User login
As the Food and Drug Administration focuses on other issues, companies, both big and small, are looking to boost physician and consumer interest in their “medical foods” – products that fall somewhere between drugs and supplements and promise to mitigate symptoms, or even address underlying pathologies, of a range of diseases.
Manufacturers now market an array of medical foods, ranging from powders and capsules for Alzheimer disease to low-protein spaghetti for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The FDA has not been completely absent; it takes a narrow view of what medical conditions qualify for treatment with food products and has warned some manufacturers that their misbranded products are acting more like unapproved drugs.
By the FDA’s definition, medical food is limited to products that provide crucial therapy for patients with inborn errors of metabolism (IEM). An example is specialized baby formula for infants with phenylketonuria. Unlike supplements, medical foods are supposed to be used under the supervision of a physician. This has prompted some sales reps to turn up in the clinic, and most manufacturers have online approval forms for doctors to sign. Manufacturers, advisers, and regulators were interviewed for a closer look at this burgeoning industry.
The market
The global market for medical foods – about $18 billion in 2019 – is expected to grow steadily in the near future. It is drawing more interest, especially in Europe, where medical foods are more accepted by physicians and consumers, Meghan Donnelly, MS, RDN, said in an interview. She is a registered dietitian who conducts physician outreach in the United States for Flavis, a division of Dr. Schär. That company, based in northern Italy, started out targeting IEMs but now also sells gluten-free foods for celiac disease and low-protein foods for CKD.
It is still a niche market in the United States – and isn’t likely to ever approach the size of the supplement market, according to Marcus Charuvastra, the managing director of Targeted Medical Pharma, which markets Theramine capsules for pain management, among many other products. But it could still be a big win for a manufacturer if they get a small slice of a big market, such as for Alzheimer disease.
Defining medical food
According to an update of the Orphan Drug Act in 1988, a medical food is “a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.” The FDA issued regulations to accompany that law in 1993 but has since only issued a guidance document that is not legally binding.
Medical foods are not drugs and they are not supplements (the latter are intended only for healthy people). The FDA doesn’t require formal approval of a medical food, but, by law, the ingredients must be generally recognized as safe, and manufacturers must follow good manufacturing practices. However, the agency has taken a narrow view of what conditions require medical foods.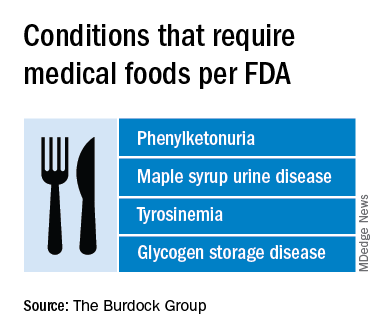
Policing medical foods hasn’t been a priority for the FDA, which is why there has been a proliferation of products that don’t meet the FDA’s view of the statutory definition of medical foods, according to Miriam Guggenheim, a food and drug law attorney in Washington, D.C. The FDA usually takes enforcement action when it sees a risk to the public’s health.
The agency’s stance has led to confusion – among manufacturers, physicians, consumers, and even regulators – making the market a kind of Wild West, according to Paul Hyman, a Washington, D.C.–based attorney who has represented medical food companies.
George A. Burdock, PhD, an Orlando-based regulatory consultant who has worked with medical food makers, believes the FDA will be forced to expand their narrow definition. He foresees a reconsideration of many medical food products in light of an October 2019 White House executive order prohibiting federal agencies from issuing guidance in lieu of rules.
Manufacturers and the FDA differ
One example of a product about which regulators and manufacturers differ is Theramine, which is described as “specially designed to supply the nervous system with the fuel it needs to meet the altered metabolic requirements of chronic pain and inflammatory disorders.”
It is not considered a medical food by the FDA, and the company has had numerous discussions with the agency about their diverging views, according to Mr. Charuvastra. “We’ve had our warning letters and we’ve had our sit downs, and we just had an inspection.”
Targeted Medical Pharma continues to market its products as medical foods but steers away from making any claims that they are like drugs, he said.
Confusion about medical foods has been exposed in the California Workers’ Compensation System by Leslie Wilson, PhD, and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco. They found that physicians regularly wrote medical food prescriptions for non–FDA-approved uses and that the system reimbursed the majority of the products at a cost of $15.5 million from 2011 to 2013. More than half of these prescriptions were for Theramine.
Dr. Wilson reported that, for most products, no evidence supported effectiveness, and they were frequently mislabeled – for all 36 that were studied, submissions for reimbursement were made using a National Drug Code, an impossibility because medical foods are not drugs, and 14 were labeled “Rx only.”
Big-name companies joining in
The FDA does not keep a list of approved medical foods or manufacturers. Both small businesses and big food companies like Danone, Nestlé, and Abbott are players. Most products are sold online.
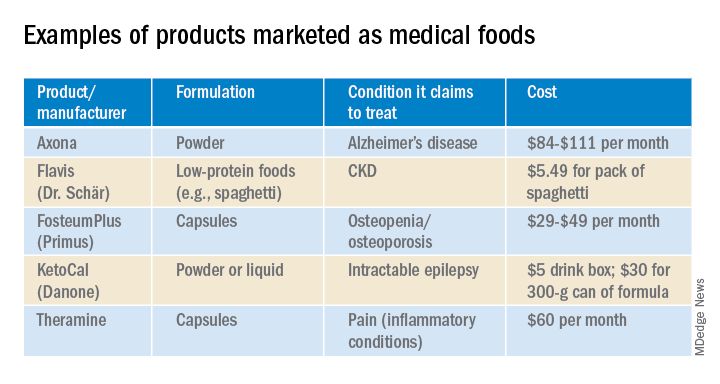
In the United States, Danone’s Nutricia division sells formulas and low-protein foods for IEMs. They also sell Ketocal, a powder or ready-to-drink liquid that is pitched as a balanced medical food to simplify and optimize the ketogenic diet for children with intractable epilepsy. Yet the FDA does not include epilepsy among the conditions that medical foods can treat.
Nestlé sells traditional medical foods for IEMs and also markets a range of what it calls nutritional therapies for such conditions as irritable bowel syndrome and dysphagia.
Nestlé is a minority shareholder in Axona, a product originally developed by Accera (Cerecin as of 2018). Jacquelyn Campo, senior director of global communications at Nestlé Health Sciences, said that the company is not actively involved in the operations management of Cerecin. However, on its website, Nestlé touts Axona, which is only available in the United States, as a “medical food” that “is intended for the clinical dietary management of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.” The Axona site claims that the main ingredient, caprylic triglyceride, is broken down into ketones that provide fuel to treat cerebral hypometabolism, a precursor to Alzheimer disease. In a 2009 study, daily dosing of a preliminary formulation was associated with improved cognitive performance compared with placebo in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.
In 2013, the FDA warned Accera that it was misbranding Axona as a medical food and that the therapeutic claims the company was making would make the product an unapproved drug. Ms. Campo said Nestlé is aware of the agency’s warning, but added, “to our knowledge, Cerecin provided answers to the issues raised by the FDA.”
With the goal of getting drug approval, Accera went on to test a tweaked formulation in a 400-patient randomized, placebo-controlled trial called NOURISH AD that ultimately failed. Nevertheless, Axona is still marketed as a medical food. It costs about $100 for a month’s supply.
Repeated requests for comment from Cerecin were not answered. Danielle Schor, an FDA spokesperson, said the agency will not discuss the status of individual products.
More disputes and insurance coverage
Mary Ann DeMarco, executive director of sales and marketing for the Scottsdale, Ariz.–based medical food maker Primus Pharmaceuticals, said the company believes its products fit within the FDA’s medical foods rubric.
These include Fosteum Plus capsules, which it markets “for the clinical dietary management of the metabolic processes of osteopenia and osteoporosis.” The capsules contain a combination of genistein, zinc, calcium, phosphate, vitamin K2, and vitamin D. As proof of effectiveness, the company cites clinical data on some of the ingredients – not the product itself.
Primus has run afoul of the FDA before when it similarly positioned another product, called Limbrel, as a medical food for osteoarthritis. From 2007 to 2017, the FDA received 194 adverse event reports associated with Limbrel, including reports of drug-induced liver injury, pancreatitis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In December 2017, the agency urged Primus to recall Limbrel, a move that it said was “necessary to protect the public health and welfare.” Primus withdrew the product but laid out a defense of Limbrel on a devoted website.
The FDA would not comment any further, said Ms. Schor. Ms. DeMarco said that Primus is working with the FDA to bring Limbrel back to market.
A lack of insurance coverage – even for approved medical foods for IEMs – has frustrated advocates, parents, and manufacturers. They are putting their weight behind the Medical Nutrition Equity Act, which would mandate public and private payer coverage of medical foods for IEMs and digestive conditions such as Crohn disease. That 2019 House bill has 56 cosponsors; there is no Senate companion bill.
“If you can get reimbursement, it really makes the market,” for Primus and the other manufacturers, Mr. Hyman said.
Primus Pharmaceuticals has launched its own campaign, Cover My Medical Foods, to enlist consumers and others to the cause.
Partnering with advocates
Although its low-protein breads, pastas, and baking products are not considered medical foods by the FDA, Dr. Schär is marketing them as such in the United States. They are trying to make a mark in CKD, according to Ms. Donnelly. She added that Dr. Schär has been successful in Europe, where nutrition therapy is more integrated in the health care system.
In 2019, Flavis and the National Kidney Foundation joined forces to raise awareness of nutritional interventions and to build enthusiasm for the Flavis products. The partnership has now ended, mostly because Flavis could no longer afford it, according to Ms. Donnelly.
“Information on diet and nutrition is the most requested subject matter from the NKF,” said Anthony Gucciardo, senior vice president of strategic partnerships at the foundation. The partnership “has never been necessarily about promoting their products per se; it’s promoting a healthy diet and really a diet specific for CKD.”
The NKF developed cobranded materials on low-protein foods for physicians and a teaching tool they could use with patients. Consumers could access nutrition information and a discount on Flavis products on a dedicated webpage. The foundation didn’t describe the low-protein products as medical foods, said Mr. Gucciardo, even if Flavis promoted them as such.
In patients with CKD, dietary management can help prevent the progression to end-stage renal disease. Although Medicare covers medical nutrition therapy – in which patients receive personalized assessments and dietary advice – uptake is abysmally low, according to a 2018 study.
Dr. Burdock thinks low-protein foods for CKD do meet the FDA’s criteria for a medical food but that the agency might not necessarily agree with him. The FDA would not comment.
Physician beware
When it comes to medical foods, the FDA has often looked the other way because the ingredients may already have been proven safe and the danger to an individual or to the public’s health is relatively low, according to Dr. Burdock and Mr. Hyman.
However, if the agency “feels that a medical food will prevent people from seeking medical care or there is potential to defraud the public, it is justified in taking action against the company,” said Dr. Burdock.
According to Dr. Wilson, the pharmacist who reported on the inappropriate medical food prescriptions in the California system, the FDA could help by creating a list of approved medical foods. Physicians should take time to learn about the difference between medical foods and supplements, she said, adding that they should also not hesitate to “question the veracity of the claims for them.”
Ms. Guggenheim believed doctors need to know that, for the most part, these are not FDA-approved products. She emphasized the importance of evaluating the products and looking at the data of their impact on a disease or condition.
“Many of these companies strongly believe that the products work and help people, so clinicians need to be very data driven,” she said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As the Food and Drug Administration focuses on other issues, companies, both big and small, are looking to boost physician and consumer interest in their “medical foods” – products that fall somewhere between drugs and supplements and promise to mitigate symptoms, or even address underlying pathologies, of a range of diseases.
Manufacturers now market an array of medical foods, ranging from powders and capsules for Alzheimer disease to low-protein spaghetti for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The FDA has not been completely absent; it takes a narrow view of what medical conditions qualify for treatment with food products and has warned some manufacturers that their misbranded products are acting more like unapproved drugs.
By the FDA’s definition, medical food is limited to products that provide crucial therapy for patients with inborn errors of metabolism (IEM). An example is specialized baby formula for infants with phenylketonuria. Unlike supplements, medical foods are supposed to be used under the supervision of a physician. This has prompted some sales reps to turn up in the clinic, and most manufacturers have online approval forms for doctors to sign. Manufacturers, advisers, and regulators were interviewed for a closer look at this burgeoning industry.
The market
The global market for medical foods – about $18 billion in 2019 – is expected to grow steadily in the near future. It is drawing more interest, especially in Europe, where medical foods are more accepted by physicians and consumers, Meghan Donnelly, MS, RDN, said in an interview. She is a registered dietitian who conducts physician outreach in the United States for Flavis, a division of Dr. Schär. That company, based in northern Italy, started out targeting IEMs but now also sells gluten-free foods for celiac disease and low-protein foods for CKD.
It is still a niche market in the United States – and isn’t likely to ever approach the size of the supplement market, according to Marcus Charuvastra, the managing director of Targeted Medical Pharma, which markets Theramine capsules for pain management, among many other products. But it could still be a big win for a manufacturer if they get a small slice of a big market, such as for Alzheimer disease.
Defining medical food
According to an update of the Orphan Drug Act in 1988, a medical food is “a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.” The FDA issued regulations to accompany that law in 1993 but has since only issued a guidance document that is not legally binding.
Medical foods are not drugs and they are not supplements (the latter are intended only for healthy people). The FDA doesn’t require formal approval of a medical food, but, by law, the ingredients must be generally recognized as safe, and manufacturers must follow good manufacturing practices. However, the agency has taken a narrow view of what conditions require medical foods.
Policing medical foods hasn’t been a priority for the FDA, which is why there has been a proliferation of products that don’t meet the FDA’s view of the statutory definition of medical foods, according to Miriam Guggenheim, a food and drug law attorney in Washington, D.C. The FDA usually takes enforcement action when it sees a risk to the public’s health.
The agency’s stance has led to confusion – among manufacturers, physicians, consumers, and even regulators – making the market a kind of Wild West, according to Paul Hyman, a Washington, D.C.–based attorney who has represented medical food companies.
George A. Burdock, PhD, an Orlando-based regulatory consultant who has worked with medical food makers, believes the FDA will be forced to expand their narrow definition. He foresees a reconsideration of many medical food products in light of an October 2019 White House executive order prohibiting federal agencies from issuing guidance in lieu of rules.
Manufacturers and the FDA differ
One example of a product about which regulators and manufacturers differ is Theramine, which is described as “specially designed to supply the nervous system with the fuel it needs to meet the altered metabolic requirements of chronic pain and inflammatory disorders.”
It is not considered a medical food by the FDA, and the company has had numerous discussions with the agency about their diverging views, according to Mr. Charuvastra. “We’ve had our warning letters and we’ve had our sit downs, and we just had an inspection.”
Targeted Medical Pharma continues to market its products as medical foods but steers away from making any claims that they are like drugs, he said.
Confusion about medical foods has been exposed in the California Workers’ Compensation System by Leslie Wilson, PhD, and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco. They found that physicians regularly wrote medical food prescriptions for non–FDA-approved uses and that the system reimbursed the majority of the products at a cost of $15.5 million from 2011 to 2013. More than half of these prescriptions were for Theramine.
Dr. Wilson reported that, for most products, no evidence supported effectiveness, and they were frequently mislabeled – for all 36 that were studied, submissions for reimbursement were made using a National Drug Code, an impossibility because medical foods are not drugs, and 14 were labeled “Rx only.”
Big-name companies joining in
The FDA does not keep a list of approved medical foods or manufacturers. Both small businesses and big food companies like Danone, Nestlé, and Abbott are players. Most products are sold online.

In the United States, Danone’s Nutricia division sells formulas and low-protein foods for IEMs. They also sell Ketocal, a powder or ready-to-drink liquid that is pitched as a balanced medical food to simplify and optimize the ketogenic diet for children with intractable epilepsy. Yet the FDA does not include epilepsy among the conditions that medical foods can treat.
Nestlé sells traditional medical foods for IEMs and also markets a range of what it calls nutritional therapies for such conditions as irritable bowel syndrome and dysphagia.
Nestlé is a minority shareholder in Axona, a product originally developed by Accera (Cerecin as of 2018). Jacquelyn Campo, senior director of global communications at Nestlé Health Sciences, said that the company is not actively involved in the operations management of Cerecin. However, on its website, Nestlé touts Axona, which is only available in the United States, as a “medical food” that “is intended for the clinical dietary management of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.” The Axona site claims that the main ingredient, caprylic triglyceride, is broken down into ketones that provide fuel to treat cerebral hypometabolism, a precursor to Alzheimer disease. In a 2009 study, daily dosing of a preliminary formulation was associated with improved cognitive performance compared with placebo in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.
In 2013, the FDA warned Accera that it was misbranding Axona as a medical food and that the therapeutic claims the company was making would make the product an unapproved drug. Ms. Campo said Nestlé is aware of the agency’s warning, but added, “to our knowledge, Cerecin provided answers to the issues raised by the FDA.”
With the goal of getting drug approval, Accera went on to test a tweaked formulation in a 400-patient randomized, placebo-controlled trial called NOURISH AD that ultimately failed. Nevertheless, Axona is still marketed as a medical food. It costs about $100 for a month’s supply.
Repeated requests for comment from Cerecin were not answered. Danielle Schor, an FDA spokesperson, said the agency will not discuss the status of individual products.
More disputes and insurance coverage
Mary Ann DeMarco, executive director of sales and marketing for the Scottsdale, Ariz.–based medical food maker Primus Pharmaceuticals, said the company believes its products fit within the FDA’s medical foods rubric.
These include Fosteum Plus capsules, which it markets “for the clinical dietary management of the metabolic processes of osteopenia and osteoporosis.” The capsules contain a combination of genistein, zinc, calcium, phosphate, vitamin K2, and vitamin D. As proof of effectiveness, the company cites clinical data on some of the ingredients – not the product itself.
Primus has run afoul of the FDA before when it similarly positioned another product, called Limbrel, as a medical food for osteoarthritis. From 2007 to 2017, the FDA received 194 adverse event reports associated with Limbrel, including reports of drug-induced liver injury, pancreatitis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In December 2017, the agency urged Primus to recall Limbrel, a move that it said was “necessary to protect the public health and welfare.” Primus withdrew the product but laid out a defense of Limbrel on a devoted website.
The FDA would not comment any further, said Ms. Schor. Ms. DeMarco said that Primus is working with the FDA to bring Limbrel back to market.
A lack of insurance coverage – even for approved medical foods for IEMs – has frustrated advocates, parents, and manufacturers. They are putting their weight behind the Medical Nutrition Equity Act, which would mandate public and private payer coverage of medical foods for IEMs and digestive conditions such as Crohn disease. That 2019 House bill has 56 cosponsors; there is no Senate companion bill.
“If you can get reimbursement, it really makes the market,” for Primus and the other manufacturers, Mr. Hyman said.
Primus Pharmaceuticals has launched its own campaign, Cover My Medical Foods, to enlist consumers and others to the cause.
Partnering with advocates
Although its low-protein breads, pastas, and baking products are not considered medical foods by the FDA, Dr. Schär is marketing them as such in the United States. They are trying to make a mark in CKD, according to Ms. Donnelly. She added that Dr. Schär has been successful in Europe, where nutrition therapy is more integrated in the health care system.
In 2019, Flavis and the National Kidney Foundation joined forces to raise awareness of nutritional interventions and to build enthusiasm for the Flavis products. The partnership has now ended, mostly because Flavis could no longer afford it, according to Ms. Donnelly.
“Information on diet and nutrition is the most requested subject matter from the NKF,” said Anthony Gucciardo, senior vice president of strategic partnerships at the foundation. The partnership “has never been necessarily about promoting their products per se; it’s promoting a healthy diet and really a diet specific for CKD.”
The NKF developed cobranded materials on low-protein foods for physicians and a teaching tool they could use with patients. Consumers could access nutrition information and a discount on Flavis products on a dedicated webpage. The foundation didn’t describe the low-protein products as medical foods, said Mr. Gucciardo, even if Flavis promoted them as such.
In patients with CKD, dietary management can help prevent the progression to end-stage renal disease. Although Medicare covers medical nutrition therapy – in which patients receive personalized assessments and dietary advice – uptake is abysmally low, according to a 2018 study.
Dr. Burdock thinks low-protein foods for CKD do meet the FDA’s criteria for a medical food but that the agency might not necessarily agree with him. The FDA would not comment.
Physician beware
When it comes to medical foods, the FDA has often looked the other way because the ingredients may already have been proven safe and the danger to an individual or to the public’s health is relatively low, according to Dr. Burdock and Mr. Hyman.
However, if the agency “feels that a medical food will prevent people from seeking medical care or there is potential to defraud the public, it is justified in taking action against the company,” said Dr. Burdock.
According to Dr. Wilson, the pharmacist who reported on the inappropriate medical food prescriptions in the California system, the FDA could help by creating a list of approved medical foods. Physicians should take time to learn about the difference between medical foods and supplements, she said, adding that they should also not hesitate to “question the veracity of the claims for them.”
Ms. Guggenheim believed doctors need to know that, for the most part, these are not FDA-approved products. She emphasized the importance of evaluating the products and looking at the data of their impact on a disease or condition.
“Many of these companies strongly believe that the products work and help people, so clinicians need to be very data driven,” she said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
As the Food and Drug Administration focuses on other issues, companies, both big and small, are looking to boost physician and consumer interest in their “medical foods” – products that fall somewhere between drugs and supplements and promise to mitigate symptoms, or even address underlying pathologies, of a range of diseases.
Manufacturers now market an array of medical foods, ranging from powders and capsules for Alzheimer disease to low-protein spaghetti for chronic kidney disease (CKD). The FDA has not been completely absent; it takes a narrow view of what medical conditions qualify for treatment with food products and has warned some manufacturers that their misbranded products are acting more like unapproved drugs.
By the FDA’s definition, medical food is limited to products that provide crucial therapy for patients with inborn errors of metabolism (IEM). An example is specialized baby formula for infants with phenylketonuria. Unlike supplements, medical foods are supposed to be used under the supervision of a physician. This has prompted some sales reps to turn up in the clinic, and most manufacturers have online approval forms for doctors to sign. Manufacturers, advisers, and regulators were interviewed for a closer look at this burgeoning industry.
The market
The global market for medical foods – about $18 billion in 2019 – is expected to grow steadily in the near future. It is drawing more interest, especially in Europe, where medical foods are more accepted by physicians and consumers, Meghan Donnelly, MS, RDN, said in an interview. She is a registered dietitian who conducts physician outreach in the United States for Flavis, a division of Dr. Schär. That company, based in northern Italy, started out targeting IEMs but now also sells gluten-free foods for celiac disease and low-protein foods for CKD.
It is still a niche market in the United States – and isn’t likely to ever approach the size of the supplement market, according to Marcus Charuvastra, the managing director of Targeted Medical Pharma, which markets Theramine capsules for pain management, among many other products. But it could still be a big win for a manufacturer if they get a small slice of a big market, such as for Alzheimer disease.
Defining medical food
According to an update of the Orphan Drug Act in 1988, a medical food is “a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.” The FDA issued regulations to accompany that law in 1993 but has since only issued a guidance document that is not legally binding.
Medical foods are not drugs and they are not supplements (the latter are intended only for healthy people). The FDA doesn’t require formal approval of a medical food, but, by law, the ingredients must be generally recognized as safe, and manufacturers must follow good manufacturing practices. However, the agency has taken a narrow view of what conditions require medical foods.
Policing medical foods hasn’t been a priority for the FDA, which is why there has been a proliferation of products that don’t meet the FDA’s view of the statutory definition of medical foods, according to Miriam Guggenheim, a food and drug law attorney in Washington, D.C. The FDA usually takes enforcement action when it sees a risk to the public’s health.
The agency’s stance has led to confusion – among manufacturers, physicians, consumers, and even regulators – making the market a kind of Wild West, according to Paul Hyman, a Washington, D.C.–based attorney who has represented medical food companies.
George A. Burdock, PhD, an Orlando-based regulatory consultant who has worked with medical food makers, believes the FDA will be forced to expand their narrow definition. He foresees a reconsideration of many medical food products in light of an October 2019 White House executive order prohibiting federal agencies from issuing guidance in lieu of rules.
Manufacturers and the FDA differ
One example of a product about which regulators and manufacturers differ is Theramine, which is described as “specially designed to supply the nervous system with the fuel it needs to meet the altered metabolic requirements of chronic pain and inflammatory disorders.”
It is not considered a medical food by the FDA, and the company has had numerous discussions with the agency about their diverging views, according to Mr. Charuvastra. “We’ve had our warning letters and we’ve had our sit downs, and we just had an inspection.”
Targeted Medical Pharma continues to market its products as medical foods but steers away from making any claims that they are like drugs, he said.
Confusion about medical foods has been exposed in the California Workers’ Compensation System by Leslie Wilson, PhD, and colleagues at the University of California, San Francisco. They found that physicians regularly wrote medical food prescriptions for non–FDA-approved uses and that the system reimbursed the majority of the products at a cost of $15.5 million from 2011 to 2013. More than half of these prescriptions were for Theramine.
Dr. Wilson reported that, for most products, no evidence supported effectiveness, and they were frequently mislabeled – for all 36 that were studied, submissions for reimbursement were made using a National Drug Code, an impossibility because medical foods are not drugs, and 14 were labeled “Rx only.”
Big-name companies joining in
The FDA does not keep a list of approved medical foods or manufacturers. Both small businesses and big food companies like Danone, Nestlé, and Abbott are players. Most products are sold online.

In the United States, Danone’s Nutricia division sells formulas and low-protein foods for IEMs. They also sell Ketocal, a powder or ready-to-drink liquid that is pitched as a balanced medical food to simplify and optimize the ketogenic diet for children with intractable epilepsy. Yet the FDA does not include epilepsy among the conditions that medical foods can treat.
Nestlé sells traditional medical foods for IEMs and also markets a range of what it calls nutritional therapies for such conditions as irritable bowel syndrome and dysphagia.
Nestlé is a minority shareholder in Axona, a product originally developed by Accera (Cerecin as of 2018). Jacquelyn Campo, senior director of global communications at Nestlé Health Sciences, said that the company is not actively involved in the operations management of Cerecin. However, on its website, Nestlé touts Axona, which is only available in the United States, as a “medical food” that “is intended for the clinical dietary management of mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.” The Axona site claims that the main ingredient, caprylic triglyceride, is broken down into ketones that provide fuel to treat cerebral hypometabolism, a precursor to Alzheimer disease. In a 2009 study, daily dosing of a preliminary formulation was associated with improved cognitive performance compared with placebo in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer disease.
In 2013, the FDA warned Accera that it was misbranding Axona as a medical food and that the therapeutic claims the company was making would make the product an unapproved drug. Ms. Campo said Nestlé is aware of the agency’s warning, but added, “to our knowledge, Cerecin provided answers to the issues raised by the FDA.”
With the goal of getting drug approval, Accera went on to test a tweaked formulation in a 400-patient randomized, placebo-controlled trial called NOURISH AD that ultimately failed. Nevertheless, Axona is still marketed as a medical food. It costs about $100 for a month’s supply.
Repeated requests for comment from Cerecin were not answered. Danielle Schor, an FDA spokesperson, said the agency will not discuss the status of individual products.
More disputes and insurance coverage
Mary Ann DeMarco, executive director of sales and marketing for the Scottsdale, Ariz.–based medical food maker Primus Pharmaceuticals, said the company believes its products fit within the FDA’s medical foods rubric.
These include Fosteum Plus capsules, which it markets “for the clinical dietary management of the metabolic processes of osteopenia and osteoporosis.” The capsules contain a combination of genistein, zinc, calcium, phosphate, vitamin K2, and vitamin D. As proof of effectiveness, the company cites clinical data on some of the ingredients – not the product itself.
Primus has run afoul of the FDA before when it similarly positioned another product, called Limbrel, as a medical food for osteoarthritis. From 2007 to 2017, the FDA received 194 adverse event reports associated with Limbrel, including reports of drug-induced liver injury, pancreatitis, and hypersensitivity pneumonitis. In December 2017, the agency urged Primus to recall Limbrel, a move that it said was “necessary to protect the public health and welfare.” Primus withdrew the product but laid out a defense of Limbrel on a devoted website.
The FDA would not comment any further, said Ms. Schor. Ms. DeMarco said that Primus is working with the FDA to bring Limbrel back to market.
A lack of insurance coverage – even for approved medical foods for IEMs – has frustrated advocates, parents, and manufacturers. They are putting their weight behind the Medical Nutrition Equity Act, which would mandate public and private payer coverage of medical foods for IEMs and digestive conditions such as Crohn disease. That 2019 House bill has 56 cosponsors; there is no Senate companion bill.
“If you can get reimbursement, it really makes the market,” for Primus and the other manufacturers, Mr. Hyman said.
Primus Pharmaceuticals has launched its own campaign, Cover My Medical Foods, to enlist consumers and others to the cause.
Partnering with advocates
Although its low-protein breads, pastas, and baking products are not considered medical foods by the FDA, Dr. Schär is marketing them as such in the United States. They are trying to make a mark in CKD, according to Ms. Donnelly. She added that Dr. Schär has been successful in Europe, where nutrition therapy is more integrated in the health care system.
In 2019, Flavis and the National Kidney Foundation joined forces to raise awareness of nutritional interventions and to build enthusiasm for the Flavis products. The partnership has now ended, mostly because Flavis could no longer afford it, according to Ms. Donnelly.
“Information on diet and nutrition is the most requested subject matter from the NKF,” said Anthony Gucciardo, senior vice president of strategic partnerships at the foundation. The partnership “has never been necessarily about promoting their products per se; it’s promoting a healthy diet and really a diet specific for CKD.”
The NKF developed cobranded materials on low-protein foods for physicians and a teaching tool they could use with patients. Consumers could access nutrition information and a discount on Flavis products on a dedicated webpage. The foundation didn’t describe the low-protein products as medical foods, said Mr. Gucciardo, even if Flavis promoted them as such.
In patients with CKD, dietary management can help prevent the progression to end-stage renal disease. Although Medicare covers medical nutrition therapy – in which patients receive personalized assessments and dietary advice – uptake is abysmally low, according to a 2018 study.
Dr. Burdock thinks low-protein foods for CKD do meet the FDA’s criteria for a medical food but that the agency might not necessarily agree with him. The FDA would not comment.
Physician beware
When it comes to medical foods, the FDA has often looked the other way because the ingredients may already have been proven safe and the danger to an individual or to the public’s health is relatively low, according to Dr. Burdock and Mr. Hyman.
However, if the agency “feels that a medical food will prevent people from seeking medical care or there is potential to defraud the public, it is justified in taking action against the company,” said Dr. Burdock.
According to Dr. Wilson, the pharmacist who reported on the inappropriate medical food prescriptions in the California system, the FDA could help by creating a list of approved medical foods. Physicians should take time to learn about the difference between medical foods and supplements, she said, adding that they should also not hesitate to “question the veracity of the claims for them.”
Ms. Guggenheim believed doctors need to know that, for the most part, these are not FDA-approved products. She emphasized the importance of evaluating the products and looking at the data of their impact on a disease or condition.
“Many of these companies strongly believe that the products work and help people, so clinicians need to be very data driven,” she said.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.