User login
Virtual Dermatology: A COVID-19 Update
The growing threat of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), now commonly known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has forced Americans to stay home due to quarantine, especially older individuals and those who are immunocompromised or have an underlying health problem such as pulmonary or cardiac disease. The federal government’s estimated $2 trillion CARES Act (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act)1 will provide a much-needed boost to health care and the economy; prior recent legislation approved an $8.6 billion emergency relief bill,2 HR 6074 (Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2020), which expands Medicare coverage of telehealth to patients in their home rather than having them travel to a designated site, covers both established and new patients, allows physicians to waive or reduce co-payments and cost-sharing requirements, and reimburses the same as an in-person visit.
Federal emergency legislation temporarily relaxed the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA),3,4 allowing physicians to use Facetime and Skype for Medicare patients. In addition, Medicare will reimburse telehealth services for out-of-state-providers; however, cross-state licensure is governed by the patient’s home state.5 As of March 25, 2020, emergency legislation to temporarily allow out-of-state physicians to provide care, whether or not it relates to COVID-19, was enacted in 13 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Maryland, Minnesota, New York, North Carolina, and North Dakota.6 Ongoing legislation is rapidly changing; for daily updates on licensing laws, refer to the Federation of State Medical Boards website. Check your own institutional policies and malpractice provider prior to offering telehealth, as local laws and regulations may vary. Herein, we offer suggestions for using teledermatology.
Reimbursement
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, 16 states—Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Hawaii, Kentucky, Maine, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, Tennessee, Utah, and Virginia—had true payment parity laws,7 which reimbursed telehealth as a regular office visit using modifier -95. Several states have enacted emergency telehealth expansion laws to discourage COVID-19 spread8; some states such as New Jersey now prohibit co-payments or out-of-pocket deductibles from all in-network insurance plans (commercial Medicare and Medicaid).9,10 Updated legislation about COVID-19 and telemedicine can be found on the Center for Connected Health Policy website. An interactive map of laws and reimbursement policies also is available on the websites of the American Telehealth Association and the American Academy of Dermatology. The ability to charge a patient directly for telehealth services depends on the insurance provider agreement. If telehealth is a covered service, you cannot charge these patients out-of-pocket.
Teledermatology Options
For many conditions, the effectiveness and quality of teledermatology is comparable to a conventional face-to-face visit.11 There are 3 types of telehealth visits:
• Store and forward: The clinician reviews images or videos and responds asynchronously,12 similar to an email chain.
• Live interactive: The clinician uses 2-way video synchronously.12 In states with parity laws, this method is reimbursed equally to an in-person visit.
• Remote patient monitoring: Health-related data are collected and transmitted to a remote clinician, similar to remote intensive care unit management.12 Dermatologists are unlikely to utilize this modality.
The Virtual Visit
Follow these guidelines for practicing teledermatology: (1) ensure that the image or video is clear and that there is proper lighting, a monochromatic background, and a clear view of the anatomy necessary to evaluate; (2) dress in appropriate attire as if you were in clinic, such as scrubs, a white coat, or other professional attire; (3) begin the telehealth encounter by obtaining informed consent,13 according to state14 or Medicare guidelines; (4) document the location of the patient and provider; (5) for live virtual visits, document similarly to an in-person visit5; (6) for all other virtual care, document minutes spent on each task; and (7) select only 1 billing code per visit.
In some states, regulations for commercial and/or Medicaid plans require that other modifiers be added to billing codes, which vary plan-by-plan:
• Modifier GQ: For asynchronous care (store and forward).
• Modifier GT: For synchronous live telehealth visits.
• Modifier -95: In states where there are equal parity laws or if you are billing a commercial insurance payer (may vary by plan).
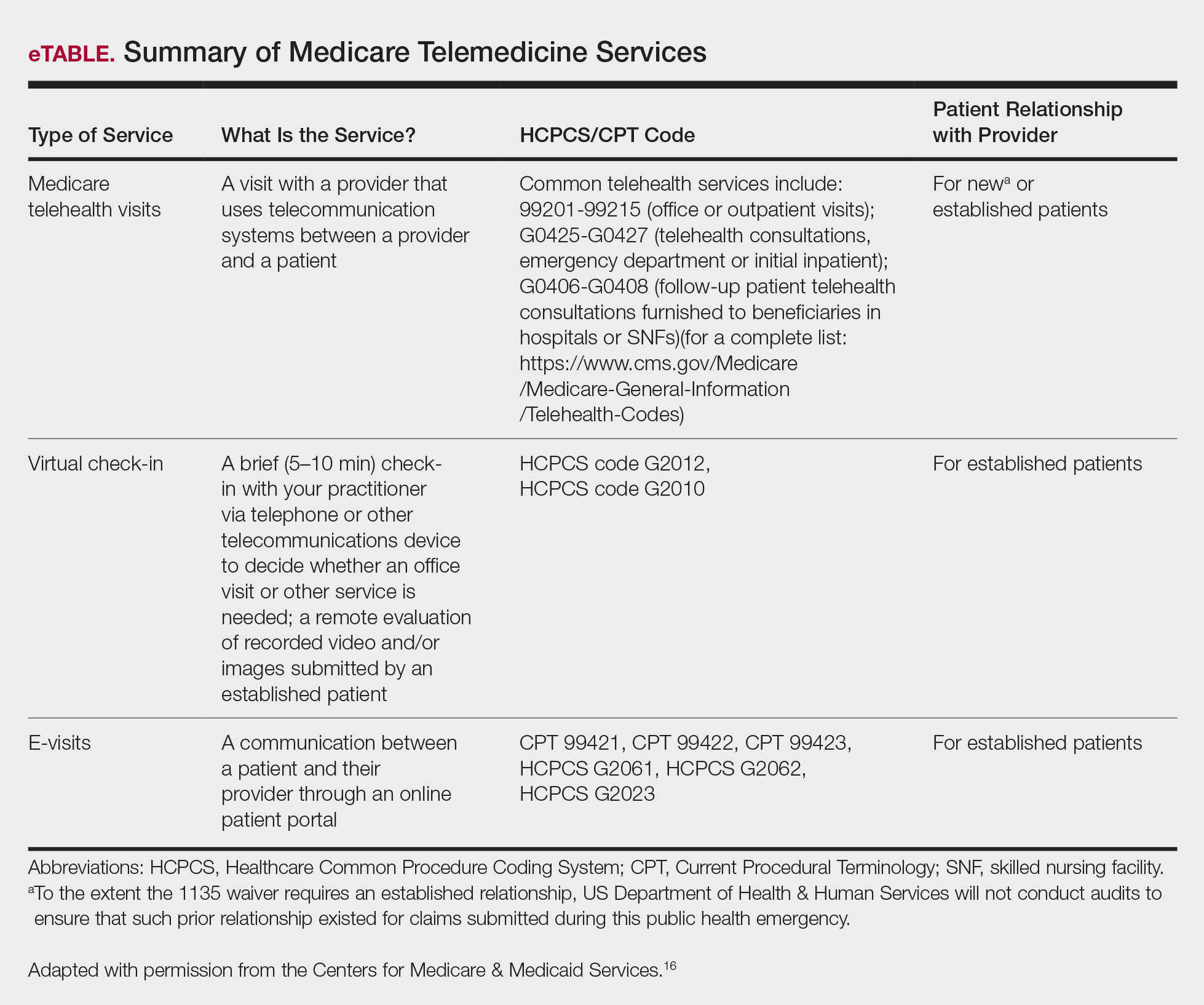
Medicare does not require any additional modifiers.15 If the plan reimburses telemedicine equally to a face-to-face visit, use regular office visit codes. The eTable16 lists billing codes and Medicare reimbursement rates.
Secure Software
Several electronic medical record systems already include secure patient communication. Other HIPAA-compliant communication options with a variety of features are available to clinicians:
• Klara allows for HIPAA-secure texting, group messaging, photograph uploads, and telephone calls.
• Doximity offers free calling and faxes.
• G Suite for health care offers HIPAA-compliant texting, emailing, and video calls through Google Voice and Google Hangouts Meet.
• Secure video chat is available on Zoom for Healthcare, VSee, Doxy.me, and other platforms.
• Multiservice platforms such as DermEngine include billing, payments, teledermatology, and teledermoscopy and allow for interprofessional consultation.
The Bottom Line
Telehealth readiness is playing a key role in containing the spread of COVID-19. In-person dermatology visits are now being limited to urgent conditions only, as per institutional guidelines.4
Acknowledgment
We thank Garfunkel Wild, P.C. (Great Neck, New York), for their expertise and assistance.
- Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, 2020. HR 748, 116th Cong, 2nd Sess (2020). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/116/hr748. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act, 2020. HR 6074, 116th Cong, 2nd Sess (2020). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/116/hr6074/text. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- Azar AM II. Waiver or Modification of Requirements Under Section 1135 of the Social Security Act. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2020. https://www.phe.gov/emergency/news/healthactions
/section1135/Pages/covid19-13March20.aspx. Accessed March 25, 2020. - American Academy of Dermatology Association. Can dermatologists use telemedicine to mitigate COVID-19 outbreaks? https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/toolkit. Updated March 28, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- American Medical Association. AMA quick guide to telemedicine in practice. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/ama-quick-guide-telemedicine-practice?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social_ama
&utm_term=3207044834&utm_campaign=Public+Health. Updated March 26, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020. - Federation of State Medical Boards. States waiving licensure requirements in response to COVID-19. http://www.fsmb.org/sitassets/advocacy/pdf/state-emergency-declarations-licensures-requimentscovid-19.pdf. Updated March 30, 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- American Telemedicine Association. 2019 State of the States: coverage & reimbursement. https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/5096139/Files/Thought Leadership_ATA/2019 State of the States summary_final.pdf. Published July 18, 2019. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- COVID-19 related state actions. Center for Connected Health Policy website. https://www.cchpca.org/resources/covid-19-related-state-actions. Updated March 27, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Governor Murphy announces departmental actions to expand access to telehealth and tele-mental health services in response to COVID-19 [news release]. Trenton, NJ: State of New Jersey; March 22, 2020. https://www.nj.gov/governor/news/news/562020/20200322b.shtml. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Caride M. Use of telemedicine and telehealth to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. State of New Jersey website. https://www.state.nj.us/dobi/bulletins/blt20_07.pdf. Published March 22, 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Tongdee E, Siegel DM, Markowitz O. New diagnostic procedure codes and reimbursement. Cutis. 2019;103:208-211.
- Telemedicine forms. American Telemedicine Association Web site. http://hub.americantelemed.org/thesource/resources/telemedicine-forms. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- State telemedicine laws, simplified. eVisit Web site. https://evisit.com/state-telemedicine-policy/. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) Response to the Public Health Emergency on the Coronavirus (COVID-19). March 20, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/se20011.pdf. Accessed March 29, 2020.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare telemedicine health care provider fact sheet. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/medicare-telemedicine-health-care-provider-fact-sheet. Published March 17, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
The growing threat of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), now commonly known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has forced Americans to stay home due to quarantine, especially older individuals and those who are immunocompromised or have an underlying health problem such as pulmonary or cardiac disease. The federal government’s estimated $2 trillion CARES Act (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act)1 will provide a much-needed boost to health care and the economy; prior recent legislation approved an $8.6 billion emergency relief bill,2 HR 6074 (Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2020), which expands Medicare coverage of telehealth to patients in their home rather than having them travel to a designated site, covers both established and new patients, allows physicians to waive or reduce co-payments and cost-sharing requirements, and reimburses the same as an in-person visit.
Federal emergency legislation temporarily relaxed the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA),3,4 allowing physicians to use Facetime and Skype for Medicare patients. In addition, Medicare will reimburse telehealth services for out-of-state-providers; however, cross-state licensure is governed by the patient’s home state.5 As of March 25, 2020, emergency legislation to temporarily allow out-of-state physicians to provide care, whether or not it relates to COVID-19, was enacted in 13 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Maryland, Minnesota, New York, North Carolina, and North Dakota.6 Ongoing legislation is rapidly changing; for daily updates on licensing laws, refer to the Federation of State Medical Boards website. Check your own institutional policies and malpractice provider prior to offering telehealth, as local laws and regulations may vary. Herein, we offer suggestions for using teledermatology.
Reimbursement
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, 16 states—Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Hawaii, Kentucky, Maine, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, Tennessee, Utah, and Virginia—had true payment parity laws,7 which reimbursed telehealth as a regular office visit using modifier -95. Several states have enacted emergency telehealth expansion laws to discourage COVID-19 spread8; some states such as New Jersey now prohibit co-payments or out-of-pocket deductibles from all in-network insurance plans (commercial Medicare and Medicaid).9,10 Updated legislation about COVID-19 and telemedicine can be found on the Center for Connected Health Policy website. An interactive map of laws and reimbursement policies also is available on the websites of the American Telehealth Association and the American Academy of Dermatology. The ability to charge a patient directly for telehealth services depends on the insurance provider agreement. If telehealth is a covered service, you cannot charge these patients out-of-pocket.
Teledermatology Options
For many conditions, the effectiveness and quality of teledermatology is comparable to a conventional face-to-face visit.11 There are 3 types of telehealth visits:
• Store and forward: The clinician reviews images or videos and responds asynchronously,12 similar to an email chain.
• Live interactive: The clinician uses 2-way video synchronously.12 In states with parity laws, this method is reimbursed equally to an in-person visit.
• Remote patient monitoring: Health-related data are collected and transmitted to a remote clinician, similar to remote intensive care unit management.12 Dermatologists are unlikely to utilize this modality.
The Virtual Visit
Follow these guidelines for practicing teledermatology: (1) ensure that the image or video is clear and that there is proper lighting, a monochromatic background, and a clear view of the anatomy necessary to evaluate; (2) dress in appropriate attire as if you were in clinic, such as scrubs, a white coat, or other professional attire; (3) begin the telehealth encounter by obtaining informed consent,13 according to state14 or Medicare guidelines; (4) document the location of the patient and provider; (5) for live virtual visits, document similarly to an in-person visit5; (6) for all other virtual care, document minutes spent on each task; and (7) select only 1 billing code per visit.
In some states, regulations for commercial and/or Medicaid plans require that other modifiers be added to billing codes, which vary plan-by-plan:
• Modifier GQ: For asynchronous care (store and forward).
• Modifier GT: For synchronous live telehealth visits.
• Modifier -95: In states where there are equal parity laws or if you are billing a commercial insurance payer (may vary by plan).
Medicare does not require any additional modifiers.15 If the plan reimburses telemedicine equally to a face-to-face visit, use regular office visit codes. The eTable16 lists billing codes and Medicare reimbursement rates.

Secure Software
Several electronic medical record systems already include secure patient communication. Other HIPAA-compliant communication options with a variety of features are available to clinicians:
• Klara allows for HIPAA-secure texting, group messaging, photograph uploads, and telephone calls.
• Doximity offers free calling and faxes.
• G Suite for health care offers HIPAA-compliant texting, emailing, and video calls through Google Voice and Google Hangouts Meet.
• Secure video chat is available on Zoom for Healthcare, VSee, Doxy.me, and other platforms.
• Multiservice platforms such as DermEngine include billing, payments, teledermatology, and teledermoscopy and allow for interprofessional consultation.
The Bottom Line
Telehealth readiness is playing a key role in containing the spread of COVID-19. In-person dermatology visits are now being limited to urgent conditions only, as per institutional guidelines.4
Acknowledgment
We thank Garfunkel Wild, P.C. (Great Neck, New York), for their expertise and assistance.
The growing threat of novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), now commonly known as coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), has forced Americans to stay home due to quarantine, especially older individuals and those who are immunocompromised or have an underlying health problem such as pulmonary or cardiac disease. The federal government’s estimated $2 trillion CARES Act (Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act)1 will provide a much-needed boost to health care and the economy; prior recent legislation approved an $8.6 billion emergency relief bill,2 HR 6074 (Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act of 2020), which expands Medicare coverage of telehealth to patients in their home rather than having them travel to a designated site, covers both established and new patients, allows physicians to waive or reduce co-payments and cost-sharing requirements, and reimburses the same as an in-person visit.
Federal emergency legislation temporarily relaxed the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA),3,4 allowing physicians to use Facetime and Skype for Medicare patients. In addition, Medicare will reimburse telehealth services for out-of-state-providers; however, cross-state licensure is governed by the patient’s home state.5 As of March 25, 2020, emergency legislation to temporarily allow out-of-state physicians to provide care, whether or not it relates to COVID-19, was enacted in 13 states: California, Colorado, Connecticut, Delaware, Hawaii, Idaho, Indiana, Iowa, Maryland, Minnesota, New York, North Carolina, and North Dakota.6 Ongoing legislation is rapidly changing; for daily updates on licensing laws, refer to the Federation of State Medical Boards website. Check your own institutional policies and malpractice provider prior to offering telehealth, as local laws and regulations may vary. Herein, we offer suggestions for using teledermatology.
Reimbursement
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, 16 states—Arkansas, Colorado, Delaware, Hawaii, Kentucky, Maine, Minnesota, Mississippi, Missouri, Montana, Nevada, New Jersey, New Mexico, Tennessee, Utah, and Virginia—had true payment parity laws,7 which reimbursed telehealth as a regular office visit using modifier -95. Several states have enacted emergency telehealth expansion laws to discourage COVID-19 spread8; some states such as New Jersey now prohibit co-payments or out-of-pocket deductibles from all in-network insurance plans (commercial Medicare and Medicaid).9,10 Updated legislation about COVID-19 and telemedicine can be found on the Center for Connected Health Policy website. An interactive map of laws and reimbursement policies also is available on the websites of the American Telehealth Association and the American Academy of Dermatology. The ability to charge a patient directly for telehealth services depends on the insurance provider agreement. If telehealth is a covered service, you cannot charge these patients out-of-pocket.
Teledermatology Options
For many conditions, the effectiveness and quality of teledermatology is comparable to a conventional face-to-face visit.11 There are 3 types of telehealth visits:
• Store and forward: The clinician reviews images or videos and responds asynchronously,12 similar to an email chain.
• Live interactive: The clinician uses 2-way video synchronously.12 In states with parity laws, this method is reimbursed equally to an in-person visit.
• Remote patient monitoring: Health-related data are collected and transmitted to a remote clinician, similar to remote intensive care unit management.12 Dermatologists are unlikely to utilize this modality.
The Virtual Visit
Follow these guidelines for practicing teledermatology: (1) ensure that the image or video is clear and that there is proper lighting, a monochromatic background, and a clear view of the anatomy necessary to evaluate; (2) dress in appropriate attire as if you were in clinic, such as scrubs, a white coat, or other professional attire; (3) begin the telehealth encounter by obtaining informed consent,13 according to state14 or Medicare guidelines; (4) document the location of the patient and provider; (5) for live virtual visits, document similarly to an in-person visit5; (6) for all other virtual care, document minutes spent on each task; and (7) select only 1 billing code per visit.
In some states, regulations for commercial and/or Medicaid plans require that other modifiers be added to billing codes, which vary plan-by-plan:
• Modifier GQ: For asynchronous care (store and forward).
• Modifier GT: For synchronous live telehealth visits.
• Modifier -95: In states where there are equal parity laws or if you are billing a commercial insurance payer (may vary by plan).
Medicare does not require any additional modifiers.15 If the plan reimburses telemedicine equally to a face-to-face visit, use regular office visit codes. The eTable16 lists billing codes and Medicare reimbursement rates.

Secure Software
Several electronic medical record systems already include secure patient communication. Other HIPAA-compliant communication options with a variety of features are available to clinicians:
• Klara allows for HIPAA-secure texting, group messaging, photograph uploads, and telephone calls.
• Doximity offers free calling and faxes.
• G Suite for health care offers HIPAA-compliant texting, emailing, and video calls through Google Voice and Google Hangouts Meet.
• Secure video chat is available on Zoom for Healthcare, VSee, Doxy.me, and other platforms.
• Multiservice platforms such as DermEngine include billing, payments, teledermatology, and teledermoscopy and allow for interprofessional consultation.
The Bottom Line
Telehealth readiness is playing a key role in containing the spread of COVID-19. In-person dermatology visits are now being limited to urgent conditions only, as per institutional guidelines.4
Acknowledgment
We thank Garfunkel Wild, P.C. (Great Neck, New York), for their expertise and assistance.
- Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, 2020. HR 748, 116th Cong, 2nd Sess (2020). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/116/hr748. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act, 2020. HR 6074, 116th Cong, 2nd Sess (2020). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/116/hr6074/text. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- Azar AM II. Waiver or Modification of Requirements Under Section 1135 of the Social Security Act. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2020. https://www.phe.gov/emergency/news/healthactions
/section1135/Pages/covid19-13March20.aspx. Accessed March 25, 2020. - American Academy of Dermatology Association. Can dermatologists use telemedicine to mitigate COVID-19 outbreaks? https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/toolkit. Updated March 28, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- American Medical Association. AMA quick guide to telemedicine in practice. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/ama-quick-guide-telemedicine-practice?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social_ama
&utm_term=3207044834&utm_campaign=Public+Health. Updated March 26, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020. - Federation of State Medical Boards. States waiving licensure requirements in response to COVID-19. http://www.fsmb.org/sitassets/advocacy/pdf/state-emergency-declarations-licensures-requimentscovid-19.pdf. Updated March 30, 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- American Telemedicine Association. 2019 State of the States: coverage & reimbursement. https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/5096139/Files/Thought Leadership_ATA/2019 State of the States summary_final.pdf. Published July 18, 2019. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- COVID-19 related state actions. Center for Connected Health Policy website. https://www.cchpca.org/resources/covid-19-related-state-actions. Updated March 27, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Governor Murphy announces departmental actions to expand access to telehealth and tele-mental health services in response to COVID-19 [news release]. Trenton, NJ: State of New Jersey; March 22, 2020. https://www.nj.gov/governor/news/news/562020/20200322b.shtml. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Caride M. Use of telemedicine and telehealth to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. State of New Jersey website. https://www.state.nj.us/dobi/bulletins/blt20_07.pdf. Published March 22, 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Tongdee E, Siegel DM, Markowitz O. New diagnostic procedure codes and reimbursement. Cutis. 2019;103:208-211.
- Telemedicine forms. American Telemedicine Association Web site. http://hub.americantelemed.org/thesource/resources/telemedicine-forms. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- State telemedicine laws, simplified. eVisit Web site. https://evisit.com/state-telemedicine-policy/. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) Response to the Public Health Emergency on the Coronavirus (COVID-19). March 20, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/se20011.pdf. Accessed March 29, 2020.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare telemedicine health care provider fact sheet. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/medicare-telemedicine-health-care-provider-fact-sheet. Published March 17, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.
- Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security Act, 2020. HR 748, 116th Cong, 2nd Sess (2020). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/116/hr748. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Coronavirus Preparedness and Response Supplemental Appropriations Act, 2020. HR 6074, 116th Cong, 2nd Sess (2020). https://www.govtrack.us/congress/bills/116/hr6074/text. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- Azar AM II. Waiver or Modification of Requirements Under Section 1135 of the Social Security Act. Washington, DC: US Department of Health and Human Services; 2020. https://www.phe.gov/emergency/news/healthactions
/section1135/Pages/covid19-13March20.aspx. Accessed March 25, 2020. - American Academy of Dermatology Association. Can dermatologists use telemedicine to mitigate COVID-19 outbreaks? https://www.aad.org/member/practice/telederm/toolkit. Updated March 28, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- American Medical Association. AMA quick guide to telemedicine in practice. https://www.ama-assn.org/practice-management/digital/ama-quick-guide-telemedicine-practice?utm_source=twitter&utm_medium=social_ama
&utm_term=3207044834&utm_campaign=Public+Health. Updated March 26, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020. - Federation of State Medical Boards. States waiving licensure requirements in response to COVID-19. http://www.fsmb.org/sitassets/advocacy/pdf/state-emergency-declarations-licensures-requimentscovid-19.pdf. Updated March 30, 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- American Telemedicine Association. 2019 State of the States: coverage & reimbursement. https://cdn2.hubspot.net/hubfs/5096139/Files/Thought Leadership_ATA/2019 State of the States summary_final.pdf. Published July 18, 2019. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- COVID-19 related state actions. Center for Connected Health Policy website. https://www.cchpca.org/resources/covid-19-related-state-actions. Updated March 27, 2020. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Governor Murphy announces departmental actions to expand access to telehealth and tele-mental health services in response to COVID-19 [news release]. Trenton, NJ: State of New Jersey; March 22, 2020. https://www.nj.gov/governor/news/news/562020/20200322b.shtml. Accessed March 26, 2020.
- Caride M. Use of telemedicine and telehealth to respond to the COVID-19 pandemic. State of New Jersey website. https://www.state.nj.us/dobi/bulletins/blt20_07.pdf. Published March 22, 2020. Accessed March 30, 2020.
- Lee JJ, English JC 3rd. Teledermatology: a review and update. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2018;19:253-260.
- Tongdee E, Siegel DM, Markowitz O. New diagnostic procedure codes and reimbursement. Cutis. 2019;103:208-211.
- Telemedicine forms. American Telemedicine Association Web site. http://hub.americantelemed.org/thesource/resources/telemedicine-forms. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- State telemedicine laws, simplified. eVisit Web site. https://evisit.com/state-telemedicine-policy/. Accessed March 22, 2020.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare Fee-for-Service (FFS) Response to the Public Health Emergency on the Coronavirus (COVID-19). March 20, 2020. https://www.cms.gov/files/document/se20011.pdf. Accessed March 29, 2020.
- Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Medicare telemedicine health care provider fact sheet. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/fact-sheets/medicare-telemedicine-health-care-provider-fact-sheet. Published March 17, 2020. Accessed March 20, 2020.