User login
ID Practitioner is an independent news source that provides infectious disease specialists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on the infectious disease specialist’s practice. Specialty focus topics include antimicrobial resistance, emerging infections, global ID, hepatitis, HIV, hospital-acquired infections, immunizations and vaccines, influenza, mycoses, pediatric infections, and STIs. Infectious Diseases News is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
sofosbuvir
ritonavir with dasabuvir
discount
support path
program
ritonavir
greedy
ledipasvir
assistance
viekira pak
vpak
advocacy
needy
protest
abbvie
paritaprevir
ombitasvir
direct-acting antivirals
dasabuvir
gilead
fake-ovir
support
v pak
oasis
harvoni
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-medstat-latest-articles-articles-section')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-idp')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-idp')]
CMS issues guidance on containing spread of coronavirus
The first guidance document, “Guidance for Infection Control and Prevention Concerning Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): FAQs and Considerations for Patient Triage, Placement and Hospital Discharge,” issued March 4, provides some basic guidance, including identifying which patients are at risk, how facilities should screen for COVID-19, how facilities should monitor or restrict health care facility staff, and other recommendations for infection prevention and control.
“Hospitals should identify visitors and patients at risk for having COVID-19 infection before or immediately upon arrival to the healthcare facility,” the guidance document notes. “For patients, implement respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette (i.e., placing a face mask over the patient’s nose and mouth if that has not already been done) and isolate the patient in an examination room with the door closed. If the patient cannot be immediately moved to an examination room, ensure they are not allowed to wait among other patients seeking care.”
The document offers further information regarding the care of patients and provides numerous links to existing guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The second document, “Guidance for Infection Control and Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Nursing Homes,” issued the same day, provides information on how to limit and monitor visitors as well as monitor and restrict health staff. It details when to transfer residents with suspected or confirmed coronavirus infection, and when a nursing home should accept a resident diagnosed with COVID-19.
Facilities “should contact their local health department if they have questions or suspect a resident of a nursing home has COVID-19,” the document states. “Per CDC, prompt detection, triage and isolation of potentially infectious patients are essential to prevent unnecessary exposure among patients, healthcare personnel, and visitors at the facility.”
The CMS also announced that it is suspending all nonemergency survey activity.
“CMS is suspending nonemergency inspections across the country, allowing inspectors to turn their focus on the most serious health and safety threats like infectious diseases and abuse,” the agency stated in a March 4 memo. “This shift in approach will also allow inspectors to focus on addressing the spread of ... COVID-19. CMS is issuing this memorandum to State Survey Agencies to provide important guidelines for the inspection process in situations in which a COVID-19 is suspected.”
In a statement, CMS Administrator Seema Verma said these actions “represent a call to action across the health care system. All health care providers must immediately review their procedures to ensure compliance with CMS’ infection control requirements, as well as the guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.”
The first guidance document, “Guidance for Infection Control and Prevention Concerning Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): FAQs and Considerations for Patient Triage, Placement and Hospital Discharge,” issued March 4, provides some basic guidance, including identifying which patients are at risk, how facilities should screen for COVID-19, how facilities should monitor or restrict health care facility staff, and other recommendations for infection prevention and control.
“Hospitals should identify visitors and patients at risk for having COVID-19 infection before or immediately upon arrival to the healthcare facility,” the guidance document notes. “For patients, implement respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette (i.e., placing a face mask over the patient’s nose and mouth if that has not already been done) and isolate the patient in an examination room with the door closed. If the patient cannot be immediately moved to an examination room, ensure they are not allowed to wait among other patients seeking care.”
The document offers further information regarding the care of patients and provides numerous links to existing guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The second document, “Guidance for Infection Control and Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Nursing Homes,” issued the same day, provides information on how to limit and monitor visitors as well as monitor and restrict health staff. It details when to transfer residents with suspected or confirmed coronavirus infection, and when a nursing home should accept a resident diagnosed with COVID-19.
Facilities “should contact their local health department if they have questions or suspect a resident of a nursing home has COVID-19,” the document states. “Per CDC, prompt detection, triage and isolation of potentially infectious patients are essential to prevent unnecessary exposure among patients, healthcare personnel, and visitors at the facility.”
The CMS also announced that it is suspending all nonemergency survey activity.
“CMS is suspending nonemergency inspections across the country, allowing inspectors to turn their focus on the most serious health and safety threats like infectious diseases and abuse,” the agency stated in a March 4 memo. “This shift in approach will also allow inspectors to focus on addressing the spread of ... COVID-19. CMS is issuing this memorandum to State Survey Agencies to provide important guidelines for the inspection process in situations in which a COVID-19 is suspected.”
In a statement, CMS Administrator Seema Verma said these actions “represent a call to action across the health care system. All health care providers must immediately review their procedures to ensure compliance with CMS’ infection control requirements, as well as the guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.”
The first guidance document, “Guidance for Infection Control and Prevention Concerning Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): FAQs and Considerations for Patient Triage, Placement and Hospital Discharge,” issued March 4, provides some basic guidance, including identifying which patients are at risk, how facilities should screen for COVID-19, how facilities should monitor or restrict health care facility staff, and other recommendations for infection prevention and control.
“Hospitals should identify visitors and patients at risk for having COVID-19 infection before or immediately upon arrival to the healthcare facility,” the guidance document notes. “For patients, implement respiratory hygiene and cough etiquette (i.e., placing a face mask over the patient’s nose and mouth if that has not already been done) and isolate the patient in an examination room with the door closed. If the patient cannot be immediately moved to an examination room, ensure they are not allowed to wait among other patients seeking care.”
The document offers further information regarding the care of patients and provides numerous links to existing guidance from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The second document, “Guidance for Infection Control and Prevention of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Nursing Homes,” issued the same day, provides information on how to limit and monitor visitors as well as monitor and restrict health staff. It details when to transfer residents with suspected or confirmed coronavirus infection, and when a nursing home should accept a resident diagnosed with COVID-19.
Facilities “should contact their local health department if they have questions or suspect a resident of a nursing home has COVID-19,” the document states. “Per CDC, prompt detection, triage and isolation of potentially infectious patients are essential to prevent unnecessary exposure among patients, healthcare personnel, and visitors at the facility.”
The CMS also announced that it is suspending all nonemergency survey activity.
“CMS is suspending nonemergency inspections across the country, allowing inspectors to turn their focus on the most serious health and safety threats like infectious diseases and abuse,” the agency stated in a March 4 memo. “This shift in approach will also allow inspectors to focus on addressing the spread of ... COVID-19. CMS is issuing this memorandum to State Survey Agencies to provide important guidelines for the inspection process in situations in which a COVID-19 is suspected.”
In a statement, CMS Administrator Seema Verma said these actions “represent a call to action across the health care system. All health care providers must immediately review their procedures to ensure compliance with CMS’ infection control requirements, as well as the guidelines from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.”
Monthly injection therapy for HIV found noninferior to daily oral dosing
Two international phase 3 randomized trials of according to reports published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine after Oral Induction for HIV-1 Infection (FLAIR) study and the Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine for Maintenance of HIV-1 Suppression (ATLAS) study looked at a separate facet of the use of a monthly therapeutic injection as a replacement for daily oral HIV therapy.
The FLAIR trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02938520) was a phase 3, randomized, open-label study in which adults with HIV-1 infection who had not previously received antiretroviral therapy were given 20 weeks of daily oral induction therapy with dolutegravir–abacavir–lamivudine. Those patients with an HIV-1 RNA level of less than 50 copies per milliliter after 16 weeks were then randomly assigned (1:1) to continue their current oral therapy or switch to oral cabotegravir plus rilpivirine for 1 month followed by monthly intramuscular injections of long-acting cabotegravir, an HIV-1 integrase strand-transfer inhibitor, and rilpivirine, a nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor.
At week 48, an HIV-1 RNA level of 50 copies per milliliter or higher was found in 6 of 283 patients (2.1%) who received the long-acting therapy and in 7 of 283 (2.5%) who received oral therapy, which met the criterion for noninferiority for the primary endpoint. An HIV-1 RNA level of less than 50 copies per milliliter at week 48 was found in 93.6% of patients who received long-acting therapy and in 93.3% who received oral therapy, which also met the criterion for noninferiority, according to the study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Injection site reactions were reported in 86% of the long-acting therapy patients, 4 of whom withdrew from the trial for injection-related reasons. Grade 3 or higher adverse events and events that met liver-related stopping criteria occurred in 11% and 2%, respectively, of those who received long-acting therapy and in 4% and 1% of those who received oral therapy.
An assessment of treatment satisfaction at 48 weeks showed that 91% of the patients who switched to long-acting therapy preferred it to their daily oral therapy.
The ATLAS trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02951052) was a phase 3, open-label, multicenter, noninferiority trial involving patients who had plasma HIV-1 RNA levels of less than 50 copies per milliliter for at least 6 months while taking standard oral antiretroviral therapy. These patients were randomized (308 in each group) to the long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine injection therapy or daily oral therapy.
At 48 weeks, HIV-1 RNA levels of 50 copies per milliliter or higher were found in five participants (1.6%) receiving long-acting therapy and in three (1.0%) receiving oral therapy, which met the criterion for noninferiority for the primary endpoint, according to a study reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
HIV-1 RNA levels of less than 50 copies per milliliter at week 48 occurred in 92.5% of patients on long-acting therapy and in 95.5% of those receiving oral therapy, which also met the criterion for noninferiority for this endpoint. Three patients in the long-acting therapy group had virologic failure, compared with four participants who received oral therapy.
Adverse events were more common in the long-acting–therapy group and included injection-site pain, which occurred in 231 recipients (75%) of long-acting therapy. This was mild or moderate in most cases, according to the authors. However, 1% of the participants in this group withdrew because of it. Overall, serious adverse events were reported in no more than 5% of participants in each group.
Together, the ATLAS and the FLAIR trials show that long-acting intramuscular injection therapy is noninferior to oral therapy as both an early regimen for HIV treatment, as well as for later, maintenance dosing. The use of long-acting therapy may improve patient adherence to treatment, according to both sets of study authors.
The ATLAS and FLAIR trials were funded by ViiV Healthcare and Janssen. The authors of both studies reported ties to pharmaceutical associations, and some authors are employees of the two funding sources.
SOURCE: Orkin C et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1909512 and Swindells S et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1904398.
Two international phase 3 randomized trials of according to reports published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine after Oral Induction for HIV-1 Infection (FLAIR) study and the Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine for Maintenance of HIV-1 Suppression (ATLAS) study looked at a separate facet of the use of a monthly therapeutic injection as a replacement for daily oral HIV therapy.
The FLAIR trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02938520) was a phase 3, randomized, open-label study in which adults with HIV-1 infection who had not previously received antiretroviral therapy were given 20 weeks of daily oral induction therapy with dolutegravir–abacavir–lamivudine. Those patients with an HIV-1 RNA level of less than 50 copies per milliliter after 16 weeks were then randomly assigned (1:1) to continue their current oral therapy or switch to oral cabotegravir plus rilpivirine for 1 month followed by monthly intramuscular injections of long-acting cabotegravir, an HIV-1 integrase strand-transfer inhibitor, and rilpivirine, a nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor.
At week 48, an HIV-1 RNA level of 50 copies per milliliter or higher was found in 6 of 283 patients (2.1%) who received the long-acting therapy and in 7 of 283 (2.5%) who received oral therapy, which met the criterion for noninferiority for the primary endpoint. An HIV-1 RNA level of less than 50 copies per milliliter at week 48 was found in 93.6% of patients who received long-acting therapy and in 93.3% who received oral therapy, which also met the criterion for noninferiority, according to the study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Injection site reactions were reported in 86% of the long-acting therapy patients, 4 of whom withdrew from the trial for injection-related reasons. Grade 3 or higher adverse events and events that met liver-related stopping criteria occurred in 11% and 2%, respectively, of those who received long-acting therapy and in 4% and 1% of those who received oral therapy.
An assessment of treatment satisfaction at 48 weeks showed that 91% of the patients who switched to long-acting therapy preferred it to their daily oral therapy.
The ATLAS trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02951052) was a phase 3, open-label, multicenter, noninferiority trial involving patients who had plasma HIV-1 RNA levels of less than 50 copies per milliliter for at least 6 months while taking standard oral antiretroviral therapy. These patients were randomized (308 in each group) to the long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine injection therapy or daily oral therapy.
At 48 weeks, HIV-1 RNA levels of 50 copies per milliliter or higher were found in five participants (1.6%) receiving long-acting therapy and in three (1.0%) receiving oral therapy, which met the criterion for noninferiority for the primary endpoint, according to a study reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
HIV-1 RNA levels of less than 50 copies per milliliter at week 48 occurred in 92.5% of patients on long-acting therapy and in 95.5% of those receiving oral therapy, which also met the criterion for noninferiority for this endpoint. Three patients in the long-acting therapy group had virologic failure, compared with four participants who received oral therapy.
Adverse events were more common in the long-acting–therapy group and included injection-site pain, which occurred in 231 recipients (75%) of long-acting therapy. This was mild or moderate in most cases, according to the authors. However, 1% of the participants in this group withdrew because of it. Overall, serious adverse events were reported in no more than 5% of participants in each group.
Together, the ATLAS and the FLAIR trials show that long-acting intramuscular injection therapy is noninferior to oral therapy as both an early regimen for HIV treatment, as well as for later, maintenance dosing. The use of long-acting therapy may improve patient adherence to treatment, according to both sets of study authors.
The ATLAS and FLAIR trials were funded by ViiV Healthcare and Janssen. The authors of both studies reported ties to pharmaceutical associations, and some authors are employees of the two funding sources.
SOURCE: Orkin C et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1909512 and Swindells S et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1904398.
Two international phase 3 randomized trials of according to reports published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine after Oral Induction for HIV-1 Infection (FLAIR) study and the Long-Acting Cabotegravir and Rilpivirine for Maintenance of HIV-1 Suppression (ATLAS) study looked at a separate facet of the use of a monthly therapeutic injection as a replacement for daily oral HIV therapy.
The FLAIR trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02938520) was a phase 3, randomized, open-label study in which adults with HIV-1 infection who had not previously received antiretroviral therapy were given 20 weeks of daily oral induction therapy with dolutegravir–abacavir–lamivudine. Those patients with an HIV-1 RNA level of less than 50 copies per milliliter after 16 weeks were then randomly assigned (1:1) to continue their current oral therapy or switch to oral cabotegravir plus rilpivirine for 1 month followed by monthly intramuscular injections of long-acting cabotegravir, an HIV-1 integrase strand-transfer inhibitor, and rilpivirine, a nonnucleoside reverse-transcriptase inhibitor.
At week 48, an HIV-1 RNA level of 50 copies per milliliter or higher was found in 6 of 283 patients (2.1%) who received the long-acting therapy and in 7 of 283 (2.5%) who received oral therapy, which met the criterion for noninferiority for the primary endpoint. An HIV-1 RNA level of less than 50 copies per milliliter at week 48 was found in 93.6% of patients who received long-acting therapy and in 93.3% who received oral therapy, which also met the criterion for noninferiority, according to the study published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Injection site reactions were reported in 86% of the long-acting therapy patients, 4 of whom withdrew from the trial for injection-related reasons. Grade 3 or higher adverse events and events that met liver-related stopping criteria occurred in 11% and 2%, respectively, of those who received long-acting therapy and in 4% and 1% of those who received oral therapy.
An assessment of treatment satisfaction at 48 weeks showed that 91% of the patients who switched to long-acting therapy preferred it to their daily oral therapy.
The ATLAS trial (ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT02951052) was a phase 3, open-label, multicenter, noninferiority trial involving patients who had plasma HIV-1 RNA levels of less than 50 copies per milliliter for at least 6 months while taking standard oral antiretroviral therapy. These patients were randomized (308 in each group) to the long-acting cabotegravir plus rilpivirine injection therapy or daily oral therapy.
At 48 weeks, HIV-1 RNA levels of 50 copies per milliliter or higher were found in five participants (1.6%) receiving long-acting therapy and in three (1.0%) receiving oral therapy, which met the criterion for noninferiority for the primary endpoint, according to a study reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
HIV-1 RNA levels of less than 50 copies per milliliter at week 48 occurred in 92.5% of patients on long-acting therapy and in 95.5% of those receiving oral therapy, which also met the criterion for noninferiority for this endpoint. Three patients in the long-acting therapy group had virologic failure, compared with four participants who received oral therapy.
Adverse events were more common in the long-acting–therapy group and included injection-site pain, which occurred in 231 recipients (75%) of long-acting therapy. This was mild or moderate in most cases, according to the authors. However, 1% of the participants in this group withdrew because of it. Overall, serious adverse events were reported in no more than 5% of participants in each group.
Together, the ATLAS and the FLAIR trials show that long-acting intramuscular injection therapy is noninferior to oral therapy as both an early regimen for HIV treatment, as well as for later, maintenance dosing. The use of long-acting therapy may improve patient adherence to treatment, according to both sets of study authors.
The ATLAS and FLAIR trials were funded by ViiV Healthcare and Janssen. The authors of both studies reported ties to pharmaceutical associations, and some authors are employees of the two funding sources.
SOURCE: Orkin C et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1909512 and Swindells S et al. N Engl J Med. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1904398.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Survey: 2020 will see more attacks on ACA
When physicians gaze into their crystal balls to predict what’s coming in 2020, they see continued efforts to defund the Affordable Care Act – meaning the ACA will still be around to be defunded – but they don’t see a lot of support for universal health care, according to health care market research company InCrowd.
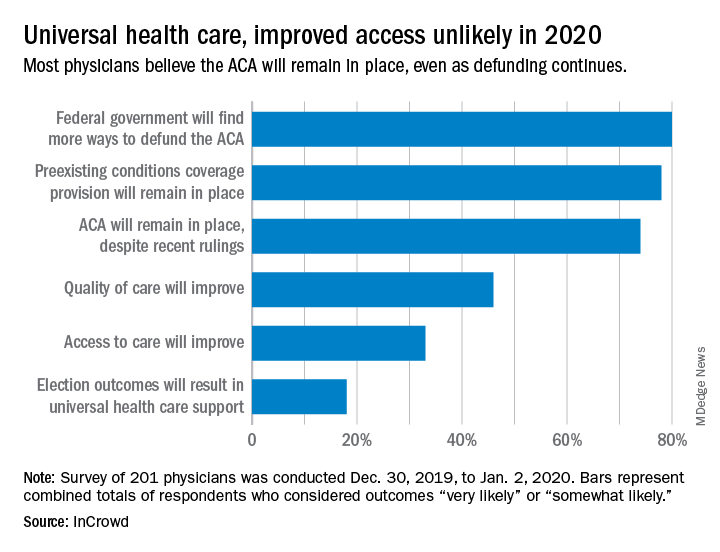
Expectations for universal health care came in at 18% of the 100 generalists and 101 specialists who responded to InCrowd’s fifth annual health care predictions survey, which left 82% who thought that “election outcomes will result in universal healthcare support” was somewhat or very unlikely in 2020.
One respondent, a specialist from California, commented that “the global data on universal healthcare for all shows that it results in overall improved population health. Unfortunately, we are so polarized in the US against universal healthcare driven by bias from health insurance companies and decision makers that are quick to ignore scientific data.”
This was the first time InCrowd asked physicians about universal health care, but ACA-related predictions have been included before, and all three scenarios presented were deemed to be increasingly likely, compared with 2019.
Respondents thought that federal government defunding was more likely to occur in 2020 (80%) than in 2019 (73%), but increased majorities also said that preexisting conditions coverage would continue (78% in 2020 vs. 70% in 2019) and that the ACA would remain in place (74% in 2020 vs. 60% in 2019), InCrowd reported after the survey, which was conducted from Dec. 30, 2019, to Jan. 2, 2020.
A respondent who thought the ACA will be eliminated said, “I have as many uninsured today as before the ACA. They are just different. Mainly younger patients who spend less in a year on healthcare than one month’s premium.” Another suggested that eliminateing it “will limit access to care and overload [emergency departments]. More people will die.”
Cost was addressed in a separate survey question that asked how physicians could help to reduce health care spending in 2020.
The leading answer, given by 37% of respondents, was for physicians to “inform themselves of costs and adapt cost-saving prescription practices.” Next came “limit use of expensive tests and scans” with 21%, followed by “prescribe generics when possible” at 20%, which was a substantial drop from the 38% it garnered in 2019, InCrowd noted.
“Participation in [shared savings] programs and risk-based incentive programs and pay-for-performance programs” would provide “better stewardship of resources,” a primary care physician from Michigan wrote.
When the survey turned to pharmaceutical industry predictions for 2020, cost was the major issue.
“What’s interesting about this year’s data is that we’re seeing less emphasis on the importance of bringing innovative, new therapies to market faster … versus expanding affordability, which was nearly a unanimous top priority for respondents,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, InCrowd’s CEO and president, said in a separate statement.
When physicians gaze into their crystal balls to predict what’s coming in 2020, they see continued efforts to defund the Affordable Care Act – meaning the ACA will still be around to be defunded – but they don’t see a lot of support for universal health care, according to health care market research company InCrowd.

Expectations for universal health care came in at 18% of the 100 generalists and 101 specialists who responded to InCrowd’s fifth annual health care predictions survey, which left 82% who thought that “election outcomes will result in universal healthcare support” was somewhat or very unlikely in 2020.
One respondent, a specialist from California, commented that “the global data on universal healthcare for all shows that it results in overall improved population health. Unfortunately, we are so polarized in the US against universal healthcare driven by bias from health insurance companies and decision makers that are quick to ignore scientific data.”
This was the first time InCrowd asked physicians about universal health care, but ACA-related predictions have been included before, and all three scenarios presented were deemed to be increasingly likely, compared with 2019.
Respondents thought that federal government defunding was more likely to occur in 2020 (80%) than in 2019 (73%), but increased majorities also said that preexisting conditions coverage would continue (78% in 2020 vs. 70% in 2019) and that the ACA would remain in place (74% in 2020 vs. 60% in 2019), InCrowd reported after the survey, which was conducted from Dec. 30, 2019, to Jan. 2, 2020.
A respondent who thought the ACA will be eliminated said, “I have as many uninsured today as before the ACA. They are just different. Mainly younger patients who spend less in a year on healthcare than one month’s premium.” Another suggested that eliminateing it “will limit access to care and overload [emergency departments]. More people will die.”
Cost was addressed in a separate survey question that asked how physicians could help to reduce health care spending in 2020.
The leading answer, given by 37% of respondents, was for physicians to “inform themselves of costs and adapt cost-saving prescription practices.” Next came “limit use of expensive tests and scans” with 21%, followed by “prescribe generics when possible” at 20%, which was a substantial drop from the 38% it garnered in 2019, InCrowd noted.
“Participation in [shared savings] programs and risk-based incentive programs and pay-for-performance programs” would provide “better stewardship of resources,” a primary care physician from Michigan wrote.
When the survey turned to pharmaceutical industry predictions for 2020, cost was the major issue.
“What’s interesting about this year’s data is that we’re seeing less emphasis on the importance of bringing innovative, new therapies to market faster … versus expanding affordability, which was nearly a unanimous top priority for respondents,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, InCrowd’s CEO and president, said in a separate statement.
When physicians gaze into their crystal balls to predict what’s coming in 2020, they see continued efforts to defund the Affordable Care Act – meaning the ACA will still be around to be defunded – but they don’t see a lot of support for universal health care, according to health care market research company InCrowd.

Expectations for universal health care came in at 18% of the 100 generalists and 101 specialists who responded to InCrowd’s fifth annual health care predictions survey, which left 82% who thought that “election outcomes will result in universal healthcare support” was somewhat or very unlikely in 2020.
One respondent, a specialist from California, commented that “the global data on universal healthcare for all shows that it results in overall improved population health. Unfortunately, we are so polarized in the US against universal healthcare driven by bias from health insurance companies and decision makers that are quick to ignore scientific data.”
This was the first time InCrowd asked physicians about universal health care, but ACA-related predictions have been included before, and all three scenarios presented were deemed to be increasingly likely, compared with 2019.
Respondents thought that federal government defunding was more likely to occur in 2020 (80%) than in 2019 (73%), but increased majorities also said that preexisting conditions coverage would continue (78% in 2020 vs. 70% in 2019) and that the ACA would remain in place (74% in 2020 vs. 60% in 2019), InCrowd reported after the survey, which was conducted from Dec. 30, 2019, to Jan. 2, 2020.
A respondent who thought the ACA will be eliminated said, “I have as many uninsured today as before the ACA. They are just different. Mainly younger patients who spend less in a year on healthcare than one month’s premium.” Another suggested that eliminateing it “will limit access to care and overload [emergency departments]. More people will die.”
Cost was addressed in a separate survey question that asked how physicians could help to reduce health care spending in 2020.
The leading answer, given by 37% of respondents, was for physicians to “inform themselves of costs and adapt cost-saving prescription practices.” Next came “limit use of expensive tests and scans” with 21%, followed by “prescribe generics when possible” at 20%, which was a substantial drop from the 38% it garnered in 2019, InCrowd noted.
“Participation in [shared savings] programs and risk-based incentive programs and pay-for-performance programs” would provide “better stewardship of resources,” a primary care physician from Michigan wrote.
When the survey turned to pharmaceutical industry predictions for 2020, cost was the major issue.
“What’s interesting about this year’s data is that we’re seeing less emphasis on the importance of bringing innovative, new therapies to market faster … versus expanding affordability, which was nearly a unanimous top priority for respondents,” Daniel S. Fitzgerald, InCrowd’s CEO and president, said in a separate statement.
FDA moves to expand coronavirus testing capacity; CDC clarifies testing criteria
The White House Coronavirus Task Force appeared at a press briefing March 2 to provide updates about testing strategies and public health coordination to address the current outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19. Speaking at the briefing, led by Vice President Mike Pence, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Robert Redfield, MD, said, “Working with our public health partners we continue to be able to identify new community cases and use our public health efforts to aggressively confirm, isolate, and do contact tracking.” Calling state, local, tribal, and territorial public health departments “the backbone of the public health system in our country,” Dr. Redfield noted that he expected many more confirmed COVID-19 cases to emerge.

At least some of the expected increase in confirmed cases of COVID-19 will occur because of expanded testing capacity, noted several of the task force members. On Feb. 29, the Food and Drug Administration issued a the virus that is causing the current outbreak of COVID-19.
Highly qualified laboratories, including both those run by public agencies and private labs, are now authorized to begin using their own validated test for the virus as long as they submit an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to the Food and Drug Administration within 15 days of notifying the agency of validation.
“To effectively respond to the COVID-19 outbreak, rapid detection of cases and contacts, appropriate clinical management and infection control, and implementation of community mitigation efforts are critical. This can best be achieved with wide availability of testing capabilities in health care settings, reference and commercial laboratories, and at the point of care,” the agency wrote in a press announcement of the expedited test expansion.
On Feb. 4, the Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services declared a coronavirus public health emergency. The FDA was then authorized to allow individual laboratories with validated coronavirus tests to begin testing samples immediately. The goal is a more rapid and expanded testing capacity in the United States.
“The global emergence of COVID-19 is concerning, and we appreciate the efforts of the FDA to help bring more testing capability to the U.S.,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), said in the press release.
The new guidance that permits the immediate use of clinical tests after individual development and validation, said the FDA, only applies to labs already certified to perform high complexity testing under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. Many governmental, academic, and private laboratories fall into this category, however.
“Under this policy, we expect certain laboratories who develop validated tests for coronavirus would begin using them right away prior to FDA review,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “We believe this action will support laboratories across the country working on this urgent public health situation,” he added in the press release.
“By the end of this week, close to a million tests will be available,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said during the March 2 briefing.*
Updated criteria
The CDC is maintaining updated criteria for the virus testing on its website. Testing criteria are based both on clinical features and epidemiologic risk.
Individuals with less severe clinical features – those who have either fever or signs and symptoms of lower respiratory disease such as cough or shortness of breath, but who don’t require hospitalization – should be tested if they have high epidemiologic risk. “High risk” is defined by the CDC as any individual, including health care workers, who has had close contact with a person with confirmed COVID-19 within the past 2 weeks. For health care workers, testing can be considered even if they have relatively mild respiratory symptoms or have had contact with a person who is suspected, but not yet confirmed, to have coronavirus.
In its testing guidance, the CDC recognizes that defining close contact is difficult. General guidelines are that individuals are considered to have been in close contact with a person who has COVID-19 if they were within about six feet of the person for a prolonged period, or cared for or have spent a prolonged amount of time in the same room or house as a person with confirmed COVID-19.
Individuals who have both fever and signs or symptoms of lower respiratory illness who require hospitalization should be tested if they have a history of travel from any affected geographic area within 14 days of the onset of their symptoms. The CDC now defines “affected geographic area” as any country or region that has at least a CDC Level 2 Travel Health Notice for COVID-19, so that the testing criteria themselves don’t need to be updated when new geographic areas are included in these alerts. As of March 3, China, Iran, Italy, Japan, and South Korea all have Level 2 or 3 travel alerts.
The CDC now recommends that any patient who has severe acute lower respiratory illness that requires hospitalization and doesn’t have an alternative diagnosis should be tested, even without any identified source of exposure.
“Despite seeing these new cases, the risk to the American people is low,” said the CDC’s Dr. Redfield. In response to a question from the press about how fast the coronavirus will spread across the United States, Dr. Redfield said, “From the beginning we’ve anticipated seeing community cases pop up.” He added that as these cases arise, testing and public health strategies will focus on unearthing linkages and contacts to learn how the virus is spreading. “We’ll use the public health strategies that we can to limit that transmission,” he said.
*An earlier version of this article misattributed this quote.
The White House Coronavirus Task Force appeared at a press briefing March 2 to provide updates about testing strategies and public health coordination to address the current outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19. Speaking at the briefing, led by Vice President Mike Pence, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Robert Redfield, MD, said, “Working with our public health partners we continue to be able to identify new community cases and use our public health efforts to aggressively confirm, isolate, and do contact tracking.” Calling state, local, tribal, and territorial public health departments “the backbone of the public health system in our country,” Dr. Redfield noted that he expected many more confirmed COVID-19 cases to emerge.

At least some of the expected increase in confirmed cases of COVID-19 will occur because of expanded testing capacity, noted several of the task force members. On Feb. 29, the Food and Drug Administration issued a the virus that is causing the current outbreak of COVID-19.
Highly qualified laboratories, including both those run by public agencies and private labs, are now authorized to begin using their own validated test for the virus as long as they submit an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to the Food and Drug Administration within 15 days of notifying the agency of validation.
“To effectively respond to the COVID-19 outbreak, rapid detection of cases and contacts, appropriate clinical management and infection control, and implementation of community mitigation efforts are critical. This can best be achieved with wide availability of testing capabilities in health care settings, reference and commercial laboratories, and at the point of care,” the agency wrote in a press announcement of the expedited test expansion.
On Feb. 4, the Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services declared a coronavirus public health emergency. The FDA was then authorized to allow individual laboratories with validated coronavirus tests to begin testing samples immediately. The goal is a more rapid and expanded testing capacity in the United States.
“The global emergence of COVID-19 is concerning, and we appreciate the efforts of the FDA to help bring more testing capability to the U.S.,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), said in the press release.
The new guidance that permits the immediate use of clinical tests after individual development and validation, said the FDA, only applies to labs already certified to perform high complexity testing under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. Many governmental, academic, and private laboratories fall into this category, however.
“Under this policy, we expect certain laboratories who develop validated tests for coronavirus would begin using them right away prior to FDA review,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “We believe this action will support laboratories across the country working on this urgent public health situation,” he added in the press release.
“By the end of this week, close to a million tests will be available,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said during the March 2 briefing.*
Updated criteria
The CDC is maintaining updated criteria for the virus testing on its website. Testing criteria are based both on clinical features and epidemiologic risk.
Individuals with less severe clinical features – those who have either fever or signs and symptoms of lower respiratory disease such as cough or shortness of breath, but who don’t require hospitalization – should be tested if they have high epidemiologic risk. “High risk” is defined by the CDC as any individual, including health care workers, who has had close contact with a person with confirmed COVID-19 within the past 2 weeks. For health care workers, testing can be considered even if they have relatively mild respiratory symptoms or have had contact with a person who is suspected, but not yet confirmed, to have coronavirus.
In its testing guidance, the CDC recognizes that defining close contact is difficult. General guidelines are that individuals are considered to have been in close contact with a person who has COVID-19 if they were within about six feet of the person for a prolonged period, or cared for or have spent a prolonged amount of time in the same room or house as a person with confirmed COVID-19.
Individuals who have both fever and signs or symptoms of lower respiratory illness who require hospitalization should be tested if they have a history of travel from any affected geographic area within 14 days of the onset of their symptoms. The CDC now defines “affected geographic area” as any country or region that has at least a CDC Level 2 Travel Health Notice for COVID-19, so that the testing criteria themselves don’t need to be updated when new geographic areas are included in these alerts. As of March 3, China, Iran, Italy, Japan, and South Korea all have Level 2 or 3 travel alerts.
The CDC now recommends that any patient who has severe acute lower respiratory illness that requires hospitalization and doesn’t have an alternative diagnosis should be tested, even without any identified source of exposure.
“Despite seeing these new cases, the risk to the American people is low,” said the CDC’s Dr. Redfield. In response to a question from the press about how fast the coronavirus will spread across the United States, Dr. Redfield said, “From the beginning we’ve anticipated seeing community cases pop up.” He added that as these cases arise, testing and public health strategies will focus on unearthing linkages and contacts to learn how the virus is spreading. “We’ll use the public health strategies that we can to limit that transmission,” he said.
*An earlier version of this article misattributed this quote.
The White House Coronavirus Task Force appeared at a press briefing March 2 to provide updates about testing strategies and public health coordination to address the current outbreak of the coronavirus COVID-19. Speaking at the briefing, led by Vice President Mike Pence, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) director Robert Redfield, MD, said, “Working with our public health partners we continue to be able to identify new community cases and use our public health efforts to aggressively confirm, isolate, and do contact tracking.” Calling state, local, tribal, and territorial public health departments “the backbone of the public health system in our country,” Dr. Redfield noted that he expected many more confirmed COVID-19 cases to emerge.

At least some of the expected increase in confirmed cases of COVID-19 will occur because of expanded testing capacity, noted several of the task force members. On Feb. 29, the Food and Drug Administration issued a the virus that is causing the current outbreak of COVID-19.
Highly qualified laboratories, including both those run by public agencies and private labs, are now authorized to begin using their own validated test for the virus as long as they submit an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to the Food and Drug Administration within 15 days of notifying the agency of validation.
“To effectively respond to the COVID-19 outbreak, rapid detection of cases and contacts, appropriate clinical management and infection control, and implementation of community mitigation efforts are critical. This can best be achieved with wide availability of testing capabilities in health care settings, reference and commercial laboratories, and at the point of care,” the agency wrote in a press announcement of the expedited test expansion.
On Feb. 4, the Secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services declared a coronavirus public health emergency. The FDA was then authorized to allow individual laboratories with validated coronavirus tests to begin testing samples immediately. The goal is a more rapid and expanded testing capacity in the United States.
“The global emergence of COVID-19 is concerning, and we appreciate the efforts of the FDA to help bring more testing capability to the U.S.,” Nancy Messonnier, MD, director of the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases (NCIRD), said in the press release.
The new guidance that permits the immediate use of clinical tests after individual development and validation, said the FDA, only applies to labs already certified to perform high complexity testing under Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments. Many governmental, academic, and private laboratories fall into this category, however.
“Under this policy, we expect certain laboratories who develop validated tests for coronavirus would begin using them right away prior to FDA review,” said Jeffrey Shuren, MD, JD, director of the FDA’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health. “We believe this action will support laboratories across the country working on this urgent public health situation,” he added in the press release.
“By the end of this week, close to a million tests will be available,” FDA Commissioner Stephen M. Hahn, MD, said during the March 2 briefing.*
Updated criteria
The CDC is maintaining updated criteria for the virus testing on its website. Testing criteria are based both on clinical features and epidemiologic risk.
Individuals with less severe clinical features – those who have either fever or signs and symptoms of lower respiratory disease such as cough or shortness of breath, but who don’t require hospitalization – should be tested if they have high epidemiologic risk. “High risk” is defined by the CDC as any individual, including health care workers, who has had close contact with a person with confirmed COVID-19 within the past 2 weeks. For health care workers, testing can be considered even if they have relatively mild respiratory symptoms or have had contact with a person who is suspected, but not yet confirmed, to have coronavirus.
In its testing guidance, the CDC recognizes that defining close contact is difficult. General guidelines are that individuals are considered to have been in close contact with a person who has COVID-19 if they were within about six feet of the person for a prolonged period, or cared for or have spent a prolonged amount of time in the same room or house as a person with confirmed COVID-19.
Individuals who have both fever and signs or symptoms of lower respiratory illness who require hospitalization should be tested if they have a history of travel from any affected geographic area within 14 days of the onset of their symptoms. The CDC now defines “affected geographic area” as any country or region that has at least a CDC Level 2 Travel Health Notice for COVID-19, so that the testing criteria themselves don’t need to be updated when new geographic areas are included in these alerts. As of March 3, China, Iran, Italy, Japan, and South Korea all have Level 2 or 3 travel alerts.
The CDC now recommends that any patient who has severe acute lower respiratory illness that requires hospitalization and doesn’t have an alternative diagnosis should be tested, even without any identified source of exposure.
“Despite seeing these new cases, the risk to the American people is low,” said the CDC’s Dr. Redfield. In response to a question from the press about how fast the coronavirus will spread across the United States, Dr. Redfield said, “From the beginning we’ve anticipated seeing community cases pop up.” He added that as these cases arise, testing and public health strategies will focus on unearthing linkages and contacts to learn how the virus is spreading. “We’ll use the public health strategies that we can to limit that transmission,” he said.
*An earlier version of this article misattributed this quote.
FROM A PRESS BRIEFING BY THE WHITE HOUSE CORONAVIRUS TASK FORCE
What medical conferences are being canceled by coronavirus?
In a typical year, March marks the start of conference season, made all the more attractive by collegial gatherings and travel to warmer climes. But 2020 has already proven anything but typical as the number of novel coronavirus cases continues to increase around the globe. As a potential pandemic looms, these meetings – full of handshakes and crowded lecture halls – are also nirvana for opportunistic viruses. As are the airports, airplanes, and cabs required to get there.
So, as COVID-19 continues to spread, medical and scientific societies must make some difficult decisions. In Europe, at least a few societies have already suspended their upcoming meetings, while France has temporarily banned all gatherings over 5000 people.
In the United States, however, most medical conferences are moving forward as planned – at least for now. But one conference of 10,000 attendees, the American Physical Society annual meeting, which was scheduled for March 2-6 in Denver, was canceled the day before the meeting started. Although it’s not a medical conference, it speaks to the “rapidly escalating health concerns” that all conference organizers must grapple with.
APS Physics Meetings
@APSMeetings
Due to rapidly escalating health concerns relating to the spread of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), the 2020 APS March Meeting in Denver, CO, has been canceled. Please do not travel to Denver to attend the March Meeting. More information will follow shortly. #apsmarch
734 9:59 PM - Feb 29, 2020
Just one smaller medical meeting, the Ataxia Conference, which was scheduled for March 6-7 in Denver, has been canceled.
Most societies hosting these meetings have put out statements to their attendees saying that they’re monitoring the situation and will adapt as necessary. The United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, which is holding its annual meeting in Los Angeles this week, sent out an email beforehand asking international travelers to consider staying home. The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Global Health Conference, which is slated to have about 50,000 attendees from around the world, has declared itself a “handshake-free” conference but otherwise intends to move ahead as planned.
All of these conferences will be pushing forward without at least one prominent group of attendees. New York University’s Langone Health has removed its employees from the decision-making process and instead is taking a proactive stance: The health system just declared a 60-day (minimum) ban preventing employees from attending any meetings or conferences and from all domestic and international work-related travel.
Here’s what some of the societies have said to attendees about their intent to proceed or modify their plans:
- Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), Boston, 3/8/20 - 3/11/20: Monitoring the situation and seeking input from local, state, and federal infectious-disease and public-health experts. Final decision expected by the evening of March 3.
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI), Philadelphia, 3/13/20 - 3/16/20: Monitoring developments but no plans to cancel or postpone at this time.
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS), Orlando, 3/24/20 - 3/28/20: Proceeding as planned.
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), Denver, 3/20/20 - 3/24/20: The AAD’s 2020 Annual Meeting is scheduled to take place as planned. The organization will increase the number of hand-sanitizing stations throughout the convention center, and it is adding a nursing station specifically designated for anyone with flu-like symptoms.
- American College of Cardiology (ACC), Chicago, 3/28/20 - 3/30/20: The organization is working with attendees, faculty, exhibitors, and other stakeholders in affected countries to ensure access to research and education from the meeting, but is otherwise proceeding as planned.
- Endocrine Society (ENDO), San Francisco, 3/28/20 - 3/31/20: ENDO 2020 will take place as scheduled, but this is an evolving situation worldwide. The society will continue to monitor and provide updates on its FAQ page.
- American College of Physicians Internal Medicine (ACP IM), Los Angeles, 4/23/20 - 4/25/20: ACP leadership is closely monitoring the COVID-19 situation and is actively working with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to ensure authoritative communication of safety updates and recommendations as the situation evolves.
- American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), San Diego, 4/24/20 - 4/29/20: At this time, there is no plan to cancel or postpone any scheduled AACR meetings. The organization is tracking all travel restrictions as well as information and guidance from the CDC and World Health Organization.
- American Academy of Neurology (AAN), Toronto, 4/25/20 - 5/1/20: The group is continuing to closely monitor the situation in Toronto and will provide updates as the situation warrants.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a typical year, March marks the start of conference season, made all the more attractive by collegial gatherings and travel to warmer climes. But 2020 has already proven anything but typical as the number of novel coronavirus cases continues to increase around the globe. As a potential pandemic looms, these meetings – full of handshakes and crowded lecture halls – are also nirvana for opportunistic viruses. As are the airports, airplanes, and cabs required to get there.
So, as COVID-19 continues to spread, medical and scientific societies must make some difficult decisions. In Europe, at least a few societies have already suspended their upcoming meetings, while France has temporarily banned all gatherings over 5000 people.
In the United States, however, most medical conferences are moving forward as planned – at least for now. But one conference of 10,000 attendees, the American Physical Society annual meeting, which was scheduled for March 2-6 in Denver, was canceled the day before the meeting started. Although it’s not a medical conference, it speaks to the “rapidly escalating health concerns” that all conference organizers must grapple with.
APS Physics Meetings
@APSMeetings
Due to rapidly escalating health concerns relating to the spread of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), the 2020 APS March Meeting in Denver, CO, has been canceled. Please do not travel to Denver to attend the March Meeting. More information will follow shortly. #apsmarch
734 9:59 PM - Feb 29, 2020
Just one smaller medical meeting, the Ataxia Conference, which was scheduled for March 6-7 in Denver, has been canceled.
Most societies hosting these meetings have put out statements to their attendees saying that they’re monitoring the situation and will adapt as necessary. The United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, which is holding its annual meeting in Los Angeles this week, sent out an email beforehand asking international travelers to consider staying home. The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Global Health Conference, which is slated to have about 50,000 attendees from around the world, has declared itself a “handshake-free” conference but otherwise intends to move ahead as planned.
All of these conferences will be pushing forward without at least one prominent group of attendees. New York University’s Langone Health has removed its employees from the decision-making process and instead is taking a proactive stance: The health system just declared a 60-day (minimum) ban preventing employees from attending any meetings or conferences and from all domestic and international work-related travel.
Here’s what some of the societies have said to attendees about their intent to proceed or modify their plans:
- Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), Boston, 3/8/20 - 3/11/20: Monitoring the situation and seeking input from local, state, and federal infectious-disease and public-health experts. Final decision expected by the evening of March 3.
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI), Philadelphia, 3/13/20 - 3/16/20: Monitoring developments but no plans to cancel or postpone at this time.
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS), Orlando, 3/24/20 - 3/28/20: Proceeding as planned.
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), Denver, 3/20/20 - 3/24/20: The AAD’s 2020 Annual Meeting is scheduled to take place as planned. The organization will increase the number of hand-sanitizing stations throughout the convention center, and it is adding a nursing station specifically designated for anyone with flu-like symptoms.
- American College of Cardiology (ACC), Chicago, 3/28/20 - 3/30/20: The organization is working with attendees, faculty, exhibitors, and other stakeholders in affected countries to ensure access to research and education from the meeting, but is otherwise proceeding as planned.
- Endocrine Society (ENDO), San Francisco, 3/28/20 - 3/31/20: ENDO 2020 will take place as scheduled, but this is an evolving situation worldwide. The society will continue to monitor and provide updates on its FAQ page.
- American College of Physicians Internal Medicine (ACP IM), Los Angeles, 4/23/20 - 4/25/20: ACP leadership is closely monitoring the COVID-19 situation and is actively working with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to ensure authoritative communication of safety updates and recommendations as the situation evolves.
- American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), San Diego, 4/24/20 - 4/29/20: At this time, there is no plan to cancel or postpone any scheduled AACR meetings. The organization is tracking all travel restrictions as well as information and guidance from the CDC and World Health Organization.
- American Academy of Neurology (AAN), Toronto, 4/25/20 - 5/1/20: The group is continuing to closely monitor the situation in Toronto and will provide updates as the situation warrants.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In a typical year, March marks the start of conference season, made all the more attractive by collegial gatherings and travel to warmer climes. But 2020 has already proven anything but typical as the number of novel coronavirus cases continues to increase around the globe. As a potential pandemic looms, these meetings – full of handshakes and crowded lecture halls – are also nirvana for opportunistic viruses. As are the airports, airplanes, and cabs required to get there.
So, as COVID-19 continues to spread, medical and scientific societies must make some difficult decisions. In Europe, at least a few societies have already suspended their upcoming meetings, while France has temporarily banned all gatherings over 5000 people.
In the United States, however, most medical conferences are moving forward as planned – at least for now. But one conference of 10,000 attendees, the American Physical Society annual meeting, which was scheduled for March 2-6 in Denver, was canceled the day before the meeting started. Although it’s not a medical conference, it speaks to the “rapidly escalating health concerns” that all conference organizers must grapple with.
APS Physics Meetings
@APSMeetings
Due to rapidly escalating health concerns relating to the spread of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19), the 2020 APS March Meeting in Denver, CO, has been canceled. Please do not travel to Denver to attend the March Meeting. More information will follow shortly. #apsmarch
734 9:59 PM - Feb 29, 2020
Just one smaller medical meeting, the Ataxia Conference, which was scheduled for March 6-7 in Denver, has been canceled.
Most societies hosting these meetings have put out statements to their attendees saying that they’re monitoring the situation and will adapt as necessary. The United States and Canadian Academy of Pathology, which is holding its annual meeting in Los Angeles this week, sent out an email beforehand asking international travelers to consider staying home. The Healthcare Information and Management Systems Society (HIMSS) Global Health Conference, which is slated to have about 50,000 attendees from around the world, has declared itself a “handshake-free” conference but otherwise intends to move ahead as planned.
All of these conferences will be pushing forward without at least one prominent group of attendees. New York University’s Langone Health has removed its employees from the decision-making process and instead is taking a proactive stance: The health system just declared a 60-day (minimum) ban preventing employees from attending any meetings or conferences and from all domestic and international work-related travel.
Here’s what some of the societies have said to attendees about their intent to proceed or modify their plans:
- Conference on Retroviruses and Opportunistic Infections (CROI), Boston, 3/8/20 - 3/11/20: Monitoring the situation and seeking input from local, state, and federal infectious-disease and public-health experts. Final decision expected by the evening of March 3.
- American Academy of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (AAAAI), Philadelphia, 3/13/20 - 3/16/20: Monitoring developments but no plans to cancel or postpone at this time.
- American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons (AAOS), Orlando, 3/24/20 - 3/28/20: Proceeding as planned.
- American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), Denver, 3/20/20 - 3/24/20: The AAD’s 2020 Annual Meeting is scheduled to take place as planned. The organization will increase the number of hand-sanitizing stations throughout the convention center, and it is adding a nursing station specifically designated for anyone with flu-like symptoms.
- American College of Cardiology (ACC), Chicago, 3/28/20 - 3/30/20: The organization is working with attendees, faculty, exhibitors, and other stakeholders in affected countries to ensure access to research and education from the meeting, but is otherwise proceeding as planned.
- Endocrine Society (ENDO), San Francisco, 3/28/20 - 3/31/20: ENDO 2020 will take place as scheduled, but this is an evolving situation worldwide. The society will continue to monitor and provide updates on its FAQ page.
- American College of Physicians Internal Medicine (ACP IM), Los Angeles, 4/23/20 - 4/25/20: ACP leadership is closely monitoring the COVID-19 situation and is actively working with the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) to ensure authoritative communication of safety updates and recommendations as the situation evolves.
- American Association for Cancer Research (AACR), San Diego, 4/24/20 - 4/29/20: At this time, there is no plan to cancel or postpone any scheduled AACR meetings. The organization is tracking all travel restrictions as well as information and guidance from the CDC and World Health Organization.
- American Academy of Neurology (AAN), Toronto, 4/25/20 - 5/1/20: The group is continuing to closely monitor the situation in Toronto and will provide updates as the situation warrants.
This article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Upcoming vaccine may offset surge in polio subtypes
Although wild poliovirus type 3 has not been detected globally for 7 years, the number of wild type 1 cases increased from 33 in 2018 to 173 in 2019. In response, a modified oral vaccine is being developed, according to Stephen Cochi, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Center for Global Health.
Several factors, including a Taliban ban on house-to-house vaccination in Afghanistan and a delay of large-scale vaccinations in Pakistan contributed to the surge in polio infections, Dr. Cochi said in a presentation at the February meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
In addition, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) outbreaks have occurred in multiple countries including sub-Saharan Africa, China, Pakistan, and the Philippines. These outbreaks threaten the success of the bivalent oral polio vaccine introduced in April 2016 in 155 countries, Dr. Cochi said.
Outbreaks tend to occur just outside targeted areas for campaigns, caused by decreasing population immunity, he said.
The novel OPV2 (nOPV2) is a genetic modification of the existing OPV2 vaccine designed to improve genetic stability, Dr. Cochi explained. The modifications would “decrease the risk of seeding new cVDPVs and the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP),” he said.
The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) was developed by the World Health Organization in response to the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016 and is the fastest way to obtain regulatory review and approval of drug products, said Dr. Cochi.
A pilot plant has been established in Indonesia, and upon EUL approval, 4-8 million doses of the nOPV2 should be available for use in the second quarter of 2020, he concluded.
Dr. Cochi had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Although wild poliovirus type 3 has not been detected globally for 7 years, the number of wild type 1 cases increased from 33 in 2018 to 173 in 2019. In response, a modified oral vaccine is being developed, according to Stephen Cochi, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Center for Global Health.
Several factors, including a Taliban ban on house-to-house vaccination in Afghanistan and a delay of large-scale vaccinations in Pakistan contributed to the surge in polio infections, Dr. Cochi said in a presentation at the February meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
In addition, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) outbreaks have occurred in multiple countries including sub-Saharan Africa, China, Pakistan, and the Philippines. These outbreaks threaten the success of the bivalent oral polio vaccine introduced in April 2016 in 155 countries, Dr. Cochi said.
Outbreaks tend to occur just outside targeted areas for campaigns, caused by decreasing population immunity, he said.
The novel OPV2 (nOPV2) is a genetic modification of the existing OPV2 vaccine designed to improve genetic stability, Dr. Cochi explained. The modifications would “decrease the risk of seeding new cVDPVs and the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP),” he said.
The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) was developed by the World Health Organization in response to the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016 and is the fastest way to obtain regulatory review and approval of drug products, said Dr. Cochi.
A pilot plant has been established in Indonesia, and upon EUL approval, 4-8 million doses of the nOPV2 should be available for use in the second quarter of 2020, he concluded.
Dr. Cochi had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Although wild poliovirus type 3 has not been detected globally for 7 years, the number of wild type 1 cases increased from 33 in 2018 to 173 in 2019. In response, a modified oral vaccine is being developed, according to Stephen Cochi, MD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Center for Global Health.
Several factors, including a Taliban ban on house-to-house vaccination in Afghanistan and a delay of large-scale vaccinations in Pakistan contributed to the surge in polio infections, Dr. Cochi said in a presentation at the February meeting of the CDC’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
In addition, circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV) outbreaks have occurred in multiple countries including sub-Saharan Africa, China, Pakistan, and the Philippines. These outbreaks threaten the success of the bivalent oral polio vaccine introduced in April 2016 in 155 countries, Dr. Cochi said.
Outbreaks tend to occur just outside targeted areas for campaigns, caused by decreasing population immunity, he said.
The novel OPV2 (nOPV2) is a genetic modification of the existing OPV2 vaccine designed to improve genetic stability, Dr. Cochi explained. The modifications would “decrease the risk of seeding new cVDPVs and the risk of vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis (VAPP),” he said.
The Emergency Use Listing (EUL) was developed by the World Health Organization in response to the Ebola virus outbreak in 2014-2016 and is the fastest way to obtain regulatory review and approval of drug products, said Dr. Cochi.
A pilot plant has been established in Indonesia, and upon EUL approval, 4-8 million doses of the nOPV2 should be available for use in the second quarter of 2020, he concluded.
Dr. Cochi had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
Dengue vaccine deemed acceptable by most doctors, fewer parents
Adults are interested in a dengue vaccine for themselves and their children, and physicians recognize that dengue is a public health problem, according to data from parents and physicians in Puerto Rico. Most doctors, but fewer parents, found the idea of protecting children with Dengue vaccine acceptable.
Lack of detailed information about the vaccine is the greatest barrier to parents’ consent to vaccination, noted Ines Esquilin, MD, of the University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, in a presentation at the February meeting of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The ACIP dengue vaccines work group reviewed data from 102 physicians in Puerto Rico, 82% of which were pediatricians, regarding potential dengue vaccination. Overall, 98% said they considered dengue a significant public health problem in Puerto Rico, and 73% said they would recommend the dengue vaccine to patients if a laboratory test with acceptable specificity were available. Among the physicians who said they would not recommend the vaccine, the most common reason (71%) was concern about the risks of vaccinating individuals with false-positive tests.
The availability of a test that can be performed in the medical office and avoid repeat visits is a major factor in the feasibility of dengue vaccination, Dr. Esquilin said.
The ACIP dengue vaccines work group also sought public opinion on the acceptability of a generic dengue vaccine through focus group sessions with parents of children aged 9-16 years in Puerto Rico, said Dr. Esquilin.
Approximately one-third of the parents said they were willing to vaccinate their children, one-third were unwilling, and one-third were unsure. The most commonly identified barriers to vaccination included lack of information or inconsistent information about the vaccine, high cost/lack of insurance coverage, time-consuming lab test to confirm infection, side effects, potential for false-positive lab results, and low vaccine effectiveness.
Motivating factors for vaccination included correct information about the vaccine, desire to prevent infection, lab-confirmed positive test, support from public health organizations, the presence of a dengue epidemic, and educational forums.
Based in part on these findings, the ACIP dengue vaccines work group noted that the need for an acceptably specific screening lab test is the greatest concern in their consideration of recommendations, and the work group expects to review a CDC assessment of laboratory tests for prevaccination screening at a future meeting.
Dr. Esquilin had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Esquilin E. 2020. February meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) presentation.
Adults are interested in a dengue vaccine for themselves and their children, and physicians recognize that dengue is a public health problem, according to data from parents and physicians in Puerto Rico. Most doctors, but fewer parents, found the idea of protecting children with Dengue vaccine acceptable.
Lack of detailed information about the vaccine is the greatest barrier to parents’ consent to vaccination, noted Ines Esquilin, MD, of the University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, in a presentation at the February meeting of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The ACIP dengue vaccines work group reviewed data from 102 physicians in Puerto Rico, 82% of which were pediatricians, regarding potential dengue vaccination. Overall, 98% said they considered dengue a significant public health problem in Puerto Rico, and 73% said they would recommend the dengue vaccine to patients if a laboratory test with acceptable specificity were available. Among the physicians who said they would not recommend the vaccine, the most common reason (71%) was concern about the risks of vaccinating individuals with false-positive tests.
The availability of a test that can be performed in the medical office and avoid repeat visits is a major factor in the feasibility of dengue vaccination, Dr. Esquilin said.
The ACIP dengue vaccines work group also sought public opinion on the acceptability of a generic dengue vaccine through focus group sessions with parents of children aged 9-16 years in Puerto Rico, said Dr. Esquilin.
Approximately one-third of the parents said they were willing to vaccinate their children, one-third were unwilling, and one-third were unsure. The most commonly identified barriers to vaccination included lack of information or inconsistent information about the vaccine, high cost/lack of insurance coverage, time-consuming lab test to confirm infection, side effects, potential for false-positive lab results, and low vaccine effectiveness.
Motivating factors for vaccination included correct information about the vaccine, desire to prevent infection, lab-confirmed positive test, support from public health organizations, the presence of a dengue epidemic, and educational forums.
Based in part on these findings, the ACIP dengue vaccines work group noted that the need for an acceptably specific screening lab test is the greatest concern in their consideration of recommendations, and the work group expects to review a CDC assessment of laboratory tests for prevaccination screening at a future meeting.
Dr. Esquilin had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Esquilin E. 2020. February meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) presentation.
Adults are interested in a dengue vaccine for themselves and their children, and physicians recognize that dengue is a public health problem, according to data from parents and physicians in Puerto Rico. Most doctors, but fewer parents, found the idea of protecting children with Dengue vaccine acceptable.
Lack of detailed information about the vaccine is the greatest barrier to parents’ consent to vaccination, noted Ines Esquilin, MD, of the University of Puerto Rico, San Juan, in a presentation at the February meeting of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP).
The ACIP dengue vaccines work group reviewed data from 102 physicians in Puerto Rico, 82% of which were pediatricians, regarding potential dengue vaccination. Overall, 98% said they considered dengue a significant public health problem in Puerto Rico, and 73% said they would recommend the dengue vaccine to patients if a laboratory test with acceptable specificity were available. Among the physicians who said they would not recommend the vaccine, the most common reason (71%) was concern about the risks of vaccinating individuals with false-positive tests.
The availability of a test that can be performed in the medical office and avoid repeat visits is a major factor in the feasibility of dengue vaccination, Dr. Esquilin said.
The ACIP dengue vaccines work group also sought public opinion on the acceptability of a generic dengue vaccine through focus group sessions with parents of children aged 9-16 years in Puerto Rico, said Dr. Esquilin.
Approximately one-third of the parents said they were willing to vaccinate their children, one-third were unwilling, and one-third were unsure. The most commonly identified barriers to vaccination included lack of information or inconsistent information about the vaccine, high cost/lack of insurance coverage, time-consuming lab test to confirm infection, side effects, potential for false-positive lab results, and low vaccine effectiveness.
Motivating factors for vaccination included correct information about the vaccine, desire to prevent infection, lab-confirmed positive test, support from public health organizations, the presence of a dengue epidemic, and educational forums.
Based in part on these findings, the ACIP dengue vaccines work group noted that the need for an acceptably specific screening lab test is the greatest concern in their consideration of recommendations, and the work group expects to review a CDC assessment of laboratory tests for prevaccination screening at a future meeting.
Dr. Esquilin had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Esquilin E. 2020. February meeting of the CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) presentation.
FROM AN ACIP MEETING
Intervention improves antibiotics use in UTIs
A multifaceted intervention significantly changed clinicians’ use of antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children, according to data from more than 2,000 cases observed between January 2014 and September 2018.
“Changing clinicians’ antibiotic prescribing practices can be challenging; barriers to change include lack of awareness of new evidence, competing clinical demands, and concern about treatment failure,” wrote Matthew F. Daley, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
To promote judicious antibiotic use, the researchers designed an intervention including the development of new local UTI guidelines; a live, case-based educational session; emailed knowledge assessments before and after the session; and a specific UTI order set in the EHR.
The researchers divided the study period into a preintervention period (January 1, 2014, to April 25, 2017) and a postintervention period (April 26, 2017, to September 30, 2018). They collected data on 2,142 incident outpatient UTIs; 1,636 from the preintervention period and 506 from the postintervention period. The patients were younger than 18 years and older than 60 days, and children with complicated urologic or neurologic conditions were excluded.
(P less than .0001). In particular, the use of first-line, narrow spectrum cephalexin increased significantly from 29% during the preintervention period to 53% during the postintervention period (P less than .0001). In addition, use of broad spectrum cefixime decreased from 17% during the preintervention period to 3% during the postintervention period (P less than .0001). These changes in prescribing patterns continued through the end of the study period, the researchers said.
The study was limited by several factors, notably that “the interrupted time-series design prevents us from inferring that the intervention caused the observed change in practice,” the researchers wrote. However, other factors including the immediate change in prescribing patterns after the intervention, multiple time points, large sample size, and consistent UTI case mix support the impact of the intervention, they suggested. Although the results might not translate completely to other settings, “developing a UTI-specific EHR order set is relatively straightforward” and might be applied elsewhere, they noted.
“Despite the limitations inherent in a nonexperimental study design, the methods and interventions developed in the current study may be informative to other learning health systems and other content areas when conducting organization-wide quality improvement initiatives,” they concluded.
The study was supported by unrestricted internal resources from the Colorado Permanente Medical Group. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Daley MF et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 3. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2503.
A multifaceted intervention significantly changed clinicians’ use of antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children, according to data from more than 2,000 cases observed between January 2014 and September 2018.
“Changing clinicians’ antibiotic prescribing practices can be challenging; barriers to change include lack of awareness of new evidence, competing clinical demands, and concern about treatment failure,” wrote Matthew F. Daley, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
To promote judicious antibiotic use, the researchers designed an intervention including the development of new local UTI guidelines; a live, case-based educational session; emailed knowledge assessments before and after the session; and a specific UTI order set in the EHR.
The researchers divided the study period into a preintervention period (January 1, 2014, to April 25, 2017) and a postintervention period (April 26, 2017, to September 30, 2018). They collected data on 2,142 incident outpatient UTIs; 1,636 from the preintervention period and 506 from the postintervention period. The patients were younger than 18 years and older than 60 days, and children with complicated urologic or neurologic conditions were excluded.
(P less than .0001). In particular, the use of first-line, narrow spectrum cephalexin increased significantly from 29% during the preintervention period to 53% during the postintervention period (P less than .0001). In addition, use of broad spectrum cefixime decreased from 17% during the preintervention period to 3% during the postintervention period (P less than .0001). These changes in prescribing patterns continued through the end of the study period, the researchers said.
The study was limited by several factors, notably that “the interrupted time-series design prevents us from inferring that the intervention caused the observed change in practice,” the researchers wrote. However, other factors including the immediate change in prescribing patterns after the intervention, multiple time points, large sample size, and consistent UTI case mix support the impact of the intervention, they suggested. Although the results might not translate completely to other settings, “developing a UTI-specific EHR order set is relatively straightforward” and might be applied elsewhere, they noted.
“Despite the limitations inherent in a nonexperimental study design, the methods and interventions developed in the current study may be informative to other learning health systems and other content areas when conducting organization-wide quality improvement initiatives,” they concluded.
The study was supported by unrestricted internal resources from the Colorado Permanente Medical Group. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Daley MF et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 3. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2503.
A multifaceted intervention significantly changed clinicians’ use of antibiotics to treat urinary tract infections (UTIs) in children, according to data from more than 2,000 cases observed between January 2014 and September 2018.
“Changing clinicians’ antibiotic prescribing practices can be challenging; barriers to change include lack of awareness of new evidence, competing clinical demands, and concern about treatment failure,” wrote Matthew F. Daley, MD, of Kaiser Permanente Colorado, Aurora, and colleagues in Pediatrics.
To promote judicious antibiotic use, the researchers designed an intervention including the development of new local UTI guidelines; a live, case-based educational session; emailed knowledge assessments before and after the session; and a specific UTI order set in the EHR.
The researchers divided the study period into a preintervention period (January 1, 2014, to April 25, 2017) and a postintervention period (April 26, 2017, to September 30, 2018). They collected data on 2,142 incident outpatient UTIs; 1,636 from the preintervention period and 506 from the postintervention period. The patients were younger than 18 years and older than 60 days, and children with complicated urologic or neurologic conditions were excluded.
(P less than .0001). In particular, the use of first-line, narrow spectrum cephalexin increased significantly from 29% during the preintervention period to 53% during the postintervention period (P less than .0001). In addition, use of broad spectrum cefixime decreased from 17% during the preintervention period to 3% during the postintervention period (P less than .0001). These changes in prescribing patterns continued through the end of the study period, the researchers said.
The study was limited by several factors, notably that “the interrupted time-series design prevents us from inferring that the intervention caused the observed change in practice,” the researchers wrote. However, other factors including the immediate change in prescribing patterns after the intervention, multiple time points, large sample size, and consistent UTI case mix support the impact of the intervention, they suggested. Although the results might not translate completely to other settings, “developing a UTI-specific EHR order set is relatively straightforward” and might be applied elsewhere, they noted.
“Despite the limitations inherent in a nonexperimental study design, the methods and interventions developed in the current study may be informative to other learning health systems and other content areas when conducting organization-wide quality improvement initiatives,” they concluded.
The study was supported by unrestricted internal resources from the Colorado Permanente Medical Group. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Daley MF et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 3. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2503.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Key clinical point: After an educational intervention, approximately 62% of clinicians prescribed first-line antibiotics, up from 43% before the intervention.
Major finding: Cephalexin use increased from 29% before the intervention to 53% after the intervention.
Study details: The data come from a review of 2,142 incident outpatient cases of urinary tract infection in patients aged older than 60 days up to 18 years.
Disclosures: The study was supported by unrestricted internal resources from the Colorado Permanente Medical Group. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Source: Daley MF et al. Pediatrics. 2020 Mar 3. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2503.
Washington State grapples with coronavirus outbreak
As the first COVID-19 outbreak in the United States emerges in Washington State, the city of Seattle, King County, and Washington State health officials provided the beginnings of a roadmap for how the region will address the rapidly evolving health crisis.
Health officials announced that four new cases were reported over the weekend in King County, Wash. There have now been 10 hospitalizations and 6 COVID-19 deaths at Evergreen Health, Kirkland, Wash. Of the deaths, five were King County residents and one was a resident of Snohomish County. Three patients died on March 1; all were in their 70s or 80s with comorbidities. Two had been residents of the Life Care senior residential facility that is at the center of the Kirkland outbreak. The number of cases in Washington now totals 18, with four cases in Snohomish County and the balance in neighboring King County.
Approximately 29 cases are under investigation with test results pending; a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) team is on-site.
Speaking at a news conference March 2, officials sought to strike a balance between giving the community a realistic appraisal of the likely scope of the COVID-19 outbreak and avoiding sparking a panic.
“This is a complex and unprecedented challenge nationally, globally, and locally. The vast majority of the infected have mild or moderate disease and do not need hospitalization,” said Jeffrey Duchin, MD, health officer and chief, Communicable Disease EPI/Immunization Section, Public Health, Seattle and King County, and a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Washington, Seattle. “On the other hand, it’s obvious that this infection can cause very serious disease in people who are older and have underlying health conditions. We expect cases to continue to increase. We are taking the situation extremely seriously; the risk for all of us becoming infected is increasing. ...There is the potential for many to become ill at the same time.”
Among the measures being taken immediately are the purchase by King County of a hotel to house individuals who require isolation and those who are convalescing from the virus. Officials are also placing a number of prefabricated stand-alone housing units on public grounds in Seattle, with the recognition that the area has a large transient and homeless community. The stand-alone units will house homeless individuals who need isolation, treatment, or recuperation but who aren’t ill enough to be hospitalized.
Dr. Duchin said that testing capacity is ramping up rapidly in Washington State: The state lab can now accommodate up to about 200 tests daily, and expects to be able to do up to 1,000 daily soon. The University of Washington’s testing capacity will come online March 2 or 3 as a testing facility with similar initial and future peak testing capacities.
The testing strategy will continue to include very ill individuals with pneumonia or other respiratory illness of unknown etiology, but will also expand to include less ill people. This shift is being made in accordance with a shift in CDC guidelines, because of increased testing capacity, and to provide a better picture of the severity, scope, geography, and timing of the current COVID-19 outbreak in the greater Seattle area.
No school closures or cancellation of gatherings are currently recommended by public health authorities. There are currently no COVID-19 cases in Washington schools. The expectation is that any recommendations regarding closures will be re-evaluated as the outbreak progresses.
Repeatedly, officials asked the general public to employ basic measures such as handwashing and avoidance of touching the face, and to spare masks for the ill and for those who care for them. “The vast majority of people will not have serious illness. In turn we need to do everything we can to help those health care workers. I’m asking the public to do things like save the masks for our health care workers. …We need assets for our front-line health care workers and also for those who may be needing them,” said King County Health Department director Patty Hayes, RN, MN.
Now is also the time for households to initiate basic emergency preparedness measures, such as having adequate food and medication, and to make arrangements for childcare in the event of school closures, said several officials.
“We can decrease the impact on our health care system by reducing our individual risk. We are making individual- and community-level recommendations to limit the spread of disease. These are very similar to what we recommend for influenza,” said Dr. Duchin.
Ettore Palazzo, MD, chief medical and quality officer at EvergreenHealth, gave a sense of how the hospital is coping with being Ground Zero for COVID-19 in the United States. “We have made adjustments for airborne precautions,” he said, including transforming the entire critical care unit to a negative pressure unit. “We have these capabilities in other parts of the hospital as well.” Staff are working hard, but thus far staffing has kept pace with demand, he said, but all are feeling the strain already.
Dr. Duchin made the point that Washington is relatively well equipped to handle the increasingly likely scenario of a large spike in coronavirus cases, since it’s part of the Northwest Healthcare Response Network. The network is planning for sharing resources such as staff, respirators, and intensive care unit beds as circumstances warrant.
“What you just heard illustrates the challenge of this disease,” said Dr. Duchin, summing up. “The public health service and clinical health care delivery systems don’t have the capacity to track down every case in the community. I’m guessing we will see more cases of coronavirus than we see of influenza. At some point we will be shifting from counting every case” to focusing on outbreaks and the critically ill in hospitals, he said.
“We are still trying to contain the outbreak, but we are at the same time pivoting to a more community-based approach,” similar to the approach with influenza, said Dr. Duchin.
A summary of deaths and ongoing cases, drawn from the press release, is below:
The four new cases are:
• A male in his 50s, hospitalized at Highline Hospital. He has no known exposures. He is in stable but critical condition. He had no underlying health conditions.
• A male in his 70s, a resident of Life Care, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The man had underlying health conditions, and died March 1.
• A female in her 70s, a resident of Life Care, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The woman had underlying health conditions, and died March 1.
• A female in her 80s, a resident of Life Care, was hospitalized at EvergreenHealth. She is in critical condition.
In addition, a woman in her 80s, who was already reported as in critical condition at Evergreen, has died. She died on March 1.
Ten other cases, already reported earlier by Public Health, include:
• A female in her 80s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. This person has now died, and is reported as such above.
• A female in her 90s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The woman has underlying health conditions, and is in critical condition.
• A male in his 70s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The man has underlying health conditions, and is in critical condition.
• A male in his 70s was hospitalized at EvergreenHealth. He had underlying health conditions and died on Feb. 29.
• A man in his 60s, hospitalized at Valley Medical Center in Renton.
• A man in 60s, hospitalized at Virginia Mason Medical Center.
• A woman in her 50s, who had traveled to South Korea; recovering at home.
• A woman in her 70s, who was a resident of Life Care in Kirkland, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth.
• A woman in her 40s, employed by Life Care, who is hospitalized at Overlake Medical Center.
• A man in his 50s, who was hospitalized and died at EvergreenHealth.
As the first COVID-19 outbreak in the United States emerges in Washington State, the city of Seattle, King County, and Washington State health officials provided the beginnings of a roadmap for how the region will address the rapidly evolving health crisis.
Health officials announced that four new cases were reported over the weekend in King County, Wash. There have now been 10 hospitalizations and 6 COVID-19 deaths at Evergreen Health, Kirkland, Wash. Of the deaths, five were King County residents and one was a resident of Snohomish County. Three patients died on March 1; all were in their 70s or 80s with comorbidities. Two had been residents of the Life Care senior residential facility that is at the center of the Kirkland outbreak. The number of cases in Washington now totals 18, with four cases in Snohomish County and the balance in neighboring King County.
Approximately 29 cases are under investigation with test results pending; a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) team is on-site.
Speaking at a news conference March 2, officials sought to strike a balance between giving the community a realistic appraisal of the likely scope of the COVID-19 outbreak and avoiding sparking a panic.
“This is a complex and unprecedented challenge nationally, globally, and locally. The vast majority of the infected have mild or moderate disease and do not need hospitalization,” said Jeffrey Duchin, MD, health officer and chief, Communicable Disease EPI/Immunization Section, Public Health, Seattle and King County, and a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Washington, Seattle. “On the other hand, it’s obvious that this infection can cause very serious disease in people who are older and have underlying health conditions. We expect cases to continue to increase. We are taking the situation extremely seriously; the risk for all of us becoming infected is increasing. ...There is the potential for many to become ill at the same time.”
Among the measures being taken immediately are the purchase by King County of a hotel to house individuals who require isolation and those who are convalescing from the virus. Officials are also placing a number of prefabricated stand-alone housing units on public grounds in Seattle, with the recognition that the area has a large transient and homeless community. The stand-alone units will house homeless individuals who need isolation, treatment, or recuperation but who aren’t ill enough to be hospitalized.
Dr. Duchin said that testing capacity is ramping up rapidly in Washington State: The state lab can now accommodate up to about 200 tests daily, and expects to be able to do up to 1,000 daily soon. The University of Washington’s testing capacity will come online March 2 or 3 as a testing facility with similar initial and future peak testing capacities.
The testing strategy will continue to include very ill individuals with pneumonia or other respiratory illness of unknown etiology, but will also expand to include less ill people. This shift is being made in accordance with a shift in CDC guidelines, because of increased testing capacity, and to provide a better picture of the severity, scope, geography, and timing of the current COVID-19 outbreak in the greater Seattle area.
No school closures or cancellation of gatherings are currently recommended by public health authorities. There are currently no COVID-19 cases in Washington schools. The expectation is that any recommendations regarding closures will be re-evaluated as the outbreak progresses.
Repeatedly, officials asked the general public to employ basic measures such as handwashing and avoidance of touching the face, and to spare masks for the ill and for those who care for them. “The vast majority of people will not have serious illness. In turn we need to do everything we can to help those health care workers. I’m asking the public to do things like save the masks for our health care workers. …We need assets for our front-line health care workers and also for those who may be needing them,” said King County Health Department director Patty Hayes, RN, MN.
Now is also the time for households to initiate basic emergency preparedness measures, such as having adequate food and medication, and to make arrangements for childcare in the event of school closures, said several officials.
“We can decrease the impact on our health care system by reducing our individual risk. We are making individual- and community-level recommendations to limit the spread of disease. These are very similar to what we recommend for influenza,” said Dr. Duchin.
Ettore Palazzo, MD, chief medical and quality officer at EvergreenHealth, gave a sense of how the hospital is coping with being Ground Zero for COVID-19 in the United States. “We have made adjustments for airborne precautions,” he said, including transforming the entire critical care unit to a negative pressure unit. “We have these capabilities in other parts of the hospital as well.” Staff are working hard, but thus far staffing has kept pace with demand, he said, but all are feeling the strain already.
Dr. Duchin made the point that Washington is relatively well equipped to handle the increasingly likely scenario of a large spike in coronavirus cases, since it’s part of the Northwest Healthcare Response Network. The network is planning for sharing resources such as staff, respirators, and intensive care unit beds as circumstances warrant.
“What you just heard illustrates the challenge of this disease,” said Dr. Duchin, summing up. “The public health service and clinical health care delivery systems don’t have the capacity to track down every case in the community. I’m guessing we will see more cases of coronavirus than we see of influenza. At some point we will be shifting from counting every case” to focusing on outbreaks and the critically ill in hospitals, he said.
“We are still trying to contain the outbreak, but we are at the same time pivoting to a more community-based approach,” similar to the approach with influenza, said Dr. Duchin.
A summary of deaths and ongoing cases, drawn from the press release, is below:
The four new cases are:
• A male in his 50s, hospitalized at Highline Hospital. He has no known exposures. He is in stable but critical condition. He had no underlying health conditions.
• A male in his 70s, a resident of Life Care, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The man had underlying health conditions, and died March 1.
• A female in her 70s, a resident of Life Care, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The woman had underlying health conditions, and died March 1.
• A female in her 80s, a resident of Life Care, was hospitalized at EvergreenHealth. She is in critical condition.
In addition, a woman in her 80s, who was already reported as in critical condition at Evergreen, has died. She died on March 1.
Ten other cases, already reported earlier by Public Health, include:
• A female in her 80s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. This person has now died, and is reported as such above.
• A female in her 90s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The woman has underlying health conditions, and is in critical condition.
• A male in his 70s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The man has underlying health conditions, and is in critical condition.
• A male in his 70s was hospitalized at EvergreenHealth. He had underlying health conditions and died on Feb. 29.
• A man in his 60s, hospitalized at Valley Medical Center in Renton.
• A man in 60s, hospitalized at Virginia Mason Medical Center.
• A woman in her 50s, who had traveled to South Korea; recovering at home.
• A woman in her 70s, who was a resident of Life Care in Kirkland, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth.
• A woman in her 40s, employed by Life Care, who is hospitalized at Overlake Medical Center.
• A man in his 50s, who was hospitalized and died at EvergreenHealth.
As the first COVID-19 outbreak in the United States emerges in Washington State, the city of Seattle, King County, and Washington State health officials provided the beginnings of a roadmap for how the region will address the rapidly evolving health crisis.
Health officials announced that four new cases were reported over the weekend in King County, Wash. There have now been 10 hospitalizations and 6 COVID-19 deaths at Evergreen Health, Kirkland, Wash. Of the deaths, five were King County residents and one was a resident of Snohomish County. Three patients died on March 1; all were in their 70s or 80s with comorbidities. Two had been residents of the Life Care senior residential facility that is at the center of the Kirkland outbreak. The number of cases in Washington now totals 18, with four cases in Snohomish County and the balance in neighboring King County.
Approximately 29 cases are under investigation with test results pending; a Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) team is on-site.
Speaking at a news conference March 2, officials sought to strike a balance between giving the community a realistic appraisal of the likely scope of the COVID-19 outbreak and avoiding sparking a panic.
“This is a complex and unprecedented challenge nationally, globally, and locally. The vast majority of the infected have mild or moderate disease and do not need hospitalization,” said Jeffrey Duchin, MD, health officer and chief, Communicable Disease EPI/Immunization Section, Public Health, Seattle and King County, and a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Washington, Seattle. “On the other hand, it’s obvious that this infection can cause very serious disease in people who are older and have underlying health conditions. We expect cases to continue to increase. We are taking the situation extremely seriously; the risk for all of us becoming infected is increasing. ...There is the potential for many to become ill at the same time.”
Among the measures being taken immediately are the purchase by King County of a hotel to house individuals who require isolation and those who are convalescing from the virus. Officials are also placing a number of prefabricated stand-alone housing units on public grounds in Seattle, with the recognition that the area has a large transient and homeless community. The stand-alone units will house homeless individuals who need isolation, treatment, or recuperation but who aren’t ill enough to be hospitalized.
Dr. Duchin said that testing capacity is ramping up rapidly in Washington State: The state lab can now accommodate up to about 200 tests daily, and expects to be able to do up to 1,000 daily soon. The University of Washington’s testing capacity will come online March 2 or 3 as a testing facility with similar initial and future peak testing capacities.
The testing strategy will continue to include very ill individuals with pneumonia or other respiratory illness of unknown etiology, but will also expand to include less ill people. This shift is being made in accordance with a shift in CDC guidelines, because of increased testing capacity, and to provide a better picture of the severity, scope, geography, and timing of the current COVID-19 outbreak in the greater Seattle area.
No school closures or cancellation of gatherings are currently recommended by public health authorities. There are currently no COVID-19 cases in Washington schools. The expectation is that any recommendations regarding closures will be re-evaluated as the outbreak progresses.
Repeatedly, officials asked the general public to employ basic measures such as handwashing and avoidance of touching the face, and to spare masks for the ill and for those who care for them. “The vast majority of people will not have serious illness. In turn we need to do everything we can to help those health care workers. I’m asking the public to do things like save the masks for our health care workers. …We need assets for our front-line health care workers and also for those who may be needing them,” said King County Health Department director Patty Hayes, RN, MN.
Now is also the time for households to initiate basic emergency preparedness measures, such as having adequate food and medication, and to make arrangements for childcare in the event of school closures, said several officials.
“We can decrease the impact on our health care system by reducing our individual risk. We are making individual- and community-level recommendations to limit the spread of disease. These are very similar to what we recommend for influenza,” said Dr. Duchin.
Ettore Palazzo, MD, chief medical and quality officer at EvergreenHealth, gave a sense of how the hospital is coping with being Ground Zero for COVID-19 in the United States. “We have made adjustments for airborne precautions,” he said, including transforming the entire critical care unit to a negative pressure unit. “We have these capabilities in other parts of the hospital as well.” Staff are working hard, but thus far staffing has kept pace with demand, he said, but all are feeling the strain already.
Dr. Duchin made the point that Washington is relatively well equipped to handle the increasingly likely scenario of a large spike in coronavirus cases, since it’s part of the Northwest Healthcare Response Network. The network is planning for sharing resources such as staff, respirators, and intensive care unit beds as circumstances warrant.
“What you just heard illustrates the challenge of this disease,” said Dr. Duchin, summing up. “The public health service and clinical health care delivery systems don’t have the capacity to track down every case in the community. I’m guessing we will see more cases of coronavirus than we see of influenza. At some point we will be shifting from counting every case” to focusing on outbreaks and the critically ill in hospitals, he said.
“We are still trying to contain the outbreak, but we are at the same time pivoting to a more community-based approach,” similar to the approach with influenza, said Dr. Duchin.
A summary of deaths and ongoing cases, drawn from the press release, is below:
The four new cases are:
• A male in his 50s, hospitalized at Highline Hospital. He has no known exposures. He is in stable but critical condition. He had no underlying health conditions.
• A male in his 70s, a resident of Life Care, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The man had underlying health conditions, and died March 1.
• A female in her 70s, a resident of Life Care, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The woman had underlying health conditions, and died March 1.
• A female in her 80s, a resident of Life Care, was hospitalized at EvergreenHealth. She is in critical condition.
In addition, a woman in her 80s, who was already reported as in critical condition at Evergreen, has died. She died on March 1.
Ten other cases, already reported earlier by Public Health, include:
• A female in her 80s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. This person has now died, and is reported as such above.
• A female in her 90s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The woman has underlying health conditions, and is in critical condition.
• A male in his 70s, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth in Kirkland. The man has underlying health conditions, and is in critical condition.
• A male in his 70s was hospitalized at EvergreenHealth. He had underlying health conditions and died on Feb. 29.
• A man in his 60s, hospitalized at Valley Medical Center in Renton.
• A man in 60s, hospitalized at Virginia Mason Medical Center.
• A woman in her 50s, who had traveled to South Korea; recovering at home.
• A woman in her 70s, who was a resident of Life Care in Kirkland, hospitalized at EvergreenHealth.
• A woman in her 40s, employed by Life Care, who is hospitalized at Overlake Medical Center.
• A man in his 50s, who was hospitalized and died at EvergreenHealth.
FROM A KING COUNTY, WASH. NEWS BRIEFING
The fate of the ACA now rests with the U.S. Supreme Court
The U.S. Supreme Court has agreed to hear Texas v. California, a closely watched case that could upend the Affordable Care Act.
The justices will hear oral arguments in the case in fall 2020, with a ruling likely in 2021.
The Texas case, consolidated with a similar challenge, stems from a lawsuit by 20 Republican state attorneys general and governors that was filed after Congress zeroed out the ACA’s individual mandate penalty in 2017. The plaintiffs contend the now-valueless mandate is no longer constitutional and thus, the entire ACA should be struck down. Since the Trump administration declined to defend the ACA, a coalition of Democratic attorneys general and governors intervened in the case as defendants.
In 2018, a Texas district court ruled in favor of the plaintiffs and declared the entire health care law invalid. The 5th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals partially affirmed the district court’s decision, ruling that the mandate was unconstitutional, but sending the case back to the lower court for more analysis on severability. On March 2, the U.S. Supreme Court granted two petitions by the defendants requesting that the high court review the appeals court decision.
The review follows a previous look at the ACA’s mandate by the Supreme Court in 2012. In National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius, justices upheld the ACA’s insurance mandate as constitutional, ruling the requirement was authorized by Congress’ power to levy taxes. The vote was 5-4, with Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. in agreement with the court’s four more liberal members.
The U.S. Supreme Court has agreed to hear Texas v. California, a closely watched case that could upend the Affordable Care Act.
The justices will hear oral arguments in the case in fall 2020, with a ruling likely in 2021.
The Texas case, consolidated with a similar challenge, stems from a lawsuit by 20 Republican state attorneys general and governors that was filed after Congress zeroed out the ACA’s individual mandate penalty in 2017. The plaintiffs contend the now-valueless mandate is no longer constitutional and thus, the entire ACA should be struck down. Since the Trump administration declined to defend the ACA, a coalition of Democratic attorneys general and governors intervened in the case as defendants.
In 2018, a Texas district court ruled in favor of the plaintiffs and declared the entire health care law invalid. The 5th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals partially affirmed the district court’s decision, ruling that the mandate was unconstitutional, but sending the case back to the lower court for more analysis on severability. On March 2, the U.S. Supreme Court granted two petitions by the defendants requesting that the high court review the appeals court decision.
The review follows a previous look at the ACA’s mandate by the Supreme Court in 2012. In National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius, justices upheld the ACA’s insurance mandate as constitutional, ruling the requirement was authorized by Congress’ power to levy taxes. The vote was 5-4, with Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. in agreement with the court’s four more liberal members.
The U.S. Supreme Court has agreed to hear Texas v. California, a closely watched case that could upend the Affordable Care Act.
The justices will hear oral arguments in the case in fall 2020, with a ruling likely in 2021.
The Texas case, consolidated with a similar challenge, stems from a lawsuit by 20 Republican state attorneys general and governors that was filed after Congress zeroed out the ACA’s individual mandate penalty in 2017. The plaintiffs contend the now-valueless mandate is no longer constitutional and thus, the entire ACA should be struck down. Since the Trump administration declined to defend the ACA, a coalition of Democratic attorneys general and governors intervened in the case as defendants.
In 2018, a Texas district court ruled in favor of the plaintiffs and declared the entire health care law invalid. The 5th U.S. Circuit Court of Appeals partially affirmed the district court’s decision, ruling that the mandate was unconstitutional, but sending the case back to the lower court for more analysis on severability. On March 2, the U.S. Supreme Court granted two petitions by the defendants requesting that the high court review the appeals court decision.
The review follows a previous look at the ACA’s mandate by the Supreme Court in 2012. In National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius, justices upheld the ACA’s insurance mandate as constitutional, ruling the requirement was authorized by Congress’ power to levy taxes. The vote was 5-4, with Chief Justice John G. Roberts Jr. in agreement with the court’s four more liberal members.