User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
Powered by CHEST Physician, Clinician Reviews, MDedge Family Medicine, Internal Medicine News, and The Journal of Clinical Outcomes Management.
Two COVID-19 outpatient antibody drugs show encouraging results
Two COVID-19 antibody treatments, one developed by Regeneron and the other by Eli Lilly, show promise in the outpatient setting in results released on Oct. 28.
Regeneron, in a randomized, double-blind trial, is assessing the effect of adding its investigational antibody cocktail REGN-COV2 to usual standard of care in comparison with adding placebo to standard of care. A descriptive analysis from the first 275 patients was previously reported. The data described on Oct. 28, which involve an additional 524 patients, show that the trial met all of the first nine endpoints.
Regeneron announced prospective results from its phase 2/3 trial showing REGN-COV2 significantly reduced viral load and patient medical visits, which included hospitalizations, visits to an emergency department, visits for urgent care, and/or physician office/telemedicine visits.
Interest in the cocktail spiked after President Donald Trump extolled its benefits after it was used in his own COVID-19 treatment earlier in October.
Trump received the highest dose of the drug, 8 g, but, according to a Regeneron news release announcing the latest findings, “results showed no significant difference in virologic or clinical efficacy between the REGN-COV2 high dose (8 grams) and low dose (2.4 grams).”
The company described further results of the industry-funded study in the release: “On the primary endpoint, the average daily change in viral load through day 7 (mean time-weighted average change from baseline) in patients with high viral load (defined as greater than107 copies/mL) was a 0.68 log10 copies/mL greater reduction with REGN-COV2 compared to placebo (combined dose groups; P < .0001). There was a 1.08 log greater reduction with REGN-COV2 treatment by day 5, which corresponds to REGN-COV2 patients having, on average, a greater than 10-fold reduction in viral load, compared to placebo.”
The treatment appears to be most effective in patients most at risk, whether because of high viral load, ineffective baseline antibody immune response, or preexisting conditions, according to the researchers.
According to the press release, these results have not been peer reviewed but have been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration, which is reviewing a potential emergency use authorization for the treatment in high-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s treatment and vaccine program, contracted in July with Regeneron for up to 300,000 doses of its antibody cocktail.
Lilly treatment shows drop in hospitalizations, symptoms
Another treatment, also given in the outpatient setting, shows promise as well.
Patients recently diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 who received Eli Lilly’s antibody treatment LY-CoV555 had fewer hospitalizations and symptoms compared with a group that received placebo, an interim analysis of a phase 2 trial indicates.
Peter Chen, MD, with the Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues found that the most profound effects were in the high-risk groups.
The interim findings of the BLAZE-1 study, which was funded by Eli Lilly, were published online October 28 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers randomly assigned 452 patients to receive an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 in one of three doses (700 mg, 2800 mg, or 7000 mg) or placebo.
In the interim analysis, the researchers found that for the entire population, more than 99.97% of viral RNA was eliminated.
For patients who received the 2800-mg dose, the difference from placebo in the decrease from baseline was −0.53 (95% CI, −0.98 to −0.08; P = .02), for a log viral load that was lower by a factor of 3.4. Benefit over placebo was not significant with the other doses.
At day 29, according to the investigators, the percentage of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 was 1.6% (5 of 309 patients) in the treatment group compared with 6.3% (9 of 143 patients) in the placebo group.
Data indicate that the safety profile was similar whether patients received the active treatment or placebo.
“If these results are confirmed in additional analyses in this trial, LY-CoV555 could become a useful treatment for emergency use in patients with recently diagnosed Covid-19,” the authors write.
Deborah Fuller, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, told Medscape Medical News the findings are «exciting» but only part of the treatment solution.
“What’s remarkable about these two studies and others I’ve seen,” she said, “is how consistent they are in terms of the window of time they will be effective, and that’s because they are just targeting the virus itself. They do not have an effect on the inflammation unless they stop the replication early enough.”
The treatments are effective when they are given near the time of diagnosis, she pointed out.
“Once the virus has started that inflammatory cascade in your body, then that train has left the station and you have to deal with the inflammation,” Fuller said.
She says future treatments will likely have to include both the antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and physicians will have to assess what’s best, given the stage of the the patient’s disease.
The trial of REGN-COV2 is funded by Regeneron. The BLAZE-1 study is funded by Eli Lilly. Many of the authors have financial ties to Eli Lilly. Fuller has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two COVID-19 antibody treatments, one developed by Regeneron and the other by Eli Lilly, show promise in the outpatient setting in results released on Oct. 28.
Regeneron, in a randomized, double-blind trial, is assessing the effect of adding its investigational antibody cocktail REGN-COV2 to usual standard of care in comparison with adding placebo to standard of care. A descriptive analysis from the first 275 patients was previously reported. The data described on Oct. 28, which involve an additional 524 patients, show that the trial met all of the first nine endpoints.
Regeneron announced prospective results from its phase 2/3 trial showing REGN-COV2 significantly reduced viral load and patient medical visits, which included hospitalizations, visits to an emergency department, visits for urgent care, and/or physician office/telemedicine visits.
Interest in the cocktail spiked after President Donald Trump extolled its benefits after it was used in his own COVID-19 treatment earlier in October.
Trump received the highest dose of the drug, 8 g, but, according to a Regeneron news release announcing the latest findings, “results showed no significant difference in virologic or clinical efficacy between the REGN-COV2 high dose (8 grams) and low dose (2.4 grams).”
The company described further results of the industry-funded study in the release: “On the primary endpoint, the average daily change in viral load through day 7 (mean time-weighted average change from baseline) in patients with high viral load (defined as greater than107 copies/mL) was a 0.68 log10 copies/mL greater reduction with REGN-COV2 compared to placebo (combined dose groups; P < .0001). There was a 1.08 log greater reduction with REGN-COV2 treatment by day 5, which corresponds to REGN-COV2 patients having, on average, a greater than 10-fold reduction in viral load, compared to placebo.”
The treatment appears to be most effective in patients most at risk, whether because of high viral load, ineffective baseline antibody immune response, or preexisting conditions, according to the researchers.
According to the press release, these results have not been peer reviewed but have been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration, which is reviewing a potential emergency use authorization for the treatment in high-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s treatment and vaccine program, contracted in July with Regeneron for up to 300,000 doses of its antibody cocktail.
Lilly treatment shows drop in hospitalizations, symptoms
Another treatment, also given in the outpatient setting, shows promise as well.
Patients recently diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 who received Eli Lilly’s antibody treatment LY-CoV555 had fewer hospitalizations and symptoms compared with a group that received placebo, an interim analysis of a phase 2 trial indicates.
Peter Chen, MD, with the Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues found that the most profound effects were in the high-risk groups.
The interim findings of the BLAZE-1 study, which was funded by Eli Lilly, were published online October 28 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers randomly assigned 452 patients to receive an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 in one of three doses (700 mg, 2800 mg, or 7000 mg) or placebo.
In the interim analysis, the researchers found that for the entire population, more than 99.97% of viral RNA was eliminated.
For patients who received the 2800-mg dose, the difference from placebo in the decrease from baseline was −0.53 (95% CI, −0.98 to −0.08; P = .02), for a log viral load that was lower by a factor of 3.4. Benefit over placebo was not significant with the other doses.
At day 29, according to the investigators, the percentage of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 was 1.6% (5 of 309 patients) in the treatment group compared with 6.3% (9 of 143 patients) in the placebo group.
Data indicate that the safety profile was similar whether patients received the active treatment or placebo.
“If these results are confirmed in additional analyses in this trial, LY-CoV555 could become a useful treatment for emergency use in patients with recently diagnosed Covid-19,” the authors write.
Deborah Fuller, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, told Medscape Medical News the findings are «exciting» but only part of the treatment solution.
“What’s remarkable about these two studies and others I’ve seen,” she said, “is how consistent they are in terms of the window of time they will be effective, and that’s because they are just targeting the virus itself. They do not have an effect on the inflammation unless they stop the replication early enough.”
The treatments are effective when they are given near the time of diagnosis, she pointed out.
“Once the virus has started that inflammatory cascade in your body, then that train has left the station and you have to deal with the inflammation,” Fuller said.
She says future treatments will likely have to include both the antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and physicians will have to assess what’s best, given the stage of the the patient’s disease.
The trial of REGN-COV2 is funded by Regeneron. The BLAZE-1 study is funded by Eli Lilly. Many of the authors have financial ties to Eli Lilly. Fuller has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two COVID-19 antibody treatments, one developed by Regeneron and the other by Eli Lilly, show promise in the outpatient setting in results released on Oct. 28.
Regeneron, in a randomized, double-blind trial, is assessing the effect of adding its investigational antibody cocktail REGN-COV2 to usual standard of care in comparison with adding placebo to standard of care. A descriptive analysis from the first 275 patients was previously reported. The data described on Oct. 28, which involve an additional 524 patients, show that the trial met all of the first nine endpoints.
Regeneron announced prospective results from its phase 2/3 trial showing REGN-COV2 significantly reduced viral load and patient medical visits, which included hospitalizations, visits to an emergency department, visits for urgent care, and/or physician office/telemedicine visits.
Interest in the cocktail spiked after President Donald Trump extolled its benefits after it was used in his own COVID-19 treatment earlier in October.
Trump received the highest dose of the drug, 8 g, but, according to a Regeneron news release announcing the latest findings, “results showed no significant difference in virologic or clinical efficacy between the REGN-COV2 high dose (8 grams) and low dose (2.4 grams).”
The company described further results of the industry-funded study in the release: “On the primary endpoint, the average daily change in viral load through day 7 (mean time-weighted average change from baseline) in patients with high viral load (defined as greater than107 copies/mL) was a 0.68 log10 copies/mL greater reduction with REGN-COV2 compared to placebo (combined dose groups; P < .0001). There was a 1.08 log greater reduction with REGN-COV2 treatment by day 5, which corresponds to REGN-COV2 patients having, on average, a greater than 10-fold reduction in viral load, compared to placebo.”
The treatment appears to be most effective in patients most at risk, whether because of high viral load, ineffective baseline antibody immune response, or preexisting conditions, according to the researchers.
According to the press release, these results have not been peer reviewed but have been submitted to the US Food and Drug Administration, which is reviewing a potential emergency use authorization for the treatment in high-risk adults with mild to moderate COVID-19.
Operation Warp Speed, the Trump administration’s treatment and vaccine program, contracted in July with Regeneron for up to 300,000 doses of its antibody cocktail.
Lilly treatment shows drop in hospitalizations, symptoms
Another treatment, also given in the outpatient setting, shows promise as well.
Patients recently diagnosed with mild to moderate COVID-19 who received Eli Lilly’s antibody treatment LY-CoV555 had fewer hospitalizations and symptoms compared with a group that received placebo, an interim analysis of a phase 2 trial indicates.
Peter Chen, MD, with the Department of Medicine, Women’s Guild Lung Institute at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, California, and colleagues found that the most profound effects were in the high-risk groups.
The interim findings of the BLAZE-1 study, which was funded by Eli Lilly, were published online October 28 in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Researchers randomly assigned 452 patients to receive an intravenous infusion of LY-CoV555 in one of three doses (700 mg, 2800 mg, or 7000 mg) or placebo.
In the interim analysis, the researchers found that for the entire population, more than 99.97% of viral RNA was eliminated.
For patients who received the 2800-mg dose, the difference from placebo in the decrease from baseline was −0.53 (95% CI, −0.98 to −0.08; P = .02), for a log viral load that was lower by a factor of 3.4. Benefit over placebo was not significant with the other doses.
At day 29, according to the investigators, the percentage of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 was 1.6% (5 of 309 patients) in the treatment group compared with 6.3% (9 of 143 patients) in the placebo group.
Data indicate that the safety profile was similar whether patients received the active treatment or placebo.
“If these results are confirmed in additional analyses in this trial, LY-CoV555 could become a useful treatment for emergency use in patients with recently diagnosed Covid-19,” the authors write.
Deborah Fuller, PhD, professor in the Department of Microbiology at the University of Washington School of Medicine in Seattle, told Medscape Medical News the findings are «exciting» but only part of the treatment solution.
“What’s remarkable about these two studies and others I’ve seen,” she said, “is how consistent they are in terms of the window of time they will be effective, and that’s because they are just targeting the virus itself. They do not have an effect on the inflammation unless they stop the replication early enough.”
The treatments are effective when they are given near the time of diagnosis, she pointed out.
“Once the virus has started that inflammatory cascade in your body, then that train has left the station and you have to deal with the inflammation,” Fuller said.
She says future treatments will likely have to include both the antiviral and anti-inflammatory properties, and physicians will have to assess what’s best, given the stage of the the patient’s disease.
The trial of REGN-COV2 is funded by Regeneron. The BLAZE-1 study is funded by Eli Lilly. Many of the authors have financial ties to Eli Lilly. Fuller has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No evidence to guide selection of biologic for severe asthma
Although “biologics have been really revolutionary for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma, we still don’t have evidence to know the right drug for the right patient,” said Wendy Moore, MD, of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“You start with your best guess and then switch,” she said in an interview.
There are no real-world contemporary measurements of biologic therapy in the United States at this time, Dr. Moore explained during her presentation of findings from the CHRONICLE trial at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST 2020), held virtually this year.
The agents have different targets: omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E, mepolizumab and reslizumab target interleukin (IL)-5, benralizumab targets the IL-5 receptor, and dupilumab targets the common receptor IL-4 receptor A for IL-4 and IL-13.
When the starting biologic doesn’t get the desired results, there is no evidence to show whether another will work better. What we say is, “This one is not working as well as I’d like, let’s try something new?” said Dr. Moore.
However, when looking at data on patients with severe asthma who change from one biologic to another, “I was actually pleased to see that only 10% are switching,” she said in an interview.
But, she added, “if you add that up with the 8% who are stopping, that means that almost 20% don’t get the clinical response they want.”
CHRONICLE trial
In the ongoing observational CHRONICLE trial, Dr. Moore and colleagues assessed biologic initiations, discontinuations, and switches to a different agent.
All 1,884 study participants had a diagnosis of severe asthma and were being treated by an allergist/immunologist or a pulmonologist. All were taking high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and additional controllers, or had received an Food and Drug Administration–approved monoclonal antibody, systemic corticosteroid, or another systemic immunosuppressant for at least half of the previous 12 months.
In the study cohort, 1,219 participants were receiving one biologic and 27 were receiving two.
Before November 2018, “it was almost universally all benralizumab being prescribed.” An earlier preference was omalizumab, which was prescribed to 99% of patients before November 2015 and to 45% from November 2017 to November 2018.
“As new drugs were introduced, patients were switched if the desired outcome was not achieved,” Dr. Moore explained.
Over the 2-year period from February 2018 to February 2020, 134 patients – about 10% of all participants taking a biologic – made 148 switches to another biologic.
“The most common reasons reported for switching were lack of efficacy, worsening of asthma control, or waning efficacy,” Dr. Moore reported.
Of the 101 patients (8%) who discontinued 106 biologics, reasons cited were a worsening of asthma symptoms, a desire to change to a cheaper medication, and a waning of effectiveness.
“It seems that the biologic used depended on when you started and whether you were prescribed by an immunologist or pulmonologist,” said Dr. Moore. “I don’t think we understand the perfect patient for any one of these drugs.”
Large-population studies need to be done on each of the drugs. “You have to look at who’s the super responder, the partial responder, compared with the nonresponders, for each medication, but those comparative studies are unlikely to happen,” she said.
In her own practice, her 175 patients are “pretty evenly split between dupilumab, benralizumab, and mepolizumab.”
I have opinions on what works, said Dr. Moore, but none of it is evidence-based. “Those with upper airway involvement with chronic sinusitis tend to do better with mepolizumab than benralizumab. My opinion,” she emphasized.
“People with nasal problems may do better with dupilumab and mepolizumab,” she added. “Also in my opinion.
“But more likely, the issue is you have a partial responder who’s on a T2 high drug but has a T2 low problem too.”
PATHWAY study
Findings from the phase 2B PATHWAY study showed that tezepelumab reduced exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled asthma better than inhaled corticosteroids, and improved forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
“Adherence was monitored very carefully,” said investigator Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who presented the PATHWAY data. This could explain, in part, why some patients in the control group “showed improvement from baseline.”
Before switching to a biologic, “we should always consider some of these issues that might contribute to better asthma control, like patient adherence or the inability to use an inhaler properly,” Dr. Corren said.
Some people have never been “shown how to use their inhalers properly,” said Moore. “Some of them come back fine when we show them.”
Dr. Moore has been on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Corren reports receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Although “biologics have been really revolutionary for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma, we still don’t have evidence to know the right drug for the right patient,” said Wendy Moore, MD, of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“You start with your best guess and then switch,” she said in an interview.
There are no real-world contemporary measurements of biologic therapy in the United States at this time, Dr. Moore explained during her presentation of findings from the CHRONICLE trial at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST 2020), held virtually this year.
The agents have different targets: omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E, mepolizumab and reslizumab target interleukin (IL)-5, benralizumab targets the IL-5 receptor, and dupilumab targets the common receptor IL-4 receptor A for IL-4 and IL-13.
When the starting biologic doesn’t get the desired results, there is no evidence to show whether another will work better. What we say is, “This one is not working as well as I’d like, let’s try something new?” said Dr. Moore.
However, when looking at data on patients with severe asthma who change from one biologic to another, “I was actually pleased to see that only 10% are switching,” she said in an interview.
But, she added, “if you add that up with the 8% who are stopping, that means that almost 20% don’t get the clinical response they want.”
CHRONICLE trial
In the ongoing observational CHRONICLE trial, Dr. Moore and colleagues assessed biologic initiations, discontinuations, and switches to a different agent.
All 1,884 study participants had a diagnosis of severe asthma and were being treated by an allergist/immunologist or a pulmonologist. All were taking high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and additional controllers, or had received an Food and Drug Administration–approved monoclonal antibody, systemic corticosteroid, or another systemic immunosuppressant for at least half of the previous 12 months.
In the study cohort, 1,219 participants were receiving one biologic and 27 were receiving two.
Before November 2018, “it was almost universally all benralizumab being prescribed.” An earlier preference was omalizumab, which was prescribed to 99% of patients before November 2015 and to 45% from November 2017 to November 2018.
“As new drugs were introduced, patients were switched if the desired outcome was not achieved,” Dr. Moore explained.
Over the 2-year period from February 2018 to February 2020, 134 patients – about 10% of all participants taking a biologic – made 148 switches to another biologic.
“The most common reasons reported for switching were lack of efficacy, worsening of asthma control, or waning efficacy,” Dr. Moore reported.
Of the 101 patients (8%) who discontinued 106 biologics, reasons cited were a worsening of asthma symptoms, a desire to change to a cheaper medication, and a waning of effectiveness.
“It seems that the biologic used depended on when you started and whether you were prescribed by an immunologist or pulmonologist,” said Dr. Moore. “I don’t think we understand the perfect patient for any one of these drugs.”
Large-population studies need to be done on each of the drugs. “You have to look at who’s the super responder, the partial responder, compared with the nonresponders, for each medication, but those comparative studies are unlikely to happen,” she said.
In her own practice, her 175 patients are “pretty evenly split between dupilumab, benralizumab, and mepolizumab.”
I have opinions on what works, said Dr. Moore, but none of it is evidence-based. “Those with upper airway involvement with chronic sinusitis tend to do better with mepolizumab than benralizumab. My opinion,” she emphasized.
“People with nasal problems may do better with dupilumab and mepolizumab,” she added. “Also in my opinion.
“But more likely, the issue is you have a partial responder who’s on a T2 high drug but has a T2 low problem too.”
PATHWAY study
Findings from the phase 2B PATHWAY study showed that tezepelumab reduced exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled asthma better than inhaled corticosteroids, and improved forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
“Adherence was monitored very carefully,” said investigator Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who presented the PATHWAY data. This could explain, in part, why some patients in the control group “showed improvement from baseline.”
Before switching to a biologic, “we should always consider some of these issues that might contribute to better asthma control, like patient adherence or the inability to use an inhaler properly,” Dr. Corren said.
Some people have never been “shown how to use their inhalers properly,” said Moore. “Some of them come back fine when we show them.”
Dr. Moore has been on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Corren reports receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Although “biologics have been really revolutionary for the treatment of severe uncontrolled asthma, we still don’t have evidence to know the right drug for the right patient,” said Wendy Moore, MD, of Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, N.C.
“You start with your best guess and then switch,” she said in an interview.
There are no real-world contemporary measurements of biologic therapy in the United States at this time, Dr. Moore explained during her presentation of findings from the CHRONICLE trial at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST 2020), held virtually this year.
The agents have different targets: omalizumab targets immunoglobulin E, mepolizumab and reslizumab target interleukin (IL)-5, benralizumab targets the IL-5 receptor, and dupilumab targets the common receptor IL-4 receptor A for IL-4 and IL-13.
When the starting biologic doesn’t get the desired results, there is no evidence to show whether another will work better. What we say is, “This one is not working as well as I’d like, let’s try something new?” said Dr. Moore.
However, when looking at data on patients with severe asthma who change from one biologic to another, “I was actually pleased to see that only 10% are switching,” she said in an interview.
But, she added, “if you add that up with the 8% who are stopping, that means that almost 20% don’t get the clinical response they want.”
CHRONICLE trial
In the ongoing observational CHRONICLE trial, Dr. Moore and colleagues assessed biologic initiations, discontinuations, and switches to a different agent.
All 1,884 study participants had a diagnosis of severe asthma and were being treated by an allergist/immunologist or a pulmonologist. All were taking high-dose inhaled corticosteroids and additional controllers, or had received an Food and Drug Administration–approved monoclonal antibody, systemic corticosteroid, or another systemic immunosuppressant for at least half of the previous 12 months.
In the study cohort, 1,219 participants were receiving one biologic and 27 were receiving two.
Before November 2018, “it was almost universally all benralizumab being prescribed.” An earlier preference was omalizumab, which was prescribed to 99% of patients before November 2015 and to 45% from November 2017 to November 2018.
“As new drugs were introduced, patients were switched if the desired outcome was not achieved,” Dr. Moore explained.
Over the 2-year period from February 2018 to February 2020, 134 patients – about 10% of all participants taking a biologic – made 148 switches to another biologic.
“The most common reasons reported for switching were lack of efficacy, worsening of asthma control, or waning efficacy,” Dr. Moore reported.
Of the 101 patients (8%) who discontinued 106 biologics, reasons cited were a worsening of asthma symptoms, a desire to change to a cheaper medication, and a waning of effectiveness.
“It seems that the biologic used depended on when you started and whether you were prescribed by an immunologist or pulmonologist,” said Dr. Moore. “I don’t think we understand the perfect patient for any one of these drugs.”
Large-population studies need to be done on each of the drugs. “You have to look at who’s the super responder, the partial responder, compared with the nonresponders, for each medication, but those comparative studies are unlikely to happen,” she said.
In her own practice, her 175 patients are “pretty evenly split between dupilumab, benralizumab, and mepolizumab.”
I have opinions on what works, said Dr. Moore, but none of it is evidence-based. “Those with upper airway involvement with chronic sinusitis tend to do better with mepolizumab than benralizumab. My opinion,” she emphasized.
“People with nasal problems may do better with dupilumab and mepolizumab,” she added. “Also in my opinion.
“But more likely, the issue is you have a partial responder who’s on a T2 high drug but has a T2 low problem too.”
PATHWAY study
Findings from the phase 2B PATHWAY study showed that tezepelumab reduced exacerbations in patients with uncontrolled asthma better than inhaled corticosteroids, and improved forced expiratory volume in 1 second.
“Adherence was monitored very carefully,” said investigator Jonathan Corren, MD, of the University of California, Los Angeles, who presented the PATHWAY data. This could explain, in part, why some patients in the control group “showed improvement from baseline.”
Before switching to a biologic, “we should always consider some of these issues that might contribute to better asthma control, like patient adherence or the inability to use an inhaler properly,” Dr. Corren said.
Some people have never been “shown how to use their inhalers properly,” said Moore. “Some of them come back fine when we show them.”
Dr. Moore has been on the advisory board for AstraZeneca, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Regeneron, and Sanofi. Dr. Corren reports receiving honoraria from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Skin symptoms common in COVID-19 ‘long-haulers’
for more than 150 days, a new analysis revealed.
Evaluating data from an international registry of COVID-19 patients with dermatologic symptoms, researchers found that retiform purpura rashes are linked to severe COVID-19, with 100% of these patients requiring hospitalization and 82% experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile, pernio/chilblains rashes, dubbed “COVID toes,” are associated with milder disease and a 16% hospitalization rate. For all COVID-19–related skin symptoms, the average duration is 12 days.
“The skin is another organ system that we didn’t know could have long COVID” effects, said principal investigator Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“The skin is really a window into how the body is working overall, so the fact that we could visually see persistent inflammation in long-hauler patients is particularly fascinating and gives us a chance to explore what’s going on,” Dr. Freeman said in an interview. “It certainly makes sense to me, knowing what we know about other organ systems, that there might be some long-lasting inflammation” in the skin as well.
The study is a result of the collaboration between the American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies, the international registry launched this past April. While the study included provider-supplied data from 990 cases spanning 39 countries, the registry now encompasses more than 1,000 patients from 41 countries, Dr. Freeman noted.
Dr. Freeman presented the data at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Many studies have reported dermatologic effects of COVID-19 infection, but information was lacking about duration. The registry represents the largest dataset to date detailing these persistent skin symptoms and offers insight about how COVID-19 can affect many different organ systems even after patients recover from acute infection, Dr. Freeman said.
Eight different types of skin rashes were noted in the study group, of which 303 were lab-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms. Of those, 224 total cases and 90 lab-confirmed cases included information on how long skin symptoms lasted. Lab tests for SARS-CoV-2 included polymerase chain reaction and serum antibody assays.
Dr. Freeman and associates defined “long-haulers” as patients with dermatologic symptoms of COVID-19 lasting 60 days or longer. These “outliers” are likely more prevalent than the registry suggests, she said, since not all providers initially reporting skin symptoms in patients updated that information over time.
“It’s important to understand that the registry is probably significantly underreporting the duration of symptoms and number of long-hauler patients,” she explained. “A registry is often a glimpse into a moment in time to these patients. To combat that, we followed up by email twice with providers to ask if patients’ symptoms were still ongoing or completed.”
Results showed a wide spectrum in average duration of symptoms among lab-confirmed COVID-19 patients, depending on specific rash. Urticaria lasted for a median of 4 days; morbilliform eruptions, 7 days; pernio/chilblains, 10 days; and papulosquamous eruptions, 20 days, with one long-hauler case lasting 70 days.
Five patients with pernio/chilblains were long-haulers, with toe symptoms enduring 60 days or longer. Only one went beyond 133 days with severe pernio and fatigue.
“The fact that we’re not necessarily seeing these long-hauler symptoms across every type of skin rash makes sense,” Dr. Freeman said. “Hives, for example, usually comes on acutely and leaves pretty rapidly. There are no reports of long-hauler hives.”
“That we’re really seeing these long-hauler symptoms in certain skin rashes really suggests that there’s a certain pathophysiology going in within that group of patients,” she added.
Dr. Freeman said not enough data have yet been generated to correlate long-standing COVID-19 skin symptoms with lasting cardiac, neurologic, or other symptoms of prolonged inflammation stemming from the virus.
Meanwhile, an EADV survey of 490 dermatologists revealed that just over one-third have seen patients presenting with skin signs of COVID-19. Moreover, 4% of dermatologists themselves tested positive for the virus.
Dr. Freeman encouraged all frontline clinicians assessing COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms to enter patients into the registry. But despite its strengths, the registry “can’t tell us what percentage of everyone who gets COVID will develop a skin finding or what percentage will be a long-hauler,” she said.
“A registry doesn’t have a denominator, so it’s like a giant case series,” she added.
“It will be very helpful going forward, as many places around the world experience second or third waves of COVID-19, to follow patients prospectively, acknowledge that patients will have symptoms lasting different amounts of time, and be aware these symptoms can occur on the skin,” she said.
Christopher Griffiths, MD, of the University of Manchester (England), praised the international registry as a valuable tool that will help clinicians better manage patients with COVID-19–related skin effects and predict prognosis.
“This has really brought the international dermatology community together, working on a focused goal relevant to all of us around the world,” Dr. Griffiths said in an interview. “It shows the power of communication and collaboration and what can be achieved in a short period of time.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Griffiths disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
for more than 150 days, a new analysis revealed.
Evaluating data from an international registry of COVID-19 patients with dermatologic symptoms, researchers found that retiform purpura rashes are linked to severe COVID-19, with 100% of these patients requiring hospitalization and 82% experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile, pernio/chilblains rashes, dubbed “COVID toes,” are associated with milder disease and a 16% hospitalization rate. For all COVID-19–related skin symptoms, the average duration is 12 days.
“The skin is another organ system that we didn’t know could have long COVID” effects, said principal investigator Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“The skin is really a window into how the body is working overall, so the fact that we could visually see persistent inflammation in long-hauler patients is particularly fascinating and gives us a chance to explore what’s going on,” Dr. Freeman said in an interview. “It certainly makes sense to me, knowing what we know about other organ systems, that there might be some long-lasting inflammation” in the skin as well.
The study is a result of the collaboration between the American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies, the international registry launched this past April. While the study included provider-supplied data from 990 cases spanning 39 countries, the registry now encompasses more than 1,000 patients from 41 countries, Dr. Freeman noted.
Dr. Freeman presented the data at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Many studies have reported dermatologic effects of COVID-19 infection, but information was lacking about duration. The registry represents the largest dataset to date detailing these persistent skin symptoms and offers insight about how COVID-19 can affect many different organ systems even after patients recover from acute infection, Dr. Freeman said.
Eight different types of skin rashes were noted in the study group, of which 303 were lab-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms. Of those, 224 total cases and 90 lab-confirmed cases included information on how long skin symptoms lasted. Lab tests for SARS-CoV-2 included polymerase chain reaction and serum antibody assays.
Dr. Freeman and associates defined “long-haulers” as patients with dermatologic symptoms of COVID-19 lasting 60 days or longer. These “outliers” are likely more prevalent than the registry suggests, she said, since not all providers initially reporting skin symptoms in patients updated that information over time.
“It’s important to understand that the registry is probably significantly underreporting the duration of symptoms and number of long-hauler patients,” she explained. “A registry is often a glimpse into a moment in time to these patients. To combat that, we followed up by email twice with providers to ask if patients’ symptoms were still ongoing or completed.”
Results showed a wide spectrum in average duration of symptoms among lab-confirmed COVID-19 patients, depending on specific rash. Urticaria lasted for a median of 4 days; morbilliform eruptions, 7 days; pernio/chilblains, 10 days; and papulosquamous eruptions, 20 days, with one long-hauler case lasting 70 days.
Five patients with pernio/chilblains were long-haulers, with toe symptoms enduring 60 days or longer. Only one went beyond 133 days with severe pernio and fatigue.
“The fact that we’re not necessarily seeing these long-hauler symptoms across every type of skin rash makes sense,” Dr. Freeman said. “Hives, for example, usually comes on acutely and leaves pretty rapidly. There are no reports of long-hauler hives.”
“That we’re really seeing these long-hauler symptoms in certain skin rashes really suggests that there’s a certain pathophysiology going in within that group of patients,” she added.
Dr. Freeman said not enough data have yet been generated to correlate long-standing COVID-19 skin symptoms with lasting cardiac, neurologic, or other symptoms of prolonged inflammation stemming from the virus.
Meanwhile, an EADV survey of 490 dermatologists revealed that just over one-third have seen patients presenting with skin signs of COVID-19. Moreover, 4% of dermatologists themselves tested positive for the virus.
Dr. Freeman encouraged all frontline clinicians assessing COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms to enter patients into the registry. But despite its strengths, the registry “can’t tell us what percentage of everyone who gets COVID will develop a skin finding or what percentage will be a long-hauler,” she said.
“A registry doesn’t have a denominator, so it’s like a giant case series,” she added.
“It will be very helpful going forward, as many places around the world experience second or third waves of COVID-19, to follow patients prospectively, acknowledge that patients will have symptoms lasting different amounts of time, and be aware these symptoms can occur on the skin,” she said.
Christopher Griffiths, MD, of the University of Manchester (England), praised the international registry as a valuable tool that will help clinicians better manage patients with COVID-19–related skin effects and predict prognosis.
“This has really brought the international dermatology community together, working on a focused goal relevant to all of us around the world,” Dr. Griffiths said in an interview. “It shows the power of communication and collaboration and what can be achieved in a short period of time.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Griffiths disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
for more than 150 days, a new analysis revealed.
Evaluating data from an international registry of COVID-19 patients with dermatologic symptoms, researchers found that retiform purpura rashes are linked to severe COVID-19, with 100% of these patients requiring hospitalization and 82% experiencing acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
Meanwhile, pernio/chilblains rashes, dubbed “COVID toes,” are associated with milder disease and a 16% hospitalization rate. For all COVID-19–related skin symptoms, the average duration is 12 days.
“The skin is another organ system that we didn’t know could have long COVID” effects, said principal investigator Esther Freeman, MD, PhD, of the department of dermatology, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
“The skin is really a window into how the body is working overall, so the fact that we could visually see persistent inflammation in long-hauler patients is particularly fascinating and gives us a chance to explore what’s going on,” Dr. Freeman said in an interview. “It certainly makes sense to me, knowing what we know about other organ systems, that there might be some long-lasting inflammation” in the skin as well.
The study is a result of the collaboration between the American Academy of Dermatology and the International League of Dermatological Societies, the international registry launched this past April. While the study included provider-supplied data from 990 cases spanning 39 countries, the registry now encompasses more than 1,000 patients from 41 countries, Dr. Freeman noted.
Dr. Freeman presented the data at the annual congress of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Many studies have reported dermatologic effects of COVID-19 infection, but information was lacking about duration. The registry represents the largest dataset to date detailing these persistent skin symptoms and offers insight about how COVID-19 can affect many different organ systems even after patients recover from acute infection, Dr. Freeman said.
Eight different types of skin rashes were noted in the study group, of which 303 were lab-confirmed or suspected COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms. Of those, 224 total cases and 90 lab-confirmed cases included information on how long skin symptoms lasted. Lab tests for SARS-CoV-2 included polymerase chain reaction and serum antibody assays.
Dr. Freeman and associates defined “long-haulers” as patients with dermatologic symptoms of COVID-19 lasting 60 days or longer. These “outliers” are likely more prevalent than the registry suggests, she said, since not all providers initially reporting skin symptoms in patients updated that information over time.
“It’s important to understand that the registry is probably significantly underreporting the duration of symptoms and number of long-hauler patients,” she explained. “A registry is often a glimpse into a moment in time to these patients. To combat that, we followed up by email twice with providers to ask if patients’ symptoms were still ongoing or completed.”
Results showed a wide spectrum in average duration of symptoms among lab-confirmed COVID-19 patients, depending on specific rash. Urticaria lasted for a median of 4 days; morbilliform eruptions, 7 days; pernio/chilblains, 10 days; and papulosquamous eruptions, 20 days, with one long-hauler case lasting 70 days.
Five patients with pernio/chilblains were long-haulers, with toe symptoms enduring 60 days or longer. Only one went beyond 133 days with severe pernio and fatigue.
“The fact that we’re not necessarily seeing these long-hauler symptoms across every type of skin rash makes sense,” Dr. Freeman said. “Hives, for example, usually comes on acutely and leaves pretty rapidly. There are no reports of long-hauler hives.”
“That we’re really seeing these long-hauler symptoms in certain skin rashes really suggests that there’s a certain pathophysiology going in within that group of patients,” she added.
Dr. Freeman said not enough data have yet been generated to correlate long-standing COVID-19 skin symptoms with lasting cardiac, neurologic, or other symptoms of prolonged inflammation stemming from the virus.
Meanwhile, an EADV survey of 490 dermatologists revealed that just over one-third have seen patients presenting with skin signs of COVID-19. Moreover, 4% of dermatologists themselves tested positive for the virus.
Dr. Freeman encouraged all frontline clinicians assessing COVID-19 patients with skin symptoms to enter patients into the registry. But despite its strengths, the registry “can’t tell us what percentage of everyone who gets COVID will develop a skin finding or what percentage will be a long-hauler,” she said.
“A registry doesn’t have a denominator, so it’s like a giant case series,” she added.
“It will be very helpful going forward, as many places around the world experience second or third waves of COVID-19, to follow patients prospectively, acknowledge that patients will have symptoms lasting different amounts of time, and be aware these symptoms can occur on the skin,” she said.
Christopher Griffiths, MD, of the University of Manchester (England), praised the international registry as a valuable tool that will help clinicians better manage patients with COVID-19–related skin effects and predict prognosis.
“This has really brought the international dermatology community together, working on a focused goal relevant to all of us around the world,” Dr. Griffiths said in an interview. “It shows the power of communication and collaboration and what can be achieved in a short period of time.”
Dr. Freeman and Dr. Griffiths disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE EADV CONGRESS
COVID-19 diagnosed on CTA scan in stroke patients
A routine scan used to evaluate some acute stroke patients can also detect SARS-CoV-2 infection in the upper lungs, a new study shows.
“As part of the stroke evaluation workup process, we were able to diagnose COVID-19 at the same time at no extra cost or additional workload,” lead author Charles Esenwa, MD, commented to Medscape Medical News. “This is an objective way to screen for COVID-19 in the acute stroke setting,” he added.
Esenwa is an assistant professor and a stroke neurologist at the Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City.
He explained that, during the COVID-19 surge earlier this year, assessment of patients with severe acute stroke using computed tomography angiogram (CTA) scans – used to evaluate suitability for endovascular stroke therapy – also showed findings in the upper lung consistent with viral infection in some patients.
“We then assumed that these patients had COVID-19 and took extra precautions to keep them isolated and to protect staff involved in their care. It also allowed us to triage these patients more quickly than waiting for the COVID-19 swab test and arrange the most appropriate care for them,” Esenwa said.
The researchers have now gone back and analyzed their data on acute stroke patients who underwent CTA at their institution during the COVID-19 surge. They found that the changes identified in the lungs were highly specific for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study was published online on Oct. 29 in Stroke.
“Stroke patients are normally screened for COVID-19 on hospitalization, but the swab test result can take several hours or longer to come back, and it is very useful for us to know if a patient could be infected,” Esenwa noted.
“When we do a CTA, we look at the blood vessels supplying the brain, but the scan also covers the top of the lung, as it starts at the aortic arch. We don’t normally look closely at that area, but we started to notice signs of active lung infection which could have been COVID-19,” he said. “For this paper, we went back to assess how accurate this approach actually was vs. the COVID-19 PCR test.”
The researchers report on 57 patients who presented to three Montefiore Health System hospitals in the Bronx, in New York City, with acute ischemic stroke and who underwent CTA of the head and neck in March and April 2020, the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak there. The patients also underwent PCR testing for COVID-19.
Results showed that 30 patients had a positive COVID-19 test result and that 27 had a negative result. Lung findings highly or very highly suspicious for COVID-19 pneumonia were identified during the CTA scan in 20 (67%) of the COVID-19–positive patients and in two (7%) of the COVID-19–negative patients.
These findings, when used in isolation, yielded a sensitivity of 0.67 and a specificity of 0.93. They had a positive predictive value of 0.19, a negative predictive value of 0.99, and accuracy of 0.92 for the diagnosis of COVID-19.
When apical lung assessment was combined with self-reported clinical symptoms of cough or dyspnea, sensitivity for the diagnosis of COVID-19 for patients presenting to the hospital for acute ischemic stroke increased to 0.83.
“We wondered whether looking at the whole lung would have found better results, but other studies which have done this actually found similar numbers to ours, so we think actually just looking at the top of the lungs, which can be seen in a stroke CTA, may be sufficient,” Esenwa said.
He emphasized the importance of establishing whether an acute stroke patient has COVID-19. “If we had a high suspicion of COVID-19 infection, we would take more precautions during any procedures, such as thrombectomy, and make sure to keep the patient isolated afterwards. It doesn’t necessarily affect the treatment given for stroke, but it affects the safety of the patients and everyone caring for them,” he commented.
Esenwa explained that intubation – which is sometime necessary during thrombectomy – can expose everyone in the room to aerosolized droplets. “So we would take much higher safety precautions if we thought the patient was COVID-19 positive,” he said.
“Early COVID-19 diagnosis also means patients can be given supportive treatment more quickly, admitted to ICU if appropriate, and we can all keep a close eye on pulmonary issues. So having that information is important in many ways,” he added.
Esenwa advises that any medical center that evaluates acute stroke patients for thrombectomy and is experiencing a COVID-19 surge can use this technique as a screening method for COVID-19.
He pointed out that the Montefiore Health System had a very high rate of COVID-19. That part of New York City was one of the worst hit areas of the world, and the CTA approach for identifying COVID-19 has been validated only in areas with such a high local incidence of COVID. If used in an area of lower prevalence, the accuracy would likely be less.
“We don’t know if this approach would work as well at times of low COVID-19 infection, where any lung findings would be more likely to be caused by other conditions, such as pneumonia due to other causes or congestive heart failure. So there would be more false positives,” Esenwa said.
“But when COVID-19 prevalence is high, the lung findings are much more likely to be a sign of COVID-19 infection. As COVID-19 numbers are now rising for a second time, it is likely to become a useful strategy again.”
The study was approved by the Albert Einstein College of Medicine/Montefiore Medical Center Institutional Review Board and had no external funding. Esenwa has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A routine scan used to evaluate some acute stroke patients can also detect SARS-CoV-2 infection in the upper lungs, a new study shows.
“As part of the stroke evaluation workup process, we were able to diagnose COVID-19 at the same time at no extra cost or additional workload,” lead author Charles Esenwa, MD, commented to Medscape Medical News. “This is an objective way to screen for COVID-19 in the acute stroke setting,” he added.
Esenwa is an assistant professor and a stroke neurologist at the Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City.
He explained that, during the COVID-19 surge earlier this year, assessment of patients with severe acute stroke using computed tomography angiogram (CTA) scans – used to evaluate suitability for endovascular stroke therapy – also showed findings in the upper lung consistent with viral infection in some patients.
“We then assumed that these patients had COVID-19 and took extra precautions to keep them isolated and to protect staff involved in their care. It also allowed us to triage these patients more quickly than waiting for the COVID-19 swab test and arrange the most appropriate care for them,” Esenwa said.
The researchers have now gone back and analyzed their data on acute stroke patients who underwent CTA at their institution during the COVID-19 surge. They found that the changes identified in the lungs were highly specific for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study was published online on Oct. 29 in Stroke.
“Stroke patients are normally screened for COVID-19 on hospitalization, but the swab test result can take several hours or longer to come back, and it is very useful for us to know if a patient could be infected,” Esenwa noted.
“When we do a CTA, we look at the blood vessels supplying the brain, but the scan also covers the top of the lung, as it starts at the aortic arch. We don’t normally look closely at that area, but we started to notice signs of active lung infection which could have been COVID-19,” he said. “For this paper, we went back to assess how accurate this approach actually was vs. the COVID-19 PCR test.”
The researchers report on 57 patients who presented to three Montefiore Health System hospitals in the Bronx, in New York City, with acute ischemic stroke and who underwent CTA of the head and neck in March and April 2020, the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak there. The patients also underwent PCR testing for COVID-19.
Results showed that 30 patients had a positive COVID-19 test result and that 27 had a negative result. Lung findings highly or very highly suspicious for COVID-19 pneumonia were identified during the CTA scan in 20 (67%) of the COVID-19–positive patients and in two (7%) of the COVID-19–negative patients.
These findings, when used in isolation, yielded a sensitivity of 0.67 and a specificity of 0.93. They had a positive predictive value of 0.19, a negative predictive value of 0.99, and accuracy of 0.92 for the diagnosis of COVID-19.
When apical lung assessment was combined with self-reported clinical symptoms of cough or dyspnea, sensitivity for the diagnosis of COVID-19 for patients presenting to the hospital for acute ischemic stroke increased to 0.83.
“We wondered whether looking at the whole lung would have found better results, but other studies which have done this actually found similar numbers to ours, so we think actually just looking at the top of the lungs, which can be seen in a stroke CTA, may be sufficient,” Esenwa said.
He emphasized the importance of establishing whether an acute stroke patient has COVID-19. “If we had a high suspicion of COVID-19 infection, we would take more precautions during any procedures, such as thrombectomy, and make sure to keep the patient isolated afterwards. It doesn’t necessarily affect the treatment given for stroke, but it affects the safety of the patients and everyone caring for them,” he commented.
Esenwa explained that intubation – which is sometime necessary during thrombectomy – can expose everyone in the room to aerosolized droplets. “So we would take much higher safety precautions if we thought the patient was COVID-19 positive,” he said.
“Early COVID-19 diagnosis also means patients can be given supportive treatment more quickly, admitted to ICU if appropriate, and we can all keep a close eye on pulmonary issues. So having that information is important in many ways,” he added.
Esenwa advises that any medical center that evaluates acute stroke patients for thrombectomy and is experiencing a COVID-19 surge can use this technique as a screening method for COVID-19.
He pointed out that the Montefiore Health System had a very high rate of COVID-19. That part of New York City was one of the worst hit areas of the world, and the CTA approach for identifying COVID-19 has been validated only in areas with such a high local incidence of COVID. If used in an area of lower prevalence, the accuracy would likely be less.
“We don’t know if this approach would work as well at times of low COVID-19 infection, where any lung findings would be more likely to be caused by other conditions, such as pneumonia due to other causes or congestive heart failure. So there would be more false positives,” Esenwa said.
“But when COVID-19 prevalence is high, the lung findings are much more likely to be a sign of COVID-19 infection. As COVID-19 numbers are now rising for a second time, it is likely to become a useful strategy again.”
The study was approved by the Albert Einstein College of Medicine/Montefiore Medical Center Institutional Review Board and had no external funding. Esenwa has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A routine scan used to evaluate some acute stroke patients can also detect SARS-CoV-2 infection in the upper lungs, a new study shows.
“As part of the stroke evaluation workup process, we were able to diagnose COVID-19 at the same time at no extra cost or additional workload,” lead author Charles Esenwa, MD, commented to Medscape Medical News. “This is an objective way to screen for COVID-19 in the acute stroke setting,” he added.
Esenwa is an assistant professor and a stroke neurologist at the Montefiore Medical Center/Albert Einstein College of Medicine in New York City.
He explained that, during the COVID-19 surge earlier this year, assessment of patients with severe acute stroke using computed tomography angiogram (CTA) scans – used to evaluate suitability for endovascular stroke therapy – also showed findings in the upper lung consistent with viral infection in some patients.
“We then assumed that these patients had COVID-19 and took extra precautions to keep them isolated and to protect staff involved in their care. It also allowed us to triage these patients more quickly than waiting for the COVID-19 swab test and arrange the most appropriate care for them,” Esenwa said.
The researchers have now gone back and analyzed their data on acute stroke patients who underwent CTA at their institution during the COVID-19 surge. They found that the changes identified in the lungs were highly specific for diagnosing SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The study was published online on Oct. 29 in Stroke.
“Stroke patients are normally screened for COVID-19 on hospitalization, but the swab test result can take several hours or longer to come back, and it is very useful for us to know if a patient could be infected,” Esenwa noted.
“When we do a CTA, we look at the blood vessels supplying the brain, but the scan also covers the top of the lung, as it starts at the aortic arch. We don’t normally look closely at that area, but we started to notice signs of active lung infection which could have been COVID-19,” he said. “For this paper, we went back to assess how accurate this approach actually was vs. the COVID-19 PCR test.”
The researchers report on 57 patients who presented to three Montefiore Health System hospitals in the Bronx, in New York City, with acute ischemic stroke and who underwent CTA of the head and neck in March and April 2020, the peak of the COVID-19 outbreak there. The patients also underwent PCR testing for COVID-19.
Results showed that 30 patients had a positive COVID-19 test result and that 27 had a negative result. Lung findings highly or very highly suspicious for COVID-19 pneumonia were identified during the CTA scan in 20 (67%) of the COVID-19–positive patients and in two (7%) of the COVID-19–negative patients.
These findings, when used in isolation, yielded a sensitivity of 0.67 and a specificity of 0.93. They had a positive predictive value of 0.19, a negative predictive value of 0.99, and accuracy of 0.92 for the diagnosis of COVID-19.
When apical lung assessment was combined with self-reported clinical symptoms of cough or dyspnea, sensitivity for the diagnosis of COVID-19 for patients presenting to the hospital for acute ischemic stroke increased to 0.83.
“We wondered whether looking at the whole lung would have found better results, but other studies which have done this actually found similar numbers to ours, so we think actually just looking at the top of the lungs, which can be seen in a stroke CTA, may be sufficient,” Esenwa said.
He emphasized the importance of establishing whether an acute stroke patient has COVID-19. “If we had a high suspicion of COVID-19 infection, we would take more precautions during any procedures, such as thrombectomy, and make sure to keep the patient isolated afterwards. It doesn’t necessarily affect the treatment given for stroke, but it affects the safety of the patients and everyone caring for them,” he commented.
Esenwa explained that intubation – which is sometime necessary during thrombectomy – can expose everyone in the room to aerosolized droplets. “So we would take much higher safety precautions if we thought the patient was COVID-19 positive,” he said.
“Early COVID-19 diagnosis also means patients can be given supportive treatment more quickly, admitted to ICU if appropriate, and we can all keep a close eye on pulmonary issues. So having that information is important in many ways,” he added.
Esenwa advises that any medical center that evaluates acute stroke patients for thrombectomy and is experiencing a COVID-19 surge can use this technique as a screening method for COVID-19.
He pointed out that the Montefiore Health System had a very high rate of COVID-19. That part of New York City was one of the worst hit areas of the world, and the CTA approach for identifying COVID-19 has been validated only in areas with such a high local incidence of COVID. If used in an area of lower prevalence, the accuracy would likely be less.
“We don’t know if this approach would work as well at times of low COVID-19 infection, where any lung findings would be more likely to be caused by other conditions, such as pneumonia due to other causes or congestive heart failure. So there would be more false positives,” Esenwa said.
“But when COVID-19 prevalence is high, the lung findings are much more likely to be a sign of COVID-19 infection. As COVID-19 numbers are now rising for a second time, it is likely to become a useful strategy again.”
The study was approved by the Albert Einstein College of Medicine/Montefiore Medical Center Institutional Review Board and had no external funding. Esenwa has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
More mask wearing could save 130,000 US lives by end of February
A cumulative 511,000 lives could be lost from COVID-19 in the United States by the end of February 2021, a new prediction study reveals.
However, if universal mask wearing is adopted — defined as 95% of Americans complying with the protective measure — along with social distancing mandates as warranted, nearly 130,000 of those lives could be saved.
And if even 85% of Americans comply, an additional 95,800 lives would be spared before March of next year, researchers at the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) report.
The study was published online October 23 in Nature Medicine.
“The study is sound and makes the case for mandatory mask policies,” said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a professor of bioethics at NYU Langone Health in New York City, who frequently provides commentary for Medscape.
Without mandatory mask requirements, he added, “we will see a pandemic slaughter and an overwhelmed healthcare system and workforce.”
The IHME team evaluated COVID-19 data for cases and related deaths between February 1 and September 21. Based on this data, they predicted the likely future of SARS-CoV-2 infections on a state level from September 22, 2020, to February 2021.
An Optimistic Projection
Lead author Robert C. Reiner Jr and colleagues looked at five scenarios. For example, they calculated likely deaths associated with COVID-19 if adoption of mask and social distancing recommendations were nearly universal. They note that Singapore achieved a 95% compliance rate with masks and used this as their “best-case scenario” model.
An estimated 129,574 (range, 85,284–170,867) additional lives could be saved if 95% of Americans wore masks in public, their research reveals. This optimistic scenario includes a “plausible reference” in which any US state reaching 8 COVID-19 deaths per 1 million residents would enact 6 weeks of social distancing mandates (SDMs).
Achieving this level of mask compliance in the United States “could be sufficient to ameliorate the worst effects of epidemic resurgences in many states,” the researchers note.
In contrast, the proportion of Americans wearing masks in public as of September 22 was 49%, according to IHME data.
Universal mask use unlikely
“I’m not a modeling expert, but it is an interesting, and as far as I can judge, well-conducted study which looks, state by state, at what might happen in various scenarios around masking policies going forward — and in particular the effect that mandated masking might have,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“However, the scenario is a thought experiment. Near-universal mask use is not going to happen in the USA, nor indeed in any individual state, right now, given how emotive the issue has become,” added Greenhalgh, professor in the Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences at Oxford University, UK. She was not affiliated with the study.
“Hence, whilst I am broadly supportive of the science,” she said, “I’m not confident that this paper will be able to change policy.”
Other ‘What if?’ scenarios
The authors also predicted the mortality implications associated with lower adherence to masks, the presence or absence of SDMs, and what could happen if mandates continue to ease at their current rate.
For example, they considered a scenario with less-than-universal mask use in public, 85%, along with SDMs being reinstated based on the mortality rate threshold. In this instance, they found an additional 95,814 (range, 60,731–133,077) lives could be spared by February 28.
Another calculation looked at outcomes if 95% of Americans wore masks going forward without states instituting SDMs at any point. In this case, the researchers predict that 490,437 Americans would die from COVID-19 by February 2021.
A fourth analysis revealed what would happen without greater mask use if the mortality threshold triggered 6 weeks of SDMs as warranted. Under this ‘plausible reference’ calculation, a total 511,373 Americans would die from COVID-19 by the end of February.
A fifth scenario predicted potential mortality if states continue easing SDMs at the current pace. “This is an alternative scenario to the more probable situation where states are expected to respond to an impending health crisis by reinstating some SDMs,” the authors note. The predicted number of American deaths appears more dire in this calculation. The investigators predict cumulative total deaths could reach 1,053,206 (range, 759,693–1,452,397) by the end of February 2021.
The death toll would likely vary among states in this scenario. California, Florida, and Pennsylvania would like account for approximately one third of all deaths.
All the modeling scenarios considered other factors including pneumonia seasonality, mobility, testing rates, and mask use per capita.
“I have seen the IHME study and I agree with the broad conclusions,” Richard Stutt, PhD, of the Epidemiology and Modelling Group at the University of Cambridge, UK, told Medscape Medical News.
“Case numbers are climbing in the US, and without further intervention, there will be a significant number of deaths over the coming months,” he said.
Masks are low cost and widely available, Stutt said. “I am hopeful that even if masks are not widely adopted, we will not see as many deaths as predicted here, as these outbreaks can be significantly reduced by increased social distancing or lockdowns.”
“However this comes at a far higher economic cost than the use of masks, and still requires action,” added Stutt, who authored a study in June that modeled facemasks in combination with “lock-down” measures for managing the COVID-19 pandemic.
Modeling study results depend on the assumptions researchers make, and the IHME team rightly tested a number of different assumptions, Greenhalgh said.
“The key conclusion,” she added, “is here: ‘The implementation of SDMs as soon as individual states reach a threshold of 8 daily deaths per million could dramatically ameliorate the effects of the disease; achieving near-universal mask use could delay, or in many states, possibly prevent, this threshold from being reached and has the potential to save the most lives while minimizing damage to the economy.’ “
“This is a useful piece of information and I think is borne out by their data,” added Greenhalgh, lead author of an April study on face masks for the public during the pandemic.
You can visit the IHME website for the most current mortality projections.
Caplan, Greenhalgh, and Stutt have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A cumulative 511,000 lives could be lost from COVID-19 in the United States by the end of February 2021, a new prediction study reveals.
However, if universal mask wearing is adopted — defined as 95% of Americans complying with the protective measure — along with social distancing mandates as warranted, nearly 130,000 of those lives could be saved.
And if even 85% of Americans comply, an additional 95,800 lives would be spared before March of next year, researchers at the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) report.
The study was published online October 23 in Nature Medicine.
“The study is sound and makes the case for mandatory mask policies,” said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a professor of bioethics at NYU Langone Health in New York City, who frequently provides commentary for Medscape.
Without mandatory mask requirements, he added, “we will see a pandemic slaughter and an overwhelmed healthcare system and workforce.”
The IHME team evaluated COVID-19 data for cases and related deaths between February 1 and September 21. Based on this data, they predicted the likely future of SARS-CoV-2 infections on a state level from September 22, 2020, to February 2021.
An Optimistic Projection
Lead author Robert C. Reiner Jr and colleagues looked at five scenarios. For example, they calculated likely deaths associated with COVID-19 if adoption of mask and social distancing recommendations were nearly universal. They note that Singapore achieved a 95% compliance rate with masks and used this as their “best-case scenario” model.
An estimated 129,574 (range, 85,284–170,867) additional lives could be saved if 95% of Americans wore masks in public, their research reveals. This optimistic scenario includes a “plausible reference” in which any US state reaching 8 COVID-19 deaths per 1 million residents would enact 6 weeks of social distancing mandates (SDMs).
Achieving this level of mask compliance in the United States “could be sufficient to ameliorate the worst effects of epidemic resurgences in many states,” the researchers note.
In contrast, the proportion of Americans wearing masks in public as of September 22 was 49%, according to IHME data.
Universal mask use unlikely
“I’m not a modeling expert, but it is an interesting, and as far as I can judge, well-conducted study which looks, state by state, at what might happen in various scenarios around masking policies going forward — and in particular the effect that mandated masking might have,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“However, the scenario is a thought experiment. Near-universal mask use is not going to happen in the USA, nor indeed in any individual state, right now, given how emotive the issue has become,” added Greenhalgh, professor in the Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences at Oxford University, UK. She was not affiliated with the study.
“Hence, whilst I am broadly supportive of the science,” she said, “I’m not confident that this paper will be able to change policy.”
Other ‘What if?’ scenarios
The authors also predicted the mortality implications associated with lower adherence to masks, the presence or absence of SDMs, and what could happen if mandates continue to ease at their current rate.
For example, they considered a scenario with less-than-universal mask use in public, 85%, along with SDMs being reinstated based on the mortality rate threshold. In this instance, they found an additional 95,814 (range, 60,731–133,077) lives could be spared by February 28.
Another calculation looked at outcomes if 95% of Americans wore masks going forward without states instituting SDMs at any point. In this case, the researchers predict that 490,437 Americans would die from COVID-19 by February 2021.
A fourth analysis revealed what would happen without greater mask use if the mortality threshold triggered 6 weeks of SDMs as warranted. Under this ‘plausible reference’ calculation, a total 511,373 Americans would die from COVID-19 by the end of February.
A fifth scenario predicted potential mortality if states continue easing SDMs at the current pace. “This is an alternative scenario to the more probable situation where states are expected to respond to an impending health crisis by reinstating some SDMs,” the authors note. The predicted number of American deaths appears more dire in this calculation. The investigators predict cumulative total deaths could reach 1,053,206 (range, 759,693–1,452,397) by the end of February 2021.
The death toll would likely vary among states in this scenario. California, Florida, and Pennsylvania would like account for approximately one third of all deaths.
All the modeling scenarios considered other factors including pneumonia seasonality, mobility, testing rates, and mask use per capita.
“I have seen the IHME study and I agree with the broad conclusions,” Richard Stutt, PhD, of the Epidemiology and Modelling Group at the University of Cambridge, UK, told Medscape Medical News.
“Case numbers are climbing in the US, and without further intervention, there will be a significant number of deaths over the coming months,” he said.
Masks are low cost and widely available, Stutt said. “I am hopeful that even if masks are not widely adopted, we will not see as many deaths as predicted here, as these outbreaks can be significantly reduced by increased social distancing or lockdowns.”
“However this comes at a far higher economic cost than the use of masks, and still requires action,” added Stutt, who authored a study in June that modeled facemasks in combination with “lock-down” measures for managing the COVID-19 pandemic.
Modeling study results depend on the assumptions researchers make, and the IHME team rightly tested a number of different assumptions, Greenhalgh said.
“The key conclusion,” she added, “is here: ‘The implementation of SDMs as soon as individual states reach a threshold of 8 daily deaths per million could dramatically ameliorate the effects of the disease; achieving near-universal mask use could delay, or in many states, possibly prevent, this threshold from being reached and has the potential to save the most lives while minimizing damage to the economy.’ “
“This is a useful piece of information and I think is borne out by their data,” added Greenhalgh, lead author of an April study on face masks for the public during the pandemic.
You can visit the IHME website for the most current mortality projections.
Caplan, Greenhalgh, and Stutt have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A cumulative 511,000 lives could be lost from COVID-19 in the United States by the end of February 2021, a new prediction study reveals.
However, if universal mask wearing is adopted — defined as 95% of Americans complying with the protective measure — along with social distancing mandates as warranted, nearly 130,000 of those lives could be saved.
And if even 85% of Americans comply, an additional 95,800 lives would be spared before March of next year, researchers at the University of Washington Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) report.
The study was published online October 23 in Nature Medicine.
“The study is sound and makes the case for mandatory mask policies,” said Arthur L. Caplan, PhD, a professor of bioethics at NYU Langone Health in New York City, who frequently provides commentary for Medscape.
Without mandatory mask requirements, he added, “we will see a pandemic slaughter and an overwhelmed healthcare system and workforce.”
The IHME team evaluated COVID-19 data for cases and related deaths between February 1 and September 21. Based on this data, they predicted the likely future of SARS-CoV-2 infections on a state level from September 22, 2020, to February 2021.
An Optimistic Projection
Lead author Robert C. Reiner Jr and colleagues looked at five scenarios. For example, they calculated likely deaths associated with COVID-19 if adoption of mask and social distancing recommendations were nearly universal. They note that Singapore achieved a 95% compliance rate with masks and used this as their “best-case scenario” model.
An estimated 129,574 (range, 85,284–170,867) additional lives could be saved if 95% of Americans wore masks in public, their research reveals. This optimistic scenario includes a “plausible reference” in which any US state reaching 8 COVID-19 deaths per 1 million residents would enact 6 weeks of social distancing mandates (SDMs).
Achieving this level of mask compliance in the United States “could be sufficient to ameliorate the worst effects of epidemic resurgences in many states,” the researchers note.
In contrast, the proportion of Americans wearing masks in public as of September 22 was 49%, according to IHME data.
Universal mask use unlikely
“I’m not a modeling expert, but it is an interesting, and as far as I can judge, well-conducted study which looks, state by state, at what might happen in various scenarios around masking policies going forward — and in particular the effect that mandated masking might have,” Trish Greenhalgh, MD, told Medscape Medical News.
“However, the scenario is a thought experiment. Near-universal mask use is not going to happen in the USA, nor indeed in any individual state, right now, given how emotive the issue has become,” added Greenhalgh, professor in the Nuffield Department of Primary Care Health Sciences at Oxford University, UK. She was not affiliated with the study.
“Hence, whilst I am broadly supportive of the science,” she said, “I’m not confident that this paper will be able to change policy.”
Other ‘What if?’ scenarios
The authors also predicted the mortality implications associated with lower adherence to masks, the presence or absence of SDMs, and what could happen if mandates continue to ease at their current rate.
For example, they considered a scenario with less-than-universal mask use in public, 85%, along with SDMs being reinstated based on the mortality rate threshold. In this instance, they found an additional 95,814 (range, 60,731–133,077) lives could be spared by February 28.
Another calculation looked at outcomes if 95% of Americans wore masks going forward without states instituting SDMs at any point. In this case, the researchers predict that 490,437 Americans would die from COVID-19 by February 2021.
A fourth analysis revealed what would happen without greater mask use if the mortality threshold triggered 6 weeks of SDMs as warranted. Under this ‘plausible reference’ calculation, a total 511,373 Americans would die from COVID-19 by the end of February.
A fifth scenario predicted potential mortality if states continue easing SDMs at the current pace. “This is an alternative scenario to the more probable situation where states are expected to respond to an impending health crisis by reinstating some SDMs,” the authors note. The predicted number of American deaths appears more dire in this calculation. The investigators predict cumulative total deaths could reach 1,053,206 (range, 759,693–1,452,397) by the end of February 2021.
The death toll would likely vary among states in this scenario. California, Florida, and Pennsylvania would like account for approximately one third of all deaths.
All the modeling scenarios considered other factors including pneumonia seasonality, mobility, testing rates, and mask use per capita.
“I have seen the IHME study and I agree with the broad conclusions,” Richard Stutt, PhD, of the Epidemiology and Modelling Group at the University of Cambridge, UK, told Medscape Medical News.
“Case numbers are climbing in the US, and without further intervention, there will be a significant number of deaths over the coming months,” he said.
Masks are low cost and widely available, Stutt said. “I am hopeful that even if masks are not widely adopted, we will not see as many deaths as predicted here, as these outbreaks can be significantly reduced by increased social distancing or lockdowns.”
“However this comes at a far higher economic cost than the use of masks, and still requires action,” added Stutt, who authored a study in June that modeled facemasks in combination with “lock-down” measures for managing the COVID-19 pandemic.
Modeling study results depend on the assumptions researchers make, and the IHME team rightly tested a number of different assumptions, Greenhalgh said.
“The key conclusion,” she added, “is here: ‘The implementation of SDMs as soon as individual states reach a threshold of 8 daily deaths per million could dramatically ameliorate the effects of the disease; achieving near-universal mask use could delay, or in many states, possibly prevent, this threshold from being reached and has the potential to save the most lives while minimizing damage to the economy.’ “
“This is a useful piece of information and I think is borne out by their data,” added Greenhalgh, lead author of an April study on face masks for the public during the pandemic.
You can visit the IHME website for the most current mortality projections.
Caplan, Greenhalgh, and Stutt have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tocilizumab stumbles as COVID-19 treatment, narrow role possible
Tocilizumab (Actemra/RoActemra) was not found to have any clear role as a treatment for COVID-19 in four new studies.
Three randomized controlled trials showed that the drug either had no benefit or only a modest one, contradicting a large retrospective study that had hinted at a more robust effect.
“This is not a blockbuster,” said David Cennimo, MD, an infectious disease expert at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey. “This is not something that’s going to revolutionize our treatment of COVID-19.”
But some researchers still regard these studies as showing evidence that the drug benefits certain patients with severe inflammation.
The immune response to SARS-CoV-2 includes elevated levels of the cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6). In some patients, this response becomes a nonspecific inflammation, a “cytokine storm,” involving edema and inflammatory cell infiltration in the lungs. These cases are among the most severe.
Dexamethasone has proved effective in controlling this inflammation in some patients. Researchers have theorized that a more targeted suppression of IL-6 could be even more effective or work in cases that don’t respond to dexamethasone.
A recombinant monoclonal antibody, tocilizumab blocks IL-6 receptors. It is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with rheumatologic disorders and cytokine release syndrome induced by chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
Current National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines recommend against the use of tocilizumab as a treatment for COVID-19, despite earlier observational studies that suggested the drug might help patients with moderate to severe disease. Controlled trials were lacking until now.
The most hopeful results in this batch came from the CORIMUNO-19 platform of open-label, randomized controlled trials of immune modulatory treatments for moderate or severe COVID-19 in France.
Published in JAMA Internal Medicine , the trial recruited patients from nine French hospitals. Patients were eligible if they required at least 3 L/min of oxygen without ventilation or admission to the intensive care unit.
The investigators randomly assigned 64 patients to receive tocilizumab 8 mg/kg body weight intravenously plus usual care and 67 patients to usual care alone. Usual care included antibiotic agents, antiviral agents, corticosteroids, vasopressor support, and anticoagulants.
After 4 days, the investigators scored patients on the World Health Organization 10-point Clinical Progression Scale. Twelve of the patients who received tocilizumab scored higher than 5 vs 19 of the patients in the usual care group, with higher scores indicating clinical deterioration.
After 14 days, 24% of the patients taking tocilizumab required either noninvasive ventilation or mechanical ventilation or had died, vs 36% in the usual care group (median posterior hazard ratio [HR], 0.58; 90% credible interval, 0.33 – 1.00).
“We reduced the risk of dying or requiring mechanical ventilation, so for me, the study was positive,” said Olivier Hermine, MD, PhD, a professor of hematology at Paris Descartes University in Paris, France.
However, there was no difference in mortality at 28 days. Hermine hopes to have longer-term outcomes soon, he told Medscape Medical News.
A second randomized controlled trial, also published in JAMA Internal Medicine , provided less hope. In this RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 Study Group trial, conducted at 24 Italian centers, patients were enrolled if their partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratios were between 200 and 300 mm Hg and if their inflammatory phenotypes were defined by fever and elevated C-reactive protein level.
The investigators randomly assigned 60 patients to receive tocilizumab 8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg within 8 hours of randomization, followed by a second dose after 12 hours. They assigned 66 patients to a control group that received supportive care until clinical worsening, at which point patients could receive tocilizumab as a rescue therapy.
Of the patients who received tocilizumab, 28.3% showed clinical worsening within 14 days, compared to 27.0% in the control group (rate ratio, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.59 – 1.86). There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the proportion admitted to intensive care. The researchers stopped the trial prematurely because tocilizumab did not seem to be making a difference.
The BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial was conducted at seven Boston hospitals. The results, which were published in The New England Journal of Medicine, were also discouraging.
In that trial, enrolled patients met two sets of parameters. First, the patients had at least one of the following signs: C-reactive protein level higher than 50 mg/L, ferritin level higher than 500 ng/mL, D-dimer level higher than 1000 ng/mL, or a lactate dehydrogenase level higher than 250 U/L. Second, the patients had to have at least two of the following signs: body temperature >38° C, pulmonary infiltrates, or the need for supplemental oxygen to maintain an oxygen saturation greater than 92%.
The investigators randomly assigned 161 patients to receive intravenous tocilizumab 8 mg/kg up to 800 mg and 81 to receive a placebo.
They didn’t find a statistically significant difference between the groups. The hazard ratio for intubation or death in the tocilizumab group as compared with the placebo group was 0.83 (95% CI, 0.38 – 1.81; P = .64). The hazard ratio for disease worsening was 1.11 (95% CI, 0.59 – 2.10; P = .73). At 14 days, the conditions of 18.0% of the patients who received tocilizumab and 14.9% of the patients who received the placebo worsened.
In contrast to these randomized trials, STOP-COVID, a retrospective analysis of 3924 patients, also published in JAMA Internal Medicine, found that the risk for death was lower for patients treated with tocilizumab compared with those not treated with tocilizumab (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.56 – 0.92) over a median follow-up period of 27 days.
Also on the bright side, none of the new studies showed significant adverse reactions to tocilizumab.
More randomized clinical trials are underway. In press releases announcing topline data, Roche reported mostly negative results in its phase 3 COVACTA trial but noted a 44% reduction in the risk for progression to death or ventilation in its phase 3 IMPACTA trial. Roche did not comment on the ethnicity of its COVACTA patients; it said IMPACTA enrolled a majority of Hispanic patients and included large representations of Native American and Black patients.
Results don’t support routine use
Commenting on the new studies, editorialists in both JAMA Internal Medicine and The New England Journal of Medicine concluded that the tocilizumab results were not strong enough to support routine use.
“My take-home point from looking at all of these together is that, even if it does help, it’s most likely in a small subset of the population and/or a small effect,” Cennimo told Medscape Medical News.
But the NIH recommendation against tocilizumab goes too far, argued Cristina Mussini, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia in Italy, who is a coauthor of a cohort study of tocilizumab and served on the CORIMUNO-19 Data Safety and Monitoring Board.
“I really think it’s too early to recommend against it because at least two clinical trials showed protection against mechanical ventilation and death,” she said.
She prescribes tocilizumab for patients who have not been helped by dexamethasone. “It’s just a rescue drug,” she told Medscape Medical News. “It’s not something you use for everybody, but it’s the only weapon we have now when the patient is really going to the intensive care unit.”
The BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial was funded by Genentech/Roche. Genentech/Roche provided the drug for the CORIMUNO and RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 trials. The STOP-COVID study was supported by grants from the NIH and by the Frankel Cardiovascular Center COVID-19: Impact Research Ignitor. Cennimo, Hermine, and Mussini have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tocilizumab (Actemra/RoActemra) was not found to have any clear role as a treatment for COVID-19 in four new studies.
Three randomized controlled trials showed that the drug either had no benefit or only a modest one, contradicting a large retrospective study that had hinted at a more robust effect.
“This is not a blockbuster,” said David Cennimo, MD, an infectious disease expert at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey. “This is not something that’s going to revolutionize our treatment of COVID-19.”
But some researchers still regard these studies as showing evidence that the drug benefits certain patients with severe inflammation.
The immune response to SARS-CoV-2 includes elevated levels of the cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6). In some patients, this response becomes a nonspecific inflammation, a “cytokine storm,” involving edema and inflammatory cell infiltration in the lungs. These cases are among the most severe.
Dexamethasone has proved effective in controlling this inflammation in some patients. Researchers have theorized that a more targeted suppression of IL-6 could be even more effective or work in cases that don’t respond to dexamethasone.
A recombinant monoclonal antibody, tocilizumab blocks IL-6 receptors. It is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with rheumatologic disorders and cytokine release syndrome induced by chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
Current National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines recommend against the use of tocilizumab as a treatment for COVID-19, despite earlier observational studies that suggested the drug might help patients with moderate to severe disease. Controlled trials were lacking until now.
The most hopeful results in this batch came from the CORIMUNO-19 platform of open-label, randomized controlled trials of immune modulatory treatments for moderate or severe COVID-19 in France.
Published in JAMA Internal Medicine , the trial recruited patients from nine French hospitals. Patients were eligible if they required at least 3 L/min of oxygen without ventilation or admission to the intensive care unit.
The investigators randomly assigned 64 patients to receive tocilizumab 8 mg/kg body weight intravenously plus usual care and 67 patients to usual care alone. Usual care included antibiotic agents, antiviral agents, corticosteroids, vasopressor support, and anticoagulants.
After 4 days, the investigators scored patients on the World Health Organization 10-point Clinical Progression Scale. Twelve of the patients who received tocilizumab scored higher than 5 vs 19 of the patients in the usual care group, with higher scores indicating clinical deterioration.
After 14 days, 24% of the patients taking tocilizumab required either noninvasive ventilation or mechanical ventilation or had died, vs 36% in the usual care group (median posterior hazard ratio [HR], 0.58; 90% credible interval, 0.33 – 1.00).
“We reduced the risk of dying or requiring mechanical ventilation, so for me, the study was positive,” said Olivier Hermine, MD, PhD, a professor of hematology at Paris Descartes University in Paris, France.
However, there was no difference in mortality at 28 days. Hermine hopes to have longer-term outcomes soon, he told Medscape Medical News.
A second randomized controlled trial, also published in JAMA Internal Medicine , provided less hope. In this RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 Study Group trial, conducted at 24 Italian centers, patients were enrolled if their partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratios were between 200 and 300 mm Hg and if their inflammatory phenotypes were defined by fever and elevated C-reactive protein level.
The investigators randomly assigned 60 patients to receive tocilizumab 8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg within 8 hours of randomization, followed by a second dose after 12 hours. They assigned 66 patients to a control group that received supportive care until clinical worsening, at which point patients could receive tocilizumab as a rescue therapy.
Of the patients who received tocilizumab, 28.3% showed clinical worsening within 14 days, compared to 27.0% in the control group (rate ratio, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.59 – 1.86). There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the proportion admitted to intensive care. The researchers stopped the trial prematurely because tocilizumab did not seem to be making a difference.
The BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial was conducted at seven Boston hospitals. The results, which were published in The New England Journal of Medicine, were also discouraging.
In that trial, enrolled patients met two sets of parameters. First, the patients had at least one of the following signs: C-reactive protein level higher than 50 mg/L, ferritin level higher than 500 ng/mL, D-dimer level higher than 1000 ng/mL, or a lactate dehydrogenase level higher than 250 U/L. Second, the patients had to have at least two of the following signs: body temperature >38° C, pulmonary infiltrates, or the need for supplemental oxygen to maintain an oxygen saturation greater than 92%.
The investigators randomly assigned 161 patients to receive intravenous tocilizumab 8 mg/kg up to 800 mg and 81 to receive a placebo.
They didn’t find a statistically significant difference between the groups. The hazard ratio for intubation or death in the tocilizumab group as compared with the placebo group was 0.83 (95% CI, 0.38 – 1.81; P = .64). The hazard ratio for disease worsening was 1.11 (95% CI, 0.59 – 2.10; P = .73). At 14 days, the conditions of 18.0% of the patients who received tocilizumab and 14.9% of the patients who received the placebo worsened.
In contrast to these randomized trials, STOP-COVID, a retrospective analysis of 3924 patients, also published in JAMA Internal Medicine, found that the risk for death was lower for patients treated with tocilizumab compared with those not treated with tocilizumab (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.56 – 0.92) over a median follow-up period of 27 days.
Also on the bright side, none of the new studies showed significant adverse reactions to tocilizumab.
More randomized clinical trials are underway. In press releases announcing topline data, Roche reported mostly negative results in its phase 3 COVACTA trial but noted a 44% reduction in the risk for progression to death or ventilation in its phase 3 IMPACTA trial. Roche did not comment on the ethnicity of its COVACTA patients; it said IMPACTA enrolled a majority of Hispanic patients and included large representations of Native American and Black patients.
Results don’t support routine use
Commenting on the new studies, editorialists in both JAMA Internal Medicine and The New England Journal of Medicine concluded that the tocilizumab results were not strong enough to support routine use.
“My take-home point from looking at all of these together is that, even if it does help, it’s most likely in a small subset of the population and/or a small effect,” Cennimo told Medscape Medical News.
But the NIH recommendation against tocilizumab goes too far, argued Cristina Mussini, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia in Italy, who is a coauthor of a cohort study of tocilizumab and served on the CORIMUNO-19 Data Safety and Monitoring Board.
“I really think it’s too early to recommend against it because at least two clinical trials showed protection against mechanical ventilation and death,” she said.
She prescribes tocilizumab for patients who have not been helped by dexamethasone. “It’s just a rescue drug,” she told Medscape Medical News. “It’s not something you use for everybody, but it’s the only weapon we have now when the patient is really going to the intensive care unit.”
The BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial was funded by Genentech/Roche. Genentech/Roche provided the drug for the CORIMUNO and RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 trials. The STOP-COVID study was supported by grants from the NIH and by the Frankel Cardiovascular Center COVID-19: Impact Research Ignitor. Cennimo, Hermine, and Mussini have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tocilizumab (Actemra/RoActemra) was not found to have any clear role as a treatment for COVID-19 in four new studies.
Three randomized controlled trials showed that the drug either had no benefit or only a modest one, contradicting a large retrospective study that had hinted at a more robust effect.
“This is not a blockbuster,” said David Cennimo, MD, an infectious disease expert at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey. “This is not something that’s going to revolutionize our treatment of COVID-19.”
But some researchers still regard these studies as showing evidence that the drug benefits certain patients with severe inflammation.
The immune response to SARS-CoV-2 includes elevated levels of the cytokine interleukin-6 (IL-6). In some patients, this response becomes a nonspecific inflammation, a “cytokine storm,” involving edema and inflammatory cell infiltration in the lungs. These cases are among the most severe.
Dexamethasone has proved effective in controlling this inflammation in some patients. Researchers have theorized that a more targeted suppression of IL-6 could be even more effective or work in cases that don’t respond to dexamethasone.
A recombinant monoclonal antibody, tocilizumab blocks IL-6 receptors. It is approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for use in patients with rheumatologic disorders and cytokine release syndrome induced by chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy.
Current National Institutes of Health (NIH) guidelines recommend against the use of tocilizumab as a treatment for COVID-19, despite earlier observational studies that suggested the drug might help patients with moderate to severe disease. Controlled trials were lacking until now.
The most hopeful results in this batch came from the CORIMUNO-19 platform of open-label, randomized controlled trials of immune modulatory treatments for moderate or severe COVID-19 in France.
Published in JAMA Internal Medicine , the trial recruited patients from nine French hospitals. Patients were eligible if they required at least 3 L/min of oxygen without ventilation or admission to the intensive care unit.
The investigators randomly assigned 64 patients to receive tocilizumab 8 mg/kg body weight intravenously plus usual care and 67 patients to usual care alone. Usual care included antibiotic agents, antiviral agents, corticosteroids, vasopressor support, and anticoagulants.
After 4 days, the investigators scored patients on the World Health Organization 10-point Clinical Progression Scale. Twelve of the patients who received tocilizumab scored higher than 5 vs 19 of the patients in the usual care group, with higher scores indicating clinical deterioration.
After 14 days, 24% of the patients taking tocilizumab required either noninvasive ventilation or mechanical ventilation or had died, vs 36% in the usual care group (median posterior hazard ratio [HR], 0.58; 90% credible interval, 0.33 – 1.00).
“We reduced the risk of dying or requiring mechanical ventilation, so for me, the study was positive,” said Olivier Hermine, MD, PhD, a professor of hematology at Paris Descartes University in Paris, France.
However, there was no difference in mortality at 28 days. Hermine hopes to have longer-term outcomes soon, he told Medscape Medical News.
A second randomized controlled trial, also published in JAMA Internal Medicine , provided less hope. In this RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 Study Group trial, conducted at 24 Italian centers, patients were enrolled if their partial pressure of arterial oxygen to fraction of inspired oxygen (PaO2/FiO2) ratios were between 200 and 300 mm Hg and if their inflammatory phenotypes were defined by fever and elevated C-reactive protein level.
The investigators randomly assigned 60 patients to receive tocilizumab 8 mg/kg up to a maximum of 800 mg within 8 hours of randomization, followed by a second dose after 12 hours. They assigned 66 patients to a control group that received supportive care until clinical worsening, at which point patients could receive tocilizumab as a rescue therapy.
Of the patients who received tocilizumab, 28.3% showed clinical worsening within 14 days, compared to 27.0% in the control group (rate ratio, 1.05; 95% CI, 0.59 – 1.86). There was no significant difference between the groups in terms of the proportion admitted to intensive care. The researchers stopped the trial prematurely because tocilizumab did not seem to be making a difference.
The BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial was conducted at seven Boston hospitals. The results, which were published in The New England Journal of Medicine, were also discouraging.
In that trial, enrolled patients met two sets of parameters. First, the patients had at least one of the following signs: C-reactive protein level higher than 50 mg/L, ferritin level higher than 500 ng/mL, D-dimer level higher than 1000 ng/mL, or a lactate dehydrogenase level higher than 250 U/L. Second, the patients had to have at least two of the following signs: body temperature >38° C, pulmonary infiltrates, or the need for supplemental oxygen to maintain an oxygen saturation greater than 92%.
The investigators randomly assigned 161 patients to receive intravenous tocilizumab 8 mg/kg up to 800 mg and 81 to receive a placebo.
They didn’t find a statistically significant difference between the groups. The hazard ratio for intubation or death in the tocilizumab group as compared with the placebo group was 0.83 (95% CI, 0.38 – 1.81; P = .64). The hazard ratio for disease worsening was 1.11 (95% CI, 0.59 – 2.10; P = .73). At 14 days, the conditions of 18.0% of the patients who received tocilizumab and 14.9% of the patients who received the placebo worsened.
In contrast to these randomized trials, STOP-COVID, a retrospective analysis of 3924 patients, also published in JAMA Internal Medicine, found that the risk for death was lower for patients treated with tocilizumab compared with those not treated with tocilizumab (HR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.56 – 0.92) over a median follow-up period of 27 days.
Also on the bright side, none of the new studies showed significant adverse reactions to tocilizumab.
More randomized clinical trials are underway. In press releases announcing topline data, Roche reported mostly negative results in its phase 3 COVACTA trial but noted a 44% reduction in the risk for progression to death or ventilation in its phase 3 IMPACTA trial. Roche did not comment on the ethnicity of its COVACTA patients; it said IMPACTA enrolled a majority of Hispanic patients and included large representations of Native American and Black patients.
Results don’t support routine use
Commenting on the new studies, editorialists in both JAMA Internal Medicine and The New England Journal of Medicine concluded that the tocilizumab results were not strong enough to support routine use.
“My take-home point from looking at all of these together is that, even if it does help, it’s most likely in a small subset of the population and/or a small effect,” Cennimo told Medscape Medical News.
But the NIH recommendation against tocilizumab goes too far, argued Cristina Mussini, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at the University of Modena and Reggio Emilia in Italy, who is a coauthor of a cohort study of tocilizumab and served on the CORIMUNO-19 Data Safety and Monitoring Board.
“I really think it’s too early to recommend against it because at least two clinical trials showed protection against mechanical ventilation and death,” she said.
She prescribes tocilizumab for patients who have not been helped by dexamethasone. “It’s just a rescue drug,” she told Medscape Medical News. “It’s not something you use for everybody, but it’s the only weapon we have now when the patient is really going to the intensive care unit.”
The BACC Bay Tocilizumab Trial was funded by Genentech/Roche. Genentech/Roche provided the drug for the CORIMUNO and RCT-TCZ-COVID-19 trials. The STOP-COVID study was supported by grants from the NIH and by the Frankel Cardiovascular Center COVID-19: Impact Research Ignitor. Cennimo, Hermine, and Mussini have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Lilly stops antibody trial in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, other trials continue
Eli Lilly announced it will halt its ACTIV-3 trial evaluating the antibody bamlanivimab in combination with remdesivir for people hospitalized with COVID-19, after new evidence regarding efficacy emerged.
The new data from the National Institutes of Health suggest that the experimental neutralizing antibody therapy does not offer significant clinical benefit for people with more advanced COVID-19 illness, according to a company statement.
Eli Lilly also announced it plans to continue its other trials evaluating the antibody, including those assessing a potential role in treating people in the earlier stages of COVID-19.
“While there was insufficient evidence that bamlanivimab improved clinical outcomes when added to other treatments in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, we remain confident based on data from Lilly’s BLAZE-1 study that bamlanivimab monotherapy may prevent progression of disease for those earlier in the course of COVID-19,” the statement reads.
The ACTIV-3 trial was paused on October 13 after a data and safety monitoring board cited safety concerns.
The most recent data update that triggered an end to the trial did not reveal any significant differences in safety, though.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eli Lilly announced it will halt its ACTIV-3 trial evaluating the antibody bamlanivimab in combination with remdesivir for people hospitalized with COVID-19, after new evidence regarding efficacy emerged.
The new data from the National Institutes of Health suggest that the experimental neutralizing antibody therapy does not offer significant clinical benefit for people with more advanced COVID-19 illness, according to a company statement.
Eli Lilly also announced it plans to continue its other trials evaluating the antibody, including those assessing a potential role in treating people in the earlier stages of COVID-19.
“While there was insufficient evidence that bamlanivimab improved clinical outcomes when added to other treatments in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, we remain confident based on data from Lilly’s BLAZE-1 study that bamlanivimab monotherapy may prevent progression of disease for those earlier in the course of COVID-19,” the statement reads.
The ACTIV-3 trial was paused on October 13 after a data and safety monitoring board cited safety concerns.
The most recent data update that triggered an end to the trial did not reveal any significant differences in safety, though.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eli Lilly announced it will halt its ACTIV-3 trial evaluating the antibody bamlanivimab in combination with remdesivir for people hospitalized with COVID-19, after new evidence regarding efficacy emerged.
The new data from the National Institutes of Health suggest that the experimental neutralizing antibody therapy does not offer significant clinical benefit for people with more advanced COVID-19 illness, according to a company statement.
Eli Lilly also announced it plans to continue its other trials evaluating the antibody, including those assessing a potential role in treating people in the earlier stages of COVID-19.
“While there was insufficient evidence that bamlanivimab improved clinical outcomes when added to other treatments in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, we remain confident based on data from Lilly’s BLAZE-1 study that bamlanivimab monotherapy may prevent progression of disease for those earlier in the course of COVID-19,” the statement reads.
The ACTIV-3 trial was paused on October 13 after a data and safety monitoring board cited safety concerns.
The most recent data update that triggered an end to the trial did not reveal any significant differences in safety, though.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Vertebral fractures in COVID-19 linked to mortality
Vertebral fractures appear to be common in people with severe COVID-19, and also raise the mortality risk, findings from a retrospective cohort suggest.
Among 114 patients with COVID-19 who underwent lateral chest x-rays at the San Raffaele Hospital ED in Milan, more than a third were found to have thoracic vertebral fractures. And, those individuals were more than twice as likely to die as were those without vertebral fractures.
“Morphometric vertebral fractures are one of the most common comorbidities among adults hospitalized with COVID-19, and the presence of such fractures may predict the severity of disease outcomes,” lead investigator Andrea Giustina, MD, said in an interview.
This is the first study to examine vertebral fracture prevalence in any coronavirus disease, but such fractures have been linked to an increased risk of pneumonia and impaired respiratory function, including restrictive pulmonary dysfunction. One possible mechanism may be that they cause anatomical changes, such as kyphosis, which negatively impact respiratory function by decreasing vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in 1 second, and inspiratory time, explained Dr. Giustina, professor of endocrinology, San Raffaele Vita Salute University, Milan, and president of the European Society of Endocrinology. The results were published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Clinically, the findings suggest that all patients with COVID-19 who are undergoing chest x-rays should have morphometric vertebral x-ray evaluation, said Dr. Giustina.
“One interesting aspect of the study is that without morphometry, approximatively two thirds of vertebral fractures [would have been] missed. Therefore, they are largely underestimated in clinical practice,” he noted.
Thoracic vertebral fractures assessed via lateral chest x-rays
The 114 study subjects included were those whose lateral chest x-rays allowed for a high-quality assessment and in which all the thoracic tract of T4-T12 were viewable and assessable. None had been using glucocorticoids and only 3% had a prior diagnosis of osteoporosis.
The majority (75%) were male, and median age was 57 years. Most (79%) were hospitalized after evaluation in the ED. Of those, 12% (13) were admitted to the ICU and 15% (16) died.
Thoracic vertebral fractures were detected on the lateral chest x-rays in 36% (41) of the patients. In contrast, in studies of women aged 50 years and older from the general European population, morphometric vertebral fracture prevalence ranged from 18% to 26%, the investigators noted.
Of the total 65 vertebral fractures detected, 60% were classified as mild (height ratio decrease <25%), 33.3% as moderate (25%-40% decrease) and 7.7% as severe (>40%). Patients with more than one vertebral fracture were classified by their most severe one.
Those with versus without vertebral fractures didn’t differ by sex, body mass index, or clinical or biological parameters evaluated in the ED. But, compared with those without vertebral fractures, those with them were significantly older (68 vs. 54 years) and were more likely to have arterial hypertension (56% vs. 30%) and coronary artery disease (22% vs. 7%).
In multivariate analysis, age was the only statistically significant predictor of vertebral fractures (odds ratio, 1.04; P < .001).
Mortality doubled, though not significantly
Those with vertebral fractures were more likely to be hospitalized, although not significantly (88% vs. 74%). There was no significant difference in ICU admission (11% vs. 12.5%).
However, those with vertebral fractures required noninvasive mechanical ventilation significantly more often (48.8% vs. 27.4%; P = .02), and were more than twice as likely to die (22% vs. 10%; P = .07). While the difference in overall mortality wasn’t quite statistically significant, those with severe vertebral fractures were significantly more likely to die, compared with those with mild or moderate fractures (60%, 7%, 24%, respectively, for severe, moderate, and mild; P = .04), despite no significant differences in clinical or laboratory parameters.
“Our data from the field reinforce the need of implementing previously published recommendations concerning the importance of bone fragility care during the COVID pandemic with at least those patients already treated with antiosteoporotic drugs maintaining their adherence to treatments including vitamin D, which have also been suggested very recently to have no relevant predisposing effect on COVID-19,” Dr. Giustina and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, they added, “continuity of care should also include bone density monitoring despite very restricted access to clinical facilities, during the COVID-19 pandemic. Finally, all patients with fractures should start antiresorptive treatment right away, even during hospital stay.”
The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Giustina A et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa738.
Vertebral fractures appear to be common in people with severe COVID-19, and also raise the mortality risk, findings from a retrospective cohort suggest.
Among 114 patients with COVID-19 who underwent lateral chest x-rays at the San Raffaele Hospital ED in Milan, more than a third were found to have thoracic vertebral fractures. And, those individuals were more than twice as likely to die as were those without vertebral fractures.
“Morphometric vertebral fractures are one of the most common comorbidities among adults hospitalized with COVID-19, and the presence of such fractures may predict the severity of disease outcomes,” lead investigator Andrea Giustina, MD, said in an interview.
This is the first study to examine vertebral fracture prevalence in any coronavirus disease, but such fractures have been linked to an increased risk of pneumonia and impaired respiratory function, including restrictive pulmonary dysfunction. One possible mechanism may be that they cause anatomical changes, such as kyphosis, which negatively impact respiratory function by decreasing vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in 1 second, and inspiratory time, explained Dr. Giustina, professor of endocrinology, San Raffaele Vita Salute University, Milan, and president of the European Society of Endocrinology. The results were published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Clinically, the findings suggest that all patients with COVID-19 who are undergoing chest x-rays should have morphometric vertebral x-ray evaluation, said Dr. Giustina.
“One interesting aspect of the study is that without morphometry, approximatively two thirds of vertebral fractures [would have been] missed. Therefore, they are largely underestimated in clinical practice,” he noted.
Thoracic vertebral fractures assessed via lateral chest x-rays
The 114 study subjects included were those whose lateral chest x-rays allowed for a high-quality assessment and in which all the thoracic tract of T4-T12 were viewable and assessable. None had been using glucocorticoids and only 3% had a prior diagnosis of osteoporosis.
The majority (75%) were male, and median age was 57 years. Most (79%) were hospitalized after evaluation in the ED. Of those, 12% (13) were admitted to the ICU and 15% (16) died.
Thoracic vertebral fractures were detected on the lateral chest x-rays in 36% (41) of the patients. In contrast, in studies of women aged 50 years and older from the general European population, morphometric vertebral fracture prevalence ranged from 18% to 26%, the investigators noted.
Of the total 65 vertebral fractures detected, 60% were classified as mild (height ratio decrease <25%), 33.3% as moderate (25%-40% decrease) and 7.7% as severe (>40%). Patients with more than one vertebral fracture were classified by their most severe one.
Those with versus without vertebral fractures didn’t differ by sex, body mass index, or clinical or biological parameters evaluated in the ED. But, compared with those without vertebral fractures, those with them were significantly older (68 vs. 54 years) and were more likely to have arterial hypertension (56% vs. 30%) and coronary artery disease (22% vs. 7%).
In multivariate analysis, age was the only statistically significant predictor of vertebral fractures (odds ratio, 1.04; P < .001).
Mortality doubled, though not significantly
Those with vertebral fractures were more likely to be hospitalized, although not significantly (88% vs. 74%). There was no significant difference in ICU admission (11% vs. 12.5%).
However, those with vertebral fractures required noninvasive mechanical ventilation significantly more often (48.8% vs. 27.4%; P = .02), and were more than twice as likely to die (22% vs. 10%; P = .07). While the difference in overall mortality wasn’t quite statistically significant, those with severe vertebral fractures were significantly more likely to die, compared with those with mild or moderate fractures (60%, 7%, 24%, respectively, for severe, moderate, and mild; P = .04), despite no significant differences in clinical or laboratory parameters.
“Our data from the field reinforce the need of implementing previously published recommendations concerning the importance of bone fragility care during the COVID pandemic with at least those patients already treated with antiosteoporotic drugs maintaining their adherence to treatments including vitamin D, which have also been suggested very recently to have no relevant predisposing effect on COVID-19,” Dr. Giustina and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, they added, “continuity of care should also include bone density monitoring despite very restricted access to clinical facilities, during the COVID-19 pandemic. Finally, all patients with fractures should start antiresorptive treatment right away, even during hospital stay.”
The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Giustina A et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa738.
Vertebral fractures appear to be common in people with severe COVID-19, and also raise the mortality risk, findings from a retrospective cohort suggest.
Among 114 patients with COVID-19 who underwent lateral chest x-rays at the San Raffaele Hospital ED in Milan, more than a third were found to have thoracic vertebral fractures. And, those individuals were more than twice as likely to die as were those without vertebral fractures.
“Morphometric vertebral fractures are one of the most common comorbidities among adults hospitalized with COVID-19, and the presence of such fractures may predict the severity of disease outcomes,” lead investigator Andrea Giustina, MD, said in an interview.
This is the first study to examine vertebral fracture prevalence in any coronavirus disease, but such fractures have been linked to an increased risk of pneumonia and impaired respiratory function, including restrictive pulmonary dysfunction. One possible mechanism may be that they cause anatomical changes, such as kyphosis, which negatively impact respiratory function by decreasing vital capacity, forced expiratory volume in 1 second, and inspiratory time, explained Dr. Giustina, professor of endocrinology, San Raffaele Vita Salute University, Milan, and president of the European Society of Endocrinology. The results were published in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
Clinically, the findings suggest that all patients with COVID-19 who are undergoing chest x-rays should have morphometric vertebral x-ray evaluation, said Dr. Giustina.
“One interesting aspect of the study is that without morphometry, approximatively two thirds of vertebral fractures [would have been] missed. Therefore, they are largely underestimated in clinical practice,” he noted.
Thoracic vertebral fractures assessed via lateral chest x-rays
The 114 study subjects included were those whose lateral chest x-rays allowed for a high-quality assessment and in which all the thoracic tract of T4-T12 were viewable and assessable. None had been using glucocorticoids and only 3% had a prior diagnosis of osteoporosis.
The majority (75%) were male, and median age was 57 years. Most (79%) were hospitalized after evaluation in the ED. Of those, 12% (13) were admitted to the ICU and 15% (16) died.
Thoracic vertebral fractures were detected on the lateral chest x-rays in 36% (41) of the patients. In contrast, in studies of women aged 50 years and older from the general European population, morphometric vertebral fracture prevalence ranged from 18% to 26%, the investigators noted.
Of the total 65 vertebral fractures detected, 60% were classified as mild (height ratio decrease <25%), 33.3% as moderate (25%-40% decrease) and 7.7% as severe (>40%). Patients with more than one vertebral fracture were classified by their most severe one.
Those with versus without vertebral fractures didn’t differ by sex, body mass index, or clinical or biological parameters evaluated in the ED. But, compared with those without vertebral fractures, those with them were significantly older (68 vs. 54 years) and were more likely to have arterial hypertension (56% vs. 30%) and coronary artery disease (22% vs. 7%).
In multivariate analysis, age was the only statistically significant predictor of vertebral fractures (odds ratio, 1.04; P < .001).
Mortality doubled, though not significantly
Those with vertebral fractures were more likely to be hospitalized, although not significantly (88% vs. 74%). There was no significant difference in ICU admission (11% vs. 12.5%).
However, those with vertebral fractures required noninvasive mechanical ventilation significantly more often (48.8% vs. 27.4%; P = .02), and were more than twice as likely to die (22% vs. 10%; P = .07). While the difference in overall mortality wasn’t quite statistically significant, those with severe vertebral fractures were significantly more likely to die, compared with those with mild or moderate fractures (60%, 7%, 24%, respectively, for severe, moderate, and mild; P = .04), despite no significant differences in clinical or laboratory parameters.
“Our data from the field reinforce the need of implementing previously published recommendations concerning the importance of bone fragility care during the COVID pandemic with at least those patients already treated with antiosteoporotic drugs maintaining their adherence to treatments including vitamin D, which have also been suggested very recently to have no relevant predisposing effect on COVID-19,” Dr. Giustina and colleagues wrote.
Moreover, they added, “continuity of care should also include bone density monitoring despite very restricted access to clinical facilities, during the COVID-19 pandemic. Finally, all patients with fractures should start antiresorptive treatment right away, even during hospital stay.”
The authors reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Giustina A et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020 Oct 21. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa738.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ENDOCRINOLOGY AND METABOLISM
The new one-percenters: Children with COVID-19
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.
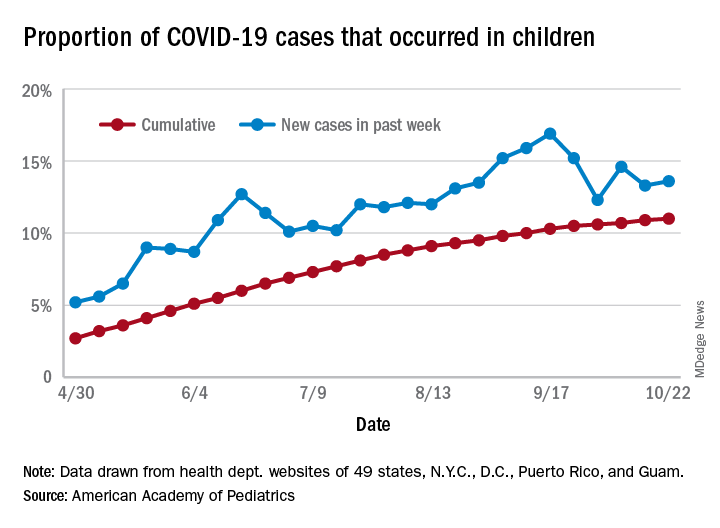
There have been 1,052 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 22, and that works out to 1.05% of all children in the country. The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 792,188, and children now represent 11% of all COVID-19 cases, the AAP and the CHA reported Oct. 26.
There were just over 50,000 new child cases reported in the week ending Oct. 22, which was 13.6% of the national total of almost 370,000. That’s up slightly from the 13.3% the previous week but still down from the spike seen in mid-September, based on the data collected from the websites of 49 state health departments (New York does not report ages), along with the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The state-level data show that California has had more COVID-19 cases in children (92,864) than any other state, although Texas has reported ages for only 7% of its confirmed cases. Illinois is next with 46,006 cases, followed by Florida at 45,575, although Florida is using an age range of 0-14 years to define a child case, the AAP and CHA noted.
Other measures largely put small states at the extremes:
- North Dakota has the highest cumulative rate: 2,954 cases per 100,000 children.
- Vermont has the lowest cumulative rate: 190.5 per 100,000.
- Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children: 27.7%.
- New Jersey has the lowest proportion of child cases: 4.6%.
There were no COVID-19–related deaths in children reported the week ending Oct. 22, so the total number remains at 120, which is just 0.06% of the total for all ages, based on data from 42 states and New York City. Hospitalization figures put admissions at almost 5,600 in children, or 1.7% of all hospitalizations, although those data come from just 24 states and New York City, the AAP and CHA said.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

There have been 1,052 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 22, and that works out to 1.05% of all children in the country. The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 792,188, and children now represent 11% of all COVID-19 cases, the AAP and the CHA reported Oct. 26.
There were just over 50,000 new child cases reported in the week ending Oct. 22, which was 13.6% of the national total of almost 370,000. That’s up slightly from the 13.3% the previous week but still down from the spike seen in mid-September, based on the data collected from the websites of 49 state health departments (New York does not report ages), along with the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The state-level data show that California has had more COVID-19 cases in children (92,864) than any other state, although Texas has reported ages for only 7% of its confirmed cases. Illinois is next with 46,006 cases, followed by Florida at 45,575, although Florida is using an age range of 0-14 years to define a child case, the AAP and CHA noted.
Other measures largely put small states at the extremes:
- North Dakota has the highest cumulative rate: 2,954 cases per 100,000 children.
- Vermont has the lowest cumulative rate: 190.5 per 100,000.
- Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children: 27.7%.
- New Jersey has the lowest proportion of child cases: 4.6%.
There were no COVID-19–related deaths in children reported the week ending Oct. 22, so the total number remains at 120, which is just 0.06% of the total for all ages, based on data from 42 states and New York City. Hospitalization figures put admissions at almost 5,600 in children, or 1.7% of all hospitalizations, although those data come from just 24 states and New York City, the AAP and CHA said.
according to a report from the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association.

There have been 1,052 cases of COVID-19 per 100,000 children as of Oct. 22, and that works out to 1.05% of all children in the country. The cumulative number of pediatric cases is 792,188, and children now represent 11% of all COVID-19 cases, the AAP and the CHA reported Oct. 26.
There were just over 50,000 new child cases reported in the week ending Oct. 22, which was 13.6% of the national total of almost 370,000. That’s up slightly from the 13.3% the previous week but still down from the spike seen in mid-September, based on the data collected from the websites of 49 state health departments (New York does not report ages), along with the District of Columbia, New York City, Puerto Rico, and Guam.
The state-level data show that California has had more COVID-19 cases in children (92,864) than any other state, although Texas has reported ages for only 7% of its confirmed cases. Illinois is next with 46,006 cases, followed by Florida at 45,575, although Florida is using an age range of 0-14 years to define a child case, the AAP and CHA noted.
Other measures largely put small states at the extremes:
- North Dakota has the highest cumulative rate: 2,954 cases per 100,000 children.
- Vermont has the lowest cumulative rate: 190.5 per 100,000.
- Wyoming has the highest proportion of cases in children: 27.7%.
- New Jersey has the lowest proportion of child cases: 4.6%.
There were no COVID-19–related deaths in children reported the week ending Oct. 22, so the total number remains at 120, which is just 0.06% of the total for all ages, based on data from 42 states and New York City. Hospitalization figures put admissions at almost 5,600 in children, or 1.7% of all hospitalizations, although those data come from just 24 states and New York City, the AAP and CHA said.
COVID-19: Thromboembolic events high despite prophylaxis
in a new large observational U.S. study.
“Despite very high rate of antithrombotic prophylaxis there were a high rate of thromboembolic events suggesting that we are probably not providing enough thromboprophylaxis,” lead author Gregory Piazza, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Standard prophylaxis as recommended in the guidelines is a low dose of low-molecular-weight heparin once daily, but these results suggest [patients] probably need higher doses,” he added.
However, Dr. Piazza cautioned that this is an observational study and randomized trials are needed to make changes in treatment strategies. Several such trials are currently underway.
The current study was published online ahead of print in the Nov. 3 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Rates similar to other very sick patients
The study showed that while thromboembolic complications were high, they were not as high as seen in some of the earlier studies from Asia and Europe, Dr. Piazza noted.
“The numbers we were seeing in early reports were so high we couldn’t figure out how that was possible,” he said. “Our study suggests that, in a U.S. population receiving thromboprophylaxis, the rate of thromboembolic complications [are] more in line with what we would expect to see in other very sick patients who end up in ICU.”
He suggested that the very high rates of thromboembolic complications in the early studies from Asia may have been because of the lack of thromboprophylaxis, which is not routine in hospitalized patients there. “Some of the earlier studies also used routine ultrasound and so picked up asymptomatic thrombotic events, which was not the case in our study. So our results are more representative of the U.S. population.”
Dr. Piazza attributed the high rate of thromboembolic complications being reported with COVID-19 to the sheer number of very sick patients being admitted to the hospital.
“We are accustomed to seeing a rare case of thrombosis despite prophylaxis in hospitalized patients, but we are seeing more in COVID patients. This is probably just because we have more critically ill patients,” he said.
“We are seeing an incredible influx of patients to the ICU that we have never experienced before, so the increase in thromboembolic complications is more obvious. In prior years we probably haven’t had enough critically ill patients at any one time to raise the flag about thromboprophylaxis,” he commented.
The study also found a high rate of cardiovascular complications. They are seeing an increase in the risk of MI, which is to be expected in such sick patients, but they also see quite a bit of new atrial fibrillation, myocarditis, and heart failure in patients who don’t always have underlying cardiovascular disease, he said.
“So this virus does appear to have a predilection to causing cardiovascular complications, but this is probably because it is making patients so sick,” Dr. Piazza said. “If flu was this virulent and resulted in such high rates of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), we would probably see similar cardiovascular complication rates.”
For the current report, the researchers analyzed a retrospective cohort of 1,114 patients with COVID-19 diagnosed through the Mass General Brigham integrated health network. Of these, 170 had been admitted to the ICU, 229 had been hospitalized but not treated in ICU, and 715 were outpatients. In terms of ethnicity, 22% were Hispanic/Latino and 44% were non-White.
Cardiovascular risk factors were common, with 36% of patients having hypertension, 29% hyperlipidemia, and 18% diabetes. Prophylactic anticoagulation was prescribed in 89% of patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care cohort and 85% of those in the hospitalized non–intensive care setting.
Results showed that major arterial or venous thromboembolism (VTE) occurred in 35% of the intensive care cohort, 2.6% of those hospitalized but not treated in ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
Major adverse cardiovascular events occurred in 46% of the intensive care cohort, 6.1% of those hospitalized but non-ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
Symptomatic VTE occurred in 27% of those admitted to ICU, 2.2% of those hospitalized but non-ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
“We found that outpatients had a very low rate of thromboembolic complications, with the vast majority of the risk being in hospitalized patients, especially those in ICU,” Dr. Piazza said.
“These results suggest that we don’t need routine thromboprophylaxis for all outpatients with COVID-19, but there will probably be some patients who need it – those with risk factors for thromboembolism.”
Catheter- and device-associated deep vein thrombosis accounted for 76.9% of the DVTs observed in the study.
“Our finding of high frequency of catheter-associated DVT supports the judicious use of central venous catheters that have been widely implemented, especially in the ICU, to minimize recurrent health care team exposure and facilitate monitoring,” the researchers wrote.
ARDS biggest risk factor
Of all the markers of disease severity, the presence of ARDS had the strongest association with adverse outcomes, including major arterial or VTE, major adverse cardiovascular events, symptomatic VTE, and death.
“The severe inflammatory state associated with ARDS and other complications of COVID-19 and its resultant hypercoagulability may explain, at least in part, the high frequency of thromboembolic events. Improved risk stratification, utilizing biochemical markers of inflammation and activated coagulation as well as clinical indicators, such as ARDS, may play an important role in the early identification of patients with an increased likelihood of developing symptomatic VTE or arterial thrombosis,” the researchers wrote. “They may benefit from full- or intermediate-intensity antithrombotic therapy rather than prophylactic anticoagulation.”
They point out that this study provides a cross-sectional view of the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 in a large health care network, consisting of two academic medical centers serving the greater Boston area, several community hospitals, and numerous outpatient care sites.
“The study incorporates a wide scope of clinically meaningful cardiovascular endpoints and utilizes a rigorous process of event adjudication. Although data on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU have been the subject of most reports, our study provides insights into the broad spectrum of all hospitalized and outpatient populations,” the authors noted.
“The high frequency of arterial or venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients despite routine thromboprophylaxis suggests the need for improved risk stratification and enhanced preventive efforts,” they concluded.
The study is continuing, and the researchers expect to have data on 10,000 patients by the end of winter.
Wait for randomized trials
In an accompanying editorial, Robert McBane, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that these data provide important real-world arterial and venous thrombotic event rates across a large, integrated health care network and an experienced roster of clinician-scientists devoted to thrombosis research.
Noting that whether to interpret these results as alarming or reassuring requires a comparison of expected thromboembolic event rates separate from the pandemic, he pointed out that, while the overall VTE rate among ICU patients was high, the vast majority of these events were attributable to central venous lines, and apart from these, the event rates do not appear inflated relative to prior published incidence rates from the pre–COVID-19 era.
“It is therefore important to resist the urge to overprevent or overtreat patients and expose them to the serious risks of major bleeding,” Dr. McBane wrote, adding that “the systematized approach to delivery of guideline-driven VTE prophylaxis across this large, integrated health network likely contributed to the relatively low rates of serious thrombotic outcomes reported.”
He further noted that, as the majority of VTE events were related to central venous lines in ICU patients, “this underscores the importance of a bundled care approach to central venous line management with daily assessment of the continued necessity of central access.
“A number of important clinical trials aimed at optimizing thromboprophylaxis during hospitalization, following hospital dismissal, and in ambulatory settings are underway. Until available, the lessons of thoughtful anticoagulant prophylaxis and treatment guidelines harvested from years of clinical research appear to apply,” he concluded.
This study was funded, in part, by a research grant from Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Piazza has received research grant support from EKOS Corporation, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Portola Pharmaceuticals, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals; and has received consulting fees from Amgen, Pfizer, Boston Scientific, Agile, and Thrombolex. Dr. McBane reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new large observational U.S. study.
“Despite very high rate of antithrombotic prophylaxis there were a high rate of thromboembolic events suggesting that we are probably not providing enough thromboprophylaxis,” lead author Gregory Piazza, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Standard prophylaxis as recommended in the guidelines is a low dose of low-molecular-weight heparin once daily, but these results suggest [patients] probably need higher doses,” he added.
However, Dr. Piazza cautioned that this is an observational study and randomized trials are needed to make changes in treatment strategies. Several such trials are currently underway.
The current study was published online ahead of print in the Nov. 3 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Rates similar to other very sick patients
The study showed that while thromboembolic complications were high, they were not as high as seen in some of the earlier studies from Asia and Europe, Dr. Piazza noted.
“The numbers we were seeing in early reports were so high we couldn’t figure out how that was possible,” he said. “Our study suggests that, in a U.S. population receiving thromboprophylaxis, the rate of thromboembolic complications [are] more in line with what we would expect to see in other very sick patients who end up in ICU.”
He suggested that the very high rates of thromboembolic complications in the early studies from Asia may have been because of the lack of thromboprophylaxis, which is not routine in hospitalized patients there. “Some of the earlier studies also used routine ultrasound and so picked up asymptomatic thrombotic events, which was not the case in our study. So our results are more representative of the U.S. population.”
Dr. Piazza attributed the high rate of thromboembolic complications being reported with COVID-19 to the sheer number of very sick patients being admitted to the hospital.
“We are accustomed to seeing a rare case of thrombosis despite prophylaxis in hospitalized patients, but we are seeing more in COVID patients. This is probably just because we have more critically ill patients,” he said.
“We are seeing an incredible influx of patients to the ICU that we have never experienced before, so the increase in thromboembolic complications is more obvious. In prior years we probably haven’t had enough critically ill patients at any one time to raise the flag about thromboprophylaxis,” he commented.
The study also found a high rate of cardiovascular complications. They are seeing an increase in the risk of MI, which is to be expected in such sick patients, but they also see quite a bit of new atrial fibrillation, myocarditis, and heart failure in patients who don’t always have underlying cardiovascular disease, he said.
“So this virus does appear to have a predilection to causing cardiovascular complications, but this is probably because it is making patients so sick,” Dr. Piazza said. “If flu was this virulent and resulted in such high rates of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), we would probably see similar cardiovascular complication rates.”
For the current report, the researchers analyzed a retrospective cohort of 1,114 patients with COVID-19 diagnosed through the Mass General Brigham integrated health network. Of these, 170 had been admitted to the ICU, 229 had been hospitalized but not treated in ICU, and 715 were outpatients. In terms of ethnicity, 22% were Hispanic/Latino and 44% were non-White.
Cardiovascular risk factors were common, with 36% of patients having hypertension, 29% hyperlipidemia, and 18% diabetes. Prophylactic anticoagulation was prescribed in 89% of patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care cohort and 85% of those in the hospitalized non–intensive care setting.
Results showed that major arterial or venous thromboembolism (VTE) occurred in 35% of the intensive care cohort, 2.6% of those hospitalized but not treated in ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
Major adverse cardiovascular events occurred in 46% of the intensive care cohort, 6.1% of those hospitalized but non-ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
Symptomatic VTE occurred in 27% of those admitted to ICU, 2.2% of those hospitalized but non-ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
“We found that outpatients had a very low rate of thromboembolic complications, with the vast majority of the risk being in hospitalized patients, especially those in ICU,” Dr. Piazza said.
“These results suggest that we don’t need routine thromboprophylaxis for all outpatients with COVID-19, but there will probably be some patients who need it – those with risk factors for thromboembolism.”
Catheter- and device-associated deep vein thrombosis accounted for 76.9% of the DVTs observed in the study.
“Our finding of high frequency of catheter-associated DVT supports the judicious use of central venous catheters that have been widely implemented, especially in the ICU, to minimize recurrent health care team exposure and facilitate monitoring,” the researchers wrote.
ARDS biggest risk factor
Of all the markers of disease severity, the presence of ARDS had the strongest association with adverse outcomes, including major arterial or VTE, major adverse cardiovascular events, symptomatic VTE, and death.
“The severe inflammatory state associated with ARDS and other complications of COVID-19 and its resultant hypercoagulability may explain, at least in part, the high frequency of thromboembolic events. Improved risk stratification, utilizing biochemical markers of inflammation and activated coagulation as well as clinical indicators, such as ARDS, may play an important role in the early identification of patients with an increased likelihood of developing symptomatic VTE or arterial thrombosis,” the researchers wrote. “They may benefit from full- or intermediate-intensity antithrombotic therapy rather than prophylactic anticoagulation.”
They point out that this study provides a cross-sectional view of the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 in a large health care network, consisting of two academic medical centers serving the greater Boston area, several community hospitals, and numerous outpatient care sites.
“The study incorporates a wide scope of clinically meaningful cardiovascular endpoints and utilizes a rigorous process of event adjudication. Although data on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU have been the subject of most reports, our study provides insights into the broad spectrum of all hospitalized and outpatient populations,” the authors noted.
“The high frequency of arterial or venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients despite routine thromboprophylaxis suggests the need for improved risk stratification and enhanced preventive efforts,” they concluded.
The study is continuing, and the researchers expect to have data on 10,000 patients by the end of winter.
Wait for randomized trials
In an accompanying editorial, Robert McBane, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that these data provide important real-world arterial and venous thrombotic event rates across a large, integrated health care network and an experienced roster of clinician-scientists devoted to thrombosis research.
Noting that whether to interpret these results as alarming or reassuring requires a comparison of expected thromboembolic event rates separate from the pandemic, he pointed out that, while the overall VTE rate among ICU patients was high, the vast majority of these events were attributable to central venous lines, and apart from these, the event rates do not appear inflated relative to prior published incidence rates from the pre–COVID-19 era.
“It is therefore important to resist the urge to overprevent or overtreat patients and expose them to the serious risks of major bleeding,” Dr. McBane wrote, adding that “the systematized approach to delivery of guideline-driven VTE prophylaxis across this large, integrated health network likely contributed to the relatively low rates of serious thrombotic outcomes reported.”
He further noted that, as the majority of VTE events were related to central venous lines in ICU patients, “this underscores the importance of a bundled care approach to central venous line management with daily assessment of the continued necessity of central access.
“A number of important clinical trials aimed at optimizing thromboprophylaxis during hospitalization, following hospital dismissal, and in ambulatory settings are underway. Until available, the lessons of thoughtful anticoagulant prophylaxis and treatment guidelines harvested from years of clinical research appear to apply,” he concluded.
This study was funded, in part, by a research grant from Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Piazza has received research grant support from EKOS Corporation, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Portola Pharmaceuticals, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals; and has received consulting fees from Amgen, Pfizer, Boston Scientific, Agile, and Thrombolex. Dr. McBane reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
in a new large observational U.S. study.
“Despite very high rate of antithrombotic prophylaxis there were a high rate of thromboembolic events suggesting that we are probably not providing enough thromboprophylaxis,” lead author Gregory Piazza, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, said in an interview.
“Standard prophylaxis as recommended in the guidelines is a low dose of low-molecular-weight heparin once daily, but these results suggest [patients] probably need higher doses,” he added.
However, Dr. Piazza cautioned that this is an observational study and randomized trials are needed to make changes in treatment strategies. Several such trials are currently underway.
The current study was published online ahead of print in the Nov. 3 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Rates similar to other very sick patients
The study showed that while thromboembolic complications were high, they were not as high as seen in some of the earlier studies from Asia and Europe, Dr. Piazza noted.
“The numbers we were seeing in early reports were so high we couldn’t figure out how that was possible,” he said. “Our study suggests that, in a U.S. population receiving thromboprophylaxis, the rate of thromboembolic complications [are] more in line with what we would expect to see in other very sick patients who end up in ICU.”
He suggested that the very high rates of thromboembolic complications in the early studies from Asia may have been because of the lack of thromboprophylaxis, which is not routine in hospitalized patients there. “Some of the earlier studies also used routine ultrasound and so picked up asymptomatic thrombotic events, which was not the case in our study. So our results are more representative of the U.S. population.”
Dr. Piazza attributed the high rate of thromboembolic complications being reported with COVID-19 to the sheer number of very sick patients being admitted to the hospital.
“We are accustomed to seeing a rare case of thrombosis despite prophylaxis in hospitalized patients, but we are seeing more in COVID patients. This is probably just because we have more critically ill patients,” he said.
“We are seeing an incredible influx of patients to the ICU that we have never experienced before, so the increase in thromboembolic complications is more obvious. In prior years we probably haven’t had enough critically ill patients at any one time to raise the flag about thromboprophylaxis,” he commented.
The study also found a high rate of cardiovascular complications. They are seeing an increase in the risk of MI, which is to be expected in such sick patients, but they also see quite a bit of new atrial fibrillation, myocarditis, and heart failure in patients who don’t always have underlying cardiovascular disease, he said.
“So this virus does appear to have a predilection to causing cardiovascular complications, but this is probably because it is making patients so sick,” Dr. Piazza said. “If flu was this virulent and resulted in such high rates of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), we would probably see similar cardiovascular complication rates.”
For the current report, the researchers analyzed a retrospective cohort of 1,114 patients with COVID-19 diagnosed through the Mass General Brigham integrated health network. Of these, 170 had been admitted to the ICU, 229 had been hospitalized but not treated in ICU, and 715 were outpatients. In terms of ethnicity, 22% were Hispanic/Latino and 44% were non-White.
Cardiovascular risk factors were common, with 36% of patients having hypertension, 29% hyperlipidemia, and 18% diabetes. Prophylactic anticoagulation was prescribed in 89% of patients with COVID-19 in the intensive care cohort and 85% of those in the hospitalized non–intensive care setting.
Results showed that major arterial or venous thromboembolism (VTE) occurred in 35% of the intensive care cohort, 2.6% of those hospitalized but not treated in ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
Major adverse cardiovascular events occurred in 46% of the intensive care cohort, 6.1% of those hospitalized but non-ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
Symptomatic VTE occurred in 27% of those admitted to ICU, 2.2% of those hospitalized but non-ICU, and 0% of outpatients.
“We found that outpatients had a very low rate of thromboembolic complications, with the vast majority of the risk being in hospitalized patients, especially those in ICU,” Dr. Piazza said.
“These results suggest that we don’t need routine thromboprophylaxis for all outpatients with COVID-19, but there will probably be some patients who need it – those with risk factors for thromboembolism.”
Catheter- and device-associated deep vein thrombosis accounted for 76.9% of the DVTs observed in the study.
“Our finding of high frequency of catheter-associated DVT supports the judicious use of central venous catheters that have been widely implemented, especially in the ICU, to minimize recurrent health care team exposure and facilitate monitoring,” the researchers wrote.
ARDS biggest risk factor
Of all the markers of disease severity, the presence of ARDS had the strongest association with adverse outcomes, including major arterial or VTE, major adverse cardiovascular events, symptomatic VTE, and death.
“The severe inflammatory state associated with ARDS and other complications of COVID-19 and its resultant hypercoagulability may explain, at least in part, the high frequency of thromboembolic events. Improved risk stratification, utilizing biochemical markers of inflammation and activated coagulation as well as clinical indicators, such as ARDS, may play an important role in the early identification of patients with an increased likelihood of developing symptomatic VTE or arterial thrombosis,” the researchers wrote. “They may benefit from full- or intermediate-intensity antithrombotic therapy rather than prophylactic anticoagulation.”
They point out that this study provides a cross-sectional view of the cardiovascular complications of COVID-19 in a large health care network, consisting of two academic medical centers serving the greater Boston area, several community hospitals, and numerous outpatient care sites.
“The study incorporates a wide scope of clinically meaningful cardiovascular endpoints and utilizes a rigorous process of event adjudication. Although data on patients with COVID-19 in the ICU have been the subject of most reports, our study provides insights into the broad spectrum of all hospitalized and outpatient populations,” the authors noted.
“The high frequency of arterial or venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients despite routine thromboprophylaxis suggests the need for improved risk stratification and enhanced preventive efforts,” they concluded.
The study is continuing, and the researchers expect to have data on 10,000 patients by the end of winter.
Wait for randomized trials
In an accompanying editorial, Robert McBane, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that these data provide important real-world arterial and venous thrombotic event rates across a large, integrated health care network and an experienced roster of clinician-scientists devoted to thrombosis research.
Noting that whether to interpret these results as alarming or reassuring requires a comparison of expected thromboembolic event rates separate from the pandemic, he pointed out that, while the overall VTE rate among ICU patients was high, the vast majority of these events were attributable to central venous lines, and apart from these, the event rates do not appear inflated relative to prior published incidence rates from the pre–COVID-19 era.
“It is therefore important to resist the urge to overprevent or overtreat patients and expose them to the serious risks of major bleeding,” Dr. McBane wrote, adding that “the systematized approach to delivery of guideline-driven VTE prophylaxis across this large, integrated health network likely contributed to the relatively low rates of serious thrombotic outcomes reported.”
He further noted that, as the majority of VTE events were related to central venous lines in ICU patients, “this underscores the importance of a bundled care approach to central venous line management with daily assessment of the continued necessity of central access.
“A number of important clinical trials aimed at optimizing thromboprophylaxis during hospitalization, following hospital dismissal, and in ambulatory settings are underway. Until available, the lessons of thoughtful anticoagulant prophylaxis and treatment guidelines harvested from years of clinical research appear to apply,” he concluded.
This study was funded, in part, by a research grant from Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Piazza has received research grant support from EKOS Corporation, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/Pfizer, Portola Pharmaceuticals, and Janssen Pharmaceuticals; and has received consulting fees from Amgen, Pfizer, Boston Scientific, Agile, and Thrombolex. Dr. McBane reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.