User login
Zanubrutinib receives breakthrough designation for MCL
The (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed by BeiGene as a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies.
Researchers have evaluated zanubrutinib in a phase 2 trial (NCT03206970) of patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 148).
As of March 27, 2018, 86 patients had been enrolled in the trial and received treatment. They had a median of two prior lines of therapy and they received zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily.
Eighty-five patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 83.5% (71/85), and the complete response rate was 58.8% (50/85). At a median follow-up of 24.1 weeks, the median duration of response and median progression-free survival had not been reached. The estimated 24-week progression-free survival rate was 82%. The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were decrease in neutrophil count (31.4%), rash (29.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (29.1%), and decrease in platelet count (22.1%). Common grade 3 or higher AEs included neutrophil count decrease (11.6%) and lung infection (5.8%).
Four patients had fatal treatment-emergent AEs. One death was caused by a traffic accident, one was due to cerebral hemorrhage, and one resulted from pneumonia. The fourth death occurred in a patient with infection, but the cause of death was unknown.
Breakthrough therapy designation is designed to expedite the development and review of a therapy for a serious or life-threatening disease, following preliminary clinical evidence indicating it demonstrates substantial improvement over existing therapies.
The (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed by BeiGene as a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies.
Researchers have evaluated zanubrutinib in a phase 2 trial (NCT03206970) of patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 148).
As of March 27, 2018, 86 patients had been enrolled in the trial and received treatment. They had a median of two prior lines of therapy and they received zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily.
Eighty-five patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 83.5% (71/85), and the complete response rate was 58.8% (50/85). At a median follow-up of 24.1 weeks, the median duration of response and median progression-free survival had not been reached. The estimated 24-week progression-free survival rate was 82%. The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were decrease in neutrophil count (31.4%), rash (29.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (29.1%), and decrease in platelet count (22.1%). Common grade 3 or higher AEs included neutrophil count decrease (11.6%) and lung infection (5.8%).
Four patients had fatal treatment-emergent AEs. One death was caused by a traffic accident, one was due to cerebral hemorrhage, and one resulted from pneumonia. The fourth death occurred in a patient with infection, but the cause of death was unknown.
Breakthrough therapy designation is designed to expedite the development and review of a therapy for a serious or life-threatening disease, following preliminary clinical evidence indicating it demonstrates substantial improvement over existing therapies.
The (MCL) who have received at least one prior therapy.
Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor being developed by BeiGene as a potential treatment for B-cell malignancies.
Researchers have evaluated zanubrutinib in a phase 2 trial (NCT03206970) of patients with relapsed/refractory MCL. Results from this trial were presented at the 2018 annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (Abstract 148).
As of March 27, 2018, 86 patients had been enrolled in the trial and received treatment. They had a median of two prior lines of therapy and they received zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily.
Eighty-five patients were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 83.5% (71/85), and the complete response rate was 58.8% (50/85). At a median follow-up of 24.1 weeks, the median duration of response and median progression-free survival had not been reached. The estimated 24-week progression-free survival rate was 82%. The most common adverse events (AEs) in this trial were decrease in neutrophil count (31.4%), rash (29.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (29.1%), and decrease in platelet count (22.1%). Common grade 3 or higher AEs included neutrophil count decrease (11.6%) and lung infection (5.8%).
Four patients had fatal treatment-emergent AEs. One death was caused by a traffic accident, one was due to cerebral hemorrhage, and one resulted from pneumonia. The fourth death occurred in a patient with infection, but the cause of death was unknown.
Breakthrough therapy designation is designed to expedite the development and review of a therapy for a serious or life-threatening disease, following preliminary clinical evidence indicating it demonstrates substantial improvement over existing therapies.
Chidamide may be more effective in PTCL than previously thought
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Real-world data suggest chidamide may be more effective against relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) than a pivotal study indicated.
Single-agent chidamide produced an overall response rate of 47.0% in a real-world study of more than 1,000 patients, compared with the 28.0% overall response rate that was observed in the phase 2 study of chidamide (Ann Oncol. 2015 Aug;26[8]:1766-71).
Yuqin Song, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute in Beijing, China, presented data from the real-world study at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Song said this study is the largest cohort of real-world patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL. She and her colleagues analyzed data on 1,064 patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
The patients had a median age of 54 years, 63.9% were male, and 88.1% had stage III-IV disease.
Disease subtypes included PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS, 38.0%), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, 29.1%), extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL, 13.4%), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL, 9.1%), and others (10.3%), including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
Fifty-two percent of patients (n = 553) received chidamide as a single agent, and 48% (n = 511) received the drug with other agents. The most common treatment regimens combined with chidamide were the following
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP, 20.7%).
- Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP, 11.8%).
- Etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH, 9.8%).
- Patients with ENKTL received chidamide with L-asparaginase (35.4%) or without it (64.5%).
The median follow-up was 4.9 months (range, 0-36.2 months). Across disease subtypes, the overall response rate was 47.0% with single-agent chidamide and 65.4% when chidamide was given in combination with other agents (P less than .01).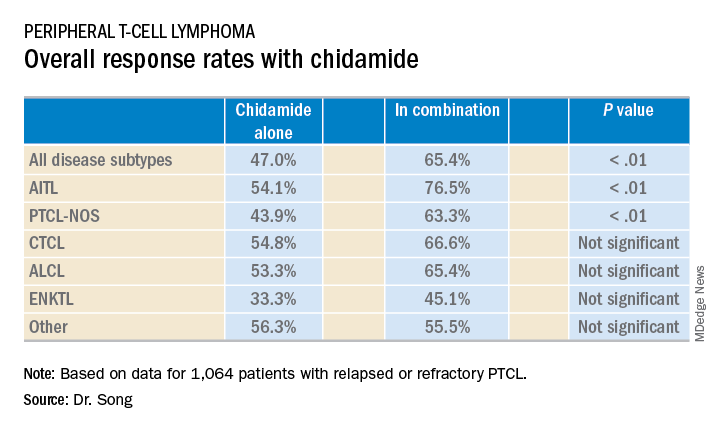
The median overall survival was 400 days for all patients, 342 days for patients treated with chidamide alone, and 457 days for patients who received combination therapy. The 1-year overall survival rates were 52%, 48%, and 56%, respectively.
Dr. Song said these data verify the efficacy of chidamide as a single agent and suggest chidamide might lead to improved survival in refractory or relapsed PTCLs.
Chidamide was generally well tolerated in this study, Dr. Song said. There were no unexpected adverse events (AEs) and most were grade 1 or 2.
The most common AEs (of any grade) observed with single-agent chidamide were neutropenia (42.9%), thrombocytopenia (40.5%), fatigue (38.3%), anemia (31.6%), and nausea/vomiting (21.0%).
The most common AEs observed with chidamide in combination were neutropenia (61.4%), thrombocytopenia (58.5%), fatigue (56.2%), anemia (54.2%), nausea/vomiting (30.7%), and fever (22.1%).
This study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Real-world data suggest chidamide may be more effective against relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) than a pivotal study indicated.
Single-agent chidamide produced an overall response rate of 47.0% in a real-world study of more than 1,000 patients, compared with the 28.0% overall response rate that was observed in the phase 2 study of chidamide (Ann Oncol. 2015 Aug;26[8]:1766-71).
Yuqin Song, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute in Beijing, China, presented data from the real-world study at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Song said this study is the largest cohort of real-world patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL. She and her colleagues analyzed data on 1,064 patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
The patients had a median age of 54 years, 63.9% were male, and 88.1% had stage III-IV disease.
Disease subtypes included PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS, 38.0%), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, 29.1%), extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL, 13.4%), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL, 9.1%), and others (10.3%), including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
Fifty-two percent of patients (n = 553) received chidamide as a single agent, and 48% (n = 511) received the drug with other agents. The most common treatment regimens combined with chidamide were the following
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP, 20.7%).
- Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP, 11.8%).
- Etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH, 9.8%).
- Patients with ENKTL received chidamide with L-asparaginase (35.4%) or without it (64.5%).
The median follow-up was 4.9 months (range, 0-36.2 months). Across disease subtypes, the overall response rate was 47.0% with single-agent chidamide and 65.4% when chidamide was given in combination with other agents (P less than .01).
The median overall survival was 400 days for all patients, 342 days for patients treated with chidamide alone, and 457 days for patients who received combination therapy. The 1-year overall survival rates were 52%, 48%, and 56%, respectively.
Dr. Song said these data verify the efficacy of chidamide as a single agent and suggest chidamide might lead to improved survival in refractory or relapsed PTCLs.
Chidamide was generally well tolerated in this study, Dr. Song said. There were no unexpected adverse events (AEs) and most were grade 1 or 2.
The most common AEs (of any grade) observed with single-agent chidamide were neutropenia (42.9%), thrombocytopenia (40.5%), fatigue (38.3%), anemia (31.6%), and nausea/vomiting (21.0%).
The most common AEs observed with chidamide in combination were neutropenia (61.4%), thrombocytopenia (58.5%), fatigue (56.2%), anemia (54.2%), nausea/vomiting (30.7%), and fever (22.1%).
This study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
LA JOLLA, CALIF. – Real-world data suggest chidamide may be more effective against relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) than a pivotal study indicated.
Single-agent chidamide produced an overall response rate of 47.0% in a real-world study of more than 1,000 patients, compared with the 28.0% overall response rate that was observed in the phase 2 study of chidamide (Ann Oncol. 2015 Aug;26[8]:1766-71).
Yuqin Song, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital and Institute in Beijing, China, presented data from the real-world study at the annual T-cell Lymphoma Forum.
Dr. Song said this study is the largest cohort of real-world patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL. She and her colleagues analyzed data on 1,064 patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
The patients had a median age of 54 years, 63.9% were male, and 88.1% had stage III-IV disease.
Disease subtypes included PTCL not otherwise specified (NOS, 38.0%), angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL, 29.1%), extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL, 13.4%), anaplastic large-cell lymphoma (ALCL, 9.1%), and others (10.3%), including cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL).
Fifty-two percent of patients (n = 553) received chidamide as a single agent, and 48% (n = 511) received the drug with other agents. The most common treatment regimens combined with chidamide were the following
- Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP, 20.7%).
- Gemcitabine, dexamethasone, and cisplatin (GDP, 11.8%).
- Etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin (EPOCH, 9.8%).
- Patients with ENKTL received chidamide with L-asparaginase (35.4%) or without it (64.5%).
The median follow-up was 4.9 months (range, 0-36.2 months). Across disease subtypes, the overall response rate was 47.0% with single-agent chidamide and 65.4% when chidamide was given in combination with other agents (P less than .01).
The median overall survival was 400 days for all patients, 342 days for patients treated with chidamide alone, and 457 days for patients who received combination therapy. The 1-year overall survival rates were 52%, 48%, and 56%, respectively.
Dr. Song said these data verify the efficacy of chidamide as a single agent and suggest chidamide might lead to improved survival in refractory or relapsed PTCLs.
Chidamide was generally well tolerated in this study, Dr. Song said. There were no unexpected adverse events (AEs) and most were grade 1 or 2.
The most common AEs (of any grade) observed with single-agent chidamide were neutropenia (42.9%), thrombocytopenia (40.5%), fatigue (38.3%), anemia (31.6%), and nausea/vomiting (21.0%).
The most common AEs observed with chidamide in combination were neutropenia (61.4%), thrombocytopenia (58.5%), fatigue (56.2%), anemia (54.2%), nausea/vomiting (30.7%), and fever (22.1%).
This study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
The T-cell Lymphoma Forum is organized by Jonathan Wood & Associates, which is owned by the same company as this news organization.
REPORTING FROM TCLF 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Single-agent chidamide had an overall response rate of 47.0% among relapsed/refractory PTCL patients, compared with 65.4% when used in combination with other agents (P less than .01).
Study details: A real-world cohort of 1,064 relapsed/refractory PTCL patients treated at 216 sites across China between February 2015 and December 2017.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Union for China Lymphoma Investigators and the Chinese Society of Clinical Oncology. Dr. Song did not disclose any conflicts of interest.
Armored CAR protects T cells, induces remissions
SAN DIEGO – A second-generation CD19-specific “armored” chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell construct was associated with high complete remission rates in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in a phase 1 trial.
The CAR T construct – labeled 1928z-41BBL – also induced “encouraging” complete remission rates in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with Richter’s transformation, reported Jae H. Park, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), New York, and his colleagues.
“Interestingly and encouragingly, severe [cytokine release syndrome] was not seen and grade 3 neurotoxicity was observed in less than 10%, with no grade 4 neurotoxicity, so there appears to be a favorable side effect profile,” Dr. Park said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Just as armored cars are designed to protect their valuable contents from people with bad intent, armored CAR T cells are engineered to protect the modified T-cells from a hostile tumor microenvironment and simultaneously recruit non-modified T cells to the target to produce a more robust immune response against malignant cells.
MSKCC investigators had previously shown that in contrast to other CAR T-cell constructs, the 1928z-41BBL configuration, which consists of two signaling domains (CD28 and CD3zeta) and the 4-1BB ligand, hit the sweet spot between tumor-killing function and T-cell persistence (Cancer Cell. 2015 Oct 12;28[4]:415-28).
In the current study, they enrolled 35 adults with relapsed or refractory CD19-positive hematologic malignancies, 29 of whom eventually underwent CAR T-cell infusions. The treated population comprised 14 patients with CLL (4 of whom had Richter’s transformation), 9 with DLBCL, 5 with indolent NHL, and 1 with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
The patients with CLL had received a median of 5.5 prior lines of therapy, including ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta).
There were 15 complete remissions (CR), with CR rates of 78% in DLBCL, 20% in CLL, 67% in CLL with Richter’s transformation, 60% in patients with indolent NHL, as well as CR in the single patient with ALL.
There were eight partial remissions. One patient with CLL had stable disease, and four patients had disease progression (one patient each with DLBCL, CLL, CLL with Richter’s, and indolent NHL).
Dr. Park noted that T cells are being detected in peripheral blood more than 6 months after T-cell infusion.
There were no cases of severe cytokine release syndrome, defined as requiring vasopressors and/or mechanical ventilation for hypoxia, and just three cases of grade 3 neurotoxicity. There were no cases of grade 4 neurotoxicity, no deaths related to neurotoxicity, and no cases of cerebral edema – a serious complication that has been seen in earlier CAR T-cell studies.
Split or multiple infusions of CAR T cells or incorporation of the technique into earlier lines of therapy might generate higher response rates, Dr. Park said.
The study was supported by Juno Therapeutics. Dr. Park reported consulting for and research funding from Juno, and financial relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Park JH et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 224.
SAN DIEGO – A second-generation CD19-specific “armored” chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell construct was associated with high complete remission rates in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in a phase 1 trial.
The CAR T construct – labeled 1928z-41BBL – also induced “encouraging” complete remission rates in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with Richter’s transformation, reported Jae H. Park, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), New York, and his colleagues.
“Interestingly and encouragingly, severe [cytokine release syndrome] was not seen and grade 3 neurotoxicity was observed in less than 10%, with no grade 4 neurotoxicity, so there appears to be a favorable side effect profile,” Dr. Park said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Just as armored cars are designed to protect their valuable contents from people with bad intent, armored CAR T cells are engineered to protect the modified T-cells from a hostile tumor microenvironment and simultaneously recruit non-modified T cells to the target to produce a more robust immune response against malignant cells.
MSKCC investigators had previously shown that in contrast to other CAR T-cell constructs, the 1928z-41BBL configuration, which consists of two signaling domains (CD28 and CD3zeta) and the 4-1BB ligand, hit the sweet spot between tumor-killing function and T-cell persistence (Cancer Cell. 2015 Oct 12;28[4]:415-28).
In the current study, they enrolled 35 adults with relapsed or refractory CD19-positive hematologic malignancies, 29 of whom eventually underwent CAR T-cell infusions. The treated population comprised 14 patients with CLL (4 of whom had Richter’s transformation), 9 with DLBCL, 5 with indolent NHL, and 1 with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
The patients with CLL had received a median of 5.5 prior lines of therapy, including ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta).
There were 15 complete remissions (CR), with CR rates of 78% in DLBCL, 20% in CLL, 67% in CLL with Richter’s transformation, 60% in patients with indolent NHL, as well as CR in the single patient with ALL.
There were eight partial remissions. One patient with CLL had stable disease, and four patients had disease progression (one patient each with DLBCL, CLL, CLL with Richter’s, and indolent NHL).
Dr. Park noted that T cells are being detected in peripheral blood more than 6 months after T-cell infusion.
There were no cases of severe cytokine release syndrome, defined as requiring vasopressors and/or mechanical ventilation for hypoxia, and just three cases of grade 3 neurotoxicity. There were no cases of grade 4 neurotoxicity, no deaths related to neurotoxicity, and no cases of cerebral edema – a serious complication that has been seen in earlier CAR T-cell studies.
Split or multiple infusions of CAR T cells or incorporation of the technique into earlier lines of therapy might generate higher response rates, Dr. Park said.
The study was supported by Juno Therapeutics. Dr. Park reported consulting for and research funding from Juno, and financial relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Park JH et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 224.
SAN DIEGO – A second-generation CD19-specific “armored” chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell construct was associated with high complete remission rates in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) and indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) in a phase 1 trial.
The CAR T construct – labeled 1928z-41BBL – also induced “encouraging” complete remission rates in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) with Richter’s transformation, reported Jae H. Park, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC), New York, and his colleagues.
“Interestingly and encouragingly, severe [cytokine release syndrome] was not seen and grade 3 neurotoxicity was observed in less than 10%, with no grade 4 neurotoxicity, so there appears to be a favorable side effect profile,” Dr. Park said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Just as armored cars are designed to protect their valuable contents from people with bad intent, armored CAR T cells are engineered to protect the modified T-cells from a hostile tumor microenvironment and simultaneously recruit non-modified T cells to the target to produce a more robust immune response against malignant cells.
MSKCC investigators had previously shown that in contrast to other CAR T-cell constructs, the 1928z-41BBL configuration, which consists of two signaling domains (CD28 and CD3zeta) and the 4-1BB ligand, hit the sweet spot between tumor-killing function and T-cell persistence (Cancer Cell. 2015 Oct 12;28[4]:415-28).
In the current study, they enrolled 35 adults with relapsed or refractory CD19-positive hematologic malignancies, 29 of whom eventually underwent CAR T-cell infusions. The treated population comprised 14 patients with CLL (4 of whom had Richter’s transformation), 9 with DLBCL, 5 with indolent NHL, and 1 with acute lymphoblastic leukemia.
The patients with CLL had received a median of 5.5 prior lines of therapy, including ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta).
There were 15 complete remissions (CR), with CR rates of 78% in DLBCL, 20% in CLL, 67% in CLL with Richter’s transformation, 60% in patients with indolent NHL, as well as CR in the single patient with ALL.
There were eight partial remissions. One patient with CLL had stable disease, and four patients had disease progression (one patient each with DLBCL, CLL, CLL with Richter’s, and indolent NHL).
Dr. Park noted that T cells are being detected in peripheral blood more than 6 months after T-cell infusion.
There were no cases of severe cytokine release syndrome, defined as requiring vasopressors and/or mechanical ventilation for hypoxia, and just three cases of grade 3 neurotoxicity. There were no cases of grade 4 neurotoxicity, no deaths related to neurotoxicity, and no cases of cerebral edema – a serious complication that has been seen in earlier CAR T-cell studies.
Split or multiple infusions of CAR T cells or incorporation of the technique into earlier lines of therapy might generate higher response rates, Dr. Park said.
The study was supported by Juno Therapeutics. Dr. Park reported consulting for and research funding from Juno, and financial relationships with other companies.
SOURCE: Park JH et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 224.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point: The 1928z-41BBL CAR T-cell construct induced high rates of complete remissions.
Major finding: The CAR T product was associated with a 78% complete remission rate in patients with heavily pretreated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
Study details: A phase 1 trial in 29 patients with CD19-positive hematologic malignancies.
Disclosures: Juno Therapeutics supported the study. Dr. Park reported consulting for and research funding from Juno, and financial relationships with other companies.
Source: Park JH et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 224.
CMT provides survival benefit in young HL patients
Combined modality therapy (CMT) can improve survival in young patients with early stage Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), according to research published in JAMA Oncology.
In a retrospective study, researchers compared chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy—CMT—to chemotherapy alone in more than 5,600 HL patients age 21 and younger.
There was a significant improvement in 5-year overall survival (OS) among patients who received CMT.
The treatment appeared particularly beneficial for adolescents and young adults as well as patients with low-risk disease.
However, the researchers observed a nearly 25% decrease in the use of CMT over the period studied.
“Nationwide, there has been a notable decrease in combined modality therapy, especially in clinical trials, many of which are designed to avoid this strategy,” said Rahul Parikh, MD, of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey in New Brunswick.
“This form of treatment has shown to be effective, with event-free survival rates greater than 80% and overall survival rates greater than 95%. The question then becomes, ‘does treatment benefit outweigh the risk of long-term side effects?”
With this in mind, Dr. Parikh and his colleagues compared CMT to chemotherapy alone using data from the National Cancer Database spanning the period from 2004 to 2015.
The researchers analyzed 5,657 patients with stage I/II classical HL who had a mean age of 17.1.
Roughly half of patients received CMT (50.3%, n=2845), and the other half received chemotherapy alone (49.7%, n=2812).
The median radiotherapy dose was 21.0 Gy, and the most common modality was photon therapy (59.0%).
Patients who received CMT were significantly more likely to be younger than 16 (P<0.001), be male (P<0.001), have stage II disease (P=0.02), and have private health insurance (P=0.002).
Results
The median follow-up was 5.1 years.
The 5-year OS was 94.5% for patients who received chemotherapy alone and 97.3% for patients treated with CMT.
CMT was significantly associated with improved OS in both univariate (hazard ratio [HR]=0.58, P<0.001) and multivariate analyses (HR=0.57, P<0.001).
In a sensitivity analysis, the researchers found the greatest benefits of CMT were in adolescents and young adults (age 14 and older, adjusted HR=0.47) and patients with low-risk disease (stage I-IIA, adjusted HR=0.59).
The researchers noted that this study was limited by their inability to control for unreported prognostic factors, such as the number of nodal sites and bulk of disease.
Another limitation was the duration of follow-up, which did not allow the researchers to fully assess secondary late effects of CMT and their potential impact on survival.
Still, Dr. Parikh said this study demonstrates a survival benefit for young HL patients treated with CMT.
“With that, physicians should be encouraged to discuss combined modality therapy as one of the many treatment options [for young HL patients],” he said.
“Investigators may also consider designing future clinical trials for this population to include combined modality therapy as a standard arm with the inclusion of interim treatment response assessment (PET scans, etc.). And as multiple disparities to the use of combined modality therapy have been identified through this work, future studies should address improving access to care for all pediatric patients.”
Dr. Parikh and his colleagues declared no conflicts of interest for the current study.
Combined modality therapy (CMT) can improve survival in young patients with early stage Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), according to research published in JAMA Oncology.
In a retrospective study, researchers compared chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy—CMT—to chemotherapy alone in more than 5,600 HL patients age 21 and younger.
There was a significant improvement in 5-year overall survival (OS) among patients who received CMT.
The treatment appeared particularly beneficial for adolescents and young adults as well as patients with low-risk disease.
However, the researchers observed a nearly 25% decrease in the use of CMT over the period studied.
“Nationwide, there has been a notable decrease in combined modality therapy, especially in clinical trials, many of which are designed to avoid this strategy,” said Rahul Parikh, MD, of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey in New Brunswick.
“This form of treatment has shown to be effective, with event-free survival rates greater than 80% and overall survival rates greater than 95%. The question then becomes, ‘does treatment benefit outweigh the risk of long-term side effects?”
With this in mind, Dr. Parikh and his colleagues compared CMT to chemotherapy alone using data from the National Cancer Database spanning the period from 2004 to 2015.
The researchers analyzed 5,657 patients with stage I/II classical HL who had a mean age of 17.1.
Roughly half of patients received CMT (50.3%, n=2845), and the other half received chemotherapy alone (49.7%, n=2812).
The median radiotherapy dose was 21.0 Gy, and the most common modality was photon therapy (59.0%).
Patients who received CMT were significantly more likely to be younger than 16 (P<0.001), be male (P<0.001), have stage II disease (P=0.02), and have private health insurance (P=0.002).
Results
The median follow-up was 5.1 years.
The 5-year OS was 94.5% for patients who received chemotherapy alone and 97.3% for patients treated with CMT.
CMT was significantly associated with improved OS in both univariate (hazard ratio [HR]=0.58, P<0.001) and multivariate analyses (HR=0.57, P<0.001).
In a sensitivity analysis, the researchers found the greatest benefits of CMT were in adolescents and young adults (age 14 and older, adjusted HR=0.47) and patients with low-risk disease (stage I-IIA, adjusted HR=0.59).
The researchers noted that this study was limited by their inability to control for unreported prognostic factors, such as the number of nodal sites and bulk of disease.
Another limitation was the duration of follow-up, which did not allow the researchers to fully assess secondary late effects of CMT and their potential impact on survival.
Still, Dr. Parikh said this study demonstrates a survival benefit for young HL patients treated with CMT.
“With that, physicians should be encouraged to discuss combined modality therapy as one of the many treatment options [for young HL patients],” he said.
“Investigators may also consider designing future clinical trials for this population to include combined modality therapy as a standard arm with the inclusion of interim treatment response assessment (PET scans, etc.). And as multiple disparities to the use of combined modality therapy have been identified through this work, future studies should address improving access to care for all pediatric patients.”
Dr. Parikh and his colleagues declared no conflicts of interest for the current study.
Combined modality therapy (CMT) can improve survival in young patients with early stage Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), according to research published in JAMA Oncology.
In a retrospective study, researchers compared chemotherapy followed by radiotherapy—CMT—to chemotherapy alone in more than 5,600 HL patients age 21 and younger.
There was a significant improvement in 5-year overall survival (OS) among patients who received CMT.
The treatment appeared particularly beneficial for adolescents and young adults as well as patients with low-risk disease.
However, the researchers observed a nearly 25% decrease in the use of CMT over the period studied.
“Nationwide, there has been a notable decrease in combined modality therapy, especially in clinical trials, many of which are designed to avoid this strategy,” said Rahul Parikh, MD, of Rutgers Cancer Institute of New Jersey in New Brunswick.
“This form of treatment has shown to be effective, with event-free survival rates greater than 80% and overall survival rates greater than 95%. The question then becomes, ‘does treatment benefit outweigh the risk of long-term side effects?”
With this in mind, Dr. Parikh and his colleagues compared CMT to chemotherapy alone using data from the National Cancer Database spanning the period from 2004 to 2015.
The researchers analyzed 5,657 patients with stage I/II classical HL who had a mean age of 17.1.
Roughly half of patients received CMT (50.3%, n=2845), and the other half received chemotherapy alone (49.7%, n=2812).
The median radiotherapy dose was 21.0 Gy, and the most common modality was photon therapy (59.0%).
Patients who received CMT were significantly more likely to be younger than 16 (P<0.001), be male (P<0.001), have stage II disease (P=0.02), and have private health insurance (P=0.002).
Results
The median follow-up was 5.1 years.
The 5-year OS was 94.5% for patients who received chemotherapy alone and 97.3% for patients treated with CMT.
CMT was significantly associated with improved OS in both univariate (hazard ratio [HR]=0.58, P<0.001) and multivariate analyses (HR=0.57, P<0.001).
In a sensitivity analysis, the researchers found the greatest benefits of CMT were in adolescents and young adults (age 14 and older, adjusted HR=0.47) and patients with low-risk disease (stage I-IIA, adjusted HR=0.59).
The researchers noted that this study was limited by their inability to control for unreported prognostic factors, such as the number of nodal sites and bulk of disease.
Another limitation was the duration of follow-up, which did not allow the researchers to fully assess secondary late effects of CMT and their potential impact on survival.
Still, Dr. Parikh said this study demonstrates a survival benefit for young HL patients treated with CMT.
“With that, physicians should be encouraged to discuss combined modality therapy as one of the many treatment options [for young HL patients],” he said.
“Investigators may also consider designing future clinical trials for this population to include combined modality therapy as a standard arm with the inclusion of interim treatment response assessment (PET scans, etc.). And as multiple disparities to the use of combined modality therapy have been identified through this work, future studies should address improving access to care for all pediatric patients.”
Dr. Parikh and his colleagues declared no conflicts of interest for the current study.
Group proposes new grading systems for CRS, neurotoxicity
A group of experts has proposed new consensus definitions and grading systems for cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity related to immune effector cell therapies.
The group hopes their recommendations will be widely accepted and used in both trials and the clinical setting.
The recommendations were devised by 49 experts at a meeting supported by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (ASBMT), compiled by a writing group, and reviewed by stakeholders.
Daniel W. Lee, MD, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville, and his colleagues described the ASBMT consensus definitions and grading systems in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
CRS
The ASBMT consensus definition for CRS is “a supraphysiologic response following any immune therapy that results in the activation or engagement of endogenous or infused T cells and/or other immune effector cells.”
To be diagnosed with CRS, a patient must have a fever and may have the following symptoms:
- Hypotension
- Capillary leak (hypoxia)
- End organ dysfunction.
The ASBMT consensus for grading CRS is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a fever, defined as a temperature of 38.0°C or higher
- Grade 2—Patient has a fever, hypotension that doesn’t require vasopressors, and/or hypoxia that requires oxygen delivered by low-flow nasal cannula (≤6 L/min) or blow-by
- Grade 3—Patient has a fever, hypotension requiring one vasopressor (with or without vasopressin), and/or hypoxia (not attributable to any other cause) that requires high-flow nasal cannula (>6 L/min), facemask, non-rebreather mask, or venturi mask
- Grade 4—Patient has a fever, hypotension requiring multiple vasopressors (excluding vasopressin), and/or hypoxia (not attributable to any other cause) requiring positive-pressure ventilation
- Grade 5—Death due to CRS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Typically, severe CRS can be considered resolved if “fever, oxygen, and pressor requirements have resolved,” Dr. Lee and his coauthors said.
The authors also stressed that neurotoxicity that occurs with or after CRS “does not inform the grade of CRS but is instead captured separately in the neurotoxicity scale.”
Neurotoxicity
Dr. Lee and his coauthors said neurotoxicity in this setting is called “immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).”
The ASBMT consensus definition for ICANs is “a disorder characterized by a pathologic process involving the central nervous system following any immune therapy that results in the activation or engagement of endogenous or infused T cells and/or other immune effector cells.”
Symptoms of ICANS may include:
- Aphasia
- Altered level of consciousness
- Impairment of cognitive skills
- Motor weakness
- Seizures
- Cerebral edema.
The ASBMT consensus for grading ICANS in adults and children age 12 and older is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a score of 7-9 on the 10-point immune effector cell-associated encephalopathy (ICE) assessment and awakens spontaneously
- Grade 2—Patient has a score of 3-6 on the ICE assessment and will awaken to the sound of a voice
- Grade 3—Patient has a score of 0-2 on the ICE assessment, awakens only to tactile stimulus, has any clinical seizure that resolves rapidly or non-convulsive seizures that resolve with intervention, has focal/local edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 4—Patient is unable to perform the ICE assessment, is unarousable or requires “vigorous stimuli” to be aroused, has life-threatening seizure (lasting more than 5 minutes) or repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between, has deep focal motor weakness, and/or has decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, Cushing’s triad, or signs of diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 5—Death due to ICANS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Dr. Lee and his coauthors noted that the ICE assessment is not suitable for children younger than 12. For these patients (and older patients with baseline developmental delays), ICANS can be assessed using the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium (CAPD).
The ASBMT consensus for grading ICANS in children younger than 12 (or older patients with developmental delays) is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a CAPD score lower than 9 and awakens spontaneously
- Grade 2—Patient has a CAPD score lower than 9 and will awaken to the sound of a voice
- Grade 3—Patient has a CAPD score of 9 or higher, awakens only to tactile stimulus, has any clinical seizure that resolves rapidly or non-convulsive seizures that resolve with intervention, and/or has focal/local edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 4—Patient is unable to perform CAPD, is unarousable or requires “vigorous stimuli” to be aroused, has life-threatening seizure (lasting more than 5 minutes) or repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between, has deep focal motor weakness, and/or has decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, Cushing’s triad, or signs of diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 5—Death due to ICANS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Dr. Lee and his coauthors reported relationships with a range of companies.
A group of experts has proposed new consensus definitions and grading systems for cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity related to immune effector cell therapies.
The group hopes their recommendations will be widely accepted and used in both trials and the clinical setting.
The recommendations were devised by 49 experts at a meeting supported by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (ASBMT), compiled by a writing group, and reviewed by stakeholders.
Daniel W. Lee, MD, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville, and his colleagues described the ASBMT consensus definitions and grading systems in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
CRS
The ASBMT consensus definition for CRS is “a supraphysiologic response following any immune therapy that results in the activation or engagement of endogenous or infused T cells and/or other immune effector cells.”
To be diagnosed with CRS, a patient must have a fever and may have the following symptoms:
- Hypotension
- Capillary leak (hypoxia)
- End organ dysfunction.
The ASBMT consensus for grading CRS is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a fever, defined as a temperature of 38.0°C or higher
- Grade 2—Patient has a fever, hypotension that doesn’t require vasopressors, and/or hypoxia that requires oxygen delivered by low-flow nasal cannula (≤6 L/min) or blow-by
- Grade 3—Patient has a fever, hypotension requiring one vasopressor (with or without vasopressin), and/or hypoxia (not attributable to any other cause) that requires high-flow nasal cannula (>6 L/min), facemask, non-rebreather mask, or venturi mask
- Grade 4—Patient has a fever, hypotension requiring multiple vasopressors (excluding vasopressin), and/or hypoxia (not attributable to any other cause) requiring positive-pressure ventilation
- Grade 5—Death due to CRS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Typically, severe CRS can be considered resolved if “fever, oxygen, and pressor requirements have resolved,” Dr. Lee and his coauthors said.
The authors also stressed that neurotoxicity that occurs with or after CRS “does not inform the grade of CRS but is instead captured separately in the neurotoxicity scale.”
Neurotoxicity
Dr. Lee and his coauthors said neurotoxicity in this setting is called “immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).”
The ASBMT consensus definition for ICANs is “a disorder characterized by a pathologic process involving the central nervous system following any immune therapy that results in the activation or engagement of endogenous or infused T cells and/or other immune effector cells.”
Symptoms of ICANS may include:
- Aphasia
- Altered level of consciousness
- Impairment of cognitive skills
- Motor weakness
- Seizures
- Cerebral edema.
The ASBMT consensus for grading ICANS in adults and children age 12 and older is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a score of 7-9 on the 10-point immune effector cell-associated encephalopathy (ICE) assessment and awakens spontaneously
- Grade 2—Patient has a score of 3-6 on the ICE assessment and will awaken to the sound of a voice
- Grade 3—Patient has a score of 0-2 on the ICE assessment, awakens only to tactile stimulus, has any clinical seizure that resolves rapidly or non-convulsive seizures that resolve with intervention, has focal/local edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 4—Patient is unable to perform the ICE assessment, is unarousable or requires “vigorous stimuli” to be aroused, has life-threatening seizure (lasting more than 5 minutes) or repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between, has deep focal motor weakness, and/or has decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, Cushing’s triad, or signs of diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 5—Death due to ICANS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Dr. Lee and his coauthors noted that the ICE assessment is not suitable for children younger than 12. For these patients (and older patients with baseline developmental delays), ICANS can be assessed using the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium (CAPD).
The ASBMT consensus for grading ICANS in children younger than 12 (or older patients with developmental delays) is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a CAPD score lower than 9 and awakens spontaneously
- Grade 2—Patient has a CAPD score lower than 9 and will awaken to the sound of a voice
- Grade 3—Patient has a CAPD score of 9 or higher, awakens only to tactile stimulus, has any clinical seizure that resolves rapidly or non-convulsive seizures that resolve with intervention, and/or has focal/local edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 4—Patient is unable to perform CAPD, is unarousable or requires “vigorous stimuli” to be aroused, has life-threatening seizure (lasting more than 5 minutes) or repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between, has deep focal motor weakness, and/or has decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, Cushing’s triad, or signs of diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 5—Death due to ICANS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Dr. Lee and his coauthors reported relationships with a range of companies.
A group of experts has proposed new consensus definitions and grading systems for cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity related to immune effector cell therapies.
The group hopes their recommendations will be widely accepted and used in both trials and the clinical setting.
The recommendations were devised by 49 experts at a meeting supported by the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (ASBMT), compiled by a writing group, and reviewed by stakeholders.
Daniel W. Lee, MD, of the University of Virginia School of Medicine in Charlottesville, and his colleagues described the ASBMT consensus definitions and grading systems in Biology of Blood and Marrow Transplantation.
CRS
The ASBMT consensus definition for CRS is “a supraphysiologic response following any immune therapy that results in the activation or engagement of endogenous or infused T cells and/or other immune effector cells.”
To be diagnosed with CRS, a patient must have a fever and may have the following symptoms:
- Hypotension
- Capillary leak (hypoxia)
- End organ dysfunction.
The ASBMT consensus for grading CRS is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a fever, defined as a temperature of 38.0°C or higher
- Grade 2—Patient has a fever, hypotension that doesn’t require vasopressors, and/or hypoxia that requires oxygen delivered by low-flow nasal cannula (≤6 L/min) or blow-by
- Grade 3—Patient has a fever, hypotension requiring one vasopressor (with or without vasopressin), and/or hypoxia (not attributable to any other cause) that requires high-flow nasal cannula (>6 L/min), facemask, non-rebreather mask, or venturi mask
- Grade 4—Patient has a fever, hypotension requiring multiple vasopressors (excluding vasopressin), and/or hypoxia (not attributable to any other cause) requiring positive-pressure ventilation
- Grade 5—Death due to CRS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Typically, severe CRS can be considered resolved if “fever, oxygen, and pressor requirements have resolved,” Dr. Lee and his coauthors said.
The authors also stressed that neurotoxicity that occurs with or after CRS “does not inform the grade of CRS but is instead captured separately in the neurotoxicity scale.”
Neurotoxicity
Dr. Lee and his coauthors said neurotoxicity in this setting is called “immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS).”
The ASBMT consensus definition for ICANs is “a disorder characterized by a pathologic process involving the central nervous system following any immune therapy that results in the activation or engagement of endogenous or infused T cells and/or other immune effector cells.”
Symptoms of ICANS may include:
- Aphasia
- Altered level of consciousness
- Impairment of cognitive skills
- Motor weakness
- Seizures
- Cerebral edema.
The ASBMT consensus for grading ICANS in adults and children age 12 and older is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a score of 7-9 on the 10-point immune effector cell-associated encephalopathy (ICE) assessment and awakens spontaneously
- Grade 2—Patient has a score of 3-6 on the ICE assessment and will awaken to the sound of a voice
- Grade 3—Patient has a score of 0-2 on the ICE assessment, awakens only to tactile stimulus, has any clinical seizure that resolves rapidly or non-convulsive seizures that resolve with intervention, has focal/local edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 4—Patient is unable to perform the ICE assessment, is unarousable or requires “vigorous stimuli” to be aroused, has life-threatening seizure (lasting more than 5 minutes) or repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between, has deep focal motor weakness, and/or has decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, Cushing’s triad, or signs of diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 5—Death due to ICANS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Dr. Lee and his coauthors noted that the ICE assessment is not suitable for children younger than 12. For these patients (and older patients with baseline developmental delays), ICANS can be assessed using the Cornell Assessment of Pediatric Delirium (CAPD).
The ASBMT consensus for grading ICANS in children younger than 12 (or older patients with developmental delays) is as follows:
- Grade 1—Patient has a CAPD score lower than 9 and awakens spontaneously
- Grade 2—Patient has a CAPD score lower than 9 and will awaken to the sound of a voice
- Grade 3—Patient has a CAPD score of 9 or higher, awakens only to tactile stimulus, has any clinical seizure that resolves rapidly or non-convulsive seizures that resolve with intervention, and/or has focal/local edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 4—Patient is unable to perform CAPD, is unarousable or requires “vigorous stimuli” to be aroused, has life-threatening seizure (lasting more than 5 minutes) or repetitive clinical or electrical seizures without return to baseline in between, has deep focal motor weakness, and/or has decerebrate or decorticate posturing, cranial nerve VI palsy, papilledema, Cushing’s triad, or signs of diffuse cerebral edema on neuroimaging
- Grade 5—Death due to ICANS when there is no other “principle factor” leading to death.
Dr. Lee and his coauthors reported relationships with a range of companies.
Lenalidomide maintenance improves MCL survival after ASCT
SAN DIEGO – For patients 65 years or younger with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have undergone autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), maintenance therapy with lenalidomide (Revlimid) can significantly improve progression-free survival (PFS), suggest results of the phase, 3 randomized MCL0208 trial.
After a median follow-up of 39 months, the 3-year PFS in an intention-to-treat analysis was 80% for patients treated with ASCT and lenalidomide maintenance, compared with 64% for patients treated with ASCT alone, reported Marco Ladetto, MD, of Azienda Ospedaliera Nazionale SS. Antonio e Biagio e Cesare Arrigo in Alessandria, Italy.
“Lenalidomide maintenance after autologous stem cell transplant has substantial clinical activity in mantle cell lymphoma in terms of progression-free survival,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. “Follow-up is still too short for meaningful overall survival considerations.”
Dr. Ladetto and his colleagues at centers in Italy and Portugal enrolled patients aged 18-65 years with previously untreated MCL stage III or IV, or stage II with bulky disease (5 cm or greater), and good performance status.
The patients first underwent induction with three cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone), which was followed by treatment with rituximab plus high-dose cyclophosphamide and two cycles of rituximab with high-dose cytarabine. Stem cells were collected after the first course of the latter regimen.
The patients then underwent conditioning with BEAM (carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, melphalan) and ASCT.
Following ASCT, patients with complete or partial remissions were randomized either to maintenance therapy with lenalidomide 15 mg for 21 of 28 days for each cycle or to observation.
Of the 303 patients initially enrolled, 248 went on to ASCT, and 205 went on to randomization – 104 assigned to maintenance and 101 assigned to observation.
A total of 52 patients completed 2 years of maintenance: Of the rest, 2 patients died from toxicities (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and pneumonia), 7 had disease progression, 41 dropped out for nonprogression reasons, and 2 patients were still in maintenance at the time of the data cutoff. In this arm, 6 of 8 patients with partial responses converted to complete responses by the end of maintenance. More than a quarter of patients (28%) received less than 25% of the planned lenalidomide dose.
In the observation arm, 1 patient died from pneumonia, 20 had disease progression, 3 were lost to follow-up, 6 were still under observation, and 71 completed observation. In this arm, 1 of 4 patients with a partial response converted to a complete response at the end of the observation period.
Despite suboptimal dosing in a large proportion of patients, the PFS primary endpoint showed significant benefit for lenalidomide, with an unstratified hazard ratio of 0.52 (P = .015) and a stratified HR of 0.51 (P = .013).
At a median follow-up of 39 months from randomization, 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 93% with lenalidomide and 86% with observation, a difference that was not statistically significant.
Grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicities occurred in 63% of patients in the lenalidomide arm, compared with 11% in the observation arm. The respective rates of granulocytopenia were 59% vs. 10%. Nonhematological grade 3 toxicity was comparable in the two arms except for grade 3 or 4 infections, which were more common with lenalidomide. Seven patients in the lenalidomide arm and three patients in the observation arm developed second cancers.
Dr. Ladetto noted that difficulties in delivering the planned dose of lenalidomide may have been caused by an already-stressed hematopoietic compartment; he commented that the question of the relative benefit of a fixed lenalidomide schedule or an until-progression approach still needs to be answered.
Additionally, the induction schedule used in the trial, while feasible, is not superior to “less cumbersome and possibly less toxic regimens,” he said.
The study was supported by the Italian Lymphoma Foundation (Fondazione Italiana Linfomi) with the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. Dr. Ladetto reported honoraria from Roche, Celgene, Acerta, Janssen, AbbVie, and Sandoz, as well as off-label use of lenalidomide.
SOURCE: Ladetto M et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 401.
SAN DIEGO – For patients 65 years or younger with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have undergone autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), maintenance therapy with lenalidomide (Revlimid) can significantly improve progression-free survival (PFS), suggest results of the phase, 3 randomized MCL0208 trial.
After a median follow-up of 39 months, the 3-year PFS in an intention-to-treat analysis was 80% for patients treated with ASCT and lenalidomide maintenance, compared with 64% for patients treated with ASCT alone, reported Marco Ladetto, MD, of Azienda Ospedaliera Nazionale SS. Antonio e Biagio e Cesare Arrigo in Alessandria, Italy.
“Lenalidomide maintenance after autologous stem cell transplant has substantial clinical activity in mantle cell lymphoma in terms of progression-free survival,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. “Follow-up is still too short for meaningful overall survival considerations.”
Dr. Ladetto and his colleagues at centers in Italy and Portugal enrolled patients aged 18-65 years with previously untreated MCL stage III or IV, or stage II with bulky disease (5 cm or greater), and good performance status.
The patients first underwent induction with three cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone), which was followed by treatment with rituximab plus high-dose cyclophosphamide and two cycles of rituximab with high-dose cytarabine. Stem cells were collected after the first course of the latter regimen.
The patients then underwent conditioning with BEAM (carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, melphalan) and ASCT.
Following ASCT, patients with complete or partial remissions were randomized either to maintenance therapy with lenalidomide 15 mg for 21 of 28 days for each cycle or to observation.
Of the 303 patients initially enrolled, 248 went on to ASCT, and 205 went on to randomization – 104 assigned to maintenance and 101 assigned to observation.
A total of 52 patients completed 2 years of maintenance: Of the rest, 2 patients died from toxicities (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and pneumonia), 7 had disease progression, 41 dropped out for nonprogression reasons, and 2 patients were still in maintenance at the time of the data cutoff. In this arm, 6 of 8 patients with partial responses converted to complete responses by the end of maintenance. More than a quarter of patients (28%) received less than 25% of the planned lenalidomide dose.
In the observation arm, 1 patient died from pneumonia, 20 had disease progression, 3 were lost to follow-up, 6 were still under observation, and 71 completed observation. In this arm, 1 of 4 patients with a partial response converted to a complete response at the end of the observation period.
Despite suboptimal dosing in a large proportion of patients, the PFS primary endpoint showed significant benefit for lenalidomide, with an unstratified hazard ratio of 0.52 (P = .015) and a stratified HR of 0.51 (P = .013).
At a median follow-up of 39 months from randomization, 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 93% with lenalidomide and 86% with observation, a difference that was not statistically significant.
Grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicities occurred in 63% of patients in the lenalidomide arm, compared with 11% in the observation arm. The respective rates of granulocytopenia were 59% vs. 10%. Nonhematological grade 3 toxicity was comparable in the two arms except for grade 3 or 4 infections, which were more common with lenalidomide. Seven patients in the lenalidomide arm and three patients in the observation arm developed second cancers.
Dr. Ladetto noted that difficulties in delivering the planned dose of lenalidomide may have been caused by an already-stressed hematopoietic compartment; he commented that the question of the relative benefit of a fixed lenalidomide schedule or an until-progression approach still needs to be answered.
Additionally, the induction schedule used in the trial, while feasible, is not superior to “less cumbersome and possibly less toxic regimens,” he said.
The study was supported by the Italian Lymphoma Foundation (Fondazione Italiana Linfomi) with the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. Dr. Ladetto reported honoraria from Roche, Celgene, Acerta, Janssen, AbbVie, and Sandoz, as well as off-label use of lenalidomide.
SOURCE: Ladetto M et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 401.
SAN DIEGO – For patients 65 years or younger with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) who have undergone autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT), maintenance therapy with lenalidomide (Revlimid) can significantly improve progression-free survival (PFS), suggest results of the phase, 3 randomized MCL0208 trial.
After a median follow-up of 39 months, the 3-year PFS in an intention-to-treat analysis was 80% for patients treated with ASCT and lenalidomide maintenance, compared with 64% for patients treated with ASCT alone, reported Marco Ladetto, MD, of Azienda Ospedaliera Nazionale SS. Antonio e Biagio e Cesare Arrigo in Alessandria, Italy.
“Lenalidomide maintenance after autologous stem cell transplant has substantial clinical activity in mantle cell lymphoma in terms of progression-free survival,” he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. “Follow-up is still too short for meaningful overall survival considerations.”
Dr. Ladetto and his colleagues at centers in Italy and Portugal enrolled patients aged 18-65 years with previously untreated MCL stage III or IV, or stage II with bulky disease (5 cm or greater), and good performance status.
The patients first underwent induction with three cycles of R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone), which was followed by treatment with rituximab plus high-dose cyclophosphamide and two cycles of rituximab with high-dose cytarabine. Stem cells were collected after the first course of the latter regimen.
The patients then underwent conditioning with BEAM (carmustine, etoposide, cytarabine, melphalan) and ASCT.
Following ASCT, patients with complete or partial remissions were randomized either to maintenance therapy with lenalidomide 15 mg for 21 of 28 days for each cycle or to observation.
Of the 303 patients initially enrolled, 248 went on to ASCT, and 205 went on to randomization – 104 assigned to maintenance and 101 assigned to observation.
A total of 52 patients completed 2 years of maintenance: Of the rest, 2 patients died from toxicities (thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and pneumonia), 7 had disease progression, 41 dropped out for nonprogression reasons, and 2 patients were still in maintenance at the time of the data cutoff. In this arm, 6 of 8 patients with partial responses converted to complete responses by the end of maintenance. More than a quarter of patients (28%) received less than 25% of the planned lenalidomide dose.
In the observation arm, 1 patient died from pneumonia, 20 had disease progression, 3 were lost to follow-up, 6 were still under observation, and 71 completed observation. In this arm, 1 of 4 patients with a partial response converted to a complete response at the end of the observation period.
Despite suboptimal dosing in a large proportion of patients, the PFS primary endpoint showed significant benefit for lenalidomide, with an unstratified hazard ratio of 0.52 (P = .015) and a stratified HR of 0.51 (P = .013).
At a median follow-up of 39 months from randomization, 3-year overall survival (OS) rates were 93% with lenalidomide and 86% with observation, a difference that was not statistically significant.
Grade 3 or 4 hematologic toxicities occurred in 63% of patients in the lenalidomide arm, compared with 11% in the observation arm. The respective rates of granulocytopenia were 59% vs. 10%. Nonhematological grade 3 toxicity was comparable in the two arms except for grade 3 or 4 infections, which were more common with lenalidomide. Seven patients in the lenalidomide arm and three patients in the observation arm developed second cancers.
Dr. Ladetto noted that difficulties in delivering the planned dose of lenalidomide may have been caused by an already-stressed hematopoietic compartment; he commented that the question of the relative benefit of a fixed lenalidomide schedule or an until-progression approach still needs to be answered.
Additionally, the induction schedule used in the trial, while feasible, is not superior to “less cumbersome and possibly less toxic regimens,” he said.
The study was supported by the Italian Lymphoma Foundation (Fondazione Italiana Linfomi) with the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. Dr. Ladetto reported honoraria from Roche, Celgene, Acerta, Janssen, AbbVie, and Sandoz, as well as off-label use of lenalidomide.
SOURCE: Ladetto M et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 401.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The 3-year PFS rate was 80% for patients on lenalidomide maintenance, compared with 64% for patients on observation alone.
Study details: An open-label, randomized, phase 3 trial with 205 patients randomized to lenalidomide or observation.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Italian Lymphoma Foundation (Fondazione Italiana Linfomi) with the European Mantle Cell Lymphoma Network. Dr. Ladetto reported honoraria from Roche, Celgene, Acerta, Janssen, AbbVie, and Sandoz, as well as off-label use of lenalidomide.
Source: Ladetto M et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 401.
Risk of second cancers in Hodgkin lymphoma survivors
Survivors of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) have a 14-fold higher risk of second cancers compared to the general population, according to new research.
The subsequent malignant neoplasms (SMNs) observed in HL survivors tended to follow specific patterns depending on the patient’s age at treatment, sex, treatment modality, and region of the body treated.
And although the risk of SMNs appears to be somewhat lower for HL patients treated in more recent decades, it is still significantly higher than the risk in the general population, according to investigators.
Anna S. Holmqvist, MD, PhD, of the University of Lund in Sweden, and her colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Cancer.
The investigators looked at data from the Late Effects Study Group, a multinational cohort of patients age 16 or younger who were treated for HL and other cancers from 1955 through 1986.
The current report is the third update from an expanded cohort including data on 1,136 patients with a median follow-up of 26.6 years. The median patient age at diagnosis was 11 years (range, birth to 16 years), and the patients were followed for 23,212 person-years after HL diagnosis.
In all, 162 patients developed 196 SMNs, including breast cancer (n=54), basal cell carcinoma (n=34), thyroid cancer (n=30), colorectal cancer (n=15), lung cancer (n=11), and other malignancies (n=40). The disease site was not available in 12 cases.
The cumulative incidence of any SMN 40 years after HL diagnosis was 26.4%. By age 50, the cumulative incidence of any SMN was 27.2%.
The standardized incidence ratio for the entire cohort was 14.0, compared with the general population as derived from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database.
Risk factors by cancer type
Females treated with chest radiotherapy between the ages of 10 and 16 who did not receive alkylating agents or received low doses of alkylating agents had the highest risk of developing breast cancer. The cumulative incidence of breast cancer by age 50 was 45.3% in these patients.
The patients with the highest risk for subsequent lung cancer were males treated with chest radiotherapy before age 10. The cumulative incidence of lung cancer by age 50 was 4.2% in these patients.
Patients with the highest risk for colorectal cancer had received abdominal/pelvic radiotherapy and high-dose alkylating agents. The cumulative incidence of colorectal cancer by age 50 was 9.5% in these patients.
Patients with the highest risk for thyroid cancers were females who had been treated with radiotherapy to the neck before the age of 10. The cumulative incidence of thyroid cancer by age 50 was 17.3% in these patients.
The investigators noted that HL patients treated more recently are likely to have received lower doses and volumes of radiotherapy compared to patients treated in the 1950s, ’60s and ’70s.
“However, for the cohort of patients treated between 1955 and 1986, it is clear that continued surveillance for SMNs is essential because their risk continues to increase as these survivors enter their fourth and subsequent decades of life,” the investigators wrote.
They did not report a funding source for this research or make any conflict-of-interest disclosures.
Survivors of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) have a 14-fold higher risk of second cancers compared to the general population, according to new research.
The subsequent malignant neoplasms (SMNs) observed in HL survivors tended to follow specific patterns depending on the patient’s age at treatment, sex, treatment modality, and region of the body treated.
And although the risk of SMNs appears to be somewhat lower for HL patients treated in more recent decades, it is still significantly higher than the risk in the general population, according to investigators.
Anna S. Holmqvist, MD, PhD, of the University of Lund in Sweden, and her colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Cancer.
The investigators looked at data from the Late Effects Study Group, a multinational cohort of patients age 16 or younger who were treated for HL and other cancers from 1955 through 1986.
The current report is the third update from an expanded cohort including data on 1,136 patients with a median follow-up of 26.6 years. The median patient age at diagnosis was 11 years (range, birth to 16 years), and the patients were followed for 23,212 person-years after HL diagnosis.
In all, 162 patients developed 196 SMNs, including breast cancer (n=54), basal cell carcinoma (n=34), thyroid cancer (n=30), colorectal cancer (n=15), lung cancer (n=11), and other malignancies (n=40). The disease site was not available in 12 cases.
The cumulative incidence of any SMN 40 years after HL diagnosis was 26.4%. By age 50, the cumulative incidence of any SMN was 27.2%.
The standardized incidence ratio for the entire cohort was 14.0, compared with the general population as derived from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database.
Risk factors by cancer type
Females treated with chest radiotherapy between the ages of 10 and 16 who did not receive alkylating agents or received low doses of alkylating agents had the highest risk of developing breast cancer. The cumulative incidence of breast cancer by age 50 was 45.3% in these patients.
The patients with the highest risk for subsequent lung cancer were males treated with chest radiotherapy before age 10. The cumulative incidence of lung cancer by age 50 was 4.2% in these patients.
Patients with the highest risk for colorectal cancer had received abdominal/pelvic radiotherapy and high-dose alkylating agents. The cumulative incidence of colorectal cancer by age 50 was 9.5% in these patients.
Patients with the highest risk for thyroid cancers were females who had been treated with radiotherapy to the neck before the age of 10. The cumulative incidence of thyroid cancer by age 50 was 17.3% in these patients.
The investigators noted that HL patients treated more recently are likely to have received lower doses and volumes of radiotherapy compared to patients treated in the 1950s, ’60s and ’70s.
“However, for the cohort of patients treated between 1955 and 1986, it is clear that continued surveillance for SMNs is essential because their risk continues to increase as these survivors enter their fourth and subsequent decades of life,” the investigators wrote.
They did not report a funding source for this research or make any conflict-of-interest disclosures.
Survivors of childhood Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) have a 14-fold higher risk of second cancers compared to the general population, according to new research.
The subsequent malignant neoplasms (SMNs) observed in HL survivors tended to follow specific patterns depending on the patient’s age at treatment, sex, treatment modality, and region of the body treated.
And although the risk of SMNs appears to be somewhat lower for HL patients treated in more recent decades, it is still significantly higher than the risk in the general population, according to investigators.
Anna S. Holmqvist, MD, PhD, of the University of Lund in Sweden, and her colleagues conducted this research and reported the results in Cancer.
The investigators looked at data from the Late Effects Study Group, a multinational cohort of patients age 16 or younger who were treated for HL and other cancers from 1955 through 1986.
The current report is the third update from an expanded cohort including data on 1,136 patients with a median follow-up of 26.6 years. The median patient age at diagnosis was 11 years (range, birth to 16 years), and the patients were followed for 23,212 person-years after HL diagnosis.
In all, 162 patients developed 196 SMNs, including breast cancer (n=54), basal cell carcinoma (n=34), thyroid cancer (n=30), colorectal cancer (n=15), lung cancer (n=11), and other malignancies (n=40). The disease site was not available in 12 cases.
The cumulative incidence of any SMN 40 years after HL diagnosis was 26.4%. By age 50, the cumulative incidence of any SMN was 27.2%.
The standardized incidence ratio for the entire cohort was 14.0, compared with the general population as derived from the Surveillance, Epidemiology and End Results database.
Risk factors by cancer type
Females treated with chest radiotherapy between the ages of 10 and 16 who did not receive alkylating agents or received low doses of alkylating agents had the highest risk of developing breast cancer. The cumulative incidence of breast cancer by age 50 was 45.3% in these patients.
The patients with the highest risk for subsequent lung cancer were males treated with chest radiotherapy before age 10. The cumulative incidence of lung cancer by age 50 was 4.2% in these patients.
Patients with the highest risk for colorectal cancer had received abdominal/pelvic radiotherapy and high-dose alkylating agents. The cumulative incidence of colorectal cancer by age 50 was 9.5% in these patients.
Patients with the highest risk for thyroid cancers were females who had been treated with radiotherapy to the neck before the age of 10. The cumulative incidence of thyroid cancer by age 50 was 17.3% in these patients.
The investigators noted that HL patients treated more recently are likely to have received lower doses and volumes of radiotherapy compared to patients treated in the 1950s, ’60s and ’70s.
“However, for the cohort of patients treated between 1955 and 1986, it is clear that continued surveillance for SMNs is essential because their risk continues to increase as these survivors enter their fourth and subsequent decades of life,” the investigators wrote.
They did not report a funding source for this research or make any conflict-of-interest disclosures.
Frailty-adjusted treatment strategy emerges in myeloma
SAN DIEGO – Switching to lenalidomide maintenance after nine cycles of lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd) may avoid toxicity without sacrificing survival benefit in elderly multiple myeloma patients of intermediate fitness, results from a randomized trial showed.
The Rd-R strategy yielded a “slight improvement” in event-free survival due largely to fewer adverse events, and no significant differences in progression-free or overall survival versus continuous Rd, reported Alessandra Larocca, MD, of GIMEMA/European Myeloma Network in Italy.
That finding suggests the promise of adapting myeloma treatment to a patient’s level of frailty or fitness, as determined by a myeloma frailty score, Dr. Larocca said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“A frailty-adjusted treatment approach is important in intermediate-fit patients to balance efficacy and safety,” she said.
The frailty score, developed by the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG), classifies individuals as fit, intermediate, or frail based on age, comorbidities, cognitive status, and functional status. In a 2015 report in Blood, the IMWG frailty score was shown to predict mortality and treatment-related toxicity in elderly myeloma patients.
Dr. Larocca described results of the RV-MM-PI-0752 phase 3 study, which enrolled 199 newly diagnosed myeloma patients of intermediate fitness and randomized them to continuous Rd or nine cycles of Rd induction followed by lenalidomide maintenance (Rd-R).
The goal was to see if Rd could be “further optimized” for elderly, intermediate-fit patients, Dr. Larocca said.
The primary endpoint of RV-MM-PI-0752 was event-free survival, which included grade 4 hematologic and grade 3-4 nonhematologic adverse events, lenalidomide discontinuation, disease progression, or death.
Median event-free survival was 9.3 months for the Rd-R strategy, compared with 6.6 months for continuous Rd (hazard ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.99; P = .044), Dr. Larocca reported.
No difference was seen in survival outcomes, she added. The 20-month progression-free survival was 43% and 42% for Rd-R and continuous Rd, respectively. The 20-month overall survival was 84% vs. 79%, with P values that were not significant for either comparison.
Patients in the Rd-R group had a somewhat higher incidence of grade 3 or greater neutropenia, but the continuous Rd group had a somewhat higher rate of nonhematologic adverse events, leading to slightly higher rates of lenalidomide discontinuation and dose reduction, Dr. Larocca said.
Overall, 9% of patients dropped out of the RV-MM-PI-0752 trial within the first 60 days, due mainly to toxicity, she added.
“We have to evaluate how to better prevent toxicity, potentially enabling patients to stay on therapy longer,” Dr. Larocca said. “Probably we have to evaluate, in prospective clinical trials, the role of up-front dose adjustment or dose reduction, and subsequent dose increase in a subgroup of patients.”
Dr. Larocca reported disclosures related to Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, and Amgen.
SOURCE: Larocca A, et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 305.
SAN DIEGO – Switching to lenalidomide maintenance after nine cycles of lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd) may avoid toxicity without sacrificing survival benefit in elderly multiple myeloma patients of intermediate fitness, results from a randomized trial showed.
The Rd-R strategy yielded a “slight improvement” in event-free survival due largely to fewer adverse events, and no significant differences in progression-free or overall survival versus continuous Rd, reported Alessandra Larocca, MD, of GIMEMA/European Myeloma Network in Italy.
That finding suggests the promise of adapting myeloma treatment to a patient’s level of frailty or fitness, as determined by a myeloma frailty score, Dr. Larocca said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“A frailty-adjusted treatment approach is important in intermediate-fit patients to balance efficacy and safety,” she said.
The frailty score, developed by the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG), classifies individuals as fit, intermediate, or frail based on age, comorbidities, cognitive status, and functional status. In a 2015 report in Blood, the IMWG frailty score was shown to predict mortality and treatment-related toxicity in elderly myeloma patients.
Dr. Larocca described results of the RV-MM-PI-0752 phase 3 study, which enrolled 199 newly diagnosed myeloma patients of intermediate fitness and randomized them to continuous Rd or nine cycles of Rd induction followed by lenalidomide maintenance (Rd-R).
The goal was to see if Rd could be “further optimized” for elderly, intermediate-fit patients, Dr. Larocca said.
The primary endpoint of RV-MM-PI-0752 was event-free survival, which included grade 4 hematologic and grade 3-4 nonhematologic adverse events, lenalidomide discontinuation, disease progression, or death.
Median event-free survival was 9.3 months for the Rd-R strategy, compared with 6.6 months for continuous Rd (hazard ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.99; P = .044), Dr. Larocca reported.
No difference was seen in survival outcomes, she added. The 20-month progression-free survival was 43% and 42% for Rd-R and continuous Rd, respectively. The 20-month overall survival was 84% vs. 79%, with P values that were not significant for either comparison.
Patients in the Rd-R group had a somewhat higher incidence of grade 3 or greater neutropenia, but the continuous Rd group had a somewhat higher rate of nonhematologic adverse events, leading to slightly higher rates of lenalidomide discontinuation and dose reduction, Dr. Larocca said.
Overall, 9% of patients dropped out of the RV-MM-PI-0752 trial within the first 60 days, due mainly to toxicity, she added.
“We have to evaluate how to better prevent toxicity, potentially enabling patients to stay on therapy longer,” Dr. Larocca said. “Probably we have to evaluate, in prospective clinical trials, the role of up-front dose adjustment or dose reduction, and subsequent dose increase in a subgroup of patients.”
Dr. Larocca reported disclosures related to Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, and Amgen.
SOURCE: Larocca A, et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 305.
SAN DIEGO – Switching to lenalidomide maintenance after nine cycles of lenalidomide/dexamethasone (Rd) may avoid toxicity without sacrificing survival benefit in elderly multiple myeloma patients of intermediate fitness, results from a randomized trial showed.
The Rd-R strategy yielded a “slight improvement” in event-free survival due largely to fewer adverse events, and no significant differences in progression-free or overall survival versus continuous Rd, reported Alessandra Larocca, MD, of GIMEMA/European Myeloma Network in Italy.
That finding suggests the promise of adapting myeloma treatment to a patient’s level of frailty or fitness, as determined by a myeloma frailty score, Dr. Larocca said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“A frailty-adjusted treatment approach is important in intermediate-fit patients to balance efficacy and safety,” she said.
The frailty score, developed by the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG), classifies individuals as fit, intermediate, or frail based on age, comorbidities, cognitive status, and functional status. In a 2015 report in Blood, the IMWG frailty score was shown to predict mortality and treatment-related toxicity in elderly myeloma patients.
Dr. Larocca described results of the RV-MM-PI-0752 phase 3 study, which enrolled 199 newly diagnosed myeloma patients of intermediate fitness and randomized them to continuous Rd or nine cycles of Rd induction followed by lenalidomide maintenance (Rd-R).
The goal was to see if Rd could be “further optimized” for elderly, intermediate-fit patients, Dr. Larocca said.
The primary endpoint of RV-MM-PI-0752 was event-free survival, which included grade 4 hematologic and grade 3-4 nonhematologic adverse events, lenalidomide discontinuation, disease progression, or death.
Median event-free survival was 9.3 months for the Rd-R strategy, compared with 6.6 months for continuous Rd (hazard ratio, 0.72; 95% confidence interval, 0.52-0.99; P = .044), Dr. Larocca reported.
No difference was seen in survival outcomes, she added. The 20-month progression-free survival was 43% and 42% for Rd-R and continuous Rd, respectively. The 20-month overall survival was 84% vs. 79%, with P values that were not significant for either comparison.
Patients in the Rd-R group had a somewhat higher incidence of grade 3 or greater neutropenia, but the continuous Rd group had a somewhat higher rate of nonhematologic adverse events, leading to slightly higher rates of lenalidomide discontinuation and dose reduction, Dr. Larocca said.
Overall, 9% of patients dropped out of the RV-MM-PI-0752 trial within the first 60 days, due mainly to toxicity, she added.
“We have to evaluate how to better prevent toxicity, potentially enabling patients to stay on therapy longer,” Dr. Larocca said. “Probably we have to evaluate, in prospective clinical trials, the role of up-front dose adjustment or dose reduction, and subsequent dose increase in a subgroup of patients.”
Dr. Larocca reported disclosures related to Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, and Amgen.
SOURCE: Larocca A, et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 305.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Median event-free survival was 9.3 months for the Rd induction followed by lenalidomide maintenance, compared with 6.6 months for continuous Rd (P = .044).
Study details: Results of the RV-MM-PI-0752 phase 3 study, which enrolled 199 newly diagnosed multiple myeloma patients of intermediate fitness.
Disclosures: Dr. Larocca reported disclosures related to Celgene, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Janssen-Cilag, Takeda, and Amgen.
Source: Larocca A et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 305.
Checkmate 436: Two-drug combo is ‘promising’ for PMBCL
SAN DIEGO – Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin may be a new treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to investigators from the CheckMate 436 trial.
Interim results from this phase 1/2 trial revealed an overall response rate of 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
“It’s very promising ... to see this level of activity in this advanced, relapsed/refractory population,” said Joseph E. Eid, MD, senior vice president of Bristol-Myers Squibb, which is sponsoring CheckMate 436 in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
Dr. Eid noted that adverse events (AEs) observed with this regimen were consistent with the safety profiles of nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin alone.
These results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Eid noted that patients with relapsed or refractory PMBCL have limited treatment options.
“The initial therapy works well in 70% to 80% of patients but the patients who fail don’t have good options,” he said.
Prior research has shown that PMBCL is often characterized by overexpression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and most PMBCL expresses CD30.
Dr. Eid said CheckMate 436 (NCT02581631) was designed to “take advantage” of these characteristics by employing the anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and the anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin.
The interim analysis of this trial included 30 patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Their median age at enrollment was 35.5 and 57% of patients were female. More than half of the patients (60%) had refractory disease, 23% had relapsed disease, and 17% had both.
The median number of prior therapies was two and 13% of patients had prior autologous stem cell transplant.
The patients received nivolumab at 240 mg and brentuximab vedotin at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 6.1 months, 10 patients were still on treatment. Reasons for discontinuation included maximum clinical benefit, disease progression, AEs unrelated to treatment, patient request, and other concerns.
The rate of treatment-related AEs was 83%. The most common of these were neutropenia (27%), peripheral neuropathy (20%), hyperthyroidism (13%), rash (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs included neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (7%), decreased neutrophil count (7%), hypersensitivity (3%), diarrhea (3%), and maculopapular rash (3%).
The rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 10%. This included grade 3-4 diarrhea and maculopapular rash and grade 5 acute kidney injury.
The acute kidney injury was the only fatal AE considered treatment related. There were three other deaths in the trial, but they were considered unrelated to treatment.
The complete response rate was 27% (n = 8), and the partial response rate was 43% (n = 13), for an overall response rate of 70% (n = 21).
“The early indication is that 70% response is a pretty good outcome in a relapsed/refractory population that, otherwise, their outcome is pretty dismal,” Dr. Eid said.
Ten percent of patients (n = 3) had stable disease, 13% (n = 4) progressed, and investigators were unable to determine the status for 7% of patients (n = 2).
The median time to response was 1.3 months, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. The median duration of response and complete response were not reached.
Overall and progression-free survival data are not yet mature.
Still, the investigators concluded that nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin “may provide a new treatment option” for patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL.
This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics. Investigators reported relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Seattle Genetics, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Moskowitz AJ et al. ASH 2018. Abstract 1691.
SAN DIEGO – Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin may be a new treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to investigators from the CheckMate 436 trial.
Interim results from this phase 1/2 trial revealed an overall response rate of 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
“It’s very promising ... to see this level of activity in this advanced, relapsed/refractory population,” said Joseph E. Eid, MD, senior vice president of Bristol-Myers Squibb, which is sponsoring CheckMate 436 in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
Dr. Eid noted that adverse events (AEs) observed with this regimen were consistent with the safety profiles of nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin alone.
These results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Eid noted that patients with relapsed or refractory PMBCL have limited treatment options.
“The initial therapy works well in 70% to 80% of patients but the patients who fail don’t have good options,” he said.
Prior research has shown that PMBCL is often characterized by overexpression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and most PMBCL expresses CD30.
Dr. Eid said CheckMate 436 (NCT02581631) was designed to “take advantage” of these characteristics by employing the anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and the anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin.
The interim analysis of this trial included 30 patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Their median age at enrollment was 35.5 and 57% of patients were female. More than half of the patients (60%) had refractory disease, 23% had relapsed disease, and 17% had both.
The median number of prior therapies was two and 13% of patients had prior autologous stem cell transplant.
The patients received nivolumab at 240 mg and brentuximab vedotin at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 6.1 months, 10 patients were still on treatment. Reasons for discontinuation included maximum clinical benefit, disease progression, AEs unrelated to treatment, patient request, and other concerns.
The rate of treatment-related AEs was 83%. The most common of these were neutropenia (27%), peripheral neuropathy (20%), hyperthyroidism (13%), rash (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs included neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (7%), decreased neutrophil count (7%), hypersensitivity (3%), diarrhea (3%), and maculopapular rash (3%).
The rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 10%. This included grade 3-4 diarrhea and maculopapular rash and grade 5 acute kidney injury.
The acute kidney injury was the only fatal AE considered treatment related. There were three other deaths in the trial, but they were considered unrelated to treatment.
The complete response rate was 27% (n = 8), and the partial response rate was 43% (n = 13), for an overall response rate of 70% (n = 21).
“The early indication is that 70% response is a pretty good outcome in a relapsed/refractory population that, otherwise, their outcome is pretty dismal,” Dr. Eid said.
Ten percent of patients (n = 3) had stable disease, 13% (n = 4) progressed, and investigators were unable to determine the status for 7% of patients (n = 2).
The median time to response was 1.3 months, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. The median duration of response and complete response were not reached.
Overall and progression-free survival data are not yet mature.
Still, the investigators concluded that nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin “may provide a new treatment option” for patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL.
This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics. Investigators reported relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Seattle Genetics, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Moskowitz AJ et al. ASH 2018. Abstract 1691.
SAN DIEGO – Nivolumab plus brentuximab vedotin may be a new treatment option for patients with relapsed/refractory primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (PMBCL), according to investigators from the CheckMate 436 trial.
Interim results from this phase 1/2 trial revealed an overall response rate of 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
“It’s very promising ... to see this level of activity in this advanced, relapsed/refractory population,” said Joseph E. Eid, MD, senior vice president of Bristol-Myers Squibb, which is sponsoring CheckMate 436 in collaboration with Seattle Genetics.
Dr. Eid noted that adverse events (AEs) observed with this regimen were consistent with the safety profiles of nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin alone.
These results were presented as a poster at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Dr. Eid noted that patients with relapsed or refractory PMBCL have limited treatment options.
“The initial therapy works well in 70% to 80% of patients but the patients who fail don’t have good options,” he said.
Prior research has shown that PMBCL is often characterized by overexpression of the PD-1 ligands PD-L1 and PD-L2, and most PMBCL expresses CD30.
Dr. Eid said CheckMate 436 (NCT02581631) was designed to “take advantage” of these characteristics by employing the anti-PD-1 checkpoint inhibitor nivolumab and the anti-CD30 antibody-drug conjugate brentuximab vedotin.
The interim analysis of this trial included 30 patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL. Their median age at enrollment was 35.5 and 57% of patients were female. More than half of the patients (60%) had refractory disease, 23% had relapsed disease, and 17% had both.
The median number of prior therapies was two and 13% of patients had prior autologous stem cell transplant.
The patients received nivolumab at 240 mg and brentuximab vedotin at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks until progression or unacceptable toxicity.
At a median follow-up of 6.1 months, 10 patients were still on treatment. Reasons for discontinuation included maximum clinical benefit, disease progression, AEs unrelated to treatment, patient request, and other concerns.
The rate of treatment-related AEs was 83%. The most common of these were neutropenia (27%), peripheral neuropathy (20%), hyperthyroidism (13%), rash (10%), and thrombocytopenia (10%).
Grade 3-4 treatment-related AEs included neutropenia (27%), thrombocytopenia (7%), decreased neutrophil count (7%), hypersensitivity (3%), diarrhea (3%), and maculopapular rash (3%).
The rate of serious treatment-related AEs was 10%. This included grade 3-4 diarrhea and maculopapular rash and grade 5 acute kidney injury.
The acute kidney injury was the only fatal AE considered treatment related. There were three other deaths in the trial, but they were considered unrelated to treatment.
The complete response rate was 27% (n = 8), and the partial response rate was 43% (n = 13), for an overall response rate of 70% (n = 21).
“The early indication is that 70% response is a pretty good outcome in a relapsed/refractory population that, otherwise, their outcome is pretty dismal,” Dr. Eid said.
Ten percent of patients (n = 3) had stable disease, 13% (n = 4) progressed, and investigators were unable to determine the status for 7% of patients (n = 2).
The median time to response was 1.3 months, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. The median duration of response and complete response were not reached.
Overall and progression-free survival data are not yet mature.
Still, the investigators concluded that nivolumab and brentuximab vedotin “may provide a new treatment option” for patients with relapsed/refractory PMBCL.
This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics. Investigators reported relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb, Seattle Genetics, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Moskowitz AJ et al. ASH 2018. Abstract 1691.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response rate was 70%, including a complete response rate of 27%.
Study details: A phase 1/2 study of 30 patients.
Disclosures: This trial is supported by Bristol-Myers Squibb in collaboration with Seattle Genetics, and investigators reported relationships with a range of other companies.
Source: Moskowitz AJ et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 1691.
ECHELON-2: BV-CHP boosts survival in PTCL
SAN DIEGO – A newly approved treatment regimen provides a survival benefit over standard therapy for patients with CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In the ECHELON-2 trial, patients who received brentuximab vedotin (BV) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHP) had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), compared with patients who received standard treatment with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP).
These results supported the recent U.S. approval of BV in combination with CHP for adults with previously untreated, systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma or other CD30-expressing PTCLs.
“ECHELON-2 is the first prospective trial in peripheral T-cell lymphoma to show an overall survival benefit over CHOP,” said Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, with locations in New York and New Jersey.
Dr. Horwitz presented data from this trial at the ASH meeting. Results were simultaneously published in the Lancet (2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]32984-2).
ECHELON-2 (NCT01777152) enrolled 452 patients with previously untreated, CD30-positive PTCL. Subtypes included ALK-positive or ALK-negative systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, PTCL not otherwise specified, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
Patients were randomized to receive BV-CHP plus placebo (n = 226) or CHOP plus placebo (n = 226) every 3 weeks for six to eight cycles.
At baseline, the median age was 58 in the BV-CHP arm and the CHOP arm. The majority of patients were male – 59% in the BV-CHP arm and 67% in the CHOP arm – and most patients had stage III/IV disease, 81% and 80%, respectively.
In all, 89% of patients in the BV-CHP arm and 81% in the CHOP arm completed six or more cycles of their assigned treatment.
The overall response rate was 83% in the BV-CHP arm and 72% in the CHOP arm (P = .0032). The complete response rates were 68% and 56%, respectively (P = .0066).
At a median follow-up of 36.2 months, the median PFS was 48.2 months in the BV-CHP arm and 20.8 months in the CHOP arm. The rate of death or progression was 42% in the BV-CHP arm and 55% in the CHOP arm (hazard ratio = 0.71, P = .011).
At a median follow-up of 42.1 months, the median OS was not reached in either treatment arm. The rate of death was 23% in the BV-CHP arm and 32% in the CHOP arm (HR = 0.66, P = .0244).
Dr. Horwitz noted that this study was not powered to determine differences in PFS or OS by PTCL subtypes.
BV-CHP had a safety profile comparable with that of CHOP, Dr. Horwitz said.
The rate of adverse events (AEs) was 99% in the BV-CHP arm and 98% in the CHOP arm. Grade 3 or higher AEs occurred in 66% and 65% of patients, respectively. Serious AEs occurred in 39% and 38%, respectively.
Three percent of patients in the BV-CHP arm and 4% of those in the CHOP arm had fatal AEs.
The study was funded by Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Horwitz reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and other companies.
SOURCE: Horwitz S et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 997.
SAN DIEGO – A newly approved treatment regimen provides a survival benefit over standard therapy for patients with CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In the ECHELON-2 trial, patients who received brentuximab vedotin (BV) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHP) had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), compared with patients who received standard treatment with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP).
These results supported the recent U.S. approval of BV in combination with CHP for adults with previously untreated, systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma or other CD30-expressing PTCLs.
“ECHELON-2 is the first prospective trial in peripheral T-cell lymphoma to show an overall survival benefit over CHOP,” said Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, with locations in New York and New Jersey.
Dr. Horwitz presented data from this trial at the ASH meeting. Results were simultaneously published in the Lancet (2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]32984-2).
ECHELON-2 (NCT01777152) enrolled 452 patients with previously untreated, CD30-positive PTCL. Subtypes included ALK-positive or ALK-negative systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, PTCL not otherwise specified, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
Patients were randomized to receive BV-CHP plus placebo (n = 226) or CHOP plus placebo (n = 226) every 3 weeks for six to eight cycles.
At baseline, the median age was 58 in the BV-CHP arm and the CHOP arm. The majority of patients were male – 59% in the BV-CHP arm and 67% in the CHOP arm – and most patients had stage III/IV disease, 81% and 80%, respectively.
In all, 89% of patients in the BV-CHP arm and 81% in the CHOP arm completed six or more cycles of their assigned treatment.
The overall response rate was 83% in the BV-CHP arm and 72% in the CHOP arm (P = .0032). The complete response rates were 68% and 56%, respectively (P = .0066).
At a median follow-up of 36.2 months, the median PFS was 48.2 months in the BV-CHP arm and 20.8 months in the CHOP arm. The rate of death or progression was 42% in the BV-CHP arm and 55% in the CHOP arm (hazard ratio = 0.71, P = .011).
At a median follow-up of 42.1 months, the median OS was not reached in either treatment arm. The rate of death was 23% in the BV-CHP arm and 32% in the CHOP arm (HR = 0.66, P = .0244).
Dr. Horwitz noted that this study was not powered to determine differences in PFS or OS by PTCL subtypes.
BV-CHP had a safety profile comparable with that of CHOP, Dr. Horwitz said.
The rate of adverse events (AEs) was 99% in the BV-CHP arm and 98% in the CHOP arm. Grade 3 or higher AEs occurred in 66% and 65% of patients, respectively. Serious AEs occurred in 39% and 38%, respectively.
Three percent of patients in the BV-CHP arm and 4% of those in the CHOP arm had fatal AEs.
The study was funded by Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Horwitz reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and other companies.
SOURCE: Horwitz S et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 997.
SAN DIEGO – A newly approved treatment regimen provides a survival benefit over standard therapy for patients with CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphomas (PTCLs), according to new research presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In the ECHELON-2 trial, patients who received brentuximab vedotin (BV) plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, and prednisone (CHP) had superior progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS), compared with patients who received standard treatment with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (CHOP).
These results supported the recent U.S. approval of BV in combination with CHP for adults with previously untreated, systemic anaplastic large cell lymphoma or other CD30-expressing PTCLs.
“ECHELON-2 is the first prospective trial in peripheral T-cell lymphoma to show an overall survival benefit over CHOP,” said Steven M. Horwitz, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, with locations in New York and New Jersey.
Dr. Horwitz presented data from this trial at the ASH meeting. Results were simultaneously published in the Lancet (2018 Dec 3. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[18]32984-2).
ECHELON-2 (NCT01777152) enrolled 452 patients with previously untreated, CD30-positive PTCL. Subtypes included ALK-positive or ALK-negative systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma, PTCL not otherwise specified, angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma, enteropathy-associated T-cell lymphoma, and adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma.
Patients were randomized to receive BV-CHP plus placebo (n = 226) or CHOP plus placebo (n = 226) every 3 weeks for six to eight cycles.
At baseline, the median age was 58 in the BV-CHP arm and the CHOP arm. The majority of patients were male – 59% in the BV-CHP arm and 67% in the CHOP arm – and most patients had stage III/IV disease, 81% and 80%, respectively.
In all, 89% of patients in the BV-CHP arm and 81% in the CHOP arm completed six or more cycles of their assigned treatment.
The overall response rate was 83% in the BV-CHP arm and 72% in the CHOP arm (P = .0032). The complete response rates were 68% and 56%, respectively (P = .0066).
At a median follow-up of 36.2 months, the median PFS was 48.2 months in the BV-CHP arm and 20.8 months in the CHOP arm. The rate of death or progression was 42% in the BV-CHP arm and 55% in the CHOP arm (hazard ratio = 0.71, P = .011).
At a median follow-up of 42.1 months, the median OS was not reached in either treatment arm. The rate of death was 23% in the BV-CHP arm and 32% in the CHOP arm (HR = 0.66, P = .0244).
Dr. Horwitz noted that this study was not powered to determine differences in PFS or OS by PTCL subtypes.
BV-CHP had a safety profile comparable with that of CHOP, Dr. Horwitz said.
The rate of adverse events (AEs) was 99% in the BV-CHP arm and 98% in the CHOP arm. Grade 3 or higher AEs occurred in 66% and 65% of patients, respectively. Serious AEs occurred in 39% and 38%, respectively.
Three percent of patients in the BV-CHP arm and 4% of those in the CHOP arm had fatal AEs.
The study was funded by Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Horwitz reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and other companies.
SOURCE: Horwitz S et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 997.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2018
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The rate of death or progression was 42% in the BV-CHP arm and 55% in the CHOP arm (hazard ratio = 0.71, P = .011), while the rate of death alone was 23% and 32%, respectively (HR = 0.66, P = .0244).
Study details: A phase 3 trial of 452 patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma.
Disclosures: The study was funded by Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Horwitz reported relationships with Seattle Genetics, Millennium Pharmaceuticals, and other companies.
Source: Horwitz S et al. ASH 2018, Abstract 997.