User login
Short Interval Repeat Colonoscopy After Inadequate Bowel Preparation Is Low Among Veterans
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
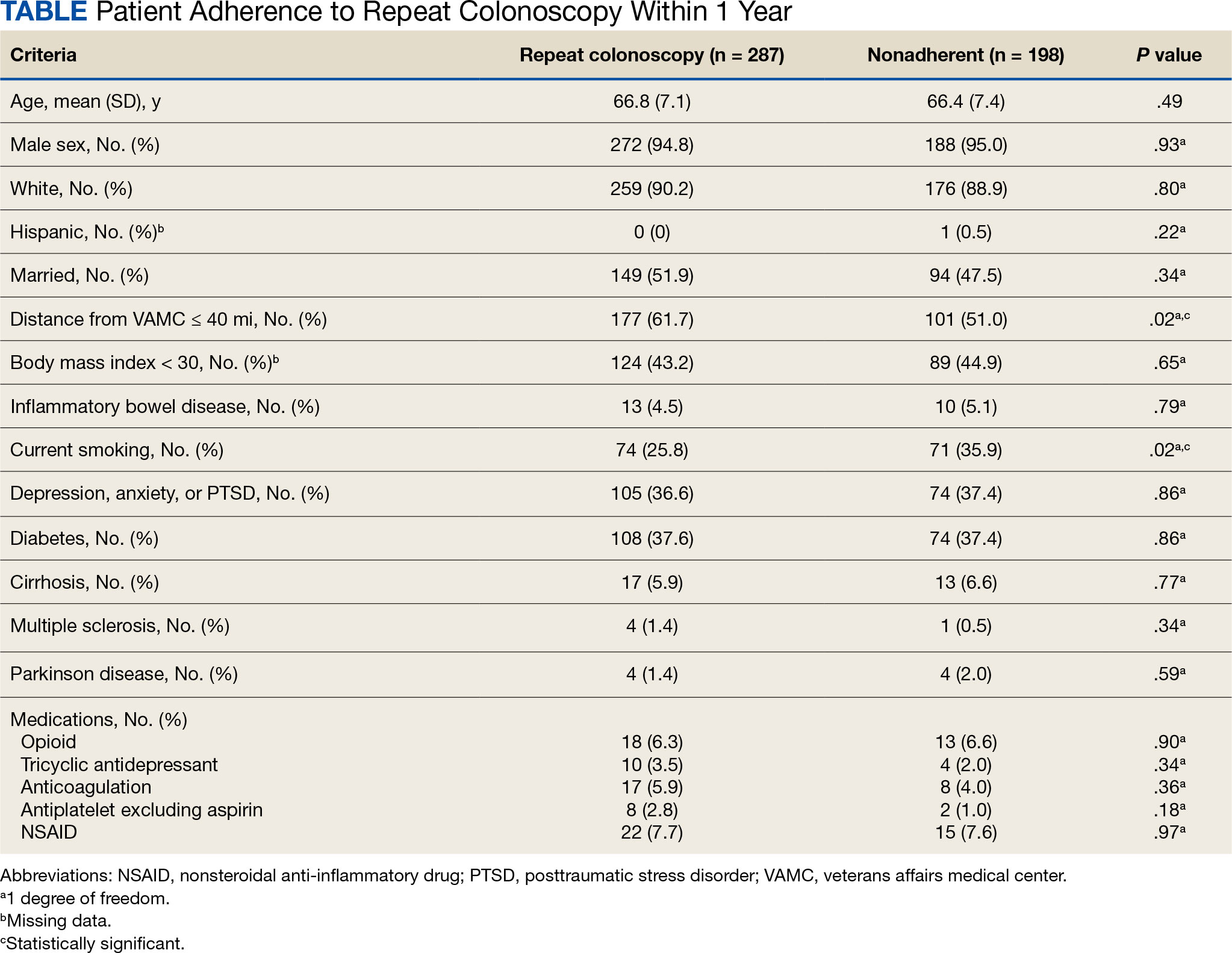
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.
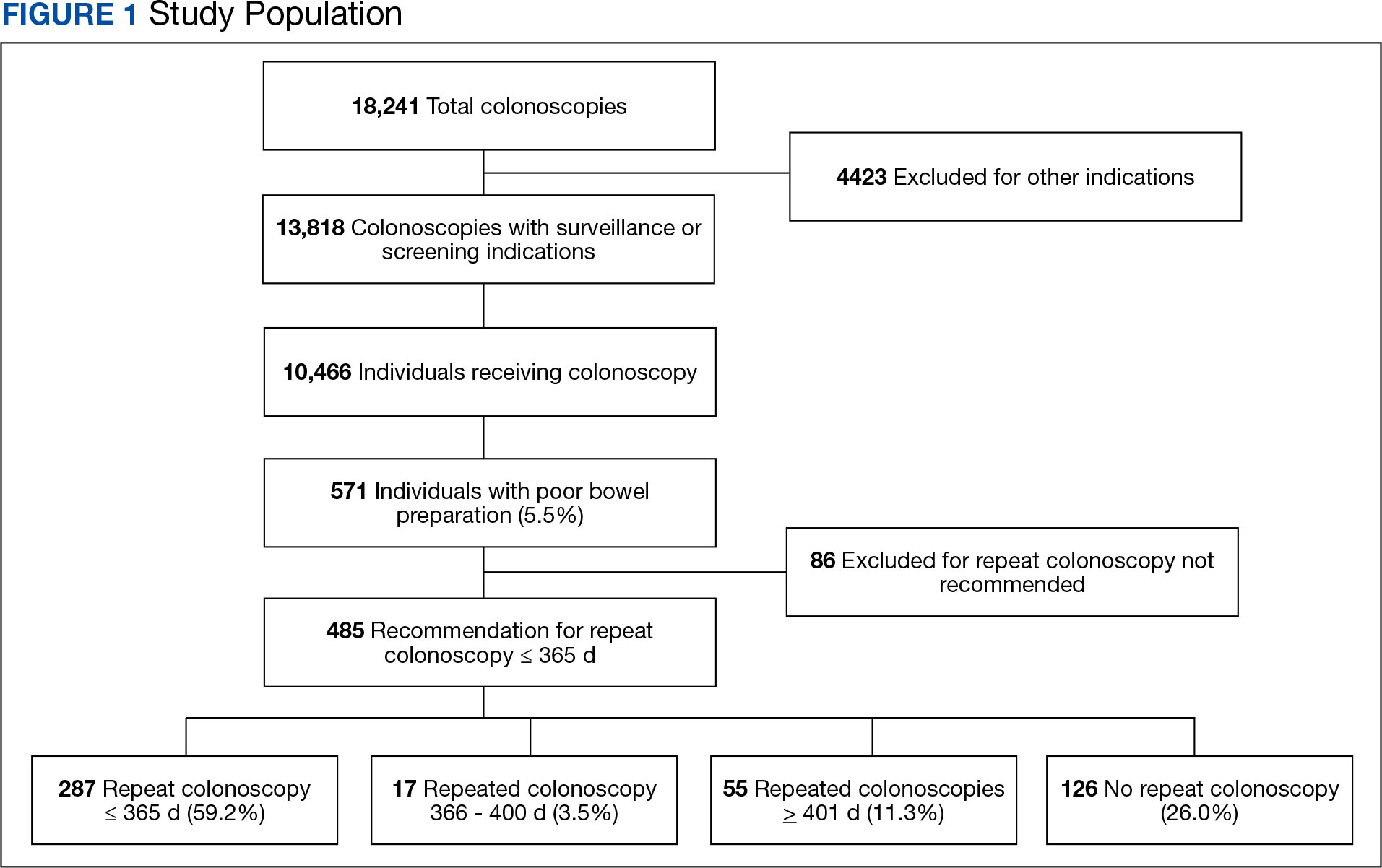
Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
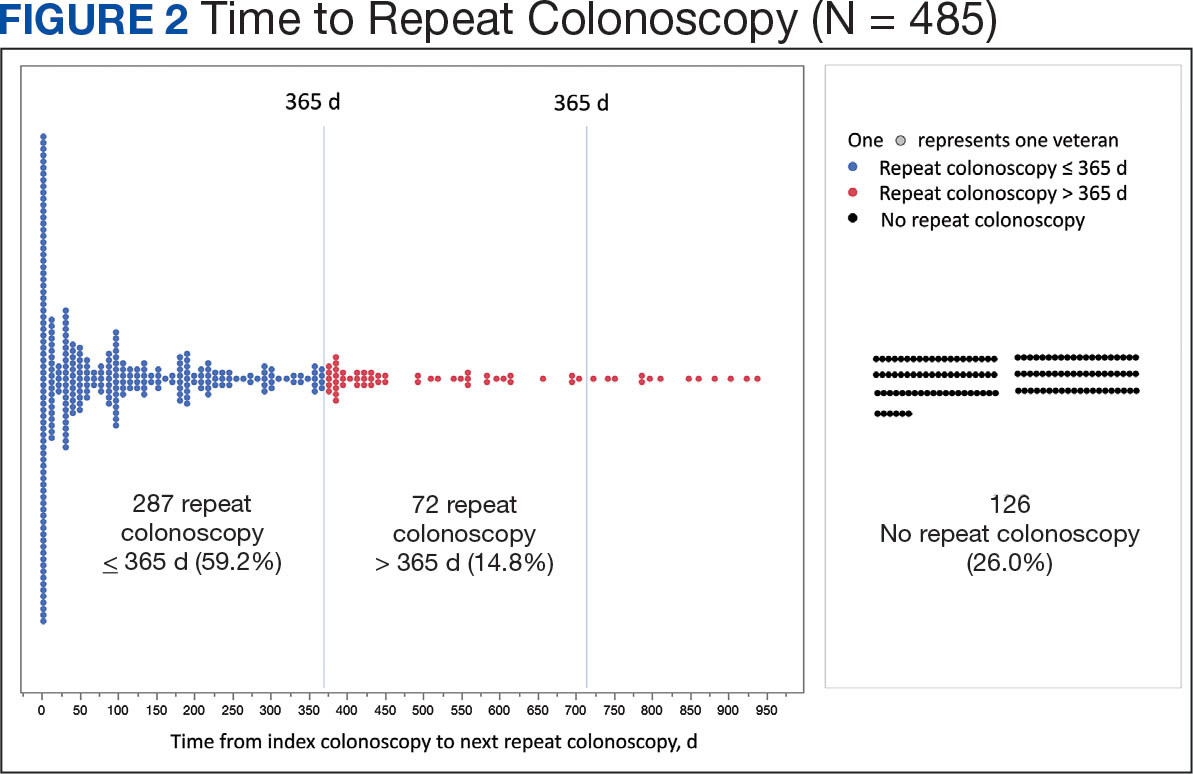
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).
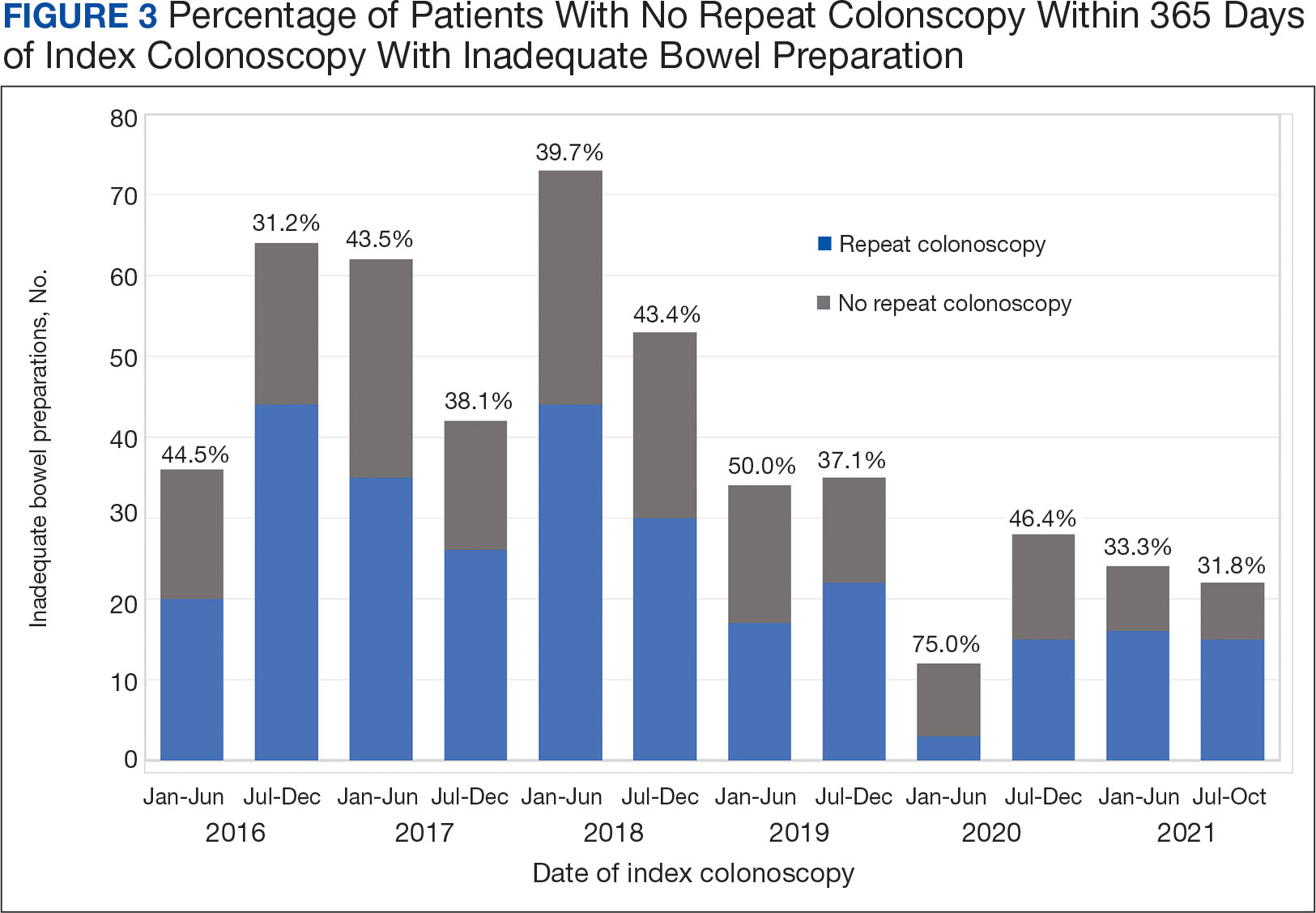
To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).
Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.


Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).

To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).

Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third-most diagnosed cancer after breast and lung cancer, and is the second leading cause of global cancer related deaths.1 In 2023 in the United States, > 150,000 individuals were diagnosed with CRC and 52,000 died.2
Colonoscopy is an effective CRC screening method and the lone method recommended for polyp surveillance. Inadequate bowel preparation (IBP) has been estimated to occur in about 6% to 26% of colonoscopies. 3,4 The prevalence varies based on a variety of comorbidities, including immobility, diabetes mellitus, neurologic disorders, and use of opioids, with more occurrences of IBP noted in older adult, non-English speaking, and male individuals.4-6
The quality of bowel preparation is integral to the effectiveness of screening and surveillance colonoscopies. IBP has been associated with missed adenomas and significantly lower adenoma detection rates.7-9 In particular, IBP is independently associated with an increased risk of CRC in the future.3 Accordingly, the US Multisociety Task Force recommends repeat colonoscopies for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 Ensuring that these individuals receive repeat colonoscopies is an essential part of CRC prevention. The benefit of repeat colonoscopy after IBP is highlighted by a retrospective analysis from Fung and colleagues that showed 81% of repeat colonoscopies had adequate bowel preparation, with higher numbers of adenomas detected on repeat compared to initial colonoscopies.11
Given the impact of bowel preparation quality on the diagnostic capability of the colonoscopy, adherence to guidelines for repeat colonoscopies in cases of IBP is paramount for effective CRC prevention. This study aims to measure the frequency of repeat colonoscopy after IBP and the factors associated with adherence to recommendations.
METHODS
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy at the Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center (MVAMC) from January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, were identified to allow for 400 days of follow-up from the index colonoscopy to the data collection date. During the COVID-19 pandemic, the colonoscopy procedure capacity was reduced by 50% from June 1, 2020, to December 1, 2020, delaying nonurgent procedures, including screening and surveillance colonoscopies.
Individuals who underwent colonoscopy for CRC screening or polyp surveillance, or following a positive fecal immunohistochemistry test (FIT) or virtual computed tomography colonoscopy were included. Patients with colonoscopy indications for iron deficiency anemia, gastrointestinal bleeding, disease activity assessment of inflammatory bowel disease, abdominal pain, or changes in bowel movement pattern were excluded. IBP was defined as recording a Boston Bowel Preparation Scale (BBPS) score of < 6, or < 2 in any segment, or described as poor or inadequate using the Aronchick scale.
Age, sex, race, marital status, distance to MVAMC, smoking status, comorbidities, and concurrent medication use, including antiplatelet, anticoagulation, and prescription opiates at the time of index colonoscopy were obtained from the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Corporate Data Warehouse (CDW) using structured query language processing of colonoscopy procedure notes to extract preparation scores and other procedure information. The CDW contains extracts from VHA clinical and administrative systems that contain complete clinical data from October 1999.12 Current smoking status was defined as any smoking activity at the time the questionnaire was administered during a routine clinic visit within 400 days from the index colonoscopy.
Only individuals who were recommended to have repeat colonoscopy within 1 year were included. The intervals of 365 days and 400 days (1 year + about 1 additional month) were used in the event that the individual had a delay in scheduling their 1-year repeat colonoscopy. For individuals who did not undergo a colonoscopy at MVAMC within 400 days, a manual chart review of all available records was performed to determine whether a colonoscopy was performed at a non-VA facility.
Patients received written instructions for bowel preparation 2 weeks prior to the procedure. The preparation included magnesium citrate and a split dose of 4 liters of polyethylene glycol. Patients were also advised to start a low-fiber diet 3 days prior to the procedure and a clear liquid diet the day before the procedure. Patients with a history of IBP or those undergoing procedures with anesthesia received an additional 2 liters for a total of 6 liters of polyethylene glycol.
Statistical analysis
Baseline characteristics were reported as mean (SD) or median and IQR for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. Individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were compared to those who did not identify factors associated with adherence to recommendations. The data on individuals who returned for colonoscopy within 400 days were also analyzed for additional minor delays in the timing of the repeat colonoscopy. Continuous data were compared using Mann-Whitney U tests. Categorical data were compared using X2 or Fisher exact tests. Missing data were imputed from the analyses. All analyses were performed using SAS JMP Pro version 16. P < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
There were 18,241 total colonoscopies performed between January 1, 2016, to October 19, 2021, and 13,818 colonoscopies had indications for screening for colon cancer, positive FIT, virtual colonoscopy, or surveillance. Of the 10,466 unique patients there were 5369 patients for polyp surveillance, 4054 patients for CRC screening, and 1043 patients for positive FIT or virtual colonoscopy. Of these, 571 individuals (5.5%) had IBP. Repeat colonoscopy within 1 year was recommended for 485 individuals (84.9%) who were included in this study (153 CRC screenings and 46 positive FITs) but not for 86 individuals (15.1%) (Figure 1). Among included patients, the mean (SD) age was 66.6 (7.2) years, and the majority were male (460 [94.8%]) and White (435 [89.7%]) (Table). Two hundred and forty-three (50.1%) were married.


Adherence to Recommended Interval Colonoscopy
Of the 485 patients with IBP who were recommended for follow-up colonoscopy, 287 (59.2%) had a colonoscopy within 1 year, and 198 (40.8%) did not; 17 patients (13.5%) had repeat colonoscopy within 366 to 400 days. Five (1.0%) individuals had a repeat colonoscopy the next day, and 77 (15.9%) had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days. One hundred and twentysix (26.0%) individuals underwent no repeat colonoscopy during the study period (Figure 2).

To account for the COVID-19 pandemic, the adherence rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year prepandemic (January 1, 2016, to December 1, 2018) was calculated along with the adherence rate postpandemic (January 1, 2019 to the end of the study). The rates were similar: 199 of 330 (60.3%) individuals prepandemic vs 88 of 155 (56.8%) individuals postpandemic (Figure 3).

Significant Associations
Age, sex, and race were not associated with adherence to repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Individuals living ≤ 40 miles from the endoscopy center were more likely to undergo a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year compared with those who lived > 40 miles away (61.7% vs 51.0%, P = .02). Current smoking status was associated with a lower rate of repeat colonoscopy within 1 year (25.8% vs 35.9%; P = .02). There were no differences with respect to inflammatory bowel disease diagnosis, mental health diagnosis, diabetes mellitus, cirrhosis, or medications used, including opioids, anticoagulation, and antiplatelet therapy.
Outcomes
Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy the day after the index colonoscopy, 53 of 56 individuals (94.6%) had adequate bowel preparation. Among individuals who had a repeat colonoscopy within 7 days, 70 of 77 (90.9%) had adequate bowel preparation. Of 287 individuals with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year, 251 (87.5%) had adequate bowel preparation on the repeat colonoscopy. By 400 days after the index colonoscopy, 268 of 304 individuals (88.2%) had adequate bowel preparation.
In this study conducted at a large VA medical center, we found that 5.6% of individuals undergoing colonoscopies had IBP, a rate comparable to prior studies (6% to 26%).3,4 Only 59.2% of individuals underwent repeat colonoscopies within 1 year, as recommended after an index colonoscopy with IBP. Smoking and living longer distances (> 40 miles) from the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation.
Current guidelines recommend repeat colonoscopy for individuals with IBP within 1 year.10 In cases of IBP, the advanced adenoma miss rate is 36% upon repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.13 Despite the importance of a follow-up colonoscopy, clinician adherence with this recommendation remains low.10,14,15 However, in this study cohort, 485 of 571 individuals with IBP (84.9%) received recommendations for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. In the US, only 31.9% of 260,314 colonoscopies with IBP included recommendations for a follow-up colonoscopy within 1 year.14 This could be related to variations in endoscopist practice as well as patient risk factors for developing polyps, including family history of cancer and personal history of prior polyps. The findings of multiple polyps, high-risk adenomas, and cancer on the index colonoscopy also influences the endoscopist for repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.14
The timing for repeat colonoscopies within 1 year will be determined by the patients, clinicians, and available scheduling. In this study, the earlier repeat colonoscopies, especially those occurring the day after the index colonoscopy, had the highest success rate of adequate bowel preparation. In a prior study, repeating colonoscopies within the same day or the next day was also found to have a higher rate of adequate bowel preparation than repeat colonoscopies within 1 year (88.9% vs 83.5%).16
Ensuring the return of individuals with IBP for repeat colonoscopy is a challenging task. We identified that individuals who live further away from MVAMC and current smokers had a decreased probability of returning for a repeat colonoscopy. Toro and colleagues found a 68.7% return rate for a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year with individuals age ≥ 60 years, and patients who were White were less likely to proceed with a repeat colonoscopy within 1 year.17 The study did not provide data regarding smoking status or distance to the endoscopy center.17 In a prior study of veterans, the dual diagnosis of psychiatric disorders and substance abuse was associated with missed and canceled colonoscopy appointments.18 The distance to the endoscopy center has also been previously identified as a barrier to a colonoscopy following an abnormal FIT.19 Although not identified in this study due to the homogenous demographic profile, social determinants of health such as socioeconomic status, education, and insurance coverage are known barriers to cancer screening but were not evaluated in this study.20
Based on the identified risk factors, we have created a model for utilizing those risk factors to identify individuals at higher risk for noncompliance (ie, those who live further away from the endoscopy center or currently smoke). These individuals are proactively offered to use an intraprocedural bowel cleansing device to achieve adequate bowel preparation or priority rescheduling for a next-day colonoscopy.
Limitations
This study was a single-center study of the veteran population, which is predominantly White and male, thus limiting generalizability. The study is also limited by minimal available data on adenoma detection and colon cancer incidence on subsequent colonoscopies.
CONCLUSIONS
The rate of IBP was 5.5% in individuals undergoing colonoscopy for colon cancer screening, surveillance, positive FIT, or computed tomography colonography. Only 59.2% of those with IBP underwent the recommended repeat colonoscopy within 1 year. Smoking and distance to the endoscopy center were associated with a decreased adherence to the repeat colonoscopy recommendation. Additional efforts are needed to ensure that individuals with IBP return for timely repeat colonoscopy.
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209-249. doi:10.3322/caac.21660
- Siegel RL, Wagle NS, Cercek A, Smith RA, Jemal A. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023;73(3):233-254. doi:10.3322/caac.21772
- Atkin W, Wooldrage K, Brenner A, et al. Adenoma surveillance and colorectal cancer incidence: a retrospective, multicentre, cohort study. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18(6):823- 834. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30187-0
- Froehlich F, Wietlisbach V, Gonvers JJ, Burnand B, Vader JP. Impact of colonic cleansing on quality and diagnostic yield of colonoscopy: the European Panel of Appropriateness of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy European multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005;61(3):378- 384. doi:10.1016/s0016-5107(04)02776-2
- Mahmood S, Farooqui SM, Madhoun MF. Predictors of inadequate bowel preparation for colonoscopy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;30(8):819-826. doi:10.1097/MEG.0000000000001175
- ASGE Standards of Practice Committee, Saltzman JR, Cash BD, et al. Bowel preparation before colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015;81(4):781-794. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2014.09.048
- Clark BT, Protiva P, Nagar A, et al. Quantification of Adequate Bowel Preparation for Screening or Surveillance Colonoscopy in Men. Gastroenterology. 2016;150(2):396- e15. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2015.09.041
- Sulz MC, Kröger A, Prakash M, Manser CN, Heinrich H, Misselwitz B. Meta-Analysis of the Effect of Bowel Preparation on Adenoma Detection: Early Adenomas Affected Stronger than Advanced Adenomas. PLoS One. 2016;11(6):e0154149. Published 2016 Jun 3. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0154149
- Chokshi RV, Hovis CE, Hollander T, Early DS, Wang JS. Prevalence of missed adenomas in patients with inadequate bowel preparation on screening colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012;75(6):1197-1203. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2012.01.005
- Lieberman DA, Rex DK, Winawer SJ, Giardiello FM, Johnson DA, Levin TR. Guidelines for colonoscopy surveillance after screening and polypectomy: a consensus update by the US Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2012;143(3):844-857. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2012.06.001
- Fung P, Syed A, Cole R, Farah K. Poor bowel prep: are you really going to come back within a year? Abstract presented at American Gastroenterological Association DDW 2021, May 21-23, 2021. doi:10.1016/S0016-5085(21)01204-X
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, VA Health Systems Research. Corporate data warehouse (CDW). Updated January 11, 2023. Accessed August 6, 2024. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/for_researchers/cdw.cfm
- Lebwohl B, Kastrinos F, Glick M, Rosenbaum AJ, Wang T, Neugut AI. The impact of suboptimal bowel preparation on adenoma miss rates and the factors associated with early repeat colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011;73(6):1207-1214. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2011.01.051
- Calderwood AH, Holub JL, Greenwald DA. Recommendations for follow-up interval after colonoscopy with inadequate bowel preparation in a national colonoscopy quality registry. Gastrointest Endosc. 2022;95(2):360-367. e2. doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.09.027
- Latorre M, Roy A, Spyrou E, Garcia-Carrasquillo R, Rosenberg R, Lebwohl B. Adherence to guidelines after poor colonoscopy preparation: experience from a patient navigator program. Gastroenterology. 2016;151(1):P196. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2016.05.027
- Bouquet E, Tomal J, Choksi Y. Next-day screening colonoscopy following inadequate bowel preparation may improve quality of preparation and adenoma detection in a veteran population. Am J Gastroenterol. 2020;115:S259. doi:10.14309/ajg.0000000000000853
- Toro B, Dawkins G, Friedenberg FK, Ehrlich AC. Risk factors for failure to return after a poor preparation colonoscopy: experience in a safety-net hospital, 255. Abstract presented at ACG October 2016. https://journals.lww.com/ajg/fulltext/2016/10001/risk_factors_for_failure_to_return_after_a_poor.255.aspx
- Partin MR, Gravely A, Gellad ZF, et al. Factors Associated With Missed and Cancelled Colonoscopy Appointments at Veterans Health Administration Facilities. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14(2):259-267. doi:10.1016/j.cgh.2015.07.051
- Idos GE, Bonner JD, Haghighat S, et al. Bridging the Gap: Patient Navigation Increases Colonoscopy Follow-up After Abnormal FIT. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12(2):e00307. doi:10.14309/ctg.0000000000000307
- Islami F, Baeker Bispo J, Lee H, et al. American Cancer Society’s report on the status of cancer disparities in the United States, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024;74(2):136- 166. doi:10.3322/caac.21812
Presence of Central Sensitization Should Be Considered During PsA Treatment
Key clinical point: Nearly two out of three patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had clinically significant central sensitization (CS), with the severity of psoriasis, anxiety level, and sleep quality being independent predictors of worse CS Inventory (CSI) scores.
Major finding: Overall, 65.1% patients had clinically significant CS, with a CSI score ≥ 40, with the severity of psoriasis and disease activity scores for PsA being positively associated with CSI scores (correlation coefficient 0.393-0.652; P < .001). The Psoriasis Area Severity Index (odds ratio [OR] 9.70; P = .017), General Anxiety Disorder-7 (OR 2.89; P = .014), and Insomnia Severity Index (OR 5.56; P = .041) scores were independent predictors of CS.
Study details: This cross-sectional observational study included 103 patients with PsA (age 18-75 years) with a mean CSI score of 45.4.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any financial support. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kaya MN, Tecer D, Kılıç Ö, et al. Impact of central sensitization on clinical and functional aspects of psoriatic arthritis. Medicina. 2024;60(9):1449 (Sept 4). Source
Key clinical point: Nearly two out of three patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had clinically significant central sensitization (CS), with the severity of psoriasis, anxiety level, and sleep quality being independent predictors of worse CS Inventory (CSI) scores.
Major finding: Overall, 65.1% patients had clinically significant CS, with a CSI score ≥ 40, with the severity of psoriasis and disease activity scores for PsA being positively associated with CSI scores (correlation coefficient 0.393-0.652; P < .001). The Psoriasis Area Severity Index (odds ratio [OR] 9.70; P = .017), General Anxiety Disorder-7 (OR 2.89; P = .014), and Insomnia Severity Index (OR 5.56; P = .041) scores were independent predictors of CS.
Study details: This cross-sectional observational study included 103 patients with PsA (age 18-75 years) with a mean CSI score of 45.4.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any financial support. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kaya MN, Tecer D, Kılıç Ö, et al. Impact of central sensitization on clinical and functional aspects of psoriatic arthritis. Medicina. 2024;60(9):1449 (Sept 4). Source
Key clinical point: Nearly two out of three patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) had clinically significant central sensitization (CS), with the severity of psoriasis, anxiety level, and sleep quality being independent predictors of worse CS Inventory (CSI) scores.
Major finding: Overall, 65.1% patients had clinically significant CS, with a CSI score ≥ 40, with the severity of psoriasis and disease activity scores for PsA being positively associated with CSI scores (correlation coefficient 0.393-0.652; P < .001). The Psoriasis Area Severity Index (odds ratio [OR] 9.70; P = .017), General Anxiety Disorder-7 (OR 2.89; P = .014), and Insomnia Severity Index (OR 5.56; P = .041) scores were independent predictors of CS.
Study details: This cross-sectional observational study included 103 patients with PsA (age 18-75 years) with a mean CSI score of 45.4.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any financial support. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kaya MN, Tecer D, Kılıç Ö, et al. Impact of central sensitization on clinical and functional aspects of psoriatic arthritis. Medicina. 2024;60(9):1449 (Sept 4). Source
Bimekizumab Shows Long-Term Safety and Efficacy in Biologic-Naive and TNFi-IR PsA Patients
Key clinical point: Bimekizumab demonstrated consistent safety and sustained efficacy for up to 2 years in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were biologic-naive or inadequately responsive to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: From weeks 52 to 104, the incidence of treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) was consistent with previous studies, with no new safety signals. SARS-CoV2 infection (18.6 per 100 patient-years) was the most common TEAE. Approximately 50% biologic-naive and TNFi-IR patients maintained a ≥50% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology response.
Study details: This open-label extension (BE-VITAL) of two phase 3 trials included biologic-naive (n = 852) and TNFi-IR (n = 400) patients with PsA who were randomly assigned to receive bimekizumab, placebo with crossover to bimekizumab at week 16, or adalimumab followed by bimekizumab at week 52.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by UCB Pharma. Five authors declared being employees or shareholders of UCB Pharma. LC Coates declared being an editorial board member of Rheumatology and Therapy. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including UCB.
Source: Mease PJ, Merola JF, Tanaka Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of bimekizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis: 2-year results from two phase 3 studies. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Aug 31). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00708-8 Source
Key clinical point: Bimekizumab demonstrated consistent safety and sustained efficacy for up to 2 years in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were biologic-naive or inadequately responsive to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: From weeks 52 to 104, the incidence of treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) was consistent with previous studies, with no new safety signals. SARS-CoV2 infection (18.6 per 100 patient-years) was the most common TEAE. Approximately 50% biologic-naive and TNFi-IR patients maintained a ≥50% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology response.
Study details: This open-label extension (BE-VITAL) of two phase 3 trials included biologic-naive (n = 852) and TNFi-IR (n = 400) patients with PsA who were randomly assigned to receive bimekizumab, placebo with crossover to bimekizumab at week 16, or adalimumab followed by bimekizumab at week 52.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by UCB Pharma. Five authors declared being employees or shareholders of UCB Pharma. LC Coates declared being an editorial board member of Rheumatology and Therapy. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including UCB.
Source: Mease PJ, Merola JF, Tanaka Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of bimekizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis: 2-year results from two phase 3 studies. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Aug 31). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00708-8 Source
Key clinical point: Bimekizumab demonstrated consistent safety and sustained efficacy for up to 2 years in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were biologic-naive or inadequately responsive to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: From weeks 52 to 104, the incidence of treatment emergent adverse events (TEAE) was consistent with previous studies, with no new safety signals. SARS-CoV2 infection (18.6 per 100 patient-years) was the most common TEAE. Approximately 50% biologic-naive and TNFi-IR patients maintained a ≥50% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology response.
Study details: This open-label extension (BE-VITAL) of two phase 3 trials included biologic-naive (n = 852) and TNFi-IR (n = 400) patients with PsA who were randomly assigned to receive bimekizumab, placebo with crossover to bimekizumab at week 16, or adalimumab followed by bimekizumab at week 52.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by UCB Pharma. Five authors declared being employees or shareholders of UCB Pharma. LC Coates declared being an editorial board member of Rheumatology and Therapy. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including UCB.
Source: Mease PJ, Merola JF, Tanaka Y, et al. Safety and efficacy of bimekizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis: 2-year results from two phase 3 studies. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Aug 31). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00708-8 Source
Guselkumab Shows Early and Sustained Efficacy in PsA
Key clinical point: Guselkumab treatment every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W/Q8W) showed minimal clinically important improvements (MCII) in Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA) after the first dose and sustained disease control for up to 1 year in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: Both guselkumab doses (Q4W and Q8W) vs placebo led to early achievement of MCII in cDAPSA (hazard ratio 1.6-1.7; all P < .0001), with higher response rates at week 4 (P < .01). Achieving early MCII in cDAPSA was associated with sustained disease control at 24 and 52 weeks (odds ratio 1.4-3.5; all P < .05).
Study details: This post hoc analysis of phase 3 trials, DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, included 1120 patients with active PsA who received guselkumab (Q4W or Q8W) or placebo with a crossover to guselkumab Q4W at week 24.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development (JRD), LLC. Four authors declared being employees or shareholders of JRD or other sources. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including JRD.
Source: Curtis JR, Deodhar A, Soriano ER, et al. Early Improvements with guselkumab associate with sustained control of psoriatic arthritis: Post hoc analyses of two phase 3 trials. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Sept 11). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00702-0 Source
Key clinical point: Guselkumab treatment every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W/Q8W) showed minimal clinically important improvements (MCII) in Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA) after the first dose and sustained disease control for up to 1 year in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: Both guselkumab doses (Q4W and Q8W) vs placebo led to early achievement of MCII in cDAPSA (hazard ratio 1.6-1.7; all P < .0001), with higher response rates at week 4 (P < .01). Achieving early MCII in cDAPSA was associated with sustained disease control at 24 and 52 weeks (odds ratio 1.4-3.5; all P < .05).
Study details: This post hoc analysis of phase 3 trials, DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, included 1120 patients with active PsA who received guselkumab (Q4W or Q8W) or placebo with a crossover to guselkumab Q4W at week 24.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development (JRD), LLC. Four authors declared being employees or shareholders of JRD or other sources. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including JRD.
Source: Curtis JR, Deodhar A, Soriano ER, et al. Early Improvements with guselkumab associate with sustained control of psoriatic arthritis: Post hoc analyses of two phase 3 trials. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Sept 11). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00702-0 Source
Key clinical point: Guselkumab treatment every 4 or 8 weeks (Q4W/Q8W) showed minimal clinically important improvements (MCII) in Clinical Disease Activity Index for Psoriatic Arthritis (cDAPSA) after the first dose and sustained disease control for up to 1 year in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: Both guselkumab doses (Q4W and Q8W) vs placebo led to early achievement of MCII in cDAPSA (hazard ratio 1.6-1.7; all P < .0001), with higher response rates at week 4 (P < .01). Achieving early MCII in cDAPSA was associated with sustained disease control at 24 and 52 weeks (odds ratio 1.4-3.5; all P < .05).
Study details: This post hoc analysis of phase 3 trials, DISCOVER-1 and DISCOVER-2, included 1120 patients with active PsA who received guselkumab (Q4W or Q8W) or placebo with a crossover to guselkumab Q4W at week 24.
Disclosures: This study was supported by Janssen Research & Development (JRD), LLC. Four authors declared being employees or shareholders of JRD or other sources. Several authors declared having ties with various sources, including JRD.
Source: Curtis JR, Deodhar A, Soriano ER, et al. Early Improvements with guselkumab associate with sustained control of psoriatic arthritis: Post hoc analyses of two phase 3 trials. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Sept 11). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00702-0 Source
Potential Predictive Biomarkers for Biologic Treatment Response in PsA
Key clinical point: Treatment with biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i), altered serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3), S100 calcium-binding protein A8 (S100A8), acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant (ACP5), and CXC motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10), with initial levels of these biomarkers effectively predicting treatment response to biologics in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: The serum levels of MMP3, S100A8, ACP5, CCL2, and CXCL10 were significantly reduced with TNFi (all P < .05), whereas ACP5 and CCL2 levels increased with IL-17i (both P < .05). The baseline levels of MMP3, S100A8, ACP5, and CXCL10 effectively predicted response to biologic treatment (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve > 0.8).
Study details: This study retrospectively analyzed data from 205 patients with PsA who did (n = 130) or did not (n = 75) receive biologics or conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and 56 patients with psoriasis without arthritis, of whom 28 patients received biologics.
Disclosures: This study was partially funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, with additional funding provided by the Krembil Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Offenheim R, Cruz-Correa OF, Ganatra D, Gladman DD. Candidate biomarkers for response to treatment in psoriatic disease. J Rheumatol. 2024 (Sept 1). doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2024-0396 Source
Key clinical point: Treatment with biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i), altered serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3), S100 calcium-binding protein A8 (S100A8), acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant (ACP5), and CXC motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10), with initial levels of these biomarkers effectively predicting treatment response to biologics in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: The serum levels of MMP3, S100A8, ACP5, CCL2, and CXCL10 were significantly reduced with TNFi (all P < .05), whereas ACP5 and CCL2 levels increased with IL-17i (both P < .05). The baseline levels of MMP3, S100A8, ACP5, and CXCL10 effectively predicted response to biologic treatment (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve > 0.8).
Study details: This study retrospectively analyzed data from 205 patients with PsA who did (n = 130) or did not (n = 75) receive biologics or conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and 56 patients with psoriasis without arthritis, of whom 28 patients received biologics.
Disclosures: This study was partially funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, with additional funding provided by the Krembil Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Offenheim R, Cruz-Correa OF, Ganatra D, Gladman DD. Candidate biomarkers for response to treatment in psoriatic disease. J Rheumatol. 2024 (Sept 1). doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2024-0396 Source
Key clinical point: Treatment with biologics, such as tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi) and interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i), altered serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 (MMP3), S100 calcium-binding protein A8 (S100A8), acid phosphatase 5, tartrate resistant (ACP5), and CXC motif chemokine 10 (CXCL10), with initial levels of these biomarkers effectively predicting treatment response to biologics in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
Major finding: The serum levels of MMP3, S100A8, ACP5, CCL2, and CXCL10 were significantly reduced with TNFi (all P < .05), whereas ACP5 and CCL2 levels increased with IL-17i (both P < .05). The baseline levels of MMP3, S100A8, ACP5, and CXCL10 effectively predicted response to biologic treatment (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve > 0.8).
Study details: This study retrospectively analyzed data from 205 patients with PsA who did (n = 130) or did not (n = 75) receive biologics or conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and 56 patients with psoriasis without arthritis, of whom 28 patients received biologics.
Disclosures: This study was partially funded by the Canadian Institute of Health Research, with additional funding provided by the Krembil Foundation. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Offenheim R, Cruz-Correa OF, Ganatra D, Gladman DD. Candidate biomarkers for response to treatment in psoriatic disease. J Rheumatol. 2024 (Sept 1). doi: 10.3899/jrheum.2024-0396 Source
PsA Patients Initiating bDMARD Face High Risk for Interstitial Lung Disease
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) initiating biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) had a significantly higher risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) than control individuals in the general population; with methotrexate co-medication not being a risk factor for ILD.
Major finding: The 5-year risk for ILD was significantly higher in patients with PsA vs individuals in the general population (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 4.4; 95% CI 2.8-7.0). The risk for ILD did not increase among patients with PsA who did vs did not use methotrexate as co-medication (aHR 1.0; 95% CI 0.4-2.2).
Study details: This observational cohort study included 10,919 patients with PsA and 29,478 patients with rheumatoid arthritis from five Nordic rheumatology registers (all age ≥ 18 years) who initiated bDMARD treatment, along with 362,087 control individuals from the general population.
Disclosures: This study was supported by NordForsk, Foreum, and other sources. Several authors declared receiving grants, honoraria, or consulting fees from or having other ties with various sources.
Source: Provan SA, Ljung L, Kristianslund EK, et al. Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis patients initiating biologics, and controls - Data from five Nordic registries. J Rheumatol. 2024 (Sept 1). doi: 0.3899/jrheum.2024-0252 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) initiating biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) had a significantly higher risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) than control individuals in the general population; with methotrexate co-medication not being a risk factor for ILD.
Major finding: The 5-year risk for ILD was significantly higher in patients with PsA vs individuals in the general population (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 4.4; 95% CI 2.8-7.0). The risk for ILD did not increase among patients with PsA who did vs did not use methotrexate as co-medication (aHR 1.0; 95% CI 0.4-2.2).
Study details: This observational cohort study included 10,919 patients with PsA and 29,478 patients with rheumatoid arthritis from five Nordic rheumatology registers (all age ≥ 18 years) who initiated bDMARD treatment, along with 362,087 control individuals from the general population.
Disclosures: This study was supported by NordForsk, Foreum, and other sources. Several authors declared receiving grants, honoraria, or consulting fees from or having other ties with various sources.
Source: Provan SA, Ljung L, Kristianslund EK, et al. Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis patients initiating biologics, and controls - Data from five Nordic registries. J Rheumatol. 2024 (Sept 1). doi: 0.3899/jrheum.2024-0252 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) initiating biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARD) had a significantly higher risk for interstitial lung disease (ILD) than control individuals in the general population; with methotrexate co-medication not being a risk factor for ILD.
Major finding: The 5-year risk for ILD was significantly higher in patients with PsA vs individuals in the general population (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 4.4; 95% CI 2.8-7.0). The risk for ILD did not increase among patients with PsA who did vs did not use methotrexate as co-medication (aHR 1.0; 95% CI 0.4-2.2).
Study details: This observational cohort study included 10,919 patients with PsA and 29,478 patients with rheumatoid arthritis from five Nordic rheumatology registers (all age ≥ 18 years) who initiated bDMARD treatment, along with 362,087 control individuals from the general population.
Disclosures: This study was supported by NordForsk, Foreum, and other sources. Several authors declared receiving grants, honoraria, or consulting fees from or having other ties with various sources.
Source: Provan SA, Ljung L, Kristianslund EK, et al. Interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid or psoriatic arthritis patients initiating biologics, and controls - Data from five Nordic registries. J Rheumatol. 2024 (Sept 1). doi: 0.3899/jrheum.2024-0252 Source
Bimekizumab Bests Risankizumab in PsA
Key clinical point: Bimekizumab showed better clinical efficacy outcomes than risankizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were biologic-naive or showed inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: At week 52, bimekizumab vs risankizumab led to a higher likelihood of achieving ≥70% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology response in biologic-naive (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.80; P < .001) and TNFi-IR (aOR 3.69; P < .001) patients. It was also linked to greater odds of minimal disease activity response in TNFi-IR patients (aOR 2.43; P = .003).
Study details: This matching-adjusted indirect comparison of data from four phase 3 trials (BE OPTIMAL, BE COMPLETE, KEEPsAKE-1, and KEEPsAKE-2) that involved biologic-naive or TNFi-IR patients with PsA who received bimekizumab (n = 698) or risankizumab (n = 589).
Disclosures: This study was supported by UCB Pharma and the National Institute of Health and Care Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre, UK. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of UCB Pharma. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including UCB Pharma.
Source: Mease PJ, Warren RB, Nash P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of bimekizumab and risankizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis at 52 weeks assessed using a matching-adjusted indirect comparison. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Aug 9). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00706-w Source
Key clinical point: Bimekizumab showed better clinical efficacy outcomes than risankizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were biologic-naive or showed inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: At week 52, bimekizumab vs risankizumab led to a higher likelihood of achieving ≥70% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology response in biologic-naive (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.80; P < .001) and TNFi-IR (aOR 3.69; P < .001) patients. It was also linked to greater odds of minimal disease activity response in TNFi-IR patients (aOR 2.43; P = .003).
Study details: This matching-adjusted indirect comparison of data from four phase 3 trials (BE OPTIMAL, BE COMPLETE, KEEPsAKE-1, and KEEPsAKE-2) that involved biologic-naive or TNFi-IR patients with PsA who received bimekizumab (n = 698) or risankizumab (n = 589).
Disclosures: This study was supported by UCB Pharma and the National Institute of Health and Care Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre, UK. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of UCB Pharma. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including UCB Pharma.
Source: Mease PJ, Warren RB, Nash P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of bimekizumab and risankizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis at 52 weeks assessed using a matching-adjusted indirect comparison. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Aug 9). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00706-w Source
Key clinical point: Bimekizumab showed better clinical efficacy outcomes than risankizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were biologic-naive or showed inadequate response to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Major finding: At week 52, bimekizumab vs risankizumab led to a higher likelihood of achieving ≥70% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology response in biologic-naive (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 1.80; P < .001) and TNFi-IR (aOR 3.69; P < .001) patients. It was also linked to greater odds of minimal disease activity response in TNFi-IR patients (aOR 2.43; P = .003).
Study details: This matching-adjusted indirect comparison of data from four phase 3 trials (BE OPTIMAL, BE COMPLETE, KEEPsAKE-1, and KEEPsAKE-2) that involved biologic-naive or TNFi-IR patients with PsA who received bimekizumab (n = 698) or risankizumab (n = 589).
Disclosures: This study was supported by UCB Pharma and the National Institute of Health and Care Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre, UK. Four authors declared being employees and shareholders of UCB Pharma. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including UCB Pharma.
Source: Mease PJ, Warren RB, Nash P, et al. Comparative effectiveness of bimekizumab and risankizumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis at 52 weeks assessed using a matching-adjusted indirect comparison. Rheumatol Ther. 2024 (Aug 9). doi: 10.1007/s40744-024-00706-w Source
DMARD-Naive and DMARD-Failure PsA Patients Show Similar Imaging Profile
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive or non-responders to previous conventional synthetic DMARD treatment (DMARD-failure) showed similar inflammation and structural damage on imaging.
Major finding: After adjusting for patient characteristics, structural imaging parameters including Achilles tendon structural damage and Joint Space Narrowing scores (both P > .6) were similar in DMARD-naive and DMARD-failure patients. Additionally, inflammatory imaging parameters (P > .2) showed no significant differences between the two groups, indicating that failing a DMARD was not associated with worsened imaging outcomes.
Study details: This cross-sectional study evaluated 80 patients with PsA from TOFA-PREDICT trial who were either DMARD-naive (n = 40) or DMARD non-responders (n = 40).
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pfizer. The collaboration project was co-funded by the public-private partnerships allowance by Health~Holland, Top Sector Life Sciences & Health. Six authors declared receiving research grants, consulting fees, and support from various sources, including Pfizer. Other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Renkli NÖ, Kleinrensink NJ, Spierings J, et al, and the TOFA-PREDICT author group. Multimodal imaging of structural damage and inflammation in psoriatic arthritis: A comparison of DMARD-naive and DMARD-failure patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 (Aug 17). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae450 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive or non-responders to previous conventional synthetic DMARD treatment (DMARD-failure) showed similar inflammation and structural damage on imaging.
Major finding: After adjusting for patient characteristics, structural imaging parameters including Achilles tendon structural damage and Joint Space Narrowing scores (both P > .6) were similar in DMARD-naive and DMARD-failure patients. Additionally, inflammatory imaging parameters (P > .2) showed no significant differences between the two groups, indicating that failing a DMARD was not associated with worsened imaging outcomes.
Study details: This cross-sectional study evaluated 80 patients with PsA from TOFA-PREDICT trial who were either DMARD-naive (n = 40) or DMARD non-responders (n = 40).
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pfizer. The collaboration project was co-funded by the public-private partnerships allowance by Health~Holland, Top Sector Life Sciences & Health. Six authors declared receiving research grants, consulting fees, and support from various sources, including Pfizer. Other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Renkli NÖ, Kleinrensink NJ, Spierings J, et al, and the TOFA-PREDICT author group. Multimodal imaging of structural damage and inflammation in psoriatic arthritis: A comparison of DMARD-naive and DMARD-failure patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 (Aug 17). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae450 Source
Key clinical point: Patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) who were disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive or non-responders to previous conventional synthetic DMARD treatment (DMARD-failure) showed similar inflammation and structural damage on imaging.
Major finding: After adjusting for patient characteristics, structural imaging parameters including Achilles tendon structural damage and Joint Space Narrowing scores (both P > .6) were similar in DMARD-naive and DMARD-failure patients. Additionally, inflammatory imaging parameters (P > .2) showed no significant differences between the two groups, indicating that failing a DMARD was not associated with worsened imaging outcomes.
Study details: This cross-sectional study evaluated 80 patients with PsA from TOFA-PREDICT trial who were either DMARD-naive (n = 40) or DMARD non-responders (n = 40).
Disclosures: This study was supported by Pfizer. The collaboration project was co-funded by the public-private partnerships allowance by Health~Holland, Top Sector Life Sciences & Health. Six authors declared receiving research grants, consulting fees, and support from various sources, including Pfizer. Other authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Renkli NÖ, Kleinrensink NJ, Spierings J, et al, and the TOFA-PREDICT author group. Multimodal imaging of structural damage and inflammation in psoriatic arthritis: A comparison of DMARD-naive and DMARD-failure patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2024 (Aug 17). doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keae450 Source
Risankizumab Safe for Long-Term Use in PsA
Key clinical point: This largest and longest safety analysis on risankizumab demonstrated its long-term safety in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), consistent with previously published reports.
Major finding: The rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AE) was 142.6 events per 100 patient-years (E/100 PY), serious AE was 8.6 E/100 PY, and AE leading to discontinuation was 1.8 E/100 PY. The rates of serious infections, cancer, major cardiovascular events, and hepatic events remained consistent or decreased in frequency through 6 months or 1 year. No additional safety concerns were reported.
Study details: This integrated safety analysis used data from four phase 2-3 trials involving 1542 patients with PsA and 20 phase 1-4 trials involving 3658 patients with plaque psoriasis, all of whom received ≥1 dose of risankizumab.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Risankizumab was jointly developed by AbbVie and Boehringer Ingelheim. Five authors declared being full-time employees of and may own stock or stock options of AbbVie. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Bachelez H, et al. Long-term safety of risankizumab in patients with psoriatic disease: A comprehensive analysis from clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14:2523-2538 (Aug 17). doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01238-5 Source
Key clinical point: This largest and longest safety analysis on risankizumab demonstrated its long-term safety in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), consistent with previously published reports.
Major finding: The rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AE) was 142.6 events per 100 patient-years (E/100 PY), serious AE was 8.6 E/100 PY, and AE leading to discontinuation was 1.8 E/100 PY. The rates of serious infections, cancer, major cardiovascular events, and hepatic events remained consistent or decreased in frequency through 6 months or 1 year. No additional safety concerns were reported.
Study details: This integrated safety analysis used data from four phase 2-3 trials involving 1542 patients with PsA and 20 phase 1-4 trials involving 3658 patients with plaque psoriasis, all of whom received ≥1 dose of risankizumab.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Risankizumab was jointly developed by AbbVie and Boehringer Ingelheim. Five authors declared being full-time employees of and may own stock or stock options of AbbVie. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Bachelez H, et al. Long-term safety of risankizumab in patients with psoriatic disease: A comprehensive analysis from clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14:2523-2538 (Aug 17). doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01238-5 Source
Key clinical point: This largest and longest safety analysis on risankizumab demonstrated its long-term safety in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), consistent with previously published reports.
Major finding: The rate of treatment-emergent adverse events (AE) was 142.6 events per 100 patient-years (E/100 PY), serious AE was 8.6 E/100 PY, and AE leading to discontinuation was 1.8 E/100 PY. The rates of serious infections, cancer, major cardiovascular events, and hepatic events remained consistent or decreased in frequency through 6 months or 1 year. No additional safety concerns were reported.
Study details: This integrated safety analysis used data from four phase 2-3 trials involving 1542 patients with PsA and 20 phase 1-4 trials involving 3658 patients with plaque psoriasis, all of whom received ≥1 dose of risankizumab.
Disclosures: This study was funded by AbbVie. Risankizumab was jointly developed by AbbVie and Boehringer Ingelheim. Five authors declared being full-time employees of and may own stock or stock options of AbbVie. Other authors declared having ties with various sources, including AbbVie.
Source: Gordon KB, Blauvelt A, Bachelez H, et al. Long-term safety of risankizumab in patients with psoriatic disease: A comprehensive analysis from clinical trials. Dermatol Ther (Heidelb). 2024;14:2523-2538 (Aug 17). doi: 10.1007/s13555-024-01238-5 Source
Incidence and Risk Factors Associated With Switching Between b/tsDMARD in PsA
Key clinical point: Switching between biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD) was common due to treatment inefficacy in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), with concomitant therapies and multiple prior treatments being significant risk factors.
Major finding: Overall, 40% of patients switched between b/tsDMARD, with 85.1% switches due to treatment inefficacy. The risk for switching was not affected by b/tsDMARD type (P > .05) but increased with multiple b/tsDMARD courses (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.22; P = .010), concomitant glucocorticoids (aHR 2.05; P = .001), and sulfalazine use (aHR 2.25; P = .006). Women and those with inflammatory back pain also faced an increased risk for switching.
Study details: This longitudinal retrospective study included 141 patients with PsA (age ≥ 16 years) who were treated with b/tsDMARD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministry of Health, Spain, and Red de Enfermedades Inflamatorias, with co-funding from el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Freites-Nuñez D, Leon L, Toledano E, et al. Switching related to inefficacy in biologics and targeted synthetic therapies for psoriatic arthritis: A comparative real-life study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024 (Aug 31). doi:10.1177/1759720X241273083 Source
Key clinical point: Switching between biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD) was common due to treatment inefficacy in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), with concomitant therapies and multiple prior treatments being significant risk factors.
Major finding: Overall, 40% of patients switched between b/tsDMARD, with 85.1% switches due to treatment inefficacy. The risk for switching was not affected by b/tsDMARD type (P > .05) but increased with multiple b/tsDMARD courses (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.22; P = .010), concomitant glucocorticoids (aHR 2.05; P = .001), and sulfalazine use (aHR 2.25; P = .006). Women and those with inflammatory back pain also faced an increased risk for switching.
Study details: This longitudinal retrospective study included 141 patients with PsA (age ≥ 16 years) who were treated with b/tsDMARD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministry of Health, Spain, and Red de Enfermedades Inflamatorias, with co-funding from el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Freites-Nuñez D, Leon L, Toledano E, et al. Switching related to inefficacy in biologics and targeted synthetic therapies for psoriatic arthritis: A comparative real-life study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024 (Aug 31). doi:10.1177/1759720X241273083 Source
Key clinical point: Switching between biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARD) was common due to treatment inefficacy in patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), with concomitant therapies and multiple prior treatments being significant risk factors.
Major finding: Overall, 40% of patients switched between b/tsDMARD, with 85.1% switches due to treatment inefficacy. The risk for switching was not affected by b/tsDMARD type (P > .05) but increased with multiple b/tsDMARD courses (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.22; P = .010), concomitant glucocorticoids (aHR 2.05; P = .001), and sulfalazine use (aHR 2.25; P = .006). Women and those with inflammatory back pain also faced an increased risk for switching.
Study details: This longitudinal retrospective study included 141 patients with PsA (age ≥ 16 years) who were treated with b/tsDMARD.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Ministry of Health, Spain, and Red de Enfermedades Inflamatorias, with co-funding from el Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Freites-Nuñez D, Leon L, Toledano E, et al. Switching related to inefficacy in biologics and targeted synthetic therapies for psoriatic arthritis: A comparative real-life study. Ther Adv Musculoskelet Dis. 2024 (Aug 31). doi:10.1177/1759720X241273083 Source