User login
Nail-Patella Syndrome: Clinical Clues for Making the Diagnosis
Nail-patella syndrome (NPS), also known as hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia syndrome, is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder with an estimated incidence of 1 per 50,000 individuals in the United States. Nail-patella syndrome presents due to a heterozygous loss-of-function mutation in the LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta gene, LMX1B, on chromosome 9q34.1 LMX1B gene mutations are fully penetrant, but there is variable expressivity, even within families.2
Case Report
A 69-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic for a routine skin cancer screening. The patient’s history was remarkable for dystrophic fingernails and toenails since birth. In his 20s he developed progressively worsening instability of the left knee and chronic back pain due to scoliosis, lumbar lordosis, and spinal disc herniation. Since then, he underwent knee surgery and 7 back surgeries for rheumatologic disease. His medical history also was remarkable for osteoporosis, hypertension, and glaucoma. Family history was notable for similar findings in the patient’s sister; mother; and maternal aunt, uncle, and grandmother, all with varying disease severity.
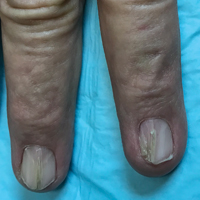
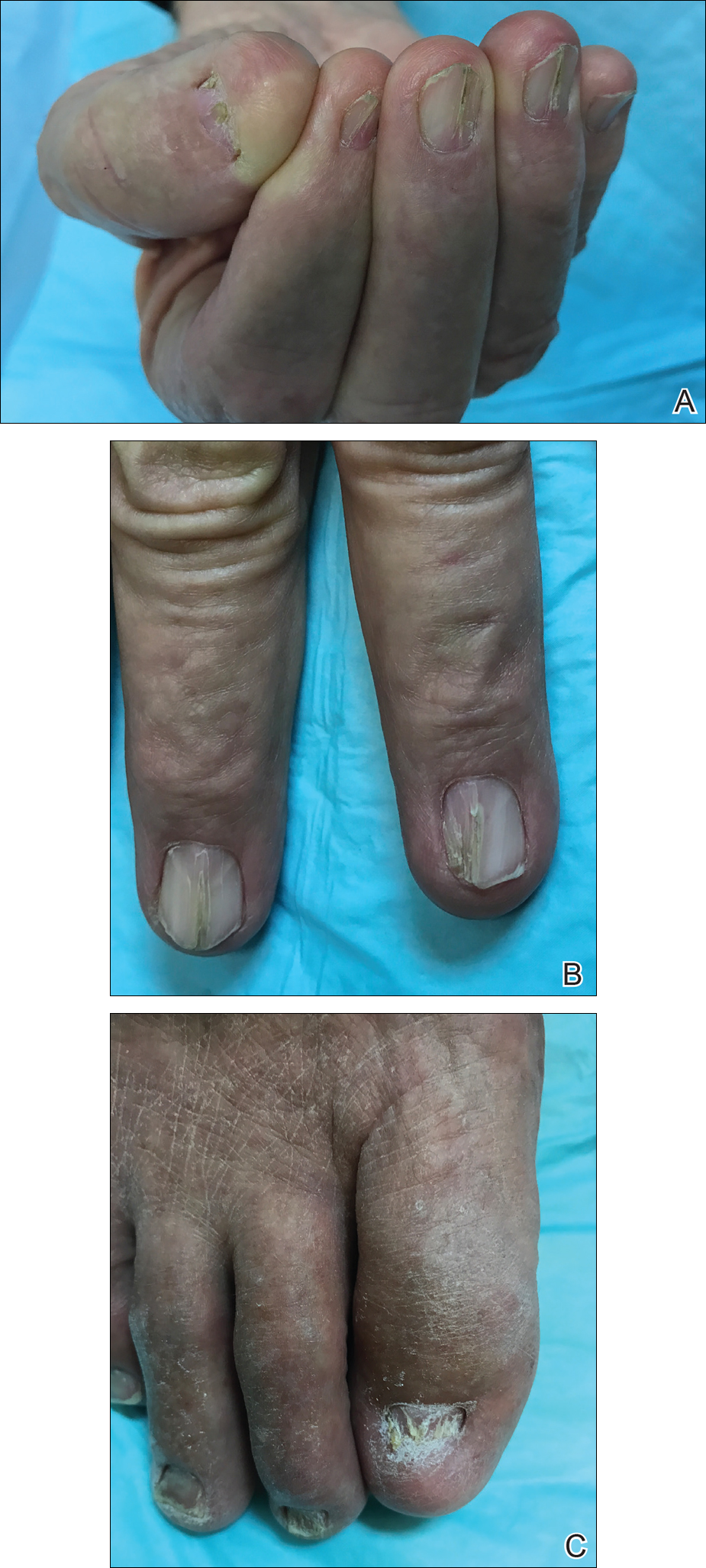
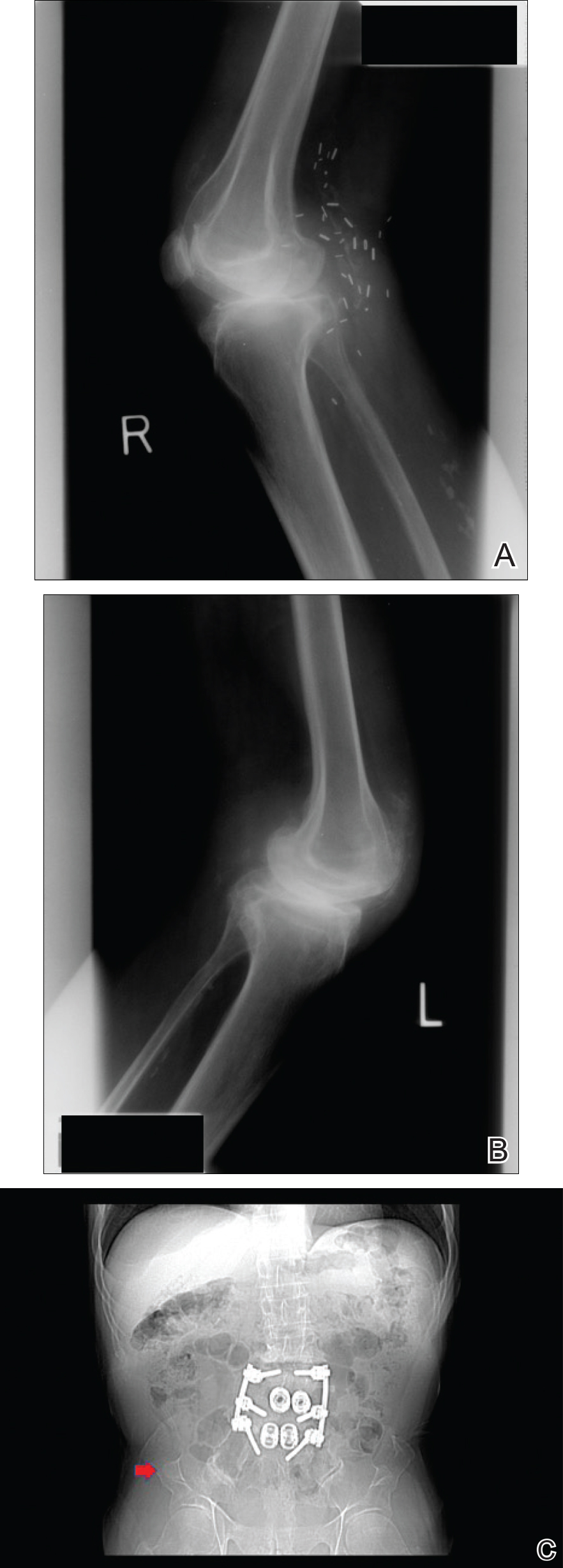
Physical examination was remarkable for bilateral fingernail hypoplasia that was most prominent on the thumb, with improvement in each nail on progression toward the fifth digit (Figure 1A). Triangular fingernail lunulae, longitudinal ridging, and nail splitting were present (Figure 1A and 1B). Hypoplastic crumbly toenails also were appreciated (Figure 1C). Skin creases over the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and toes were conspicuously absent. Limited range of motion was noted in multiple joints, with profound limitation of bilateral elbow extension. Review of prior imaging reports revealed bilateral iliac horns as well as left patellar absence and right patellar hypoplasia (Figure 2). Urinalysis was remarkable for proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Given the constellation of examination findings and positive family history, a diagnosis of NPS was made.
Comment
Nail-patella syndrome is characterized by variable dermatologic, neurologic, nephrogenic, ophthalmologic, and orthopedic clinical manifestations.3 Almost all patients with NPS have bilateral and symmetric nail changes, including absent or hypoplastic nails with ridging, splitting, or discoloration and triangular-shaped lunulae.1,4 Nail findings are the most consistent findings of NPS, as they are present in more than 98% of patients.5 The thumb often is the most severely affected nail, with improvement appreciated on progression toward the fifth digit, as seen in our patient (Figure 1A).5 Each individual nail usually is more severely affected on its ulnar side. When toenails are involved, the abnormalities tend to be less severe, and the little toenail is most commonly affected. Distal digital changes also are observed in almost all patients. Loss of dorsal creases in the skin overlying the distal interphalangeal joints can be considered as a diagnostic clue.3,4
There are a variety of orthopedic manifestations of NPS. Hypoplastic or absent patellae leading to recurrent subluxations or dislocations is a common finding.4 Bilateral symmetric bone formations (horns) arising from the iliac crest are pathognomonic but only found on radiography 70% of the time.6 Occasionally these protuberances can be palpated on physical examination,5 though this finding was not appreciated in our patient. Dysplasia of the elbows may result in limited elbow extension and limited pronation and supination. Early degenerative arthritis, lumbar lordosis, and scoliosis also are not uncommon. In addition, skeletal integrity is compromised, leading to early osteoporosis and increased risk for fractures.5
Nephropathy develops in approximately 30% to 40% of patients and is a major determinant of mortality in these patients.2 Mutations in the LMX1B gene lead to abnormal development of podocytes and reduction in collagen in the glomerular basement membrane. The first sign of renal involvement usually is proteinuria, with or without microscopic hematuria. As in our patient, many patients develop hypertension. Patients may progress to develop nephrotic syndrome and end-stage renal failure (5%–10%).7 Death from NPS-related nephropathy has occurred, even in childhood.4,5
Primary open-angle glaucoma has been recognized as a feature of NPS.8 It is the most frequent ocular abnormality observed, followed by ocular hypertension and Lester sign of the iris.3,5 These conditions also are more common in younger patients with NPS than in the general population.5 Important neurologic findings include epilepsy, peripheral neuropathy, attention deficit disorder, major depressive disorder, and vasomotor problems.9
Our case highlights the importance of recognizing this rare condition to provide a multidisciplinary approach to care that addresses all aspects of LMX1B-associated disease in affected individuals. Nail findings may be the first clue to the need for additional screenings in these patients. Nail-patella syndrome patients should undergo thorough ophthalmologic examinations every 2 years, including measurement of intraocular pressure, examination of the optic disc, and assessment of visual fields. Given the variability in severity of joint problems and the unpredictable anatomy of the joints, magnetic resonance imaging of the joints is recommended prior to orthopedic intervention. Most importantly, physicians should recognize this genodermatosis to implement periodic screenings for renal disease, as up to 40% of NPS patients develop kidney failure. Annual blood pressure measurements, urinalysis, and measurement of the protein to creatinine ratio in the urine are recommended. For patients with end-stage renal failure, renal transplantation results in cure of nephropathy and may even result in nail regrowth.10 Further, this case is notable in that it describes a patient with NPS who is older than most other individuals presenting with the condition, thereby revealing novel information about NPS in its more advanced stages.
- Harita Y, Kitanaka S, Isojima T, et al. Spectrum of LMX1B mutations: from nail-patella syndrome to isolated nephropathy [published online July 23, 2016]. Pediatr Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s00467-016-3462-x.
- Ghoumid J, Petit F, Holder-Espinasse M, et al. Nail-patella syndrome: clinical and molecular data in 55 families raising the hypothesis of a genetic heterogeneity [published online April 22, 2015]. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016;24:44-50.
- Tong SY, Luk HM, Tong TM, et al. The nail points to the diagnosis. Fong disease or hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia. Hong Kong Med J. 2015;21:573.e3-573.e5.
- Figueroa-Silva O, Vicente A, Agudo A, et al. Nail-patella syndrome: report of 11 pediatric cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1614-1617.
- Sweeney E, Fryer A, Mountford R, et al. Nail patella syndrome: a review of the phenotype aided by developmental biology. J Med Genet. 2003;40:153-162.
- Tigchelaar S, Lenting A, Bongers EM, et al. Nail patella syndrome: knee symptoms and surgical outcomes. a questionnaire-based survey [published online November 17, 2015]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101:959-962.
- Lemley KV. Kidney disease in nail-patella syndrome [published online June 6, 2008]. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:2345-2354.
- Sweeney E, Hoover-Fong JE, McIntosh I. Nail-patella syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al, eds. GeneReviews. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 2003. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1132/. Updated November 13, 2014. Accessed January 30, 2018.
- Lopez-Arvizu C, Sparrow EP, Strube MJ, et al. Increased symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and major depressive disorder symptoms in nail-patella syndrome: potential association with LMX1B loss-of-function [published online November 2, 2010]. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011;156B:59-66.
- Chan PC, Chan KW, Cheng IK, et al. Living-related renal transplantation in a patient with nail-patella syndrome. Nephron. 1988;50:164-166.
Nail-patella syndrome (NPS), also known as hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia syndrome, is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder with an estimated incidence of 1 per 50,000 individuals in the United States. Nail-patella syndrome presents due to a heterozygous loss-of-function mutation in the LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta gene, LMX1B, on chromosome 9q34.1 LMX1B gene mutations are fully penetrant, but there is variable expressivity, even within families.2
Case Report
A 69-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic for a routine skin cancer screening. The patient’s history was remarkable for dystrophic fingernails and toenails since birth. In his 20s he developed progressively worsening instability of the left knee and chronic back pain due to scoliosis, lumbar lordosis, and spinal disc herniation. Since then, he underwent knee surgery and 7 back surgeries for rheumatologic disease. His medical history also was remarkable for osteoporosis, hypertension, and glaucoma. Family history was notable for similar findings in the patient’s sister; mother; and maternal aunt, uncle, and grandmother, all with varying disease severity.
Physical examination was remarkable for bilateral fingernail hypoplasia that was most prominent on the thumb, with improvement in each nail on progression toward the fifth digit (Figure 1A). Triangular fingernail lunulae, longitudinal ridging, and nail splitting were present (Figure 1A and 1B). Hypoplastic crumbly toenails also were appreciated (Figure 1C). Skin creases over the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and toes were conspicuously absent. Limited range of motion was noted in multiple joints, with profound limitation of bilateral elbow extension. Review of prior imaging reports revealed bilateral iliac horns as well as left patellar absence and right patellar hypoplasia (Figure 2). Urinalysis was remarkable for proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Given the constellation of examination findings and positive family history, a diagnosis of NPS was made.


Comment
Nail-patella syndrome is characterized by variable dermatologic, neurologic, nephrogenic, ophthalmologic, and orthopedic clinical manifestations.3 Almost all patients with NPS have bilateral and symmetric nail changes, including absent or hypoplastic nails with ridging, splitting, or discoloration and triangular-shaped lunulae.1,4 Nail findings are the most consistent findings of NPS, as they are present in more than 98% of patients.5 The thumb often is the most severely affected nail, with improvement appreciated on progression toward the fifth digit, as seen in our patient (Figure 1A).5 Each individual nail usually is more severely affected on its ulnar side. When toenails are involved, the abnormalities tend to be less severe, and the little toenail is most commonly affected. Distal digital changes also are observed in almost all patients. Loss of dorsal creases in the skin overlying the distal interphalangeal joints can be considered as a diagnostic clue.3,4
There are a variety of orthopedic manifestations of NPS. Hypoplastic or absent patellae leading to recurrent subluxations or dislocations is a common finding.4 Bilateral symmetric bone formations (horns) arising from the iliac crest are pathognomonic but only found on radiography 70% of the time.6 Occasionally these protuberances can be palpated on physical examination,5 though this finding was not appreciated in our patient. Dysplasia of the elbows may result in limited elbow extension and limited pronation and supination. Early degenerative arthritis, lumbar lordosis, and scoliosis also are not uncommon. In addition, skeletal integrity is compromised, leading to early osteoporosis and increased risk for fractures.5
Nephropathy develops in approximately 30% to 40% of patients and is a major determinant of mortality in these patients.2 Mutations in the LMX1B gene lead to abnormal development of podocytes and reduction in collagen in the glomerular basement membrane. The first sign of renal involvement usually is proteinuria, with or without microscopic hematuria. As in our patient, many patients develop hypertension. Patients may progress to develop nephrotic syndrome and end-stage renal failure (5%–10%).7 Death from NPS-related nephropathy has occurred, even in childhood.4,5
Primary open-angle glaucoma has been recognized as a feature of NPS.8 It is the most frequent ocular abnormality observed, followed by ocular hypertension and Lester sign of the iris.3,5 These conditions also are more common in younger patients with NPS than in the general population.5 Important neurologic findings include epilepsy, peripheral neuropathy, attention deficit disorder, major depressive disorder, and vasomotor problems.9
Our case highlights the importance of recognizing this rare condition to provide a multidisciplinary approach to care that addresses all aspects of LMX1B-associated disease in affected individuals. Nail findings may be the first clue to the need for additional screenings in these patients. Nail-patella syndrome patients should undergo thorough ophthalmologic examinations every 2 years, including measurement of intraocular pressure, examination of the optic disc, and assessment of visual fields. Given the variability in severity of joint problems and the unpredictable anatomy of the joints, magnetic resonance imaging of the joints is recommended prior to orthopedic intervention. Most importantly, physicians should recognize this genodermatosis to implement periodic screenings for renal disease, as up to 40% of NPS patients develop kidney failure. Annual blood pressure measurements, urinalysis, and measurement of the protein to creatinine ratio in the urine are recommended. For patients with end-stage renal failure, renal transplantation results in cure of nephropathy and may even result in nail regrowth.10 Further, this case is notable in that it describes a patient with NPS who is older than most other individuals presenting with the condition, thereby revealing novel information about NPS in its more advanced stages.
Nail-patella syndrome (NPS), also known as hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia syndrome, is a rare autosomal-dominant disorder with an estimated incidence of 1 per 50,000 individuals in the United States. Nail-patella syndrome presents due to a heterozygous loss-of-function mutation in the LIM homeobox transcription factor 1 beta gene, LMX1B, on chromosome 9q34.1 LMX1B gene mutations are fully penetrant, but there is variable expressivity, even within families.2
Case Report
A 69-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic for a routine skin cancer screening. The patient’s history was remarkable for dystrophic fingernails and toenails since birth. In his 20s he developed progressively worsening instability of the left knee and chronic back pain due to scoliosis, lumbar lordosis, and spinal disc herniation. Since then, he underwent knee surgery and 7 back surgeries for rheumatologic disease. His medical history also was remarkable for osteoporosis, hypertension, and glaucoma. Family history was notable for similar findings in the patient’s sister; mother; and maternal aunt, uncle, and grandmother, all with varying disease severity.
Physical examination was remarkable for bilateral fingernail hypoplasia that was most prominent on the thumb, with improvement in each nail on progression toward the fifth digit (Figure 1A). Triangular fingernail lunulae, longitudinal ridging, and nail splitting were present (Figure 1A and 1B). Hypoplastic crumbly toenails also were appreciated (Figure 1C). Skin creases over the distal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and toes were conspicuously absent. Limited range of motion was noted in multiple joints, with profound limitation of bilateral elbow extension. Review of prior imaging reports revealed bilateral iliac horns as well as left patellar absence and right patellar hypoplasia (Figure 2). Urinalysis was remarkable for proteinuria and microscopic hematuria. Given the constellation of examination findings and positive family history, a diagnosis of NPS was made.


Comment
Nail-patella syndrome is characterized by variable dermatologic, neurologic, nephrogenic, ophthalmologic, and orthopedic clinical manifestations.3 Almost all patients with NPS have bilateral and symmetric nail changes, including absent or hypoplastic nails with ridging, splitting, or discoloration and triangular-shaped lunulae.1,4 Nail findings are the most consistent findings of NPS, as they are present in more than 98% of patients.5 The thumb often is the most severely affected nail, with improvement appreciated on progression toward the fifth digit, as seen in our patient (Figure 1A).5 Each individual nail usually is more severely affected on its ulnar side. When toenails are involved, the abnormalities tend to be less severe, and the little toenail is most commonly affected. Distal digital changes also are observed in almost all patients. Loss of dorsal creases in the skin overlying the distal interphalangeal joints can be considered as a diagnostic clue.3,4
There are a variety of orthopedic manifestations of NPS. Hypoplastic or absent patellae leading to recurrent subluxations or dislocations is a common finding.4 Bilateral symmetric bone formations (horns) arising from the iliac crest are pathognomonic but only found on radiography 70% of the time.6 Occasionally these protuberances can be palpated on physical examination,5 though this finding was not appreciated in our patient. Dysplasia of the elbows may result in limited elbow extension and limited pronation and supination. Early degenerative arthritis, lumbar lordosis, and scoliosis also are not uncommon. In addition, skeletal integrity is compromised, leading to early osteoporosis and increased risk for fractures.5
Nephropathy develops in approximately 30% to 40% of patients and is a major determinant of mortality in these patients.2 Mutations in the LMX1B gene lead to abnormal development of podocytes and reduction in collagen in the glomerular basement membrane. The first sign of renal involvement usually is proteinuria, with or without microscopic hematuria. As in our patient, many patients develop hypertension. Patients may progress to develop nephrotic syndrome and end-stage renal failure (5%–10%).7 Death from NPS-related nephropathy has occurred, even in childhood.4,5
Primary open-angle glaucoma has been recognized as a feature of NPS.8 It is the most frequent ocular abnormality observed, followed by ocular hypertension and Lester sign of the iris.3,5 These conditions also are more common in younger patients with NPS than in the general population.5 Important neurologic findings include epilepsy, peripheral neuropathy, attention deficit disorder, major depressive disorder, and vasomotor problems.9
Our case highlights the importance of recognizing this rare condition to provide a multidisciplinary approach to care that addresses all aspects of LMX1B-associated disease in affected individuals. Nail findings may be the first clue to the need for additional screenings in these patients. Nail-patella syndrome patients should undergo thorough ophthalmologic examinations every 2 years, including measurement of intraocular pressure, examination of the optic disc, and assessment of visual fields. Given the variability in severity of joint problems and the unpredictable anatomy of the joints, magnetic resonance imaging of the joints is recommended prior to orthopedic intervention. Most importantly, physicians should recognize this genodermatosis to implement periodic screenings for renal disease, as up to 40% of NPS patients develop kidney failure. Annual blood pressure measurements, urinalysis, and measurement of the protein to creatinine ratio in the urine are recommended. For patients with end-stage renal failure, renal transplantation results in cure of nephropathy and may even result in nail regrowth.10 Further, this case is notable in that it describes a patient with NPS who is older than most other individuals presenting with the condition, thereby revealing novel information about NPS in its more advanced stages.
- Harita Y, Kitanaka S, Isojima T, et al. Spectrum of LMX1B mutations: from nail-patella syndrome to isolated nephropathy [published online July 23, 2016]. Pediatr Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s00467-016-3462-x.
- Ghoumid J, Petit F, Holder-Espinasse M, et al. Nail-patella syndrome: clinical and molecular data in 55 families raising the hypothesis of a genetic heterogeneity [published online April 22, 2015]. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016;24:44-50.
- Tong SY, Luk HM, Tong TM, et al. The nail points to the diagnosis. Fong disease or hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia. Hong Kong Med J. 2015;21:573.e3-573.e5.
- Figueroa-Silva O, Vicente A, Agudo A, et al. Nail-patella syndrome: report of 11 pediatric cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1614-1617.
- Sweeney E, Fryer A, Mountford R, et al. Nail patella syndrome: a review of the phenotype aided by developmental biology. J Med Genet. 2003;40:153-162.
- Tigchelaar S, Lenting A, Bongers EM, et al. Nail patella syndrome: knee symptoms and surgical outcomes. a questionnaire-based survey [published online November 17, 2015]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101:959-962.
- Lemley KV. Kidney disease in nail-patella syndrome [published online June 6, 2008]. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:2345-2354.
- Sweeney E, Hoover-Fong JE, McIntosh I. Nail-patella syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al, eds. GeneReviews. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 2003. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1132/. Updated November 13, 2014. Accessed January 30, 2018.
- Lopez-Arvizu C, Sparrow EP, Strube MJ, et al. Increased symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and major depressive disorder symptoms in nail-patella syndrome: potential association with LMX1B loss-of-function [published online November 2, 2010]. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011;156B:59-66.
- Chan PC, Chan KW, Cheng IK, et al. Living-related renal transplantation in a patient with nail-patella syndrome. Nephron. 1988;50:164-166.
- Harita Y, Kitanaka S, Isojima T, et al. Spectrum of LMX1B mutations: from nail-patella syndrome to isolated nephropathy [published online July 23, 2016]. Pediatr Nephrol. doi:10.1007/s00467-016-3462-x.
- Ghoumid J, Petit F, Holder-Espinasse M, et al. Nail-patella syndrome: clinical and molecular data in 55 families raising the hypothesis of a genetic heterogeneity [published online April 22, 2015]. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016;24:44-50.
- Tong SY, Luk HM, Tong TM, et al. The nail points to the diagnosis. Fong disease or hereditary osteo-onychodysplasia. Hong Kong Med J. 2015;21:573.e3-573.e5.
- Figueroa-Silva O, Vicente A, Agudo A, et al. Nail-patella syndrome: report of 11 pediatric cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2016;30:1614-1617.
- Sweeney E, Fryer A, Mountford R, et al. Nail patella syndrome: a review of the phenotype aided by developmental biology. J Med Genet. 2003;40:153-162.
- Tigchelaar S, Lenting A, Bongers EM, et al. Nail patella syndrome: knee symptoms and surgical outcomes. a questionnaire-based survey [published online November 17, 2015]. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res. 2015;101:959-962.
- Lemley KV. Kidney disease in nail-patella syndrome [published online June 6, 2008]. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:2345-2354.
- Sweeney E, Hoover-Fong JE, McIntosh I. Nail-patella syndrome. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al, eds. GeneReviews. Seattle, WA: University of Washington, Seattle; 2003. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1132/. Updated November 13, 2014. Accessed January 30, 2018.
- Lopez-Arvizu C, Sparrow EP, Strube MJ, et al. Increased symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder and major depressive disorder symptoms in nail-patella syndrome: potential association with LMX1B loss-of-function [published online November 2, 2010]. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2011;156B:59-66.
- Chan PC, Chan KW, Cheng IK, et al. Living-related renal transplantation in a patient with nail-patella syndrome. Nephron. 1988;50:164-166.
Practice Points
- Nail-patella syndrome (NPS) is a multisystem disease.
- Nail findings (eg, triangular lunulae) may be the first clue to NPS and should prompt investigation of associated renal, ocular, neurologic, skeletal, and orthopedic abnormalities.
- Early intervention and a multidisciplinary approach to care can improve morbidity and mortality in patients with NPS.
Sun Protection for Infants: Parent Behaviors and Beliefs in Miami, Florida
Sun exposure and sunburns sustained during childhood are linked to an increased risk for development of skin cancers in adulthood. In infants, the skin is particularly vulnerable and is considered to be at increased risk for UV radiation damage,1 even as early as the first 6 months of life.2 Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 To effectively teach parents proper sun-safe practices, it is essential to understand their existing perceptions and behaviors. This study sought to examine differences in infant sun-safety practices during the first 6 months of life among black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic white (NHW) parents in Miami, Florida.
Methods
Parents presenting to the University of Miami general pediatrics clinic from February 2015 through April 2015 with a child younger than 5 years were administered a 15-item questionnaire that included items on demographics, sun-safety strategies, sunburns and tanning, beliefs and limitations regarding sunscreen, and primary information source regarding sun safety (eg, physician, Internet, media, instincts). Parents were approached by the investigators consecutively for participation in scheduled blocks, with the exception of those who were otherwise engaged in appointment-related tasks (eg, paperwork). The study was approved by the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine institutional review board. The primary objective of this study was to determine the sun protection behaviors that black and Hispanic parents in Miami, Florida, employ in infants younger than 6 months. Secondary objectives included determining if this patient population is at risk for infant sunburns and tanning, beliefs among parents regarding sunscreen's efficacy in the prevention of skin cancers, and limitations of sunscreen use.
All data were analyzed using SAS software version 9.3. Wilcoxon signed rank test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Fisher exact test, and proportional-odds cumulative logit model were used to compare nonparametric data. Parents reporting on the full first 6 months of life (ie, the child was older than 6 months at the time of study completion) were included for analysis of sun-safety strategies. All survey respondents were included for analysis of secondary objectives. Responses from parents of infants of mixed racial and ethnic backgrounds were excluded from applicable subgroup analyses.
Results
Ninety-eight parents were approached for participation in the study; 97 consented to participate and 95 completed the survey. Seventy parents had children who were at least 6 months of age and were included for analysis of the primary objectives (ie, sun-protection strategies in the first 6 months of life). The cohort included 49 Hispanic parents, 26 black parents, and 9 NHW parents; 5 parents indicated their child was of mixed racial and ethnic background. Six respondents indicated another minority group (eg, Native American, Pacific Islander). Eighty-three respondents were mothers, 72 were educated beyond high school, and 14 were Spanish-speaking only. Four reported a known family history of skin cancer.
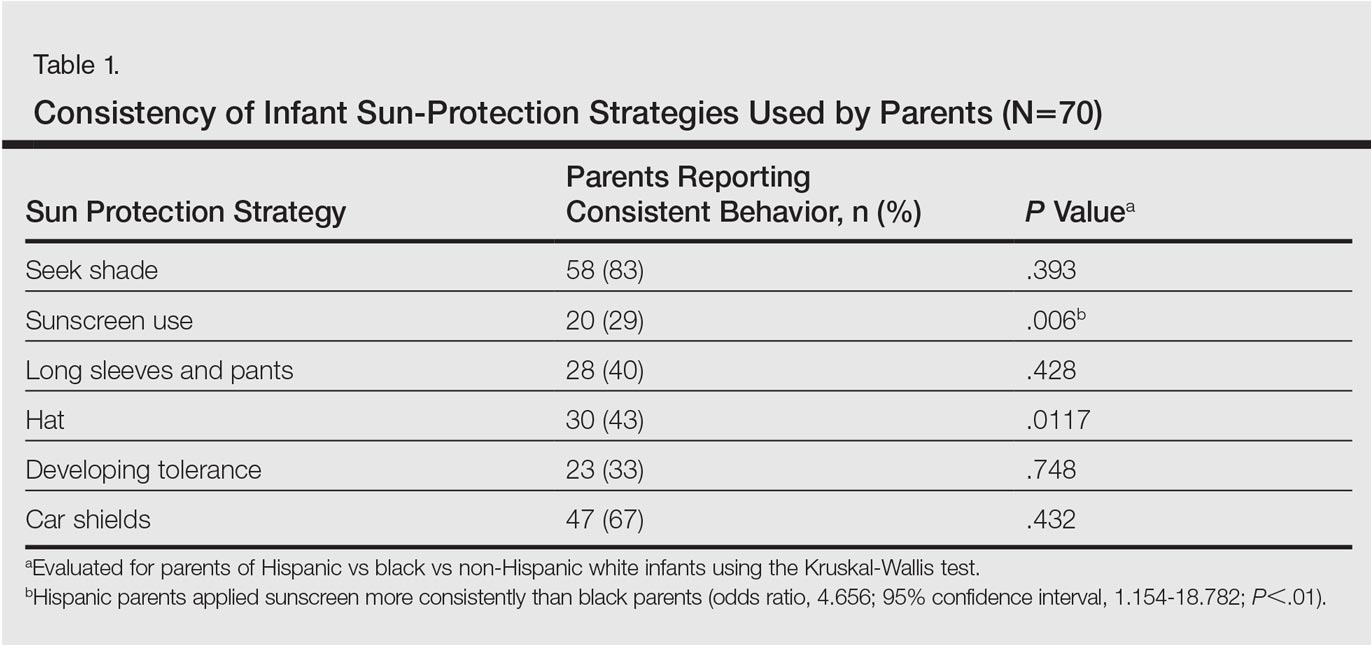
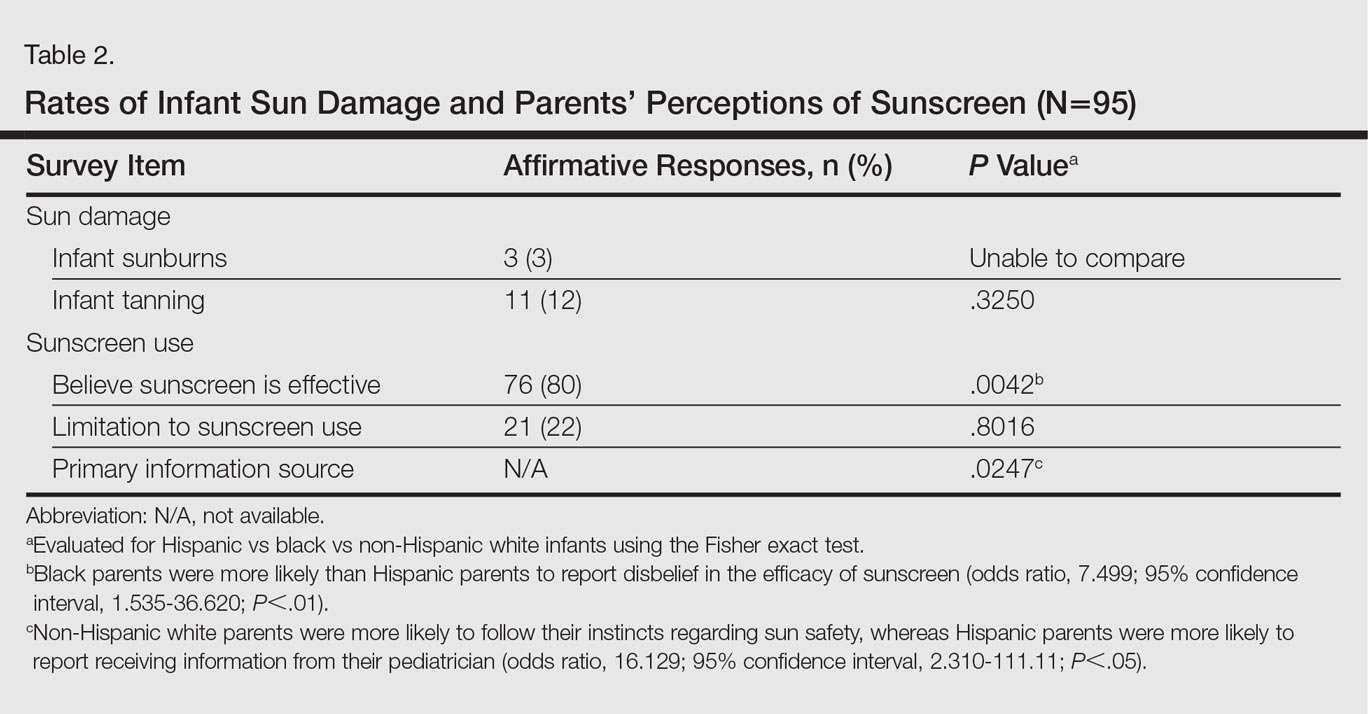
There were notable differences in application of sunscreen, belief in the efficacy of sunscreen, and primary source of information between parents (Tables 1 and 2). Hispanic parents reported applying sunscreen more consistently than black parents (odds ratio, 4.656; 95% confidence interval, 1.154-18.782; P<.01). Hispanic parents also were more likely than black parents to believe sunscreen is effective in the prevention of skin cancers (odds ratio, 7.499; 95% confidence interval, 1.535-36.620; P<.01). Hispanic parents were more likely to report receiving information regarding sun-safety practices for infants from their pediatrician, whereas NHW parents were more likely to follow their instincts regarding how and if infants should be exposed to the sun (P<.05). No significant differences were found in the reported primary source of information in black versus Hispanic parents or in black versus NHW parents. Three percent (3/95) of respondents reported a sunburn in the infant's first 6 months of life, and 12% (11/95) reported tanning of infants' skin from sun exposure. Tanning was associated with inconsistent shade (P<.01), inconsistent clothing coverage (P<.01), and consistently allowing infants to "develop tolerance to the sun's rays by slowly increasing sun exposure each day" (P<.05).
Comment
The survey results indicated suboptimal sun-protection practices among parents of black and Hispanic infants in Miami. Although the majority of respondents (83% [58/70]) reported keeping their infants in the shade, less than half of parents consistently covered their infants adequately with clothing and hats (40% [28/70] and 43% [30/70], respectively). More alarmingly, one-third of parents reported intentionally increasing their infant's level of sun exposure to develop his/her tolerance to the sun. A minority of parents reported sunburns (3%) and tanning (12%) within the first 6 months of life. Twenty-nine percent of parents (20/70) reported consistently applying sunscreen to their infants who were younger than 6 months despite limited safety data available for this age group.
Although our study included a limited sample size and represents a narrow geographic distribution, these results suggest that shortcomings in current practices in sun protection for black and Hispanic infants younger than 6 months may be a widespread problem. Black and Hispanic patients have a lower incidence of skin cancer, but the diagnosis often is delayed and the mortality is higher when skin cancer does occur.4 The common perception among laypeople as well as many health care providers that black and Hispanic individuals are not at risk for skin cancer may limit sun-safety counseling as well as the overall knowledge base of this patient demographic. As demonstrated by the results of this study, there is a need for counseling on sun-safe behaviors from a young age among this population.
Conclusion
This study highlights potential shortcomings in current sun-protection practices for black and Hispanic infants younger than 6 months. Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 Additional studies are needed to further define sun-safety behaviors in black and Hispanic children across the United States. Further, additional studies should focus on developing interventions that positively influence sun-safety behaviors in this patient population.
- Paller AS, Hawk JL, Honig P, et al. New insights about infant and toddler skin: implications for sun protection. Pediatrics. 2011;128:92-102.
- Benjes LS, Brooks DR, Zhang Z, et al. Changing patterns of sun protection between the first and second summers for very young children. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:925-930.
- Oliveria SA, Saraiya M, Geller AC, et al. Sun exposure and risk of melanoma. Arch Dis Child. 2006;91:131-138.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37.
Sun exposure and sunburns sustained during childhood are linked to an increased risk for development of skin cancers in adulthood. In infants, the skin is particularly vulnerable and is considered to be at increased risk for UV radiation damage,1 even as early as the first 6 months of life.2 Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 To effectively teach parents proper sun-safe practices, it is essential to understand their existing perceptions and behaviors. This study sought to examine differences in infant sun-safety practices during the first 6 months of life among black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic white (NHW) parents in Miami, Florida.
Methods
Parents presenting to the University of Miami general pediatrics clinic from February 2015 through April 2015 with a child younger than 5 years were administered a 15-item questionnaire that included items on demographics, sun-safety strategies, sunburns and tanning, beliefs and limitations regarding sunscreen, and primary information source regarding sun safety (eg, physician, Internet, media, instincts). Parents were approached by the investigators consecutively for participation in scheduled blocks, with the exception of those who were otherwise engaged in appointment-related tasks (eg, paperwork). The study was approved by the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine institutional review board. The primary objective of this study was to determine the sun protection behaviors that black and Hispanic parents in Miami, Florida, employ in infants younger than 6 months. Secondary objectives included determining if this patient population is at risk for infant sunburns and tanning, beliefs among parents regarding sunscreen's efficacy in the prevention of skin cancers, and limitations of sunscreen use.
All data were analyzed using SAS software version 9.3. Wilcoxon signed rank test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Fisher exact test, and proportional-odds cumulative logit model were used to compare nonparametric data. Parents reporting on the full first 6 months of life (ie, the child was older than 6 months at the time of study completion) were included for analysis of sun-safety strategies. All survey respondents were included for analysis of secondary objectives. Responses from parents of infants of mixed racial and ethnic backgrounds were excluded from applicable subgroup analyses.
Results
Ninety-eight parents were approached for participation in the study; 97 consented to participate and 95 completed the survey. Seventy parents had children who were at least 6 months of age and were included for analysis of the primary objectives (ie, sun-protection strategies in the first 6 months of life). The cohort included 49 Hispanic parents, 26 black parents, and 9 NHW parents; 5 parents indicated their child was of mixed racial and ethnic background. Six respondents indicated another minority group (eg, Native American, Pacific Islander). Eighty-three respondents were mothers, 72 were educated beyond high school, and 14 were Spanish-speaking only. Four reported a known family history of skin cancer.
There were notable differences in application of sunscreen, belief in the efficacy of sunscreen, and primary source of information between parents (Tables 1 and 2). Hispanic parents reported applying sunscreen more consistently than black parents (odds ratio, 4.656; 95% confidence interval, 1.154-18.782; P<.01). Hispanic parents also were more likely than black parents to believe sunscreen is effective in the prevention of skin cancers (odds ratio, 7.499; 95% confidence interval, 1.535-36.620; P<.01). Hispanic parents were more likely to report receiving information regarding sun-safety practices for infants from their pediatrician, whereas NHW parents were more likely to follow their instincts regarding how and if infants should be exposed to the sun (P<.05). No significant differences were found in the reported primary source of information in black versus Hispanic parents or in black versus NHW parents. Three percent (3/95) of respondents reported a sunburn in the infant's first 6 months of life, and 12% (11/95) reported tanning of infants' skin from sun exposure. Tanning was associated with inconsistent shade (P<.01), inconsistent clothing coverage (P<.01), and consistently allowing infants to "develop tolerance to the sun's rays by slowly increasing sun exposure each day" (P<.05).


Comment
The survey results indicated suboptimal sun-protection practices among parents of black and Hispanic infants in Miami. Although the majority of respondents (83% [58/70]) reported keeping their infants in the shade, less than half of parents consistently covered their infants adequately with clothing and hats (40% [28/70] and 43% [30/70], respectively). More alarmingly, one-third of parents reported intentionally increasing their infant's level of sun exposure to develop his/her tolerance to the sun. A minority of parents reported sunburns (3%) and tanning (12%) within the first 6 months of life. Twenty-nine percent of parents (20/70) reported consistently applying sunscreen to their infants who were younger than 6 months despite limited safety data available for this age group.
Although our study included a limited sample size and represents a narrow geographic distribution, these results suggest that shortcomings in current practices in sun protection for black and Hispanic infants younger than 6 months may be a widespread problem. Black and Hispanic patients have a lower incidence of skin cancer, but the diagnosis often is delayed and the mortality is higher when skin cancer does occur.4 The common perception among laypeople as well as many health care providers that black and Hispanic individuals are not at risk for skin cancer may limit sun-safety counseling as well as the overall knowledge base of this patient demographic. As demonstrated by the results of this study, there is a need for counseling on sun-safe behaviors from a young age among this population.
Conclusion
This study highlights potential shortcomings in current sun-protection practices for black and Hispanic infants younger than 6 months. Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 Additional studies are needed to further define sun-safety behaviors in black and Hispanic children across the United States. Further, additional studies should focus on developing interventions that positively influence sun-safety behaviors in this patient population.
Sun exposure and sunburns sustained during childhood are linked to an increased risk for development of skin cancers in adulthood. In infants, the skin is particularly vulnerable and is considered to be at increased risk for UV radiation damage,1 even as early as the first 6 months of life.2 Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 To effectively teach parents proper sun-safe practices, it is essential to understand their existing perceptions and behaviors. This study sought to examine differences in infant sun-safety practices during the first 6 months of life among black, Hispanic, and non-Hispanic white (NHW) parents in Miami, Florida.
Methods
Parents presenting to the University of Miami general pediatrics clinic from February 2015 through April 2015 with a child younger than 5 years were administered a 15-item questionnaire that included items on demographics, sun-safety strategies, sunburns and tanning, beliefs and limitations regarding sunscreen, and primary information source regarding sun safety (eg, physician, Internet, media, instincts). Parents were approached by the investigators consecutively for participation in scheduled blocks, with the exception of those who were otherwise engaged in appointment-related tasks (eg, paperwork). The study was approved by the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine institutional review board. The primary objective of this study was to determine the sun protection behaviors that black and Hispanic parents in Miami, Florida, employ in infants younger than 6 months. Secondary objectives included determining if this patient population is at risk for infant sunburns and tanning, beliefs among parents regarding sunscreen's efficacy in the prevention of skin cancers, and limitations of sunscreen use.
All data were analyzed using SAS software version 9.3. Wilcoxon signed rank test, Kruskal-Wallis test, Fisher exact test, and proportional-odds cumulative logit model were used to compare nonparametric data. Parents reporting on the full first 6 months of life (ie, the child was older than 6 months at the time of study completion) were included for analysis of sun-safety strategies. All survey respondents were included for analysis of secondary objectives. Responses from parents of infants of mixed racial and ethnic backgrounds were excluded from applicable subgroup analyses.
Results
Ninety-eight parents were approached for participation in the study; 97 consented to participate and 95 completed the survey. Seventy parents had children who were at least 6 months of age and were included for analysis of the primary objectives (ie, sun-protection strategies in the first 6 months of life). The cohort included 49 Hispanic parents, 26 black parents, and 9 NHW parents; 5 parents indicated their child was of mixed racial and ethnic background. Six respondents indicated another minority group (eg, Native American, Pacific Islander). Eighty-three respondents were mothers, 72 were educated beyond high school, and 14 were Spanish-speaking only. Four reported a known family history of skin cancer.
There were notable differences in application of sunscreen, belief in the efficacy of sunscreen, and primary source of information between parents (Tables 1 and 2). Hispanic parents reported applying sunscreen more consistently than black parents (odds ratio, 4.656; 95% confidence interval, 1.154-18.782; P<.01). Hispanic parents also were more likely than black parents to believe sunscreen is effective in the prevention of skin cancers (odds ratio, 7.499; 95% confidence interval, 1.535-36.620; P<.01). Hispanic parents were more likely to report receiving information regarding sun-safety practices for infants from their pediatrician, whereas NHW parents were more likely to follow their instincts regarding how and if infants should be exposed to the sun (P<.05). No significant differences were found in the reported primary source of information in black versus Hispanic parents or in black versus NHW parents. Three percent (3/95) of respondents reported a sunburn in the infant's first 6 months of life, and 12% (11/95) reported tanning of infants' skin from sun exposure. Tanning was associated with inconsistent shade (P<.01), inconsistent clothing coverage (P<.01), and consistently allowing infants to "develop tolerance to the sun's rays by slowly increasing sun exposure each day" (P<.05).


Comment
The survey results indicated suboptimal sun-protection practices among parents of black and Hispanic infants in Miami. Although the majority of respondents (83% [58/70]) reported keeping their infants in the shade, less than half of parents consistently covered their infants adequately with clothing and hats (40% [28/70] and 43% [30/70], respectively). More alarmingly, one-third of parents reported intentionally increasing their infant's level of sun exposure to develop his/her tolerance to the sun. A minority of parents reported sunburns (3%) and tanning (12%) within the first 6 months of life. Twenty-nine percent of parents (20/70) reported consistently applying sunscreen to their infants who were younger than 6 months despite limited safety data available for this age group.
Although our study included a limited sample size and represents a narrow geographic distribution, these results suggest that shortcomings in current practices in sun protection for black and Hispanic infants younger than 6 months may be a widespread problem. Black and Hispanic patients have a lower incidence of skin cancer, but the diagnosis often is delayed and the mortality is higher when skin cancer does occur.4 The common perception among laypeople as well as many health care providers that black and Hispanic individuals are not at risk for skin cancer may limit sun-safety counseling as well as the overall knowledge base of this patient demographic. As demonstrated by the results of this study, there is a need for counseling on sun-safe behaviors from a young age among this population.
Conclusion
This study highlights potential shortcomings in current sun-protection practices for black and Hispanic infants younger than 6 months. Sun-safe behaviors instituted from a young age may help reduce the risk for future skin cancers.3 Additional studies are needed to further define sun-safety behaviors in black and Hispanic children across the United States. Further, additional studies should focus on developing interventions that positively influence sun-safety behaviors in this patient population.
- Paller AS, Hawk JL, Honig P, et al. New insights about infant and toddler skin: implications for sun protection. Pediatrics. 2011;128:92-102.
- Benjes LS, Brooks DR, Zhang Z, et al. Changing patterns of sun protection between the first and second summers for very young children. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:925-930.
- Oliveria SA, Saraiya M, Geller AC, et al. Sun exposure and risk of melanoma. Arch Dis Child. 2006;91:131-138.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37.
- Paller AS, Hawk JL, Honig P, et al. New insights about infant and toddler skin: implications for sun protection. Pediatrics. 2011;128:92-102.
- Benjes LS, Brooks DR, Zhang Z, et al. Changing patterns of sun protection between the first and second summers for very young children. Arch Dermatol. 2004;140:925-930.
- Oliveria SA, Saraiya M, Geller AC, et al. Sun exposure and risk of melanoma. Arch Dis Child. 2006;91:131-138.
- Wu XC, Eide MJ, King J, et al. Racial and ethnic variations in incidence and survival of cutaneous melanoma in the United States, 1999-2006. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2011;65(5 suppl 1):S26-S37.
Practice Points
- Infants of all racial and ethnic backgrounds need protection from the sun's rays. Remember to counsel parents on the importance of sun protection.
- Instruct parents to keep infants in the shade when outdoors and to dress infants in a long-sleeved shirt, pants, and a hat. Intentional sun exposure for infants is not recommended.
- The American Academy of Dermatology currently recommends that parents begin sunscreen application when their child reaches 6 months of age. Broad-spectrum barrier sunscreens containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide are preferred and should provide a sun protection factor of 30 or greater.