User login
Should Hospitalists Who Fail to Provide a Standard of Care Be Paid for Subsequent Care?
A 72-year-old male with a history of CHF is admitted for elective total hip arthroplasty. On postoperative day one, he develops dyspnea and hypoxia, and is diagnosed with acute pulmonary edema by the hospitalist co-managing his care. Furosemide is prescribed, and he improves, and by day four is ready for discharge following another dose of diuretics. Overnight, he develops acute onset of shortness of breath and is diagnosed with a pulmonary embolism (PE). Under new regulations, the hospital will not be reimbursed for the extra cost associated with subsequent patient care. Should the hospitalist be paid for the subsequent care?
PRO
Nonpayment won’t improve quality or significantly decrease costs
The real essence of the question raised in the clinical case above is “Should doctors profit from errors?” The answer might be “It’s better than the alternative.” Allow me to explain. There essentially are two reasons to withhold payment in this scenario: one, as a mechanism for promoting quality; two, as a mechanism for decreasing costs to the payor.
The quality argument assumes the physician will deliver higher-quality care (i.e., prescribe chemical thromboprophylaxis) if a threat of nonpayment exists. This concept is simply hogwash. If expensive medical malpractice threats fail as quality-improvement (QI) mechanisms, it is absurd to think withholding a few subsequent-care charges will generate better results.
The key issue is the type of error involved. As defined by Lucien Leape, MD, in his celebrated 1994 article on medical errors, “mistakes” reflect failures during attentional behaviors, or incorrect choices.1 “Slips” reflect lapses in concentration. “Slips occur in the face of competing sensory or emotional distractions, fatigue, and stress,” and “reducing the risk of slips requires attention to the designs of protocols, devices, and work environments.”
Misjudging the type of error—in this case, a slip (find me a hospitalist who doesn’t know total hip arthroplasty requires thrombophrophylaxis)—and misapplying corrective actions will have little to no effect on outcomes. Thus, pay-withholding schemes can have a negative net effect by diverting resources from QI projects that truly improve patient outcomes.
Withholding payment in this case generates approximately $160 in direct savings to the payor (assuming Medicare payments for one 99233 and two 99232 subsequent care visits), yet the operational costs are not negligible and must be factored into the equation. The payor needs to first determine who is truly at fault: the hospitalist or the orthopedic surgeon. Answering that question requires the payor to review the co-management agreement, perhaps aided by an attorney. That’s a costly endeavor.
For the sake of argument, let’s assume in this case the hospitalist is at fault. The next step is determining if the hospitalist who failed to prescribe prophylaxis prior to the PE is the same hospitalist caring for the patient after the PE. It is inappropriate to withhold payment to hospitalist A if hospitalist B made the error. Again, significant manpower will be required to determine fault, as this is not information one finds on a UB-04 claim form submitted to Medicare.
Further eroding the $160 savings is the cost of determining whether a contraindication exists: Bleeding ulcer? Subdural hematoma? Heparinoid allergy? Let us not forget the additional costs in copying, shipping, warehousing, and eventual shredding of the records. One can readily see that the operational costs can quickly negate the $160 anticipated savings. In fact, it’s likely a negative return on investment.
Clearly, withholding payment in this scenario is an ineffective mechanism for improving quality or decreasing cost. I am not generally a proponent of rewarding failure, and perhaps as we usher in a new era of healthcare reform, the system will be redesigned in such a way that better aligns quality and cost-control measures. However, under the current system, payment denial as outlined above likely does more harm than good.
CON
Withhold payment when medical errors are easily identifiable
When I first learned of the proposal to withhold Medicare payment for hospital-acquired conditions (HACs), I had mixed emotions. On the one hand, I firmly believe that physicians should be accountable for their work; on the other hand, this policy seems to conflict sharply with the “no blame” mantra that has been prevalent in patient safety for more than a decade.2 More recently, though, many have argued for balancing the pursuit of system fixes for quality and patient-safety issues with the development of a culture of accountability.3
In theory, the HACs should meet the following criteria: They should be high-cost conditions, high-volume conditions, or both; they should be identifiable through ICD-9-CM coding as complicating conditions (CCs) or major complicating conditions (MCCs) that result in a higher-paying MS-DRG; and they should be reasonably preventable through the application of evidence-based guidelines. Some HACs are jaw-dropping lapses in care (e.g., leaving foreign bodies in during surgery). Other HACs seem to me to be much less preventable, especially fall injuries and catheter-associated urinary tract infections (UTIs). Several experts have written eloquently regarding the limitations of these new measures, particularly emphasizing the potential for increased administrative burden on hospitals and the potential for unintended consequences.4,5
However, in the case described above involving a hospitalist, I have no reservations in limiting payment to the provider. To me, failing to prescribe VTE prophylaxis in an elderly, immobilized, post-op hip replacement patient with a CHF exacerbation is the hospitalist’s equivalent to a surgeon leaving behind a sponge in an appendectomy. It also meets the elements outlined in the HAC withholding program:
- It is high-cost. The 2007 MS-DRG payment for elective hip arthroplasty was $9,863, but adding an MCC increased that cost by one-third.6
- It is readily identifiable, though one concern might be that hospitals would perform unnecessary pre-operative testing to identify asymptomatic DVT, incurring increased testing and treatment costs and increasing the incidence of bleeding complications.
- It is very preventable. Without thromboprophylaxis, 40% to 60% of hip arthroplasty patients will develop an asymptomatic DVT, and 1 in 300 will die from a PE. However, such fatal events are exceedingly rare with appropriate prevention.7
Ultimately, I think a policy of nonpayment for this case keeps with the culture of accountability we need to foster in healthcare. The financial implications of nonpayment will drive hospital innovation and force the hospital to police provider behavior in more effective ways. This is likely to be a painful process, similar to the tribulations experienced with implementing pay-for-performance programs. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) needs to be flexible in adding—and removing—new HACs based on good evidence.
Regardless, the goal of achieving a safer, more effective healthcare system remains.
References
- Leape LL. Error in medicine. JAMA. 1994;272(23):1851-1857.
- Institute of Medicine. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Healthcare System. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2000.
- Wachter RM, Pronovost PJ. Balancing “no blame” with accountability in patient safety. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1401-1406.
- Saint S, Meddings JA, Calfee D, Kowalski CP, Krein SL. Catheter-associated urinary tract infection and the Medicare rule changes. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(12):877-884.
- Inouye SK, Brown CJ, Tinetti ME. Medicare nonpayment, hospital falls, and unintended consequences. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(23):2390-2393.
- Wachter RM, Foster NE, Dudley RA. Medicare’s decision to withhold payment for hospital errors: the devil is in the det. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(2):116-123.
- Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):381S-453S.
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not represent those of SHM or The Hospitalist.
A 72-year-old male with a history of CHF is admitted for elective total hip arthroplasty. On postoperative day one, he develops dyspnea and hypoxia, and is diagnosed with acute pulmonary edema by the hospitalist co-managing his care. Furosemide is prescribed, and he improves, and by day four is ready for discharge following another dose of diuretics. Overnight, he develops acute onset of shortness of breath and is diagnosed with a pulmonary embolism (PE). Under new regulations, the hospital will not be reimbursed for the extra cost associated with subsequent patient care. Should the hospitalist be paid for the subsequent care?
PRO
Nonpayment won’t improve quality or significantly decrease costs
The real essence of the question raised in the clinical case above is “Should doctors profit from errors?” The answer might be “It’s better than the alternative.” Allow me to explain. There essentially are two reasons to withhold payment in this scenario: one, as a mechanism for promoting quality; two, as a mechanism for decreasing costs to the payor.
The quality argument assumes the physician will deliver higher-quality care (i.e., prescribe chemical thromboprophylaxis) if a threat of nonpayment exists. This concept is simply hogwash. If expensive medical malpractice threats fail as quality-improvement (QI) mechanisms, it is absurd to think withholding a few subsequent-care charges will generate better results.
The key issue is the type of error involved. As defined by Lucien Leape, MD, in his celebrated 1994 article on medical errors, “mistakes” reflect failures during attentional behaviors, or incorrect choices.1 “Slips” reflect lapses in concentration. “Slips occur in the face of competing sensory or emotional distractions, fatigue, and stress,” and “reducing the risk of slips requires attention to the designs of protocols, devices, and work environments.”
Misjudging the type of error—in this case, a slip (find me a hospitalist who doesn’t know total hip arthroplasty requires thrombophrophylaxis)—and misapplying corrective actions will have little to no effect on outcomes. Thus, pay-withholding schemes can have a negative net effect by diverting resources from QI projects that truly improve patient outcomes.
Withholding payment in this case generates approximately $160 in direct savings to the payor (assuming Medicare payments for one 99233 and two 99232 subsequent care visits), yet the operational costs are not negligible and must be factored into the equation. The payor needs to first determine who is truly at fault: the hospitalist or the orthopedic surgeon. Answering that question requires the payor to review the co-management agreement, perhaps aided by an attorney. That’s a costly endeavor.
For the sake of argument, let’s assume in this case the hospitalist is at fault. The next step is determining if the hospitalist who failed to prescribe prophylaxis prior to the PE is the same hospitalist caring for the patient after the PE. It is inappropriate to withhold payment to hospitalist A if hospitalist B made the error. Again, significant manpower will be required to determine fault, as this is not information one finds on a UB-04 claim form submitted to Medicare.
Further eroding the $160 savings is the cost of determining whether a contraindication exists: Bleeding ulcer? Subdural hematoma? Heparinoid allergy? Let us not forget the additional costs in copying, shipping, warehousing, and eventual shredding of the records. One can readily see that the operational costs can quickly negate the $160 anticipated savings. In fact, it’s likely a negative return on investment.
Clearly, withholding payment in this scenario is an ineffective mechanism for improving quality or decreasing cost. I am not generally a proponent of rewarding failure, and perhaps as we usher in a new era of healthcare reform, the system will be redesigned in such a way that better aligns quality and cost-control measures. However, under the current system, payment denial as outlined above likely does more harm than good.
CON
Withhold payment when medical errors are easily identifiable
When I first learned of the proposal to withhold Medicare payment for hospital-acquired conditions (HACs), I had mixed emotions. On the one hand, I firmly believe that physicians should be accountable for their work; on the other hand, this policy seems to conflict sharply with the “no blame” mantra that has been prevalent in patient safety for more than a decade.2 More recently, though, many have argued for balancing the pursuit of system fixes for quality and patient-safety issues with the development of a culture of accountability.3
In theory, the HACs should meet the following criteria: They should be high-cost conditions, high-volume conditions, or both; they should be identifiable through ICD-9-CM coding as complicating conditions (CCs) or major complicating conditions (MCCs) that result in a higher-paying MS-DRG; and they should be reasonably preventable through the application of evidence-based guidelines. Some HACs are jaw-dropping lapses in care (e.g., leaving foreign bodies in during surgery). Other HACs seem to me to be much less preventable, especially fall injuries and catheter-associated urinary tract infections (UTIs). Several experts have written eloquently regarding the limitations of these new measures, particularly emphasizing the potential for increased administrative burden on hospitals and the potential for unintended consequences.4,5
However, in the case described above involving a hospitalist, I have no reservations in limiting payment to the provider. To me, failing to prescribe VTE prophylaxis in an elderly, immobilized, post-op hip replacement patient with a CHF exacerbation is the hospitalist’s equivalent to a surgeon leaving behind a sponge in an appendectomy. It also meets the elements outlined in the HAC withholding program:
- It is high-cost. The 2007 MS-DRG payment for elective hip arthroplasty was $9,863, but adding an MCC increased that cost by one-third.6
- It is readily identifiable, though one concern might be that hospitals would perform unnecessary pre-operative testing to identify asymptomatic DVT, incurring increased testing and treatment costs and increasing the incidence of bleeding complications.
- It is very preventable. Without thromboprophylaxis, 40% to 60% of hip arthroplasty patients will develop an asymptomatic DVT, and 1 in 300 will die from a PE. However, such fatal events are exceedingly rare with appropriate prevention.7
Ultimately, I think a policy of nonpayment for this case keeps with the culture of accountability we need to foster in healthcare. The financial implications of nonpayment will drive hospital innovation and force the hospital to police provider behavior in more effective ways. This is likely to be a painful process, similar to the tribulations experienced with implementing pay-for-performance programs. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) needs to be flexible in adding—and removing—new HACs based on good evidence.
Regardless, the goal of achieving a safer, more effective healthcare system remains.
References
- Leape LL. Error in medicine. JAMA. 1994;272(23):1851-1857.
- Institute of Medicine. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Healthcare System. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2000.
- Wachter RM, Pronovost PJ. Balancing “no blame” with accountability in patient safety. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1401-1406.
- Saint S, Meddings JA, Calfee D, Kowalski CP, Krein SL. Catheter-associated urinary tract infection and the Medicare rule changes. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(12):877-884.
- Inouye SK, Brown CJ, Tinetti ME. Medicare nonpayment, hospital falls, and unintended consequences. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(23):2390-2393.
- Wachter RM, Foster NE, Dudley RA. Medicare’s decision to withhold payment for hospital errors: the devil is in the det. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(2):116-123.
- Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):381S-453S.
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not represent those of SHM or The Hospitalist.
A 72-year-old male with a history of CHF is admitted for elective total hip arthroplasty. On postoperative day one, he develops dyspnea and hypoxia, and is diagnosed with acute pulmonary edema by the hospitalist co-managing his care. Furosemide is prescribed, and he improves, and by day four is ready for discharge following another dose of diuretics. Overnight, he develops acute onset of shortness of breath and is diagnosed with a pulmonary embolism (PE). Under new regulations, the hospital will not be reimbursed for the extra cost associated with subsequent patient care. Should the hospitalist be paid for the subsequent care?
PRO
Nonpayment won’t improve quality or significantly decrease costs
The real essence of the question raised in the clinical case above is “Should doctors profit from errors?” The answer might be “It’s better than the alternative.” Allow me to explain. There essentially are two reasons to withhold payment in this scenario: one, as a mechanism for promoting quality; two, as a mechanism for decreasing costs to the payor.
The quality argument assumes the physician will deliver higher-quality care (i.e., prescribe chemical thromboprophylaxis) if a threat of nonpayment exists. This concept is simply hogwash. If expensive medical malpractice threats fail as quality-improvement (QI) mechanisms, it is absurd to think withholding a few subsequent-care charges will generate better results.
The key issue is the type of error involved. As defined by Lucien Leape, MD, in his celebrated 1994 article on medical errors, “mistakes” reflect failures during attentional behaviors, or incorrect choices.1 “Slips” reflect lapses in concentration. “Slips occur in the face of competing sensory or emotional distractions, fatigue, and stress,” and “reducing the risk of slips requires attention to the designs of protocols, devices, and work environments.”
Misjudging the type of error—in this case, a slip (find me a hospitalist who doesn’t know total hip arthroplasty requires thrombophrophylaxis)—and misapplying corrective actions will have little to no effect on outcomes. Thus, pay-withholding schemes can have a negative net effect by diverting resources from QI projects that truly improve patient outcomes.
Withholding payment in this case generates approximately $160 in direct savings to the payor (assuming Medicare payments for one 99233 and two 99232 subsequent care visits), yet the operational costs are not negligible and must be factored into the equation. The payor needs to first determine who is truly at fault: the hospitalist or the orthopedic surgeon. Answering that question requires the payor to review the co-management agreement, perhaps aided by an attorney. That’s a costly endeavor.
For the sake of argument, let’s assume in this case the hospitalist is at fault. The next step is determining if the hospitalist who failed to prescribe prophylaxis prior to the PE is the same hospitalist caring for the patient after the PE. It is inappropriate to withhold payment to hospitalist A if hospitalist B made the error. Again, significant manpower will be required to determine fault, as this is not information one finds on a UB-04 claim form submitted to Medicare.
Further eroding the $160 savings is the cost of determining whether a contraindication exists: Bleeding ulcer? Subdural hematoma? Heparinoid allergy? Let us not forget the additional costs in copying, shipping, warehousing, and eventual shredding of the records. One can readily see that the operational costs can quickly negate the $160 anticipated savings. In fact, it’s likely a negative return on investment.
Clearly, withholding payment in this scenario is an ineffective mechanism for improving quality or decreasing cost. I am not generally a proponent of rewarding failure, and perhaps as we usher in a new era of healthcare reform, the system will be redesigned in such a way that better aligns quality and cost-control measures. However, under the current system, payment denial as outlined above likely does more harm than good.
CON
Withhold payment when medical errors are easily identifiable
When I first learned of the proposal to withhold Medicare payment for hospital-acquired conditions (HACs), I had mixed emotions. On the one hand, I firmly believe that physicians should be accountable for their work; on the other hand, this policy seems to conflict sharply with the “no blame” mantra that has been prevalent in patient safety for more than a decade.2 More recently, though, many have argued for balancing the pursuit of system fixes for quality and patient-safety issues with the development of a culture of accountability.3
In theory, the HACs should meet the following criteria: They should be high-cost conditions, high-volume conditions, or both; they should be identifiable through ICD-9-CM coding as complicating conditions (CCs) or major complicating conditions (MCCs) that result in a higher-paying MS-DRG; and they should be reasonably preventable through the application of evidence-based guidelines. Some HACs are jaw-dropping lapses in care (e.g., leaving foreign bodies in during surgery). Other HACs seem to me to be much less preventable, especially fall injuries and catheter-associated urinary tract infections (UTIs). Several experts have written eloquently regarding the limitations of these new measures, particularly emphasizing the potential for increased administrative burden on hospitals and the potential for unintended consequences.4,5
However, in the case described above involving a hospitalist, I have no reservations in limiting payment to the provider. To me, failing to prescribe VTE prophylaxis in an elderly, immobilized, post-op hip replacement patient with a CHF exacerbation is the hospitalist’s equivalent to a surgeon leaving behind a sponge in an appendectomy. It also meets the elements outlined in the HAC withholding program:
- It is high-cost. The 2007 MS-DRG payment for elective hip arthroplasty was $9,863, but adding an MCC increased that cost by one-third.6
- It is readily identifiable, though one concern might be that hospitals would perform unnecessary pre-operative testing to identify asymptomatic DVT, incurring increased testing and treatment costs and increasing the incidence of bleeding complications.
- It is very preventable. Without thromboprophylaxis, 40% to 60% of hip arthroplasty patients will develop an asymptomatic DVT, and 1 in 300 will die from a PE. However, such fatal events are exceedingly rare with appropriate prevention.7
Ultimately, I think a policy of nonpayment for this case keeps with the culture of accountability we need to foster in healthcare. The financial implications of nonpayment will drive hospital innovation and force the hospital to police provider behavior in more effective ways. This is likely to be a painful process, similar to the tribulations experienced with implementing pay-for-performance programs. The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) needs to be flexible in adding—and removing—new HACs based on good evidence.
Regardless, the goal of achieving a safer, more effective healthcare system remains.
References
- Leape LL. Error in medicine. JAMA. 1994;272(23):1851-1857.
- Institute of Medicine. To Err Is Human: Building a Safer Healthcare System. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press; 2000.
- Wachter RM, Pronovost PJ. Balancing “no blame” with accountability in patient safety. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:1401-1406.
- Saint S, Meddings JA, Calfee D, Kowalski CP, Krein SL. Catheter-associated urinary tract infection and the Medicare rule changes. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(12):877-884.
- Inouye SK, Brown CJ, Tinetti ME. Medicare nonpayment, hospital falls, and unintended consequences. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(23):2390-2393.
- Wachter RM, Foster NE, Dudley RA. Medicare’s decision to withhold payment for hospital errors: the devil is in the det. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf. 2008;34(2):116-123.
- Geerts WH, Bergqvist D, Pineo GF, et al. Prevention of venous thromboembolism: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th Edition). Chest. 2008;133(6 Suppl):381S-453S.
The opinions expressed herein are those of the authors and do not represent those of SHM or The Hospitalist.
Admit Documentation
In light of the recent elimination of consultation codes from the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, physicians of all specialties are being asked to report initial hospital care services (99221-99223) for their first encounter with a patient.1 This leaves hospitalists with questions about the billing and financial implications of reporting admissions services.
Here’s a typical scenario: Dr. A admits a Medicare patient to the hospital from the ED for hyperglycemia and dehydration in the setting of uncontrolled diabetes. He performs and documents an initial hospital-care service on day one of the admission. On day two, another hospitalist, Dr. B, who works in the same HM group, sees the patient for the first time. What should each of the physicians report for their first encounter with the patient?
Each hospitalist should select the CPT code that best fits the service and their role in the case. Remember, only one physician is named “attending of record” or “admitting physician.”
When billing during the course of the hospitalization, consider all physicians of the same specialty in the same provider group as the “admitting physician/group.”
Admissions Service
On day one, Dr. A admits the patient. He performs and documents a comprehensive history, a comprehensive exam, and medical decision-making of high complexity. The documentation corresponds to the highest initial admission service, 99223. Given the recent Medicare billing changes, the attending of record is required to append modifier “AI” (principal physician of record) to the admission service (e.g., 99223-AI).
The purpose of this modifier is “to identify the physician who oversees the patient’s care from all other physicians who may be furnishing specialty care.”2 This modifier has no financial implications. It does not increase or decrease the payment associated with the reported visit level (i.e., 99223 is reimbursed at a national rate of approximately $190, with or without modifier AI).
Initial Encounter by Team Members
As previously stated, the elimination of consultation services requires physicians to report their initial hospital encounter with an initial hospital-care code (i.e., 99221-99223). However, Medicare states that “physicians in the same group practice who are in the same specialty must bill and be paid as though they were a single physician.”3 This means followup services performed on days subsequent to a group member’s initial admission service must be reported with subsequent hospital-care codes (99231-99233). Therefore, in the scenario above, Dr. B is obligated to report the appropriate subsequent hospital-care code for his patient encounter on day two.
Incomplete Documentation
Initial hospital-care services (99221-99223) require the physician to obtain, perform, and document the necessary elements of history, physical exam, and medical decision-making in support of the code reported on the claim. There are occasions when the physician’s documentation does not support the lowest code (i.e., 99221). A reasonable approach is to report the service with an unlisted E&M code (99499). “Unlisted” codes do not have a payor-recognized code description or fee. When reporting an unlisted code, the biller must manually enter a charge description (e.g., expanded problem-focused admissions service) and a fee. A payor-prompted request for documentation is likely before payment is made.
Some payors have more specific references to the situation and allow for options. Two options exist for coding services that do not meet the work and/or medical necessity requirements of 99221-99223: report an unlisted E&M service (99499); or report a subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233) that appropriately reflects physician work and medical necessity for the service, and avoids mandatory medical record submission and manual medical review.4
In fact, Medicare Administrator Contractor TrailBlazer Health’s Web site (www.trailblazerhealth.com) offers guidance to physicians who are unsure if subsequent hospital care is an appropriate choice for this dilemma: “TrailBlazer recognizes provider reluctance to miscode initial hospital care as subsequent hospital care. However, doing so is preferable in that it allows Medicare to process and pay the claims much more efficiently. For those concerned about miscoding these services, please understand that TrailBlazer will not find fault with providers who choose this option when records appropriately demonstrate the work and medical necessity of the subsequent code chosen.”4 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She also is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- CMS announces payment, policy changes for physicians services to Medicare beneficiaries in 2010. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/apps/media/ press/release.asp?Counter=3539&intNumPerPage=10&checkDate=&checkKey=&srchType=1&numDays=3500&srchOpt=0&srchData=&keywordType=All&chkNewsType=1%2C+2%2C+3%2C+4%2C+5&intPage=&showAll=&pYear=&year=&desc=&cboOrder=date. Accessed Nov. 12, 2009.
- Revisions to Consultation Services Payment Policy. Medicare Learning Network Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNMattersArticles/downloads/ MM6740.pdf. Accessed Jan. 16, 2010.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.5. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Jan. 16, 2010.
- Update-evaluation and management services formerly coded as consultations. Trailblazer Health Enterprises Web site. Available at: www.trailblazerhealth.com/Tools/Notices.aspx?DomainID=1. Accessed Jan. 17, 2010.
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2009;14-15.
In light of the recent elimination of consultation codes from the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, physicians of all specialties are being asked to report initial hospital care services (99221-99223) for their first encounter with a patient.1 This leaves hospitalists with questions about the billing and financial implications of reporting admissions services.
Here’s a typical scenario: Dr. A admits a Medicare patient to the hospital from the ED for hyperglycemia and dehydration in the setting of uncontrolled diabetes. He performs and documents an initial hospital-care service on day one of the admission. On day two, another hospitalist, Dr. B, who works in the same HM group, sees the patient for the first time. What should each of the physicians report for their first encounter with the patient?
Each hospitalist should select the CPT code that best fits the service and their role in the case. Remember, only one physician is named “attending of record” or “admitting physician.”
When billing during the course of the hospitalization, consider all physicians of the same specialty in the same provider group as the “admitting physician/group.”
Admissions Service
On day one, Dr. A admits the patient. He performs and documents a comprehensive history, a comprehensive exam, and medical decision-making of high complexity. The documentation corresponds to the highest initial admission service, 99223. Given the recent Medicare billing changes, the attending of record is required to append modifier “AI” (principal physician of record) to the admission service (e.g., 99223-AI).
The purpose of this modifier is “to identify the physician who oversees the patient’s care from all other physicians who may be furnishing specialty care.”2 This modifier has no financial implications. It does not increase or decrease the payment associated with the reported visit level (i.e., 99223 is reimbursed at a national rate of approximately $190, with or without modifier AI).
Initial Encounter by Team Members
As previously stated, the elimination of consultation services requires physicians to report their initial hospital encounter with an initial hospital-care code (i.e., 99221-99223). However, Medicare states that “physicians in the same group practice who are in the same specialty must bill and be paid as though they were a single physician.”3 This means followup services performed on days subsequent to a group member’s initial admission service must be reported with subsequent hospital-care codes (99231-99233). Therefore, in the scenario above, Dr. B is obligated to report the appropriate subsequent hospital-care code for his patient encounter on day two.
Incomplete Documentation
Initial hospital-care services (99221-99223) require the physician to obtain, perform, and document the necessary elements of history, physical exam, and medical decision-making in support of the code reported on the claim. There are occasions when the physician’s documentation does not support the lowest code (i.e., 99221). A reasonable approach is to report the service with an unlisted E&M code (99499). “Unlisted” codes do not have a payor-recognized code description or fee. When reporting an unlisted code, the biller must manually enter a charge description (e.g., expanded problem-focused admissions service) and a fee. A payor-prompted request for documentation is likely before payment is made.
Some payors have more specific references to the situation and allow for options. Two options exist for coding services that do not meet the work and/or medical necessity requirements of 99221-99223: report an unlisted E&M service (99499); or report a subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233) that appropriately reflects physician work and medical necessity for the service, and avoids mandatory medical record submission and manual medical review.4
In fact, Medicare Administrator Contractor TrailBlazer Health’s Web site (www.trailblazerhealth.com) offers guidance to physicians who are unsure if subsequent hospital care is an appropriate choice for this dilemma: “TrailBlazer recognizes provider reluctance to miscode initial hospital care as subsequent hospital care. However, doing so is preferable in that it allows Medicare to process and pay the claims much more efficiently. For those concerned about miscoding these services, please understand that TrailBlazer will not find fault with providers who choose this option when records appropriately demonstrate the work and medical necessity of the subsequent code chosen.”4 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She also is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- CMS announces payment, policy changes for physicians services to Medicare beneficiaries in 2010. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/apps/media/ press/release.asp?Counter=3539&intNumPerPage=10&checkDate=&checkKey=&srchType=1&numDays=3500&srchOpt=0&srchData=&keywordType=All&chkNewsType=1%2C+2%2C+3%2C+4%2C+5&intPage=&showAll=&pYear=&year=&desc=&cboOrder=date. Accessed Nov. 12, 2009.
- Revisions to Consultation Services Payment Policy. Medicare Learning Network Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNMattersArticles/downloads/ MM6740.pdf. Accessed Jan. 16, 2010.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.5. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Jan. 16, 2010.
- Update-evaluation and management services formerly coded as consultations. Trailblazer Health Enterprises Web site. Available at: www.trailblazerhealth.com/Tools/Notices.aspx?DomainID=1. Accessed Jan. 17, 2010.
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2009;14-15.
In light of the recent elimination of consultation codes from the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule, physicians of all specialties are being asked to report initial hospital care services (99221-99223) for their first encounter with a patient.1 This leaves hospitalists with questions about the billing and financial implications of reporting admissions services.
Here’s a typical scenario: Dr. A admits a Medicare patient to the hospital from the ED for hyperglycemia and dehydration in the setting of uncontrolled diabetes. He performs and documents an initial hospital-care service on day one of the admission. On day two, another hospitalist, Dr. B, who works in the same HM group, sees the patient for the first time. What should each of the physicians report for their first encounter with the patient?
Each hospitalist should select the CPT code that best fits the service and their role in the case. Remember, only one physician is named “attending of record” or “admitting physician.”
When billing during the course of the hospitalization, consider all physicians of the same specialty in the same provider group as the “admitting physician/group.”
Admissions Service
On day one, Dr. A admits the patient. He performs and documents a comprehensive history, a comprehensive exam, and medical decision-making of high complexity. The documentation corresponds to the highest initial admission service, 99223. Given the recent Medicare billing changes, the attending of record is required to append modifier “AI” (principal physician of record) to the admission service (e.g., 99223-AI).
The purpose of this modifier is “to identify the physician who oversees the patient’s care from all other physicians who may be furnishing specialty care.”2 This modifier has no financial implications. It does not increase or decrease the payment associated with the reported visit level (i.e., 99223 is reimbursed at a national rate of approximately $190, with or without modifier AI).
Initial Encounter by Team Members
As previously stated, the elimination of consultation services requires physicians to report their initial hospital encounter with an initial hospital-care code (i.e., 99221-99223). However, Medicare states that “physicians in the same group practice who are in the same specialty must bill and be paid as though they were a single physician.”3 This means followup services performed on days subsequent to a group member’s initial admission service must be reported with subsequent hospital-care codes (99231-99233). Therefore, in the scenario above, Dr. B is obligated to report the appropriate subsequent hospital-care code for his patient encounter on day two.
Incomplete Documentation
Initial hospital-care services (99221-99223) require the physician to obtain, perform, and document the necessary elements of history, physical exam, and medical decision-making in support of the code reported on the claim. There are occasions when the physician’s documentation does not support the lowest code (i.e., 99221). A reasonable approach is to report the service with an unlisted E&M code (99499). “Unlisted” codes do not have a payor-recognized code description or fee. When reporting an unlisted code, the biller must manually enter a charge description (e.g., expanded problem-focused admissions service) and a fee. A payor-prompted request for documentation is likely before payment is made.
Some payors have more specific references to the situation and allow for options. Two options exist for coding services that do not meet the work and/or medical necessity requirements of 99221-99223: report an unlisted E&M service (99499); or report a subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233) that appropriately reflects physician work and medical necessity for the service, and avoids mandatory medical record submission and manual medical review.4
In fact, Medicare Administrator Contractor TrailBlazer Health’s Web site (www.trailblazerhealth.com) offers guidance to physicians who are unsure if subsequent hospital care is an appropriate choice for this dilemma: “TrailBlazer recognizes provider reluctance to miscode initial hospital care as subsequent hospital care. However, doing so is preferable in that it allows Medicare to process and pay the claims much more efficiently. For those concerned about miscoding these services, please understand that TrailBlazer will not find fault with providers who choose this option when records appropriately demonstrate the work and medical necessity of the subsequent code chosen.”4 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She also is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- CMS announces payment, policy changes for physicians services to Medicare beneficiaries in 2010. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/apps/media/ press/release.asp?Counter=3539&intNumPerPage=10&checkDate=&checkKey=&srchType=1&numDays=3500&srchOpt=0&srchData=&keywordType=All&chkNewsType=1%2C+2%2C+3%2C+4%2C+5&intPage=&showAll=&pYear=&year=&desc=&cboOrder=date. Accessed Nov. 12, 2009.
- Revisions to Consultation Services Payment Policy. Medicare Learning Network Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNMattersArticles/downloads/ MM6740.pdf. Accessed Jan. 16, 2010.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.5. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Jan. 16, 2010.
- Update-evaluation and management services formerly coded as consultations. Trailblazer Health Enterprises Web site. Available at: www.trailblazerhealth.com/Tools/Notices.aspx?DomainID=1. Accessed Jan. 17, 2010.
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2009;14-15.
Patient Distribution
Editor’s note: This is the first of a three-part series.
My experience is that some, maybe even most, hospitalists tend to assume there is a standard or “right” way to organize things like work schedules, compensation, or even the assignment of patients among the group’s providers. Some will say things like “SHM says the best hospitalist schedule is …” or “The best way to compensate hospitalists is …”
But there really isn’t a “best” way to manage any particular attribute of a practice. Don’t make the mistake of assuming your method is best, or that it’s the way “everybody else does it.” Although scheduling and compensation are marquee issues for hospitalists, approaches to distributing new patients is much less visible. Many groups tend to assume their method is the only reasonable approach. The best approach, however, varies from one practice to the next. You should be open to hearing approaches to scheduling that are different from your own.
Assign Patients by “Load Leveling”
I’ve come across a lot—and I mean a lot—of different approaches to distributing new patients in HM groups around the country, but it seems pretty clear that the most common method is to undertake “load leveling” on a daily or ongoing basis.
For example, groups that have a separate night shift (the night doctor performs no daytime work the day before or the day after a night shift) typically distribute the night’s new patients with the intent of having each daytime doctor start with the same number of patients. The group might more heavily weight some patients, such as those in the ICU (e.g., each ICU patient counts as 1.5 or two non-ICU patients), but most groups don’t. Over the course of the day shift, new referrals will be distributed evenly among the doctors one at a time, sort of like dealing a deck of cards.
This approach aims to avoid significant imbalances in patient loads and has the potential cultural benefit of everyone sharing equally in busy and slow days. Groups that use it tend to see it as the best option because it is the fairest way to divide up the workload.
Practices that use load-leveling almost always use a schedule built on shifts of a predetermined and fixed duration. For example, say the day shift always works from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. This schedule usually has the majority of compensation paid via a fixed annual salary or fixed shift rate. One potential problem with this approach is that the doctor who is efficient and discharges a lot of patients today is “rewarded” with more new patients tomorrow. Hospitalists who are allergic to work might have an incentive to have a patient wait until tomorrow to discharge to avoid having to assume the care of yet another patient tomorrow morning. Hospital executives who are focused on length-of-stay management might be concerned if they knew this was a potential issue. Of course, the reverse is true as well. In a practice that doesn’t aggressively undertake load-leveling, a less-than-admirable hospitalist could push patients to discharge earlier than optimal just to have one less patient the next day.
Another cost of this approach is that the distribution of patients can be time-consuming each morning. It also offers the opportunity for some in the group to decide they’re treated unfairly. For instance, you might hear the occasional “just last Tuesday, I started with 16 patients, compared with 15 for everyone else. Now you want me to do it again? You’re being unfair to me; it’s someone else’s turn to take the extra patient.”
Assignment by Location
Groups that use “unit-based” hospitalists distribute patients according to the unit the patient is admitted to—and the hospitalist covering that unit. The pros and cons of unit-based hospitalists are many (see “A Unit-Based Approach,” September 2007), but there is an obvious tension between keeping patient loads even among hospitalists and ensuring that all of a hospitalist’s patients are on “their” unit. Practicality usually requires a compromise between pure unit-based assignment and load-leveling.
Uneven Assignments
Some groups assign patients according to a predetermined algorithm and employ load-leveling only when patient loads become extremely unbalanced. For example, Dr. Jones gets all the new referrals today, and Dr. James gets them tomorrow. The idea is that patient loads end up close to even over time, even if they’re unbalanced on any given day.
A system like this allows everyone, including the hospitalists themselves, ED staff, etc., to know who will take the next patient. It decreases the need to communicate the “who’s next” information time after time during the course of the day. In small- to medium-sized practices, it could mean no one needs to function as the triage doctor (i.e., the person who inefficiently answers the service calls, scribbles down clinical information, then calls the hospitalist who is due to take the next patient and relays all the pertinent patient info). This system allows the
hospitalists to know which days will be harder (e.g., taking on the care of new patients) and which days will be easier (e.g., rounding but not assuming care of new patients). Allowing uneven loads also eliminates the need to spend energy working to even the loads and risking that some in the group feel as if they aren’t being treated fairly.
Uncommon yet Intriguing Approaches
Pair referring primary-care physicians (PCPs) with specific hospitalists. I’ve encountered two groups that had hospitalists always admit patients from the same PCPs. In other words, hospitalist Dr. Hancock always serves as attending for patients referred by the same nine PCPs, and hospitalist Dr. Franklin always attends to patients from a different set of PCPs. It seems to me that there could be tremendous benefit in working closely with the same PCPs, most notably getting to know the PCPs’ office staff. But this system raises the risk of creating out-of-balance patient loads, among other problems. It is really attractive to me, but most groups will decide its costs outweigh its benefits.
Hospitalist and patient stay connected during admission. I’m not aware of any group that uses this method (let me know if you do!), but there could be benefits to having each patient see the same hospitalist during each hospital stay. Of course, that is assuming the hospitalist is on duty. Hospitalist and patient could be paired upon the patient’s first admission. The hospitalist could form an excellent relationship with the patient and family; the time spent by the hospitalist getting to know patients on admission would be reduced, and I suspect there might be some benefit in the quality of care.
This method, however, likely results in the most uneven patient loads, and load-leveling would be difficult, if not impossible. Even if hospitalist and patient did form a tight bond, there is a high probability that the hospitalist would be off for the duration of the patient’s next admission. So despite what I suspect are tremendous benefits, this approach may not be feasible for any group.
In next month’s column, I will discuss issues related to the way patients are distributed. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is co-founder and past president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm (www.nelsonflores.com). He is co-director and faculty for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
Editor’s note: This is the first of a three-part series.
My experience is that some, maybe even most, hospitalists tend to assume there is a standard or “right” way to organize things like work schedules, compensation, or even the assignment of patients among the group’s providers. Some will say things like “SHM says the best hospitalist schedule is …” or “The best way to compensate hospitalists is …”
But there really isn’t a “best” way to manage any particular attribute of a practice. Don’t make the mistake of assuming your method is best, or that it’s the way “everybody else does it.” Although scheduling and compensation are marquee issues for hospitalists, approaches to distributing new patients is much less visible. Many groups tend to assume their method is the only reasonable approach. The best approach, however, varies from one practice to the next. You should be open to hearing approaches to scheduling that are different from your own.
Assign Patients by “Load Leveling”
I’ve come across a lot—and I mean a lot—of different approaches to distributing new patients in HM groups around the country, but it seems pretty clear that the most common method is to undertake “load leveling” on a daily or ongoing basis.
For example, groups that have a separate night shift (the night doctor performs no daytime work the day before or the day after a night shift) typically distribute the night’s new patients with the intent of having each daytime doctor start with the same number of patients. The group might more heavily weight some patients, such as those in the ICU (e.g., each ICU patient counts as 1.5 or two non-ICU patients), but most groups don’t. Over the course of the day shift, new referrals will be distributed evenly among the doctors one at a time, sort of like dealing a deck of cards.
This approach aims to avoid significant imbalances in patient loads and has the potential cultural benefit of everyone sharing equally in busy and slow days. Groups that use it tend to see it as the best option because it is the fairest way to divide up the workload.
Practices that use load-leveling almost always use a schedule built on shifts of a predetermined and fixed duration. For example, say the day shift always works from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. This schedule usually has the majority of compensation paid via a fixed annual salary or fixed shift rate. One potential problem with this approach is that the doctor who is efficient and discharges a lot of patients today is “rewarded” with more new patients tomorrow. Hospitalists who are allergic to work might have an incentive to have a patient wait until tomorrow to discharge to avoid having to assume the care of yet another patient tomorrow morning. Hospital executives who are focused on length-of-stay management might be concerned if they knew this was a potential issue. Of course, the reverse is true as well. In a practice that doesn’t aggressively undertake load-leveling, a less-than-admirable hospitalist could push patients to discharge earlier than optimal just to have one less patient the next day.
Another cost of this approach is that the distribution of patients can be time-consuming each morning. It also offers the opportunity for some in the group to decide they’re treated unfairly. For instance, you might hear the occasional “just last Tuesday, I started with 16 patients, compared with 15 for everyone else. Now you want me to do it again? You’re being unfair to me; it’s someone else’s turn to take the extra patient.”
Assignment by Location
Groups that use “unit-based” hospitalists distribute patients according to the unit the patient is admitted to—and the hospitalist covering that unit. The pros and cons of unit-based hospitalists are many (see “A Unit-Based Approach,” September 2007), but there is an obvious tension between keeping patient loads even among hospitalists and ensuring that all of a hospitalist’s patients are on “their” unit. Practicality usually requires a compromise between pure unit-based assignment and load-leveling.
Uneven Assignments
Some groups assign patients according to a predetermined algorithm and employ load-leveling only when patient loads become extremely unbalanced. For example, Dr. Jones gets all the new referrals today, and Dr. James gets them tomorrow. The idea is that patient loads end up close to even over time, even if they’re unbalanced on any given day.
A system like this allows everyone, including the hospitalists themselves, ED staff, etc., to know who will take the next patient. It decreases the need to communicate the “who’s next” information time after time during the course of the day. In small- to medium-sized practices, it could mean no one needs to function as the triage doctor (i.e., the person who inefficiently answers the service calls, scribbles down clinical information, then calls the hospitalist who is due to take the next patient and relays all the pertinent patient info). This system allows the
hospitalists to know which days will be harder (e.g., taking on the care of new patients) and which days will be easier (e.g., rounding but not assuming care of new patients). Allowing uneven loads also eliminates the need to spend energy working to even the loads and risking that some in the group feel as if they aren’t being treated fairly.
Uncommon yet Intriguing Approaches
Pair referring primary-care physicians (PCPs) with specific hospitalists. I’ve encountered two groups that had hospitalists always admit patients from the same PCPs. In other words, hospitalist Dr. Hancock always serves as attending for patients referred by the same nine PCPs, and hospitalist Dr. Franklin always attends to patients from a different set of PCPs. It seems to me that there could be tremendous benefit in working closely with the same PCPs, most notably getting to know the PCPs’ office staff. But this system raises the risk of creating out-of-balance patient loads, among other problems. It is really attractive to me, but most groups will decide its costs outweigh its benefits.
Hospitalist and patient stay connected during admission. I’m not aware of any group that uses this method (let me know if you do!), but there could be benefits to having each patient see the same hospitalist during each hospital stay. Of course, that is assuming the hospitalist is on duty. Hospitalist and patient could be paired upon the patient’s first admission. The hospitalist could form an excellent relationship with the patient and family; the time spent by the hospitalist getting to know patients on admission would be reduced, and I suspect there might be some benefit in the quality of care.
This method, however, likely results in the most uneven patient loads, and load-leveling would be difficult, if not impossible. Even if hospitalist and patient did form a tight bond, there is a high probability that the hospitalist would be off for the duration of the patient’s next admission. So despite what I suspect are tremendous benefits, this approach may not be feasible for any group.
In next month’s column, I will discuss issues related to the way patients are distributed. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is co-founder and past president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm (www.nelsonflores.com). He is co-director and faculty for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
Editor’s note: This is the first of a three-part series.
My experience is that some, maybe even most, hospitalists tend to assume there is a standard or “right” way to organize things like work schedules, compensation, or even the assignment of patients among the group’s providers. Some will say things like “SHM says the best hospitalist schedule is …” or “The best way to compensate hospitalists is …”
But there really isn’t a “best” way to manage any particular attribute of a practice. Don’t make the mistake of assuming your method is best, or that it’s the way “everybody else does it.” Although scheduling and compensation are marquee issues for hospitalists, approaches to distributing new patients is much less visible. Many groups tend to assume their method is the only reasonable approach. The best approach, however, varies from one practice to the next. You should be open to hearing approaches to scheduling that are different from your own.
Assign Patients by “Load Leveling”
I’ve come across a lot—and I mean a lot—of different approaches to distributing new patients in HM groups around the country, but it seems pretty clear that the most common method is to undertake “load leveling” on a daily or ongoing basis.
For example, groups that have a separate night shift (the night doctor performs no daytime work the day before or the day after a night shift) typically distribute the night’s new patients with the intent of having each daytime doctor start with the same number of patients. The group might more heavily weight some patients, such as those in the ICU (e.g., each ICU patient counts as 1.5 or two non-ICU patients), but most groups don’t. Over the course of the day shift, new referrals will be distributed evenly among the doctors one at a time, sort of like dealing a deck of cards.
This approach aims to avoid significant imbalances in patient loads and has the potential cultural benefit of everyone sharing equally in busy and slow days. Groups that use it tend to see it as the best option because it is the fairest way to divide up the workload.
Practices that use load-leveling almost always use a schedule built on shifts of a predetermined and fixed duration. For example, say the day shift always works from 7 a.m. to 7 p.m. This schedule usually has the majority of compensation paid via a fixed annual salary or fixed shift rate. One potential problem with this approach is that the doctor who is efficient and discharges a lot of patients today is “rewarded” with more new patients tomorrow. Hospitalists who are allergic to work might have an incentive to have a patient wait until tomorrow to discharge to avoid having to assume the care of yet another patient tomorrow morning. Hospital executives who are focused on length-of-stay management might be concerned if they knew this was a potential issue. Of course, the reverse is true as well. In a practice that doesn’t aggressively undertake load-leveling, a less-than-admirable hospitalist could push patients to discharge earlier than optimal just to have one less patient the next day.
Another cost of this approach is that the distribution of patients can be time-consuming each morning. It also offers the opportunity for some in the group to decide they’re treated unfairly. For instance, you might hear the occasional “just last Tuesday, I started with 16 patients, compared with 15 for everyone else. Now you want me to do it again? You’re being unfair to me; it’s someone else’s turn to take the extra patient.”
Assignment by Location
Groups that use “unit-based” hospitalists distribute patients according to the unit the patient is admitted to—and the hospitalist covering that unit. The pros and cons of unit-based hospitalists are many (see “A Unit-Based Approach,” September 2007), but there is an obvious tension between keeping patient loads even among hospitalists and ensuring that all of a hospitalist’s patients are on “their” unit. Practicality usually requires a compromise between pure unit-based assignment and load-leveling.
Uneven Assignments
Some groups assign patients according to a predetermined algorithm and employ load-leveling only when patient loads become extremely unbalanced. For example, Dr. Jones gets all the new referrals today, and Dr. James gets them tomorrow. The idea is that patient loads end up close to even over time, even if they’re unbalanced on any given day.
A system like this allows everyone, including the hospitalists themselves, ED staff, etc., to know who will take the next patient. It decreases the need to communicate the “who’s next” information time after time during the course of the day. In small- to medium-sized practices, it could mean no one needs to function as the triage doctor (i.e., the person who inefficiently answers the service calls, scribbles down clinical information, then calls the hospitalist who is due to take the next patient and relays all the pertinent patient info). This system allows the
hospitalists to know which days will be harder (e.g., taking on the care of new patients) and which days will be easier (e.g., rounding but not assuming care of new patients). Allowing uneven loads also eliminates the need to spend energy working to even the loads and risking that some in the group feel as if they aren’t being treated fairly.
Uncommon yet Intriguing Approaches
Pair referring primary-care physicians (PCPs) with specific hospitalists. I’ve encountered two groups that had hospitalists always admit patients from the same PCPs. In other words, hospitalist Dr. Hancock always serves as attending for patients referred by the same nine PCPs, and hospitalist Dr. Franklin always attends to patients from a different set of PCPs. It seems to me that there could be tremendous benefit in working closely with the same PCPs, most notably getting to know the PCPs’ office staff. But this system raises the risk of creating out-of-balance patient loads, among other problems. It is really attractive to me, but most groups will decide its costs outweigh its benefits.
Hospitalist and patient stay connected during admission. I’m not aware of any group that uses this method (let me know if you do!), but there could be benefits to having each patient see the same hospitalist during each hospital stay. Of course, that is assuming the hospitalist is on duty. Hospitalist and patient could be paired upon the patient’s first admission. The hospitalist could form an excellent relationship with the patient and family; the time spent by the hospitalist getting to know patients on admission would be reduced, and I suspect there might be some benefit in the quality of care.
This method, however, likely results in the most uneven patient loads, and load-leveling would be difficult, if not impossible. Even if hospitalist and patient did form a tight bond, there is a high probability that the hospitalist would be off for the duration of the patient’s next admission. So despite what I suspect are tremendous benefits, this approach may not be feasible for any group.
In next month’s column, I will discuss issues related to the way patients are distributed. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is co-founder and past president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm (www.nelsonflores.com). He is co-director and faculty for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
Necessary Evil: Change
The amount and complexity of medical knowledge we need to keep up with is changing and growing at a remarkable rate. I was trained in an era in which it was taken as a given that congestive heart failure patients should not receive beta-blockers; now it is a big mistake if we don’t prescribe them in most cases. But even before starting medical school, most of us realize that things will change a lot, and many of us see that as a good thing. It keeps our work interesting. Just recently, our hospital had a guest speaker who talked about potential medical applications of nanotechnology. It was way over my head, but it sounded pretty cool.
While I was prepared for ongoing changes in medical knowledge, I failed to anticipate how quickly the business of medicine would change during my career. I think the need to keep up with ever-increasing financial and regulatory issues siphons a lot of time and energy that could be used to keep up with the medical knowledge base. I wasn’t prepared for this when I started my career.
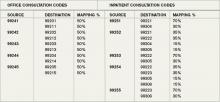
Because it is the start of a new year, I thought I would highlight one issue related to CPT coding: Medicare stopped recognizing consult codes as of Jan. 1 (see “Consultation Elimination,” p. 31).
What It Means for Hospitalists
The good news is that we can just use initial hospital visit codes, inpatient or observation, for all new visits. For example, it won’t matter anymore whether I’m admitting and serving as attending for a patient, or whether a surgeon admitted the patient and asked me to consult for preoperative medical evaluation (“clearance”). I should use the same CPT code in either situation, simply appending a modifier if I’m the admitting physician. And for billing purposes, we won’t have to worry about documenting which doctor requested that we see the patient, though it is a good idea to document it as part of the clinical record anyway.
But it gets a little more complicated. The codes aren’t going away or being removed from the CPT “bible” published by the American Medical Association (AMA). Instead, Medicare simply won’t recognize them anymore. Other payors probably will follow suit within a few months, but that isn’t certain. So it is possible that when asked by a surgeon to provide a preoperative evaluation, you will need to bill an initial hospital (or office or nursing facility) care visit if the patient is on Medicare but bill a consult code if the patient has other insurance. You should check with your billers to ensure you’re doing this correctly.
Medicare-paid consults are at a slightly higher rate than the equivalent service billed as initial hospital care (e.g., when the hospitalist is attending). So a higher reimbursing code has been replaced with one that pays a little less. For example, a 99253 consultation code requires a detailed history, detailed examination, and medical decision-making of low complexity; last year, 99253 was reimbursed by Medicare at an average rate of $114.69. The equivalent admission code for a detailed history, detailed examination, and low-complexity medical decision-making is a 99221 code, for which Medicare pays about $99.90. This represents a difference of about 14%.
However, the net financial impact of this change probably will be positive for most HM groups because you probably bill very few initial consult codes, and instead were stuck billing a follow-up visit code when seeing co-management “consults” (i.e., a patient admitted by a surgeon who asks you to follow and manage diabetes and other medical issues). Now, at least in the case of Medicare, it is appropriate for us to bill an initial hospital visit code, which provides significantly higher reimbursement than follow-up codes.
In addition, there is a modest (about 0.3%) proposed increase in work relative value units attached to the initial hospital visit codes, which will benefit us not only when we’re consulting, but also when we admit and serve as a patient’s attending.
Some specialists may be less interested in consulting on our patients because the initial visit codes will reimburse a little less than similar consultation codes. I don’t anticipate this will be a significant problem for most of us, particularly since many specialists bill the highest level of consultation code (99255), which pays about the same as the equivalent admission code (99223).
Although I think elimination of the use of consultation codes seems like a reasonable step toward simplifying how hospitalists bill for our services, keeping up with these frequent coding changes requires a high level of diligence on our part, and on the part of our administrative and clerical staffs. And it consumes time and resources that I—and my team—could better spend keeping up with changes in clinical practice.
Perhaps when all the dust settles around the healthcare reform debate, we will begin to move toward new, more creative payment models that will allow us to focus on what we do best. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is cofounder and past president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm (www.nelsonflores.com). He is also course co-director and faculty for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
The amount and complexity of medical knowledge we need to keep up with is changing and growing at a remarkable rate. I was trained in an era in which it was taken as a given that congestive heart failure patients should not receive beta-blockers; now it is a big mistake if we don’t prescribe them in most cases. But even before starting medical school, most of us realize that things will change a lot, and many of us see that as a good thing. It keeps our work interesting. Just recently, our hospital had a guest speaker who talked about potential medical applications of nanotechnology. It was way over my head, but it sounded pretty cool.
While I was prepared for ongoing changes in medical knowledge, I failed to anticipate how quickly the business of medicine would change during my career. I think the need to keep up with ever-increasing financial and regulatory issues siphons a lot of time and energy that could be used to keep up with the medical knowledge base. I wasn’t prepared for this when I started my career.
Because it is the start of a new year, I thought I would highlight one issue related to CPT coding: Medicare stopped recognizing consult codes as of Jan. 1 (see “Consultation Elimination,” p. 31).
What It Means for Hospitalists
The good news is that we can just use initial hospital visit codes, inpatient or observation, for all new visits. For example, it won’t matter anymore whether I’m admitting and serving as attending for a patient, or whether a surgeon admitted the patient and asked me to consult for preoperative medical evaluation (“clearance”). I should use the same CPT code in either situation, simply appending a modifier if I’m the admitting physician. And for billing purposes, we won’t have to worry about documenting which doctor requested that we see the patient, though it is a good idea to document it as part of the clinical record anyway.
But it gets a little more complicated. The codes aren’t going away or being removed from the CPT “bible” published by the American Medical Association (AMA). Instead, Medicare simply won’t recognize them anymore. Other payors probably will follow suit within a few months, but that isn’t certain. So it is possible that when asked by a surgeon to provide a preoperative evaluation, you will need to bill an initial hospital (or office or nursing facility) care visit if the patient is on Medicare but bill a consult code if the patient has other insurance. You should check with your billers to ensure you’re doing this correctly.
Medicare-paid consults are at a slightly higher rate than the equivalent service billed as initial hospital care (e.g., when the hospitalist is attending). So a higher reimbursing code has been replaced with one that pays a little less. For example, a 99253 consultation code requires a detailed history, detailed examination, and medical decision-making of low complexity; last year, 99253 was reimbursed by Medicare at an average rate of $114.69. The equivalent admission code for a detailed history, detailed examination, and low-complexity medical decision-making is a 99221 code, for which Medicare pays about $99.90. This represents a difference of about 14%.
However, the net financial impact of this change probably will be positive for most HM groups because you probably bill very few initial consult codes, and instead were stuck billing a follow-up visit code when seeing co-management “consults” (i.e., a patient admitted by a surgeon who asks you to follow and manage diabetes and other medical issues). Now, at least in the case of Medicare, it is appropriate for us to bill an initial hospital visit code, which provides significantly higher reimbursement than follow-up codes.
In addition, there is a modest (about 0.3%) proposed increase in work relative value units attached to the initial hospital visit codes, which will benefit us not only when we’re consulting, but also when we admit and serve as a patient’s attending.
Some specialists may be less interested in consulting on our patients because the initial visit codes will reimburse a little less than similar consultation codes. I don’t anticipate this will be a significant problem for most of us, particularly since many specialists bill the highest level of consultation code (99255), which pays about the same as the equivalent admission code (99223).
Although I think elimination of the use of consultation codes seems like a reasonable step toward simplifying how hospitalists bill for our services, keeping up with these frequent coding changes requires a high level of diligence on our part, and on the part of our administrative and clerical staffs. And it consumes time and resources that I—and my team—could better spend keeping up with changes in clinical practice.
Perhaps when all the dust settles around the healthcare reform debate, we will begin to move toward new, more creative payment models that will allow us to focus on what we do best. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is cofounder and past president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm (www.nelsonflores.com). He is also course co-director and faculty for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
The amount and complexity of medical knowledge we need to keep up with is changing and growing at a remarkable rate. I was trained in an era in which it was taken as a given that congestive heart failure patients should not receive beta-blockers; now it is a big mistake if we don’t prescribe them in most cases. But even before starting medical school, most of us realize that things will change a lot, and many of us see that as a good thing. It keeps our work interesting. Just recently, our hospital had a guest speaker who talked about potential medical applications of nanotechnology. It was way over my head, but it sounded pretty cool.
While I was prepared for ongoing changes in medical knowledge, I failed to anticipate how quickly the business of medicine would change during my career. I think the need to keep up with ever-increasing financial and regulatory issues siphons a lot of time and energy that could be used to keep up with the medical knowledge base. I wasn’t prepared for this when I started my career.
Because it is the start of a new year, I thought I would highlight one issue related to CPT coding: Medicare stopped recognizing consult codes as of Jan. 1 (see “Consultation Elimination,” p. 31).
What It Means for Hospitalists
The good news is that we can just use initial hospital visit codes, inpatient or observation, for all new visits. For example, it won’t matter anymore whether I’m admitting and serving as attending for a patient, or whether a surgeon admitted the patient and asked me to consult for preoperative medical evaluation (“clearance”). I should use the same CPT code in either situation, simply appending a modifier if I’m the admitting physician. And for billing purposes, we won’t have to worry about documenting which doctor requested that we see the patient, though it is a good idea to document it as part of the clinical record anyway.
But it gets a little more complicated. The codes aren’t going away or being removed from the CPT “bible” published by the American Medical Association (AMA). Instead, Medicare simply won’t recognize them anymore. Other payors probably will follow suit within a few months, but that isn’t certain. So it is possible that when asked by a surgeon to provide a preoperative evaluation, you will need to bill an initial hospital (or office or nursing facility) care visit if the patient is on Medicare but bill a consult code if the patient has other insurance. You should check with your billers to ensure you’re doing this correctly.
Medicare-paid consults are at a slightly higher rate than the equivalent service billed as initial hospital care (e.g., when the hospitalist is attending). So a higher reimbursing code has been replaced with one that pays a little less. For example, a 99253 consultation code requires a detailed history, detailed examination, and medical decision-making of low complexity; last year, 99253 was reimbursed by Medicare at an average rate of $114.69. The equivalent admission code for a detailed history, detailed examination, and low-complexity medical decision-making is a 99221 code, for which Medicare pays about $99.90. This represents a difference of about 14%.
However, the net financial impact of this change probably will be positive for most HM groups because you probably bill very few initial consult codes, and instead were stuck billing a follow-up visit code when seeing co-management “consults” (i.e., a patient admitted by a surgeon who asks you to follow and manage diabetes and other medical issues). Now, at least in the case of Medicare, it is appropriate for us to bill an initial hospital visit code, which provides significantly higher reimbursement than follow-up codes.
In addition, there is a modest (about 0.3%) proposed increase in work relative value units attached to the initial hospital visit codes, which will benefit us not only when we’re consulting, but also when we admit and serve as a patient’s attending.
Some specialists may be less interested in consulting on our patients because the initial visit codes will reimburse a little less than similar consultation codes. I don’t anticipate this will be a significant problem for most of us, particularly since many specialists bill the highest level of consultation code (99255), which pays about the same as the equivalent admission code (99223).
Although I think elimination of the use of consultation codes seems like a reasonable step toward simplifying how hospitalists bill for our services, keeping up with these frequent coding changes requires a high level of diligence on our part, and on the part of our administrative and clerical staffs. And it consumes time and resources that I—and my team—could better spend keeping up with changes in clinical practice.
Perhaps when all the dust settles around the healthcare reform debate, we will begin to move toward new, more creative payment models that will allow us to focus on what we do best. TH
Dr. Nelson has been a practicing hospitalist since 1988 and is cofounder and past president of SHM. He is a principal in Nelson Flores Hospital Medicine Consultants, a national hospitalist practice management consulting firm (www.nelsonflores.com). He is also course co-director and faculty for SHM’s “Best Practices in Managing a Hospital Medicine Program” course. This column represents his views and is not intended to reflect an official position of SHM.
Consultation Elimination
As of Jan. 1, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) ceased physician payment for consultations. The elimination of consult codes will affect physician group payments as well as relative-value-unit (RVU)-based incentive payments to individual physicians.
The Medicare-designated status of outpatient consultation (99241-99245) and inpatient consultation (99251-99255) codes has changed from “A” (separately payable under the physician fee schedule, when covered) to “I” (not valid for Medicare purposes; Medicare uses another code for the reporting of and the payment for these services). So if you submit consultation codes for Medicare beneficiaries, the result will be nonpayment.
While many physicians fear the negative impact of this ruling, hospitalists should consider its potential. Let’s take a look at a scenario hospitalists encounter on a routine basis.
Typical HM Scenario
A surgeon admits a 76-year-old man for aortic valve replacement. The patient’s history also includes well-controlled hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Postoperatively, the patient experiences an exacerbation of COPD related to anesthesia, elevated blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. The surgeon requests the hospitalist’s advice on appropriate medical interventions of these conditions. How should the hospitalist report the initial encounter with this Medicare beneficiary?
The hospitalist should select the CPT code that best fits the service and the payor. While most physicians regard this requested service as an inpatient consultation (99251-99255), Medicare no longer recognizes those codes. Instead, the hospitalist should report this encounter as an initial hospital care service (99221-99223).
Comanagement Issues
CMS and Medicare administrative contractors regularly uncover reporting errors for co-management requests. CMS decided the nature of these services were not consultative because the surgeon is not asking the physician or qualified nonphysician provider’s (NPP’s) opinion or advice for the surgeon’s use in treating the patient. Instead, these services constituted concurrent care and should have been billed using subsequent hospital care codes (99231-99233) in the hospital inpatient setting, subsequent NF care codes (99307-99310) in the SNF/NF setting, or office or other outpatient visit codes (99201-99215) in the office or outpatient settings.1
The new ruling simplifies coding and reduces reporting errors. The initial encounter with the patient is reported as such. Regardless of who is the attending of record or the consultant, the first physician from a particular provider group reports initial hospital care codes (i.e., 99221-99223) to represent the first patient encounter, even when this encounter does not occur on the admission date. Other physicians of the same specialty within the same provider group will not be permitted to report initial hospital care codes for their own initial encounter if someone from the group and specialty has already seen the patient during that hospitalization. In other words, the first hospitalist in the provider group reports 9922x, while the remaining hospitalists use subsequent hospital care codes (9923x).
In order to differentiate “consultant” services from “attending” services, CMS will be creating a modifier. The anticipated “AI” modifier must be appended to the attending physician’s initial encounter. Other initial hospital care codes reported throughout the hospital stay, as appropriate, are presumed to be that of “consultants” (i.e., physicians with a different specialty designation than the attending physician) participating in the case. Therefore, the hospitalist now can rightfully recover the increased work effort of the initial patient encounter (99223: 3.79 relative value units, ~$147 vs. 99233: 2.0 relative value units, ~$78, based on 2010 Medicare rates). Physicians will be required to meet the minimum documentation required for the selected visit code.
Other and Undefined Service Locations
Consultations in nursing facilities are handled much like inpatient hospital care. Physicians should report initial nursing facility services (99203-99306) for the first patient encounter, and subsequent nursing facility care codes (99307-99310) for each encounter thereafter. The attending physician of record appends the assigned modifier (presumed to be “AI”) when submitting their initial care service. All other initial care codes are presumed to be those of “consulting” physicians.
Initial information from CMS does not address observation services. Logically, these hospital-based services would follow the same methodology as inpatient care: report initial observation care (99218-99220) for the first “consulting” encounter. However, this might not be appropriate given Medicare’s existing rules for observation services, which guide physicians other than the admitting physician/group to “bill the office and other outpatient service codes or outpatient consultation codes as appropriate when they provide services to the patient.”2 With Medicare’s elimination of consultation codes, the consultant reports “office and other outpatient service codes” (i.e., new patient, 99201-99205, or established patient codes, 99212-99215) by default.
Without further clarification on observation services, hospitalists should report new or established patient service codes, depending on whether the patient has been seen by a group member within the last three years.
Medicare also has existing guidelines for the ED, which suggest that any physician not meeting the consultation criteria report ED service codes (99281-99285). Without further clarification, hospitalists should continue to follow this instruction for Medicare beneficiaries.
Nonphysician Providers
Medicare’s split/shared billing guidelines apply to most hospital inpatient, hospital outpatient, and ED evaluation and management (E/M) services, with consultations as one exception. Now, in accordance with the new ruling, hospitalists should select the appropriate initial service codes that correspond to patient’s location (e.g., 99223 for inpatients). NPPs can participate in the initial service provided to patients in these locations without the hospitalist having to replicate the entire service. The hospitalist can submit the claim in their name after selecting the visit level based upon the cumulative service personally provided on the same calendar day by both the NPP and the physician. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She also is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.10I. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/ manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Nov. 14, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.8A. CMS Web site. Available at: www. cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Nov. 14, 2009.
- PFS Federal Regulation Notices: Proposed Revisions to Payment Policies Under the Physician Fee Schedule and Part B for CY 2010. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/PhysicianFeeSched/PFSFRN/itemdetail.asp?filterType=none&filterByDID=99&sortByDID=4&sortOrder=descending&itemID=CMS1223902&intNumPerPage=10. Accessed Nov. 12, 2009.
- Payment Policies Under the Physician Fee Schedule and Other Revisions to Part B (for CY 2010). CMS Web site. Available at: www.federalregister.gov/OFR Upload/OFRData/2009-26502_PI.pdf. Accessed Nov. 10, 2009.
As of Jan. 1, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) ceased physician payment for consultations. The elimination of consult codes will affect physician group payments as well as relative-value-unit (RVU)-based incentive payments to individual physicians.
The Medicare-designated status of outpatient consultation (99241-99245) and inpatient consultation (99251-99255) codes has changed from “A” (separately payable under the physician fee schedule, when covered) to “I” (not valid for Medicare purposes; Medicare uses another code for the reporting of and the payment for these services). So if you submit consultation codes for Medicare beneficiaries, the result will be nonpayment.
While many physicians fear the negative impact of this ruling, hospitalists should consider its potential. Let’s take a look at a scenario hospitalists encounter on a routine basis.
Typical HM Scenario
A surgeon admits a 76-year-old man for aortic valve replacement. The patient’s history also includes well-controlled hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Postoperatively, the patient experiences an exacerbation of COPD related to anesthesia, elevated blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. The surgeon requests the hospitalist’s advice on appropriate medical interventions of these conditions. How should the hospitalist report the initial encounter with this Medicare beneficiary?
The hospitalist should select the CPT code that best fits the service and the payor. While most physicians regard this requested service as an inpatient consultation (99251-99255), Medicare no longer recognizes those codes. Instead, the hospitalist should report this encounter as an initial hospital care service (99221-99223).
Comanagement Issues
CMS and Medicare administrative contractors regularly uncover reporting errors for co-management requests. CMS decided the nature of these services were not consultative because the surgeon is not asking the physician or qualified nonphysician provider’s (NPP’s) opinion or advice for the surgeon’s use in treating the patient. Instead, these services constituted concurrent care and should have been billed using subsequent hospital care codes (99231-99233) in the hospital inpatient setting, subsequent NF care codes (99307-99310) in the SNF/NF setting, or office or other outpatient visit codes (99201-99215) in the office or outpatient settings.1
The new ruling simplifies coding and reduces reporting errors. The initial encounter with the patient is reported as such. Regardless of who is the attending of record or the consultant, the first physician from a particular provider group reports initial hospital care codes (i.e., 99221-99223) to represent the first patient encounter, even when this encounter does not occur on the admission date. Other physicians of the same specialty within the same provider group will not be permitted to report initial hospital care codes for their own initial encounter if someone from the group and specialty has already seen the patient during that hospitalization. In other words, the first hospitalist in the provider group reports 9922x, while the remaining hospitalists use subsequent hospital care codes (9923x).
In order to differentiate “consultant” services from “attending” services, CMS will be creating a modifier. The anticipated “AI” modifier must be appended to the attending physician’s initial encounter. Other initial hospital care codes reported throughout the hospital stay, as appropriate, are presumed to be that of “consultants” (i.e., physicians with a different specialty designation than the attending physician) participating in the case. Therefore, the hospitalist now can rightfully recover the increased work effort of the initial patient encounter (99223: 3.79 relative value units, ~$147 vs. 99233: 2.0 relative value units, ~$78, based on 2010 Medicare rates). Physicians will be required to meet the minimum documentation required for the selected visit code.
Other and Undefined Service Locations
Consultations in nursing facilities are handled much like inpatient hospital care. Physicians should report initial nursing facility services (99203-99306) for the first patient encounter, and subsequent nursing facility care codes (99307-99310) for each encounter thereafter. The attending physician of record appends the assigned modifier (presumed to be “AI”) when submitting their initial care service. All other initial care codes are presumed to be those of “consulting” physicians.
Initial information from CMS does not address observation services. Logically, these hospital-based services would follow the same methodology as inpatient care: report initial observation care (99218-99220) for the first “consulting” encounter. However, this might not be appropriate given Medicare’s existing rules for observation services, which guide physicians other than the admitting physician/group to “bill the office and other outpatient service codes or outpatient consultation codes as appropriate when they provide services to the patient.”2 With Medicare’s elimination of consultation codes, the consultant reports “office and other outpatient service codes” (i.e., new patient, 99201-99205, or established patient codes, 99212-99215) by default.
Without further clarification on observation services, hospitalists should report new or established patient service codes, depending on whether the patient has been seen by a group member within the last three years.
Medicare also has existing guidelines for the ED, which suggest that any physician not meeting the consultation criteria report ED service codes (99281-99285). Without further clarification, hospitalists should continue to follow this instruction for Medicare beneficiaries.
Nonphysician Providers
Medicare’s split/shared billing guidelines apply to most hospital inpatient, hospital outpatient, and ED evaluation and management (E/M) services, with consultations as one exception. Now, in accordance with the new ruling, hospitalists should select the appropriate initial service codes that correspond to patient’s location (e.g., 99223 for inpatients). NPPs can participate in the initial service provided to patients in these locations without the hospitalist having to replicate the entire service. The hospitalist can submit the claim in their name after selecting the visit level based upon the cumulative service personally provided on the same calendar day by both the NPP and the physician. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She also is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.10I. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/ manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Nov. 14, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.8A. CMS Web site. Available at: www. cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Nov. 14, 2009.
- PFS Federal Regulation Notices: Proposed Revisions to Payment Policies Under the Physician Fee Schedule and Part B for CY 2010. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/PhysicianFeeSched/PFSFRN/itemdetail.asp?filterType=none&filterByDID=99&sortByDID=4&sortOrder=descending&itemID=CMS1223902&intNumPerPage=10. Accessed Nov. 12, 2009.
- Payment Policies Under the Physician Fee Schedule and Other Revisions to Part B (for CY 2010). CMS Web site. Available at: www.federalregister.gov/OFR Upload/OFRData/2009-26502_PI.pdf. Accessed Nov. 10, 2009.
As of Jan. 1, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) ceased physician payment for consultations. The elimination of consult codes will affect physician group payments as well as relative-value-unit (RVU)-based incentive payments to individual physicians.
The Medicare-designated status of outpatient consultation (99241-99245) and inpatient consultation (99251-99255) codes has changed from “A” (separately payable under the physician fee schedule, when covered) to “I” (not valid for Medicare purposes; Medicare uses another code for the reporting of and the payment for these services). So if you submit consultation codes for Medicare beneficiaries, the result will be nonpayment.
While many physicians fear the negative impact of this ruling, hospitalists should consider its potential. Let’s take a look at a scenario hospitalists encounter on a routine basis.
Typical HM Scenario
A surgeon admits a 76-year-old man for aortic valve replacement. The patient’s history also includes well-controlled hypertension and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Postoperatively, the patient experiences an exacerbation of COPD related to anesthesia, elevated blood pressure, and hyperglycemia. The surgeon requests the hospitalist’s advice on appropriate medical interventions of these conditions. How should the hospitalist report the initial encounter with this Medicare beneficiary?
The hospitalist should select the CPT code that best fits the service and the payor. While most physicians regard this requested service as an inpatient consultation (99251-99255), Medicare no longer recognizes those codes. Instead, the hospitalist should report this encounter as an initial hospital care service (99221-99223).
Comanagement Issues
CMS and Medicare administrative contractors regularly uncover reporting errors for co-management requests. CMS decided the nature of these services were not consultative because the surgeon is not asking the physician or qualified nonphysician provider’s (NPP’s) opinion or advice for the surgeon’s use in treating the patient. Instead, these services constituted concurrent care and should have been billed using subsequent hospital care codes (99231-99233) in the hospital inpatient setting, subsequent NF care codes (99307-99310) in the SNF/NF setting, or office or other outpatient visit codes (99201-99215) in the office or outpatient settings.1
The new ruling simplifies coding and reduces reporting errors. The initial encounter with the patient is reported as such. Regardless of who is the attending of record or the consultant, the first physician from a particular provider group reports initial hospital care codes (i.e., 99221-99223) to represent the first patient encounter, even when this encounter does not occur on the admission date. Other physicians of the same specialty within the same provider group will not be permitted to report initial hospital care codes for their own initial encounter if someone from the group and specialty has already seen the patient during that hospitalization. In other words, the first hospitalist in the provider group reports 9922x, while the remaining hospitalists use subsequent hospital care codes (9923x).
In order to differentiate “consultant” services from “attending” services, CMS will be creating a modifier. The anticipated “AI” modifier must be appended to the attending physician’s initial encounter. Other initial hospital care codes reported throughout the hospital stay, as appropriate, are presumed to be that of “consultants” (i.e., physicians with a different specialty designation than the attending physician) participating in the case. Therefore, the hospitalist now can rightfully recover the increased work effort of the initial patient encounter (99223: 3.79 relative value units, ~$147 vs. 99233: 2.0 relative value units, ~$78, based on 2010 Medicare rates). Physicians will be required to meet the minimum documentation required for the selected visit code.
Other and Undefined Service Locations
Consultations in nursing facilities are handled much like inpatient hospital care. Physicians should report initial nursing facility services (99203-99306) for the first patient encounter, and subsequent nursing facility care codes (99307-99310) for each encounter thereafter. The attending physician of record appends the assigned modifier (presumed to be “AI”) when submitting their initial care service. All other initial care codes are presumed to be those of “consulting” physicians.
Initial information from CMS does not address observation services. Logically, these hospital-based services would follow the same methodology as inpatient care: report initial observation care (99218-99220) for the first “consulting” encounter. However, this might not be appropriate given Medicare’s existing rules for observation services, which guide physicians other than the admitting physician/group to “bill the office and other outpatient service codes or outpatient consultation codes as appropriate when they provide services to the patient.”2 With Medicare’s elimination of consultation codes, the consultant reports “office and other outpatient service codes” (i.e., new patient, 99201-99205, or established patient codes, 99212-99215) by default.
Without further clarification on observation services, hospitalists should report new or established patient service codes, depending on whether the patient has been seen by a group member within the last three years.
Medicare also has existing guidelines for the ED, which suggest that any physician not meeting the consultation criteria report ED service codes (99281-99285). Without further clarification, hospitalists should continue to follow this instruction for Medicare beneficiaries.
Nonphysician Providers
Medicare’s split/shared billing guidelines apply to most hospital inpatient, hospital outpatient, and ED evaluation and management (E/M) services, with consultations as one exception. Now, in accordance with the new ruling, hospitalists should select the appropriate initial service codes that correspond to patient’s location (e.g., 99223 for inpatients). NPPs can participate in the initial service provided to patients in these locations without the hospitalist having to replicate the entire service. The hospitalist can submit the claim in their name after selecting the visit level based upon the cumulative service personally provided on the same calendar day by both the NPP and the physician. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She also is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.10I. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/ manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Nov. 14, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.8A. CMS Web site. Available at: www. cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed Nov. 14, 2009.
- PFS Federal Regulation Notices: Proposed Revisions to Payment Policies Under the Physician Fee Schedule and Part B for CY 2010. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/PhysicianFeeSched/PFSFRN/itemdetail.asp?filterType=none&filterByDID=99&sortByDID=4&sortOrder=descending&itemID=CMS1223902&intNumPerPage=10. Accessed Nov. 12, 2009.
- Payment Policies Under the Physician Fee Schedule and Other Revisions to Part B (for CY 2010). CMS Web site. Available at: www.federalregister.gov/OFR Upload/OFRData/2009-26502_PI.pdf. Accessed Nov. 10, 2009.
Submission Support
Physicians receive requests for documentation on a daily basis. Insurer requests need particular attention, as they can be directly related to reimbursement. If the documentation supports the service, payment is rendered (pre-payment request) or maintained (post-payment request). If the documentation is not supportive, payment is denied (pre-payment request) or refunded (post-payment request).
The two most common reasons submitted documentation is not supportive: It lacks information or only a portion of the documentation was submitted.
Not Enough Documentation
“Insufficient documentation” can take many forms. Each visit category (e.g., initial hospital care or subsequent hospital care) and level of service (e.g., 99221-99233) has corresponding documentation requirements. A full list of requirements is available on the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site (www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNProducts/Downloads/1995dg.pdf). Selecting an evaluation and management (E/M) level is focused on either upon the content of three key components: history, exam, and decision-making; time can also be a consideration but only when counseling or coordination of care dominate more than 50% of the physician’s total visit time.1 Failure to document any essential element in a given visit level (e.g., family history required but missing for 99222 and 99223) might result in a reviewer down-coding or denying the service.
Dates and signatures are vital to each encounter. The reviewer must be able to identify each individual who performs, documents, and bills for a service, as well as when the service occurred. Notes that lack dates or signatures are not considered in support of a billed service. Notes that contain an illegible signature are equally problematic. If the legibility of a signature prevents the reviewer from correctly identifying the rendering physician, the service can be denied.
It is advisable for the physician to print their name alongside the signature on the encounter note, or include a separate signature sheet with the requested documentation to assist the reviewer in deciphering the physician’s scrawl. Keep in mind that stamped signatures are not acceptable. Medicare accepts handwritten signatures, electronic signatures, or facsimiles of original written or electronic signatures.2
A service is questioned when two different sets of handwriting appear on a note and only one signature is provided. Because the reviewer cannot confirm the credentials of the unidentified individual and cannot be sure which portion belongs to the identified individual, the entire note is disregarded.
Incomplete Submission
Many times, an encounter note does not contain the cumulative information representing the reported service. For example, other pieces of pertinent information might be included in the data section or order section of the chart. If the individual responsible for gathering the requested documentation does not review the information before submitting it, those other important entries could be missed, and the complexity of the billed service might not be justified.
To avoid this, have the designated individual review the note for specific references to information housed in different areas of the chart. The provider should submit any entry with the same date as the requested documentation: labs, diagnostic testing, physician orders, patient instructions, nursing notes, resident notes, notes by other physicians in the same group, discharge summaries, etc.
Legibility is crucial when the documentation is sent for review. Note that the reviewer will not contact the provider if the information is not readable. Most reviewers seek another reviewer’s assistance in translating the handwriting, but they are not obligated to do this. If the note is deemed incomprehensible, the service is denied.
Electronic health records (EHR) are assisting physicians and other providers with legibility issues, and can help take the guesswork out of the note’s content. If a physician is still writing notes by hand, a transcription could be sent along with the documentation to prevent unnecessary denials. It is not advisable to do this for all requests, but only for requests involving providers who have particularly problematic handwriting.
Timeliness of Response
Once the documentation request is received, the physician has a small window of opportunity to review the request, collect the information, and issue a response. A lack of physician response always results in a service denial or a refund request. Once denied, the physician must go through the proper channels of appeal (with a different insurer reviewing department). Requests for refunds are more difficult to overturn. It is difficult to “open” a case that has been “closed.” Denials resulting from a failure to respond to a pre-payment request are a bit easier to resolve because the resulting denial is typically the payor’s initial determination of the claim. The physician usually is allowed an appeal of the payor’s initial determination. However, it is not a cost-effective process to handle prepayment requests in this manner. Always attempt to respond to the initial request within the designated time frame. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Pohlig, C. Documentation and Coding Evaluation and Management Services. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, Ill.: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;79-109.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services: CR 5971 Clarification-Signature Requirements. Medicare Learning Network Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNMattersArticles/downloads/SE0829.pdf. Accessed Sept. 1, 2009.
- Pohlig C. Evaluation and Management Services: An Overview. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, Ill.: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008; 65-78.
Physicians receive requests for documentation on a daily basis. Insurer requests need particular attention, as they can be directly related to reimbursement. If the documentation supports the service, payment is rendered (pre-payment request) or maintained (post-payment request). If the documentation is not supportive, payment is denied (pre-payment request) or refunded (post-payment request).
The two most common reasons submitted documentation is not supportive: It lacks information or only a portion of the documentation was submitted.
Not Enough Documentation
“Insufficient documentation” can take many forms. Each visit category (e.g., initial hospital care or subsequent hospital care) and level of service (e.g., 99221-99233) has corresponding documentation requirements. A full list of requirements is available on the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site (www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNProducts/Downloads/1995dg.pdf). Selecting an evaluation and management (E/M) level is focused on either upon the content of three key components: history, exam, and decision-making; time can also be a consideration but only when counseling or coordination of care dominate more than 50% of the physician’s total visit time.1 Failure to document any essential element in a given visit level (e.g., family history required but missing for 99222 and 99223) might result in a reviewer down-coding or denying the service.
Dates and signatures are vital to each encounter. The reviewer must be able to identify each individual who performs, documents, and bills for a service, as well as when the service occurred. Notes that lack dates or signatures are not considered in support of a billed service. Notes that contain an illegible signature are equally problematic. If the legibility of a signature prevents the reviewer from correctly identifying the rendering physician, the service can be denied.
It is advisable for the physician to print their name alongside the signature on the encounter note, or include a separate signature sheet with the requested documentation to assist the reviewer in deciphering the physician’s scrawl. Keep in mind that stamped signatures are not acceptable. Medicare accepts handwritten signatures, electronic signatures, or facsimiles of original written or electronic signatures.2
A service is questioned when two different sets of handwriting appear on a note and only one signature is provided. Because the reviewer cannot confirm the credentials of the unidentified individual and cannot be sure which portion belongs to the identified individual, the entire note is disregarded.
Incomplete Submission
Many times, an encounter note does not contain the cumulative information representing the reported service. For example, other pieces of pertinent information might be included in the data section or order section of the chart. If the individual responsible for gathering the requested documentation does not review the information before submitting it, those other important entries could be missed, and the complexity of the billed service might not be justified.
To avoid this, have the designated individual review the note for specific references to information housed in different areas of the chart. The provider should submit any entry with the same date as the requested documentation: labs, diagnostic testing, physician orders, patient instructions, nursing notes, resident notes, notes by other physicians in the same group, discharge summaries, etc.
Legibility is crucial when the documentation is sent for review. Note that the reviewer will not contact the provider if the information is not readable. Most reviewers seek another reviewer’s assistance in translating the handwriting, but they are not obligated to do this. If the note is deemed incomprehensible, the service is denied.
Electronic health records (EHR) are assisting physicians and other providers with legibility issues, and can help take the guesswork out of the note’s content. If a physician is still writing notes by hand, a transcription could be sent along with the documentation to prevent unnecessary denials. It is not advisable to do this for all requests, but only for requests involving providers who have particularly problematic handwriting.
Timeliness of Response
Once the documentation request is received, the physician has a small window of opportunity to review the request, collect the information, and issue a response. A lack of physician response always results in a service denial or a refund request. Once denied, the physician must go through the proper channels of appeal (with a different insurer reviewing department). Requests for refunds are more difficult to overturn. It is difficult to “open” a case that has been “closed.” Denials resulting from a failure to respond to a pre-payment request are a bit easier to resolve because the resulting denial is typically the payor’s initial determination of the claim. The physician usually is allowed an appeal of the payor’s initial determination. However, it is not a cost-effective process to handle prepayment requests in this manner. Always attempt to respond to the initial request within the designated time frame. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Pohlig, C. Documentation and Coding Evaluation and Management Services. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, Ill.: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;79-109.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services: CR 5971 Clarification-Signature Requirements. Medicare Learning Network Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNMattersArticles/downloads/SE0829.pdf. Accessed Sept. 1, 2009.
- Pohlig C. Evaluation and Management Services: An Overview. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, Ill.: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008; 65-78.
Physicians receive requests for documentation on a daily basis. Insurer requests need particular attention, as they can be directly related to reimbursement. If the documentation supports the service, payment is rendered (pre-payment request) or maintained (post-payment request). If the documentation is not supportive, payment is denied (pre-payment request) or refunded (post-payment request).
The two most common reasons submitted documentation is not supportive: It lacks information or only a portion of the documentation was submitted.
Not Enough Documentation
“Insufficient documentation” can take many forms. Each visit category (e.g., initial hospital care or subsequent hospital care) and level of service (e.g., 99221-99233) has corresponding documentation requirements. A full list of requirements is available on the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services Web site (www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNProducts/Downloads/1995dg.pdf). Selecting an evaluation and management (E/M) level is focused on either upon the content of three key components: history, exam, and decision-making; time can also be a consideration but only when counseling or coordination of care dominate more than 50% of the physician’s total visit time.1 Failure to document any essential element in a given visit level (e.g., family history required but missing for 99222 and 99223) might result in a reviewer down-coding or denying the service.
Dates and signatures are vital to each encounter. The reviewer must be able to identify each individual who performs, documents, and bills for a service, as well as when the service occurred. Notes that lack dates or signatures are not considered in support of a billed service. Notes that contain an illegible signature are equally problematic. If the legibility of a signature prevents the reviewer from correctly identifying the rendering physician, the service can be denied.
It is advisable for the physician to print their name alongside the signature on the encounter note, or include a separate signature sheet with the requested documentation to assist the reviewer in deciphering the physician’s scrawl. Keep in mind that stamped signatures are not acceptable. Medicare accepts handwritten signatures, electronic signatures, or facsimiles of original written or electronic signatures.2
A service is questioned when two different sets of handwriting appear on a note and only one signature is provided. Because the reviewer cannot confirm the credentials of the unidentified individual and cannot be sure which portion belongs to the identified individual, the entire note is disregarded.
Incomplete Submission
Many times, an encounter note does not contain the cumulative information representing the reported service. For example, other pieces of pertinent information might be included in the data section or order section of the chart. If the individual responsible for gathering the requested documentation does not review the information before submitting it, those other important entries could be missed, and the complexity of the billed service might not be justified.
To avoid this, have the designated individual review the note for specific references to information housed in different areas of the chart. The provider should submit any entry with the same date as the requested documentation: labs, diagnostic testing, physician orders, patient instructions, nursing notes, resident notes, notes by other physicians in the same group, discharge summaries, etc.
Legibility is crucial when the documentation is sent for review. Note that the reviewer will not contact the provider if the information is not readable. Most reviewers seek another reviewer’s assistance in translating the handwriting, but they are not obligated to do this. If the note is deemed incomprehensible, the service is denied.
Electronic health records (EHR) are assisting physicians and other providers with legibility issues, and can help take the guesswork out of the note’s content. If a physician is still writing notes by hand, a transcription could be sent along with the documentation to prevent unnecessary denials. It is not advisable to do this for all requests, but only for requests involving providers who have particularly problematic handwriting.
Timeliness of Response
Once the documentation request is received, the physician has a small window of opportunity to review the request, collect the information, and issue a response. A lack of physician response always results in a service denial or a refund request. Once denied, the physician must go through the proper channels of appeal (with a different insurer reviewing department). Requests for refunds are more difficult to overturn. It is difficult to “open” a case that has been “closed.” Denials resulting from a failure to respond to a pre-payment request are a bit easier to resolve because the resulting denial is typically the payor’s initial determination of the claim. The physician usually is allowed an appeal of the payor’s initial determination. However, it is not a cost-effective process to handle prepayment requests in this manner. Always attempt to respond to the initial request within the designated time frame. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Pohlig, C. Documentation and Coding Evaluation and Management Services. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, Ill.: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;79-109.
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services: CR 5971 Clarification-Signature Requirements. Medicare Learning Network Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNMattersArticles/downloads/SE0829.pdf. Accessed Sept. 1, 2009.
- Pohlig C. Evaluation and Management Services: An Overview. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, Ill.: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008; 65-78.
Document Inspection
One constant in all the modifications to billing and reimbursement guidelines for evaluation and management (E/M) services provided by hospitalists is that a face-to-face patient encounter by the billing provider is required. Exceptions do occur (e.g., telehealth services, care plan oversight, home health certification) but are infrequently reported by hospitalist teams. Do not get caught misreporting the following services due to the absence of a physician presence.
Discharge Day Management
Hospital discharge day management (CPT 99238-99239) is a face-to-face E/M service between the attending physician and the patient. Document the date of the actual physician visit even if the patient is discharged from the facility on a different date.1 Documentation must substantiate this personal patient encounter.
A hospitalist can choose to record the face-to-face encounter in a handwritten progress note or make note of it in the formal discharge summary. When relying solely upon the dictated summary, physicians often fail to identify personal contact with the patient. Although an examination need only be performed “as appropriate” on the day of discharge, it is the best indicator of a face-to-face encounter. Such statements as “Upon discharge, the patient appeared well, vital signs stable, lungs clear” or “Patient seen and examined by me on discharge day” clearly illustrate this service.
It is important to note that only the attending physician of record reports the discharge day management service. Physicians or qualified non-physician practitioners (NPPs), other than the attending physician, who have been managing concurrent healthcare problems not primarily managed by the attending physician and who are not acting on behalf of the attending physician should use subsequent hospital care codes (99231-99233) for a final visit.2
Death pronouncement can be reported with discharge day management codes (99238-99239), but only when this service involves a physician-patient encounter. Physicians should report the most appropriate discharge code on the actual day of pronouncement.
Shared/Split Services
Shared/split Medicare services occur when two providers from the same specialty and group practice perform a portion of a facility-based (outpatient hospital, inpatient hospital, or ED) patient encounter on the same day. One provider must be a physician; the other must be a qualified and certified NPP (e.g., nurse practitioner, physician assistant, clinical nurse specialist, certified nurse midwife).
The culmination of the two portions of service must fulfill the requirements of a single E/M service (consultations, critical care, and other time-based services excluded). The physician has the option to report the shared/split service to Medicare under their name for 100% of the allowable reimbursement rate, or under the NPP’s name for 85% of the allowable reimbursement rate.
In order to utilize this billing model, the physician and the NPP must provide a face-to-face encounter on the same day. If there is no face-to-face encounter between the patient and the physician, then the service can only be billed under the NPP’s name at 85% of the allowable reimbursement rate.3
Documentation must clearly identify each provider involved in the shared/split service, along with the presence and the portion of each individual’s service. The NPP and the physician should each indicate the extent of their involvement (e.g., “Patient seen and examined by me … ”) in the patient’s care and sign their portion of the note. If the NPP and physician each write a separate note, each note should refer to the other provider. That way, the supporting documentation for the service rendered encompasses the summation of both notes.4
Teaching Physician Services
A different type of shared service can occur under the teaching physician rules, whereby an attending physician and a “resident” are involved in the same patient encounter. The term “resident” also includes interns and fellows in recognized graduate medical education (GME) programs, as approved for purposes of direct GME payments made by the fiscal intermediary.5 As with services shared with NPPs, the attending physician must provide a face-to-face encounter and participate in a key portion of the service.
The attending physician can perform their portion of the service concurrently or independent of the resident but is allowed to discuss the case (teaching service) with the resident, as appropriate. If the attending physician does not physically see the patient, the service cannot be reported. Payment is made only for the teaching physician’s involvement in the patient’s care.
Instead of detailing the entire encounter, the teaching physician should write a short, legible linking or tethering statement specifically referencing the resident’s note. Physicians must demonstrate their physical presence (e.g., “Patient seen and examined by me. Agree with note by Dr. Jones”) and comment on the patient’s evaluation and their active involvement in the care plan.6 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.15.1C. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.2B. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.1B. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Pohlig, C. Nonphysician Providers in Your Practice. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, IL: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;265-271.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 100. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Manaker, S. Teaching Physician Regulations. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, IL: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;299-305.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1D. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2008.
One constant in all the modifications to billing and reimbursement guidelines for evaluation and management (E/M) services provided by hospitalists is that a face-to-face patient encounter by the billing provider is required. Exceptions do occur (e.g., telehealth services, care plan oversight, home health certification) but are infrequently reported by hospitalist teams. Do not get caught misreporting the following services due to the absence of a physician presence.
Discharge Day Management
Hospital discharge day management (CPT 99238-99239) is a face-to-face E/M service between the attending physician and the patient. Document the date of the actual physician visit even if the patient is discharged from the facility on a different date.1 Documentation must substantiate this personal patient encounter.
A hospitalist can choose to record the face-to-face encounter in a handwritten progress note or make note of it in the formal discharge summary. When relying solely upon the dictated summary, physicians often fail to identify personal contact with the patient. Although an examination need only be performed “as appropriate” on the day of discharge, it is the best indicator of a face-to-face encounter. Such statements as “Upon discharge, the patient appeared well, vital signs stable, lungs clear” or “Patient seen and examined by me on discharge day” clearly illustrate this service.
It is important to note that only the attending physician of record reports the discharge day management service. Physicians or qualified non-physician practitioners (NPPs), other than the attending physician, who have been managing concurrent healthcare problems not primarily managed by the attending physician and who are not acting on behalf of the attending physician should use subsequent hospital care codes (99231-99233) for a final visit.2
Death pronouncement can be reported with discharge day management codes (99238-99239), but only when this service involves a physician-patient encounter. Physicians should report the most appropriate discharge code on the actual day of pronouncement.
Shared/Split Services
Shared/split Medicare services occur when two providers from the same specialty and group practice perform a portion of a facility-based (outpatient hospital, inpatient hospital, or ED) patient encounter on the same day. One provider must be a physician; the other must be a qualified and certified NPP (e.g., nurse practitioner, physician assistant, clinical nurse specialist, certified nurse midwife).
The culmination of the two portions of service must fulfill the requirements of a single E/M service (consultations, critical care, and other time-based services excluded). The physician has the option to report the shared/split service to Medicare under their name for 100% of the allowable reimbursement rate, or under the NPP’s name for 85% of the allowable reimbursement rate.
In order to utilize this billing model, the physician and the NPP must provide a face-to-face encounter on the same day. If there is no face-to-face encounter between the patient and the physician, then the service can only be billed under the NPP’s name at 85% of the allowable reimbursement rate.3
Documentation must clearly identify each provider involved in the shared/split service, along with the presence and the portion of each individual’s service. The NPP and the physician should each indicate the extent of their involvement (e.g., “Patient seen and examined by me … ”) in the patient’s care and sign their portion of the note. If the NPP and physician each write a separate note, each note should refer to the other provider. That way, the supporting documentation for the service rendered encompasses the summation of both notes.4
Teaching Physician Services
A different type of shared service can occur under the teaching physician rules, whereby an attending physician and a “resident” are involved in the same patient encounter. The term “resident” also includes interns and fellows in recognized graduate medical education (GME) programs, as approved for purposes of direct GME payments made by the fiscal intermediary.5 As with services shared with NPPs, the attending physician must provide a face-to-face encounter and participate in a key portion of the service.
The attending physician can perform their portion of the service concurrently or independent of the resident but is allowed to discuss the case (teaching service) with the resident, as appropriate. If the attending physician does not physically see the patient, the service cannot be reported. Payment is made only for the teaching physician’s involvement in the patient’s care.
Instead of detailing the entire encounter, the teaching physician should write a short, legible linking or tethering statement specifically referencing the resident’s note. Physicians must demonstrate their physical presence (e.g., “Patient seen and examined by me. Agree with note by Dr. Jones”) and comment on the patient’s evaluation and their active involvement in the care plan.6 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.15.1C. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.2B. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.1B. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Pohlig, C. Nonphysician Providers in Your Practice. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, IL: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;265-271.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 100. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Manaker, S. Teaching Physician Regulations. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, IL: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;299-305.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1D. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2008.
One constant in all the modifications to billing and reimbursement guidelines for evaluation and management (E/M) services provided by hospitalists is that a face-to-face patient encounter by the billing provider is required. Exceptions do occur (e.g., telehealth services, care plan oversight, home health certification) but are infrequently reported by hospitalist teams. Do not get caught misreporting the following services due to the absence of a physician presence.
Discharge Day Management
Hospital discharge day management (CPT 99238-99239) is a face-to-face E/M service between the attending physician and the patient. Document the date of the actual physician visit even if the patient is discharged from the facility on a different date.1 Documentation must substantiate this personal patient encounter.
A hospitalist can choose to record the face-to-face encounter in a handwritten progress note or make note of it in the formal discharge summary. When relying solely upon the dictated summary, physicians often fail to identify personal contact with the patient. Although an examination need only be performed “as appropriate” on the day of discharge, it is the best indicator of a face-to-face encounter. Such statements as “Upon discharge, the patient appeared well, vital signs stable, lungs clear” or “Patient seen and examined by me on discharge day” clearly illustrate this service.
It is important to note that only the attending physician of record reports the discharge day management service. Physicians or qualified non-physician practitioners (NPPs), other than the attending physician, who have been managing concurrent healthcare problems not primarily managed by the attending physician and who are not acting on behalf of the attending physician should use subsequent hospital care codes (99231-99233) for a final visit.2
Death pronouncement can be reported with discharge day management codes (99238-99239), but only when this service involves a physician-patient encounter. Physicians should report the most appropriate discharge code on the actual day of pronouncement.
Shared/Split Services
Shared/split Medicare services occur when two providers from the same specialty and group practice perform a portion of a facility-based (outpatient hospital, inpatient hospital, or ED) patient encounter on the same day. One provider must be a physician; the other must be a qualified and certified NPP (e.g., nurse practitioner, physician assistant, clinical nurse specialist, certified nurse midwife).
The culmination of the two portions of service must fulfill the requirements of a single E/M service (consultations, critical care, and other time-based services excluded). The physician has the option to report the shared/split service to Medicare under their name for 100% of the allowable reimbursement rate, or under the NPP’s name for 85% of the allowable reimbursement rate.
In order to utilize this billing model, the physician and the NPP must provide a face-to-face encounter on the same day. If there is no face-to-face encounter between the patient and the physician, then the service can only be billed under the NPP’s name at 85% of the allowable reimbursement rate.3
Documentation must clearly identify each provider involved in the shared/split service, along with the presence and the portion of each individual’s service. The NPP and the physician should each indicate the extent of their involvement (e.g., “Patient seen and examined by me … ”) in the patient’s care and sign their portion of the note. If the NPP and physician each write a separate note, each note should refer to the other provider. That way, the supporting documentation for the service rendered encompasses the summation of both notes.4
Teaching Physician Services
A different type of shared service can occur under the teaching physician rules, whereby an attending physician and a “resident” are involved in the same patient encounter. The term “resident” also includes interns and fellows in recognized graduate medical education (GME) programs, as approved for purposes of direct GME payments made by the fiscal intermediary.5 As with services shared with NPPs, the attending physician must provide a face-to-face encounter and participate in a key portion of the service.
The attending physician can perform their portion of the service concurrently or independent of the resident but is allowed to discuss the case (teaching service) with the resident, as appropriate. If the attending physician does not physically see the patient, the service cannot be reported. Payment is made only for the teaching physician’s involvement in the patient’s care.
Instead of detailing the entire encounter, the teaching physician should write a short, legible linking or tethering statement specifically referencing the resident’s note. Physicians must demonstrate their physical presence (e.g., “Patient seen and examined by me. Agree with note by Dr. Jones”) and comment on the patient’s evaluation and their active involvement in the care plan.6 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center, Philadelphia. She is faculty for SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.15.1C. Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.2B. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.1B. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Pohlig, C. Nonphysician Providers in Your Practice. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, IL: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;265-271.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 100. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Manaker, S. Teaching Physician Regulations. In: Coding for Chest Medicine 2009. Northbrook, IL: American College of Chest Physicians, 2008;299-305.
- Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1D. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12. pdf. Accessed July 5, 2009.
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2008.
Revenue Essentials
As physicians take on more extensive roles outside of patient care (e.g., administrative, academic, and billing compliance), involvement in the revenue cycle might diminish or even fail to commence. It is crucial for physicians to keep abreast of revenue cycle issues, but more often than not, they go unnoticed until a physician’s bottom line is affected.
The risk of inappropriately billed claims and corresponding reimbursement is increased until the problem is identified and resolved. In an effort to prevent this from occurring, physicians should get involved with or oversee their billing service or staff. Some of the revenue cycle essentials that require physician attention are:1
- Periodic reports of claims billed on the physician’s behalf and data regarding payments;
- Changes in procedure codes, diagnosis codes, or other information furnished by the physician without the physician’s knowledge and consent; and
- Information received from Medicare and other payors.
Feedback
One of the most common billing-related physician complaints involves the lack of feedback. Most physicians want to receive information regarding their quarterly billings: the volume and frequency of specific reported services, and corresponding payments or denials. Physicians prefer to know how they rank as individuals and as a group. Although they might not be experts in coding and documentation, this information offers physicians a feeling of security, as it permits them to identify typical billing patterns or highlight outlier patterns.
Establish communication with the manager/coder/biller to better assist with feedback. Appoint a physician leader to spearhead this effort; ensure feedback is provided quarterly, at a minimum. If the coders/billers feel that they have an approachable contact, they’re more likely to offer feedback before formal reports are generated. A quick resolution of potential problems lessens the financial burden on the HM group, as well as the resource-intensive education process that ensues.
Discrepancy Notation
Physicians should be notified whenever coding changes take place. Discrepancies occur when the physician employs coders to select the service or diagnosis codes, and the selected codes differ from the physician-intended codes. Discrepancies also occur when billers change the original physician-selected codes to codes that are considered covered or medically necessary by the pay0r. Physicians need to instruct coders to only report codes that are supported by the documentation.
Physicians must be aware that delegating any portion of the billing to an employee or a billing company does not alleviate physicians’ personal responsibility for erroneously submitted claims or receipt of overpayments. Physicians should regularly review information submitted by the designated employee or billing service to ensure consistency with their own records, and also keep complete administrative records for the claims a billing service files on their behalf.1 Physicians also should meet with staff to resolve discrepancies and reinforce the billing education process. If biller/coder performance becomes a recurring problem, the physician should question the competency of the employee or company with whom the billing is entrusted.
Accounts Receivable
Physicians do not necessarily recognize the need for involvement in the accounts receivable (A/R) component of the revenue cycle. Physicians should be aware of denials, and the reasons for the denials. Some services are denied because of issues that can be easily corrected (e.g., truncated diagnoses, two physicians of the same specialty billing on the same date, missing modifiers). These denial types might require physician assistance in changing the codes originally submitted. If the denied services can be corrected with the appropriate information and resubmitted electronically, payment might be recovered quickly. Other types of denials require submission of the documentation to support the service billed.
Billers should know the difference between the types of denials and the required action for each denial type. Physicians should feel confident that such denials will be handled in the correct manner. Be mindful of billing staff that accepts denials and surrenders the reimbursement efforts without hesitation. As a physician, do not default to the idea that “no news is good news.” Do not assume the billing manager (physician employee or outsourced firm) will let the group know if there is a problem. Develop a standard that requires monthly feedback of denials.
Only a short window of time exists for the appeals process to occur. Do not lose the potential to recover monies because the information was not provided to the physician in a timely manner. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Protecting Your Practice. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNProducts/downloads/Protectingpracbroch508-09.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
- Office of Inspector General. Work Plan Health Care Financing Administration Projects Fiscal Year 1999. Physicians: Billing Service Companies. Available at: http://oig.hhs.gov/publications/docs/workplan/1999/99hcfawp.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
- Office of Inspector General. OIG Compliance Program Guidance for Third-Party Medical Billing Companies in Federal Register, December 1998, Vol. 63; pages 70138-70152. Available at: http://oig.hhs.gov/fraud/docs/complianceguidance/thirdparty.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
As physicians take on more extensive roles outside of patient care (e.g., administrative, academic, and billing compliance), involvement in the revenue cycle might diminish or even fail to commence. It is crucial for physicians to keep abreast of revenue cycle issues, but more often than not, they go unnoticed until a physician’s bottom line is affected.
The risk of inappropriately billed claims and corresponding reimbursement is increased until the problem is identified and resolved. In an effort to prevent this from occurring, physicians should get involved with or oversee their billing service or staff. Some of the revenue cycle essentials that require physician attention are:1
- Periodic reports of claims billed on the physician’s behalf and data regarding payments;
- Changes in procedure codes, diagnosis codes, or other information furnished by the physician without the physician’s knowledge and consent; and
- Information received from Medicare and other payors.
Feedback
One of the most common billing-related physician complaints involves the lack of feedback. Most physicians want to receive information regarding their quarterly billings: the volume and frequency of specific reported services, and corresponding payments or denials. Physicians prefer to know how they rank as individuals and as a group. Although they might not be experts in coding and documentation, this information offers physicians a feeling of security, as it permits them to identify typical billing patterns or highlight outlier patterns.
Establish communication with the manager/coder/biller to better assist with feedback. Appoint a physician leader to spearhead this effort; ensure feedback is provided quarterly, at a minimum. If the coders/billers feel that they have an approachable contact, they’re more likely to offer feedback before formal reports are generated. A quick resolution of potential problems lessens the financial burden on the HM group, as well as the resource-intensive education process that ensues.
Discrepancy Notation
Physicians should be notified whenever coding changes take place. Discrepancies occur when the physician employs coders to select the service or diagnosis codes, and the selected codes differ from the physician-intended codes. Discrepancies also occur when billers change the original physician-selected codes to codes that are considered covered or medically necessary by the pay0r. Physicians need to instruct coders to only report codes that are supported by the documentation.
Physicians must be aware that delegating any portion of the billing to an employee or a billing company does not alleviate physicians’ personal responsibility for erroneously submitted claims or receipt of overpayments. Physicians should regularly review information submitted by the designated employee or billing service to ensure consistency with their own records, and also keep complete administrative records for the claims a billing service files on their behalf.1 Physicians also should meet with staff to resolve discrepancies and reinforce the billing education process. If biller/coder performance becomes a recurring problem, the physician should question the competency of the employee or company with whom the billing is entrusted.
Accounts Receivable
Physicians do not necessarily recognize the need for involvement in the accounts receivable (A/R) component of the revenue cycle. Physicians should be aware of denials, and the reasons for the denials. Some services are denied because of issues that can be easily corrected (e.g., truncated diagnoses, two physicians of the same specialty billing on the same date, missing modifiers). These denial types might require physician assistance in changing the codes originally submitted. If the denied services can be corrected with the appropriate information and resubmitted electronically, payment might be recovered quickly. Other types of denials require submission of the documentation to support the service billed.
Billers should know the difference between the types of denials and the required action for each denial type. Physicians should feel confident that such denials will be handled in the correct manner. Be mindful of billing staff that accepts denials and surrenders the reimbursement efforts without hesitation. As a physician, do not default to the idea that “no news is good news.” Do not assume the billing manager (physician employee or outsourced firm) will let the group know if there is a problem. Develop a standard that requires monthly feedback of denials.
Only a short window of time exists for the appeals process to occur. Do not lose the potential to recover monies because the information was not provided to the physician in a timely manner. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Protecting Your Practice. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNProducts/downloads/Protectingpracbroch508-09.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
- Office of Inspector General. Work Plan Health Care Financing Administration Projects Fiscal Year 1999. Physicians: Billing Service Companies. Available at: http://oig.hhs.gov/publications/docs/workplan/1999/99hcfawp.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
- Office of Inspector General. OIG Compliance Program Guidance for Third-Party Medical Billing Companies in Federal Register, December 1998, Vol. 63; pages 70138-70152. Available at: http://oig.hhs.gov/fraud/docs/complianceguidance/thirdparty.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
As physicians take on more extensive roles outside of patient care (e.g., administrative, academic, and billing compliance), involvement in the revenue cycle might diminish or even fail to commence. It is crucial for physicians to keep abreast of revenue cycle issues, but more often than not, they go unnoticed until a physician’s bottom line is affected.
The risk of inappropriately billed claims and corresponding reimbursement is increased until the problem is identified and resolved. In an effort to prevent this from occurring, physicians should get involved with or oversee their billing service or staff. Some of the revenue cycle essentials that require physician attention are:1
- Periodic reports of claims billed on the physician’s behalf and data regarding payments;
- Changes in procedure codes, diagnosis codes, or other information furnished by the physician without the physician’s knowledge and consent; and
- Information received from Medicare and other payors.
Feedback
One of the most common billing-related physician complaints involves the lack of feedback. Most physicians want to receive information regarding their quarterly billings: the volume and frequency of specific reported services, and corresponding payments or denials. Physicians prefer to know how they rank as individuals and as a group. Although they might not be experts in coding and documentation, this information offers physicians a feeling of security, as it permits them to identify typical billing patterns or highlight outlier patterns.
Establish communication with the manager/coder/biller to better assist with feedback. Appoint a physician leader to spearhead this effort; ensure feedback is provided quarterly, at a minimum. If the coders/billers feel that they have an approachable contact, they’re more likely to offer feedback before formal reports are generated. A quick resolution of potential problems lessens the financial burden on the HM group, as well as the resource-intensive education process that ensues.
Discrepancy Notation
Physicians should be notified whenever coding changes take place. Discrepancies occur when the physician employs coders to select the service or diagnosis codes, and the selected codes differ from the physician-intended codes. Discrepancies also occur when billers change the original physician-selected codes to codes that are considered covered or medically necessary by the pay0r. Physicians need to instruct coders to only report codes that are supported by the documentation.
Physicians must be aware that delegating any portion of the billing to an employee or a billing company does not alleviate physicians’ personal responsibility for erroneously submitted claims or receipt of overpayments. Physicians should regularly review information submitted by the designated employee or billing service to ensure consistency with their own records, and also keep complete administrative records for the claims a billing service files on their behalf.1 Physicians also should meet with staff to resolve discrepancies and reinforce the billing education process. If biller/coder performance becomes a recurring problem, the physician should question the competency of the employee or company with whom the billing is entrusted.
Accounts Receivable
Physicians do not necessarily recognize the need for involvement in the accounts receivable (A/R) component of the revenue cycle. Physicians should be aware of denials, and the reasons for the denials. Some services are denied because of issues that can be easily corrected (e.g., truncated diagnoses, two physicians of the same specialty billing on the same date, missing modifiers). These denial types might require physician assistance in changing the codes originally submitted. If the denied services can be corrected with the appropriate information and resubmitted electronically, payment might be recovered quickly. Other types of denials require submission of the documentation to support the service billed.
Billers should know the difference between the types of denials and the required action for each denial type. Physicians should feel confident that such denials will be handled in the correct manner. Be mindful of billing staff that accepts denials and surrenders the reimbursement efforts without hesitation. As a physician, do not default to the idea that “no news is good news.” Do not assume the billing manager (physician employee or outsourced firm) will let the group know if there is a problem. Develop a standard that requires monthly feedback of denials.
Only a short window of time exists for the appeals process to occur. Do not lose the potential to recover monies because the information was not provided to the physician in a timely manner. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is also on the faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Protecting Your Practice. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/MLNProducts/downloads/Protectingpracbroch508-09.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
- Office of Inspector General. Work Plan Health Care Financing Administration Projects Fiscal Year 1999. Physicians: Billing Service Companies. Available at: http://oig.hhs.gov/publications/docs/workplan/1999/99hcfawp.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
- Office of Inspector General. OIG Compliance Program Guidance for Third-Party Medical Billing Companies in Federal Register, December 1998, Vol. 63; pages 70138-70152. Available at: http://oig.hhs.gov/fraud/docs/complianceguidance/thirdparty.pdf. Accessed Aug. 2, 2009.
Facility Transfers
Patient care provided in the acute setting might not always end with discharge to the patient’s home. Frequently, a hospitalist will transfer the patient to a different unit in the hospital or an off-site facility to receive additional services before returning to their home. When the patient’s condition requires a transfer to a physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) unit, a psychiatric unit, a long-term acute-care facility, or a skilled nursing facility, it is important for the hospitalist to identify their role, if any, in the new area of care. Physician billing will depend on several factors:
- A shared medical record;
- The attending of record in each setting; and
- The care rendered by the hospitalist in each setting.
Intrafacility
A hospitalist serves as the “attending of record” in an inpatient hospital where acute care is required for a 68-year-old male with hypertension and diabetes who sustained a hip fracture. The care plan includes post-discharge therapy and rehabilitation. When the hospitalist transfers care to a PM&R unit within the same facility for which the hospitalist is no longer the attending of record, they might be asked to provide ongoing care for the patient’s medical conditions (e.g., diabetes and hypertension). The hospitalist’s knee-jerk reaction is to bill for an inpatient consultation for the initial service provided in the transferred setting. This would only be appropriate if the request for opinion or advice involved an unrelated, new condition, and the requesting physician’s intent is for opinion or advice on how to manage the patient and not the a priori intent for the hospitalist to assume the patient’s medical care.
If consultation requirements are met (see “Consulataion Reminder,” p. 20), the hospitalist can report an inpatient consultation code (99251-99255). However, when circumstances do not fully represent the intent or need for consultative services but rather a continuity of the medical care provided during the acute phase of the hospitalization, report the most appropriate subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233) for the initial rehab visit and all follow-up services.
On occasion, the hospitalist will be asked to perform and provide the history and physical (H&P) for the patient’s “sub-acute” phase of care, even though the hospitalist is not the attending of record. This usually happens when the attending of record cannot complete the medical requirements of the H&P, either at all or as comprehensively as the hospitalist. When this occurs, the hospitalist should not report an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) because they are not the attending of record—the physician who admits the patient and is responsible for the patient’s stay in the transferred location.
Additionally, a consultation service (99251-99255) should not be reported, because the request involves the completion of a facility-mandated form and not an opinion or advice on caring for the patient. If medical issues require the hospitalist’s evaluation and management, there is medical necessity for capturing the hospitalist’s participation as subsequent hospital care (99231-99233). If no medical conditions present for the hospitalist to manage, the service will not be considered “medically necessary” by the payor.
Interfacility
Hospitalist groups provide patient care and coverage in a variety of facilities. Confusion often arises when the attending of record during acute care and the sub-acute setting are different hospitalists from the same HM group. The hospitalist who receives the patient in the transfer facility may err on the side of caution and report subsequent hospital care (99231-99233) because the group has provided ongoing patient care. In this scenario, the hospitalist group might lose revenue if an admission service (99221-99223) was not reported.
Day of Transfer Billing
A single hospitalist or two hospitalists from the same group might bill both the hospital discharge management code (99238-99239) and an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) when the discharge and admission do not occur on the same day if the transfer is between:
- Different hospitals;
- Different facilities under common ownership that do not have merged records;* or
- Between the acute-care hospital and a prospective payment system (PPS)-exempt unit within the same hospital when there are no merged records.
In all other transfer circumstances that do not meet the elements noted above, the physician should bill only the appropriate level of subsequent hospital care (99231-99233) for the date of transfer.1 Of note, Medicare Part A covers inpatient care in psychiatric, rehabilitation, critical access, and long-term-care hospitals. Each of these specialty hospitals is exempt from the PPS established for acute-care hospitals in 1983.2 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
*Editor’s note: “Merged record” is not equivalent to commonly accessible charts via an electronic health record system. If the medical record for the patient’s acute stay is “closed” and the patient is given a separate medical record and registration for the stay in the transferred facility, consider the transfer stay as a separate admission.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1E. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
- Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General: Oversight of Medicare PPS-Exempt Hospital Services. HHS Web site. Available at: www.oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-12-02-00170.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
- CMS. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1H. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
Patient care provided in the acute setting might not always end with discharge to the patient’s home. Frequently, a hospitalist will transfer the patient to a different unit in the hospital or an off-site facility to receive additional services before returning to their home. When the patient’s condition requires a transfer to a physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) unit, a psychiatric unit, a long-term acute-care facility, or a skilled nursing facility, it is important for the hospitalist to identify their role, if any, in the new area of care. Physician billing will depend on several factors:
- A shared medical record;
- The attending of record in each setting; and
- The care rendered by the hospitalist in each setting.
Intrafacility
A hospitalist serves as the “attending of record” in an inpatient hospital where acute care is required for a 68-year-old male with hypertension and diabetes who sustained a hip fracture. The care plan includes post-discharge therapy and rehabilitation. When the hospitalist transfers care to a PM&R unit within the same facility for which the hospitalist is no longer the attending of record, they might be asked to provide ongoing care for the patient’s medical conditions (e.g., diabetes and hypertension). The hospitalist’s knee-jerk reaction is to bill for an inpatient consultation for the initial service provided in the transferred setting. This would only be appropriate if the request for opinion or advice involved an unrelated, new condition, and the requesting physician’s intent is for opinion or advice on how to manage the patient and not the a priori intent for the hospitalist to assume the patient’s medical care.
If consultation requirements are met (see “Consulataion Reminder,” p. 20), the hospitalist can report an inpatient consultation code (99251-99255). However, when circumstances do not fully represent the intent or need for consultative services but rather a continuity of the medical care provided during the acute phase of the hospitalization, report the most appropriate subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233) for the initial rehab visit and all follow-up services.
On occasion, the hospitalist will be asked to perform and provide the history and physical (H&P) for the patient’s “sub-acute” phase of care, even though the hospitalist is not the attending of record. This usually happens when the attending of record cannot complete the medical requirements of the H&P, either at all or as comprehensively as the hospitalist. When this occurs, the hospitalist should not report an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) because they are not the attending of record—the physician who admits the patient and is responsible for the patient’s stay in the transferred location.
Additionally, a consultation service (99251-99255) should not be reported, because the request involves the completion of a facility-mandated form and not an opinion or advice on caring for the patient. If medical issues require the hospitalist’s evaluation and management, there is medical necessity for capturing the hospitalist’s participation as subsequent hospital care (99231-99233). If no medical conditions present for the hospitalist to manage, the service will not be considered “medically necessary” by the payor.
Interfacility
Hospitalist groups provide patient care and coverage in a variety of facilities. Confusion often arises when the attending of record during acute care and the sub-acute setting are different hospitalists from the same HM group. The hospitalist who receives the patient in the transfer facility may err on the side of caution and report subsequent hospital care (99231-99233) because the group has provided ongoing patient care. In this scenario, the hospitalist group might lose revenue if an admission service (99221-99223) was not reported.
Day of Transfer Billing
A single hospitalist or two hospitalists from the same group might bill both the hospital discharge management code (99238-99239) and an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) when the discharge and admission do not occur on the same day if the transfer is between:
- Different hospitals;
- Different facilities under common ownership that do not have merged records;* or
- Between the acute-care hospital and a prospective payment system (PPS)-exempt unit within the same hospital when there are no merged records.
In all other transfer circumstances that do not meet the elements noted above, the physician should bill only the appropriate level of subsequent hospital care (99231-99233) for the date of transfer.1 Of note, Medicare Part A covers inpatient care in psychiatric, rehabilitation, critical access, and long-term-care hospitals. Each of these specialty hospitals is exempt from the PPS established for acute-care hospitals in 1983.2 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
*Editor’s note: “Merged record” is not equivalent to commonly accessible charts via an electronic health record system. If the medical record for the patient’s acute stay is “closed” and the patient is given a separate medical record and registration for the stay in the transferred facility, consider the transfer stay as a separate admission.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1E. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
- Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General: Oversight of Medicare PPS-Exempt Hospital Services. HHS Web site. Available at: www.oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-12-02-00170.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
- CMS. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1H. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
Patient care provided in the acute setting might not always end with discharge to the patient’s home. Frequently, a hospitalist will transfer the patient to a different unit in the hospital or an off-site facility to receive additional services before returning to their home. When the patient’s condition requires a transfer to a physical medicine and rehabilitation (PM&R) unit, a psychiatric unit, a long-term acute-care facility, or a skilled nursing facility, it is important for the hospitalist to identify their role, if any, in the new area of care. Physician billing will depend on several factors:
- A shared medical record;
- The attending of record in each setting; and
- The care rendered by the hospitalist in each setting.
Intrafacility
A hospitalist serves as the “attending of record” in an inpatient hospital where acute care is required for a 68-year-old male with hypertension and diabetes who sustained a hip fracture. The care plan includes post-discharge therapy and rehabilitation. When the hospitalist transfers care to a PM&R unit within the same facility for which the hospitalist is no longer the attending of record, they might be asked to provide ongoing care for the patient’s medical conditions (e.g., diabetes and hypertension). The hospitalist’s knee-jerk reaction is to bill for an inpatient consultation for the initial service provided in the transferred setting. This would only be appropriate if the request for opinion or advice involved an unrelated, new condition, and the requesting physician’s intent is for opinion or advice on how to manage the patient and not the a priori intent for the hospitalist to assume the patient’s medical care.
If consultation requirements are met (see “Consulataion Reminder,” p. 20), the hospitalist can report an inpatient consultation code (99251-99255). However, when circumstances do not fully represent the intent or need for consultative services but rather a continuity of the medical care provided during the acute phase of the hospitalization, report the most appropriate subsequent hospital care code (99231-99233) for the initial rehab visit and all follow-up services.
On occasion, the hospitalist will be asked to perform and provide the history and physical (H&P) for the patient’s “sub-acute” phase of care, even though the hospitalist is not the attending of record. This usually happens when the attending of record cannot complete the medical requirements of the H&P, either at all or as comprehensively as the hospitalist. When this occurs, the hospitalist should not report an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) because they are not the attending of record—the physician who admits the patient and is responsible for the patient’s stay in the transferred location.
Additionally, a consultation service (99251-99255) should not be reported, because the request involves the completion of a facility-mandated form and not an opinion or advice on caring for the patient. If medical issues require the hospitalist’s evaluation and management, there is medical necessity for capturing the hospitalist’s participation as subsequent hospital care (99231-99233). If no medical conditions present for the hospitalist to manage, the service will not be considered “medically necessary” by the payor.
Interfacility
Hospitalist groups provide patient care and coverage in a variety of facilities. Confusion often arises when the attending of record during acute care and the sub-acute setting are different hospitalists from the same HM group. The hospitalist who receives the patient in the transfer facility may err on the side of caution and report subsequent hospital care (99231-99233) because the group has provided ongoing patient care. In this scenario, the hospitalist group might lose revenue if an admission service (99221-99223) was not reported.
Day of Transfer Billing
A single hospitalist or two hospitalists from the same group might bill both the hospital discharge management code (99238-99239) and an initial hospital care code (99221-99223) when the discharge and admission do not occur on the same day if the transfer is between:
- Different hospitals;
- Different facilities under common ownership that do not have merged records;* or
- Between the acute-care hospital and a prospective payment system (PPS)-exempt unit within the same hospital when there are no merged records.
In all other transfer circumstances that do not meet the elements noted above, the physician should bill only the appropriate level of subsequent hospital care (99231-99233) for the date of transfer.1 Of note, Medicare Part A covers inpatient care in psychiatric, rehabilitation, critical access, and long-term-care hospitals. Each of these specialty hospitals is exempt from the PPS established for acute-care hospitals in 1983.2 TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
*Editor’s note: “Merged record” is not equivalent to commonly accessible charts via an electronic health record system. If the medical record for the patient’s acute stay is “closed” and the patient is given a separate medical record and registration for the stay in the transferred facility, consider the transfer stay as a separate admission.
References
- Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1E. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
- Department of Health and Human Services. Office of Inspector General: Oversight of Medicare PPS-Exempt Hospital Services. HHS Web site. Available at: www.oig.hhs.gov/oei/reports/oei-12-02-00170.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
- CMS. Medicare Claims Processing Manual: Chapter 12, Section 30.6.9.1H. CMS Web site. Available at: www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c12.pdf. Accessed June 1, 2009.
Investigate Claim Denials
In order to recover the appropriate payment for services provided by hospitalists, the following must occur:
- The billing provider renders service fully, or jointly with a resident under the teaching physician guidelines or nonphysician provider under the shared/split billing rules;
- The service is completely and accurately documented in the medical record;
- The correct information is entered on the claim form that is submitted to the payor; and
- The service is determined to be a covered benefit and eligible for payment.
Claims frequently are rejected or denied. Even more frequently, the physician or billing staff does not understand the reason for the denial. The typical reaction to claim denial is twofold: “appeal with paper” and “write off.” In other words, send a copy of the physician notes to the payor and consider the claim unsuccessful and payment unable to be obtained.
Examining and understanding the payor’s initial claim determination might prompt a more successful response. Presuming the patient demographics are entered without error, the insurance information is correct, the patient is eligible for coverage, and all precertifications and authorizations were obtained, check for these other common errors.
Medical Necessity
Denials for “medical necessity” are not always what they seem. Individuals often assume that the physician reported an incorrect diagnosis code. Consider the service/procedure code when trying to formulate a response to the denial. When dealing with procedure codes, it is likely the denial is received for a mismatched diagnosis.
For example, a payor might deny a claim for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (92950) that is associated with a diagnosis code of congestive heart failure (428.0), despite this being the underlying condition that prompted the decline in the patient’s condition. The payor might only accept “cardiac arrest” (427.5) as the diagnosis for cardiopulmonary resuscitation because it was the direct reason for the procedure. After you ensure that the documentation supports the diagnosis, the claim should be resubmitted with the corrected diagnosis code.
If the “medical necessity” denial involves a covered evaluation and management (E/M) visit, it is less likely that the diagnosis code is the issue. When dealing with Medicare in particular, this type of denial likely is the result of a failure to respond to a prepayment request for documentation. Medicare issues prepayment requests for documentation for the following inpatient CPT codes: 99255, 99254, 99233, 99232, 99223, 99239, and 99292. If the documentation isn’t provided to the Medicare review department within the designated time frame, the claim is automatically denied. The reason for denial is cited as “not deemed a medical necessity.” Some providers misunderstand this remittance remark and assume that the physician assigned an incorrect diagnosis code. Although that might be true, it probably is due to a failure to respond to the prepayment documentation request. Appealing these claims requires the submission of documentation to the Medicare appeals department. Once the supporting documentation is reviewed, reimbursement is granted.
Bundling
The National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) identifies edits that ultimately affect claims submission and payment. The Column One/Column Two Correct Coding Edits and the Mutually Exclusive Edits list code pairs that should not be reported together on the same date by either a single physician or physicians of the same specialty within a provider group. Under some well-documented circumstances, the physician is allowed to “unbundle” the services by appending the appropriate modifier.
When services are denied as being “incidental/integral” to another reimbursed service (e.g., bundled), the claim should not automatically be resubmitted with a modifier appended to the “bundled” procedure code.
Documentation should be reviewed to determine if the denied service is separately reportable from the paid service. Only when supported by documentation can the physician append the appropriate modifier and resubmit the claim. For example, a hospitalist evaluated a patient with congestive heart failure and pleural effusions. The hospitalist determined that the patient requires placement of a central venous catheter (36556). Because the patient’s underlying condition was evaluated and resulted in the decision to place a central venous catheter, both the visit (99233) and the procedure (36556) can be reported. If submitted without modifiers, some payors may deny payment for the visit because it was not “integral” to the catheter placement. You should resubmit those claims with modifier 25.
Place of Service
Ensure that the place of service (POS) matches the service/procedure code. For example, say a hospitalist performs a consultation in the ED and determines that the patient does not need to be treated as an inpatient but provides recommendations for ED care and outpatient followup. Avoid a mismatch of the service code and the location. Consults performed in the ED should be reported with outpatient consultation codes (99241-99245) as appropriate. The correct POS should be the ED, not the inpatient hospital. Reporting outpatient codes with an inpatient POS (e.g., 21: inpatient hospital, 31: skilled nursing facility) will result in claim denial.
The same is true when trying to report inpatient consultation codes (99251-99255) in an outpatient location (e.g., 23-ED). The appropriate response for this type of denial is to resubmit the claim with the correct the POS and service/procedure code. A complete list of POS codes and corresponding definitions can be found in Chapter 26, Section 10.5 of the Medicare Claims Processing Manual, available at www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c26.pdf.
Provider Enrollment
Provider enrollment issues occur when a physician’s national provider identifier (NPI) is not properly linked to the group practice. More often than not, the group practice receives claim rejections for enrollment issues when services involve nurse practitioners or physician assistants who have not enrolled with Medicare or cannot enroll with non-Medicare payors.
For example, a nurse practitioner independently provides a subsequent hospital-care service (e.g., 99232). The claim is submitted and Medicare reimburses the service at the correct amount as a primary insurer. The remaining balance is submitted to the secondary insurer. Because the submitted claim identifies the service provider as a nonphysician provider, who likely is not enrolled with the non-Medicare payor, the claim is rejected.
If the physician group has a contractual agreement to recognize nonphysician provider services by reporting them under the collaborating physician’s name, the claim can be resubmitted in the physician’s name. In absence of such an agreement, the claim should be written off. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
Reference
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2008.
In order to recover the appropriate payment for services provided by hospitalists, the following must occur:
- The billing provider renders service fully, or jointly with a resident under the teaching physician guidelines or nonphysician provider under the shared/split billing rules;
- The service is completely and accurately documented in the medical record;
- The correct information is entered on the claim form that is submitted to the payor; and
- The service is determined to be a covered benefit and eligible for payment.
Claims frequently are rejected or denied. Even more frequently, the physician or billing staff does not understand the reason for the denial. The typical reaction to claim denial is twofold: “appeal with paper” and “write off.” In other words, send a copy of the physician notes to the payor and consider the claim unsuccessful and payment unable to be obtained.
Examining and understanding the payor’s initial claim determination might prompt a more successful response. Presuming the patient demographics are entered without error, the insurance information is correct, the patient is eligible for coverage, and all precertifications and authorizations were obtained, check for these other common errors.
Medical Necessity
Denials for “medical necessity” are not always what they seem. Individuals often assume that the physician reported an incorrect diagnosis code. Consider the service/procedure code when trying to formulate a response to the denial. When dealing with procedure codes, it is likely the denial is received for a mismatched diagnosis.
For example, a payor might deny a claim for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (92950) that is associated with a diagnosis code of congestive heart failure (428.0), despite this being the underlying condition that prompted the decline in the patient’s condition. The payor might only accept “cardiac arrest” (427.5) as the diagnosis for cardiopulmonary resuscitation because it was the direct reason for the procedure. After you ensure that the documentation supports the diagnosis, the claim should be resubmitted with the corrected diagnosis code.
If the “medical necessity” denial involves a covered evaluation and management (E/M) visit, it is less likely that the diagnosis code is the issue. When dealing with Medicare in particular, this type of denial likely is the result of a failure to respond to a prepayment request for documentation. Medicare issues prepayment requests for documentation for the following inpatient CPT codes: 99255, 99254, 99233, 99232, 99223, 99239, and 99292. If the documentation isn’t provided to the Medicare review department within the designated time frame, the claim is automatically denied. The reason for denial is cited as “not deemed a medical necessity.” Some providers misunderstand this remittance remark and assume that the physician assigned an incorrect diagnosis code. Although that might be true, it probably is due to a failure to respond to the prepayment documentation request. Appealing these claims requires the submission of documentation to the Medicare appeals department. Once the supporting documentation is reviewed, reimbursement is granted.
Bundling
The National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) identifies edits that ultimately affect claims submission and payment. The Column One/Column Two Correct Coding Edits and the Mutually Exclusive Edits list code pairs that should not be reported together on the same date by either a single physician or physicians of the same specialty within a provider group. Under some well-documented circumstances, the physician is allowed to “unbundle” the services by appending the appropriate modifier.
When services are denied as being “incidental/integral” to another reimbursed service (e.g., bundled), the claim should not automatically be resubmitted with a modifier appended to the “bundled” procedure code.
Documentation should be reviewed to determine if the denied service is separately reportable from the paid service. Only when supported by documentation can the physician append the appropriate modifier and resubmit the claim. For example, a hospitalist evaluated a patient with congestive heart failure and pleural effusions. The hospitalist determined that the patient requires placement of a central venous catheter (36556). Because the patient’s underlying condition was evaluated and resulted in the decision to place a central venous catheter, both the visit (99233) and the procedure (36556) can be reported. If submitted without modifiers, some payors may deny payment for the visit because it was not “integral” to the catheter placement. You should resubmit those claims with modifier 25.
Place of Service
Ensure that the place of service (POS) matches the service/procedure code. For example, say a hospitalist performs a consultation in the ED and determines that the patient does not need to be treated as an inpatient but provides recommendations for ED care and outpatient followup. Avoid a mismatch of the service code and the location. Consults performed in the ED should be reported with outpatient consultation codes (99241-99245) as appropriate. The correct POS should be the ED, not the inpatient hospital. Reporting outpatient codes with an inpatient POS (e.g., 21: inpatient hospital, 31: skilled nursing facility) will result in claim denial.
The same is true when trying to report inpatient consultation codes (99251-99255) in an outpatient location (e.g., 23-ED). The appropriate response for this type of denial is to resubmit the claim with the correct the POS and service/procedure code. A complete list of POS codes and corresponding definitions can be found in Chapter 26, Section 10.5 of the Medicare Claims Processing Manual, available at www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c26.pdf.
Provider Enrollment
Provider enrollment issues occur when a physician’s national provider identifier (NPI) is not properly linked to the group practice. More often than not, the group practice receives claim rejections for enrollment issues when services involve nurse practitioners or physician assistants who have not enrolled with Medicare or cannot enroll with non-Medicare payors.
For example, a nurse practitioner independently provides a subsequent hospital-care service (e.g., 99232). The claim is submitted and Medicare reimburses the service at the correct amount as a primary insurer. The remaining balance is submitted to the secondary insurer. Because the submitted claim identifies the service provider as a nonphysician provider, who likely is not enrolled with the non-Medicare payor, the claim is rejected.
If the physician group has a contractual agreement to recognize nonphysician provider services by reporting them under the collaborating physician’s name, the claim can be resubmitted in the physician’s name. In absence of such an agreement, the claim should be written off. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
Reference
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2008.
In order to recover the appropriate payment for services provided by hospitalists, the following must occur:
- The billing provider renders service fully, or jointly with a resident under the teaching physician guidelines or nonphysician provider under the shared/split billing rules;
- The service is completely and accurately documented in the medical record;
- The correct information is entered on the claim form that is submitted to the payor; and
- The service is determined to be a covered benefit and eligible for payment.
Claims frequently are rejected or denied. Even more frequently, the physician or billing staff does not understand the reason for the denial. The typical reaction to claim denial is twofold: “appeal with paper” and “write off.” In other words, send a copy of the physician notes to the payor and consider the claim unsuccessful and payment unable to be obtained.
Examining and understanding the payor’s initial claim determination might prompt a more successful response. Presuming the patient demographics are entered without error, the insurance information is correct, the patient is eligible for coverage, and all precertifications and authorizations were obtained, check for these other common errors.
Medical Necessity
Denials for “medical necessity” are not always what they seem. Individuals often assume that the physician reported an incorrect diagnosis code. Consider the service/procedure code when trying to formulate a response to the denial. When dealing with procedure codes, it is likely the denial is received for a mismatched diagnosis.
For example, a payor might deny a claim for cardiopulmonary resuscitation (92950) that is associated with a diagnosis code of congestive heart failure (428.0), despite this being the underlying condition that prompted the decline in the patient’s condition. The payor might only accept “cardiac arrest” (427.5) as the diagnosis for cardiopulmonary resuscitation because it was the direct reason for the procedure. After you ensure that the documentation supports the diagnosis, the claim should be resubmitted with the corrected diagnosis code.
If the “medical necessity” denial involves a covered evaluation and management (E/M) visit, it is less likely that the diagnosis code is the issue. When dealing with Medicare in particular, this type of denial likely is the result of a failure to respond to a prepayment request for documentation. Medicare issues prepayment requests for documentation for the following inpatient CPT codes: 99255, 99254, 99233, 99232, 99223, 99239, and 99292. If the documentation isn’t provided to the Medicare review department within the designated time frame, the claim is automatically denied. The reason for denial is cited as “not deemed a medical necessity.” Some providers misunderstand this remittance remark and assume that the physician assigned an incorrect diagnosis code. Although that might be true, it probably is due to a failure to respond to the prepayment documentation request. Appealing these claims requires the submission of documentation to the Medicare appeals department. Once the supporting documentation is reviewed, reimbursement is granted.
Bundling
The National Correct Coding Initiative (NCCI) identifies edits that ultimately affect claims submission and payment. The Column One/Column Two Correct Coding Edits and the Mutually Exclusive Edits list code pairs that should not be reported together on the same date by either a single physician or physicians of the same specialty within a provider group. Under some well-documented circumstances, the physician is allowed to “unbundle” the services by appending the appropriate modifier.
When services are denied as being “incidental/integral” to another reimbursed service (e.g., bundled), the claim should not automatically be resubmitted with a modifier appended to the “bundled” procedure code.
Documentation should be reviewed to determine if the denied service is separately reportable from the paid service. Only when supported by documentation can the physician append the appropriate modifier and resubmit the claim. For example, a hospitalist evaluated a patient with congestive heart failure and pleural effusions. The hospitalist determined that the patient requires placement of a central venous catheter (36556). Because the patient’s underlying condition was evaluated and resulted in the decision to place a central venous catheter, both the visit (99233) and the procedure (36556) can be reported. If submitted without modifiers, some payors may deny payment for the visit because it was not “integral” to the catheter placement. You should resubmit those claims with modifier 25.
Place of Service
Ensure that the place of service (POS) matches the service/procedure code. For example, say a hospitalist performs a consultation in the ED and determines that the patient does not need to be treated as an inpatient but provides recommendations for ED care and outpatient followup. Avoid a mismatch of the service code and the location. Consults performed in the ED should be reported with outpatient consultation codes (99241-99245) as appropriate. The correct POS should be the ED, not the inpatient hospital. Reporting outpatient codes with an inpatient POS (e.g., 21: inpatient hospital, 31: skilled nursing facility) will result in claim denial.
The same is true when trying to report inpatient consultation codes (99251-99255) in an outpatient location (e.g., 23-ED). The appropriate response for this type of denial is to resubmit the claim with the correct the POS and service/procedure code. A complete list of POS codes and corresponding definitions can be found in Chapter 26, Section 10.5 of the Medicare Claims Processing Manual, available at www.cms.hhs.gov/manuals/downloads/clm104c26.pdf.
Provider Enrollment
Provider enrollment issues occur when a physician’s national provider identifier (NPI) is not properly linked to the group practice. More often than not, the group practice receives claim rejections for enrollment issues when services involve nurse practitioners or physician assistants who have not enrolled with Medicare or cannot enroll with non-Medicare payors.
For example, a nurse practitioner independently provides a subsequent hospital-care service (e.g., 99232). The claim is submitted and Medicare reimburses the service at the correct amount as a primary insurer. The remaining balance is submitted to the secondary insurer. Because the submitted claim identifies the service provider as a nonphysician provider, who likely is not enrolled with the non-Medicare payor, the claim is rejected.
If the physician group has a contractual agreement to recognize nonphysician provider services by reporting them under the collaborating physician’s name, the claim can be resubmitted in the physician’s name. In absence of such an agreement, the claim should be written off. TH
Carol Pohlig is a billing and coding expert with the University of Pennsylvania Medical Center in Philadelphia. She is faculty of SHM’s inpatient coding course.
Reference
- Beebe M, Dalton J, Espronceda M, Evans D, Glenn R. Current Procedural Terminology Professional Edition. Chicago: American Medical Association Press; 2008.