User login
The Diagnosis: Reactive Perforating Collagenosis
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) may be either acquired or inherited. It is 1 of 4 classical forms of transepithelial elimination, which also includes elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS) as well as perforating folliculitis and Kyrle disease. These 4 forms of transepithelial elimination share characteristics of the elimination of altered dermal components through the epidermis.1 The acquired subtype of RPC frequently occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease,2 both present in our patient.
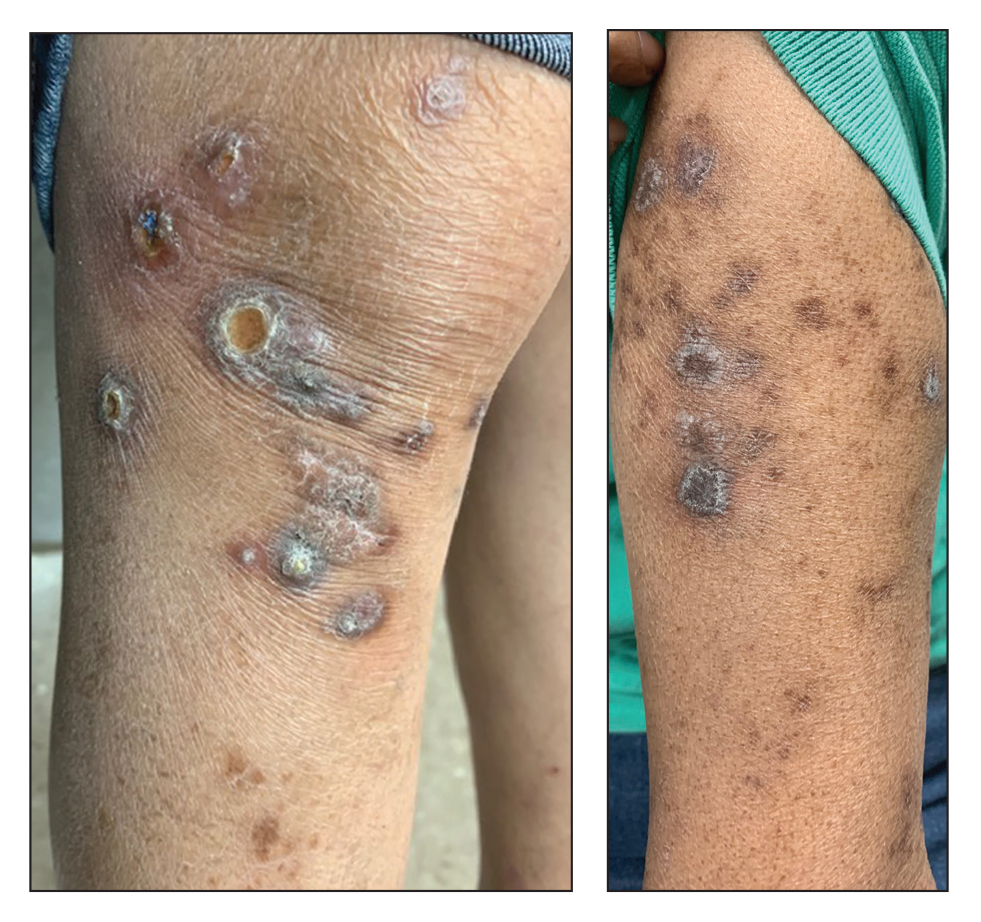
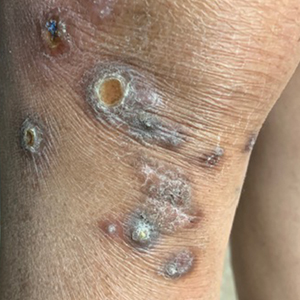
Clinical presentation typically shows pruritic hyperkeratotic papules with a central crater filled with crust that frequently are distributed on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, often in a linear pattern.3 The perforating papules and nodules occasionally may involve the trunk and face.4 Histopathologic examination is characterized by the elimination of altered collagen through the epidermis. Established lesions may show a cup-shaped depression of the epidermis filled with a keratin plug. The underlying dermis will show vertically oriented basophilic collagen fibers with focal extrusion through the epidermis, and elastic fibers will be absent.5 The exact pathophysiology of this disease is unknown, but it may represent a cutaneous response to superficial trauma caused by intense scratching.6
Standard treatment protocols are not well established for this condition, but some evidence shows that a combination of treatments can help ameliorate symptoms, even if they are not curative.7 Treatments without strong evidence have included a wide range of topical, systemic, and other therapies. Case series and anecdotal reports have used retinoids, corticosteroids, menthol, antibiotics, allopurinol antihistamines, cryotherapy, and lasers.8 One case was treated with a combination of narrowband UVB phototherapy and doxycycline with resolution in approximately 6 weeks.9 Other cases have been cured using triple therapy with antihistamines, topical or injected steroids, and emollients or oral antibiotics.7 Evidence shows that there may be benefit to combining multiple different treatment types that target pruritus, inflammation, and collagen damage.7,9 This disease usually cannot be cured, but it may be improved by the available treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes delusional parasitosis, EPS, perforating folliculitis, and prurigo nodularis. Delusional parasitosis also can be characterized by excoriated plaques and a sensation of parasites infesting the skin, as our patient described.10 However, it can be differentiated from RPC by the fact that it is a diagnosis of exclusion, which would not have the histopathologic findings of the elimination of collagen from the epidermis, as was demonstrated in our patient.11 Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is in the same family of perforating diseases as RPC; however, EPS typically appears in children or young adults and often is associated with other genetic disorders. Physical examination in a patient with EPS would reveal keratotic papules in a serpiginous pattern, whereas our patient had discrete lesions without any serpiginous pattern. The histopathologic appearance of EPS would reveal plugs of elastic fibers rather than collagen fibers, as was demonstrated in our patient.8 Perforating folliculitis, while also demonstrating transepithelial elimination similar to RPC, would appear as erythematous follicular papules with small central keratotic plugs and histopathologic findings of a widely dilated follicle with a mass of keratotic debris.12 Prurigo nodularis would appear as dome-shaped papulonodules with varying degrees of scale, crust, and erosion, with a histopathologic appearance of hyperplasia and thick hyperkeratosis.11
Overall, the histopathology is paramount in differentiating RPC from the alternative diagnoses, with the extrusion of collagen from the epidermis not being seen in these other conditions. The coupling of the medical history (type 2 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease) with the clinical presentation and skin biopsy findings confirmed the diagnosis of RPC.
- Fei C, Wang Y, Gong Y, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a report of a typical case. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E4305.
- Matsui A, Nakano H, Aizu T, et al. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with 308‐nm excimer laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:820-821.
- Dey AK. Reactive perforating collagenosis: an important differential diagnosis in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:422-425.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education LLC; 2012.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Demos Medical Publishing LLC; 2012.
- Kreuter A, Gambichler T. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. CMAJ. 2010;182:E184.
- Zhang X, Yang Y, Shao S. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:E20391.
- Rapini RP. Perforating diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1690-1696.
- Gao L, Gu L, Chen Z, et al. Doxycycline combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:917-921.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Psychocutaneous disorders. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:50-55. 11. Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Pruritus and dysesthesia. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:39-49. 12. Rubio FA, Herranz P, Robayna G, et al. Perforating folliculitis: report of a case in an HIV-infected man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:300-302.
The Diagnosis: Reactive Perforating Collagenosis
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) may be either acquired or inherited. It is 1 of 4 classical forms of transepithelial elimination, which also includes elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS) as well as perforating folliculitis and Kyrle disease. These 4 forms of transepithelial elimination share characteristics of the elimination of altered dermal components through the epidermis.1 The acquired subtype of RPC frequently occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease,2 both present in our patient.
Clinical presentation typically shows pruritic hyperkeratotic papules with a central crater filled with crust that frequently are distributed on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, often in a linear pattern.3 The perforating papules and nodules occasionally may involve the trunk and face.4 Histopathologic examination is characterized by the elimination of altered collagen through the epidermis. Established lesions may show a cup-shaped depression of the epidermis filled with a keratin plug. The underlying dermis will show vertically oriented basophilic collagen fibers with focal extrusion through the epidermis, and elastic fibers will be absent.5 The exact pathophysiology of this disease is unknown, but it may represent a cutaneous response to superficial trauma caused by intense scratching.6
Standard treatment protocols are not well established for this condition, but some evidence shows that a combination of treatments can help ameliorate symptoms, even if they are not curative.7 Treatments without strong evidence have included a wide range of topical, systemic, and other therapies. Case series and anecdotal reports have used retinoids, corticosteroids, menthol, antibiotics, allopurinol antihistamines, cryotherapy, and lasers.8 One case was treated with a combination of narrowband UVB phototherapy and doxycycline with resolution in approximately 6 weeks.9 Other cases have been cured using triple therapy with antihistamines, topical or injected steroids, and emollients or oral antibiotics.7 Evidence shows that there may be benefit to combining multiple different treatment types that target pruritus, inflammation, and collagen damage.7,9 This disease usually cannot be cured, but it may be improved by the available treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes delusional parasitosis, EPS, perforating folliculitis, and prurigo nodularis. Delusional parasitosis also can be characterized by excoriated plaques and a sensation of parasites infesting the skin, as our patient described.10 However, it can be differentiated from RPC by the fact that it is a diagnosis of exclusion, which would not have the histopathologic findings of the elimination of collagen from the epidermis, as was demonstrated in our patient.11 Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is in the same family of perforating diseases as RPC; however, EPS typically appears in children or young adults and often is associated with other genetic disorders. Physical examination in a patient with EPS would reveal keratotic papules in a serpiginous pattern, whereas our patient had discrete lesions without any serpiginous pattern. The histopathologic appearance of EPS would reveal plugs of elastic fibers rather than collagen fibers, as was demonstrated in our patient.8 Perforating folliculitis, while also demonstrating transepithelial elimination similar to RPC, would appear as erythematous follicular papules with small central keratotic plugs and histopathologic findings of a widely dilated follicle with a mass of keratotic debris.12 Prurigo nodularis would appear as dome-shaped papulonodules with varying degrees of scale, crust, and erosion, with a histopathologic appearance of hyperplasia and thick hyperkeratosis.11
Overall, the histopathology is paramount in differentiating RPC from the alternative diagnoses, with the extrusion of collagen from the epidermis not being seen in these other conditions. The coupling of the medical history (type 2 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease) with the clinical presentation and skin biopsy findings confirmed the diagnosis of RPC.
The Diagnosis: Reactive Perforating Collagenosis
Reactive perforating collagenosis (RPC) may be either acquired or inherited. It is 1 of 4 classical forms of transepithelial elimination, which also includes elastosis perforans serpiginosa (EPS) as well as perforating folliculitis and Kyrle disease. These 4 forms of transepithelial elimination share characteristics of the elimination of altered dermal components through the epidermis.1 The acquired subtype of RPC frequently occurs in patients with diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease,2 both present in our patient.
Clinical presentation typically shows pruritic hyperkeratotic papules with a central crater filled with crust that frequently are distributed on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, often in a linear pattern.3 The perforating papules and nodules occasionally may involve the trunk and face.4 Histopathologic examination is characterized by the elimination of altered collagen through the epidermis. Established lesions may show a cup-shaped depression of the epidermis filled with a keratin plug. The underlying dermis will show vertically oriented basophilic collagen fibers with focal extrusion through the epidermis, and elastic fibers will be absent.5 The exact pathophysiology of this disease is unknown, but it may represent a cutaneous response to superficial trauma caused by intense scratching.6
Standard treatment protocols are not well established for this condition, but some evidence shows that a combination of treatments can help ameliorate symptoms, even if they are not curative.7 Treatments without strong evidence have included a wide range of topical, systemic, and other therapies. Case series and anecdotal reports have used retinoids, corticosteroids, menthol, antibiotics, allopurinol antihistamines, cryotherapy, and lasers.8 One case was treated with a combination of narrowband UVB phototherapy and doxycycline with resolution in approximately 6 weeks.9 Other cases have been cured using triple therapy with antihistamines, topical or injected steroids, and emollients or oral antibiotics.7 Evidence shows that there may be benefit to combining multiple different treatment types that target pruritus, inflammation, and collagen damage.7,9 This disease usually cannot be cured, but it may be improved by the available treatments.
The differential diagnosis includes delusional parasitosis, EPS, perforating folliculitis, and prurigo nodularis. Delusional parasitosis also can be characterized by excoriated plaques and a sensation of parasites infesting the skin, as our patient described.10 However, it can be differentiated from RPC by the fact that it is a diagnosis of exclusion, which would not have the histopathologic findings of the elimination of collagen from the epidermis, as was demonstrated in our patient.11 Elastosis perforans serpiginosa is in the same family of perforating diseases as RPC; however, EPS typically appears in children or young adults and often is associated with other genetic disorders. Physical examination in a patient with EPS would reveal keratotic papules in a serpiginous pattern, whereas our patient had discrete lesions without any serpiginous pattern. The histopathologic appearance of EPS would reveal plugs of elastic fibers rather than collagen fibers, as was demonstrated in our patient.8 Perforating folliculitis, while also demonstrating transepithelial elimination similar to RPC, would appear as erythematous follicular papules with small central keratotic plugs and histopathologic findings of a widely dilated follicle with a mass of keratotic debris.12 Prurigo nodularis would appear as dome-shaped papulonodules with varying degrees of scale, crust, and erosion, with a histopathologic appearance of hyperplasia and thick hyperkeratosis.11
Overall, the histopathology is paramount in differentiating RPC from the alternative diagnoses, with the extrusion of collagen from the epidermis not being seen in these other conditions. The coupling of the medical history (type 2 diabetes mellitus and end-stage renal disease) with the clinical presentation and skin biopsy findings confirmed the diagnosis of RPC.
- Fei C, Wang Y, Gong Y, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a report of a typical case. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E4305.
- Matsui A, Nakano H, Aizu T, et al. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with 308‐nm excimer laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:820-821.
- Dey AK. Reactive perforating collagenosis: an important differential diagnosis in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:422-425.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education LLC; 2012.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Demos Medical Publishing LLC; 2012.
- Kreuter A, Gambichler T. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. CMAJ. 2010;182:E184.
- Zhang X, Yang Y, Shao S. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:E20391.
- Rapini RP. Perforating diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1690-1696.
- Gao L, Gu L, Chen Z, et al. Doxycycline combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:917-921.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Psychocutaneous disorders. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:50-55. 11. Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Pruritus and dysesthesia. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:39-49. 12. Rubio FA, Herranz P, Robayna G, et al. Perforating folliculitis: report of a case in an HIV-infected man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:300-302.
- Fei C, Wang Y, Gong Y, et al. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a report of a typical case. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95:E4305.
- Matsui A, Nakano H, Aizu T, et al. Treatment of acquired reactive perforating collagenosis with 308‐nm excimer laser. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2016;41:820-821.
- Dey AK. Reactive perforating collagenosis: an important differential diagnosis in hemodialysis patients. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2018;29:422-425.
- Kang S, Amagai M, Bruckner AL, et al, eds. Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine. 9th ed. McGraw-Hill Education LLC; 2012.
- Plaza JA, Prieto VG. Inflammatory Skin Disorders. Demos Medical Publishing LLC; 2012.
- Kreuter A, Gambichler T. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. CMAJ. 2010;182:E184.
- Zhang X, Yang Y, Shao S. Acquired reactive perforating collagenosis: a case report and review of the literature. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020;99:E20391.
- Rapini RP. Perforating diseases. In: Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Cerroni L, eds. Dermatology. 4th ed. Elsevier; 2018:1690-1696.
- Gao L, Gu L, Chen Z, et al. Doxycycline combined with NB-UVB phototherapy for acquired reactive perforating collagenosis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2020;16:917-921.
- Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Psychocutaneous disorders. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:50-55. 11. Bolognia JL, Schaffer JV, Duncan KO, et al. Pruritus and dysesthesia. Dermatology Essentials. Elsevier; 2014:39-49. 12. Rubio FA, Herranz P, Robayna G, et al. Perforating folliculitis: report of a case in an HIV-infected man. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40:300-302.
A 73-year-old woman presented for evaluation of a rash on the arms and legs of 3 months’ duration. The rash had developed abruptly, and she believed it was caused by bugs in the skin; her husband noted that she constantly picked at her arms and legs. She had a medical history of hypertension, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and endstage renal disease on dialysis. Physical examination revealed multiple pigmented papules and plaques, some with keratotic scale, on the lower legs (left) and arms, with greater involvement on the left arm (right). The lesions were of various sizes and shapes, some with a central keratotic core, and several lesions demonstrated erosion, excoriation, or ulceration. Histopathologic examination revealed slight attenuation of the epidermis with loss of normal rete peg architecture, alternating areas of hypergranulosis and hypogranulosis, central ulceration with inflammatory cells, and a basophilic hue to the ulcer base with sweeping up of the collagen fibers.