User login
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by flushing, telangiectasia, erythema, papules, and pustules, most classically of the central face. Fair-skinned individuals and women are more commonly affected than are men, with age of onset typically around 30 years and older.1 In children and adolescents, rosacea is rare, especially among prepubertal children, so other papulopustular disorders should be considered when a rosacealike picture is present.2 Recurrent chalazia are seen with ocular rosacea and may be a clue to the diagnosis of acne rosacea. An individual’s subtype of rosacea also may transform with time to a different or an additional subtype.
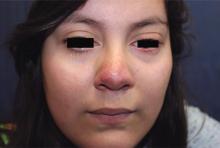
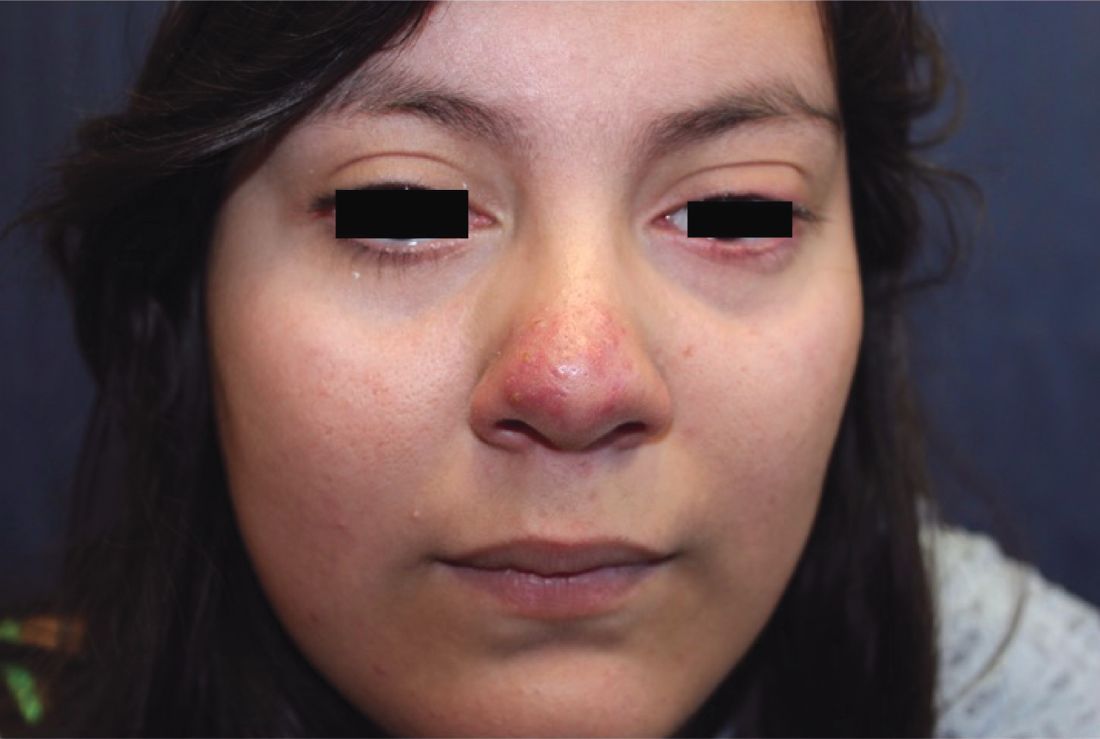
Papulopustular rosacea (subtype II) is characterized by the presence of erythematous, dome-shaped papules distributed in crops in the central facial region. Cheeks, nasolabial folds, and the chin are most commonly affected. Pustules may or may not be present, but comedones are notably absent in an exclusively rosacea disease process. If comedones are present, a diagnosis of acne vulgaris should be considered instead of, or in addition to, rosacea. Pediatric patients with rosacea frequently present with papules and/or pustules, following the development of flushing.2
Ocular rosacea (subtype IV) may range in severity from mild blepharitis to severe keratitis and corneal vascularization. Patients may complain of a foreign body sensation. On external exam, lid margin telangiectasias, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, conjunctival injection, and recurrent chalazia may be frequently seen.3 Ocular rosacea may present without any signs of cutaneous disease; it may be the only form of rosacea (15% of patients in one study of 20 patients had only ocular rosacea)4 or may herald the development of cutaneous involvement. In fact, in children, ocular rosacea is frequently the first sign of disease. (A total of 55% of patients in the same study had both ocular and cutaneous rosacea, with ocular symptoms manifesting before the cutaneous disease). Thus an index of suspicion for rosacea should be maintained when a child presents with ocular findings.2
Other dermatitides resembling rosacea include steroid rosacea, perioral dermatitis, and idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma. Steroid rosacea, also known as iatrosacea, describes an eruption of erythema, papules, and telangiectasias that is clinically indistinguishable from rosacea.6 It results from chronic use of topical steroids, generally high potency, or abrupt withdrawal of steroids. Steroid rosacea should be treated by discontinuation of the steroid via tapered withdrawal.7 Perioral dermatitis, also known as periorificial dermatitis, may also appear rosacea-form. It usually is located around the perioral and perinasal areas, but may extend to the periocular area.8 Idiopathic facial septic granuloma describes erythematous to violaceous nodules of the cheeks and eyelid in children, with chalazia frequently present; it is thought to be associated with rosacea.9
Although the exact pathophysiology of rosacea is unknown, it is clear that the dysregulation of the innate immune system plays a key role in the pathogenesis of rosacea. Studies have found that patients with rosacea have increased expression of cathelicidin, and its activating serine protease, kallikrein.5 Interestingly, UV light, a known trigger of rosacea, induces expression of cathelicidin and its inflammatory cascade.5 Neurovascular signaling is also aberrantly upregulated; vanilloid and ankyrin receptors have been shown to be active in rosacea, and are activated by rosacea-exacerbating stimuli, such as heat, inflammation, and spices. Higher levels of Demodex folliculorum and Staphylococcus epidermis also have been consistently found on the skin of rosacea patients, compared with healthy subjects, though it is unclear what role these pathogens play in the development of rosacea.
Treatment of rosacea is very important given its profound impact on quality of life; one study found that the odds ratio for depression in individuals with rosacea is 4.81.10 Patient education is essential, and patients should be encouraged to identify specific triggers so they can minimize exposure when feasible. Common triggers include hot and cold temperature, sunlight, wind, spicy foods, alcohol, exercise, emotional stress, and certain medications such as niacin. Topical steroids frequently are exacerbating, so patients should be encouraged to avoid them and use moisturizers often, given their skin’s increased transepidermal water loss and susceptibility to irritation. In addition, sunscreens are essential to reduce inflammation from reactive oxygen species, which aggravate rosacea.11 For pharmaceutical therapeutics, topical sodium sulfacetamide, metronidazole, and azelaic acid have been shown to be effective in rosacea. For persistent erythema, topical alpha-adrenergic receptor agonists including brimonidine tartrate and oxymetazoline have been shown to reduce erythema by vasoconstricting blood vessels, although some products are associated with a rebound erythema on treatment discontinuation. For moderate to severe rosacea, low-dose oral doxycycline at anti-inflammatory doses (less than 50 mg daily) is the mainstay of therapy. Other oral antibiotics and topical permethrin have been used, and topical ivermectin 1% cream has been approved for inflammatory rosacea.11 Oral beta-blockers also have been successfully used in some patients to reduce erythema and flushing, as well as isotretinoin for refractory, severe rosacea with improvement.
Allison Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Ms. Han or Dr. Eichenfield.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jan;78(1):148-55.
2. Cutis. 2016 Jul;98(1):49-53.
3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Oct;31(10):1732-8.
4. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2011 Dec;34(10):703-10.
5. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May;72(5):749-58.
6. Indian J Dermatol. 2011 Jan;56(1):30-2.
7. Cutis, 2004. 74(2):99-103.
8. Pediatr Dermatol. 1992 Mar;9(1):22-6.
9. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):e136-9.
10. Br J Dermatol. 2005 Dec;153(6):1176-81.
11. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May;72(5):761-70.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by flushing, telangiectasia, erythema, papules, and pustules, most classically of the central face. Fair-skinned individuals and women are more commonly affected than are men, with age of onset typically around 30 years and older.1 In children and adolescents, rosacea is rare, especially among prepubertal children, so other papulopustular disorders should be considered when a rosacealike picture is present.2 Recurrent chalazia are seen with ocular rosacea and may be a clue to the diagnosis of acne rosacea. An individual’s subtype of rosacea also may transform with time to a different or an additional subtype.
Papulopustular rosacea (subtype II) is characterized by the presence of erythematous, dome-shaped papules distributed in crops in the central facial region. Cheeks, nasolabial folds, and the chin are most commonly affected. Pustules may or may not be present, but comedones are notably absent in an exclusively rosacea disease process. If comedones are present, a diagnosis of acne vulgaris should be considered instead of, or in addition to, rosacea. Pediatric patients with rosacea frequently present with papules and/or pustules, following the development of flushing.2
Ocular rosacea (subtype IV) may range in severity from mild blepharitis to severe keratitis and corneal vascularization. Patients may complain of a foreign body sensation. On external exam, lid margin telangiectasias, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, conjunctival injection, and recurrent chalazia may be frequently seen.3 Ocular rosacea may present without any signs of cutaneous disease; it may be the only form of rosacea (15% of patients in one study of 20 patients had only ocular rosacea)4 or may herald the development of cutaneous involvement. In fact, in children, ocular rosacea is frequently the first sign of disease. (A total of 55% of patients in the same study had both ocular and cutaneous rosacea, with ocular symptoms manifesting before the cutaneous disease). Thus an index of suspicion for rosacea should be maintained when a child presents with ocular findings.2
Other dermatitides resembling rosacea include steroid rosacea, perioral dermatitis, and idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma. Steroid rosacea, also known as iatrosacea, describes an eruption of erythema, papules, and telangiectasias that is clinically indistinguishable from rosacea.6 It results from chronic use of topical steroids, generally high potency, or abrupt withdrawal of steroids. Steroid rosacea should be treated by discontinuation of the steroid via tapered withdrawal.7 Perioral dermatitis, also known as periorificial dermatitis, may also appear rosacea-form. It usually is located around the perioral and perinasal areas, but may extend to the periocular area.8 Idiopathic facial septic granuloma describes erythematous to violaceous nodules of the cheeks and eyelid in children, with chalazia frequently present; it is thought to be associated with rosacea.9
Although the exact pathophysiology of rosacea is unknown, it is clear that the dysregulation of the innate immune system plays a key role in the pathogenesis of rosacea. Studies have found that patients with rosacea have increased expression of cathelicidin, and its activating serine protease, kallikrein.5 Interestingly, UV light, a known trigger of rosacea, induces expression of cathelicidin and its inflammatory cascade.5 Neurovascular signaling is also aberrantly upregulated; vanilloid and ankyrin receptors have been shown to be active in rosacea, and are activated by rosacea-exacerbating stimuli, such as heat, inflammation, and spices. Higher levels of Demodex folliculorum and Staphylococcus epidermis also have been consistently found on the skin of rosacea patients, compared with healthy subjects, though it is unclear what role these pathogens play in the development of rosacea.
Treatment of rosacea is very important given its profound impact on quality of life; one study found that the odds ratio for depression in individuals with rosacea is 4.81.10 Patient education is essential, and patients should be encouraged to identify specific triggers so they can minimize exposure when feasible. Common triggers include hot and cold temperature, sunlight, wind, spicy foods, alcohol, exercise, emotional stress, and certain medications such as niacin. Topical steroids frequently are exacerbating, so patients should be encouraged to avoid them and use moisturizers often, given their skin’s increased transepidermal water loss and susceptibility to irritation. In addition, sunscreens are essential to reduce inflammation from reactive oxygen species, which aggravate rosacea.11 For pharmaceutical therapeutics, topical sodium sulfacetamide, metronidazole, and azelaic acid have been shown to be effective in rosacea. For persistent erythema, topical alpha-adrenergic receptor agonists including brimonidine tartrate and oxymetazoline have been shown to reduce erythema by vasoconstricting blood vessels, although some products are associated with a rebound erythema on treatment discontinuation. For moderate to severe rosacea, low-dose oral doxycycline at anti-inflammatory doses (less than 50 mg daily) is the mainstay of therapy. Other oral antibiotics and topical permethrin have been used, and topical ivermectin 1% cream has been approved for inflammatory rosacea.11 Oral beta-blockers also have been successfully used in some patients to reduce erythema and flushing, as well as isotretinoin for refractory, severe rosacea with improvement.
Allison Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Ms. Han or Dr. Eichenfield.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jan;78(1):148-55.
2. Cutis. 2016 Jul;98(1):49-53.
3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Oct;31(10):1732-8.
4. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2011 Dec;34(10):703-10.
5. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May;72(5):749-58.
6. Indian J Dermatol. 2011 Jan;56(1):30-2.
7. Cutis, 2004. 74(2):99-103.
8. Pediatr Dermatol. 1992 Mar;9(1):22-6.
9. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):e136-9.
10. Br J Dermatol. 2005 Dec;153(6):1176-81.
11. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May;72(5):761-70.
Rosacea is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by flushing, telangiectasia, erythema, papules, and pustules, most classically of the central face. Fair-skinned individuals and women are more commonly affected than are men, with age of onset typically around 30 years and older.1 In children and adolescents, rosacea is rare, especially among prepubertal children, so other papulopustular disorders should be considered when a rosacealike picture is present.2 Recurrent chalazia are seen with ocular rosacea and may be a clue to the diagnosis of acne rosacea. An individual’s subtype of rosacea also may transform with time to a different or an additional subtype.
Papulopustular rosacea (subtype II) is characterized by the presence of erythematous, dome-shaped papules distributed in crops in the central facial region. Cheeks, nasolabial folds, and the chin are most commonly affected. Pustules may or may not be present, but comedones are notably absent in an exclusively rosacea disease process. If comedones are present, a diagnosis of acne vulgaris should be considered instead of, or in addition to, rosacea. Pediatric patients with rosacea frequently present with papules and/or pustules, following the development of flushing.2
Ocular rosacea (subtype IV) may range in severity from mild blepharitis to severe keratitis and corneal vascularization. Patients may complain of a foreign body sensation. On external exam, lid margin telangiectasias, blepharitis, conjunctivitis, conjunctival injection, and recurrent chalazia may be frequently seen.3 Ocular rosacea may present without any signs of cutaneous disease; it may be the only form of rosacea (15% of patients in one study of 20 patients had only ocular rosacea)4 or may herald the development of cutaneous involvement. In fact, in children, ocular rosacea is frequently the first sign of disease. (A total of 55% of patients in the same study had both ocular and cutaneous rosacea, with ocular symptoms manifesting before the cutaneous disease). Thus an index of suspicion for rosacea should be maintained when a child presents with ocular findings.2
Other dermatitides resembling rosacea include steroid rosacea, perioral dermatitis, and idiopathic facial aseptic granuloma. Steroid rosacea, also known as iatrosacea, describes an eruption of erythema, papules, and telangiectasias that is clinically indistinguishable from rosacea.6 It results from chronic use of topical steroids, generally high potency, or abrupt withdrawal of steroids. Steroid rosacea should be treated by discontinuation of the steroid via tapered withdrawal.7 Perioral dermatitis, also known as periorificial dermatitis, may also appear rosacea-form. It usually is located around the perioral and perinasal areas, but may extend to the periocular area.8 Idiopathic facial septic granuloma describes erythematous to violaceous nodules of the cheeks and eyelid in children, with chalazia frequently present; it is thought to be associated with rosacea.9
Although the exact pathophysiology of rosacea is unknown, it is clear that the dysregulation of the innate immune system plays a key role in the pathogenesis of rosacea. Studies have found that patients with rosacea have increased expression of cathelicidin, and its activating serine protease, kallikrein.5 Interestingly, UV light, a known trigger of rosacea, induces expression of cathelicidin and its inflammatory cascade.5 Neurovascular signaling is also aberrantly upregulated; vanilloid and ankyrin receptors have been shown to be active in rosacea, and are activated by rosacea-exacerbating stimuli, such as heat, inflammation, and spices. Higher levels of Demodex folliculorum and Staphylococcus epidermis also have been consistently found on the skin of rosacea patients, compared with healthy subjects, though it is unclear what role these pathogens play in the development of rosacea.
Treatment of rosacea is very important given its profound impact on quality of life; one study found that the odds ratio for depression in individuals with rosacea is 4.81.10 Patient education is essential, and patients should be encouraged to identify specific triggers so they can minimize exposure when feasible. Common triggers include hot and cold temperature, sunlight, wind, spicy foods, alcohol, exercise, emotional stress, and certain medications such as niacin. Topical steroids frequently are exacerbating, so patients should be encouraged to avoid them and use moisturizers often, given their skin’s increased transepidermal water loss and susceptibility to irritation. In addition, sunscreens are essential to reduce inflammation from reactive oxygen species, which aggravate rosacea.11 For pharmaceutical therapeutics, topical sodium sulfacetamide, metronidazole, and azelaic acid have been shown to be effective in rosacea. For persistent erythema, topical alpha-adrenergic receptor agonists including brimonidine tartrate and oxymetazoline have been shown to reduce erythema by vasoconstricting blood vessels, although some products are associated with a rebound erythema on treatment discontinuation. For moderate to severe rosacea, low-dose oral doxycycline at anti-inflammatory doses (less than 50 mg daily) is the mainstay of therapy. Other oral antibiotics and topical permethrin have been used, and topical ivermectin 1% cream has been approved for inflammatory rosacea.11 Oral beta-blockers also have been successfully used in some patients to reduce erythema and flushing, as well as isotretinoin for refractory, severe rosacea with improvement.
Allison Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Ms. Han or Dr. Eichenfield.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2018 Jan;78(1):148-55.
2. Cutis. 2016 Jul;98(1):49-53.
3. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2017 Oct;31(10):1732-8.
4. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2011 Dec;34(10):703-10.
5. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May;72(5):749-58.
6. Indian J Dermatol. 2011 Jan;56(1):30-2.
7. Cutis, 2004. 74(2):99-103.
8. Pediatr Dermatol. 1992 Mar;9(1):22-6.
9. Pediatr Dermatol. 2015 Jul-Aug;32(4):e136-9.
10. Br J Dermatol. 2005 Dec;153(6):1176-81.
11. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2015 May;72(5):761-70.
A 16-year-old girl presented with a 6-month history of an erythematous eruption of small papules and pustules around the cheeks and nose. She states the erythema had started first, with periods of feeling flushed that became worse with sun exposure. She saw her primary care physician who prescribed topical steroids. After using the steroids, the rash became worse, and she developed papules and pustules.