User login
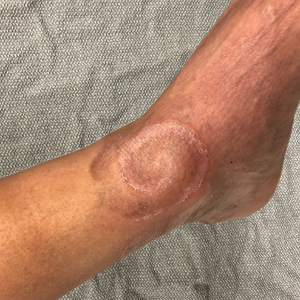
Spiral Plaque on the Left Ankle
The Diagnosis: Recurrent Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma
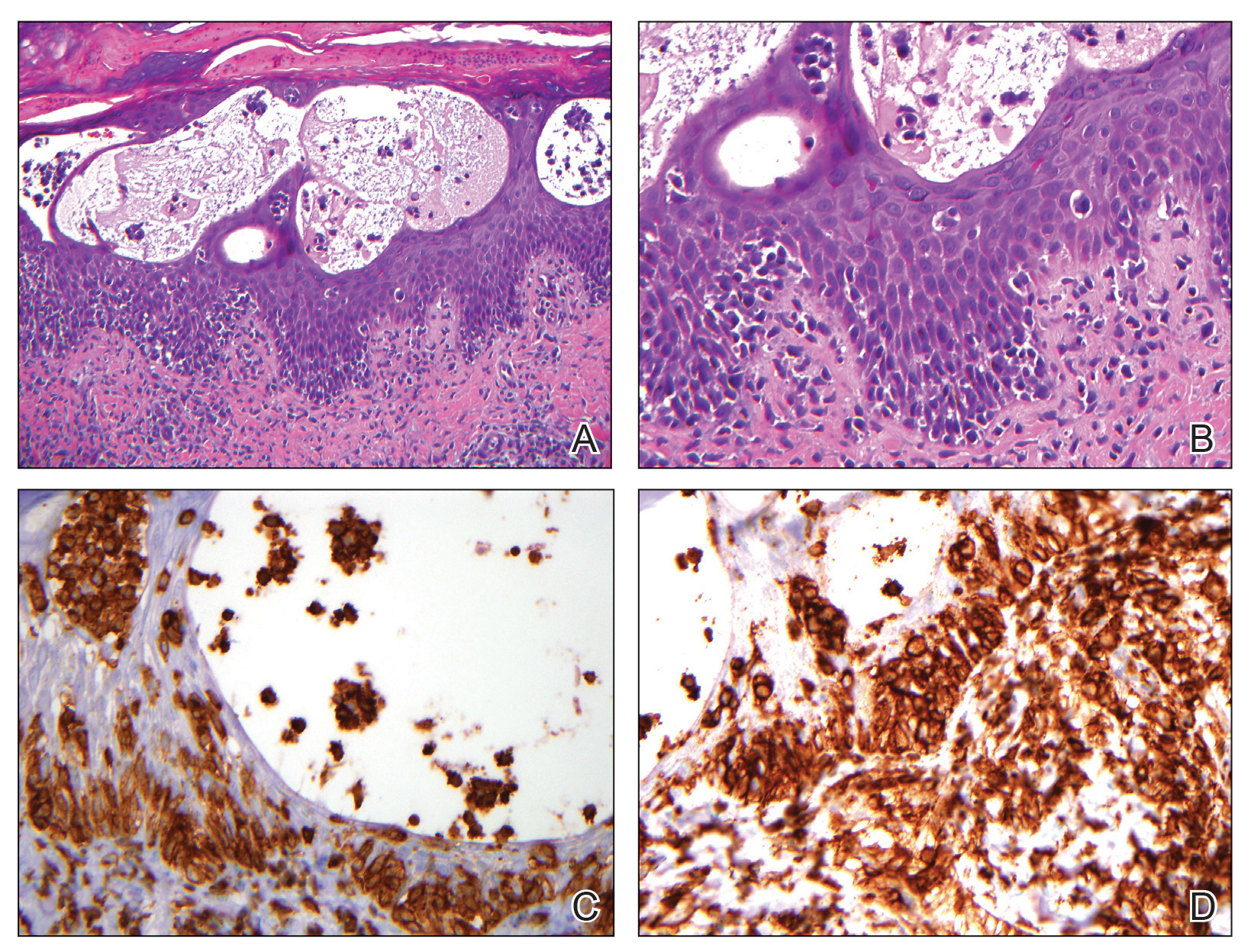
The skin biopsy revealed alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis with mild to moderate spongiosis and intraepidermal vesiculation as well as individual and nested atypical mononuclear cells with moderately enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei in the epidermis. There was a superficial interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate with occasional enlarged cells (Figure, A and B), and atypical cells in the epidermis and dermis stained with antibodies against CD3 and CD4 (Figure, C and D) but not against CD20 or CD8. These histopathologic findings were consistent with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), mycosis fungoides (MF) type. Additional application of bexarotene gel on days the patient received narrowband UVB was recommended with noted improvement of the skin.
Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are a heterogenous group of diseases with monoclonal proliferation of T lymphocytes that largely are confined to the skin at the time of diagnosis.1 The incidence of CTCL rose steadily for more than 25 years, with an annual age-adjusted incidence of 6.4 to 9.6 cases per million individuals in the United States from 1973 to 2002.2 Mycosis fungoides is the most common classification of CTCL. It usually is characterized by patches or plaques of scaly erythema or poikiloderma; however, it also can present with annular, arcuate, concentrative, annular and linear morphologies. Mycosis fungoides tumor cells typically express a mature memory T helper cell phenotype of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8−, but there are different variants that have been discovered.3 Mycosis fungoides distributed in a spiral pattern is a distinctly unusual manifestation. Mechanisms of such dynamic morphologies are unknown but may represent an interplay between malignant cell proliferation and lost immune responses in temporospatial relationships.
The presence of keratotic gyrate lesions on acral surfaces should raise the possibility of pagetoid reticulosis. However, our patient had a history of MF involving areas of the body beyond the extremities, making this diagnosis less likely. Pagetoid reticulosis is categorized as an MF variant under the current World Health Organization– European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer classification for cutaneous lymphomas.4 Pagetoid reticulosis clinically presents as a solitary psoriasiform or hyperkeratotic patch or plaque that affects the distal extremities. Variable immunophenotypes have been shown in pagetoid reticulosis, such as CD4−/CD8+ and CD4−/CD8−, while classic MF typically shows CD4+/CD8−, as in our case.5
Tinea pedis is a superficial fungal infection usually caused by anthropophilic dermatophytes, with Trichophyton rubrum being the most common organism. Four common clinical presentations of tinea pedis have been identified: interdigital, moccasin, vesicular, and acute ulcerative. Clinical presentation ranges from macerations, ulcerations, and erosions in the toe web spaces to dry hyperkeratotic scaling and fissures on the plantar foot.6 Tinea pedis primarily affects the plantar and interdigital spaces, sparing the dorsal foot and ankle. Treatment is recommended to alleviate symptoms and limit the spread of infection; topical antifungals for 4 weeks is the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is common, and maintenance therapy often is indicated. Oral antifungals or a combination of both topical and oral medications may be needed in certain cases.7
Erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) is a rare dermatologic disease described as erythematous or urticarial papules that can enlarge centrifugally to form annular lesions that clear centrally. Thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction to an underlying condition, EAC has been associated with fungal infections, various cutaneous diseases, and even internal malignancies. Clinically, EAC can be divided into 2 forms: deep and superficial. Deep gyrate erythema is characterized by a firm indurated border with rare scaling and pruritus that histologically shows perivascular lymphocytic infiltration in the upper and deep dermis. Superficial gyrate erythema has minimally elevated lesions with an indistinct border and trailing scales and pruritus; histopathologic findings present a dense, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltration restricted to the upper dermis.8 Therapy for EAC is directed at relieving symptoms and treating the underlying condition if there is one associated.
Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common skin disorder classically characterized by ringed erythematous plaques, though many variants have been identified. Localized GA is the most common variant and presents with pink-red, nonscaly, annular patches or plaques, typically affecting the hands and feet. Generalized GA is characterized as diffuse annular patches or plaques classically affecting the trunk and extremities. Histology is notable for mucin with a palisading or interstitial pattern of granulomatous inflammation, which was not evident in our patient.9 Topical or intralesional corticosteroids are the first-line treatment of localized GA; however, localized GA generally is self-limited, and treatment often is not necessary. Treatment with cryosurgery, laser therapy, and topical dapsone and tacrolimus also has been described, but evidence of the efficacy of these agents is limited. For generalized GA, phototherapy currently is the most reliable therapy. Systemic therapies include antimalarials, fumaric acid esters, biologics, antimicrobials, and isotretinoin.10
Erythema gyratum repens (EGR) is a rare dermatologic disease described as erythematous concentric bands arranged in parallel rings that can be annular, figurate, or gyrate, with a fine scale trailing the leading edge. Histopathologic features of EGR are nonspecific but are characterized by a perivascular, superficial, mononuclear dermatitis. Diagnosis is based on its characteristic clinical presentation. Although EGR commonly is associated with internal malignancies such as bronchial carcinoma, it also may be associated with benign conditions.11 Improvement often is seen with successful therapy of the underlying associated malignancy.12
Treatment of MF is based on tumor-node-metastasisblood classification, prognostic factors, and clinical stage at the time of diagnosis. Early-stage MF (IA–IIA) commonly is treated with skin-directed therapies such as topical corticosteroids, topical mechlorethamine, topical retinoids, UV phototherapy, and localized radiotherapy. In late stages (IIB–IV), systemic therapy is indicated and includes systemic retinoids, interferon alfa, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, and psoralen plus UVA.13 In many cases, patients may require combination therapy to achieve remission or better control of their condition, as in our patient.
The Diagnosis: Recurrent Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma
The skin biopsy revealed alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis with mild to moderate spongiosis and intraepidermal vesiculation as well as individual and nested atypical mononuclear cells with moderately enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei in the epidermis. There was a superficial interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate with occasional enlarged cells (Figure, A and B), and atypical cells in the epidermis and dermis stained with antibodies against CD3 and CD4 (Figure, C and D) but not against CD20 or CD8. These histopathologic findings were consistent with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), mycosis fungoides (MF) type. Additional application of bexarotene gel on days the patient received narrowband UVB was recommended with noted improvement of the skin.

Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are a heterogenous group of diseases with monoclonal proliferation of T lymphocytes that largely are confined to the skin at the time of diagnosis.1 The incidence of CTCL rose steadily for more than 25 years, with an annual age-adjusted incidence of 6.4 to 9.6 cases per million individuals in the United States from 1973 to 2002.2 Mycosis fungoides is the most common classification of CTCL. It usually is characterized by patches or plaques of scaly erythema or poikiloderma; however, it also can present with annular, arcuate, concentrative, annular and linear morphologies. Mycosis fungoides tumor cells typically express a mature memory T helper cell phenotype of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8−, but there are different variants that have been discovered.3 Mycosis fungoides distributed in a spiral pattern is a distinctly unusual manifestation. Mechanisms of such dynamic morphologies are unknown but may represent an interplay between malignant cell proliferation and lost immune responses in temporospatial relationships.
The presence of keratotic gyrate lesions on acral surfaces should raise the possibility of pagetoid reticulosis. However, our patient had a history of MF involving areas of the body beyond the extremities, making this diagnosis less likely. Pagetoid reticulosis is categorized as an MF variant under the current World Health Organization– European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer classification for cutaneous lymphomas.4 Pagetoid reticulosis clinically presents as a solitary psoriasiform or hyperkeratotic patch or plaque that affects the distal extremities. Variable immunophenotypes have been shown in pagetoid reticulosis, such as CD4−/CD8+ and CD4−/CD8−, while classic MF typically shows CD4+/CD8−, as in our case.5
Tinea pedis is a superficial fungal infection usually caused by anthropophilic dermatophytes, with Trichophyton rubrum being the most common organism. Four common clinical presentations of tinea pedis have been identified: interdigital, moccasin, vesicular, and acute ulcerative. Clinical presentation ranges from macerations, ulcerations, and erosions in the toe web spaces to dry hyperkeratotic scaling and fissures on the plantar foot.6 Tinea pedis primarily affects the plantar and interdigital spaces, sparing the dorsal foot and ankle. Treatment is recommended to alleviate symptoms and limit the spread of infection; topical antifungals for 4 weeks is the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is common, and maintenance therapy often is indicated. Oral antifungals or a combination of both topical and oral medications may be needed in certain cases.7
Erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) is a rare dermatologic disease described as erythematous or urticarial papules that can enlarge centrifugally to form annular lesions that clear centrally. Thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction to an underlying condition, EAC has been associated with fungal infections, various cutaneous diseases, and even internal malignancies. Clinically, EAC can be divided into 2 forms: deep and superficial. Deep gyrate erythema is characterized by a firm indurated border with rare scaling and pruritus that histologically shows perivascular lymphocytic infiltration in the upper and deep dermis. Superficial gyrate erythema has minimally elevated lesions with an indistinct border and trailing scales and pruritus; histopathologic findings present a dense, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltration restricted to the upper dermis.8 Therapy for EAC is directed at relieving symptoms and treating the underlying condition if there is one associated.
Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common skin disorder classically characterized by ringed erythematous plaques, though many variants have been identified. Localized GA is the most common variant and presents with pink-red, nonscaly, annular patches or plaques, typically affecting the hands and feet. Generalized GA is characterized as diffuse annular patches or plaques classically affecting the trunk and extremities. Histology is notable for mucin with a palisading or interstitial pattern of granulomatous inflammation, which was not evident in our patient.9 Topical or intralesional corticosteroids are the first-line treatment of localized GA; however, localized GA generally is self-limited, and treatment often is not necessary. Treatment with cryosurgery, laser therapy, and topical dapsone and tacrolimus also has been described, but evidence of the efficacy of these agents is limited. For generalized GA, phototherapy currently is the most reliable therapy. Systemic therapies include antimalarials, fumaric acid esters, biologics, antimicrobials, and isotretinoin.10
Erythema gyratum repens (EGR) is a rare dermatologic disease described as erythematous concentric bands arranged in parallel rings that can be annular, figurate, or gyrate, with a fine scale trailing the leading edge. Histopathologic features of EGR are nonspecific but are characterized by a perivascular, superficial, mononuclear dermatitis. Diagnosis is based on its characteristic clinical presentation. Although EGR commonly is associated with internal malignancies such as bronchial carcinoma, it also may be associated with benign conditions.11 Improvement often is seen with successful therapy of the underlying associated malignancy.12
Treatment of MF is based on tumor-node-metastasisblood classification, prognostic factors, and clinical stage at the time of diagnosis. Early-stage MF (IA–IIA) commonly is treated with skin-directed therapies such as topical corticosteroids, topical mechlorethamine, topical retinoids, UV phototherapy, and localized radiotherapy. In late stages (IIB–IV), systemic therapy is indicated and includes systemic retinoids, interferon alfa, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, and psoralen plus UVA.13 In many cases, patients may require combination therapy to achieve remission or better control of their condition, as in our patient.
The Diagnosis: Recurrent Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma
The skin biopsy revealed alternating orthokeratosis and parakeratosis with mild to moderate spongiosis and intraepidermal vesiculation as well as individual and nested atypical mononuclear cells with moderately enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei in the epidermis. There was a superficial interstitial lymphocytic infiltrate with occasional enlarged cells (Figure, A and B), and atypical cells in the epidermis and dermis stained with antibodies against CD3 and CD4 (Figure, C and D) but not against CD20 or CD8. These histopathologic findings were consistent with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (CTCL), mycosis fungoides (MF) type. Additional application of bexarotene gel on days the patient received narrowband UVB was recommended with noted improvement of the skin.

Cutaneous T-cell lymphomas are a heterogenous group of diseases with monoclonal proliferation of T lymphocytes that largely are confined to the skin at the time of diagnosis.1 The incidence of CTCL rose steadily for more than 25 years, with an annual age-adjusted incidence of 6.4 to 9.6 cases per million individuals in the United States from 1973 to 2002.2 Mycosis fungoides is the most common classification of CTCL. It usually is characterized by patches or plaques of scaly erythema or poikiloderma; however, it also can present with annular, arcuate, concentrative, annular and linear morphologies. Mycosis fungoides tumor cells typically express a mature memory T helper cell phenotype of CD3+, CD4+, and CD8−, but there are different variants that have been discovered.3 Mycosis fungoides distributed in a spiral pattern is a distinctly unusual manifestation. Mechanisms of such dynamic morphologies are unknown but may represent an interplay between malignant cell proliferation and lost immune responses in temporospatial relationships.
The presence of keratotic gyrate lesions on acral surfaces should raise the possibility of pagetoid reticulosis. However, our patient had a history of MF involving areas of the body beyond the extremities, making this diagnosis less likely. Pagetoid reticulosis is categorized as an MF variant under the current World Health Organization– European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer classification for cutaneous lymphomas.4 Pagetoid reticulosis clinically presents as a solitary psoriasiform or hyperkeratotic patch or plaque that affects the distal extremities. Variable immunophenotypes have been shown in pagetoid reticulosis, such as CD4−/CD8+ and CD4−/CD8−, while classic MF typically shows CD4+/CD8−, as in our case.5
Tinea pedis is a superficial fungal infection usually caused by anthropophilic dermatophytes, with Trichophyton rubrum being the most common organism. Four common clinical presentations of tinea pedis have been identified: interdigital, moccasin, vesicular, and acute ulcerative. Clinical presentation ranges from macerations, ulcerations, and erosions in the toe web spaces to dry hyperkeratotic scaling and fissures on the plantar foot.6 Tinea pedis primarily affects the plantar and interdigital spaces, sparing the dorsal foot and ankle. Treatment is recommended to alleviate symptoms and limit the spread of infection; topical antifungals for 4 weeks is the treatment of choice. However, recurrence is common, and maintenance therapy often is indicated. Oral antifungals or a combination of both topical and oral medications may be needed in certain cases.7
Erythema annulare centrifugum (EAC) is a rare dermatologic disease described as erythematous or urticarial papules that can enlarge centrifugally to form annular lesions that clear centrally. Thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction to an underlying condition, EAC has been associated with fungal infections, various cutaneous diseases, and even internal malignancies. Clinically, EAC can be divided into 2 forms: deep and superficial. Deep gyrate erythema is characterized by a firm indurated border with rare scaling and pruritus that histologically shows perivascular lymphocytic infiltration in the upper and deep dermis. Superficial gyrate erythema has minimally elevated lesions with an indistinct border and trailing scales and pruritus; histopathologic findings present a dense, perivascular, lymphocytic infiltration restricted to the upper dermis.8 Therapy for EAC is directed at relieving symptoms and treating the underlying condition if there is one associated.
Granuloma annulare (GA) is a common skin disorder classically characterized by ringed erythematous plaques, though many variants have been identified. Localized GA is the most common variant and presents with pink-red, nonscaly, annular patches or plaques, typically affecting the hands and feet. Generalized GA is characterized as diffuse annular patches or plaques classically affecting the trunk and extremities. Histology is notable for mucin with a palisading or interstitial pattern of granulomatous inflammation, which was not evident in our patient.9 Topical or intralesional corticosteroids are the first-line treatment of localized GA; however, localized GA generally is self-limited, and treatment often is not necessary. Treatment with cryosurgery, laser therapy, and topical dapsone and tacrolimus also has been described, but evidence of the efficacy of these agents is limited. For generalized GA, phototherapy currently is the most reliable therapy. Systemic therapies include antimalarials, fumaric acid esters, biologics, antimicrobials, and isotretinoin.10
Erythema gyratum repens (EGR) is a rare dermatologic disease described as erythematous concentric bands arranged in parallel rings that can be annular, figurate, or gyrate, with a fine scale trailing the leading edge. Histopathologic features of EGR are nonspecific but are characterized by a perivascular, superficial, mononuclear dermatitis. Diagnosis is based on its characteristic clinical presentation. Although EGR commonly is associated with internal malignancies such as bronchial carcinoma, it also may be associated with benign conditions.11 Improvement often is seen with successful therapy of the underlying associated malignancy.12
Treatment of MF is based on tumor-node-metastasisblood classification, prognostic factors, and clinical stage at the time of diagnosis. Early-stage MF (IA–IIA) commonly is treated with skin-directed therapies such as topical corticosteroids, topical mechlorethamine, topical retinoids, UV phototherapy, and localized radiotherapy. In late stages (IIB–IV), systemic therapy is indicated and includes systemic retinoids, interferon alfa, chemotherapy, monoclonal antibodies, and psoralen plus UVA.13 In many cases, patients may require combination therapy to achieve remission or better control of their condition, as in our patient.
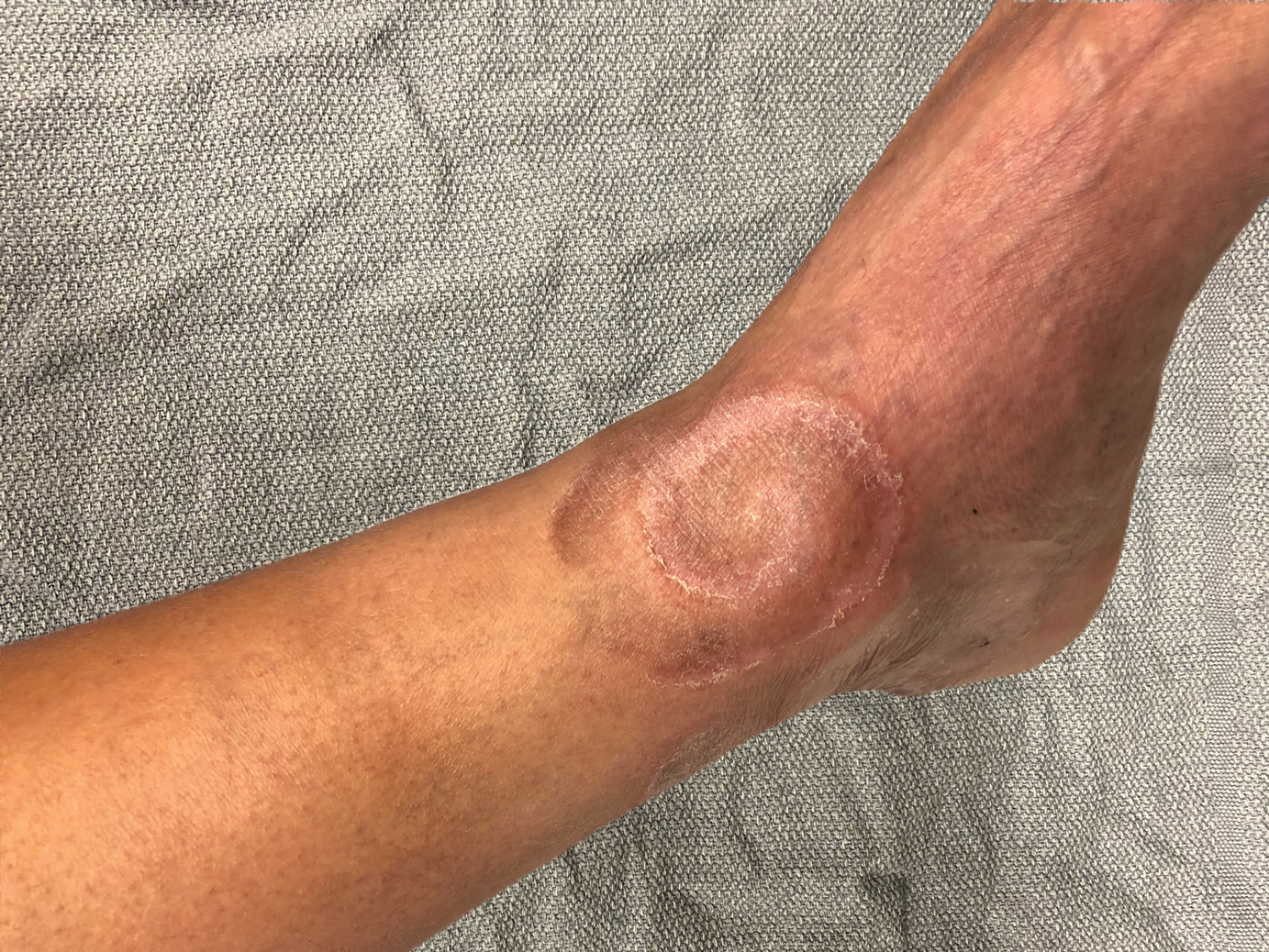
A 60-year-old man presented with a whorl-like plaque on the left ankle that he had noticed while undergoing treatment with narrowband UVB every other week and nitrogen mustard gel daily for stage IB cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, mycosis fungoides type. He denied pain, pruritus, and any other associated symptoms at the site. He denied recent illness, new medications, or changes in diet. His medical history included multiple sclerosis, vascular disease, and stroke. Physical examination revealed an 8×6-cm, welldemarcated, slightly scaly, erythematous plaque with a spiral appearance and peripheral hyperpigmentation involving the left ankle. The remainder of the examination was notable for well-controlled mycosis fungoides with several hyperpigmented patches at sites of prior involvement on the trunk and upper and lower extremities. No cervical, axillary, or inguinal lymphadenopathy was noted. A 4-mm punch biopsy was performed and sent for histopathologic examination.
Rapidly developing vesicular eruption
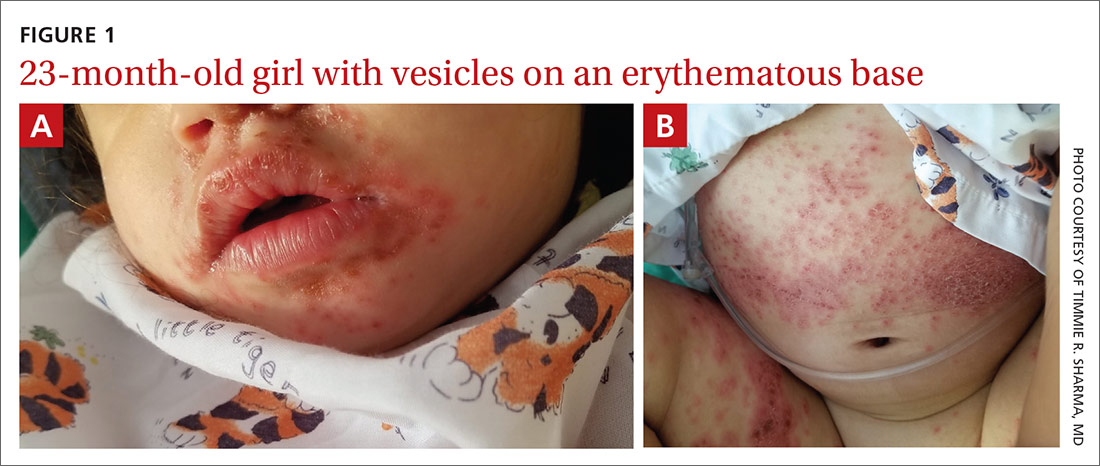
A 23-month-old girl with a history of well-controlled atopic dermatitis was admitted to the hospital with fever and a widespread vesicular eruption of 2 days’ duration. Two days prior to admission, the patient had 3 episodes of nonbloody diarrhea and redness in the diaper area. The child’s parents reported that the red areas spread to her arms and legs later that day, and that she subsequently developed a fever, cough, and rhinorrhea. She was taken to an urgent care facility where she was diagnosed with vulvovaginitis and an upper respiratory infection; amoxicillin was prescribed. Shortly thereafter, the patient developed more lesions in and around the mouth, as well as on the trunk, prompting the parents to bring her to the emergency department.
The history revealed that the patient had spent time with her aunt and cousins who had “red spots” on their palms and soles. The patient’s sister had a flare of “cold sores,” about 2 weeks prior to the current presentation. The patient had received a varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine several months earlier.
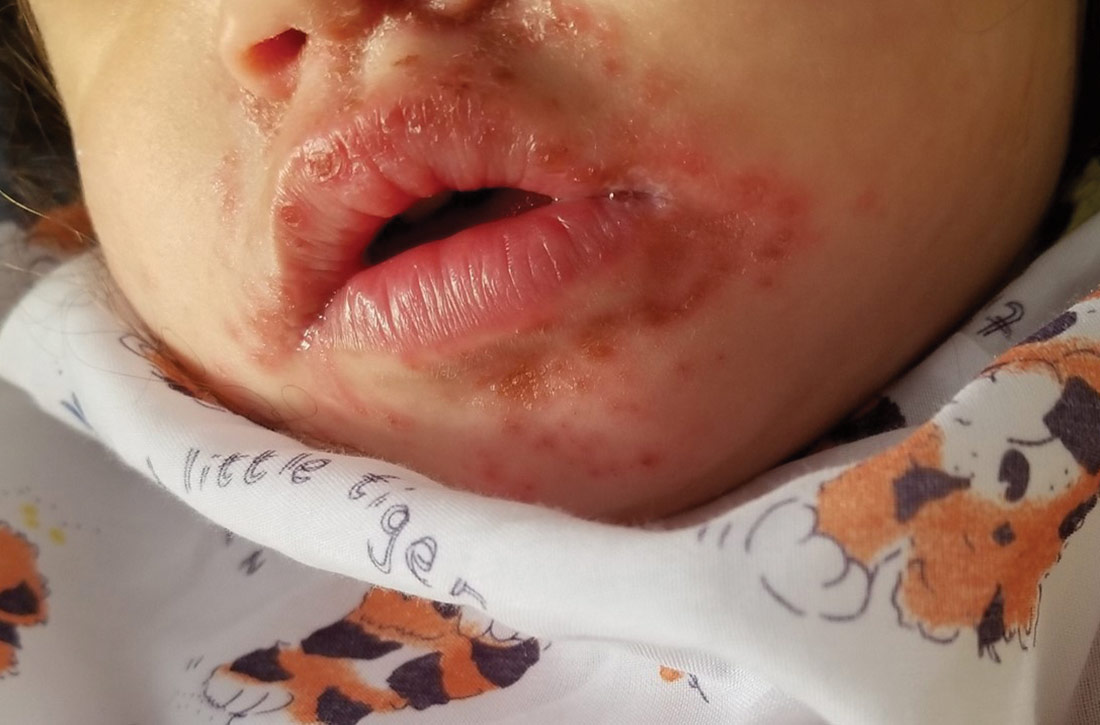
Physical examination was notable for an uncomfortable infant with erythematous macules on the bilateral palms and soles and an erythematous hard palate. The child also had scattered vesicles on an erythematous base with confluent crusted plaques on her lips, perioral skin (FIGURE 1A), abdomen, back, buttocks, arms, legs (FIGURE 1B), and dorsal aspects of her hands and feet.
WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Eczema coxsackium
Given the history of atopic dermatitis; prodromal diarrhea/rhinorrhea; papulovesicular eruption involving areas of prior dermatitis as well as the palms, soles, and mouth; recent contacts with suspected hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD); and history of VZV vaccination, the favored diagnosis was eczema coxsackium.
Eczema coxsackium is an atypical form of HFMD that occurs in patients with a history of eczema. Classic HFMD usually is caused by coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71, while atypical HFMD often is caused by coxsackievirus A6.1,2,3 Patients with HFMD present with painful oral vesicles and ulcers and a papulovesicular eruption on the palms, soles, and sometimes the buttocks and genitalia. Patients may have prodromal fever, fussiness, and diarrhea. Painful oral lesions may result in poor oral intake.1,2
Differential includes viral eruptions
Other conditions may manifest similarly to eczema coxsackium and must be ruled out before initiating proper treatment.
Eczema herpeticum (EH). In atypical HFMD, the virus can show tropism for active or previously inflamed areas of eczematous skin, leading to a widespread vesicular eruption, which can be difficult to distinguish from EH.1 Similar to EH, eczema coxsackium does not exclusively affect children with atopic dermatitis. It also has been described in adults and patients with Darier disease, incontinentia pigmenti, and epidermolytic ichthyosis.4-6
In cases of vesicular eruptions in eczema patients, it is imperative to rule out EH. One prospective study of atypical HFMD compared similarities of the conditions. Both have a predilection for mucosa during primary infection and develop vesicular eruptions on cutaneous eczematous skin.1 One key difference between eczema coxsackium and EH is that EH tends to produce intraoral vesicles beyond simple erythema; it also tends to predominate in the area of the head and neck.7
Continue to: Eczema varicellicum
Eczema varicellicum has been reported, and it has been suggested that some cases of EH may actually be caused by VZV as the 2 are clinically indistinguishable and less than half of EH cases are diagnosed with laboratory confirmation.8
Confirm Dx before you treat
To guide management, cases of suspected eczema coxsackium should be confirmed, and HSV/VZV should be ruled out.9 Testing modalities include swabbing vesicular fluid for enterovirus polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis (preferred modality), oropharyngeal swab up to 2 weeks after infection, or viral isolate from stool samples up to 3 months after infection.2,3
Treatment for eczema coxsackium involves supportive care such as intravenous (IV) hydration and antipyretics. Some studies show potential benefit with IV immunoglobulin in treating severe HFMD, while other studies show the exacerbation of widespread HFMD with this treatment.7,10
Prompt diagnosis and treatment for eczema coxsackium is critical to prevent unnecessary antiviral therapy and to help guide monitoring for associated morbidities including Gianotti-Crosti syndrome–like eruptions, purpuric eruptions, and onychomadesis.
Our patient. Because EH was in the differential, our patient was started on empiric IV acyclovir 10 mg/kg every 8 hours while test results were pending. In addition, she received acetaminophen, IV fluids, gentle sponge baths, and diligent emollient application. Scraping from a vesicle revealed negative herpes simplex virus 1/2 PCR, negative VZV direct fluorescent antibody, and a positive enterovirus PCR—confirming the diagnosis of eczema coxsackium. Interestingly, a viral culture was negative in our patient, consistent with prior reports of enterovirus being difficult to culture.11
With confirmation of the diagnosis of eczema coxsackium, the IV acyclovir was discontinued, and symptoms resolved after 7 days.
CORRESPONDENCE
Shane M. Swink, DO, MS, Division of Dermatology, 1200 South Cedar Crest Boulevard, Allentown, PA 18103; [email protected]
1. Neri I, Dondi A, Wollenberg A, et al. Atypical forms of hand, foot, and mouth disease: a prospective study of 47 Italian children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:429-437.
2. Nassef C, Ziemer C, Morrell DS. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: a new look at a classic viral rash. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2015;27:486-491.
3. Horsten H, Fisker N, Bygu, A. Eczema coxsackium caused by coxsackievirus A6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:230-231.
4. Jefferson J, Grossberg A. Incontinentia pigmenti coxsackium. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:E280-E281.
5. Ganguly S, Kuruvila S. Eczema coxsackium. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:682-683.
6. Harris P, Wang AD, Yin M, et al. Atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease: eczema coxsackium can also occur in adults. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:1043.
7. Wollenberg A, Zoch C, Wetzel S, et al. Predisposing factors and clinical features of eczema herpeticum: a retrospective analysis of 100 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:198-205.
8. Austin TA, Steele RW. Eczema varicella/zoster (varicellicum). Clin Pediatr. 2017;56:579-581.
9. Leung DYM. Why is eczema herpeticum unexpectedly rare? Antiviral Res. 2013;98:153-157.
10. Cao RY, Dong DY, Liu RJ, et al. Human IgG subclasses against enterovirus type 71: neutralization versus antibody dependent enhancement of infection. PLoS One. 2013;8:E64024.
11. Mathes EF, Oza V, Frieden IJ, et al. Eczema coxsackium and unusual cutaneous findings in an enterovirus outbreak. Pediatrics. 2013;132:149-157.
A 23-month-old girl with a history of well-controlled atopic dermatitis was admitted to the hospital with fever and a widespread vesicular eruption of 2 days’ duration. Two days prior to admission, the patient had 3 episodes of nonbloody diarrhea and redness in the diaper area. The child’s parents reported that the red areas spread to her arms and legs later that day, and that she subsequently developed a fever, cough, and rhinorrhea. She was taken to an urgent care facility where she was diagnosed with vulvovaginitis and an upper respiratory infection; amoxicillin was prescribed. Shortly thereafter, the patient developed more lesions in and around the mouth, as well as on the trunk, prompting the parents to bring her to the emergency department.
The history revealed that the patient had spent time with her aunt and cousins who had “red spots” on their palms and soles. The patient’s sister had a flare of “cold sores,” about 2 weeks prior to the current presentation. The patient had received a varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine several months earlier.
Physical examination was notable for an uncomfortable infant with erythematous macules on the bilateral palms and soles and an erythematous hard palate. The child also had scattered vesicles on an erythematous base with confluent crusted plaques on her lips, perioral skin (FIGURE 1A), abdomen, back, buttocks, arms, legs (FIGURE 1B), and dorsal aspects of her hands and feet.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Eczema coxsackium
Given the history of atopic dermatitis; prodromal diarrhea/rhinorrhea; papulovesicular eruption involving areas of prior dermatitis as well as the palms, soles, and mouth; recent contacts with suspected hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD); and history of VZV vaccination, the favored diagnosis was eczema coxsackium.
Eczema coxsackium is an atypical form of HFMD that occurs in patients with a history of eczema. Classic HFMD usually is caused by coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71, while atypical HFMD often is caused by coxsackievirus A6.1,2,3 Patients with HFMD present with painful oral vesicles and ulcers and a papulovesicular eruption on the palms, soles, and sometimes the buttocks and genitalia. Patients may have prodromal fever, fussiness, and diarrhea. Painful oral lesions may result in poor oral intake.1,2
Differential includes viral eruptions
Other conditions may manifest similarly to eczema coxsackium and must be ruled out before initiating proper treatment.
Eczema herpeticum (EH). In atypical HFMD, the virus can show tropism for active or previously inflamed areas of eczematous skin, leading to a widespread vesicular eruption, which can be difficult to distinguish from EH.1 Similar to EH, eczema coxsackium does not exclusively affect children with atopic dermatitis. It also has been described in adults and patients with Darier disease, incontinentia pigmenti, and epidermolytic ichthyosis.4-6
In cases of vesicular eruptions in eczema patients, it is imperative to rule out EH. One prospective study of atypical HFMD compared similarities of the conditions. Both have a predilection for mucosa during primary infection and develop vesicular eruptions on cutaneous eczematous skin.1 One key difference between eczema coxsackium and EH is that EH tends to produce intraoral vesicles beyond simple erythema; it also tends to predominate in the area of the head and neck.7
Continue to: Eczema varicellicum
Eczema varicellicum has been reported, and it has been suggested that some cases of EH may actually be caused by VZV as the 2 are clinically indistinguishable and less than half of EH cases are diagnosed with laboratory confirmation.8
Confirm Dx before you treat
To guide management, cases of suspected eczema coxsackium should be confirmed, and HSV/VZV should be ruled out.9 Testing modalities include swabbing vesicular fluid for enterovirus polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis (preferred modality), oropharyngeal swab up to 2 weeks after infection, or viral isolate from stool samples up to 3 months after infection.2,3
Treatment for eczema coxsackium involves supportive care such as intravenous (IV) hydration and antipyretics. Some studies show potential benefit with IV immunoglobulin in treating severe HFMD, while other studies show the exacerbation of widespread HFMD with this treatment.7,10
Prompt diagnosis and treatment for eczema coxsackium is critical to prevent unnecessary antiviral therapy and to help guide monitoring for associated morbidities including Gianotti-Crosti syndrome–like eruptions, purpuric eruptions, and onychomadesis.
Our patient. Because EH was in the differential, our patient was started on empiric IV acyclovir 10 mg/kg every 8 hours while test results were pending. In addition, she received acetaminophen, IV fluids, gentle sponge baths, and diligent emollient application. Scraping from a vesicle revealed negative herpes simplex virus 1/2 PCR, negative VZV direct fluorescent antibody, and a positive enterovirus PCR—confirming the diagnosis of eczema coxsackium. Interestingly, a viral culture was negative in our patient, consistent with prior reports of enterovirus being difficult to culture.11
With confirmation of the diagnosis of eczema coxsackium, the IV acyclovir was discontinued, and symptoms resolved after 7 days.
CORRESPONDENCE
Shane M. Swink, DO, MS, Division of Dermatology, 1200 South Cedar Crest Boulevard, Allentown, PA 18103; [email protected]
A 23-month-old girl with a history of well-controlled atopic dermatitis was admitted to the hospital with fever and a widespread vesicular eruption of 2 days’ duration. Two days prior to admission, the patient had 3 episodes of nonbloody diarrhea and redness in the diaper area. The child’s parents reported that the red areas spread to her arms and legs later that day, and that she subsequently developed a fever, cough, and rhinorrhea. She was taken to an urgent care facility where she was diagnosed with vulvovaginitis and an upper respiratory infection; amoxicillin was prescribed. Shortly thereafter, the patient developed more lesions in and around the mouth, as well as on the trunk, prompting the parents to bring her to the emergency department.
The history revealed that the patient had spent time with her aunt and cousins who had “red spots” on their palms and soles. The patient’s sister had a flare of “cold sores,” about 2 weeks prior to the current presentation. The patient had received a varicella zoster virus (VZV) vaccine several months earlier.
Physical examination was notable for an uncomfortable infant with erythematous macules on the bilateral palms and soles and an erythematous hard palate. The child also had scattered vesicles on an erythematous base with confluent crusted plaques on her lips, perioral skin (FIGURE 1A), abdomen, back, buttocks, arms, legs (FIGURE 1B), and dorsal aspects of her hands and feet.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Eczema coxsackium
Given the history of atopic dermatitis; prodromal diarrhea/rhinorrhea; papulovesicular eruption involving areas of prior dermatitis as well as the palms, soles, and mouth; recent contacts with suspected hand-foot-mouth disease (HFMD); and history of VZV vaccination, the favored diagnosis was eczema coxsackium.
Eczema coxsackium is an atypical form of HFMD that occurs in patients with a history of eczema. Classic HFMD usually is caused by coxsackievirus A16 or enterovirus 71, while atypical HFMD often is caused by coxsackievirus A6.1,2,3 Patients with HFMD present with painful oral vesicles and ulcers and a papulovesicular eruption on the palms, soles, and sometimes the buttocks and genitalia. Patients may have prodromal fever, fussiness, and diarrhea. Painful oral lesions may result in poor oral intake.1,2
Differential includes viral eruptions
Other conditions may manifest similarly to eczema coxsackium and must be ruled out before initiating proper treatment.
Eczema herpeticum (EH). In atypical HFMD, the virus can show tropism for active or previously inflamed areas of eczematous skin, leading to a widespread vesicular eruption, which can be difficult to distinguish from EH.1 Similar to EH, eczema coxsackium does not exclusively affect children with atopic dermatitis. It also has been described in adults and patients with Darier disease, incontinentia pigmenti, and epidermolytic ichthyosis.4-6
In cases of vesicular eruptions in eczema patients, it is imperative to rule out EH. One prospective study of atypical HFMD compared similarities of the conditions. Both have a predilection for mucosa during primary infection and develop vesicular eruptions on cutaneous eczematous skin.1 One key difference between eczema coxsackium and EH is that EH tends to produce intraoral vesicles beyond simple erythema; it also tends to predominate in the area of the head and neck.7
Continue to: Eczema varicellicum
Eczema varicellicum has been reported, and it has been suggested that some cases of EH may actually be caused by VZV as the 2 are clinically indistinguishable and less than half of EH cases are diagnosed with laboratory confirmation.8
Confirm Dx before you treat
To guide management, cases of suspected eczema coxsackium should be confirmed, and HSV/VZV should be ruled out.9 Testing modalities include swabbing vesicular fluid for enterovirus polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis (preferred modality), oropharyngeal swab up to 2 weeks after infection, or viral isolate from stool samples up to 3 months after infection.2,3
Treatment for eczema coxsackium involves supportive care such as intravenous (IV) hydration and antipyretics. Some studies show potential benefit with IV immunoglobulin in treating severe HFMD, while other studies show the exacerbation of widespread HFMD with this treatment.7,10
Prompt diagnosis and treatment for eczema coxsackium is critical to prevent unnecessary antiviral therapy and to help guide monitoring for associated morbidities including Gianotti-Crosti syndrome–like eruptions, purpuric eruptions, and onychomadesis.
Our patient. Because EH was in the differential, our patient was started on empiric IV acyclovir 10 mg/kg every 8 hours while test results were pending. In addition, she received acetaminophen, IV fluids, gentle sponge baths, and diligent emollient application. Scraping from a vesicle revealed negative herpes simplex virus 1/2 PCR, negative VZV direct fluorescent antibody, and a positive enterovirus PCR—confirming the diagnosis of eczema coxsackium. Interestingly, a viral culture was negative in our patient, consistent with prior reports of enterovirus being difficult to culture.11
With confirmation of the diagnosis of eczema coxsackium, the IV acyclovir was discontinued, and symptoms resolved after 7 days.
CORRESPONDENCE
Shane M. Swink, DO, MS, Division of Dermatology, 1200 South Cedar Crest Boulevard, Allentown, PA 18103; [email protected]
1. Neri I, Dondi A, Wollenberg A, et al. Atypical forms of hand, foot, and mouth disease: a prospective study of 47 Italian children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:429-437.
2. Nassef C, Ziemer C, Morrell DS. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: a new look at a classic viral rash. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2015;27:486-491.
3. Horsten H, Fisker N, Bygu, A. Eczema coxsackium caused by coxsackievirus A6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:230-231.
4. Jefferson J, Grossberg A. Incontinentia pigmenti coxsackium. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:E280-E281.
5. Ganguly S, Kuruvila S. Eczema coxsackium. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:682-683.
6. Harris P, Wang AD, Yin M, et al. Atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease: eczema coxsackium can also occur in adults. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:1043.
7. Wollenberg A, Zoch C, Wetzel S, et al. Predisposing factors and clinical features of eczema herpeticum: a retrospective analysis of 100 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:198-205.
8. Austin TA, Steele RW. Eczema varicella/zoster (varicellicum). Clin Pediatr. 2017;56:579-581.
9. Leung DYM. Why is eczema herpeticum unexpectedly rare? Antiviral Res. 2013;98:153-157.
10. Cao RY, Dong DY, Liu RJ, et al. Human IgG subclasses against enterovirus type 71: neutralization versus antibody dependent enhancement of infection. PLoS One. 2013;8:E64024.
11. Mathes EF, Oza V, Frieden IJ, et al. Eczema coxsackium and unusual cutaneous findings in an enterovirus outbreak. Pediatrics. 2013;132:149-157.
1. Neri I, Dondi A, Wollenberg A, et al. Atypical forms of hand, foot, and mouth disease: a prospective study of 47 Italian children. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:429-437.
2. Nassef C, Ziemer C, Morrell DS. Hand-foot-and-mouth disease: a new look at a classic viral rash. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2015;27:486-491.
3. Horsten H, Fisker N, Bygu, A. Eczema coxsackium caused by coxsackievirus A6. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:230-231.
4. Jefferson J, Grossberg A. Incontinentia pigmenti coxsackium. Pediatr Dermatol. 2016;33:E280-E281.
5. Ganguly S, Kuruvila S. Eczema coxsackium. Indian J Dermatol. 2016;61:682-683.
6. Harris P, Wang AD, Yin M, et al. Atypical hand, foot, and mouth disease: eczema coxsackium can also occur in adults. Lancet Infect Dis. 2014;14:1043.
7. Wollenberg A, Zoch C, Wetzel S, et al. Predisposing factors and clinical features of eczema herpeticum: a retrospective analysis of 100 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2003;49:198-205.
8. Austin TA, Steele RW. Eczema varicella/zoster (varicellicum). Clin Pediatr. 2017;56:579-581.
9. Leung DYM. Why is eczema herpeticum unexpectedly rare? Antiviral Res. 2013;98:153-157.
10. Cao RY, Dong DY, Liu RJ, et al. Human IgG subclasses against enterovirus type 71: neutralization versus antibody dependent enhancement of infection. PLoS One. 2013;8:E64024.
11. Mathes EF, Oza V, Frieden IJ, et al. Eczema coxsackium and unusual cutaneous findings in an enterovirus outbreak. Pediatrics. 2013;132:149-157.