User login
On Jan. 20, 2020, the first confirmed case of the 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States was admitted to Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash. Less than 3 months later, the COVID-19 pandemic has put enormous stress on the U.S. health care system, which is confronting acute resource shortage because of the surge of acute and critically ill patients, health care provider safety and burnout, and an ongoing need for managing vulnerable populations while minimizing the infection spread.
With the onset of these unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a powerful new resource for health care providers, hospitals, and health care systems across the country. This article offers a summary of government regulations that enabled telehealth expansion, and provides an overview of how two health care organizations, Providence St. Joseph Health and Sound Physicians, are employing telehealth services to combat the COVID-19 health care crisis.
The government response: Telehealth expansion
In response to the pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have significantly increased access to telehealth services for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. CMS swiftly put measures in place such as:
- Expanding telehealth beyond rural areas.
- Adding 80 services that can be provided in all settings, including patient homes
- Allowing providers to bill for telehealth visits at the same rate as in-person visits.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services also aided this effort by:
- Waiving requirements that physicians or other health care professionals must have licenses in the state in which they provide services, if they have an equivalent license from another state.
- Waving penalties for HIPAA violations against health care providers that serve patients in good faith through everyday communications technologies, such as FaceTime or Skype
Without prior regulatory and reimbursement restrictions, telehealth rapidly became a powerful tool in helping to solve some of the problems brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Providence Telehealth for COVID-19
Providence St. Joseph Health is a not-for-profit health care system operating 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics across Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington. Providence has developed an enterprise telemedicine network with more than 100 virtual programs. Several of these services – including Telestroke, Telepsychiatry, TeleICU, and Telehospitalist – have been scaled across several states as a clinical cloud. More than 400 telemedicine endpoints are deployed, such as robotic carts and fixed InTouch TVs. In fact, the first U.S. COVID-19 patient was treated at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash., using the telemedical robot Vici from InTouch Health.
According to Todd Czartoski, MD, chief medical technology officer at Providence, “while telehealth has been around for many years, COVID-19 opened a lot of people’s eyes to the value of virtual care delivery.”
Providence’s telehealth response to COVID-19 has encompassed five main areas: COVID-19 home care, COVID-19 acute care, ambulatory virtual visits, behavioral health concierge (BHC) expansion, and additional support for outside partnerships.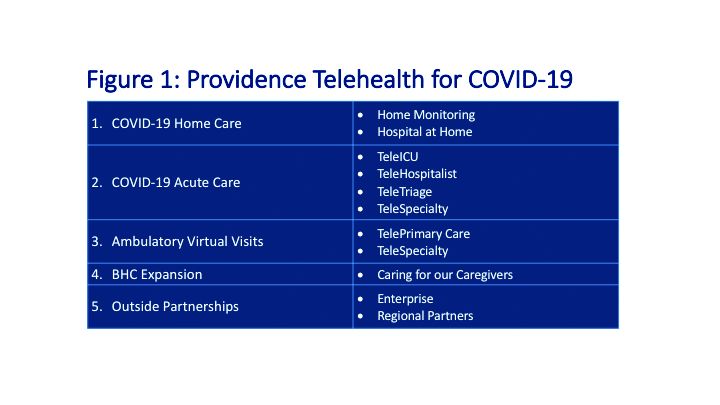
COVID-19 Home Care
Providence rapidly deployed home monitoring for nearly 2,000 positive or presumptive COVID-19 patients. Those symptomatic, clinically stable patients are given a thermometer and a pulse oximeter, and are monitored from home by a central team of nurses and physicians using the Xealth and Twistle programs.
Providence is evaluating expansion of home monitoring to other diagnoses, including higher acuity conditions.
COVID-19 Acute Care
TeleTriage expedites the triage of suspected COVID-19 patients and reduces the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by 50% per patient per day. To date, TeleTriage has resulted in the conservation of more than 90,000 PPE units.
TeleHospitalist services expanded from traditional night coverage to caring for patients in COVID-19 units around the clock. Currently, there are 25 telehospitalists who practice both in-person and virtual medicine.
TeleICU offers remote management of more than 180 ICU beds across 17 hospitals from two central command centers in Washington state and Alaska. The services include night-time intensivist and ICU nurse coverage, including medication and ventilator management, and family conferences. COVID-19 increased the demand for TeleICU, with anticipated expansion to more than 300 beds.
Core TeleSpecialty services include TeleStroke and TelePsychiatry across 135 remote sites.
Ambulatory Virtual Visits
Providence launched the COVID-19 hub microsite to help educate patients by providing accurate and timely information. A chatbot named Grace helps screen patients who are worried about COVID-19. Grace also suggests next steps, such as a video visit with a patient’s primary care provider or a visit using Express Care/Virtual team, a direct-to-consumer service available to patients within and outside of the health care system.
In less than 2 weeks, Providence enabled virtual visits for more than 7,000 outpatient providers, with more than 14,000 alternative visits now occurring daily. This has allowed primary and specialty providers to continue to manage their patient panels remotely. The number of Express Care/Virtual visits increased from 60 to more than 1,000 per day.
BHC Expansion
In the effort to improve care for its caregivers, Providence launched a behavioral health concierge (BHC) service that offers employees and their dependents virtual access to licensed mental health professionals. Over the last half of 2019, BHC provided more than 1,000 phone and virtual visits, depending on the individual preference of patients. Notably, 21% percent of users were physicians; 65% of users were seen the same day and 100% of users were seen within 48 hours.
COVID-19 increased demand for services that initially started in Seattle and rapidly expanded to Montana, Oregon, and California.
Outside Partnerships
Providence has established partnerships with outside facilities by providing services to 135 sites across eight states. COVID-19 accelerated the employment of new services, including TeleICU.
Telemedicine at Sound Physicians
Sound Physicians is a national physician-founded and -led organization that provides emergency medicine, critical care, hospital medicine, population health, and physician advisory services. Five years ago, Sound launched a telemedicine service line. I spoke with Brian Carpenter, MD, national medical director for TeleHospitalist Services at Sound, to learn about his experience implementing Telehospitalist programs across 22 hospitals and 22 skilled nursing facilities.
Prior to COVID-19, Sound offered a spectrum of telemedicine services including night-time telephonic cross coverage, as well as video-assisted admissions, transfers, and rapid responses. In 2019, Sound Telehospitalists received 88,000 connect requests, including 6,400 video-assisted new admissions and 82 rapid responses. Typically, one physician covers four to eight hospitals with back-up available for surges. The team uses a predictive model for staffing and developed an acuity-based algorithm to ensure that patients in distress are evaluated immediately, new stable admissions on average are seen within 12 minutes, and order clarifications are provided within 30 minutes.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an urgent demand for providers to support an overwhelmed health care system. Without the traditional barriers to implementation – such as lack of acceptance by medical staff, nurses and patients, strict state licensing and technology requirements, lack of reimbursement, and delays in hospital credentialing – Sound was able to develop a rapid implementation model for telemedicine services. Currently, four new hospitals are in the active implementation phase, with 40 more hospitals in the pipeline.
Implementing a telemedicine program at your hospital
In order to successfully launch a telemedicine program, Dr. Carpenter outlined the following critical implementation steps:
- In collaboration with local leadership, define the problem you are trying to solve, which helps inform the scope of the telemedicine practice and technology requirements (for example, night-time cross-coverage vs. full telemedicine service).
- Complete a discovery process (for example, existing workflow for patient admission and transfer) with the end-goal of developing a workflow and rules of engagement.
- Obtain hospital credentialing/privileges and EMR access.
- Train end-users, including physicians and nurse telepresenters.
Dr. Carpenter offered this advice to those considering a telemedicine program: “Telemedicine is not just about technology; a true telemedicine program encompasses change management, workflow development, end-user training, compliance, and mechanisms for continuous process improvement. We want to make things better for the physicians, nurses, and patients.”
Telehealth is offering support to health care providers on the front lines, patients in need of care, and health care systems managing the unprecedented surges in volume.
Dr. Farah is a hospitalist, physician adviser, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. She is a performance improvement consultant based in Corvallis, Ore., and a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
On Jan. 20, 2020, the first confirmed case of the 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States was admitted to Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash. Less than 3 months later, the COVID-19 pandemic has put enormous stress on the U.S. health care system, which is confronting acute resource shortage because of the surge of acute and critically ill patients, health care provider safety and burnout, and an ongoing need for managing vulnerable populations while minimizing the infection spread.
With the onset of these unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a powerful new resource for health care providers, hospitals, and health care systems across the country. This article offers a summary of government regulations that enabled telehealth expansion, and provides an overview of how two health care organizations, Providence St. Joseph Health and Sound Physicians, are employing telehealth services to combat the COVID-19 health care crisis.
The government response: Telehealth expansion
In response to the pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have significantly increased access to telehealth services for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. CMS swiftly put measures in place such as:
- Expanding telehealth beyond rural areas.
- Adding 80 services that can be provided in all settings, including patient homes
- Allowing providers to bill for telehealth visits at the same rate as in-person visits.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services also aided this effort by:
- Waiving requirements that physicians or other health care professionals must have licenses in the state in which they provide services, if they have an equivalent license from another state.
- Waving penalties for HIPAA violations against health care providers that serve patients in good faith through everyday communications technologies, such as FaceTime or Skype
Without prior regulatory and reimbursement restrictions, telehealth rapidly became a powerful tool in helping to solve some of the problems brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Providence Telehealth for COVID-19
Providence St. Joseph Health is a not-for-profit health care system operating 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics across Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington. Providence has developed an enterprise telemedicine network with more than 100 virtual programs. Several of these services – including Telestroke, Telepsychiatry, TeleICU, and Telehospitalist – have been scaled across several states as a clinical cloud. More than 400 telemedicine endpoints are deployed, such as robotic carts and fixed InTouch TVs. In fact, the first U.S. COVID-19 patient was treated at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash., using the telemedical robot Vici from InTouch Health.
According to Todd Czartoski, MD, chief medical technology officer at Providence, “while telehealth has been around for many years, COVID-19 opened a lot of people’s eyes to the value of virtual care delivery.”
Providence’s telehealth response to COVID-19 has encompassed five main areas: COVID-19 home care, COVID-19 acute care, ambulatory virtual visits, behavioral health concierge (BHC) expansion, and additional support for outside partnerships.
COVID-19 Home Care
Providence rapidly deployed home monitoring for nearly 2,000 positive or presumptive COVID-19 patients. Those symptomatic, clinically stable patients are given a thermometer and a pulse oximeter, and are monitored from home by a central team of nurses and physicians using the Xealth and Twistle programs.
Providence is evaluating expansion of home monitoring to other diagnoses, including higher acuity conditions.
COVID-19 Acute Care
TeleTriage expedites the triage of suspected COVID-19 patients and reduces the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by 50% per patient per day. To date, TeleTriage has resulted in the conservation of more than 90,000 PPE units.
TeleHospitalist services expanded from traditional night coverage to caring for patients in COVID-19 units around the clock. Currently, there are 25 telehospitalists who practice both in-person and virtual medicine.
TeleICU offers remote management of more than 180 ICU beds across 17 hospitals from two central command centers in Washington state and Alaska. The services include night-time intensivist and ICU nurse coverage, including medication and ventilator management, and family conferences. COVID-19 increased the demand for TeleICU, with anticipated expansion to more than 300 beds.
Core TeleSpecialty services include TeleStroke and TelePsychiatry across 135 remote sites.
Ambulatory Virtual Visits
Providence launched the COVID-19 hub microsite to help educate patients by providing accurate and timely information. A chatbot named Grace helps screen patients who are worried about COVID-19. Grace also suggests next steps, such as a video visit with a patient’s primary care provider or a visit using Express Care/Virtual team, a direct-to-consumer service available to patients within and outside of the health care system.
In less than 2 weeks, Providence enabled virtual visits for more than 7,000 outpatient providers, with more than 14,000 alternative visits now occurring daily. This has allowed primary and specialty providers to continue to manage their patient panels remotely. The number of Express Care/Virtual visits increased from 60 to more than 1,000 per day.
BHC Expansion
In the effort to improve care for its caregivers, Providence launched a behavioral health concierge (BHC) service that offers employees and their dependents virtual access to licensed mental health professionals. Over the last half of 2019, BHC provided more than 1,000 phone and virtual visits, depending on the individual preference of patients. Notably, 21% percent of users were physicians; 65% of users were seen the same day and 100% of users were seen within 48 hours.
COVID-19 increased demand for services that initially started in Seattle and rapidly expanded to Montana, Oregon, and California.
Outside Partnerships
Providence has established partnerships with outside facilities by providing services to 135 sites across eight states. COVID-19 accelerated the employment of new services, including TeleICU.
Telemedicine at Sound Physicians
Sound Physicians is a national physician-founded and -led organization that provides emergency medicine, critical care, hospital medicine, population health, and physician advisory services. Five years ago, Sound launched a telemedicine service line. I spoke with Brian Carpenter, MD, national medical director for TeleHospitalist Services at Sound, to learn about his experience implementing Telehospitalist programs across 22 hospitals and 22 skilled nursing facilities.
Prior to COVID-19, Sound offered a spectrum of telemedicine services including night-time telephonic cross coverage, as well as video-assisted admissions, transfers, and rapid responses. In 2019, Sound Telehospitalists received 88,000 connect requests, including 6,400 video-assisted new admissions and 82 rapid responses. Typically, one physician covers four to eight hospitals with back-up available for surges. The team uses a predictive model for staffing and developed an acuity-based algorithm to ensure that patients in distress are evaluated immediately, new stable admissions on average are seen within 12 minutes, and order clarifications are provided within 30 minutes.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an urgent demand for providers to support an overwhelmed health care system. Without the traditional barriers to implementation – such as lack of acceptance by medical staff, nurses and patients, strict state licensing and technology requirements, lack of reimbursement, and delays in hospital credentialing – Sound was able to develop a rapid implementation model for telemedicine services. Currently, four new hospitals are in the active implementation phase, with 40 more hospitals in the pipeline.
Implementing a telemedicine program at your hospital
In order to successfully launch a telemedicine program, Dr. Carpenter outlined the following critical implementation steps:
- In collaboration with local leadership, define the problem you are trying to solve, which helps inform the scope of the telemedicine practice and technology requirements (for example, night-time cross-coverage vs. full telemedicine service).
- Complete a discovery process (for example, existing workflow for patient admission and transfer) with the end-goal of developing a workflow and rules of engagement.
- Obtain hospital credentialing/privileges and EMR access.
- Train end-users, including physicians and nurse telepresenters.
Dr. Carpenter offered this advice to those considering a telemedicine program: “Telemedicine is not just about technology; a true telemedicine program encompasses change management, workflow development, end-user training, compliance, and mechanisms for continuous process improvement. We want to make things better for the physicians, nurses, and patients.”
Telehealth is offering support to health care providers on the front lines, patients in need of care, and health care systems managing the unprecedented surges in volume.
Dr. Farah is a hospitalist, physician adviser, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. She is a performance improvement consultant based in Corvallis, Ore., and a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.
On Jan. 20, 2020, the first confirmed case of the 2019 novel coronavirus in the United States was admitted to Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash. Less than 3 months later, the COVID-19 pandemic has put enormous stress on the U.S. health care system, which is confronting acute resource shortage because of the surge of acute and critically ill patients, health care provider safety and burnout, and an ongoing need for managing vulnerable populations while minimizing the infection spread.
With the onset of these unprecedented challenges, telehealth has emerged as a powerful new resource for health care providers, hospitals, and health care systems across the country. This article offers a summary of government regulations that enabled telehealth expansion, and provides an overview of how two health care organizations, Providence St. Joseph Health and Sound Physicians, are employing telehealth services to combat the COVID-19 health care crisis.
The government response: Telehealth expansion
In response to the pandemic, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) have significantly increased access to telehealth services for Medicare and Medicaid beneficiaries. CMS swiftly put measures in place such as:
- Expanding telehealth beyond rural areas.
- Adding 80 services that can be provided in all settings, including patient homes
- Allowing providers to bill for telehealth visits at the same rate as in-person visits.
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services also aided this effort by:
- Waiving requirements that physicians or other health care professionals must have licenses in the state in which they provide services, if they have an equivalent license from another state.
- Waving penalties for HIPAA violations against health care providers that serve patients in good faith through everyday communications technologies, such as FaceTime or Skype
Without prior regulatory and reimbursement restrictions, telehealth rapidly became a powerful tool in helping to solve some of the problems brought about by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Providence Telehealth for COVID-19
Providence St. Joseph Health is a not-for-profit health care system operating 51 hospitals and 1,085 clinics across Alaska, California, Montana, New Mexico, Oregon, Texas, and Washington. Providence has developed an enterprise telemedicine network with more than 100 virtual programs. Several of these services – including Telestroke, Telepsychiatry, TeleICU, and Telehospitalist – have been scaled across several states as a clinical cloud. More than 400 telemedicine endpoints are deployed, such as robotic carts and fixed InTouch TVs. In fact, the first U.S. COVID-19 patient was treated at Providence Regional Medical Center in Everett, Wash., using the telemedical robot Vici from InTouch Health.
According to Todd Czartoski, MD, chief medical technology officer at Providence, “while telehealth has been around for many years, COVID-19 opened a lot of people’s eyes to the value of virtual care delivery.”
Providence’s telehealth response to COVID-19 has encompassed five main areas: COVID-19 home care, COVID-19 acute care, ambulatory virtual visits, behavioral health concierge (BHC) expansion, and additional support for outside partnerships.
COVID-19 Home Care
Providence rapidly deployed home monitoring for nearly 2,000 positive or presumptive COVID-19 patients. Those symptomatic, clinically stable patients are given a thermometer and a pulse oximeter, and are monitored from home by a central team of nurses and physicians using the Xealth and Twistle programs.
Providence is evaluating expansion of home monitoring to other diagnoses, including higher acuity conditions.
COVID-19 Acute Care
TeleTriage expedites the triage of suspected COVID-19 patients and reduces the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) by 50% per patient per day. To date, TeleTriage has resulted in the conservation of more than 90,000 PPE units.
TeleHospitalist services expanded from traditional night coverage to caring for patients in COVID-19 units around the clock. Currently, there are 25 telehospitalists who practice both in-person and virtual medicine.
TeleICU offers remote management of more than 180 ICU beds across 17 hospitals from two central command centers in Washington state and Alaska. The services include night-time intensivist and ICU nurse coverage, including medication and ventilator management, and family conferences. COVID-19 increased the demand for TeleICU, with anticipated expansion to more than 300 beds.
Core TeleSpecialty services include TeleStroke and TelePsychiatry across 135 remote sites.
Ambulatory Virtual Visits
Providence launched the COVID-19 hub microsite to help educate patients by providing accurate and timely information. A chatbot named Grace helps screen patients who are worried about COVID-19. Grace also suggests next steps, such as a video visit with a patient’s primary care provider or a visit using Express Care/Virtual team, a direct-to-consumer service available to patients within and outside of the health care system.
In less than 2 weeks, Providence enabled virtual visits for more than 7,000 outpatient providers, with more than 14,000 alternative visits now occurring daily. This has allowed primary and specialty providers to continue to manage their patient panels remotely. The number of Express Care/Virtual visits increased from 60 to more than 1,000 per day.
BHC Expansion
In the effort to improve care for its caregivers, Providence launched a behavioral health concierge (BHC) service that offers employees and their dependents virtual access to licensed mental health professionals. Over the last half of 2019, BHC provided more than 1,000 phone and virtual visits, depending on the individual preference of patients. Notably, 21% percent of users were physicians; 65% of users were seen the same day and 100% of users were seen within 48 hours.
COVID-19 increased demand for services that initially started in Seattle and rapidly expanded to Montana, Oregon, and California.
Outside Partnerships
Providence has established partnerships with outside facilities by providing services to 135 sites across eight states. COVID-19 accelerated the employment of new services, including TeleICU.
Telemedicine at Sound Physicians
Sound Physicians is a national physician-founded and -led organization that provides emergency medicine, critical care, hospital medicine, population health, and physician advisory services. Five years ago, Sound launched a telemedicine service line. I spoke with Brian Carpenter, MD, national medical director for TeleHospitalist Services at Sound, to learn about his experience implementing Telehospitalist programs across 22 hospitals and 22 skilled nursing facilities.
Prior to COVID-19, Sound offered a spectrum of telemedicine services including night-time telephonic cross coverage, as well as video-assisted admissions, transfers, and rapid responses. In 2019, Sound Telehospitalists received 88,000 connect requests, including 6,400 video-assisted new admissions and 82 rapid responses. Typically, one physician covers four to eight hospitals with back-up available for surges. The team uses a predictive model for staffing and developed an acuity-based algorithm to ensure that patients in distress are evaluated immediately, new stable admissions on average are seen within 12 minutes, and order clarifications are provided within 30 minutes.
The COVID-19 pandemic created an urgent demand for providers to support an overwhelmed health care system. Without the traditional barriers to implementation – such as lack of acceptance by medical staff, nurses and patients, strict state licensing and technology requirements, lack of reimbursement, and delays in hospital credentialing – Sound was able to develop a rapid implementation model for telemedicine services. Currently, four new hospitals are in the active implementation phase, with 40 more hospitals in the pipeline.
Implementing a telemedicine program at your hospital
In order to successfully launch a telemedicine program, Dr. Carpenter outlined the following critical implementation steps:
- In collaboration with local leadership, define the problem you are trying to solve, which helps inform the scope of the telemedicine practice and technology requirements (for example, night-time cross-coverage vs. full telemedicine service).
- Complete a discovery process (for example, existing workflow for patient admission and transfer) with the end-goal of developing a workflow and rules of engagement.
- Obtain hospital credentialing/privileges and EMR access.
- Train end-users, including physicians and nurse telepresenters.
Dr. Carpenter offered this advice to those considering a telemedicine program: “Telemedicine is not just about technology; a true telemedicine program encompasses change management, workflow development, end-user training, compliance, and mechanisms for continuous process improvement. We want to make things better for the physicians, nurses, and patients.”
Telehealth is offering support to health care providers on the front lines, patients in need of care, and health care systems managing the unprecedented surges in volume.
Dr. Farah is a hospitalist, physician adviser, and Lean Six Sigma Black Belt. She is a performance improvement consultant based in Corvallis, Ore., and a member of The Hospitalist’s editorial advisory board.



