User login
Why some COVID-19 vaccines seem occasionally to cause a distinctive form of myocarditis, and why adolescent boys and young men appear most vulnerable, remain a mystery. But the entity’s prevalence, nuances of presentation, and likely clinical course have come into sharper view after recent additions to the literature.
Two new publications all but confirm that the rare cases of myocarditis closely following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, primarily with one of the mRNA-based vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, is a clinically different creature from myocarditis physicians were likely to see before the pandemic.
A third report unveils rates of hospitalization for myocarditis linked to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in the 12- to 15-year age group, based on active surveillance across Israel. Of note, the rates were lower than corresponding numbers among the country’s 16- to 19-year-olds published in late 2021 by the same authors.
No link with CoronaVac
A case-control study covering almost the entire population of Hong Kong from February to August 2021 confirms a slight but significant excess risk for myocarditis and, to a lesser degree, pericarditis, after injections of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. As consistently reported from other studies, the risks were highest in adolescent and young adult males and after a second dose.
The study estimated an overall carditis incidence of 5.7 cases per million doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, for a risk 3.5 times that in the unvaccinated Hong Kong population. Carditis rates after a first dose were about 2.5 per million and 10 per million after a second dose.
Hong Kong launched its public SARS-CoV-2 immunization program in late February 2021 with the Chinese-made CoronaVac (Sinovac) inactivated-virus vaccine, and introduced the mRNA-based alternative several weeks later. By August 2021, the vaccines had reached about 3.3 million people in the region – 49% of the Hong Kong population at least 12 years of age.
In a novel finding, there were no excesses in carditis cases after CoronaVac vaccination. The difference between vaccines likely isn’t caused by chance, because three-fourths of the carditis-associated Pfizer-BioNTech injections arose within a week, whereas “71% of cases following the use of CoronaVac occurred more than 30 days after vaccination,” senior author Ian Chi Kei Wong, PhD, University of Hong Kong, said in an interview.
“This onset distribution for cases having received CoronaVac demonstrates that it is highly unlikely the carditis cases are related to the vaccine,” he said. And that “plausibly implies a specific underlying mechanism between vaccination and carditis that may only be applicable to mRNA vaccines.”
That inference is in line with case reports and other research, including large population-based studies from Israel and Denmark, although a recent study from the United Kingdom hinted at a potential excess myocarditis risk associated with the adenovirus-based AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
The Hong Kong study identified 160 patients age 12 or older with a first diagnosis of carditis during February to August 2021, in electronic health records covering nearly the entire region.
“We used laboratory test results of troponin levels to further eliminate unlikely cases of carditis,” Dr. Wong said. The health records were linked to a “population-based vaccination record” maintained by the government’s department of health.
About 10 control patients from among all hospitalized patients without carditis were matched by age, sex, and admission date to each of the 160 carditis cases. About 83% of cases and 92% of the controls were unvaccinated.
Among those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, representing 12.5% of cases and 4.2% of controls, the estimated carditis incidence was 0.57 per 100,000 doses. For those who received CoronaVac, representing 4.4% of cases and 3.9% of controls, it was 0.31 per 100,000 doses.
In adjusted analysis, the odds ratios for carditis among Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients, compared with unvaccinated controls, were 3.57 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-6.60) overall, 4.68 (95% CI, 2.25-9.71) for males, 2.22 (95% CI, 0.57-8.69) for females, 2.41 (95% CI, 1.18-4.90) for ages 18 and older, and 13.8 (95% CI, 2.86-110.4) for ages 12-17
Myocarditis accounted for most of the excess cases, with an overall OR of 9.29 (95% CI, 3.94-21.9). The OR reached only 1.06 (95% CI, 0.35-3.22) for pericarditis alone.
The case-control study is noteworthy for its design, which contrasts with the many recent case series and passive or active surveillance studies, and even the more robust population-based studies of vaccine-related myocarditis, observed Dongngan Truong, MD, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, both in Salt Lake City, who wasn’t part of the study.
Among its strengths, she said in an interview, are its linkage of comprehensive hospital and vaccination data sets for two different vaccines; and that it corroborates other research suggesting there is “something in particular about mRNA vaccination that seems to be associated with the development of myocarditis.”
Active surveillance in Israel
In an October 2021 report based on an Israeli Ministry of Health database covering up to May 2021, rates of myocarditis arising within 21 days of a second Pfizer-BioNTech dose in 16- to 19-year-olds reached about 1 per 6,637 males and 1 per 99,853 females. Those numbers compared with 1 per 26,000 males and 1 per 218,000 females across all age groups.
Now authors led by Dror Mevorach, MD, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, have published corresponding numbers from the same data base for myocarditis associated with the same vaccine in males and females aged 12-15.
Their research covers 404,407 people in that age group who received a first dose of the mRNA-based vaccine and 326,463 who received the second dose from June to October, 2021. Only 18 cases of myocarditis were observed within 21 days of either dose.
The estimated rates for males were 0.56 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 8.09 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
For females, the estimates were 0 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 0.69 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
“The pattern observed, mainly following the second vaccination in males, suggests causality,” the group wrote.
Leveraging passive surveillance reports
Another new report adds a twist to updated numbers from the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Prevalences derived from the passive-surveillance data base, known for including case records of inconsistent quality or completeness, are considered especially prone to reporting bias, the authors acknowledged.
The current analysis, however, plunges deep into VAERS-reported cases of presumed SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated myocarditis to help clarify “more of the characteristics of the patients and some of the treatments and short-term outcomes,” Matthew E. Oster, MD, MPH, said in an interview.
Dr. Oster, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Emory University, Atlanta, is lead author on the study’s Jan. 25, 2022, publication in JAMA.
The group reviewed charts and interviewed involved clinicians to adjudicate and document presentations, therapies, and the clinical course of cases reported as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–associated myocarditis from December 2020 to August 2021. Out of the nearly 2000 reports, which were limited to patients younger than 30, the group identified 1,626 likely cases of such myocarditis arising within 7 days of a second mRNA vaccine dose.
The confirmed cases consistently represented higher prevalences than expected compared with prepandemic myocarditis claims data for both sexes and across age groups spanning 12-29 years.
For example, rates were highest for adolescent males – about 106 and 71 cases per million second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in those aged 16-17 and 12-16, respectively, for example. They were lowest for women aged 25-29, at 2.23 cases per million second Pfizer-BioNTech doses; the highest rate among females was about 11 per million for the 16-17 age group.
The observed rates, Dr. Oster said, represent an update to VAERS numbers published June 2021 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report covering cases through June 2021.
“Overall, the general risk of having myocarditis from the vaccines is still extremely low. Even in the highest risk groups, it is still extremely low, and still lower than the risk of having cardiac complications from COVID,” he noted.
How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.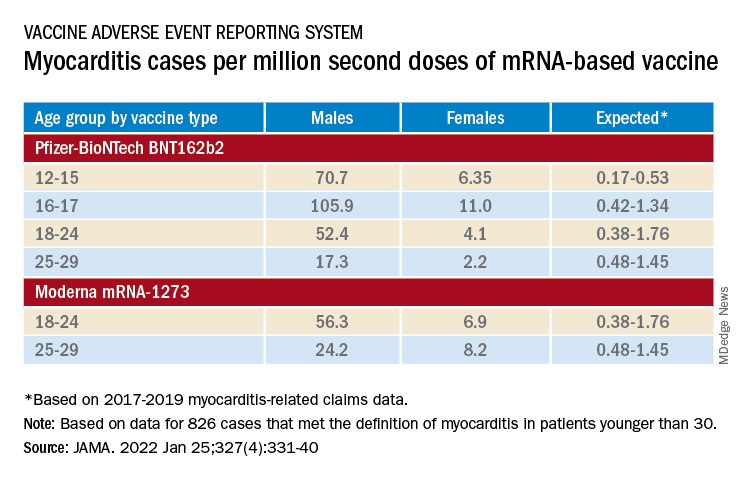
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why some COVID-19 vaccines seem occasionally to cause a distinctive form of myocarditis, and why adolescent boys and young men appear most vulnerable, remain a mystery. But the entity’s prevalence, nuances of presentation, and likely clinical course have come into sharper view after recent additions to the literature.
Two new publications all but confirm that the rare cases of myocarditis closely following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, primarily with one of the mRNA-based vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, is a clinically different creature from myocarditis physicians were likely to see before the pandemic.
A third report unveils rates of hospitalization for myocarditis linked to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in the 12- to 15-year age group, based on active surveillance across Israel. Of note, the rates were lower than corresponding numbers among the country’s 16- to 19-year-olds published in late 2021 by the same authors.
No link with CoronaVac
A case-control study covering almost the entire population of Hong Kong from February to August 2021 confirms a slight but significant excess risk for myocarditis and, to a lesser degree, pericarditis, after injections of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. As consistently reported from other studies, the risks were highest in adolescent and young adult males and after a second dose.
The study estimated an overall carditis incidence of 5.7 cases per million doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, for a risk 3.5 times that in the unvaccinated Hong Kong population. Carditis rates after a first dose were about 2.5 per million and 10 per million after a second dose.
Hong Kong launched its public SARS-CoV-2 immunization program in late February 2021 with the Chinese-made CoronaVac (Sinovac) inactivated-virus vaccine, and introduced the mRNA-based alternative several weeks later. By August 2021, the vaccines had reached about 3.3 million people in the region – 49% of the Hong Kong population at least 12 years of age.
In a novel finding, there were no excesses in carditis cases after CoronaVac vaccination. The difference between vaccines likely isn’t caused by chance, because three-fourths of the carditis-associated Pfizer-BioNTech injections arose within a week, whereas “71% of cases following the use of CoronaVac occurred more than 30 days after vaccination,” senior author Ian Chi Kei Wong, PhD, University of Hong Kong, said in an interview.
“This onset distribution for cases having received CoronaVac demonstrates that it is highly unlikely the carditis cases are related to the vaccine,” he said. And that “plausibly implies a specific underlying mechanism between vaccination and carditis that may only be applicable to mRNA vaccines.”
That inference is in line with case reports and other research, including large population-based studies from Israel and Denmark, although a recent study from the United Kingdom hinted at a potential excess myocarditis risk associated with the adenovirus-based AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
The Hong Kong study identified 160 patients age 12 or older with a first diagnosis of carditis during February to August 2021, in electronic health records covering nearly the entire region.
“We used laboratory test results of troponin levels to further eliminate unlikely cases of carditis,” Dr. Wong said. The health records were linked to a “population-based vaccination record” maintained by the government’s department of health.
About 10 control patients from among all hospitalized patients without carditis were matched by age, sex, and admission date to each of the 160 carditis cases. About 83% of cases and 92% of the controls were unvaccinated.
Among those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, representing 12.5% of cases and 4.2% of controls, the estimated carditis incidence was 0.57 per 100,000 doses. For those who received CoronaVac, representing 4.4% of cases and 3.9% of controls, it was 0.31 per 100,000 doses.
In adjusted analysis, the odds ratios for carditis among Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients, compared with unvaccinated controls, were 3.57 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-6.60) overall, 4.68 (95% CI, 2.25-9.71) for males, 2.22 (95% CI, 0.57-8.69) for females, 2.41 (95% CI, 1.18-4.90) for ages 18 and older, and 13.8 (95% CI, 2.86-110.4) for ages 12-17
Myocarditis accounted for most of the excess cases, with an overall OR of 9.29 (95% CI, 3.94-21.9). The OR reached only 1.06 (95% CI, 0.35-3.22) for pericarditis alone.
The case-control study is noteworthy for its design, which contrasts with the many recent case series and passive or active surveillance studies, and even the more robust population-based studies of vaccine-related myocarditis, observed Dongngan Truong, MD, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, both in Salt Lake City, who wasn’t part of the study.
Among its strengths, she said in an interview, are its linkage of comprehensive hospital and vaccination data sets for two different vaccines; and that it corroborates other research suggesting there is “something in particular about mRNA vaccination that seems to be associated with the development of myocarditis.”
Active surveillance in Israel
In an October 2021 report based on an Israeli Ministry of Health database covering up to May 2021, rates of myocarditis arising within 21 days of a second Pfizer-BioNTech dose in 16- to 19-year-olds reached about 1 per 6,637 males and 1 per 99,853 females. Those numbers compared with 1 per 26,000 males and 1 per 218,000 females across all age groups.
Now authors led by Dror Mevorach, MD, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, have published corresponding numbers from the same data base for myocarditis associated with the same vaccine in males and females aged 12-15.
Their research covers 404,407 people in that age group who received a first dose of the mRNA-based vaccine and 326,463 who received the second dose from June to October, 2021. Only 18 cases of myocarditis were observed within 21 days of either dose.
The estimated rates for males were 0.56 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 8.09 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
For females, the estimates were 0 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 0.69 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
“The pattern observed, mainly following the second vaccination in males, suggests causality,” the group wrote.
Leveraging passive surveillance reports
Another new report adds a twist to updated numbers from the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Prevalences derived from the passive-surveillance data base, known for including case records of inconsistent quality or completeness, are considered especially prone to reporting bias, the authors acknowledged.
The current analysis, however, plunges deep into VAERS-reported cases of presumed SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated myocarditis to help clarify “more of the characteristics of the patients and some of the treatments and short-term outcomes,” Matthew E. Oster, MD, MPH, said in an interview.
Dr. Oster, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Emory University, Atlanta, is lead author on the study’s Jan. 25, 2022, publication in JAMA.
The group reviewed charts and interviewed involved clinicians to adjudicate and document presentations, therapies, and the clinical course of cases reported as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–associated myocarditis from December 2020 to August 2021. Out of the nearly 2000 reports, which were limited to patients younger than 30, the group identified 1,626 likely cases of such myocarditis arising within 7 days of a second mRNA vaccine dose.
The confirmed cases consistently represented higher prevalences than expected compared with prepandemic myocarditis claims data for both sexes and across age groups spanning 12-29 years.
For example, rates were highest for adolescent males – about 106 and 71 cases per million second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in those aged 16-17 and 12-16, respectively, for example. They were lowest for women aged 25-29, at 2.23 cases per million second Pfizer-BioNTech doses; the highest rate among females was about 11 per million for the 16-17 age group.
The observed rates, Dr. Oster said, represent an update to VAERS numbers published June 2021 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report covering cases through June 2021.
“Overall, the general risk of having myocarditis from the vaccines is still extremely low. Even in the highest risk groups, it is still extremely low, and still lower than the risk of having cardiac complications from COVID,” he noted.
How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why some COVID-19 vaccines seem occasionally to cause a distinctive form of myocarditis, and why adolescent boys and young men appear most vulnerable, remain a mystery. But the entity’s prevalence, nuances of presentation, and likely clinical course have come into sharper view after recent additions to the literature.
Two new publications all but confirm that the rare cases of myocarditis closely following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, primarily with one of the mRNA-based vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, is a clinically different creature from myocarditis physicians were likely to see before the pandemic.
A third report unveils rates of hospitalization for myocarditis linked to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in the 12- to 15-year age group, based on active surveillance across Israel. Of note, the rates were lower than corresponding numbers among the country’s 16- to 19-year-olds published in late 2021 by the same authors.
No link with CoronaVac
A case-control study covering almost the entire population of Hong Kong from February to August 2021 confirms a slight but significant excess risk for myocarditis and, to a lesser degree, pericarditis, after injections of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. As consistently reported from other studies, the risks were highest in adolescent and young adult males and after a second dose.
The study estimated an overall carditis incidence of 5.7 cases per million doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, for a risk 3.5 times that in the unvaccinated Hong Kong population. Carditis rates after a first dose were about 2.5 per million and 10 per million after a second dose.
Hong Kong launched its public SARS-CoV-2 immunization program in late February 2021 with the Chinese-made CoronaVac (Sinovac) inactivated-virus vaccine, and introduced the mRNA-based alternative several weeks later. By August 2021, the vaccines had reached about 3.3 million people in the region – 49% of the Hong Kong population at least 12 years of age.
In a novel finding, there were no excesses in carditis cases after CoronaVac vaccination. The difference between vaccines likely isn’t caused by chance, because three-fourths of the carditis-associated Pfizer-BioNTech injections arose within a week, whereas “71% of cases following the use of CoronaVac occurred more than 30 days after vaccination,” senior author Ian Chi Kei Wong, PhD, University of Hong Kong, said in an interview.
“This onset distribution for cases having received CoronaVac demonstrates that it is highly unlikely the carditis cases are related to the vaccine,” he said. And that “plausibly implies a specific underlying mechanism between vaccination and carditis that may only be applicable to mRNA vaccines.”
That inference is in line with case reports and other research, including large population-based studies from Israel and Denmark, although a recent study from the United Kingdom hinted at a potential excess myocarditis risk associated with the adenovirus-based AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
The Hong Kong study identified 160 patients age 12 or older with a first diagnosis of carditis during February to August 2021, in electronic health records covering nearly the entire region.
“We used laboratory test results of troponin levels to further eliminate unlikely cases of carditis,” Dr. Wong said. The health records were linked to a “population-based vaccination record” maintained by the government’s department of health.
About 10 control patients from among all hospitalized patients without carditis were matched by age, sex, and admission date to each of the 160 carditis cases. About 83% of cases and 92% of the controls were unvaccinated.
Among those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, representing 12.5% of cases and 4.2% of controls, the estimated carditis incidence was 0.57 per 100,000 doses. For those who received CoronaVac, representing 4.4% of cases and 3.9% of controls, it was 0.31 per 100,000 doses.
In adjusted analysis, the odds ratios for carditis among Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients, compared with unvaccinated controls, were 3.57 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-6.60) overall, 4.68 (95% CI, 2.25-9.71) for males, 2.22 (95% CI, 0.57-8.69) for females, 2.41 (95% CI, 1.18-4.90) for ages 18 and older, and 13.8 (95% CI, 2.86-110.4) for ages 12-17
Myocarditis accounted for most of the excess cases, with an overall OR of 9.29 (95% CI, 3.94-21.9). The OR reached only 1.06 (95% CI, 0.35-3.22) for pericarditis alone.
The case-control study is noteworthy for its design, which contrasts with the many recent case series and passive or active surveillance studies, and even the more robust population-based studies of vaccine-related myocarditis, observed Dongngan Truong, MD, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, both in Salt Lake City, who wasn’t part of the study.
Among its strengths, she said in an interview, are its linkage of comprehensive hospital and vaccination data sets for two different vaccines; and that it corroborates other research suggesting there is “something in particular about mRNA vaccination that seems to be associated with the development of myocarditis.”
Active surveillance in Israel
In an October 2021 report based on an Israeli Ministry of Health database covering up to May 2021, rates of myocarditis arising within 21 days of a second Pfizer-BioNTech dose in 16- to 19-year-olds reached about 1 per 6,637 males and 1 per 99,853 females. Those numbers compared with 1 per 26,000 males and 1 per 218,000 females across all age groups.
Now authors led by Dror Mevorach, MD, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, have published corresponding numbers from the same data base for myocarditis associated with the same vaccine in males and females aged 12-15.
Their research covers 404,407 people in that age group who received a first dose of the mRNA-based vaccine and 326,463 who received the second dose from June to October, 2021. Only 18 cases of myocarditis were observed within 21 days of either dose.
The estimated rates for males were 0.56 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 8.09 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
For females, the estimates were 0 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 0.69 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
“The pattern observed, mainly following the second vaccination in males, suggests causality,” the group wrote.
Leveraging passive surveillance reports
Another new report adds a twist to updated numbers from the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Prevalences derived from the passive-surveillance data base, known for including case records of inconsistent quality or completeness, are considered especially prone to reporting bias, the authors acknowledged.
The current analysis, however, plunges deep into VAERS-reported cases of presumed SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated myocarditis to help clarify “more of the characteristics of the patients and some of the treatments and short-term outcomes,” Matthew E. Oster, MD, MPH, said in an interview.
Dr. Oster, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Emory University, Atlanta, is lead author on the study’s Jan. 25, 2022, publication in JAMA.
The group reviewed charts and interviewed involved clinicians to adjudicate and document presentations, therapies, and the clinical course of cases reported as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–associated myocarditis from December 2020 to August 2021. Out of the nearly 2000 reports, which were limited to patients younger than 30, the group identified 1,626 likely cases of such myocarditis arising within 7 days of a second mRNA vaccine dose.
The confirmed cases consistently represented higher prevalences than expected compared with prepandemic myocarditis claims data for both sexes and across age groups spanning 12-29 years.
For example, rates were highest for adolescent males – about 106 and 71 cases per million second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in those aged 16-17 and 12-16, respectively, for example. They were lowest for women aged 25-29, at 2.23 cases per million second Pfizer-BioNTech doses; the highest rate among females was about 11 per million for the 16-17 age group.
The observed rates, Dr. Oster said, represent an update to VAERS numbers published June 2021 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report covering cases through June 2021.
“Overall, the general risk of having myocarditis from the vaccines is still extremely low. Even in the highest risk groups, it is still extremely low, and still lower than the risk of having cardiac complications from COVID,” he noted.
How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.