User login
The march of immunotherapy continues at ESMO 2020
The use of immunotherapy for upper gastrointestinal tumors and renal cancer, ALK- and EGFR-targeted agents in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and the next step in personalized prostate cancer management will all be subjects of headlining presentations at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
The conference will, like so many other major events, be held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
John B. Haanen, PhD, ESMO 2020 scientific chair, who is from the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, told Medscape Medical News that, because the congress is being held online this year, fewer abstracts were submitted; nevertheless, “We were very happy to see ... that the quality was very good.”
The number of submissions was not the only problem the organizing committee had to face in transforming the ESMO Congress into a virtual meeting.
They were unable to fit the scientific and educational programs together and so have had to split them over two consecutive weekends. Moreover, many of the sessions were highly interactive and needed to be either adapted or omitted.
“So the program is somewhat different,” Haanen said. He noted that “the presentations were also made shorter, especially on the educational sessions, because...we can’t expect people to sit behind screens for hours listening to long presentations.”
He added: “That was out of the question.”
Haanen is nevertheless hopeful that the virtual meeting will be “very exciting.”
Solange Peters, MD, PhD, ESMO president, who is also affiliated with the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois, Lausanne, Switzerland, said in a press conference that it was a “sacrifice” to move ESMO 2020 online and that “there were very sad moments” when deciding on the content.
However, there were some benefits from the change.
She said that all of the ESMO meetings this year have seen “huge” increases in the number of attendees and the geographical span or reach of each of the conferences.
“So suddenly you also realize that, what is one of the missions of ESMO being to convey education globally ... was probably better reached, better achieved with the virtual format,” she commented.
Presidential symposia
Turning to the program, Haanen first picked out the third presidential symposium, which will be held on Monday, September 21. This will focus entirely on upper gastrointestinal tumors in both the adjuvant and metastatic setting.
He said that in recent years, “very little progress has been made” in this area, with treatment mostly consisting of chemotherapy and chemoradiotherapy.
However, this year’s presentations will explore the addition of immunotherapy either to chemotherapy or as an adjuvant treatment following completion of standard-of-care treatment for local disease.
Haanen said that the results will be “very interesting ... and may change current practice,” something that “is very important for both doctors and their patients.”
On Saturday, September 19, the first presidential symposium will include two presentations on lung cancer that Haanen said will offer some “exciting new [results] that I am sure will change clinical practice.”
One will be on the CROWN phase 3 trial comparing lorlatinib and crizotinib in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC.
The other will present results on central nervous system disease recurrence from the ADAURA phase 3 trial of osimertinib adjuvant therapy in patients with resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
The same session will also see new data in advanced renal cell carcinoma from CheckMate 9ER, in which the c-Met and VEGFR2 inhibitor cabozantinib (Cabometyx) was combined with nivolumab (Opdivo) and compared to sunitinib (Sutent) in untreated patients.
“Last year, there were already some exciting results of the combination of axitinib [Inlyta], either with pembrolizumab [Keytruda] or with avelumab [Bavencio]...in the first-line setting in metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer,” Hannen said.
“Clearly there was a survival advantage over the standard of care, sunitinib,” he added.
This year, not only will efficacy data from CheckMate 9ER be presented but also quality-of-life results.
“That’s very important, because what everybody is afraid of is that, by adding drugs, you always get more impact on the quality of life, but you will see that the quality-of-life results are very exciting,” he said.
The second presidential symposium will feature studies on prostate cancer, notably the phase 3 IPATential150 trial of abiraterone (Zytiga) plus either ipatasertib or placebo in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Ipatasertib targets Akt, and Haanen said that “by adding it to, let’s say, standard-of-care treatment ... the question of course of will be, Does that have a better outcome?”
He believes the results will be a “very nice illustration” that prostate cancer management is heading in the direction of personalized treatment.
Alongside the presidential symposia, there will be a number of proffered paper sessions on the latest results in all aspects of oncology, including results from the ASCENT trial in triple-negative breast cancer, as well as a dedicated COVID-19 track.
Haanen said that the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020, coming after the AACR and ASCO annual meetings, has the “advantage” of being able to present the latest outcomes of patients treated with chemotherapy and immunotherapy against the backdrop of the pandemic.
This will include a study from the ESMO Resilience Task Force on the impact of COVID-19 on oncology professionals both in terms of their personal distress and burnout and their job performance.
“I think that is very important,” Haanen said, “especially because the whole thing with COVID-19 is not yet over, and everybody is preparing for a second wave in the fall and winter.
“It may help us give us clues on how we can protect ourselves or each other to prevent burnout or other problems that we as healthcare caregivers face in this difficult period.”
Next year
For next year, Peters remains hopeful that the ESMO 2021 meeting will take place as planned in Paris.
She anticipates that, indeed, ESMO meetings will be able to take place from spring next year.
This will depend on a vaccine for COVID-19 becoming widely available, although oncologists in some countries may still not be able to travel.
This means “starting probably with hybrid formats, with some of the faculty being on site and some not, [and] the same thing for the attendees,” Peters said.
She suggested that, for ESMO Congress 2021 to work as an on-site meeting, it will require at least half or two-thirds of the originally anticipated number of attendees.
“I hope that Paris next year will happen,” Peters said, adding that it “will probably happen with less attendees – that’s fine, but [still] with a large number of faculty and attendees.”
The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The use of immunotherapy for upper gastrointestinal tumors and renal cancer, ALK- and EGFR-targeted agents in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and the next step in personalized prostate cancer management will all be subjects of headlining presentations at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
The conference will, like so many other major events, be held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
John B. Haanen, PhD, ESMO 2020 scientific chair, who is from the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, told Medscape Medical News that, because the congress is being held online this year, fewer abstracts were submitted; nevertheless, “We were very happy to see ... that the quality was very good.”
The number of submissions was not the only problem the organizing committee had to face in transforming the ESMO Congress into a virtual meeting.
They were unable to fit the scientific and educational programs together and so have had to split them over two consecutive weekends. Moreover, many of the sessions were highly interactive and needed to be either adapted or omitted.
“So the program is somewhat different,” Haanen said. He noted that “the presentations were also made shorter, especially on the educational sessions, because...we can’t expect people to sit behind screens for hours listening to long presentations.”
He added: “That was out of the question.”
Haanen is nevertheless hopeful that the virtual meeting will be “very exciting.”
Solange Peters, MD, PhD, ESMO president, who is also affiliated with the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois, Lausanne, Switzerland, said in a press conference that it was a “sacrifice” to move ESMO 2020 online and that “there were very sad moments” when deciding on the content.
However, there were some benefits from the change.
She said that all of the ESMO meetings this year have seen “huge” increases in the number of attendees and the geographical span or reach of each of the conferences.
“So suddenly you also realize that, what is one of the missions of ESMO being to convey education globally ... was probably better reached, better achieved with the virtual format,” she commented.
Presidential symposia
Turning to the program, Haanen first picked out the third presidential symposium, which will be held on Monday, September 21. This will focus entirely on upper gastrointestinal tumors in both the adjuvant and metastatic setting.
He said that in recent years, “very little progress has been made” in this area, with treatment mostly consisting of chemotherapy and chemoradiotherapy.
However, this year’s presentations will explore the addition of immunotherapy either to chemotherapy or as an adjuvant treatment following completion of standard-of-care treatment for local disease.
Haanen said that the results will be “very interesting ... and may change current practice,” something that “is very important for both doctors and their patients.”
On Saturday, September 19, the first presidential symposium will include two presentations on lung cancer that Haanen said will offer some “exciting new [results] that I am sure will change clinical practice.”
One will be on the CROWN phase 3 trial comparing lorlatinib and crizotinib in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC.
The other will present results on central nervous system disease recurrence from the ADAURA phase 3 trial of osimertinib adjuvant therapy in patients with resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
The same session will also see new data in advanced renal cell carcinoma from CheckMate 9ER, in which the c-Met and VEGFR2 inhibitor cabozantinib (Cabometyx) was combined with nivolumab (Opdivo) and compared to sunitinib (Sutent) in untreated patients.
“Last year, there were already some exciting results of the combination of axitinib [Inlyta], either with pembrolizumab [Keytruda] or with avelumab [Bavencio]...in the first-line setting in metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer,” Hannen said.
“Clearly there was a survival advantage over the standard of care, sunitinib,” he added.
This year, not only will efficacy data from CheckMate 9ER be presented but also quality-of-life results.
“That’s very important, because what everybody is afraid of is that, by adding drugs, you always get more impact on the quality of life, but you will see that the quality-of-life results are very exciting,” he said.
The second presidential symposium will feature studies on prostate cancer, notably the phase 3 IPATential150 trial of abiraterone (Zytiga) plus either ipatasertib or placebo in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Ipatasertib targets Akt, and Haanen said that “by adding it to, let’s say, standard-of-care treatment ... the question of course of will be, Does that have a better outcome?”
He believes the results will be a “very nice illustration” that prostate cancer management is heading in the direction of personalized treatment.
Alongside the presidential symposia, there will be a number of proffered paper sessions on the latest results in all aspects of oncology, including results from the ASCENT trial in triple-negative breast cancer, as well as a dedicated COVID-19 track.
Haanen said that the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020, coming after the AACR and ASCO annual meetings, has the “advantage” of being able to present the latest outcomes of patients treated with chemotherapy and immunotherapy against the backdrop of the pandemic.
This will include a study from the ESMO Resilience Task Force on the impact of COVID-19 on oncology professionals both in terms of their personal distress and burnout and their job performance.
“I think that is very important,” Haanen said, “especially because the whole thing with COVID-19 is not yet over, and everybody is preparing for a second wave in the fall and winter.
“It may help us give us clues on how we can protect ourselves or each other to prevent burnout or other problems that we as healthcare caregivers face in this difficult period.”
Next year
For next year, Peters remains hopeful that the ESMO 2021 meeting will take place as planned in Paris.
She anticipates that, indeed, ESMO meetings will be able to take place from spring next year.
This will depend on a vaccine for COVID-19 becoming widely available, although oncologists in some countries may still not be able to travel.
This means “starting probably with hybrid formats, with some of the faculty being on site and some not, [and] the same thing for the attendees,” Peters said.
She suggested that, for ESMO Congress 2021 to work as an on-site meeting, it will require at least half or two-thirds of the originally anticipated number of attendees.
“I hope that Paris next year will happen,” Peters said, adding that it “will probably happen with less attendees – that’s fine, but [still] with a large number of faculty and attendees.”
The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The use of immunotherapy for upper gastrointestinal tumors and renal cancer, ALK- and EGFR-targeted agents in non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and the next step in personalized prostate cancer management will all be subjects of headlining presentations at the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020.
The conference will, like so many other major events, be held online this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
John B. Haanen, PhD, ESMO 2020 scientific chair, who is from the Netherlands Cancer Institute, Amsterdam, the Netherlands, told Medscape Medical News that, because the congress is being held online this year, fewer abstracts were submitted; nevertheless, “We were very happy to see ... that the quality was very good.”
The number of submissions was not the only problem the organizing committee had to face in transforming the ESMO Congress into a virtual meeting.
They were unable to fit the scientific and educational programs together and so have had to split them over two consecutive weekends. Moreover, many of the sessions were highly interactive and needed to be either adapted or omitted.
“So the program is somewhat different,” Haanen said. He noted that “the presentations were also made shorter, especially on the educational sessions, because...we can’t expect people to sit behind screens for hours listening to long presentations.”
He added: “That was out of the question.”
Haanen is nevertheless hopeful that the virtual meeting will be “very exciting.”
Solange Peters, MD, PhD, ESMO president, who is also affiliated with the Centre Hospitalier Universitaire Vaudois, Lausanne, Switzerland, said in a press conference that it was a “sacrifice” to move ESMO 2020 online and that “there were very sad moments” when deciding on the content.
However, there were some benefits from the change.
She said that all of the ESMO meetings this year have seen “huge” increases in the number of attendees and the geographical span or reach of each of the conferences.
“So suddenly you also realize that, what is one of the missions of ESMO being to convey education globally ... was probably better reached, better achieved with the virtual format,” she commented.
Presidential symposia
Turning to the program, Haanen first picked out the third presidential symposium, which will be held on Monday, September 21. This will focus entirely on upper gastrointestinal tumors in both the adjuvant and metastatic setting.
He said that in recent years, “very little progress has been made” in this area, with treatment mostly consisting of chemotherapy and chemoradiotherapy.
However, this year’s presentations will explore the addition of immunotherapy either to chemotherapy or as an adjuvant treatment following completion of standard-of-care treatment for local disease.
Haanen said that the results will be “very interesting ... and may change current practice,” something that “is very important for both doctors and their patients.”
On Saturday, September 19, the first presidential symposium will include two presentations on lung cancer that Haanen said will offer some “exciting new [results] that I am sure will change clinical practice.”
One will be on the CROWN phase 3 trial comparing lorlatinib and crizotinib in the first-line treatment of patients with advanced ALK-positive NSCLC.
The other will present results on central nervous system disease recurrence from the ADAURA phase 3 trial of osimertinib adjuvant therapy in patients with resected EGFR-mutated NSCLC.
The same session will also see new data in advanced renal cell carcinoma from CheckMate 9ER, in which the c-Met and VEGFR2 inhibitor cabozantinib (Cabometyx) was combined with nivolumab (Opdivo) and compared to sunitinib (Sutent) in untreated patients.
“Last year, there were already some exciting results of the combination of axitinib [Inlyta], either with pembrolizumab [Keytruda] or with avelumab [Bavencio]...in the first-line setting in metastatic clear cell renal cell cancer,” Hannen said.
“Clearly there was a survival advantage over the standard of care, sunitinib,” he added.
This year, not only will efficacy data from CheckMate 9ER be presented but also quality-of-life results.
“That’s very important, because what everybody is afraid of is that, by adding drugs, you always get more impact on the quality of life, but you will see that the quality-of-life results are very exciting,” he said.
The second presidential symposium will feature studies on prostate cancer, notably the phase 3 IPATential150 trial of abiraterone (Zytiga) plus either ipatasertib or placebo in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Ipatasertib targets Akt, and Haanen said that “by adding it to, let’s say, standard-of-care treatment ... the question of course of will be, Does that have a better outcome?”
He believes the results will be a “very nice illustration” that prostate cancer management is heading in the direction of personalized treatment.
Alongside the presidential symposia, there will be a number of proffered paper sessions on the latest results in all aspects of oncology, including results from the ASCENT trial in triple-negative breast cancer, as well as a dedicated COVID-19 track.
Haanen said that the ESMO Virtual Congress 2020, coming after the AACR and ASCO annual meetings, has the “advantage” of being able to present the latest outcomes of patients treated with chemotherapy and immunotherapy against the backdrop of the pandemic.
This will include a study from the ESMO Resilience Task Force on the impact of COVID-19 on oncology professionals both in terms of their personal distress and burnout and their job performance.
“I think that is very important,” Haanen said, “especially because the whole thing with COVID-19 is not yet over, and everybody is preparing for a second wave in the fall and winter.
“It may help us give us clues on how we can protect ourselves or each other to prevent burnout or other problems that we as healthcare caregivers face in this difficult period.”
Next year
For next year, Peters remains hopeful that the ESMO 2021 meeting will take place as planned in Paris.
She anticipates that, indeed, ESMO meetings will be able to take place from spring next year.
This will depend on a vaccine for COVID-19 becoming widely available, although oncologists in some countries may still not be able to travel.
This means “starting probably with hybrid formats, with some of the faculty being on site and some not, [and] the same thing for the attendees,” Peters said.
She suggested that, for ESMO Congress 2021 to work as an on-site meeting, it will require at least half or two-thirds of the originally anticipated number of attendees.
“I hope that Paris next year will happen,” Peters said, adding that it “will probably happen with less attendees – that’s fine, but [still] with a large number of faculty and attendees.”
The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESMO 2020
Immunotherapy should not be withheld because of sex, age, or PS
The improvement in survival in many cancer types that is seen with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), when compared to control therapies, is not affected by the patient’s sex, age, or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), according to a new meta-analysis.
Therefore, treatment with these immunotherapies should not be withheld on the basis of these factors, the authors concluded.
Asked whether there have been such instances of withholding ICIs, lead author Yucai Wang, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, told Medscape Medical News: “We did this study solely based on scientific questions we had and not because we were seeing any bias at the moment in the use of ICIs.
“And we saw that the survival benefits were very similar across all of the categories [we analyzed], with a survival benefit of about 20% from immunotherapy across the board, which is clinically meaningful,” he added.
The study was published online August 7 in JAMA Network Open.
“The comparable survival advantage between patients of different sex, age, and ECOG PS may encourage more patients to receive ICI treatment regardless of cancer types, lines of therapy, agents of immunotherapy, and intervention therapies,” the authors commented.
Wang noted that there have been conflicting reports in the literature suggesting that male patients may benefit more from immunotherapy than female patients and that older patients may benefit more from the same treatment than younger patients.
However, there are also suggestions in the literature that women experience a stronger immune response than men and that, with aging, the immune system generally undergoes immunosenescence.
In addition, the PS of oncology patients has been implicated in how well patients respond to immunotherapy.
Wang noted that the findings of past studies have contradicted each other.
Findings of the Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis included 37 randomized clinical trials that involved a total of 23,760 patients with a variety of advanced cancers. “Most of the trials were phase 3 (n = 34) and conduced for subsequent lines of therapy (n = 22),” the authors explained.
The most common cancers treated with an ICI were non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
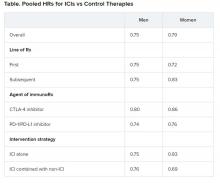
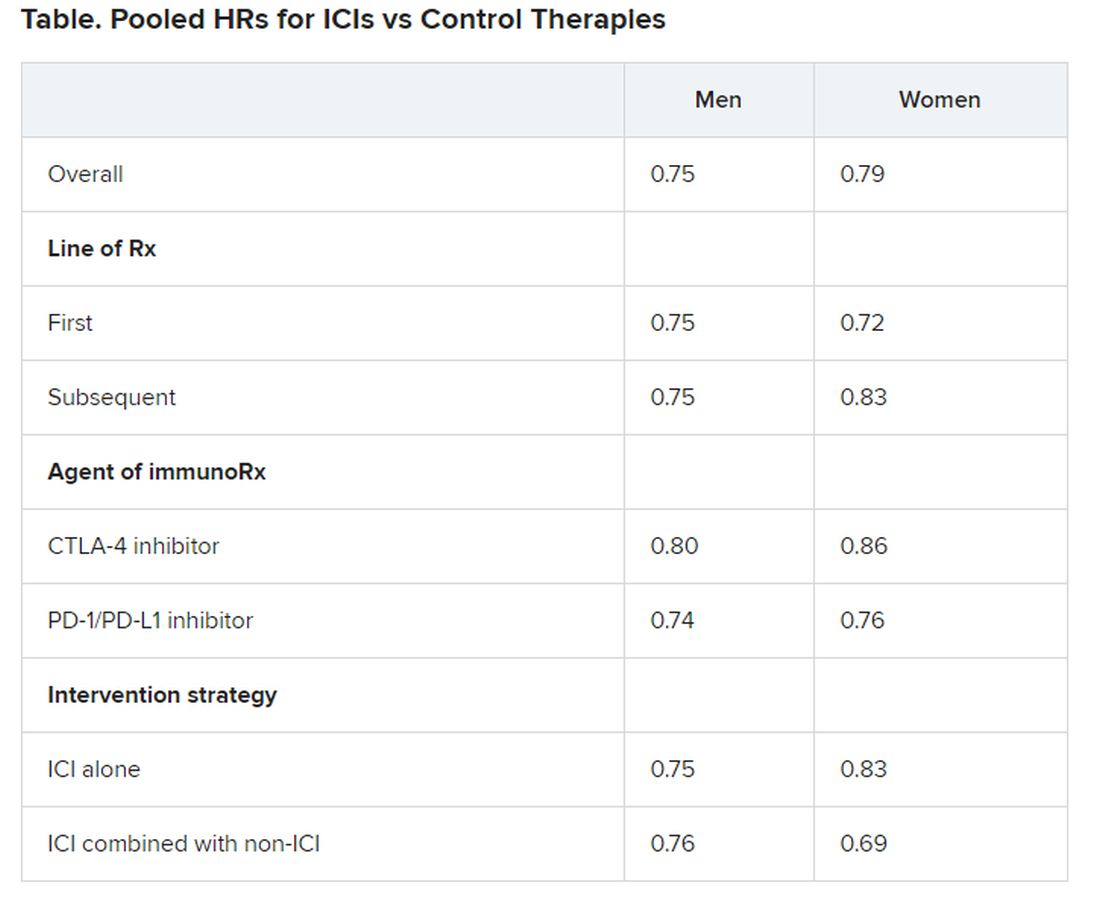
Pooled overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated on the basis of sex, age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older), and an ECOG PS of 0 and 1 or higher.
Responses were stratified on the basis of cancer type, line of therapy, the ICI used, and the immunotherapy strategy used in the ICI arm.
Most of the drugs evaluated were PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. The specific drugs assessed included ipilimumab, tremelimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab.
A total of 32 trials that involved more than 20,000 patients reported HRs for death according to the patients’ sex. Thirty-four trials that involved more than 21,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ age, and 30 trials that involved more than 19,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ ECOG PS.
No significant differences in OS benefit were seen by cancer type, line of therapy, agent of immunotherapy, or intervention strategy, the investigators pointed out.
There were also no differences in survival benefit associated with immunotherapy vs control therapies for patients with an ECOG PS of 0 and an ECOG PS of 1 or greater. The OS benefit was 0.81 for those with an ECOG PS of 0 and 0.79 for those with an ECOG PS of 1 or greater.
Wang has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com .
The improvement in survival in many cancer types that is seen with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), when compared to control therapies, is not affected by the patient’s sex, age, or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), according to a new meta-analysis.
Therefore, treatment with these immunotherapies should not be withheld on the basis of these factors, the authors concluded.
Asked whether there have been such instances of withholding ICIs, lead author Yucai Wang, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, told Medscape Medical News: “We did this study solely based on scientific questions we had and not because we were seeing any bias at the moment in the use of ICIs.
“And we saw that the survival benefits were very similar across all of the categories [we analyzed], with a survival benefit of about 20% from immunotherapy across the board, which is clinically meaningful,” he added.
The study was published online August 7 in JAMA Network Open.
“The comparable survival advantage between patients of different sex, age, and ECOG PS may encourage more patients to receive ICI treatment regardless of cancer types, lines of therapy, agents of immunotherapy, and intervention therapies,” the authors commented.
Wang noted that there have been conflicting reports in the literature suggesting that male patients may benefit more from immunotherapy than female patients and that older patients may benefit more from the same treatment than younger patients.
However, there are also suggestions in the literature that women experience a stronger immune response than men and that, with aging, the immune system generally undergoes immunosenescence.
In addition, the PS of oncology patients has been implicated in how well patients respond to immunotherapy.
Wang noted that the findings of past studies have contradicted each other.
Findings of the Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis included 37 randomized clinical trials that involved a total of 23,760 patients with a variety of advanced cancers. “Most of the trials were phase 3 (n = 34) and conduced for subsequent lines of therapy (n = 22),” the authors explained.
The most common cancers treated with an ICI were non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
Pooled overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated on the basis of sex, age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older), and an ECOG PS of 0 and 1 or higher.
Responses were stratified on the basis of cancer type, line of therapy, the ICI used, and the immunotherapy strategy used in the ICI arm.
Most of the drugs evaluated were PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. The specific drugs assessed included ipilimumab, tremelimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab.
A total of 32 trials that involved more than 20,000 patients reported HRs for death according to the patients’ sex. Thirty-four trials that involved more than 21,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ age, and 30 trials that involved more than 19,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ ECOG PS.
No significant differences in OS benefit were seen by cancer type, line of therapy, agent of immunotherapy, or intervention strategy, the investigators pointed out.
There were also no differences in survival benefit associated with immunotherapy vs control therapies for patients with an ECOG PS of 0 and an ECOG PS of 1 or greater. The OS benefit was 0.81 for those with an ECOG PS of 0 and 0.79 for those with an ECOG PS of 1 or greater.
Wang has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com .
The improvement in survival in many cancer types that is seen with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), when compared to control therapies, is not affected by the patient’s sex, age, or Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status (PS), according to a new meta-analysis.
Therefore, treatment with these immunotherapies should not be withheld on the basis of these factors, the authors concluded.
Asked whether there have been such instances of withholding ICIs, lead author Yucai Wang, MD, PhD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota, told Medscape Medical News: “We did this study solely based on scientific questions we had and not because we were seeing any bias at the moment in the use of ICIs.
“And we saw that the survival benefits were very similar across all of the categories [we analyzed], with a survival benefit of about 20% from immunotherapy across the board, which is clinically meaningful,” he added.
The study was published online August 7 in JAMA Network Open.
“The comparable survival advantage between patients of different sex, age, and ECOG PS may encourage more patients to receive ICI treatment regardless of cancer types, lines of therapy, agents of immunotherapy, and intervention therapies,” the authors commented.
Wang noted that there have been conflicting reports in the literature suggesting that male patients may benefit more from immunotherapy than female patients and that older patients may benefit more from the same treatment than younger patients.
However, there are also suggestions in the literature that women experience a stronger immune response than men and that, with aging, the immune system generally undergoes immunosenescence.
In addition, the PS of oncology patients has been implicated in how well patients respond to immunotherapy.
Wang noted that the findings of past studies have contradicted each other.
Findings of the Meta-Analysis
The meta-analysis included 37 randomized clinical trials that involved a total of 23,760 patients with a variety of advanced cancers. “Most of the trials were phase 3 (n = 34) and conduced for subsequent lines of therapy (n = 22),” the authors explained.
The most common cancers treated with an ICI were non–small cell lung cancer and melanoma.
Pooled overall survival (OS) hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated on the basis of sex, age (younger than 65 years and 65 years and older), and an ECOG PS of 0 and 1 or higher.
Responses were stratified on the basis of cancer type, line of therapy, the ICI used, and the immunotherapy strategy used in the ICI arm.
Most of the drugs evaluated were PD-1 and PD-L1 inhibitors. The specific drugs assessed included ipilimumab, tremelimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab, atezolizumab, durvalumab, and avelumab.
A total of 32 trials that involved more than 20,000 patients reported HRs for death according to the patients’ sex. Thirty-four trials that involved more than 21,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ age, and 30 trials that involved more than 19,000 patients reported HRs for death according to patients’ ECOG PS.
No significant differences in OS benefit were seen by cancer type, line of therapy, agent of immunotherapy, or intervention strategy, the investigators pointed out.
There were also no differences in survival benefit associated with immunotherapy vs control therapies for patients with an ECOG PS of 0 and an ECOG PS of 1 or greater. The OS benefit was 0.81 for those with an ECOG PS of 0 and 0.79 for those with an ECOG PS of 1 or greater.
Wang has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com .
FDA approves new indications for pembrolizumab
The Food and Drug Administration recently announced two new types of cancer that can be treated by the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab.
The new indications expand the use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to include treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden–high (TMB-H) solid tumors as well as patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The FDA announced the new indications just 8 days apart, on June 16 and June 24.
In addition, on June 29, the FDA approved a third new indication for pembrolizumab, this time as first-line treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer.
The new approvals add to a wide range of oncology indications for which pembrolizumab can be used.
Accelerated approval to treat solid tumors
The FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab to treat children and adults with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H solid tumors that progressed after previous treatment or in instances where there are no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The tumor mutational burden must be confirmed by an FDA-approved test. To that end, the FDA approved the FoundationOneCDx assay, which is designed to help physicians determine which patients meet the threshold for TMB-H malignancies (10 or more mutations per megabase).
The efficacy of pembrolizumab in TMB-H solid tumors was investigated in 10 cohorts from the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-158 trial. Participants received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until their disease progressed or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
Within this population, 102 patients had tumors that met the TMB-H definition. In this group, the overall response rate was 29%, including a 25% partial response rate and a 4% complete response rate.
The median duration of response was not reached, but 57% of participants experienced a response lasting 12 months or longer, and 50% had a response lasting 24 months or longer.
The most common adverse events associated with pembrolizumab in this trial were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. Pembrolizumab is associated with immune-mediated side effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and skin adverse reactions, the FDA noted.
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in pediatric patients with TMB-H central nervous system cancers have not been established.
New option for recurrent or metastatic cSCC
Physicians treating patients with cSCC that is not curable by surgery or radiation now have pembrolizumab to consider as another treatment option.
The cSCC approval is based on results of the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-629 trial. The dosage regimen was 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until cancer progressed, unacceptable toxicity arose, or 24 months of treatment were completed.
The objective response rate was 34%, and the median duration of response was not reached.
Adverse events were similar to those occurring in patients who received pembrolizumab as a single agent in other clinical trials, the FDA noted.
The Food and Drug Administration recently announced two new types of cancer that can be treated by the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab.
The new indications expand the use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to include treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden–high (TMB-H) solid tumors as well as patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The FDA announced the new indications just 8 days apart, on June 16 and June 24.
In addition, on June 29, the FDA approved a third new indication for pembrolizumab, this time as first-line treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer.
The new approvals add to a wide range of oncology indications for which pembrolizumab can be used.
Accelerated approval to treat solid tumors
The FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab to treat children and adults with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H solid tumors that progressed after previous treatment or in instances where there are no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The tumor mutational burden must be confirmed by an FDA-approved test. To that end, the FDA approved the FoundationOneCDx assay, which is designed to help physicians determine which patients meet the threshold for TMB-H malignancies (10 or more mutations per megabase).
The efficacy of pembrolizumab in TMB-H solid tumors was investigated in 10 cohorts from the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-158 trial. Participants received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until their disease progressed or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
Within this population, 102 patients had tumors that met the TMB-H definition. In this group, the overall response rate was 29%, including a 25% partial response rate and a 4% complete response rate.
The median duration of response was not reached, but 57% of participants experienced a response lasting 12 months or longer, and 50% had a response lasting 24 months or longer.
The most common adverse events associated with pembrolizumab in this trial were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. Pembrolizumab is associated with immune-mediated side effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and skin adverse reactions, the FDA noted.
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in pediatric patients with TMB-H central nervous system cancers have not been established.
New option for recurrent or metastatic cSCC
Physicians treating patients with cSCC that is not curable by surgery or radiation now have pembrolizumab to consider as another treatment option.
The cSCC approval is based on results of the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-629 trial. The dosage regimen was 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until cancer progressed, unacceptable toxicity arose, or 24 months of treatment were completed.
The objective response rate was 34%, and the median duration of response was not reached.
Adverse events were similar to those occurring in patients who received pembrolizumab as a single agent in other clinical trials, the FDA noted.
The Food and Drug Administration recently announced two new types of cancer that can be treated by the anti–PD-1 antibody pembrolizumab.
The new indications expand the use of pembrolizumab (Keytruda) to include treatment of patients with unresectable or metastatic tumor mutational burden–high (TMB-H) solid tumors as well as patients with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC). The FDA announced the new indications just 8 days apart, on June 16 and June 24.
In addition, on June 29, the FDA approved a third new indication for pembrolizumab, this time as first-line treatment for patients with unresectable or metastatic microsatellite instability–high or mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer.
The new approvals add to a wide range of oncology indications for which pembrolizumab can be used.
Accelerated approval to treat solid tumors
The FDA granted accelerated approval for pembrolizumab to treat children and adults with unresectable or metastatic TMB-H solid tumors that progressed after previous treatment or in instances where there are no satisfactory alternative treatment options.
The tumor mutational burden must be confirmed by an FDA-approved test. To that end, the FDA approved the FoundationOneCDx assay, which is designed to help physicians determine which patients meet the threshold for TMB-H malignancies (10 or more mutations per megabase).
The efficacy of pembrolizumab in TMB-H solid tumors was investigated in 10 cohorts from the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-158 trial. Participants received 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until their disease progressed or they experienced unacceptable toxicity.
Within this population, 102 patients had tumors that met the TMB-H definition. In this group, the overall response rate was 29%, including a 25% partial response rate and a 4% complete response rate.
The median duration of response was not reached, but 57% of participants experienced a response lasting 12 months or longer, and 50% had a response lasting 24 months or longer.
The most common adverse events associated with pembrolizumab in this trial were fatigue, musculoskeletal pain, decreased appetite, pruritus, diarrhea, nausea, rash, pyrexia, cough, dyspnea, constipation, pain, and abdominal pain. Pembrolizumab is associated with immune-mediated side effects, including pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, and skin adverse reactions, the FDA noted.
Safety and efficacy of pembrolizumab in pediatric patients with TMB-H central nervous system cancers have not been established.
New option for recurrent or metastatic cSCC
Physicians treating patients with cSCC that is not curable by surgery or radiation now have pembrolizumab to consider as another treatment option.
The cSCC approval is based on results of the multicenter, open-label KEYNOTE-629 trial. The dosage regimen was 200 mg of pembrolizumab intravenously every 3 weeks until cancer progressed, unacceptable toxicity arose, or 24 months of treatment were completed.
The objective response rate was 34%, and the median duration of response was not reached.
Adverse events were similar to those occurring in patients who received pembrolizumab as a single agent in other clinical trials, the FDA noted.
Personalized cancer vaccine may enhance checkpoint inhibitor activity
Combining a personalized cancer vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor induced neoantigen-specific immune responses in most patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1b study.
Only two clinical responses were seen in this early investigation of the vaccine, RO7198457, combined with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab. However, T-cell responses were observed in about three-quarters of the patients evaluated, according to study investigator Juanita Lopez, MB BChir, PhD.
Those immune responses, coupled with preliminary evidence of infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells into tumors, suggest the viability of this individualized anticancer strategy, according to Dr. Lopez, a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
“Failure of T-cell priming is a major cause of lack of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Lopez said in an interview. “We hoped that, by eliciting a tumor-specific T-cell response, we would be able to overcome this.”
Preclinical data suggested the combination of vaccine and immune checkpoint inhibitors improved outcomes, which prompted the current study, added Dr. Lopez, who presented results from this study at the American Association for Cancer Research virtual meeting II.
Dr. Lopez noted that mutated neoantigens are recognized as foreign and have been shown to induce stronger T-cell responses, compared with shared antigens, likely because of a lack of central tolerance.
“Most of these mutated neoantigens are not shared between the patients, and therefore, targeted neoantigen-specific therapy requires an individualized approach,” she explained.
RO7198457 is manufactured on a per-patient basis and includes as many as 20 tumor-specific neoepitopes.
Study details
Dr. Lopez presented results from dose-escalation and expansion cohorts of the study, which included 142 patients with advanced solid tumors. The patients had colorectal, skin, kidney, lung, urothelial, breast, gynecologic, and head and neck cancers.
Most patients had low or no PD-L1 expression, and nearly 40% had received prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Patients received nine doses of RO7198457 at 25-50 mcg during the 12-week induction stage. They then received RO7198457 every eight cycles until disease progression. Patients received atezolizumab at 1,200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle.
Induction of proinflammatory cytokines was observed at each dose tested, and ex vivo T-cell responses were noted in 46 of 63 patients evaluated, or 73%.
T-cell receptors specific to RO7198457 were present posttreatment in a patient with rectal cancer, providing some preliminary evidence suggesting infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells in the tumor, Dr. Lopez said.
There were two clinical responses. A patient with rectal cancer had a complete response, and a patient with triple-negative breast cancer had a partial response.
The combination of RO7198457 with atezolizumab was generally well tolerated, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached, Dr. Lopez said. Most adverse events were grade 1/2, and immune-mediated adverse events were rare.
Implications and next steps
This study furthers earlier observations from neoantigen vaccine studies by linking dosing of the vaccine to dosing with immune checkpoint inhibitor, rather than giving the vaccine in the period leading up to immune checkpoint inhibitor administration, according to former AACR President Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, both in Columbus.
That said, the implications for clinical practice remain unclear, according to Dr. Mardis.
“This combination did elicit an immune response that was highly specific for the neoantigen vaccine, but most patients did not receive a clinical benefit of disease response,” Dr. Mardis said in an interview. “This tells us the combination approach used was, overall, not quite right, and we need to continue to innovate in this area.”
The low clinical response rate in the study was likely caused in part by the fact that patients had very advanced disease and were heavily pretreated, according to Dr. Lopez
Randomized phase 2 studies of RO7198457 are now underway, Dr. Lopez said. One is a study of RO7198457 plus atezolizumab as adjuvant treatment for non–small cell lung cancer (NCT04267237). Another is testing RO7198457 in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for melanoma (NCT03815058).
The current study was funded by Genentech and BioNTech. Dr. Lopez reported disclosures related to Roche/Genentech, Basilea Pharmaceutica, and Genmab. Dr. Mardis reported disclosures related to Quiagen NV, PACT Pharma, Kiadis Pharma NV, and Interpreta.
SOURCE: Lopez J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT301.
Combining a personalized cancer vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor induced neoantigen-specific immune responses in most patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1b study.
Only two clinical responses were seen in this early investigation of the vaccine, RO7198457, combined with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab. However, T-cell responses were observed in about three-quarters of the patients evaluated, according to study investigator Juanita Lopez, MB BChir, PhD.
Those immune responses, coupled with preliminary evidence of infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells into tumors, suggest the viability of this individualized anticancer strategy, according to Dr. Lopez, a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
“Failure of T-cell priming is a major cause of lack of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Lopez said in an interview. “We hoped that, by eliciting a tumor-specific T-cell response, we would be able to overcome this.”
Preclinical data suggested the combination of vaccine and immune checkpoint inhibitors improved outcomes, which prompted the current study, added Dr. Lopez, who presented results from this study at the American Association for Cancer Research virtual meeting II.
Dr. Lopez noted that mutated neoantigens are recognized as foreign and have been shown to induce stronger T-cell responses, compared with shared antigens, likely because of a lack of central tolerance.
“Most of these mutated neoantigens are not shared between the patients, and therefore, targeted neoantigen-specific therapy requires an individualized approach,” she explained.
RO7198457 is manufactured on a per-patient basis and includes as many as 20 tumor-specific neoepitopes.
Study details
Dr. Lopez presented results from dose-escalation and expansion cohorts of the study, which included 142 patients with advanced solid tumors. The patients had colorectal, skin, kidney, lung, urothelial, breast, gynecologic, and head and neck cancers.
Most patients had low or no PD-L1 expression, and nearly 40% had received prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Patients received nine doses of RO7198457 at 25-50 mcg during the 12-week induction stage. They then received RO7198457 every eight cycles until disease progression. Patients received atezolizumab at 1,200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle.
Induction of proinflammatory cytokines was observed at each dose tested, and ex vivo T-cell responses were noted in 46 of 63 patients evaluated, or 73%.
T-cell receptors specific to RO7198457 were present posttreatment in a patient with rectal cancer, providing some preliminary evidence suggesting infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells in the tumor, Dr. Lopez said.
There were two clinical responses. A patient with rectal cancer had a complete response, and a patient with triple-negative breast cancer had a partial response.
The combination of RO7198457 with atezolizumab was generally well tolerated, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached, Dr. Lopez said. Most adverse events were grade 1/2, and immune-mediated adverse events were rare.
Implications and next steps
This study furthers earlier observations from neoantigen vaccine studies by linking dosing of the vaccine to dosing with immune checkpoint inhibitor, rather than giving the vaccine in the period leading up to immune checkpoint inhibitor administration, according to former AACR President Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, both in Columbus.
That said, the implications for clinical practice remain unclear, according to Dr. Mardis.
“This combination did elicit an immune response that was highly specific for the neoantigen vaccine, but most patients did not receive a clinical benefit of disease response,” Dr. Mardis said in an interview. “This tells us the combination approach used was, overall, not quite right, and we need to continue to innovate in this area.”
The low clinical response rate in the study was likely caused in part by the fact that patients had very advanced disease and were heavily pretreated, according to Dr. Lopez
Randomized phase 2 studies of RO7198457 are now underway, Dr. Lopez said. One is a study of RO7198457 plus atezolizumab as adjuvant treatment for non–small cell lung cancer (NCT04267237). Another is testing RO7198457 in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for melanoma (NCT03815058).
The current study was funded by Genentech and BioNTech. Dr. Lopez reported disclosures related to Roche/Genentech, Basilea Pharmaceutica, and Genmab. Dr. Mardis reported disclosures related to Quiagen NV, PACT Pharma, Kiadis Pharma NV, and Interpreta.
SOURCE: Lopez J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT301.
Combining a personalized cancer vaccine with an immune checkpoint inhibitor induced neoantigen-specific immune responses in most patients with advanced solid tumors in a phase 1b study.
Only two clinical responses were seen in this early investigation of the vaccine, RO7198457, combined with the PD-L1 inhibitor atezolizumab. However, T-cell responses were observed in about three-quarters of the patients evaluated, according to study investigator Juanita Lopez, MB BChir, PhD.
Those immune responses, coupled with preliminary evidence of infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells into tumors, suggest the viability of this individualized anticancer strategy, according to Dr. Lopez, a consultant medical oncologist at The Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust and The Institute of Cancer Research, London.
“Failure of T-cell priming is a major cause of lack of response to immune checkpoint inhibitors,” Dr. Lopez said in an interview. “We hoped that, by eliciting a tumor-specific T-cell response, we would be able to overcome this.”
Preclinical data suggested the combination of vaccine and immune checkpoint inhibitors improved outcomes, which prompted the current study, added Dr. Lopez, who presented results from this study at the American Association for Cancer Research virtual meeting II.
Dr. Lopez noted that mutated neoantigens are recognized as foreign and have been shown to induce stronger T-cell responses, compared with shared antigens, likely because of a lack of central tolerance.
“Most of these mutated neoantigens are not shared between the patients, and therefore, targeted neoantigen-specific therapy requires an individualized approach,” she explained.
RO7198457 is manufactured on a per-patient basis and includes as many as 20 tumor-specific neoepitopes.
Study details
Dr. Lopez presented results from dose-escalation and expansion cohorts of the study, which included 142 patients with advanced solid tumors. The patients had colorectal, skin, kidney, lung, urothelial, breast, gynecologic, and head and neck cancers.
Most patients had low or no PD-L1 expression, and nearly 40% had received prior treatment with a checkpoint inhibitor.
Patients received nine doses of RO7198457 at 25-50 mcg during the 12-week induction stage. They then received RO7198457 every eight cycles until disease progression. Patients received atezolizumab at 1,200 mg on day 1 of each 21-day cycle.
Induction of proinflammatory cytokines was observed at each dose tested, and ex vivo T-cell responses were noted in 46 of 63 patients evaluated, or 73%.
T-cell receptors specific to RO7198457 were present posttreatment in a patient with rectal cancer, providing some preliminary evidence suggesting infiltration of RO7198457-stimulated T cells in the tumor, Dr. Lopez said.
There were two clinical responses. A patient with rectal cancer had a complete response, and a patient with triple-negative breast cancer had a partial response.
The combination of RO7198457 with atezolizumab was generally well tolerated, and the maximum tolerated dose was not reached, Dr. Lopez said. Most adverse events were grade 1/2, and immune-mediated adverse events were rare.
Implications and next steps
This study furthers earlier observations from neoantigen vaccine studies by linking dosing of the vaccine to dosing with immune checkpoint inhibitor, rather than giving the vaccine in the period leading up to immune checkpoint inhibitor administration, according to former AACR President Elaine R. Mardis, PhD, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital and The Ohio State University College of Medicine, both in Columbus.
That said, the implications for clinical practice remain unclear, according to Dr. Mardis.
“This combination did elicit an immune response that was highly specific for the neoantigen vaccine, but most patients did not receive a clinical benefit of disease response,” Dr. Mardis said in an interview. “This tells us the combination approach used was, overall, not quite right, and we need to continue to innovate in this area.”
The low clinical response rate in the study was likely caused in part by the fact that patients had very advanced disease and were heavily pretreated, according to Dr. Lopez
Randomized phase 2 studies of RO7198457 are now underway, Dr. Lopez said. One is a study of RO7198457 plus atezolizumab as adjuvant treatment for non–small cell lung cancer (NCT04267237). Another is testing RO7198457 in combination with pembrolizumab as first-line treatment for melanoma (NCT03815058).
The current study was funded by Genentech and BioNTech. Dr. Lopez reported disclosures related to Roche/Genentech, Basilea Pharmaceutica, and Genmab. Dr. Mardis reported disclosures related to Quiagen NV, PACT Pharma, Kiadis Pharma NV, and Interpreta.
SOURCE: Lopez J et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT301.
FROM AACR 2020
New registry focuses on rheumatic immune-related AEs of cancer therapy
Its first findings were reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
“We have limited knowledge on the interrelationships between malignant and rheumatic diseases on both the clinical and molecular level, and we have a large unmet need for management guidelines in the case of the coincidence of both disease entities,” noted lead author Karolina Benesova, MD, of the department of hematology, oncology, and rheumatology at University Hospital Heidelberg (Germany).
The TRheuMa registry – Therapy-Induced Rheumatic Symptoms in Patients with Malignancy – is one of three registries in a multicenter observational project exploring various contexts between malignant and rheumatic diseases. Over its first 22 months, the registry recruited 69 patients having rheumatic symptoms as a result of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy or other cancer therapies.
Registry findings
The largest shares of patients had non–small cell lung cancer (38%) or melanoma (33%), Dr. Benesova reported. The immune checkpoint inhibitors most commonly received were pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo), and ipilimumab (Yervoy).
The immune-related adverse events usually presented with symptoms of de novo spondyloarthritis or psoriatic arthritis (42%), late-onset RA (17%), or polymyalgia rheumatica (14%). But 16% of the patients were experiencing a flare of a preexisting rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease.
Laboratory findings differed somewhat from those of classical rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, according to Dr. Benesova. Specific findings were rare; in particular, most patients did not have detectable autoantibodies. However, 76% had an elevated C-reactive protein level and 39% had an elevated soluble CD25 level. In addition, nearly all patients (96%) undergoing joint ultrasound had pathologic findings.
“Based on our experiences from interdisciplinary care together with our local oncologists, we have developed a therapeutic algorithm for rheumatic immune-related adverse events,” she reported, noting that the algorithm is consistent with recently published recommendations in this area.
The large majority of patients were adequately treated with prednisone at a dose greater than 10 mg (40%) or at a dose of 10 mg or less with or without an NSAID (40%), while some received NSAID monotherapy (14%).
“We have a growing proportion of patients on conventional or biological [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs],” Dr. Benesova noted. “These are mostly patients with preexisting rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease or highly suspected de novo classical rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease under checkpoint inhibitor therapy.”
Patients with melanoma having a rheumatic immune-related adverse event had a better response to their therapy than historical counterparts who did not have such events: 39% of the former had a complete response, relative to merely 4% of the latter.
Only a small proportion of patients overall (9%) had to discontinue immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy because of their adverse event, and some of them may be eligible for rechallenge if their cancer progresses, Dr. Benesova noted.
“There is still a lot to be done,” she stated, such as better elucidating the nature of these adverse events [whether transient side effects or a triggering of chronic rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases], the need for a defensive treatment strategy, and the advisability of closer monitoring of high-risk patients given immune checkpoint inhibitors. “We are aiming at solving these questions in the next few years,” she concluded.
Findings in context
“Registries are important to gain prospective data on patient outcomes,” Sabina Sandigursky, MD, an instructor in the division of rheumatology at the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University, commented in an interview. “One must be careful, while interpreting these data, especially since they are not randomized, controlled trials.”
Patterns may differ at other centers, too, she pointed out. “The German registry reported a predominance of spondyloarthritis-like disease; however, our patients have a predominance of small-joint involvement. It is unclear what accounts for this difference.”
Individual institutions in North America are similarly collecting data on this patient population, with efforts underway to compile those data to provide a larger picture, according to Dr. Sandigursky.
“Many of the syndromes that we consider to be rheumatic immune-related adverse events have been well described by groups from the U.S., Canada, Australia, and European Union,” she concluded. “From this registry, we can observe how patients are being treated in real time since this information is largely consensus based.”
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Benesova disclosed grant/research support from AbbVie, Novartis, Rheumaliga Baden-Wurttemberg, and the University of Heidelberg, and consultancies, speaker fees, and/or travel reimbursements from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Medac, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Some of her coauthors also disclosed financial relationships with industry. Dr. Sandigursky disclosed having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Benesova K et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79[suppl 1]:168-9, Abstract OP0270.
Its first findings were reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
“We have limited knowledge on the interrelationships between malignant and rheumatic diseases on both the clinical and molecular level, and we have a large unmet need for management guidelines in the case of the coincidence of both disease entities,” noted lead author Karolina Benesova, MD, of the department of hematology, oncology, and rheumatology at University Hospital Heidelberg (Germany).
The TRheuMa registry – Therapy-Induced Rheumatic Symptoms in Patients with Malignancy – is one of three registries in a multicenter observational project exploring various contexts between malignant and rheumatic diseases. Over its first 22 months, the registry recruited 69 patients having rheumatic symptoms as a result of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy or other cancer therapies.
Registry findings
The largest shares of patients had non–small cell lung cancer (38%) or melanoma (33%), Dr. Benesova reported. The immune checkpoint inhibitors most commonly received were pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo), and ipilimumab (Yervoy).
The immune-related adverse events usually presented with symptoms of de novo spondyloarthritis or psoriatic arthritis (42%), late-onset RA (17%), or polymyalgia rheumatica (14%). But 16% of the patients were experiencing a flare of a preexisting rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease.
Laboratory findings differed somewhat from those of classical rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, according to Dr. Benesova. Specific findings were rare; in particular, most patients did not have detectable autoantibodies. However, 76% had an elevated C-reactive protein level and 39% had an elevated soluble CD25 level. In addition, nearly all patients (96%) undergoing joint ultrasound had pathologic findings.
“Based on our experiences from interdisciplinary care together with our local oncologists, we have developed a therapeutic algorithm for rheumatic immune-related adverse events,” she reported, noting that the algorithm is consistent with recently published recommendations in this area.
The large majority of patients were adequately treated with prednisone at a dose greater than 10 mg (40%) or at a dose of 10 mg or less with or without an NSAID (40%), while some received NSAID monotherapy (14%).
“We have a growing proportion of patients on conventional or biological [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs],” Dr. Benesova noted. “These are mostly patients with preexisting rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease or highly suspected de novo classical rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease under checkpoint inhibitor therapy.”
Patients with melanoma having a rheumatic immune-related adverse event had a better response to their therapy than historical counterparts who did not have such events: 39% of the former had a complete response, relative to merely 4% of the latter.
Only a small proportion of patients overall (9%) had to discontinue immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy because of their adverse event, and some of them may be eligible for rechallenge if their cancer progresses, Dr. Benesova noted.
“There is still a lot to be done,” she stated, such as better elucidating the nature of these adverse events [whether transient side effects or a triggering of chronic rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases], the need for a defensive treatment strategy, and the advisability of closer monitoring of high-risk patients given immune checkpoint inhibitors. “We are aiming at solving these questions in the next few years,” she concluded.
Findings in context
“Registries are important to gain prospective data on patient outcomes,” Sabina Sandigursky, MD, an instructor in the division of rheumatology at the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University, commented in an interview. “One must be careful, while interpreting these data, especially since they are not randomized, controlled trials.”
Patterns may differ at other centers, too, she pointed out. “The German registry reported a predominance of spondyloarthritis-like disease; however, our patients have a predominance of small-joint involvement. It is unclear what accounts for this difference.”
Individual institutions in North America are similarly collecting data on this patient population, with efforts underway to compile those data to provide a larger picture, according to Dr. Sandigursky.
“Many of the syndromes that we consider to be rheumatic immune-related adverse events have been well described by groups from the U.S., Canada, Australia, and European Union,” she concluded. “From this registry, we can observe how patients are being treated in real time since this information is largely consensus based.”
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Benesova disclosed grant/research support from AbbVie, Novartis, Rheumaliga Baden-Wurttemberg, and the University of Heidelberg, and consultancies, speaker fees, and/or travel reimbursements from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Medac, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Some of her coauthors also disclosed financial relationships with industry. Dr. Sandigursky disclosed having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Benesova K et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79[suppl 1]:168-9, Abstract OP0270.
Its first findings were reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology, held online this year due to COVID-19.
“We have limited knowledge on the interrelationships between malignant and rheumatic diseases on both the clinical and molecular level, and we have a large unmet need for management guidelines in the case of the coincidence of both disease entities,” noted lead author Karolina Benesova, MD, of the department of hematology, oncology, and rheumatology at University Hospital Heidelberg (Germany).
The TRheuMa registry – Therapy-Induced Rheumatic Symptoms in Patients with Malignancy – is one of three registries in a multicenter observational project exploring various contexts between malignant and rheumatic diseases. Over its first 22 months, the registry recruited 69 patients having rheumatic symptoms as a result of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy or other cancer therapies.
Registry findings
The largest shares of patients had non–small cell lung cancer (38%) or melanoma (33%), Dr. Benesova reported. The immune checkpoint inhibitors most commonly received were pembrolizumab (Keytruda), nivolumab (Opdivo), and ipilimumab (Yervoy).
The immune-related adverse events usually presented with symptoms of de novo spondyloarthritis or psoriatic arthritis (42%), late-onset RA (17%), or polymyalgia rheumatica (14%). But 16% of the patients were experiencing a flare of a preexisting rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease.
Laboratory findings differed somewhat from those of classical rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases, according to Dr. Benesova. Specific findings were rare; in particular, most patients did not have detectable autoantibodies. However, 76% had an elevated C-reactive protein level and 39% had an elevated soluble CD25 level. In addition, nearly all patients (96%) undergoing joint ultrasound had pathologic findings.
“Based on our experiences from interdisciplinary care together with our local oncologists, we have developed a therapeutic algorithm for rheumatic immune-related adverse events,” she reported, noting that the algorithm is consistent with recently published recommendations in this area.
The large majority of patients were adequately treated with prednisone at a dose greater than 10 mg (40%) or at a dose of 10 mg or less with or without an NSAID (40%), while some received NSAID monotherapy (14%).
“We have a growing proportion of patients on conventional or biological [disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs],” Dr. Benesova noted. “These are mostly patients with preexisting rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease or highly suspected de novo classical rheumatic and musculoskeletal disease under checkpoint inhibitor therapy.”
Patients with melanoma having a rheumatic immune-related adverse event had a better response to their therapy than historical counterparts who did not have such events: 39% of the former had a complete response, relative to merely 4% of the latter.
Only a small proportion of patients overall (9%) had to discontinue immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy because of their adverse event, and some of them may be eligible for rechallenge if their cancer progresses, Dr. Benesova noted.
“There is still a lot to be done,” she stated, such as better elucidating the nature of these adverse events [whether transient side effects or a triggering of chronic rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases], the need for a defensive treatment strategy, and the advisability of closer monitoring of high-risk patients given immune checkpoint inhibitors. “We are aiming at solving these questions in the next few years,” she concluded.
Findings in context
“Registries are important to gain prospective data on patient outcomes,” Sabina Sandigursky, MD, an instructor in the division of rheumatology at the Laura and Isaac Perlmutter Cancer Center at New York University, commented in an interview. “One must be careful, while interpreting these data, especially since they are not randomized, controlled trials.”
Patterns may differ at other centers, too, she pointed out. “The German registry reported a predominance of spondyloarthritis-like disease; however, our patients have a predominance of small-joint involvement. It is unclear what accounts for this difference.”
Individual institutions in North America are similarly collecting data on this patient population, with efforts underway to compile those data to provide a larger picture, according to Dr. Sandigursky.
“Many of the syndromes that we consider to be rheumatic immune-related adverse events have been well described by groups from the U.S., Canada, Australia, and European Union,” she concluded. “From this registry, we can observe how patients are being treated in real time since this information is largely consensus based.”
The study did not receive any specific funding. Dr. Benesova disclosed grant/research support from AbbVie, Novartis, Rheumaliga Baden-Wurttemberg, and the University of Heidelberg, and consultancies, speaker fees, and/or travel reimbursements from AbbVie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Gilead, Janssen, Medac, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Mundipharma, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche, and UCB. Some of her coauthors also disclosed financial relationships with industry. Dr. Sandigursky disclosed having no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Benesova K et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2020;79[suppl 1]:168-9, Abstract OP0270.
FROM THE EULAR 2020 E-CONGRESS
FDA approves immunotherapy combo for liver cancer
Patients with advanced liver cancer have a new treatment option – the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) and ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval of the combination for use in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have previously been treated with sorafenib (Nexavar, Bayer). Nivolumab is already approved as monotherapy for use in advanced HCC in patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The immunotherapy combination has shown a response rate that is more than twice that seen with nivolumab alone. The combination was tested at three different dosage schedules in the single-arm phase 1/2 trial known as CheckMate-040, which was conducted in 148 patients with advanced HCC who had previously been treated with sorafenib.
The approval was based on one arm of this trial, a cohort of 49 patients who were treated with nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV and ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
After a minimum follow-up of 28 months, 33% (16/49) of these patients showed a response, with 8% (4/49) showing a complete response and 24% (12/49) a partial response.
In terms of duration of responses, 88% of the responses lasted at least 6 months, 56% at least 12 months, and 31% at least 24 months, according to the company.
The results that led to the 2017 approval of nivolumab monotherapy for advanced HCC, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News, come from a cohort of 154 patients who received nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
The overall response rate was 14.3% (22 of 154 patients), with three patients (1.9%) showing a complete response and 19 patients (12.3%) a partial response. The duration of the responses ranged from 3.2 to 38.2+ months; 91% of those patients had responses of 6 months or longer, and 55% had responses of 12 months or longer.
Notably, patient responses in all arms were achieved regardless of baseline tumor PD-L1 status.
Aggressive disease, incidence is rising
“HCC is an aggressive disease in need of different treatment approaches,” said Anthony B. El-Khoueiry, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, in a company press statement.“The overall response rate observed in the Opdivo + Yervoy cohort of the CheckMate-040 trial underscores the potential of this dual immunotherapy as a possible treatment option for patients,” he commented. El-Khoueiry was lead investigator of the study and has received honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
“The incidence of liver cancer is rising in the United States, and HCC is the most common and aggressive form of the disease,” said Andrea Wilson, president and founder, Blue Faery: The Adrienne Wilson Liver Cancer Association.
“Today’s approval provides a new option for patients with HCC previously treated with sorafenib, giving the community more hope,” she said in the company press statement.
Safety profile
The nivolumab-ipilimumab combination had an “acceptable” safety profile overall in the CheckMate-040 trial, wrote lead study author Thomas Yao, MD, of the University at Hong Kong, China, and colleagues in their study abstract, which was presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Yao has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and has served as a consultant to the company.
According to those data, 37% of patients had a grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), the most common of which were pruritus and rash; 5% had grade 3–4 TRAEs that led to discontinuation.
Nivolumab is associated with pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, renal dysfunction, skin adverse reactions, encephalitis, other adverse reactions, and infusion-related reactions, as well as embryo-fetal toxicity. Ipilimumab has a boxed warning for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Nivolumab alone is approved for use in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is also approved for use in the treatment of melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with advanced liver cancer have a new treatment option – the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) and ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval of the combination for use in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have previously been treated with sorafenib (Nexavar, Bayer). Nivolumab is already approved as monotherapy for use in advanced HCC in patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The immunotherapy combination has shown a response rate that is more than twice that seen with nivolumab alone. The combination was tested at three different dosage schedules in the single-arm phase 1/2 trial known as CheckMate-040, which was conducted in 148 patients with advanced HCC who had previously been treated with sorafenib.
The approval was based on one arm of this trial, a cohort of 49 patients who were treated with nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV and ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
After a minimum follow-up of 28 months, 33% (16/49) of these patients showed a response, with 8% (4/49) showing a complete response and 24% (12/49) a partial response.
In terms of duration of responses, 88% of the responses lasted at least 6 months, 56% at least 12 months, and 31% at least 24 months, according to the company.
The results that led to the 2017 approval of nivolumab monotherapy for advanced HCC, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News, come from a cohort of 154 patients who received nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
The overall response rate was 14.3% (22 of 154 patients), with three patients (1.9%) showing a complete response and 19 patients (12.3%) a partial response. The duration of the responses ranged from 3.2 to 38.2+ months; 91% of those patients had responses of 6 months or longer, and 55% had responses of 12 months or longer.
Notably, patient responses in all arms were achieved regardless of baseline tumor PD-L1 status.
Aggressive disease, incidence is rising
“HCC is an aggressive disease in need of different treatment approaches,” said Anthony B. El-Khoueiry, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, in a company press statement.“The overall response rate observed in the Opdivo + Yervoy cohort of the CheckMate-040 trial underscores the potential of this dual immunotherapy as a possible treatment option for patients,” he commented. El-Khoueiry was lead investigator of the study and has received honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
“The incidence of liver cancer is rising in the United States, and HCC is the most common and aggressive form of the disease,” said Andrea Wilson, president and founder, Blue Faery: The Adrienne Wilson Liver Cancer Association.
“Today’s approval provides a new option for patients with HCC previously treated with sorafenib, giving the community more hope,” she said in the company press statement.
Safety profile
The nivolumab-ipilimumab combination had an “acceptable” safety profile overall in the CheckMate-040 trial, wrote lead study author Thomas Yao, MD, of the University at Hong Kong, China, and colleagues in their study abstract, which was presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Yao has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and has served as a consultant to the company.
According to those data, 37% of patients had a grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), the most common of which were pruritus and rash; 5% had grade 3–4 TRAEs that led to discontinuation.
Nivolumab is associated with pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, renal dysfunction, skin adverse reactions, encephalitis, other adverse reactions, and infusion-related reactions, as well as embryo-fetal toxicity. Ipilimumab has a boxed warning for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Nivolumab alone is approved for use in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is also approved for use in the treatment of melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with advanced liver cancer have a new treatment option – the immunotherapy combination of nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol-Myers Squibb) and ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol-Myers Squibb).
The US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted an accelerated approval of the combination for use in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) who have previously been treated with sorafenib (Nexavar, Bayer). Nivolumab is already approved as monotherapy for use in advanced HCC in patients who have previously been treated with sorafenib.
The immunotherapy combination has shown a response rate that is more than twice that seen with nivolumab alone. The combination was tested at three different dosage schedules in the single-arm phase 1/2 trial known as CheckMate-040, which was conducted in 148 patients with advanced HCC who had previously been treated with sorafenib.
The approval was based on one arm of this trial, a cohort of 49 patients who were treated with nivolumab 1 mg/kg IV and ipilimumab 3 mg/kg IV every 3 weeks for four doses, followed by nivolumab 240 mg every 2 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
After a minimum follow-up of 28 months, 33% (16/49) of these patients showed a response, with 8% (4/49) showing a complete response and 24% (12/49) a partial response.
In terms of duration of responses, 88% of the responses lasted at least 6 months, 56% at least 12 months, and 31% at least 24 months, according to the company.
The results that led to the 2017 approval of nivolumab monotherapy for advanced HCC, as previously reported by Medscape Medical News, come from a cohort of 154 patients who received nivolumab 3 mg/kg administered intravenously every 2 weeks.
The overall response rate was 14.3% (22 of 154 patients), with three patients (1.9%) showing a complete response and 19 patients (12.3%) a partial response. The duration of the responses ranged from 3.2 to 38.2+ months; 91% of those patients had responses of 6 months or longer, and 55% had responses of 12 months or longer.
Notably, patient responses in all arms were achieved regardless of baseline tumor PD-L1 status.
Aggressive disease, incidence is rising
“HCC is an aggressive disease in need of different treatment approaches,” said Anthony B. El-Khoueiry, MD, of the Norris Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of Southern California, Los Angeles, in a company press statement.“The overall response rate observed in the Opdivo + Yervoy cohort of the CheckMate-040 trial underscores the potential of this dual immunotherapy as a possible treatment option for patients,” he commented. El-Khoueiry was lead investigator of the study and has received honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb.
“The incidence of liver cancer is rising in the United States, and HCC is the most common and aggressive form of the disease,” said Andrea Wilson, president and founder, Blue Faery: The Adrienne Wilson Liver Cancer Association.
“Today’s approval provides a new option for patients with HCC previously treated with sorafenib, giving the community more hope,” she said in the company press statement.
Safety profile
The nivolumab-ipilimumab combination had an “acceptable” safety profile overall in the CheckMate-040 trial, wrote lead study author Thomas Yao, MD, of the University at Hong Kong, China, and colleagues in their study abstract, which was presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. Yao has received honoraria from Bristol-Myers Squibb and has served as a consultant to the company.
According to those data, 37% of patients had a grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse event (TRAE), the most common of which were pruritus and rash; 5% had grade 3–4 TRAEs that led to discontinuation.
Nivolumab is associated with pneumonitis, colitis, hepatitis, endocrinopathies, nephritis, renal dysfunction, skin adverse reactions, encephalitis, other adverse reactions, and infusion-related reactions, as well as embryo-fetal toxicity. Ipilimumab has a boxed warning for immune-mediated adverse reactions.
Nivolumab alone is approved for use in the treatment of unresectable or metastatic melanoma, non–small cell lung cancer, small cell lung cancer, and classical Hodgkin lymphoma.
The combination of nivolumab with ipilimumab is also approved for use in the treatment of melanoma and renal cell carcinoma.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cancer increase observed in modern era of MS drugs
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Cancer incidence among patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) treated after the advent of immune therapies showed an increase, compared with prior generations, according to a large study of Norwegian MS patients.
“We detected a similar cancer risk among MS patients, compared to the general Norwegian population before 1996, [however] MS patients had increased risk of cancer compared to the general population after 1996,” first author Nina Grytten, PhD, of the department of neurology at the Norwegian Multiple Sclerosis Centre, Bergen, Norway, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
“This finding suggests that clinicians should be aware of this increased risk of cancer when caring for MS patients.”
With the widespread use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in patients with MS, such findings are always of interest to clinicians and patients alike, commented ACTRIMS president, Jeffrey A. Cohen, MD.
“Something that’s already on the mind of most people with MS is what are the long-term safety characteristics of these medicines because we’re talking about a life-long therapy for most people,” Dr. Cohen, who is the director of Experimental Therapeutics at the Mellen Center for MS Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“With such a large sample size and such a long study, this is on one hand reassuring and tells us the cancer risk is likely low, but it also suggests that it’s something we should pay attention to,” he said.
In previous research, Dr. Grytten and her team identified an increased risk of cancer among patients with MS in Norway, but conflicting results have been reported in other studies looking at cancer risk and MS.
The authors therefore sought to dig deeper into the risk in the Norwegian population, looking into the specifics of cancer incidence according to sex and the period of diagnosis.
For the study, they identified a total of 6,638 patients with MS from previous prevalence studies in Norway, as well as in the Norwegian MS Registry and Biobank.
The data from the cohort was matched with 36,957 Norwegian citizens without MS in a 5:1 ratio, with the participants matched according to age, gender, and county. The cohort was further linked to data from the Norwegian Cancer Registry for additional information on the year and type of cancer diagnosis, as well as cause and year of death data. The participants were born between 1930 and 1979.
Over the course of the full 65-year observation period, the cancer diagnosis rates were similar between participants with MS (774; 11.2%) and those without MS (4,017; 10.6%).
And in looking at cancer incidence rate ratios of those with MS, compared with controls between the years 1953 and 1995, the rate was similar (IRR, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.97-1.14). However, after 1995, the rate increased, with a higher cancer incidence among MS patients, compared with those without MS (IRR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.30-1.51).
Cancer rates were additionally higher among those with MS in cancers of various organs, including the brain (IRR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.28-2.40), meninges (IRR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.47-3.53), urinary organs (IRR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.52-2.79), digestive system (IRR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.20-1.80), endocrine glands (IRR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.06-2.54), and respiratory organs (IRR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.55-2.07).
Dr. Grytten noted, however, that the study cannot rule out various other possible causes for the differences. For instance, “cancer in urinary system and respiratory organs showed increased risk in MS both before and after introduction of disease-modifying therapies,” she noted. “Those are possibly caused by smoking, which is a habit more common among MS patients in Norway.”
Furthermore, “increased cancer in the central nervous system in MS could possibly be explained by frequent use of magnetic resonance imaging and the ability to detect CNS cancer at early stages.”
“There is increasing evidence that patients with MS are also more susceptible to other diseases, and increased cancer risk seems to be one of these comorbidities.”
However, the finding that increased cancers were observed after 1996 in other organs in MS patients as well does raise the issue of a possible role of DMTs.
Of note, mitoxantrone has been associated with an increased risk of leukemia and colorectal cancer.
And “other immunosuppressant drugs, including the MS drug fingolimod, are believed to possibly be linked to an increased cancer risk, although evidence has not yet been established,” Dr. Grytten said.
“The increased risk of cancer associated with MS was detected in the era of disease-modifying treatment of MS, and this association suggests that DMTs might possibly increase cancer risk.”
In general, “clinicians should be aware of comorbidity in MS,” Dr. Grytten said. “More data is needed on the long-time effects of immunomodulatory treatment.”
Dr. Cohen added that, in addition to mitoxantrone, azathioprine and cyclophosphamide have shown risk, but “clinical trials and follow-up studies of individual MS DMTs have not shown clear cut increased risk of cancer, which is reassuring.”
“Nevertheless, this study suggests that, in aggregate, there may be a mild increased risk. There are many other potential explanations, so the research needs to be followed up,” he said.
Dr. Cohen reported receiving personal compensation for consulting for Adamas, Convelo, MedDay, Mylan, and Population Council; and serving as an Editor of Multiple Sclerosis Journal.
SOURCE: Torkildsen NG et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2020, Abstract P126.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Cancer incidence among patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) treated after the advent of immune therapies showed an increase, compared with prior generations, according to a large study of Norwegian MS patients.
“We detected a similar cancer risk among MS patients, compared to the general Norwegian population before 1996, [however] MS patients had increased risk of cancer compared to the general population after 1996,” first author Nina Grytten, PhD, of the department of neurology at the Norwegian Multiple Sclerosis Centre, Bergen, Norway, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
“This finding suggests that clinicians should be aware of this increased risk of cancer when caring for MS patients.”
With the widespread use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in patients with MS, such findings are always of interest to clinicians and patients alike, commented ACTRIMS president, Jeffrey A. Cohen, MD.
“Something that’s already on the mind of most people with MS is what are the long-term safety characteristics of these medicines because we’re talking about a life-long therapy for most people,” Dr. Cohen, who is the director of Experimental Therapeutics at the Mellen Center for MS Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“With such a large sample size and such a long study, this is on one hand reassuring and tells us the cancer risk is likely low, but it also suggests that it’s something we should pay attention to,” he said.
In previous research, Dr. Grytten and her team identified an increased risk of cancer among patients with MS in Norway, but conflicting results have been reported in other studies looking at cancer risk and MS.
The authors therefore sought to dig deeper into the risk in the Norwegian population, looking into the specifics of cancer incidence according to sex and the period of diagnosis.
For the study, they identified a total of 6,638 patients with MS from previous prevalence studies in Norway, as well as in the Norwegian MS Registry and Biobank.
The data from the cohort was matched with 36,957 Norwegian citizens without MS in a 5:1 ratio, with the participants matched according to age, gender, and county. The cohort was further linked to data from the Norwegian Cancer Registry for additional information on the year and type of cancer diagnosis, as well as cause and year of death data. The participants were born between 1930 and 1979.
Over the course of the full 65-year observation period, the cancer diagnosis rates were similar between participants with MS (774; 11.2%) and those without MS (4,017; 10.6%).
And in looking at cancer incidence rate ratios of those with MS, compared with controls between the years 1953 and 1995, the rate was similar (IRR, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.97-1.14). However, after 1995, the rate increased, with a higher cancer incidence among MS patients, compared with those without MS (IRR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.30-1.51).
Cancer rates were additionally higher among those with MS in cancers of various organs, including the brain (IRR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.28-2.40), meninges (IRR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.47-3.53), urinary organs (IRR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.52-2.79), digestive system (IRR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.20-1.80), endocrine glands (IRR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.06-2.54), and respiratory organs (IRR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.55-2.07).
Dr. Grytten noted, however, that the study cannot rule out various other possible causes for the differences. For instance, “cancer in urinary system and respiratory organs showed increased risk in MS both before and after introduction of disease-modifying therapies,” she noted. “Those are possibly caused by smoking, which is a habit more common among MS patients in Norway.”
Furthermore, “increased cancer in the central nervous system in MS could possibly be explained by frequent use of magnetic resonance imaging and the ability to detect CNS cancer at early stages.”
“There is increasing evidence that patients with MS are also more susceptible to other diseases, and increased cancer risk seems to be one of these comorbidities.”
However, the finding that increased cancers were observed after 1996 in other organs in MS patients as well does raise the issue of a possible role of DMTs.
Of note, mitoxantrone has been associated with an increased risk of leukemia and colorectal cancer.
And “other immunosuppressant drugs, including the MS drug fingolimod, are believed to possibly be linked to an increased cancer risk, although evidence has not yet been established,” Dr. Grytten said.
“The increased risk of cancer associated with MS was detected in the era of disease-modifying treatment of MS, and this association suggests that DMTs might possibly increase cancer risk.”
In general, “clinicians should be aware of comorbidity in MS,” Dr. Grytten said. “More data is needed on the long-time effects of immunomodulatory treatment.”
Dr. Cohen added that, in addition to mitoxantrone, azathioprine and cyclophosphamide have shown risk, but “clinical trials and follow-up studies of individual MS DMTs have not shown clear cut increased risk of cancer, which is reassuring.”
“Nevertheless, this study suggests that, in aggregate, there may be a mild increased risk. There are many other potential explanations, so the research needs to be followed up,” he said.
Dr. Cohen reported receiving personal compensation for consulting for Adamas, Convelo, MedDay, Mylan, and Population Council; and serving as an Editor of Multiple Sclerosis Journal.
SOURCE: Torkildsen NG et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2020, Abstract P126.
WEST PALM BEACH, FLA. – Cancer incidence among patients with multiple sclerosis (MS) treated after the advent of immune therapies showed an increase, compared with prior generations, according to a large study of Norwegian MS patients.
“We detected a similar cancer risk among MS patients, compared to the general Norwegian population before 1996, [however] MS patients had increased risk of cancer compared to the general population after 1996,” first author Nina Grytten, PhD, of the department of neurology at the Norwegian Multiple Sclerosis Centre, Bergen, Norway, said in an interview at the meeting held by the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis.
“This finding suggests that clinicians should be aware of this increased risk of cancer when caring for MS patients.”
With the widespread use of disease-modifying therapies (DMTs) in patients with MS, such findings are always of interest to clinicians and patients alike, commented ACTRIMS president, Jeffrey A. Cohen, MD.
“Something that’s already on the mind of most people with MS is what are the long-term safety characteristics of these medicines because we’re talking about a life-long therapy for most people,” Dr. Cohen, who is the director of Experimental Therapeutics at the Mellen Center for MS Treatment and Research at the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview.
“With such a large sample size and such a long study, this is on one hand reassuring and tells us the cancer risk is likely low, but it also suggests that it’s something we should pay attention to,” he said.
In previous research, Dr. Grytten and her team identified an increased risk of cancer among patients with MS in Norway, but conflicting results have been reported in other studies looking at cancer risk and MS.
The authors therefore sought to dig deeper into the risk in the Norwegian population, looking into the specifics of cancer incidence according to sex and the period of diagnosis.
For the study, they identified a total of 6,638 patients with MS from previous prevalence studies in Norway, as well as in the Norwegian MS Registry and Biobank.
The data from the cohort was matched with 36,957 Norwegian citizens without MS in a 5:1 ratio, with the participants matched according to age, gender, and county. The cohort was further linked to data from the Norwegian Cancer Registry for additional information on the year and type of cancer diagnosis, as well as cause and year of death data. The participants were born between 1930 and 1979.
Over the course of the full 65-year observation period, the cancer diagnosis rates were similar between participants with MS (774; 11.2%) and those without MS (4,017; 10.6%).
And in looking at cancer incidence rate ratios of those with MS, compared with controls between the years 1953 and 1995, the rate was similar (IRR, 1.05; 95% confidence interval, 0.97-1.14). However, after 1995, the rate increased, with a higher cancer incidence among MS patients, compared with those without MS (IRR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.30-1.51).
Cancer rates were additionally higher among those with MS in cancers of various organs, including the brain (IRR, 1.75; 95% CI, 1.28-2.40), meninges (IRR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.47-3.53), urinary organs (IRR, 2.06; 95% CI, 1.52-2.79), digestive system (IRR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.20-1.80), endocrine glands (IRR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.06-2.54), and respiratory organs (IRR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.55-2.07).
Dr. Grytten noted, however, that the study cannot rule out various other possible causes for the differences. For instance, “cancer in urinary system and respiratory organs showed increased risk in MS both before and after introduction of disease-modifying therapies,” she noted. “Those are possibly caused by smoking, which is a habit more common among MS patients in Norway.”
Furthermore, “increased cancer in the central nervous system in MS could possibly be explained by frequent use of magnetic resonance imaging and the ability to detect CNS cancer at early stages.”
“There is increasing evidence that patients with MS are also more susceptible to other diseases, and increased cancer risk seems to be one of these comorbidities.”
However, the finding that increased cancers were observed after 1996 in other organs in MS patients as well does raise the issue of a possible role of DMTs.
Of note, mitoxantrone has been associated with an increased risk of leukemia and colorectal cancer.
And “other immunosuppressant drugs, including the MS drug fingolimod, are believed to possibly be linked to an increased cancer risk, although evidence has not yet been established,” Dr. Grytten said.
“The increased risk of cancer associated with MS was detected in the era of disease-modifying treatment of MS, and this association suggests that DMTs might possibly increase cancer risk.”
In general, “clinicians should be aware of comorbidity in MS,” Dr. Grytten said. “More data is needed on the long-time effects of immunomodulatory treatment.”
Dr. Cohen added that, in addition to mitoxantrone, azathioprine and cyclophosphamide have shown risk, but “clinical trials and follow-up studies of individual MS DMTs have not shown clear cut increased risk of cancer, which is reassuring.”
“Nevertheless, this study suggests that, in aggregate, there may be a mild increased risk. There are many other potential explanations, so the research needs to be followed up,” he said.
Dr. Cohen reported receiving personal compensation for consulting for Adamas, Convelo, MedDay, Mylan, and Population Council; and serving as an Editor of Multiple Sclerosis Journal.
SOURCE: Torkildsen NG et al. ACTRIMS Forum 2020, Abstract P126.
REPORTING FROM ACTRIMS FORUM 2020
Tumor neoantigenicity metric improves prediction of response to immunotherapy
A new tumor neoantigenicity metric may improve prediction of response to immunotherapy in patients with melanoma, lung cancer, and kidney cancer, a retrospective analysis suggests.
The new metric, known as the Cauchy-Schwarz index of neoantigens (CSiN) score, incorporates both immunogenicity and clonality, according to lead study author Tianshi Lu, a PhD candidate at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues.
“The major biological insight from this study is that the neoantigen clonal structure in each tumor specimen and the immunogenicity of the neoantigens (represented by the MHC-binding strength in our study) are predictive of response to checkpoint inhibitors and prognosis,” the investigators wrote in Science Immunology.
The study involved 2,479 patients with various cancers, including immunogenic types such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and nonimmunogenic types, such as pediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia.
The investigators first evaluated CSiN in relation to clinical outcome among patients with immunogenic cancers who received immunotherapy. Drawing data from multiple cohorts, the investigators found that patients who had better responses to therapy were significantly more likely to have above average CSiN scores than those who had worse responses.
In one cohort of patients with melanoma who received anti–CTLA-4 therapy, those with better responses were more likely to have high CSiN scores (P = .009). In another cohort of melanoma patients who received anti–CTLA-4 therapy, those with higher CSiN scores were more likely to achieve durable clinical benefit (response or stable disease for more than 6 months), compared with patients who had lower CSiN scores (P = .033).
Among patients with clear cell RCC treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, there was a significant positive association between higher CSiN scores and better response (P = .036). Among T effector-high patients with metastatic clear cell RCC, there was a significant association between higher CSiN scores and better response to atezolizumab (P = .028) but not sunitinib (P = .890).
In a cohort of patients with non–small cell lung cancer treated with checkpoint inhibitors, those with sustained responses were more likely to have higher CSiN scores than were patients with short-term progression (P = .015).
The investigators also compared the predictive power of CSiN with existing neoantigenicity metrics, ultimately concluding that CSiN was superior.
“Overall, the neoantigen load and neoantigen fitness models were not as strongly predictive of treatment response as CSiN,” the investigators wrote.
Again using data from patients with immunogenic cancers, the investigators looked for an association between CSiN score and overall survival. Indeed, patients with higher-than-average CSiN scores had significantly better survival than that of those with lower scores (P less than .001). This finding was maintained in a multivariate analysis that accounted for disease type, stage, sex, and age.
In contrast with the above findings, CSiN did not predict survival among patients with nonimmunogenic cancer types.
“Overall, our work offers a rigorous methodology of predicting response to immunotherapy and prognosis from routine patient samples and should be useful for personalizing medicine in the modern era of immunotherapy,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas, and the American Cancer Society. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lu et al. Sci Immunol. 2020 Feb 21. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaz3199.
A new tumor neoantigenicity metric may improve prediction of response to immunotherapy in patients with melanoma, lung cancer, and kidney cancer, a retrospective analysis suggests.
The new metric, known as the Cauchy-Schwarz index of neoantigens (CSiN) score, incorporates both immunogenicity and clonality, according to lead study author Tianshi Lu, a PhD candidate at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues.
“The major biological insight from this study is that the neoantigen clonal structure in each tumor specimen and the immunogenicity of the neoantigens (represented by the MHC-binding strength in our study) are predictive of response to checkpoint inhibitors and prognosis,” the investigators wrote in Science Immunology.
The study involved 2,479 patients with various cancers, including immunogenic types such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and nonimmunogenic types, such as pediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia.
The investigators first evaluated CSiN in relation to clinical outcome among patients with immunogenic cancers who received immunotherapy. Drawing data from multiple cohorts, the investigators found that patients who had better responses to therapy were significantly more likely to have above average CSiN scores than those who had worse responses.
In one cohort of patients with melanoma who received anti–CTLA-4 therapy, those with better responses were more likely to have high CSiN scores (P = .009). In another cohort of melanoma patients who received anti–CTLA-4 therapy, those with higher CSiN scores were more likely to achieve durable clinical benefit (response or stable disease for more than 6 months), compared with patients who had lower CSiN scores (P = .033).
Among patients with clear cell RCC treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, there was a significant positive association between higher CSiN scores and better response (P = .036). Among T effector-high patients with metastatic clear cell RCC, there was a significant association between higher CSiN scores and better response to atezolizumab (P = .028) but not sunitinib (P = .890).
In a cohort of patients with non–small cell lung cancer treated with checkpoint inhibitors, those with sustained responses were more likely to have higher CSiN scores than were patients with short-term progression (P = .015).
The investigators also compared the predictive power of CSiN with existing neoantigenicity metrics, ultimately concluding that CSiN was superior.
“Overall, the neoantigen load and neoantigen fitness models were not as strongly predictive of treatment response as CSiN,” the investigators wrote.
Again using data from patients with immunogenic cancers, the investigators looked for an association between CSiN score and overall survival. Indeed, patients with higher-than-average CSiN scores had significantly better survival than that of those with lower scores (P less than .001). This finding was maintained in a multivariate analysis that accounted for disease type, stage, sex, and age.
In contrast with the above findings, CSiN did not predict survival among patients with nonimmunogenic cancer types.
“Overall, our work offers a rigorous methodology of predicting response to immunotherapy and prognosis from routine patient samples and should be useful for personalizing medicine in the modern era of immunotherapy,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas, and the American Cancer Society. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lu et al. Sci Immunol. 2020 Feb 21. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaz3199.
A new tumor neoantigenicity metric may improve prediction of response to immunotherapy in patients with melanoma, lung cancer, and kidney cancer, a retrospective analysis suggests.
The new metric, known as the Cauchy-Schwarz index of neoantigens (CSiN) score, incorporates both immunogenicity and clonality, according to lead study author Tianshi Lu, a PhD candidate at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas, and colleagues.
“The major biological insight from this study is that the neoantigen clonal structure in each tumor specimen and the immunogenicity of the neoantigens (represented by the MHC-binding strength in our study) are predictive of response to checkpoint inhibitors and prognosis,” the investigators wrote in Science Immunology.
The study involved 2,479 patients with various cancers, including immunogenic types such as renal cell carcinoma (RCC), and nonimmunogenic types, such as pediatric acute lymphocytic leukemia.
The investigators first evaluated CSiN in relation to clinical outcome among patients with immunogenic cancers who received immunotherapy. Drawing data from multiple cohorts, the investigators found that patients who had better responses to therapy were significantly more likely to have above average CSiN scores than those who had worse responses.
In one cohort of patients with melanoma who received anti–CTLA-4 therapy, those with better responses were more likely to have high CSiN scores (P = .009). In another cohort of melanoma patients who received anti–CTLA-4 therapy, those with higher CSiN scores were more likely to achieve durable clinical benefit (response or stable disease for more than 6 months), compared with patients who had lower CSiN scores (P = .033).
Among patients with clear cell RCC treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy, there was a significant positive association between higher CSiN scores and better response (P = .036). Among T effector-high patients with metastatic clear cell RCC, there was a significant association between higher CSiN scores and better response to atezolizumab (P = .028) but not sunitinib (P = .890).
In a cohort of patients with non–small cell lung cancer treated with checkpoint inhibitors, those with sustained responses were more likely to have higher CSiN scores than were patients with short-term progression (P = .015).
The investigators also compared the predictive power of CSiN with existing neoantigenicity metrics, ultimately concluding that CSiN was superior.
“Overall, the neoantigen load and neoantigen fitness models were not as strongly predictive of treatment response as CSiN,” the investigators wrote.
Again using data from patients with immunogenic cancers, the investigators looked for an association between CSiN score and overall survival. Indeed, patients with higher-than-average CSiN scores had significantly better survival than that of those with lower scores (P less than .001). This finding was maintained in a multivariate analysis that accounted for disease type, stage, sex, and age.
In contrast with the above findings, CSiN did not predict survival among patients with nonimmunogenic cancer types.
“Overall, our work offers a rigorous methodology of predicting response to immunotherapy and prognosis from routine patient samples and should be useful for personalizing medicine in the modern era of immunotherapy,” the investigators concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas, and the American Cancer Society. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lu et al. Sci Immunol. 2020 Feb 21. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.aaz3199.
FROM SCIENCE IMMUNOLOGY
Experts break down latest CAR T-cell advances in lymphoma
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASH 2019
New toxicity subscale measures QOL in cancer patients on checkpoint inhibitors
developed based on direct patient involvement, picks up on cutaneous and other side effects that would be missed using traditional quality of life questionnaires, investigators say.
The 25-item list represents the first-ever health-related quality of life (HRQOL) toxicity subscale developed for patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, according to the investigators, led by Aaron R. Hansen, MBBS, of the division of medical oncology and hematology in the department of medicine at the University of Toronto.
The toxicity subscale is combined with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–General (FACT-G), which measures physical, emotional, family and social, and functional domains, to form the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Immune Checkpoint Modulator (FACT-ICM), Dr. Hansen stated in a recent report that describes initial development and early validation efforts.
The FACT-ICM could become an important tool for measuring HRQOL in patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, depending on results of further investigations including more patients, the authors wrote in that report.
“Currently, we would recommend that our toxicity subscale be validated first before use in clinical care, or in trials with QOL as a primary or secondary endpoint,” wrote Dr. Hansen and colleagues in the report, which appears in Cancer.
The toxicity subscale asks patients to rate items such as “I am bothered by dry skin,” “I feel pain, soreness or aches in some of my muscles,” and “My fatigue keeps me from doing the things I want do” on a scale of 0 (not at all) to 4 (very much).
Development of the toxicity subscale was based on focus groups and interviews with 37 patients with a variety of cancer types who were being treated with a PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Sixteen physicians were surveyed to evaluate the patient input, while 11 of them also participated in follow-up interviews.
“At every step in this process, the patients were central,” the investigators wrote in their report.
According to the investigators, that approach is in line with guidance from the Food and Drug Administration, which has said that meaningful patient input should be used in the upfront development of patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures, rather than obtaining patient endorsement after the fact.
By contrast, an electronic PRO immune-oncology module recently developed, based on 19 immune-related adverse events from drug labels and clinical trial reports, had “no evaluation” of effects on HRQOL, according to Dr. Hansen and coauthors, who added that the tool “did not adhere” to the FDA call for meaningful patient input.
Some previous studies of quality of life in immune checkpoint inhibitor–treated patients have used tumor-specific PROs and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire–Core 30 Items (EORTC-QLQ-C30).
The new, immune checkpoint inhibitor–specific toxicity subscale has “broader coverage” of side effects that reportedly affect HRQOL in patients treated with these agents, including taste disturbance, cough, and fever or chills, according to the investigators.
Moreover, the EORTC-QLQ-C30 and the EORTC head and neck cancer–specific-35 module (EORTC QLQ-H&N35), do not include items related to cutaneous adverse events such as itch, rash, and dry skin that have been seen in some checkpoint inhibitor clinical trials, they noted.
“This represents a clear limitation of such preexisting PRO instruments, which should be addressed with our immune checkpoint moduator–specific tool,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant from the University of Toronto. Authors of the study provided disclosures related to Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Karyopharm, Boston Biomedical, Novartis, Genentech, Hoffmann La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and others.
SOURCE: Hansen AR et al. Cancer. 2020 Jan 8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32692.
developed based on direct patient involvement, picks up on cutaneous and other side effects that would be missed using traditional quality of life questionnaires, investigators say.
The 25-item list represents the first-ever health-related quality of life (HRQOL) toxicity subscale developed for patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, according to the investigators, led by Aaron R. Hansen, MBBS, of the division of medical oncology and hematology in the department of medicine at the University of Toronto.
The toxicity subscale is combined with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–General (FACT-G), which measures physical, emotional, family and social, and functional domains, to form the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Immune Checkpoint Modulator (FACT-ICM), Dr. Hansen stated in a recent report that describes initial development and early validation efforts.
The FACT-ICM could become an important tool for measuring HRQOL in patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, depending on results of further investigations including more patients, the authors wrote in that report.
“Currently, we would recommend that our toxicity subscale be validated first before use in clinical care, or in trials with QOL as a primary or secondary endpoint,” wrote Dr. Hansen and colleagues in the report, which appears in Cancer.
The toxicity subscale asks patients to rate items such as “I am bothered by dry skin,” “I feel pain, soreness or aches in some of my muscles,” and “My fatigue keeps me from doing the things I want do” on a scale of 0 (not at all) to 4 (very much).
Development of the toxicity subscale was based on focus groups and interviews with 37 patients with a variety of cancer types who were being treated with a PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Sixteen physicians were surveyed to evaluate the patient input, while 11 of them also participated in follow-up interviews.
“At every step in this process, the patients were central,” the investigators wrote in their report.
According to the investigators, that approach is in line with guidance from the Food and Drug Administration, which has said that meaningful patient input should be used in the upfront development of patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures, rather than obtaining patient endorsement after the fact.
By contrast, an electronic PRO immune-oncology module recently developed, based on 19 immune-related adverse events from drug labels and clinical trial reports, had “no evaluation” of effects on HRQOL, according to Dr. Hansen and coauthors, who added that the tool “did not adhere” to the FDA call for meaningful patient input.
Some previous studies of quality of life in immune checkpoint inhibitor–treated patients have used tumor-specific PROs and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire–Core 30 Items (EORTC-QLQ-C30).
The new, immune checkpoint inhibitor–specific toxicity subscale has “broader coverage” of side effects that reportedly affect HRQOL in patients treated with these agents, including taste disturbance, cough, and fever or chills, according to the investigators.
Moreover, the EORTC-QLQ-C30 and the EORTC head and neck cancer–specific-35 module (EORTC QLQ-H&N35), do not include items related to cutaneous adverse events such as itch, rash, and dry skin that have been seen in some checkpoint inhibitor clinical trials, they noted.
“This represents a clear limitation of such preexisting PRO instruments, which should be addressed with our immune checkpoint moduator–specific tool,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant from the University of Toronto. Authors of the study provided disclosures related to Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Karyopharm, Boston Biomedical, Novartis, Genentech, Hoffmann La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and others.
SOURCE: Hansen AR et al. Cancer. 2020 Jan 8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32692.
developed based on direct patient involvement, picks up on cutaneous and other side effects that would be missed using traditional quality of life questionnaires, investigators say.
The 25-item list represents the first-ever health-related quality of life (HRQOL) toxicity subscale developed for patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, according to the investigators, led by Aaron R. Hansen, MBBS, of the division of medical oncology and hematology in the department of medicine at the University of Toronto.
The toxicity subscale is combined with the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–General (FACT-G), which measures physical, emotional, family and social, and functional domains, to form the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy–Immune Checkpoint Modulator (FACT-ICM), Dr. Hansen stated in a recent report that describes initial development and early validation efforts.
The FACT-ICM could become an important tool for measuring HRQOL in patients receiving checkpoint inhibitors, depending on results of further investigations including more patients, the authors wrote in that report.
“Currently, we would recommend that our toxicity subscale be validated first before use in clinical care, or in trials with QOL as a primary or secondary endpoint,” wrote Dr. Hansen and colleagues in the report, which appears in Cancer.
The toxicity subscale asks patients to rate items such as “I am bothered by dry skin,” “I feel pain, soreness or aches in some of my muscles,” and “My fatigue keeps me from doing the things I want do” on a scale of 0 (not at all) to 4 (very much).
Development of the toxicity subscale was based on focus groups and interviews with 37 patients with a variety of cancer types who were being treated with a PD-1, PD-L1, and CTLA-4 immune checkpoint inhibitors. Sixteen physicians were surveyed to evaluate the patient input, while 11 of them also participated in follow-up interviews.
“At every step in this process, the patients were central,” the investigators wrote in their report.
According to the investigators, that approach is in line with guidance from the Food and Drug Administration, which has said that meaningful patient input should be used in the upfront development of patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures, rather than obtaining patient endorsement after the fact.
By contrast, an electronic PRO immune-oncology module recently developed, based on 19 immune-related adverse events from drug labels and clinical trial reports, had “no evaluation” of effects on HRQOL, according to Dr. Hansen and coauthors, who added that the tool “did not adhere” to the FDA call for meaningful patient input.
Some previous studies of quality of life in immune checkpoint inhibitor–treated patients have used tumor-specific PROs and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire–Core 30 Items (EORTC-QLQ-C30).
The new, immune checkpoint inhibitor–specific toxicity subscale has “broader coverage” of side effects that reportedly affect HRQOL in patients treated with these agents, including taste disturbance, cough, and fever or chills, according to the investigators.
Moreover, the EORTC-QLQ-C30 and the EORTC head and neck cancer–specific-35 module (EORTC QLQ-H&N35), do not include items related to cutaneous adverse events such as itch, rash, and dry skin that have been seen in some checkpoint inhibitor clinical trials, they noted.
“This represents a clear limitation of such preexisting PRO instruments, which should be addressed with our immune checkpoint moduator–specific tool,” they wrote.
The study was supported by a grant from the University of Toronto. Authors of the study provided disclosures related to Merck, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Karyopharm, Boston Biomedical, Novartis, Genentech, Hoffmann La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, and others.
SOURCE: Hansen AR et al. Cancer. 2020 Jan 8. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32692.
FROM CANCER