User login
Want to see what COVID strain you have? The government says no
Every day, more than 140,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with COVID-19. But no matter how curious they are about which variant they are fighting, none of them will find out.
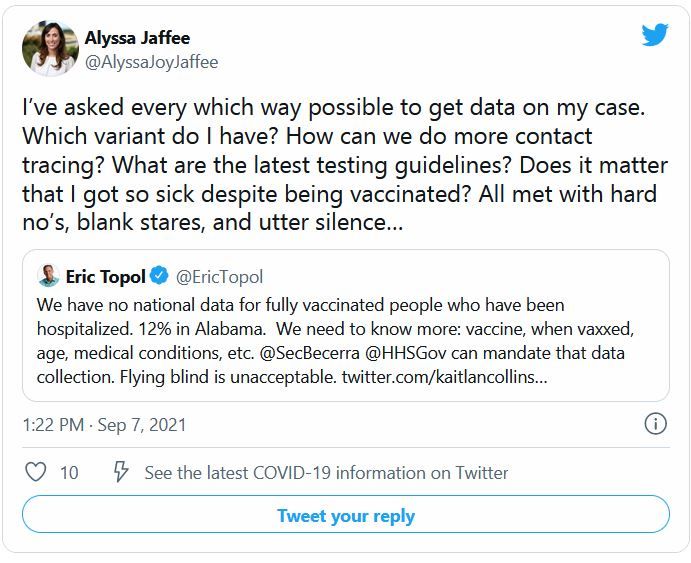
The country is dotted with labs that sequence the genomes of COVID-19 cases, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tracks those results. But federal rules say those results are not allowed to make their way back to patients or doctors.
According to public health and infectious disease experts, this is unlikely to change any time soon.
“I know people want to know – I’ve had a lot of friends or family who’ve asked me how they can find out,” says Aubree Gordon, PhD, an epidemiology specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think it’s an interesting thing to find out, for sure. And it would certainly be nice to know. But because it probably isn’t necessary, there is little motivation to change the rules.”
Because the tests that are used have not been approved as diagnostic tools under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments program, which is overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they can only be used for research purposes.
In fact, the scientists doing the sequencing rarely have any patient information, Dr. Gordon says. For example, the Lauring Lab at University of Michigan – run by Adam Lauring, MD – focuses on viral evolution and currently tests for variants. But this is not done for the sake of the patient or the doctors treating the patient.
“The samples come in ... and they’ve been de-identified,”Dr. Gordon says. “This is just for research purposes. Not much patient information is shared with the researchers.”
But as of now, aside from sheer curiosity, there is not a reason to change this, says Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at University of California, Los Angeles.
Although there are emerging variants – including the new Mu variant, also known as B.1.621 and recently classified as a “variant of interest” – the Delta variant accounts for about 99% of U.S. cases.
In addition, Dr. Brewer says, treatments are the same for all COVID-19 patients, regardless of the variant.
“There would have to be some clinical significance for there to be a good reason to give this information,” he says. “That would mean we would be doing something different treatment-wise depending on the variant. As of now, that is not the case.”
There is a loophole that allows labs to release variant information: They can develop their own tests. But they then must go through a lengthy validation process that proves their tests are as effective as the gold standard, says Mark Pandori, PhD, director of the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
But even with validation, it is too time-consuming and costly to sequence large numbers of cases, he says.
“The reason we’re not doing it routinely is there’s no way to do the genomic analysis on all the positives,” Dr. Pandori says. “It is about $110 dollars to do a sequence. It’s not like a standard PCR test.”
There is a hypothetical situation that may warrant the release of these results, Dr. Brewer says: If a variant emerges that evades vaccines.
“That would be a real public health issue,” he says. “You want to make sure there aren’t variants emerging somewhere that are escaping immunity.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Every day, more than 140,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with COVID-19. But no matter how curious they are about which variant they are fighting, none of them will find out.

The country is dotted with labs that sequence the genomes of COVID-19 cases, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tracks those results. But federal rules say those results are not allowed to make their way back to patients or doctors.
According to public health and infectious disease experts, this is unlikely to change any time soon.
“I know people want to know – I’ve had a lot of friends or family who’ve asked me how they can find out,” says Aubree Gordon, PhD, an epidemiology specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think it’s an interesting thing to find out, for sure. And it would certainly be nice to know. But because it probably isn’t necessary, there is little motivation to change the rules.”
Because the tests that are used have not been approved as diagnostic tools under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments program, which is overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they can only be used for research purposes.
In fact, the scientists doing the sequencing rarely have any patient information, Dr. Gordon says. For example, the Lauring Lab at University of Michigan – run by Adam Lauring, MD – focuses on viral evolution and currently tests for variants. But this is not done for the sake of the patient or the doctors treating the patient.
“The samples come in ... and they’ve been de-identified,”Dr. Gordon says. “This is just for research purposes. Not much patient information is shared with the researchers.”
But as of now, aside from sheer curiosity, there is not a reason to change this, says Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at University of California, Los Angeles.
Although there are emerging variants – including the new Mu variant, also known as B.1.621 and recently classified as a “variant of interest” – the Delta variant accounts for about 99% of U.S. cases.
In addition, Dr. Brewer says, treatments are the same for all COVID-19 patients, regardless of the variant.
“There would have to be some clinical significance for there to be a good reason to give this information,” he says. “That would mean we would be doing something different treatment-wise depending on the variant. As of now, that is not the case.”
There is a loophole that allows labs to release variant information: They can develop their own tests. But they then must go through a lengthy validation process that proves their tests are as effective as the gold standard, says Mark Pandori, PhD, director of the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
But even with validation, it is too time-consuming and costly to sequence large numbers of cases, he says.
“The reason we’re not doing it routinely is there’s no way to do the genomic analysis on all the positives,” Dr. Pandori says. “It is about $110 dollars to do a sequence. It’s not like a standard PCR test.”
There is a hypothetical situation that may warrant the release of these results, Dr. Brewer says: If a variant emerges that evades vaccines.
“That would be a real public health issue,” he says. “You want to make sure there aren’t variants emerging somewhere that are escaping immunity.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Every day, more than 140,000 people in the United States are diagnosed with COVID-19. But no matter how curious they are about which variant they are fighting, none of them will find out.

The country is dotted with labs that sequence the genomes of COVID-19 cases, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention tracks those results. But federal rules say those results are not allowed to make their way back to patients or doctors.
According to public health and infectious disease experts, this is unlikely to change any time soon.
“I know people want to know – I’ve had a lot of friends or family who’ve asked me how they can find out,” says Aubree Gordon, PhD, an epidemiology specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor. “I think it’s an interesting thing to find out, for sure. And it would certainly be nice to know. But because it probably isn’t necessary, there is little motivation to change the rules.”
Because the tests that are used have not been approved as diagnostic tools under the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments program, which is overseen by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services, they can only be used for research purposes.
In fact, the scientists doing the sequencing rarely have any patient information, Dr. Gordon says. For example, the Lauring Lab at University of Michigan – run by Adam Lauring, MD – focuses on viral evolution and currently tests for variants. But this is not done for the sake of the patient or the doctors treating the patient.
“The samples come in ... and they’ve been de-identified,”Dr. Gordon says. “This is just for research purposes. Not much patient information is shared with the researchers.”
But as of now, aside from sheer curiosity, there is not a reason to change this, says Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at University of California, Los Angeles.
Although there are emerging variants – including the new Mu variant, also known as B.1.621 and recently classified as a “variant of interest” – the Delta variant accounts for about 99% of U.S. cases.
In addition, Dr. Brewer says, treatments are the same for all COVID-19 patients, regardless of the variant.
“There would have to be some clinical significance for there to be a good reason to give this information,” he says. “That would mean we would be doing something different treatment-wise depending on the variant. As of now, that is not the case.”
There is a loophole that allows labs to release variant information: They can develop their own tests. But they then must go through a lengthy validation process that proves their tests are as effective as the gold standard, says Mark Pandori, PhD, director of the Nevada State Public Health Laboratory.
But even with validation, it is too time-consuming and costly to sequence large numbers of cases, he says.
“The reason we’re not doing it routinely is there’s no way to do the genomic analysis on all the positives,” Dr. Pandori says. “It is about $110 dollars to do a sequence. It’s not like a standard PCR test.”
There is a hypothetical situation that may warrant the release of these results, Dr. Brewer says: If a variant emerges that evades vaccines.
“That would be a real public health issue,” he says. “You want to make sure there aren’t variants emerging somewhere that are escaping immunity.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA authorizes booster shot for immunocompromised Americans
The decision, which came late on Aug. 12, was not unexpected and a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) panel meeting Aug. 13 is expected to approve directions to doctors and health care providers on who should receive the booster shot.
“The country has entered yet another wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the FDA is especially cognizant that immunocompromised people are particularly at risk for severe disease. After a thorough review of the available data, the FDA determined that this small, vulnerable group may benefit from a third dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna Vaccines,” acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said in a statement.
Those eligible for a third dose include solid organ transplant recipients, those undergoing cancer treatments, and people with autoimmune diseases that suppress their immune systems.
Meanwhile, White House officials said Aug. 12 they “have supply and are prepared” to give all U.S. residents COVID-19 boosters -- which, as of now, are likely to be authorized first only for immunocompromised people.
“We believe sooner or later you will need a booster,” Anthony Fauci, MD, said at a news briefing Aug. 12. “Right now, we are evaluating this on a day-by-day, week-by-week, month-by-month basis.”
He added: “Right at this moment, apart from the immunocompromised -- elderly or not elderly -- people do not need a booster.” But, he said, “We’re preparing for the eventuality of doing that.”
White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said officials “have supply and are prepared” to at some point provide widespread access to boosters.
The immunocompromised population is very small -- less than 3% of adults, said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 rates continue to rise. Dr. Walensky reported that the 7-day average of daily cases is 132,384 -- an increase of 24% from the previous week. Average daily hospitalizations are up 31%, at 9,700, and deaths are up to 452 -- an increase of 22%.
In the past week, Florida has had more COVID-19 cases than the 30 states with the lowest case rates combined, Mr. Zients said. Florida and Texas alone have accounted for nearly 40% of new hospitalizations across the country.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The decision, which came late on Aug. 12, was not unexpected and a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) panel meeting Aug. 13 is expected to approve directions to doctors and health care providers on who should receive the booster shot.
“The country has entered yet another wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the FDA is especially cognizant that immunocompromised people are particularly at risk for severe disease. After a thorough review of the available data, the FDA determined that this small, vulnerable group may benefit from a third dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna Vaccines,” acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said in a statement.
Those eligible for a third dose include solid organ transplant recipients, those undergoing cancer treatments, and people with autoimmune diseases that suppress their immune systems.
Meanwhile, White House officials said Aug. 12 they “have supply and are prepared” to give all U.S. residents COVID-19 boosters -- which, as of now, are likely to be authorized first only for immunocompromised people.
“We believe sooner or later you will need a booster,” Anthony Fauci, MD, said at a news briefing Aug. 12. “Right now, we are evaluating this on a day-by-day, week-by-week, month-by-month basis.”
He added: “Right at this moment, apart from the immunocompromised -- elderly or not elderly -- people do not need a booster.” But, he said, “We’re preparing for the eventuality of doing that.”
White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said officials “have supply and are prepared” to at some point provide widespread access to boosters.
The immunocompromised population is very small -- less than 3% of adults, said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 rates continue to rise. Dr. Walensky reported that the 7-day average of daily cases is 132,384 -- an increase of 24% from the previous week. Average daily hospitalizations are up 31%, at 9,700, and deaths are up to 452 -- an increase of 22%.
In the past week, Florida has had more COVID-19 cases than the 30 states with the lowest case rates combined, Mr. Zients said. Florida and Texas alone have accounted for nearly 40% of new hospitalizations across the country.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The decision, which came late on Aug. 12, was not unexpected and a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) panel meeting Aug. 13 is expected to approve directions to doctors and health care providers on who should receive the booster shot.
“The country has entered yet another wave of the COVID-19 pandemic, and the FDA is especially cognizant that immunocompromised people are particularly at risk for severe disease. After a thorough review of the available data, the FDA determined that this small, vulnerable group may benefit from a third dose of the Pfizer-BioNTech or Moderna Vaccines,” acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock, MD, said in a statement.
Those eligible for a third dose include solid organ transplant recipients, those undergoing cancer treatments, and people with autoimmune diseases that suppress their immune systems.
Meanwhile, White House officials said Aug. 12 they “have supply and are prepared” to give all U.S. residents COVID-19 boosters -- which, as of now, are likely to be authorized first only for immunocompromised people.
“We believe sooner or later you will need a booster,” Anthony Fauci, MD, said at a news briefing Aug. 12. “Right now, we are evaluating this on a day-by-day, week-by-week, month-by-month basis.”
He added: “Right at this moment, apart from the immunocompromised -- elderly or not elderly -- people do not need a booster.” But, he said, “We’re preparing for the eventuality of doing that.”
White House COVID-19 Response Coordinator Jeff Zients said officials “have supply and are prepared” to at some point provide widespread access to boosters.
The immunocompromised population is very small -- less than 3% of adults, said CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD.
Meanwhile, COVID-19 rates continue to rise. Dr. Walensky reported that the 7-day average of daily cases is 132,384 -- an increase of 24% from the previous week. Average daily hospitalizations are up 31%, at 9,700, and deaths are up to 452 -- an increase of 22%.
In the past week, Florida has had more COVID-19 cases than the 30 states with the lowest case rates combined, Mr. Zients said. Florida and Texas alone have accounted for nearly 40% of new hospitalizations across the country.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Health anxiety common as COVID restrictions loosen
As restrictions lift and mask mandates become scarce, Americans are filling their social calendars and booking vacations. While some are rejoicing, health care professionals say others are emerging from the pandemic with more health-related fears.
COVID-19 has caused more anxiety and depression for many over the course of the pandemic. A survey from the CDC and the Census Bureau found the percentage of adults with symptoms of an anxiety or depressive disorder increased from 36.4% to 41.5% from August 2020 to February 2021.
But this phenomenon will not just disappear as COVID-19 cases decrease, said Reese Druckenmiller, a clinical social worker for the Mayo Clinic Health System.
“There are still people out there not wanting to leave home,” she said. “Some folks inherently struggle with anxiety more than others, and we know anxiety can come from different experiences and traumas.
Though there is little research on the psychological effects of pandemic outbreaks, scientists are beginning to explore this. A recent review published in the International Journal of Cognitive Therapy concluded that, based on available research and the effects of previous pandemics, COVID-19 will likely have a significant effect on people’s mental health, particularly those who already have obsessive-compulsive disorder and health anxiety, along with people on the front line of health care.
According to the authors, since the virus doesn’t have symptoms among certain populations, there’s more anxiety about becoming infected and unknowingly spreading it to vulnerable people.
Not to mention the influx of anxiety-provoking news over the past year, Ms. Druckenmiller noted.
“One thing I noticed during the pandemic: The news changed. There were still regular news stories, but at the forefront of every single newscast was the numbers, how many people have died, how many people are hospitalized,” she said.
Some of Ms. Druckenmiller’s own patients who are more health-focused saw this as an added burden – another source of anxiety.
For those still uncomfortable with an abrupt reentry into public spaces, Ms. Druckenmiller recommended taking small steps. Start leaving the house every day, she suggested, even if it’s just for a walk. It is also important to be honest with loved ones about your own comfort level.
“Our brain is very flexible and fluid, but it also doesn’t just switch on a dime,” she said. “If I’ve been told over the past year this is a horrible thing that could kill me, my brain can’t adjust that fast. We need evidence through experience.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As restrictions lift and mask mandates become scarce, Americans are filling their social calendars and booking vacations. While some are rejoicing, health care professionals say others are emerging from the pandemic with more health-related fears.
COVID-19 has caused more anxiety and depression for many over the course of the pandemic. A survey from the CDC and the Census Bureau found the percentage of adults with symptoms of an anxiety or depressive disorder increased from 36.4% to 41.5% from August 2020 to February 2021.
But this phenomenon will not just disappear as COVID-19 cases decrease, said Reese Druckenmiller, a clinical social worker for the Mayo Clinic Health System.
“There are still people out there not wanting to leave home,” she said. “Some folks inherently struggle with anxiety more than others, and we know anxiety can come from different experiences and traumas.
Though there is little research on the psychological effects of pandemic outbreaks, scientists are beginning to explore this. A recent review published in the International Journal of Cognitive Therapy concluded that, based on available research and the effects of previous pandemics, COVID-19 will likely have a significant effect on people’s mental health, particularly those who already have obsessive-compulsive disorder and health anxiety, along with people on the front line of health care.
According to the authors, since the virus doesn’t have symptoms among certain populations, there’s more anxiety about becoming infected and unknowingly spreading it to vulnerable people.
Not to mention the influx of anxiety-provoking news over the past year, Ms. Druckenmiller noted.
“One thing I noticed during the pandemic: The news changed. There were still regular news stories, but at the forefront of every single newscast was the numbers, how many people have died, how many people are hospitalized,” she said.
Some of Ms. Druckenmiller’s own patients who are more health-focused saw this as an added burden – another source of anxiety.
For those still uncomfortable with an abrupt reentry into public spaces, Ms. Druckenmiller recommended taking small steps. Start leaving the house every day, she suggested, even if it’s just for a walk. It is also important to be honest with loved ones about your own comfort level.
“Our brain is very flexible and fluid, but it also doesn’t just switch on a dime,” she said. “If I’ve been told over the past year this is a horrible thing that could kill me, my brain can’t adjust that fast. We need evidence through experience.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
As restrictions lift and mask mandates become scarce, Americans are filling their social calendars and booking vacations. While some are rejoicing, health care professionals say others are emerging from the pandemic with more health-related fears.
COVID-19 has caused more anxiety and depression for many over the course of the pandemic. A survey from the CDC and the Census Bureau found the percentage of adults with symptoms of an anxiety or depressive disorder increased from 36.4% to 41.5% from August 2020 to February 2021.
But this phenomenon will not just disappear as COVID-19 cases decrease, said Reese Druckenmiller, a clinical social worker for the Mayo Clinic Health System.
“There are still people out there not wanting to leave home,” she said. “Some folks inherently struggle with anxiety more than others, and we know anxiety can come from different experiences and traumas.
Though there is little research on the psychological effects of pandemic outbreaks, scientists are beginning to explore this. A recent review published in the International Journal of Cognitive Therapy concluded that, based on available research and the effects of previous pandemics, COVID-19 will likely have a significant effect on people’s mental health, particularly those who already have obsessive-compulsive disorder and health anxiety, along with people on the front line of health care.
According to the authors, since the virus doesn’t have symptoms among certain populations, there’s more anxiety about becoming infected and unknowingly spreading it to vulnerable people.
Not to mention the influx of anxiety-provoking news over the past year, Ms. Druckenmiller noted.
“One thing I noticed during the pandemic: The news changed. There were still regular news stories, but at the forefront of every single newscast was the numbers, how many people have died, how many people are hospitalized,” she said.
Some of Ms. Druckenmiller’s own patients who are more health-focused saw this as an added burden – another source of anxiety.
For those still uncomfortable with an abrupt reentry into public spaces, Ms. Druckenmiller recommended taking small steps. Start leaving the house every day, she suggested, even if it’s just for a walk. It is also important to be honest with loved ones about your own comfort level.
“Our brain is very flexible and fluid, but it also doesn’t just switch on a dime,” she said. “If I’ve been told over the past year this is a horrible thing that could kill me, my brain can’t adjust that fast. We need evidence through experience.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Supreme Court upholds Affordable Care Act
The challengers were comprised of 18 GOP-dominated states, led by Texas, that took issue with the ACA’s individual mandate – which required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a tax penalty.
But Congress reduced the penalty to zero in 2017. Challengers argued that without the mandate, the rest of the law should be scrapped, too. The court ruled that eliminated the harm the states were claiming.
“To have standing, a plaintiff must ‘allege personal injury fairly traceable to the defendant’s allegedly unlawful conduct and likely to be redressed by the requested relief,’” the majority wrote. “No plaintiff has shown such an injury ‘fairly traceable’ to the ‘allegedly unlawful conduct’ challenged here.”
Justice Stephen Breyer authored the opinion. Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch dissented.
The decision said that the mandate in question did not require the 18 states that brought the complaint to pay anything, and therefore they had no standing.
President Joe Biden has said he plans to build on the ACA – which was enacted while he was vice president – to offer coverage to more Americans.
This marks the third time the Supreme Court spared the Obama-era law from GOP attacks. The mandate was also upheld in 2012 in a 5 to 4 ruling.
American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, also called for building on the ruling to expand the law.
“With yet another court decision upholding the ACA now behind us, we remain committed to strengthening the current law and look forward to policymakers advancing solutions to improve the ACA,” Dr. Harmon said in a statement. “The AMA will continue working to expand access to health care and ensure that all Americans have meaningful, comprehensive, and affordable health coverage to improve the health of the nation.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.), a longtime advocate for the ACA, called the decision a “landmark victory for Democrats.”
“Thanks to the tireless advocacy of Americans across the country and Democrats in Congress, the Affordable Care Act endures as a pillar of American health and economic security alongside Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security,” she said in a statement.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) also celebrated the ruling.
“The Affordable Care Act has won. The Supreme Court has just ruled: the ACA is here to stay and now we’re going to try to make it bigger and better,” he said, according to CNN. “For more than a decade, the assault on our health care law was relentless from Republicans in Congress, from the executive branch itself and from Republican attorneys general in the courts. Each time in each arena, the ACA has prevailed.”
This article was updated June 17, 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The challengers were comprised of 18 GOP-dominated states, led by Texas, that took issue with the ACA’s individual mandate – which required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a tax penalty.
But Congress reduced the penalty to zero in 2017. Challengers argued that without the mandate, the rest of the law should be scrapped, too. The court ruled that eliminated the harm the states were claiming.
“To have standing, a plaintiff must ‘allege personal injury fairly traceable to the defendant’s allegedly unlawful conduct and likely to be redressed by the requested relief,’” the majority wrote. “No plaintiff has shown such an injury ‘fairly traceable’ to the ‘allegedly unlawful conduct’ challenged here.”
Justice Stephen Breyer authored the opinion. Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch dissented.
The decision said that the mandate in question did not require the 18 states that brought the complaint to pay anything, and therefore they had no standing.
President Joe Biden has said he plans to build on the ACA – which was enacted while he was vice president – to offer coverage to more Americans.
This marks the third time the Supreme Court spared the Obama-era law from GOP attacks. The mandate was also upheld in 2012 in a 5 to 4 ruling.
American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, also called for building on the ruling to expand the law.
“With yet another court decision upholding the ACA now behind us, we remain committed to strengthening the current law and look forward to policymakers advancing solutions to improve the ACA,” Dr. Harmon said in a statement. “The AMA will continue working to expand access to health care and ensure that all Americans have meaningful, comprehensive, and affordable health coverage to improve the health of the nation.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.), a longtime advocate for the ACA, called the decision a “landmark victory for Democrats.”
“Thanks to the tireless advocacy of Americans across the country and Democrats in Congress, the Affordable Care Act endures as a pillar of American health and economic security alongside Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security,” she said in a statement.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) also celebrated the ruling.
“The Affordable Care Act has won. The Supreme Court has just ruled: the ACA is here to stay and now we’re going to try to make it bigger and better,” he said, according to CNN. “For more than a decade, the assault on our health care law was relentless from Republicans in Congress, from the executive branch itself and from Republican attorneys general in the courts. Each time in each arena, the ACA has prevailed.”
This article was updated June 17, 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The challengers were comprised of 18 GOP-dominated states, led by Texas, that took issue with the ACA’s individual mandate – which required most Americans to have health insurance or pay a tax penalty.
But Congress reduced the penalty to zero in 2017. Challengers argued that without the mandate, the rest of the law should be scrapped, too. The court ruled that eliminated the harm the states were claiming.
“To have standing, a plaintiff must ‘allege personal injury fairly traceable to the defendant’s allegedly unlawful conduct and likely to be redressed by the requested relief,’” the majority wrote. “No plaintiff has shown such an injury ‘fairly traceable’ to the ‘allegedly unlawful conduct’ challenged here.”
Justice Stephen Breyer authored the opinion. Justices Samuel Alito and Neil Gorsuch dissented.
The decision said that the mandate in question did not require the 18 states that brought the complaint to pay anything, and therefore they had no standing.
President Joe Biden has said he plans to build on the ACA – which was enacted while he was vice president – to offer coverage to more Americans.
This marks the third time the Supreme Court spared the Obama-era law from GOP attacks. The mandate was also upheld in 2012 in a 5 to 4 ruling.
American Medical Association president Gerald Harmon, MD, also called for building on the ruling to expand the law.
“With yet another court decision upholding the ACA now behind us, we remain committed to strengthening the current law and look forward to policymakers advancing solutions to improve the ACA,” Dr. Harmon said in a statement. “The AMA will continue working to expand access to health care and ensure that all Americans have meaningful, comprehensive, and affordable health coverage to improve the health of the nation.”
House Speaker Nancy Pelosi (D-Calif.), a longtime advocate for the ACA, called the decision a “landmark victory for Democrats.”
“Thanks to the tireless advocacy of Americans across the country and Democrats in Congress, the Affordable Care Act endures as a pillar of American health and economic security alongside Medicare, Medicaid and Social Security,” she said in a statement.
Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer (D-N.Y.) also celebrated the ruling.
“The Affordable Care Act has won. The Supreme Court has just ruled: the ACA is here to stay and now we’re going to try to make it bigger and better,” he said, according to CNN. “For more than a decade, the assault on our health care law was relentless from Republicans in Congress, from the executive branch itself and from Republican attorneys general in the courts. Each time in each arena, the ACA has prevailed.”
This article was updated June 17, 2021.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
CDC: Vaccinated? You don’t need a mask indoors
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the CDC announced on May 13.
“Anyone who is fully vaccinated can participate in indoor and outdoor activities, large or small, without wearing a mask or physically distancing,” CDC director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said at a press briefing. “We have all longed for this moment when we can get back to some sense of normalcy.
“This is an exciting and powerful moment,” she added, “It could only happen because of the work from so many who made sure we had the rapid administration of three safe and effective vaccines.”
Dr. Walensky cited three large studies on the effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against the original virus and its variants. One study from Israel found the vaccine to be 97% effective against symptomatic infection.
Those who are symptomatic should still wear masks, Dr. Walensky said, and those who are immunocompromised should talk to their doctors for further guidance. The CDC still advises travelers to wear masks while on airplanes or trains.
The COVID-19 death rates are now the lowest they have been since April 2020.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
JAMA editor resigns over controversial podcast
JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD, apologized to JAMA staff and stakeholders and asked for and received Dr. Livingston’s resignation, according to a statement from AMA CEO James Madara.
More than 2,000 people have signed a petition on Change.org calling for an investigation at JAMA over the podcast, called “Structural Racism for Doctors: What Is It?”
It appears they are now getting their wish. Dr. Bauchner announced that the journal’s oversight committee is investigating how the podcast and a tweet promoting the episode were developed, reviewed, and ultimately posted.
“This investigation and report of its findings will be thorough and completed rapidly,” Dr. Bauchner said.
Dr. Livingston, the host of the podcast, has been heavily criticized across social media. During the podcast, Dr. Livingston, who is White, said: “Structural racism is an unfortunate term. Personally, I think taking racism out of the conversation will help. Many of us are offended by the concept that we are racist.”
The audio of the podcast has been deleted from JAMA’s website. In its place is audio of a statement from Dr. Bauchner. In his statement, which he released last week, he said the comments in the podcast, which also featured Mitch Katz, MD, were “inaccurate, offensive, hurtful, and inconsistent with the standards of JAMA.”
Dr. Katz is an editor at JAMA Internal Medicine and CEO of NYC Health + Hospitals in New York.
Also deleted was a JAMA tweet promoting the podcast episode. The tweet said: “No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast.”
The incident was met with anger and confusion in the medical community.
Herbert C. Smitherman, MD, vice dean of diversity and community affairs at Wayne State University, Detroit, noted after hearing the podcast that it was a symptom of a much larger problem.
“At its core, this podcast had racist tendencies. Those attitudes are why you don’t have as many articles by Black and Brown people in JAMA,” he said. “People’s attitudes, whether conscious or unconscious, are what drive the policies and practices which create the structural racism.”
Dr. Katz responded to the backlash last week with the following statement: “Systemic racism exists in our country. The disparate effects of the pandemic have made this painfully clear in New York City and across the country.
“As clinicians, we must understand how these structures and policies have a direct impact on the health outcomes of the patients and communities we serve. It is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it, or that we should avoid the term ‘systematic racism’ because it makes people uncomfortable. We must and can do better.”
JAMA, an independent arm of the AMA, is taking other steps to address concerns. Its executive publisher, Thomas Easley, held an employee town hall this week, and said JAMA acknowledges that “structural racism is real, pernicious, and pervasive in health care.” The journal is also starting an “end-to-end review” of all editorial processes across all JAMA publications. Finally, the journal will also create a new associate editor’s position who will provide “insight and counsel” on racism and structural racism in health care.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD, apologized to JAMA staff and stakeholders and asked for and received Dr. Livingston’s resignation, according to a statement from AMA CEO James Madara.
More than 2,000 people have signed a petition on Change.org calling for an investigation at JAMA over the podcast, called “Structural Racism for Doctors: What Is It?”
It appears they are now getting their wish. Dr. Bauchner announced that the journal’s oversight committee is investigating how the podcast and a tweet promoting the episode were developed, reviewed, and ultimately posted.
“This investigation and report of its findings will be thorough and completed rapidly,” Dr. Bauchner said.
Dr. Livingston, the host of the podcast, has been heavily criticized across social media. During the podcast, Dr. Livingston, who is White, said: “Structural racism is an unfortunate term. Personally, I think taking racism out of the conversation will help. Many of us are offended by the concept that we are racist.”
The audio of the podcast has been deleted from JAMA’s website. In its place is audio of a statement from Dr. Bauchner. In his statement, which he released last week, he said the comments in the podcast, which also featured Mitch Katz, MD, were “inaccurate, offensive, hurtful, and inconsistent with the standards of JAMA.”
Dr. Katz is an editor at JAMA Internal Medicine and CEO of NYC Health + Hospitals in New York.
Also deleted was a JAMA tweet promoting the podcast episode. The tweet said: “No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast.”
The incident was met with anger and confusion in the medical community.
Herbert C. Smitherman, MD, vice dean of diversity and community affairs at Wayne State University, Detroit, noted after hearing the podcast that it was a symptom of a much larger problem.
“At its core, this podcast had racist tendencies. Those attitudes are why you don’t have as many articles by Black and Brown people in JAMA,” he said. “People’s attitudes, whether conscious or unconscious, are what drive the policies and practices which create the structural racism.”
Dr. Katz responded to the backlash last week with the following statement: “Systemic racism exists in our country. The disparate effects of the pandemic have made this painfully clear in New York City and across the country.
“As clinicians, we must understand how these structures and policies have a direct impact on the health outcomes of the patients and communities we serve. It is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it, or that we should avoid the term ‘systematic racism’ because it makes people uncomfortable. We must and can do better.”
JAMA, an independent arm of the AMA, is taking other steps to address concerns. Its executive publisher, Thomas Easley, held an employee town hall this week, and said JAMA acknowledges that “structural racism is real, pernicious, and pervasive in health care.” The journal is also starting an “end-to-end review” of all editorial processes across all JAMA publications. Finally, the journal will also create a new associate editor’s position who will provide “insight and counsel” on racism and structural racism in health care.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
JAMA editor in chief Howard Bauchner, MD, apologized to JAMA staff and stakeholders and asked for and received Dr. Livingston’s resignation, according to a statement from AMA CEO James Madara.
More than 2,000 people have signed a petition on Change.org calling for an investigation at JAMA over the podcast, called “Structural Racism for Doctors: What Is It?”
It appears they are now getting their wish. Dr. Bauchner announced that the journal’s oversight committee is investigating how the podcast and a tweet promoting the episode were developed, reviewed, and ultimately posted.
“This investigation and report of its findings will be thorough and completed rapidly,” Dr. Bauchner said.
Dr. Livingston, the host of the podcast, has been heavily criticized across social media. During the podcast, Dr. Livingston, who is White, said: “Structural racism is an unfortunate term. Personally, I think taking racism out of the conversation will help. Many of us are offended by the concept that we are racist.”
The audio of the podcast has been deleted from JAMA’s website. In its place is audio of a statement from Dr. Bauchner. In his statement, which he released last week, he said the comments in the podcast, which also featured Mitch Katz, MD, were “inaccurate, offensive, hurtful, and inconsistent with the standards of JAMA.”
Dr. Katz is an editor at JAMA Internal Medicine and CEO of NYC Health + Hospitals in New York.
Also deleted was a JAMA tweet promoting the podcast episode. The tweet said: “No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast.”
The incident was met with anger and confusion in the medical community.
Herbert C. Smitherman, MD, vice dean of diversity and community affairs at Wayne State University, Detroit, noted after hearing the podcast that it was a symptom of a much larger problem.
“At its core, this podcast had racist tendencies. Those attitudes are why you don’t have as many articles by Black and Brown people in JAMA,” he said. “People’s attitudes, whether conscious or unconscious, are what drive the policies and practices which create the structural racism.”
Dr. Katz responded to the backlash last week with the following statement: “Systemic racism exists in our country. The disparate effects of the pandemic have made this painfully clear in New York City and across the country.
“As clinicians, we must understand how these structures and policies have a direct impact on the health outcomes of the patients and communities we serve. It is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it, or that we should avoid the term ‘systematic racism’ because it makes people uncomfortable. We must and can do better.”
JAMA, an independent arm of the AMA, is taking other steps to address concerns. Its executive publisher, Thomas Easley, held an employee town hall this week, and said JAMA acknowledges that “structural racism is real, pernicious, and pervasive in health care.” The journal is also starting an “end-to-end review” of all editorial processes across all JAMA publications. Finally, the journal will also create a new associate editor’s position who will provide “insight and counsel” on racism and structural racism in health care.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com .
CDC: Vaccinated people can gather indoors without masks
People who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 can safely gather unmasked and inside with nonvulnerable people who are not yet immunized, according to long-awaited guidance released by the CDC.
“Today’s action represents an important first step. It is not our final destination,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said March 8 at a White House briefing. “As more people get vaccinated, levels of COVID-19 infection decline in communities, and as our understanding of COVID immunity improves, we look forward to updating these recommendations to the public.”
According to the new guidance, people who are at least 2 weeks out from their last dose can:
- Visit with other fully vaccinated people indoors without wearing masks or physical distancing.
- Visit with unvaccinated people from a single household who are at low risk for severe COVID-19 disease indoors without wearing masks or physical distancing
- Avoid quarantine and testing following exposure to someone if they remain asymptomatic.
However, there are still restrictions that will remain until further data are collected. Those who are fully vaccinated must still:
- Wear masks and physically distance in public settings and around people at high risk for severe disease.
- Wear masks and physically distance when visiting unvaccinated people from more than one household.
- Avoid medium- and large-sized gatherings.
- Avoid travel.
People considered at high risk for severe disease include older adults and those with cancer, chronic kidney disease, COPD, Down syndrome, heart disease, heart failure, a weakened immune system, obesity, sickle cell disease, and type 2 diabetes. The category also includes pregnant women and smokers.
“In public spaces, fully vaccinated people should continue to follow guidance to protect themselves and others, including wearing a well-fitted mask, physical distancing (at least 6 feet), avoiding crowds, avoiding poorly ventilated spaces, covering coughs and sneezes, washing hands often, and following any applicable workplace or school guidance,” the guidance says. “Fully vaccinated people should still watch for symptoms of COVID-19, especially following an exposure to someone with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.”
Respecting travel restrictions is still crucial, Dr. Walensky said, given past surges and variants that have emerged after periods of increased travel.
"We would like to give the opportunity for vaccinated grandparents to visit children and grandchildren who are healthy and local,” Dr. Walensky said.
But, she said, “It’s important to realize as we’re working through this that over 90% of the population is not yet vaccinated.”
For now, there are not enough data on transmission rates from those who are vaccinated to the rest of the public. However, Anthony Fauci, MD, said at a briefing last month that preliminary data are “pointing in a very favorable direction.”
Studies from Spain and Israel published last month showed the amount of viral load – or the amount of the COVID-19 virus in someone’s body – is significantly lower if someone gets infected after they’ve been vaccinated, compared with people who get infected and didn’t have the vaccine. Lower viral load means much lower chances of passing the virus to someone else, Dr. Fauci said.
“The science of COVID-19 is complex,” Dr. Walensky said, “and our understanding of it continues to evolve.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 can safely gather unmasked and inside with nonvulnerable people who are not yet immunized, according to long-awaited guidance released by the CDC.
“Today’s action represents an important first step. It is not our final destination,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said March 8 at a White House briefing. “As more people get vaccinated, levels of COVID-19 infection decline in communities, and as our understanding of COVID immunity improves, we look forward to updating these recommendations to the public.”
According to the new guidance, people who are at least 2 weeks out from their last dose can:
- Visit with other fully vaccinated people indoors without wearing masks or physical distancing.
- Visit with unvaccinated people from a single household who are at low risk for severe COVID-19 disease indoors without wearing masks or physical distancing
- Avoid quarantine and testing following exposure to someone if they remain asymptomatic.
However, there are still restrictions that will remain until further data are collected. Those who are fully vaccinated must still:
- Wear masks and physically distance in public settings and around people at high risk for severe disease.
- Wear masks and physically distance when visiting unvaccinated people from more than one household.
- Avoid medium- and large-sized gatherings.
- Avoid travel.
People considered at high risk for severe disease include older adults and those with cancer, chronic kidney disease, COPD, Down syndrome, heart disease, heart failure, a weakened immune system, obesity, sickle cell disease, and type 2 diabetes. The category also includes pregnant women and smokers.
“In public spaces, fully vaccinated people should continue to follow guidance to protect themselves and others, including wearing a well-fitted mask, physical distancing (at least 6 feet), avoiding crowds, avoiding poorly ventilated spaces, covering coughs and sneezes, washing hands often, and following any applicable workplace or school guidance,” the guidance says. “Fully vaccinated people should still watch for symptoms of COVID-19, especially following an exposure to someone with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.”
Respecting travel restrictions is still crucial, Dr. Walensky said, given past surges and variants that have emerged after periods of increased travel.
"We would like to give the opportunity for vaccinated grandparents to visit children and grandchildren who are healthy and local,” Dr. Walensky said.
But, she said, “It’s important to realize as we’re working through this that over 90% of the population is not yet vaccinated.”
For now, there are not enough data on transmission rates from those who are vaccinated to the rest of the public. However, Anthony Fauci, MD, said at a briefing last month that preliminary data are “pointing in a very favorable direction.”
Studies from Spain and Israel published last month showed the amount of viral load – or the amount of the COVID-19 virus in someone’s body – is significantly lower if someone gets infected after they’ve been vaccinated, compared with people who get infected and didn’t have the vaccine. Lower viral load means much lower chances of passing the virus to someone else, Dr. Fauci said.
“The science of COVID-19 is complex,” Dr. Walensky said, “and our understanding of it continues to evolve.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
People who are fully vaccinated against COVID-19 can safely gather unmasked and inside with nonvulnerable people who are not yet immunized, according to long-awaited guidance released by the CDC.
“Today’s action represents an important first step. It is not our final destination,” CDC Director Rochelle Walensky, MD, said March 8 at a White House briefing. “As more people get vaccinated, levels of COVID-19 infection decline in communities, and as our understanding of COVID immunity improves, we look forward to updating these recommendations to the public.”
According to the new guidance, people who are at least 2 weeks out from their last dose can:
- Visit with other fully vaccinated people indoors without wearing masks or physical distancing.
- Visit with unvaccinated people from a single household who are at low risk for severe COVID-19 disease indoors without wearing masks or physical distancing
- Avoid quarantine and testing following exposure to someone if they remain asymptomatic.
However, there are still restrictions that will remain until further data are collected. Those who are fully vaccinated must still:
- Wear masks and physically distance in public settings and around people at high risk for severe disease.
- Wear masks and physically distance when visiting unvaccinated people from more than one household.
- Avoid medium- and large-sized gatherings.
- Avoid travel.
People considered at high risk for severe disease include older adults and those with cancer, chronic kidney disease, COPD, Down syndrome, heart disease, heart failure, a weakened immune system, obesity, sickle cell disease, and type 2 diabetes. The category also includes pregnant women and smokers.
“In public spaces, fully vaccinated people should continue to follow guidance to protect themselves and others, including wearing a well-fitted mask, physical distancing (at least 6 feet), avoiding crowds, avoiding poorly ventilated spaces, covering coughs and sneezes, washing hands often, and following any applicable workplace or school guidance,” the guidance says. “Fully vaccinated people should still watch for symptoms of COVID-19, especially following an exposure to someone with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.”
Respecting travel restrictions is still crucial, Dr. Walensky said, given past surges and variants that have emerged after periods of increased travel.
"We would like to give the opportunity for vaccinated grandparents to visit children and grandchildren who are healthy and local,” Dr. Walensky said.
But, she said, “It’s important to realize as we’re working through this that over 90% of the population is not yet vaccinated.”
For now, there are not enough data on transmission rates from those who are vaccinated to the rest of the public. However, Anthony Fauci, MD, said at a briefing last month that preliminary data are “pointing in a very favorable direction.”
Studies from Spain and Israel published last month showed the amount of viral load – or the amount of the COVID-19 virus in someone’s body – is significantly lower if someone gets infected after they’ve been vaccinated, compared with people who get infected and didn’t have the vaccine. Lower viral load means much lower chances of passing the virus to someone else, Dr. Fauci said.
“The science of COVID-19 is complex,” Dr. Walensky said, “and our understanding of it continues to evolve.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
JAMA podcast on racism in medicine faces backlash
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.
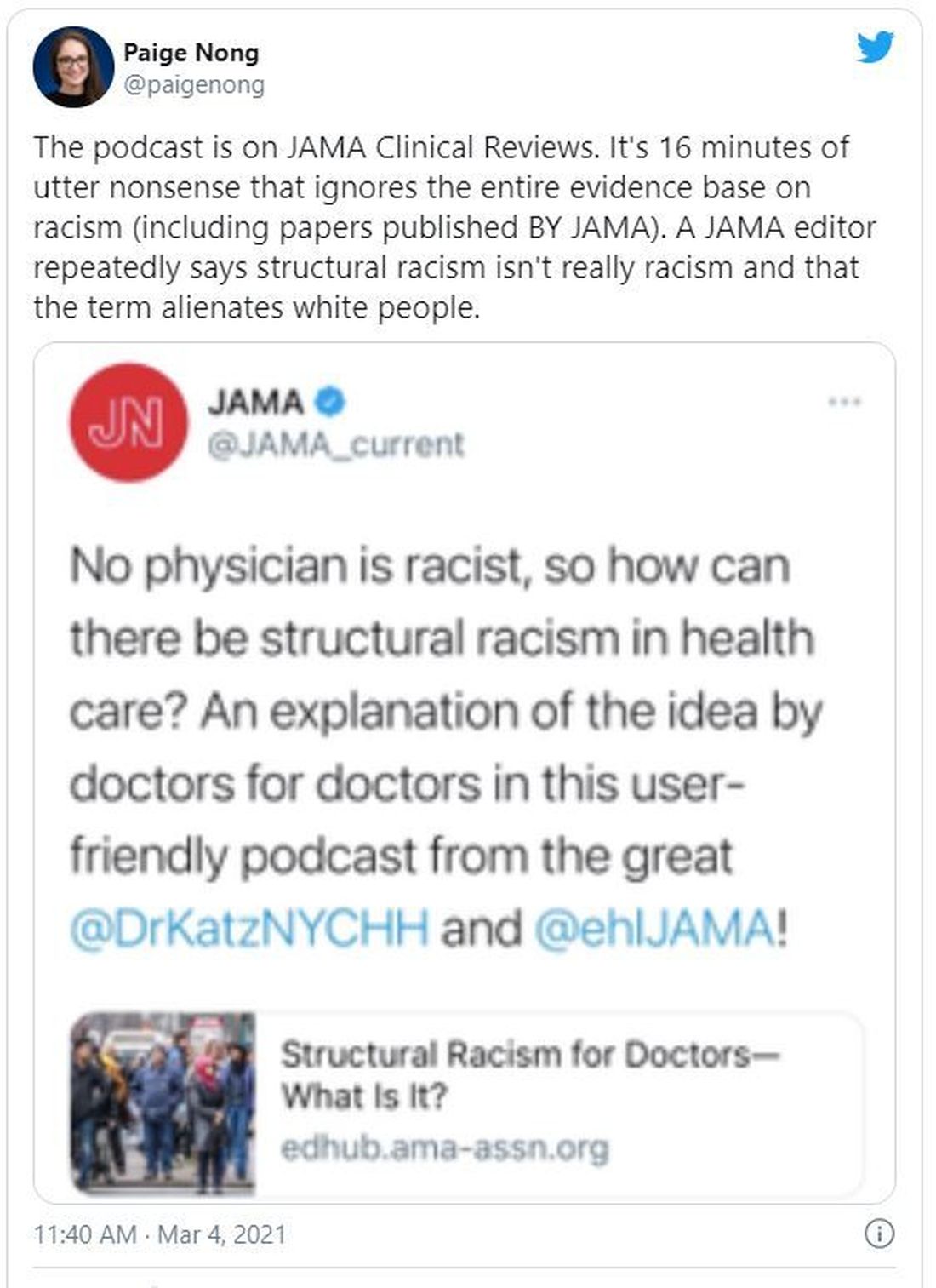
The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.

The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Published on Feb. 23, the episode is hosted on JAMA’s learning platform for doctors and is available for continuing medical education credits.
“No physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care? An explanation of the idea by doctors for doctors in this user-friendly podcast,” JAMA wrote in a Twitter post to promote the episode. That tweet has since been deleted.

The episode features host Ed Livingston, MD, deputy editor for clinical reviews and education at JAMA, and guest Mitchell Katz, MD, president and CEO for NYC Health + Hospitals and deputy editor for JAMA Internal Medicine. Dr. Livingston approaches the episode as “structural racism for skeptics,” and Dr. Katz tries to explain how structural racism deepens health disparities and what health systems can do about it.
“Many physicians are skeptical of structural racism, the idea that economic, educational, and other societal systems preferentially disadvantage Black Americans and other communities of color,” the episode description says.
In the podcast, Dr. Livingston and Dr. Katz speak about health care disparities and racial inequality. Dr. Livingston, who says he “didn’t understand the concept” going into the episode, suggests that racism was made illegal in the 1960s and that the discussion of “structural racism” should shift away from the term “racism” and focus on socioeconomic status instead.
“What you’re talking about isn’t so much racism ... it isn’t their race, it isn’t their color, it’s their socioeconomic status,” Dr. Livingston says. “Is that a fair statement?”
But Dr. Katz says that “acknowledging structural racism can be helpful to us. Structural racism refers to a system in which policies or practices or how we look at people perpetuates racial inequality.”
Dr. Katz points to the creation of a hospital in San Francisco in the 1880s to treat patients of Chinese ethnicity separately. Outside of health care, he talks about environmental racism between neighborhoods with inequalities in hospitals, schools, and social services.
“All of those things have an impact on that minority person,” Dr. Katz says. “The big thing we can all do is move away from trying to interrogate each other’s opinions and move to a place where we are looking at the policies of our institutions and making sure that they promote equality.”
Dr. Livingston concludes the episode by reemphasizing that “racism” should be taken out of the conversation and it should instead focus on the “structural” aspect of socioeconomics.
“Minorities ... aren’t [in those neighborhoods] because they’re not allowed to buy houses or they can’t get a job because they’re Black or Hispanic. That would be illegal,” Dr. Livingston says. “But disproportionality does exist.”
Efforts to reach Dr. Livingston were unsuccessful. Dr. Katz distanced himself from Dr. Livingston in a statement released on March 4.
“Systemic and interpersonal racism both still exist in our country — they must be rooted out. I do not share the JAMA host’s belief of doing away with the word ‘racism’ will help us be more successful in ending inequities that exists across racial and ethnic lines,” Dr. Katz said. “Further, I believe that we will only produce an equitable society when social and political structures do not continue to produce and perpetuate disparate results based on social race and ethnicity.”
Dr. Katz reiterated that both interpersonal and structural racism continue to exist in the United States, “and it is woefully naive to say that no physician is a racist just because the Civil Rights Act of 1964 forbade it.”
He also recommended JAMA use this controversy “as a learning opportunity for continued dialogue and create another podcast series as an open conversation that invites diverse experts in the field to have an open discussion about structural racism in healthcare.”
The podcast and JAMA’s tweet promoting it were widely criticized on Twitter. In interviews with WebMD, many doctors expressed disbelief that such a respected journal would lend its name to this podcast episode.
B. Bobby Chiong, MD, a radiologist in New York, said although JAMA’s effort to engage with its audience about racism is laudable, it missed the mark.
“I think the backlash comes from how they tried to make a podcast about the subject and somehow made themselves an example of unconscious bias and unfamiliarity with just how embedded in our system is structural racism,” he said.
Perhaps the podcast’s worst offense was its failure to address the painful history of racial bias in this country that still permeates the medical community, says Tamara Saint-Surin, MD, assistant professor at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill.
“For physicians in leadership to have the belief that structural racism does not exist in medicine, they don’t really appreciate what affects their patients and what their patients were dealing with,” Dr. Saint-Surin said in an interview. “It was a very harmful podcast and goes to show we still have so much work to do.”
Along with a flawed premise, she says, the podcast was not nearly long enough to address such a nuanced issue. And Dr. Livingston focused on interpersonal racism rather than structural racism, she said, failing to address widespread problems such as higher rates of asthma among Black populations living in areas with poor air quality.
The number of Black doctors remains low and the lack of representation adds to an environment already rife with racism, according to many medical professionals.
Shirlene Obuobi, MD, an internal medicine doctor in Chicago, said JAMA failed to live up to its own standards by publishing material that lacked research and expertise.
“I can’t submit a clinical trial to JAMA without them combing through methods with a fine-tooth comb,” Dr. Obuobi said. “They didn’t uphold the standards they normally apply to anyone else.”
Both the editor of JAMA and the head of the American Medical Association issued statements criticizing the episode and the tweet that promoted it.
JAMA Editor-in-Chief Howard Bauchner, MD, said, “The language of the tweet, and some portions of the podcast, do not reflect my commitment as editorial leader of JAMA and JAMA Network to call out and discuss the adverse effects of injustice, inequity, and racism in society and medicine as JAMA has done for many years.” He said JAMA will schedule a future podcast to address the concerns raised about the recent episode.
AMA CEO James L. Madara, MD, said, “The AMA’s House of Delegates passed policy stating that racism is structural, systemic, cultural, and interpersonal, and we are deeply disturbed – and angered – by a recent JAMA podcast that questioned the existence of structural racism and the affiliated tweet that promoted the podcast and stated ‘no physician is racist, so how can there be structural racism in health care?’ ”
He continued: “JAMA has editorial independence from AMA, but this tweet and podcast are inconsistent with the policies and views of AMA, and I’m concerned about and acknowledge the harms they have caused. Structural racism in health care and our society exists, and it is incumbent on all of us to fix it.”
This article was updated 3/5/21.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.

