User login
Transgender patients report stigma, voyeurism in medical care
Transgender patients in the United States and Canada told researchers that they often face voyeuristic and stigmatizing treatment in medical clinics and they fear they’re getting substandard care.
“Transgender people feel that their care worsens when clinicians learn that they are transgender, and thus they often have to choose between stigma if clinicians learn that they are transgender and potentially ineffective clinical problem-solving if they do not,” said Yale Cancer Center instructor of medicine Ash B. Alpert, MD, MFA, lead author of the study, which was published in Annals of Family Medicine. For the qualitative study, researchers held seven online focus groups with 30 transgender adults (median age, 31; age range, 20-67; 40% people of color; and 47% with incomes of more than $40,000 a year). All but one were from the United States.
According to the study, the participants said clinicians often ask “irrelevant” questions, sometimes with intentions that appear voyeuristic. “I saw a pulmonologist earlier in the year and one of his first questions was, ‘When are you getting genital surgery?’ and I was like, ‘I’m here for my lungs,’ ” said a White, nonbinary participant. A White male participant said “As soon as I walk in, no matter what I’m there for, the first [order] of business is for them to determine my gender or sex assigned at birth ... and ... once they ... know they’re ... much more at ease.”
Participants also described how medical encounters went awry once clinicians realized they were transgender. “It wasn’t until after I told the doctor that I was on hormones for transition that I started being ‘he’d.’ ” Before that, it was “she,” said a Black transgender woman.
One participant, a Black person who declined to identify by gender, said “I don’t feel comfortable sharing medical records with physicians anyway because it’s a guarantee that I’m not gonna get services. So I lost [my medical records] and they’re good wherever they are now, far away from me.”
Ten participants were clinicians. “Many seemed concerned that transgender people are being put in distressing and difficult situations in medical settings and also seemed dubious that health care for transgender people would improve without a complete overhaul,” Dr. Alpert said.
In an interview, Boston University assistant professor of medicine C. Streed Jr., MD, MPH, who studies gender and health, praised the study. He said it plays an early role in revealing the problems faced by transgender people in the health system.
“We do not fully know the experience of transgender persons accessing care in various contexts, especially in specialty care such as oncology, pulmonology, nephrology, etc.” Dr. Streed said. “We do not know how they identify specialists who are welcoming, compassionate, and competent in care for transgender persons.”
The results aren’t surprising, Dr. Streed said, “given the lack of training in medical school, residency, and fellowship specific to the unique needs of transgender persons.”
How can clinicians improve interactions with transgender people?
What can clinicians do to help transgender patients feel comfortable? Dr. Alpert suggested they “ask [only] for medically relevant information and to explain to patients why it is medically relevant.”
“This is important because transgender people are often weighing the risks and benefits of disclosing information that could be used to stigmatize them,” Dr. Alpert said.
What if a clinician wants to create a personal connection with a patient by asking questions about their life? “If you as a clinician think it’s important to ask for nonmedical information to get to know a patient, explicitly clarify that your questions are optional and not medically relevant,” Dr. Alpert said. “That way patients have the ability to consent or not to questions that likely will not directly benefit their care.”
Dr. Streed offered a similar perspective. “Clinicians should only be asking questions of patients that will affect the care the patient is seeking and for which the clinician is trained to provide,” he said. “Having a transgender patient is not an opportunity for a clinician to satisfy their curiosity when it is not related to the care the patient is seeking or needs.”
More specifically, Dr. Streed offered an example: Clinicians should not be asking about a patient’s genitals if they are seeking care related to their asthma diagnosis.
Dr. Streed referred clinicians to resources from the American Medical Association and the Human Rights Campaign for guidelines on caring for transgender patients.
The study was funded by Conquer Cancer. The study authors and Dr. Streed have no relevant disclosures.
Transgender patients in the United States and Canada told researchers that they often face voyeuristic and stigmatizing treatment in medical clinics and they fear they’re getting substandard care.
“Transgender people feel that their care worsens when clinicians learn that they are transgender, and thus they often have to choose between stigma if clinicians learn that they are transgender and potentially ineffective clinical problem-solving if they do not,” said Yale Cancer Center instructor of medicine Ash B. Alpert, MD, MFA, lead author of the study, which was published in Annals of Family Medicine. For the qualitative study, researchers held seven online focus groups with 30 transgender adults (median age, 31; age range, 20-67; 40% people of color; and 47% with incomes of more than $40,000 a year). All but one were from the United States.
According to the study, the participants said clinicians often ask “irrelevant” questions, sometimes with intentions that appear voyeuristic. “I saw a pulmonologist earlier in the year and one of his first questions was, ‘When are you getting genital surgery?’ and I was like, ‘I’m here for my lungs,’ ” said a White, nonbinary participant. A White male participant said “As soon as I walk in, no matter what I’m there for, the first [order] of business is for them to determine my gender or sex assigned at birth ... and ... once they ... know they’re ... much more at ease.”
Participants also described how medical encounters went awry once clinicians realized they were transgender. “It wasn’t until after I told the doctor that I was on hormones for transition that I started being ‘he’d.’ ” Before that, it was “she,” said a Black transgender woman.
One participant, a Black person who declined to identify by gender, said “I don’t feel comfortable sharing medical records with physicians anyway because it’s a guarantee that I’m not gonna get services. So I lost [my medical records] and they’re good wherever they are now, far away from me.”
Ten participants were clinicians. “Many seemed concerned that transgender people are being put in distressing and difficult situations in medical settings and also seemed dubious that health care for transgender people would improve without a complete overhaul,” Dr. Alpert said.
In an interview, Boston University assistant professor of medicine C. Streed Jr., MD, MPH, who studies gender and health, praised the study. He said it plays an early role in revealing the problems faced by transgender people in the health system.
“We do not fully know the experience of transgender persons accessing care in various contexts, especially in specialty care such as oncology, pulmonology, nephrology, etc.” Dr. Streed said. “We do not know how they identify specialists who are welcoming, compassionate, and competent in care for transgender persons.”
The results aren’t surprising, Dr. Streed said, “given the lack of training in medical school, residency, and fellowship specific to the unique needs of transgender persons.”
How can clinicians improve interactions with transgender people?
What can clinicians do to help transgender patients feel comfortable? Dr. Alpert suggested they “ask [only] for medically relevant information and to explain to patients why it is medically relevant.”
“This is important because transgender people are often weighing the risks and benefits of disclosing information that could be used to stigmatize them,” Dr. Alpert said.
What if a clinician wants to create a personal connection with a patient by asking questions about their life? “If you as a clinician think it’s important to ask for nonmedical information to get to know a patient, explicitly clarify that your questions are optional and not medically relevant,” Dr. Alpert said. “That way patients have the ability to consent or not to questions that likely will not directly benefit their care.”
Dr. Streed offered a similar perspective. “Clinicians should only be asking questions of patients that will affect the care the patient is seeking and for which the clinician is trained to provide,” he said. “Having a transgender patient is not an opportunity for a clinician to satisfy their curiosity when it is not related to the care the patient is seeking or needs.”
More specifically, Dr. Streed offered an example: Clinicians should not be asking about a patient’s genitals if they are seeking care related to their asthma diagnosis.
Dr. Streed referred clinicians to resources from the American Medical Association and the Human Rights Campaign for guidelines on caring for transgender patients.
The study was funded by Conquer Cancer. The study authors and Dr. Streed have no relevant disclosures.
Transgender patients in the United States and Canada told researchers that they often face voyeuristic and stigmatizing treatment in medical clinics and they fear they’re getting substandard care.
“Transgender people feel that their care worsens when clinicians learn that they are transgender, and thus they often have to choose between stigma if clinicians learn that they are transgender and potentially ineffective clinical problem-solving if they do not,” said Yale Cancer Center instructor of medicine Ash B. Alpert, MD, MFA, lead author of the study, which was published in Annals of Family Medicine. For the qualitative study, researchers held seven online focus groups with 30 transgender adults (median age, 31; age range, 20-67; 40% people of color; and 47% with incomes of more than $40,000 a year). All but one were from the United States.
According to the study, the participants said clinicians often ask “irrelevant” questions, sometimes with intentions that appear voyeuristic. “I saw a pulmonologist earlier in the year and one of his first questions was, ‘When are you getting genital surgery?’ and I was like, ‘I’m here for my lungs,’ ” said a White, nonbinary participant. A White male participant said “As soon as I walk in, no matter what I’m there for, the first [order] of business is for them to determine my gender or sex assigned at birth ... and ... once they ... know they’re ... much more at ease.”
Participants also described how medical encounters went awry once clinicians realized they were transgender. “It wasn’t until after I told the doctor that I was on hormones for transition that I started being ‘he’d.’ ” Before that, it was “she,” said a Black transgender woman.
One participant, a Black person who declined to identify by gender, said “I don’t feel comfortable sharing medical records with physicians anyway because it’s a guarantee that I’m not gonna get services. So I lost [my medical records] and they’re good wherever they are now, far away from me.”
Ten participants were clinicians. “Many seemed concerned that transgender people are being put in distressing and difficult situations in medical settings and also seemed dubious that health care for transgender people would improve without a complete overhaul,” Dr. Alpert said.
In an interview, Boston University assistant professor of medicine C. Streed Jr., MD, MPH, who studies gender and health, praised the study. He said it plays an early role in revealing the problems faced by transgender people in the health system.
“We do not fully know the experience of transgender persons accessing care in various contexts, especially in specialty care such as oncology, pulmonology, nephrology, etc.” Dr. Streed said. “We do not know how they identify specialists who are welcoming, compassionate, and competent in care for transgender persons.”
The results aren’t surprising, Dr. Streed said, “given the lack of training in medical school, residency, and fellowship specific to the unique needs of transgender persons.”
How can clinicians improve interactions with transgender people?
What can clinicians do to help transgender patients feel comfortable? Dr. Alpert suggested they “ask [only] for medically relevant information and to explain to patients why it is medically relevant.”
“This is important because transgender people are often weighing the risks and benefits of disclosing information that could be used to stigmatize them,” Dr. Alpert said.
What if a clinician wants to create a personal connection with a patient by asking questions about their life? “If you as a clinician think it’s important to ask for nonmedical information to get to know a patient, explicitly clarify that your questions are optional and not medically relevant,” Dr. Alpert said. “That way patients have the ability to consent or not to questions that likely will not directly benefit their care.”
Dr. Streed offered a similar perspective. “Clinicians should only be asking questions of patients that will affect the care the patient is seeking and for which the clinician is trained to provide,” he said. “Having a transgender patient is not an opportunity for a clinician to satisfy their curiosity when it is not related to the care the patient is seeking or needs.”
More specifically, Dr. Streed offered an example: Clinicians should not be asking about a patient’s genitals if they are seeking care related to their asthma diagnosis.
Dr. Streed referred clinicians to resources from the American Medical Association and the Human Rights Campaign for guidelines on caring for transgender patients.
The study was funded by Conquer Cancer. The study authors and Dr. Streed have no relevant disclosures.
FROM ANNALS OF FAMILY MEDICINE
Are cellular therapies the future of autoimmune disease?
A revolutionary treatment for cancers may also be able to treat and reset the immune system to provide long-term remission or possibly even cure certain autoimmune diseases.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has offered a novel approach to treating hematologic cancers since 2017, but there are early signs that these cellular immunotherapies could be repurposed for B-cell mediated autoimmune diseases.
In September of last year, researchers in Germany reported that five patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated with CAR T-cell therapy all achieved drug-free remission. At the time of publication, no patients had relapsed for up to 17 months after treatment. The authors described seroconversion of antinuclear antibodies in two patients with the longest follow-up, “indicating that abrogation of autoimmune B-cell clones may lead to a more widespread correction of autoimmunity,” the researchers write.
In another case study published in June, researchers used CD-19 targeted CAR-T cells to treat a 41-year-old man with refractory antisynthetase syndrome with progressive myositis and interstitial lung disease. Six months after treatment, there were no signs of myositis on MRI and a chest CT scan showed full regression of alveolitis.
Since then, two biotechnology companies – Cabaletta Bio in Philadelphia and Kyverna Therapeutics in Emeryville, Calif. – have already been granted fast-track designations from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for CAR T-cell therapy for SLE and lupus nephritis. Bristol-Myers Squibb is also conducting a phase 1 trial in patients with severe, refractory SLE. Several biotechnology companies and hospitals in China are also conducting clinical trials for SLE. But this is only the tip of the iceberg regarding cellular therapies for autoimmune disease, said Max Konig, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“It’s an incredibly exciting time. It’s unprecedented in the history of autoimmunity,” he noted.
A ‘reboot’ for the immune system
B-cell targeted therapies have been around since the early 2000s with drugs like rituximab, a monoclonal antibody medication that targets CD20, an antigen expressed on the surface of B cells. The CAR T cells currently available target another surface antigen, CD19, and are a much more potent therapy. Both are effective at depleting B cells in blood, but these engineered CD19-targeted T cells can reach B cells sitting in tissues in a way that antibody therapies cannot, Dr. Konig explained.
“If you have a patient with myositis, for example, where autoreactive B cells are sitting in the inflamed muscle, or a patient with rheumatoid arthritis, where you have disease-relevant B cells in hard-to-reach tissues like the synovium, those cells are much harder to deplete with an antibody, compared to a T cell that evolved to surveil and effectively kill in all tissues,” he explained.
In this process, T cells are collected from patients via leukapheresis and then re-engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors. A few days before these modified T cells are infused back into the patient, the patients are given a low-dose chemotherapy (lymphodepletion) regimen to help increase the effectiveness of the therapy. The one-time infusion is generally given on an inpatient basis, and patients are then monitored in hospital for side effects.
Once B cells are depleted, disease symptoms improve. But in the case studies published to date, once B cells re-emerge, they are naïve and no longer producing autoreactive B cells.
“Maybe it’s like a tabula rasa: You wipe [the B cells] out and start with a clean slate. Then, the immune system reboots, and now it’s working, whereas before it was messed up,” said Carl June, MD, who directs the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies at the at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. June and his research team led the development of CAR T-cell therapies for blood cancers.
The findings suggest that autoantibodies “might not be hardwired into the immune system,” he said.
But Dr. Konig stressed that we are still in the early days of clinical trials, and more research is necessary to understand the safety and efficacy of these therapies.
“There’s an incredible buzz around CAR T cells at the moment in rheumatology, which is great because I think that’s where the future is,” he said. “But we still need to learn how to appropriately apply these therapies in randomized, controlled trials.”
So far, the evidence behind CD19 CAR T-cell therapies in autoimmune disease is from case studies and phase 1 trials in a very small number of selected patients. (The upcoming Cabaletta and Kyverna trials in lupus will also be small, consisting of 12 patients each.)
Risks of intensive therapy
But while these therapies show promise, the process is very intensive. The lymphodepleting regimen increases the risk for infection and patients are commonly hospitalized for a week or more following infusion for toxicity monitoring. Serious adverse events such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) can occur days to weeks after CAR T-cell infusion. In the five-patient case series reported in 2022, patients were hospitalized for 10 days following treatment.
The patient with antisynthetase syndrome, as well as three of five patients in the SLE case series study experienced mild CRS following infusion. Patients are also at a high risk for infection, as the engineered T cells target all B cells, not just the autoreactive immune cells.
The inability to differentiate between disease-causing and protective immune cells is an issue for all currently available drugs treating autoimmune disease, Dr. Konig said. But scientists are already working on how to make these potent cellular therapies safer and more precise.
Alternatives to standard CAR T-cell therapies
Engineering T cells with RNA is a new approach to limit the side effects and toxicity of CAR T-cell therapy, said Chris Jewell, PhD, the chief scientific officer at Cartesian Therapeutics, a biotechnology company based in Gaithersburg, Md. The company’s RNA CAR T-cell (rCAR-T) therapy – called DESCARTES-08 – is in phase 2 clinical trials for treatment of myasthenia gravis. Once these rCAR-T cells are infused in patients, as they divide, the RNAnaturally decays, he explained, meaning that after a certain point, the CAR is no longer expressed.
DESCARTES-08 targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), which is primarily expressed on plasma cells, rather than all B cells, Dr. Jewell said.
“Targeting BCMA, we actually have a more selective profile,” he explained. “We are targeting the cells primarily responsible for the pathogenicity; many plasma cells – such as long-lived plasma cells – also take a long time to repopulate.”
This therapy also does not require lymphodepletion prior to infusion and can be done in an outpatient setting. The therapy is given in multiple infusions, once per week.
In the most recent clinical trial, patients with myasthenia gravis received six infusions over 6 weeks and experienced notable decreases in myasthenia gravis severity scale at up to 9 months of follow-up.
While standard CAR T-cell therapies under clinical investigational up to now all use effector T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) can also be engineered to target autoimmune disease. Abata Therapeutics, based in Boston, is using this approach for therapies for progressive multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. These engineered Tregs express a T-cell receptor (TCR) that recognizes tissue-specific antigens and suppress inflammation at the site of the disease. “Treg-based cell therapies are really harnessing the natural power of regulatory cells to reset immune tolerance and recalibrate the immune system,” said their chief medical officer, Leonard Dragone, MD, PhD.
These therapies are derived from terminally differentiated cells that have limited capacity to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-2 or interferon gamma, Dr. Dragone explained. “CRS is difficult to envision from engineered Treg products and hasn’t been observed in any clinical experience with polyclonal Tregs,” he said.
This approach also does not require lymphodepletion prior to treatment. The company’s Treg cellular therapy for progressive MS is currently in investigational new drug-enabling studies, and they aim to dose their first patients in 2024.
Precision immunotherapy
For B-cell driven autoimmune diseases where the autoantibody is known, researchers have begun to re-engineer T cells to recognize only autoreactive B cells. While CD19 CAR T cells act more like a sledgehammer, these precision cellular immunotherapies are “like a razor’s strike,” Dr. June said.
“The chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) approach targets autoantibodies that are expressed only on the surface of autoimmune B cells and are not expressed on normal B cells, which ideally should lead to precision targeting of just the cells that cause autoimmune disease,” explained Aimee Payne, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and director of the Penn Clinical Autoimmunity Center of Excellence at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She and her research team used this approach to develop a treatment for mucosal pemphigus vulgaris, an autoimmune blistering disease of mucous membranes driven by autoantibodies against desmoglein 3.
“The current standard of care for pemphigus is to treat with steroids and rituximab, an infusion therapy that results in global, but temporary, B-cell depletion,” she said. “By expressing desmoglein 3 (DSG3) on the surface of the CAAR T-cell therapy, we target just the anti-DSG3 B cells that cause disease in mucosal pemphigus vulgaris and spare the healthy B cells.”
The therapy – called DSG3-CAART – is being developed by Cabaletta Bio and is now in phase 1 clinical trials. The approach is also being investigated to treat certain types of myasthenia gravis and membranous nephropathy.
Dr. Konig’s lab at Johns Hopkins developed and is now exploring a new precision cellular immunotherapy approach, chimeric autoantigen-T cell receptor (CATCR) T-cell therapy, to treat antiphospholipid syndrome, which is in preclinical stages. In this approach, Dr. Konig and his team are “re-engineering the natural T-cell receptor to selectively kill disease-causing B cells that drive antiphospholipid syndrome,” he explained.
He anticipates the CD19 CAR T-cell therapies currently in clinical trials will help to pave the way for this new generation of precision cellular therapies. The ultimate goal of these therapies, he said, is to uncouple therapeutic potency from infection risk.
“That’s really the holy grail in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. It’s tantalizingly close, but we’re not there yet.”
Dr. June is an inventor on patents and/or patent applications licensed to Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research and receives license revenue from such licenses. Dr. June is a scientific founder of Tmunity Therapeutics and Capstan Therapeutics and is a member of the scientific advisory boards of AC Immune SA, Alaunos, BlueSphere Bio, Cabaletta, Carisma, Cartography Biosciences, Cellares, Celldex, Decheng Capital, Poseida, Verismo, and WIRB-Copernicus Group. Dr. Konig is a consultant for argenx and Revel and is listed as inventor for patent applications filed by John Hopkins University. Dr. Payne holds equity, grants, payments, and patent licensing from Cabaletta Bio and consults for Janssen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A revolutionary treatment for cancers may also be able to treat and reset the immune system to provide long-term remission or possibly even cure certain autoimmune diseases.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has offered a novel approach to treating hematologic cancers since 2017, but there are early signs that these cellular immunotherapies could be repurposed for B-cell mediated autoimmune diseases.
In September of last year, researchers in Germany reported that five patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated with CAR T-cell therapy all achieved drug-free remission. At the time of publication, no patients had relapsed for up to 17 months after treatment. The authors described seroconversion of antinuclear antibodies in two patients with the longest follow-up, “indicating that abrogation of autoimmune B-cell clones may lead to a more widespread correction of autoimmunity,” the researchers write.
In another case study published in June, researchers used CD-19 targeted CAR-T cells to treat a 41-year-old man with refractory antisynthetase syndrome with progressive myositis and interstitial lung disease. Six months after treatment, there were no signs of myositis on MRI and a chest CT scan showed full regression of alveolitis.
Since then, two biotechnology companies – Cabaletta Bio in Philadelphia and Kyverna Therapeutics in Emeryville, Calif. – have already been granted fast-track designations from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for CAR T-cell therapy for SLE and lupus nephritis. Bristol-Myers Squibb is also conducting a phase 1 trial in patients with severe, refractory SLE. Several biotechnology companies and hospitals in China are also conducting clinical trials for SLE. But this is only the tip of the iceberg regarding cellular therapies for autoimmune disease, said Max Konig, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“It’s an incredibly exciting time. It’s unprecedented in the history of autoimmunity,” he noted.
A ‘reboot’ for the immune system
B-cell targeted therapies have been around since the early 2000s with drugs like rituximab, a monoclonal antibody medication that targets CD20, an antigen expressed on the surface of B cells. The CAR T cells currently available target another surface antigen, CD19, and are a much more potent therapy. Both are effective at depleting B cells in blood, but these engineered CD19-targeted T cells can reach B cells sitting in tissues in a way that antibody therapies cannot, Dr. Konig explained.
“If you have a patient with myositis, for example, where autoreactive B cells are sitting in the inflamed muscle, or a patient with rheumatoid arthritis, where you have disease-relevant B cells in hard-to-reach tissues like the synovium, those cells are much harder to deplete with an antibody, compared to a T cell that evolved to surveil and effectively kill in all tissues,” he explained.
In this process, T cells are collected from patients via leukapheresis and then re-engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors. A few days before these modified T cells are infused back into the patient, the patients are given a low-dose chemotherapy (lymphodepletion) regimen to help increase the effectiveness of the therapy. The one-time infusion is generally given on an inpatient basis, and patients are then monitored in hospital for side effects.
Once B cells are depleted, disease symptoms improve. But in the case studies published to date, once B cells re-emerge, they are naïve and no longer producing autoreactive B cells.
“Maybe it’s like a tabula rasa: You wipe [the B cells] out and start with a clean slate. Then, the immune system reboots, and now it’s working, whereas before it was messed up,” said Carl June, MD, who directs the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies at the at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. June and his research team led the development of CAR T-cell therapies for blood cancers.
The findings suggest that autoantibodies “might not be hardwired into the immune system,” he said.
But Dr. Konig stressed that we are still in the early days of clinical trials, and more research is necessary to understand the safety and efficacy of these therapies.
“There’s an incredible buzz around CAR T cells at the moment in rheumatology, which is great because I think that’s where the future is,” he said. “But we still need to learn how to appropriately apply these therapies in randomized, controlled trials.”
So far, the evidence behind CD19 CAR T-cell therapies in autoimmune disease is from case studies and phase 1 trials in a very small number of selected patients. (The upcoming Cabaletta and Kyverna trials in lupus will also be small, consisting of 12 patients each.)
Risks of intensive therapy
But while these therapies show promise, the process is very intensive. The lymphodepleting regimen increases the risk for infection and patients are commonly hospitalized for a week or more following infusion for toxicity monitoring. Serious adverse events such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) can occur days to weeks after CAR T-cell infusion. In the five-patient case series reported in 2022, patients were hospitalized for 10 days following treatment.
The patient with antisynthetase syndrome, as well as three of five patients in the SLE case series study experienced mild CRS following infusion. Patients are also at a high risk for infection, as the engineered T cells target all B cells, not just the autoreactive immune cells.
The inability to differentiate between disease-causing and protective immune cells is an issue for all currently available drugs treating autoimmune disease, Dr. Konig said. But scientists are already working on how to make these potent cellular therapies safer and more precise.
Alternatives to standard CAR T-cell therapies
Engineering T cells with RNA is a new approach to limit the side effects and toxicity of CAR T-cell therapy, said Chris Jewell, PhD, the chief scientific officer at Cartesian Therapeutics, a biotechnology company based in Gaithersburg, Md. The company’s RNA CAR T-cell (rCAR-T) therapy – called DESCARTES-08 – is in phase 2 clinical trials for treatment of myasthenia gravis. Once these rCAR-T cells are infused in patients, as they divide, the RNAnaturally decays, he explained, meaning that after a certain point, the CAR is no longer expressed.
DESCARTES-08 targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), which is primarily expressed on plasma cells, rather than all B cells, Dr. Jewell said.
“Targeting BCMA, we actually have a more selective profile,” he explained. “We are targeting the cells primarily responsible for the pathogenicity; many plasma cells – such as long-lived plasma cells – also take a long time to repopulate.”
This therapy also does not require lymphodepletion prior to infusion and can be done in an outpatient setting. The therapy is given in multiple infusions, once per week.
In the most recent clinical trial, patients with myasthenia gravis received six infusions over 6 weeks and experienced notable decreases in myasthenia gravis severity scale at up to 9 months of follow-up.
While standard CAR T-cell therapies under clinical investigational up to now all use effector T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) can also be engineered to target autoimmune disease. Abata Therapeutics, based in Boston, is using this approach for therapies for progressive multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. These engineered Tregs express a T-cell receptor (TCR) that recognizes tissue-specific antigens and suppress inflammation at the site of the disease. “Treg-based cell therapies are really harnessing the natural power of regulatory cells to reset immune tolerance and recalibrate the immune system,” said their chief medical officer, Leonard Dragone, MD, PhD.
These therapies are derived from terminally differentiated cells that have limited capacity to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-2 or interferon gamma, Dr. Dragone explained. “CRS is difficult to envision from engineered Treg products and hasn’t been observed in any clinical experience with polyclonal Tregs,” he said.
This approach also does not require lymphodepletion prior to treatment. The company’s Treg cellular therapy for progressive MS is currently in investigational new drug-enabling studies, and they aim to dose their first patients in 2024.
Precision immunotherapy
For B-cell driven autoimmune diseases where the autoantibody is known, researchers have begun to re-engineer T cells to recognize only autoreactive B cells. While CD19 CAR T cells act more like a sledgehammer, these precision cellular immunotherapies are “like a razor’s strike,” Dr. June said.
“The chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) approach targets autoantibodies that are expressed only on the surface of autoimmune B cells and are not expressed on normal B cells, which ideally should lead to precision targeting of just the cells that cause autoimmune disease,” explained Aimee Payne, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and director of the Penn Clinical Autoimmunity Center of Excellence at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She and her research team used this approach to develop a treatment for mucosal pemphigus vulgaris, an autoimmune blistering disease of mucous membranes driven by autoantibodies against desmoglein 3.
“The current standard of care for pemphigus is to treat with steroids and rituximab, an infusion therapy that results in global, but temporary, B-cell depletion,” she said. “By expressing desmoglein 3 (DSG3) on the surface of the CAAR T-cell therapy, we target just the anti-DSG3 B cells that cause disease in mucosal pemphigus vulgaris and spare the healthy B cells.”
The therapy – called DSG3-CAART – is being developed by Cabaletta Bio and is now in phase 1 clinical trials. The approach is also being investigated to treat certain types of myasthenia gravis and membranous nephropathy.
Dr. Konig’s lab at Johns Hopkins developed and is now exploring a new precision cellular immunotherapy approach, chimeric autoantigen-T cell receptor (CATCR) T-cell therapy, to treat antiphospholipid syndrome, which is in preclinical stages. In this approach, Dr. Konig and his team are “re-engineering the natural T-cell receptor to selectively kill disease-causing B cells that drive antiphospholipid syndrome,” he explained.
He anticipates the CD19 CAR T-cell therapies currently in clinical trials will help to pave the way for this new generation of precision cellular therapies. The ultimate goal of these therapies, he said, is to uncouple therapeutic potency from infection risk.
“That’s really the holy grail in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. It’s tantalizingly close, but we’re not there yet.”
Dr. June is an inventor on patents and/or patent applications licensed to Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research and receives license revenue from such licenses. Dr. June is a scientific founder of Tmunity Therapeutics and Capstan Therapeutics and is a member of the scientific advisory boards of AC Immune SA, Alaunos, BlueSphere Bio, Cabaletta, Carisma, Cartography Biosciences, Cellares, Celldex, Decheng Capital, Poseida, Verismo, and WIRB-Copernicus Group. Dr. Konig is a consultant for argenx and Revel and is listed as inventor for patent applications filed by John Hopkins University. Dr. Payne holds equity, grants, payments, and patent licensing from Cabaletta Bio and consults for Janssen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A revolutionary treatment for cancers may also be able to treat and reset the immune system to provide long-term remission or possibly even cure certain autoimmune diseases.
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy has offered a novel approach to treating hematologic cancers since 2017, but there are early signs that these cellular immunotherapies could be repurposed for B-cell mediated autoimmune diseases.
In September of last year, researchers in Germany reported that five patients with refractory systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated with CAR T-cell therapy all achieved drug-free remission. At the time of publication, no patients had relapsed for up to 17 months after treatment. The authors described seroconversion of antinuclear antibodies in two patients with the longest follow-up, “indicating that abrogation of autoimmune B-cell clones may lead to a more widespread correction of autoimmunity,” the researchers write.
In another case study published in June, researchers used CD-19 targeted CAR-T cells to treat a 41-year-old man with refractory antisynthetase syndrome with progressive myositis and interstitial lung disease. Six months after treatment, there were no signs of myositis on MRI and a chest CT scan showed full regression of alveolitis.
Since then, two biotechnology companies – Cabaletta Bio in Philadelphia and Kyverna Therapeutics in Emeryville, Calif. – have already been granted fast-track designations from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for CAR T-cell therapy for SLE and lupus nephritis. Bristol-Myers Squibb is also conducting a phase 1 trial in patients with severe, refractory SLE. Several biotechnology companies and hospitals in China are also conducting clinical trials for SLE. But this is only the tip of the iceberg regarding cellular therapies for autoimmune disease, said Max Konig, MD, PhD, an assistant professor of medicine in the division of rheumatology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore.
“It’s an incredibly exciting time. It’s unprecedented in the history of autoimmunity,” he noted.
A ‘reboot’ for the immune system
B-cell targeted therapies have been around since the early 2000s with drugs like rituximab, a monoclonal antibody medication that targets CD20, an antigen expressed on the surface of B cells. The CAR T cells currently available target another surface antigen, CD19, and are a much more potent therapy. Both are effective at depleting B cells in blood, but these engineered CD19-targeted T cells can reach B cells sitting in tissues in a way that antibody therapies cannot, Dr. Konig explained.
“If you have a patient with myositis, for example, where autoreactive B cells are sitting in the inflamed muscle, or a patient with rheumatoid arthritis, where you have disease-relevant B cells in hard-to-reach tissues like the synovium, those cells are much harder to deplete with an antibody, compared to a T cell that evolved to surveil and effectively kill in all tissues,” he explained.
In this process, T cells are collected from patients via leukapheresis and then re-engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors. A few days before these modified T cells are infused back into the patient, the patients are given a low-dose chemotherapy (lymphodepletion) regimen to help increase the effectiveness of the therapy. The one-time infusion is generally given on an inpatient basis, and patients are then monitored in hospital for side effects.
Once B cells are depleted, disease symptoms improve. But in the case studies published to date, once B cells re-emerge, they are naïve and no longer producing autoreactive B cells.
“Maybe it’s like a tabula rasa: You wipe [the B cells] out and start with a clean slate. Then, the immune system reboots, and now it’s working, whereas before it was messed up,” said Carl June, MD, who directs the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies at the at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. June and his research team led the development of CAR T-cell therapies for blood cancers.
The findings suggest that autoantibodies “might not be hardwired into the immune system,” he said.
But Dr. Konig stressed that we are still in the early days of clinical trials, and more research is necessary to understand the safety and efficacy of these therapies.
“There’s an incredible buzz around CAR T cells at the moment in rheumatology, which is great because I think that’s where the future is,” he said. “But we still need to learn how to appropriately apply these therapies in randomized, controlled trials.”
So far, the evidence behind CD19 CAR T-cell therapies in autoimmune disease is from case studies and phase 1 trials in a very small number of selected patients. (The upcoming Cabaletta and Kyverna trials in lupus will also be small, consisting of 12 patients each.)
Risks of intensive therapy
But while these therapies show promise, the process is very intensive. The lymphodepleting regimen increases the risk for infection and patients are commonly hospitalized for a week or more following infusion for toxicity monitoring. Serious adverse events such as cytokine release syndrome (CRS) can occur days to weeks after CAR T-cell infusion. In the five-patient case series reported in 2022, patients were hospitalized for 10 days following treatment.
The patient with antisynthetase syndrome, as well as three of five patients in the SLE case series study experienced mild CRS following infusion. Patients are also at a high risk for infection, as the engineered T cells target all B cells, not just the autoreactive immune cells.
The inability to differentiate between disease-causing and protective immune cells is an issue for all currently available drugs treating autoimmune disease, Dr. Konig said. But scientists are already working on how to make these potent cellular therapies safer and more precise.
Alternatives to standard CAR T-cell therapies
Engineering T cells with RNA is a new approach to limit the side effects and toxicity of CAR T-cell therapy, said Chris Jewell, PhD, the chief scientific officer at Cartesian Therapeutics, a biotechnology company based in Gaithersburg, Md. The company’s RNA CAR T-cell (rCAR-T) therapy – called DESCARTES-08 – is in phase 2 clinical trials for treatment of myasthenia gravis. Once these rCAR-T cells are infused in patients, as they divide, the RNAnaturally decays, he explained, meaning that after a certain point, the CAR is no longer expressed.
DESCARTES-08 targets B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA), which is primarily expressed on plasma cells, rather than all B cells, Dr. Jewell said.
“Targeting BCMA, we actually have a more selective profile,” he explained. “We are targeting the cells primarily responsible for the pathogenicity; many plasma cells – such as long-lived plasma cells – also take a long time to repopulate.”
This therapy also does not require lymphodepletion prior to infusion and can be done in an outpatient setting. The therapy is given in multiple infusions, once per week.
In the most recent clinical trial, patients with myasthenia gravis received six infusions over 6 weeks and experienced notable decreases in myasthenia gravis severity scale at up to 9 months of follow-up.
While standard CAR T-cell therapies under clinical investigational up to now all use effector T cells, regulatory T cells (Tregs) can also be engineered to target autoimmune disease. Abata Therapeutics, based in Boston, is using this approach for therapies for progressive multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes. These engineered Tregs express a T-cell receptor (TCR) that recognizes tissue-specific antigens and suppress inflammation at the site of the disease. “Treg-based cell therapies are really harnessing the natural power of regulatory cells to reset immune tolerance and recalibrate the immune system,” said their chief medical officer, Leonard Dragone, MD, PhD.
These therapies are derived from terminally differentiated cells that have limited capacity to produce pro-inflammatory cytokines including interleukin-2 or interferon gamma, Dr. Dragone explained. “CRS is difficult to envision from engineered Treg products and hasn’t been observed in any clinical experience with polyclonal Tregs,” he said.
This approach also does not require lymphodepletion prior to treatment. The company’s Treg cellular therapy for progressive MS is currently in investigational new drug-enabling studies, and they aim to dose their first patients in 2024.
Precision immunotherapy
For B-cell driven autoimmune diseases where the autoantibody is known, researchers have begun to re-engineer T cells to recognize only autoreactive B cells. While CD19 CAR T cells act more like a sledgehammer, these precision cellular immunotherapies are “like a razor’s strike,” Dr. June said.
“The chimeric autoantibody receptor (CAAR) approach targets autoantibodies that are expressed only on the surface of autoimmune B cells and are not expressed on normal B cells, which ideally should lead to precision targeting of just the cells that cause autoimmune disease,” explained Aimee Payne, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology and director of the Penn Clinical Autoimmunity Center of Excellence at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
She and her research team used this approach to develop a treatment for mucosal pemphigus vulgaris, an autoimmune blistering disease of mucous membranes driven by autoantibodies against desmoglein 3.
“The current standard of care for pemphigus is to treat with steroids and rituximab, an infusion therapy that results in global, but temporary, B-cell depletion,” she said. “By expressing desmoglein 3 (DSG3) on the surface of the CAAR T-cell therapy, we target just the anti-DSG3 B cells that cause disease in mucosal pemphigus vulgaris and spare the healthy B cells.”
The therapy – called DSG3-CAART – is being developed by Cabaletta Bio and is now in phase 1 clinical trials. The approach is also being investigated to treat certain types of myasthenia gravis and membranous nephropathy.
Dr. Konig’s lab at Johns Hopkins developed and is now exploring a new precision cellular immunotherapy approach, chimeric autoantigen-T cell receptor (CATCR) T-cell therapy, to treat antiphospholipid syndrome, which is in preclinical stages. In this approach, Dr. Konig and his team are “re-engineering the natural T-cell receptor to selectively kill disease-causing B cells that drive antiphospholipid syndrome,” he explained.
He anticipates the CD19 CAR T-cell therapies currently in clinical trials will help to pave the way for this new generation of precision cellular therapies. The ultimate goal of these therapies, he said, is to uncouple therapeutic potency from infection risk.
“That’s really the holy grail in the treatment of autoimmune diseases. It’s tantalizingly close, but we’re not there yet.”
Dr. June is an inventor on patents and/or patent applications licensed to Novartis Institutes of Biomedical Research and receives license revenue from such licenses. Dr. June is a scientific founder of Tmunity Therapeutics and Capstan Therapeutics and is a member of the scientific advisory boards of AC Immune SA, Alaunos, BlueSphere Bio, Cabaletta, Carisma, Cartography Biosciences, Cellares, Celldex, Decheng Capital, Poseida, Verismo, and WIRB-Copernicus Group. Dr. Konig is a consultant for argenx and Revel and is listed as inventor for patent applications filed by John Hopkins University. Dr. Payne holds equity, grants, payments, and patent licensing from Cabaletta Bio and consults for Janssen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
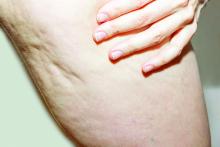
A glimpse at devices designed to tackle cellulite
SAN DIEGO –
A noninvasive treatment, rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) technology (RESONIC), was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in 2021 for short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite. The device emits rapid acoustic pulses (shock waves) that are transmitted through the skin to rupture or shear the fibrotic septa; release of the septa results in the smoothing of skin dimples, Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. RAP, however, was “taken off the market temporarily to refine the design.”
According to Dr. Ortiz, RAP’s repetition rate and short rise time provides microscopic mechanical disruption to the targeted cellular level structures and vacuoles, while high peak pressure and the fast repetition rate exploit the viscoelastic nature of tissue. Compressed pulses from electronic filtering and the reflector shape eliminate cavitation, heat, and pain. Researchers have postulated that the procedure stimulates collagenesis and angiogenesis.
“There’s no heat to this; it just uses sound,” Dr. Ortiz explained. “It’s also time dependent. The longer you do the treatment, the more disruption of the septa you see. The procedure takes 20-30 minutes. Unlike other treatments, it’s not just for discreet dimples. You can treat entire areas like the buttock or posterior leg,” said Dr. Ortiz, who did not use the RAP device in her practice.
Another device, targeted verifiable subcision (TVS, marketed as Avéli), is FDA cleared for temporary reduction in the appearance of cellulite in the buttock and thigh areas of adult women. “But studies show lasting results, at least through a year,” Dr. Ortiz said. The device features a light-guided probe and a hook. The light enables clinicians to navigate under the skin, while the hook releases a tiny blade that severs the septa. “Once you find the septa, then you activate the blade and release the septa. You go right to left because the direction of the blade is on the left of the probe. Then you go back to verify that you got everything that was creating that dimple.”
Previous devices, she said, would “blindly shear the area, so you would find the dimple and blindly cut, so there was no way to verify that you got the target dimple. The results were sometimes mediocre because you didn’t really know if you effectively treated the area.”
She emphasized that TVS is only useful for discreet dimples. “Many patients who come in asking for cellulite treatment have a lot of laxity and rippled texture,” said Dr. Ortiz, who is also president-elect of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is not going to be appropriate for those cases. Setting expectations is important. If patients have laxity and discreet dimples and it’s just the dimples that bother them, that’s fine. They just need to understand the difference,” she said, noting that this is “safe for all skin types.”
Tumescent anesthesia is used to control pain during the procedure. The most common adverse events are bruising and soreness. Results from a pivotal trial showed that clinically significant improvements in the primary endpoint, Cellulite Severity Scale scores, were sustained 1 year after treatment. “Hemosiderin staining can occur, but it eventually dissipates on its own,” Dr. Ortiz added. “You can use laser to speed up healing but sometimes that can make it worse, so you want to be careful with that. Most of the time I have patients wait it out; it does go away on its own.”
She noted that the development of RAP and TVS have helped clinicians better understand the makeup of septa. “We used to think of septa as singular bands that are vertically oriented in cellulite, but what we’ve realized is that it’s more like a network of septa,” she said.
Another noninvasive technology, synchronous parallel ultrasound beam technology from Sofwave (marketed as SUPERB), was FDA cleared in December 2022 for the short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite. The device has seven parallel beam transducers that increase tissue temperatures of the treatment area to 60-70° C, inducing collagen remodeling and collagen denaturation, she said.
In the pivotal study of 68 women, two blinded reviewers reported an 89% improvement rate for both cellulite and skin laxity, after two treatments 2-4 weeks apart, according to data she presented at the meeting. The mean pain score during treatment was 4.55 on a scale of 1-10. No safety issues were observed and immediate responses were limited to erythema and edema.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies, including receipt of speaker fees and honoraria from Sofwave. She is also cochair of MOAS.
SAN DIEGO –
A noninvasive treatment, rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) technology (RESONIC), was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in 2021 for short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite. The device emits rapid acoustic pulses (shock waves) that are transmitted through the skin to rupture or shear the fibrotic septa; release of the septa results in the smoothing of skin dimples, Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. RAP, however, was “taken off the market temporarily to refine the design.”
According to Dr. Ortiz, RAP’s repetition rate and short rise time provides microscopic mechanical disruption to the targeted cellular level structures and vacuoles, while high peak pressure and the fast repetition rate exploit the viscoelastic nature of tissue. Compressed pulses from electronic filtering and the reflector shape eliminate cavitation, heat, and pain. Researchers have postulated that the procedure stimulates collagenesis and angiogenesis.
“There’s no heat to this; it just uses sound,” Dr. Ortiz explained. “It’s also time dependent. The longer you do the treatment, the more disruption of the septa you see. The procedure takes 20-30 minutes. Unlike other treatments, it’s not just for discreet dimples. You can treat entire areas like the buttock or posterior leg,” said Dr. Ortiz, who did not use the RAP device in her practice.
Another device, targeted verifiable subcision (TVS, marketed as Avéli), is FDA cleared for temporary reduction in the appearance of cellulite in the buttock and thigh areas of adult women. “But studies show lasting results, at least through a year,” Dr. Ortiz said. The device features a light-guided probe and a hook. The light enables clinicians to navigate under the skin, while the hook releases a tiny blade that severs the septa. “Once you find the septa, then you activate the blade and release the septa. You go right to left because the direction of the blade is on the left of the probe. Then you go back to verify that you got everything that was creating that dimple.”
Previous devices, she said, would “blindly shear the area, so you would find the dimple and blindly cut, so there was no way to verify that you got the target dimple. The results were sometimes mediocre because you didn’t really know if you effectively treated the area.”
She emphasized that TVS is only useful for discreet dimples. “Many patients who come in asking for cellulite treatment have a lot of laxity and rippled texture,” said Dr. Ortiz, who is also president-elect of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is not going to be appropriate for those cases. Setting expectations is important. If patients have laxity and discreet dimples and it’s just the dimples that bother them, that’s fine. They just need to understand the difference,” she said, noting that this is “safe for all skin types.”
Tumescent anesthesia is used to control pain during the procedure. The most common adverse events are bruising and soreness. Results from a pivotal trial showed that clinically significant improvements in the primary endpoint, Cellulite Severity Scale scores, were sustained 1 year after treatment. “Hemosiderin staining can occur, but it eventually dissipates on its own,” Dr. Ortiz added. “You can use laser to speed up healing but sometimes that can make it worse, so you want to be careful with that. Most of the time I have patients wait it out; it does go away on its own.”
She noted that the development of RAP and TVS have helped clinicians better understand the makeup of septa. “We used to think of septa as singular bands that are vertically oriented in cellulite, but what we’ve realized is that it’s more like a network of septa,” she said.
Another noninvasive technology, synchronous parallel ultrasound beam technology from Sofwave (marketed as SUPERB), was FDA cleared in December 2022 for the short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite. The device has seven parallel beam transducers that increase tissue temperatures of the treatment area to 60-70° C, inducing collagen remodeling and collagen denaturation, she said.
In the pivotal study of 68 women, two blinded reviewers reported an 89% improvement rate for both cellulite and skin laxity, after two treatments 2-4 weeks apart, according to data she presented at the meeting. The mean pain score during treatment was 4.55 on a scale of 1-10. No safety issues were observed and immediate responses were limited to erythema and edema.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies, including receipt of speaker fees and honoraria from Sofwave. She is also cochair of MOAS.
SAN DIEGO –
A noninvasive treatment, rapid acoustic pulse (RAP) technology (RESONIC), was cleared by the Food and Drug Administration in 2021 for short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite. The device emits rapid acoustic pulses (shock waves) that are transmitted through the skin to rupture or shear the fibrotic septa; release of the septa results in the smoothing of skin dimples, Arisa E. Ortiz, MD, director of laser and cosmetic dermatology at the University of California, San Diego, said at the annual Masters of Aesthetics Symposium. RAP, however, was “taken off the market temporarily to refine the design.”
According to Dr. Ortiz, RAP’s repetition rate and short rise time provides microscopic mechanical disruption to the targeted cellular level structures and vacuoles, while high peak pressure and the fast repetition rate exploit the viscoelastic nature of tissue. Compressed pulses from electronic filtering and the reflector shape eliminate cavitation, heat, and pain. Researchers have postulated that the procedure stimulates collagenesis and angiogenesis.
“There’s no heat to this; it just uses sound,” Dr. Ortiz explained. “It’s also time dependent. The longer you do the treatment, the more disruption of the septa you see. The procedure takes 20-30 minutes. Unlike other treatments, it’s not just for discreet dimples. You can treat entire areas like the buttock or posterior leg,” said Dr. Ortiz, who did not use the RAP device in her practice.
Another device, targeted verifiable subcision (TVS, marketed as Avéli), is FDA cleared for temporary reduction in the appearance of cellulite in the buttock and thigh areas of adult women. “But studies show lasting results, at least through a year,” Dr. Ortiz said. The device features a light-guided probe and a hook. The light enables clinicians to navigate under the skin, while the hook releases a tiny blade that severs the septa. “Once you find the septa, then you activate the blade and release the septa. You go right to left because the direction of the blade is on the left of the probe. Then you go back to verify that you got everything that was creating that dimple.”
Previous devices, she said, would “blindly shear the area, so you would find the dimple and blindly cut, so there was no way to verify that you got the target dimple. The results were sometimes mediocre because you didn’t really know if you effectively treated the area.”
She emphasized that TVS is only useful for discreet dimples. “Many patients who come in asking for cellulite treatment have a lot of laxity and rippled texture,” said Dr. Ortiz, who is also president-elect of the American Society for Laser Medicine and Surgery. “This is not going to be appropriate for those cases. Setting expectations is important. If patients have laxity and discreet dimples and it’s just the dimples that bother them, that’s fine. They just need to understand the difference,” she said, noting that this is “safe for all skin types.”
Tumescent anesthesia is used to control pain during the procedure. The most common adverse events are bruising and soreness. Results from a pivotal trial showed that clinically significant improvements in the primary endpoint, Cellulite Severity Scale scores, were sustained 1 year after treatment. “Hemosiderin staining can occur, but it eventually dissipates on its own,” Dr. Ortiz added. “You can use laser to speed up healing but sometimes that can make it worse, so you want to be careful with that. Most of the time I have patients wait it out; it does go away on its own.”
She noted that the development of RAP and TVS have helped clinicians better understand the makeup of septa. “We used to think of septa as singular bands that are vertically oriented in cellulite, but what we’ve realized is that it’s more like a network of septa,” she said.
Another noninvasive technology, synchronous parallel ultrasound beam technology from Sofwave (marketed as SUPERB), was FDA cleared in December 2022 for the short-term improvement in the appearance of cellulite. The device has seven parallel beam transducers that increase tissue temperatures of the treatment area to 60-70° C, inducing collagen remodeling and collagen denaturation, she said.
In the pivotal study of 68 women, two blinded reviewers reported an 89% improvement rate for both cellulite and skin laxity, after two treatments 2-4 weeks apart, according to data she presented at the meeting. The mean pain score during treatment was 4.55 on a scale of 1-10. No safety issues were observed and immediate responses were limited to erythema and edema.
Dr. Ortiz disclosed having financial relationships with several pharmaceutical and device companies, including receipt of speaker fees and honoraria from Sofwave. She is also cochair of MOAS.
AT MOAS 2023
Lack of medical device tracking leaves patients vulnerable
.
As a result of this siloing of information, patients are not getting the expected benefits of a regulation finalized over a decade ago by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
In 2013, the agency ordered companies to include unique device identifiers (UDIs) in plain-text and barcode format on some device labels, starting with implanted devices that are considered life-sustaining. The FDA said that tracking of UDI information would speed detection of complications linked to devices.
But identifiers are rarely on devices. At the time of the regulation creation, the FDA also said it expected this data would be integrated into EHRs. But only a few pioneer organizations such as Duke University and Mercy Health have so far attempted to track any UDI data in an organized way, researchers say.
Richard J. Kovacs, MD, the chief medical officer of the American College of Cardiology, contrasted the lack of useful implementation of UDI data with the speedy transfers of information that happen routinely in other industries. For example, employees of car rental agencies use handheld devices to gather detailed information about the vehicles being returned.
“But if you go to an emergency room with a medical device in your body, no one knows what it is or where it came from or anything about it,” Dr. Kovacs said in an interview.
Many physicians with expertise in device research have pushed for years to have insurers like Medicare require identification information on medical claims.
Even researchers face multiple obstacles in trying to investigate how well UDIs have been incorporated into EHRs and outcomes tied to certain devices.
In August, a Harvard team published a study in JAMA Internal Medicine, attempting to analyze the risks of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) devices. They reported an 11.6% risk for serious blood leaks with AFX Endovascular AAA System aneurysm devices, more than double the 5.7% risk estimated for competing products. The team selected EVAR devices for the study due in part to their known safety concerns. Endologix, the maker of the devices, declined to comment for this story.
The Harvard team used data from the Veterans Affairs health system, which is considered more well organized than most other health systems. But UDI information was found for only 19 of the 13,941 patients whose records were studied. In those cases, only partial information was included.
The researchers developed natural language processing tools, which they used to scrounge clinical notes for information about which devices patients received.
Using this method isn’t feasible for most clinicians, given that records from independent hospitals might not provide this kind of data and descriptions to search, according to the authors of an editorial accompanying the paper. Those researchers urged Congress to pass a law mandating inclusion of UDIs for all devices on claims forms as a condition for reimbursement by federal health care programs.
Setback for advocates
The movement toward UDI suffered a setback in June.
An influential, but little known federal advisory panel, the National Committee on Vital Health Statistics (NCVHS), opted to not recommend use of this information in claims, saying the FDA should consider the matter further.
Gaining an NCVHS recommendation would have been a win, said Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), Sen. Charles E. Grassley (R-IA), and Rep. Bill Pascrell Jr. (D-NJ), in a December 2022 letter to the panel.
Including UDI data would let researchers track patients’ interactions with a health system and could be used to establish population-level correlations between a particular device and a long-term outcome or side effect, the lawmakers said.
That view had the support of at least one major maker of devices, Cook Group, which sells products for a variety of specialties, including cardiology.
In a comment to NCVHS, Cook urged for the inclusion identifiers in Medicare claims.
“While some have argued that the UDI is better suited for inclusion in the electronic health records, Cook believes this argument sets up a false choice between the two,” wrote Stephen L. Ferguson, JD, the chairman of Cook’s board. “Inclusion of the UDI in both electronic health records and claims forms will lead to a more robust system of real-world data.”
In contrast, AdvaMed, the trade group for device makers, told the NCVHS that it did not support adding the information to payment claims submissions, instead just supporting the inclusion in EHRs.
Dr. Kovacs of the ACC said one potential drawback to more transparency could be challenges in interpreting reports of complications in certain cases, at least initially. Reports about a flaw or even a suspected flaw in a device might lead patients to become concerned about their implanted devices, potentially registering unfounded complaints.
But this concern can be addressed through using “scientific rigor and safeguards” and is outweighed by the potential safety benefits for patients, Dr. Kovacs said.
Patients should ask health care systems to track and share information about their implanted devices, Dr. Kovacs suggested.
“I feel it would be my right to demand that that device information follows my electronic medical record, so that it’s readily available to anyone who’s taking care of me,” Dr. Kovacs said. “They would know what it is that’s in me, whether it’s a lens in my eye or a prosthesis in my hip or a highly complicated implantable cardiac electronic device.”
The Harvard study was supported by the FDA and National Institutes of Health. Authors of the study reported receiving fees from the FDA, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and Harvard-MIT Center for Regulatory Science outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Authors of the editorial reported past and present connections with F-Prime Capital, FDA, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Devices Innovation Consortium; the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Arnold Ventures, as well being an expert witness at in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen. Authors of the Viewpoint reported past and present connections with the National Evaluation System for Health Technology Coordinating Center (NESTcc), which is part of the Medical Device Innovation Consortium (MDIC); AIM North America UDI Advisory Committee, Mass General Brigham, Arnold Ventures; the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review California Technology Assessment Forum; Yale University, Johnson & Johnson, FD, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; as well as having been an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
As a result of this siloing of information, patients are not getting the expected benefits of a regulation finalized over a decade ago by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
In 2013, the agency ordered companies to include unique device identifiers (UDIs) in plain-text and barcode format on some device labels, starting with implanted devices that are considered life-sustaining. The FDA said that tracking of UDI information would speed detection of complications linked to devices.
But identifiers are rarely on devices. At the time of the regulation creation, the FDA also said it expected this data would be integrated into EHRs. But only a few pioneer organizations such as Duke University and Mercy Health have so far attempted to track any UDI data in an organized way, researchers say.
Richard J. Kovacs, MD, the chief medical officer of the American College of Cardiology, contrasted the lack of useful implementation of UDI data with the speedy transfers of information that happen routinely in other industries. For example, employees of car rental agencies use handheld devices to gather detailed information about the vehicles being returned.
“But if you go to an emergency room with a medical device in your body, no one knows what it is or where it came from or anything about it,” Dr. Kovacs said in an interview.
Many physicians with expertise in device research have pushed for years to have insurers like Medicare require identification information on medical claims.
Even researchers face multiple obstacles in trying to investigate how well UDIs have been incorporated into EHRs and outcomes tied to certain devices.
In August, a Harvard team published a study in JAMA Internal Medicine, attempting to analyze the risks of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) devices. They reported an 11.6% risk for serious blood leaks with AFX Endovascular AAA System aneurysm devices, more than double the 5.7% risk estimated for competing products. The team selected EVAR devices for the study due in part to their known safety concerns. Endologix, the maker of the devices, declined to comment for this story.
The Harvard team used data from the Veterans Affairs health system, which is considered more well organized than most other health systems. But UDI information was found for only 19 of the 13,941 patients whose records were studied. In those cases, only partial information was included.
The researchers developed natural language processing tools, which they used to scrounge clinical notes for information about which devices patients received.
Using this method isn’t feasible for most clinicians, given that records from independent hospitals might not provide this kind of data and descriptions to search, according to the authors of an editorial accompanying the paper. Those researchers urged Congress to pass a law mandating inclusion of UDIs for all devices on claims forms as a condition for reimbursement by federal health care programs.
Setback for advocates
The movement toward UDI suffered a setback in June.
An influential, but little known federal advisory panel, the National Committee on Vital Health Statistics (NCVHS), opted to not recommend use of this information in claims, saying the FDA should consider the matter further.
Gaining an NCVHS recommendation would have been a win, said Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), Sen. Charles E. Grassley (R-IA), and Rep. Bill Pascrell Jr. (D-NJ), in a December 2022 letter to the panel.
Including UDI data would let researchers track patients’ interactions with a health system and could be used to establish population-level correlations between a particular device and a long-term outcome or side effect, the lawmakers said.
That view had the support of at least one major maker of devices, Cook Group, which sells products for a variety of specialties, including cardiology.
In a comment to NCVHS, Cook urged for the inclusion identifiers in Medicare claims.
“While some have argued that the UDI is better suited for inclusion in the electronic health records, Cook believes this argument sets up a false choice between the two,” wrote Stephen L. Ferguson, JD, the chairman of Cook’s board. “Inclusion of the UDI in both electronic health records and claims forms will lead to a more robust system of real-world data.”
In contrast, AdvaMed, the trade group for device makers, told the NCVHS that it did not support adding the information to payment claims submissions, instead just supporting the inclusion in EHRs.
Dr. Kovacs of the ACC said one potential drawback to more transparency could be challenges in interpreting reports of complications in certain cases, at least initially. Reports about a flaw or even a suspected flaw in a device might lead patients to become concerned about their implanted devices, potentially registering unfounded complaints.
But this concern can be addressed through using “scientific rigor and safeguards” and is outweighed by the potential safety benefits for patients, Dr. Kovacs said.
Patients should ask health care systems to track and share information about their implanted devices, Dr. Kovacs suggested.
“I feel it would be my right to demand that that device information follows my electronic medical record, so that it’s readily available to anyone who’s taking care of me,” Dr. Kovacs said. “They would know what it is that’s in me, whether it’s a lens in my eye or a prosthesis in my hip or a highly complicated implantable cardiac electronic device.”
The Harvard study was supported by the FDA and National Institutes of Health. Authors of the study reported receiving fees from the FDA, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and Harvard-MIT Center for Regulatory Science outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Authors of the editorial reported past and present connections with F-Prime Capital, FDA, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Devices Innovation Consortium; the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Arnold Ventures, as well being an expert witness at in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen. Authors of the Viewpoint reported past and present connections with the National Evaluation System for Health Technology Coordinating Center (NESTcc), which is part of the Medical Device Innovation Consortium (MDIC); AIM North America UDI Advisory Committee, Mass General Brigham, Arnold Ventures; the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review California Technology Assessment Forum; Yale University, Johnson & Johnson, FD, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; as well as having been an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
.
As a result of this siloing of information, patients are not getting the expected benefits of a regulation finalized over a decade ago by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
In 2013, the agency ordered companies to include unique device identifiers (UDIs) in plain-text and barcode format on some device labels, starting with implanted devices that are considered life-sustaining. The FDA said that tracking of UDI information would speed detection of complications linked to devices.
But identifiers are rarely on devices. At the time of the regulation creation, the FDA also said it expected this data would be integrated into EHRs. But only a few pioneer organizations such as Duke University and Mercy Health have so far attempted to track any UDI data in an organized way, researchers say.
Richard J. Kovacs, MD, the chief medical officer of the American College of Cardiology, contrasted the lack of useful implementation of UDI data with the speedy transfers of information that happen routinely in other industries. For example, employees of car rental agencies use handheld devices to gather detailed information about the vehicles being returned.
“But if you go to an emergency room with a medical device in your body, no one knows what it is or where it came from or anything about it,” Dr. Kovacs said in an interview.
Many physicians with expertise in device research have pushed for years to have insurers like Medicare require identification information on medical claims.
Even researchers face multiple obstacles in trying to investigate how well UDIs have been incorporated into EHRs and outcomes tied to certain devices.
In August, a Harvard team published a study in JAMA Internal Medicine, attempting to analyze the risks of endovascular aortic repair (EVAR) devices. They reported an 11.6% risk for serious blood leaks with AFX Endovascular AAA System aneurysm devices, more than double the 5.7% risk estimated for competing products. The team selected EVAR devices for the study due in part to their known safety concerns. Endologix, the maker of the devices, declined to comment for this story.
The Harvard team used data from the Veterans Affairs health system, which is considered more well organized than most other health systems. But UDI information was found for only 19 of the 13,941 patients whose records were studied. In those cases, only partial information was included.
The researchers developed natural language processing tools, which they used to scrounge clinical notes for information about which devices patients received.
Using this method isn’t feasible for most clinicians, given that records from independent hospitals might not provide this kind of data and descriptions to search, according to the authors of an editorial accompanying the paper. Those researchers urged Congress to pass a law mandating inclusion of UDIs for all devices on claims forms as a condition for reimbursement by federal health care programs.
Setback for advocates
The movement toward UDI suffered a setback in June.
An influential, but little known federal advisory panel, the National Committee on Vital Health Statistics (NCVHS), opted to not recommend use of this information in claims, saying the FDA should consider the matter further.
Gaining an NCVHS recommendation would have been a win, said Sen. Elizabeth Warren (D-MA), Sen. Charles E. Grassley (R-IA), and Rep. Bill Pascrell Jr. (D-NJ), in a December 2022 letter to the panel.
Including UDI data would let researchers track patients’ interactions with a health system and could be used to establish population-level correlations between a particular device and a long-term outcome or side effect, the lawmakers said.
That view had the support of at least one major maker of devices, Cook Group, which sells products for a variety of specialties, including cardiology.
In a comment to NCVHS, Cook urged for the inclusion identifiers in Medicare claims.
“While some have argued that the UDI is better suited for inclusion in the electronic health records, Cook believes this argument sets up a false choice between the two,” wrote Stephen L. Ferguson, JD, the chairman of Cook’s board. “Inclusion of the UDI in both electronic health records and claims forms will lead to a more robust system of real-world data.”
In contrast, AdvaMed, the trade group for device makers, told the NCVHS that it did not support adding the information to payment claims submissions, instead just supporting the inclusion in EHRs.
Dr. Kovacs of the ACC said one potential drawback to more transparency could be challenges in interpreting reports of complications in certain cases, at least initially. Reports about a flaw or even a suspected flaw in a device might lead patients to become concerned about their implanted devices, potentially registering unfounded complaints.
But this concern can be addressed through using “scientific rigor and safeguards” and is outweighed by the potential safety benefits for patients, Dr. Kovacs said.
Patients should ask health care systems to track and share information about their implanted devices, Dr. Kovacs suggested.
“I feel it would be my right to demand that that device information follows my electronic medical record, so that it’s readily available to anyone who’s taking care of me,” Dr. Kovacs said. “They would know what it is that’s in me, whether it’s a lens in my eye or a prosthesis in my hip or a highly complicated implantable cardiac electronic device.”
The Harvard study was supported by the FDA and National Institutes of Health. Authors of the study reported receiving fees from the FDA, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, and Harvard-MIT Center for Regulatory Science outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported. Authors of the editorial reported past and present connections with F-Prime Capital, FDA, Johnson & Johnson, the Medical Devices Innovation Consortium; the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Arnold Ventures, as well being an expert witness at in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against Biogen. Authors of the Viewpoint reported past and present connections with the National Evaluation System for Health Technology Coordinating Center (NESTcc), which is part of the Medical Device Innovation Consortium (MDIC); AIM North America UDI Advisory Committee, Mass General Brigham, Arnold Ventures; the Institute for Clinical and Economic Review California Technology Assessment Forum; Yale University, Johnson & Johnson, FD, Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health; as well as having been an expert witness in a qui tam suit alleging violations of the False Claims Act and Anti-Kickback Statute against.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Does continuity of care affect outcomes after arthroplasty?
according to new research.
In a retrospective cohort study that included more than 45,000 surgeries, the likelihood of visiting the ED within 90 days was 40% lower for patients who had unbroken continuity of primary care before knee replacement and 35% lower for patients who had unbroken continuity of primary care before hip replacement, compared with those who had several primary care clinicians. Continuity of primary care was defined as having one primary care clinician in the 3 years before surgery.
The findings highlight the critical need for improved access to primary care in Canada, lead author Lynn Lethbridge, from the department of surgery at Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., said in an interview. “The primary care providers have been aware that continuity of care matters, but I’m not sure that surgeons are,” she said. “If they become aware, the surgical team could develop strategies to help prevent somebody from coming back to the ED by discussing primary care provisions during the presurgical consultation.”
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Surgery.
Discontinuity a disadvantage
“There’s been a lot of news for the last few years here in Nova Scotia and all across Canada on the difficulties of getting and keeping a regular primary care provider, and there has also been a lot of coverage about overcrowded emergency departments and efforts to reduce the need for emergency care,” said Ms. Lethbridge. “The number of joint replacement procedures is expected to rise in the coming years, and we wanted to know if there was an association between not having a regular primary care provider and the chance of returning to the ED after joint replacement, so we undertook the study.”
The researchers accessed data on all patients in Nova Scotia who underwent nonemergency hip and knee procedures from 2005 to 2020. The study outcome was any ED visit within 90 days after discharge.
The investigators looked at 3 years of primary care history before surgery and calculated the Modified Modified Continuity Index (MMCI), which represents the number of primary care clinicians adjusted for the total number of visits, for each patient. The maximum value of the MMCI is 1, meaning that the patient saw the same doctor throughout the period examined. Lower scores mean that the patient saw different health care providers during that period.
Of the patients who underwent the 28,574 knee procedures included in the analysis, 13.9% had an ED visit within 90 days. Of the patients who underwent the 16,767 hip procedures included in the analysis, 13.5% had an ED visit within 90 days.
For patients undergoing knee procedures, the mean MMCI was 0.868, and 10.7% of patients had a perfect MMCI score of 1. For patients undergoing hip replacement, the mean MMCI was 0.864, and 13.5% had an MMCI of 1.
After controlling for confounders such as age, comorbidities, distance to hospital, and neighborhood income, the researchers found a statistically significant negative association between greater continuity of care and the probability of an ED visit.
A knee replacement patient with an MMCI score of 1 had a 90-day ED visit probability of 12.8%. A patient who had visited multiple primary care clinicians before surgery had a probability of 15.2%.
‘Quarterbacks’ needed
Commenting on the findings, Harman Chaudhry, MD, MSc, an orthopedic surgeon at Sunnybrook Health Science Center, Toronto, said: “Their main message quantified what many of us in health care already sense is true: That patients do benefit when there’s somebody, specifically a primary care provider, to quarterback their health care, look over the entirety of their care, and really know the patient.
“These are elective procedures, and joint replacement is a very siloed and episodic instance of care where we, as surgeons in hospitals, think we can control a lot of the presurgical and postsurgical care and really optimize patients,” he added. “But it’s clear that despite that, patients are still benefiting from having somebody who has known them for a longer period of time.”
The longstanding shortage of family physicians in Canada has worsened, especially since the beginning of the pandemic. The shortage means that many people are denied access to a family doctor of their own, said Dr. Chaudhry, who was not involved in the research.
“In Canada, there’s a large chunk of the population that is having difficulty accessing a primary care physician, so those patients have created their own primary care experience, taking advantage of walk-in clinics, perhaps urgent care centers, EDs when they need emergency care, and locum [tenens] physicians that may come into the community once in a while. And so, they have created their own primary care experience, but there is not a single person or single medical home where they’ve been seen for a period of years,” he said.
“Many of the patients in this study who were in the ED had nobody that the surgeon could communicate with or send his notes to,” Dr. Chaudhry concluded.
No source of funding for this study was reported. Ms. Lethbridge and Dr. Chaudhry reported no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor received travel support from Stryker and DePuy Synthes, has stock or stock options in Stryker, and participated in a data safety monitoring board for Hip Innovation Technology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to new research.
In a retrospective cohort study that included more than 45,000 surgeries, the likelihood of visiting the ED within 90 days was 40% lower for patients who had unbroken continuity of primary care before knee replacement and 35% lower for patients who had unbroken continuity of primary care before hip replacement, compared with those who had several primary care clinicians. Continuity of primary care was defined as having one primary care clinician in the 3 years before surgery.
The findings highlight the critical need for improved access to primary care in Canada, lead author Lynn Lethbridge, from the department of surgery at Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., said in an interview. “The primary care providers have been aware that continuity of care matters, but I’m not sure that surgeons are,” she said. “If they become aware, the surgical team could develop strategies to help prevent somebody from coming back to the ED by discussing primary care provisions during the presurgical consultation.”
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Surgery.
Discontinuity a disadvantage
“There’s been a lot of news for the last few years here in Nova Scotia and all across Canada on the difficulties of getting and keeping a regular primary care provider, and there has also been a lot of coverage about overcrowded emergency departments and efforts to reduce the need for emergency care,” said Ms. Lethbridge. “The number of joint replacement procedures is expected to rise in the coming years, and we wanted to know if there was an association between not having a regular primary care provider and the chance of returning to the ED after joint replacement, so we undertook the study.”
The researchers accessed data on all patients in Nova Scotia who underwent nonemergency hip and knee procedures from 2005 to 2020. The study outcome was any ED visit within 90 days after discharge.
The investigators looked at 3 years of primary care history before surgery and calculated the Modified Modified Continuity Index (MMCI), which represents the number of primary care clinicians adjusted for the total number of visits, for each patient. The maximum value of the MMCI is 1, meaning that the patient saw the same doctor throughout the period examined. Lower scores mean that the patient saw different health care providers during that period.
Of the patients who underwent the 28,574 knee procedures included in the analysis, 13.9% had an ED visit within 90 days. Of the patients who underwent the 16,767 hip procedures included in the analysis, 13.5% had an ED visit within 90 days.
For patients undergoing knee procedures, the mean MMCI was 0.868, and 10.7% of patients had a perfect MMCI score of 1. For patients undergoing hip replacement, the mean MMCI was 0.864, and 13.5% had an MMCI of 1.
After controlling for confounders such as age, comorbidities, distance to hospital, and neighborhood income, the researchers found a statistically significant negative association between greater continuity of care and the probability of an ED visit.
A knee replacement patient with an MMCI score of 1 had a 90-day ED visit probability of 12.8%. A patient who had visited multiple primary care clinicians before surgery had a probability of 15.2%.
‘Quarterbacks’ needed
Commenting on the findings, Harman Chaudhry, MD, MSc, an orthopedic surgeon at Sunnybrook Health Science Center, Toronto, said: “Their main message quantified what many of us in health care already sense is true: That patients do benefit when there’s somebody, specifically a primary care provider, to quarterback their health care, look over the entirety of their care, and really know the patient.
“These are elective procedures, and joint replacement is a very siloed and episodic instance of care where we, as surgeons in hospitals, think we can control a lot of the presurgical and postsurgical care and really optimize patients,” he added. “But it’s clear that despite that, patients are still benefiting from having somebody who has known them for a longer period of time.”
The longstanding shortage of family physicians in Canada has worsened, especially since the beginning of the pandemic. The shortage means that many people are denied access to a family doctor of their own, said Dr. Chaudhry, who was not involved in the research.
“In Canada, there’s a large chunk of the population that is having difficulty accessing a primary care physician, so those patients have created their own primary care experience, taking advantage of walk-in clinics, perhaps urgent care centers, EDs when they need emergency care, and locum [tenens] physicians that may come into the community once in a while. And so, they have created their own primary care experience, but there is not a single person or single medical home where they’ve been seen for a period of years,” he said.
“Many of the patients in this study who were in the ED had nobody that the surgeon could communicate with or send his notes to,” Dr. Chaudhry concluded.
No source of funding for this study was reported. Ms. Lethbridge and Dr. Chaudhry reported no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor received travel support from Stryker and DePuy Synthes, has stock or stock options in Stryker, and participated in a data safety monitoring board for Hip Innovation Technology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to new research.
In a retrospective cohort study that included more than 45,000 surgeries, the likelihood of visiting the ED within 90 days was 40% lower for patients who had unbroken continuity of primary care before knee replacement and 35% lower for patients who had unbroken continuity of primary care before hip replacement, compared with those who had several primary care clinicians. Continuity of primary care was defined as having one primary care clinician in the 3 years before surgery.
The findings highlight the critical need for improved access to primary care in Canada, lead author Lynn Lethbridge, from the department of surgery at Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S., said in an interview. “The primary care providers have been aware that continuity of care matters, but I’m not sure that surgeons are,” she said. “If they become aware, the surgical team could develop strategies to help prevent somebody from coming back to the ED by discussing primary care provisions during the presurgical consultation.”
The study was published online in the Canadian Journal of Surgery.
Discontinuity a disadvantage
“There’s been a lot of news for the last few years here in Nova Scotia and all across Canada on the difficulties of getting and keeping a regular primary care provider, and there has also been a lot of coverage about overcrowded emergency departments and efforts to reduce the need for emergency care,” said Ms. Lethbridge. “The number of joint replacement procedures is expected to rise in the coming years, and we wanted to know if there was an association between not having a regular primary care provider and the chance of returning to the ED after joint replacement, so we undertook the study.”
The researchers accessed data on all patients in Nova Scotia who underwent nonemergency hip and knee procedures from 2005 to 2020. The study outcome was any ED visit within 90 days after discharge.
The investigators looked at 3 years of primary care history before surgery and calculated the Modified Modified Continuity Index (MMCI), which represents the number of primary care clinicians adjusted for the total number of visits, for each patient. The maximum value of the MMCI is 1, meaning that the patient saw the same doctor throughout the period examined. Lower scores mean that the patient saw different health care providers during that period.
Of the patients who underwent the 28,574 knee procedures included in the analysis, 13.9% had an ED visit within 90 days. Of the patients who underwent the 16,767 hip procedures included in the analysis, 13.5% had an ED visit within 90 days.
For patients undergoing knee procedures, the mean MMCI was 0.868, and 10.7% of patients had a perfect MMCI score of 1. For patients undergoing hip replacement, the mean MMCI was 0.864, and 13.5% had an MMCI of 1.
After controlling for confounders such as age, comorbidities, distance to hospital, and neighborhood income, the researchers found a statistically significant negative association between greater continuity of care and the probability of an ED visit.
A knee replacement patient with an MMCI score of 1 had a 90-day ED visit probability of 12.8%. A patient who had visited multiple primary care clinicians before surgery had a probability of 15.2%.
‘Quarterbacks’ needed
Commenting on the findings, Harman Chaudhry, MD, MSc, an orthopedic surgeon at Sunnybrook Health Science Center, Toronto, said: “Their main message quantified what many of us in health care already sense is true: That patients do benefit when there’s somebody, specifically a primary care provider, to quarterback their health care, look over the entirety of their care, and really know the patient.
“These are elective procedures, and joint replacement is a very siloed and episodic instance of care where we, as surgeons in hospitals, think we can control a lot of the presurgical and postsurgical care and really optimize patients,” he added. “But it’s clear that despite that, patients are still benefiting from having somebody who has known them for a longer period of time.”
The longstanding shortage of family physicians in Canada has worsened, especially since the beginning of the pandemic. The shortage means that many people are denied access to a family doctor of their own, said Dr. Chaudhry, who was not involved in the research.
“In Canada, there’s a large chunk of the population that is having difficulty accessing a primary care physician, so those patients have created their own primary care experience, taking advantage of walk-in clinics, perhaps urgent care centers, EDs when they need emergency care, and locum [tenens] physicians that may come into the community once in a while. And so, they have created their own primary care experience, but there is not a single person or single medical home where they’ve been seen for a period of years,” he said.
“Many of the patients in this study who were in the ED had nobody that the surgeon could communicate with or send his notes to,” Dr. Chaudhry concluded.
No source of funding for this study was reported. Ms. Lethbridge and Dr. Chaudhry reported no relevant financial relationships. One coauthor received travel support from Stryker and DePuy Synthes, has stock or stock options in Stryker, and participated in a data safety monitoring board for Hip Innovation Technology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN JOURNAL OF SURGERY
Hormone replacement therapy for postmenopausal osteoporosis
The actress Sally Field recently described her struggles with postmenopausal osteoporosis – she was given the diagnosis when she was 60 years old despite being physically active and engaging in activities such as biking, hiking, and yoga. As a slim, White woman in her sixth decade of life, she certainly had several risk factors for osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis, a condition associated with weak bones and an increased risk for fracture, is common in women after menopause. It’s defined as a bone mineral density (BMD) T-score of less than or equal to –2.5 on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan, occurrence of a spine or hip fracture regardless of BMD, or a BMD T-score between –1 and –2.5, along with a history of certain kinds of fractures or increased fracture risk based on the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX).
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2013 to 2014 reported that 16.5 % of women aged 50 years or older in the U.S. have osteoporosis (vs. only 5% of men of a similar age), with an increasing prevalence with increasing age. For example, the risk for osteoporosis of the hip increases from about 7% in women 50-59 years of age to about 35% in those aged 80 years or older. The risk for postmenopausal osteoporosis is reported to be highest in Asian women (40%), followed by Hispanic (20.5%), non-Hispanic White (17%), and non-Hispanic Black women (8.2%).
Why increased fracture risk in postmenopausal women?
The primary cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis is the cessation of estrogen production by the ovaries around the menopausal transition. Estrogen is very important for bone health. It reduces bone loss by reducing levels of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and sclerostin, and it probably also increases bone formation through its effects on sclerostin.
Around menopause, the decrease in estrogen levels results in an increase in RANKL and sclerostin, with a consequent increase in bone loss at a pace that exceeds the rate of bone formation, thereby leading to osteoporosis.
Many factors further increase the risk for osteoporosis and fracture in postmenopausal women. These include a sedentary lifestyle, lower body weight, family history of osteoporosis, smoking, and certain medications and diseases. Medications that adversely affect bone health at this age include (but are not limited to) glucocorticoids such as hydrocortisone, prednisone, and dexamethasone; letrozole; excess thyroid hormone; certain drugs used to treat cancer; immunosuppressive drugs; certain antiseizure medications; proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazole); sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and certain other drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes; and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (used to treat anxiety and depression).
Diseases associated with increased osteoporosis risk include certain genetic conditions affecting bone, a history of early ovarian insufficiency, hyperthyroidism, high levels of cortisol, diabetes, hyperparathyroidism, eating disorders, obesity, calcium and vitamin D deficiency, excess urinary excretion of calcium, malabsorption and certain gastrointestinal surgeries, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, certain types of cancer, and frailty.
Furthermore, older age, low bone density, a previous history of fracture, a family history of hip fracture, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake increase the risk for an osteoporotic fracture in a postmenopausal woman.
Bone density assessment using DXA is recommended in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk for low bone density and fracture. Monitoring of bone density is typically initiated about 5 years after the menopausal transition but should be considered earlier in those at high risk for osteoporosis. Women who are aged 70 or older, and those who have had significant height loss, should also get radiography of the spine to look for vertebral fractures.
Optimal nutrition is important for all postmenopausal women. Weight extremes are to be avoided. Although the use of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in postmenopausal women is still debated, the Institute of Medicine recommends that women 51-70 years of age take 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 400-600 IU of vitamin D daily, and that those older than 70 years take 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 400-800 IU of vitamin D daily.
Women with low vitamin D levels often require higher doses of vitamin D. It’s very important to avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Optimizing protein intake and exercises that improve muscle strength and improve balance can reduce the risk for falls, a key contributor to osteoporotic fractures.
Estrogen to prevent fracture risk
Because estrogen deficiency is a key cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis, estrogen replacement therapy has been used to prevent this condition, particularly early in the menopausal transition (51-60 years). Different formulations of estrogen given via oral or transdermal routes have been demonstrated to prevent osteoporosis; transdermal estrogen is often preferred because of a lower risk for blood clots and stroke. Women who have an intact uterus should also receive a progestin preparation either daily or cyclically, because estrogen alone can increase the risk for uterine cancer in the long run. Estrogen replacement has been associated with a 34% reduction in vertebral, hip, and total fractures in women of this age group.
Sally Field did receive hormone replacement therapy, which was helpful for her bones. However, as typically happens, her bone density dropped again when she discontinued hormone replacement. She also had low vitamin D levels, but vitamin D supplementation was not helpful. She received other medical intervention, with recovery back to good bone health.
Raloxifene is a medication that acts on the estrogen receptor, with beneficial effects on bone, and is approved for prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Medications that reduce bone loss (antiresorptive drugs), such as bisphosphonates and denosumab, and those that increase bone formation (osteoanabolic drugs), such as teriparatide, abaloparatide, and romosozumab, are used alone or in combination in women whose osteoporosis doesn’t respond to lifestyle and preventive strategies. The osteoanabolic drugs are typically reserved for women at very high risk for fractures, such as those with a BMD T-score ≤ less than or equal to –3, older women with recent fractures, and those with other risk factors. Treatment is typically lifelong.
(such as fractures of the spine and hip). It’s important to recognize those at greatest risk for this condition; implement bone health monitoring in a timely fashion; and ensure optimal nutrition, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and exercises that optimize muscle strength and balance. Hormone replacement therapy is a consideration in many women. Some women will require antiresorptive or osteoanabolic drugs to manage this condition. With optimal treatment, older women can live long and productive lives.
Dr. Misra is Chief, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, Mass General for Children; Associate Director, Harvard Catalyst Translation and Clinical Research Center; Director, Pediatric Endocrine-Sports Endocrine-Neuroendocrine Lab, Mass General Hospital; Professor, department of pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. She has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Sanofi; Ipsen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The actress Sally Field recently described her struggles with postmenopausal osteoporosis – she was given the diagnosis when she was 60 years old despite being physically active and engaging in activities such as biking, hiking, and yoga. As a slim, White woman in her sixth decade of life, she certainly had several risk factors for osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis, a condition associated with weak bones and an increased risk for fracture, is common in women after menopause. It’s defined as a bone mineral density (BMD) T-score of less than or equal to –2.5 on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan, occurrence of a spine or hip fracture regardless of BMD, or a BMD T-score between –1 and –2.5, along with a history of certain kinds of fractures or increased fracture risk based on the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX).
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2013 to 2014 reported that 16.5 % of women aged 50 years or older in the U.S. have osteoporosis (vs. only 5% of men of a similar age), with an increasing prevalence with increasing age. For example, the risk for osteoporosis of the hip increases from about 7% in women 50-59 years of age to about 35% in those aged 80 years or older. The risk for postmenopausal osteoporosis is reported to be highest in Asian women (40%), followed by Hispanic (20.5%), non-Hispanic White (17%), and non-Hispanic Black women (8.2%).
Why increased fracture risk in postmenopausal women?
The primary cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis is the cessation of estrogen production by the ovaries around the menopausal transition. Estrogen is very important for bone health. It reduces bone loss by reducing levels of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and sclerostin, and it probably also increases bone formation through its effects on sclerostin.
Around menopause, the decrease in estrogen levels results in an increase in RANKL and sclerostin, with a consequent increase in bone loss at a pace that exceeds the rate of bone formation, thereby leading to osteoporosis.
Many factors further increase the risk for osteoporosis and fracture in postmenopausal women. These include a sedentary lifestyle, lower body weight, family history of osteoporosis, smoking, and certain medications and diseases. Medications that adversely affect bone health at this age include (but are not limited to) glucocorticoids such as hydrocortisone, prednisone, and dexamethasone; letrozole; excess thyroid hormone; certain drugs used to treat cancer; immunosuppressive drugs; certain antiseizure medications; proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazole); sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and certain other drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes; and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (used to treat anxiety and depression).
Diseases associated with increased osteoporosis risk include certain genetic conditions affecting bone, a history of early ovarian insufficiency, hyperthyroidism, high levels of cortisol, diabetes, hyperparathyroidism, eating disorders, obesity, calcium and vitamin D deficiency, excess urinary excretion of calcium, malabsorption and certain gastrointestinal surgeries, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, certain types of cancer, and frailty.
Furthermore, older age, low bone density, a previous history of fracture, a family history of hip fracture, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake increase the risk for an osteoporotic fracture in a postmenopausal woman.
Bone density assessment using DXA is recommended in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk for low bone density and fracture. Monitoring of bone density is typically initiated about 5 years after the menopausal transition but should be considered earlier in those at high risk for osteoporosis. Women who are aged 70 or older, and those who have had significant height loss, should also get radiography of the spine to look for vertebral fractures.
Optimal nutrition is important for all postmenopausal women. Weight extremes are to be avoided. Although the use of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in postmenopausal women is still debated, the Institute of Medicine recommends that women 51-70 years of age take 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 400-600 IU of vitamin D daily, and that those older than 70 years take 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 400-800 IU of vitamin D daily.
Women with low vitamin D levels often require higher doses of vitamin D. It’s very important to avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Optimizing protein intake and exercises that improve muscle strength and improve balance can reduce the risk for falls, a key contributor to osteoporotic fractures.
Estrogen to prevent fracture risk
Because estrogen deficiency is a key cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis, estrogen replacement therapy has been used to prevent this condition, particularly early in the menopausal transition (51-60 years). Different formulations of estrogen given via oral or transdermal routes have been demonstrated to prevent osteoporosis; transdermal estrogen is often preferred because of a lower risk for blood clots and stroke. Women who have an intact uterus should also receive a progestin preparation either daily or cyclically, because estrogen alone can increase the risk for uterine cancer in the long run. Estrogen replacement has been associated with a 34% reduction in vertebral, hip, and total fractures in women of this age group.
Sally Field did receive hormone replacement therapy, which was helpful for her bones. However, as typically happens, her bone density dropped again when she discontinued hormone replacement. She also had low vitamin D levels, but vitamin D supplementation was not helpful. She received other medical intervention, with recovery back to good bone health.
Raloxifene is a medication that acts on the estrogen receptor, with beneficial effects on bone, and is approved for prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Medications that reduce bone loss (antiresorptive drugs), such as bisphosphonates and denosumab, and those that increase bone formation (osteoanabolic drugs), such as teriparatide, abaloparatide, and romosozumab, are used alone or in combination in women whose osteoporosis doesn’t respond to lifestyle and preventive strategies. The osteoanabolic drugs are typically reserved for women at very high risk for fractures, such as those with a BMD T-score ≤ less than or equal to –3, older women with recent fractures, and those with other risk factors. Treatment is typically lifelong.
(such as fractures of the spine and hip). It’s important to recognize those at greatest risk for this condition; implement bone health monitoring in a timely fashion; and ensure optimal nutrition, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and exercises that optimize muscle strength and balance. Hormone replacement therapy is a consideration in many women. Some women will require antiresorptive or osteoanabolic drugs to manage this condition. With optimal treatment, older women can live long and productive lives.
Dr. Misra is Chief, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, Mass General for Children; Associate Director, Harvard Catalyst Translation and Clinical Research Center; Director, Pediatric Endocrine-Sports Endocrine-Neuroendocrine Lab, Mass General Hospital; Professor, department of pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. She has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Sanofi; Ipsen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The actress Sally Field recently described her struggles with postmenopausal osteoporosis – she was given the diagnosis when she was 60 years old despite being physically active and engaging in activities such as biking, hiking, and yoga. As a slim, White woman in her sixth decade of life, she certainly had several risk factors for osteoporosis.
Osteoporosis, a condition associated with weak bones and an increased risk for fracture, is common in women after menopause. It’s defined as a bone mineral density (BMD) T-score of less than or equal to –2.5 on dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA) scan, occurrence of a spine or hip fracture regardless of BMD, or a BMD T-score between –1 and –2.5, along with a history of certain kinds of fractures or increased fracture risk based on the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX).
The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2013 to 2014 reported that 16.5 % of women aged 50 years or older in the U.S. have osteoporosis (vs. only 5% of men of a similar age), with an increasing prevalence with increasing age. For example, the risk for osteoporosis of the hip increases from about 7% in women 50-59 years of age to about 35% in those aged 80 years or older. The risk for postmenopausal osteoporosis is reported to be highest in Asian women (40%), followed by Hispanic (20.5%), non-Hispanic White (17%), and non-Hispanic Black women (8.2%).
Why increased fracture risk in postmenopausal women?
The primary cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis is the cessation of estrogen production by the ovaries around the menopausal transition. Estrogen is very important for bone health. It reduces bone loss by reducing levels of receptor activator of NF-kappa B ligand (RANKL) and sclerostin, and it probably also increases bone formation through its effects on sclerostin.
Around menopause, the decrease in estrogen levels results in an increase in RANKL and sclerostin, with a consequent increase in bone loss at a pace that exceeds the rate of bone formation, thereby leading to osteoporosis.
Many factors further increase the risk for osteoporosis and fracture in postmenopausal women. These include a sedentary lifestyle, lower body weight, family history of osteoporosis, smoking, and certain medications and diseases. Medications that adversely affect bone health at this age include (but are not limited to) glucocorticoids such as hydrocortisone, prednisone, and dexamethasone; letrozole; excess thyroid hormone; certain drugs used to treat cancer; immunosuppressive drugs; certain antiseizure medications; proton pump inhibitors (such as omeprazole); sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and certain other drugs used to treat type 2 diabetes; and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (used to treat anxiety and depression).
Diseases associated with increased osteoporosis risk include certain genetic conditions affecting bone, a history of early ovarian insufficiency, hyperthyroidism, high levels of cortisol, diabetes, hyperparathyroidism, eating disorders, obesity, calcium and vitamin D deficiency, excess urinary excretion of calcium, malabsorption and certain gastrointestinal surgeries, chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, certain types of cancer, and frailty.
Furthermore, older age, low bone density, a previous history of fracture, a family history of hip fracture, smoking, and excessive alcohol intake increase the risk for an osteoporotic fracture in a postmenopausal woman.
Bone density assessment using DXA is recommended in postmenopausal women who are at increased risk for low bone density and fracture. Monitoring of bone density is typically initiated about 5 years after the menopausal transition but should be considered earlier in those at high risk for osteoporosis. Women who are aged 70 or older, and those who have had significant height loss, should also get radiography of the spine to look for vertebral fractures.
Optimal nutrition is important for all postmenopausal women. Weight extremes are to be avoided. Although the use of calcium and vitamin D supplementation in postmenopausal women is still debated, the Institute of Medicine recommends that women 51-70 years of age take 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 400-600 IU of vitamin D daily, and that those older than 70 years take 1,000-1,200 mg of calcium and 400-800 IU of vitamin D daily.
Women with low vitamin D levels often require higher doses of vitamin D. It’s very important to avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Optimizing protein intake and exercises that improve muscle strength and improve balance can reduce the risk for falls, a key contributor to osteoporotic fractures.
Estrogen to prevent fracture risk
Because estrogen deficiency is a key cause of postmenopausal osteoporosis, estrogen replacement therapy has been used to prevent this condition, particularly early in the menopausal transition (51-60 years). Different formulations of estrogen given via oral or transdermal routes have been demonstrated to prevent osteoporosis; transdermal estrogen is often preferred because of a lower risk for blood clots and stroke. Women who have an intact uterus should also receive a progestin preparation either daily or cyclically, because estrogen alone can increase the risk for uterine cancer in the long run. Estrogen replacement has been associated with a 34% reduction in vertebral, hip, and total fractures in women of this age group.
Sally Field did receive hormone replacement therapy, which was helpful for her bones. However, as typically happens, her bone density dropped again when she discontinued hormone replacement. She also had low vitamin D levels, but vitamin D supplementation was not helpful. She received other medical intervention, with recovery back to good bone health.
Raloxifene is a medication that acts on the estrogen receptor, with beneficial effects on bone, and is approved for prevention and treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis.
Medications that reduce bone loss (antiresorptive drugs), such as bisphosphonates and denosumab, and those that increase bone formation (osteoanabolic drugs), such as teriparatide, abaloparatide, and romosozumab, are used alone or in combination in women whose osteoporosis doesn’t respond to lifestyle and preventive strategies. The osteoanabolic drugs are typically reserved for women at very high risk for fractures, such as those with a BMD T-score ≤ less than or equal to –3, older women with recent fractures, and those with other risk factors. Treatment is typically lifelong.
(such as fractures of the spine and hip). It’s important to recognize those at greatest risk for this condition; implement bone health monitoring in a timely fashion; and ensure optimal nutrition, calcium and vitamin D supplementation, and exercises that optimize muscle strength and balance. Hormone replacement therapy is a consideration in many women. Some women will require antiresorptive or osteoanabolic drugs to manage this condition. With optimal treatment, older women can live long and productive lives.
Dr. Misra is Chief, Division of Pediatric Endocrinology, Mass General for Children; Associate Director, Harvard Catalyst Translation and Clinical Research Center; Director, Pediatric Endocrine-Sports Endocrine-Neuroendocrine Lab, Mass General Hospital; Professor, department of pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. She has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships: Serve(d) as a director, officer, partner, employee, advisor, consultant, or trustee for: AbbVie; Sanofi; Ipsen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Footprints
Early Monday morning was my usual start-the-week routine: Set up things at the office, update my computer, check the mail, review the week’s schedule.
I was rolling the phones when a text passed by on my screen that a friend had died.
He wasn’t a close friend, but still someone I liked and got along with on the occasional times we ran into each other. Good neurologist, all-around nice person. It was a shock. I’d just seen him a week ago when we crossed paths and briefly chatted about life, the universe, and everything, before going on with our days.
We’d trained together back in the mid-90s. He was 2 years younger than I. I was in my last year of residency when he started the program. I remember being at different gatherings back then with him and his wife, a few with his then-young son, too.
And now he’s gone.
Along with the grief, you think about your own mortality. What can I be doing to hang around longer? To be better? To enjoy whatever time that I have left?
Why a mensch like him?
These are questions we all face at different times. Questions that have no answers (or at least not easy ones). There’s a lot of “why” in the universe.
There are people out there whom you don’t see often, but still consider friends, and enjoy seeing when you encounter them. Sometimes you’re bound by a common interest, or background, or who knows what. You may not think of them much, but it’s somehow reassuring to know they’re out there. And upsetting when you suddenly realize they aren’t.
You feel awful for them and their families. You wish there was a reason, or that something, anything, good will come out of the loss. But right now you don’t see any.
Our time here is never long enough. We make the best of what we have and wish for a better tomorrow.
As Longfellow wrote, the best we can hope for is to leave “footprints on the sands of time.”
I’ll miss you, friend.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Early Monday morning was my usual start-the-week routine: Set up things at the office, update my computer, check the mail, review the week’s schedule.
I was rolling the phones when a text passed by on my screen that a friend had died.
He wasn’t a close friend, but still someone I liked and got along with on the occasional times we ran into each other. Good neurologist, all-around nice person. It was a shock. I’d just seen him a week ago when we crossed paths and briefly chatted about life, the universe, and everything, before going on with our days.
We’d trained together back in the mid-90s. He was 2 years younger than I. I was in my last year of residency when he started the program. I remember being at different gatherings back then with him and his wife, a few with his then-young son, too.
And now he’s gone.
Along with the grief, you think about your own mortality. What can I be doing to hang around longer? To be better? To enjoy whatever time that I have left?
Why a mensch like him?
These are questions we all face at different times. Questions that have no answers (or at least not easy ones). There’s a lot of “why” in the universe.
There are people out there whom you don’t see often, but still consider friends, and enjoy seeing when you encounter them. Sometimes you’re bound by a common interest, or background, or who knows what. You may not think of them much, but it’s somehow reassuring to know they’re out there. And upsetting when you suddenly realize they aren’t.
You feel awful for them and their families. You wish there was a reason, or that something, anything, good will come out of the loss. But right now you don’t see any.
Our time here is never long enough. We make the best of what we have and wish for a better tomorrow.
As Longfellow wrote, the best we can hope for is to leave “footprints on the sands of time.”
I’ll miss you, friend.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Early Monday morning was my usual start-the-week routine: Set up things at the office, update my computer, check the mail, review the week’s schedule.
I was rolling the phones when a text passed by on my screen that a friend had died.
He wasn’t a close friend, but still someone I liked and got along with on the occasional times we ran into each other. Good neurologist, all-around nice person. It was a shock. I’d just seen him a week ago when we crossed paths and briefly chatted about life, the universe, and everything, before going on with our days.
We’d trained together back in the mid-90s. He was 2 years younger than I. I was in my last year of residency when he started the program. I remember being at different gatherings back then with him and his wife, a few with his then-young son, too.
And now he’s gone.
Along with the grief, you think about your own mortality. What can I be doing to hang around longer? To be better? To enjoy whatever time that I have left?
Why a mensch like him?
These are questions we all face at different times. Questions that have no answers (or at least not easy ones). There’s a lot of “why” in the universe.
There are people out there whom you don’t see often, but still consider friends, and enjoy seeing when you encounter them. Sometimes you’re bound by a common interest, or background, or who knows what. You may not think of them much, but it’s somehow reassuring to know they’re out there. And upsetting when you suddenly realize they aren’t.
You feel awful for them and their families. You wish there was a reason, or that something, anything, good will come out of the loss. But right now you don’t see any.
Our time here is never long enough. We make the best of what we have and wish for a better tomorrow.
As Longfellow wrote, the best we can hope for is to leave “footprints on the sands of time.”
I’ll miss you, friend.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Hidradenitis suppurativa experts reach consensus on treatment outcome measures
TOPLINE:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) experts collaborated to reach consensus on a core set of outcome measures, with the intent of improving the management of HS in clinical practice.
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) experts collaborated to reach consensus on a core set of outcome measures, with the intent of improving the management of HS in clinical practice.
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) experts collaborated to reach consensus on a core set of outcome measures, with the intent of improving the management of HS in clinical practice.
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Hidradenitis suppurativa experts reach consensus on treatment outcome measures
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY
Hidradenitis suppurativa experts reach consensus on treatment outcome measures
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
METHODOLOGY:
- Participants in the study were 55 HS experts from the HiSTORIC group (dermatologists, internists, surgeons, and nurses) and 24 patient research partners.
- The group identified clinician- and patient-reported HS outcome measures in the literature, then participated in an online item reduction survey, followed by an electronic Delphi survey to reach consensus on which measures should be used in clinical practice. Consensus was defined as at least 67% of participants agreeing/strongly agreeing or disagreeing/strongly disagreeing about the use of a measure in clinical practice.
- The initial literature search yielded 11 HS studies with clinician-reported outcome measures and 12 with patient-reported outcomes; of these, eight and five, respectively, were included in the final reduction survey.
TAKEAWAY:
- The group reached consensus on two HS outcome measures for use in clinical practice: the HS Investigator Global Assessment (HS-IGA) score, a clinician-reported outcome measure selected by the HS experts, and the HS Quality of Life (HiSQOL) score, a patient-reported outcome measure selected by the patient research partners.
- The HS-IGA score uses a number between 0 and 5 based on the sum of abscesses, inflammatory and noninflammatory nodules, and tunnels in regions of the upper or lower body.
- The HiSQOL, a disease-specific quality-of-life measure for adults with HS, is designed to capture unique features of HS, including symptoms (such as pain, itch, odor, and drainage) and psychosocial outcomes and activities that may be affected by the disease.
IN PRACTICE:
“The intent of these recommendations is to provide an objective framework with both clinician and patient input that can facilitate bidirectional discussion, trust building, and decision making on the current treatment strategy and the need to adjust or escalate treatment in an appropriate time frame,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was published online in JAMA Dermatology. The lead author was Nicole Mastacouris, MS, and the corresponding author was Amit Garg, MD, both of Northwell Health, New Hyde Park, N.Y.
LIMITATIONS:
The consensus results may have been affected by variations in HS management by region. Neither measure has been studied in clinical practice, and practice variability may limit their implementation.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from UCB and AbbVie. Ms. Mastacouris had no financial disclosures. Dr. Garg disclosed grant support from AbbVie and UCB during the conduct of the study, as well as personal fees from AbbVie, UCB, Aclaris Therapeutics, Anaptys Bio, Aristea Therapeutics, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Incyte, Insmed, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Sonoma Biotherapeutics, Union Therapeutics, Ventyx Biosciences, and Viela Biosciences during the conduct of the study; Dr. Garg also holds patents for HS-IGA and HiSQOL. Many other coauthors disclosed relationships with multiple companies, including AbbVie and UCB, and some also disclosed patents, including patents for HiSQOL and HS Area and Severity Index.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA DERMATOLOGY