User login
BET inhibitors may target oncogene in ABC-like DLBCL
(ABC-like DLBCL).
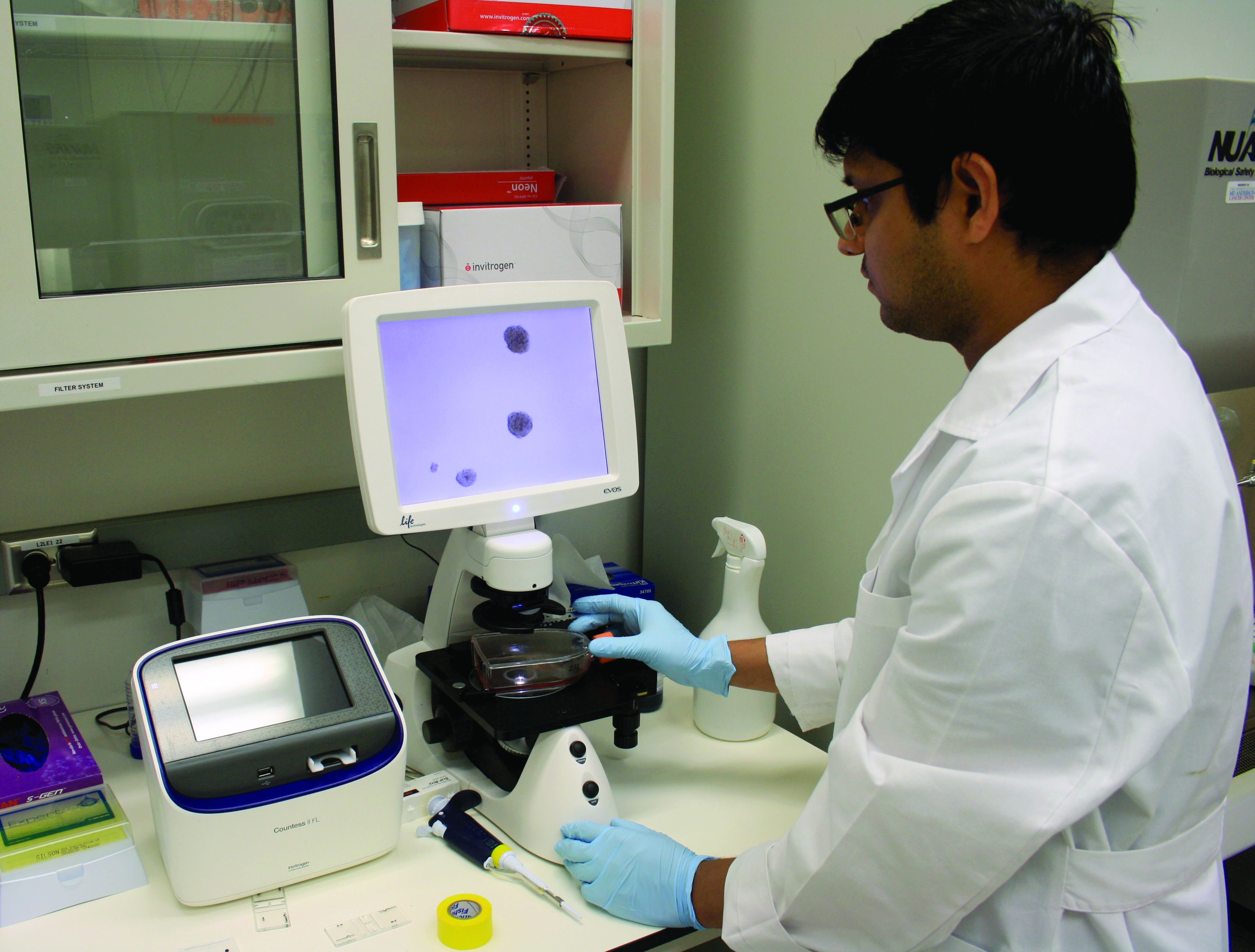
Researchers found the TCF4 (E2-2) transcription factor is an oncogene in ABC-like DLBCL, and TCF4 can be targeted via BET inhibition.
The BET protein degrader ARV771 reduced TCF4 expression and exhibited activity against ABC-like DLBCL in vitro and in vivo.
Neeraj Jain, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and colleagues reported these findings in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers performed a genomic analysis of 1,000 DLBCL tumors and discovered that gains of 18q21.2 were the most frequent genetic alteration in ABC-like DLBCL. In analyzing another 249 tumors, the researchers found that TCF4 was the target of the 18q21.2 gains.
Additional experiments with primary DLBCL tumors and DLBCL cell lines indicated that TCF4 regulates IGHM and MYC expression. The researchers also found that the TCF4 gene was “one of the most highly BRD4-loaded genes in DLBCL,” and knocking down BRD4 in DLBCL cell lines reduced TCF4 expression.
These findings prompted the team to test small-molecule BET inhibitors – JQ1 and OTX015 – and a BET protein degrader – ARV771 – in ABC-like DLBCL cell lines with a high TCF4 copy number.
Treatment with JQ1 and OTX015 resulted in upregulation of BRD4, but ARV771 treatment did not. As a result, subsequent experiments were performed with ARV771.
The researchers found that ARV771 induced apoptosis in the cell lines and reduced the expression of TCF4, IgM, and MYC. However, enforced TCF4 expression during ARV771 treatment rescued IgM and MYC expression. This suggests that “reduction of TCF4 is one of the mechanisms by which BET inhibition reduces IgM and MYC expression and induces apoptosis,” according to the researchers.
The team also tested ARV771 in mouse models of ABC-like DLBCL with high TCF4 expression. ARV771 significantly reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival (P less than .05 for both), and there were no signs of toxicity in ARV771-treated mice.
“Our data provide a clear functional rationale for BET inhibition in ABC-like DLBCL,” the researchers wrote. They did note, however, that BCL2 overexpression is associated with resistance to BET inhibitors, and most of the 18q DNA copy number gains the researchers observed in DLBCL encompass TCF4 and BCL2. The team therefore theorized that combining a BET inhibitor with a BCL2 inhibitor could be a promising treatment approach in ABC-like DLBCL and is worthy of further investigation.
This research was supported by the Nebraska Department of Health & Human Services, the Schweitzer Family Fund, the Fred & Pamela Buffet Cancer Center Support Grant, and the MD Anderson Cancer Center NCI CORE Grant. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest related to the study.
SOURCE: Jain N et al. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav5599.
(ABC-like DLBCL).
Researchers found the TCF4 (E2-2) transcription factor is an oncogene in ABC-like DLBCL, and TCF4 can be targeted via BET inhibition.
The BET protein degrader ARV771 reduced TCF4 expression and exhibited activity against ABC-like DLBCL in vitro and in vivo.
Neeraj Jain, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and colleagues reported these findings in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers performed a genomic analysis of 1,000 DLBCL tumors and discovered that gains of 18q21.2 were the most frequent genetic alteration in ABC-like DLBCL. In analyzing another 249 tumors, the researchers found that TCF4 was the target of the 18q21.2 gains.
Additional experiments with primary DLBCL tumors and DLBCL cell lines indicated that TCF4 regulates IGHM and MYC expression. The researchers also found that the TCF4 gene was “one of the most highly BRD4-loaded genes in DLBCL,” and knocking down BRD4 in DLBCL cell lines reduced TCF4 expression.
These findings prompted the team to test small-molecule BET inhibitors – JQ1 and OTX015 – and a BET protein degrader – ARV771 – in ABC-like DLBCL cell lines with a high TCF4 copy number.
Treatment with JQ1 and OTX015 resulted in upregulation of BRD4, but ARV771 treatment did not. As a result, subsequent experiments were performed with ARV771.
The researchers found that ARV771 induced apoptosis in the cell lines and reduced the expression of TCF4, IgM, and MYC. However, enforced TCF4 expression during ARV771 treatment rescued IgM and MYC expression. This suggests that “reduction of TCF4 is one of the mechanisms by which BET inhibition reduces IgM and MYC expression and induces apoptosis,” according to the researchers.
The team also tested ARV771 in mouse models of ABC-like DLBCL with high TCF4 expression. ARV771 significantly reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival (P less than .05 for both), and there were no signs of toxicity in ARV771-treated mice.
“Our data provide a clear functional rationale for BET inhibition in ABC-like DLBCL,” the researchers wrote. They did note, however, that BCL2 overexpression is associated with resistance to BET inhibitors, and most of the 18q DNA copy number gains the researchers observed in DLBCL encompass TCF4 and BCL2. The team therefore theorized that combining a BET inhibitor with a BCL2 inhibitor could be a promising treatment approach in ABC-like DLBCL and is worthy of further investigation.
This research was supported by the Nebraska Department of Health & Human Services, the Schweitzer Family Fund, the Fred & Pamela Buffet Cancer Center Support Grant, and the MD Anderson Cancer Center NCI CORE Grant. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest related to the study.
SOURCE: Jain N et al. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav5599.
(ABC-like DLBCL).
Researchers found the TCF4 (E2-2) transcription factor is an oncogene in ABC-like DLBCL, and TCF4 can be targeted via BET inhibition.
The BET protein degrader ARV771 reduced TCF4 expression and exhibited activity against ABC-like DLBCL in vitro and in vivo.
Neeraj Jain, PhD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston and colleagues reported these findings in Science Translational Medicine.
The researchers performed a genomic analysis of 1,000 DLBCL tumors and discovered that gains of 18q21.2 were the most frequent genetic alteration in ABC-like DLBCL. In analyzing another 249 tumors, the researchers found that TCF4 was the target of the 18q21.2 gains.
Additional experiments with primary DLBCL tumors and DLBCL cell lines indicated that TCF4 regulates IGHM and MYC expression. The researchers also found that the TCF4 gene was “one of the most highly BRD4-loaded genes in DLBCL,” and knocking down BRD4 in DLBCL cell lines reduced TCF4 expression.
These findings prompted the team to test small-molecule BET inhibitors – JQ1 and OTX015 – and a BET protein degrader – ARV771 – in ABC-like DLBCL cell lines with a high TCF4 copy number.
Treatment with JQ1 and OTX015 resulted in upregulation of BRD4, but ARV771 treatment did not. As a result, subsequent experiments were performed with ARV771.
The researchers found that ARV771 induced apoptosis in the cell lines and reduced the expression of TCF4, IgM, and MYC. However, enforced TCF4 expression during ARV771 treatment rescued IgM and MYC expression. This suggests that “reduction of TCF4 is one of the mechanisms by which BET inhibition reduces IgM and MYC expression and induces apoptosis,” according to the researchers.
The team also tested ARV771 in mouse models of ABC-like DLBCL with high TCF4 expression. ARV771 significantly reduced tumor growth and prolonged survival (P less than .05 for both), and there were no signs of toxicity in ARV771-treated mice.
“Our data provide a clear functional rationale for BET inhibition in ABC-like DLBCL,” the researchers wrote. They did note, however, that BCL2 overexpression is associated with resistance to BET inhibitors, and most of the 18q DNA copy number gains the researchers observed in DLBCL encompass TCF4 and BCL2. The team therefore theorized that combining a BET inhibitor with a BCL2 inhibitor could be a promising treatment approach in ABC-like DLBCL and is worthy of further investigation.
This research was supported by the Nebraska Department of Health & Human Services, the Schweitzer Family Fund, the Fred & Pamela Buffet Cancer Center Support Grant, and the MD Anderson Cancer Center NCI CORE Grant. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest related to the study.
SOURCE: Jain N et al. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019 Jun 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav5599.
FROM SCIENCE TRANSLATIONAL MEDICINE
Bispecific CAR T-cell therapy yields complete responses in relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas
CHICAGO – A bispecific anti-CD19, anti-CD20 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell approach is safe and produced complete responses in the majority of patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a phase 1 study, an investigator reported.
Eleven of 17 assessable patients had a response to treatment with the bispecific lentiviral CAR T cell (LV20.19CAR) at day 28, and of those 11 patients, 9 had complete responses, all of which are ongoing, said Nirav Niranjan Shah, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
“To date, there’s no dose-limiting toxicity, no ICU-level care, no deaths attributed to treatment, no grade 3 to 4 cytokine release syndrome, and only two patients had reversible grade 3 neurotoxicity,” Dr. Shah said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Patients who did relapse or progress on treatment maintained CD19 or CD20 positivity, with no observed downregulation of target receptors, he reported in an oral abstract session.
Of note, the CAR T cells were produced locally at the point of care, with a 100% success rate and a set 14-day manufacturing time, he added.
Bispecific targeting of CD19 and CD20 is a new approach being investigated at a time when there are already two CD19-specific CAR T cell therapies approved for aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, Dr. Shah told attendees.
“Despite the great promise of CD19 CAR T cell therapies, very quickly after the development of these therapies, we discovered mechanisms of resistance—specifically, the development of a CD19 negative relapse,” he said.
The hypothesis that targeting more than one B-cell antigen could potentially mitigate that effect stemmed from preclinical studies showing that targeting both CD19 and CD20 decreased downregulation of CD19 but not other B-cell antigens, he added.
In the present phase 1 study of the first-in-human, bispecific tandem CAR T cell against CD19 and CD20, patients have been treated at several dose levels, some with a split infusion over 2 days to evaluate safety, and some with a single infusion, Dr. Shah said.
A total of 17 patients have been treated with a lymphodepletion regimen followed by LV20.19CAR: 8 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, 6 with mantle cell lymphoma, 2 with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and 1 with follicular lymphoma, according to the investigator. The median age of patients is 59 years, and patients had received at least 3 and up to 11 prior lines of therapy.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities to date with dosing up to the target of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, Dr. Shah reported, adding that there has been no grade 3-4 cytokine release syndrome and no grade 4 neurotoxicity. Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome has been seen in 11 patients, while grade 3 neurotoxicity occurred in 2 patients.
Fourteen of 17 patients had a response, including 11 complete responses and 3 partial responses. Eleven patients were treated at the target dose of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, and of those, 9 had a complete response and 1 had a partial response (overall response rate, Dr. Shah said.
To date, all patients in complete response have remained in a complete response, with durations of response of 1 to 18 months.
Next, investigators plan to conduct phase 2 studies in more specific cohorts, including patients with mantle cell lymphoma, and patients who have relapsed after CD19 CAR T cell therapy, Dr. Shah said.
Dr. Shah reported disclosures related to Cidara Therapeutics, Exelixis, Geron, Oncosec, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, and Miltenyi Biotec.
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. ASCO 2019. Abstract 2510.
This article was updated on 7/8/2019
CHICAGO – A bispecific anti-CD19, anti-CD20 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell approach is safe and produced complete responses in the majority of patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a phase 1 study, an investigator reported.
Eleven of 17 assessable patients had a response to treatment with the bispecific lentiviral CAR T cell (LV20.19CAR) at day 28, and of those 11 patients, 9 had complete responses, all of which are ongoing, said Nirav Niranjan Shah, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
“To date, there’s no dose-limiting toxicity, no ICU-level care, no deaths attributed to treatment, no grade 3 to 4 cytokine release syndrome, and only two patients had reversible grade 3 neurotoxicity,” Dr. Shah said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Patients who did relapse or progress on treatment maintained CD19 or CD20 positivity, with no observed downregulation of target receptors, he reported in an oral abstract session.
Of note, the CAR T cells were produced locally at the point of care, with a 100% success rate and a set 14-day manufacturing time, he added.
Bispecific targeting of CD19 and CD20 is a new approach being investigated at a time when there are already two CD19-specific CAR T cell therapies approved for aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, Dr. Shah told attendees.
“Despite the great promise of CD19 CAR T cell therapies, very quickly after the development of these therapies, we discovered mechanisms of resistance—specifically, the development of a CD19 negative relapse,” he said.
The hypothesis that targeting more than one B-cell antigen could potentially mitigate that effect stemmed from preclinical studies showing that targeting both CD19 and CD20 decreased downregulation of CD19 but not other B-cell antigens, he added.
In the present phase 1 study of the first-in-human, bispecific tandem CAR T cell against CD19 and CD20, patients have been treated at several dose levels, some with a split infusion over 2 days to evaluate safety, and some with a single infusion, Dr. Shah said.
A total of 17 patients have been treated with a lymphodepletion regimen followed by LV20.19CAR: 8 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, 6 with mantle cell lymphoma, 2 with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and 1 with follicular lymphoma, according to the investigator. The median age of patients is 59 years, and patients had received at least 3 and up to 11 prior lines of therapy.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities to date with dosing up to the target of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, Dr. Shah reported, adding that there has been no grade 3-4 cytokine release syndrome and no grade 4 neurotoxicity. Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome has been seen in 11 patients, while grade 3 neurotoxicity occurred in 2 patients.
Fourteen of 17 patients had a response, including 11 complete responses and 3 partial responses. Eleven patients were treated at the target dose of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, and of those, 9 had a complete response and 1 had a partial response (overall response rate, Dr. Shah said.
To date, all patients in complete response have remained in a complete response, with durations of response of 1 to 18 months.
Next, investigators plan to conduct phase 2 studies in more specific cohorts, including patients with mantle cell lymphoma, and patients who have relapsed after CD19 CAR T cell therapy, Dr. Shah said.
Dr. Shah reported disclosures related to Cidara Therapeutics, Exelixis, Geron, Oncosec, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, and Miltenyi Biotec.
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. ASCO 2019. Abstract 2510.
This article was updated on 7/8/2019
CHICAGO – A bispecific anti-CD19, anti-CD20 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell approach is safe and produced complete responses in the majority of patients with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma in a phase 1 study, an investigator reported.
Eleven of 17 assessable patients had a response to treatment with the bispecific lentiviral CAR T cell (LV20.19CAR) at day 28, and of those 11 patients, 9 had complete responses, all of which are ongoing, said Nirav Niranjan Shah, MD, of the Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee.
“To date, there’s no dose-limiting toxicity, no ICU-level care, no deaths attributed to treatment, no grade 3 to 4 cytokine release syndrome, and only two patients had reversible grade 3 neurotoxicity,” Dr. Shah said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Patients who did relapse or progress on treatment maintained CD19 or CD20 positivity, with no observed downregulation of target receptors, he reported in an oral abstract session.
Of note, the CAR T cells were produced locally at the point of care, with a 100% success rate and a set 14-day manufacturing time, he added.
Bispecific targeting of CD19 and CD20 is a new approach being investigated at a time when there are already two CD19-specific CAR T cell therapies approved for aggressive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas, Dr. Shah told attendees.
“Despite the great promise of CD19 CAR T cell therapies, very quickly after the development of these therapies, we discovered mechanisms of resistance—specifically, the development of a CD19 negative relapse,” he said.
The hypothesis that targeting more than one B-cell antigen could potentially mitigate that effect stemmed from preclinical studies showing that targeting both CD19 and CD20 decreased downregulation of CD19 but not other B-cell antigens, he added.
In the present phase 1 study of the first-in-human, bispecific tandem CAR T cell against CD19 and CD20, patients have been treated at several dose levels, some with a split infusion over 2 days to evaluate safety, and some with a single infusion, Dr. Shah said.
A total of 17 patients have been treated with a lymphodepletion regimen followed by LV20.19CAR: 8 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, 6 with mantle cell lymphoma, 2 with chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and 1 with follicular lymphoma, according to the investigator. The median age of patients is 59 years, and patients had received at least 3 and up to 11 prior lines of therapy.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities to date with dosing up to the target of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, Dr. Shah reported, adding that there has been no grade 3-4 cytokine release syndrome and no grade 4 neurotoxicity. Grade 1-2 cytokine release syndrome has been seen in 11 patients, while grade 3 neurotoxicity occurred in 2 patients.
Fourteen of 17 patients had a response, including 11 complete responses and 3 partial responses. Eleven patients were treated at the target dose of 2.5 x 106 cells/kg, and of those, 9 had a complete response and 1 had a partial response (overall response rate, Dr. Shah said.
To date, all patients in complete response have remained in a complete response, with durations of response of 1 to 18 months.
Next, investigators plan to conduct phase 2 studies in more specific cohorts, including patients with mantle cell lymphoma, and patients who have relapsed after CD19 CAR T cell therapy, Dr. Shah said.
Dr. Shah reported disclosures related to Cidara Therapeutics, Exelixis, Geron, Oncosec, Incyte, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Juno Therapeutics, Kite Pharma, and Miltenyi Biotec.
SOURCE: Shah NN et al. ASCO 2019. Abstract 2510.
This article was updated on 7/8/2019
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
5F9 plus rituximab take a bite out of drug-resistant NHL
AMSTERDAM – The novel monoclonal antibody , thereby thwarting a mechanism that non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) use to evade immune surveillance, investigators report.
Among 97 patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive or indolent lymphomas in a phase 1b/2 trial who were treated with Hu5F9 (5F9) plus rituximab, the objective response rate (ORR) was 45%, reported Mark Roschewski, MD, of the National Cancer Institute’s Center for Cancer Research in Bethesda, Md.
5F9 is an immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets CD47, the “don’t eat me” signal that inhibits macrophages from carrying out their crucial phagocytosis role.
“Rituximab, through its activity on the Fc receptor, places an extrinsic ‘eat me’ signal, so when you give these two things together you’re blocking the ‘don’t eat me’ signal and you’re placing the ‘eat me’ signal, and then the cell becomes susceptible to phagocytosis,” he said in a briefing prior to his presentation of the data at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
5F9 is the first agent in its class and the most advanced in clinical trials, but several similar agents are also in development. As previously reported, a similar molecule labeled TTI-621 has shown early activity in the treatment of T-cell lymphomas.
In an interview, Dr. Roschewski explained that the therapeutic approach shows promise for the treatment of NHL and nonmalignant diseases.
“This target isn’t even specific to cancer. There is rationale for using this to treat infections or other conditions. Basically, anything that your innate immune system should normally chew up, if that cell has always been evading it using that signal, this removes that [evasion] mechanism,” he said.
In preclinical studies, 5F9 showed the most activity against NHL and acute myeloid leukemia, he noted.
Results of the phase 1b portion of the study were reported in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018;379:1711-21). At the EHA Congress, Dr. Roschewski reported on extended follow-up of the phase 1b cohort and preliminary phase 2 data.
In phase 2, the investigators enrolled patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that was either primary refractory to standard therapy or relapsed/refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were not eligible for chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. They also enrolled a smaller cohort of patients with the indolent lymphoma histologies follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) whose disease was relapsed or refractory to at least two prior lines.
Dr. Roschewski reported on pooled data for 115 patients enrolled in phases 1b and 2: 70 with DLBCL, 41 with FL, and 4 with MZL.
The patients were heavily pretreated with a median of three prior lines of therapy. Of the patients with DLBCL, 59% had primary refractory disease, and 89% of the patients with DLBCL in phase 2 were not eligible for CAR T-cell therapy.
Among all patients in this analysis, 85% had disease that was refractory to a prior rituximab-containing regimen, and the majority had disease that was refractory to the last rituximab-containing regimen.
Among 97 patients evaluable for response (59 with DLBCL, 35 with FL, and 3 with MZL), the ORR was 45%, including 19% CR and 27% partial responses (PR). An additional 17% of patients had stable disease, and 38% experienced disease progression.
The ORR for DLBCL patients was 35%, consisting of 15% CR and 20% PR. An additional 12% of patients with DLBCL had stable disease, and 53% experienced progression.
Of the patients with indolent lymphomas, the ORR was 61%, including 24% CR and 37% PR. Of this group, 24% had stable disease, and 16% had disease progression.
For all patients, the median time to response was 1.8 months (range 1.6-7.3 months).
Efficacy among patients with DLBCL was similar across subtypes and for patients with primary refractory vs. acquired refractory disease. The responses also were similar irrespective of prior lines of therapy.
Patients tolerated the combination well, with no maximum tolerated dose at up to 45 mg/kg of 5F9, and no significant dose-related toxicities.
Most adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse events included expected on-target anemia, caused by clearance of aging red blood cells, which are cleared by the CD47-blocking effects of 5F9. This anemia can be mitigated with an initial priming dose of 1 mg/kg 5FP that causes a transient mild decline in hemoglobin and a temporary reticulocytosis that soon resolves. Hemoglobin levels return to baseline even with continued 5F9 at doses much higher than the priming dose, Dr. Roschewski said.
Other adverse events were infusion reactions and related symptoms. There were no autoimmune adverse events, and just 8 of the 115 patients available for the safety analysis (7%) had to discontinue therapy.
Enrollment in the phase 2 trial is continuing, and a 30-mg/kg maintenance dose of 5F9 has been selected for a trial in patients with DLBCL who are either ineligible for CAR T-cell therapy or have disease that progressed on three or more prior lines of therapy.
The study is funded by Forty Seven and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. Dr. Roschewski reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Roschewski M et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S867.
AMSTERDAM – The novel monoclonal antibody , thereby thwarting a mechanism that non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) use to evade immune surveillance, investigators report.
Among 97 patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive or indolent lymphomas in a phase 1b/2 trial who were treated with Hu5F9 (5F9) plus rituximab, the objective response rate (ORR) was 45%, reported Mark Roschewski, MD, of the National Cancer Institute’s Center for Cancer Research in Bethesda, Md.
5F9 is an immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets CD47, the “don’t eat me” signal that inhibits macrophages from carrying out their crucial phagocytosis role.
“Rituximab, through its activity on the Fc receptor, places an extrinsic ‘eat me’ signal, so when you give these two things together you’re blocking the ‘don’t eat me’ signal and you’re placing the ‘eat me’ signal, and then the cell becomes susceptible to phagocytosis,” he said in a briefing prior to his presentation of the data at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
5F9 is the first agent in its class and the most advanced in clinical trials, but several similar agents are also in development. As previously reported, a similar molecule labeled TTI-621 has shown early activity in the treatment of T-cell lymphomas.
In an interview, Dr. Roschewski explained that the therapeutic approach shows promise for the treatment of NHL and nonmalignant diseases.
“This target isn’t even specific to cancer. There is rationale for using this to treat infections or other conditions. Basically, anything that your innate immune system should normally chew up, if that cell has always been evading it using that signal, this removes that [evasion] mechanism,” he said.
In preclinical studies, 5F9 showed the most activity against NHL and acute myeloid leukemia, he noted.
Results of the phase 1b portion of the study were reported in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018;379:1711-21). At the EHA Congress, Dr. Roschewski reported on extended follow-up of the phase 1b cohort and preliminary phase 2 data.
In phase 2, the investigators enrolled patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that was either primary refractory to standard therapy or relapsed/refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were not eligible for chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. They also enrolled a smaller cohort of patients with the indolent lymphoma histologies follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) whose disease was relapsed or refractory to at least two prior lines.
Dr. Roschewski reported on pooled data for 115 patients enrolled in phases 1b and 2: 70 with DLBCL, 41 with FL, and 4 with MZL.
The patients were heavily pretreated with a median of three prior lines of therapy. Of the patients with DLBCL, 59% had primary refractory disease, and 89% of the patients with DLBCL in phase 2 were not eligible for CAR T-cell therapy.
Among all patients in this analysis, 85% had disease that was refractory to a prior rituximab-containing regimen, and the majority had disease that was refractory to the last rituximab-containing regimen.
Among 97 patients evaluable for response (59 with DLBCL, 35 with FL, and 3 with MZL), the ORR was 45%, including 19% CR and 27% partial responses (PR). An additional 17% of patients had stable disease, and 38% experienced disease progression.
The ORR for DLBCL patients was 35%, consisting of 15% CR and 20% PR. An additional 12% of patients with DLBCL had stable disease, and 53% experienced progression.
Of the patients with indolent lymphomas, the ORR was 61%, including 24% CR and 37% PR. Of this group, 24% had stable disease, and 16% had disease progression.
For all patients, the median time to response was 1.8 months (range 1.6-7.3 months).
Efficacy among patients with DLBCL was similar across subtypes and for patients with primary refractory vs. acquired refractory disease. The responses also were similar irrespective of prior lines of therapy.
Patients tolerated the combination well, with no maximum tolerated dose at up to 45 mg/kg of 5F9, and no significant dose-related toxicities.
Most adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse events included expected on-target anemia, caused by clearance of aging red blood cells, which are cleared by the CD47-blocking effects of 5F9. This anemia can be mitigated with an initial priming dose of 1 mg/kg 5FP that causes a transient mild decline in hemoglobin and a temporary reticulocytosis that soon resolves. Hemoglobin levels return to baseline even with continued 5F9 at doses much higher than the priming dose, Dr. Roschewski said.
Other adverse events were infusion reactions and related symptoms. There were no autoimmune adverse events, and just 8 of the 115 patients available for the safety analysis (7%) had to discontinue therapy.
Enrollment in the phase 2 trial is continuing, and a 30-mg/kg maintenance dose of 5F9 has been selected for a trial in patients with DLBCL who are either ineligible for CAR T-cell therapy or have disease that progressed on three or more prior lines of therapy.
The study is funded by Forty Seven and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. Dr. Roschewski reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Roschewski M et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S867.
AMSTERDAM – The novel monoclonal antibody , thereby thwarting a mechanism that non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHL) use to evade immune surveillance, investigators report.
Among 97 patients with relapsed or refractory aggressive or indolent lymphomas in a phase 1b/2 trial who were treated with Hu5F9 (5F9) plus rituximab, the objective response rate (ORR) was 45%, reported Mark Roschewski, MD, of the National Cancer Institute’s Center for Cancer Research in Bethesda, Md.
5F9 is an immune checkpoint inhibitor that targets CD47, the “don’t eat me” signal that inhibits macrophages from carrying out their crucial phagocytosis role.
“Rituximab, through its activity on the Fc receptor, places an extrinsic ‘eat me’ signal, so when you give these two things together you’re blocking the ‘don’t eat me’ signal and you’re placing the ‘eat me’ signal, and then the cell becomes susceptible to phagocytosis,” he said in a briefing prior to his presentation of the data at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
5F9 is the first agent in its class and the most advanced in clinical trials, but several similar agents are also in development. As previously reported, a similar molecule labeled TTI-621 has shown early activity in the treatment of T-cell lymphomas.
In an interview, Dr. Roschewski explained that the therapeutic approach shows promise for the treatment of NHL and nonmalignant diseases.
“This target isn’t even specific to cancer. There is rationale for using this to treat infections or other conditions. Basically, anything that your innate immune system should normally chew up, if that cell has always been evading it using that signal, this removes that [evasion] mechanism,” he said.
In preclinical studies, 5F9 showed the most activity against NHL and acute myeloid leukemia, he noted.
Results of the phase 1b portion of the study were reported in the New England Journal of Medicine (2018;379:1711-21). At the EHA Congress, Dr. Roschewski reported on extended follow-up of the phase 1b cohort and preliminary phase 2 data.
In phase 2, the investigators enrolled patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) that was either primary refractory to standard therapy or relapsed/refractory after two or more prior lines of therapy and who were not eligible for chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. They also enrolled a smaller cohort of patients with the indolent lymphoma histologies follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) whose disease was relapsed or refractory to at least two prior lines.
Dr. Roschewski reported on pooled data for 115 patients enrolled in phases 1b and 2: 70 with DLBCL, 41 with FL, and 4 with MZL.
The patients were heavily pretreated with a median of three prior lines of therapy. Of the patients with DLBCL, 59% had primary refractory disease, and 89% of the patients with DLBCL in phase 2 were not eligible for CAR T-cell therapy.
Among all patients in this analysis, 85% had disease that was refractory to a prior rituximab-containing regimen, and the majority had disease that was refractory to the last rituximab-containing regimen.
Among 97 patients evaluable for response (59 with DLBCL, 35 with FL, and 3 with MZL), the ORR was 45%, including 19% CR and 27% partial responses (PR). An additional 17% of patients had stable disease, and 38% experienced disease progression.
The ORR for DLBCL patients was 35%, consisting of 15% CR and 20% PR. An additional 12% of patients with DLBCL had stable disease, and 53% experienced progression.
Of the patients with indolent lymphomas, the ORR was 61%, including 24% CR and 37% PR. Of this group, 24% had stable disease, and 16% had disease progression.
For all patients, the median time to response was 1.8 months (range 1.6-7.3 months).
Efficacy among patients with DLBCL was similar across subtypes and for patients with primary refractory vs. acquired refractory disease. The responses also were similar irrespective of prior lines of therapy.
Patients tolerated the combination well, with no maximum tolerated dose at up to 45 mg/kg of 5F9, and no significant dose-related toxicities.
Most adverse events were grade 1 or 2. The most common adverse events included expected on-target anemia, caused by clearance of aging red blood cells, which are cleared by the CD47-blocking effects of 5F9. This anemia can be mitigated with an initial priming dose of 1 mg/kg 5FP that causes a transient mild decline in hemoglobin and a temporary reticulocytosis that soon resolves. Hemoglobin levels return to baseline even with continued 5F9 at doses much higher than the priming dose, Dr. Roschewski said.
Other adverse events were infusion reactions and related symptoms. There were no autoimmune adverse events, and just 8 of the 115 patients available for the safety analysis (7%) had to discontinue therapy.
Enrollment in the phase 2 trial is continuing, and a 30-mg/kg maintenance dose of 5F9 has been selected for a trial in patients with DLBCL who are either ineligible for CAR T-cell therapy or have disease that progressed on three or more prior lines of therapy.
The study is funded by Forty Seven and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. Dr. Roschewski reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Roschewski M et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S867.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Key clinical point: The combination of Hu5F9 and rituximab shows activity in heavily pretreated, relapsed/refractory lymphomas.
Major finding: Among all evaluable patients, the objective response rate was 45%. The objective response rate for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma was 35%.
Study details: A pooled analysis of data from phase 1b/2 studies in patients with aggressive and indolent lymphomas. Among 97 patients evaluable for response, there were 59 patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, 35 with follicular lymphoma, and 3 with marginal zone lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study is funded by Forty Seven and the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society. Dr. Roschewski reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Roschewski M et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S867.
Obinutuzumab provides strong early responses in untreated MCL
Amsterdam – For patients with untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody obinutuzumab may one day offer an alternative to rituximab, according to investigators.
Patients in the LYMA-101 trial were given four cycles of obinutuzumab in combination with dexamethasone, high-dose aracytine, and platinum chemotherapy (O-DHAP), followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and maintenance obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 14.6 months, ranging from 3.8 to 24.4 months, 85% of evaluable patients had achieved minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow, reported lead author Steven Le Gouill, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Nantes, and his colleagues.
In this disease population, an MRD rate of 85% is “unprecedented,” Dr. Le Gouill said during his presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. Based on findings from LYMA-101 and preclinical data, Dr. Le Gouill suggested that obinutuzumab may become an alternative to rituximab, the current standard anti-CD20 antibody.
“There are few data of interest for obinutuzumab in MCL, but there is a strong rationale in the lab as obinutuzumab has a different mechanism of action against tumor cells [than rituximab], with more efficacy against MCL cells,” Dr. Le Gouill said.
Data from the ongoing phase 2 trial were drawn from 85 patients with untreated MCL who were 65 years or younger at the time of enrollment. More specifically, median patient age was 55.5 years and 17.4% of patients had blastoid disease. All patients were given the O-DHAP/ASCT/obinutuzumab protocol, with a maintenance period of 3 years. Thereafter, MRD-positive patients may receive obinutuzumab on-demand.
The primary endpoint was MRD in bone marrow after induction therapy, measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). Secondary endpoints included response rates, survival measures, incidence of stem cell collection failure after O-DHAP, and MRD rates at additional therapeutic time points.
Owing to the ongoing nature of the study, Dr. Le Gouill focused on the primary endpoint during his presentation.
Analysis showed that 75% and 85% of evaluable patients had achieved negative MRD in bone marrow after induction, according to qPCR and ddPCR, respectively.
These early findings give “a flavor of the results in terms of efficacy,” Dr. Le Gouill said, noting that “the median follow-up is pretty short.”
Still, 1-year findings were “very promising,” he said, with a progression-free survival of 93.4% and overall survival of 96%.
Twelve patients stopped treatment before ASCT, three prior to maintenance, and nine during maintenance. Of these 24 patients, 13 stopped treatment because of adverse events. The remaining 11 patients halted therapy because of disease progression, other malignancies, or death.
From the original 85 patients, 3 patients died and 3 progressed. Considering all of these findings, and that no major toxicities were encountered, the investigators concluded that the regimen was safe.
Overall, the results suggest that further research is needed, Dr. Le Gouill concluded. “Maybe this is where obinutuzumab may have stronger efficacy in MCL, as compared to rituximab,” he said.
The study is sponsored by the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The investigators reported relationships with Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Gilead, Servier, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Le Gouill S et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S103.
Amsterdam – For patients with untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody obinutuzumab may one day offer an alternative to rituximab, according to investigators.
Patients in the LYMA-101 trial were given four cycles of obinutuzumab in combination with dexamethasone, high-dose aracytine, and platinum chemotherapy (O-DHAP), followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and maintenance obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 14.6 months, ranging from 3.8 to 24.4 months, 85% of evaluable patients had achieved minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow, reported lead author Steven Le Gouill, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Nantes, and his colleagues.
In this disease population, an MRD rate of 85% is “unprecedented,” Dr. Le Gouill said during his presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. Based on findings from LYMA-101 and preclinical data, Dr. Le Gouill suggested that obinutuzumab may become an alternative to rituximab, the current standard anti-CD20 antibody.
“There are few data of interest for obinutuzumab in MCL, but there is a strong rationale in the lab as obinutuzumab has a different mechanism of action against tumor cells [than rituximab], with more efficacy against MCL cells,” Dr. Le Gouill said.
Data from the ongoing phase 2 trial were drawn from 85 patients with untreated MCL who were 65 years or younger at the time of enrollment. More specifically, median patient age was 55.5 years and 17.4% of patients had blastoid disease. All patients were given the O-DHAP/ASCT/obinutuzumab protocol, with a maintenance period of 3 years. Thereafter, MRD-positive patients may receive obinutuzumab on-demand.
The primary endpoint was MRD in bone marrow after induction therapy, measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). Secondary endpoints included response rates, survival measures, incidence of stem cell collection failure after O-DHAP, and MRD rates at additional therapeutic time points.
Owing to the ongoing nature of the study, Dr. Le Gouill focused on the primary endpoint during his presentation.
Analysis showed that 75% and 85% of evaluable patients had achieved negative MRD in bone marrow after induction, according to qPCR and ddPCR, respectively.
These early findings give “a flavor of the results in terms of efficacy,” Dr. Le Gouill said, noting that “the median follow-up is pretty short.”
Still, 1-year findings were “very promising,” he said, with a progression-free survival of 93.4% and overall survival of 96%.
Twelve patients stopped treatment before ASCT, three prior to maintenance, and nine during maintenance. Of these 24 patients, 13 stopped treatment because of adverse events. The remaining 11 patients halted therapy because of disease progression, other malignancies, or death.
From the original 85 patients, 3 patients died and 3 progressed. Considering all of these findings, and that no major toxicities were encountered, the investigators concluded that the regimen was safe.
Overall, the results suggest that further research is needed, Dr. Le Gouill concluded. “Maybe this is where obinutuzumab may have stronger efficacy in MCL, as compared to rituximab,” he said.
The study is sponsored by the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The investigators reported relationships with Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Gilead, Servier, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Le Gouill S et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S103.
Amsterdam – For patients with untreated mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody obinutuzumab may one day offer an alternative to rituximab, according to investigators.
Patients in the LYMA-101 trial were given four cycles of obinutuzumab in combination with dexamethasone, high-dose aracytine, and platinum chemotherapy (O-DHAP), followed by autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) and maintenance obinutuzumab. After a median follow-up of 14.6 months, ranging from 3.8 to 24.4 months, 85% of evaluable patients had achieved minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow, reported lead author Steven Le Gouill, MD, PhD, of the University Hospital of Nantes, and his colleagues.
In this disease population, an MRD rate of 85% is “unprecedented,” Dr. Le Gouill said during his presentation at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association. Based on findings from LYMA-101 and preclinical data, Dr. Le Gouill suggested that obinutuzumab may become an alternative to rituximab, the current standard anti-CD20 antibody.
“There are few data of interest for obinutuzumab in MCL, but there is a strong rationale in the lab as obinutuzumab has a different mechanism of action against tumor cells [than rituximab], with more efficacy against MCL cells,” Dr. Le Gouill said.
Data from the ongoing phase 2 trial were drawn from 85 patients with untreated MCL who were 65 years or younger at the time of enrollment. More specifically, median patient age was 55.5 years and 17.4% of patients had blastoid disease. All patients were given the O-DHAP/ASCT/obinutuzumab protocol, with a maintenance period of 3 years. Thereafter, MRD-positive patients may receive obinutuzumab on-demand.
The primary endpoint was MRD in bone marrow after induction therapy, measured by quantitative PCR (qPCR) and droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). Secondary endpoints included response rates, survival measures, incidence of stem cell collection failure after O-DHAP, and MRD rates at additional therapeutic time points.
Owing to the ongoing nature of the study, Dr. Le Gouill focused on the primary endpoint during his presentation.
Analysis showed that 75% and 85% of evaluable patients had achieved negative MRD in bone marrow after induction, according to qPCR and ddPCR, respectively.
These early findings give “a flavor of the results in terms of efficacy,” Dr. Le Gouill said, noting that “the median follow-up is pretty short.”
Still, 1-year findings were “very promising,” he said, with a progression-free survival of 93.4% and overall survival of 96%.
Twelve patients stopped treatment before ASCT, three prior to maintenance, and nine during maintenance. Of these 24 patients, 13 stopped treatment because of adverse events. The remaining 11 patients halted therapy because of disease progression, other malignancies, or death.
From the original 85 patients, 3 patients died and 3 progressed. Considering all of these findings, and that no major toxicities were encountered, the investigators concluded that the regimen was safe.
Overall, the results suggest that further research is needed, Dr. Le Gouill concluded. “Maybe this is where obinutuzumab may have stronger efficacy in MCL, as compared to rituximab,” he said.
The study is sponsored by the Lymphoma Academic Research Organisation. The investigators reported relationships with Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Gilead, Servier, and Novartis.
SOURCE: Le Gouill S et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S103.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Out of 73 patients, 62 (85%) achieved negative minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow based on ddPCR.
Study details: LYMA-101 is an ongoing phase 2 trial involving 85 patients with untreated mantle cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The investigators reported relationships with Roche, Janssen-Cilag, Gilead, Servier, and Novartis.
Source: Le Gouill S et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S103.
‘Encouraging’ responses seen with durvalumab plus R-CHOP in DLBCL
CHICAGO – A six-drug combination produced complete responses in previously untreated, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients in a phase 2 trial.
Induction with durvalumab and R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) produced complete response rates of 54% in the entire cohort and 41% in patients with double- or triple-hit lymphoma. Immune-related adverse events (AEs) were common with this regimen, but no unexpected AEs occurred, according to researchers.
Grzegorz S. Nowakowski, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Treatment
The phase 2 trial (NCT03003520) was designed to assess durvalumab plus R-CHOP as well as durvalumab plus R-CHOP and lenalidomide (R2-CHOP) in patients with previously untreated, high-risk DLBCL. However, the R2-CHOP arm was closed early.
In cycle one, all patients received durvalumab plus R-CHOP. For subsequent cycles, patients with activated B-cell (ABC) DLBCL were assigned to durvalumab plus R2-CHOP, while patients with non-ABC DLBCL continued on durvalumab plus R-CHOP.
The R2-CHOP arm was closed early due to safety issues observed in trials combining checkpoint inhibitors with immunomodulatory agents. A partial clinical hold was placed on the R2-CHOP arm, but patients could continue on the regimen if they experienced a clinical benefit. Any patients with ABC DLBCL who were enrolled after the partial hold received treatment with durvalumab plus R-CHOP.
Induction was given for up to eight cycles and was followed by consolidation with durvalumab alone for up to 12 months from the start of induction.
Patient characteristics
The researchers presented data on 43 patients in the durvalumab plus R-CHOP arm. The patients’ median age was 62 years, and 61% were men.
“I think it’s worth noting that 46% of patients in the durvalumab plus R-CHOP group had very high-risk features, including double-hit or triple-hit genetic features,” said Justin Kline, MD, of the University of Chicago Medicine who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
Specifically, 30% of patients had double-hit lymphoma, and 16% had triple-hit lymphoma. Most patients had a high-intermediate-risk (49%) or high-risk (21%) International Prognostic Index score, and 79% of patients had Ann Arbor stage IV disease.
Efficacy
As of Aug. 2, 2018, 70% of patients had completed induction, 2% had completed consolidation, 44% remained on treatment, and 54% had discontinued therapy. The most common reasons for stopping treatment were progression (16%), AEs (14%), and consent withdrawal (12%).
“The combination of durvalumab plus R-CHOP demonstrated encouraging response rates … in subjects with high-risk DLBCL, including double- and triple-hit lymphomas,” Dr. Kline said.
The complete response rate was 54% (20/37) at the end of induction and 68% (n = 25) at the end of consolidation. The partial response rate at the end of consolidation was 30% (n = 11).
In patients with double- or triple-hit lymphoma, the complete response rate at the end of induction was 41% (7/17). The overall response rate in this group was 88% (n = 15).
Safety
“The safety profile was as expected for the components of the combination, and no new safety signals were observed,” Dr. Kline said.
He noted that AEs of special interest, or immune-related AEs, occurred in 61% of patients, but most of these events were grade 1 or 2.
AEs of special interest included diarrhea (28%), rash (23%), infusion-related reactions (16%), dermatitis (12%), hypothyroidism (5%), myocarditis (5%), adrenal insufficiency (2%), and hepatitis (2%).
Grade 3 or 4 AEs of special interest included infusion-related reactions (5%), rash (2%), diarrhea (2%), and hepatitis (2%).
The safety and efficacy results support further evaluation of durvalumab plus R-CHOP, although it will be important to identify DLBCL patients who are more likely to derive a clinical benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade, Dr. Kline said.
“This early study showed that the combination is feasible,” Dr. Nowakowski added. “I think, down the road, we’ll need to identify patients who can actually benefit from this combination. We definitely have clinical evidence of exceptional responses to PD-1 blockade.”
The trial was sponsored by Celgene. Dr. Nowakowski reported relationships with Celgene, Genentech, MorphoSys, and NanoString Technologies. Dr. Kline reported relationships with Cardinal Health, Merck, Seattle Genetics, Kite/Gilead, ITeos Therapeutics, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Nowakowski GS et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7520.
CHICAGO – A six-drug combination produced complete responses in previously untreated, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients in a phase 2 trial.
Induction with durvalumab and R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) produced complete response rates of 54% in the entire cohort and 41% in patients with double- or triple-hit lymphoma. Immune-related adverse events (AEs) were common with this regimen, but no unexpected AEs occurred, according to researchers.
Grzegorz S. Nowakowski, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Treatment
The phase 2 trial (NCT03003520) was designed to assess durvalumab plus R-CHOP as well as durvalumab plus R-CHOP and lenalidomide (R2-CHOP) in patients with previously untreated, high-risk DLBCL. However, the R2-CHOP arm was closed early.
In cycle one, all patients received durvalumab plus R-CHOP. For subsequent cycles, patients with activated B-cell (ABC) DLBCL were assigned to durvalumab plus R2-CHOP, while patients with non-ABC DLBCL continued on durvalumab plus R-CHOP.
The R2-CHOP arm was closed early due to safety issues observed in trials combining checkpoint inhibitors with immunomodulatory agents. A partial clinical hold was placed on the R2-CHOP arm, but patients could continue on the regimen if they experienced a clinical benefit. Any patients with ABC DLBCL who were enrolled after the partial hold received treatment with durvalumab plus R-CHOP.
Induction was given for up to eight cycles and was followed by consolidation with durvalumab alone for up to 12 months from the start of induction.
Patient characteristics
The researchers presented data on 43 patients in the durvalumab plus R-CHOP arm. The patients’ median age was 62 years, and 61% were men.
“I think it’s worth noting that 46% of patients in the durvalumab plus R-CHOP group had very high-risk features, including double-hit or triple-hit genetic features,” said Justin Kline, MD, of the University of Chicago Medicine who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
Specifically, 30% of patients had double-hit lymphoma, and 16% had triple-hit lymphoma. Most patients had a high-intermediate-risk (49%) or high-risk (21%) International Prognostic Index score, and 79% of patients had Ann Arbor stage IV disease.
Efficacy
As of Aug. 2, 2018, 70% of patients had completed induction, 2% had completed consolidation, 44% remained on treatment, and 54% had discontinued therapy. The most common reasons for stopping treatment were progression (16%), AEs (14%), and consent withdrawal (12%).
“The combination of durvalumab plus R-CHOP demonstrated encouraging response rates … in subjects with high-risk DLBCL, including double- and triple-hit lymphomas,” Dr. Kline said.
The complete response rate was 54% (20/37) at the end of induction and 68% (n = 25) at the end of consolidation. The partial response rate at the end of consolidation was 30% (n = 11).
In patients with double- or triple-hit lymphoma, the complete response rate at the end of induction was 41% (7/17). The overall response rate in this group was 88% (n = 15).
Safety
“The safety profile was as expected for the components of the combination, and no new safety signals were observed,” Dr. Kline said.
He noted that AEs of special interest, or immune-related AEs, occurred in 61% of patients, but most of these events were grade 1 or 2.
AEs of special interest included diarrhea (28%), rash (23%), infusion-related reactions (16%), dermatitis (12%), hypothyroidism (5%), myocarditis (5%), adrenal insufficiency (2%), and hepatitis (2%).
Grade 3 or 4 AEs of special interest included infusion-related reactions (5%), rash (2%), diarrhea (2%), and hepatitis (2%).
The safety and efficacy results support further evaluation of durvalumab plus R-CHOP, although it will be important to identify DLBCL patients who are more likely to derive a clinical benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade, Dr. Kline said.
“This early study showed that the combination is feasible,” Dr. Nowakowski added. “I think, down the road, we’ll need to identify patients who can actually benefit from this combination. We definitely have clinical evidence of exceptional responses to PD-1 blockade.”
The trial was sponsored by Celgene. Dr. Nowakowski reported relationships with Celgene, Genentech, MorphoSys, and NanoString Technologies. Dr. Kline reported relationships with Cardinal Health, Merck, Seattle Genetics, Kite/Gilead, ITeos Therapeutics, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Nowakowski GS et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7520.
CHICAGO – A six-drug combination produced complete responses in previously untreated, high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) patients in a phase 2 trial.
Induction with durvalumab and R-CHOP (rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone) produced complete response rates of 54% in the entire cohort and 41% in patients with double- or triple-hit lymphoma. Immune-related adverse events (AEs) were common with this regimen, but no unexpected AEs occurred, according to researchers.
Grzegorz S. Nowakowski, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Treatment
The phase 2 trial (NCT03003520) was designed to assess durvalumab plus R-CHOP as well as durvalumab plus R-CHOP and lenalidomide (R2-CHOP) in patients with previously untreated, high-risk DLBCL. However, the R2-CHOP arm was closed early.
In cycle one, all patients received durvalumab plus R-CHOP. For subsequent cycles, patients with activated B-cell (ABC) DLBCL were assigned to durvalumab plus R2-CHOP, while patients with non-ABC DLBCL continued on durvalumab plus R-CHOP.
The R2-CHOP arm was closed early due to safety issues observed in trials combining checkpoint inhibitors with immunomodulatory agents. A partial clinical hold was placed on the R2-CHOP arm, but patients could continue on the regimen if they experienced a clinical benefit. Any patients with ABC DLBCL who were enrolled after the partial hold received treatment with durvalumab plus R-CHOP.
Induction was given for up to eight cycles and was followed by consolidation with durvalumab alone for up to 12 months from the start of induction.
Patient characteristics
The researchers presented data on 43 patients in the durvalumab plus R-CHOP arm. The patients’ median age was 62 years, and 61% were men.
“I think it’s worth noting that 46% of patients in the durvalumab plus R-CHOP group had very high-risk features, including double-hit or triple-hit genetic features,” said Justin Kline, MD, of the University of Chicago Medicine who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
Specifically, 30% of patients had double-hit lymphoma, and 16% had triple-hit lymphoma. Most patients had a high-intermediate-risk (49%) or high-risk (21%) International Prognostic Index score, and 79% of patients had Ann Arbor stage IV disease.
Efficacy
As of Aug. 2, 2018, 70% of patients had completed induction, 2% had completed consolidation, 44% remained on treatment, and 54% had discontinued therapy. The most common reasons for stopping treatment were progression (16%), AEs (14%), and consent withdrawal (12%).
“The combination of durvalumab plus R-CHOP demonstrated encouraging response rates … in subjects with high-risk DLBCL, including double- and triple-hit lymphomas,” Dr. Kline said.
The complete response rate was 54% (20/37) at the end of induction and 68% (n = 25) at the end of consolidation. The partial response rate at the end of consolidation was 30% (n = 11).
In patients with double- or triple-hit lymphoma, the complete response rate at the end of induction was 41% (7/17). The overall response rate in this group was 88% (n = 15).
Safety
“The safety profile was as expected for the components of the combination, and no new safety signals were observed,” Dr. Kline said.
He noted that AEs of special interest, or immune-related AEs, occurred in 61% of patients, but most of these events were grade 1 or 2.
AEs of special interest included diarrhea (28%), rash (23%), infusion-related reactions (16%), dermatitis (12%), hypothyroidism (5%), myocarditis (5%), adrenal insufficiency (2%), and hepatitis (2%).
Grade 3 or 4 AEs of special interest included infusion-related reactions (5%), rash (2%), diarrhea (2%), and hepatitis (2%).
The safety and efficacy results support further evaluation of durvalumab plus R-CHOP, although it will be important to identify DLBCL patients who are more likely to derive a clinical benefit from PD-1 or PD-L1 blockade, Dr. Kline said.
“This early study showed that the combination is feasible,” Dr. Nowakowski added. “I think, down the road, we’ll need to identify patients who can actually benefit from this combination. We definitely have clinical evidence of exceptional responses to PD-1 blockade.”
The trial was sponsored by Celgene. Dr. Nowakowski reported relationships with Celgene, Genentech, MorphoSys, and NanoString Technologies. Dr. Kline reported relationships with Cardinal Health, Merck, Seattle Genetics, Kite/Gilead, ITeos Therapeutics, and Bristol-Myers Squibb.
SOURCE: Nowakowski GS et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7520.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
R2 appears active in high-risk FL and MZL
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide plus rituximab (R2) demonstrated activity against relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) in the phase 3b MAGNIFY trial.
R2 produced responses in FL and MZL patients, including those who had previously experienced early relapse and patients who were refractory to rituximab or both lenalidomide and rituximab at baseline.
David Jacob Andorsky, MD, of Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers in Boulder, Colo., and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The ongoing MAGNIFY trial has enrolled 370 patients with relapsed/refractory FL (grade 1-3a) or MZL.
For induction, patients receive lenalidomide (20 mg per day on days 1-21 for 12 cycles) and rituximab (375 mg/m2 per week in cycle 1 and then on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11). Patients who achieve stable disease or better on R2 induction are randomized to maintenance with R2 or rituximab alone.
Dr. Andorsky and colleagues presented results of R2 induction in 310 evaluable patients – 247 with FL and 63 with MZL.
The patients had a median age of 66 years (range, 35-91 years) at baseline, and they had received a median of two prior therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had experienced early relapse (37%, n = 115), were refractory to rituximab (36%, n = 113), or were refractory to both rituximab and lenalidomide (20%, n = 63) at baseline.
Results
At a median follow-up of 16.7 months, the overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 45%. The overall response rate was 74% in FL patients, 65% in MZL patients, 63% in rituximab-refractory patients, 51% in double-refractory patients, and 68% in patients with an early relapse.
The median duration of response was 36.8 months in all patients, 35.8 months in MZL patients, and not reached in FL patients. The median duration of response was 35.8 months in patients who were rituximab refractory and was not reached in patients who were not refractory to rituximab.
The median progression-free survival was 36 months overall, 30 months in FL patients, 38 months in MZL patients, 23 months in patients with early relapse, and 15.5 months in double-refractory patients.
“While these [subgroup analyses of efficacy] were exploratory endpoints, I think this suggests that [R2] is a promising regimen for patients that are in the high-risk subgroup,” said Carla Casulo, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
The most common adverse events in this trial were fatigue (48%), neutropenia (40%), diarrhea (35%), nausea (30%), and constipation (29%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse event was neutropenia (34%).
The MAGNIFY trial is sponsored by Celgene. Dr. Andorsky reported financial relationships with Celgene, CTI BioPharma, and Gilead Sciences. Dr. Casulo reported financial relationships with Gilead Sciences, Celgene, and Roche.
SOURCE: Andorsky DJ et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7513.
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide plus rituximab (R2) demonstrated activity against relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) in the phase 3b MAGNIFY trial.
R2 produced responses in FL and MZL patients, including those who had previously experienced early relapse and patients who were refractory to rituximab or both lenalidomide and rituximab at baseline.
David Jacob Andorsky, MD, of Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers in Boulder, Colo., and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The ongoing MAGNIFY trial has enrolled 370 patients with relapsed/refractory FL (grade 1-3a) or MZL.
For induction, patients receive lenalidomide (20 mg per day on days 1-21 for 12 cycles) and rituximab (375 mg/m2 per week in cycle 1 and then on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11). Patients who achieve stable disease or better on R2 induction are randomized to maintenance with R2 or rituximab alone.
Dr. Andorsky and colleagues presented results of R2 induction in 310 evaluable patients – 247 with FL and 63 with MZL.
The patients had a median age of 66 years (range, 35-91 years) at baseline, and they had received a median of two prior therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had experienced early relapse (37%, n = 115), were refractory to rituximab (36%, n = 113), or were refractory to both rituximab and lenalidomide (20%, n = 63) at baseline.
Results
At a median follow-up of 16.7 months, the overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 45%. The overall response rate was 74% in FL patients, 65% in MZL patients, 63% in rituximab-refractory patients, 51% in double-refractory patients, and 68% in patients with an early relapse.
The median duration of response was 36.8 months in all patients, 35.8 months in MZL patients, and not reached in FL patients. The median duration of response was 35.8 months in patients who were rituximab refractory and was not reached in patients who were not refractory to rituximab.
The median progression-free survival was 36 months overall, 30 months in FL patients, 38 months in MZL patients, 23 months in patients with early relapse, and 15.5 months in double-refractory patients.
“While these [subgroup analyses of efficacy] were exploratory endpoints, I think this suggests that [R2] is a promising regimen for patients that are in the high-risk subgroup,” said Carla Casulo, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
The most common adverse events in this trial were fatigue (48%), neutropenia (40%), diarrhea (35%), nausea (30%), and constipation (29%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse event was neutropenia (34%).
The MAGNIFY trial is sponsored by Celgene. Dr. Andorsky reported financial relationships with Celgene, CTI BioPharma, and Gilead Sciences. Dr. Casulo reported financial relationships with Gilead Sciences, Celgene, and Roche.
SOURCE: Andorsky DJ et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7513.
CHICAGO – Lenalidomide plus rituximab (R2) demonstrated activity against relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma (FL) and marginal zone lymphoma (MZL) in the phase 3b MAGNIFY trial.
R2 produced responses in FL and MZL patients, including those who had previously experienced early relapse and patients who were refractory to rituximab or both lenalidomide and rituximab at baseline.
David Jacob Andorsky, MD, of Rocky Mountain Cancer Centers in Boulder, Colo., and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The ongoing MAGNIFY trial has enrolled 370 patients with relapsed/refractory FL (grade 1-3a) or MZL.
For induction, patients receive lenalidomide (20 mg per day on days 1-21 for 12 cycles) and rituximab (375 mg/m2 per week in cycle 1 and then on day 1 of cycles 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11). Patients who achieve stable disease or better on R2 induction are randomized to maintenance with R2 or rituximab alone.
Dr. Andorsky and colleagues presented results of R2 induction in 310 evaluable patients – 247 with FL and 63 with MZL.
The patients had a median age of 66 years (range, 35-91 years) at baseline, and they had received a median of two prior therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had experienced early relapse (37%, n = 115), were refractory to rituximab (36%, n = 113), or were refractory to both rituximab and lenalidomide (20%, n = 63) at baseline.
Results
At a median follow-up of 16.7 months, the overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 45%. The overall response rate was 74% in FL patients, 65% in MZL patients, 63% in rituximab-refractory patients, 51% in double-refractory patients, and 68% in patients with an early relapse.
The median duration of response was 36.8 months in all patients, 35.8 months in MZL patients, and not reached in FL patients. The median duration of response was 35.8 months in patients who were rituximab refractory and was not reached in patients who were not refractory to rituximab.
The median progression-free survival was 36 months overall, 30 months in FL patients, 38 months in MZL patients, 23 months in patients with early relapse, and 15.5 months in double-refractory patients.
“While these [subgroup analyses of efficacy] were exploratory endpoints, I think this suggests that [R2] is a promising regimen for patients that are in the high-risk subgroup,” said Carla Casulo, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
The most common adverse events in this trial were fatigue (48%), neutropenia (40%), diarrhea (35%), nausea (30%), and constipation (29%). The most common grade 3/4 adverse event was neutropenia (34%).
The MAGNIFY trial is sponsored by Celgene. Dr. Andorsky reported financial relationships with Celgene, CTI BioPharma, and Gilead Sciences. Dr. Casulo reported financial relationships with Gilead Sciences, Celgene, and Roche.
SOURCE: Andorsky DJ et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7513.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
Triplet offers longest PFS yet seen in relapsed/refractory myeloma
CHICAGO – Adding isatuximab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, to pomalidomide and dexamethasone can prolong progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, a phase 3 trial suggests.
The median PFS was 11.53 months among patients who received isatuximab (isa) plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone (Pd), compared with 6.47 months in patients who received Pd alone (P = .001).
“[W]e now have the first randomized, phase 3 study demonstrating a significant prolonged PFS benefit of CD38 targeting combined with pomalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory myeloma,” said Paul Richardson, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“The PFS was the longest observed in this population to date ..., and ... this PFS benefit was consistent among subgroups.”
Dr. Richardson presented these results from the ICARIA-MM trial at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers enrolled 307 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. The patients had a median age of 67 years (range, 36-86 years) and a median time from diagnosis of 4.23 years (range, 0.5-20.5 years).
The patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, 2-11 for the isa-Pd arm and 2-10 for the Pd arm). All patients had previously received a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent.
The patients received isatuximab at 10 mg/kg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 in cycle 1, then on days 1 and 15 for subsequent cycles. Pomalidomide and dexamethasone were given at standard doses in both treatment arms.
At a median follow-up of 11.6 months, 42.2% of patients were still receiving isa-Pd, and 22.9% of patients were still on Pd alone. The most common reason for stopping either treatment was disease progression (42.9% in the isa-Pd arm and 57.5% in the Pd arm).
Efficacy
The overall response rate was 60.4% in the isa-Pd arm and 35.3% in the Pd arm (P less than .0001). The rates of complete response/stringent complete response were 4.5% and 2.0%, respectively. The rates of minimal residual disease negativity were 5.2% and 0%, respectively.
The median time to next treatment was 9.1 months in the Pd arm and was not reached in the isa-Pd arm (hazard ratio, 0.538).
The median PFS was 11.53 months in the isa-Pd arm and 6.47 months in the Pd arm (HR, 0.596; P = .001). There was a PFS benefit with isa-Pd across subgroups, including in patients with renal dysfunction, those with high-risk cytogenetics, and patients who were refractory to lenalidomide.
The median overall survival was not reached in either treatment arm. The overall survival rate was 72% in the isa-Pd arm and 63% in the Pd arm (HR, 0.687).
Safety
There were more grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) with isa-Pd. However, as Dr. Richardson noted, adding isa to Pd did not increase the rates of TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation or death.
The incidence of grade 3 or higher TEAEs was 86.8% in the isa-Pd arm and 70.5% in the Pd arm. The rate of serious TEAEs was 61.8% and 53.7%, respectively.
TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 7.2% of patients in the isa-Pd arm and 12.8% in the Pd arm. TEAEs leading to death occurred in 7.9% and 9.4%, respectively.
Grade 3 TEAEs (in the isa-Pd and Pd arms, respectively) included upper respiratory tract infection (3.3% and 0.7%), diarrhea (2.0% and 0.7%), bronchitis (3.3% and 0.7%), pneumonia (15.1% and 13.4%), fatigue (3.9% and 0%), back pain (2.0% and 1.3%), asthenia (3.3% and 2.7%), and dyspnea (3.9% and 1.3%).
The only grade 4 TEAE was pneumonia (1.3% in both arms).
Based on the safety and efficacy results, Dr. Richardson concluded that isa-Pd “is an important new treatment option for our patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma.”
This study was funded by Sanofi. Dr. Richardson reported financial relationships with Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. His coinvestigators reported relationships with a range of companies.
SOURCE: Richardson P et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 8004.
CHICAGO – Adding isatuximab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, to pomalidomide and dexamethasone can prolong progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, a phase 3 trial suggests.
The median PFS was 11.53 months among patients who received isatuximab (isa) plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone (Pd), compared with 6.47 months in patients who received Pd alone (P = .001).
“[W]e now have the first randomized, phase 3 study demonstrating a significant prolonged PFS benefit of CD38 targeting combined with pomalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory myeloma,” said Paul Richardson, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“The PFS was the longest observed in this population to date ..., and ... this PFS benefit was consistent among subgroups.”
Dr. Richardson presented these results from the ICARIA-MM trial at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers enrolled 307 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. The patients had a median age of 67 years (range, 36-86 years) and a median time from diagnosis of 4.23 years (range, 0.5-20.5 years).
The patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, 2-11 for the isa-Pd arm and 2-10 for the Pd arm). All patients had previously received a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent.
The patients received isatuximab at 10 mg/kg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 in cycle 1, then on days 1 and 15 for subsequent cycles. Pomalidomide and dexamethasone were given at standard doses in both treatment arms.
At a median follow-up of 11.6 months, 42.2% of patients were still receiving isa-Pd, and 22.9% of patients were still on Pd alone. The most common reason for stopping either treatment was disease progression (42.9% in the isa-Pd arm and 57.5% in the Pd arm).
Efficacy
The overall response rate was 60.4% in the isa-Pd arm and 35.3% in the Pd arm (P less than .0001). The rates of complete response/stringent complete response were 4.5% and 2.0%, respectively. The rates of minimal residual disease negativity were 5.2% and 0%, respectively.
The median time to next treatment was 9.1 months in the Pd arm and was not reached in the isa-Pd arm (hazard ratio, 0.538).
The median PFS was 11.53 months in the isa-Pd arm and 6.47 months in the Pd arm (HR, 0.596; P = .001). There was a PFS benefit with isa-Pd across subgroups, including in patients with renal dysfunction, those with high-risk cytogenetics, and patients who were refractory to lenalidomide.
The median overall survival was not reached in either treatment arm. The overall survival rate was 72% in the isa-Pd arm and 63% in the Pd arm (HR, 0.687).
Safety
There were more grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) with isa-Pd. However, as Dr. Richardson noted, adding isa to Pd did not increase the rates of TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation or death.
The incidence of grade 3 or higher TEAEs was 86.8% in the isa-Pd arm and 70.5% in the Pd arm. The rate of serious TEAEs was 61.8% and 53.7%, respectively.
TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 7.2% of patients in the isa-Pd arm and 12.8% in the Pd arm. TEAEs leading to death occurred in 7.9% and 9.4%, respectively.
Grade 3 TEAEs (in the isa-Pd and Pd arms, respectively) included upper respiratory tract infection (3.3% and 0.7%), diarrhea (2.0% and 0.7%), bronchitis (3.3% and 0.7%), pneumonia (15.1% and 13.4%), fatigue (3.9% and 0%), back pain (2.0% and 1.3%), asthenia (3.3% and 2.7%), and dyspnea (3.9% and 1.3%).
The only grade 4 TEAE was pneumonia (1.3% in both arms).
Based on the safety and efficacy results, Dr. Richardson concluded that isa-Pd “is an important new treatment option for our patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma.”
This study was funded by Sanofi. Dr. Richardson reported financial relationships with Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. His coinvestigators reported relationships with a range of companies.
SOURCE: Richardson P et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 8004.
CHICAGO – Adding isatuximab, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, to pomalidomide and dexamethasone can prolong progression-free survival (PFS) in patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma, a phase 3 trial suggests.
The median PFS was 11.53 months among patients who received isatuximab (isa) plus pomalidomide and dexamethasone (Pd), compared with 6.47 months in patients who received Pd alone (P = .001).
“[W]e now have the first randomized, phase 3 study demonstrating a significant prolonged PFS benefit of CD38 targeting combined with pomalidomide and dexamethasone in relapsed/refractory myeloma,” said Paul Richardson, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston.
“The PFS was the longest observed in this population to date ..., and ... this PFS benefit was consistent among subgroups.”
Dr. Richardson presented these results from the ICARIA-MM trial at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers enrolled 307 patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. The patients had a median age of 67 years (range, 36-86 years) and a median time from diagnosis of 4.23 years (range, 0.5-20.5 years).
The patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, 2-11 for the isa-Pd arm and 2-10 for the Pd arm). All patients had previously received a proteasome inhibitor and an immunomodulatory agent.
The patients received isatuximab at 10 mg/kg on days 1, 8, 15, and 22 in cycle 1, then on days 1 and 15 for subsequent cycles. Pomalidomide and dexamethasone were given at standard doses in both treatment arms.
At a median follow-up of 11.6 months, 42.2% of patients were still receiving isa-Pd, and 22.9% of patients were still on Pd alone. The most common reason for stopping either treatment was disease progression (42.9% in the isa-Pd arm and 57.5% in the Pd arm).
Efficacy
The overall response rate was 60.4% in the isa-Pd arm and 35.3% in the Pd arm (P less than .0001). The rates of complete response/stringent complete response were 4.5% and 2.0%, respectively. The rates of minimal residual disease negativity were 5.2% and 0%, respectively.
The median time to next treatment was 9.1 months in the Pd arm and was not reached in the isa-Pd arm (hazard ratio, 0.538).
The median PFS was 11.53 months in the isa-Pd arm and 6.47 months in the Pd arm (HR, 0.596; P = .001). There was a PFS benefit with isa-Pd across subgroups, including in patients with renal dysfunction, those with high-risk cytogenetics, and patients who were refractory to lenalidomide.
The median overall survival was not reached in either treatment arm. The overall survival rate was 72% in the isa-Pd arm and 63% in the Pd arm (HR, 0.687).
Safety
There were more grade 3 or higher treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) with isa-Pd. However, as Dr. Richardson noted, adding isa to Pd did not increase the rates of TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation or death.
The incidence of grade 3 or higher TEAEs was 86.8% in the isa-Pd arm and 70.5% in the Pd arm. The rate of serious TEAEs was 61.8% and 53.7%, respectively.
TEAEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 7.2% of patients in the isa-Pd arm and 12.8% in the Pd arm. TEAEs leading to death occurred in 7.9% and 9.4%, respectively.
Grade 3 TEAEs (in the isa-Pd and Pd arms, respectively) included upper respiratory tract infection (3.3% and 0.7%), diarrhea (2.0% and 0.7%), bronchitis (3.3% and 0.7%), pneumonia (15.1% and 13.4%), fatigue (3.9% and 0%), back pain (2.0% and 1.3%), asthenia (3.3% and 2.7%), and dyspnea (3.9% and 1.3%).
The only grade 4 TEAE was pneumonia (1.3% in both arms).
Based on the safety and efficacy results, Dr. Richardson concluded that isa-Pd “is an important new treatment option for our patients with relapsed/refractory myeloma.”
This study was funded by Sanofi. Dr. Richardson reported financial relationships with Celgene, Janssen, and Takeda. His coinvestigators reported relationships with a range of companies.
SOURCE: Richardson P et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 8004.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
Four-drug combo bests triplet in newly diagnosed myeloma
CHICAGO – Daratumumab plus bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (D-VTd) provided a “robust clinical benefit” over bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone alone (VTd) in a phase 3 trial of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to the trial’s principal investigator.
D-VTd produced significantly higher rates of stringent complete response (sCR) and progression-free survival (PFS) than did VTd, said Philippe Moreau, MD, of the University Hospital of Nantes (France).
Dr. Moreau presented these results, from the CASSIOPEIA trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. The findings were simultaneously published in the Lancet (2019 Jun 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[19]31240-1).
CASSIOPEIA enrolled 1,085 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who were eligible for high-dose chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). This is a two-part trial, and Dr. Moreau presented final results from part 1.
In part 1, patients were randomized to induction with D-VTd or VTd, followed by autologous HSCT and consolidation with D-VTd or VTd. In part 2, which is ongoing, patients who achieve a partial response or better are randomized to observation or maintenance with daratumumab for up to 2 years.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the D-VTd and VTd arms. The median age was 59 years (range, 22-65) and 58 years (range, 26-65), respectively. Most patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1, and most had an International Staging System stage of I or II.
The median follow-up was 18.8 months. Most patients completed induction – 85% in the D-VTd arm and 81% in the VTd arm – and went on to HSCT – 90% and 89%, respectively. The most common reasons for treatment discontinuation in both arms were adverse events and progression.
Response and survival
The primary endpoint for part 1 was the rate of sCR at 100 days after HSCT. The sCR rate was significantly higher in the D-VTd arm than it was in the VTd arm – 29% and 20%, respectively (odds ratio, 1.60; P less than .0010).
The overall response rate was significantly higher in the D-VTd arm than in the VTd arm – 93% and 90%, respectively (P less than .0001) – as was the rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity – 64% and 44%, respectively (P less than .0001).
Dr. Moreau noted that sCR and MRD negativity rates were superior with D-VTd across all subgroups except among patients with high-risk cytogenetics and International Staging System stage III disease.
“Dara-VTd resulted in a robust clinical benefit with a higher rate of response, including stringent CR, including MRD negativity,” Dr. Moreau said. “And this translated into a better progression-free survival, with a 53% reduction in the risk of progression or death.”
The 18-month PFS was 93% in the D-VTd arm and 85% in the VTd arm (hazard ratio, 0.47; P less than .0001). D-VTd reduced the risk of progression or death across all subgroups.
The median overall survival (OS) was not reached in either treatment arm. The 18-month OS rate was 98% in the D-VTd arm and 95% in the VTd arm. The 24-month OS rate was 97% and 93%, respectively.
“These results are the best ever reported in the setting of stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Moreau said.
Safety
The most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VTd and VTd arms, respectively) were neutropenia (28% and 15%), lymphopenia (17% and 10%), stomatitis (13% and 16%), and thrombocytopenia (11% and 7%).
The rate of infusion-related reactions was 35% in the D-VTd arm and 0% in the VTd arm. The rate of infections was 66% and 57%, respectively. The most common serious infection was pneumonia, which occurred in 4% and 2% of patients, respectively. The rate of second primary malignancies was 2% in both arms.
Based on the safety and efficacy results, Dr. Moreau concluded that D-VTd “should be considered a valid treatment option” for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients who are eligible for HSCT.
Dr. Moreau reported relationships with Amgen, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Takeda. The study is sponsored by the French Intergroupe Francophone du Myelome in collaboration with the Dutch-Belgian Cooperative Trial Group for Hematology Oncology and Janssen Research & Development.
SOURCE: Moreau P et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 8003.
CHICAGO – Daratumumab plus bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (D-VTd) provided a “robust clinical benefit” over bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone alone (VTd) in a phase 3 trial of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to the trial’s principal investigator.
D-VTd produced significantly higher rates of stringent complete response (sCR) and progression-free survival (PFS) than did VTd, said Philippe Moreau, MD, of the University Hospital of Nantes (France).
Dr. Moreau presented these results, from the CASSIOPEIA trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. The findings were simultaneously published in the Lancet (2019 Jun 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[19]31240-1).
CASSIOPEIA enrolled 1,085 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who were eligible for high-dose chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). This is a two-part trial, and Dr. Moreau presented final results from part 1.
In part 1, patients were randomized to induction with D-VTd or VTd, followed by autologous HSCT and consolidation with D-VTd or VTd. In part 2, which is ongoing, patients who achieve a partial response or better are randomized to observation or maintenance with daratumumab for up to 2 years.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the D-VTd and VTd arms. The median age was 59 years (range, 22-65) and 58 years (range, 26-65), respectively. Most patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1, and most had an International Staging System stage of I or II.
The median follow-up was 18.8 months. Most patients completed induction – 85% in the D-VTd arm and 81% in the VTd arm – and went on to HSCT – 90% and 89%, respectively. The most common reasons for treatment discontinuation in both arms were adverse events and progression.
Response and survival
The primary endpoint for part 1 was the rate of sCR at 100 days after HSCT. The sCR rate was significantly higher in the D-VTd arm than it was in the VTd arm – 29% and 20%, respectively (odds ratio, 1.60; P less than .0010).
The overall response rate was significantly higher in the D-VTd arm than in the VTd arm – 93% and 90%, respectively (P less than .0001) – as was the rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity – 64% and 44%, respectively (P less than .0001).
Dr. Moreau noted that sCR and MRD negativity rates were superior with D-VTd across all subgroups except among patients with high-risk cytogenetics and International Staging System stage III disease.
“Dara-VTd resulted in a robust clinical benefit with a higher rate of response, including stringent CR, including MRD negativity,” Dr. Moreau said. “And this translated into a better progression-free survival, with a 53% reduction in the risk of progression or death.”
The 18-month PFS was 93% in the D-VTd arm and 85% in the VTd arm (hazard ratio, 0.47; P less than .0001). D-VTd reduced the risk of progression or death across all subgroups.
The median overall survival (OS) was not reached in either treatment arm. The 18-month OS rate was 98% in the D-VTd arm and 95% in the VTd arm. The 24-month OS rate was 97% and 93%, respectively.
“These results are the best ever reported in the setting of stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Moreau said.
Safety
The most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VTd and VTd arms, respectively) were neutropenia (28% and 15%), lymphopenia (17% and 10%), stomatitis (13% and 16%), and thrombocytopenia (11% and 7%).
The rate of infusion-related reactions was 35% in the D-VTd arm and 0% in the VTd arm. The rate of infections was 66% and 57%, respectively. The most common serious infection was pneumonia, which occurred in 4% and 2% of patients, respectively. The rate of second primary malignancies was 2% in both arms.
Based on the safety and efficacy results, Dr. Moreau concluded that D-VTd “should be considered a valid treatment option” for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients who are eligible for HSCT.
Dr. Moreau reported relationships with Amgen, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Takeda. The study is sponsored by the French Intergroupe Francophone du Myelome in collaboration with the Dutch-Belgian Cooperative Trial Group for Hematology Oncology and Janssen Research & Development.
SOURCE: Moreau P et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 8003.
CHICAGO – Daratumumab plus bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone (D-VTd) provided a “robust clinical benefit” over bortezomib, thalidomide, and dexamethasone alone (VTd) in a phase 3 trial of patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma, according to the trial’s principal investigator.
D-VTd produced significantly higher rates of stringent complete response (sCR) and progression-free survival (PFS) than did VTd, said Philippe Moreau, MD, of the University Hospital of Nantes (France).
Dr. Moreau presented these results, from the CASSIOPEIA trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. The findings were simultaneously published in the Lancet (2019 Jun 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[19]31240-1).
CASSIOPEIA enrolled 1,085 patients with newly diagnosed multiple myeloma who were eligible for high-dose chemotherapy and hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT). This is a two-part trial, and Dr. Moreau presented final results from part 1.
In part 1, patients were randomized to induction with D-VTd or VTd, followed by autologous HSCT and consolidation with D-VTd or VTd. In part 2, which is ongoing, patients who achieve a partial response or better are randomized to observation or maintenance with daratumumab for up to 2 years.
Baseline characteristics were well balanced between the D-VTd and VTd arms. The median age was 59 years (range, 22-65) and 58 years (range, 26-65), respectively. Most patients had an Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status of 0 or 1, and most had an International Staging System stage of I or II.
The median follow-up was 18.8 months. Most patients completed induction – 85% in the D-VTd arm and 81% in the VTd arm – and went on to HSCT – 90% and 89%, respectively. The most common reasons for treatment discontinuation in both arms were adverse events and progression.
Response and survival
The primary endpoint for part 1 was the rate of sCR at 100 days after HSCT. The sCR rate was significantly higher in the D-VTd arm than it was in the VTd arm – 29% and 20%, respectively (odds ratio, 1.60; P less than .0010).
The overall response rate was significantly higher in the D-VTd arm than in the VTd arm – 93% and 90%, respectively (P less than .0001) – as was the rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity – 64% and 44%, respectively (P less than .0001).
Dr. Moreau noted that sCR and MRD negativity rates were superior with D-VTd across all subgroups except among patients with high-risk cytogenetics and International Staging System stage III disease.
“Dara-VTd resulted in a robust clinical benefit with a higher rate of response, including stringent CR, including MRD negativity,” Dr. Moreau said. “And this translated into a better progression-free survival, with a 53% reduction in the risk of progression or death.”
The 18-month PFS was 93% in the D-VTd arm and 85% in the VTd arm (hazard ratio, 0.47; P less than .0001). D-VTd reduced the risk of progression or death across all subgroups.
The median overall survival (OS) was not reached in either treatment arm. The 18-month OS rate was 98% in the D-VTd arm and 95% in the VTd arm. The 24-month OS rate was 97% and 93%, respectively.
“These results are the best ever reported in the setting of stem cell transplantation,” Dr. Moreau said.
Safety
The most common grade 3/4 treatment-emergent adverse events (in the D-VTd and VTd arms, respectively) were neutropenia (28% and 15%), lymphopenia (17% and 10%), stomatitis (13% and 16%), and thrombocytopenia (11% and 7%).
The rate of infusion-related reactions was 35% in the D-VTd arm and 0% in the VTd arm. The rate of infections was 66% and 57%, respectively. The most common serious infection was pneumonia, which occurred in 4% and 2% of patients, respectively. The rate of second primary malignancies was 2% in both arms.
Based on the safety and efficacy results, Dr. Moreau concluded that D-VTd “should be considered a valid treatment option” for newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients who are eligible for HSCT.
Dr. Moreau reported relationships with Amgen, Celgene, Janssen-Cilag, Novartis, and Takeda. The study is sponsored by the French Intergroupe Francophone du Myelome in collaboration with the Dutch-Belgian Cooperative Trial Group for Hematology Oncology and Janssen Research & Development.
SOURCE: Moreau P et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 8003.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
Inhibitor produces high response rate in relapsed/refractory FL
CHICAGO – The phosphoinositide 3-kinase–delta inhibitor ME-401, given with or without rituximab, produced an overall response rate of 80% in a phase 1b trial of patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.
Response rates were similar between patients who received ME-401 alone and those who received it in combination with rituximab.
Response rates were also similar between patients on an intermittent dosing schedule and those on a continuous dosing schedule. However, intermittent dosing decreased the rate of delayed grade 3 adverse events (AEs).
“The idea that continuous inhibition of target is absolutely essential for activity of this class of drugs has not been proven,” said Andrew Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“The promising results of this somewhat novel intermittent schedule that we used with ME-401 suggests to me that we can maintain efficacy and reduce toxicity.”
Dr. Zelenetz and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Patients and dosing
Data were presented for 54 patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma enrolled on this study. The patients had a median age of 63.5 years, and 80% were male. They had received a median of 2 prior therapies (range, 1-10).
Initially, patients received ME-401 at 60 mg, 120 mg, or 180 mg once daily continuously on a 28-day cycle. However, the dose-escalation portion of the study was closed because response rates were comparable among the three doses, the safety profile was similar, and there were no dose-limiting toxicities.
Two additional groups of patients received ME-401 at 60 mg daily for two cycles, followed by an intermittent schedule (IS) of 60 mg on days 1-7, repeated every 28 days.
The researchers had observed delayed grade 3 AEs on the continuous schedule (CS), and they hypothesized that the IS might prevent these events. Patients could revert to the CS if they had stable disease or progressed on the IS.
“One of the advantages of this particular agent is the very long half-life,” Dr. Zelenetz said. “So, essentially, we have 2 weeks on drug and 2 weeks off [with the IS]. It takes about a week to clear the drug because it has about a 30-hour half-life.”
In all, 40 patients received ME-401 monotherapy, and 14 received ME-401 plus rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks and then on day 1 of cycles 3-6. There were 31 patients who received ME-401 on the CS and 23 who received ME-401 on the IS.
Results
A total of 50 patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate in these patients was 80% (40/50), and 20% (10/50) achieved a complete response.
The overall response rate was 79% (30/38) in patients who received ME-401 alone, 83% (10/12) in those who received ME-401 plus rituximab, 83% (25/30) in patients on the CS, and 75% (15/20) in those on the IS.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival have not been reached. The median follow-up for response duration is 8.8 months in the IS group and 8.3 months in the CS group. The median follow-up for progression-free survival is 5.5 months and 6.5 months, respectively.
A total of 18 patients on the IS (78%) were still on therapy at the data cutoff, as were 14 patients (45%) on the CS.
Seven patients (23%) on the CS and two patients (9%) on the IS discontinued treatment due to progression. Four patients in the IS group and two in the CS group who were switched to IS dosing reverted to CS dosing after experiencing progression.
Four CS patients (13%) discontinued treatment because of AEs, but none of the IS patients did.
AEs occurring in at least 15% of patients were diarrhea/colitis (40.7%), fatigue (35.2%), cough (33.3%), rash (24.1%), ALT increase (24.1%), nausea (24.1%), AST increase (22.2%), and decreased appetite (16.7%).
There were no grade 4-5 AEs. Grade 3 drug-related AEs of special interest (in the CS and IS groups, respectively) were diarrhea/colitis (16.1% and 8.7%), rash (12.9% and 0%), ALT increase (6.5% and 4.3%), AST increase (6.5% and 0%), pneumonia (6.5% and 0%), and mucositis (1.9% and 0%).
“[W]hile the grade 3 immune-related events seem to be very consistent in terms of class effects, they did seem to improve with transition to intermittent schedule,” said Carla Casulo, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
“And I think that this novel design helps to create an opportunity to limit treatment and mitigate toxicity without necessarily compromising efficacy.”
The phase 1b trial is sponsored by MEI Pharma. Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with MEI Pharma and several other companies. Dr. Casulo reported relationships with Gilead Sciences, Celgene, and Roche.
SOURCE: Zelenetz A et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7512.
CHICAGO – The phosphoinositide 3-kinase–delta inhibitor ME-401, given with or without rituximab, produced an overall response rate of 80% in a phase 1b trial of patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.
Response rates were similar between patients who received ME-401 alone and those who received it in combination with rituximab.
Response rates were also similar between patients on an intermittent dosing schedule and those on a continuous dosing schedule. However, intermittent dosing decreased the rate of delayed grade 3 adverse events (AEs).
“The idea that continuous inhibition of target is absolutely essential for activity of this class of drugs has not been proven,” said Andrew Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“The promising results of this somewhat novel intermittent schedule that we used with ME-401 suggests to me that we can maintain efficacy and reduce toxicity.”
Dr. Zelenetz and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Patients and dosing
Data were presented for 54 patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma enrolled on this study. The patients had a median age of 63.5 years, and 80% were male. They had received a median of 2 prior therapies (range, 1-10).
Initially, patients received ME-401 at 60 mg, 120 mg, or 180 mg once daily continuously on a 28-day cycle. However, the dose-escalation portion of the study was closed because response rates were comparable among the three doses, the safety profile was similar, and there were no dose-limiting toxicities.
Two additional groups of patients received ME-401 at 60 mg daily for two cycles, followed by an intermittent schedule (IS) of 60 mg on days 1-7, repeated every 28 days.
The researchers had observed delayed grade 3 AEs on the continuous schedule (CS), and they hypothesized that the IS might prevent these events. Patients could revert to the CS if they had stable disease or progressed on the IS.
“One of the advantages of this particular agent is the very long half-life,” Dr. Zelenetz said. “So, essentially, we have 2 weeks on drug and 2 weeks off [with the IS]. It takes about a week to clear the drug because it has about a 30-hour half-life.”
In all, 40 patients received ME-401 monotherapy, and 14 received ME-401 plus rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks and then on day 1 of cycles 3-6. There were 31 patients who received ME-401 on the CS and 23 who received ME-401 on the IS.
Results
A total of 50 patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate in these patients was 80% (40/50), and 20% (10/50) achieved a complete response.
The overall response rate was 79% (30/38) in patients who received ME-401 alone, 83% (10/12) in those who received ME-401 plus rituximab, 83% (25/30) in patients on the CS, and 75% (15/20) in those on the IS.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival have not been reached. The median follow-up for response duration is 8.8 months in the IS group and 8.3 months in the CS group. The median follow-up for progression-free survival is 5.5 months and 6.5 months, respectively.
A total of 18 patients on the IS (78%) were still on therapy at the data cutoff, as were 14 patients (45%) on the CS.
Seven patients (23%) on the CS and two patients (9%) on the IS discontinued treatment due to progression. Four patients in the IS group and two in the CS group who were switched to IS dosing reverted to CS dosing after experiencing progression.
Four CS patients (13%) discontinued treatment because of AEs, but none of the IS patients did.
AEs occurring in at least 15% of patients were diarrhea/colitis (40.7%), fatigue (35.2%), cough (33.3%), rash (24.1%), ALT increase (24.1%), nausea (24.1%), AST increase (22.2%), and decreased appetite (16.7%).
There were no grade 4-5 AEs. Grade 3 drug-related AEs of special interest (in the CS and IS groups, respectively) were diarrhea/colitis (16.1% and 8.7%), rash (12.9% and 0%), ALT increase (6.5% and 4.3%), AST increase (6.5% and 0%), pneumonia (6.5% and 0%), and mucositis (1.9% and 0%).
“[W]hile the grade 3 immune-related events seem to be very consistent in terms of class effects, they did seem to improve with transition to intermittent schedule,” said Carla Casulo, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
“And I think that this novel design helps to create an opportunity to limit treatment and mitigate toxicity without necessarily compromising efficacy.”
The phase 1b trial is sponsored by MEI Pharma. Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with MEI Pharma and several other companies. Dr. Casulo reported relationships with Gilead Sciences, Celgene, and Roche.
SOURCE: Zelenetz A et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7512.
CHICAGO – The phosphoinositide 3-kinase–delta inhibitor ME-401, given with or without rituximab, produced an overall response rate of 80% in a phase 1b trial of patients with relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma.
Response rates were similar between patients who received ME-401 alone and those who received it in combination with rituximab.
Response rates were also similar between patients on an intermittent dosing schedule and those on a continuous dosing schedule. However, intermittent dosing decreased the rate of delayed grade 3 adverse events (AEs).
“The idea that continuous inhibition of target is absolutely essential for activity of this class of drugs has not been proven,” said Andrew Zelenetz, MD, PhD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
“The promising results of this somewhat novel intermittent schedule that we used with ME-401 suggests to me that we can maintain efficacy and reduce toxicity.”
Dr. Zelenetz and colleagues presented these results in a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Patients and dosing
Data were presented for 54 patients with relapsed/refractory follicular lymphoma enrolled on this study. The patients had a median age of 63.5 years, and 80% were male. They had received a median of 2 prior therapies (range, 1-10).
Initially, patients received ME-401 at 60 mg, 120 mg, or 180 mg once daily continuously on a 28-day cycle. However, the dose-escalation portion of the study was closed because response rates were comparable among the three doses, the safety profile was similar, and there were no dose-limiting toxicities.
Two additional groups of patients received ME-401 at 60 mg daily for two cycles, followed by an intermittent schedule (IS) of 60 mg on days 1-7, repeated every 28 days.
The researchers had observed delayed grade 3 AEs on the continuous schedule (CS), and they hypothesized that the IS might prevent these events. Patients could revert to the CS if they had stable disease or progressed on the IS.
“One of the advantages of this particular agent is the very long half-life,” Dr. Zelenetz said. “So, essentially, we have 2 weeks on drug and 2 weeks off [with the IS]. It takes about a week to clear the drug because it has about a 30-hour half-life.”
In all, 40 patients received ME-401 monotherapy, and 14 received ME-401 plus rituximab at 375 mg/m2 weekly for 4 weeks and then on day 1 of cycles 3-6. There were 31 patients who received ME-401 on the CS and 23 who received ME-401 on the IS.
Results
A total of 50 patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate in these patients was 80% (40/50), and 20% (10/50) achieved a complete response.
The overall response rate was 79% (30/38) in patients who received ME-401 alone, 83% (10/12) in those who received ME-401 plus rituximab, 83% (25/30) in patients on the CS, and 75% (15/20) in those on the IS.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival have not been reached. The median follow-up for response duration is 8.8 months in the IS group and 8.3 months in the CS group. The median follow-up for progression-free survival is 5.5 months and 6.5 months, respectively.
A total of 18 patients on the IS (78%) were still on therapy at the data cutoff, as were 14 patients (45%) on the CS.
Seven patients (23%) on the CS and two patients (9%) on the IS discontinued treatment due to progression. Four patients in the IS group and two in the CS group who were switched to IS dosing reverted to CS dosing after experiencing progression.
Four CS patients (13%) discontinued treatment because of AEs, but none of the IS patients did.
AEs occurring in at least 15% of patients were diarrhea/colitis (40.7%), fatigue (35.2%), cough (33.3%), rash (24.1%), ALT increase (24.1%), nausea (24.1%), AST increase (22.2%), and decreased appetite (16.7%).
There were no grade 4-5 AEs. Grade 3 drug-related AEs of special interest (in the CS and IS groups, respectively) were diarrhea/colitis (16.1% and 8.7%), rash (12.9% and 0%), ALT increase (6.5% and 4.3%), AST increase (6.5% and 0%), pneumonia (6.5% and 0%), and mucositis (1.9% and 0%).
“[W]hile the grade 3 immune-related events seem to be very consistent in terms of class effects, they did seem to improve with transition to intermittent schedule,” said Carla Casulo, MD, of the University of Rochester (N.Y.), who reviewed this study in a poster discussion session.
“And I think that this novel design helps to create an opportunity to limit treatment and mitigate toxicity without necessarily compromising efficacy.”
The phase 1b trial is sponsored by MEI Pharma. Dr. Zelenetz reported relationships with MEI Pharma and several other companies. Dr. Casulo reported relationships with Gilead Sciences, Celgene, and Roche.
SOURCE: Zelenetz A et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7512.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
FDA approves Polivy for DLBCL
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval to Polivy (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq), in conjunction with bendamustine and a rituximab product, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who have undergone at least two prior therapies.
The FDA approval is based on results of an open-label, multicenter clinical trial of 80 patients with DLBCL who had undergone at least one prior regimen. Patients received either Polivy plus bendamustine and rituximab or only bendamustine and rituximab for six 21-day cycles. At the completion of therapy, 40% of patients who received Polivy in conjunction with bendamustine and rituximab achieved a complete response, compared with 18% of patients who received only bendamustine and rituximab; total response was 63% in those who received Polivy and 25% in those who did not.
The most common adverse events included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, decreased appetite, and pneumonia. Serious adverse events occurred in 64% of patients, most commonly from infection; the most common cause for treatment discontinuation was cytopenia.
The recommended dose of Polivy is 1.8 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 90 minutes every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product, the FDA said. Subsequent infusions may be administered over 30 minutes if the previous infusion is tolerated.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval to Polivy (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq), in conjunction with bendamustine and a rituximab product, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who have undergone at least two prior therapies.
The FDA approval is based on results of an open-label, multicenter clinical trial of 80 patients with DLBCL who had undergone at least one prior regimen. Patients received either Polivy plus bendamustine and rituximab or only bendamustine and rituximab for six 21-day cycles. At the completion of therapy, 40% of patients who received Polivy in conjunction with bendamustine and rituximab achieved a complete response, compared with 18% of patients who received only bendamustine and rituximab; total response was 63% in those who received Polivy and 25% in those who did not.
The most common adverse events included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, decreased appetite, and pneumonia. Serious adverse events occurred in 64% of patients, most commonly from infection; the most common cause for treatment discontinuation was cytopenia.
The recommended dose of Polivy is 1.8 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 90 minutes every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product, the FDA said. Subsequent infusions may be administered over 30 minutes if the previous infusion is tolerated.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted accelerated approval to Polivy (polatuzumab vedotin-piiq), in conjunction with bendamustine and a rituximab product, for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) who have undergone at least two prior therapies.
The FDA approval is based on results of an open-label, multicenter clinical trial of 80 patients with DLBCL who had undergone at least one prior regimen. Patients received either Polivy plus bendamustine and rituximab or only bendamustine and rituximab for six 21-day cycles. At the completion of therapy, 40% of patients who received Polivy in conjunction with bendamustine and rituximab achieved a complete response, compared with 18% of patients who received only bendamustine and rituximab; total response was 63% in those who received Polivy and 25% in those who did not.
The most common adverse events included neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, peripheral neuropathy, fatigue, diarrhea, pyrexia, decreased appetite, and pneumonia. Serious adverse events occurred in 64% of patients, most commonly from infection; the most common cause for treatment discontinuation was cytopenia.
The recommended dose of Polivy is 1.8 mg/kg as an intravenous infusion over 90 minutes every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product, the FDA said. Subsequent infusions may be administered over 30 minutes if the previous infusion is tolerated.
Find the full press release on the FDA website.