User login
Emerging sickle cell agents target new pathways
CONCORD, N.C. – Approved treatments for sickle cell disease have been extremely limited, but there are several therapies in the research pipeline that use new pathways to target the disease.
“We do have much better understanding of the pathophysiology, which is getting us a few more targets to aim at,” Julie Kanter, MD, director of sickle cell research at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. These targets include influencing how cells interact with the vascular endothelium, inhibiting platelets, and preventing cell sickling and inflammation.
“I’m waiting to see who’s willing to take it just because it is a lot of powder that the patient has to mix and drink twice a day, but it does look promising to reduce inflammation,” Dr. Kanter said.
SCD pipeline
Deeper in the sickle cell pipeline is a class of antisickling agents known as hemoglobin modifiers. “We’re tying to change the way hemoglobin binds to oxygen, and if we can keep hemoglobin binding to oxygen longer, it actually decreases the risk of hemoglobin sickling and polymerizing in the cell,” Dr. Kanter explained.
One hemoglobin modifier is voxelotor (previously called GBT440), a once-daily oral agent that Global Blood Therapeutics has in development.
Another category of antisickling agents that researchers are looking at is anti-inflammatory moderators, Dr. Kanter said. These include nitric oxide donors like sildenafil, which did not “quite work” in SCD, and arginine and glutamine, which increase the amount of nitric oxide once in the body “and hopefully reduce the risk of sickling,” she said. “If we can improve inflammation, we might be able to improve the risk of crisis.”
Cell adhesion modifiers are a drug class that aims to prevent cells from binding to each other. These include platelet inhibitors and endothelial blockers. “There are several antiplatelet agents that are approved really for stroke prevention or heart attack prevention, and we’re trying to see if we can repurpose these in sickle cell disease in a specific pathway that allows the platelet to stick to the endothelium, but if we only inhibit one pathway it should not increase the risk of bleeding,” Dr. Kanter said.
One platelet inhibition pathway that researchers are focused on is the P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate blockade, which the platelet inhibitor prasugrel (Effient) acts on. A 2016 study of this pathway in SCD “wasn’t successful,” Dr. Kanter said, “but it had some interesting results” – namely that the drug may be most effective in adolescents (N Engl J Med. 2016 Feb 18;374[7]:625-35).
Selectin-blocking medications are a drug class that act on white blood cell adhesion to, and movement through, the endothelium, Dr. Kanter said. “Neutrophils can instigate a sickle cell crisis, so if we can interrupt some of this rolling or sticking, could we decrease the risk of a sickle cell crisis?” The drug GMI-1070 is currently being studied in a phase III trial and so far has shown “a significant decrease in the amount of opioids used by those individuals who received the study drug,” she said.
Crizanlizumab (also known as SelG1) is a humanized monoclonal antibody with an affinity to P-selectin and is the subject of the phase II SUSTAIN trial, which included a cohort that also was taking hydroxyurea. Treatment with high-dose crizanlizumab resulted in an annual rate of sickle cell–related pain crises that was more than 45% lower than with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:429-39).
Stem cell transplants
Besides drugs, stem cell transplants to treat SCD have advanced in recent years to the point where cure rates are exceeding 90%, Dr. Kanter noted. “However, the real issue with stem cells is that patients still don’t have enough donors,” she said.
SCD is also potentially amenable to gene therapy, Dr. Kanter said, noting that SCD gene therapy trials in progress are looking at harvesting patients’ own bone marrow, using the lentivirus viral vector, inserting a gene to increase production of nonsickle hemoglobin, and using myeloablative chemotherapy to remove old marrow and replace it with new, manipulated bone marrow.
Several programs are investigating using a gene editing technique, known as CRISPR/Cas9, to alter the BCL11A gene to maintain fetal hemoglobin production.
“We all make fetal hemoglobin at birth, and then over 6 months to 1 year of life, our bodies convert fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin,” she said. “In sickle cell disease, it converts to sickle hemoglobin. What if we could prevent that conversion and keep the fetal hemoglobin turned on?” That could potentially eradicate the complications of SCD starting at an early age, Dr. Kanter said.
Dr. Kanter, who has been involved in several of the SCD trials, reported relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bluebird Bio, Global Blood Therapeutics, Novartis, Guidepoint, GLG, ApoPharma, and Purdue Pharma.
CONCORD, N.C. – Approved treatments for sickle cell disease have been extremely limited, but there are several therapies in the research pipeline that use new pathways to target the disease.
“We do have much better understanding of the pathophysiology, which is getting us a few more targets to aim at,” Julie Kanter, MD, director of sickle cell research at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. These targets include influencing how cells interact with the vascular endothelium, inhibiting platelets, and preventing cell sickling and inflammation.
“I’m waiting to see who’s willing to take it just because it is a lot of powder that the patient has to mix and drink twice a day, but it does look promising to reduce inflammation,” Dr. Kanter said.
SCD pipeline
Deeper in the sickle cell pipeline is a class of antisickling agents known as hemoglobin modifiers. “We’re tying to change the way hemoglobin binds to oxygen, and if we can keep hemoglobin binding to oxygen longer, it actually decreases the risk of hemoglobin sickling and polymerizing in the cell,” Dr. Kanter explained.
One hemoglobin modifier is voxelotor (previously called GBT440), a once-daily oral agent that Global Blood Therapeutics has in development.
Another category of antisickling agents that researchers are looking at is anti-inflammatory moderators, Dr. Kanter said. These include nitric oxide donors like sildenafil, which did not “quite work” in SCD, and arginine and glutamine, which increase the amount of nitric oxide once in the body “and hopefully reduce the risk of sickling,” she said. “If we can improve inflammation, we might be able to improve the risk of crisis.”
Cell adhesion modifiers are a drug class that aims to prevent cells from binding to each other. These include platelet inhibitors and endothelial blockers. “There are several antiplatelet agents that are approved really for stroke prevention or heart attack prevention, and we’re trying to see if we can repurpose these in sickle cell disease in a specific pathway that allows the platelet to stick to the endothelium, but if we only inhibit one pathway it should not increase the risk of bleeding,” Dr. Kanter said.
One platelet inhibition pathway that researchers are focused on is the P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate blockade, which the platelet inhibitor prasugrel (Effient) acts on. A 2016 study of this pathway in SCD “wasn’t successful,” Dr. Kanter said, “but it had some interesting results” – namely that the drug may be most effective in adolescents (N Engl J Med. 2016 Feb 18;374[7]:625-35).
Selectin-blocking medications are a drug class that act on white blood cell adhesion to, and movement through, the endothelium, Dr. Kanter said. “Neutrophils can instigate a sickle cell crisis, so if we can interrupt some of this rolling or sticking, could we decrease the risk of a sickle cell crisis?” The drug GMI-1070 is currently being studied in a phase III trial and so far has shown “a significant decrease in the amount of opioids used by those individuals who received the study drug,” she said.
Crizanlizumab (also known as SelG1) is a humanized monoclonal antibody with an affinity to P-selectin and is the subject of the phase II SUSTAIN trial, which included a cohort that also was taking hydroxyurea. Treatment with high-dose crizanlizumab resulted in an annual rate of sickle cell–related pain crises that was more than 45% lower than with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:429-39).
Stem cell transplants
Besides drugs, stem cell transplants to treat SCD have advanced in recent years to the point where cure rates are exceeding 90%, Dr. Kanter noted. “However, the real issue with stem cells is that patients still don’t have enough donors,” she said.
SCD is also potentially amenable to gene therapy, Dr. Kanter said, noting that SCD gene therapy trials in progress are looking at harvesting patients’ own bone marrow, using the lentivirus viral vector, inserting a gene to increase production of nonsickle hemoglobin, and using myeloablative chemotherapy to remove old marrow and replace it with new, manipulated bone marrow.
Several programs are investigating using a gene editing technique, known as CRISPR/Cas9, to alter the BCL11A gene to maintain fetal hemoglobin production.
“We all make fetal hemoglobin at birth, and then over 6 months to 1 year of life, our bodies convert fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin,” she said. “In sickle cell disease, it converts to sickle hemoglobin. What if we could prevent that conversion and keep the fetal hemoglobin turned on?” That could potentially eradicate the complications of SCD starting at an early age, Dr. Kanter said.
Dr. Kanter, who has been involved in several of the SCD trials, reported relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bluebird Bio, Global Blood Therapeutics, Novartis, Guidepoint, GLG, ApoPharma, and Purdue Pharma.
CONCORD, N.C. – Approved treatments for sickle cell disease have been extremely limited, but there are several therapies in the research pipeline that use new pathways to target the disease.
“We do have much better understanding of the pathophysiology, which is getting us a few more targets to aim at,” Julie Kanter, MD, director of sickle cell research at the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, said at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System. These targets include influencing how cells interact with the vascular endothelium, inhibiting platelets, and preventing cell sickling and inflammation.
“I’m waiting to see who’s willing to take it just because it is a lot of powder that the patient has to mix and drink twice a day, but it does look promising to reduce inflammation,” Dr. Kanter said.
SCD pipeline
Deeper in the sickle cell pipeline is a class of antisickling agents known as hemoglobin modifiers. “We’re tying to change the way hemoglobin binds to oxygen, and if we can keep hemoglobin binding to oxygen longer, it actually decreases the risk of hemoglobin sickling and polymerizing in the cell,” Dr. Kanter explained.
One hemoglobin modifier is voxelotor (previously called GBT440), a once-daily oral agent that Global Blood Therapeutics has in development.
Another category of antisickling agents that researchers are looking at is anti-inflammatory moderators, Dr. Kanter said. These include nitric oxide donors like sildenafil, which did not “quite work” in SCD, and arginine and glutamine, which increase the amount of nitric oxide once in the body “and hopefully reduce the risk of sickling,” she said. “If we can improve inflammation, we might be able to improve the risk of crisis.”
Cell adhesion modifiers are a drug class that aims to prevent cells from binding to each other. These include platelet inhibitors and endothelial blockers. “There are several antiplatelet agents that are approved really for stroke prevention or heart attack prevention, and we’re trying to see if we can repurpose these in sickle cell disease in a specific pathway that allows the platelet to stick to the endothelium, but if we only inhibit one pathway it should not increase the risk of bleeding,” Dr. Kanter said.
One platelet inhibition pathway that researchers are focused on is the P2Y12 adenosine diphosphate blockade, which the platelet inhibitor prasugrel (Effient) acts on. A 2016 study of this pathway in SCD “wasn’t successful,” Dr. Kanter said, “but it had some interesting results” – namely that the drug may be most effective in adolescents (N Engl J Med. 2016 Feb 18;374[7]:625-35).
Selectin-blocking medications are a drug class that act on white blood cell adhesion to, and movement through, the endothelium, Dr. Kanter said. “Neutrophils can instigate a sickle cell crisis, so if we can interrupt some of this rolling or sticking, could we decrease the risk of a sickle cell crisis?” The drug GMI-1070 is currently being studied in a phase III trial and so far has shown “a significant decrease in the amount of opioids used by those individuals who received the study drug,” she said.
Crizanlizumab (also known as SelG1) is a humanized monoclonal antibody with an affinity to P-selectin and is the subject of the phase II SUSTAIN trial, which included a cohort that also was taking hydroxyurea. Treatment with high-dose crizanlizumab resulted in an annual rate of sickle cell–related pain crises that was more than 45% lower than with placebo (N Engl J Med. 2017 Feb 2;376[5]:429-39).
Stem cell transplants
Besides drugs, stem cell transplants to treat SCD have advanced in recent years to the point where cure rates are exceeding 90%, Dr. Kanter noted. “However, the real issue with stem cells is that patients still don’t have enough donors,” she said.
SCD is also potentially amenable to gene therapy, Dr. Kanter said, noting that SCD gene therapy trials in progress are looking at harvesting patients’ own bone marrow, using the lentivirus viral vector, inserting a gene to increase production of nonsickle hemoglobin, and using myeloablative chemotherapy to remove old marrow and replace it with new, manipulated bone marrow.
Several programs are investigating using a gene editing technique, known as CRISPR/Cas9, to alter the BCL11A gene to maintain fetal hemoglobin production.
“We all make fetal hemoglobin at birth, and then over 6 months to 1 year of life, our bodies convert fetal hemoglobin to adult hemoglobin,” she said. “In sickle cell disease, it converts to sickle hemoglobin. What if we could prevent that conversion and keep the fetal hemoglobin turned on?” That could potentially eradicate the complications of SCD starting at an early age, Dr. Kanter said.
Dr. Kanter, who has been involved in several of the SCD trials, reported relationships with Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Bluebird Bio, Global Blood Therapeutics, Novartis, Guidepoint, GLG, ApoPharma, and Purdue Pharma.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON SICKLE CELL DISEASE
Dedicated sickle cell center offers roadmap for care
CONCORD, N.C. – A care center for acute sickle cell pain management, which includes a dedicated emergency room and a daytime management unit in the hospital, decreased health system costs and the frequency of acute care visits by sickle cell patients, James Eckman, MD, reported at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System.
“In the first 5 years of the center, acute care visits dropped from 16 per patient per year to 10, and admissions per active patient per year dropped from 2.1 to less than one,” said Dr. Eckman, former medical director of the Georgia Comprehensive Sickle Cell Center at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
By 2011, those numbers had dropped further, falling to less than four acute care visits per patient per year and less than 0.5 admissions per patient per year.
The results Dr. Eckman reported are based on 37 years of his experience at Grady Health System, which included setting up an emergency room dedicated to patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) and the launch of a tertiary care clinic in 1985. The Grady SCD database includes more than 4,500 patients, with about 1,000 adults active at any given time.
It’s , according to Emory University.
“We really developed a model that was very cost effective for the management of this disease,” said Dr. Eckman, professor emeritus in hematology and medical oncology at Emory University. “We actually consistently turned a profit in our budget.”
Previously, SCD patients went to the regular emergency department for their acute pain crises, and they would often wait for hours without treatment. “You need to initiate treatment rapidly in these patients,” Dr. Eckman said. “It’s really unacceptable now what’s happening in our emergency rooms, where they have to wait 3, 4, or more hours to get treated while they’re in intolerable pain.”
In 2014, an expert panel issued guidelines for pain management in SCD calling for the initiation of pain treatment for acute crisis within 30 minutes of the patient’s arrival in the emergency department (JAMA. 2014 Sep 10;312[10]:1033-48). “Our goal is 20 minutes to have a complete assessment, get a laboratory draw, and have them on therapy,” he said. “And we were relatively successful in being able to do that.”
Each patient at the center was enrolled in a care management program consisting of 35 assessment and intervention elements. Assessment includes a complete medical evaluation, along with social and psychological evaluations. Intervention entails developing a detailed problem list – including medical, social, and psychological issues – a detailed management plan, and a social support plan. The initial assessment can take 4-8 hours.
For the first decade, the program tracked acute care visits and admissions in 166 continuing patients and saw dramatic declines in both. “The data only go through 1995, but they actually look exactly the same after 1995 all the way up to 2015,” Dr. Eckman said. “This sustained a really marked decrease in health care utilization.”
The program also identified a small group of patients – fewer than 75 out of a base of 1,000 – who accounted for 90% of visits, he said.
Although the Georgia experience is based on a dedicated care center for SCD, the results can be replicated without that type of dedicated infrastructure, Dr. Eckman said. “It is not the 24-hour acute care center,” he said. “It’s the carefully thought out and implemented comprehensive care plan by a multidisciplinary care team dedicated to care of the individuals with sickle cell disease that makes the difference.”
Dr. Eckman reported having no financial disclosures.
CONCORD, N.C. – A care center for acute sickle cell pain management, which includes a dedicated emergency room and a daytime management unit in the hospital, decreased health system costs and the frequency of acute care visits by sickle cell patients, James Eckman, MD, reported at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System.
“In the first 5 years of the center, acute care visits dropped from 16 per patient per year to 10, and admissions per active patient per year dropped from 2.1 to less than one,” said Dr. Eckman, former medical director of the Georgia Comprehensive Sickle Cell Center at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
By 2011, those numbers had dropped further, falling to less than four acute care visits per patient per year and less than 0.5 admissions per patient per year.
The results Dr. Eckman reported are based on 37 years of his experience at Grady Health System, which included setting up an emergency room dedicated to patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) and the launch of a tertiary care clinic in 1985. The Grady SCD database includes more than 4,500 patients, with about 1,000 adults active at any given time.
It’s , according to Emory University.
“We really developed a model that was very cost effective for the management of this disease,” said Dr. Eckman, professor emeritus in hematology and medical oncology at Emory University. “We actually consistently turned a profit in our budget.”
Previously, SCD patients went to the regular emergency department for their acute pain crises, and they would often wait for hours without treatment. “You need to initiate treatment rapidly in these patients,” Dr. Eckman said. “It’s really unacceptable now what’s happening in our emergency rooms, where they have to wait 3, 4, or more hours to get treated while they’re in intolerable pain.”
In 2014, an expert panel issued guidelines for pain management in SCD calling for the initiation of pain treatment for acute crisis within 30 minutes of the patient’s arrival in the emergency department (JAMA. 2014 Sep 10;312[10]:1033-48). “Our goal is 20 minutes to have a complete assessment, get a laboratory draw, and have them on therapy,” he said. “And we were relatively successful in being able to do that.”
Each patient at the center was enrolled in a care management program consisting of 35 assessment and intervention elements. Assessment includes a complete medical evaluation, along with social and psychological evaluations. Intervention entails developing a detailed problem list – including medical, social, and psychological issues – a detailed management plan, and a social support plan. The initial assessment can take 4-8 hours.
For the first decade, the program tracked acute care visits and admissions in 166 continuing patients and saw dramatic declines in both. “The data only go through 1995, but they actually look exactly the same after 1995 all the way up to 2015,” Dr. Eckman said. “This sustained a really marked decrease in health care utilization.”
The program also identified a small group of patients – fewer than 75 out of a base of 1,000 – who accounted for 90% of visits, he said.
Although the Georgia experience is based on a dedicated care center for SCD, the results can be replicated without that type of dedicated infrastructure, Dr. Eckman said. “It is not the 24-hour acute care center,” he said. “It’s the carefully thought out and implemented comprehensive care plan by a multidisciplinary care team dedicated to care of the individuals with sickle cell disease that makes the difference.”
Dr. Eckman reported having no financial disclosures.
CONCORD, N.C. – A care center for acute sickle cell pain management, which includes a dedicated emergency room and a daytime management unit in the hospital, decreased health system costs and the frequency of acute care visits by sickle cell patients, James Eckman, MD, reported at Sickle Cell Disease Symposium held by Carolinas Health Care System.
“In the first 5 years of the center, acute care visits dropped from 16 per patient per year to 10, and admissions per active patient per year dropped from 2.1 to less than one,” said Dr. Eckman, former medical director of the Georgia Comprehensive Sickle Cell Center at Grady Health System in Atlanta.
By 2011, those numbers had dropped further, falling to less than four acute care visits per patient per year and less than 0.5 admissions per patient per year.
The results Dr. Eckman reported are based on 37 years of his experience at Grady Health System, which included setting up an emergency room dedicated to patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) and the launch of a tertiary care clinic in 1985. The Grady SCD database includes more than 4,500 patients, with about 1,000 adults active at any given time.
It’s , according to Emory University.
“We really developed a model that was very cost effective for the management of this disease,” said Dr. Eckman, professor emeritus in hematology and medical oncology at Emory University. “We actually consistently turned a profit in our budget.”
Previously, SCD patients went to the regular emergency department for their acute pain crises, and they would often wait for hours without treatment. “You need to initiate treatment rapidly in these patients,” Dr. Eckman said. “It’s really unacceptable now what’s happening in our emergency rooms, where they have to wait 3, 4, or more hours to get treated while they’re in intolerable pain.”
In 2014, an expert panel issued guidelines for pain management in SCD calling for the initiation of pain treatment for acute crisis within 30 minutes of the patient’s arrival in the emergency department (JAMA. 2014 Sep 10;312[10]:1033-48). “Our goal is 20 minutes to have a complete assessment, get a laboratory draw, and have them on therapy,” he said. “And we were relatively successful in being able to do that.”
Each patient at the center was enrolled in a care management program consisting of 35 assessment and intervention elements. Assessment includes a complete medical evaluation, along with social and psychological evaluations. Intervention entails developing a detailed problem list – including medical, social, and psychological issues – a detailed management plan, and a social support plan. The initial assessment can take 4-8 hours.
For the first decade, the program tracked acute care visits and admissions in 166 continuing patients and saw dramatic declines in both. “The data only go through 1995, but they actually look exactly the same after 1995 all the way up to 2015,” Dr. Eckman said. “This sustained a really marked decrease in health care utilization.”
The program also identified a small group of patients – fewer than 75 out of a base of 1,000 – who accounted for 90% of visits, he said.
Although the Georgia experience is based on a dedicated care center for SCD, the results can be replicated without that type of dedicated infrastructure, Dr. Eckman said. “It is not the 24-hour acute care center,” he said. “It’s the carefully thought out and implemented comprehensive care plan by a multidisciplinary care team dedicated to care of the individuals with sickle cell disease that makes the difference.”
Dr. Eckman reported having no financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A MEETING ON SICKLE CELL DISEASE
Study examines intestinal microbiota role post liver transplant
WASHINGTON – During and after liver transplant, the reaction of the intestinal microbiota may be a critical determinant of outcomes; preliminary data from a cohort study may provide some clarification of what modulates gut microbiota post transplantation and shed light on predictive factors.
Anna-Catrin Uhlemann, MD, PhD, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, noted that several studies in recent years sought to clarify influences on gut microbiota in people receiving liver transplants, but “there are still a number of important gaps in knowledge, including what exactly is the longitudinal evolution of the host transplant microbiome and what is the predictive value of pre- and early posttransplant dysbiosis on outcomes and complications.”
The researchers collected more than 1,000 samples to screen for colonization by the following MDR organisms: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), Enterobacteriaceae resistant to third-generation cephalosporins (ESBL), and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). Over the 1-year follow-up period, 19% (P =.031) of patients had CRE colonization associated with subsequent infection, 41% (P = .003) had ESBL colonization, and 46% (P = .021) had VRE colonization, Dr. Uhlemann said at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. The researchers then selected 484 samples for sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene to determine the composition of gut microbiota.
The study used two indexes to determine the alpha diversity of microbiota: the Chao index to estimate richness and the Shannon diversity index to determine the abundance of species in different settings. “We observed dynamic temporal evolution of alpha diversity and taxa abundance over the 1-year follow-up period,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “The diagnosis, the Child-Pugh class, and changes in perioperative antibiotics were important predictors of posttransplant alpha diversity.”
The study also found that Enterobacteriaceae and enterococci increased post transplant in general and as MDR organisms, and that a patient’s MDR status was an important modulator of the posttransplant microbiome, as was the lack of protective operational taxonomic units (OTUs).
The researchers evaluated the relative abundance of taxa and beta diversity. For example, pretransplant patients with a Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score greater than 25 showed enrichment of Enterobacteriaceae as well as different taxa of the Bacteroidiaceae, while those with MELD scores below 25 showed enrichment of Veillonellaceae. “The significance of this is not clear yet,” Dr. Uhlemann said.
Liver disease severity can also influence gut microbes. Those with Child-Pugh class C disease have the highest numbers in terms of richness and lowest in terms of diversity, Dr. Uhlemann said. “However, at the moment when we are looking at the differential abundance of the taxa, we don’t see quite as clear a pattern, although we noticed in the high group a higher abundance of Bacteroidiaceae,” she said.
Hepatitis B and C patients also presented divergent microbiota profiles. Hepatitis B virus patients “in general are always relatively healthy, and we actually see that these indices are relatively preserved,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “When we look at hepatitis C, however, we see that these patients are starting off quite low and then have an increase in alpha-diversity measures at around month 6.” A subset of patients with alcoholic liver disease also didn’t reach higher Chao and Shannon levels until 6 months after transplant.
“We also find that adjustment of periodic antibiotics for allergy or history of prior infection is significantly associated with a decrease in alpha diversity several months into the posttransplant course,” said Dr. Uhlemann. This is driven by an increase in the abundance of Enterococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae. “And when we look at MDR colonization as a predictor of alpha diversity, we see that those who have MDR colonization, irrespective of the species, also have the lower alpha diversity.”
The researchers also started to look at pretransplant alpha diversity as a predictor of transplant outcomes, and while the analysis is still in progress, the Shannon indices were significantly different between patients who died and those who survived a year. “There was a trend for significant differences for posttransplant infection and the length of the hospital stay,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “However, we did not see any association with posttransplant ICU readmission, rejection, or VRE complications.”
She added that future analyses are needed to further evaluate the interaction between the clinical comorbidities in the microbiome and vice versa.
Dr. Uhlemann disclosed links to Merck.
WASHINGTON – During and after liver transplant, the reaction of the intestinal microbiota may be a critical determinant of outcomes; preliminary data from a cohort study may provide some clarification of what modulates gut microbiota post transplantation and shed light on predictive factors.
Anna-Catrin Uhlemann, MD, PhD, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, noted that several studies in recent years sought to clarify influences on gut microbiota in people receiving liver transplants, but “there are still a number of important gaps in knowledge, including what exactly is the longitudinal evolution of the host transplant microbiome and what is the predictive value of pre- and early posttransplant dysbiosis on outcomes and complications.”
The researchers collected more than 1,000 samples to screen for colonization by the following MDR organisms: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), Enterobacteriaceae resistant to third-generation cephalosporins (ESBL), and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). Over the 1-year follow-up period, 19% (P =.031) of patients had CRE colonization associated with subsequent infection, 41% (P = .003) had ESBL colonization, and 46% (P = .021) had VRE colonization, Dr. Uhlemann said at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. The researchers then selected 484 samples for sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene to determine the composition of gut microbiota.
The study used two indexes to determine the alpha diversity of microbiota: the Chao index to estimate richness and the Shannon diversity index to determine the abundance of species in different settings. “We observed dynamic temporal evolution of alpha diversity and taxa abundance over the 1-year follow-up period,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “The diagnosis, the Child-Pugh class, and changes in perioperative antibiotics were important predictors of posttransplant alpha diversity.”
The study also found that Enterobacteriaceae and enterococci increased post transplant in general and as MDR organisms, and that a patient’s MDR status was an important modulator of the posttransplant microbiome, as was the lack of protective operational taxonomic units (OTUs).
The researchers evaluated the relative abundance of taxa and beta diversity. For example, pretransplant patients with a Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score greater than 25 showed enrichment of Enterobacteriaceae as well as different taxa of the Bacteroidiaceae, while those with MELD scores below 25 showed enrichment of Veillonellaceae. “The significance of this is not clear yet,” Dr. Uhlemann said.
Liver disease severity can also influence gut microbes. Those with Child-Pugh class C disease have the highest numbers in terms of richness and lowest in terms of diversity, Dr. Uhlemann said. “However, at the moment when we are looking at the differential abundance of the taxa, we don’t see quite as clear a pattern, although we noticed in the high group a higher abundance of Bacteroidiaceae,” she said.
Hepatitis B and C patients also presented divergent microbiota profiles. Hepatitis B virus patients “in general are always relatively healthy, and we actually see that these indices are relatively preserved,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “When we look at hepatitis C, however, we see that these patients are starting off quite low and then have an increase in alpha-diversity measures at around month 6.” A subset of patients with alcoholic liver disease also didn’t reach higher Chao and Shannon levels until 6 months after transplant.
“We also find that adjustment of periodic antibiotics for allergy or history of prior infection is significantly associated with a decrease in alpha diversity several months into the posttransplant course,” said Dr. Uhlemann. This is driven by an increase in the abundance of Enterococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae. “And when we look at MDR colonization as a predictor of alpha diversity, we see that those who have MDR colonization, irrespective of the species, also have the lower alpha diversity.”
The researchers also started to look at pretransplant alpha diversity as a predictor of transplant outcomes, and while the analysis is still in progress, the Shannon indices were significantly different between patients who died and those who survived a year. “There was a trend for significant differences for posttransplant infection and the length of the hospital stay,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “However, we did not see any association with posttransplant ICU readmission, rejection, or VRE complications.”
She added that future analyses are needed to further evaluate the interaction between the clinical comorbidities in the microbiome and vice versa.
Dr. Uhlemann disclosed links to Merck.
WASHINGTON – During and after liver transplant, the reaction of the intestinal microbiota may be a critical determinant of outcomes; preliminary data from a cohort study may provide some clarification of what modulates gut microbiota post transplantation and shed light on predictive factors.
Anna-Catrin Uhlemann, MD, PhD, of Columbia University Medical Center, New York, noted that several studies in recent years sought to clarify influences on gut microbiota in people receiving liver transplants, but “there are still a number of important gaps in knowledge, including what exactly is the longitudinal evolution of the host transplant microbiome and what is the predictive value of pre- and early posttransplant dysbiosis on outcomes and complications.”
The researchers collected more than 1,000 samples to screen for colonization by the following MDR organisms: carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE), Enterobacteriaceae resistant to third-generation cephalosporins (ESBL), and vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE). Over the 1-year follow-up period, 19% (P =.031) of patients had CRE colonization associated with subsequent infection, 41% (P = .003) had ESBL colonization, and 46% (P = .021) had VRE colonization, Dr. Uhlemann said at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. The researchers then selected 484 samples for sequencing of the 16S ribosomal RNA gene to determine the composition of gut microbiota.
The study used two indexes to determine the alpha diversity of microbiota: the Chao index to estimate richness and the Shannon diversity index to determine the abundance of species in different settings. “We observed dynamic temporal evolution of alpha diversity and taxa abundance over the 1-year follow-up period,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “The diagnosis, the Child-Pugh class, and changes in perioperative antibiotics were important predictors of posttransplant alpha diversity.”
The study also found that Enterobacteriaceae and enterococci increased post transplant in general and as MDR organisms, and that a patient’s MDR status was an important modulator of the posttransplant microbiome, as was the lack of protective operational taxonomic units (OTUs).
The researchers evaluated the relative abundance of taxa and beta diversity. For example, pretransplant patients with a Model for End-stage Liver Disease (MELD) score greater than 25 showed enrichment of Enterobacteriaceae as well as different taxa of the Bacteroidiaceae, while those with MELD scores below 25 showed enrichment of Veillonellaceae. “The significance of this is not clear yet,” Dr. Uhlemann said.
Liver disease severity can also influence gut microbes. Those with Child-Pugh class C disease have the highest numbers in terms of richness and lowest in terms of diversity, Dr. Uhlemann said. “However, at the moment when we are looking at the differential abundance of the taxa, we don’t see quite as clear a pattern, although we noticed in the high group a higher abundance of Bacteroidiaceae,” she said.
Hepatitis B and C patients also presented divergent microbiota profiles. Hepatitis B virus patients “in general are always relatively healthy, and we actually see that these indices are relatively preserved,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “When we look at hepatitis C, however, we see that these patients are starting off quite low and then have an increase in alpha-diversity measures at around month 6.” A subset of patients with alcoholic liver disease also didn’t reach higher Chao and Shannon levels until 6 months after transplant.
“We also find that adjustment of periodic antibiotics for allergy or history of prior infection is significantly associated with a decrease in alpha diversity several months into the posttransplant course,” said Dr. Uhlemann. This is driven by an increase in the abundance of Enterococcaceae and Enterobacteriaceae. “And when we look at MDR colonization as a predictor of alpha diversity, we see that those who have MDR colonization, irrespective of the species, also have the lower alpha diversity.”
The researchers also started to look at pretransplant alpha diversity as a predictor of transplant outcomes, and while the analysis is still in progress, the Shannon indices were significantly different between patients who died and those who survived a year. “There was a trend for significant differences for posttransplant infection and the length of the hospital stay,” Dr. Uhlemann said. “However, we did not see any association with posttransplant ICU readmission, rejection, or VRE complications.”
She added that future analyses are needed to further evaluate the interaction between the clinical comorbidities in the microbiome and vice versa.
Dr. Uhlemann disclosed links to Merck.
AT THE LIVER MEETING 2017
Key clinical point: The presence or lack of specific modulators of gut microbiota may influence outcomes of liver transplantation.
Major finding: Over a 1-year follow-up period, 19% of patients had colonization with carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae, 41% had Enterobacteriaceae resistant to third-generation cephalosporins, and 46% had vancomycin-resistant enterococci associated with subsequent infections.
Data source: A prospective longitudinal cohort study of 323 patients, 125 of whom completed 1 year of follow-up.
Disclosures: Dr. Uhlemann disclosed receiving research funding from Merck.
Nivolumab may extend survival in HCC patients
WASHINGTON – A multinational clinical trial has found that the metastatic cancer agent nivolumab can improve long-term survival and durable tumor responses in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) whether or not they’ve had previous treatment with a chemotherapy agent already approved for advanced primary liver cancer, a principal investigator reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Nivolumab has demonstrated clinically meaningful efficacy across etiologies in sorafenib-naive and -experienced patients with extended follow-up,” Bruno Sangro, MD, of the University of Navarra in Pamplona, Spain, said in reporting results of the CheckMate-040 trial. “The median overall survival is 15 and 15.6 months in patients who were sorafenib-experienced in both the dose-escalation and expansion cohorts.”
The dose-escalation cohort received 0.1 to 10 mg/kg of nivolumab (Opdivo) while the dose-expansion group received a steady dose of 3 mg/kg. In all, 262 patients participated in the trial, 80 of whom had never been on sorafenib (Nexavar) therapy. The survival outcome in these subgroups, Dr. Sangro said, “really speaks for the consistency and the robustness of the results.”
Trial participants had inoperable, usually metastatic HCC, with Child-Pugh scores up to and including 7 in the escalation group or up to and including 6 in the expansion group. Most of them were progressing to treatment with one or more prior systemic therapies, including sorafenib. Their aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase scores were in the upper limits of normal, and bilirubin was less than or equal to 3 mg/dL. If they had hepatitis B (HBV), their viral load had to be less than 100 IU/mL and they had to be on effective antiviral therapy. Any history of hepatic encephalopathy or clinically significant ascites and an active HBV and hepatitis C (HCV) coinfection were grounds for exclusion.
“Most patients had to discontinue nivolumab because of disease progression,” Dr. Sangro noted, so that only 36 patients, or 14%, were continuing treatment at the time of this analysis. Thirteen patients in the total population that discontinued nivolumab did so because of toxicity, he said.
“Around 20% of patients achieved an objective remission that included complete responses in all subgroups of patients; 15% of progressors and 23% of sorafenib-intolerant patients had an objective response,” Dr. Sangro said. In terms of overall response, about half of all patients in the sorafenib-experienced subgroups had a complete or partial response or stable disease: 51% in the dose-escalation subgroup and 54% in the dose-expansion subgroup.
Although tumor responses were associated with declines in alpha-fetoprotein levels, “it’s unlikely that these biomarkers will be useful either for monitoring or selecting patients for treatment,” he added. “Indeed, baseline alpha-fetoprotein levels were comparable between responders and nonresponders to nivolumab” Dr. Sangro said.
“We also showed there was some impact on HCV viral kinetics in infected individuals,” Dr. Sangro noted. “The overall safety profile for the HCC population is consistent with other tumor types in which nivolumab is approved; these include patients who are infected with hepatitis B or C viruses.”
The study showed that 36% (19/53) of HCV infected patients had a greater than 1 log decrease in viral load. No signs of additional antiviral activity were detected among HBV-infected patients already on effective antiviral treatment: only 5% (3/59) posted a up to 1 log decrease in HB surface antigen levels, and 11% (7/64) of patients had increases in viral load. “These increases occurred in the setting of low-level viremia.” Dr. Sangro said. “They were asymptomatic and [nivolumab] did not result in changes in hepatic parameters or other serious adverse events.”
With regard to adverse events (AEs), 77% of all patients had some treatment-related AEs, ranging from fatigue to rash to dry mouth to increased lab levels, but only 20% were grade 3 or 4, and 88% of those resolved in an average of 8 weeks, Dr. Sangro said.
More research into nivolumab for HCC is needed, Dr. Sangro said. “Ongoing and future studies in patients with advanced tumors will evaluate nivolumab in the first-line setting or in combination with other agents,” he said.
Dr. Sangro disclosed relationships with Bayer Schering Pharma, Onxeo, Astra Zeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bristol-Myers Squibb funded the trial, and Chrysalis Medical Communications assisted in reporting the study results.
WASHINGTON – A multinational clinical trial has found that the metastatic cancer agent nivolumab can improve long-term survival and durable tumor responses in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) whether or not they’ve had previous treatment with a chemotherapy agent already approved for advanced primary liver cancer, a principal investigator reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Nivolumab has demonstrated clinically meaningful efficacy across etiologies in sorafenib-naive and -experienced patients with extended follow-up,” Bruno Sangro, MD, of the University of Navarra in Pamplona, Spain, said in reporting results of the CheckMate-040 trial. “The median overall survival is 15 and 15.6 months in patients who were sorafenib-experienced in both the dose-escalation and expansion cohorts.”
The dose-escalation cohort received 0.1 to 10 mg/kg of nivolumab (Opdivo) while the dose-expansion group received a steady dose of 3 mg/kg. In all, 262 patients participated in the trial, 80 of whom had never been on sorafenib (Nexavar) therapy. The survival outcome in these subgroups, Dr. Sangro said, “really speaks for the consistency and the robustness of the results.”
Trial participants had inoperable, usually metastatic HCC, with Child-Pugh scores up to and including 7 in the escalation group or up to and including 6 in the expansion group. Most of them were progressing to treatment with one or more prior systemic therapies, including sorafenib. Their aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase scores were in the upper limits of normal, and bilirubin was less than or equal to 3 mg/dL. If they had hepatitis B (HBV), their viral load had to be less than 100 IU/mL and they had to be on effective antiviral therapy. Any history of hepatic encephalopathy or clinically significant ascites and an active HBV and hepatitis C (HCV) coinfection were grounds for exclusion.
“Most patients had to discontinue nivolumab because of disease progression,” Dr. Sangro noted, so that only 36 patients, or 14%, were continuing treatment at the time of this analysis. Thirteen patients in the total population that discontinued nivolumab did so because of toxicity, he said.
“Around 20% of patients achieved an objective remission that included complete responses in all subgroups of patients; 15% of progressors and 23% of sorafenib-intolerant patients had an objective response,” Dr. Sangro said. In terms of overall response, about half of all patients in the sorafenib-experienced subgroups had a complete or partial response or stable disease: 51% in the dose-escalation subgroup and 54% in the dose-expansion subgroup.
Although tumor responses were associated with declines in alpha-fetoprotein levels, “it’s unlikely that these biomarkers will be useful either for monitoring or selecting patients for treatment,” he added. “Indeed, baseline alpha-fetoprotein levels were comparable between responders and nonresponders to nivolumab” Dr. Sangro said.
“We also showed there was some impact on HCV viral kinetics in infected individuals,” Dr. Sangro noted. “The overall safety profile for the HCC population is consistent with other tumor types in which nivolumab is approved; these include patients who are infected with hepatitis B or C viruses.”
The study showed that 36% (19/53) of HCV infected patients had a greater than 1 log decrease in viral load. No signs of additional antiviral activity were detected among HBV-infected patients already on effective antiviral treatment: only 5% (3/59) posted a up to 1 log decrease in HB surface antigen levels, and 11% (7/64) of patients had increases in viral load. “These increases occurred in the setting of low-level viremia.” Dr. Sangro said. “They were asymptomatic and [nivolumab] did not result in changes in hepatic parameters or other serious adverse events.”
With regard to adverse events (AEs), 77% of all patients had some treatment-related AEs, ranging from fatigue to rash to dry mouth to increased lab levels, but only 20% were grade 3 or 4, and 88% of those resolved in an average of 8 weeks, Dr. Sangro said.
More research into nivolumab for HCC is needed, Dr. Sangro said. “Ongoing and future studies in patients with advanced tumors will evaluate nivolumab in the first-line setting or in combination with other agents,” he said.
Dr. Sangro disclosed relationships with Bayer Schering Pharma, Onxeo, Astra Zeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bristol-Myers Squibb funded the trial, and Chrysalis Medical Communications assisted in reporting the study results.
WASHINGTON – A multinational clinical trial has found that the metastatic cancer agent nivolumab can improve long-term survival and durable tumor responses in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) whether or not they’ve had previous treatment with a chemotherapy agent already approved for advanced primary liver cancer, a principal investigator reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“Nivolumab has demonstrated clinically meaningful efficacy across etiologies in sorafenib-naive and -experienced patients with extended follow-up,” Bruno Sangro, MD, of the University of Navarra in Pamplona, Spain, said in reporting results of the CheckMate-040 trial. “The median overall survival is 15 and 15.6 months in patients who were sorafenib-experienced in both the dose-escalation and expansion cohorts.”
The dose-escalation cohort received 0.1 to 10 mg/kg of nivolumab (Opdivo) while the dose-expansion group received a steady dose of 3 mg/kg. In all, 262 patients participated in the trial, 80 of whom had never been on sorafenib (Nexavar) therapy. The survival outcome in these subgroups, Dr. Sangro said, “really speaks for the consistency and the robustness of the results.”
Trial participants had inoperable, usually metastatic HCC, with Child-Pugh scores up to and including 7 in the escalation group or up to and including 6 in the expansion group. Most of them were progressing to treatment with one or more prior systemic therapies, including sorafenib. Their aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase scores were in the upper limits of normal, and bilirubin was less than or equal to 3 mg/dL. If they had hepatitis B (HBV), their viral load had to be less than 100 IU/mL and they had to be on effective antiviral therapy. Any history of hepatic encephalopathy or clinically significant ascites and an active HBV and hepatitis C (HCV) coinfection were grounds for exclusion.
“Most patients had to discontinue nivolumab because of disease progression,” Dr. Sangro noted, so that only 36 patients, or 14%, were continuing treatment at the time of this analysis. Thirteen patients in the total population that discontinued nivolumab did so because of toxicity, he said.
“Around 20% of patients achieved an objective remission that included complete responses in all subgroups of patients; 15% of progressors and 23% of sorafenib-intolerant patients had an objective response,” Dr. Sangro said. In terms of overall response, about half of all patients in the sorafenib-experienced subgroups had a complete or partial response or stable disease: 51% in the dose-escalation subgroup and 54% in the dose-expansion subgroup.
Although tumor responses were associated with declines in alpha-fetoprotein levels, “it’s unlikely that these biomarkers will be useful either for monitoring or selecting patients for treatment,” he added. “Indeed, baseline alpha-fetoprotein levels were comparable between responders and nonresponders to nivolumab” Dr. Sangro said.
“We also showed there was some impact on HCV viral kinetics in infected individuals,” Dr. Sangro noted. “The overall safety profile for the HCC population is consistent with other tumor types in which nivolumab is approved; these include patients who are infected with hepatitis B or C viruses.”
The study showed that 36% (19/53) of HCV infected patients had a greater than 1 log decrease in viral load. No signs of additional antiviral activity were detected among HBV-infected patients already on effective antiviral treatment: only 5% (3/59) posted a up to 1 log decrease in HB surface antigen levels, and 11% (7/64) of patients had increases in viral load. “These increases occurred in the setting of low-level viremia.” Dr. Sangro said. “They were asymptomatic and [nivolumab] did not result in changes in hepatic parameters or other serious adverse events.”
With regard to adverse events (AEs), 77% of all patients had some treatment-related AEs, ranging from fatigue to rash to dry mouth to increased lab levels, but only 20% were grade 3 or 4, and 88% of those resolved in an average of 8 weeks, Dr. Sangro said.
More research into nivolumab for HCC is needed, Dr. Sangro said. “Ongoing and future studies in patients with advanced tumors will evaluate nivolumab in the first-line setting or in combination with other agents,” he said.
Dr. Sangro disclosed relationships with Bayer Schering Pharma, Onxeo, Astra Zeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bristol-Myers Squibb funded the trial, and Chrysalis Medical Communications assisted in reporting the study results.
AT THE LIVER MEETING 2017
Key clinical point: Nivolumab demonstrated long-term survival, durable tumor responses, and manageable overall and hepatic safety profiles, regardless of prior sorafenib treatment, in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma.
Major finding: The 18-month overall survival rate was 57% in sorafenib-naive patients and 46% (dose-escalation) and 44% (dose-expansion) in sorafenib-experienced patients.
Data source: CheckMate-040 phase 1/2 dose-escalation and -expansion trial of 262 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Sangro disclosed relationships with Bayer Schering Pharma, Onxeo, Astra Zeneca, and Bristol-Myers Squibb. Bristol-Myers Squibb funded the trial, and Chrysalis Medical Communications assisted in reporting the study results.
Emerging oral agent reduces ALT in NAFLD
WASHINGTON – Limited treatment options for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mean that NASH is the fastest-growing reason for liver transplants in the United States, but preclinical and, now, phase 2 clinical results have shown that treatment with 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid, otherwise known as norUDCA, can improve steatosis and liver stiffness in selected patients, a principal investigator in a European study of the treatment reported at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“The norUDCA dose of 1,500 mg resulted in significant reduction of ALT [alanine aminotransferase] within 12 weeks,” said Michael Trauner, MD, head of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Medical University of Vienna, a coinventor of the drug. “The results are supported by improvement in liver stiffness and steatosis in the subsets analyzed.”
The 1,500-mg group had an average reduction in ALT of 17.4% whereas those in the 500-mg group only had a 4.2% reduction and placebo actually had an increase of 10.4%. “The reduction of the 500-mg dose was not significant,” Dr. Trauner said. “And this was emphasized in the proportion of patients reaching ALT less than 0.8 x ULN (upper limits of normal) at the end of treatment, with about 17% of patients reaching this endpoint in the higher dose group.” Among patients in the 500-mg group, 15% achieved that level, as did 5% in the placebo group.
The therapy also had an effect on lipid levels, Dr. Trauner noted. “Surprisingly, we saw a slight increase in LDL levels, with the highest in the 1,500-mg dose,” he said. “There were no significant changes in triglycerides and HDL levels, although there were some trends for reduced triglycerides and increased HDL.” Triglycerides decreased 14.6 mg/dL on average and HDL increased 2.8 mg/dL. The slight rise in LDL, 14.6 mg/dL on average, occurred in the first 2 weeks of treatment and continued through the treatment period, but then receded after discontinuation of therapy, said Dr. Trauner. “Please note that HDL cholesterol also increased in time, and the HDL-LDL ratio remained unchanged in these patients,” he added.
During the discussion, Dr. Trauner offered a possible explanation for the change in lipid levels. “One possibility could be that a slight repression of endogenous bile acid biosynthesis and subsequent upregulation of the LDL receptor,” he said, “but the changes are really very mild and subtle.”
He also noted that liver stiffness improved in a higher proportion of patients in the treatment groups than in the placebo group – 25% and 21% of patients in the 1,500- and 500-mg groups vs. 9% under placebo. Hepatic fat fraction values also improved from 21.3% to 16.3% (relative reduction of 23.5%) from baseline to end of treatment in the 1,500-mg group in a subset of patients undergoing more extensive MRI and spectroscopy studies – a degree of reduction that other studies have shown to be predictive of histologic improvement, Dr. Trauner said. Patients in this exploratory study did not have liver biopsies.
Overall, the drug was well tolerated, Dr. Trauner said. “There were slightly higher potentially adverse drug reactions in the 1,500-mg group, mainly due to higher rate of headache, nausea, and rash,” he said. Based on these results, a phase 2b study with histologic endpoints is underway, he added.
Dr. Trauner disclosed relationships with Gilead, Albireo, Takeda, Falk Pharma, Genfit, Intercept, MSD, Novartis, Roche, and Phenex.
WASHINGTON – Limited treatment options for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mean that NASH is the fastest-growing reason for liver transplants in the United States, but preclinical and, now, phase 2 clinical results have shown that treatment with 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid, otherwise known as norUDCA, can improve steatosis and liver stiffness in selected patients, a principal investigator in a European study of the treatment reported at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“The norUDCA dose of 1,500 mg resulted in significant reduction of ALT [alanine aminotransferase] within 12 weeks,” said Michael Trauner, MD, head of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Medical University of Vienna, a coinventor of the drug. “The results are supported by improvement in liver stiffness and steatosis in the subsets analyzed.”
The 1,500-mg group had an average reduction in ALT of 17.4% whereas those in the 500-mg group only had a 4.2% reduction and placebo actually had an increase of 10.4%. “The reduction of the 500-mg dose was not significant,” Dr. Trauner said. “And this was emphasized in the proportion of patients reaching ALT less than 0.8 x ULN (upper limits of normal) at the end of treatment, with about 17% of patients reaching this endpoint in the higher dose group.” Among patients in the 500-mg group, 15% achieved that level, as did 5% in the placebo group.
The therapy also had an effect on lipid levels, Dr. Trauner noted. “Surprisingly, we saw a slight increase in LDL levels, with the highest in the 1,500-mg dose,” he said. “There were no significant changes in triglycerides and HDL levels, although there were some trends for reduced triglycerides and increased HDL.” Triglycerides decreased 14.6 mg/dL on average and HDL increased 2.8 mg/dL. The slight rise in LDL, 14.6 mg/dL on average, occurred in the first 2 weeks of treatment and continued through the treatment period, but then receded after discontinuation of therapy, said Dr. Trauner. “Please note that HDL cholesterol also increased in time, and the HDL-LDL ratio remained unchanged in these patients,” he added.
During the discussion, Dr. Trauner offered a possible explanation for the change in lipid levels. “One possibility could be that a slight repression of endogenous bile acid biosynthesis and subsequent upregulation of the LDL receptor,” he said, “but the changes are really very mild and subtle.”
He also noted that liver stiffness improved in a higher proportion of patients in the treatment groups than in the placebo group – 25% and 21% of patients in the 1,500- and 500-mg groups vs. 9% under placebo. Hepatic fat fraction values also improved from 21.3% to 16.3% (relative reduction of 23.5%) from baseline to end of treatment in the 1,500-mg group in a subset of patients undergoing more extensive MRI and spectroscopy studies – a degree of reduction that other studies have shown to be predictive of histologic improvement, Dr. Trauner said. Patients in this exploratory study did not have liver biopsies.
Overall, the drug was well tolerated, Dr. Trauner said. “There were slightly higher potentially adverse drug reactions in the 1,500-mg group, mainly due to higher rate of headache, nausea, and rash,” he said. Based on these results, a phase 2b study with histologic endpoints is underway, he added.
Dr. Trauner disclosed relationships with Gilead, Albireo, Takeda, Falk Pharma, Genfit, Intercept, MSD, Novartis, Roche, and Phenex.
WASHINGTON – Limited treatment options for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease mean that NASH is the fastest-growing reason for liver transplants in the United States, but preclinical and, now, phase 2 clinical results have shown that treatment with 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid, otherwise known as norUDCA, can improve steatosis and liver stiffness in selected patients, a principal investigator in a European study of the treatment reported at the 2017 annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“The norUDCA dose of 1,500 mg resulted in significant reduction of ALT [alanine aminotransferase] within 12 weeks,” said Michael Trauner, MD, head of the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Medical University of Vienna, a coinventor of the drug. “The results are supported by improvement in liver stiffness and steatosis in the subsets analyzed.”
The 1,500-mg group had an average reduction in ALT of 17.4% whereas those in the 500-mg group only had a 4.2% reduction and placebo actually had an increase of 10.4%. “The reduction of the 500-mg dose was not significant,” Dr. Trauner said. “And this was emphasized in the proportion of patients reaching ALT less than 0.8 x ULN (upper limits of normal) at the end of treatment, with about 17% of patients reaching this endpoint in the higher dose group.” Among patients in the 500-mg group, 15% achieved that level, as did 5% in the placebo group.
The therapy also had an effect on lipid levels, Dr. Trauner noted. “Surprisingly, we saw a slight increase in LDL levels, with the highest in the 1,500-mg dose,” he said. “There were no significant changes in triglycerides and HDL levels, although there were some trends for reduced triglycerides and increased HDL.” Triglycerides decreased 14.6 mg/dL on average and HDL increased 2.8 mg/dL. The slight rise in LDL, 14.6 mg/dL on average, occurred in the first 2 weeks of treatment and continued through the treatment period, but then receded after discontinuation of therapy, said Dr. Trauner. “Please note that HDL cholesterol also increased in time, and the HDL-LDL ratio remained unchanged in these patients,” he added.
During the discussion, Dr. Trauner offered a possible explanation for the change in lipid levels. “One possibility could be that a slight repression of endogenous bile acid biosynthesis and subsequent upregulation of the LDL receptor,” he said, “but the changes are really very mild and subtle.”
He also noted that liver stiffness improved in a higher proportion of patients in the treatment groups than in the placebo group – 25% and 21% of patients in the 1,500- and 500-mg groups vs. 9% under placebo. Hepatic fat fraction values also improved from 21.3% to 16.3% (relative reduction of 23.5%) from baseline to end of treatment in the 1,500-mg group in a subset of patients undergoing more extensive MRI and spectroscopy studies – a degree of reduction that other studies have shown to be predictive of histologic improvement, Dr. Trauner said. Patients in this exploratory study did not have liver biopsies.
Overall, the drug was well tolerated, Dr. Trauner said. “There were slightly higher potentially adverse drug reactions in the 1,500-mg group, mainly due to higher rate of headache, nausea, and rash,” he said. Based on these results, a phase 2b study with histologic endpoints is underway, he added.
Dr. Trauner disclosed relationships with Gilead, Albireo, Takeda, Falk Pharma, Genfit, Intercept, MSD, Novartis, Roche, and Phenex.
AT THE LIVER MEETING 2017
Key clinical point: Treatment with oral 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid (norUDCA) resulted in a significant reduction of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Major finding: Mean value of hepatic fat fraction decreased 23.5% in a subset of patients treated with 1,500 mg norUDCA.
Data source: Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept phase 2 dose-finding study of 198 patients receiving treatment over 12 weeks.
Disclosures: Dr. Trauner disclosed relationships with Gilead, Albireo, Takeda, Falk Pharma, Genfit, Intercept, MSD, Novartis, Roche, and Phenex, and is listed as a coinventor on patents filed for the medical use of 24-nor-ursodeoxycholic acid.
Novel metabolite may be key in NAFLD
WASHINGTON – A newly identified metabolite of the gut microbiome may be a potentially useful biomarker in determining the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and may provide a new treatment target, according to results of an analysis of serum metabolites isolated from 100 pairs of twins presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The researchers at the NAFLD Research Center at the University of California at San Diego isolated a metabolite derived from the gut microbiome, known as 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate, from 713 serum metabolites they analyzed, 440 of which were identified as heritable, said Cyrielle Caussy, MD, PhD. The researchers further winnowed that pool down to 94 associated with fibrosis alone and 170 associated with hepatic steatosis alone, 56 of which overlapped to have a shared gene effect with both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, six of which derived from the gut microbiome.
Of the four heritable serum metabolites the researchers found to be significantly associated with NAFLD after adjustment for age, sex and Hispanic ethnicity, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate had the highest odds ratio (95% confidence interval): 4.29 (1.87-9.81, P = .0006) vs. phenyllactate (OR 2.12, 1.09-4.10, P = .0258), palmitic acid (2.58, 1.31-5.17, P = .0065) and gamma-glutamylisoleucine (2.98, 1.36-6.51, P = .0062).
Dr. Caussy noted that previous studies have found a strong correlation between bacterial species in the gut and advanced fibrosis in NAFLD (Cell Metab. 2017;25:1054-62). This latest research takes those findings to the next level, Dr. Caussy said. “This metabolite could be a useful biomarker of the severity of NAFLD and may be a target for future treatment of NAFLD and could be used to monitor a treatment response,” she added.
The goal of the study was to determine if any serum metabolites have a shared genetic effect with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, Dr. Caussy said. “The heritability of serum metabolites associated with NAFLD and their shared gene effect with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis have not been assessed yet,” she noted. The researchers isolated the serum metabolites from a cohort of 100 pairs of twins and 56 other relatives in the Southern California Twins Register, and validated the data in a cohort of 156 patients who had biopsy-proven NAFLD.
Dr. Caussy reported having no financial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – A newly identified metabolite of the gut microbiome may be a potentially useful biomarker in determining the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and may provide a new treatment target, according to results of an analysis of serum metabolites isolated from 100 pairs of twins presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The researchers at the NAFLD Research Center at the University of California at San Diego isolated a metabolite derived from the gut microbiome, known as 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate, from 713 serum metabolites they analyzed, 440 of which were identified as heritable, said Cyrielle Caussy, MD, PhD. The researchers further winnowed that pool down to 94 associated with fibrosis alone and 170 associated with hepatic steatosis alone, 56 of which overlapped to have a shared gene effect with both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, six of which derived from the gut microbiome.
Of the four heritable serum metabolites the researchers found to be significantly associated with NAFLD after adjustment for age, sex and Hispanic ethnicity, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate had the highest odds ratio (95% confidence interval): 4.29 (1.87-9.81, P = .0006) vs. phenyllactate (OR 2.12, 1.09-4.10, P = .0258), palmitic acid (2.58, 1.31-5.17, P = .0065) and gamma-glutamylisoleucine (2.98, 1.36-6.51, P = .0062).
Dr. Caussy noted that previous studies have found a strong correlation between bacterial species in the gut and advanced fibrosis in NAFLD (Cell Metab. 2017;25:1054-62). This latest research takes those findings to the next level, Dr. Caussy said. “This metabolite could be a useful biomarker of the severity of NAFLD and may be a target for future treatment of NAFLD and could be used to monitor a treatment response,” she added.
The goal of the study was to determine if any serum metabolites have a shared genetic effect with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, Dr. Caussy said. “The heritability of serum metabolites associated with NAFLD and their shared gene effect with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis have not been assessed yet,” she noted. The researchers isolated the serum metabolites from a cohort of 100 pairs of twins and 56 other relatives in the Southern California Twins Register, and validated the data in a cohort of 156 patients who had biopsy-proven NAFLD.
Dr. Caussy reported having no financial disclosures.
WASHINGTON – A newly identified metabolite of the gut microbiome may be a potentially useful biomarker in determining the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and may provide a new treatment target, according to results of an analysis of serum metabolites isolated from 100 pairs of twins presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The researchers at the NAFLD Research Center at the University of California at San Diego isolated a metabolite derived from the gut microbiome, known as 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate, from 713 serum metabolites they analyzed, 440 of which were identified as heritable, said Cyrielle Caussy, MD, PhD. The researchers further winnowed that pool down to 94 associated with fibrosis alone and 170 associated with hepatic steatosis alone, 56 of which overlapped to have a shared gene effect with both hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, six of which derived from the gut microbiome.
Of the four heritable serum metabolites the researchers found to be significantly associated with NAFLD after adjustment for age, sex and Hispanic ethnicity, 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate had the highest odds ratio (95% confidence interval): 4.29 (1.87-9.81, P = .0006) vs. phenyllactate (OR 2.12, 1.09-4.10, P = .0258), palmitic acid (2.58, 1.31-5.17, P = .0065) and gamma-glutamylisoleucine (2.98, 1.36-6.51, P = .0062).
Dr. Caussy noted that previous studies have found a strong correlation between bacterial species in the gut and advanced fibrosis in NAFLD (Cell Metab. 2017;25:1054-62). This latest research takes those findings to the next level, Dr. Caussy said. “This metabolite could be a useful biomarker of the severity of NAFLD and may be a target for future treatment of NAFLD and could be used to monitor a treatment response,” she added.
The goal of the study was to determine if any serum metabolites have a shared genetic effect with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis, Dr. Caussy said. “The heritability of serum metabolites associated with NAFLD and their shared gene effect with hepatic steatosis and fibrosis have not been assessed yet,” she noted. The researchers isolated the serum metabolites from a cohort of 100 pairs of twins and 56 other relatives in the Southern California Twins Register, and validated the data in a cohort of 156 patients who had biopsy-proven NAFLD.
Dr. Caussy reported having no financial disclosures.
AT THE LIVER MEETING 2017
Key clinical point: Researchers have identified a novel serum metabolite that may be the key to linking the role of the gut microbiome with the presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)–related fibrosis.
Major finding: An analysis of 713 serum metabolites identified a novel, gut microbiome–derived serum metabolite known as 3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)lactate that had an odds ratio of 4.29 for NAFLD.
Data source: Cross-sectional analysis of a prospective cohort of 156 subjects in the Southern California Twin Study Cohort.
Disclosures: Dr. Caussy reported having no financial disclosures.
Hispanics bear brunt of NAFLD disease burden
WASHINGTON — Significant racial and ethnic disparities exist in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence and severity in the United States, with Hispanics at highest risk and blacks at the lowest, but the risk of death from NAFLD is highest in whites, according to a meta-analysis of 34 studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The findings are based on a meta-analysis of studies in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases from inception through August 2016 that included 368,569 unique patients that characterized disparities in NAFLD prevalence, severity, or prognosis, Dr. Rich said.
When the researchers drilled down into the data, they found the disparities dissipated somewhat. “When we looked at the severity of NAFLD we looked at two things: whether there was NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) present, or if there was the presence of advanced fibrosis,” Dr. Rich said. “We found there was no significant difference in the risk of NASH in Hispanic patients, compared to white patients; however, the proportion of Hispanic NAFLD patients that had NASH was 45.4%, compared to 32.2% in whites.” The pooled relative risk was 1.09.
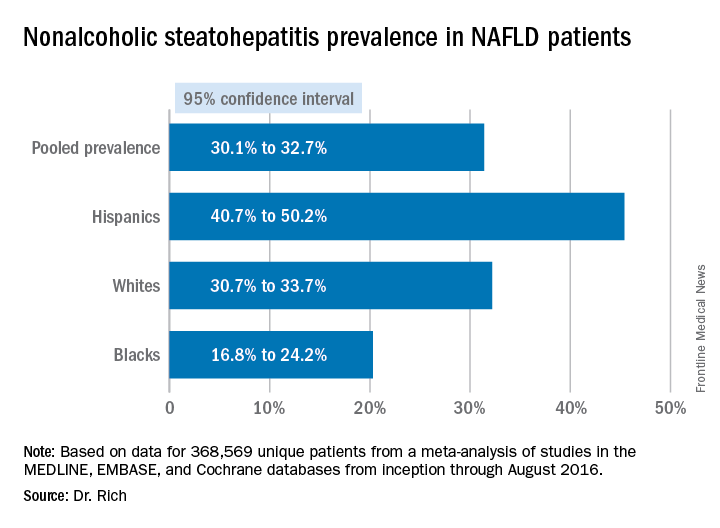
The meta-analysis tended to attenuate the disparities found in disease severity, compared with the disparities the researchers found in prevalence, Dr. Rich said. “Data are limited and discordant on racial and ethnic differences in NAFLD prognosis and outcomes,” she said. “In the current literature the studies have notable limitations, highlighting the need for future high-quality data in this area, and further studies are needed to determine the need and pathways to reduce NAFLD disparities in the future,” she said.
Dr. Rich had no financial relationships to disclose.
WASHINGTON — Significant racial and ethnic disparities exist in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence and severity in the United States, with Hispanics at highest risk and blacks at the lowest, but the risk of death from NAFLD is highest in whites, according to a meta-analysis of 34 studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The findings are based on a meta-analysis of studies in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases from inception through August 2016 that included 368,569 unique patients that characterized disparities in NAFLD prevalence, severity, or prognosis, Dr. Rich said.
When the researchers drilled down into the data, they found the disparities dissipated somewhat. “When we looked at the severity of NAFLD we looked at two things: whether there was NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) present, or if there was the presence of advanced fibrosis,” Dr. Rich said. “We found there was no significant difference in the risk of NASH in Hispanic patients, compared to white patients; however, the proportion of Hispanic NAFLD patients that had NASH was 45.4%, compared to 32.2% in whites.” The pooled relative risk was 1.09.

The meta-analysis tended to attenuate the disparities found in disease severity, compared with the disparities the researchers found in prevalence, Dr. Rich said. “Data are limited and discordant on racial and ethnic differences in NAFLD prognosis and outcomes,” she said. “In the current literature the studies have notable limitations, highlighting the need for future high-quality data in this area, and further studies are needed to determine the need and pathways to reduce NAFLD disparities in the future,” she said.
Dr. Rich had no financial relationships to disclose.
WASHINGTON — Significant racial and ethnic disparities exist in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease prevalence and severity in the United States, with Hispanics at highest risk and blacks at the lowest, but the risk of death from NAFLD is highest in whites, according to a meta-analysis of 34 studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
The findings are based on a meta-analysis of studies in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases from inception through August 2016 that included 368,569 unique patients that characterized disparities in NAFLD prevalence, severity, or prognosis, Dr. Rich said.
When the researchers drilled down into the data, they found the disparities dissipated somewhat. “When we looked at the severity of NAFLD we looked at two things: whether there was NASH (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis) present, or if there was the presence of advanced fibrosis,” Dr. Rich said. “We found there was no significant difference in the risk of NASH in Hispanic patients, compared to white patients; however, the proportion of Hispanic NAFLD patients that had NASH was 45.4%, compared to 32.2% in whites.” The pooled relative risk was 1.09.

The meta-analysis tended to attenuate the disparities found in disease severity, compared with the disparities the researchers found in prevalence, Dr. Rich said. “Data are limited and discordant on racial and ethnic differences in NAFLD prognosis and outcomes,” she said. “In the current literature the studies have notable limitations, highlighting the need for future high-quality data in this area, and further studies are needed to determine the need and pathways to reduce NAFLD disparities in the future,” she said.
Dr. Rich had no financial relationships to disclose.
AT THE LIVER MEETING 2017
Key clinical point: Hispanics have a much higher incidence of fatty liver disease than other ethnic groups.
Major finding: NAFLD prevalence is highest in Hispanics and lower in blacks, compared with whites, although differences between groups are smaller in high-risk cohorts (range, 47.6%-55.5%) than in population-based cohorts (range, 13.0%-22.9%).
Data source: Meta-analysis of 34 studies in the MEDLINE, EMBASE, and Cochrane databases from inception through August 2016 that involved 368,569 patients.
Disclosures: Dr. Rich had no financial relationships to disclose.
Why VADS is gaining ground in pediatrics
The miniaturization of continuous-flow ventricular assist devices has launched the era of continuous-flow VAD support in pediatric patients, and the trend may accelerate with the introduction of a continuous-flow device designed specifically for small children. In an expert opinion in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Iki Adachi, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, said the emerging science of continuous-flow VADs in children promises to solve problems like device size mismatch, hospital-only VADs, and chronic therapy (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 Oct;154:1358-61). “With ongoing device miniaturization, enthusiasm has been growing among pediatric physicians for the use of continuous-flow VADs in children,” Dr. Adachi said. He noted the introduction of a continuous-flow device for small children, the Infant Jarvik 2015, “may further accelerate the trend.”
Dr. Adachi cited PediMACS reports that stated that more than half of the long-term devices now registered are continuous-flow devices, and that continuous-flow VADs comprised 62% of all durable VAD implants in the third quarter of 2016. “With the encouraging results recorded to date, the use of continuous-flow devices in the pediatric population is rapidly increasing,” he said.
Miniaturization has addressed the problem of size mismatch when using continuous-flow VAD devices in children, he said, noting that use of the Infant Jarvik device may be expanded even further to children as small at 8 kg or less. The PumpKIN trial(Pumps for Kids, Infants, and Neonates), which is evaluating the Infant Jarvik 2015 vs. the Berlin Heart EXCOR, could provide answers on the feasibility of continuous-flow VADs in small children.
“Based on experience with the chronic animal model, I believe that the Infant Jarvik device will properly fit the patients included in the trial,” he said.
Continuous-flow VAD in children also holds potential for managing these patients outside the hospital setting. “Outpatient management of children with continuous-flow VADs has been shown to be feasible,” he said, adding that the PediMACS registry has reported that only 45% of patients have been managed this way. “Nonetheless, with maturation of the pediatric field, outpatient management will become routine rather than the exception,” he said.
Greater use of continuous-flow VADs also may create opportunities to improve the status and suitability for transplantation of children with severe heart failure, he said. He gave as an example his group’s practice at Houston’s Texas Children’s Hospital, which is to deactivate patients on the transplant wait list for 3 months once they start continuous-flow VAD support. “A postoperative ‘grace period’ affords protected opportunities for both physical and psychological recovery,” he said. This timeout of sorts also affords the care team time to assess the myocardium for possible functional recovery.
In patients who are not good candidates for transplantation, durable continuous-flow VADs may provide chronic therapy, and in time, these patients may become suitable transplant candidates, said Dr. Adachi. “Bypassing such an unfavorable period for transplantation with prolonged VAD support may be a reasonable approach,” he said.
Patients with failing single-ventricle circulation also may benefit from VAD support, although the challenges facing this population are more profound than in other groups, Dr. Adachi said. VAD support for single-ventricle disease is sparse, but these patients require careful evaluation of the nature of their condition. “If systolic dysfunction is the predominant cause of circulatory failure, then VAD support for the failing systemic ventricle will likely improve hemodynamics,” said Dr. Adachi. VAD support also could help the patient move through the various stages of palliation.
“Again, the emphasis is not just on simply keeping the patient alive until a donor organ becomes available; rather, attention is refocused on overall health beyond survival, which may eventually affect transplantation candidacy and even post transplantation outcome,” Dr. Adachi concluded.
Dr. Adachi serves as a consultant and proctor for Berlin Heart and HeartWare, and as a consultant for the New England Research Institute related to the PumpKIN trial.
The miniaturization of continuous-flow ventricular assist devices has launched the era of continuous-flow VAD support in pediatric patients, and the trend may accelerate with the introduction of a continuous-flow device designed specifically for small children. In an expert opinion in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Iki Adachi, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, said the emerging science of continuous-flow VADs in children promises to solve problems like device size mismatch, hospital-only VADs, and chronic therapy (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 Oct;154:1358-61). “With ongoing device miniaturization, enthusiasm has been growing among pediatric physicians for the use of continuous-flow VADs in children,” Dr. Adachi said. He noted the introduction of a continuous-flow device for small children, the Infant Jarvik 2015, “may further accelerate the trend.”
Dr. Adachi cited PediMACS reports that stated that more than half of the long-term devices now registered are continuous-flow devices, and that continuous-flow VADs comprised 62% of all durable VAD implants in the third quarter of 2016. “With the encouraging results recorded to date, the use of continuous-flow devices in the pediatric population is rapidly increasing,” he said.
Miniaturization has addressed the problem of size mismatch when using continuous-flow VAD devices in children, he said, noting that use of the Infant Jarvik device may be expanded even further to children as small at 8 kg or less. The PumpKIN trial(Pumps for Kids, Infants, and Neonates), which is evaluating the Infant Jarvik 2015 vs. the Berlin Heart EXCOR, could provide answers on the feasibility of continuous-flow VADs in small children.
“Based on experience with the chronic animal model, I believe that the Infant Jarvik device will properly fit the patients included in the trial,” he said.
Continuous-flow VAD in children also holds potential for managing these patients outside the hospital setting. “Outpatient management of children with continuous-flow VADs has been shown to be feasible,” he said, adding that the PediMACS registry has reported that only 45% of patients have been managed this way. “Nonetheless, with maturation of the pediatric field, outpatient management will become routine rather than the exception,” he said.
Greater use of continuous-flow VADs also may create opportunities to improve the status and suitability for transplantation of children with severe heart failure, he said. He gave as an example his group’s practice at Houston’s Texas Children’s Hospital, which is to deactivate patients on the transplant wait list for 3 months once they start continuous-flow VAD support. “A postoperative ‘grace period’ affords protected opportunities for both physical and psychological recovery,” he said. This timeout of sorts also affords the care team time to assess the myocardium for possible functional recovery.
In patients who are not good candidates for transplantation, durable continuous-flow VADs may provide chronic therapy, and in time, these patients may become suitable transplant candidates, said Dr. Adachi. “Bypassing such an unfavorable period for transplantation with prolonged VAD support may be a reasonable approach,” he said.
Patients with failing single-ventricle circulation also may benefit from VAD support, although the challenges facing this population are more profound than in other groups, Dr. Adachi said. VAD support for single-ventricle disease is sparse, but these patients require careful evaluation of the nature of their condition. “If systolic dysfunction is the predominant cause of circulatory failure, then VAD support for the failing systemic ventricle will likely improve hemodynamics,” said Dr. Adachi. VAD support also could help the patient move through the various stages of palliation.
“Again, the emphasis is not just on simply keeping the patient alive until a donor organ becomes available; rather, attention is refocused on overall health beyond survival, which may eventually affect transplantation candidacy and even post transplantation outcome,” Dr. Adachi concluded.
Dr. Adachi serves as a consultant and proctor for Berlin Heart and HeartWare, and as a consultant for the New England Research Institute related to the PumpKIN trial.
The miniaturization of continuous-flow ventricular assist devices has launched the era of continuous-flow VAD support in pediatric patients, and the trend may accelerate with the introduction of a continuous-flow device designed specifically for small children. In an expert opinion in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Iki Adachi, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine in Houston, said the emerging science of continuous-flow VADs in children promises to solve problems like device size mismatch, hospital-only VADs, and chronic therapy (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017 Oct;154:1358-61). “With ongoing device miniaturization, enthusiasm has been growing among pediatric physicians for the use of continuous-flow VADs in children,” Dr. Adachi said. He noted the introduction of a continuous-flow device for small children, the Infant Jarvik 2015, “may further accelerate the trend.”
Dr. Adachi cited PediMACS reports that stated that more than half of the long-term devices now registered are continuous-flow devices, and that continuous-flow VADs comprised 62% of all durable VAD implants in the third quarter of 2016. “With the encouraging results recorded to date, the use of continuous-flow devices in the pediatric population is rapidly increasing,” he said.
Miniaturization has addressed the problem of size mismatch when using continuous-flow VAD devices in children, he said, noting that use of the Infant Jarvik device may be expanded even further to children as small at 8 kg or less. The PumpKIN trial(Pumps for Kids, Infants, and Neonates), which is evaluating the Infant Jarvik 2015 vs. the Berlin Heart EXCOR, could provide answers on the feasibility of continuous-flow VADs in small children.
“Based on experience with the chronic animal model, I believe that the Infant Jarvik device will properly fit the patients included in the trial,” he said.
Continuous-flow VAD in children also holds potential for managing these patients outside the hospital setting. “Outpatient management of children with continuous-flow VADs has been shown to be feasible,” he said, adding that the PediMACS registry has reported that only 45% of patients have been managed this way. “Nonetheless, with maturation of the pediatric field, outpatient management will become routine rather than the exception,” he said.
Greater use of continuous-flow VADs also may create opportunities to improve the status and suitability for transplantation of children with severe heart failure, he said. He gave as an example his group’s practice at Houston’s Texas Children’s Hospital, which is to deactivate patients on the transplant wait list for 3 months once they start continuous-flow VAD support. “A postoperative ‘grace period’ affords protected opportunities for both physical and psychological recovery,” he said. This timeout of sorts also affords the care team time to assess the myocardium for possible functional recovery.
In patients who are not good candidates for transplantation, durable continuous-flow VADs may provide chronic therapy, and in time, these patients may become suitable transplant candidates, said Dr. Adachi. “Bypassing such an unfavorable period for transplantation with prolonged VAD support may be a reasonable approach,” he said.
Patients with failing single-ventricle circulation also may benefit from VAD support, although the challenges facing this population are more profound than in other groups, Dr. Adachi said. VAD support for single-ventricle disease is sparse, but these patients require careful evaluation of the nature of their condition. “If systolic dysfunction is the predominant cause of circulatory failure, then VAD support for the failing systemic ventricle will likely improve hemodynamics,” said Dr. Adachi. VAD support also could help the patient move through the various stages of palliation.
“Again, the emphasis is not just on simply keeping the patient alive until a donor organ becomes available; rather, attention is refocused on overall health beyond survival, which may eventually affect transplantation candidacy and even post transplantation outcome,” Dr. Adachi concluded.
Dr. Adachi serves as a consultant and proctor for Berlin Heart and HeartWare, and as a consultant for the New England Research Institute related to the PumpKIN trial.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: Advances in continuous-flow ventricular assist devices (VADs) promise a paradigm shift in pediatrics.
Major finding: Device miniaturization is solving problems such as size mismatch, inpatients on VADs, and chronic therapy.
Data source: Expert opinion drawing on PediMACS reports and published trials of continuous-flow VAD.
Disclosures: Dr. Adachi serves as a consultant and proctor for Berlin Heart and HeartWare and as a consultant for the New England Research Institute related to the PumpKIN trial.
Challenges of validating cerebral protection for TAVI
While using cerebral embolic protection during transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) seems appealing to reduce the risk of stroke, which has been reported to be higher than in open aortic valve replacement, the challenge of developing practical CEP devices and then designing appropriate trials may be insurmountable, according to a featured expert opinion in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2017;154;880-3).
Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie reviewed completed trials of five different CEP devices in 630 patients, noting that the trials confirmed the difficulty of “designing a trial that can prove a clinical benefit.” They noted 30-day stroke rates ranged from 4% to 6.7%, although prospective, nonrandomized European registries reported rates of 3.4% to 4.1%, and a large U.S. registry reported a rate of 2.5%. These results suggest “that some neurologic complications are going undetected or underreported in routine clinical practice.”
That may be a function of the different methods the trials used to determine complications. “There are little data to define best practice, but direct comprehensive assessment by a neurologist is likely the most accurate and sensitive method for detecting clinical stroke,” they added.
Another important factor is the timing of the assessment. They pointed out that half of all 30-day stroke events in TAVI are detected within 2 days of the procedure, but mild or transient symptoms can be missed if the only evaluation occurs just before discharge. “Unfortunately, in most studies this is when the neurologic assessment is performed,” Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie wrote. They added that long-term effects of these strokes have not been well studied.
What’s more, many TAVI patients have subclinical ischemic injury that only neuroimaging can detect. “Studies of MRI performed early after TAVI have demonstrated acute infarcts in 68% to 97% of patients,” the stated. While small and multiple, these microinfarcts may not be totally silent. “Additional studies to assess the long-term implications of clinically silent infarcts are clearly needed,” the coauthors said.
They also noted that a trial of stenting vs. endarterectomy for carotid stenosis raises caution about CEP devices (Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:353-62), as patients who had angioplasty and stenting and were treated with a CEP device had higher rates of acute infarct detected on MRI than those who did not have the CEP. Placing the CEP device through a severely stenosed and symptomatic carotid artery may have led to additional cerebral emboli.
“Placing a cerebral protection device in the aorta for a TAVI procedure also could be problematic in the presence of severe aortic arch disease or variant anatomy,” Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie commented. With two large trials of embolic protection in TAVI currently underway, the coauthors said, “the field eagerly awaits these results.”
Dr. Messé has received research support from GlaxoSmithKline and Direct Flow Medical. Both Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie have participated in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke–sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgery Network.
Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie pointed out the difficulty of quantifying the incidence of stroke during TAVI. But the long-term impact of stroke is more important because TAVI, as opposed to surgical aortic valve replacement, is more likely to be performed in a younger, healthier population, John Bozinovski, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Victoria said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:484-5).
While Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie make a valid point that clinically significant stroke, as opposed to diagnostically apparent stroke, is an important outcome of trials of embolic protection in TAVI, the long-term impact of silent strokes identified only with neuroimaging is unknown, “As such, ‘clinically significant’ stroke carries a nebulous definition,” Dr. Bozinovski said.
Nonetheless, CEP devices may become standard “even without good evidence” to support their use, Dr. Bozinovski said, “or perhaps they will be used infrequently or not at all.” Their uptake by cardiac surgeons will depend on the supporting evidence and their treatment effect. “Not only is it difficult to design an effective device, it is possible that we may not know whether a device is effective or what is the size of that effect,” he said. As Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie point out, “Designing and successfully conducting the trial to do so might never occur.”
Dr. Bozinovski disclosed he was a paid consultant with Edwards Life Sciences.
Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie pointed out the difficulty of quantifying the incidence of stroke during TAVI. But the long-term impact of stroke is more important because TAVI, as opposed to surgical aortic valve replacement, is more likely to be performed in a younger, healthier population, John Bozinovski, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Victoria said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:484-5).
While Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie make a valid point that clinically significant stroke, as opposed to diagnostically apparent stroke, is an important outcome of trials of embolic protection in TAVI, the long-term impact of silent strokes identified only with neuroimaging is unknown, “As such, ‘clinically significant’ stroke carries a nebulous definition,” Dr. Bozinovski said.
Nonetheless, CEP devices may become standard “even without good evidence” to support their use, Dr. Bozinovski said, “or perhaps they will be used infrequently or not at all.” Their uptake by cardiac surgeons will depend on the supporting evidence and their treatment effect. “Not only is it difficult to design an effective device, it is possible that we may not know whether a device is effective or what is the size of that effect,” he said. As Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie point out, “Designing and successfully conducting the trial to do so might never occur.”
Dr. Bozinovski disclosed he was a paid consultant with Edwards Life Sciences.
Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie pointed out the difficulty of quantifying the incidence of stroke during TAVI. But the long-term impact of stroke is more important because TAVI, as opposed to surgical aortic valve replacement, is more likely to be performed in a younger, healthier population, John Bozinovski, MD, of the University of British Columbia in Victoria said in his invited commentary (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154:484-5).
While Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie make a valid point that clinically significant stroke, as opposed to diagnostically apparent stroke, is an important outcome of trials of embolic protection in TAVI, the long-term impact of silent strokes identified only with neuroimaging is unknown, “As such, ‘clinically significant’ stroke carries a nebulous definition,” Dr. Bozinovski said.
Nonetheless, CEP devices may become standard “even without good evidence” to support their use, Dr. Bozinovski said, “or perhaps they will be used infrequently or not at all.” Their uptake by cardiac surgeons will depend on the supporting evidence and their treatment effect. “Not only is it difficult to design an effective device, it is possible that we may not know whether a device is effective or what is the size of that effect,” he said. As Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie point out, “Designing and successfully conducting the trial to do so might never occur.”
Dr. Bozinovski disclosed he was a paid consultant with Edwards Life Sciences.
While using cerebral embolic protection during transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) seems appealing to reduce the risk of stroke, which has been reported to be higher than in open aortic valve replacement, the challenge of developing practical CEP devices and then designing appropriate trials may be insurmountable, according to a featured expert opinion in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2017;154;880-3).
Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie reviewed completed trials of five different CEP devices in 630 patients, noting that the trials confirmed the difficulty of “designing a trial that can prove a clinical benefit.” They noted 30-day stroke rates ranged from 4% to 6.7%, although prospective, nonrandomized European registries reported rates of 3.4% to 4.1%, and a large U.S. registry reported a rate of 2.5%. These results suggest “that some neurologic complications are going undetected or underreported in routine clinical practice.”
That may be a function of the different methods the trials used to determine complications. “There are little data to define best practice, but direct comprehensive assessment by a neurologist is likely the most accurate and sensitive method for detecting clinical stroke,” they added.
Another important factor is the timing of the assessment. They pointed out that half of all 30-day stroke events in TAVI are detected within 2 days of the procedure, but mild or transient symptoms can be missed if the only evaluation occurs just before discharge. “Unfortunately, in most studies this is when the neurologic assessment is performed,” Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie wrote. They added that long-term effects of these strokes have not been well studied.
What’s more, many TAVI patients have subclinical ischemic injury that only neuroimaging can detect. “Studies of MRI performed early after TAVI have demonstrated acute infarcts in 68% to 97% of patients,” the stated. While small and multiple, these microinfarcts may not be totally silent. “Additional studies to assess the long-term implications of clinically silent infarcts are clearly needed,” the coauthors said.
They also noted that a trial of stenting vs. endarterectomy for carotid stenosis raises caution about CEP devices (Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:353-62), as patients who had angioplasty and stenting and were treated with a CEP device had higher rates of acute infarct detected on MRI than those who did not have the CEP. Placing the CEP device through a severely stenosed and symptomatic carotid artery may have led to additional cerebral emboli.
“Placing a cerebral protection device in the aorta for a TAVI procedure also could be problematic in the presence of severe aortic arch disease or variant anatomy,” Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie commented. With two large trials of embolic protection in TAVI currently underway, the coauthors said, “the field eagerly awaits these results.”
Dr. Messé has received research support from GlaxoSmithKline and Direct Flow Medical. Both Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie have participated in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke–sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgery Network.
While using cerebral embolic protection during transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) seems appealing to reduce the risk of stroke, which has been reported to be higher than in open aortic valve replacement, the challenge of developing practical CEP devices and then designing appropriate trials may be insurmountable, according to a featured expert opinion in the Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (2017;154;880-3).
Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie reviewed completed trials of five different CEP devices in 630 patients, noting that the trials confirmed the difficulty of “designing a trial that can prove a clinical benefit.” They noted 30-day stroke rates ranged from 4% to 6.7%, although prospective, nonrandomized European registries reported rates of 3.4% to 4.1%, and a large U.S. registry reported a rate of 2.5%. These results suggest “that some neurologic complications are going undetected or underreported in routine clinical practice.”
That may be a function of the different methods the trials used to determine complications. “There are little data to define best practice, but direct comprehensive assessment by a neurologist is likely the most accurate and sensitive method for detecting clinical stroke,” they added.
Another important factor is the timing of the assessment. They pointed out that half of all 30-day stroke events in TAVI are detected within 2 days of the procedure, but mild or transient symptoms can be missed if the only evaluation occurs just before discharge. “Unfortunately, in most studies this is when the neurologic assessment is performed,” Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie wrote. They added that long-term effects of these strokes have not been well studied.
What’s more, many TAVI patients have subclinical ischemic injury that only neuroimaging can detect. “Studies of MRI performed early after TAVI have demonstrated acute infarcts in 68% to 97% of patients,” the stated. While small and multiple, these microinfarcts may not be totally silent. “Additional studies to assess the long-term implications of clinically silent infarcts are clearly needed,” the coauthors said.
They also noted that a trial of stenting vs. endarterectomy for carotid stenosis raises caution about CEP devices (Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:353-62), as patients who had angioplasty and stenting and were treated with a CEP device had higher rates of acute infarct detected on MRI than those who did not have the CEP. Placing the CEP device through a severely stenosed and symptomatic carotid artery may have led to additional cerebral emboli.
“Placing a cerebral protection device in the aorta for a TAVI procedure also could be problematic in the presence of severe aortic arch disease or variant anatomy,” Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie commented. With two large trials of embolic protection in TAVI currently underway, the coauthors said, “the field eagerly awaits these results.”
Dr. Messé has received research support from GlaxoSmithKline and Direct Flow Medical. Both Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie have participated in the National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute/National Institute of Neurologic Disorders and Stroke–sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgery Network.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THORACIC AND CARDIOVASCULAR SURGERY
Key clinical point: Cerebral embolic protection during TAVI is an appealing concept that faces challenges.
Major finding: Developing practical and safe devices and testing them in adequately powered trials are daunting tasks.
Data source: Review of five completed and two ongoing clinical trials of 603 and 613 patients, respectively.
Disclosures: Dr. Messé has received research support from GlaxoSmithKline and Direct Flow Medical. Both Dr. Messé and Dr. Furie have participated in the NIH/NHLBI/NINDS-sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgery Network.
Vascular risks heightened in fibrotic NAFLD
WASHINGTON – The true impact of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis advancing to serious hepatic and nonhepatic complications in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease remains somewhat a mystery, but a multinational prospective cohort study has found that patients with bridging fibrosis are at risk of nonhepatic malignancies and vascular problems while patients with cirrhosis are prone to predominantly liver-related complications that result in higher rates of death and liver transplant, according to a report presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“NAFLD patients with biopsy-proven cirrhosis have a higher mortality and liver-related complications than those with bridging fibrosis, whereas vascular events and nonhepatic malignancies are the commonest complications in those with bridging fibrosis,” said Eduardo Vilar-Gomez, MD, PhD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis. “Among compensated cirrhotic patients, those with Child-Pugh (CP) A6 are at highest risk of liver-related outcomes and mortality.”
Dr. Vilar-Gomez reported on a multicenter, international prospective cohort study of 458 NAFLD patients, 159 with biopsy-proven bridging fibrosis and 299 with compensated cirrhosis (222 with CP A5 and 77 with CP A6) who were followed at six academic centers in four different countries between April 1995 and December 2016.
During a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 41 patients died, 43 had liver transplants, 90 had initial hepatic decompensation events, 42 were diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), 14 had major vascular events, and 30 were diagnosed with nonhepatic cancers. The overall death or transplant rates were 3% (four) in the bridging fibrosis group, 14% (32) in the cirrhosis and CP A5 group, and 62% (48) in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group.
Liver-related death rates were also highest among patients with cirrhosis, Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. While the four deaths in the fibrosis patients were evenly split between liver- and non–liver-related causes, 79% of deaths (15) in the cirrhosis and CP A5 patients were liver related, as were all 18 deaths in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group.
“Cirrhotic patients displayed the highest rates of hepatic outcomes overall as compared to those with bridging fibrosis,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. Rates of hepatic decompensation were 3% (5) for bridging fibrosis, 18% (40) for cirrhosis and CP A5, and 58% (48) for cirrhosis and CP A6. Likewise, HCC rates were also highest in cirrhotic patients: 9% (21) and 25% (19) for those with CP A5 and CP A6 disease, respectively, vs. 1% (2) for those with bridging fibrosis.
But nonhepatic outcomes were highest among the bridging fibrosis patients, Dr. Vilar-Gomez noted. “These include higher rates of major vascular events – 5% (eight) for those with bridging fibrosis vs. 2% (five) and 1% (one) for those with cirrhosis and CP A5 or CP A6 disease, respectively,” he said. “Rates of nonhepatic malignancies were comparable: 8% (13) for those with bridging fibrosis, 5% (10) for those with cirrhosis and CP5 disease and 9% (7) for those with cirrhosis and CP6 disease.
“Cirrhosis increased the risk of death/transplant, decompensation, and hepatocellular carcinoma by 4.3-, 4.5-, and 3.9-fold, respectively,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said, “but was associated with a lower risk of vascular events.”
He noted that the study identified a number of risk factors associated with overall mortality and severity of liver disease in cirrhosis compared with bridging fibrosis. Cirrhosis patients tended to be 2-3 years older, had lower body mass index and blood pressure, had higher rates of type 2 diabetes, had lower lipid levels, and had worse liver and renal function.
“Type 2 diabetes and steatosis severity on liver histology, among other factors, were independent predictors for liver-related outcomes,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. The findings have implications in assessing patients with advanced NAFLD and for the design and interpretation of clinical trials, he added.
Dr. Vilar-Gomez had no financial relationships to disclose.
WASHINGTON – The true impact of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis advancing to serious hepatic and nonhepatic complications in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease remains somewhat a mystery, but a multinational prospective cohort study has found that patients with bridging fibrosis are at risk of nonhepatic malignancies and vascular problems while patients with cirrhosis are prone to predominantly liver-related complications that result in higher rates of death and liver transplant, according to a report presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“NAFLD patients with biopsy-proven cirrhosis have a higher mortality and liver-related complications than those with bridging fibrosis, whereas vascular events and nonhepatic malignancies are the commonest complications in those with bridging fibrosis,” said Eduardo Vilar-Gomez, MD, PhD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis. “Among compensated cirrhotic patients, those with Child-Pugh (CP) A6 are at highest risk of liver-related outcomes and mortality.”
Dr. Vilar-Gomez reported on a multicenter, international prospective cohort study of 458 NAFLD patients, 159 with biopsy-proven bridging fibrosis and 299 with compensated cirrhosis (222 with CP A5 and 77 with CP A6) who were followed at six academic centers in four different countries between April 1995 and December 2016.
During a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 41 patients died, 43 had liver transplants, 90 had initial hepatic decompensation events, 42 were diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), 14 had major vascular events, and 30 were diagnosed with nonhepatic cancers. The overall death or transplant rates were 3% (four) in the bridging fibrosis group, 14% (32) in the cirrhosis and CP A5 group, and 62% (48) in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group.
Liver-related death rates were also highest among patients with cirrhosis, Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. While the four deaths in the fibrosis patients were evenly split between liver- and non–liver-related causes, 79% of deaths (15) in the cirrhosis and CP A5 patients were liver related, as were all 18 deaths in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group.
“Cirrhotic patients displayed the highest rates of hepatic outcomes overall as compared to those with bridging fibrosis,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. Rates of hepatic decompensation were 3% (5) for bridging fibrosis, 18% (40) for cirrhosis and CP A5, and 58% (48) for cirrhosis and CP A6. Likewise, HCC rates were also highest in cirrhotic patients: 9% (21) and 25% (19) for those with CP A5 and CP A6 disease, respectively, vs. 1% (2) for those with bridging fibrosis.
But nonhepatic outcomes were highest among the bridging fibrosis patients, Dr. Vilar-Gomez noted. “These include higher rates of major vascular events – 5% (eight) for those with bridging fibrosis vs. 2% (five) and 1% (one) for those with cirrhosis and CP A5 or CP A6 disease, respectively,” he said. “Rates of nonhepatic malignancies were comparable: 8% (13) for those with bridging fibrosis, 5% (10) for those with cirrhosis and CP5 disease and 9% (7) for those with cirrhosis and CP6 disease.
“Cirrhosis increased the risk of death/transplant, decompensation, and hepatocellular carcinoma by 4.3-, 4.5-, and 3.9-fold, respectively,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said, “but was associated with a lower risk of vascular events.”
He noted that the study identified a number of risk factors associated with overall mortality and severity of liver disease in cirrhosis compared with bridging fibrosis. Cirrhosis patients tended to be 2-3 years older, had lower body mass index and blood pressure, had higher rates of type 2 diabetes, had lower lipid levels, and had worse liver and renal function.
“Type 2 diabetes and steatosis severity on liver histology, among other factors, were independent predictors for liver-related outcomes,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. The findings have implications in assessing patients with advanced NAFLD and for the design and interpretation of clinical trials, he added.
Dr. Vilar-Gomez had no financial relationships to disclose.
WASHINGTON – The true impact of advanced fibrosis and cirrhosis advancing to serious hepatic and nonhepatic complications in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease remains somewhat a mystery, but a multinational prospective cohort study has found that patients with bridging fibrosis are at risk of nonhepatic malignancies and vascular problems while patients with cirrhosis are prone to predominantly liver-related complications that result in higher rates of death and liver transplant, according to a report presented at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
“NAFLD patients with biopsy-proven cirrhosis have a higher mortality and liver-related complications than those with bridging fibrosis, whereas vascular events and nonhepatic malignancies are the commonest complications in those with bridging fibrosis,” said Eduardo Vilar-Gomez, MD, PhD, of Indiana University, Indianapolis. “Among compensated cirrhotic patients, those with Child-Pugh (CP) A6 are at highest risk of liver-related outcomes and mortality.”
Dr. Vilar-Gomez reported on a multicenter, international prospective cohort study of 458 NAFLD patients, 159 with biopsy-proven bridging fibrosis and 299 with compensated cirrhosis (222 with CP A5 and 77 with CP A6) who were followed at six academic centers in four different countries between April 1995 and December 2016.
During a mean follow-up of 5.7 years, 41 patients died, 43 had liver transplants, 90 had initial hepatic decompensation events, 42 were diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), 14 had major vascular events, and 30 were diagnosed with nonhepatic cancers. The overall death or transplant rates were 3% (four) in the bridging fibrosis group, 14% (32) in the cirrhosis and CP A5 group, and 62% (48) in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group.
Liver-related death rates were also highest among patients with cirrhosis, Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. While the four deaths in the fibrosis patients were evenly split between liver- and non–liver-related causes, 79% of deaths (15) in the cirrhosis and CP A5 patients were liver related, as were all 18 deaths in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group.
“Cirrhotic patients displayed the highest rates of hepatic outcomes overall as compared to those with bridging fibrosis,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. Rates of hepatic decompensation were 3% (5) for bridging fibrosis, 18% (40) for cirrhosis and CP A5, and 58% (48) for cirrhosis and CP A6. Likewise, HCC rates were also highest in cirrhotic patients: 9% (21) and 25% (19) for those with CP A5 and CP A6 disease, respectively, vs. 1% (2) for those with bridging fibrosis.
But nonhepatic outcomes were highest among the bridging fibrosis patients, Dr. Vilar-Gomez noted. “These include higher rates of major vascular events – 5% (eight) for those with bridging fibrosis vs. 2% (five) and 1% (one) for those with cirrhosis and CP A5 or CP A6 disease, respectively,” he said. “Rates of nonhepatic malignancies were comparable: 8% (13) for those with bridging fibrosis, 5% (10) for those with cirrhosis and CP5 disease and 9% (7) for those with cirrhosis and CP6 disease.
“Cirrhosis increased the risk of death/transplant, decompensation, and hepatocellular carcinoma by 4.3-, 4.5-, and 3.9-fold, respectively,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said, “but was associated with a lower risk of vascular events.”
He noted that the study identified a number of risk factors associated with overall mortality and severity of liver disease in cirrhosis compared with bridging fibrosis. Cirrhosis patients tended to be 2-3 years older, had lower body mass index and blood pressure, had higher rates of type 2 diabetes, had lower lipid levels, and had worse liver and renal function.
“Type 2 diabetes and steatosis severity on liver histology, among other factors, were independent predictors for liver-related outcomes,” Dr. Vilar-Gomez said. The findings have implications in assessing patients with advanced NAFLD and for the design and interpretation of clinical trials, he added.
Dr. Vilar-Gomez had no financial relationships to disclose.
AT THE LIVER MEETING 2017
Key clinical point: Cirrhotic patients with advanced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease are at higher risk for liver-related adverse outcomes whereas patients with bridging fibrosis are more prone to nonhepatic malignancies and vascular events.
Major finding: Overall death or transplant rates were 3% in the bridging fibrosis group, 14% in the cirrhosis and Child-Pugh (CP) A5 group, and 62% in the cirrhosis and CP A6 group
Data source: Multicenter, international prospective cohort study of 458 NAFLD patients with biopsy-proven bridging fibrosis or compensated cirrhosis.
Disclosures: Dr. Vilar-Gomez had no financial relationships to disclose.


















