User login
The Diagnosis: Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare histiocytic proliferative disorder of unknown etiology. It has 2 forms: limited cutaneous and systemic. The systemic form, also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, affects the lymph nodes and other organs at times. The disease is characterized by a proliferation of histiocytes in the lymph nodes, most commonly in the cervical basin1; however, the inguinal, axillary, mediastinal, or para-aortic nodes also may be affected.1,2 The skin is the most common site of extranodal disease, seen in approximately 10% of cases.1 Cutaneous involvement often is in the facial area but also can be found on the trunk, ears, neck, arms, legs, and genitals. Clinically, skin lesions appear as papules, plaques, and/or nodules.2
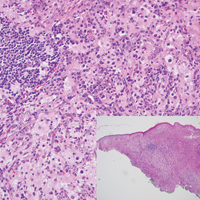
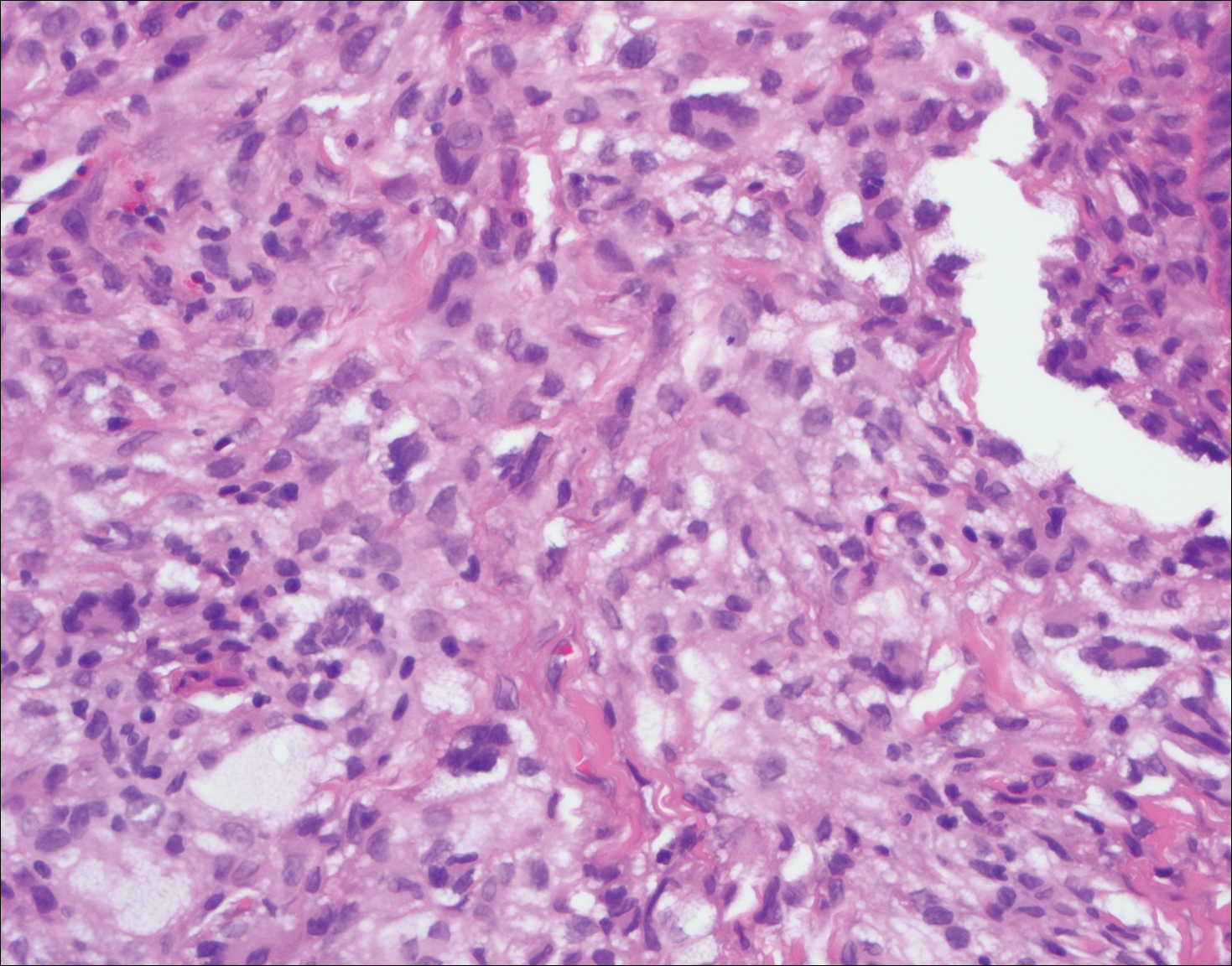
Histopathologic examination of Rosai-Dorfman disease generally shows a dense sheetlike dermal infiltrate of large polygonal histiocytes (Figure 1). Histiocytes may display pale pink or clear cytoplasm. The pathognomonic finding is emperipolesis, which consists of histiocytes with engulfed lymphocytes, erythrocytes, plasma cells, and/or granulocytes surrounded by a clear halo. Immunohistochemical staining also is characteristic, with lesional histiocytes showing expression of S-100 protein (Figure 1, inset) and CD68. The associated inflammatory infiltrate is mixed, containing primarily plasma cells but also lymphocytes, neutrophils, and eosinophils.
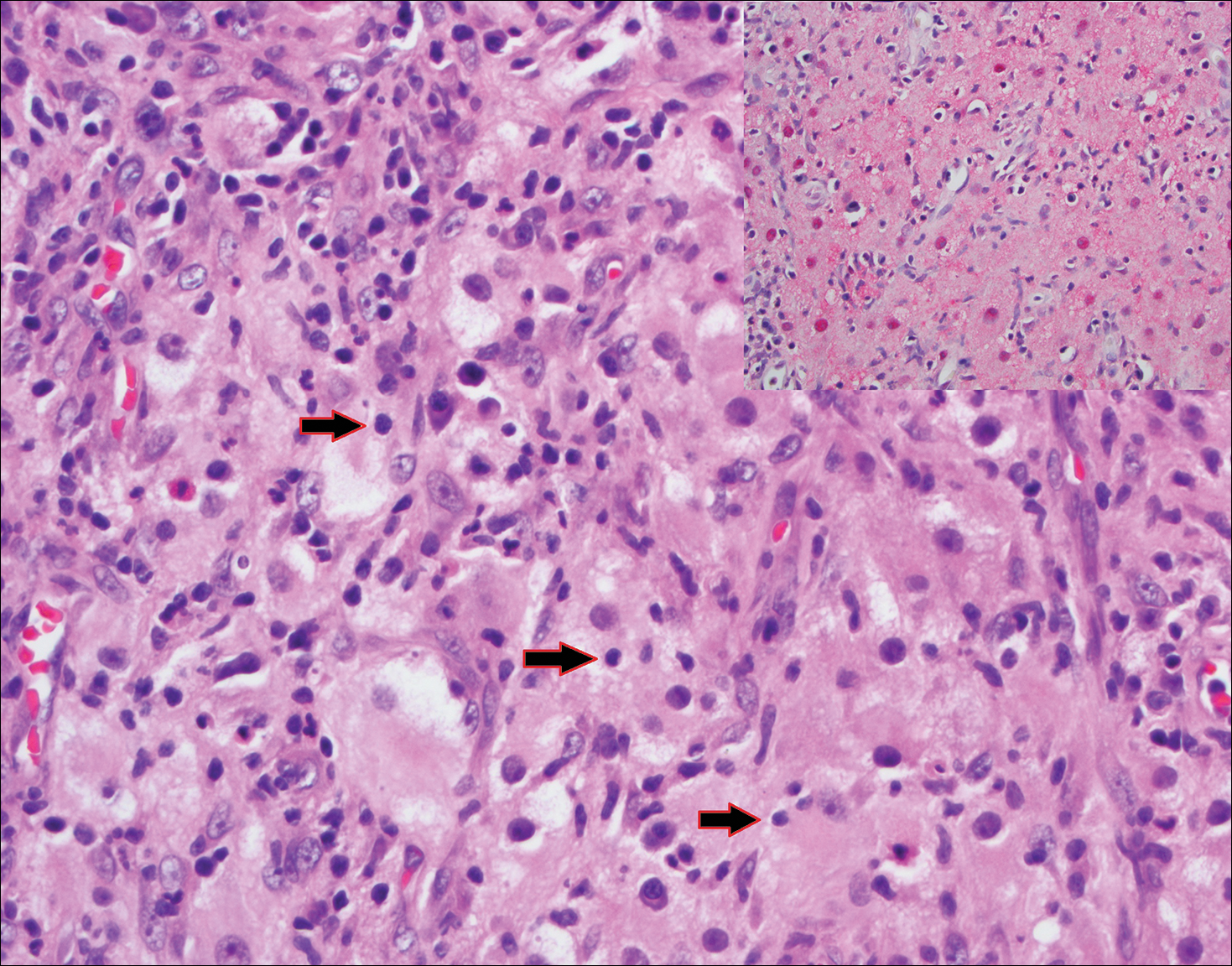
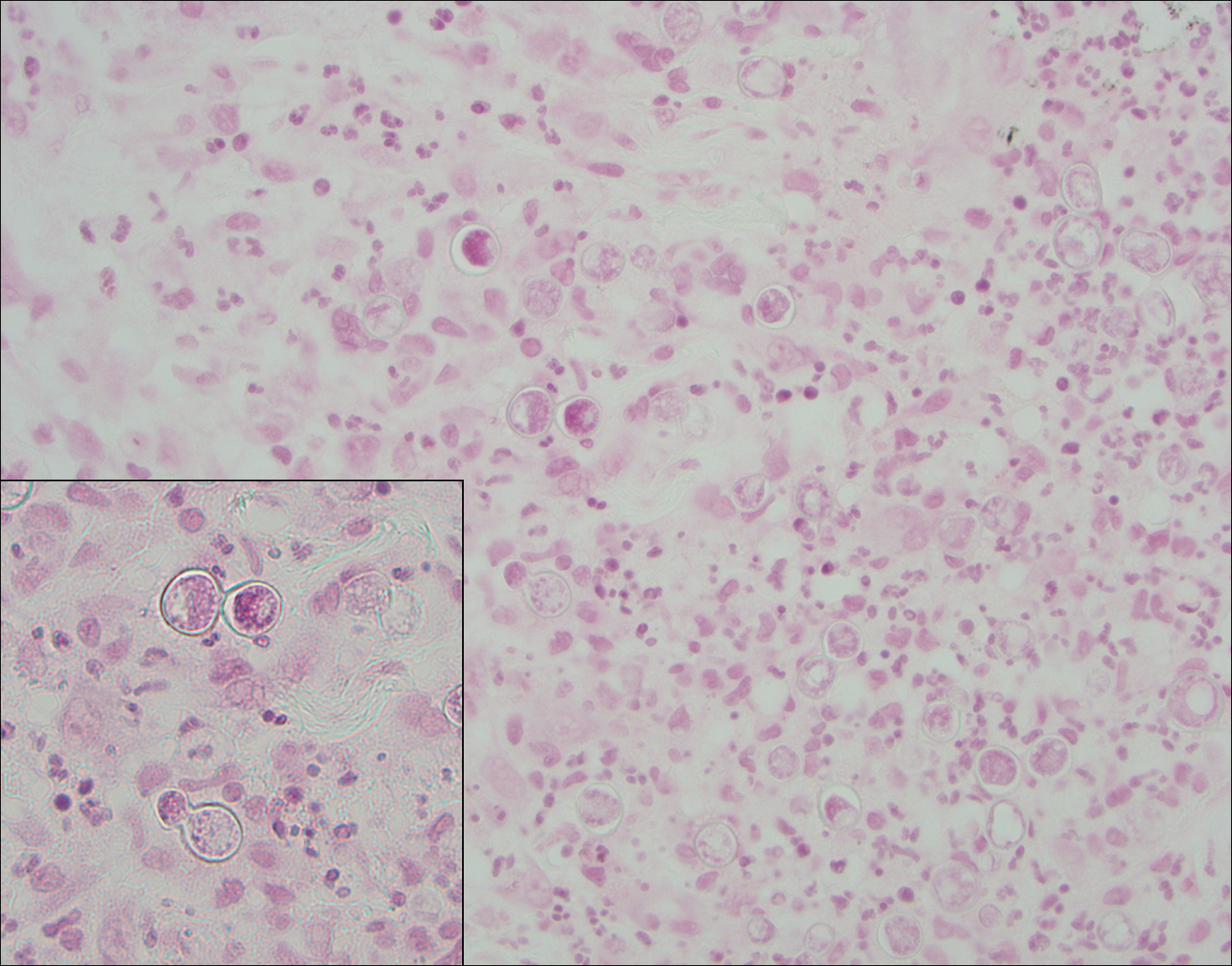
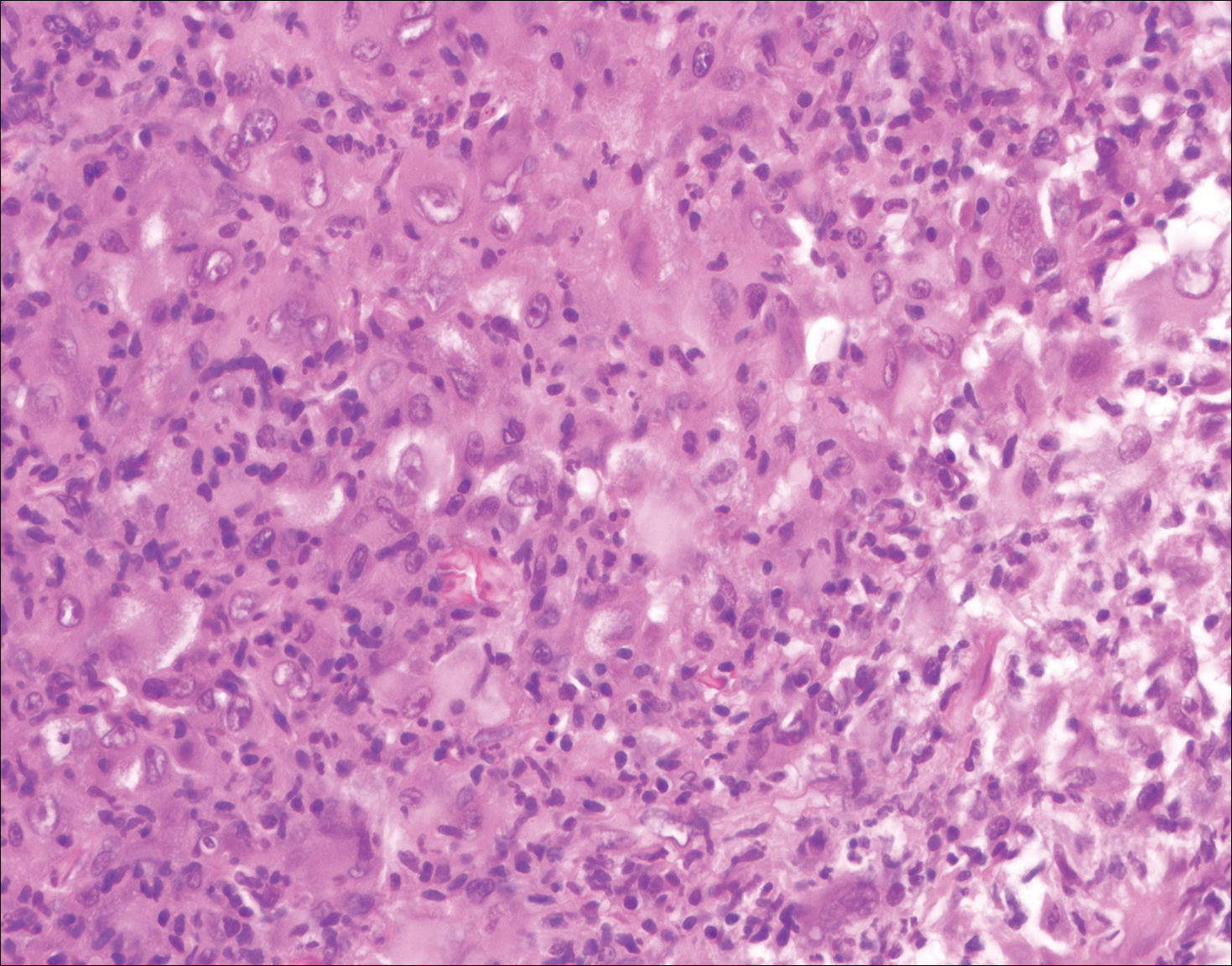
Blastomycosis (Figure 2) is a systemic infection due to inhalation of Blastomyces dermatitidis conidia. Primary infection occurs in the lungs, and with dissemination the skin is the most common subsequently involved organ.3 Cutaneous blastomycosis shows pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with neutrophilic microabscesses and a dense dermal infiltrate containing suppurative granulomatous inflammation. The nonpigmented yeast phase typically is 8 to 15 µm in length with a refractile cell wall and characteristic single, broad-based budding.3
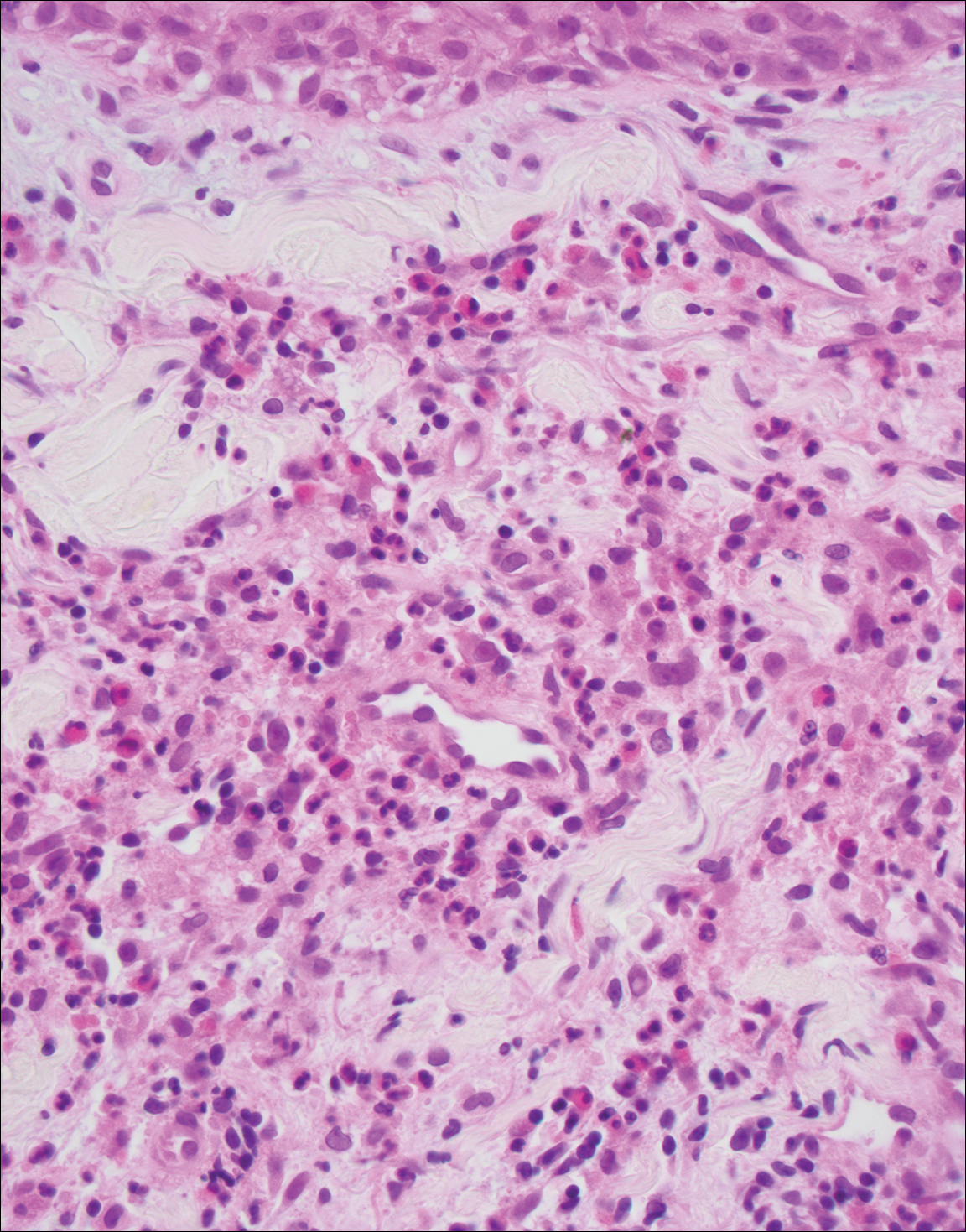
Granuloma faciale (Figure 3) is a rare disease with unknown etiology characterized by reddish brown plaques or nodules most commonly occurring on the face.4,5 Histology shows a dense nodular dermal infiltrate with a grenz zone. The infiltrate is mixed, containing mostly neutrophils with leukocytoclasis and eosinophils. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis is present with associated extravasated erythrocytes. In chronic fibrosing granuloma faciale, lesions can demonstrate fibrosis and hemosiderin deposition, similar to erythema elevatum diutinum.
Juvenile xanthogranuloma (Figure 4) is a common histiocytic disease of early childhood, though adult cases have been reported.6 Tumors are found on the head and trunk and are typically firm, reddish yellow papules or nodules.6,7 Histologic examination shows a nodular infiltrate of foamy histiocytes in the superficial dermis. Touton-type multinucleated giant cells with a peripheral rim of xanthomatized foamy cytoplasm and a wreathlike arrangement of nuclei are characteristic. Associated eosinophils are seen. No emperipolesis is present.
Reticulohistiocytoma (Figure 5) is a benign dermal lesion that presents as solitary or less commonly multiple red-brown papules or nodules.8 Lesions consist of well-delineated nodular aggregates of histiocytes containing a finely granular eosinophilic ground glass cytoplasm. Few, if any, eosinophils are found. The lack of Touton multinucleated giant cells or emperipolesis and lack of expression of S-100 protein helps to distinguish reticulohistiocytoma from other entities in the differential diagnosis.
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:19-73.
- Kutlubay Z, Bairamov O, Sevim A, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report with nodal and cutaneous involvement and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:353-357.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015.
- Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
- Marcoval J, Moreno A, Peyrí J. Granuloma faciale: a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:269-273.
- Rodriguez J, Ackerman AB. Xanthogranuloma in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:43-44.
- Tanz WS, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. Cutis. 1994;54:241-245.
- Cohen PR, Lee RA. Adult-onset reticulohistiocytoma presenting as a solitary asymptomatic red knee nodule: report and review of clinical presentations and immunohistochemistry staining features of reticulohistiocytosis. Dermatology Online J. 2014;20. pii:doj_21725.
The Diagnosis: Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare histiocytic proliferative disorder of unknown etiology. It has 2 forms: limited cutaneous and systemic. The systemic form, also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, affects the lymph nodes and other organs at times. The disease is characterized by a proliferation of histiocytes in the lymph nodes, most commonly in the cervical basin1; however, the inguinal, axillary, mediastinal, or para-aortic nodes also may be affected.1,2 The skin is the most common site of extranodal disease, seen in approximately 10% of cases.1 Cutaneous involvement often is in the facial area but also can be found on the trunk, ears, neck, arms, legs, and genitals. Clinically, skin lesions appear as papules, plaques, and/or nodules.2
Histopathologic examination of Rosai-Dorfman disease generally shows a dense sheetlike dermal infiltrate of large polygonal histiocytes (Figure 1). Histiocytes may display pale pink or clear cytoplasm. The pathognomonic finding is emperipolesis, which consists of histiocytes with engulfed lymphocytes, erythrocytes, plasma cells, and/or granulocytes surrounded by a clear halo. Immunohistochemical staining also is characteristic, with lesional histiocytes showing expression of S-100 protein (Figure 1, inset) and CD68. The associated inflammatory infiltrate is mixed, containing primarily plasma cells but also lymphocytes, neutrophils, and eosinophils.

Blastomycosis (Figure 2) is a systemic infection due to inhalation of Blastomyces dermatitidis conidia. Primary infection occurs in the lungs, and with dissemination the skin is the most common subsequently involved organ.3 Cutaneous blastomycosis shows pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with neutrophilic microabscesses and a dense dermal infiltrate containing suppurative granulomatous inflammation. The nonpigmented yeast phase typically is 8 to 15 µm in length with a refractile cell wall and characteristic single, broad-based budding.3

Granuloma faciale (Figure 3) is a rare disease with unknown etiology characterized by reddish brown plaques or nodules most commonly occurring on the face.4,5 Histology shows a dense nodular dermal infiltrate with a grenz zone. The infiltrate is mixed, containing mostly neutrophils with leukocytoclasis and eosinophils. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis is present with associated extravasated erythrocytes. In chronic fibrosing granuloma faciale, lesions can demonstrate fibrosis and hemosiderin deposition, similar to erythema elevatum diutinum.

Juvenile xanthogranuloma (Figure 4) is a common histiocytic disease of early childhood, though adult cases have been reported.6 Tumors are found on the head and trunk and are typically firm, reddish yellow papules or nodules.6,7 Histologic examination shows a nodular infiltrate of foamy histiocytes in the superficial dermis. Touton-type multinucleated giant cells with a peripheral rim of xanthomatized foamy cytoplasm and a wreathlike arrangement of nuclei are characteristic. Associated eosinophils are seen. No emperipolesis is present.

Reticulohistiocytoma (Figure 5) is a benign dermal lesion that presents as solitary or less commonly multiple red-brown papules or nodules.8 Lesions consist of well-delineated nodular aggregates of histiocytes containing a finely granular eosinophilic ground glass cytoplasm. Few, if any, eosinophils are found. The lack of Touton multinucleated giant cells or emperipolesis and lack of expression of S-100 protein helps to distinguish reticulohistiocytoma from other entities in the differential diagnosis.

The Diagnosis: Rosai-Dorfman Disease
Rosai-Dorfman disease is a rare histiocytic proliferative disorder of unknown etiology. It has 2 forms: limited cutaneous and systemic. The systemic form, also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, affects the lymph nodes and other organs at times. The disease is characterized by a proliferation of histiocytes in the lymph nodes, most commonly in the cervical basin1; however, the inguinal, axillary, mediastinal, or para-aortic nodes also may be affected.1,2 The skin is the most common site of extranodal disease, seen in approximately 10% of cases.1 Cutaneous involvement often is in the facial area but also can be found on the trunk, ears, neck, arms, legs, and genitals. Clinically, skin lesions appear as papules, plaques, and/or nodules.2
Histopathologic examination of Rosai-Dorfman disease generally shows a dense sheetlike dermal infiltrate of large polygonal histiocytes (Figure 1). Histiocytes may display pale pink or clear cytoplasm. The pathognomonic finding is emperipolesis, which consists of histiocytes with engulfed lymphocytes, erythrocytes, plasma cells, and/or granulocytes surrounded by a clear halo. Immunohistochemical staining also is characteristic, with lesional histiocytes showing expression of S-100 protein (Figure 1, inset) and CD68. The associated inflammatory infiltrate is mixed, containing primarily plasma cells but also lymphocytes, neutrophils, and eosinophils.

Blastomycosis (Figure 2) is a systemic infection due to inhalation of Blastomyces dermatitidis conidia. Primary infection occurs in the lungs, and with dissemination the skin is the most common subsequently involved organ.3 Cutaneous blastomycosis shows pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia with neutrophilic microabscesses and a dense dermal infiltrate containing suppurative granulomatous inflammation. The nonpigmented yeast phase typically is 8 to 15 µm in length with a refractile cell wall and characteristic single, broad-based budding.3

Granuloma faciale (Figure 3) is a rare disease with unknown etiology characterized by reddish brown plaques or nodules most commonly occurring on the face.4,5 Histology shows a dense nodular dermal infiltrate with a grenz zone. The infiltrate is mixed, containing mostly neutrophils with leukocytoclasis and eosinophils. Leukocytoclastic vasculitis is present with associated extravasated erythrocytes. In chronic fibrosing granuloma faciale, lesions can demonstrate fibrosis and hemosiderin deposition, similar to erythema elevatum diutinum.

Juvenile xanthogranuloma (Figure 4) is a common histiocytic disease of early childhood, though adult cases have been reported.6 Tumors are found on the head and trunk and are typically firm, reddish yellow papules or nodules.6,7 Histologic examination shows a nodular infiltrate of foamy histiocytes in the superficial dermis. Touton-type multinucleated giant cells with a peripheral rim of xanthomatized foamy cytoplasm and a wreathlike arrangement of nuclei are characteristic. Associated eosinophils are seen. No emperipolesis is present.

Reticulohistiocytoma (Figure 5) is a benign dermal lesion that presents as solitary or less commonly multiple red-brown papules or nodules.8 Lesions consist of well-delineated nodular aggregates of histiocytes containing a finely granular eosinophilic ground glass cytoplasm. Few, if any, eosinophils are found. The lack of Touton multinucleated giant cells or emperipolesis and lack of expression of S-100 protein helps to distinguish reticulohistiocytoma from other entities in the differential diagnosis.

- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:19-73.
- Kutlubay Z, Bairamov O, Sevim A, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report with nodal and cutaneous involvement and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:353-357.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015.
- Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
- Marcoval J, Moreno A, Peyrí J. Granuloma faciale: a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:269-273.
- Rodriguez J, Ackerman AB. Xanthogranuloma in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:43-44.
- Tanz WS, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. Cutis. 1994;54:241-245.
- Cohen PR, Lee RA. Adult-onset reticulohistiocytoma presenting as a solitary asymptomatic red knee nodule: report and review of clinical presentations and immunohistochemistry staining features of reticulohistiocytosis. Dermatology Online J. 2014;20. pii:doj_21725.
- Foucar E, Rosai J, Dorfman R. Sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy (Rosai-Dorfman disease): review of the entity. Semin Diagn Pathol. 1990;7:19-73.
- Kutlubay Z, Bairamov O, Sevim A, et al. Rosai-Dorfman disease: a case report with nodal and cutaneous involvement and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2014;36:353-357.
- James WD, Berger TG, Elston DM, eds. Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: Clinical Dermatology. 12th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2015.
- Wolff K, Johnson R, Saavedra AP. Fitzpatrick's Color Atlas and Synopsis of Clinical Dermatology. 7th ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013.
- Marcoval J, Moreno A, Peyrí J. Granuloma faciale: a clinicopathological study of 11 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;51:269-273.
- Rodriguez J, Ackerman AB. Xanthogranuloma in adults. Arch Dermatol. 1976;112:43-44.
- Tanz WS, Schwartz RA, Janniger CK. Juvenile xanthogranuloma. Cutis. 1994;54:241-245.
- Cohen PR, Lee RA. Adult-onset reticulohistiocytoma presenting as a solitary asymptomatic red knee nodule: report and review of clinical presentations and immunohistochemistry staining features of reticulohistiocytosis. Dermatology Online J. 2014;20. pii:doj_21725.
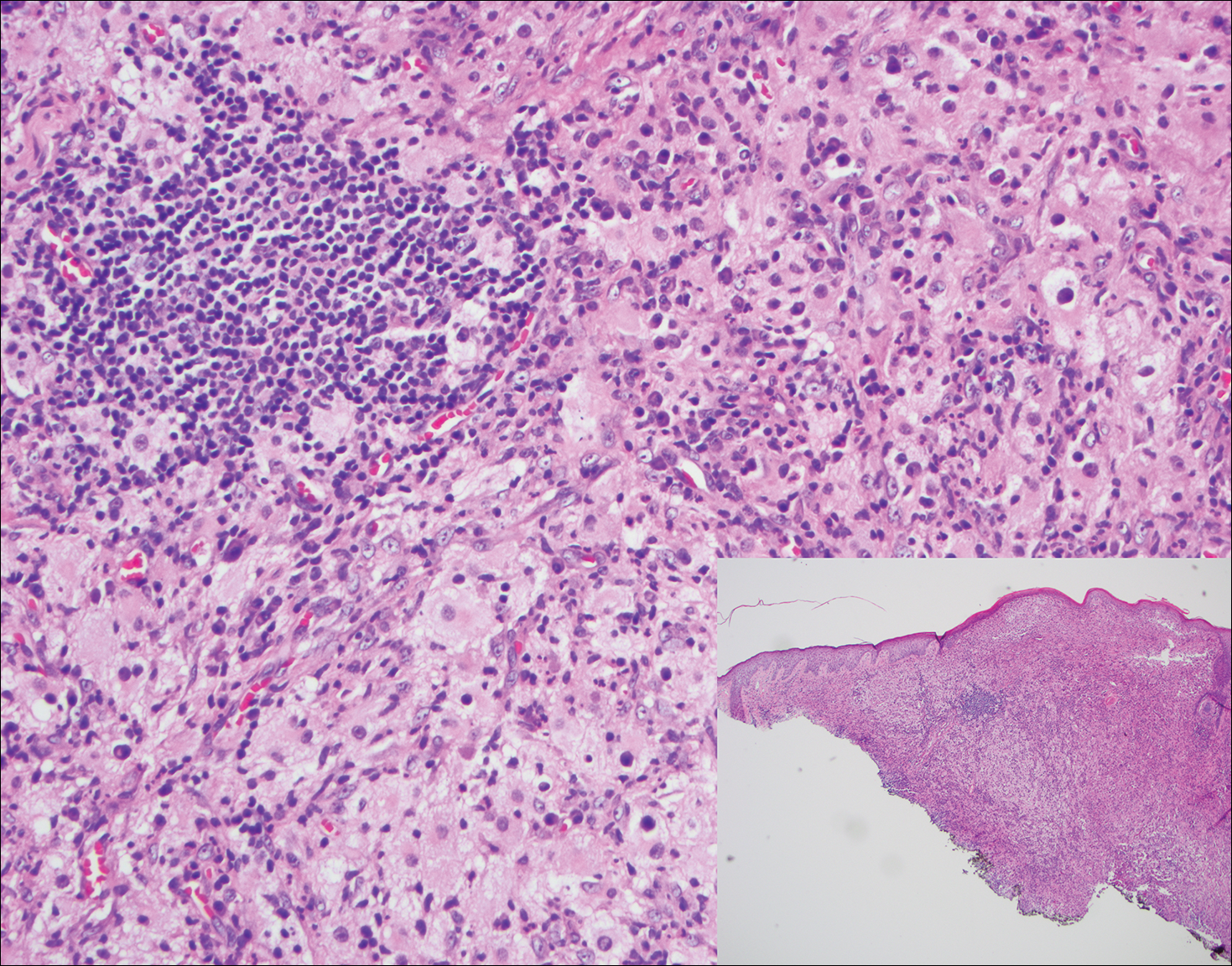
A 59-year-old man presented with itchy and mildly painful nodules on the head and neck of 7 months' duration. The patient denied fever, chills, unintentional weight loss, night sweats, and other systemic symptoms. Physical examination revealed multiple firm pink-orange nodules of varying sizes distributed on the scalp, face, and neck. Right-sided, painless, bulky cervical lymphadenopathy also was noted. An incisional biopsy was performed.