User login
A biopsy of the lesion was performed that showed a well-defined nodulocystic tumor composed of nests of basaloid cells that are undergoing trichilemmal keratinization. Shadow cells are seen as well as small areas of calcification. There is also a histiocytic infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells. The histologic diagnosis is of a pilomatrixoma.
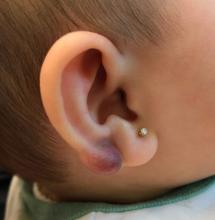
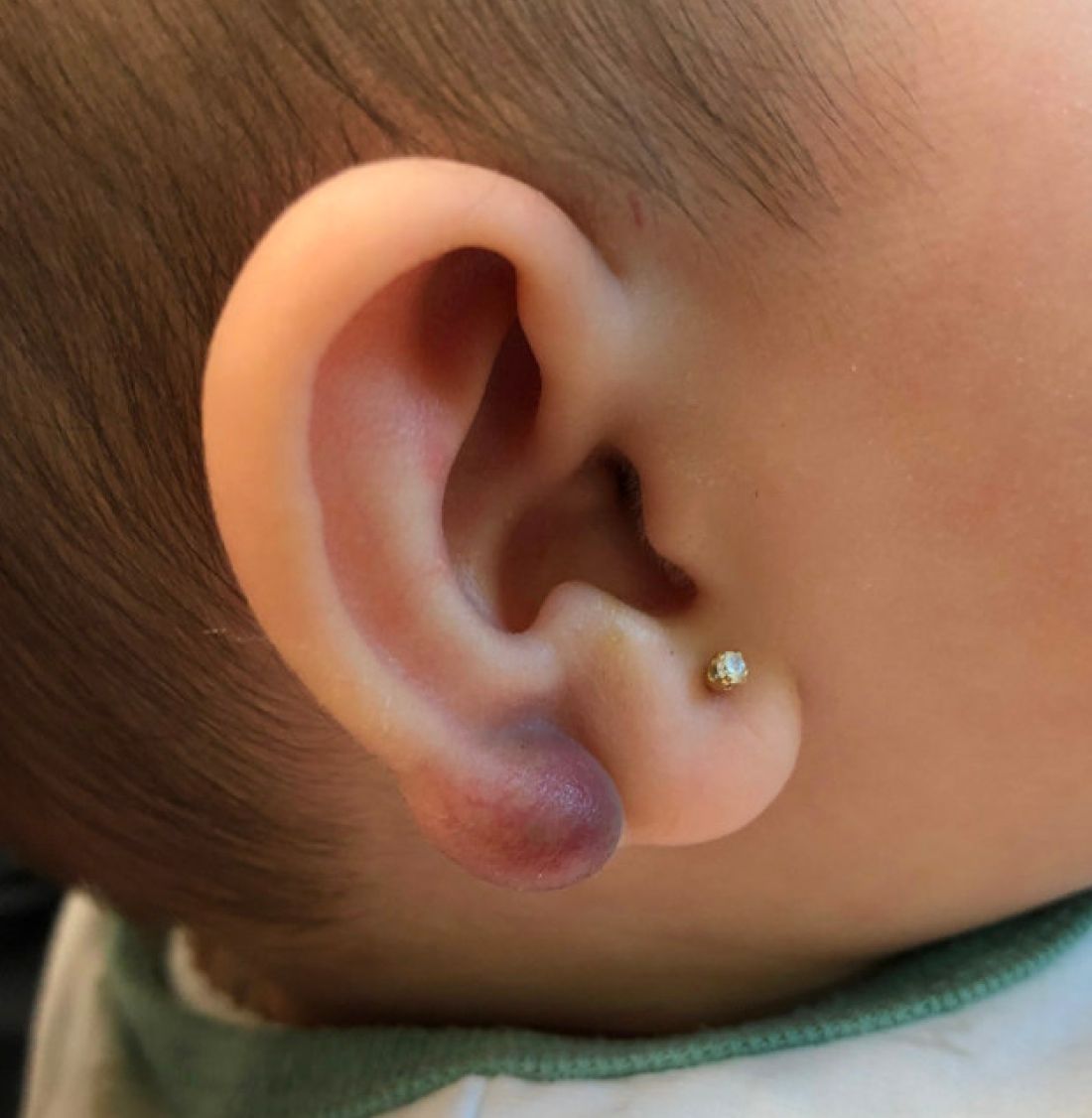
Pilomatrixoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, was first described in 1880, as a tumor of sebaceous gland origin. Later, in 1961, Robert Forbis Jr, MD, and Elson B. Helwig, MD, coined the term pilomatrixoma to describe the hair follicle matrix as the source of the tumor. Pilomatrixomas are commonly seen in the pediatric population, usually in children between 8 and 13 years of age. Our patient is one of the youngest described. The lesions are commonly seen on the face and neck in about 70% of the cases followed by the upper extremities, back, and legs. Clinically, the lesions appear as a firm dermal papule or nodule, which moves freely and may have associated erythema on the skin surface or a blueish gray hue on the underlying skin.
Most pilomatrixomas that have been studied have shown a mutation in Exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1). The beta-catenin molecule is a subunit of the cadherin protein, which is part of an important pathway in the terminal hair follicle differentiation. Beta-catenin also plays an important role in the Wnt pathway, which regulates cell fate as well as early embryonic patterning. Beta-catenin is responsible for forming adhesion junctions among cells. There have also been immunohistochemical studies that have shown a BCL2 proto-oncogene overexpression to pilomatrixoma.
There are several genetic syndromes that have been associated with the presence of pilomatrixomas: Turner syndrome (XO chromosome abnormality associated with short stature and cardiac defects), Gardner syndrome (polyposis coli and colon and rectal cancer), myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (characterized by broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability), and trisomy 9. On physical examination our patient didn’t present with any of the typical features or history that could suggest any of these syndromes. A close follow-up and evaluation by a geneticist was recommended because after the initial visit she developed a second lesion on the forehead.
The differential diagnosis for this lesion includes other cysts that may occur on the ear such as epidermal inclusion cyst or dermoid cysts, though these lesions do not tend to be as firm as pilomatrixomas are, which can help with the diagnosis. Dermoid cysts are made of dermal and epidermal components. They are usually present at birth and are commonly seen on the scalp and the periorbital face.
Keloids are rubbery nodules of scar tissue that can form on sites of trauma, and although the lesion occurred after she had her ears pierced, the consistency and rapid growth of the lesion as well as the pathological description made this benign fibrous growth less likely.
When pilomatrixomas are inflamed they can be confused with vascular growths: in this particular case, a hemangioma or another vascular tumor such as a tufted angioma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. An ultrasound of the lesion could have helped in the differential diagnosis of the lesion.
Pilomatrixomas can grow significantly and in some cases get inflamed or infected. Surgical management of pilomatrixomas is often required because the lesions do not regress spontaneously.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Forbis R Jr and Helwig EB. Arch Dermatol 1961;83:606-18.
Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;85:148-53.
A biopsy of the lesion was performed that showed a well-defined nodulocystic tumor composed of nests of basaloid cells that are undergoing trichilemmal keratinization. Shadow cells are seen as well as small areas of calcification. There is also a histiocytic infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells. The histologic diagnosis is of a pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, was first described in 1880, as a tumor of sebaceous gland origin. Later, in 1961, Robert Forbis Jr, MD, and Elson B. Helwig, MD, coined the term pilomatrixoma to describe the hair follicle matrix as the source of the tumor. Pilomatrixomas are commonly seen in the pediatric population, usually in children between 8 and 13 years of age. Our patient is one of the youngest described. The lesions are commonly seen on the face and neck in about 70% of the cases followed by the upper extremities, back, and legs. Clinically, the lesions appear as a firm dermal papule or nodule, which moves freely and may have associated erythema on the skin surface or a blueish gray hue on the underlying skin.
Most pilomatrixomas that have been studied have shown a mutation in Exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1). The beta-catenin molecule is a subunit of the cadherin protein, which is part of an important pathway in the terminal hair follicle differentiation. Beta-catenin also plays an important role in the Wnt pathway, which regulates cell fate as well as early embryonic patterning. Beta-catenin is responsible for forming adhesion junctions among cells. There have also been immunohistochemical studies that have shown a BCL2 proto-oncogene overexpression to pilomatrixoma.
There are several genetic syndromes that have been associated with the presence of pilomatrixomas: Turner syndrome (XO chromosome abnormality associated with short stature and cardiac defects), Gardner syndrome (polyposis coli and colon and rectal cancer), myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (characterized by broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability), and trisomy 9. On physical examination our patient didn’t present with any of the typical features or history that could suggest any of these syndromes. A close follow-up and evaluation by a geneticist was recommended because after the initial visit she developed a second lesion on the forehead.
The differential diagnosis for this lesion includes other cysts that may occur on the ear such as epidermal inclusion cyst or dermoid cysts, though these lesions do not tend to be as firm as pilomatrixomas are, which can help with the diagnosis. Dermoid cysts are made of dermal and epidermal components. They are usually present at birth and are commonly seen on the scalp and the periorbital face.
Keloids are rubbery nodules of scar tissue that can form on sites of trauma, and although the lesion occurred after she had her ears pierced, the consistency and rapid growth of the lesion as well as the pathological description made this benign fibrous growth less likely.
When pilomatrixomas are inflamed they can be confused with vascular growths: in this particular case, a hemangioma or another vascular tumor such as a tufted angioma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. An ultrasound of the lesion could have helped in the differential diagnosis of the lesion.
Pilomatrixomas can grow significantly and in some cases get inflamed or infected. Surgical management of pilomatrixomas is often required because the lesions do not regress spontaneously.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Forbis R Jr and Helwig EB. Arch Dermatol 1961;83:606-18.
Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;85:148-53.
A biopsy of the lesion was performed that showed a well-defined nodulocystic tumor composed of nests of basaloid cells that are undergoing trichilemmal keratinization. Shadow cells are seen as well as small areas of calcification. There is also a histiocytic infiltrate with multinucleated giant cells. The histologic diagnosis is of a pilomatrixoma.
Pilomatrixoma, also known as calcifying epithelioma of Malherbe, was first described in 1880, as a tumor of sebaceous gland origin. Later, in 1961, Robert Forbis Jr, MD, and Elson B. Helwig, MD, coined the term pilomatrixoma to describe the hair follicle matrix as the source of the tumor. Pilomatrixomas are commonly seen in the pediatric population, usually in children between 8 and 13 years of age. Our patient is one of the youngest described. The lesions are commonly seen on the face and neck in about 70% of the cases followed by the upper extremities, back, and legs. Clinically, the lesions appear as a firm dermal papule or nodule, which moves freely and may have associated erythema on the skin surface or a blueish gray hue on the underlying skin.
Most pilomatrixomas that have been studied have shown a mutation in Exon 3 of the beta-catenin gene (CTNNB1). The beta-catenin molecule is a subunit of the cadherin protein, which is part of an important pathway in the terminal hair follicle differentiation. Beta-catenin also plays an important role in the Wnt pathway, which regulates cell fate as well as early embryonic patterning. Beta-catenin is responsible for forming adhesion junctions among cells. There have also been immunohistochemical studies that have shown a BCL2 proto-oncogene overexpression to pilomatrixoma.
There are several genetic syndromes that have been associated with the presence of pilomatrixomas: Turner syndrome (XO chromosome abnormality associated with short stature and cardiac defects), Gardner syndrome (polyposis coli and colon and rectal cancer), myotonic dystrophy, Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (characterized by broad thumbs and toes, short stature, distinctive facial features, and varying degrees of intellectual disability), and trisomy 9. On physical examination our patient didn’t present with any of the typical features or history that could suggest any of these syndromes. A close follow-up and evaluation by a geneticist was recommended because after the initial visit she developed a second lesion on the forehead.
The differential diagnosis for this lesion includes other cysts that may occur on the ear such as epidermal inclusion cyst or dermoid cysts, though these lesions do not tend to be as firm as pilomatrixomas are, which can help with the diagnosis. Dermoid cysts are made of dermal and epidermal components. They are usually present at birth and are commonly seen on the scalp and the periorbital face.
Keloids are rubbery nodules of scar tissue that can form on sites of trauma, and although the lesion occurred after she had her ears pierced, the consistency and rapid growth of the lesion as well as the pathological description made this benign fibrous growth less likely.
When pilomatrixomas are inflamed they can be confused with vascular growths: in this particular case, a hemangioma or another vascular tumor such as a tufted angioma or kaposiform hemangioendothelioma. An ultrasound of the lesion could have helped in the differential diagnosis of the lesion.
Pilomatrixomas can grow significantly and in some cases get inflamed or infected. Surgical management of pilomatrixomas is often required because the lesions do not regress spontaneously.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
Forbis R Jr and Helwig EB. Arch Dermatol 1961;83:606-18.
Schwarz Y et al. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2016 Jun;85:148-53.
A 4-month-old female was referred to our clinic for evaluation of a bump on the right ear. The lesion was first noted at 2 months of age as a little pimple. She was evaluated by her pediatrician and was treated with topical and oral antibiotics without resolution of the lesion. The bump continued to grow and seemed tender to palpation, so she was referred to dermatology for evaluation.
She was born via normal vaginal delivery at 40 weeks. Her mother has no medical conditions and the pregnancy was uneventful. She has been growing and developing well. She takes vitamin D and is currently breast fed.
There have been no other family members with similar lesions. She had her ears pierced at a month of age without any complications.
On skin examination she has a firm red nodule on the right ear that appears slightly tender to touch. She has no other skin lesions of concern. She has normal muscle tone and there are no other abnormalities noted on the physical exam. She has no hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, or lymphadenopathy.