User login
Experts break down latest CAR T-cell advances in lymphoma
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
ORLANDO – There’s now mature data surrounding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in lymphoma, and the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology brought forth additional information from real-world studies, insights about what is driving relapse, and promising data on mantle cell lymphoma.

The roundtable participants included Brian Hill, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Center; Frederick L. Locke, MD, of the Moffit Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.; and Peter Riedell, MD, of the University of Chicago.
Among the studies highlighted by the panel was the Transcend NHL 001 study (Abstract 241), which looked at third-line use of lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, transformed follicular lymphoma, and other indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma subtypes. More than 300 patients were enrolled, and liso-cel met all primary and secondary efficacy endpoints, with an overall response rate of more than 70%. The notable take-home point from the study was the safety profile, Dr. Riedell noted. Liso-cel was associated with a lower rate of cytokine release syndrome and neurologic toxicity, compared with the currently approved products.
Since patients in the study had a lower incidence and later onset of cytokine release syndrome, liso-cel could be a candidate for outpatient administration, Dr. Locke said. However, doing that would require “significant infrastructure” in hospitals and clinics to properly support patients, especially given that the treatment-related mortality on the study was similar to approved CAR T-cell products at about 3%. “You have to be ready to admit the patient to the hospital very rapidly, and you have to have the providers and the nurses who are vigilant when the patient is not in the hospital,” he said.
Another notable study presented at ASH examined the characteristics and outcomes of patients receiving bridging therapy while awaiting treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 245). This real-world study adds interesting information to the field because, in some of the studies that were pivotal to the approval of CAR T-cell therapy, bridging therapy was not allowed, Dr. Locke said.
In this analysis, researchers found that the overall survival was worse among patients who received bridging. This finding suggests that patients who received bridging therapy had a different biology or that the therapy itself may have had an effect on the host or tumor microenvironment that affected the efficacy of the CAR T-cell therapy, the researchers reported.
The panel also highlighted the Zuma-2 study, which looked at KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy, among more than 70 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who had failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor (Abstract 754). “This was, I thought, kind of a sleeper study at ASH,” said Dr. Hill, who was one of the authors of the study.
The overall response rate was 93% with about two-thirds of patients achieving a complete response. Researchers found that the response was consistent across subgroups, including Ki-67 and patients with prior use of steroids or bridging therapy. Dr. Locke, who was also a study author, said the results are a “game changer.”
“I’m very excited about it,” Dr. Riedell said, noting that these are patients without a lot of treatment options.
The panel also discussed other studies from ASH, including an analysis of tumor tissue samples from patients in the ZUMA-1 trial who had responded and subsequently relapsed (Abstract 203); a multicenter prospective analysis of circulating tumor DNA in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma patients who had relapsed after treatment with axicabtagene ciloleucel (Abstract 884); and the early use of corticosteroids to prevent toxicities in patients in cohort 4 of the ZUMA-1 trial (Abstract 243).
Dr. Hill reported consulting with Juno/Celgene/BMS and Novartis and research and consulting for Kite/Gilead. Dr. Locke reported consulting for Cellular Biomedicine Group and being a scientific adviser to Kite/Gilead, Novartis, Celgene/BMS, GammaDelta Therapeutics, Calibr, and Allogene. Dr. Riedell reported consulting for Bayer and Verastem, consulting for and research funding from Novartis and BMS/Celgene, and consulting for, research funding from, and speaking for Kite.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASH 2019
LOXO-305: Next-gen BTK inhibitor safe and effective in B-cell malignancies
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
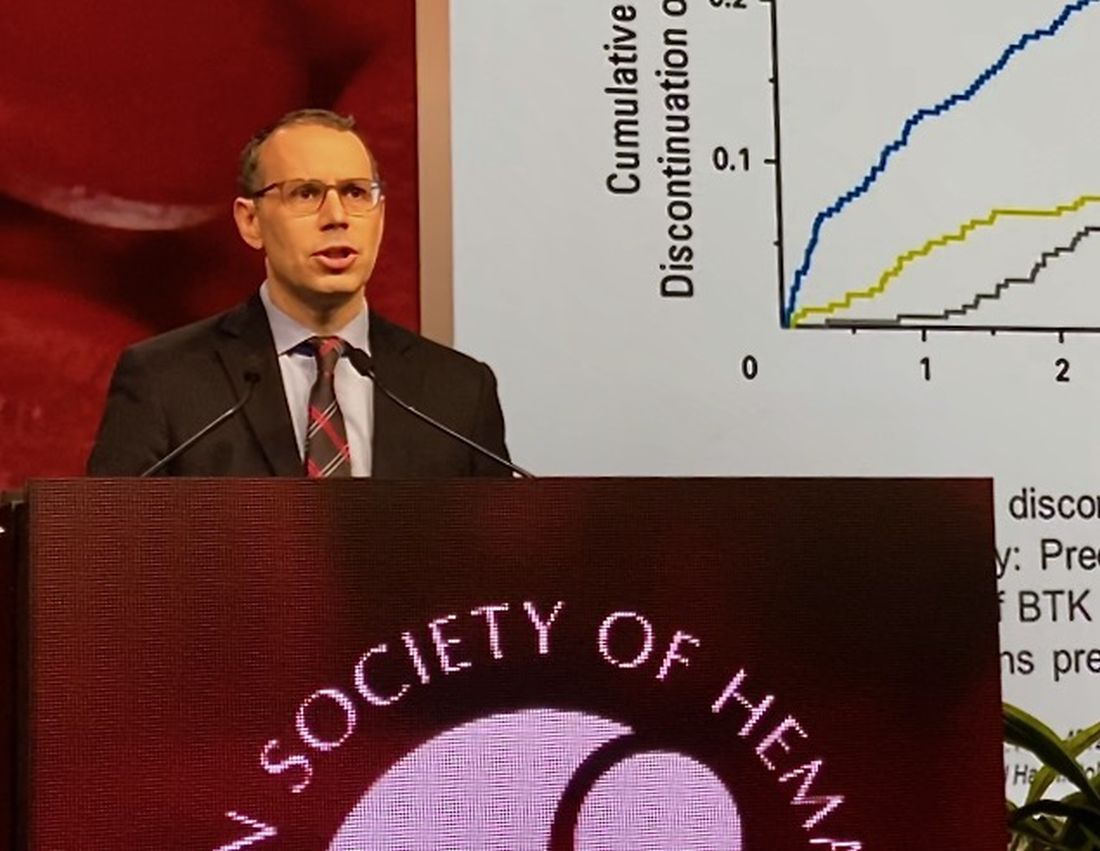
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
ORLANDO – A phase 1 trial of the next-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor LOXO-305 has demonstrated safety and provided evidence of its efficacy in heavily pretreated patients with B-cell malignancies, including some with acquired resistance to other BTK inhibitors and venetoclax, according to an investigator.
The antitumor activity of this highly selective investigational oral BTK inhibitor was significant in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), with a rapid onset of action and resolution of lymphocytosis “consistent with effective BTK target inhibition,” said Anthony R. Mato, MD, of the Center for CLL at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York.
Responses were also seen in patients with BTK C481 mutations, the primary cause of progressive CLL after BTK inhibitor use, Dr. Mato said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The safety and tolerability profile of LOXO-305 is “consistent with highly selective drug design,” with no evidence of off-target effects, he said. “Collectively, these data demonstrate that BTK remains a highly actionable target despite progression on covalent BTK inhibitors.”
While BTK inhibitors have transformed treatment of B-cell malignancies, resistance remains a major problem, said Dr. Mato, citing 5-year ibrutinib discontinuation rates of 41% in the front line setting and 53.7% in the relapsed/refractory setting.
Key reasons for discontinuation are intolerance, events such as atrial fibrillation and major bleeding, progression of disease, and the appearance of BTK C481 mutations, which prevent covalent BTK inhibitors from achieving effective target inhibition, he said. In contrast, LOXO-305 is designed to non-covalently bind to BTK, regardless of C481 status.
Dr. Mato described results of the phase 1 BRUIN trial, in which 28 adult patients with CLL or B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas received once daily oral LOXO-305 at doses ranging from 25 mg to 200 mg. All patients had received at least two lines of prior therapy and had active disease in need of treatment.
For 13 evaluable CLL patients, the overall response rate was 77% (10 patients), Dr. Mato reported. Overall response rates for MCL and other B-cell malignancies were 50%, or three out of six MCL patients and two of four patients with Waldenström macroglobulinemia, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, or marginal zone lymphoma.
Though only a small subset of CLL patients have had multiple response assessments, the available data suggest that responses “deepen over time” with continued LOXO-305 treatment, Dr. Mato said.
With the median follow-up of 2.7 months, 24 of 28 patients remain on therapy, including all responders. “Some of the responses appear to be quite durable,” Dr. Mato said.
There have been no dose-limiting toxicities, the maximum tolerated dose has not been reached, and there have been no notable adverse events characteristic of covalent BTK inhibitors – namely atrial fibrillation or major bleeding – despite frequent monitoring, according to Dr. Mato.
There were two grade 3 events (leukocytosis and neutropenia), but the remaining treatment-emergent adverse events have been grade 1-2. “Having managed many of these patients, I can tell you that these adverse events were quite manageable,” Dr. Mato told attendees.
BRUIN is a global trial that continues to enroll patients at 18 sites in 3 countries, with a plan in 2020 to incorporate “rational combinations” of agents, according to the investigator.
Dr. Mato reported disclosures related to Gilead, Pharmacyclics, AstraZeneca, AbbVie, Sunesis, Johnson & Johnson, TG Therapeutics, LOXO, DTRM Biopharma, Genentech, Janssen, Acerta, Pharmacyclics, and Celgene.
SOURCE: Mato AR et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 501.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Some MCL patients can safely stop venetoclax-ibrutinib, study suggests
ORLANDO – Updated trial results have revealed durable responses with venetoclax and ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing some patients to stop treatment.
Five of 24 patients were able to stop treatment after achieving minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative complete responses (CRs). Four of these patients remain in CR at up to 18 months off treatment, although one patient ultimately progressed and died.
“Treatment cessation was feasible for patients in MRD-negative complete responses, raising the prospect of limited-duration, targeted-agent therapy in the management of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” said Sasanka M. Handunnetti, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne. Dr. Handunnetti presented these results, from the AIM trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 24 patients. At baseline, patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 47-81 years), and 88% were men. One patient was treatment-naive, but the rest had relapsed/refractory MCL. These patients had received a median of two prior therapies (range, 1-6).
The patients received venetoclax at 400 mg daily and ibrutinib at 560 mg daily.
In the primary analysis, the CR rate was 62% at week 16 and 71% overall, according to positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. MRD negativity was achieved by 67% of patients according to flow cytometry and 38% according to allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378[13]:1211-23).
Response and survival
For the current analysis, the median follow up was 37.5 months (range, 1.4-45.3 months). The median duration of response has not been reached, the median progression-free survival is 29 months, and the median overall survival is 32 months.
Thirteen patients have died, 8 of them due to progressive disease. The remaining 11 patients are still alive, and 9 of them are still in CR. One patient is still in partial response, and one has not responded but remains on ibrutinib and venetoclax.
Dr. Handunnetti pointed out that 12 patients had TP53 aberrations, and 8 of them died, but 4 remain alive and in CR. All four patients with SMARCA4 aberrations died.
Treatment status
Five patients are still receiving treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax, and one patient is receiving only venetoclax. One patient went off study treatment due to a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome, but that patient’s MCL is still in CR.
Five patients were able to stop treatment after achieving MRD-negative CR and were placed under “stringent surveillance,” Dr. Handunnetti said.
One of the five patients who stopped treatment progressed at 7 months and died. The remaining four patients are still alive and in CR at 6 months, 13 months, 17 months, and 18 months off treatment.
Safety update
Within the first 56 weeks of treatment, 15 patients required dose adjustments. Twelve patients required an adjustment to ibrutinib, seven to venetoclax, and four to both drugs. After 56 weeks, there were no dose adjustments.
Two patients developed therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome. One patient had previously received FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and BR (bendamustine and rituximab). The other patient had received R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
This investigator-initiated trial was funded by Janssen and Abbvie. Dr. Handunnetti reported relationships with Abbvie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Handunnetti S et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 756.
ORLANDO – Updated trial results have revealed durable responses with venetoclax and ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing some patients to stop treatment.
Five of 24 patients were able to stop treatment after achieving minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative complete responses (CRs). Four of these patients remain in CR at up to 18 months off treatment, although one patient ultimately progressed and died.
“Treatment cessation was feasible for patients in MRD-negative complete responses, raising the prospect of limited-duration, targeted-agent therapy in the management of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” said Sasanka M. Handunnetti, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne. Dr. Handunnetti presented these results, from the AIM trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 24 patients. At baseline, patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 47-81 years), and 88% were men. One patient was treatment-naive, but the rest had relapsed/refractory MCL. These patients had received a median of two prior therapies (range, 1-6).
The patients received venetoclax at 400 mg daily and ibrutinib at 560 mg daily.
In the primary analysis, the CR rate was 62% at week 16 and 71% overall, according to positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. MRD negativity was achieved by 67% of patients according to flow cytometry and 38% according to allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378[13]:1211-23).
Response and survival
For the current analysis, the median follow up was 37.5 months (range, 1.4-45.3 months). The median duration of response has not been reached, the median progression-free survival is 29 months, and the median overall survival is 32 months.
Thirteen patients have died, 8 of them due to progressive disease. The remaining 11 patients are still alive, and 9 of them are still in CR. One patient is still in partial response, and one has not responded but remains on ibrutinib and venetoclax.
Dr. Handunnetti pointed out that 12 patients had TP53 aberrations, and 8 of them died, but 4 remain alive and in CR. All four patients with SMARCA4 aberrations died.
Treatment status
Five patients are still receiving treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax, and one patient is receiving only venetoclax. One patient went off study treatment due to a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome, but that patient’s MCL is still in CR.
Five patients were able to stop treatment after achieving MRD-negative CR and were placed under “stringent surveillance,” Dr. Handunnetti said.
One of the five patients who stopped treatment progressed at 7 months and died. The remaining four patients are still alive and in CR at 6 months, 13 months, 17 months, and 18 months off treatment.
Safety update
Within the first 56 weeks of treatment, 15 patients required dose adjustments. Twelve patients required an adjustment to ibrutinib, seven to venetoclax, and four to both drugs. After 56 weeks, there were no dose adjustments.
Two patients developed therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome. One patient had previously received FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and BR (bendamustine and rituximab). The other patient had received R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
This investigator-initiated trial was funded by Janssen and Abbvie. Dr. Handunnetti reported relationships with Abbvie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Handunnetti S et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 756.
ORLANDO – Updated trial results have revealed durable responses with venetoclax and ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing some patients to stop treatment.
Five of 24 patients were able to stop treatment after achieving minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative complete responses (CRs). Four of these patients remain in CR at up to 18 months off treatment, although one patient ultimately progressed and died.
“Treatment cessation was feasible for patients in MRD-negative complete responses, raising the prospect of limited-duration, targeted-agent therapy in the management of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” said Sasanka M. Handunnetti, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne. Dr. Handunnetti presented these results, from the AIM trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 24 patients. At baseline, patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 47-81 years), and 88% were men. One patient was treatment-naive, but the rest had relapsed/refractory MCL. These patients had received a median of two prior therapies (range, 1-6).
The patients received venetoclax at 400 mg daily and ibrutinib at 560 mg daily.
In the primary analysis, the CR rate was 62% at week 16 and 71% overall, according to positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. MRD negativity was achieved by 67% of patients according to flow cytometry and 38% according to allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378[13]:1211-23).
Response and survival
For the current analysis, the median follow up was 37.5 months (range, 1.4-45.3 months). The median duration of response has not been reached, the median progression-free survival is 29 months, and the median overall survival is 32 months.
Thirteen patients have died, 8 of them due to progressive disease. The remaining 11 patients are still alive, and 9 of them are still in CR. One patient is still in partial response, and one has not responded but remains on ibrutinib and venetoclax.
Dr. Handunnetti pointed out that 12 patients had TP53 aberrations, and 8 of them died, but 4 remain alive and in CR. All four patients with SMARCA4 aberrations died.
Treatment status
Five patients are still receiving treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax, and one patient is receiving only venetoclax. One patient went off study treatment due to a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome, but that patient’s MCL is still in CR.
Five patients were able to stop treatment after achieving MRD-negative CR and were placed under “stringent surveillance,” Dr. Handunnetti said.
One of the five patients who stopped treatment progressed at 7 months and died. The remaining four patients are still alive and in CR at 6 months, 13 months, 17 months, and 18 months off treatment.
Safety update
Within the first 56 weeks of treatment, 15 patients required dose adjustments. Twelve patients required an adjustment to ibrutinib, seven to venetoclax, and four to both drugs. After 56 weeks, there were no dose adjustments.
Two patients developed therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome. One patient had previously received FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and BR (bendamustine and rituximab). The other patient had received R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
This investigator-initiated trial was funded by Janssen and Abbvie. Dr. Handunnetti reported relationships with Abbvie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Handunnetti S et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 756.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
KTE-X19 produces highest response rate in MCL subgroup
ORLANDO – KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in the ZUMA-2 trial, according to an investigator involved in the study.
KTE-X19 produced a 93% overall response rate in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). This is the highest reported response rate in patients who have failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, said Michael L. Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr. Wang presented results from ZUMA-2 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Patients with relapsed/refractory MCL have very poor outcomes,” Dr. Wang noted. “In patients who progress after BTK inhibition therapy, the overall response rate is only between 25% and 42%, and the overall survival is only between 6 and 10 months. Few patients proceed to allogeneic transplantation.”
The phase 2 ZUMA-2 trial was designed to test KTE-X19 in these patients. KTE-X19 is an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy containing a CD3-zeta T-cell activation domain and a CD28 signaling domain. KTE-X19 is distinct from axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19) because the manufacturing process for KTE-X19 removes circulating tumor cells.
The trial enrolled 74 patients, and 68 of them received KTE-X19. Manufacturing failed for three patients, two patients died of progressive disease before they could receive KTE-X19, and one patient was found to be ineligible for treatment.
The 68 patients had a median age of 65 years (range, 38-79 years), and 84% were men. A majority of patients (85%) had stage IV disease and classical (59%) or blastoid (25%) morphology. Most patients (69%) had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater, and most (56%) were intermediate- or high-risk according to the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
Patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, one to five). All had been treated with a BTK inhibitor, with 85% receiving ibrutinib, 24% receiving acalabrutinib, and 9% receiving both. Most patients (68%) were refractory to BTK inhibition, and 32% relapsed on or after BTK inhibitor therapy.
In this study, patients could receive bridging therapy to keep their disease stable while KTE-X19 was being manufactured. There were 25 patients who received bridging therapy, which consisted of ibrutinib (n = 14), acalabrutinib (n = 5), dexamethasone (n = 12), and/or methylprednisolone (n = 2). Six patients received both BTK inhibitors and steroids.
All patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of KTE-X19 at 2x106.
Efficacy
Sixty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up was 12.3 months (range, 7.0-32.3 months).
The overall response rate was 93%, with 67% of patients achieving a complete response and 27% achieving a partial response. Three percent of patients had stable disease, and 3% had progressive disease.
“The overall response rate was consistent across key subgroups, without any statistical difference,” Dr. Wang said. “This includes Ki-67, MIPI, and prior use of either steroids or bridging therapy.”
The median time to response was 1.0 month, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. Responses deepened over time, with 35% of patients converting from a partial response to a complete response, and 5% converting from stable disease to complete response.
The median duration of response has not been reached. At last follow-up, 57% of all patients and 78% of complete responders were still in response.
The median progression-free and overall survival have not been reached. At 12 months, the progression-free survival rate was 61%, and the overall survival rate was 83%.
Safety
All 68 patients were evaluable for safety. The most common adverse events were pyrexia (94%), neutropenia (87%), thrombocytopenia (74%), anemia (68%), and hypotension (51%).
Grade 3/4 adverse events included pyrexia (13%), neutropenia (85%), thrombocytopenia (51%), anemia (50%), hypotension (22%), hypoxia (21%), hypophosphatemia (22%), fatigue (1%), and headache (1%).
There were two grade 5 treatment-related adverse events – organizing pneumonia on day 37 and staphylococcal bacteremia on day 134.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 91% of patients, with 15% experiencing grade 3 or higher CRS. Patients were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and all CRS events resolved.
Neurologic adverse events occurred in 63% of patients, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 31%. Neurologic events were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and 86% of neurologic events resolved.
This trial was sponsored by Kite, a Gilead company. Dr. Wang reported financial relationships with Kite and other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 754.
ORLANDO – KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in the ZUMA-2 trial, according to an investigator involved in the study.
KTE-X19 produced a 93% overall response rate in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). This is the highest reported response rate in patients who have failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, said Michael L. Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr. Wang presented results from ZUMA-2 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Patients with relapsed/refractory MCL have very poor outcomes,” Dr. Wang noted. “In patients who progress after BTK inhibition therapy, the overall response rate is only between 25% and 42%, and the overall survival is only between 6 and 10 months. Few patients proceed to allogeneic transplantation.”
The phase 2 ZUMA-2 trial was designed to test KTE-X19 in these patients. KTE-X19 is an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy containing a CD3-zeta T-cell activation domain and a CD28 signaling domain. KTE-X19 is distinct from axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19) because the manufacturing process for KTE-X19 removes circulating tumor cells.
The trial enrolled 74 patients, and 68 of them received KTE-X19. Manufacturing failed for three patients, two patients died of progressive disease before they could receive KTE-X19, and one patient was found to be ineligible for treatment.
The 68 patients had a median age of 65 years (range, 38-79 years), and 84% were men. A majority of patients (85%) had stage IV disease and classical (59%) or blastoid (25%) morphology. Most patients (69%) had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater, and most (56%) were intermediate- or high-risk according to the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
Patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, one to five). All had been treated with a BTK inhibitor, with 85% receiving ibrutinib, 24% receiving acalabrutinib, and 9% receiving both. Most patients (68%) were refractory to BTK inhibition, and 32% relapsed on or after BTK inhibitor therapy.
In this study, patients could receive bridging therapy to keep their disease stable while KTE-X19 was being manufactured. There were 25 patients who received bridging therapy, which consisted of ibrutinib (n = 14), acalabrutinib (n = 5), dexamethasone (n = 12), and/or methylprednisolone (n = 2). Six patients received both BTK inhibitors and steroids.
All patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of KTE-X19 at 2x106.
Efficacy
Sixty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up was 12.3 months (range, 7.0-32.3 months).
The overall response rate was 93%, with 67% of patients achieving a complete response and 27% achieving a partial response. Three percent of patients had stable disease, and 3% had progressive disease.
“The overall response rate was consistent across key subgroups, without any statistical difference,” Dr. Wang said. “This includes Ki-67, MIPI, and prior use of either steroids or bridging therapy.”
The median time to response was 1.0 month, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. Responses deepened over time, with 35% of patients converting from a partial response to a complete response, and 5% converting from stable disease to complete response.
The median duration of response has not been reached. At last follow-up, 57% of all patients and 78% of complete responders were still in response.
The median progression-free and overall survival have not been reached. At 12 months, the progression-free survival rate was 61%, and the overall survival rate was 83%.
Safety
All 68 patients were evaluable for safety. The most common adverse events were pyrexia (94%), neutropenia (87%), thrombocytopenia (74%), anemia (68%), and hypotension (51%).
Grade 3/4 adverse events included pyrexia (13%), neutropenia (85%), thrombocytopenia (51%), anemia (50%), hypotension (22%), hypoxia (21%), hypophosphatemia (22%), fatigue (1%), and headache (1%).
There were two grade 5 treatment-related adverse events – organizing pneumonia on day 37 and staphylococcal bacteremia on day 134.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 91% of patients, with 15% experiencing grade 3 or higher CRS. Patients were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and all CRS events resolved.
Neurologic adverse events occurred in 63% of patients, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 31%. Neurologic events were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and 86% of neurologic events resolved.
This trial was sponsored by Kite, a Gilead company. Dr. Wang reported financial relationships with Kite and other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 754.
ORLANDO – KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in the ZUMA-2 trial, according to an investigator involved in the study.
KTE-X19 produced a 93% overall response rate in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). This is the highest reported response rate in patients who have failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, said Michael L. Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr. Wang presented results from ZUMA-2 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Patients with relapsed/refractory MCL have very poor outcomes,” Dr. Wang noted. “In patients who progress after BTK inhibition therapy, the overall response rate is only between 25% and 42%, and the overall survival is only between 6 and 10 months. Few patients proceed to allogeneic transplantation.”
The phase 2 ZUMA-2 trial was designed to test KTE-X19 in these patients. KTE-X19 is an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy containing a CD3-zeta T-cell activation domain and a CD28 signaling domain. KTE-X19 is distinct from axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19) because the manufacturing process for KTE-X19 removes circulating tumor cells.
The trial enrolled 74 patients, and 68 of them received KTE-X19. Manufacturing failed for three patients, two patients died of progressive disease before they could receive KTE-X19, and one patient was found to be ineligible for treatment.
The 68 patients had a median age of 65 years (range, 38-79 years), and 84% were men. A majority of patients (85%) had stage IV disease and classical (59%) or blastoid (25%) morphology. Most patients (69%) had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater, and most (56%) were intermediate- or high-risk according to the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
Patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, one to five). All had been treated with a BTK inhibitor, with 85% receiving ibrutinib, 24% receiving acalabrutinib, and 9% receiving both. Most patients (68%) were refractory to BTK inhibition, and 32% relapsed on or after BTK inhibitor therapy.
In this study, patients could receive bridging therapy to keep their disease stable while KTE-X19 was being manufactured. There were 25 patients who received bridging therapy, which consisted of ibrutinib (n = 14), acalabrutinib (n = 5), dexamethasone (n = 12), and/or methylprednisolone (n = 2). Six patients received both BTK inhibitors and steroids.
All patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of KTE-X19 at 2x106.
Efficacy
Sixty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up was 12.3 months (range, 7.0-32.3 months).
The overall response rate was 93%, with 67% of patients achieving a complete response and 27% achieving a partial response. Three percent of patients had stable disease, and 3% had progressive disease.
“The overall response rate was consistent across key subgroups, without any statistical difference,” Dr. Wang said. “This includes Ki-67, MIPI, and prior use of either steroids or bridging therapy.”
The median time to response was 1.0 month, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. Responses deepened over time, with 35% of patients converting from a partial response to a complete response, and 5% converting from stable disease to complete response.
The median duration of response has not been reached. At last follow-up, 57% of all patients and 78% of complete responders were still in response.
The median progression-free and overall survival have not been reached. At 12 months, the progression-free survival rate was 61%, and the overall survival rate was 83%.
Safety
All 68 patients were evaluable for safety. The most common adverse events were pyrexia (94%), neutropenia (87%), thrombocytopenia (74%), anemia (68%), and hypotension (51%).
Grade 3/4 adverse events included pyrexia (13%), neutropenia (85%), thrombocytopenia (51%), anemia (50%), hypotension (22%), hypoxia (21%), hypophosphatemia (22%), fatigue (1%), and headache (1%).
There were two grade 5 treatment-related adverse events – organizing pneumonia on day 37 and staphylococcal bacteremia on day 134.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 91% of patients, with 15% experiencing grade 3 or higher CRS. Patients were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and all CRS events resolved.
Neurologic adverse events occurred in 63% of patients, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 31%. Neurologic events were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and 86% of neurologic events resolved.
This trial was sponsored by Kite, a Gilead company. Dr. Wang reported financial relationships with Kite and other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 754.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Orelabrutinib could be ‘preferred’ BTK inhibitor for MCL
ORLANDO – A novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has produced favorable results in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In a phase 2 trial, orelabrutinib produced an overall response rate of 86% and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 64%. Safety results with orelabrutinib were superior to historical results with ibrutinib.
The efficacy and safety profile of orelabrutinib, as well as its “convenient” dosing, may make it the “preferred therapeutic choice for B-cell malignancy,” said Lijuan Deng, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, who presented the phase 2 trial of orelabrutinib at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 106 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who were treated at 22 centers in China. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 62 years (range, 37-73 years), and 79.2% were men. Most patients (94.4%) had stage III-IV disease.
Prior therapies included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone)-based (69.8%), EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin)-based (22.6%), DHAP (dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (22.6%), CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone)-based (12.3%), and ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (4.7%) regimens, and 88.7% of patients had received prior anti-CD20 therapy.
Patients received orelabrutinib at 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) or 150 mg once a day (n = 86). All 106 patients were evaluable for safety, and 99 were evaluable for efficacy.
Efficacy
“Orelabrutinib achieved high response and durable remissions,” Dr. Deng said.
The overall response rate was 85.9% in the evaluable efficacy population and 83.5% in the 150-mg dosing arm. The complete response rates were 27.3% and 29.1%, respectively. The median time to response, overall, was 1.9 months.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival were not reached at a median follow-up of 10.5 months. At 12 months, 74.3% of patients were still in response, and the progression-free survival rate was 64%.
Safety
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in nature. The most common grade 3 or higher events were platelet count decrease (11.3%), neutrophil count decrease (8.5%), anemia (7.5%), hypertension (3.8%), pneumonia (2.8%), white blood count decrease (1.9%), and hypokalemia (1.9%).
Adverse events of interest included grade 3 or higher hypertension (3.8%), diarrhea (6.6%), and infection (10.4%), as well as secondary malignancy (0.9%, n = 1). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, grade 3 or higher atrial fibrillation/flutter, or grade 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Dr. Deng noted that rates of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, and infection, as well as rates of secondary malignancies, have historically been higher with ibrutinib (Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126[6]:739-45; Lancet. 2016 Feb 20;387[10020]:770-8).
“Orelabrutinib has an improved safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Dr. Deng said. “The most common adverse events were cytopenia and infections, which are considered mechanism based.”
The study was sponsored by InnoCare Pharma. Dr. Deng reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Deng L et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 755.
ORLANDO – A novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has produced favorable results in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In a phase 2 trial, orelabrutinib produced an overall response rate of 86% and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 64%. Safety results with orelabrutinib were superior to historical results with ibrutinib.
The efficacy and safety profile of orelabrutinib, as well as its “convenient” dosing, may make it the “preferred therapeutic choice for B-cell malignancy,” said Lijuan Deng, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, who presented the phase 2 trial of orelabrutinib at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 106 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who were treated at 22 centers in China. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 62 years (range, 37-73 years), and 79.2% were men. Most patients (94.4%) had stage III-IV disease.
Prior therapies included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone)-based (69.8%), EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin)-based (22.6%), DHAP (dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (22.6%), CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone)-based (12.3%), and ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (4.7%) regimens, and 88.7% of patients had received prior anti-CD20 therapy.
Patients received orelabrutinib at 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) or 150 mg once a day (n = 86). All 106 patients were evaluable for safety, and 99 were evaluable for efficacy.
Efficacy
“Orelabrutinib achieved high response and durable remissions,” Dr. Deng said.
The overall response rate was 85.9% in the evaluable efficacy population and 83.5% in the 150-mg dosing arm. The complete response rates were 27.3% and 29.1%, respectively. The median time to response, overall, was 1.9 months.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival were not reached at a median follow-up of 10.5 months. At 12 months, 74.3% of patients were still in response, and the progression-free survival rate was 64%.
Safety
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in nature. The most common grade 3 or higher events were platelet count decrease (11.3%), neutrophil count decrease (8.5%), anemia (7.5%), hypertension (3.8%), pneumonia (2.8%), white blood count decrease (1.9%), and hypokalemia (1.9%).
Adverse events of interest included grade 3 or higher hypertension (3.8%), diarrhea (6.6%), and infection (10.4%), as well as secondary malignancy (0.9%, n = 1). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, grade 3 or higher atrial fibrillation/flutter, or grade 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Dr. Deng noted that rates of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, and infection, as well as rates of secondary malignancies, have historically been higher with ibrutinib (Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126[6]:739-45; Lancet. 2016 Feb 20;387[10020]:770-8).
“Orelabrutinib has an improved safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Dr. Deng said. “The most common adverse events were cytopenia and infections, which are considered mechanism based.”
The study was sponsored by InnoCare Pharma. Dr. Deng reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Deng L et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 755.
ORLANDO – A novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has produced favorable results in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In a phase 2 trial, orelabrutinib produced an overall response rate of 86% and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 64%. Safety results with orelabrutinib were superior to historical results with ibrutinib.
The efficacy and safety profile of orelabrutinib, as well as its “convenient” dosing, may make it the “preferred therapeutic choice for B-cell malignancy,” said Lijuan Deng, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, who presented the phase 2 trial of orelabrutinib at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 106 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who were treated at 22 centers in China. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 62 years (range, 37-73 years), and 79.2% were men. Most patients (94.4%) had stage III-IV disease.
Prior therapies included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone)-based (69.8%), EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin)-based (22.6%), DHAP (dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (22.6%), CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone)-based (12.3%), and ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (4.7%) regimens, and 88.7% of patients had received prior anti-CD20 therapy.
Patients received orelabrutinib at 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) or 150 mg once a day (n = 86). All 106 patients were evaluable for safety, and 99 were evaluable for efficacy.
Efficacy
“Orelabrutinib achieved high response and durable remissions,” Dr. Deng said.
The overall response rate was 85.9% in the evaluable efficacy population and 83.5% in the 150-mg dosing arm. The complete response rates were 27.3% and 29.1%, respectively. The median time to response, overall, was 1.9 months.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival were not reached at a median follow-up of 10.5 months. At 12 months, 74.3% of patients were still in response, and the progression-free survival rate was 64%.
Safety
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in nature. The most common grade 3 or higher events were platelet count decrease (11.3%), neutrophil count decrease (8.5%), anemia (7.5%), hypertension (3.8%), pneumonia (2.8%), white blood count decrease (1.9%), and hypokalemia (1.9%).
Adverse events of interest included grade 3 or higher hypertension (3.8%), diarrhea (6.6%), and infection (10.4%), as well as secondary malignancy (0.9%, n = 1). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, grade 3 or higher atrial fibrillation/flutter, or grade 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Dr. Deng noted that rates of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, and infection, as well as rates of secondary malignancies, have historically been higher with ibrutinib (Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126[6]:739-45; Lancet. 2016 Feb 20;387[10020]:770-8).
“Orelabrutinib has an improved safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Dr. Deng said. “The most common adverse events were cytopenia and infections, which are considered mechanism based.”
The study was sponsored by InnoCare Pharma. Dr. Deng reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Deng L et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 755.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
The clinical impact of new approvals in sickle cell, MCL
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration – crizanlizumab for sickle cell patients with painful crises and zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients in relapse.
Crizanlizumab
P-selectin is an adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelial cells and platelets. It is a key molecule in the initiation of leukocyte rolling on vessel walls and promotes firm attachment and extravasation to underlying tissues during inflammation. Up-regulation of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets contributes to the cell-cell interactions involved in the pathogenesis of sickle cell pain crises.
The SUSTAIN study was a multisite, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial of two different dosage levels of intravenous crizanlizumab (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg for 52 weeks), a humanized anti–P-selectin antibody, examining its effect on pain crises in patients with sickle cell disease. The primary endpoint was the annual rate of sickle cell pain crises, with a variety of clinically relevant secondary endpoints. The target population had 2-10 pain crises in the 12 months before enrollment. Patients on a stable dose of hydroxyurea for at least the most recent 3 months were allowed to enter, but if patients were not receiving hydroxyurea, it could not be initiated during the trial. Patients who were undergoing chronic red-cell transfusion therapy were excluded.
Among 198 enrolled patients, 35% did not complete the 52 weeks of treatment. Discontinuations were equally balanced among patients assigned to the high-dose, low-dose, and placebo cohorts. Adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events occurred in 55 patients, with 5 deaths, all of which were unrelated to treatment. Crizanlizumab did not augment hemolysis or bacterial infections.
In the efficacy analysis, patients receiving high-dose crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for sickle cell pain crises, compared with 2.98 visits for placebo patients (P = .01). In comparison with placebo, high-dose crizanlizumab also delayed the first pain crisis after starting treatment (4.1 months vs. 1.4 months), delayed the median time to a second pain crisis, and decreased the median number of pain crises annually.
More than twice as many high-dose crizanlizumab patients had no pain crisis episodes, compared with placebo patients. In general, differences were more striking in patients who were not taking hydroxyurea and who had non–hemoglobin SS disease. Differences in the primary endpoint between low-dose crizanlizumab and placebo were numerically, but not statistically, different.
How these results influence practice
It has been over 20 years since a new agent (hydroxyurea) was approved for sickle cell patients and, despite its use, sickle cell pain crises remain a frequent problem. Pain crises are associated with worse quality of life and increased risk of death. A promising advance is badly needed, especially in an era in which sensitivity to providers’ role in the opioid addiction crisis is highly scrutinized and may contribute to future undertreatment of pain episodes. This is especially true for patients from areas with high levels of opioid misuse.
The SUSTAIN trial was international, multi-institutional, placebo-controlled, and inclusive. These attributes enhance the likelihood that crizanlizumab will enhance patient care in routine practice. As an intravenous agent, monitoring adherence and toxicity are less challenging than with hydroxyurea. Despite these factors, however, there are some concerns. Crizanlizumab was not free of toxicity, quality of life via the Brief Pain Inventory used in the trial was not improved, and changes in the pain-severity and pain-interference domains were small. Treatment in SUSTAIN ensued for 52 weeks, so the emergence of late neutralizing antibodies and late toxicities with longer-term therapy will require careful postmarketing assessment.
These concerns notwithstanding, anyone who has cared for sickle cell patients would be excited about the potential benefits crizanlizumab could bring to patient care.
Zanubrutinib
The FDA has approved zanubrutinib for the treatment of MCL in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy. The approval is based on the results of two studies in which overall response rate was the primary endpoint.
BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970) was a phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy. Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120) was a phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation trial of B-cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.
In the phase 2 trial, 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% confidence interval, 74%-91%), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI, 48%-70%) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI, 16.6% to not estimable). In the phase 1/2 dose-escalation trial, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI, 67%-95%), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI, 9%-40%) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI, 12.6% to not estimable). In both trials, median follow-up on study was about 18 months.
The most common adverse reactions were cytopenias, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, bruising, diarrhea, and cough. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia in 11% and hemorrhage in 5% of patients. Of 118 MCL patients, 8 stopped therapy because of an adverse event, most frequently pneumonia (3.4%).
How these results influence practice
Unfortunately, the therapy of recurrent MCL is noncurative, because of the rapid development of treatment resistance. There are multiple single-and multiagent chemotherapy regimens that may be tried, many incorporating immunotherapy options such as anti-CD20- or Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–targeted agents. Given the limited efficacy of these agents, temporary nature of remissions, and paucity of data comparing these various treatment options, participation in clinical trials is encouraged whenever possible.
Outside of a clinical trial, zanubrutinib joins ibrutinib and acalabrutinib as approved single-agent BTK inhibitors for adult MCL patients in relapse. The impressive ORR and response duration reported for zanubrutinib are similar to the results achieved with the other agents, but the toxicity pattern may be slightly different.
As in the treatment of hormonally sensitive breast cancer, clinicians and patients benefit when they have multiple similar, equally efficacious oral agents with slightly different toxicity patterns so that quality of life can be improved and treatment duration maximized before treatment resistance develops and a more toxic and/or inconvenient therapy needs to be employed.
Whether zanubrutinib has benefits beyond those for MCL patients in relapse will depend on the results of confirmatory trials and patient-reported outcome data.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration – crizanlizumab for sickle cell patients with painful crises and zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients in relapse.
Crizanlizumab
P-selectin is an adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelial cells and platelets. It is a key molecule in the initiation of leukocyte rolling on vessel walls and promotes firm attachment and extravasation to underlying tissues during inflammation. Up-regulation of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets contributes to the cell-cell interactions involved in the pathogenesis of sickle cell pain crises.
The SUSTAIN study was a multisite, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial of two different dosage levels of intravenous crizanlizumab (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg for 52 weeks), a humanized anti–P-selectin antibody, examining its effect on pain crises in patients with sickle cell disease. The primary endpoint was the annual rate of sickle cell pain crises, with a variety of clinically relevant secondary endpoints. The target population had 2-10 pain crises in the 12 months before enrollment. Patients on a stable dose of hydroxyurea for at least the most recent 3 months were allowed to enter, but if patients were not receiving hydroxyurea, it could not be initiated during the trial. Patients who were undergoing chronic red-cell transfusion therapy were excluded.
Among 198 enrolled patients, 35% did not complete the 52 weeks of treatment. Discontinuations were equally balanced among patients assigned to the high-dose, low-dose, and placebo cohorts. Adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events occurred in 55 patients, with 5 deaths, all of which were unrelated to treatment. Crizanlizumab did not augment hemolysis or bacterial infections.
In the efficacy analysis, patients receiving high-dose crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for sickle cell pain crises, compared with 2.98 visits for placebo patients (P = .01). In comparison with placebo, high-dose crizanlizumab also delayed the first pain crisis after starting treatment (4.1 months vs. 1.4 months), delayed the median time to a second pain crisis, and decreased the median number of pain crises annually.
More than twice as many high-dose crizanlizumab patients had no pain crisis episodes, compared with placebo patients. In general, differences were more striking in patients who were not taking hydroxyurea and who had non–hemoglobin SS disease. Differences in the primary endpoint between low-dose crizanlizumab and placebo were numerically, but not statistically, different.
How these results influence practice
It has been over 20 years since a new agent (hydroxyurea) was approved for sickle cell patients and, despite its use, sickle cell pain crises remain a frequent problem. Pain crises are associated with worse quality of life and increased risk of death. A promising advance is badly needed, especially in an era in which sensitivity to providers’ role in the opioid addiction crisis is highly scrutinized and may contribute to future undertreatment of pain episodes. This is especially true for patients from areas with high levels of opioid misuse.
The SUSTAIN trial was international, multi-institutional, placebo-controlled, and inclusive. These attributes enhance the likelihood that crizanlizumab will enhance patient care in routine practice. As an intravenous agent, monitoring adherence and toxicity are less challenging than with hydroxyurea. Despite these factors, however, there are some concerns. Crizanlizumab was not free of toxicity, quality of life via the Brief Pain Inventory used in the trial was not improved, and changes in the pain-severity and pain-interference domains were small. Treatment in SUSTAIN ensued for 52 weeks, so the emergence of late neutralizing antibodies and late toxicities with longer-term therapy will require careful postmarketing assessment.
These concerns notwithstanding, anyone who has cared for sickle cell patients would be excited about the potential benefits crizanlizumab could bring to patient care.
Zanubrutinib
The FDA has approved zanubrutinib for the treatment of MCL in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy. The approval is based on the results of two studies in which overall response rate was the primary endpoint.
BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970) was a phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy. Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120) was a phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation trial of B-cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.
In the phase 2 trial, 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% confidence interval, 74%-91%), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI, 48%-70%) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI, 16.6% to not estimable). In the phase 1/2 dose-escalation trial, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI, 67%-95%), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI, 9%-40%) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI, 12.6% to not estimable). In both trials, median follow-up on study was about 18 months.
The most common adverse reactions were cytopenias, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, bruising, diarrhea, and cough. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia in 11% and hemorrhage in 5% of patients. Of 118 MCL patients, 8 stopped therapy because of an adverse event, most frequently pneumonia (3.4%).
How these results influence practice
Unfortunately, the therapy of recurrent MCL is noncurative, because of the rapid development of treatment resistance. There are multiple single-and multiagent chemotherapy regimens that may be tried, many incorporating immunotherapy options such as anti-CD20- or Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–targeted agents. Given the limited efficacy of these agents, temporary nature of remissions, and paucity of data comparing these various treatment options, participation in clinical trials is encouraged whenever possible.
Outside of a clinical trial, zanubrutinib joins ibrutinib and acalabrutinib as approved single-agent BTK inhibitors for adult MCL patients in relapse. The impressive ORR and response duration reported for zanubrutinib are similar to the results achieved with the other agents, but the toxicity pattern may be slightly different.
As in the treatment of hormonally sensitive breast cancer, clinicians and patients benefit when they have multiple similar, equally efficacious oral agents with slightly different toxicity patterns so that quality of life can be improved and treatment duration maximized before treatment resistance develops and a more toxic and/or inconvenient therapy needs to be employed.
Whether zanubrutinib has benefits beyond those for MCL patients in relapse will depend on the results of confirmatory trials and patient-reported outcome data.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I Will Treat My Next Patient,” I highlight two recent drug approvals by the Food and Drug Administration – crizanlizumab for sickle cell patients with painful crises and zanubrutinib for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) patients in relapse.
Crizanlizumab
P-selectin is an adhesion molecule expressed on activated vascular endothelial cells and platelets. It is a key molecule in the initiation of leukocyte rolling on vessel walls and promotes firm attachment and extravasation to underlying tissues during inflammation. Up-regulation of P-selectin on endothelial cells and platelets contributes to the cell-cell interactions involved in the pathogenesis of sickle cell pain crises.
The SUSTAIN study was a multisite, placebo-controlled, randomized phase 2 trial of two different dosage levels of intravenous crizanlizumab (2.5 mg/kg or 5 mg/kg for 52 weeks), a humanized anti–P-selectin antibody, examining its effect on pain crises in patients with sickle cell disease. The primary endpoint was the annual rate of sickle cell pain crises, with a variety of clinically relevant secondary endpoints. The target population had 2-10 pain crises in the 12 months before enrollment. Patients on a stable dose of hydroxyurea for at least the most recent 3 months were allowed to enter, but if patients were not receiving hydroxyurea, it could not be initiated during the trial. Patients who were undergoing chronic red-cell transfusion therapy were excluded.
Among 198 enrolled patients, 35% did not complete the 52 weeks of treatment. Discontinuations were equally balanced among patients assigned to the high-dose, low-dose, and placebo cohorts. Adverse events associated with crizanlizumab included back pain, nausea, pyrexia, and arthralgia. Serious adverse events occurred in 55 patients, with 5 deaths, all of which were unrelated to treatment. Crizanlizumab did not augment hemolysis or bacterial infections.
In the efficacy analysis, patients receiving high-dose crizanlizumab had a median annual rate of 1.63 health care visits for sickle cell pain crises, compared with 2.98 visits for placebo patients (P = .01). In comparison with placebo, high-dose crizanlizumab also delayed the first pain crisis after starting treatment (4.1 months vs. 1.4 months), delayed the median time to a second pain crisis, and decreased the median number of pain crises annually.
More than twice as many high-dose crizanlizumab patients had no pain crisis episodes, compared with placebo patients. In general, differences were more striking in patients who were not taking hydroxyurea and who had non–hemoglobin SS disease. Differences in the primary endpoint between low-dose crizanlizumab and placebo were numerically, but not statistically, different.
How these results influence practice
It has been over 20 years since a new agent (hydroxyurea) was approved for sickle cell patients and, despite its use, sickle cell pain crises remain a frequent problem. Pain crises are associated with worse quality of life and increased risk of death. A promising advance is badly needed, especially in an era in which sensitivity to providers’ role in the opioid addiction crisis is highly scrutinized and may contribute to future undertreatment of pain episodes. This is especially true for patients from areas with high levels of opioid misuse.
The SUSTAIN trial was international, multi-institutional, placebo-controlled, and inclusive. These attributes enhance the likelihood that crizanlizumab will enhance patient care in routine practice. As an intravenous agent, monitoring adherence and toxicity are less challenging than with hydroxyurea. Despite these factors, however, there are some concerns. Crizanlizumab was not free of toxicity, quality of life via the Brief Pain Inventory used in the trial was not improved, and changes in the pain-severity and pain-interference domains were small. Treatment in SUSTAIN ensued for 52 weeks, so the emergence of late neutralizing antibodies and late toxicities with longer-term therapy will require careful postmarketing assessment.
These concerns notwithstanding, anyone who has cared for sickle cell patients would be excited about the potential benefits crizanlizumab could bring to patient care.
Zanubrutinib
The FDA has approved zanubrutinib for the treatment of MCL in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy. The approval is based on the results of two studies in which overall response rate was the primary endpoint.
BGB-3111-206 (NCT03206970) was a phase 2, open-label, multicenter, single-arm trial of 86 patients with MCL who received at least one prior therapy. Zanubrutinib was given orally at 160 mg twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. BGB-3111-AU-003 (NCT 02343120) was a phase 1/2, open-label, dose-escalation trial of B-cell malignancies, including 32 previously treated MCL patients treated with zanubrutinib at 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily.
In the phase 2 trial, 18fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)–PET scans were required and the ORR was 84% (95% confidence interval, 74%-91%), with a complete response rate of 59% (95% CI, 48%-70%) and a median response duration of 19.5 months (95% CI, 16.6% to not estimable). In the phase 1/2 dose-escalation trial, FDG-PET scans were not required and the ORR was 84% (95% CI, 67%-95%), with a complete response rate of 22% (95% CI, 9%-40%) and a median response duration of 18.5 months (95% CI, 12.6% to not estimable). In both trials, median follow-up on study was about 18 months.
The most common adverse reactions were cytopenias, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, bruising, diarrhea, and cough. The most common serious adverse reactions were pneumonia in 11% and hemorrhage in 5% of patients. Of 118 MCL patients, 8 stopped therapy because of an adverse event, most frequently pneumonia (3.4%).
How these results influence practice
Unfortunately, the therapy of recurrent MCL is noncurative, because of the rapid development of treatment resistance. There are multiple single-and multiagent chemotherapy regimens that may be tried, many incorporating immunotherapy options such as anti-CD20- or Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK)–targeted agents. Given the limited efficacy of these agents, temporary nature of remissions, and paucity of data comparing these various treatment options, participation in clinical trials is encouraged whenever possible.
Outside of a clinical trial, zanubrutinib joins ibrutinib and acalabrutinib as approved single-agent BTK inhibitors for adult MCL patients in relapse. The impressive ORR and response duration reported for zanubrutinib are similar to the results achieved with the other agents, but the toxicity pattern may be slightly different.
As in the treatment of hormonally sensitive breast cancer, clinicians and patients benefit when they have multiple similar, equally efficacious oral agents with slightly different toxicity patterns so that quality of life can be improved and treatment duration maximized before treatment resistance develops and a more toxic and/or inconvenient therapy needs to be employed.
Whether zanubrutinib has benefits beyond those for MCL patients in relapse will depend on the results of confirmatory trials and patient-reported outcome data.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
SOX11 shows value as diagnostic marker in MCL
SOX11 may be an accurate diagnostic marker for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing clinicians to distinguish it from other lymphoproliferative disorders, according to findings from a meta-analysis of 14 case-control studies.
Woojoo Lee, PhD, of Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea, and coinvestigators, evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of MCL. The results were published in PLoS One.
The researchers searched major databases for studies that evaluated the use of SOX11 immunohistochemistry in patients with MCL and other lymphoproliferative disorders. After applying the search parameters, the team identified 383 studies, 14 of which were included in the meta-analysis. Various data were extracted from eligible studies, including the type and clonality of anti-SOX11 antibody, number of SOX11-positive lymphomas (MCLs and other lymphoproliferative disorders), specificity, sensitivity, and others. After combining the data, the investigators calculated pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve. Among the included studies, hairy cell leukemia, Burkitt’s lymphoma, and lymphoblastic lymphoma were common among patient populations. In total, clone MRQ-58 mouse antibodies were used in five study populations.
The researchers found that the pooled specificity was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.9-0.97), and sensitivity was 0.9 (95% CI, 0.86-0.92). There was statistically significant substantial heterogeneity observed for specificity, but not for sensitivity, the investigators reported.
“The results demonstrated that SOX11 was a potential diagnostic marker for MCL,” they wrote. “Meta-regression revealed a significant inverse relationship between specificity and proportions of [Burkitt’s lymphoma, lymphoblastic lymphoma, and hairy cell leukemia].”
With respect to antibody type, the clone MRQ-58 mouse antibody showed consistently high specificity in the clinical setting, despite observed heterogeneity.
“Future studies using MRQ-58 are needed to improve our understanding of the diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry for MCL,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 program (Republic of Korea). The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lee W et al. PLoS One. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225096.
SOX11 may be an accurate diagnostic marker for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing clinicians to distinguish it from other lymphoproliferative disorders, according to findings from a meta-analysis of 14 case-control studies.
Woojoo Lee, PhD, of Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea, and coinvestigators, evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of MCL. The results were published in PLoS One.
The researchers searched major databases for studies that evaluated the use of SOX11 immunohistochemistry in patients with MCL and other lymphoproliferative disorders. After applying the search parameters, the team identified 383 studies, 14 of which were included in the meta-analysis. Various data were extracted from eligible studies, including the type and clonality of anti-SOX11 antibody, number of SOX11-positive lymphomas (MCLs and other lymphoproliferative disorders), specificity, sensitivity, and others. After combining the data, the investigators calculated pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve. Among the included studies, hairy cell leukemia, Burkitt’s lymphoma, and lymphoblastic lymphoma were common among patient populations. In total, clone MRQ-58 mouse antibodies were used in five study populations.
The researchers found that the pooled specificity was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.9-0.97), and sensitivity was 0.9 (95% CI, 0.86-0.92). There was statistically significant substantial heterogeneity observed for specificity, but not for sensitivity, the investigators reported.
“The results demonstrated that SOX11 was a potential diagnostic marker for MCL,” they wrote. “Meta-regression revealed a significant inverse relationship between specificity and proportions of [Burkitt’s lymphoma, lymphoblastic lymphoma, and hairy cell leukemia].”
With respect to antibody type, the clone MRQ-58 mouse antibody showed consistently high specificity in the clinical setting, despite observed heterogeneity.
“Future studies using MRQ-58 are needed to improve our understanding of the diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry for MCL,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 program (Republic of Korea). The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lee W et al. PLoS One. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225096.
SOX11 may be an accurate diagnostic marker for mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing clinicians to distinguish it from other lymphoproliferative disorders, according to findings from a meta-analysis of 14 case-control studies.
Woojoo Lee, PhD, of Inha University, Incheon, Republic of Korea, and coinvestigators, evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry for the diagnosis of MCL. The results were published in PLoS One.
The researchers searched major databases for studies that evaluated the use of SOX11 immunohistochemistry in patients with MCL and other lymphoproliferative disorders. After applying the search parameters, the team identified 383 studies, 14 of which were included in the meta-analysis. Various data were extracted from eligible studies, including the type and clonality of anti-SOX11 antibody, number of SOX11-positive lymphomas (MCLs and other lymphoproliferative disorders), specificity, sensitivity, and others. After combining the data, the investigators calculated pooled sensitivity, specificity, and area under the curve. Among the included studies, hairy cell leukemia, Burkitt’s lymphoma, and lymphoblastic lymphoma were common among patient populations. In total, clone MRQ-58 mouse antibodies were used in five study populations.
The researchers found that the pooled specificity was 0.95 (95% CI, 0.9-0.97), and sensitivity was 0.9 (95% CI, 0.86-0.92). There was statistically significant substantial heterogeneity observed for specificity, but not for sensitivity, the investigators reported.
“The results demonstrated that SOX11 was a potential diagnostic marker for MCL,” they wrote. “Meta-regression revealed a significant inverse relationship between specificity and proportions of [Burkitt’s lymphoma, lymphoblastic lymphoma, and hairy cell leukemia].”
With respect to antibody type, the clone MRQ-58 mouse antibody showed consistently high specificity in the clinical setting, despite observed heterogeneity.
“Future studies using MRQ-58 are needed to improve our understanding of the diagnostic accuracy of SOX11 immunohistochemistry for MCL,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 program (Republic of Korea). The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Lee W et al. PLoS One. 2019 Nov 12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0225096.
FROM PLOS ONE
Acalabrutinib may outperform other targeted therapies in MCL
For patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), second generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib may offer increased response rates and better tolerability compared with other single-agent targeted therapies, based on a recent analysis.
Improved safety could lead to long-term benefits resulting from extended treatment duration, according to lead author Claire Telford, PhD, of AstraZeneca in Gaithersburg, Md., and colleagues. AstraZeneca manufactures acalabrutinib (Calquence).
Currently, treatment for MCL is guided by a number of clinical considerations, the investigators explained in Clinical Therapeutics.
“The type of treatment recommended for relapsed/refractory MCL depends on multiple factors, namely time to the relapse, extent of disease, previous regimens, candidacy for allogeneic stem cell transplantation, and the patient’s overall health,” they wrote.
To determine how acalabrutinib stacks up with other options, the investigators drew data from the phase 2 ACE-LY-004 trial, which tested acalabrutinib in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory MCL. After matching, the investigators compared the ACE-LY-004 outcomes from 12 other trials, in which patients received different targeted therapies.
Results pointed to higher overall response and complete response rates for acalabrutinib, compared with other single-agent targeted therapy. Specifically, acalabrutinib had a higher overall response rate, compared with ibrutinib (9.3% higher), lenalidomide (38.1% higher), temsirolimus (40.7% higher), and bortezomib (50.6% higher). For each of these, complete responses also were higher.
There was no significant difference in overall response or complete response rates between acalabrutinib and rituximab combinations – bendamustine plus rituximab, ibrutinib plus rituximab, and lenalidomide plus rituximab.
The investigators also highlighted a number of safety advantages. Compared with ibrutinib, acalabrutinib was associated with significantly fewer instances of grade 3 or 4 atrial fibrillation. Risk of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia was significantly lower with acalabrutinib than with ibrutinib, bortezomib, lenalidomide, and temsirolimus.
Still, in some instances, acalabrutinib was comparatively less tolerable. It was associated with a higher risk of grade 3 or 4 infections than bendamustine plus rituximab; and anemia was more common among patients receiving acalabrutinib than among those who had lenalidomide plus rituximab or ibrutinib plus rituximab.
“This comparison of targeted therapies used in the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL has shown that acalabrutinib has the potential to provide higher response rates, with trends for longer [progression-free survival] and [overall survival], and an improved safety profile,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Telford is an employee of AstraZeneca and other authors reported financial relationships with the company.
SOURCE: Telford C et al. Clin Ther. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.09.012 .
For patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), second generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib may offer increased response rates and better tolerability compared with other single-agent targeted therapies, based on a recent analysis.
Improved safety could lead to long-term benefits resulting from extended treatment duration, according to lead author Claire Telford, PhD, of AstraZeneca in Gaithersburg, Md., and colleagues. AstraZeneca manufactures acalabrutinib (Calquence).
Currently, treatment for MCL is guided by a number of clinical considerations, the investigators explained in Clinical Therapeutics.
“The type of treatment recommended for relapsed/refractory MCL depends on multiple factors, namely time to the relapse, extent of disease, previous regimens, candidacy for allogeneic stem cell transplantation, and the patient’s overall health,” they wrote.
To determine how acalabrutinib stacks up with other options, the investigators drew data from the phase 2 ACE-LY-004 trial, which tested acalabrutinib in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory MCL. After matching, the investigators compared the ACE-LY-004 outcomes from 12 other trials, in which patients received different targeted therapies.
Results pointed to higher overall response and complete response rates for acalabrutinib, compared with other single-agent targeted therapy. Specifically, acalabrutinib had a higher overall response rate, compared with ibrutinib (9.3% higher), lenalidomide (38.1% higher), temsirolimus (40.7% higher), and bortezomib (50.6% higher). For each of these, complete responses also were higher.
There was no significant difference in overall response or complete response rates between acalabrutinib and rituximab combinations – bendamustine plus rituximab, ibrutinib plus rituximab, and lenalidomide plus rituximab.
The investigators also highlighted a number of safety advantages. Compared with ibrutinib, acalabrutinib was associated with significantly fewer instances of grade 3 or 4 atrial fibrillation. Risk of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia was significantly lower with acalabrutinib than with ibrutinib, bortezomib, lenalidomide, and temsirolimus.
Still, in some instances, acalabrutinib was comparatively less tolerable. It was associated with a higher risk of grade 3 or 4 infections than bendamustine plus rituximab; and anemia was more common among patients receiving acalabrutinib than among those who had lenalidomide plus rituximab or ibrutinib plus rituximab.
“This comparison of targeted therapies used in the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL has shown that acalabrutinib has the potential to provide higher response rates, with trends for longer [progression-free survival] and [overall survival], and an improved safety profile,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Telford is an employee of AstraZeneca and other authors reported financial relationships with the company.
SOURCE: Telford C et al. Clin Ther. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.09.012 .
For patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), second generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib may offer increased response rates and better tolerability compared with other single-agent targeted therapies, based on a recent analysis.
Improved safety could lead to long-term benefits resulting from extended treatment duration, according to lead author Claire Telford, PhD, of AstraZeneca in Gaithersburg, Md., and colleagues. AstraZeneca manufactures acalabrutinib (Calquence).
Currently, treatment for MCL is guided by a number of clinical considerations, the investigators explained in Clinical Therapeutics.
“The type of treatment recommended for relapsed/refractory MCL depends on multiple factors, namely time to the relapse, extent of disease, previous regimens, candidacy for allogeneic stem cell transplantation, and the patient’s overall health,” they wrote.
To determine how acalabrutinib stacks up with other options, the investigators drew data from the phase 2 ACE-LY-004 trial, which tested acalabrutinib in 124 patients with relapsed or refractory MCL. After matching, the investigators compared the ACE-LY-004 outcomes from 12 other trials, in which patients received different targeted therapies.
Results pointed to higher overall response and complete response rates for acalabrutinib, compared with other single-agent targeted therapy. Specifically, acalabrutinib had a higher overall response rate, compared with ibrutinib (9.3% higher), lenalidomide (38.1% higher), temsirolimus (40.7% higher), and bortezomib (50.6% higher). For each of these, complete responses also were higher.
There was no significant difference in overall response or complete response rates between acalabrutinib and rituximab combinations – bendamustine plus rituximab, ibrutinib plus rituximab, and lenalidomide plus rituximab.
The investigators also highlighted a number of safety advantages. Compared with ibrutinib, acalabrutinib was associated with significantly fewer instances of grade 3 or 4 atrial fibrillation. Risk of grade 3 or 4 thrombocytopenia was significantly lower with acalabrutinib than with ibrutinib, bortezomib, lenalidomide, and temsirolimus.
Still, in some instances, acalabrutinib was comparatively less tolerable. It was associated with a higher risk of grade 3 or 4 infections than bendamustine plus rituximab; and anemia was more common among patients receiving acalabrutinib than among those who had lenalidomide plus rituximab or ibrutinib plus rituximab.
“This comparison of targeted therapies used in the treatment of relapsed/refractory MCL has shown that acalabrutinib has the potential to provide higher response rates, with trends for longer [progression-free survival] and [overall survival], and an improved safety profile,” the investigators wrote.
The study was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Telford is an employee of AstraZeneca and other authors reported financial relationships with the company.
SOURCE: Telford C et al. Clin Ther. 2019 Nov 4. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.09.012 .
FROM CLINICAL THERAPEUTICS
FDA approves Brukinsa for relapsed, refractory MCL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved zanubrutinib (Brukinsa) for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma (MCL) in adult patients who have received at least one prior therapy.
The approval is based on results from two separate studies; in a global phase 1/2 trial, patients with relapsed or refractory MCL who received zanubrutinib had an overall response rate of 84%, with 22% experiencing a complete response and 62% experiencing partial response. Median duration of response was 18.5 months. The ORR in the second study – a multicenter phase 2 trial – was also 84%, but with 59% experiencing a complete response and 24% experiencing partial response; duration of response was 19.5 months.
The most common adverse events reported during the trials were decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, upper respiratory tract infection, decreased white blood cell count, decreased hemoglobin, rash, bruising, diarrhea, cough, musculoskeletal pain, pneumonia, urinary tract infection, hematuria, fatigue, constipation, and hemorrhage. The most common serious adverse events were pneumonia and hemorrhage.
Of the 118 patients with MCL treated with zanubrutinib over the two trials, 8 had to be discontinued because of adverse events.
The recommended dose of zanubrutinib is 320 mg, taken orally 160 mg twice daily or 320 mg once daily, with or without food.
“BTK [Bruton kinase] inhibition is an established mode of treatment for patients with MCL, but many patients treated with previously approved BTK inhibitors do not fully respond to BTK therapy or are forced to discontinue treatment early due to side effects. Today we have a new option for our adult patients who have received one prior systemic or targeted therapy and are living with MCL,” Luhua (Michael) Wang, MD, clinical trial investigator and professor in the department of lymphoma and myeloma at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, said in a statement.
Survival ‘excellent’ after rituximab-bendamustine induction in transplant-eligible MCL
The combination of rituximab and bendamustine (RB) provided “excellent” survival with less toxicity, compared with a cytarabine-based induction regimen, in transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma, according to a long-term follow-up report from randomized phase 2 trial.
The 5-year survival rates for RB were “provocatively similar” to what was achieved with the standard, intensive R-hyperCVAD regimen, investigators said in this update on the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S1106 study.
By contrast, the R-hyperCVAD regimen was associated with more toxicity and higher failure rates for stem cell mobilization, according to the report’s lead author, Manali Kamdar, MD, of the University of Colorado, Denver, and coauthors.
“Overall, S1106 demonstrated that an outpatient-based, less intensive induction therapy of bendamustine plus rituximab is highly effective, safe, and durable in untreated transplant-eligible MCL patients,” Dr. Kamdar and her colleagues reported in Blood Advances.
The results have guided the design of an upcoming study, EA4181, in which patients with mantle cell lymphoma will be treated with an RB backbone plus cytarabine, the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib, or both, according to the authors.
In the present study, S1106, patients with mantle cell lymphoma were randomized to receive RB or the R-hyperCVAD regimen, which consisted of rituximab with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, alternating with high-dose cytarabine and methotrexate. Both regimens were followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The stem cell mobilization failure rate was 29% in the R-hyperCVAD arm in an interim analysis conducted after 53 of a planned 160 patients had been enrolled, including 35 in the RB arm and 17 in the R-hyperCVAD arm, according to a report published in the British Journal of Haematology (2016 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14480). That analysis triggered a shutdown of the study, based on a rule stating that either arm would be deemed “unacceptably toxic” if the mobilization rate exceeded 10%.
Accordingly, R-hyperCVAD is “not an ideal platform” for future trials, the investigators said. At that time, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 81% versus 82% for RB and R-hyperCVAD, respectively, while overall survival (OS) was 87% versus 88%.
With additional follow-up, the 5-year PFS is 66% and 62% in the RB and R-hyperCVAD arms, respectively, while 5-year OS is 80% and 74%, according to the investigators.
The RB regimen also results in “excellent” minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, they added.
MRD status was evaluated in 12 paired pre- and postinduction therapy specimens, of which 2 pairs were from patients in the R-hyperCVAD arm, and 10 pairs were from patients in the RB arm.
In the R-hyperCVAD arm, both patients were MRD positive at baseline, and MRD negative after induction, according to the investigators. Similarly, 9 of 10 patients in the RB arm were MRD positive at baseline, and of those, 7 converted to MRD negative following induction.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, and in part by Sequenta (Adaptive Biotechnologies). Dr. Kamdar reported being on the speakers bureau of Seattle Genetics and receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Celgene, and Genentech. Co-authors of the study provided disclosures related to Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Affimed, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, and Merck, among others.
SOURCE: Kamdar M et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 22;3(20):3132-5.
The combination of rituximab and bendamustine (RB) provided “excellent” survival with less toxicity, compared with a cytarabine-based induction regimen, in transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma, according to a long-term follow-up report from randomized phase 2 trial.
The 5-year survival rates for RB were “provocatively similar” to what was achieved with the standard, intensive R-hyperCVAD regimen, investigators said in this update on the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S1106 study.
By contrast, the R-hyperCVAD regimen was associated with more toxicity and higher failure rates for stem cell mobilization, according to the report’s lead author, Manali Kamdar, MD, of the University of Colorado, Denver, and coauthors.
“Overall, S1106 demonstrated that an outpatient-based, less intensive induction therapy of bendamustine plus rituximab is highly effective, safe, and durable in untreated transplant-eligible MCL patients,” Dr. Kamdar and her colleagues reported in Blood Advances.
The results have guided the design of an upcoming study, EA4181, in which patients with mantle cell lymphoma will be treated with an RB backbone plus cytarabine, the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib, or both, according to the authors.
In the present study, S1106, patients with mantle cell lymphoma were randomized to receive RB or the R-hyperCVAD regimen, which consisted of rituximab with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, alternating with high-dose cytarabine and methotrexate. Both regimens were followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The stem cell mobilization failure rate was 29% in the R-hyperCVAD arm in an interim analysis conducted after 53 of a planned 160 patients had been enrolled, including 35 in the RB arm and 17 in the R-hyperCVAD arm, according to a report published in the British Journal of Haematology (2016 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14480). That analysis triggered a shutdown of the study, based on a rule stating that either arm would be deemed “unacceptably toxic” if the mobilization rate exceeded 10%.
Accordingly, R-hyperCVAD is “not an ideal platform” for future trials, the investigators said. At that time, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 81% versus 82% for RB and R-hyperCVAD, respectively, while overall survival (OS) was 87% versus 88%.
With additional follow-up, the 5-year PFS is 66% and 62% in the RB and R-hyperCVAD arms, respectively, while 5-year OS is 80% and 74%, according to the investigators.
The RB regimen also results in “excellent” minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, they added.
MRD status was evaluated in 12 paired pre- and postinduction therapy specimens, of which 2 pairs were from patients in the R-hyperCVAD arm, and 10 pairs were from patients in the RB arm.
In the R-hyperCVAD arm, both patients were MRD positive at baseline, and MRD negative after induction, according to the investigators. Similarly, 9 of 10 patients in the RB arm were MRD positive at baseline, and of those, 7 converted to MRD negative following induction.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, and in part by Sequenta (Adaptive Biotechnologies). Dr. Kamdar reported being on the speakers bureau of Seattle Genetics and receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Celgene, and Genentech. Co-authors of the study provided disclosures related to Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Affimed, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, and Merck, among others.
SOURCE: Kamdar M et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 22;3(20):3132-5.
The combination of rituximab and bendamustine (RB) provided “excellent” survival with less toxicity, compared with a cytarabine-based induction regimen, in transplant-eligible patients with mantle cell lymphoma, according to a long-term follow-up report from randomized phase 2 trial.
The 5-year survival rates for RB were “provocatively similar” to what was achieved with the standard, intensive R-hyperCVAD regimen, investigators said in this update on the Southwest Oncology Group (SWOG) S1106 study.
By contrast, the R-hyperCVAD regimen was associated with more toxicity and higher failure rates for stem cell mobilization, according to the report’s lead author, Manali Kamdar, MD, of the University of Colorado, Denver, and coauthors.
“Overall, S1106 demonstrated that an outpatient-based, less intensive induction therapy of bendamustine plus rituximab is highly effective, safe, and durable in untreated transplant-eligible MCL patients,” Dr. Kamdar and her colleagues reported in Blood Advances.
The results have guided the design of an upcoming study, EA4181, in which patients with mantle cell lymphoma will be treated with an RB backbone plus cytarabine, the BTK inhibitor acalabrutinib, or both, according to the authors.
In the present study, S1106, patients with mantle cell lymphoma were randomized to receive RB or the R-hyperCVAD regimen, which consisted of rituximab with hyperfractionated cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, and dexamethasone, alternating with high-dose cytarabine and methotrexate. Both regimens were followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
The stem cell mobilization failure rate was 29% in the R-hyperCVAD arm in an interim analysis conducted after 53 of a planned 160 patients had been enrolled, including 35 in the RB arm and 17 in the R-hyperCVAD arm, according to a report published in the British Journal of Haematology (2016 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/bjh.14480). That analysis triggered a shutdown of the study, based on a rule stating that either arm would be deemed “unacceptably toxic” if the mobilization rate exceeded 10%.
Accordingly, R-hyperCVAD is “not an ideal platform” for future trials, the investigators said. At that time, the estimated 2-year progression-free survival (PFS) was 81% versus 82% for RB and R-hyperCVAD, respectively, while overall survival (OS) was 87% versus 88%.
With additional follow-up, the 5-year PFS is 66% and 62% in the RB and R-hyperCVAD arms, respectively, while 5-year OS is 80% and 74%, according to the investigators.
The RB regimen also results in “excellent” minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity, they added.
MRD status was evaluated in 12 paired pre- and postinduction therapy specimens, of which 2 pairs were from patients in the R-hyperCVAD arm, and 10 pairs were from patients in the RB arm.
In the R-hyperCVAD arm, both patients were MRD positive at baseline, and MRD negative after induction, according to the investigators. Similarly, 9 of 10 patients in the RB arm were MRD positive at baseline, and of those, 7 converted to MRD negative following induction.
The research was supported by the National Cancer Institute, and in part by Sequenta (Adaptive Biotechnologies). Dr. Kamdar reported being on the speakers bureau of Seattle Genetics and receiving consultancy fees from AstraZeneca, Celgene, and Genentech. Co-authors of the study provided disclosures related to Millennium Pharmaceuticals, Affimed, Seattle Genetics, Pharmacyclics, and Merck, among others.
SOURCE: Kamdar M et al. Blood Adv. 2019 Oct 22;3(20):3132-5.
FROM BLOOD ADVANCES