User login
Ibrutinib-MTX-rituximab combo shows promise in CNS lymphoma
The three-drug combination of ibrutinib, high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX), and rituximab showed positive safety and clinical outcomes in patients with recurrent/refractory primary/secondary CNS lymphoma, according to results from a phase 1b trial.
Ibrutinib has already shown single-agent activity in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma, Christian Grommes, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, and his colleagues, wrote in Blood. “The primary objective was to determine the maximum tolerated dose of ibrutinib in combination with HD-MTX alone and ibrutinib in combination with HD-MTX and rituximab.”
With respect to ibrutinib dosing, the initial cohort was started at 560 mg daily, which was increased to 840 mg daily in successive cohorts using a 3+3 design. HD-MTX was administered every 2 weeks at 3.5 g/m2 for a total of eight infusions, or four cycles, with each cycle lasting of 28 days.
After no dose-limiting adverse effects were seen with the ibrutinib-MTX combination, the researchers added rituximab at 500 mg/m2 every 2 weeks, for a total of eight infusions, which completed the induction phase. The three-agent induction therapy was followed by daily ibrutinib monotherapy, which was maintained until discontinuation caused by malignancy progression, intolerable adverse events, or death.
“To minimize the risk of adverse events, we held ibrutinib on days of HD-MTX infusion and resumed 5 days after HD-MTX infusion or after MTX clearance,” they wrote.
After analysis, Dr. Grommes and his colleagues reported that no dose-limiting or grade 5 toxicities were detected. At a median follow-up of 19.7 months, they saw an 80% overall response rate in study patients treated with combination therapy. The median progression free survival for all 15 patients was 9.2 months and the median overall survival was not reached, with 11 of 15 patients alive.
The researchers proposed an 840-mg dose of ibrutinib for future studies.
The most frequent adverse events were lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and transaminase elevations. No fungal infections were seen during the study.
The researchers noted that two key limitations of the study were the nonrandomized design and small sample size. As a result, they reported that the degree of ibrutinib-specific activity in the three-drug combination remains unknown.
The study was supported by grant funding from Pharmacyclics to Memorial Sloan Kettering. The authors reported financial ties to AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BTH, Kite Pharma, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Grommes C et al. Blood. 2019;133(5):436-45.
The three-drug combination of ibrutinib, high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX), and rituximab showed positive safety and clinical outcomes in patients with recurrent/refractory primary/secondary CNS lymphoma, according to results from a phase 1b trial.
Ibrutinib has already shown single-agent activity in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma, Christian Grommes, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, and his colleagues, wrote in Blood. “The primary objective was to determine the maximum tolerated dose of ibrutinib in combination with HD-MTX alone and ibrutinib in combination with HD-MTX and rituximab.”
With respect to ibrutinib dosing, the initial cohort was started at 560 mg daily, which was increased to 840 mg daily in successive cohorts using a 3+3 design. HD-MTX was administered every 2 weeks at 3.5 g/m2 for a total of eight infusions, or four cycles, with each cycle lasting of 28 days.
After no dose-limiting adverse effects were seen with the ibrutinib-MTX combination, the researchers added rituximab at 500 mg/m2 every 2 weeks, for a total of eight infusions, which completed the induction phase. The three-agent induction therapy was followed by daily ibrutinib monotherapy, which was maintained until discontinuation caused by malignancy progression, intolerable adverse events, or death.
“To minimize the risk of adverse events, we held ibrutinib on days of HD-MTX infusion and resumed 5 days after HD-MTX infusion or after MTX clearance,” they wrote.
After analysis, Dr. Grommes and his colleagues reported that no dose-limiting or grade 5 toxicities were detected. At a median follow-up of 19.7 months, they saw an 80% overall response rate in study patients treated with combination therapy. The median progression free survival for all 15 patients was 9.2 months and the median overall survival was not reached, with 11 of 15 patients alive.
The researchers proposed an 840-mg dose of ibrutinib for future studies.
The most frequent adverse events were lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and transaminase elevations. No fungal infections were seen during the study.
The researchers noted that two key limitations of the study were the nonrandomized design and small sample size. As a result, they reported that the degree of ibrutinib-specific activity in the three-drug combination remains unknown.
The study was supported by grant funding from Pharmacyclics to Memorial Sloan Kettering. The authors reported financial ties to AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BTH, Kite Pharma, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Grommes C et al. Blood. 2019;133(5):436-45.
The three-drug combination of ibrutinib, high-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX), and rituximab showed positive safety and clinical outcomes in patients with recurrent/refractory primary/secondary CNS lymphoma, according to results from a phase 1b trial.
Ibrutinib has already shown single-agent activity in recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma, Christian Grommes, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, and his colleagues, wrote in Blood. “The primary objective was to determine the maximum tolerated dose of ibrutinib in combination with HD-MTX alone and ibrutinib in combination with HD-MTX and rituximab.”
With respect to ibrutinib dosing, the initial cohort was started at 560 mg daily, which was increased to 840 mg daily in successive cohorts using a 3+3 design. HD-MTX was administered every 2 weeks at 3.5 g/m2 for a total of eight infusions, or four cycles, with each cycle lasting of 28 days.
After no dose-limiting adverse effects were seen with the ibrutinib-MTX combination, the researchers added rituximab at 500 mg/m2 every 2 weeks, for a total of eight infusions, which completed the induction phase. The three-agent induction therapy was followed by daily ibrutinib monotherapy, which was maintained until discontinuation caused by malignancy progression, intolerable adverse events, or death.
“To minimize the risk of adverse events, we held ibrutinib on days of HD-MTX infusion and resumed 5 days after HD-MTX infusion or after MTX clearance,” they wrote.
After analysis, Dr. Grommes and his colleagues reported that no dose-limiting or grade 5 toxicities were detected. At a median follow-up of 19.7 months, they saw an 80% overall response rate in study patients treated with combination therapy. The median progression free survival for all 15 patients was 9.2 months and the median overall survival was not reached, with 11 of 15 patients alive.
The researchers proposed an 840-mg dose of ibrutinib for future studies.
The most frequent adverse events were lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, and transaminase elevations. No fungal infections were seen during the study.
The researchers noted that two key limitations of the study were the nonrandomized design and small sample size. As a result, they reported that the degree of ibrutinib-specific activity in the three-drug combination remains unknown.
The study was supported by grant funding from Pharmacyclics to Memorial Sloan Kettering. The authors reported financial ties to AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BTH, Kite Pharma, Pfizer, and others.
SOURCE: Grommes C et al. Blood. 2019;133(5):436-45.
FROM BLOOD
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The ibrutinib-based regimen showed an 80% overall response rate; no grade 5 adverse events were reported.
Study details: A phase 1b study of 15 patients with recurrent/refractory CNS lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was supported by grant funding from Pharmacyclics to Memorial Sloan Kettering. The authors reported financial ties to AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, BTH, Kite Pharma, Pfizer, and others.
Source: Grommes C et al. Blood. 2019;133(5):436-45.
Applying ECHELON-2 results to clinical practice
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Results from the ECHELON-2 trial led to the U.S. approval of brentuximab vedotin (BV) in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHP), but there are still questions about how to apply the trial results to practice.

At the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum, trial investigators and other physicians debated the best use of this combination.
BV-CHP is approved to treat patients with previously untreated systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (sALCL) or other CD30-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), including angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) and PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS).
Patients who received BV-CHP in ECHELON-2 had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to patients who received cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP).
These results were initially presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology and simultaneously published in The Lancet (2019 Jan 19;393[10168]:229-40).
ECHELON-2 investigator Owen O’Connor, MD, PhD, of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, also presented details on the trial at the T-cell Lymphoma Forum. His presentation was followed by a discussion with meeting attendees about applying the trial results to clinical practice.
CD30 expression
One of the issues discussed was the importance of CD30 expression in deciding which patients should receive BV.
For a patient to be eligible for ECHELON-2, the diagnostic biopsy had to show at least 10% of the neoplastic cells were CD30-positive. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not made a similar requirement for prescribing BV. PTCL patients with any level of CD30 expression are eligible for treatment with BV-CHP, according to the FDA.
“[I]t’s still a matter of great debate and controversy as to whether we have good enough data to suggest that there’s a threshold effect with regard to the expression of CD30 and responsiveness or sensitivity to brentuximab vedotin,” Dr. O’Connor said.
“This has been an issue from the very first day with this drug, which is, ‘Just how much CD30 do you need to get a response?’ I can’t speak on behalf of the FDA, but I think they are not absolutely convinced that there’s a threshold. They take [CD30-] positive as ‘good enough’ across the board.”
“The FDA has said, ‘The data we’ve seen says there’s a lot of heterogeneity [with biopsies].’ You may do a biopsy and find 30% [of cells are CD30-positive], and you may do another biopsy [in the same patient] and find less than 10%. I don’t think the regulatory agencies are convinced that a single biopsy looking at CD30 ... is representative of the entire tumor burden.”
Andrei Shustov, MD, an ECHELON-2 investigator from the University of Washington in Seattle, questioned whether CD30 expression should be considered when deciding on the use of BV in PTCL.
“Is CD30 staining relevant at all, or should we default back to studies, say, in colon cancer where we didn’t even care about EGFR because we might be missing it by current techniques?” Dr. Shustov asked. “Should we even worry about CD30 expression ... because we cannot reliably detect low levels of CD30?”
Some attendees echoed this sentiment, questioning the utility of assessing CD30 expression. Other attendees said they would defer to the trial data and only treat patients with BV-CHP if they had at least 10% CD30.
PTCL subtypes
Meeting attendees also discussed the value of BV in different PTCL subtypes.
At the request of European regulatory agencies, ECHELON-2 was largely focused on patients with sALCL. They made up 70% of the total trial population, while 16% of patients had PTCL-NOS, 12% had AITL, and a small number of patients had other subtypes. These numbers meant ECHELON-2 was not powered to determine differences in OS or PFS in non-sALCL subtypes.
As a result, some attendees expressed concerns about using BV-CHP to treat PTCL-NOS or AITL. They argued that it wasn’t clear whether patients with these subtypes would derive more benefit from BV-CHP, CHOP, or CHOP plus etoposide (CHOEP).
Other attendees said they would feel comfortable using BV-CHP in patients with PTCL-NOS or AITL based on ECHELON-2 results.
CHOP vs. CHOEP
The use of CHOP in ECHELON-2 was another point of discussion. Some attendees said CHOEP should have been used as the comparator instead.
A few individuals mentioned retrospective data suggesting CHOEP may confer a benefit over CHOP in PTCL (Blood. 2010 Nov 4;116[18]:3418-25).
Marek Trneny, MD, of Charles University General Hospital in Prague, referenced new data from the Czech National Lymphoma Registry, which showed that patients newly diagnosed with PTCL had superior PFS and OS when they received CHOEP rather than CHOP.
Based on these findings, Dr. Trneny said he would consider treating CD30-positive PTCL patients with CHOEP plus BV rather than BV-CHP.
However, most other attendees said they would not consider adding BV to CHOEP due to the absence of clinical trial data supporting this approach.
Some attendees did say they would use CHOEP instead of BV-CHP, particularly in patients with PTCL-NOS or AITL and in patients with CD30 expression below 10%.
ECHELON-2 was funded by Seattle Genetics and Millennium Pharmaceuticals, a wholly owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
Dr. O’Connor and Dr. Shustov were investigators on ECHELON-2. Dr. O’Connor is a cochair of the T-cell Lymphoma Forum. The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Results from the ECHELON-2 trial led to the U.S. approval of brentuximab vedotin (BV) in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHP), but there are still questions about how to apply the trial results to practice.

At the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum, trial investigators and other physicians debated the best use of this combination.
BV-CHP is approved to treat patients with previously untreated systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (sALCL) or other CD30-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), including angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) and PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS).
Patients who received BV-CHP in ECHELON-2 had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to patients who received cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP).
These results were initially presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology and simultaneously published in The Lancet (2019 Jan 19;393[10168]:229-40).
ECHELON-2 investigator Owen O’Connor, MD, PhD, of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, also presented details on the trial at the T-cell Lymphoma Forum. His presentation was followed by a discussion with meeting attendees about applying the trial results to clinical practice.
CD30 expression
One of the issues discussed was the importance of CD30 expression in deciding which patients should receive BV.
For a patient to be eligible for ECHELON-2, the diagnostic biopsy had to show at least 10% of the neoplastic cells were CD30-positive. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not made a similar requirement for prescribing BV. PTCL patients with any level of CD30 expression are eligible for treatment with BV-CHP, according to the FDA.
“[I]t’s still a matter of great debate and controversy as to whether we have good enough data to suggest that there’s a threshold effect with regard to the expression of CD30 and responsiveness or sensitivity to brentuximab vedotin,” Dr. O’Connor said.
“This has been an issue from the very first day with this drug, which is, ‘Just how much CD30 do you need to get a response?’ I can’t speak on behalf of the FDA, but I think they are not absolutely convinced that there’s a threshold. They take [CD30-] positive as ‘good enough’ across the board.”
“The FDA has said, ‘The data we’ve seen says there’s a lot of heterogeneity [with biopsies].’ You may do a biopsy and find 30% [of cells are CD30-positive], and you may do another biopsy [in the same patient] and find less than 10%. I don’t think the regulatory agencies are convinced that a single biopsy looking at CD30 ... is representative of the entire tumor burden.”
Andrei Shustov, MD, an ECHELON-2 investigator from the University of Washington in Seattle, questioned whether CD30 expression should be considered when deciding on the use of BV in PTCL.
“Is CD30 staining relevant at all, or should we default back to studies, say, in colon cancer where we didn’t even care about EGFR because we might be missing it by current techniques?” Dr. Shustov asked. “Should we even worry about CD30 expression ... because we cannot reliably detect low levels of CD30?”
Some attendees echoed this sentiment, questioning the utility of assessing CD30 expression. Other attendees said they would defer to the trial data and only treat patients with BV-CHP if they had at least 10% CD30.
PTCL subtypes
Meeting attendees also discussed the value of BV in different PTCL subtypes.
At the request of European regulatory agencies, ECHELON-2 was largely focused on patients with sALCL. They made up 70% of the total trial population, while 16% of patients had PTCL-NOS, 12% had AITL, and a small number of patients had other subtypes. These numbers meant ECHELON-2 was not powered to determine differences in OS or PFS in non-sALCL subtypes.
As a result, some attendees expressed concerns about using BV-CHP to treat PTCL-NOS or AITL. They argued that it wasn’t clear whether patients with these subtypes would derive more benefit from BV-CHP, CHOP, or CHOP plus etoposide (CHOEP).
Other attendees said they would feel comfortable using BV-CHP in patients with PTCL-NOS or AITL based on ECHELON-2 results.
CHOP vs. CHOEP
The use of CHOP in ECHELON-2 was another point of discussion. Some attendees said CHOEP should have been used as the comparator instead.
A few individuals mentioned retrospective data suggesting CHOEP may confer a benefit over CHOP in PTCL (Blood. 2010 Nov 4;116[18]:3418-25).
Marek Trneny, MD, of Charles University General Hospital in Prague, referenced new data from the Czech National Lymphoma Registry, which showed that patients newly diagnosed with PTCL had superior PFS and OS when they received CHOEP rather than CHOP.
Based on these findings, Dr. Trneny said he would consider treating CD30-positive PTCL patients with CHOEP plus BV rather than BV-CHP.
However, most other attendees said they would not consider adding BV to CHOEP due to the absence of clinical trial data supporting this approach.
Some attendees did say they would use CHOEP instead of BV-CHP, particularly in patients with PTCL-NOS or AITL and in patients with CD30 expression below 10%.
ECHELON-2 was funded by Seattle Genetics and Millennium Pharmaceuticals, a wholly owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
Dr. O’Connor and Dr. Shustov were investigators on ECHELON-2. Dr. O’Connor is a cochair of the T-cell Lymphoma Forum. The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Results from the ECHELON-2 trial led to the U.S. approval of brentuximab vedotin (BV) in combination with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHP), but there are still questions about how to apply the trial results to practice.

At the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum, trial investigators and other physicians debated the best use of this combination.
BV-CHP is approved to treat patients with previously untreated systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (sALCL) or other CD30-expressing peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), including angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) and PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS).
Patients who received BV-CHP in ECHELON-2 had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) compared to patients who received cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP).
These results were initially presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology and simultaneously published in The Lancet (2019 Jan 19;393[10168]:229-40).
ECHELON-2 investigator Owen O’Connor, MD, PhD, of Columbia University Medical Center in New York, also presented details on the trial at the T-cell Lymphoma Forum. His presentation was followed by a discussion with meeting attendees about applying the trial results to clinical practice.
CD30 expression
One of the issues discussed was the importance of CD30 expression in deciding which patients should receive BV.
For a patient to be eligible for ECHELON-2, the diagnostic biopsy had to show at least 10% of the neoplastic cells were CD30-positive. However, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not made a similar requirement for prescribing BV. PTCL patients with any level of CD30 expression are eligible for treatment with BV-CHP, according to the FDA.
“[I]t’s still a matter of great debate and controversy as to whether we have good enough data to suggest that there’s a threshold effect with regard to the expression of CD30 and responsiveness or sensitivity to brentuximab vedotin,” Dr. O’Connor said.
“This has been an issue from the very first day with this drug, which is, ‘Just how much CD30 do you need to get a response?’ I can’t speak on behalf of the FDA, but I think they are not absolutely convinced that there’s a threshold. They take [CD30-] positive as ‘good enough’ across the board.”
“The FDA has said, ‘The data we’ve seen says there’s a lot of heterogeneity [with biopsies].’ You may do a biopsy and find 30% [of cells are CD30-positive], and you may do another biopsy [in the same patient] and find less than 10%. I don’t think the regulatory agencies are convinced that a single biopsy looking at CD30 ... is representative of the entire tumor burden.”
Andrei Shustov, MD, an ECHELON-2 investigator from the University of Washington in Seattle, questioned whether CD30 expression should be considered when deciding on the use of BV in PTCL.
“Is CD30 staining relevant at all, or should we default back to studies, say, in colon cancer where we didn’t even care about EGFR because we might be missing it by current techniques?” Dr. Shustov asked. “Should we even worry about CD30 expression ... because we cannot reliably detect low levels of CD30?”
Some attendees echoed this sentiment, questioning the utility of assessing CD30 expression. Other attendees said they would defer to the trial data and only treat patients with BV-CHP if they had at least 10% CD30.
PTCL subtypes
Meeting attendees also discussed the value of BV in different PTCL subtypes.
At the request of European regulatory agencies, ECHELON-2 was largely focused on patients with sALCL. They made up 70% of the total trial population, while 16% of patients had PTCL-NOS, 12% had AITL, and a small number of patients had other subtypes. These numbers meant ECHELON-2 was not powered to determine differences in OS or PFS in non-sALCL subtypes.
As a result, some attendees expressed concerns about using BV-CHP to treat PTCL-NOS or AITL. They argued that it wasn’t clear whether patients with these subtypes would derive more benefit from BV-CHP, CHOP, or CHOP plus etoposide (CHOEP).
Other attendees said they would feel comfortable using BV-CHP in patients with PTCL-NOS or AITL based on ECHELON-2 results.
CHOP vs. CHOEP
The use of CHOP in ECHELON-2 was another point of discussion. Some attendees said CHOEP should have been used as the comparator instead.
A few individuals mentioned retrospective data suggesting CHOEP may confer a benefit over CHOP in PTCL (Blood. 2010 Nov 4;116[18]:3418-25).
Marek Trneny, MD, of Charles University General Hospital in Prague, referenced new data from the Czech National Lymphoma Registry, which showed that patients newly diagnosed with PTCL had superior PFS and OS when they received CHOEP rather than CHOP.
Based on these findings, Dr. Trneny said he would consider treating CD30-positive PTCL patients with CHOEP plus BV rather than BV-CHP.
However, most other attendees said they would not consider adding BV to CHOEP due to the absence of clinical trial data supporting this approach.
Some attendees did say they would use CHOEP instead of BV-CHP, particularly in patients with PTCL-NOS or AITL and in patients with CD30 expression below 10%.
ECHELON-2 was funded by Seattle Genetics and Millennium Pharmaceuticals, a wholly owned subsidiary of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company.
Dr. O’Connor and Dr. Shustov were investigators on ECHELON-2. Dr. O’Connor is a cochair of the T-cell Lymphoma Forum. The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM TCLF 2019
Novel bispecific CAR shows promise in B-cell malignancies
SAN DIEGO – A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting both CD19 and CD22 shows promising safety and efficacy for the treatment of relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies in adults, according to early findings from a phase 1 trial of the novel bispecific CAR.
Of six patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and two patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) enrolled in the single-institution dose escalation study and available for safety analysis after the bispecific CAR T-cell infusion, five developed reversible grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and one developed grade 2 CRS requiring treatment with tocilizumab, Nasheed Hossain, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Additionally, two patients developed grade 1 neurotoxicity, and one developed grade 2 neurotoxicity requiring treatment with dexamethasone.
“But no dose-limiting toxicities have been encountered thus far,” said Dr. Hossain of Loyola University Medical Center, Chicago. “With regard to efficacy, the DLBCL overall response rate is 60%, with 1 [complete response] and 2 [partial responses] at day 28 and day 90, and the ALL overall response rate is 100%, with 1 CR and 1 PR at day 28.
“With longer follow-up, five patients have relapsed and biopsies at the time of progression all showed ongoing CD19 expression,” he said, adding that all enrolled patients are alive, except for one patient who died from disease progression.
Study participants were adults aged 35-75 years with DLBCL or B-ALL that was refractory to standard therapies.
“Our primary objectives are twofold: One is to determine the feasibility of making our CAR ... and [the other] is to assess the safety using an escalating CAR dose following standard cyclophosphamide/fludarabine conditioning,” Dr. Hossain said.
The dose assessed in the current analysis was 1 x 106 CAR T cells/kg; other planned doses include 3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg and 1 x 107 CAR T cells/kg, he said.
All patients underwent lymphodepletion with cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2 daily x 3 doses) and fludarabine (30 mg/m2 daily x 3 doses) followed by CAR T-cell infusion 2 days later.
The findings of this ongoing study – the first in-human study of a bispecific loop CAR in the United States – suggest that the novel CAR has low toxicity and promising efficacy, Dr. Hossain said.
Currently approved therapies target CD19 alone, he said, noting that they all use the same anti-CD19 domain, but different costimulatory domains, and have good clinical efficacy of greater than 70% CRs in ALL and up to 52% CRs in DLBCL.
“But questions remain about determining the durability of response and the causes of therapy failure,” he said.
One common cause of treatment failure is CD19 antigen loss, and efforts to reduce such antigen loss using bispecific loop CARs targeting both CD19 and CD22 have shown promise. The CAR construct evaluated in this study was developed to target CD19 and CD22 with intracellular signaling domains incorporating 4-1BB and CD3-zeta to overcome CD19 immune escape.
“We have now escalated the dose to 3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg ... and an expansion study of 60 patients will follow,” Dr. Hossain said.
A companion phase 1 pediatric trial using the same CAR construct is also underway, with preliminary data presented at the ASH meeting demonstrating safety and tolerability in children with relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL.
Dr. Hossain reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Hossain N et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 490.
SAN DIEGO – A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting both CD19 and CD22 shows promising safety and efficacy for the treatment of relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies in adults, according to early findings from a phase 1 trial of the novel bispecific CAR.
Of six patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and two patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) enrolled in the single-institution dose escalation study and available for safety analysis after the bispecific CAR T-cell infusion, five developed reversible grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and one developed grade 2 CRS requiring treatment with tocilizumab, Nasheed Hossain, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Additionally, two patients developed grade 1 neurotoxicity, and one developed grade 2 neurotoxicity requiring treatment with dexamethasone.
“But no dose-limiting toxicities have been encountered thus far,” said Dr. Hossain of Loyola University Medical Center, Chicago. “With regard to efficacy, the DLBCL overall response rate is 60%, with 1 [complete response] and 2 [partial responses] at day 28 and day 90, and the ALL overall response rate is 100%, with 1 CR and 1 PR at day 28.
“With longer follow-up, five patients have relapsed and biopsies at the time of progression all showed ongoing CD19 expression,” he said, adding that all enrolled patients are alive, except for one patient who died from disease progression.
Study participants were adults aged 35-75 years with DLBCL or B-ALL that was refractory to standard therapies.
“Our primary objectives are twofold: One is to determine the feasibility of making our CAR ... and [the other] is to assess the safety using an escalating CAR dose following standard cyclophosphamide/fludarabine conditioning,” Dr. Hossain said.
The dose assessed in the current analysis was 1 x 106 CAR T cells/kg; other planned doses include 3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg and 1 x 107 CAR T cells/kg, he said.
All patients underwent lymphodepletion with cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2 daily x 3 doses) and fludarabine (30 mg/m2 daily x 3 doses) followed by CAR T-cell infusion 2 days later.
The findings of this ongoing study – the first in-human study of a bispecific loop CAR in the United States – suggest that the novel CAR has low toxicity and promising efficacy, Dr. Hossain said.
Currently approved therapies target CD19 alone, he said, noting that they all use the same anti-CD19 domain, but different costimulatory domains, and have good clinical efficacy of greater than 70% CRs in ALL and up to 52% CRs in DLBCL.
“But questions remain about determining the durability of response and the causes of therapy failure,” he said.
One common cause of treatment failure is CD19 antigen loss, and efforts to reduce such antigen loss using bispecific loop CARs targeting both CD19 and CD22 have shown promise. The CAR construct evaluated in this study was developed to target CD19 and CD22 with intracellular signaling domains incorporating 4-1BB and CD3-zeta to overcome CD19 immune escape.
“We have now escalated the dose to 3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg ... and an expansion study of 60 patients will follow,” Dr. Hossain said.
A companion phase 1 pediatric trial using the same CAR construct is also underway, with preliminary data presented at the ASH meeting demonstrating safety and tolerability in children with relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL.
Dr. Hossain reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Hossain N et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 490.
SAN DIEGO – A chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) targeting both CD19 and CD22 shows promising safety and efficacy for the treatment of relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies in adults, according to early findings from a phase 1 trial of the novel bispecific CAR.
Of six patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and two patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) enrolled in the single-institution dose escalation study and available for safety analysis after the bispecific CAR T-cell infusion, five developed reversible grade 1 cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and one developed grade 2 CRS requiring treatment with tocilizumab, Nasheed Hossain, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Additionally, two patients developed grade 1 neurotoxicity, and one developed grade 2 neurotoxicity requiring treatment with dexamethasone.
“But no dose-limiting toxicities have been encountered thus far,” said Dr. Hossain of Loyola University Medical Center, Chicago. “With regard to efficacy, the DLBCL overall response rate is 60%, with 1 [complete response] and 2 [partial responses] at day 28 and day 90, and the ALL overall response rate is 100%, with 1 CR and 1 PR at day 28.
“With longer follow-up, five patients have relapsed and biopsies at the time of progression all showed ongoing CD19 expression,” he said, adding that all enrolled patients are alive, except for one patient who died from disease progression.
Study participants were adults aged 35-75 years with DLBCL or B-ALL that was refractory to standard therapies.
“Our primary objectives are twofold: One is to determine the feasibility of making our CAR ... and [the other] is to assess the safety using an escalating CAR dose following standard cyclophosphamide/fludarabine conditioning,” Dr. Hossain said.
The dose assessed in the current analysis was 1 x 106 CAR T cells/kg; other planned doses include 3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg and 1 x 107 CAR T cells/kg, he said.
All patients underwent lymphodepletion with cyclophosphamide (500 mg/m2 daily x 3 doses) and fludarabine (30 mg/m2 daily x 3 doses) followed by CAR T-cell infusion 2 days later.
The findings of this ongoing study – the first in-human study of a bispecific loop CAR in the United States – suggest that the novel CAR has low toxicity and promising efficacy, Dr. Hossain said.
Currently approved therapies target CD19 alone, he said, noting that they all use the same anti-CD19 domain, but different costimulatory domains, and have good clinical efficacy of greater than 70% CRs in ALL and up to 52% CRs in DLBCL.
“But questions remain about determining the durability of response and the causes of therapy failure,” he said.
One common cause of treatment failure is CD19 antigen loss, and efforts to reduce such antigen loss using bispecific loop CARs targeting both CD19 and CD22 have shown promise. The CAR construct evaluated in this study was developed to target CD19 and CD22 with intracellular signaling domains incorporating 4-1BB and CD3-zeta to overcome CD19 immune escape.
“We have now escalated the dose to 3 x 106 CAR T cells/kg ... and an expansion study of 60 patients will follow,” Dr. Hossain said.
A companion phase 1 pediatric trial using the same CAR construct is also underway, with preliminary data presented at the ASH meeting demonstrating safety and tolerability in children with relapsed or refractory B-cell ALL.
Dr. Hossain reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Hossain N et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 490.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Grade 1 cytokine release syndrome occurred in five patients, and grade 2 CRS occurred in one patient; there were no dose-limiting toxicities.
Study details: A phase 1 dose escalation study of nine patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Hossain reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Hossain N et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 490.
Imaging, radiotherapy clarified in new PMBCL guidelines
Fertility preservation, imaging and radiotherapy guidelines, and best practices in relapse or salvage therapy for primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) are all highlighted in a new good practice paper from the British Society for Haematology.
Though PMBCL was previously thought of as a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, “gene expression profiling data has shown it to be a separate clinicopathological entity with evidence of an overlap with classic Hodgkin lymphoma,” said Kate Cwynarski, MD, PhD, of University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in England, and her coauthors. The recommendations were published in the British Journal of Haematology.
PMBCL makes up 2%-4% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas, they said; a bulky anterior mediastinal mass is the usual initial presentation. PMBCL does not usually spread beyond the thoracic cavity.
Biopsy, which should be reviewed by a hematopathologist, is required for a histological diagnosis of PMBCL. A multidisciplinary team should review the clinical presentation, pathology, and management plan, according to the good practice paper authors. This was a strong recommendation backed by a high level of evidence.
In addition, patients should receive positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET/CT) at diagnosis, before steroids are administered, if possible, as standard of care. Results from the PET/CT should be reported in accordance with international guidelines. These strong recommendations are backed by high-quality evidence.
If PET/CT is performed, then “a bone marrow biopsy is not considered essential,” said Dr. Cwynarski and her coauthors. However, if the findings would influence management, such as when there is extranodal disease that presents central nervous system opportunities, then bone marrow biopsy should be performed. It should also be performed when cytotoxic therapy was initiated before PET/CT could be done. This is a weak recommendation supported by moderate evidence.
Since patients with PMBCL are usually young adults at presentation, it’s important to consider fertility preservation in the face of chemotherapy. For males, semen preservation should be offered. Female patients may not be able to postpone treatment long enough to accomplish egg harvesting. The risk of infertility and premature ovarian failure will depend on the treatment regimen, so “the risks of each individual therapeutic regimen should be discussed with the patient,” Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues said.
If a patient is diagnosed with PMBCL while pregnant, treatment should be managed in conjunction with high-risk obstetrics and anesthesia specialists. Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) has been used in pregnancy, and immunotherapy without antimetabolites can be considered in the second and third trimesters, according to the good practice paper. These are strong fertility and pregnancy recommendations, backed by moderate to low-quality evidence.
If superior vena cava obstruction causes thrombosis, local standard of care for anticoagulation should be used, but therapy-induced thrombocytopenia should be taken into consideration.
There is a lack of prospective, randomized studies to guide treatment decisions in PMBCL, according to the paper. Still, adding rituximab improves both response rates and duration of remission, they noted.
The standard of care for treatment is six cycles of R-CHOP and involved site radiotherapy (ISRT). If the patient is being cared for at a site that can manage the complexities of dose adjustment and monitoring, dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) without ISRT is an alternative, according to the good practice paper.
All patients should be offered clinical trial participation when feasible, a strong recommendation based on high-quality evidence.
To assess the response to therapy, R-CHOP and ISRT recipients not participating in a clinical trial should receive a PET-CT scan 2-3 months after treatment is completed, and DA-EPOCH-R patients should receive their scan 6 weeks after the end of therapy. For all patients, Deauville criteria should be used in reporting response scan results. These strong recommendations about posttherapy imaging are based on moderate-quality evidence.
The rate of relapse and refractory disease is relatively low at about 10%-30%, Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues said. Relapse usually happens within the first year and is rare after 2 years; extranodal disease is common, but usually spares the central nervous system and bone marrow. The good practice paper authors strongly recommend, based on high-quality evidence, that biopsy and fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT should be performed with relapse.
Radiotherapy can be considered if the relapse is localized and the patient didn’t receive initial radiotherapy, a strong recommendation with moderate evidence to support it.
Salvage regimens for patients who have not previously achieved complete metabolic response lack a disease-specific evidence base, noted Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues. Taking this into consideration, a PMBCL salvage regimen should be the same as that offered to patients with relapsed diffused large B-cell lymphoma. High-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation is appropriate for responsive disease.
If radiotherapy had not been given previously, it should be considered either pre- or post transplant. This, along with the other salvage therapy guidance, is a weak recommendation, backed by moderate evidence.
For longer-term follow-up, asymptomatic patients should not have routine imaging, a strong recommendation with moderate evidence. “[P]atients who remain in remission may be considered for discharge back to primary care,” Dr. Cwynarski and her coauthors said, making a weak recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Patients and their primary care providers should know about the potential for such long-term complications as cardiac toxicities and second malignancies.
SOURCE: Cwynarski K et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jan 4. doi:10.1111/bjh.15731
Fertility preservation, imaging and radiotherapy guidelines, and best practices in relapse or salvage therapy for primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) are all highlighted in a new good practice paper from the British Society for Haematology.
Though PMBCL was previously thought of as a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, “gene expression profiling data has shown it to be a separate clinicopathological entity with evidence of an overlap with classic Hodgkin lymphoma,” said Kate Cwynarski, MD, PhD, of University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in England, and her coauthors. The recommendations were published in the British Journal of Haematology.
PMBCL makes up 2%-4% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas, they said; a bulky anterior mediastinal mass is the usual initial presentation. PMBCL does not usually spread beyond the thoracic cavity.
Biopsy, which should be reviewed by a hematopathologist, is required for a histological diagnosis of PMBCL. A multidisciplinary team should review the clinical presentation, pathology, and management plan, according to the good practice paper authors. This was a strong recommendation backed by a high level of evidence.
In addition, patients should receive positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET/CT) at diagnosis, before steroids are administered, if possible, as standard of care. Results from the PET/CT should be reported in accordance with international guidelines. These strong recommendations are backed by high-quality evidence.
If PET/CT is performed, then “a bone marrow biopsy is not considered essential,” said Dr. Cwynarski and her coauthors. However, if the findings would influence management, such as when there is extranodal disease that presents central nervous system opportunities, then bone marrow biopsy should be performed. It should also be performed when cytotoxic therapy was initiated before PET/CT could be done. This is a weak recommendation supported by moderate evidence.
Since patients with PMBCL are usually young adults at presentation, it’s important to consider fertility preservation in the face of chemotherapy. For males, semen preservation should be offered. Female patients may not be able to postpone treatment long enough to accomplish egg harvesting. The risk of infertility and premature ovarian failure will depend on the treatment regimen, so “the risks of each individual therapeutic regimen should be discussed with the patient,” Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues said.
If a patient is diagnosed with PMBCL while pregnant, treatment should be managed in conjunction with high-risk obstetrics and anesthesia specialists. Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) has been used in pregnancy, and immunotherapy without antimetabolites can be considered in the second and third trimesters, according to the good practice paper. These are strong fertility and pregnancy recommendations, backed by moderate to low-quality evidence.
If superior vena cava obstruction causes thrombosis, local standard of care for anticoagulation should be used, but therapy-induced thrombocytopenia should be taken into consideration.
There is a lack of prospective, randomized studies to guide treatment decisions in PMBCL, according to the paper. Still, adding rituximab improves both response rates and duration of remission, they noted.
The standard of care for treatment is six cycles of R-CHOP and involved site radiotherapy (ISRT). If the patient is being cared for at a site that can manage the complexities of dose adjustment and monitoring, dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) without ISRT is an alternative, according to the good practice paper.
All patients should be offered clinical trial participation when feasible, a strong recommendation based on high-quality evidence.
To assess the response to therapy, R-CHOP and ISRT recipients not participating in a clinical trial should receive a PET-CT scan 2-3 months after treatment is completed, and DA-EPOCH-R patients should receive their scan 6 weeks after the end of therapy. For all patients, Deauville criteria should be used in reporting response scan results. These strong recommendations about posttherapy imaging are based on moderate-quality evidence.
The rate of relapse and refractory disease is relatively low at about 10%-30%, Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues said. Relapse usually happens within the first year and is rare after 2 years; extranodal disease is common, but usually spares the central nervous system and bone marrow. The good practice paper authors strongly recommend, based on high-quality evidence, that biopsy and fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT should be performed with relapse.
Radiotherapy can be considered if the relapse is localized and the patient didn’t receive initial radiotherapy, a strong recommendation with moderate evidence to support it.
Salvage regimens for patients who have not previously achieved complete metabolic response lack a disease-specific evidence base, noted Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues. Taking this into consideration, a PMBCL salvage regimen should be the same as that offered to patients with relapsed diffused large B-cell lymphoma. High-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation is appropriate for responsive disease.
If radiotherapy had not been given previously, it should be considered either pre- or post transplant. This, along with the other salvage therapy guidance, is a weak recommendation, backed by moderate evidence.
For longer-term follow-up, asymptomatic patients should not have routine imaging, a strong recommendation with moderate evidence. “[P]atients who remain in remission may be considered for discharge back to primary care,” Dr. Cwynarski and her coauthors said, making a weak recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Patients and their primary care providers should know about the potential for such long-term complications as cardiac toxicities and second malignancies.
SOURCE: Cwynarski K et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jan 4. doi:10.1111/bjh.15731
Fertility preservation, imaging and radiotherapy guidelines, and best practices in relapse or salvage therapy for primary mediastinal B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL) are all highlighted in a new good practice paper from the British Society for Haematology.
Though PMBCL was previously thought of as a subtype of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, “gene expression profiling data has shown it to be a separate clinicopathological entity with evidence of an overlap with classic Hodgkin lymphoma,” said Kate Cwynarski, MD, PhD, of University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust in England, and her coauthors. The recommendations were published in the British Journal of Haematology.
PMBCL makes up 2%-4% of non-Hodgkin lymphomas, they said; a bulky anterior mediastinal mass is the usual initial presentation. PMBCL does not usually spread beyond the thoracic cavity.
Biopsy, which should be reviewed by a hematopathologist, is required for a histological diagnosis of PMBCL. A multidisciplinary team should review the clinical presentation, pathology, and management plan, according to the good practice paper authors. This was a strong recommendation backed by a high level of evidence.
In addition, patients should receive positron emission tomography–computed tomography (PET/CT) at diagnosis, before steroids are administered, if possible, as standard of care. Results from the PET/CT should be reported in accordance with international guidelines. These strong recommendations are backed by high-quality evidence.
If PET/CT is performed, then “a bone marrow biopsy is not considered essential,” said Dr. Cwynarski and her coauthors. However, if the findings would influence management, such as when there is extranodal disease that presents central nervous system opportunities, then bone marrow biopsy should be performed. It should also be performed when cytotoxic therapy was initiated before PET/CT could be done. This is a weak recommendation supported by moderate evidence.
Since patients with PMBCL are usually young adults at presentation, it’s important to consider fertility preservation in the face of chemotherapy. For males, semen preservation should be offered. Female patients may not be able to postpone treatment long enough to accomplish egg harvesting. The risk of infertility and premature ovarian failure will depend on the treatment regimen, so “the risks of each individual therapeutic regimen should be discussed with the patient,” Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues said.
If a patient is diagnosed with PMBCL while pregnant, treatment should be managed in conjunction with high-risk obstetrics and anesthesia specialists. Rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) has been used in pregnancy, and immunotherapy without antimetabolites can be considered in the second and third trimesters, according to the good practice paper. These are strong fertility and pregnancy recommendations, backed by moderate to low-quality evidence.
If superior vena cava obstruction causes thrombosis, local standard of care for anticoagulation should be used, but therapy-induced thrombocytopenia should be taken into consideration.
There is a lack of prospective, randomized studies to guide treatment decisions in PMBCL, according to the paper. Still, adding rituximab improves both response rates and duration of remission, they noted.
The standard of care for treatment is six cycles of R-CHOP and involved site radiotherapy (ISRT). If the patient is being cared for at a site that can manage the complexities of dose adjustment and monitoring, dose-adjusted etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and rituximab (DA-EPOCH-R) without ISRT is an alternative, according to the good practice paper.
All patients should be offered clinical trial participation when feasible, a strong recommendation based on high-quality evidence.
To assess the response to therapy, R-CHOP and ISRT recipients not participating in a clinical trial should receive a PET-CT scan 2-3 months after treatment is completed, and DA-EPOCH-R patients should receive their scan 6 weeks after the end of therapy. For all patients, Deauville criteria should be used in reporting response scan results. These strong recommendations about posttherapy imaging are based on moderate-quality evidence.
The rate of relapse and refractory disease is relatively low at about 10%-30%, Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues said. Relapse usually happens within the first year and is rare after 2 years; extranodal disease is common, but usually spares the central nervous system and bone marrow. The good practice paper authors strongly recommend, based on high-quality evidence, that biopsy and fluorodeoxyglucose-PET/CT should be performed with relapse.
Radiotherapy can be considered if the relapse is localized and the patient didn’t receive initial radiotherapy, a strong recommendation with moderate evidence to support it.
Salvage regimens for patients who have not previously achieved complete metabolic response lack a disease-specific evidence base, noted Dr. Cwynarski and her colleagues. Taking this into consideration, a PMBCL salvage regimen should be the same as that offered to patients with relapsed diffused large B-cell lymphoma. High-dose therapy and autologous stem cell transplantation is appropriate for responsive disease.
If radiotherapy had not been given previously, it should be considered either pre- or post transplant. This, along with the other salvage therapy guidance, is a weak recommendation, backed by moderate evidence.
For longer-term follow-up, asymptomatic patients should not have routine imaging, a strong recommendation with moderate evidence. “[P]atients who remain in remission may be considered for discharge back to primary care,” Dr. Cwynarski and her coauthors said, making a weak recommendation based on low-quality evidence. Patients and their primary care providers should know about the potential for such long-term complications as cardiac toxicities and second malignancies.
SOURCE: Cwynarski K et al. Br J Haematol. 2019 Jan 4. doi:10.1111/bjh.15731
FROM BRITISH JOURNAL OF HAEMATOLOGY
Combo treatment may improve quality of life in CTCL
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Treatment with brentuximab vedotin (BV) and lenalidomide (len) may improve quality of life (QOL) for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), according to the principal investigator of a phase 2 trial.

In this small trial, most CTCL patients experienced relief from pruritus after one cycle of treatment with BV-len.
Investigators also observed durable responses to the combination, although two patients experienced tumor flare prior to response.
“Because of the tumor flare, we decreased the dose of lenalidomide ... and, since then, it has not been a major problem,” said Basem M. William, MD, principal investigator of the trial and a professor at Ohio State University in Columbus.
“We’re trying to be more reassuring to patients that, if they experience a little bit of tumor flare, as long as it’s not dangerous or life-threatening, if they can hold on with the treatment, this might translate to a later durable response.”
Dr. William and his colleagues presented results from this ongoing, phase 2 trial (NCT03409432) at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Thus far, the investigators have treated 12 patients with relapsed or refractory CTCL or peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). The CTCL patients had received at least two lines of skin-directed therapy or one line of systemic therapy, and the PTCL patients had received at least one line of systemic therapy.
Dr. William and his colleagues reported results for 10 patients. Six patients had mycosis fungoides (MF), two had Sézary syndrome (SS), one had CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder, and one had systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
The patients’ median age was 59 (range, 49-74), there were nine males, and patients had received a median of 2 (range, 1-10) prior therapies.
The first seven patients received BV at 1.2 mg/kg and len at 20 mg daily every 3 weeks. However, after the investigators observed tumor flare in two patients, the dose of len was lowered to 10 mg.
Safety
The investigators said all adverse events (AEs) were reversible by stopping therapy, there were no grade 4 AEs, and none of the patients had grade 3 or higher neuropathy.
“We have not seen an excess of neuropathy, which is very important because both brentuximab and lenalidomide are known to cause neuropathy,” Dr. William said. “So we were fairly concerned that there would be a synergistic neurotoxic effect, which we don’t want, but we haven’t seen that.”
The most common treatment-related AE was neutropenia. Grade 3 neutropenia occurred in four patients.
Other grade 3 AEs, which occurred in patients on the 20 mg dose of len, were thrombocytopenia (n = 1), dyspnea (n = 1), vertigo (n = 1), drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome (n = 1), and tumor flare (n = 1).
Three patients discontinued treatment because of AEs — thrombocytopenia, tumor flare, and DRESS syndrome.
Tumor flare and response
“We did see tumor flare in two initial patients treated with the higher dose of lenalidomide, and we had to remove them from the study for their safety,” Dr. William said. “One of them had a full-blown DRESS syndrome. For their safety, we did have to remove them, but both did experience durable remissions after.”
One of the patients with tumor flare, who had MF, didn’t require treatment for 6 months after going off study. The other patient, who had SS, cleared the clone from his blood but developed DRESS syndrome.
In all, three patients achieved a response to treatment. The ALCL patient had a complete response, and two MF patients achieved a partial response.
Two MF patients and one SS patient had stable disease. The remaining four patients — two with MF, one with SS, and one with lymphoproliferative disorder — progressed.
QOL
The investigators used the Skindex-16 to assess the effect of treatment on QOL.
Five of six evaluable patients with CTCL had a 50% or greater reduction in their Skindex-16 scores after two cycles of treatment. In fact, most patients had relief from pruritus after one cycle, Dr. William said.
“Patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, their biggest problem is with the symptom burden, with pruritus,” he said. “They’re really miserable from all the itching they have. They cannot sleep at night. So we’re fairly excited that most of the patients we’ve treated so far had relief from pruritus just after one cycle.”
Dr. William said he and his colleagues are excited about the overall results they have observed with BV-len, although it’s “still pretty early” in the trial. The investigators are planning to enroll a total of 42 patients and may open the trial at a second center.
The study is sponsored by Ohio State University and the lenalidomide is provided by Celgene. Dr. William reported relationships with miRagen Therapeutics, GuidePoint, Kyowa Kirin, and Celgene.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Treatment with brentuximab vedotin (BV) and lenalidomide (len) may improve quality of life (QOL) for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), according to the principal investigator of a phase 2 trial.

In this small trial, most CTCL patients experienced relief from pruritus after one cycle of treatment with BV-len.
Investigators also observed durable responses to the combination, although two patients experienced tumor flare prior to response.
“Because of the tumor flare, we decreased the dose of lenalidomide ... and, since then, it has not been a major problem,” said Basem M. William, MD, principal investigator of the trial and a professor at Ohio State University in Columbus.
“We’re trying to be more reassuring to patients that, if they experience a little bit of tumor flare, as long as it’s not dangerous or life-threatening, if they can hold on with the treatment, this might translate to a later durable response.”
Dr. William and his colleagues presented results from this ongoing, phase 2 trial (NCT03409432) at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Thus far, the investigators have treated 12 patients with relapsed or refractory CTCL or peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). The CTCL patients had received at least two lines of skin-directed therapy or one line of systemic therapy, and the PTCL patients had received at least one line of systemic therapy.
Dr. William and his colleagues reported results for 10 patients. Six patients had mycosis fungoides (MF), two had Sézary syndrome (SS), one had CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder, and one had systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
The patients’ median age was 59 (range, 49-74), there were nine males, and patients had received a median of 2 (range, 1-10) prior therapies.
The first seven patients received BV at 1.2 mg/kg and len at 20 mg daily every 3 weeks. However, after the investigators observed tumor flare in two patients, the dose of len was lowered to 10 mg.
Safety
The investigators said all adverse events (AEs) were reversible by stopping therapy, there were no grade 4 AEs, and none of the patients had grade 3 or higher neuropathy.
“We have not seen an excess of neuropathy, which is very important because both brentuximab and lenalidomide are known to cause neuropathy,” Dr. William said. “So we were fairly concerned that there would be a synergistic neurotoxic effect, which we don’t want, but we haven’t seen that.”
The most common treatment-related AE was neutropenia. Grade 3 neutropenia occurred in four patients.
Other grade 3 AEs, which occurred in patients on the 20 mg dose of len, were thrombocytopenia (n = 1), dyspnea (n = 1), vertigo (n = 1), drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome (n = 1), and tumor flare (n = 1).
Three patients discontinued treatment because of AEs — thrombocytopenia, tumor flare, and DRESS syndrome.
Tumor flare and response
“We did see tumor flare in two initial patients treated with the higher dose of lenalidomide, and we had to remove them from the study for their safety,” Dr. William said. “One of them had a full-blown DRESS syndrome. For their safety, we did have to remove them, but both did experience durable remissions after.”
One of the patients with tumor flare, who had MF, didn’t require treatment for 6 months after going off study. The other patient, who had SS, cleared the clone from his blood but developed DRESS syndrome.
In all, three patients achieved a response to treatment. The ALCL patient had a complete response, and two MF patients achieved a partial response.
Two MF patients and one SS patient had stable disease. The remaining four patients — two with MF, one with SS, and one with lymphoproliferative disorder — progressed.
QOL
The investigators used the Skindex-16 to assess the effect of treatment on QOL.
Five of six evaluable patients with CTCL had a 50% or greater reduction in their Skindex-16 scores after two cycles of treatment. In fact, most patients had relief from pruritus after one cycle, Dr. William said.
“Patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, their biggest problem is with the symptom burden, with pruritus,” he said. “They’re really miserable from all the itching they have. They cannot sleep at night. So we’re fairly excited that most of the patients we’ve treated so far had relief from pruritus just after one cycle.”
Dr. William said he and his colleagues are excited about the overall results they have observed with BV-len, although it’s “still pretty early” in the trial. The investigators are planning to enroll a total of 42 patients and may open the trial at a second center.
The study is sponsored by Ohio State University and the lenalidomide is provided by Celgene. Dr. William reported relationships with miRagen Therapeutics, GuidePoint, Kyowa Kirin, and Celgene.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Treatment with brentuximab vedotin (BV) and lenalidomide (len) may improve quality of life (QOL) for patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), according to the principal investigator of a phase 2 trial.

In this small trial, most CTCL patients experienced relief from pruritus after one cycle of treatment with BV-len.
Investigators also observed durable responses to the combination, although two patients experienced tumor flare prior to response.
“Because of the tumor flare, we decreased the dose of lenalidomide ... and, since then, it has not been a major problem,” said Basem M. William, MD, principal investigator of the trial and a professor at Ohio State University in Columbus.
“We’re trying to be more reassuring to patients that, if they experience a little bit of tumor flare, as long as it’s not dangerous or life-threatening, if they can hold on with the treatment, this might translate to a later durable response.”
Dr. William and his colleagues presented results from this ongoing, phase 2 trial (NCT03409432) at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Thus far, the investigators have treated 12 patients with relapsed or refractory CTCL or peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). The CTCL patients had received at least two lines of skin-directed therapy or one line of systemic therapy, and the PTCL patients had received at least one line of systemic therapy.
Dr. William and his colleagues reported results for 10 patients. Six patients had mycosis fungoides (MF), two had Sézary syndrome (SS), one had CD30+ lymphoproliferative disorder, and one had systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL).
The patients’ median age was 59 (range, 49-74), there were nine males, and patients had received a median of 2 (range, 1-10) prior therapies.
The first seven patients received BV at 1.2 mg/kg and len at 20 mg daily every 3 weeks. However, after the investigators observed tumor flare in two patients, the dose of len was lowered to 10 mg.
Safety
The investigators said all adverse events (AEs) were reversible by stopping therapy, there were no grade 4 AEs, and none of the patients had grade 3 or higher neuropathy.
“We have not seen an excess of neuropathy, which is very important because both brentuximab and lenalidomide are known to cause neuropathy,” Dr. William said. “So we were fairly concerned that there would be a synergistic neurotoxic effect, which we don’t want, but we haven’t seen that.”
The most common treatment-related AE was neutropenia. Grade 3 neutropenia occurred in four patients.
Other grade 3 AEs, which occurred in patients on the 20 mg dose of len, were thrombocytopenia (n = 1), dyspnea (n = 1), vertigo (n = 1), drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS) syndrome (n = 1), and tumor flare (n = 1).
Three patients discontinued treatment because of AEs — thrombocytopenia, tumor flare, and DRESS syndrome.
Tumor flare and response
“We did see tumor flare in two initial patients treated with the higher dose of lenalidomide, and we had to remove them from the study for their safety,” Dr. William said. “One of them had a full-blown DRESS syndrome. For their safety, we did have to remove them, but both did experience durable remissions after.”
One of the patients with tumor flare, who had MF, didn’t require treatment for 6 months after going off study. The other patient, who had SS, cleared the clone from his blood but developed DRESS syndrome.
In all, three patients achieved a response to treatment. The ALCL patient had a complete response, and two MF patients achieved a partial response.
Two MF patients and one SS patient had stable disease. The remaining four patients — two with MF, one with SS, and one with lymphoproliferative disorder — progressed.
QOL
The investigators used the Skindex-16 to assess the effect of treatment on QOL.
Five of six evaluable patients with CTCL had a 50% or greater reduction in their Skindex-16 scores after two cycles of treatment. In fact, most patients had relief from pruritus after one cycle, Dr. William said.
“Patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, their biggest problem is with the symptom burden, with pruritus,” he said. “They’re really miserable from all the itching they have. They cannot sleep at night. So we’re fairly excited that most of the patients we’ve treated so far had relief from pruritus just after one cycle.”
Dr. William said he and his colleagues are excited about the overall results they have observed with BV-len, although it’s “still pretty early” in the trial. The investigators are planning to enroll a total of 42 patients and may open the trial at a second center.
The study is sponsored by Ohio State University and the lenalidomide is provided by Celgene. Dr. William reported relationships with miRagen Therapeutics, GuidePoint, Kyowa Kirin, and Celgene.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Five of six evaluable CTCL patients had a 50% or greater reduction in their Skindex-16 scores after two cycles of treatment.
Study details: A phase 2 study with results reported for 10 patients.
Disclosures: The study is sponsored by Ohio State University and the lenalidomide is provided by Celgene. The principal investigator reported relationships with miRagen Therapeutics, GuidePoint, Kyowa Kirin, and Celgene.
Are single agents better than chemo for relapsed/refractory PTCL?
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Results from the COMPLETE registry suggest newer single agents may be more effective than combination chemotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
Complete response (CR) rates and median survival times were significantly better among patients who received single agents than among those who received combination therapy.
Although researchers don’t know what is driving these differences in outcomes, they did find that outcomes were best among patients who received single-agent brentuximab vedotin (BV), and a disproportionate number of patients received BV.
The researchers also found that patients who received single-agent therapy were more likely to proceed to stem cell transplant.
Therefore, it’s still unclear if single-agent treatment is superior to combination therapy for relapsed/refractory PTCL, according to Robert Stuver, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Dr. Stuver presented data from the COMPLETE (Comprehensive Oncology Measures for Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Treatment) registry at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
The registry (NCT01110733) enrolled patients newly diagnosed with PTCL. Dr. Stuver presented results among patients who had relapsed after, or were refractory to, upfront therapy and went on to receive single-agent therapy or any combination regimen excluding those single agents. Outcome data were collected for 5 years or until death.
Patients and treatment
There were 26 patients in the combination treatment group — 10 with PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS), 6 with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), 5 with natural killer T-cell lymphoma (NKTL), 3 with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), 1 with enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), and 1 with hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL).
Patients in the combination group received gemcitabine-based therapy (n = 10), ifosfamide-based therapy (n = 7), platinum-based therapy (n = 4), CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone)-like therapy (n = 1), DHAP (dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin; n = 1), and other combinations (n = 3).
There were 31 patients in the single-agent group – 13 with PTCL-NOS, 7 with ALCL, 5 with AITL, 2 with EATL, 2 with NKTL, and 2 with HSTCL.
These patients were treated with BV (n = 12), romidepsin (n = 8), pralatrexate (n = 5), alisertib (n = 3), bendamustine (n = 1), denileukin diftitox (n = 1), and lenalidomide (n = 1).
Response
The CR rates were significantly higher among patients who received single-agent treatment than among those who received combination therapy — 41.4% (12/31) and 19.2% (5/26), respectively (P = .02). The partial response rates were 17.2% (5/31) and 26.9% (7/26), respectively. Rates of stable disease were 3.4% (1/31) and 30.8% (8/26), respectively.
Complete responders in the single-agent arm were treated with BV (n = 7), romidepsin (n = 2), pralatrexate (n = 1), alisertib (n = 1), and bendamustine (n = 1). Four of the patients treated with BV had ALCL.
“We had an enrichment of patients treated with brentuximab,” Dr. Stuver said. “So the obvious question this begs is, ‘Are the favorable results that were seen for single agents over combination therapy solely due to patients treated with brentuximab?’ ”
To investigate, Dr. Stuver and his colleagues compared responses among patients who received BV with patients who received other single agents or combination therapies.
The CR rate was 58.3% (7/12) among BV recipients, 29.4% (5/17) among patients who received other single agents, and 19.2% (5/26) among patients who received combination therapy.
“The takeaway here is that, when you do divide the single-agent group into BV and other single agents, you’re seeing that BV is doing much better than every other group,” Dr. Stuver said. “And all the other single agents are doing somewhat similarly to the combination group, although there’s still a 10% difference, 29% versus 19%.”
Survival
The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly better among patients who received single-agent therapy. The median PFS was 11.7 months in the single-agent group and 6.7 months in the combination group (P = .0197). The median OS was 38.9 months and 17.1 months, respectively (P = .0170).
A factor that may have affected survival is that patients were more likely to undergo stem cell transplant after single-agent therapy (25.8%, 8/31), compared with those who had received combination therapy (7.7%, 2/26).
Another factor that may have affected the survival differences is the enrichment of patients treated with BV.
The researchers found the median PFS was 11.9 months among BV recipients, 10.4 months among patients who received other single agents, and 6.7 months in the combination-therapy group. The median OS was 44.5 months, 19.1 months, and 17.1 months, respectively.
Dr. Stuver said these results suggest there is a role for single agents as first retreatment in the salvage setting. However, this analysis was limited by the small sample size and the enrichment of patients treated with BV.
Larger, randomized studies are needed to identify the “truly superior” treatment strategy for relapsed/refractory PTCL, Dr. Stuver said.
The COMPLETE registry is sponsored by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stuver did not declare any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Results from the COMPLETE registry suggest newer single agents may be more effective than combination chemotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
Complete response (CR) rates and median survival times were significantly better among patients who received single agents than among those who received combination therapy.
Although researchers don’t know what is driving these differences in outcomes, they did find that outcomes were best among patients who received single-agent brentuximab vedotin (BV), and a disproportionate number of patients received BV.
The researchers also found that patients who received single-agent therapy were more likely to proceed to stem cell transplant.
Therefore, it’s still unclear if single-agent treatment is superior to combination therapy for relapsed/refractory PTCL, according to Robert Stuver, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Dr. Stuver presented data from the COMPLETE (Comprehensive Oncology Measures for Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Treatment) registry at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
The registry (NCT01110733) enrolled patients newly diagnosed with PTCL. Dr. Stuver presented results among patients who had relapsed after, or were refractory to, upfront therapy and went on to receive single-agent therapy or any combination regimen excluding those single agents. Outcome data were collected for 5 years or until death.
Patients and treatment
There were 26 patients in the combination treatment group — 10 with PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS), 6 with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), 5 with natural killer T-cell lymphoma (NKTL), 3 with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), 1 with enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), and 1 with hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL).
Patients in the combination group received gemcitabine-based therapy (n = 10), ifosfamide-based therapy (n = 7), platinum-based therapy (n = 4), CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone)-like therapy (n = 1), DHAP (dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin; n = 1), and other combinations (n = 3).
There were 31 patients in the single-agent group – 13 with PTCL-NOS, 7 with ALCL, 5 with AITL, 2 with EATL, 2 with NKTL, and 2 with HSTCL.
These patients were treated with BV (n = 12), romidepsin (n = 8), pralatrexate (n = 5), alisertib (n = 3), bendamustine (n = 1), denileukin diftitox (n = 1), and lenalidomide (n = 1).
Response
The CR rates were significantly higher among patients who received single-agent treatment than among those who received combination therapy — 41.4% (12/31) and 19.2% (5/26), respectively (P = .02). The partial response rates were 17.2% (5/31) and 26.9% (7/26), respectively. Rates of stable disease were 3.4% (1/31) and 30.8% (8/26), respectively.
Complete responders in the single-agent arm were treated with BV (n = 7), romidepsin (n = 2), pralatrexate (n = 1), alisertib (n = 1), and bendamustine (n = 1). Four of the patients treated with BV had ALCL.
“We had an enrichment of patients treated with brentuximab,” Dr. Stuver said. “So the obvious question this begs is, ‘Are the favorable results that were seen for single agents over combination therapy solely due to patients treated with brentuximab?’ ”
To investigate, Dr. Stuver and his colleagues compared responses among patients who received BV with patients who received other single agents or combination therapies.
The CR rate was 58.3% (7/12) among BV recipients, 29.4% (5/17) among patients who received other single agents, and 19.2% (5/26) among patients who received combination therapy.
“The takeaway here is that, when you do divide the single-agent group into BV and other single agents, you’re seeing that BV is doing much better than every other group,” Dr. Stuver said. “And all the other single agents are doing somewhat similarly to the combination group, although there’s still a 10% difference, 29% versus 19%.”
Survival
The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly better among patients who received single-agent therapy. The median PFS was 11.7 months in the single-agent group and 6.7 months in the combination group (P = .0197). The median OS was 38.9 months and 17.1 months, respectively (P = .0170).
A factor that may have affected survival is that patients were more likely to undergo stem cell transplant after single-agent therapy (25.8%, 8/31), compared with those who had received combination therapy (7.7%, 2/26).
Another factor that may have affected the survival differences is the enrichment of patients treated with BV.
The researchers found the median PFS was 11.9 months among BV recipients, 10.4 months among patients who received other single agents, and 6.7 months in the combination-therapy group. The median OS was 44.5 months, 19.1 months, and 17.1 months, respectively.
Dr. Stuver said these results suggest there is a role for single agents as first retreatment in the salvage setting. However, this analysis was limited by the small sample size and the enrichment of patients treated with BV.
Larger, randomized studies are needed to identify the “truly superior” treatment strategy for relapsed/refractory PTCL, Dr. Stuver said.
The COMPLETE registry is sponsored by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stuver did not declare any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Results from the COMPLETE registry suggest newer single agents may be more effective than combination chemotherapy for patients with relapsed/refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL).
Complete response (CR) rates and median survival times were significantly better among patients who received single agents than among those who received combination therapy.
Although researchers don’t know what is driving these differences in outcomes, they did find that outcomes were best among patients who received single-agent brentuximab vedotin (BV), and a disproportionate number of patients received BV.
The researchers also found that patients who received single-agent therapy were more likely to proceed to stem cell transplant.
Therefore, it’s still unclear if single-agent treatment is superior to combination therapy for relapsed/refractory PTCL, according to Robert Stuver, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston.
Dr. Stuver presented data from the COMPLETE (Comprehensive Oncology Measures for Peripheral T-cell Lymphoma Treatment) registry at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
The registry (NCT01110733) enrolled patients newly diagnosed with PTCL. Dr. Stuver presented results among patients who had relapsed after, or were refractory to, upfront therapy and went on to receive single-agent therapy or any combination regimen excluding those single agents. Outcome data were collected for 5 years or until death.
Patients and treatment
There were 26 patients in the combination treatment group — 10 with PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS), 6 with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL), 5 with natural killer T-cell lymphoma (NKTL), 3 with anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL), 1 with enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma (EATL), and 1 with hepatosplenic T-cell lymphoma (HSTCL).
Patients in the combination group received gemcitabine-based therapy (n = 10), ifosfamide-based therapy (n = 7), platinum-based therapy (n = 4), CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone)-like therapy (n = 1), DHAP (dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine, and cisplatin; n = 1), and other combinations (n = 3).
There were 31 patients in the single-agent group – 13 with PTCL-NOS, 7 with ALCL, 5 with AITL, 2 with EATL, 2 with NKTL, and 2 with HSTCL.
These patients were treated with BV (n = 12), romidepsin (n = 8), pralatrexate (n = 5), alisertib (n = 3), bendamustine (n = 1), denileukin diftitox (n = 1), and lenalidomide (n = 1).
Response
The CR rates were significantly higher among patients who received single-agent treatment than among those who received combination therapy — 41.4% (12/31) and 19.2% (5/26), respectively (P = .02). The partial response rates were 17.2% (5/31) and 26.9% (7/26), respectively. Rates of stable disease were 3.4% (1/31) and 30.8% (8/26), respectively.
Complete responders in the single-agent arm were treated with BV (n = 7), romidepsin (n = 2), pralatrexate (n = 1), alisertib (n = 1), and bendamustine (n = 1). Four of the patients treated with BV had ALCL.
“We had an enrichment of patients treated with brentuximab,” Dr. Stuver said. “So the obvious question this begs is, ‘Are the favorable results that were seen for single agents over combination therapy solely due to patients treated with brentuximab?’ ”
To investigate, Dr. Stuver and his colleagues compared responses among patients who received BV with patients who received other single agents or combination therapies.
The CR rate was 58.3% (7/12) among BV recipients, 29.4% (5/17) among patients who received other single agents, and 19.2% (5/26) among patients who received combination therapy.
“The takeaway here is that, when you do divide the single-agent group into BV and other single agents, you’re seeing that BV is doing much better than every other group,” Dr. Stuver said. “And all the other single agents are doing somewhat similarly to the combination group, although there’s still a 10% difference, 29% versus 19%.”
Survival
The median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were significantly better among patients who received single-agent therapy. The median PFS was 11.7 months in the single-agent group and 6.7 months in the combination group (P = .0197). The median OS was 38.9 months and 17.1 months, respectively (P = .0170).
A factor that may have affected survival is that patients were more likely to undergo stem cell transplant after single-agent therapy (25.8%, 8/31), compared with those who had received combination therapy (7.7%, 2/26).
Another factor that may have affected the survival differences is the enrichment of patients treated with BV.
The researchers found the median PFS was 11.9 months among BV recipients, 10.4 months among patients who received other single agents, and 6.7 months in the combination-therapy group. The median OS was 44.5 months, 19.1 months, and 17.1 months, respectively.
Dr. Stuver said these results suggest there is a role for single agents as first retreatment in the salvage setting. However, this analysis was limited by the small sample size and the enrichment of patients treated with BV.
Larger, randomized studies are needed to identify the “truly superior” treatment strategy for relapsed/refractory PTCL, Dr. Stuver said.
The COMPLETE registry is sponsored by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stuver did not declare any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The complete response rate was significantly higher among patients who received single-agent treatment than it was among those who received combination therapy – 41.4% and 19.2%, respectively (P = .02).
Study details: Analysis of 57 patients with relapsed/refractory PTCL in the COMPLETE registry.
Disclosures: The COMPLETE registry is sponsored by Spectrum Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Stuver did not declare any conflicts of interest.
Four-drug combo shows durable responses in relapsed/refractory lymphomas
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Results of a phase 1 trial suggest a four-drug combination can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory T- and B-cell lymphomas.
Seven of 15 patients responded to treatment with romidepsin, gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone, including six patients who achieved a complete response (CR).
The median duration of response was 8.5 months, and three patients had responses lasting more than 24 months.
Patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) in particular responded well to the combination.
Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis, and her colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
“[I]t was thought that the addition of histone deacetylase inhibitors to traditional platinum-based chemotherapies, which tend to cause DNA damage, would increase the response of platinum-based therapies,” Dr. Shah said.
With that in mind, she and her colleagues added romidepsin to gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone and evaluated this combination in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphomas.
The trial (NCT02181218) enrolled 15 patients — 6 with peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), 6 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and 3 with AITL.
The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 55-83), and they had received a median of 2 (range, 1-4) prior therapies.
The researchers tested three dose levels of romidepsin — 8 mg/m2, 10 mg/m2, and 12 mg/m2 — given on day 2 of a 21-day cycle. The study originally included romidepsin on day 8 as well. However, the researchers discontinued the day 8 dose after patients developed grade 4 thrombocytopenia.
Patients also received gemcitabine at 1,000 mg/m2 (day 1), oxaliplatin at 100 mg/m2 (day 1), and dexamethasone at 20 mg (days 1-4). All patients received pegfilgrastim at 6 mg (day 3) as well.
The patients could receive up to eight cycles of treatment if they had stable disease or better and did not experience significant toxicity.
Safety
There was one dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) — pneumonia — at the 8 mg/m2 dose of romidepsin (given on days 2 and 8). There was one DLT — bleeding — at the 10 mg/m2 dose (day 2 only).
Two patients experienced DLTs — neutropenic fever and grade 4 thrombocytopenia — at the 12 mg/m2 dose (day 2 only).
Based on these events, 10 mg/m2 was considered the maximum-tolerated dose of romidepsin.
The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were thrombocytopenia (n = 13), electrolyte abnormalities (n = 12), liver function abnormalities (n = 10), anemia (n = 9), neutropenia (n = 8), fatigue (n = 7), nausea (n = 7), and creatinine increase (n = 5).
Grade 3/4 AEs included thrombocytopenia (n = 13), neutropenia (n = 5), anemia (n = 3), hyperglycemia (n = 2), hyperuricemia (n = 2), febrile neutropenia (n = 1), tumor lysis syndrome (n = 1), vomiting (n = 1), peripheral sensory neuropathy (n = 1), pneumonia (n = 1), sepsis (n = 1), bleeding (n = 1), and elevated troponin (n = 1).
Serious AEs requiring hospitalization included pneumonia (n = 1), nausea and vomiting (n = 1), tumor lysis syndrome (n = 1), and complications of disease progression (n = 4).
Efficacy
The overall response rate was 47% (7/15). CRs occurred in all three patients with AITL and two patients with DLBCL. One patient with PTCL-NOS had a CR, and one had a partial response.
The median duration of response was 8.5 months (range, 1.2-36.6 months). Four patients remain in CR — two with AITL, one with PTCL-NOS, and one with DLBCL.
Dr. Shah noted that the CRs in the AITL patients “have been quite prolonged.” One patient had a CR lasting 27 months, and another had a CR lasting 29 months.
Dr. Shah said these results are particularly exciting because patients discontinued study treatment after eight cycles or two cycles after they achieved a CR.
“[S]ome of these patients remained in remission for 2 years without any therapy thereafter, which is quite impressive in a population where the median survival — for patients with relapsed/refractory AITL — is thought to be 6-10 months,” Dr. Shah said.
She noted that this study is ongoing with an expansion cohort of patients with T-cell lymphomas.
This research was supported by Celgene. Dr. Shah reported relationships with Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Verastem, and Genentech.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Results of a phase 1 trial suggest a four-drug combination can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory T- and B-cell lymphomas.
Seven of 15 patients responded to treatment with romidepsin, gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone, including six patients who achieved a complete response (CR).
The median duration of response was 8.5 months, and three patients had responses lasting more than 24 months.
Patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) in particular responded well to the combination.
Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis, and her colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
“[I]t was thought that the addition of histone deacetylase inhibitors to traditional platinum-based chemotherapies, which tend to cause DNA damage, would increase the response of platinum-based therapies,” Dr. Shah said.
With that in mind, she and her colleagues added romidepsin to gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone and evaluated this combination in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphomas.
The trial (NCT02181218) enrolled 15 patients — 6 with peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), 6 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and 3 with AITL.
The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 55-83), and they had received a median of 2 (range, 1-4) prior therapies.
The researchers tested three dose levels of romidepsin — 8 mg/m2, 10 mg/m2, and 12 mg/m2 — given on day 2 of a 21-day cycle. The study originally included romidepsin on day 8 as well. However, the researchers discontinued the day 8 dose after patients developed grade 4 thrombocytopenia.
Patients also received gemcitabine at 1,000 mg/m2 (day 1), oxaliplatin at 100 mg/m2 (day 1), and dexamethasone at 20 mg (days 1-4). All patients received pegfilgrastim at 6 mg (day 3) as well.
The patients could receive up to eight cycles of treatment if they had stable disease or better and did not experience significant toxicity.
Safety
There was one dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) — pneumonia — at the 8 mg/m2 dose of romidepsin (given on days 2 and 8). There was one DLT — bleeding — at the 10 mg/m2 dose (day 2 only).
Two patients experienced DLTs — neutropenic fever and grade 4 thrombocytopenia — at the 12 mg/m2 dose (day 2 only).
Based on these events, 10 mg/m2 was considered the maximum-tolerated dose of romidepsin.
The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were thrombocytopenia (n = 13), electrolyte abnormalities (n = 12), liver function abnormalities (n = 10), anemia (n = 9), neutropenia (n = 8), fatigue (n = 7), nausea (n = 7), and creatinine increase (n = 5).
Grade 3/4 AEs included thrombocytopenia (n = 13), neutropenia (n = 5), anemia (n = 3), hyperglycemia (n = 2), hyperuricemia (n = 2), febrile neutropenia (n = 1), tumor lysis syndrome (n = 1), vomiting (n = 1), peripheral sensory neuropathy (n = 1), pneumonia (n = 1), sepsis (n = 1), bleeding (n = 1), and elevated troponin (n = 1).
Serious AEs requiring hospitalization included pneumonia (n = 1), nausea and vomiting (n = 1), tumor lysis syndrome (n = 1), and complications of disease progression (n = 4).
Efficacy
The overall response rate was 47% (7/15). CRs occurred in all three patients with AITL and two patients with DLBCL. One patient with PTCL-NOS had a CR, and one had a partial response.
The median duration of response was 8.5 months (range, 1.2-36.6 months). Four patients remain in CR — two with AITL, one with PTCL-NOS, and one with DLBCL.
Dr. Shah noted that the CRs in the AITL patients “have been quite prolonged.” One patient had a CR lasting 27 months, and another had a CR lasting 29 months.
Dr. Shah said these results are particularly exciting because patients discontinued study treatment after eight cycles or two cycles after they achieved a CR.
“[S]ome of these patients remained in remission for 2 years without any therapy thereafter, which is quite impressive in a population where the median survival — for patients with relapsed/refractory AITL — is thought to be 6-10 months,” Dr. Shah said.
She noted that this study is ongoing with an expansion cohort of patients with T-cell lymphomas.
This research was supported by Celgene. Dr. Shah reported relationships with Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Verastem, and Genentech.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. — Results of a phase 1 trial suggest a four-drug combination can produce durable responses in patients with relapsed or refractory T- and B-cell lymphomas.
Seven of 15 patients responded to treatment with romidepsin, gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone, including six patients who achieved a complete response (CR).
The median duration of response was 8.5 months, and three patients had responses lasting more than 24 months.
Patients with angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) in particular responded well to the combination.
Neha Mehta-Shah, MD, of Washington University in St. Louis, and her colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
“[I]t was thought that the addition of histone deacetylase inhibitors to traditional platinum-based chemotherapies, which tend to cause DNA damage, would increase the response of platinum-based therapies,” Dr. Shah said.
With that in mind, she and her colleagues added romidepsin to gemcitabine, oxaliplatin, and dexamethasone and evaluated this combination in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphomas.
The trial (NCT02181218) enrolled 15 patients — 6 with peripheral T-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (PTCL-NOS), 6 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and 3 with AITL.
The patients’ median age was 66 (range, 55-83), and they had received a median of 2 (range, 1-4) prior therapies.
The researchers tested three dose levels of romidepsin — 8 mg/m2, 10 mg/m2, and 12 mg/m2 — given on day 2 of a 21-day cycle. The study originally included romidepsin on day 8 as well. However, the researchers discontinued the day 8 dose after patients developed grade 4 thrombocytopenia.
Patients also received gemcitabine at 1,000 mg/m2 (day 1), oxaliplatin at 100 mg/m2 (day 1), and dexamethasone at 20 mg (days 1-4). All patients received pegfilgrastim at 6 mg (day 3) as well.
The patients could receive up to eight cycles of treatment if they had stable disease or better and did not experience significant toxicity.
Safety
There was one dose-limiting toxicity (DLT) — pneumonia — at the 8 mg/m2 dose of romidepsin (given on days 2 and 8). There was one DLT — bleeding — at the 10 mg/m2 dose (day 2 only).
Two patients experienced DLTs — neutropenic fever and grade 4 thrombocytopenia — at the 12 mg/m2 dose (day 2 only).
Based on these events, 10 mg/m2 was considered the maximum-tolerated dose of romidepsin.
The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were thrombocytopenia (n = 13), electrolyte abnormalities (n = 12), liver function abnormalities (n = 10), anemia (n = 9), neutropenia (n = 8), fatigue (n = 7), nausea (n = 7), and creatinine increase (n = 5).
Grade 3/4 AEs included thrombocytopenia (n = 13), neutropenia (n = 5), anemia (n = 3), hyperglycemia (n = 2), hyperuricemia (n = 2), febrile neutropenia (n = 1), tumor lysis syndrome (n = 1), vomiting (n = 1), peripheral sensory neuropathy (n = 1), pneumonia (n = 1), sepsis (n = 1), bleeding (n = 1), and elevated troponin (n = 1).
Serious AEs requiring hospitalization included pneumonia (n = 1), nausea and vomiting (n = 1), tumor lysis syndrome (n = 1), and complications of disease progression (n = 4).
Efficacy
The overall response rate was 47% (7/15). CRs occurred in all three patients with AITL and two patients with DLBCL. One patient with PTCL-NOS had a CR, and one had a partial response.
The median duration of response was 8.5 months (range, 1.2-36.6 months). Four patients remain in CR — two with AITL, one with PTCL-NOS, and one with DLBCL.
Dr. Shah noted that the CRs in the AITL patients “have been quite prolonged.” One patient had a CR lasting 27 months, and another had a CR lasting 29 months.
Dr. Shah said these results are particularly exciting because patients discontinued study treatment after eight cycles or two cycles after they achieved a CR.
“[S]ome of these patients remained in remission for 2 years without any therapy thereafter, which is quite impressive in a population where the median survival — for patients with relapsed/refractory AITL — is thought to be 6-10 months,” Dr. Shah said.
She noted that this study is ongoing with an expansion cohort of patients with T-cell lymphomas.
This research was supported by Celgene. Dr. Shah reported relationships with Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Verastem, and Genentech.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Seven patients responded, and three patients had responses lasting more than 24 months.
Study details: Phase 1 trial of 15 patients.
Disclosures: This research was supported by Celgene. The presenter reported relationships with Celgene, Kyowa Kirin, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Verastem, and Genentech.
Zanubrutinib receives breakthrough designation for MCL
The (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed by BeiGene as a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies.
Researchers have evaluated zanubrutinib in a phase 2 trial (NCT03206970) of patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 148).
As of March 27, 2018, 86 patients had been enrolled in the trial and received treatment. They had a median of two prior lines of therapy and they received zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily.
Eighty-five patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 83.5% (71/85), and the complete response rate was 58.8% (50/85). At a median follow-up of 24.1 weeks, the median duration of response and median progression-free survival had not been reached. The estimated 24-week progression-free survival rate was 82%. The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were decrease in neutrophil count (31.4%), rash (29.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (29.1%), and decrease in platelet count (22.1%). Common grade 3 or higher AEs included neutrophil count decrease (11.6%) and lung infection (5.8%).
Four patients had fatal treatment-emergent AEs. One death was caused by a traffic accident, one was due to cerebral hemorrhage, and one resulted from pneumonia. The fourth death occurred in a patient with infection, but the cause of death was unknown.
Breakthrough therapy designation is designed to expedite the development and review of a therapy for a serious or life-threatening disease, following preliminary clinical evidence indicating it demonstrates substantial improvement over existing therapies.
The (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed by BeiGene as a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies.
Researchers have evaluated zanubrutinib in a phase 2 trial (NCT03206970) of patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 148).
As of March 27, 2018, 86 patients had been enrolled in the trial and received treatment. They had a median of two prior lines of therapy and they received zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily.
Eighty-five patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 83.5% (71/85), and the complete response rate was 58.8% (50/85). At a median follow-up of 24.1 weeks, the median duration of response and median progression-free survival had not been reached. The estimated 24-week progression-free survival rate was 82%. The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were decrease in neutrophil count (31.4%), rash (29.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (29.1%), and decrease in platelet count (22.1%). Common grade 3 or higher AEs included neutrophil count decrease (11.6%) and lung infection (5.8%).
Four patients had fatal treatment-emergent AEs. One death was caused by a traffic accident, one was due to cerebral hemorrhage, and one resulted from pneumonia. The fourth death occurred in a patient with infection, but the cause of death was unknown.
Breakthrough therapy designation is designed to expedite the development and review of a therapy for a serious or life-threatening disease, following preliminary clinical evidence indicating it demonstrates substantial improvement over existing therapies.
The (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed by BeiGene as a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies.
Researchers have evaluated zanubrutinib in a phase 2 trial (NCT03206970) of patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 148).
As of March 27, 2018, 86 patients had been enrolled in the trial and received treatment. They had a median of two prior lines of therapy and they received zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily.
Eighty-five patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 83.5% (71/85), and the complete response rate was 58.8% (50/85). At a median follow-up of 24.1 weeks, the median duration of response and median progression-free survival had not been reached. The estimated 24-week progression-free survival rate was 82%. The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were decrease in neutrophil count (31.4%), rash (29.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (29.1%), and decrease in platelet count (22.1%). Common grade 3 or higher AEs included neutrophil count decrease (11.6%) and lung infection (5.8%).
Four patients had fatal treatment-emergent AEs. One death was caused by a traffic accident, one was due to cerebral hemorrhage, and one resulted from pneumonia. The fourth death occurred in a patient with infection, but the cause of death was unknown.
Breakthrough therapy designation is designed to expedite the development and review of a therapy for a serious or life-threatening disease, following preliminary clinical evidence indicating it demonstrates substantial improvement over existing therapies.
Chidamide may be more effective in PTCL than previously thought
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Real-world data suggest chidamide may be more effective against relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) than a pivotal study indicated.
Single-agent chidamide produced an overall response rate of 47.0% in a real-world study of more than 1,000 patients, compared with the 28.0% overall response rate that was observed in the phase 2 study of chidamide (Ann Oncol. 2015 Aug;26[8]:1766-71).
Yuqin Song, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute in Beijing, China, presented data from the real-world study at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Song said this study is the largest cohort of real-world patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL. She and her colleagues analyzed data on 1,064 patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
The patients had a median age of 54 years, 63.9% were male, and 88.1% had stage III-IV disease.
Disease subtypes included PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS, 38.0%), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, 29.1%), extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL, 13.4%), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL, 9.1%), and others (10.3%), including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
Fifty-two percent of patients (n = 553) received chidamide as a single agent, and 48% (n = 511) received the drug with other agents. The most common treatment regimens combined with chidamide were the following
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP, 20.7%).
- Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP, 11.8%).
- Etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH, 9.8%).
- Patients with ENKTL received chidamide with L-asparaginase (35.4%) or without it (64.5%).
The median follow-up was 4.9 months (range, 0-36.2 months). Across disease subtypes, the overall response rate was 47.0% with single-agent chidamide and 65.4% when chidamide was given in combination with other agents (P less than .01).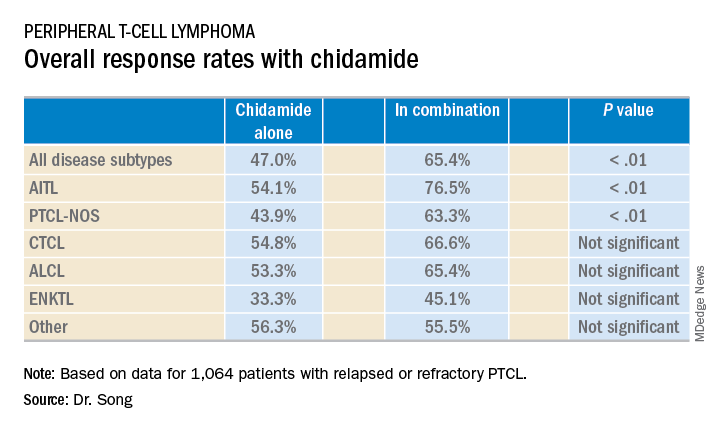
The median overall survival was 400 days for all patients, 342 days for patients treated with chidamide alone, and 457 days for patients who received combination therapy. The 1-year overall survival rates were 52%, 48%, and 56%, respectively.
Dr. Song said these data verify the efficacy of chidamide as a single agent and suggest chidamide might lead to improved survival in refractory or relapsed PTCLs.
Chidamide was generally well tolerated in this study, Dr. Song said. There were no unexpected adverse events (AEs) and most were grade 1 or 2.
The most common AEs (of any grade) observed with single-agent chidamide were neutropenia (42.9%), thrombocytopenia (40.5%), fatigue (38.3%), anemia (31.6%), and nausea/vomiting (21.0%).
The most common AEs observed with chidamide in combination were neutropenia (61.4%), thrombocytopenia (58.5%), fatigue (56.2%), anemia (54.2%), nausea/vomiting (30.7%), and fever (22.1%).
This study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Real-world data suggest chidamide may be more effective against relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) than a pivotal study indicated.
Single-agent chidamide produced an overall response rate of 47.0% in a real-world study of more than 1,000 patients, compared with the 28.0% overall response rate that was observed in the phase 2 study of chidamide (Ann Oncol. 2015 Aug;26[8]:1766-71).
Yuqin Song, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute in Beijing, China, presented data from the real-world study at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Song said this study is the largest cohort of real-world patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL. She and her colleagues analyzed data on 1,064 patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
The patients had a median age of 54 years, 63.9% were male, and 88.1% had stage III-IV disease.
Disease subtypes included PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS, 38.0%), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, 29.1%), extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL, 13.4%), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL, 9.1%), and others (10.3%), including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
Fifty-two percent of patients (n = 553) received chidamide as a single agent, and 48% (n = 511) received the drug with other agents. The most common treatment regimens combined with chidamide were the following
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP, 20.7%).
- Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP, 11.8%).
- Etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH, 9.8%).
- Patients with ENKTL received chidamide with L-asparaginase (35.4%) or without it (64.5%).
The median follow-up was 4.9 months (range, 0-36.2 months). Across disease subtypes, the overall response rate was 47.0% with single-agent chidamide and 65.4% when chidamide was given in combination with other agents (P less than .01).
The median overall survival was 400 days for all patients, 342 days for patients treated with chidamide alone, and 457 days for patients who received combination therapy. The 1-year overall survival rates were 52%, 48%, and 56%, respectively.
Dr. Song said these data verify the efficacy of chidamide as a single agent and suggest chidamide might lead to improved survival in refractory or relapsed PTCLs.
Chidamide was generally well tolerated in this study, Dr. Song said. There were no unexpected adverse events (AEs) and most were grade 1 or 2.
The most common AEs (of any grade) observed with single-agent chidamide were neutropenia (42.9%), thrombocytopenia (40.5%), fatigue (38.3%), anemia (31.6%), and nausea/vomiting (21.0%).
The most common AEs observed with chidamide in combination were neutropenia (61.4%), thrombocytopenia (58.5%), fatigue (56.2%), anemia (54.2%), nausea/vomiting (30.7%), and fever (22.1%).
This study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Real-world data suggest chidamide may be more effective against relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) than a pivotal study indicated.
Single-agent chidamide produced an overall response rate of 47.0% in a real-world study of more than 1,000 patients, compared with the 28.0% overall response rate that was observed in the phase 2 study of chidamide (Ann Oncol. 2015 Aug;26[8]:1766-71).
Yuqin Song, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute in Beijing, China, presented data from the real-world study at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Song said this study is the largest cohort of real-world patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL. She and her colleagues analyzed data on 1,064 patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
The patients had a median age of 54 years, 63.9% were male, and 88.1% had stage III-IV disease.
Disease subtypes included PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS, 38.0%), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, 29.1%), extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL, 13.4%), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL, 9.1%), and others (10.3%), including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
Fifty-two percent of patients (n = 553) received chidamide as a single agent, and 48% (n = 511) received the drug with other agents. The most common treatment regimens combined with chidamide were the following
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP, 20.7%).
- Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP, 11.8%).
- Etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH, 9.8%).
- Patients with ENKTL received chidamide with L-asparaginase (35.4%) or without it (64.5%).
The median follow-up was 4.9 months (range, 0-36.2 months). Across disease subtypes, the overall response rate was 47.0% with single-agent chidamide and 65.4% when chidamide was given in combination with other agents (P less than .01).
The median overall survival was 400 days for all patients, 342 days for patients treated with chidamide alone, and 457 days for patients who received combination therapy. The 1-year overall survival rates were 52%, 48%, and 56%, respectively.
Dr. Song said these data verify the efficacy of chidamide as a single agent and suggest chidamide might lead to improved survival in refractory or relapsed PTCLs.
Chidamide was generally well tolerated in this study, Dr. Song said. There were no unexpected adverse events (AEs) and most were grade 1 or 2.
The most common AEs (of any grade) observed with single-agent chidamide were neutropenia (42.9%), thrombocytopenia (40.5%), fatigue (38.3%), anemia (31.6%), and nausea/vomiting (21.0%).
The most common AEs observed with chidamide in combination were neutropenia (61.4%), thrombocytopenia (58.5%), fatigue (56.2%), anemia (54.2%), nausea/vomiting (30.7%), and fever (22.1%).
This study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Single-agent chidamide had an overall response rate of 47.0% among relapsed/refractory PTCL patients, compared with 65.4% when used in combination with other agents (P less than .01).
Study details: A real-world cohort of 1,064 relapsed/refractory PTCL patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
Adding umbralisib to ibrutinib produced responses in MCL, CLL
Dual B-cell receptor pathway blockade was tolerable and efficacious for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who participated in a multicenter phase 1-1b clinical study that added umbralisib to ibrutinib.
The study “is the first successful combination for two drugs targeting the B-cell receptor pathway,” Matthew S. Davids, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and his colleagues wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
Of the 21 patients with CLL, 90% (n = 19) achieved an overall response (OR), 62% (n = 13) achieved partial response (PR) or PR with lymphocytosis, and 29% (n = 6) achieved complete response (CR). All patients in complete response still had minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow. No CLL patients had progressive disease.
Of the 21 patients with MCL, 67% (n = 14) had an OR, with 19% (n = 4) showing CR and 48% (n = 10) achieving partial response. Three MCL patients (14%) had progressive disease.
Umbralisib is a next-generation phosphoinositide-3-kinase-delta inhibitor that, when added to the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) ibrutinib, offers once-daily oral dosing. The combination affords the possibility of overcoming the resistance that can come with prolonged ibrutinib monotherapy.
A total of 44 patients were enrolled, and 42 patients (21 with CLL and 21 with MCL) received at least one dose of the study drug and were included in the analysis. At enrollment, patients had received a median of two previous therapies.
Diarrhea was the most frequent adverse event, seen in 22 patients (52%), and half of all patients (n = 21) had infections.
Hematologic toxicities included neutropenia, seen in 9 (43%) of the CLL patients and 8 (38%) of the MCL patients; thrombocytopenia, seen in 6 (29%) of the CLL patients and 10 (48%) of the MCL patients; and anemia, seen in 4 (19%) of the CLL and 9 (43%) of the MCL patients. Grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicities of any type were less common, occurring in less than 20% of patients. One MCL patient developed febrile neutropenia. According to the study investigators, none of the hematologic toxicities were deemed related to the study drugs.
Adverse events did not appear to be dose-dependent for umbralisib, with the maximum tolerated dose not reached in the study, the investigators wrote. For phase 2 trials, the recommended dose of umbralisib is 800 mg given orally once daily in combination with ibrutinib.
“One unanticipated benefit of doublet B-cell receptor pathway inhibition in this study was the ability to continue one drug when a characteristic toxicity required the other drug to be held,” the investigators wrote.
For MCL patients, 67% achieved OR and 19% achieved CR, figures similar to those reported for ibrutinib monotherapy. However, “the 2-year progression-free survival of 49% and overall survival of 58% suggest that patients who made it to 1 year progression-free had few events during the second year on therapy,” the investigators wrote. They also noted that this MCL population was high risk; more than one-quarter of patients had relapsed after prior autologous stem cell transplantation.
The study was limited by small sample size and a short duration of follow-up, so durability of response can’t yet be assessed. Also, neither pharmacokinetics nor resistance mutations were tracked for participants.
Currently, the doublet regimen is designed to be continuous therapy, and although it’s not known whether this regimen would be effective as time-limited therapy, it’s unlikely because 100% of patients who had CR still had detectable minimal residual disease, the investigators noted.
Umbralisib and ibrutinib are also being explored as part of triplet therapy, with the type 2 CD20 antibody ublituximab, for relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (NCT02006485).
“These novel drug-based approaches, along with several others in development, hold promise as highly effective and well-tolerated regimens with the potential to substantially improve outcomes for patients with B-cell malignancies,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by TG Therapeutics and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Therapy Accelerator Program. The authors reported financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including TG Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Davids MS et al. Lancet Haemtol. 2019;6:e38-47.
Dual B-cell receptor pathway blockade was tolerable and efficacious for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who participated in a multicenter phase 1-1b clinical study that added umbralisib to ibrutinib.
The study “is the first successful combination for two drugs targeting the B-cell receptor pathway,” Matthew S. Davids, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and his colleagues wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
Of the 21 patients with CLL, 90% (n = 19) achieved an overall response (OR), 62% (n = 13) achieved partial response (PR) or PR with lymphocytosis, and 29% (n = 6) achieved complete response (CR). All patients in complete response still had minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow. No CLL patients had progressive disease.
Of the 21 patients with MCL, 67% (n = 14) had an OR, with 19% (n = 4) showing CR and 48% (n = 10) achieving partial response. Three MCL patients (14%) had progressive disease.
Umbralisib is a next-generation phosphoinositide-3-kinase-delta inhibitor that, when added to the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) ibrutinib, offers once-daily oral dosing. The combination affords the possibility of overcoming the resistance that can come with prolonged ibrutinib monotherapy.
A total of 44 patients were enrolled, and 42 patients (21 with CLL and 21 with MCL) received at least one dose of the study drug and were included in the analysis. At enrollment, patients had received a median of two previous therapies.
Diarrhea was the most frequent adverse event, seen in 22 patients (52%), and half of all patients (n = 21) had infections.
Hematologic toxicities included neutropenia, seen in 9 (43%) of the CLL patients and 8 (38%) of the MCL patients; thrombocytopenia, seen in 6 (29%) of the CLL patients and 10 (48%) of the MCL patients; and anemia, seen in 4 (19%) of the CLL and 9 (43%) of the MCL patients. Grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicities of any type were less common, occurring in less than 20% of patients. One MCL patient developed febrile neutropenia. According to the study investigators, none of the hematologic toxicities were deemed related to the study drugs.
Adverse events did not appear to be dose-dependent for umbralisib, with the maximum tolerated dose not reached in the study, the investigators wrote. For phase 2 trials, the recommended dose of umbralisib is 800 mg given orally once daily in combination with ibrutinib.
“One unanticipated benefit of doublet B-cell receptor pathway inhibition in this study was the ability to continue one drug when a characteristic toxicity required the other drug to be held,” the investigators wrote.
For MCL patients, 67% achieved OR and 19% achieved CR, figures similar to those reported for ibrutinib monotherapy. However, “the 2-year progression-free survival of 49% and overall survival of 58% suggest that patients who made it to 1 year progression-free had few events during the second year on therapy,” the investigators wrote. They also noted that this MCL population was high risk; more than one-quarter of patients had relapsed after prior autologous stem cell transplantation.
The study was limited by small sample size and a short duration of follow-up, so durability of response can’t yet be assessed. Also, neither pharmacokinetics nor resistance mutations were tracked for participants.
Currently, the doublet regimen is designed to be continuous therapy, and although it’s not known whether this regimen would be effective as time-limited therapy, it’s unlikely because 100% of patients who had CR still had detectable minimal residual disease, the investigators noted.
Umbralisib and ibrutinib are also being explored as part of triplet therapy, with the type 2 CD20 antibody ublituximab, for relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (NCT02006485).
“These novel drug-based approaches, along with several others in development, hold promise as highly effective and well-tolerated regimens with the potential to substantially improve outcomes for patients with B-cell malignancies,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by TG Therapeutics and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Therapy Accelerator Program. The authors reported financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including TG Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Davids MS et al. Lancet Haemtol. 2019;6:e38-47.
Dual B-cell receptor pathway blockade was tolerable and efficacious for patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who participated in a multicenter phase 1-1b clinical study that added umbralisib to ibrutinib.
The study “is the first successful combination for two drugs targeting the B-cell receptor pathway,” Matthew S. Davids, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston and his colleagues wrote in the Lancet Haematology.
Of the 21 patients with CLL, 90% (n = 19) achieved an overall response (OR), 62% (n = 13) achieved partial response (PR) or PR with lymphocytosis, and 29% (n = 6) achieved complete response (CR). All patients in complete response still had minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow. No CLL patients had progressive disease.
Of the 21 patients with MCL, 67% (n = 14) had an OR, with 19% (n = 4) showing CR and 48% (n = 10) achieving partial response. Three MCL patients (14%) had progressive disease.
Umbralisib is a next-generation phosphoinositide-3-kinase-delta inhibitor that, when added to the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor (BTKi) ibrutinib, offers once-daily oral dosing. The combination affords the possibility of overcoming the resistance that can come with prolonged ibrutinib monotherapy.
A total of 44 patients were enrolled, and 42 patients (21 with CLL and 21 with MCL) received at least one dose of the study drug and were included in the analysis. At enrollment, patients had received a median of two previous therapies.
Diarrhea was the most frequent adverse event, seen in 22 patients (52%), and half of all patients (n = 21) had infections.
Hematologic toxicities included neutropenia, seen in 9 (43%) of the CLL patients and 8 (38%) of the MCL patients; thrombocytopenia, seen in 6 (29%) of the CLL patients and 10 (48%) of the MCL patients; and anemia, seen in 4 (19%) of the CLL and 9 (43%) of the MCL patients. Grade 3 and 4 hematologic toxicities of any type were less common, occurring in less than 20% of patients. One MCL patient developed febrile neutropenia. According to the study investigators, none of the hematologic toxicities were deemed related to the study drugs.
Adverse events did not appear to be dose-dependent for umbralisib, with the maximum tolerated dose not reached in the study, the investigators wrote. For phase 2 trials, the recommended dose of umbralisib is 800 mg given orally once daily in combination with ibrutinib.
“One unanticipated benefit of doublet B-cell receptor pathway inhibition in this study was the ability to continue one drug when a characteristic toxicity required the other drug to be held,” the investigators wrote.
For MCL patients, 67% achieved OR and 19% achieved CR, figures similar to those reported for ibrutinib monotherapy. However, “the 2-year progression-free survival of 49% and overall survival of 58% suggest that patients who made it to 1 year progression-free had few events during the second year on therapy,” the investigators wrote. They also noted that this MCL population was high risk; more than one-quarter of patients had relapsed after prior autologous stem cell transplantation.
The study was limited by small sample size and a short duration of follow-up, so durability of response can’t yet be assessed. Also, neither pharmacokinetics nor resistance mutations were tracked for participants.
Currently, the doublet regimen is designed to be continuous therapy, and although it’s not known whether this regimen would be effective as time-limited therapy, it’s unlikely because 100% of patients who had CR still had detectable minimal residual disease, the investigators noted.
Umbralisib and ibrutinib are also being explored as part of triplet therapy, with the type 2 CD20 antibody ublituximab, for relapsed or refractory B-cell malignancies (NCT02006485).
“These novel drug-based approaches, along with several others in development, hold promise as highly effective and well-tolerated regimens with the potential to substantially improve outcomes for patients with B-cell malignancies,” the investigators wrote.
The study was supported by TG Therapeutics and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Therapy Accelerator Program. The authors reported financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including TG Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Davids MS et al. Lancet Haemtol. 2019;6:e38-47.
FROM LANCET HAEMATOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Of CLL patients, 90% achieved an overall response.
Study details: Phase 1-1b trial of umbralisib and ibrutinib in patients with relapsed or refractory MCL or CLL.
Disclosures: The study was supported by TG Therapeutics and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Therapy Accelerator Program. Dr. Davids and his coauthors reported financial relationships with several pharmaceutical companies, including TG Therapeutics.
Source: Davids MS et al. Lancet Haematol. 2019;6:e38-47.








