User login
Analysis of a Pilot Curriculum for Business Education in Dermatology Residency
To the Editor:
With health care constituting one of the larger segments of the US economy, medical practice is increasingly subject to business considerations.1 Patients, providers, and organizations are all required to make decisions that reflect choices beyond clinical needs alone. Given the impact of market forces, clinicians often are asked to navigate operational and business decisions. Accordingly, education about the policy and systems that shape care delivery can improve quality and help patients.2
The ability to understand the ecosystem of health care is of utmost importance for medical providers and can be achieved through resident education. Teaching fundamental business concepts enables residents to deliver care that is responsive to the constraints and opportunities encountered by patients and organizations, which ultimately will better prepare them to serve as advocates in alignment with their principal duties as physicians.
Despite the recognizable relationship between business and medicine, training has not yet been standardized to include topics in business education, and clinicians in dermatology are remarkably positioned to benefit because of the variety of practice settings and services they can provide. In dermatology, the diversity of services provided gives rise to complex coding and use of modifiers. Proper utilization of coding and billing is critical to create accurate documentation and receive appropriate reimbursement.3 Furthermore, clinicians in dermatology have to contend with the influence of insurance at many points of care, such as with coverage of pharmaceuticals. Formularies often have wide variability in coverage and are changing as new drugs come to market in the dermatologic space.4
The landscape of practice structure also has undergone change with increasing consolidation and mergers. The acquisition of practices by private equity firms has induced changes in practice infrastructure. The impact of changing organizational and managerial influences continues to be a topic of debate, with disparate opinions on how these developments shape standards of physician satisfaction and patient care.5
The convergence of these factors points to an important question that is gaining popularity: How will young dermatologists work within the context of all these parameters to best advocate and care for their patients? These questions are garnering more attention and were recently investigated through a survey of participants in a pilot program to evaluate the importance of business education in dermatology residency.
A survey of residency program directors was created by Patrinley and Dewan,6 which found that business education during residency was important and additional training should be implemented. Despite the perceived importance of business education, only half of the programs represented by survey respondents offered any structured educational opportunities, revealing a discrepancy between believed importance and practical implementation of business training, which suggests the need to develop a standardized, dermatology-specific curriculum that could be accessed by all residents in training.6
We performed a search of the medical literature to identify models of business education in residency programs. Only a few programs were identified, in which courses were predominantly instructed to trainees in primary care–based fields. According to course graduates, the programs were beneficial.7,8 Programs that had descriptive information about curriculum structure and content were chosen for further investigation and included internal medicine programs at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) and Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons (New York, New York). UCSF implemented a Program in Residency Investigation Methods and Epidemiology (PRIME program) to deliver seven 90-minute sessions dedicated to introducing residents to medical economics. Sessions were constructed with the intent of being interactive seminars that took on a variety of forms, including reading-based discussions, case-based analysis, and simulation-based learning.7 Columbia University developed a pilot program of week-long didactic sessions that were delivered to third-year internal medicine residents. These seminars featured discussions on health policy and economics, health insurance, technology and cost assessment, legal medicine, public health, community-oriented primary care, and local health department initiatives.8 We drew on both courses to build a lecture series focused on the business of dermatology that was delivered to dermatology residents at UMass Chan Medical School (Worcester, Massachusetts). Topic selection also was informed by qualitative input collected via email from recent graduates of the UMass dermatology residency program, focusing on the following areas: the US medical economy and health care costs; billing, coding, and claims processing; quality, relative value units (RVUs), reimbursement, and the merit-based incentive payment system; coverage of pharmaceuticals and teledermatology; and management. Residents were not required to prepare for any of the sessions; they were provided with handouts and slideshow presentations for reference to review at their convenience if desired. Five seminars were virtually conducted by an MD/MBA candidate at the institution (E.H.). They were recorded over the course of an academic year at 1- to 2-month intervals. Each 45-minute session was conducted in a lecture-discussion format and included case examples to help illustrate key principles and stimulate conversation. For example, the lecture on reimbursement incorporated a fee schedule calculation for a shave biopsy, using RVU and geographic pricing cost index (GCPI) multipliers. This demonstrated the variation in Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services reimbursement in relation to (1) constituents of the RVU calculation (ie, work, practice expense, and malpractice) and (2) practice in a particular location (ie, the GCPI). Following this example, a conversation ensued among participants regarding the factors that drive valuation, with particular interest in variation based on urban vs suburban locations across the United States. Participants also found it of interest to examine the percentage of the valuation dedicated to each constituent and how features such as lesion size informed the final assessment of the charge. Another stylistic choice in developing the model was to include prompts for further consideration prior to transitioning topics in the lectures. For example: when examining the burden of skin disease, the audience was prompted to consider: “What is driving cost escalations, and how will services of the clinical domain meet these evolving needs?” At another point in the introductory lecture, residents were asked: “How do different types of insurance plans impact the management of patients with dermatologic concerns?” These questions were intended to transition residents to the next topic of discussion and highlight take-home points of consideration for medical practice. The project was reviewed by the UMass institutional review board and met criteria for exemption.
Residents who participated in at least 1 lecture (N=10) were surveyed after attendance; there were 7 responses (70% response rate). Residents were asked to rate a series of statements on a scale of 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) and to provide commentary via an online form. Respondents indicated that the course was enjoyable (average score, 4.00), provided an appropriate level of detail (average score, 4.00), would be beneficial to integrate into a dermatology residency curriculum (average score, 3.86), and informed how they would practice as a clinician (average score, 3.86)(Figure). The respondents agreed that the course met the main goals of this initiative: it helped them develop knowledge about the interface between business and dermatology (4.14) and exposed residents to topics they had not learned about previously (4.71).
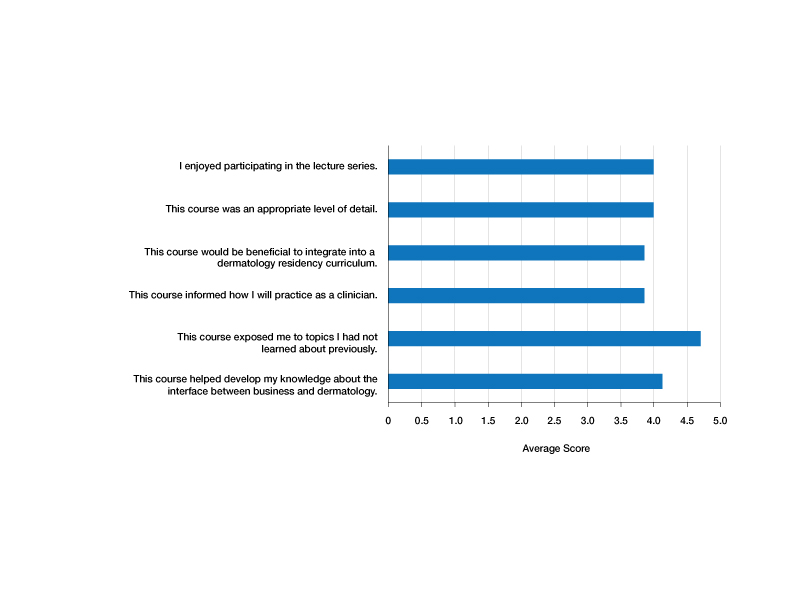
Although the course generally was well received, areas for improvement were identified from respondents’ comments, relating to audience engagement and refining the level of detail in the lectures. Recommendations included “less technical jargon and more focus on ‘big picture’ concepts, given audience’s low baseline knowledge”; “more case examples in each module”; and “more diagrams or interactive activities (polls, quizzes, break-out rooms) because the lectures were a bit dense.” This input was taken into consideration when revising the lectures for future use; they were reconstructed to have more case-based examples and prompts to encourage participation.
Resident commentary also demonstrated appreciation for education in this subject material. Statements such as “this is an important topic for future dermatologists” and “thank you so much for taking the time to implement this course” reflected the perceived value of this material during critical academic time. Another resident remarked: “This was great, thanks for putting it together.”
Given the positive experience of the residents and successful implementation of the series, this course was made available to all dermatology trainees on a network server with accompanying written documents. It is planned to be offered on a 3-year cycle in the future and will be updated to reflect inevitable changes in health care.
Although the relationship between business and medicine is increasingly important, teaching business principles has not become standardized or required in medical training. Despite the perception that this content is of value, implementation of programming has lagged behind that recognition, likely due to challenges in designing the curriculum and diffusing content into an already-saturated schedule. A model course that can be replicated in other residency programs would be valuable. We introduced a dermatology-specific lecture series to help prepare trainees for dermatology practice in a variety of clinical settings and train them with the language of business and operations that will equip them to respond to the needs of their patients, their practice, and the medical environment. Findings of this pilot study may not be generalizable to all dermatology residency programs because the sample size was small; the study was conducted at a single institution; and the content was delivered entirely online.
1. Tan S, Seiger K, Renehan P, et al. Trends in private equity acquisition of dermatology practices in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1013-1021. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1634
2. The business of health care in the United States. Harvard Online [Internet]. June 27, 2022. Accessed July 24, 2023. https://www.harvardonline.harvard.edu/blog/business-health-care-united-states
3. Ranpariya V, Cull D, Feldman SR, et al. Evaluation and management 2021 coding guidelines: key changes and implications. The Dermatologist. December 2020. Accessed July 24, 2023. https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/thederm/article/evaluation-and-management-2021-coding-guidelines-key-changes-and-implications?key=Ranpariya&elastic%5B0%5D=brand%3A73468
4. Lim HW, Collins SAB, Resneck JS Jr, et al. The burden of skin disease in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:958-972.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.043
5. Resneck JS Jr. Dermatology practice consolidation fueled by private equity investment: potential consequences for the specialty and patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:13-14. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.5558
6. Patrinely JR Jr, Dewan AK. Business education in dermatology residency: a survey of program directors. Cutis. 2021;108:E7-E19. doi:10.12788/cutis.0331
7. Kohlwes RJ, Chou CL. A curriculum in medical economics for residents. Acad Med. 2002;77:465-466. doi:10.1097/00001888-200205000-00040
8. Fiebach NH, Rao D, Hamm ME. A curriculum in health systems and public health for internal medicine residents. Am J Prev Med. 2011;41(4 suppl 3):S264-S269. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.025
To the Editor:
With health care constituting one of the larger segments of the US economy, medical practice is increasingly subject to business considerations.1 Patients, providers, and organizations are all required to make decisions that reflect choices beyond clinical needs alone. Given the impact of market forces, clinicians often are asked to navigate operational and business decisions. Accordingly, education about the policy and systems that shape care delivery can improve quality and help patients.2
The ability to understand the ecosystem of health care is of utmost importance for medical providers and can be achieved through resident education. Teaching fundamental business concepts enables residents to deliver care that is responsive to the constraints and opportunities encountered by patients and organizations, which ultimately will better prepare them to serve as advocates in alignment with their principal duties as physicians.
Despite the recognizable relationship between business and medicine, training has not yet been standardized to include topics in business education, and clinicians in dermatology are remarkably positioned to benefit because of the variety of practice settings and services they can provide. In dermatology, the diversity of services provided gives rise to complex coding and use of modifiers. Proper utilization of coding and billing is critical to create accurate documentation and receive appropriate reimbursement.3 Furthermore, clinicians in dermatology have to contend with the influence of insurance at many points of care, such as with coverage of pharmaceuticals. Formularies often have wide variability in coverage and are changing as new drugs come to market in the dermatologic space.4
The landscape of practice structure also has undergone change with increasing consolidation and mergers. The acquisition of practices by private equity firms has induced changes in practice infrastructure. The impact of changing organizational and managerial influences continues to be a topic of debate, with disparate opinions on how these developments shape standards of physician satisfaction and patient care.5
The convergence of these factors points to an important question that is gaining popularity: How will young dermatologists work within the context of all these parameters to best advocate and care for their patients? These questions are garnering more attention and were recently investigated through a survey of participants in a pilot program to evaluate the importance of business education in dermatology residency.
A survey of residency program directors was created by Patrinley and Dewan,6 which found that business education during residency was important and additional training should be implemented. Despite the perceived importance of business education, only half of the programs represented by survey respondents offered any structured educational opportunities, revealing a discrepancy between believed importance and practical implementation of business training, which suggests the need to develop a standardized, dermatology-specific curriculum that could be accessed by all residents in training.6
We performed a search of the medical literature to identify models of business education in residency programs. Only a few programs were identified, in which courses were predominantly instructed to trainees in primary care–based fields. According to course graduates, the programs were beneficial.7,8 Programs that had descriptive information about curriculum structure and content were chosen for further investigation and included internal medicine programs at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) and Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons (New York, New York). UCSF implemented a Program in Residency Investigation Methods and Epidemiology (PRIME program) to deliver seven 90-minute sessions dedicated to introducing residents to medical economics. Sessions were constructed with the intent of being interactive seminars that took on a variety of forms, including reading-based discussions, case-based analysis, and simulation-based learning.7 Columbia University developed a pilot program of week-long didactic sessions that were delivered to third-year internal medicine residents. These seminars featured discussions on health policy and economics, health insurance, technology and cost assessment, legal medicine, public health, community-oriented primary care, and local health department initiatives.8 We drew on both courses to build a lecture series focused on the business of dermatology that was delivered to dermatology residents at UMass Chan Medical School (Worcester, Massachusetts). Topic selection also was informed by qualitative input collected via email from recent graduates of the UMass dermatology residency program, focusing on the following areas: the US medical economy and health care costs; billing, coding, and claims processing; quality, relative value units (RVUs), reimbursement, and the merit-based incentive payment system; coverage of pharmaceuticals and teledermatology; and management. Residents were not required to prepare for any of the sessions; they were provided with handouts and slideshow presentations for reference to review at their convenience if desired. Five seminars were virtually conducted by an MD/MBA candidate at the institution (E.H.). They were recorded over the course of an academic year at 1- to 2-month intervals. Each 45-minute session was conducted in a lecture-discussion format and included case examples to help illustrate key principles and stimulate conversation. For example, the lecture on reimbursement incorporated a fee schedule calculation for a shave biopsy, using RVU and geographic pricing cost index (GCPI) multipliers. This demonstrated the variation in Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services reimbursement in relation to (1) constituents of the RVU calculation (ie, work, practice expense, and malpractice) and (2) practice in a particular location (ie, the GCPI). Following this example, a conversation ensued among participants regarding the factors that drive valuation, with particular interest in variation based on urban vs suburban locations across the United States. Participants also found it of interest to examine the percentage of the valuation dedicated to each constituent and how features such as lesion size informed the final assessment of the charge. Another stylistic choice in developing the model was to include prompts for further consideration prior to transitioning topics in the lectures. For example: when examining the burden of skin disease, the audience was prompted to consider: “What is driving cost escalations, and how will services of the clinical domain meet these evolving needs?” At another point in the introductory lecture, residents were asked: “How do different types of insurance plans impact the management of patients with dermatologic concerns?” These questions were intended to transition residents to the next topic of discussion and highlight take-home points of consideration for medical practice. The project was reviewed by the UMass institutional review board and met criteria for exemption.
Residents who participated in at least 1 lecture (N=10) were surveyed after attendance; there were 7 responses (70% response rate). Residents were asked to rate a series of statements on a scale of 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) and to provide commentary via an online form. Respondents indicated that the course was enjoyable (average score, 4.00), provided an appropriate level of detail (average score, 4.00), would be beneficial to integrate into a dermatology residency curriculum (average score, 3.86), and informed how they would practice as a clinician (average score, 3.86)(Figure). The respondents agreed that the course met the main goals of this initiative: it helped them develop knowledge about the interface between business and dermatology (4.14) and exposed residents to topics they had not learned about previously (4.71).

Although the course generally was well received, areas for improvement were identified from respondents’ comments, relating to audience engagement and refining the level of detail in the lectures. Recommendations included “less technical jargon and more focus on ‘big picture’ concepts, given audience’s low baseline knowledge”; “more case examples in each module”; and “more diagrams or interactive activities (polls, quizzes, break-out rooms) because the lectures were a bit dense.” This input was taken into consideration when revising the lectures for future use; they were reconstructed to have more case-based examples and prompts to encourage participation.
Resident commentary also demonstrated appreciation for education in this subject material. Statements such as “this is an important topic for future dermatologists” and “thank you so much for taking the time to implement this course” reflected the perceived value of this material during critical academic time. Another resident remarked: “This was great, thanks for putting it together.”
Given the positive experience of the residents and successful implementation of the series, this course was made available to all dermatology trainees on a network server with accompanying written documents. It is planned to be offered on a 3-year cycle in the future and will be updated to reflect inevitable changes in health care.
Although the relationship between business and medicine is increasingly important, teaching business principles has not become standardized or required in medical training. Despite the perception that this content is of value, implementation of programming has lagged behind that recognition, likely due to challenges in designing the curriculum and diffusing content into an already-saturated schedule. A model course that can be replicated in other residency programs would be valuable. We introduced a dermatology-specific lecture series to help prepare trainees for dermatology practice in a variety of clinical settings and train them with the language of business and operations that will equip them to respond to the needs of their patients, their practice, and the medical environment. Findings of this pilot study may not be generalizable to all dermatology residency programs because the sample size was small; the study was conducted at a single institution; and the content was delivered entirely online.
To the Editor:
With health care constituting one of the larger segments of the US economy, medical practice is increasingly subject to business considerations.1 Patients, providers, and organizations are all required to make decisions that reflect choices beyond clinical needs alone. Given the impact of market forces, clinicians often are asked to navigate operational and business decisions. Accordingly, education about the policy and systems that shape care delivery can improve quality and help patients.2
The ability to understand the ecosystem of health care is of utmost importance for medical providers and can be achieved through resident education. Teaching fundamental business concepts enables residents to deliver care that is responsive to the constraints and opportunities encountered by patients and organizations, which ultimately will better prepare them to serve as advocates in alignment with their principal duties as physicians.
Despite the recognizable relationship between business and medicine, training has not yet been standardized to include topics in business education, and clinicians in dermatology are remarkably positioned to benefit because of the variety of practice settings and services they can provide. In dermatology, the diversity of services provided gives rise to complex coding and use of modifiers. Proper utilization of coding and billing is critical to create accurate documentation and receive appropriate reimbursement.3 Furthermore, clinicians in dermatology have to contend with the influence of insurance at many points of care, such as with coverage of pharmaceuticals. Formularies often have wide variability in coverage and are changing as new drugs come to market in the dermatologic space.4
The landscape of practice structure also has undergone change with increasing consolidation and mergers. The acquisition of practices by private equity firms has induced changes in practice infrastructure. The impact of changing organizational and managerial influences continues to be a topic of debate, with disparate opinions on how these developments shape standards of physician satisfaction and patient care.5
The convergence of these factors points to an important question that is gaining popularity: How will young dermatologists work within the context of all these parameters to best advocate and care for their patients? These questions are garnering more attention and were recently investigated through a survey of participants in a pilot program to evaluate the importance of business education in dermatology residency.
A survey of residency program directors was created by Patrinley and Dewan,6 which found that business education during residency was important and additional training should be implemented. Despite the perceived importance of business education, only half of the programs represented by survey respondents offered any structured educational opportunities, revealing a discrepancy between believed importance and practical implementation of business training, which suggests the need to develop a standardized, dermatology-specific curriculum that could be accessed by all residents in training.6
We performed a search of the medical literature to identify models of business education in residency programs. Only a few programs were identified, in which courses were predominantly instructed to trainees in primary care–based fields. According to course graduates, the programs were beneficial.7,8 Programs that had descriptive information about curriculum structure and content were chosen for further investigation and included internal medicine programs at the University of California San Francisco (UCSF) and Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons (New York, New York). UCSF implemented a Program in Residency Investigation Methods and Epidemiology (PRIME program) to deliver seven 90-minute sessions dedicated to introducing residents to medical economics. Sessions were constructed with the intent of being interactive seminars that took on a variety of forms, including reading-based discussions, case-based analysis, and simulation-based learning.7 Columbia University developed a pilot program of week-long didactic sessions that were delivered to third-year internal medicine residents. These seminars featured discussions on health policy and economics, health insurance, technology and cost assessment, legal medicine, public health, community-oriented primary care, and local health department initiatives.8 We drew on both courses to build a lecture series focused on the business of dermatology that was delivered to dermatology residents at UMass Chan Medical School (Worcester, Massachusetts). Topic selection also was informed by qualitative input collected via email from recent graduates of the UMass dermatology residency program, focusing on the following areas: the US medical economy and health care costs; billing, coding, and claims processing; quality, relative value units (RVUs), reimbursement, and the merit-based incentive payment system; coverage of pharmaceuticals and teledermatology; and management. Residents were not required to prepare for any of the sessions; they were provided with handouts and slideshow presentations for reference to review at their convenience if desired. Five seminars were virtually conducted by an MD/MBA candidate at the institution (E.H.). They were recorded over the course of an academic year at 1- to 2-month intervals. Each 45-minute session was conducted in a lecture-discussion format and included case examples to help illustrate key principles and stimulate conversation. For example, the lecture on reimbursement incorporated a fee schedule calculation for a shave biopsy, using RVU and geographic pricing cost index (GCPI) multipliers. This demonstrated the variation in Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services reimbursement in relation to (1) constituents of the RVU calculation (ie, work, practice expense, and malpractice) and (2) practice in a particular location (ie, the GCPI). Following this example, a conversation ensued among participants regarding the factors that drive valuation, with particular interest in variation based on urban vs suburban locations across the United States. Participants also found it of interest to examine the percentage of the valuation dedicated to each constituent and how features such as lesion size informed the final assessment of the charge. Another stylistic choice in developing the model was to include prompts for further consideration prior to transitioning topics in the lectures. For example: when examining the burden of skin disease, the audience was prompted to consider: “What is driving cost escalations, and how will services of the clinical domain meet these evolving needs?” At another point in the introductory lecture, residents were asked: “How do different types of insurance plans impact the management of patients with dermatologic concerns?” These questions were intended to transition residents to the next topic of discussion and highlight take-home points of consideration for medical practice. The project was reviewed by the UMass institutional review board and met criteria for exemption.
Residents who participated in at least 1 lecture (N=10) were surveyed after attendance; there were 7 responses (70% response rate). Residents were asked to rate a series of statements on a scale of 1 (strongly disagree) to 5 (strongly agree) and to provide commentary via an online form. Respondents indicated that the course was enjoyable (average score, 4.00), provided an appropriate level of detail (average score, 4.00), would be beneficial to integrate into a dermatology residency curriculum (average score, 3.86), and informed how they would practice as a clinician (average score, 3.86)(Figure). The respondents agreed that the course met the main goals of this initiative: it helped them develop knowledge about the interface between business and dermatology (4.14) and exposed residents to topics they had not learned about previously (4.71).

Although the course generally was well received, areas for improvement were identified from respondents’ comments, relating to audience engagement and refining the level of detail in the lectures. Recommendations included “less technical jargon and more focus on ‘big picture’ concepts, given audience’s low baseline knowledge”; “more case examples in each module”; and “more diagrams or interactive activities (polls, quizzes, break-out rooms) because the lectures were a bit dense.” This input was taken into consideration when revising the lectures for future use; they were reconstructed to have more case-based examples and prompts to encourage participation.
Resident commentary also demonstrated appreciation for education in this subject material. Statements such as “this is an important topic for future dermatologists” and “thank you so much for taking the time to implement this course” reflected the perceived value of this material during critical academic time. Another resident remarked: “This was great, thanks for putting it together.”
Given the positive experience of the residents and successful implementation of the series, this course was made available to all dermatology trainees on a network server with accompanying written documents. It is planned to be offered on a 3-year cycle in the future and will be updated to reflect inevitable changes in health care.
Although the relationship between business and medicine is increasingly important, teaching business principles has not become standardized or required in medical training. Despite the perception that this content is of value, implementation of programming has lagged behind that recognition, likely due to challenges in designing the curriculum and diffusing content into an already-saturated schedule. A model course that can be replicated in other residency programs would be valuable. We introduced a dermatology-specific lecture series to help prepare trainees for dermatology practice in a variety of clinical settings and train them with the language of business and operations that will equip them to respond to the needs of their patients, their practice, and the medical environment. Findings of this pilot study may not be generalizable to all dermatology residency programs because the sample size was small; the study was conducted at a single institution; and the content was delivered entirely online.
1. Tan S, Seiger K, Renehan P, et al. Trends in private equity acquisition of dermatology practices in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1013-1021. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1634
2. The business of health care in the United States. Harvard Online [Internet]. June 27, 2022. Accessed July 24, 2023. https://www.harvardonline.harvard.edu/blog/business-health-care-united-states
3. Ranpariya V, Cull D, Feldman SR, et al. Evaluation and management 2021 coding guidelines: key changes and implications. The Dermatologist. December 2020. Accessed July 24, 2023. https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/thederm/article/evaluation-and-management-2021-coding-guidelines-key-changes-and-implications?key=Ranpariya&elastic%5B0%5D=brand%3A73468
4. Lim HW, Collins SAB, Resneck JS Jr, et al. The burden of skin disease in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:958-972.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.043
5. Resneck JS Jr. Dermatology practice consolidation fueled by private equity investment: potential consequences for the specialty and patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:13-14. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.5558
6. Patrinely JR Jr, Dewan AK. Business education in dermatology residency: a survey of program directors. Cutis. 2021;108:E7-E19. doi:10.12788/cutis.0331
7. Kohlwes RJ, Chou CL. A curriculum in medical economics for residents. Acad Med. 2002;77:465-466. doi:10.1097/00001888-200205000-00040
8. Fiebach NH, Rao D, Hamm ME. A curriculum in health systems and public health for internal medicine residents. Am J Prev Med. 2011;41(4 suppl 3):S264-S269. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.025
1. Tan S, Seiger K, Renehan P, et al. Trends in private equity acquisition of dermatology practices in the United States. JAMA Dermatol. 2019;155:1013-1021. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2019.1634
2. The business of health care in the United States. Harvard Online [Internet]. June 27, 2022. Accessed July 24, 2023. https://www.harvardonline.harvard.edu/blog/business-health-care-united-states
3. Ranpariya V, Cull D, Feldman SR, et al. Evaluation and management 2021 coding guidelines: key changes and implications. The Dermatologist. December 2020. Accessed July 24, 2023. https://www.hmpgloballearningnetwork.com/site/thederm/article/evaluation-and-management-2021-coding-guidelines-key-changes-and-implications?key=Ranpariya&elastic%5B0%5D=brand%3A73468
4. Lim HW, Collins SAB, Resneck JS Jr, et al. The burden of skin disease in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2017;76:958-972.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.043
5. Resneck JS Jr. Dermatology practice consolidation fueled by private equity investment: potential consequences for the specialty and patients. JAMA Dermatol. 2018;154:13-14. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2017.5558
6. Patrinely JR Jr, Dewan AK. Business education in dermatology residency: a survey of program directors. Cutis. 2021;108:E7-E19. doi:10.12788/cutis.0331
7. Kohlwes RJ, Chou CL. A curriculum in medical economics for residents. Acad Med. 2002;77:465-466. doi:10.1097/00001888-200205000-00040
8. Fiebach NH, Rao D, Hamm ME. A curriculum in health systems and public health for internal medicine residents. Am J Prev Med. 2011;41(4 suppl 3):S264-S269. doi:10.1016/j.amepre.2011.05.025
Practice Points
- Business education in dermatology residency promotes understanding of the health care ecosystem and can enable residents to more effectively deliver care that is responsive to the needs of their patients.
- Teaching fundamental business principles to residents can inform decision-making on patient, provider, and systems levels.
- A pilot curriculum supports implementation of business education teaching and will be particularly helpful in dermatology.