User login
Best practices in LGBT care: A guide for primary care physicians
Primary care physicians are very likely to encounter lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) patients in their practice, and must be able to provide informed, appropriate, and culturally sensitive care.
Approximately 9 million people in the United States identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual, and 700,000 adults are transgender.1 In the 2013 National Health Interview Survey,2 which queried 34,557 adults about their sexual orientation, 2.3% reported being lesbian, gay, or bisexual, with only slight differences according to age or sex: of those ages 18 through 44, 1.9% were gay or lesbian and 1.1% were bisexual; of those ages 65 and over, 0.7% were gay or lesbian and 0.2% were bisexual. By sex, 0.9% of women vs 0.4% of men identified as bisexual.2
This article identifies and corrects common myths about LGBT care, addresses disparities in healthcare access, and outlines a step-by-step approach for delivering comprehensive care to LGBT patients.
MYTHS ABOUT LGBT CARE
Myth #1: L = G = B = T
Although LGBT is a commonly used term, each group described by the abbreviation has its own unique healthcare needs. For example, lesbian and bisexual women are more likely than heterosexual women to smoke, and gay men are at increased risk for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and other sexually transmitted infections.3,4 Transgender persons have high rates of suicide.5
Primary care of the LGBT patient needs to be individualized but also informed by the knowledge of distinct risks and behaviors associated with particular groups.
Myth #2: Sexual orientation = sexual activity
Sexual identity correlates closely but not completely with sexual behavior; individuals may engage in same-sex behavior but not identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual.6,7 Many women who identify as lesbian have previously had sex with men, and men may have had same-sex encounters but consider themselves heterosexual.8,9
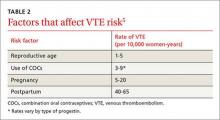
Since the risk of certain infections is related to sexual activity, providers should query patients about their sexual partners and practices in an open, nonjudgmental way, and avoid labeling patients solely according to sexual orientation. Table 1 suggests questions to use when interviewing patients.
Myth #3: Sexual orientation = gender identity
Gender identity describes a person’s inherent sense of being a woman, man, or of neither gender, whereas sexual orientation refers to how a person identifies their physical and emotional attraction to others.10,11 Conflating the two concepts can alienate patients, lead to incorrect assumptions, and result in an underestimation of an individual’s risk of sexually transmitted diseases.
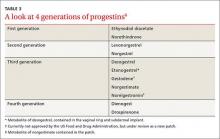
Using questions such as “Are you sexually active with men, women, or both?” or “When you are sexually active, what parts of your body do you use?” with all patients, regardless of gender identity, will facilitate open and honest conversations that allow for appropriate counseling and risk assessment. Table 2 lists commonly used gender-identity terms.
Myth #4: LGBT people have the same access to healthcare as heterosexual people
People who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender experience significant disparities in access to healthcare compared with cisgender heterosexual people. For example, lesbian women are less likely to receive the human papillomavirus vaccine, cervical cancer screening, and mammograms, and men in same-sex relationships are twice as likely to have unmet medical needs.8,12 In a national survey,5 19% of transgender individuals reported that they had been refused healthcare. Among 152 transgender adults who described their experiences with the healthcare system, 7% reported receiving substandard care.13
We can eliminate these disparities by creating a welcoming environment for all patients (Table 3), and also by being aware of the specific services that should be offered to LGBT individuals.
ADDRESSING THE NEEDS OF LGBT PATIENTS
Outlined here is an office-based approach for addressing the unique clinical concerns of adult LGBT patients. Not all of these issues need to or should be addressed at the first visit, and the sequence in which these steps are accomplished may vary.
Step #1: Screen for mental health disorders
Lesbian, bisexual, and gay people are more likely to experience depression and anxiety. According to the results of a large meta-analysis,14 the prevalence of these conditions is 1.5 times higher in this population than in heterosexual people. Risk may vary according to group, with gay and bisexual men experiencing a higher lifetime prevalence of anxiety and depression than lesbian and bisexual women.15 Suicidal attempts are also more common in gay and bisexual men, who have a lifetime risk four times higher than that of heterosexual men.14
The risk of suicide is even higher among transgender people: 41% of surveyed transgender adults reported that they had attempted suicide, with higher rates in younger individuals.5 Risk factors include experiences of harassment or physical or sexual violence, as well as poverty, low education level, and unemployment.5 The risk of suicide in transgender people who served in the military is 20 times higher than that in the general veteran population.16
It is imperative to routinely screen LGBT patients for anxiety, depression, and suicidality and to refer them to mental health providers who are sensitive to LGBT patients’ needs and concerns. Screening tools such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ2), PHQ9A, PHQ9, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD7) are useful in screening patients for depression and anxiety in addition to mnemonics such as SIGECAPS (sleep, interest, guilt, energy, concentration, appetite, psychomotor, suicidal thoughts or ideation).17
Although the same screening tools are used in cisgender heterosexual patients, factors contributing to the experience of depression or anxiety may be directly related to gender identity, gender expression, or sexual orientation. In a 2001 study, more lesbian, gay, and bisexual people reported lifetime and day-to-day experiences with discrimination than heterosexual people, and approximately 42% attributed this in part or in total to their sexual orientation.18
Step #2: Assess for substance use
Substance use is also more common in LGBT people. Lesbian and bisexual women have higher rates of tobacco abuse, exposure to second-hand smoke, and alcohol and drug dependence.3,14 In one study, compared with heterosexual individuals, the odds of lifetime alcohol and substance use disorder was three times higher in lesbian women, and the odds of lifetime drug-use disorder was 1.6 times higher in gay men.19
In a survey of transgender people, 30% reported using tobacco compared with 20% of the US adult population, and 8% reported using alcohol or drugs to cope with mistreatment and bias.5 In a study of transgender women in San Francisco, 58% used alcohol and 43% used substances, including marijuana, methamphetamine, and crack cocaine. Substance use significantly increased the odds of testing positive for HIV.20
Clinicians should carefully question LGBT patients about their use of alcohol, tobacco, and other substances and provide counseling and assistance with cessation. Several LGBT-specific resources can be used to aid patients in their efforts, and referral to substance abuse groups that are welcoming to LGBT people may increase cessation rates.19,21
Step #3: Offer appropriate screening services
Human papillomavirus (HPV). Like heterosexual women, lesbian and bisexual women are at risk of HPV infection, which is associated with cervical cancer and genital warts.8 HPV can be transmitted in several ways, including skin-to-skin and digital-to-genital contact, as well as penile-vaginal intercourse. Lesbian and bisexual women may have acquired HPV from previous male sexual partners or from female-to-female transmission.8 In a study comparing cervical cancer screening results among lesbian, bisexual, and heterosexual women, there was no significant difference in the odds for Papanicolaou (Pap) test abnormalities and only a minor decrease in the odds of HPV infection.22 Lesbian and bisexual women should receive Pap and HPV testing according to current guidelines.
Other sexually transmitted infections, including herpes simplex virus 1, herpes simplex virus 2, Trichomonas vaginalis, syphilis, and hepatitis A, can be passed between female partners; risk may vary according to sexual practices.23 Thus, providers should not assume that lesbian women are at low risk of these infections and should screen according to current guidelines.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends annual screening for Chlamydia infection for all women under age 25, as well as those at increased risk for this infection (ie, those with a new sex partner or multiple sex partners).24
Breast cancer. Studies reveal that lesbian and bisexual women are less likely to receive mammograms, and they may have several risk factors that increase their risk for breast cancer, including overweight, obesity, and excessive alcohol intake.12,18,25 Providers should discuss the risks and benefits of mammography and offer this screening service at appropriate intervals.
Screening in men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men are at increased risk for several sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, Chlamydia, anal HPV, and hepatitis B and C.4,9 The CDC recommends annual sexual health screening that includes serologic testing for HIV and syphilis, and urine, rectal, or pharyngeal testing for gonorrhea and Chlamydia according to sexual practices.24
In contrast, routine screening for anal HPV is not currently recommended because we lack data demonstrating that screening reduces mortality rates from anal carcinoma.24,26 Nevertheless, the CDC acknowledges that some clinicians may choose to perform anal Pap testing in patients who are at high risk, and guidelines from the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene suggest annual anal Pap testing in HIV-positive men who have sex with men.27
According to the results of a systematic review,28 a significant proportion of transgender women reported sexual practices that increased their risk for sexually transmitted infections, and 27.7% tested positive for HIV infection. In contrast, rates of HIV and risk behaviors were much lower among transgender men. Risk may be heightened in transgender women who have not had sexual reassignment surgery and who engage in insertive anal, vaginal, or oral intercourse.28 An awareness of an individual patient’s current anatomy and sexual practices is essential for providing appropriate counseling about sexually transmitted infections.
‘Screen what you have’
When considering screening for breast, cervical, and prostate cancer, providers should consider an individual patient’s surgical history and hormonal status. “Screen what you have” is an easy rule to help both patients and providers remember which services to consider.
Transgender men who have not had a mastectomy should discuss the risks and benefits of breast cancer screening and consider mammography as recommended by the American Cancer Society.29 Similarly, cervical cancer screening should be performed according to current guidelines, although providers should be aware that this examination can cause significant anxiety and emotional distress for the patient.30
In transgender women, guidelines for breast cancer screening for those who were previously or currently treated with hormones are lacking. The University of California-San Francisco Center of Excellence for Transgender Health recommends mammography for patients over age 50 with additional risk factors (family history, obesity, estrogen and progestin use for more than 5 years).31 Transgender women should be counseled about the risks and benefits of prostate cancer screening.
Step #4: Immunize, and promote healthy behaviors
Table 4 outlines the screening services, immunizations, and health behavior promotions that should be offered to LGBT patients.
Vaccinations. LGBT individuals should be routinely offered HPV vaccination through age 26, according to current guidelines.24 Immunization against hepatitis A and B is also recommended for men who have sex with men, if they are not already immune.24 Meningococcal vaccine should be given to men who have sex with men if they have an additional medical, occupational, or lifestyle risk factor.32
Physical activity should be encouraged, especially in lesbian and bisexual women, who are more likely to be overweight and obese.25 In a recent study,33 gay, lesbian, and bisexual youths (ages 12–22) reported 1.21 to 2.62 fewer hours of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week than their “completely heterosexual” counterparts, and were 46% to 76% less likely to participate in team sports, in part due to concerns about gender nonconformity. On the other hand, results from a recent national survey of adults ages 18 through 64 found no significant differences in physical activity according to sexual orientation.
Providers should address patients’ perceived barriers to participating in exercise programs.2
Preexposure prophylaxis against HIV. A growing number of patients and health providers are asking about preexposure prophylaxis for HIV infection. The initial CDC recommendations for the daily use of emtricitabine-tenofovir were restricted to gay and bisexual men and men who have sex with men in serodiscordant relationships or in situations where the HIV status of the patient’s partner was unknown.34 Since then, the CDC has expanded the groups who may benefit from preexposure prophylaxis.35 Assessment of the patient’s ability to adhere to a daily oral medication regimen is central to its success. Patients should be screened for hepatitis, HIV, and renal and liver function before starting emtricitabine-tenofovir and should have these tests repeated at 3-month intervals if pre-exposure prophylaxis is continued.
Step #5: Initiate or continue hormone therapy for transgender individuals
Hormone therapy often improves the quality of life for patients who desire to have their physical appearance align more closely with their gender identity.29 Moreover, abruptly stopping hormone therapy can have significant psychological consequences.36
Clinicians should feel comfortable starting hormone therapy for patients who have been diagnosed with gender dysphoria by a mental health professional, can demonstrate knowledge about and outcomes of hormone therapy, and have lived as a member of the desired gender (“real-life experience”) for at least 3 months, and preferably 12 months.29 More recently, some practitioners have advocated prescribing hormone therapy for patients without the requirement for real-life experience or a formal letter from a mental health professional recommending hormonal therapy.37 However, mental healthcare is recommended for any patient with moderate to severe mental health conditions, especially if not treated at the time of presentation.37
Providers should continue hormone therapy for patients who are already receiving it, while being aware of the appropriate treatment goals and monitoring parameters. The two main principles of hormone therapy for transgender patients are to reduce endogenous hormone levels and their associated sex characteristics and replace with hormones of the preferred sex.29 Doses and formulations are similar to those used for treatment of hypogonadism. This topic has been reviewed by Spack.10
The only absolute contraindications to hormone therapy are estrogen- or testosterone-responsive tumors. Otherwise, hormone therapy can be initiated or continued with the patient’s informed consent about its benefits and risks.
Estrogen therapy may increase the risk of thromboembolic disease, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, severe migraine headaches, liver dysfunction, and macroprolactinoma.29 In a cross-sectional study of 100 transgender patients receiving hormone therapy, 12% of transgender women experienced a thromboembolic or cardiovascular event after an average of 11 years of treatment.38 However, many of these patients had additional risk factors for these events, such as smoking. In contrast, results from a recent systematic review39 indicated a much lower rate of venous thromboembolism among transgender women receiving estrogen therapy (1.7%–6.3%). Use of transdermal estrogen may minimize the likelihood of thromboembolic disease, and cessation of hormonal care in the perioperative period is advisable, especially for procedures with greater risk of venous thromboembolism.39
Transgender men are at risk of erythrocytosis (hematocrit > 50%) as a result of testosterone therapy. Although current guidelines indicate that testosterone may increase the risk of breast or uterine cancer, results from a recent systematic review40 indicate that the overall cancer incidence in transgender men is not higher than in natal controls. Both estrogen and testosterone therapy increase insulin resistance and fasting glucose levels, whereas only estrogen increases triglyceride concentrations.40
For transgender women, estrogen levels should be maintained in the normal range for cisgender women of reproductive age (< 200 pg/mL), and testosterone levels should be suppressed to less than 55 ng/dL. Goal testosterone levels for transgender men are between 320 and 1,000 ng/dL and should be measured at intervals specific to the preparation used (ie, measured midway between injections for individuals treated with testosterone cypionate). Estradiol levels should be less than 50 ng/dL.29 Transgender women and men should have estradiol and testosterone levels measured quarterly during the first year of treatment, and then every 6 to 12 months thereafter once goal levels are achieved.
Additional monitoring for transgender women includes measuring serum prolactin at baseline and after 12 months of therapy, and serum electrolytes for those taking spironolactone as antiandrogen therapy. Complete blood cell counts and liver function tests should be done every 3 months during the first year of testosterone therapy for transgender men, and then one to two times per year.29 Reference laboratory values for the patient’s affirmed gender should be used to assess response to therapy as well as effects on end-organ function.
The marked suppression of endogenous hormone levels that occurs during therapy may have adverse effects on the bone mineral density of both transgender women and men. Clinicians should assess patients’ baseline risk for osteoporotic fracture at the time hormone therapy is started and consider bone mineral density testing if appropriate. For those at low risk for fracture, current guidelines recommend screening for osteoporosis starting at age 60.29
Providers should counsel patients who have recently initiated hormone therapy that some changes may occur gradually over time. While transgender women will notice a decrease in libido and spontaneous erections within the first 3 months of therapy, breast growth begins approximately 3 to 6 months after treatment is started. Similarly, for transgender men, fat redistribution occurs during the first 6 months of treatment, but facial and body hair growth occur more slowly and are at maximum 4 to 5 years after starting hormone therapy.29 Amenorrhea typically occurs 1 to 6 months after starting hormonal therapy for transgender men.
Some patients may be interested in surgery to continue their physical transformation to the desired sex. Patients who have used hormone therapy and participated in a real-life experience or otherwise completed social transition by living as the affirmed gender for 12 months are considered eligible for surgery if they can demonstrate a good understanding of the cost, potential complications, and expected recovery time of the procedure. Guidelines also recommend that the patient demonstrate progress in work, family, and interpersonal issues regarding their new gender.29 Available surgical options include breast augmentation, orchiectomy and penectomy, and vaginoplasty, clitoroplasty, and vulvoplasty for transgender women. Feminizing procedures include voice surgery, thyroid cartilage reduction, and facial feminization surgery. Transgender men may choose to have mastectomy, hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy, vaginectomy, scrotoplasty and testicular implant placement, and implantation of a penile prosthesis. Additional virilizing surgeries include voice surgery and pectoral implants.41
Step #6: Screen for intimate partner violence
Intimate partner violence refers to physical, sexual, and psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse, and it can occur in gay and lesbian relationships. In 2000, a National Violence Against Women survey found that 21.5% of men and 35.4% of women who reported living with a same-sex partner had experienced physical abuse.42 More recent studies confirm rates similar to those in heterosexual relationships. In an online study,43 11.8% of men who have sex with men reported physical violence from a current male partner, and about 4% reported experiencing coerced sex.
Intimate partner violence is uniquely challenging for LGBT people. In addition to the commonly described methods an abuser uses to maintain power and control, forced disclosure or “outing”—publicly revealing someone’s sexual orientation or gender identity—may result in additional psychological violence and harm. Survivors of intimate partner violence who are in same-gender intimate relationships often find that obtaining services through the police, judicial, and social services systems is challenging. Survivors may be required to disclose their sexual orientation or gender identity as part of filing a report or judicial order to obtain help or protection from the abuser. Many male and transgender survivors of intimate partner violence are unable to access traditional shelters. Female survivors may find that their same-sex abusers have the same access to resources and shelters that they do.
Intimate partner violence is associated with negative physical and mental health outcomes. Physical injuries such as bruises, fractures, and burns are some of the more obvious harms survivors sustain. However, the negative psychological impact on survivors cannot be overstated. LGBT individuals are at greater risk of depression and substance abuse as a result of intimate partner violence than their cisgender heterosexual counterparts. The stress resulting from stigmatization and discrimination can be exacerbated by intimate partner violence.44 This can be seen in health outcomes of HIV-positive men who have sex with men, in whom abuse predicts interruptions in care, more advanced HIV disease, and HIV-associated hospitalizations.45
We recommend that providers screen all LGBT patients for intimate partner violence. One commonly used tool is the Partner Violence Screen, which consists of three gender-neutral questions:
- Have you been hit, kicked, punched, or otherwise hurt by someone in the past year? If so, by whom?
- Do you feel safe in your current relationship?
- Is there a partner from a previous relationship who is making you feel unsafe now?
Like other screening tools for intimate partner violence, the Partner Violence Screen is more specific than sensitive.46 Screening and discussions about intimate partner violence should be performed in a private, confidential manner while the patient is alone.
Providers who care for LGBT patients need to be aware of not only the medical and mental health sequelae of intimate partner violence but also the social and legal issues facing survivors. Familiarity with the available community resources and their limitations can better facilitate trust and patient care for those affected by intimate partner violence. In one study, the most frequent requests for assistance from sexual and gender minority survivors were for counseling, safe housing, legal assistance, and assistance navigating the medical system.47 Providers should refer patients to LGBT-focused resources in their community as available, and when no such resources exist, initiate contact with standard domestic violence services, with patient consent, to ask about a program’s ability to assist survivors of LGBT intimate partner violence.
IN A NUTSHELL
Optimizing the care of LGBT patients requires developing both clinical and cultural competency.
Initial steps for creating an inclusive and welcoming clinical environment include becoming familiar with local resources for LGBT patients (support groups, substance and alcohol cessation groups, mental health providers; see sidebar), providing education and training for support staff and nurses, and establishing gender-neutral bathrooms. Waiting areas should include literature relevant to LGBT patients and signage that is relevant to all patients, including gender-nonconforming individuals. Providers should offer all patients universal HIV screening initially and at clinically appropriate intervals and discuss preexposure prophylaxis with emtricitabine-tenofovir for at-risk individuals.
For transgender patients, addressing them by their preferred name and pronouns is central to building rapport. General health maintenance is the same for transgender patients as for cisgender patients and can be guided by the adage “screen what you have.” Hormonal care can be offered using an informed consent method consistent with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health Standards of Care.48 Guidelines exist to assist providers in initiation and maintenance of hormonal care. Cross-gender hormonal therapy is initiated with low-dose medication that is gradually increased over time, with a goal of approximating the pubertal changes of the desired gender over a 2- to 3-year period. Some, but not all, patients may pursue various surgical procedures as part of their gender affirmation process.
- Gates GJ. How many people are lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender? Williams Institute. 2011. http://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/Gates-How-Many-People-LGBT-Apr-2011.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Ward BW, Dahlhamer JM, Galinsky AM, Joesti SS. Sexual orientation and health among U.S. Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2013. Natl Health Stat Report 2014; 77:1–10.
- Cochran SD, Bandiera FC, Mays VM. Sexual orientation-related differences in tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure among US adults aged 20-59 years: 2003–2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys. Am J Publ Health 2013; 103:1837–1844.
- Mayer KH. Sexually transmitted diseases in men who have sex with men. Clin Infect Disease 2011; 53:S79–S83.
- Grant JM, Mottet LA, Tanis J, Herman JL, Harrison J, Keisling M. National transgender discrimination survey report on health and health care. www.thetaskforce.org/static_html/downloads/reports/reports/ntds_report_on_health.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Pathela P, Hajat A, Schillinger J, Blank S, Sell R, Mostashari F. Discordance between sexual behavior and self-reported sexual identity: a population-based survey of New York City men. Ann Intern Med 2006; 145:416–425.
- Chandra A, Mosher WD, Copen C, Sionean C. Sexual behavior, sexual attraction, and sexual identity in the United States: data from the 2006–2009 National Survey of Family Growth. Natl Health Stat Report 2011; 36:1–36.
- Agenor M, Peitzmeier S, Gordon AR, Haneuse S, Potter JE, Austin SB. Sexual orientation identity disparities in awareness and initiation of the human papillomavirus vaccine among U.S. women and girls: a national survey. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:99–106.
- Ard KL, Makadon HJ. Improving the health care of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people: understanding and eliminating health disparities. www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/12-054_LGBTHealtharticle_v3_07-09-12.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Spack NP. Management of transgenderism. JAMA 2013; 309:474–484.
- National LGBT Health Education Center. Achieving health equity for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people, Module 1. www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/Achieving-Health-Equity-for-LGBT-People-1.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Buchmueller T, Carpenter CS. Disparities in health Insurance coverage, access, and outcomes for individuals in same-sex versus different-sex relationships, 2000–2007. Am J Public Health 2010; 100:489–496.
- Kosenko K, Rintamaki L, Raney S, Maness K. Transgender patient perceptions of stigma in health care contexts. Med Care 2013; 51:819–822.
- King M, Semlyen J, Tai SS, et al. A systematic review of mental disorder, suicide, and deliberate self-harm in lesbian, gay, and bisexual people. BMC Psychiatry 2008; 8:70.
- Bostwick WB, Boyd CJ, Hughes TL, McCabe SE. Dimensions of sexual orientation and the prevalence of mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. Am J Public Health 2010; 100:468–475.
- Blosnich JR, Brown GR, Shipherd JC, Kauth M, Piegari RI, Bossarte RM. Prevalence of gender identity disorder and suicide risk among transgender veterans utilizing Veterans Health Administration care. Am J Public Health 2013: 103:e27–e32.
- Maurer DM. Screening for depression. Am Fam Physician 2012; 85:139–144.
- Mays VM, Cochran SD. Mental health correlates of perceived discrimination among lesbian, gay, and bisexual adults in the United States. Am J Pub Health 2001; 91:1869–1875.
- McCabe SE, West BT, Hughes TL, Boyd CJ. Sexual orientation and substance abuse treatment utilization in the United States: results from a national survey. J Subst Abuse Treat 2013; 44:4–12.
- Santos GM, Rapues J, Wilson EC, et al. Alcohol and substance use among transgender women in San Francisco: prevalence and association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Drug Alcohol Rev 2014; 33:287–295.
- National LGBT Tobacco Control Network. www.lgbttobacco.org. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Massad LS, Xie X, Minkoff H, et al. Abnormal Pap tests and human papillomavirus infections among HIV infected and uninfected women who have sex with women. J Low Genit Tract Dis 2014; 18:50–56.
- Gorgos LM, Marrazzo JM. Sexually transmitted infections among women who have sex with women. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 53:S84–S91.
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR 2015; 64(3):1–138.
- Boehmer U, Bowen DJ, Bauer GR. Overweight and obesity in sexual-minority women: evidence from population-based data. Am J Public Health 2007; 97:1134–1140.
- Smyczek P, Singh AE, Romanowski B. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia: review and recommendations for screening and management. Int J STD AIDS 2013; 24:843–851.
- New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Preventing sexually transmitted infections. 2013; 32(4):19–27. www.nyc.gov/html/doh/html/data/chi32-4_screening.html. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Herbst JH, Jacobs ED, Finlayson TJ, McKleroy VS, Neumann MS, Crepaz N. Estimating HIV prevalence and risk behaviors of transgender persons in the United States: a systematic review. AIDS Behav 2008; 12:1–17.
- Hembree WC, Cohen-Kettenis P, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, et al. Endocrine treatment of transsexual persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94:3132–3133.
- Peitzmeier SM, Reisner SL, Harigopal P, Potter J. Female-to-male patients may have high prevalence of unsatisfactory paps compared to non-transgender females: implications for cervical cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med 2014; 29:778–784.
- UCSF Center of Excellence for Transgender Health. Primary care protocol for transgender patient care. http://transhealth.ucsf.edu/protocols. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended adult immunization schedule United States—2015. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-combined-schedule.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Calzo JP, Roberts AL, Corliss HL, Blood EA, Kroshus E, Austin SB. Physical activity disparities in heterosexual and sexual minority youth ages 12–22 years old: roles of childhood gender nonconformity and athletic self-esteem. Ann Behav Med 2014; 47:17–27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim guidance for clinicians considering the use of preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in heterosexually active adults. MMWR 2012; 61:586–589.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophlyaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2014. A clinical practice guideline. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Feldman JL, Goldberg J. Transgender primary medical care: suggested guidelines for clinicians in British Columbia. www.cwhn.ca/en/node/27567. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Coleman E, Bockting W, Botzer M, et al. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender-noncomforming people, version 7. Int J Transgenderism 2011; 13:165–232.
- Wierckx K, Mueller S, Weyers S, et al. Long-term evaluation of cross-sex hormone treatment in transsexual persons. J Sex Med 2012; 9: 2641–2651.
- Asscheman H, T’Sjoen G, Lemaire A, et al. Venous thrombo-embolism as a complication of cross-sex hormone treatment of male-to-female transsexual subjects: a review. Andrologia 2014; 46:791–795.
- Weinand JD, Safer JD. Hormone therapy in transgender adults is safe with provider supervision. A review of hormone therapy sequelae for transgender individuals. J Clin Transl Endocrinol 2015; 2:55–60.
- Unger CA. Care of the transgender patient: the role of the gynecologist. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014; 210:16–26.
- Tjaden P, Thoennes N. Extent, nature, and consequences of intimate partner violence: findings from the National Violence Against Women Survey. Washington, DC: US Department of Justice, National Institute of Justice; 2000. P. 29–31. Report No.: NCJ 181867.
- Stephenson R, Khosropour C, Sullivan P. Reporting of intimate partner violence among men who have sex with men in an online survey. West J Emerg Med 2010; 11:242–246.
- Chen PH, Jacobs A, Rovi SL. Intimate partner violence: IPV in the LGBT community. FP Essent 2013; 412:28–35.
- Siemieniuk R, Miller P, Woodman K, et al. Prevalence, clinical associations, and impact of intimate partner violence among HIV infected gay and bisexual men: a population based study. HIV Med 2013; 14:293–302.
- Rabin RF, Jennings JM, Campbell JC, Bair-Merritt MH. Intimate partner violence screening tools: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2009; 36:439–445.
- Ford CL, Slavin T, Hilton KL, Holt SL. Intimate partner violence prevention services and resources in Los Angeles: issues, needs, and challenges for assisting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender clients. Health Promot Pract 2013; 14:841–849.
- World Professional Association for Transgender Health. www.wpath.org/site_page.cfm?pk_association_webpage_menu=1351. Accessed May 19, 2016.
Primary care physicians are very likely to encounter lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) patients in their practice, and must be able to provide informed, appropriate, and culturally sensitive care.
Approximately 9 million people in the United States identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual, and 700,000 adults are transgender.1 In the 2013 National Health Interview Survey,2 which queried 34,557 adults about their sexual orientation, 2.3% reported being lesbian, gay, or bisexual, with only slight differences according to age or sex: of those ages 18 through 44, 1.9% were gay or lesbian and 1.1% were bisexual; of those ages 65 and over, 0.7% were gay or lesbian and 0.2% were bisexual. By sex, 0.9% of women vs 0.4% of men identified as bisexual.2
This article identifies and corrects common myths about LGBT care, addresses disparities in healthcare access, and outlines a step-by-step approach for delivering comprehensive care to LGBT patients.
MYTHS ABOUT LGBT CARE
Myth #1: L = G = B = T
Although LGBT is a commonly used term, each group described by the abbreviation has its own unique healthcare needs. For example, lesbian and bisexual women are more likely than heterosexual women to smoke, and gay men are at increased risk for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and other sexually transmitted infections.3,4 Transgender persons have high rates of suicide.5
Primary care of the LGBT patient needs to be individualized but also informed by the knowledge of distinct risks and behaviors associated with particular groups.
Myth #2: Sexual orientation = sexual activity
Sexual identity correlates closely but not completely with sexual behavior; individuals may engage in same-sex behavior but not identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual.6,7 Many women who identify as lesbian have previously had sex with men, and men may have had same-sex encounters but consider themselves heterosexual.8,9
Since the risk of certain infections is related to sexual activity, providers should query patients about their sexual partners and practices in an open, nonjudgmental way, and avoid labeling patients solely according to sexual orientation. Table 1 suggests questions to use when interviewing patients.
Myth #3: Sexual orientation = gender identity
Gender identity describes a person’s inherent sense of being a woman, man, or of neither gender, whereas sexual orientation refers to how a person identifies their physical and emotional attraction to others.10,11 Conflating the two concepts can alienate patients, lead to incorrect assumptions, and result in an underestimation of an individual’s risk of sexually transmitted diseases.
Using questions such as “Are you sexually active with men, women, or both?” or “When you are sexually active, what parts of your body do you use?” with all patients, regardless of gender identity, will facilitate open and honest conversations that allow for appropriate counseling and risk assessment. Table 2 lists commonly used gender-identity terms.
Myth #4: LGBT people have the same access to healthcare as heterosexual people
People who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender experience significant disparities in access to healthcare compared with cisgender heterosexual people. For example, lesbian women are less likely to receive the human papillomavirus vaccine, cervical cancer screening, and mammograms, and men in same-sex relationships are twice as likely to have unmet medical needs.8,12 In a national survey,5 19% of transgender individuals reported that they had been refused healthcare. Among 152 transgender adults who described their experiences with the healthcare system, 7% reported receiving substandard care.13
We can eliminate these disparities by creating a welcoming environment for all patients (Table 3), and also by being aware of the specific services that should be offered to LGBT individuals.
ADDRESSING THE NEEDS OF LGBT PATIENTS
Outlined here is an office-based approach for addressing the unique clinical concerns of adult LGBT patients. Not all of these issues need to or should be addressed at the first visit, and the sequence in which these steps are accomplished may vary.
Step #1: Screen for mental health disorders
Lesbian, bisexual, and gay people are more likely to experience depression and anxiety. According to the results of a large meta-analysis,14 the prevalence of these conditions is 1.5 times higher in this population than in heterosexual people. Risk may vary according to group, with gay and bisexual men experiencing a higher lifetime prevalence of anxiety and depression than lesbian and bisexual women.15 Suicidal attempts are also more common in gay and bisexual men, who have a lifetime risk four times higher than that of heterosexual men.14
The risk of suicide is even higher among transgender people: 41% of surveyed transgender adults reported that they had attempted suicide, with higher rates in younger individuals.5 Risk factors include experiences of harassment or physical or sexual violence, as well as poverty, low education level, and unemployment.5 The risk of suicide in transgender people who served in the military is 20 times higher than that in the general veteran population.16
It is imperative to routinely screen LGBT patients for anxiety, depression, and suicidality and to refer them to mental health providers who are sensitive to LGBT patients’ needs and concerns. Screening tools such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ2), PHQ9A, PHQ9, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD7) are useful in screening patients for depression and anxiety in addition to mnemonics such as SIGECAPS (sleep, interest, guilt, energy, concentration, appetite, psychomotor, suicidal thoughts or ideation).17
Although the same screening tools are used in cisgender heterosexual patients, factors contributing to the experience of depression or anxiety may be directly related to gender identity, gender expression, or sexual orientation. In a 2001 study, more lesbian, gay, and bisexual people reported lifetime and day-to-day experiences with discrimination than heterosexual people, and approximately 42% attributed this in part or in total to their sexual orientation.18
Step #2: Assess for substance use
Substance use is also more common in LGBT people. Lesbian and bisexual women have higher rates of tobacco abuse, exposure to second-hand smoke, and alcohol and drug dependence.3,14 In one study, compared with heterosexual individuals, the odds of lifetime alcohol and substance use disorder was three times higher in lesbian women, and the odds of lifetime drug-use disorder was 1.6 times higher in gay men.19
In a survey of transgender people, 30% reported using tobacco compared with 20% of the US adult population, and 8% reported using alcohol or drugs to cope with mistreatment and bias.5 In a study of transgender women in San Francisco, 58% used alcohol and 43% used substances, including marijuana, methamphetamine, and crack cocaine. Substance use significantly increased the odds of testing positive for HIV.20
Clinicians should carefully question LGBT patients about their use of alcohol, tobacco, and other substances and provide counseling and assistance with cessation. Several LGBT-specific resources can be used to aid patients in their efforts, and referral to substance abuse groups that are welcoming to LGBT people may increase cessation rates.19,21
Step #3: Offer appropriate screening services
Human papillomavirus (HPV). Like heterosexual women, lesbian and bisexual women are at risk of HPV infection, which is associated with cervical cancer and genital warts.8 HPV can be transmitted in several ways, including skin-to-skin and digital-to-genital contact, as well as penile-vaginal intercourse. Lesbian and bisexual women may have acquired HPV from previous male sexual partners or from female-to-female transmission.8 In a study comparing cervical cancer screening results among lesbian, bisexual, and heterosexual women, there was no significant difference in the odds for Papanicolaou (Pap) test abnormalities and only a minor decrease in the odds of HPV infection.22 Lesbian and bisexual women should receive Pap and HPV testing according to current guidelines.
Other sexually transmitted infections, including herpes simplex virus 1, herpes simplex virus 2, Trichomonas vaginalis, syphilis, and hepatitis A, can be passed between female partners; risk may vary according to sexual practices.23 Thus, providers should not assume that lesbian women are at low risk of these infections and should screen according to current guidelines.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends annual screening for Chlamydia infection for all women under age 25, as well as those at increased risk for this infection (ie, those with a new sex partner or multiple sex partners).24
Breast cancer. Studies reveal that lesbian and bisexual women are less likely to receive mammograms, and they may have several risk factors that increase their risk for breast cancer, including overweight, obesity, and excessive alcohol intake.12,18,25 Providers should discuss the risks and benefits of mammography and offer this screening service at appropriate intervals.
Screening in men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men are at increased risk for several sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, Chlamydia, anal HPV, and hepatitis B and C.4,9 The CDC recommends annual sexual health screening that includes serologic testing for HIV and syphilis, and urine, rectal, or pharyngeal testing for gonorrhea and Chlamydia according to sexual practices.24
In contrast, routine screening for anal HPV is not currently recommended because we lack data demonstrating that screening reduces mortality rates from anal carcinoma.24,26 Nevertheless, the CDC acknowledges that some clinicians may choose to perform anal Pap testing in patients who are at high risk, and guidelines from the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene suggest annual anal Pap testing in HIV-positive men who have sex with men.27
According to the results of a systematic review,28 a significant proportion of transgender women reported sexual practices that increased their risk for sexually transmitted infections, and 27.7% tested positive for HIV infection. In contrast, rates of HIV and risk behaviors were much lower among transgender men. Risk may be heightened in transgender women who have not had sexual reassignment surgery and who engage in insertive anal, vaginal, or oral intercourse.28 An awareness of an individual patient’s current anatomy and sexual practices is essential for providing appropriate counseling about sexually transmitted infections.
‘Screen what you have’
When considering screening for breast, cervical, and prostate cancer, providers should consider an individual patient’s surgical history and hormonal status. “Screen what you have” is an easy rule to help both patients and providers remember which services to consider.
Transgender men who have not had a mastectomy should discuss the risks and benefits of breast cancer screening and consider mammography as recommended by the American Cancer Society.29 Similarly, cervical cancer screening should be performed according to current guidelines, although providers should be aware that this examination can cause significant anxiety and emotional distress for the patient.30
In transgender women, guidelines for breast cancer screening for those who were previously or currently treated with hormones are lacking. The University of California-San Francisco Center of Excellence for Transgender Health recommends mammography for patients over age 50 with additional risk factors (family history, obesity, estrogen and progestin use for more than 5 years).31 Transgender women should be counseled about the risks and benefits of prostate cancer screening.
Step #4: Immunize, and promote healthy behaviors
Table 4 outlines the screening services, immunizations, and health behavior promotions that should be offered to LGBT patients.
Vaccinations. LGBT individuals should be routinely offered HPV vaccination through age 26, according to current guidelines.24 Immunization against hepatitis A and B is also recommended for men who have sex with men, if they are not already immune.24 Meningococcal vaccine should be given to men who have sex with men if they have an additional medical, occupational, or lifestyle risk factor.32
Physical activity should be encouraged, especially in lesbian and bisexual women, who are more likely to be overweight and obese.25 In a recent study,33 gay, lesbian, and bisexual youths (ages 12–22) reported 1.21 to 2.62 fewer hours of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week than their “completely heterosexual” counterparts, and were 46% to 76% less likely to participate in team sports, in part due to concerns about gender nonconformity. On the other hand, results from a recent national survey of adults ages 18 through 64 found no significant differences in physical activity according to sexual orientation.
Providers should address patients’ perceived barriers to participating in exercise programs.2
Preexposure prophylaxis against HIV. A growing number of patients and health providers are asking about preexposure prophylaxis for HIV infection. The initial CDC recommendations for the daily use of emtricitabine-tenofovir were restricted to gay and bisexual men and men who have sex with men in serodiscordant relationships or in situations where the HIV status of the patient’s partner was unknown.34 Since then, the CDC has expanded the groups who may benefit from preexposure prophylaxis.35 Assessment of the patient’s ability to adhere to a daily oral medication regimen is central to its success. Patients should be screened for hepatitis, HIV, and renal and liver function before starting emtricitabine-tenofovir and should have these tests repeated at 3-month intervals if pre-exposure prophylaxis is continued.
Step #5: Initiate or continue hormone therapy for transgender individuals
Hormone therapy often improves the quality of life for patients who desire to have their physical appearance align more closely with their gender identity.29 Moreover, abruptly stopping hormone therapy can have significant psychological consequences.36
Clinicians should feel comfortable starting hormone therapy for patients who have been diagnosed with gender dysphoria by a mental health professional, can demonstrate knowledge about and outcomes of hormone therapy, and have lived as a member of the desired gender (“real-life experience”) for at least 3 months, and preferably 12 months.29 More recently, some practitioners have advocated prescribing hormone therapy for patients without the requirement for real-life experience or a formal letter from a mental health professional recommending hormonal therapy.37 However, mental healthcare is recommended for any patient with moderate to severe mental health conditions, especially if not treated at the time of presentation.37
Providers should continue hormone therapy for patients who are already receiving it, while being aware of the appropriate treatment goals and monitoring parameters. The two main principles of hormone therapy for transgender patients are to reduce endogenous hormone levels and their associated sex characteristics and replace with hormones of the preferred sex.29 Doses and formulations are similar to those used for treatment of hypogonadism. This topic has been reviewed by Spack.10
The only absolute contraindications to hormone therapy are estrogen- or testosterone-responsive tumors. Otherwise, hormone therapy can be initiated or continued with the patient’s informed consent about its benefits and risks.
Estrogen therapy may increase the risk of thromboembolic disease, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, severe migraine headaches, liver dysfunction, and macroprolactinoma.29 In a cross-sectional study of 100 transgender patients receiving hormone therapy, 12% of transgender women experienced a thromboembolic or cardiovascular event after an average of 11 years of treatment.38 However, many of these patients had additional risk factors for these events, such as smoking. In contrast, results from a recent systematic review39 indicated a much lower rate of venous thromboembolism among transgender women receiving estrogen therapy (1.7%–6.3%). Use of transdermal estrogen may minimize the likelihood of thromboembolic disease, and cessation of hormonal care in the perioperative period is advisable, especially for procedures with greater risk of venous thromboembolism.39
Transgender men are at risk of erythrocytosis (hematocrit > 50%) as a result of testosterone therapy. Although current guidelines indicate that testosterone may increase the risk of breast or uterine cancer, results from a recent systematic review40 indicate that the overall cancer incidence in transgender men is not higher than in natal controls. Both estrogen and testosterone therapy increase insulin resistance and fasting glucose levels, whereas only estrogen increases triglyceride concentrations.40
For transgender women, estrogen levels should be maintained in the normal range for cisgender women of reproductive age (< 200 pg/mL), and testosterone levels should be suppressed to less than 55 ng/dL. Goal testosterone levels for transgender men are between 320 and 1,000 ng/dL and should be measured at intervals specific to the preparation used (ie, measured midway between injections for individuals treated with testosterone cypionate). Estradiol levels should be less than 50 ng/dL.29 Transgender women and men should have estradiol and testosterone levels measured quarterly during the first year of treatment, and then every 6 to 12 months thereafter once goal levels are achieved.
Additional monitoring for transgender women includes measuring serum prolactin at baseline and after 12 months of therapy, and serum electrolytes for those taking spironolactone as antiandrogen therapy. Complete blood cell counts and liver function tests should be done every 3 months during the first year of testosterone therapy for transgender men, and then one to two times per year.29 Reference laboratory values for the patient’s affirmed gender should be used to assess response to therapy as well as effects on end-organ function.
The marked suppression of endogenous hormone levels that occurs during therapy may have adverse effects on the bone mineral density of both transgender women and men. Clinicians should assess patients’ baseline risk for osteoporotic fracture at the time hormone therapy is started and consider bone mineral density testing if appropriate. For those at low risk for fracture, current guidelines recommend screening for osteoporosis starting at age 60.29
Providers should counsel patients who have recently initiated hormone therapy that some changes may occur gradually over time. While transgender women will notice a decrease in libido and spontaneous erections within the first 3 months of therapy, breast growth begins approximately 3 to 6 months after treatment is started. Similarly, for transgender men, fat redistribution occurs during the first 6 months of treatment, but facial and body hair growth occur more slowly and are at maximum 4 to 5 years after starting hormone therapy.29 Amenorrhea typically occurs 1 to 6 months after starting hormonal therapy for transgender men.
Some patients may be interested in surgery to continue their physical transformation to the desired sex. Patients who have used hormone therapy and participated in a real-life experience or otherwise completed social transition by living as the affirmed gender for 12 months are considered eligible for surgery if they can demonstrate a good understanding of the cost, potential complications, and expected recovery time of the procedure. Guidelines also recommend that the patient demonstrate progress in work, family, and interpersonal issues regarding their new gender.29 Available surgical options include breast augmentation, orchiectomy and penectomy, and vaginoplasty, clitoroplasty, and vulvoplasty for transgender women. Feminizing procedures include voice surgery, thyroid cartilage reduction, and facial feminization surgery. Transgender men may choose to have mastectomy, hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy, vaginectomy, scrotoplasty and testicular implant placement, and implantation of a penile prosthesis. Additional virilizing surgeries include voice surgery and pectoral implants.41
Step #6: Screen for intimate partner violence
Intimate partner violence refers to physical, sexual, and psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse, and it can occur in gay and lesbian relationships. In 2000, a National Violence Against Women survey found that 21.5% of men and 35.4% of women who reported living with a same-sex partner had experienced physical abuse.42 More recent studies confirm rates similar to those in heterosexual relationships. In an online study,43 11.8% of men who have sex with men reported physical violence from a current male partner, and about 4% reported experiencing coerced sex.
Intimate partner violence is uniquely challenging for LGBT people. In addition to the commonly described methods an abuser uses to maintain power and control, forced disclosure or “outing”—publicly revealing someone’s sexual orientation or gender identity—may result in additional psychological violence and harm. Survivors of intimate partner violence who are in same-gender intimate relationships often find that obtaining services through the police, judicial, and social services systems is challenging. Survivors may be required to disclose their sexual orientation or gender identity as part of filing a report or judicial order to obtain help or protection from the abuser. Many male and transgender survivors of intimate partner violence are unable to access traditional shelters. Female survivors may find that their same-sex abusers have the same access to resources and shelters that they do.
Intimate partner violence is associated with negative physical and mental health outcomes. Physical injuries such as bruises, fractures, and burns are some of the more obvious harms survivors sustain. However, the negative psychological impact on survivors cannot be overstated. LGBT individuals are at greater risk of depression and substance abuse as a result of intimate partner violence than their cisgender heterosexual counterparts. The stress resulting from stigmatization and discrimination can be exacerbated by intimate partner violence.44 This can be seen in health outcomes of HIV-positive men who have sex with men, in whom abuse predicts interruptions in care, more advanced HIV disease, and HIV-associated hospitalizations.45
We recommend that providers screen all LGBT patients for intimate partner violence. One commonly used tool is the Partner Violence Screen, which consists of three gender-neutral questions:
- Have you been hit, kicked, punched, or otherwise hurt by someone in the past year? If so, by whom?
- Do you feel safe in your current relationship?
- Is there a partner from a previous relationship who is making you feel unsafe now?
Like other screening tools for intimate partner violence, the Partner Violence Screen is more specific than sensitive.46 Screening and discussions about intimate partner violence should be performed in a private, confidential manner while the patient is alone.
Providers who care for LGBT patients need to be aware of not only the medical and mental health sequelae of intimate partner violence but also the social and legal issues facing survivors. Familiarity with the available community resources and their limitations can better facilitate trust and patient care for those affected by intimate partner violence. In one study, the most frequent requests for assistance from sexual and gender minority survivors were for counseling, safe housing, legal assistance, and assistance navigating the medical system.47 Providers should refer patients to LGBT-focused resources in their community as available, and when no such resources exist, initiate contact with standard domestic violence services, with patient consent, to ask about a program’s ability to assist survivors of LGBT intimate partner violence.
IN A NUTSHELL
Optimizing the care of LGBT patients requires developing both clinical and cultural competency.
Initial steps for creating an inclusive and welcoming clinical environment include becoming familiar with local resources for LGBT patients (support groups, substance and alcohol cessation groups, mental health providers; see sidebar), providing education and training for support staff and nurses, and establishing gender-neutral bathrooms. Waiting areas should include literature relevant to LGBT patients and signage that is relevant to all patients, including gender-nonconforming individuals. Providers should offer all patients universal HIV screening initially and at clinically appropriate intervals and discuss preexposure prophylaxis with emtricitabine-tenofovir for at-risk individuals.
For transgender patients, addressing them by their preferred name and pronouns is central to building rapport. General health maintenance is the same for transgender patients as for cisgender patients and can be guided by the adage “screen what you have.” Hormonal care can be offered using an informed consent method consistent with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health Standards of Care.48 Guidelines exist to assist providers in initiation and maintenance of hormonal care. Cross-gender hormonal therapy is initiated with low-dose medication that is gradually increased over time, with a goal of approximating the pubertal changes of the desired gender over a 2- to 3-year period. Some, but not all, patients may pursue various surgical procedures as part of their gender affirmation process.
Primary care physicians are very likely to encounter lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) patients in their practice, and must be able to provide informed, appropriate, and culturally sensitive care.
Approximately 9 million people in the United States identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual, and 700,000 adults are transgender.1 In the 2013 National Health Interview Survey,2 which queried 34,557 adults about their sexual orientation, 2.3% reported being lesbian, gay, or bisexual, with only slight differences according to age or sex: of those ages 18 through 44, 1.9% were gay or lesbian and 1.1% were bisexual; of those ages 65 and over, 0.7% were gay or lesbian and 0.2% were bisexual. By sex, 0.9% of women vs 0.4% of men identified as bisexual.2
This article identifies and corrects common myths about LGBT care, addresses disparities in healthcare access, and outlines a step-by-step approach for delivering comprehensive care to LGBT patients.
MYTHS ABOUT LGBT CARE
Myth #1: L = G = B = T
Although LGBT is a commonly used term, each group described by the abbreviation has its own unique healthcare needs. For example, lesbian and bisexual women are more likely than heterosexual women to smoke, and gay men are at increased risk for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and other sexually transmitted infections.3,4 Transgender persons have high rates of suicide.5
Primary care of the LGBT patient needs to be individualized but also informed by the knowledge of distinct risks and behaviors associated with particular groups.
Myth #2: Sexual orientation = sexual activity
Sexual identity correlates closely but not completely with sexual behavior; individuals may engage in same-sex behavior but not identify as lesbian, gay, or bisexual.6,7 Many women who identify as lesbian have previously had sex with men, and men may have had same-sex encounters but consider themselves heterosexual.8,9
Since the risk of certain infections is related to sexual activity, providers should query patients about their sexual partners and practices in an open, nonjudgmental way, and avoid labeling patients solely according to sexual orientation. Table 1 suggests questions to use when interviewing patients.
Myth #3: Sexual orientation = gender identity
Gender identity describes a person’s inherent sense of being a woman, man, or of neither gender, whereas sexual orientation refers to how a person identifies their physical and emotional attraction to others.10,11 Conflating the two concepts can alienate patients, lead to incorrect assumptions, and result in an underestimation of an individual’s risk of sexually transmitted diseases.
Using questions such as “Are you sexually active with men, women, or both?” or “When you are sexually active, what parts of your body do you use?” with all patients, regardless of gender identity, will facilitate open and honest conversations that allow for appropriate counseling and risk assessment. Table 2 lists commonly used gender-identity terms.
Myth #4: LGBT people have the same access to healthcare as heterosexual people
People who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender experience significant disparities in access to healthcare compared with cisgender heterosexual people. For example, lesbian women are less likely to receive the human papillomavirus vaccine, cervical cancer screening, and mammograms, and men in same-sex relationships are twice as likely to have unmet medical needs.8,12 In a national survey,5 19% of transgender individuals reported that they had been refused healthcare. Among 152 transgender adults who described their experiences with the healthcare system, 7% reported receiving substandard care.13
We can eliminate these disparities by creating a welcoming environment for all patients (Table 3), and also by being aware of the specific services that should be offered to LGBT individuals.
ADDRESSING THE NEEDS OF LGBT PATIENTS
Outlined here is an office-based approach for addressing the unique clinical concerns of adult LGBT patients. Not all of these issues need to or should be addressed at the first visit, and the sequence in which these steps are accomplished may vary.
Step #1: Screen for mental health disorders
Lesbian, bisexual, and gay people are more likely to experience depression and anxiety. According to the results of a large meta-analysis,14 the prevalence of these conditions is 1.5 times higher in this population than in heterosexual people. Risk may vary according to group, with gay and bisexual men experiencing a higher lifetime prevalence of anxiety and depression than lesbian and bisexual women.15 Suicidal attempts are also more common in gay and bisexual men, who have a lifetime risk four times higher than that of heterosexual men.14
The risk of suicide is even higher among transgender people: 41% of surveyed transgender adults reported that they had attempted suicide, with higher rates in younger individuals.5 Risk factors include experiences of harassment or physical or sexual violence, as well as poverty, low education level, and unemployment.5 The risk of suicide in transgender people who served in the military is 20 times higher than that in the general veteran population.16
It is imperative to routinely screen LGBT patients for anxiety, depression, and suicidality and to refer them to mental health providers who are sensitive to LGBT patients’ needs and concerns. Screening tools such as the Patient Health Questionnaire-2 (PHQ2), PHQ9A, PHQ9, and Generalized Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD7) are useful in screening patients for depression and anxiety in addition to mnemonics such as SIGECAPS (sleep, interest, guilt, energy, concentration, appetite, psychomotor, suicidal thoughts or ideation).17
Although the same screening tools are used in cisgender heterosexual patients, factors contributing to the experience of depression or anxiety may be directly related to gender identity, gender expression, or sexual orientation. In a 2001 study, more lesbian, gay, and bisexual people reported lifetime and day-to-day experiences with discrimination than heterosexual people, and approximately 42% attributed this in part or in total to their sexual orientation.18
Step #2: Assess for substance use
Substance use is also more common in LGBT people. Lesbian and bisexual women have higher rates of tobacco abuse, exposure to second-hand smoke, and alcohol and drug dependence.3,14 In one study, compared with heterosexual individuals, the odds of lifetime alcohol and substance use disorder was three times higher in lesbian women, and the odds of lifetime drug-use disorder was 1.6 times higher in gay men.19
In a survey of transgender people, 30% reported using tobacco compared with 20% of the US adult population, and 8% reported using alcohol or drugs to cope with mistreatment and bias.5 In a study of transgender women in San Francisco, 58% used alcohol and 43% used substances, including marijuana, methamphetamine, and crack cocaine. Substance use significantly increased the odds of testing positive for HIV.20
Clinicians should carefully question LGBT patients about their use of alcohol, tobacco, and other substances and provide counseling and assistance with cessation. Several LGBT-specific resources can be used to aid patients in their efforts, and referral to substance abuse groups that are welcoming to LGBT people may increase cessation rates.19,21
Step #3: Offer appropriate screening services
Human papillomavirus (HPV). Like heterosexual women, lesbian and bisexual women are at risk of HPV infection, which is associated with cervical cancer and genital warts.8 HPV can be transmitted in several ways, including skin-to-skin and digital-to-genital contact, as well as penile-vaginal intercourse. Lesbian and bisexual women may have acquired HPV from previous male sexual partners or from female-to-female transmission.8 In a study comparing cervical cancer screening results among lesbian, bisexual, and heterosexual women, there was no significant difference in the odds for Papanicolaou (Pap) test abnormalities and only a minor decrease in the odds of HPV infection.22 Lesbian and bisexual women should receive Pap and HPV testing according to current guidelines.
Other sexually transmitted infections, including herpes simplex virus 1, herpes simplex virus 2, Trichomonas vaginalis, syphilis, and hepatitis A, can be passed between female partners; risk may vary according to sexual practices.23 Thus, providers should not assume that lesbian women are at low risk of these infections and should screen according to current guidelines.
The US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends annual screening for Chlamydia infection for all women under age 25, as well as those at increased risk for this infection (ie, those with a new sex partner or multiple sex partners).24
Breast cancer. Studies reveal that lesbian and bisexual women are less likely to receive mammograms, and they may have several risk factors that increase their risk for breast cancer, including overweight, obesity, and excessive alcohol intake.12,18,25 Providers should discuss the risks and benefits of mammography and offer this screening service at appropriate intervals.
Screening in men who have sex with men
Men who have sex with men are at increased risk for several sexually transmitted infections, including HIV, syphilis, gonorrhea, Chlamydia, anal HPV, and hepatitis B and C.4,9 The CDC recommends annual sexual health screening that includes serologic testing for HIV and syphilis, and urine, rectal, or pharyngeal testing for gonorrhea and Chlamydia according to sexual practices.24
In contrast, routine screening for anal HPV is not currently recommended because we lack data demonstrating that screening reduces mortality rates from anal carcinoma.24,26 Nevertheless, the CDC acknowledges that some clinicians may choose to perform anal Pap testing in patients who are at high risk, and guidelines from the New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene suggest annual anal Pap testing in HIV-positive men who have sex with men.27
According to the results of a systematic review,28 a significant proportion of transgender women reported sexual practices that increased their risk for sexually transmitted infections, and 27.7% tested positive for HIV infection. In contrast, rates of HIV and risk behaviors were much lower among transgender men. Risk may be heightened in transgender women who have not had sexual reassignment surgery and who engage in insertive anal, vaginal, or oral intercourse.28 An awareness of an individual patient’s current anatomy and sexual practices is essential for providing appropriate counseling about sexually transmitted infections.
‘Screen what you have’
When considering screening for breast, cervical, and prostate cancer, providers should consider an individual patient’s surgical history and hormonal status. “Screen what you have” is an easy rule to help both patients and providers remember which services to consider.
Transgender men who have not had a mastectomy should discuss the risks and benefits of breast cancer screening and consider mammography as recommended by the American Cancer Society.29 Similarly, cervical cancer screening should be performed according to current guidelines, although providers should be aware that this examination can cause significant anxiety and emotional distress for the patient.30
In transgender women, guidelines for breast cancer screening for those who were previously or currently treated with hormones are lacking. The University of California-San Francisco Center of Excellence for Transgender Health recommends mammography for patients over age 50 with additional risk factors (family history, obesity, estrogen and progestin use for more than 5 years).31 Transgender women should be counseled about the risks and benefits of prostate cancer screening.
Step #4: Immunize, and promote healthy behaviors
Table 4 outlines the screening services, immunizations, and health behavior promotions that should be offered to LGBT patients.
Vaccinations. LGBT individuals should be routinely offered HPV vaccination through age 26, according to current guidelines.24 Immunization against hepatitis A and B is also recommended for men who have sex with men, if they are not already immune.24 Meningococcal vaccine should be given to men who have sex with men if they have an additional medical, occupational, or lifestyle risk factor.32
Physical activity should be encouraged, especially in lesbian and bisexual women, who are more likely to be overweight and obese.25 In a recent study,33 gay, lesbian, and bisexual youths (ages 12–22) reported 1.21 to 2.62 fewer hours of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week than their “completely heterosexual” counterparts, and were 46% to 76% less likely to participate in team sports, in part due to concerns about gender nonconformity. On the other hand, results from a recent national survey of adults ages 18 through 64 found no significant differences in physical activity according to sexual orientation.
Providers should address patients’ perceived barriers to participating in exercise programs.2
Preexposure prophylaxis against HIV. A growing number of patients and health providers are asking about preexposure prophylaxis for HIV infection. The initial CDC recommendations for the daily use of emtricitabine-tenofovir were restricted to gay and bisexual men and men who have sex with men in serodiscordant relationships or in situations where the HIV status of the patient’s partner was unknown.34 Since then, the CDC has expanded the groups who may benefit from preexposure prophylaxis.35 Assessment of the patient’s ability to adhere to a daily oral medication regimen is central to its success. Patients should be screened for hepatitis, HIV, and renal and liver function before starting emtricitabine-tenofovir and should have these tests repeated at 3-month intervals if pre-exposure prophylaxis is continued.
Step #5: Initiate or continue hormone therapy for transgender individuals
Hormone therapy often improves the quality of life for patients who desire to have their physical appearance align more closely with their gender identity.29 Moreover, abruptly stopping hormone therapy can have significant psychological consequences.36
Clinicians should feel comfortable starting hormone therapy for patients who have been diagnosed with gender dysphoria by a mental health professional, can demonstrate knowledge about and outcomes of hormone therapy, and have lived as a member of the desired gender (“real-life experience”) for at least 3 months, and preferably 12 months.29 More recently, some practitioners have advocated prescribing hormone therapy for patients without the requirement for real-life experience or a formal letter from a mental health professional recommending hormonal therapy.37 However, mental healthcare is recommended for any patient with moderate to severe mental health conditions, especially if not treated at the time of presentation.37
Providers should continue hormone therapy for patients who are already receiving it, while being aware of the appropriate treatment goals and monitoring parameters. The two main principles of hormone therapy for transgender patients are to reduce endogenous hormone levels and their associated sex characteristics and replace with hormones of the preferred sex.29 Doses and formulations are similar to those used for treatment of hypogonadism. This topic has been reviewed by Spack.10
The only absolute contraindications to hormone therapy are estrogen- or testosterone-responsive tumors. Otherwise, hormone therapy can be initiated or continued with the patient’s informed consent about its benefits and risks.
Estrogen therapy may increase the risk of thromboembolic disease, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular disease, severe migraine headaches, liver dysfunction, and macroprolactinoma.29 In a cross-sectional study of 100 transgender patients receiving hormone therapy, 12% of transgender women experienced a thromboembolic or cardiovascular event after an average of 11 years of treatment.38 However, many of these patients had additional risk factors for these events, such as smoking. In contrast, results from a recent systematic review39 indicated a much lower rate of venous thromboembolism among transgender women receiving estrogen therapy (1.7%–6.3%). Use of transdermal estrogen may minimize the likelihood of thromboembolic disease, and cessation of hormonal care in the perioperative period is advisable, especially for procedures with greater risk of venous thromboembolism.39
Transgender men are at risk of erythrocytosis (hematocrit > 50%) as a result of testosterone therapy. Although current guidelines indicate that testosterone may increase the risk of breast or uterine cancer, results from a recent systematic review40 indicate that the overall cancer incidence in transgender men is not higher than in natal controls. Both estrogen and testosterone therapy increase insulin resistance and fasting glucose levels, whereas only estrogen increases triglyceride concentrations.40
For transgender women, estrogen levels should be maintained in the normal range for cisgender women of reproductive age (< 200 pg/mL), and testosterone levels should be suppressed to less than 55 ng/dL. Goal testosterone levels for transgender men are between 320 and 1,000 ng/dL and should be measured at intervals specific to the preparation used (ie, measured midway between injections for individuals treated with testosterone cypionate). Estradiol levels should be less than 50 ng/dL.29 Transgender women and men should have estradiol and testosterone levels measured quarterly during the first year of treatment, and then every 6 to 12 months thereafter once goal levels are achieved.
Additional monitoring for transgender women includes measuring serum prolactin at baseline and after 12 months of therapy, and serum electrolytes for those taking spironolactone as antiandrogen therapy. Complete blood cell counts and liver function tests should be done every 3 months during the first year of testosterone therapy for transgender men, and then one to two times per year.29 Reference laboratory values for the patient’s affirmed gender should be used to assess response to therapy as well as effects on end-organ function.
The marked suppression of endogenous hormone levels that occurs during therapy may have adverse effects on the bone mineral density of both transgender women and men. Clinicians should assess patients’ baseline risk for osteoporotic fracture at the time hormone therapy is started and consider bone mineral density testing if appropriate. For those at low risk for fracture, current guidelines recommend screening for osteoporosis starting at age 60.29
Providers should counsel patients who have recently initiated hormone therapy that some changes may occur gradually over time. While transgender women will notice a decrease in libido and spontaneous erections within the first 3 months of therapy, breast growth begins approximately 3 to 6 months after treatment is started. Similarly, for transgender men, fat redistribution occurs during the first 6 months of treatment, but facial and body hair growth occur more slowly and are at maximum 4 to 5 years after starting hormone therapy.29 Amenorrhea typically occurs 1 to 6 months after starting hormonal therapy for transgender men.
Some patients may be interested in surgery to continue their physical transformation to the desired sex. Patients who have used hormone therapy and participated in a real-life experience or otherwise completed social transition by living as the affirmed gender for 12 months are considered eligible for surgery if they can demonstrate a good understanding of the cost, potential complications, and expected recovery time of the procedure. Guidelines also recommend that the patient demonstrate progress in work, family, and interpersonal issues regarding their new gender.29 Available surgical options include breast augmentation, orchiectomy and penectomy, and vaginoplasty, clitoroplasty, and vulvoplasty for transgender women. Feminizing procedures include voice surgery, thyroid cartilage reduction, and facial feminization surgery. Transgender men may choose to have mastectomy, hysterectomy and salpingo-oophorectomy, vaginectomy, scrotoplasty and testicular implant placement, and implantation of a penile prosthesis. Additional virilizing surgeries include voice surgery and pectoral implants.41
Step #6: Screen for intimate partner violence
Intimate partner violence refers to physical, sexual, and psychological harm by a current or former partner or spouse, and it can occur in gay and lesbian relationships. In 2000, a National Violence Against Women survey found that 21.5% of men and 35.4% of women who reported living with a same-sex partner had experienced physical abuse.42 More recent studies confirm rates similar to those in heterosexual relationships. In an online study,43 11.8% of men who have sex with men reported physical violence from a current male partner, and about 4% reported experiencing coerced sex.
Intimate partner violence is uniquely challenging for LGBT people. In addition to the commonly described methods an abuser uses to maintain power and control, forced disclosure or “outing”—publicly revealing someone’s sexual orientation or gender identity—may result in additional psychological violence and harm. Survivors of intimate partner violence who are in same-gender intimate relationships often find that obtaining services through the police, judicial, and social services systems is challenging. Survivors may be required to disclose their sexual orientation or gender identity as part of filing a report or judicial order to obtain help or protection from the abuser. Many male and transgender survivors of intimate partner violence are unable to access traditional shelters. Female survivors may find that their same-sex abusers have the same access to resources and shelters that they do.
Intimate partner violence is associated with negative physical and mental health outcomes. Physical injuries such as bruises, fractures, and burns are some of the more obvious harms survivors sustain. However, the negative psychological impact on survivors cannot be overstated. LGBT individuals are at greater risk of depression and substance abuse as a result of intimate partner violence than their cisgender heterosexual counterparts. The stress resulting from stigmatization and discrimination can be exacerbated by intimate partner violence.44 This can be seen in health outcomes of HIV-positive men who have sex with men, in whom abuse predicts interruptions in care, more advanced HIV disease, and HIV-associated hospitalizations.45
We recommend that providers screen all LGBT patients for intimate partner violence. One commonly used tool is the Partner Violence Screen, which consists of three gender-neutral questions:
- Have you been hit, kicked, punched, or otherwise hurt by someone in the past year? If so, by whom?
- Do you feel safe in your current relationship?
- Is there a partner from a previous relationship who is making you feel unsafe now?
Like other screening tools for intimate partner violence, the Partner Violence Screen is more specific than sensitive.46 Screening and discussions about intimate partner violence should be performed in a private, confidential manner while the patient is alone.
Providers who care for LGBT patients need to be aware of not only the medical and mental health sequelae of intimate partner violence but also the social and legal issues facing survivors. Familiarity with the available community resources and their limitations can better facilitate trust and patient care for those affected by intimate partner violence. In one study, the most frequent requests for assistance from sexual and gender minority survivors were for counseling, safe housing, legal assistance, and assistance navigating the medical system.47 Providers should refer patients to LGBT-focused resources in their community as available, and when no such resources exist, initiate contact with standard domestic violence services, with patient consent, to ask about a program’s ability to assist survivors of LGBT intimate partner violence.
IN A NUTSHELL
Optimizing the care of LGBT patients requires developing both clinical and cultural competency.
Initial steps for creating an inclusive and welcoming clinical environment include becoming familiar with local resources for LGBT patients (support groups, substance and alcohol cessation groups, mental health providers; see sidebar), providing education and training for support staff and nurses, and establishing gender-neutral bathrooms. Waiting areas should include literature relevant to LGBT patients and signage that is relevant to all patients, including gender-nonconforming individuals. Providers should offer all patients universal HIV screening initially and at clinically appropriate intervals and discuss preexposure prophylaxis with emtricitabine-tenofovir for at-risk individuals.
For transgender patients, addressing them by their preferred name and pronouns is central to building rapport. General health maintenance is the same for transgender patients as for cisgender patients and can be guided by the adage “screen what you have.” Hormonal care can be offered using an informed consent method consistent with the World Professional Association for Transgender Health Standards of Care.48 Guidelines exist to assist providers in initiation and maintenance of hormonal care. Cross-gender hormonal therapy is initiated with low-dose medication that is gradually increased over time, with a goal of approximating the pubertal changes of the desired gender over a 2- to 3-year period. Some, but not all, patients may pursue various surgical procedures as part of their gender affirmation process.
- Gates GJ. How many people are lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender? Williams Institute. 2011. http://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/Gates-How-Many-People-LGBT-Apr-2011.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Ward BW, Dahlhamer JM, Galinsky AM, Joesti SS. Sexual orientation and health among U.S. Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2013. Natl Health Stat Report 2014; 77:1–10.
- Cochran SD, Bandiera FC, Mays VM. Sexual orientation-related differences in tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure among US adults aged 20-59 years: 2003–2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys. Am J Publ Health 2013; 103:1837–1844.
- Mayer KH. Sexually transmitted diseases in men who have sex with men. Clin Infect Disease 2011; 53:S79–S83.
- Grant JM, Mottet LA, Tanis J, Herman JL, Harrison J, Keisling M. National transgender discrimination survey report on health and health care. www.thetaskforce.org/static_html/downloads/reports/reports/ntds_report_on_health.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Pathela P, Hajat A, Schillinger J, Blank S, Sell R, Mostashari F. Discordance between sexual behavior and self-reported sexual identity: a population-based survey of New York City men. Ann Intern Med 2006; 145:416–425.
- Chandra A, Mosher WD, Copen C, Sionean C. Sexual behavior, sexual attraction, and sexual identity in the United States: data from the 2006–2009 National Survey of Family Growth. Natl Health Stat Report 2011; 36:1–36.
- Agenor M, Peitzmeier S, Gordon AR, Haneuse S, Potter JE, Austin SB. Sexual orientation identity disparities in awareness and initiation of the human papillomavirus vaccine among U.S. women and girls: a national survey. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:99–106.
- Ard KL, Makadon HJ. Improving the health care of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people: understanding and eliminating health disparities. www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/12-054_LGBTHealtharticle_v3_07-09-12.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Spack NP. Management of transgenderism. JAMA 2013; 309:474–484.
- National LGBT Health Education Center. Achieving health equity for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people, Module 1. www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/Achieving-Health-Equity-for-LGBT-People-1.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Buchmueller T, Carpenter CS. Disparities in health Insurance coverage, access, and outcomes for individuals in same-sex versus different-sex relationships, 2000–2007. Am J Public Health 2010; 100:489–496.
- Kosenko K, Rintamaki L, Raney S, Maness K. Transgender patient perceptions of stigma in health care contexts. Med Care 2013; 51:819–822.
- King M, Semlyen J, Tai SS, et al. A systematic review of mental disorder, suicide, and deliberate self-harm in lesbian, gay, and bisexual people. BMC Psychiatry 2008; 8:70.
- Bostwick WB, Boyd CJ, Hughes TL, McCabe SE. Dimensions of sexual orientation and the prevalence of mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. Am J Public Health 2010; 100:468–475.
- Blosnich JR, Brown GR, Shipherd JC, Kauth M, Piegari RI, Bossarte RM. Prevalence of gender identity disorder and suicide risk among transgender veterans utilizing Veterans Health Administration care. Am J Public Health 2013: 103:e27–e32.
- Maurer DM. Screening for depression. Am Fam Physician 2012; 85:139–144.
- Mays VM, Cochran SD. Mental health correlates of perceived discrimination among lesbian, gay, and bisexual adults in the United States. Am J Pub Health 2001; 91:1869–1875.
- McCabe SE, West BT, Hughes TL, Boyd CJ. Sexual orientation and substance abuse treatment utilization in the United States: results from a national survey. J Subst Abuse Treat 2013; 44:4–12.
- Santos GM, Rapues J, Wilson EC, et al. Alcohol and substance use among transgender women in San Francisco: prevalence and association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Drug Alcohol Rev 2014; 33:287–295.
- National LGBT Tobacco Control Network. www.lgbttobacco.org. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Massad LS, Xie X, Minkoff H, et al. Abnormal Pap tests and human papillomavirus infections among HIV infected and uninfected women who have sex with women. J Low Genit Tract Dis 2014; 18:50–56.
- Gorgos LM, Marrazzo JM. Sexually transmitted infections among women who have sex with women. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 53:S84–S91.
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR 2015; 64(3):1–138.
- Boehmer U, Bowen DJ, Bauer GR. Overweight and obesity in sexual-minority women: evidence from population-based data. Am J Public Health 2007; 97:1134–1140.
- Smyczek P, Singh AE, Romanowski B. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia: review and recommendations for screening and management. Int J STD AIDS 2013; 24:843–851.
- New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Preventing sexually transmitted infections. 2013; 32(4):19–27. www.nyc.gov/html/doh/html/data/chi32-4_screening.html. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Herbst JH, Jacobs ED, Finlayson TJ, McKleroy VS, Neumann MS, Crepaz N. Estimating HIV prevalence and risk behaviors of transgender persons in the United States: a systematic review. AIDS Behav 2008; 12:1–17.
- Hembree WC, Cohen-Kettenis P, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, et al. Endocrine treatment of transsexual persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94:3132–3133.
- Peitzmeier SM, Reisner SL, Harigopal P, Potter J. Female-to-male patients may have high prevalence of unsatisfactory paps compared to non-transgender females: implications for cervical cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med 2014; 29:778–784.
- UCSF Center of Excellence for Transgender Health. Primary care protocol for transgender patient care. http://transhealth.ucsf.edu/protocols. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended adult immunization schedule United States—2015. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-combined-schedule.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Calzo JP, Roberts AL, Corliss HL, Blood EA, Kroshus E, Austin SB. Physical activity disparities in heterosexual and sexual minority youth ages 12–22 years old: roles of childhood gender nonconformity and athletic self-esteem. Ann Behav Med 2014; 47:17–27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim guidance for clinicians considering the use of preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in heterosexually active adults. MMWR 2012; 61:586–589.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophlyaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2014. A clinical practice guideline. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Feldman JL, Goldberg J. Transgender primary medical care: suggested guidelines for clinicians in British Columbia. www.cwhn.ca/en/node/27567. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Coleman E, Bockting W, Botzer M, et al. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender-noncomforming people, version 7. Int J Transgenderism 2011; 13:165–232.
- Wierckx K, Mueller S, Weyers S, et al. Long-term evaluation of cross-sex hormone treatment in transsexual persons. J Sex Med 2012; 9: 2641–2651.
- Asscheman H, T’Sjoen G, Lemaire A, et al. Venous thrombo-embolism as a complication of cross-sex hormone treatment of male-to-female transsexual subjects: a review. Andrologia 2014; 46:791–795.
- Weinand JD, Safer JD. Hormone therapy in transgender adults is safe with provider supervision. A review of hormone therapy sequelae for transgender individuals. J Clin Transl Endocrinol 2015; 2:55–60.
- Unger CA. Care of the transgender patient: the role of the gynecologist. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014; 210:16–26.
- Tjaden P, Thoennes N. Extent, nature, and consequences of intimate partner violence: findings from the National Violence Against Women Survey. Washington, DC: US Department of Justice, National Institute of Justice; 2000. P. 29–31. Report No.: NCJ 181867.
- Stephenson R, Khosropour C, Sullivan P. Reporting of intimate partner violence among men who have sex with men in an online survey. West J Emerg Med 2010; 11:242–246.
- Chen PH, Jacobs A, Rovi SL. Intimate partner violence: IPV in the LGBT community. FP Essent 2013; 412:28–35.
- Siemieniuk R, Miller P, Woodman K, et al. Prevalence, clinical associations, and impact of intimate partner violence among HIV infected gay and bisexual men: a population based study. HIV Med 2013; 14:293–302.
- Rabin RF, Jennings JM, Campbell JC, Bair-Merritt MH. Intimate partner violence screening tools: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2009; 36:439–445.
- Ford CL, Slavin T, Hilton KL, Holt SL. Intimate partner violence prevention services and resources in Los Angeles: issues, needs, and challenges for assisting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender clients. Health Promot Pract 2013; 14:841–849.
- World Professional Association for Transgender Health. www.wpath.org/site_page.cfm?pk_association_webpage_menu=1351. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Gates GJ. How many people are lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender? Williams Institute. 2011. http://williamsinstitute.law.ucla.edu/wp-content/uploads/Gates-How-Many-People-LGBT-Apr-2011.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Ward BW, Dahlhamer JM, Galinsky AM, Joesti SS. Sexual orientation and health among U.S. Adults: National Health Interview Survey, 2013. Natl Health Stat Report 2014; 77:1–10.
- Cochran SD, Bandiera FC, Mays VM. Sexual orientation-related differences in tobacco use and secondhand smoke exposure among US adults aged 20-59 years: 2003–2010 National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys. Am J Publ Health 2013; 103:1837–1844.
- Mayer KH. Sexually transmitted diseases in men who have sex with men. Clin Infect Disease 2011; 53:S79–S83.
- Grant JM, Mottet LA, Tanis J, Herman JL, Harrison J, Keisling M. National transgender discrimination survey report on health and health care. www.thetaskforce.org/static_html/downloads/reports/reports/ntds_report_on_health.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Pathela P, Hajat A, Schillinger J, Blank S, Sell R, Mostashari F. Discordance between sexual behavior and self-reported sexual identity: a population-based survey of New York City men. Ann Intern Med 2006; 145:416–425.
- Chandra A, Mosher WD, Copen C, Sionean C. Sexual behavior, sexual attraction, and sexual identity in the United States: data from the 2006–2009 National Survey of Family Growth. Natl Health Stat Report 2011; 36:1–36.
- Agenor M, Peitzmeier S, Gordon AR, Haneuse S, Potter JE, Austin SB. Sexual orientation identity disparities in awareness and initiation of the human papillomavirus vaccine among U.S. women and girls: a national survey. Ann Intern Med 2015; 163:99–106.
- Ard KL, Makadon HJ. Improving the health care of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) people: understanding and eliminating health disparities. www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/12-054_LGBTHealtharticle_v3_07-09-12.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Spack NP. Management of transgenderism. JAMA 2013; 309:474–484.
- National LGBT Health Education Center. Achieving health equity for lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people, Module 1. www.lgbthealtheducation.org/wp-content/uploads/Achieving-Health-Equity-for-LGBT-People-1.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Buchmueller T, Carpenter CS. Disparities in health Insurance coverage, access, and outcomes for individuals in same-sex versus different-sex relationships, 2000–2007. Am J Public Health 2010; 100:489–496.
- Kosenko K, Rintamaki L, Raney S, Maness K. Transgender patient perceptions of stigma in health care contexts. Med Care 2013; 51:819–822.
- King M, Semlyen J, Tai SS, et al. A systematic review of mental disorder, suicide, and deliberate self-harm in lesbian, gay, and bisexual people. BMC Psychiatry 2008; 8:70.
- Bostwick WB, Boyd CJ, Hughes TL, McCabe SE. Dimensions of sexual orientation and the prevalence of mood and anxiety disorders in the United States. Am J Public Health 2010; 100:468–475.
- Blosnich JR, Brown GR, Shipherd JC, Kauth M, Piegari RI, Bossarte RM. Prevalence of gender identity disorder and suicide risk among transgender veterans utilizing Veterans Health Administration care. Am J Public Health 2013: 103:e27–e32.
- Maurer DM. Screening for depression. Am Fam Physician 2012; 85:139–144.
- Mays VM, Cochran SD. Mental health correlates of perceived discrimination among lesbian, gay, and bisexual adults in the United States. Am J Pub Health 2001; 91:1869–1875.
- McCabe SE, West BT, Hughes TL, Boyd CJ. Sexual orientation and substance abuse treatment utilization in the United States: results from a national survey. J Subst Abuse Treat 2013; 44:4–12.
- Santos GM, Rapues J, Wilson EC, et al. Alcohol and substance use among transgender women in San Francisco: prevalence and association with human immunodeficiency virus infection. Drug Alcohol Rev 2014; 33:287–295.
- National LGBT Tobacco Control Network. www.lgbttobacco.org. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Massad LS, Xie X, Minkoff H, et al. Abnormal Pap tests and human papillomavirus infections among HIV infected and uninfected women who have sex with women. J Low Genit Tract Dis 2014; 18:50–56.
- Gorgos LM, Marrazzo JM. Sexually transmitted infections among women who have sex with women. Clin Infect Dis 2011; 53:S84–S91.
- Workowski KA, Bolan GA. Sexually transmitted diseases treatment guidelines, 2015. MMWR 2015; 64(3):1–138.
- Boehmer U, Bowen DJ, Bauer GR. Overweight and obesity in sexual-minority women: evidence from population-based data. Am J Public Health 2007; 97:1134–1140.
- Smyczek P, Singh AE, Romanowski B. Anal intraepithelial neoplasia: review and recommendations for screening and management. Int J STD AIDS 2013; 24:843–851.
- New York City Department of Health and Mental Hygiene. Preventing sexually transmitted infections. 2013; 32(4):19–27. www.nyc.gov/html/doh/html/data/chi32-4_screening.html. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Herbst JH, Jacobs ED, Finlayson TJ, McKleroy VS, Neumann MS, Crepaz N. Estimating HIV prevalence and risk behaviors of transgender persons in the United States: a systematic review. AIDS Behav 2008; 12:1–17.
- Hembree WC, Cohen-Kettenis P, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, et al. Endocrine treatment of transsexual persons: an Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2009; 94:3132–3133.
- Peitzmeier SM, Reisner SL, Harigopal P, Potter J. Female-to-male patients may have high prevalence of unsatisfactory paps compared to non-transgender females: implications for cervical cancer screening. J Gen Intern Med 2014; 29:778–784.
- UCSF Center of Excellence for Transgender Health. Primary care protocol for transgender patient care. http://transhealth.ucsf.edu/protocols. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Recommended adult immunization schedule United States—2015. www.cdc.gov/vaccines/schedules/downloads/adult/adult-combined-schedule.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Calzo JP, Roberts AL, Corliss HL, Blood EA, Kroshus E, Austin SB. Physical activity disparities in heterosexual and sexual minority youth ages 12–22 years old: roles of childhood gender nonconformity and athletic self-esteem. Ann Behav Med 2014; 47:17–27.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Interim guidance for clinicians considering the use of preexposure prophylaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in heterosexually active adults. MMWR 2012; 61:586–589.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and US Public Health Service. Preexposure prophlyaxis for the prevention of HIV infection in the United States—2014. A clinical practice guideline. www.cdc.gov/hiv/pdf/PrEPguidelines2014.pdf. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Feldman JL, Goldberg J. Transgender primary medical care: suggested guidelines for clinicians in British Columbia. www.cwhn.ca/en/node/27567. Accessed May 19, 2016.
- Coleman E, Bockting W, Botzer M, et al. Standards of care for the health of transsexual, transgender, and gender-noncomforming people, version 7. Int J Transgenderism 2011; 13:165–232.
- Wierckx K, Mueller S, Weyers S, et al. Long-term evaluation of cross-sex hormone treatment in transsexual persons. J Sex Med 2012; 9: 2641–2651.
- Asscheman H, T’Sjoen G, Lemaire A, et al. Venous thrombo-embolism as a complication of cross-sex hormone treatment of male-to-female transsexual subjects: a review. Andrologia 2014; 46:791–795.
- Weinand JD, Safer JD. Hormone therapy in transgender adults is safe with provider supervision. A review of hormone therapy sequelae for transgender individuals. J Clin Transl Endocrinol 2015; 2:55–60.
- Unger CA. Care of the transgender patient: the role of the gynecologist. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2014; 210:16–26.
- Tjaden P, Thoennes N. Extent, nature, and consequences of intimate partner violence: findings from the National Violence Against Women Survey. Washington, DC: US Department of Justice, National Institute of Justice; 2000. P. 29–31. Report No.: NCJ 181867.
- Stephenson R, Khosropour C, Sullivan P. Reporting of intimate partner violence among men who have sex with men in an online survey. West J Emerg Med 2010; 11:242–246.
- Chen PH, Jacobs A, Rovi SL. Intimate partner violence: IPV in the LGBT community. FP Essent 2013; 412:28–35.
- Siemieniuk R, Miller P, Woodman K, et al. Prevalence, clinical associations, and impact of intimate partner violence among HIV infected gay and bisexual men: a population based study. HIV Med 2013; 14:293–302.
- Rabin RF, Jennings JM, Campbell JC, Bair-Merritt MH. Intimate partner violence screening tools: a systematic review. Am J Prev Med 2009; 36:439–445.
- Ford CL, Slavin T, Hilton KL, Holt SL. Intimate partner violence prevention services and resources in Los Angeles: issues, needs, and challenges for assisting lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender clients. Health Promot Pract 2013; 14:841–849.
- World Professional Association for Transgender Health. www.wpath.org/site_page.cfm?pk_association_webpage_menu=1351. Accessed May 19, 2016.
KEY POINTS
- Lesbian and bisexual women are at increased risk for overweight, obesity, tobacco use, and drug and alcohol use disorders. Clinicians should screen for these conditions regularly and provide appropriate referral.
- Annual screening for HIV, syphilis, Chlamydia, and gonorrhea should be offered to men who have sex with men.
- Pre-exposure prophylaxis against HIV infection may be appropriate for some at-risk individuals who can adhere to daily therapy.
- “Screen what you have” is a rule that can help physicians to consider the appropriate screening services for transgender individuals.
- Hormone therapy (estrogen and testosterone) can benefit transgender individuals who are changing their physical appearance to their affirmed gender.
Contraception for the perimenopausal woman: What’s best?
› Consider long-acting reversible contraception, such as an intrauterine device or an implant, as a first-line option for women who have mild or no symptoms of perimenopause. A
› Unless contraindicated, prescribe combination hormonal contraceptives for women in their 40s who desire them, as they are generally safe and effective in treating perimenopausal symptoms. A
› Use the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s evidence-based recommendations to guide your choice of contraceptive for perimenopausal patients based on individual medical history. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
It is no secret that about half of all pregnancies in the United States are unintended, and that teens have the highest rate of unplanned pregnancy. What’s not so well known is that women in their 40s have the second highest rate.1
Optimal use of contraception throughout perimenopause is crucial, but finding the right method of birth control for this patient population can be a bit of a balancing act. Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), such as an intrauterine device or progestin-only implant, are preferred first-line contraceptive options when preventing pregnancy is the primary goal, given their increased efficacy and limited number of contraindications.2,3 However, women experiencing perimenopausal symptoms often need a combination hormonal contraceptive (CHC)—typically an estrogen-containing pill, a patch, or a vaginal ring—for relief of vasomotor symptoms and cycle control.
Women in their 40s should have access to a full array of options to help improve adherence. However, physicians may be reluctant to prescribe estrogen-containing products for patients who often have a more complex medical history than their younger counterparts, including increased risks for breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and venous thromboembolism (VTE).
With this in mind, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified medical conditions that may affect the use of the various types of contraceptives by perimenopausal women and issued evidence-based recommendations on the appropriateness of each method using a one-to-4 rating system (TABLE 1).2 To help you address the contraceptive needs of such patients, we review the key risk factors, CDC guidelines, and optimal choices in the 4 case studies that follow.
CASE 1 › Sara G: VTE risk
Sara G, a healthy 45-year-old, recently started dating again following her divorce. She wants to avoid pregnancy. She has no personal or family history of clotting disorders and does not smoke. However, she is obese (body mass index [BMI]=32 kg/m2), and her job as a visiting nurse requires her to spend most of the day in her car. Ms. G also has acne and wants an estrogen-containing contraceptive to help treat it.
If Ms. G were your patient, what would you offer her?
The risk for VTE increases substantially for women older than 40 years. In a recent cohort study, those ages 45 to 49 faced approximately twice the risk of women ages 25 to 29. However, the absolute risk for the older women was still low (4.7-5.3 per 10,000 woman-years).4 What’s more, the risk of VTE from the use of a CHC is substantially less than the risk associated with pregnancy and the postpartum period (TABLE 2).5
Obesity increases the risk. Women like Ms. G who are obese (BMI >30) have an increased risk for VTE associated with CHCs, but the CDC rates them as a Category 2 risk, even for obese women in their 40s—a determination that the advantages outweigh the risks.2
Progestin choice and estrogen dose matter. Combination oral contraceptives (COCs) that contain certain third-generation progestins (gestodene and desogestrel) may be more thrombophilic than those containing first- or second-generation progestins (TABLE 3).6 The relative risk (RR) for VTE with third-generation vs second-generation progestins is 1.3 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-1.8).7 Formulations containing higher doses of estrogen are also more likely to be associated with VTE.7
Drospirenone is a newer progestin. Found in several COCs, drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid properties that help to minimize bloating and fluid retention but may also lead to a hypercoagulable state.5 Numerous studies have investigated the association between drospirenone and VTE risk, with conflicting results.8 Most recently, a large international prospective observational study involving more than 85,000 women showed no increased risk for VTE among women taking COCs with drospirenone compared with pills that do not contain this progestin.9
Non-oral CHCs, including the vaginal ring and the patch, offer the convenience of weekly or monthly use while providing similar benefits to COCs. Some fear that the continuous exposure to hormones associated with these methods may increase the risk for VTE, but evidence is mixed.
A large (N=1.6 million) Danish registry study published in 2012 demonstrated a 2-fold increased risk of VTE among vaginal ring users vs women taking COCs.4 But a multinational prospective cohort study of more than 33,000 women found no increased VTE risk in ring users,10 and a recent US database study involving more than 800,000 women reported nonsignificant VTE risk estimates for both the ring (RR=1.09; 95% CI, 0.55-2.16) and the patch (RR=1.35; 95% CI, 0.90-2.02) compared with COCs.11
THE BOTTOM LINE For Ms. G, the benefits of contraception likely outweigh any small increase in her absolute risk for VTE. To minimize her risk, however, select a pill that contains a low dose (20-35 mcg) of ethinyl estradiol (EE) combined with a progestin that has not been associated with an increased VTE risk. Because of their mechanism of action, most COCs will improve acne, regardless of the progestin in the formulation.12-14
CASE 2 › Stephanie T: CV risk
Stephanie T, 47, is in need of contraception and treatment for severe hot flashes. She has no significant past medical history, but she is obese (BMI =36), her blood pressure (BP) is 130/80 mm Hg, and her most recent labs reveal a fasting glucose of 115 and a hemoglobin A1c of 6.1%. Ms. T is concerned about arterial thromboembolic disease because of her family history: Her father had a myocardial infarction (MI) at age 56 and a maternal aunt had a stroke when she was 65.
What evidence should you consider?
Baseline arterial thromboembolic events are considerably more rare in premenopausal women than VTEs (13.2 MIs vs 24.2 thrombotic strokes per 100,000 woman-years).15 Thus, a small increased RR from a CHC is unlikely to have a significant clinical impact.
A systemic review and meta-analysis of studies between 1995 and 2012 showed that the odds ratio (OR) of ischemic stroke in users of COCs vs nonusers was 1.9 (95% CI, 1.24–2.91).16 This study included very few estrogen formulations with <35 mcg EE, however; even so, no increased risk of MI was found (OR=1.34; 95% CI, 0.87–2.08).16 A 15-year retrospective cohort study of 1.6 million Danish women showed that lowering the dose of EE to 20 mcg (from 30-40 mcg) significantly reduced the risk of arterial events.15 It is unclear whether the vaginal ring is associated with an increased RR of stroke compared with COCs because studies have had mixed results.10,15 There is no compelling evidence to suggest a difference in the risk of arterial events based on the type of progestin used in the COC.15
Hypertension is a key consideration. It is important to remember that perimenopausal women may have comorbid conditions that increase their risk of arterial thromboembolic events. CHCs should be used with caution in women with hypertension, even if BP is adequately controlled—a Category 3 recommendation from the CDC. In such patients, LARC or a progestin-only pill is preferred unless there is a compelling reason to use a CHC, such as acne, vasomotor symptoms, or hirsutism.2
CHCs are contraindicated for women with a BP ≥160/100 mm Hg and/or any manifestation of vascular disease (Category 4).2 Although progestin-only methods are often preferred for women with established vascular disease, depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) is an exception (Category 3).2 DMPA is not a first-line choice for such patients because of its potential to cause weight gain and worsening lipids, glucose, and insulin metabolism. Women with hypertriglyceridemia should have follow-up testing of lipid levels after initiation of hormonal contraception, especially if it contains estrogen.
Diabetes is not an absolute contraindication. Many women with diabetes can safely use CHCs (Category 2). The exceptions: those who have vascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, or neuropathy (Category 4) or have had diabetes for >20 years and therefore have the potential for undiagnosed vascular disease.2 Generally, the use of insulin should not affect decisions regarding CHCs, and patients can be reassured that the hormones will not worsen their diabetes control.
When caring for women who have multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease, it is important to exercise clinical judgment regarding the appropriateness of CHCs (Categories 3 and 4). Progestin-only methods have a more favorable risk profile for women at the highest risk and may provide ample relief of perimenopausal symptoms.2
THE BOTTOM LINE Ms. T may benefit from a CHC due to her severe hot flashes. She should be encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, to decrease her risk of arterial thromboembolism and VTE, but she has no contraindications to the use of a CHC at this time.
CASE 3 › Leslie C: Bone health
Leslie C, age 45, is happy with the contraceptive he has used for the past 3 years—DMPA injections every 3 months. She has no perimenopausal symptoms. However, her mother had an osteoporotic hip fracture at age 70 and Ms. C is concerned about the long-term use of DMPA.
Should Ms. C be worried?
Because of DMPA’s association with bone loss, the US Food and Drug Administration issued a black box warning in 2004 recommending that this method be used for more than 2 years only by women for whom other birth control methods are deemed inappropriate.17
The bone loss may be reversed. Evidence suggests that the bone loss is reversible, however, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has stated that a potential fracture risk need not limit a woman’s use of DMPA to 2 years.18 A retrospective cohort review of 312,295 women in the United Kingdom did not find evidence of an increased risk of fracture with long-term use of DMPA.19 It is important to note, however, that because of declining estrogen levels, perimenopausal women have fewer years than their younger counterparts to recover bone density upon discontinuation of DMPA.20,21
THE BOTTOM LINE Because Ms. C has no perimenopausal symptoms, she may do well with LARC, which—like DMPA —would free her of the need to remember to take, apply, or insert a contraceptive regularly. It may help to point out that LARCs provide superior contraceptive efficacy compared with DMPA injections (99% vs 94%).3 Nonetheless, she and other women in their 40s who need ongoing contraception should not be discouraged from using DMPA if that is their preference.
CASE 4 › Alissa B: Breast cancer risk
Alissa B, 49, has polycystic ovaries and wonders if it is safe for her to continue her COC. She has been happy with the treatment for years because it gives her relief from hot flashes and regulates her cycles. Her 46-year-old sister was recently diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, however, and Ms. B is afraid that the hormones she takes put her at increased risk.
Should you recommend another method?
Breast cancer is an important concern for many women as they age. Although Ms. B’s family history increases her risk for developing breast cancer, a systematic review indicates that COCs do not add to this risk.22
Weak association between family history and OC use. The review included 10 observational studies and one meta-analysis that investigated the association between COC use and breast cancer in women with a family history of the disease. Only 2 fair-quality studies showed an association, one of which included women who had begun taking the pill before 1975, when formulations typically contained higher doses of estrogen than present-day preparations.22
Data from a recently published meta-analysis also indicate that there is no increased risk for breast cancer from COCs among women with BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutations. The summary RR for breast cancer in such patients was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.88-1.45), but OC users had a lower risk for ovarian cancer (summary RR=0.50; 95% CI, 0.33-0.75).23 Additionally, investigators found no association between specific currently used COC formulations and breast cancer.24
THE BOTTOM LINE Based on an independent review of the evidence, the CDC has given a family history of breast cancer a Category 1 rating. Thus, Ms. B can be reassured that she may safely continue taking her COC, which is unlikely to increase her breast cancer risk.
CORRESPONDENCE
Pelin Batur, MD, NCMP, CCD, Cleveland Clinic Independence Family Health Center, 5001 Rockside Road, IN30, Cleveland, OH 44131; [email protected].
1. Finer LB, Zolna MR. Unintended pregnancy in the United States: incidence and disparities, 2006. Contraception. 2011;84:478-485.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59:1-86.
3. Division of Reproductive Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2013: adapted from the World Health Organization selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2nd edition. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013;62:1-60.
4. Lidegaard O, Nielsen LH, Skovlund CW, et al. Venous thrombosis in users of non-oral hormonal contraception: follow-up study, Denmark 2001-10. BMJ. 2012;344:e2990.
5. Committee on gynecologic practice. ACOG committee opinion number 540: Risk of venous thromboembolism among users of drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
6. McNamara M, Batur P, DeSapri KT. In the clinic. Perimenopause. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:ITC1-15.
7. de Bastos M, Stegeman BH, Rosendaal FR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives: venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;3:CD010813.
8. Wu CQ, Grandi SM, Filion KB, et al. Drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills and the risk of venous and arterial thrombosis: a systematic review. BJOG. 2013;120:801-810.
9. Dinger J, Bardenheuer K, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular and general safety of a 24-day regimen of drospirenone-containing combined oral contraceptives: final results from the international active surveillance study of women taking oral contraceptives. Contraception. 2014;89:253-263.
10. Dinger J, Möhner S, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular risk associated with the use of an etonogestrel-containing vaginal ring. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:800-808.
11. Sidney S, Cheetham TC, Connell FA, et al. Recent combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) and the risk of thromboembolism and other cardiovascular events in new users. Contraception. 2013;87:93-100.
12. Arowojolu AO, Gallo MF, Lopez LM, et al. Combined oral contraceptive pills for treatment of acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;6:CD004425.
13. Koulianos GT. Treatment of acne with oral contraceptives: criteria for pill selection. Cutis. 2000;66:281-286.
14. Thorneycroft IH. Update on androgenicity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:288-294.
15. Lidegaard Ø, Løkkegaard E, Jensen A, et al. Thrombotic stroke and myocardial infarction with hormonal contraception. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2257-2266.
16. Peragallo Urrutia R, Coeytaux RR, McBroom AJ, et al. Risk of acute thromboembolic events with oral contraceptive use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:380-389.
17. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety: Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension). U.S. Food and Drug Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm154784.htm. Accessed April 20, 2015.
18. Committee Opinion No. 602: Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate and bone effects. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:1398-1402.
19. Lanza LL, McQuay LJ, Rothman KJ, et al. Use of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate contraception and incidence of bone fracture. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121:593-600.
20. Ettinger B, Pressman A, Sklarin P, et al. Associations between low levels of serum estradiol, bone density, and fractures among elderly women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:2239-2243.
21. Reginster JY, Sarlet N, Deroisy R, et al. Minimal levels of serum estradiol prevent postmenopausal bone loss. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992;51:340-343.
22. Gaffield ME, Culwell KR, Ravi A. Oral contraceptives and family history of breast cancer. Contraception. 2009;80:372-380.
23. Iodice S, Barile M, Rotmensz N, et al. Oral contraceptive use and breast or ovarian cancer risk in BRCA1/2 carriers: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:2275-2284.
24. Marchbanks PA, Curtis KM, Mandel MG, et al. Oral contraceptive formulation and risk of breast cancer. Contraception. 2012;85:342-350.
› Consider long-acting reversible contraception, such as an intrauterine device or an implant, as a first-line option for women who have mild or no symptoms of perimenopause. A
› Unless contraindicated, prescribe combination hormonal contraceptives for women in their 40s who desire them, as they are generally safe and effective in treating perimenopausal symptoms. A
› Use the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s evidence-based recommendations to guide your choice of contraceptive for perimenopausal patients based on individual medical history. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
It is no secret that about half of all pregnancies in the United States are unintended, and that teens have the highest rate of unplanned pregnancy. What’s not so well known is that women in their 40s have the second highest rate.1
Optimal use of contraception throughout perimenopause is crucial, but finding the right method of birth control for this patient population can be a bit of a balancing act. Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), such as an intrauterine device or progestin-only implant, are preferred first-line contraceptive options when preventing pregnancy is the primary goal, given their increased efficacy and limited number of contraindications.2,3 However, women experiencing perimenopausal symptoms often need a combination hormonal contraceptive (CHC)—typically an estrogen-containing pill, a patch, or a vaginal ring—for relief of vasomotor symptoms and cycle control.
Women in their 40s should have access to a full array of options to help improve adherence. However, physicians may be reluctant to prescribe estrogen-containing products for patients who often have a more complex medical history than their younger counterparts, including increased risks for breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and venous thromboembolism (VTE).
With this in mind, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified medical conditions that may affect the use of the various types of contraceptives by perimenopausal women and issued evidence-based recommendations on the appropriateness of each method using a one-to-4 rating system (TABLE 1).2 To help you address the contraceptive needs of such patients, we review the key risk factors, CDC guidelines, and optimal choices in the 4 case studies that follow.
CASE 1 › Sara G: VTE risk
Sara G, a healthy 45-year-old, recently started dating again following her divorce. She wants to avoid pregnancy. She has no personal or family history of clotting disorders and does not smoke. However, she is obese (body mass index [BMI]=32 kg/m2), and her job as a visiting nurse requires her to spend most of the day in her car. Ms. G also has acne and wants an estrogen-containing contraceptive to help treat it.
If Ms. G were your patient, what would you offer her?
The risk for VTE increases substantially for women older than 40 years. In a recent cohort study, those ages 45 to 49 faced approximately twice the risk of women ages 25 to 29. However, the absolute risk for the older women was still low (4.7-5.3 per 10,000 woman-years).4 What’s more, the risk of VTE from the use of a CHC is substantially less than the risk associated with pregnancy and the postpartum period (TABLE 2).5
Obesity increases the risk. Women like Ms. G who are obese (BMI >30) have an increased risk for VTE associated with CHCs, but the CDC rates them as a Category 2 risk, even for obese women in their 40s—a determination that the advantages outweigh the risks.2
Progestin choice and estrogen dose matter. Combination oral contraceptives (COCs) that contain certain third-generation progestins (gestodene and desogestrel) may be more thrombophilic than those containing first- or second-generation progestins (TABLE 3).6 The relative risk (RR) for VTE with third-generation vs second-generation progestins is 1.3 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-1.8).7 Formulations containing higher doses of estrogen are also more likely to be associated with VTE.7
Drospirenone is a newer progestin. Found in several COCs, drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid properties that help to minimize bloating and fluid retention but may also lead to a hypercoagulable state.5 Numerous studies have investigated the association between drospirenone and VTE risk, with conflicting results.8 Most recently, a large international prospective observational study involving more than 85,000 women showed no increased risk for VTE among women taking COCs with drospirenone compared with pills that do not contain this progestin.9
Non-oral CHCs, including the vaginal ring and the patch, offer the convenience of weekly or monthly use while providing similar benefits to COCs. Some fear that the continuous exposure to hormones associated with these methods may increase the risk for VTE, but evidence is mixed.
A large (N=1.6 million) Danish registry study published in 2012 demonstrated a 2-fold increased risk of VTE among vaginal ring users vs women taking COCs.4 But a multinational prospective cohort study of more than 33,000 women found no increased VTE risk in ring users,10 and a recent US database study involving more than 800,000 women reported nonsignificant VTE risk estimates for both the ring (RR=1.09; 95% CI, 0.55-2.16) and the patch (RR=1.35; 95% CI, 0.90-2.02) compared with COCs.11
THE BOTTOM LINE For Ms. G, the benefits of contraception likely outweigh any small increase in her absolute risk for VTE. To minimize her risk, however, select a pill that contains a low dose (20-35 mcg) of ethinyl estradiol (EE) combined with a progestin that has not been associated with an increased VTE risk. Because of their mechanism of action, most COCs will improve acne, regardless of the progestin in the formulation.12-14
CASE 2 › Stephanie T: CV risk
Stephanie T, 47, is in need of contraception and treatment for severe hot flashes. She has no significant past medical history, but she is obese (BMI =36), her blood pressure (BP) is 130/80 mm Hg, and her most recent labs reveal a fasting glucose of 115 and a hemoglobin A1c of 6.1%. Ms. T is concerned about arterial thromboembolic disease because of her family history: Her father had a myocardial infarction (MI) at age 56 and a maternal aunt had a stroke when she was 65.
What evidence should you consider?
Baseline arterial thromboembolic events are considerably more rare in premenopausal women than VTEs (13.2 MIs vs 24.2 thrombotic strokes per 100,000 woman-years).15 Thus, a small increased RR from a CHC is unlikely to have a significant clinical impact.
A systemic review and meta-analysis of studies between 1995 and 2012 showed that the odds ratio (OR) of ischemic stroke in users of COCs vs nonusers was 1.9 (95% CI, 1.24–2.91).16 This study included very few estrogen formulations with <35 mcg EE, however; even so, no increased risk of MI was found (OR=1.34; 95% CI, 0.87–2.08).16 A 15-year retrospective cohort study of 1.6 million Danish women showed that lowering the dose of EE to 20 mcg (from 30-40 mcg) significantly reduced the risk of arterial events.15 It is unclear whether the vaginal ring is associated with an increased RR of stroke compared with COCs because studies have had mixed results.10,15 There is no compelling evidence to suggest a difference in the risk of arterial events based on the type of progestin used in the COC.15
Hypertension is a key consideration. It is important to remember that perimenopausal women may have comorbid conditions that increase their risk of arterial thromboembolic events. CHCs should be used with caution in women with hypertension, even if BP is adequately controlled—a Category 3 recommendation from the CDC. In such patients, LARC or a progestin-only pill is preferred unless there is a compelling reason to use a CHC, such as acne, vasomotor symptoms, or hirsutism.2
CHCs are contraindicated for women with a BP ≥160/100 mm Hg and/or any manifestation of vascular disease (Category 4).2 Although progestin-only methods are often preferred for women with established vascular disease, depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) is an exception (Category 3).2 DMPA is not a first-line choice for such patients because of its potential to cause weight gain and worsening lipids, glucose, and insulin metabolism. Women with hypertriglyceridemia should have follow-up testing of lipid levels after initiation of hormonal contraception, especially if it contains estrogen.
Diabetes is not an absolute contraindication. Many women with diabetes can safely use CHCs (Category 2). The exceptions: those who have vascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, or neuropathy (Category 4) or have had diabetes for >20 years and therefore have the potential for undiagnosed vascular disease.2 Generally, the use of insulin should not affect decisions regarding CHCs, and patients can be reassured that the hormones will not worsen their diabetes control.
When caring for women who have multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease, it is important to exercise clinical judgment regarding the appropriateness of CHCs (Categories 3 and 4). Progestin-only methods have a more favorable risk profile for women at the highest risk and may provide ample relief of perimenopausal symptoms.2
THE BOTTOM LINE Ms. T may benefit from a CHC due to her severe hot flashes. She should be encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, to decrease her risk of arterial thromboembolism and VTE, but she has no contraindications to the use of a CHC at this time.
CASE 3 › Leslie C: Bone health
Leslie C, age 45, is happy with the contraceptive he has used for the past 3 years—DMPA injections every 3 months. She has no perimenopausal symptoms. However, her mother had an osteoporotic hip fracture at age 70 and Ms. C is concerned about the long-term use of DMPA.
Should Ms. C be worried?
Because of DMPA’s association with bone loss, the US Food and Drug Administration issued a black box warning in 2004 recommending that this method be used for more than 2 years only by women for whom other birth control methods are deemed inappropriate.17
The bone loss may be reversed. Evidence suggests that the bone loss is reversible, however, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has stated that a potential fracture risk need not limit a woman’s use of DMPA to 2 years.18 A retrospective cohort review of 312,295 women in the United Kingdom did not find evidence of an increased risk of fracture with long-term use of DMPA.19 It is important to note, however, that because of declining estrogen levels, perimenopausal women have fewer years than their younger counterparts to recover bone density upon discontinuation of DMPA.20,21
THE BOTTOM LINE Because Ms. C has no perimenopausal symptoms, she may do well with LARC, which—like DMPA —would free her of the need to remember to take, apply, or insert a contraceptive regularly. It may help to point out that LARCs provide superior contraceptive efficacy compared with DMPA injections (99% vs 94%).3 Nonetheless, she and other women in their 40s who need ongoing contraception should not be discouraged from using DMPA if that is their preference.
CASE 4 › Alissa B: Breast cancer risk
Alissa B, 49, has polycystic ovaries and wonders if it is safe for her to continue her COC. She has been happy with the treatment for years because it gives her relief from hot flashes and regulates her cycles. Her 46-year-old sister was recently diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, however, and Ms. B is afraid that the hormones she takes put her at increased risk.
Should you recommend another method?
Breast cancer is an important concern for many women as they age. Although Ms. B’s family history increases her risk for developing breast cancer, a systematic review indicates that COCs do not add to this risk.22
Weak association between family history and OC use. The review included 10 observational studies and one meta-analysis that investigated the association between COC use and breast cancer in women with a family history of the disease. Only 2 fair-quality studies showed an association, one of which included women who had begun taking the pill before 1975, when formulations typically contained higher doses of estrogen than present-day preparations.22
Data from a recently published meta-analysis also indicate that there is no increased risk for breast cancer from COCs among women with BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutations. The summary RR for breast cancer in such patients was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.88-1.45), but OC users had a lower risk for ovarian cancer (summary RR=0.50; 95% CI, 0.33-0.75).23 Additionally, investigators found no association between specific currently used COC formulations and breast cancer.24
THE BOTTOM LINE Based on an independent review of the evidence, the CDC has given a family history of breast cancer a Category 1 rating. Thus, Ms. B can be reassured that she may safely continue taking her COC, which is unlikely to increase her breast cancer risk.
CORRESPONDENCE
Pelin Batur, MD, NCMP, CCD, Cleveland Clinic Independence Family Health Center, 5001 Rockside Road, IN30, Cleveland, OH 44131; [email protected].
› Consider long-acting reversible contraception, such as an intrauterine device or an implant, as a first-line option for women who have mild or no symptoms of perimenopause. A
› Unless contraindicated, prescribe combination hormonal contraceptives for women in their 40s who desire them, as they are generally safe and effective in treating perimenopausal symptoms. A
› Use the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s evidence-based recommendations to guide your choice of contraceptive for perimenopausal patients based on individual medical history. A
Strength of recommendation (SOR)
A Good-quality patient-oriented evidence
B Inconsistent or limited-quality patient-oriented evidence
C Consensus, usual practice, opinion, disease-oriented evidence, case series
It is no secret that about half of all pregnancies in the United States are unintended, and that teens have the highest rate of unplanned pregnancy. What’s not so well known is that women in their 40s have the second highest rate.1
Optimal use of contraception throughout perimenopause is crucial, but finding the right method of birth control for this patient population can be a bit of a balancing act. Long-acting reversible contraceptives (LARCs), such as an intrauterine device or progestin-only implant, are preferred first-line contraceptive options when preventing pregnancy is the primary goal, given their increased efficacy and limited number of contraindications.2,3 However, women experiencing perimenopausal symptoms often need a combination hormonal contraceptive (CHC)—typically an estrogen-containing pill, a patch, or a vaginal ring—for relief of vasomotor symptoms and cycle control.
Women in their 40s should have access to a full array of options to help improve adherence. However, physicians may be reluctant to prescribe estrogen-containing products for patients who often have a more complex medical history than their younger counterparts, including increased risks for breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, and venous thromboembolism (VTE).
With this in mind, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has identified medical conditions that may affect the use of the various types of contraceptives by perimenopausal women and issued evidence-based recommendations on the appropriateness of each method using a one-to-4 rating system (TABLE 1).2 To help you address the contraceptive needs of such patients, we review the key risk factors, CDC guidelines, and optimal choices in the 4 case studies that follow.
CASE 1 › Sara G: VTE risk
Sara G, a healthy 45-year-old, recently started dating again following her divorce. She wants to avoid pregnancy. She has no personal or family history of clotting disorders and does not smoke. However, she is obese (body mass index [BMI]=32 kg/m2), and her job as a visiting nurse requires her to spend most of the day in her car. Ms. G also has acne and wants an estrogen-containing contraceptive to help treat it.
If Ms. G were your patient, what would you offer her?
The risk for VTE increases substantially for women older than 40 years. In a recent cohort study, those ages 45 to 49 faced approximately twice the risk of women ages 25 to 29. However, the absolute risk for the older women was still low (4.7-5.3 per 10,000 woman-years).4 What’s more, the risk of VTE from the use of a CHC is substantially less than the risk associated with pregnancy and the postpartum period (TABLE 2).5
Obesity increases the risk. Women like Ms. G who are obese (BMI >30) have an increased risk for VTE associated with CHCs, but the CDC rates them as a Category 2 risk, even for obese women in their 40s—a determination that the advantages outweigh the risks.2
Progestin choice and estrogen dose matter. Combination oral contraceptives (COCs) that contain certain third-generation progestins (gestodene and desogestrel) may be more thrombophilic than those containing first- or second-generation progestins (TABLE 3).6 The relative risk (RR) for VTE with third-generation vs second-generation progestins is 1.3 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.0-1.8).7 Formulations containing higher doses of estrogen are also more likely to be associated with VTE.7
Drospirenone is a newer progestin. Found in several COCs, drospirenone has antimineralocorticoid properties that help to minimize bloating and fluid retention but may also lead to a hypercoagulable state.5 Numerous studies have investigated the association between drospirenone and VTE risk, with conflicting results.8 Most recently, a large international prospective observational study involving more than 85,000 women showed no increased risk for VTE among women taking COCs with drospirenone compared with pills that do not contain this progestin.9
Non-oral CHCs, including the vaginal ring and the patch, offer the convenience of weekly or monthly use while providing similar benefits to COCs. Some fear that the continuous exposure to hormones associated with these methods may increase the risk for VTE, but evidence is mixed.
A large (N=1.6 million) Danish registry study published in 2012 demonstrated a 2-fold increased risk of VTE among vaginal ring users vs women taking COCs.4 But a multinational prospective cohort study of more than 33,000 women found no increased VTE risk in ring users,10 and a recent US database study involving more than 800,000 women reported nonsignificant VTE risk estimates for both the ring (RR=1.09; 95% CI, 0.55-2.16) and the patch (RR=1.35; 95% CI, 0.90-2.02) compared with COCs.11
THE BOTTOM LINE For Ms. G, the benefits of contraception likely outweigh any small increase in her absolute risk for VTE. To minimize her risk, however, select a pill that contains a low dose (20-35 mcg) of ethinyl estradiol (EE) combined with a progestin that has not been associated with an increased VTE risk. Because of their mechanism of action, most COCs will improve acne, regardless of the progestin in the formulation.12-14
CASE 2 › Stephanie T: CV risk
Stephanie T, 47, is in need of contraception and treatment for severe hot flashes. She has no significant past medical history, but she is obese (BMI =36), her blood pressure (BP) is 130/80 mm Hg, and her most recent labs reveal a fasting glucose of 115 and a hemoglobin A1c of 6.1%. Ms. T is concerned about arterial thromboembolic disease because of her family history: Her father had a myocardial infarction (MI) at age 56 and a maternal aunt had a stroke when she was 65.
What evidence should you consider?
Baseline arterial thromboembolic events are considerably more rare in premenopausal women than VTEs (13.2 MIs vs 24.2 thrombotic strokes per 100,000 woman-years).15 Thus, a small increased RR from a CHC is unlikely to have a significant clinical impact.
A systemic review and meta-analysis of studies between 1995 and 2012 showed that the odds ratio (OR) of ischemic stroke in users of COCs vs nonusers was 1.9 (95% CI, 1.24–2.91).16 This study included very few estrogen formulations with <35 mcg EE, however; even so, no increased risk of MI was found (OR=1.34; 95% CI, 0.87–2.08).16 A 15-year retrospective cohort study of 1.6 million Danish women showed that lowering the dose of EE to 20 mcg (from 30-40 mcg) significantly reduced the risk of arterial events.15 It is unclear whether the vaginal ring is associated with an increased RR of stroke compared with COCs because studies have had mixed results.10,15 There is no compelling evidence to suggest a difference in the risk of arterial events based on the type of progestin used in the COC.15
Hypertension is a key consideration. It is important to remember that perimenopausal women may have comorbid conditions that increase their risk of arterial thromboembolic events. CHCs should be used with caution in women with hypertension, even if BP is adequately controlled—a Category 3 recommendation from the CDC. In such patients, LARC or a progestin-only pill is preferred unless there is a compelling reason to use a CHC, such as acne, vasomotor symptoms, or hirsutism.2
CHCs are contraindicated for women with a BP ≥160/100 mm Hg and/or any manifestation of vascular disease (Category 4).2 Although progestin-only methods are often preferred for women with established vascular disease, depot medroxyprogesterone acetate (DMPA) is an exception (Category 3).2 DMPA is not a first-line choice for such patients because of its potential to cause weight gain and worsening lipids, glucose, and insulin metabolism. Women with hypertriglyceridemia should have follow-up testing of lipid levels after initiation of hormonal contraception, especially if it contains estrogen.
Diabetes is not an absolute contraindication. Many women with diabetes can safely use CHCs (Category 2). The exceptions: those who have vascular disease, nephropathy, retinopathy, or neuropathy (Category 4) or have had diabetes for >20 years and therefore have the potential for undiagnosed vascular disease.2 Generally, the use of insulin should not affect decisions regarding CHCs, and patients can be reassured that the hormones will not worsen their diabetes control.
When caring for women who have multiple risk factors for cardiovascular disease, it is important to exercise clinical judgment regarding the appropriateness of CHCs (Categories 3 and 4). Progestin-only methods have a more favorable risk profile for women at the highest risk and may provide ample relief of perimenopausal symptoms.2
THE BOTTOM LINE Ms. T may benefit from a CHC due to her severe hot flashes. She should be encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise, to decrease her risk of arterial thromboembolism and VTE, but she has no contraindications to the use of a CHC at this time.
CASE 3 › Leslie C: Bone health
Leslie C, age 45, is happy with the contraceptive he has used for the past 3 years—DMPA injections every 3 months. She has no perimenopausal symptoms. However, her mother had an osteoporotic hip fracture at age 70 and Ms. C is concerned about the long-term use of DMPA.
Should Ms. C be worried?
Because of DMPA’s association with bone loss, the US Food and Drug Administration issued a black box warning in 2004 recommending that this method be used for more than 2 years only by women for whom other birth control methods are deemed inappropriate.17
The bone loss may be reversed. Evidence suggests that the bone loss is reversible, however, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists has stated that a potential fracture risk need not limit a woman’s use of DMPA to 2 years.18 A retrospective cohort review of 312,295 women in the United Kingdom did not find evidence of an increased risk of fracture with long-term use of DMPA.19 It is important to note, however, that because of declining estrogen levels, perimenopausal women have fewer years than their younger counterparts to recover bone density upon discontinuation of DMPA.20,21
THE BOTTOM LINE Because Ms. C has no perimenopausal symptoms, she may do well with LARC, which—like DMPA —would free her of the need to remember to take, apply, or insert a contraceptive regularly. It may help to point out that LARCs provide superior contraceptive efficacy compared with DMPA injections (99% vs 94%).3 Nonetheless, she and other women in their 40s who need ongoing contraception should not be discouraged from using DMPA if that is their preference.
CASE 4 › Alissa B: Breast cancer risk
Alissa B, 49, has polycystic ovaries and wonders if it is safe for her to continue her COC. She has been happy with the treatment for years because it gives her relief from hot flashes and regulates her cycles. Her 46-year-old sister was recently diagnosed with invasive breast cancer, however, and Ms. B is afraid that the hormones she takes put her at increased risk.
Should you recommend another method?
Breast cancer is an important concern for many women as they age. Although Ms. B’s family history increases her risk for developing breast cancer, a systematic review indicates that COCs do not add to this risk.22
Weak association between family history and OC use. The review included 10 observational studies and one meta-analysis that investigated the association between COC use and breast cancer in women with a family history of the disease. Only 2 fair-quality studies showed an association, one of which included women who had begun taking the pill before 1975, when formulations typically contained higher doses of estrogen than present-day preparations.22
Data from a recently published meta-analysis also indicate that there is no increased risk for breast cancer from COCs among women with BRCA 1 or BRCA 2 mutations. The summary RR for breast cancer in such patients was 1.13 (95% CI, 0.88-1.45), but OC users had a lower risk for ovarian cancer (summary RR=0.50; 95% CI, 0.33-0.75).23 Additionally, investigators found no association between specific currently used COC formulations and breast cancer.24
THE BOTTOM LINE Based on an independent review of the evidence, the CDC has given a family history of breast cancer a Category 1 rating. Thus, Ms. B can be reassured that she may safely continue taking her COC, which is unlikely to increase her breast cancer risk.
CORRESPONDENCE
Pelin Batur, MD, NCMP, CCD, Cleveland Clinic Independence Family Health Center, 5001 Rockside Road, IN30, Cleveland, OH 44131; [email protected].
1. Finer LB, Zolna MR. Unintended pregnancy in the United States: incidence and disparities, 2006. Contraception. 2011;84:478-485.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59:1-86.
3. Division of Reproductive Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2013: adapted from the World Health Organization selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2nd edition. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013;62:1-60.
4. Lidegaard O, Nielsen LH, Skovlund CW, et al. Venous thrombosis in users of non-oral hormonal contraception: follow-up study, Denmark 2001-10. BMJ. 2012;344:e2990.
5. Committee on gynecologic practice. ACOG committee opinion number 540: Risk of venous thromboembolism among users of drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
6. McNamara M, Batur P, DeSapri KT. In the clinic. Perimenopause. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:ITC1-15.
7. de Bastos M, Stegeman BH, Rosendaal FR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives: venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;3:CD010813.
8. Wu CQ, Grandi SM, Filion KB, et al. Drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills and the risk of venous and arterial thrombosis: a systematic review. BJOG. 2013;120:801-810.
9. Dinger J, Bardenheuer K, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular and general safety of a 24-day regimen of drospirenone-containing combined oral contraceptives: final results from the international active surveillance study of women taking oral contraceptives. Contraception. 2014;89:253-263.
10. Dinger J, Möhner S, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular risk associated with the use of an etonogestrel-containing vaginal ring. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:800-808.
11. Sidney S, Cheetham TC, Connell FA, et al. Recent combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) and the risk of thromboembolism and other cardiovascular events in new users. Contraception. 2013;87:93-100.
12. Arowojolu AO, Gallo MF, Lopez LM, et al. Combined oral contraceptive pills for treatment of acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;6:CD004425.
13. Koulianos GT. Treatment of acne with oral contraceptives: criteria for pill selection. Cutis. 2000;66:281-286.
14. Thorneycroft IH. Update on androgenicity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:288-294.
15. Lidegaard Ø, Løkkegaard E, Jensen A, et al. Thrombotic stroke and myocardial infarction with hormonal contraception. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2257-2266.
16. Peragallo Urrutia R, Coeytaux RR, McBroom AJ, et al. Risk of acute thromboembolic events with oral contraceptive use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:380-389.
17. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety: Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension). U.S. Food and Drug Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm154784.htm. Accessed April 20, 2015.
18. Committee Opinion No. 602: Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate and bone effects. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:1398-1402.
19. Lanza LL, McQuay LJ, Rothman KJ, et al. Use of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate contraception and incidence of bone fracture. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121:593-600.
20. Ettinger B, Pressman A, Sklarin P, et al. Associations between low levels of serum estradiol, bone density, and fractures among elderly women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:2239-2243.
21. Reginster JY, Sarlet N, Deroisy R, et al. Minimal levels of serum estradiol prevent postmenopausal bone loss. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992;51:340-343.
22. Gaffield ME, Culwell KR, Ravi A. Oral contraceptives and family history of breast cancer. Contraception. 2009;80:372-380.
23. Iodice S, Barile M, Rotmensz N, et al. Oral contraceptive use and breast or ovarian cancer risk in BRCA1/2 carriers: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:2275-2284.
24. Marchbanks PA, Curtis KM, Mandel MG, et al. Oral contraceptive formulation and risk of breast cancer. Contraception. 2012;85:342-350.
1. Finer LB, Zolna MR. Unintended pregnancy in the United States: incidence and disparities, 2006. Contraception. 2011;84:478-485.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. medical eligibility criteria for contraceptive use, 2010. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2010;59:1-86.
3. Division of Reproductive Health, National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). U.S. selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2013: adapted from the World Health Organization selected practice recommendations for contraceptive use, 2nd edition. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013;62:1-60.
4. Lidegaard O, Nielsen LH, Skovlund CW, et al. Venous thrombosis in users of non-oral hormonal contraception: follow-up study, Denmark 2001-10. BMJ. 2012;344:e2990.
5. Committee on gynecologic practice. ACOG committee opinion number 540: Risk of venous thromboembolism among users of drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills. Obstet Gynecol. 2012;120:1239-1242.
6. McNamara M, Batur P, DeSapri KT. In the clinic. Perimenopause. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162:ITC1-15.
7. de Bastos M, Stegeman BH, Rosendaal FR, et al. Combined oral contraceptives: venous thrombosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;3:CD010813.
8. Wu CQ, Grandi SM, Filion KB, et al. Drospirenone-containing oral contraceptive pills and the risk of venous and arterial thrombosis: a systematic review. BJOG. 2013;120:801-810.
9. Dinger J, Bardenheuer K, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular and general safety of a 24-day regimen of drospirenone-containing combined oral contraceptives: final results from the international active surveillance study of women taking oral contraceptives. Contraception. 2014;89:253-263.
10. Dinger J, Möhner S, Heinemann K. Cardiovascular risk associated with the use of an etonogestrel-containing vaginal ring. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:800-808.
11. Sidney S, Cheetham TC, Connell FA, et al. Recent combined hormonal contraceptives (CHCs) and the risk of thromboembolism and other cardiovascular events in new users. Contraception. 2013;87:93-100.
12. Arowojolu AO, Gallo MF, Lopez LM, et al. Combined oral contraceptive pills for treatment of acne. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;6:CD004425.
13. Koulianos GT. Treatment of acne with oral contraceptives: criteria for pill selection. Cutis. 2000;66:281-286.
14. Thorneycroft IH. Update on androgenicity. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180:288-294.
15. Lidegaard Ø, Løkkegaard E, Jensen A, et al. Thrombotic stroke and myocardial infarction with hormonal contraception. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:2257-2266.
16. Peragallo Urrutia R, Coeytaux RR, McBroom AJ, et al. Risk of acute thromboembolic events with oral contraceptive use: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;122:380-389.
17. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Safety: Depo-Provera (medroxyprogesterone acetate injectable suspension). U.S. Food and Drug Administration Web site. Available at: http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm154784.htm. Accessed April 20, 2015.
18. Committee Opinion No. 602: Depot medroxyprogesterone acetate and bone effects. Obstet Gynecol. 2014;123:1398-1402.
19. Lanza LL, McQuay LJ, Rothman KJ, et al. Use of depot medroxyprogesterone acetate contraception and incidence of bone fracture. Obstet Gynecol. 2013;121:593-600.
20. Ettinger B, Pressman A, Sklarin P, et al. Associations between low levels of serum estradiol, bone density, and fractures among elderly women: the study of osteoporotic fractures. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998;83:2239-2243.
21. Reginster JY, Sarlet N, Deroisy R, et al. Minimal levels of serum estradiol prevent postmenopausal bone loss. Calcif Tissue Int. 1992;51:340-343.
22. Gaffield ME, Culwell KR, Ravi A. Oral contraceptives and family history of breast cancer. Contraception. 2009;80:372-380.
23. Iodice S, Barile M, Rotmensz N, et al. Oral contraceptive use and breast or ovarian cancer risk in BRCA1/2 carriers: a meta-analysis. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:2275-2284.
24. Marchbanks PA, Curtis KM, Mandel MG, et al. Oral contraceptive formulation and risk of breast cancer. Contraception. 2012;85:342-350.