User login
Roundtable discussion: The Pluripotent Hospitalist
In honor of National Hospitalist Day, the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Explore the Space podcast are teaming up to bring you a roundtable discussion, featuring a diverse group of hospitalists from all stages in their careers, on Thursday, March 4, at 7 p.m. ET / 4 p.m. PT.
Registration is required. Sign up here.
Hosted by Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and founder, producer, and host of Explore the Space, the roundtable will include:
- Gurpreet Dhaliwal, MD, a clinician-educator and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He studies, writes, and speaks about how doctors think – how they make diagnoses, how they develop diagnostic expertise, and what motivates them to improve their practice and the systems in which they work.
- Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She also serves as the pediatric editor of the Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly news magazine.
- Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, a clinician-researcher and clinical associate at the University of Chicago. Her research focuses on hospital-associated disability and she recently authored a perspectives piece in the Journal of Hospital Medicine with her mentor, Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, on why the COVID-19 pandemic might exacerbate this problem.
- Ndidi Unaka, MD, MEd, an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Unaka has served as the associate program director of the pediatric residency program since 2011. She is also the medical director of an inpatient unit that serves as the primary home.
For more information about SHM, please visit hospitalmedicine.org. To learn more about Explore the Space, please visit explorethespaceshow.com.
Register now.
In honor of National Hospitalist Day, the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Explore the Space podcast are teaming up to bring you a roundtable discussion, featuring a diverse group of hospitalists from all stages in their careers, on Thursday, March 4, at 7 p.m. ET / 4 p.m. PT.
Registration is required. Sign up here.
Hosted by Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and founder, producer, and host of Explore the Space, the roundtable will include:
- Gurpreet Dhaliwal, MD, a clinician-educator and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He studies, writes, and speaks about how doctors think – how they make diagnoses, how they develop diagnostic expertise, and what motivates them to improve their practice and the systems in which they work.
- Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She also serves as the pediatric editor of the Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly news magazine.
- Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, a clinician-researcher and clinical associate at the University of Chicago. Her research focuses on hospital-associated disability and she recently authored a perspectives piece in the Journal of Hospital Medicine with her mentor, Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, on why the COVID-19 pandemic might exacerbate this problem.
- Ndidi Unaka, MD, MEd, an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Unaka has served as the associate program director of the pediatric residency program since 2011. She is also the medical director of an inpatient unit that serves as the primary home.
For more information about SHM, please visit hospitalmedicine.org. To learn more about Explore the Space, please visit explorethespaceshow.com.
Register now.
In honor of National Hospitalist Day, the Society of Hospital Medicine and the Explore the Space podcast are teaming up to bring you a roundtable discussion, featuring a diverse group of hospitalists from all stages in their careers, on Thursday, March 4, at 7 p.m. ET / 4 p.m. PT.
Registration is required. Sign up here.
Hosted by Mark Shapiro, MD, hospitalist and founder, producer, and host of Explore the Space, the roundtable will include:
- Gurpreet Dhaliwal, MD, a clinician-educator and professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco. He studies, writes, and speaks about how doctors think – how they make diagnoses, how they develop diagnostic expertise, and what motivates them to improve their practice and the systems in which they work.
- Anika Kumar, MD, FHM, a clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at the Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine, and a pediatric hospitalist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. She also serves as the pediatric editor of the Hospitalist, SHM’s monthly news magazine.
- Maylyn S. Martinez, MD, a clinician-researcher and clinical associate at the University of Chicago. Her research focuses on hospital-associated disability and she recently authored a perspectives piece in the Journal of Hospital Medicine with her mentor, Vineet Arora, MD, MHM, on why the COVID-19 pandemic might exacerbate this problem.
- Ndidi Unaka, MD, MEd, an associate professor in the division of hospital medicine at Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center. Dr. Unaka has served as the associate program director of the pediatric residency program since 2011. She is also the medical director of an inpatient unit that serves as the primary home.
For more information about SHM, please visit hospitalmedicine.org. To learn more about Explore the Space, please visit explorethespaceshow.com.
Register now.
Inpatient telemedicine can help address hospitalist pain points
COVID-19 has increased confidence in the technology
Since the advent of COVID-19, health care has seen an unprecedented rise in virtual health. Telemedicine has come to the forefront of our conversations, and there are many speculations around its future state. One such discussion is around the sustainability and expansion of inpatient telemedicine programs post COVID, and if – and how – it is going to be helpful for health care.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1
A patient presents to an emergency department of a small community hospital. He needs to be seen by a specialist, but (s)he is not available, so patient gets transferred out to the ED of a different hospital several miles away from his hometown.
He is evaluated in the second ED by the specialist, has repeat testing done – some of those tests were already completed at the first hospital. After evaluating him, the specialist recommends that he does not need to be admitted to the hospital and can be safely followed up as an outpatient. The patient does not require any further intervention and is discharged from the ED.
Scenario 2
Dr. N is a hospitalist in a rural hospital that does not have intensivist support at night. She works 7 on/7 off and is on call 24/7 during her “on” week. Dr. N cannot be physically present in the hospital 24/7. She receives messages from the hospital around the clock and feels that this call schedule is no longer sustainable. She doesn’t feel comfortable admitting patients in the ICU who come to the hospital at night without physically seeing them and without ICU backup. Therefore, some of the patients who are sick enough to be admitted in ICU for closer monitoring but can be potentially handled in this rural hospital get transferred out to a different hospital.
Dr. N has been asking the hospital to provide her intensivist back up at night and to give her some flexibility in the call schedule. However, from hospital’s perspective, the volume isn’t high enough to hire a dedicated nocturnist, and because the hospital is in the small rural area, it is having a hard time attracting more intensivists. After multiple conversations between both parties, Dr. N finally resigns.
Scenario 3
Dr. A is a specialist who is on call covering different hospitals and seeing patients in clinic. His call is getting busier. He has received many new consults and also has to follow up on his other patients in hospital who he saw a day prior.
Dr. A started receiving many pages from the hospitals – some of his patients and their families are anxiously waiting on him so that he can let them go home once he sees them, while some are waiting to know what the next steps and plan of action are. He ends up canceling some of his clinic patients who had scheduled an appointment with him 3, 4, or even 5 months ago. It’s already afternoon.
Dr. A now drives to one hospital, sees his new consults, orders tests which may or may not get results the same day, follows up on other patients, reviews their test results, modifies treatment plans for some while clearing other patients for discharge. He then drives to the other hospital and follows the same process. Some of the patients aren’t happy because of the long wait, a few couldn’t arrange for the ride to go home and ended up staying in hospital 1 extra night, while the ER is getting backlogged waiting on discharges.
These scenarios highlight some of the important and prevalent pain points in health care as shown in Figure 1.
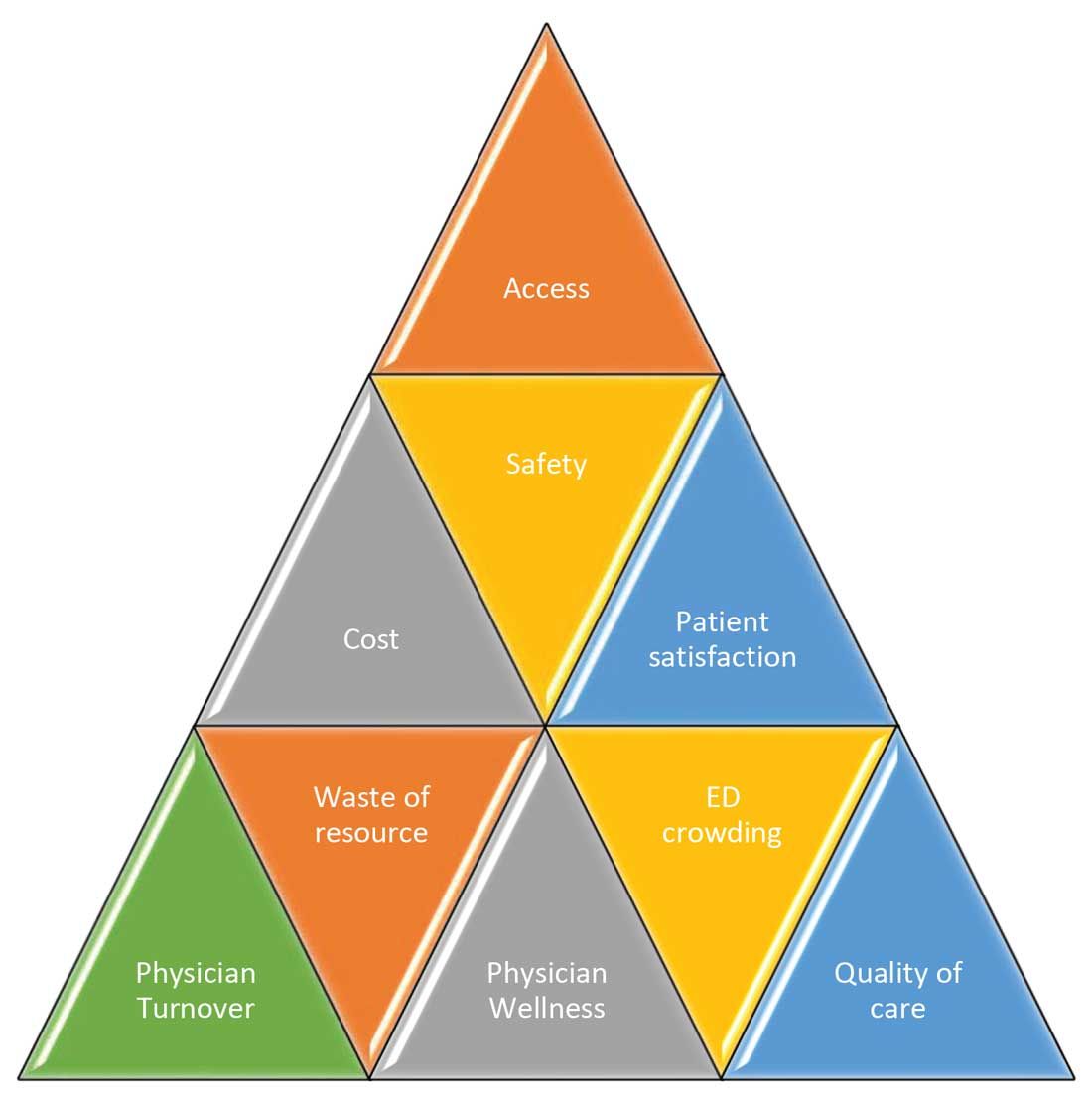
Scenario 1 and part of scenario 2 describe what is called potentially avoidable interfacility transfers. One study showed that around 8% of transferred patients (transferred from one ED to another) were discharged after ED evaluation in the second hospital, meaning they could have been retained locally without necessarily getting transferred if they could have been evaluated by the specialist.1
Transferring a patient from one hospital to another isn’t as simple as picking up a person from point A and dropping him off at point B. Rather it’s a very complicated, high-risk, capital-intensive, and time-consuming process that leads not only to excessive cost involved around transfer but also adds additional stress and burden on the patient and family. In these scenarios, having a specialist available via teleconsult could have eliminated much of this hassle and cost, allowing the patient to stay locally close to family and get access to necessary medical expertise from any part of the country in a timely manner.
Scenario 2 talks about the recruitment and retention challenges in low-volume, low-resourced locations because of call schedule and the lack of specialty support. It is reported in one study that 19% of common hospitalist admissions happen between 7:00 p.m. and 7:00 a.m. Eighty percent of admissions occurred prior to midnight. Nonrural facilities averaged 6.69 hospitalist admissions per night in that study, whereas rural facilities averaged 1.35 admissions.2 It’s like a double-edged sword for such facilities. While having a dedicated nocturnist is not a sustainable model for these hospitals, not having adequate support at night impacts physician wellness, which is already costing hospitals billions of dollars as well as leading to physician turnover: It could cost a hospital somewhere between $500,000 and $1 million to replace just one physician.3 Hence, the potential exists for a telehospitalist program in these settings to address this dilemma.
Scenario 3 sheds light on the operational issues resulting in reduced patient satisfaction and lost revenues, both on the outpatient and inpatient sides by cancellation of office visits and ED backlog. Telemedicine use in these situations can improve the turnaround time of physicians who can see some of those patients while staying at one location as they wait on other patients to show up in the clinic or wait on the operation room crew, or the procedure kit etcetera, hence improving the length of stay, ED throughput, patient satisfaction, and quality of care. This also can improve overall workflow and the wellness of physicians.
One common outcome in all these scenarios is emergency department overcrowding. There have been multiple studies that suggest that ED overcrowding can result in increased costs, lost revenues, and poor clinical outcomes, including delayed administration of antibiotics, delayed administration of analgesics to suffering patients, increased hospital length of stay, and even increased mortality.4-6 A crowded ED limits the ability of an institution to accept referrals and increases medicolegal risks. (See Figure 2.)
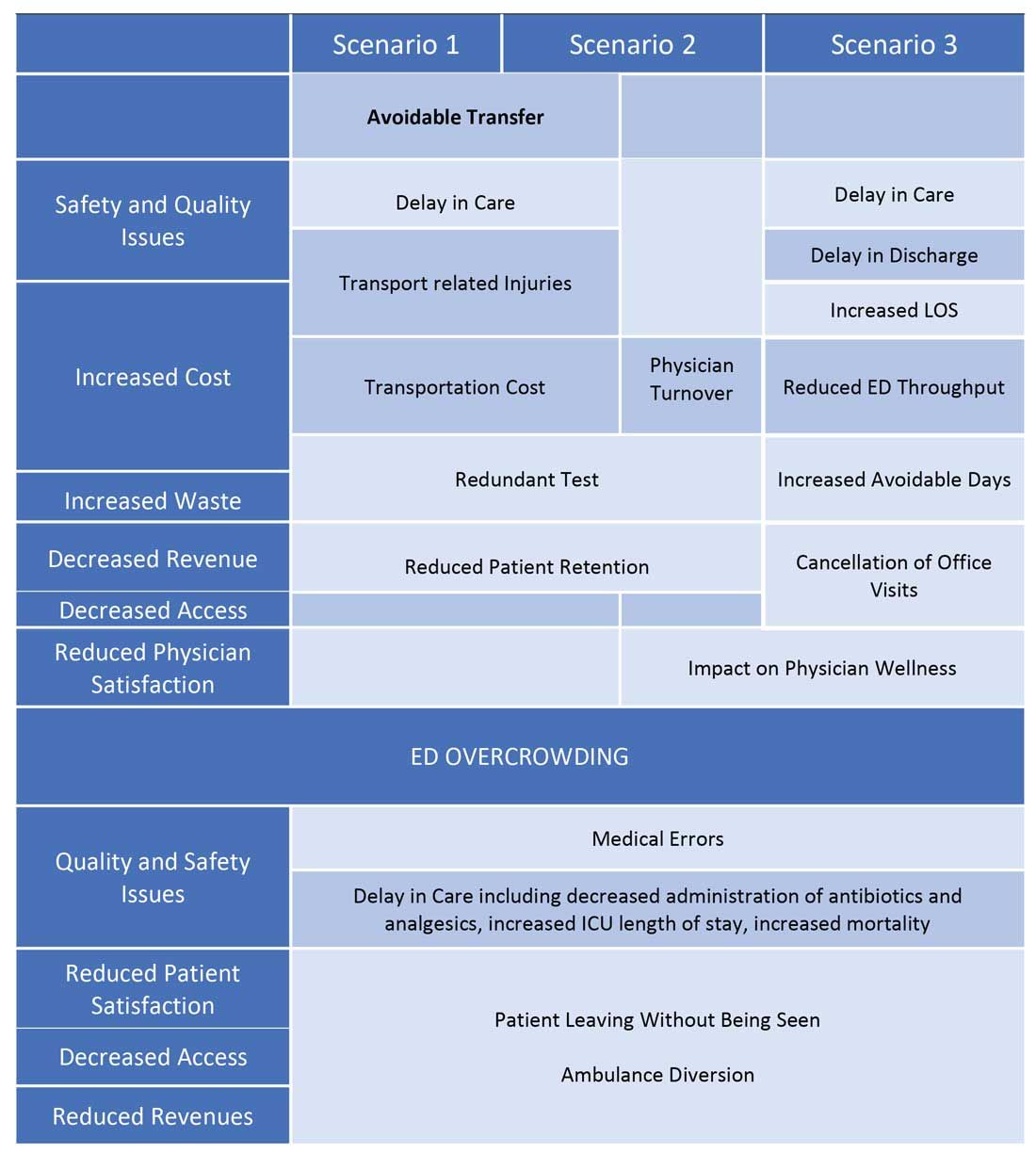
Another study showed that a 1-hour reduction in ED boarding time would result in over $9,000 of additional revenue by reducing ambulance diversion and the number of patients who left without being seen.7 Another found that using tele-emergency services can potentially result in net savings of $3,823 per avoided transfer, while accounting for the costs related to tele-emergency technology, hospital revenues, and patient-associated savings.8
There are other instances where gaps in staffing and cracks in workflow can have a negative impact on hospital operations. For example, the busier hospitals that do have a dedicated nocturnist also struggle with physician retention, since such hospitals have higher volumes and higher cross-coverage needs, and are therefore hard to manage by just one single physician at night. Since these are temporary surges, hiring another full-time nocturnist is not a viable option for the hospitals and is considered an expense in many places.
Similarly, during day shift, if a physician goes on vacation or there are surges in patient volumes, hiring a locum tenens hospitalist can be an expensive option, since the cost also includes travel and lodging. In many instances, hiring locum tenens in a given time frame is also not possible, and it leaves the physicians short staffed, fueling both physicians’ and patients’ dissatisfaction and leading to other operational and safety challenges, which I highlighted above.
Telemedicine services in these situations can provide cross-coverage while nocturnists can focus on admissions and other acute issues. Also, when physicians are on vacation or there is surge capacity (that can be forecast by using various predictive analytics models), hospitals can make plans accordingly and make use of telemedicine services. For example, Providence St. Joseph Health reported improvement in timeliness and efficiency of care after implementation of a telehospitalist program. Their 2-year study at a partner site showed a 59% improvement in patients admitted prior to midnight, about $547,000 improvement in first-day revenue capture, an increase in total revenue days and comparable patient experience scores, and a substantial increase in inpatient census and case mix index.9
Other institutions have successfully implemented some inpatient telemedicine programs – such as telepsych, telestroke, and tele-ICU – and some have also reported positive outcomes in terms of patient satisfaction, improved access, reduced length of stay in the ED, and improved quality metrics. Emory Healthcare in Atlanta reported $4.6 million savings in Medicare costs over a 15-month period from adopting a telemedicine model in the ICU, and a reduction in 60-day readmissions by 2.1%.10 Similarly, another study showed that one large health care center improved its direct contribution margins by 376% (from $7.9 million to $37.7 million) because of increased case volume, shorter lengths of stay, and higher case revenue relative to direct costs. When combined with a logistics center, they reported improved contribution margins by 665% (from $7.9 million to $60.6 million).11
There are barriers to the integration and implementation of inpatient telemedicine, including regulations, reimbursement, physician licensing, adoption of technology, and trust among staff and patients. However, I am cautiously optimistic that increased use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has allowed patients, physicians, nurses, and health care workers and leaders to gain experience with this technology, which will help them gain confidence and reduce hesitation in adapting to this new digital platform. Ultimately, the extent to which telemedicine is able to positively impact patient care will revolve around overcoming these barriers, likely through an evolution of both the technology itself and the attitudes and regulations surrounding it.
I do not suggest that telemedicine should replace the in-person encounter, but it can be implemented and used successfully in addressing the pain points in U.S. health care. (See Figure 3.)
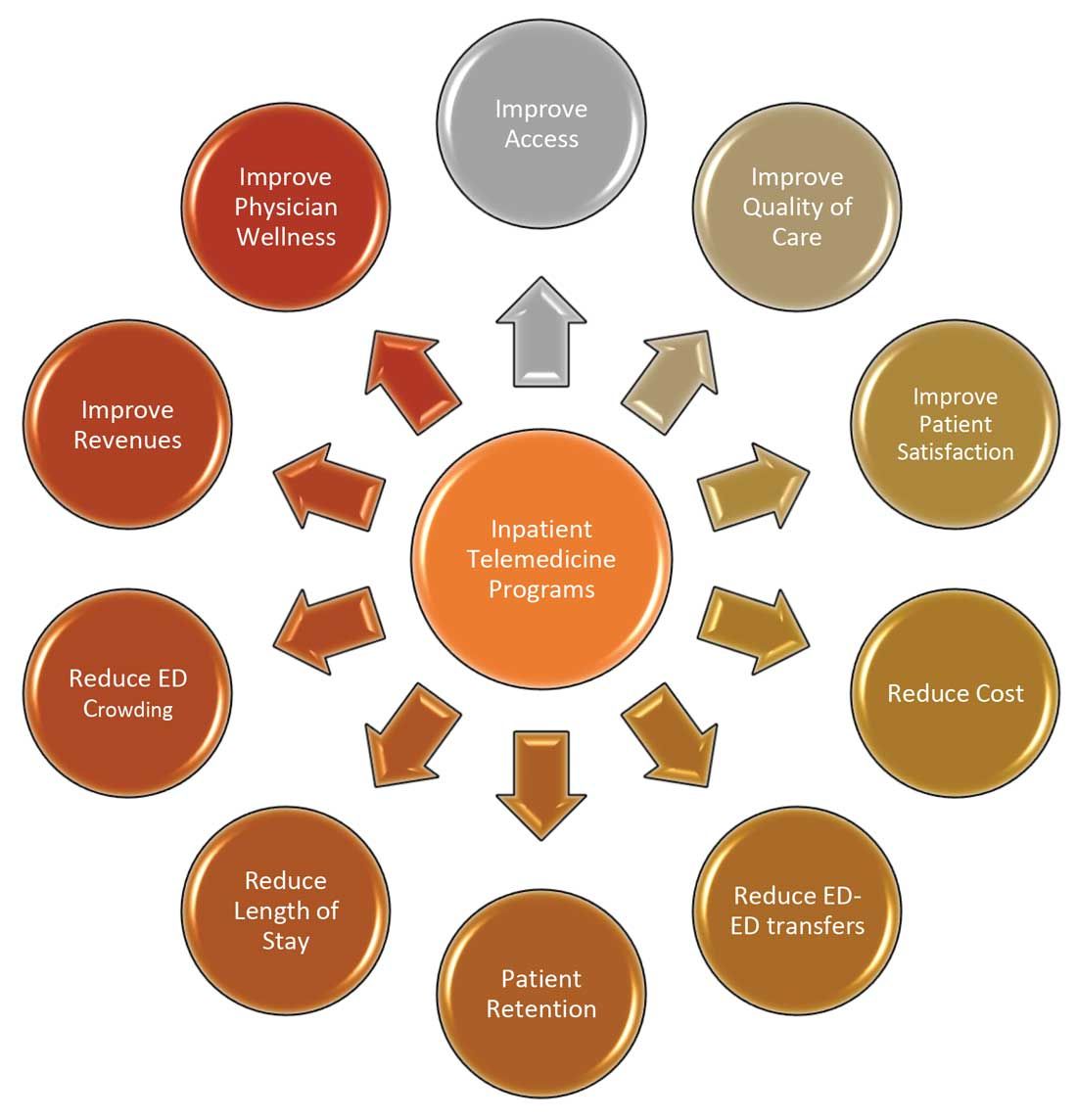
To that end, the purpose of this article is to spark discussion around different ways of implementing telemedicine in inpatient settings to solve many of the challenges that health care faces today.
Dr. Zia is an internal medicine board-certified physician, serving as a hospitalist and physician adviser in a medically underserved area. She has also served as interim medical director of the department of hospital medicine, and medical staff president, at SIH Herrin Hospital, in Herrin, Ill., part of Southern Illinois Healthcare. She has a special interest in improving access to health care in physician shortage areas.
References
1. Kindermann DR et al. Emergency department transfers and transfer relationships in United States hospitals. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(2):157-65.
2. Sanders RB et al. New hospital telemedicine services: Potential market for a nighttime hospitalist service. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Oct 1;20(10):902-8.
3. Shanafelt T et al. The business case for investing in physician well-being. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(12):1826-32.
4. Pines JM et al. The impact of emergency department crowding measures on time to antibiotics for patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Emerg Med. 2007 Nov;50(5):510-6.
5. Pines JM and Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jan;51(1):1-5.
6. Chalfin DB et al. Impact of delayed transfer of critically ill patients from the emergency department to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2007 Jun;35(6):1477-83.
7. Pines JM et al. The financial consequences of lost demand and reducing boarding in hospital emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Oct;58(4):331-40.
8. Natafgi N et al. Using tele-emergency to avoid patient transfers in rural emergency. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Apri;24(3):193-201.
9. Providence.org/telehealthhospitalistcasestudy.
10. Woodruff Health Sciences Center. CMS report: eICU program reduced hospital stays, saved millions, eased provider shortage. 2017 Apr 5.
11. Lilly CM et al. ICU telemedicine program financial outcomes. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):286-97.
COVID-19 has increased confidence in the technology
COVID-19 has increased confidence in the technology
Since the advent of COVID-19, health care has seen an unprecedented rise in virtual health. Telemedicine has come to the forefront of our conversations, and there are many speculations around its future state. One such discussion is around the sustainability and expansion of inpatient telemedicine programs post COVID, and if – and how – it is going to be helpful for health care.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1
A patient presents to an emergency department of a small community hospital. He needs to be seen by a specialist, but (s)he is not available, so patient gets transferred out to the ED of a different hospital several miles away from his hometown.
He is evaluated in the second ED by the specialist, has repeat testing done – some of those tests were already completed at the first hospital. After evaluating him, the specialist recommends that he does not need to be admitted to the hospital and can be safely followed up as an outpatient. The patient does not require any further intervention and is discharged from the ED.
Scenario 2
Dr. N is a hospitalist in a rural hospital that does not have intensivist support at night. She works 7 on/7 off and is on call 24/7 during her “on” week. Dr. N cannot be physically present in the hospital 24/7. She receives messages from the hospital around the clock and feels that this call schedule is no longer sustainable. She doesn’t feel comfortable admitting patients in the ICU who come to the hospital at night without physically seeing them and without ICU backup. Therefore, some of the patients who are sick enough to be admitted in ICU for closer monitoring but can be potentially handled in this rural hospital get transferred out to a different hospital.
Dr. N has been asking the hospital to provide her intensivist back up at night and to give her some flexibility in the call schedule. However, from hospital’s perspective, the volume isn’t high enough to hire a dedicated nocturnist, and because the hospital is in the small rural area, it is having a hard time attracting more intensivists. After multiple conversations between both parties, Dr. N finally resigns.
Scenario 3
Dr. A is a specialist who is on call covering different hospitals and seeing patients in clinic. His call is getting busier. He has received many new consults and also has to follow up on his other patients in hospital who he saw a day prior.
Dr. A started receiving many pages from the hospitals – some of his patients and their families are anxiously waiting on him so that he can let them go home once he sees them, while some are waiting to know what the next steps and plan of action are. He ends up canceling some of his clinic patients who had scheduled an appointment with him 3, 4, or even 5 months ago. It’s already afternoon.
Dr. A now drives to one hospital, sees his new consults, orders tests which may or may not get results the same day, follows up on other patients, reviews their test results, modifies treatment plans for some while clearing other patients for discharge. He then drives to the other hospital and follows the same process. Some of the patients aren’t happy because of the long wait, a few couldn’t arrange for the ride to go home and ended up staying in hospital 1 extra night, while the ER is getting backlogged waiting on discharges.
These scenarios highlight some of the important and prevalent pain points in health care as shown in Figure 1.

Scenario 1 and part of scenario 2 describe what is called potentially avoidable interfacility transfers. One study showed that around 8% of transferred patients (transferred from one ED to another) were discharged after ED evaluation in the second hospital, meaning they could have been retained locally without necessarily getting transferred if they could have been evaluated by the specialist.1
Transferring a patient from one hospital to another isn’t as simple as picking up a person from point A and dropping him off at point B. Rather it’s a very complicated, high-risk, capital-intensive, and time-consuming process that leads not only to excessive cost involved around transfer but also adds additional stress and burden on the patient and family. In these scenarios, having a specialist available via teleconsult could have eliminated much of this hassle and cost, allowing the patient to stay locally close to family and get access to necessary medical expertise from any part of the country in a timely manner.
Scenario 2 talks about the recruitment and retention challenges in low-volume, low-resourced locations because of call schedule and the lack of specialty support. It is reported in one study that 19% of common hospitalist admissions happen between 7:00 p.m. and 7:00 a.m. Eighty percent of admissions occurred prior to midnight. Nonrural facilities averaged 6.69 hospitalist admissions per night in that study, whereas rural facilities averaged 1.35 admissions.2 It’s like a double-edged sword for such facilities. While having a dedicated nocturnist is not a sustainable model for these hospitals, not having adequate support at night impacts physician wellness, which is already costing hospitals billions of dollars as well as leading to physician turnover: It could cost a hospital somewhere between $500,000 and $1 million to replace just one physician.3 Hence, the potential exists for a telehospitalist program in these settings to address this dilemma.
Scenario 3 sheds light on the operational issues resulting in reduced patient satisfaction and lost revenues, both on the outpatient and inpatient sides by cancellation of office visits and ED backlog. Telemedicine use in these situations can improve the turnaround time of physicians who can see some of those patients while staying at one location as they wait on other patients to show up in the clinic or wait on the operation room crew, or the procedure kit etcetera, hence improving the length of stay, ED throughput, patient satisfaction, and quality of care. This also can improve overall workflow and the wellness of physicians.
One common outcome in all these scenarios is emergency department overcrowding. There have been multiple studies that suggest that ED overcrowding can result in increased costs, lost revenues, and poor clinical outcomes, including delayed administration of antibiotics, delayed administration of analgesics to suffering patients, increased hospital length of stay, and even increased mortality.4-6 A crowded ED limits the ability of an institution to accept referrals and increases medicolegal risks. (See Figure 2.)

Another study showed that a 1-hour reduction in ED boarding time would result in over $9,000 of additional revenue by reducing ambulance diversion and the number of patients who left without being seen.7 Another found that using tele-emergency services can potentially result in net savings of $3,823 per avoided transfer, while accounting for the costs related to tele-emergency technology, hospital revenues, and patient-associated savings.8
There are other instances where gaps in staffing and cracks in workflow can have a negative impact on hospital operations. For example, the busier hospitals that do have a dedicated nocturnist also struggle with physician retention, since such hospitals have higher volumes and higher cross-coverage needs, and are therefore hard to manage by just one single physician at night. Since these are temporary surges, hiring another full-time nocturnist is not a viable option for the hospitals and is considered an expense in many places.
Similarly, during day shift, if a physician goes on vacation or there are surges in patient volumes, hiring a locum tenens hospitalist can be an expensive option, since the cost also includes travel and lodging. In many instances, hiring locum tenens in a given time frame is also not possible, and it leaves the physicians short staffed, fueling both physicians’ and patients’ dissatisfaction and leading to other operational and safety challenges, which I highlighted above.
Telemedicine services in these situations can provide cross-coverage while nocturnists can focus on admissions and other acute issues. Also, when physicians are on vacation or there is surge capacity (that can be forecast by using various predictive analytics models), hospitals can make plans accordingly and make use of telemedicine services. For example, Providence St. Joseph Health reported improvement in timeliness and efficiency of care after implementation of a telehospitalist program. Their 2-year study at a partner site showed a 59% improvement in patients admitted prior to midnight, about $547,000 improvement in first-day revenue capture, an increase in total revenue days and comparable patient experience scores, and a substantial increase in inpatient census and case mix index.9
Other institutions have successfully implemented some inpatient telemedicine programs – such as telepsych, telestroke, and tele-ICU – and some have also reported positive outcomes in terms of patient satisfaction, improved access, reduced length of stay in the ED, and improved quality metrics. Emory Healthcare in Atlanta reported $4.6 million savings in Medicare costs over a 15-month period from adopting a telemedicine model in the ICU, and a reduction in 60-day readmissions by 2.1%.10 Similarly, another study showed that one large health care center improved its direct contribution margins by 376% (from $7.9 million to $37.7 million) because of increased case volume, shorter lengths of stay, and higher case revenue relative to direct costs. When combined with a logistics center, they reported improved contribution margins by 665% (from $7.9 million to $60.6 million).11
There are barriers to the integration and implementation of inpatient telemedicine, including regulations, reimbursement, physician licensing, adoption of technology, and trust among staff and patients. However, I am cautiously optimistic that increased use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has allowed patients, physicians, nurses, and health care workers and leaders to gain experience with this technology, which will help them gain confidence and reduce hesitation in adapting to this new digital platform. Ultimately, the extent to which telemedicine is able to positively impact patient care will revolve around overcoming these barriers, likely through an evolution of both the technology itself and the attitudes and regulations surrounding it.
I do not suggest that telemedicine should replace the in-person encounter, but it can be implemented and used successfully in addressing the pain points in U.S. health care. (See Figure 3.)

To that end, the purpose of this article is to spark discussion around different ways of implementing telemedicine in inpatient settings to solve many of the challenges that health care faces today.
Dr. Zia is an internal medicine board-certified physician, serving as a hospitalist and physician adviser in a medically underserved area. She has also served as interim medical director of the department of hospital medicine, and medical staff president, at SIH Herrin Hospital, in Herrin, Ill., part of Southern Illinois Healthcare. She has a special interest in improving access to health care in physician shortage areas.
References
1. Kindermann DR et al. Emergency department transfers and transfer relationships in United States hospitals. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(2):157-65.
2. Sanders RB et al. New hospital telemedicine services: Potential market for a nighttime hospitalist service. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Oct 1;20(10):902-8.
3. Shanafelt T et al. The business case for investing in physician well-being. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(12):1826-32.
4. Pines JM et al. The impact of emergency department crowding measures on time to antibiotics for patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Emerg Med. 2007 Nov;50(5):510-6.
5. Pines JM and Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jan;51(1):1-5.
6. Chalfin DB et al. Impact of delayed transfer of critically ill patients from the emergency department to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2007 Jun;35(6):1477-83.
7. Pines JM et al. The financial consequences of lost demand and reducing boarding in hospital emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Oct;58(4):331-40.
8. Natafgi N et al. Using tele-emergency to avoid patient transfers in rural emergency. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Apri;24(3):193-201.
9. Providence.org/telehealthhospitalistcasestudy.
10. Woodruff Health Sciences Center. CMS report: eICU program reduced hospital stays, saved millions, eased provider shortage. 2017 Apr 5.
11. Lilly CM et al. ICU telemedicine program financial outcomes. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):286-97.
Since the advent of COVID-19, health care has seen an unprecedented rise in virtual health. Telemedicine has come to the forefront of our conversations, and there are many speculations around its future state. One such discussion is around the sustainability and expansion of inpatient telemedicine programs post COVID, and if – and how – it is going to be helpful for health care.
Consider the following scenarios:
Scenario 1
A patient presents to an emergency department of a small community hospital. He needs to be seen by a specialist, but (s)he is not available, so patient gets transferred out to the ED of a different hospital several miles away from his hometown.
He is evaluated in the second ED by the specialist, has repeat testing done – some of those tests were already completed at the first hospital. After evaluating him, the specialist recommends that he does not need to be admitted to the hospital and can be safely followed up as an outpatient. The patient does not require any further intervention and is discharged from the ED.
Scenario 2
Dr. N is a hospitalist in a rural hospital that does not have intensivist support at night. She works 7 on/7 off and is on call 24/7 during her “on” week. Dr. N cannot be physically present in the hospital 24/7. She receives messages from the hospital around the clock and feels that this call schedule is no longer sustainable. She doesn’t feel comfortable admitting patients in the ICU who come to the hospital at night without physically seeing them and without ICU backup. Therefore, some of the patients who are sick enough to be admitted in ICU for closer monitoring but can be potentially handled in this rural hospital get transferred out to a different hospital.
Dr. N has been asking the hospital to provide her intensivist back up at night and to give her some flexibility in the call schedule. However, from hospital’s perspective, the volume isn’t high enough to hire a dedicated nocturnist, and because the hospital is in the small rural area, it is having a hard time attracting more intensivists. After multiple conversations between both parties, Dr. N finally resigns.
Scenario 3
Dr. A is a specialist who is on call covering different hospitals and seeing patients in clinic. His call is getting busier. He has received many new consults and also has to follow up on his other patients in hospital who he saw a day prior.
Dr. A started receiving many pages from the hospitals – some of his patients and their families are anxiously waiting on him so that he can let them go home once he sees them, while some are waiting to know what the next steps and plan of action are. He ends up canceling some of his clinic patients who had scheduled an appointment with him 3, 4, or even 5 months ago. It’s already afternoon.
Dr. A now drives to one hospital, sees his new consults, orders tests which may or may not get results the same day, follows up on other patients, reviews their test results, modifies treatment plans for some while clearing other patients for discharge. He then drives to the other hospital and follows the same process. Some of the patients aren’t happy because of the long wait, a few couldn’t arrange for the ride to go home and ended up staying in hospital 1 extra night, while the ER is getting backlogged waiting on discharges.
These scenarios highlight some of the important and prevalent pain points in health care as shown in Figure 1.

Scenario 1 and part of scenario 2 describe what is called potentially avoidable interfacility transfers. One study showed that around 8% of transferred patients (transferred from one ED to another) were discharged after ED evaluation in the second hospital, meaning they could have been retained locally without necessarily getting transferred if they could have been evaluated by the specialist.1
Transferring a patient from one hospital to another isn’t as simple as picking up a person from point A and dropping him off at point B. Rather it’s a very complicated, high-risk, capital-intensive, and time-consuming process that leads not only to excessive cost involved around transfer but also adds additional stress and burden on the patient and family. In these scenarios, having a specialist available via teleconsult could have eliminated much of this hassle and cost, allowing the patient to stay locally close to family and get access to necessary medical expertise from any part of the country in a timely manner.
Scenario 2 talks about the recruitment and retention challenges in low-volume, low-resourced locations because of call schedule and the lack of specialty support. It is reported in one study that 19% of common hospitalist admissions happen between 7:00 p.m. and 7:00 a.m. Eighty percent of admissions occurred prior to midnight. Nonrural facilities averaged 6.69 hospitalist admissions per night in that study, whereas rural facilities averaged 1.35 admissions.2 It’s like a double-edged sword for such facilities. While having a dedicated nocturnist is not a sustainable model for these hospitals, not having adequate support at night impacts physician wellness, which is already costing hospitals billions of dollars as well as leading to physician turnover: It could cost a hospital somewhere between $500,000 and $1 million to replace just one physician.3 Hence, the potential exists for a telehospitalist program in these settings to address this dilemma.
Scenario 3 sheds light on the operational issues resulting in reduced patient satisfaction and lost revenues, both on the outpatient and inpatient sides by cancellation of office visits and ED backlog. Telemedicine use in these situations can improve the turnaround time of physicians who can see some of those patients while staying at one location as they wait on other patients to show up in the clinic or wait on the operation room crew, or the procedure kit etcetera, hence improving the length of stay, ED throughput, patient satisfaction, and quality of care. This also can improve overall workflow and the wellness of physicians.
One common outcome in all these scenarios is emergency department overcrowding. There have been multiple studies that suggest that ED overcrowding can result in increased costs, lost revenues, and poor clinical outcomes, including delayed administration of antibiotics, delayed administration of analgesics to suffering patients, increased hospital length of stay, and even increased mortality.4-6 A crowded ED limits the ability of an institution to accept referrals and increases medicolegal risks. (See Figure 2.)

Another study showed that a 1-hour reduction in ED boarding time would result in over $9,000 of additional revenue by reducing ambulance diversion and the number of patients who left without being seen.7 Another found that using tele-emergency services can potentially result in net savings of $3,823 per avoided transfer, while accounting for the costs related to tele-emergency technology, hospital revenues, and patient-associated savings.8
There are other instances where gaps in staffing and cracks in workflow can have a negative impact on hospital operations. For example, the busier hospitals that do have a dedicated nocturnist also struggle with physician retention, since such hospitals have higher volumes and higher cross-coverage needs, and are therefore hard to manage by just one single physician at night. Since these are temporary surges, hiring another full-time nocturnist is not a viable option for the hospitals and is considered an expense in many places.
Similarly, during day shift, if a physician goes on vacation or there are surges in patient volumes, hiring a locum tenens hospitalist can be an expensive option, since the cost also includes travel and lodging. In many instances, hiring locum tenens in a given time frame is also not possible, and it leaves the physicians short staffed, fueling both physicians’ and patients’ dissatisfaction and leading to other operational and safety challenges, which I highlighted above.
Telemedicine services in these situations can provide cross-coverage while nocturnists can focus on admissions and other acute issues. Also, when physicians are on vacation or there is surge capacity (that can be forecast by using various predictive analytics models), hospitals can make plans accordingly and make use of telemedicine services. For example, Providence St. Joseph Health reported improvement in timeliness and efficiency of care after implementation of a telehospitalist program. Their 2-year study at a partner site showed a 59% improvement in patients admitted prior to midnight, about $547,000 improvement in first-day revenue capture, an increase in total revenue days and comparable patient experience scores, and a substantial increase in inpatient census and case mix index.9
Other institutions have successfully implemented some inpatient telemedicine programs – such as telepsych, telestroke, and tele-ICU – and some have also reported positive outcomes in terms of patient satisfaction, improved access, reduced length of stay in the ED, and improved quality metrics. Emory Healthcare in Atlanta reported $4.6 million savings in Medicare costs over a 15-month period from adopting a telemedicine model in the ICU, and a reduction in 60-day readmissions by 2.1%.10 Similarly, another study showed that one large health care center improved its direct contribution margins by 376% (from $7.9 million to $37.7 million) because of increased case volume, shorter lengths of stay, and higher case revenue relative to direct costs. When combined with a logistics center, they reported improved contribution margins by 665% (from $7.9 million to $60.6 million).11
There are barriers to the integration and implementation of inpatient telemedicine, including regulations, reimbursement, physician licensing, adoption of technology, and trust among staff and patients. However, I am cautiously optimistic that increased use of telehealth during the COVID-19 pandemic has allowed patients, physicians, nurses, and health care workers and leaders to gain experience with this technology, which will help them gain confidence and reduce hesitation in adapting to this new digital platform. Ultimately, the extent to which telemedicine is able to positively impact patient care will revolve around overcoming these barriers, likely through an evolution of both the technology itself and the attitudes and regulations surrounding it.
I do not suggest that telemedicine should replace the in-person encounter, but it can be implemented and used successfully in addressing the pain points in U.S. health care. (See Figure 3.)

To that end, the purpose of this article is to spark discussion around different ways of implementing telemedicine in inpatient settings to solve many of the challenges that health care faces today.
Dr. Zia is an internal medicine board-certified physician, serving as a hospitalist and physician adviser in a medically underserved area. She has also served as interim medical director of the department of hospital medicine, and medical staff president, at SIH Herrin Hospital, in Herrin, Ill., part of Southern Illinois Healthcare. She has a special interest in improving access to health care in physician shortage areas.
References
1. Kindermann DR et al. Emergency department transfers and transfer relationships in United States hospitals. Acad Emerg Med. 2015 Feb;22(2):157-65.
2. Sanders RB et al. New hospital telemedicine services: Potential market for a nighttime hospitalist service. Telemed J E Health. 2014 Oct 1;20(10):902-8.
3. Shanafelt T et al. The business case for investing in physician well-being. JAMA Intern Med. 2017;177(12):1826-32.
4. Pines JM et al. The impact of emergency department crowding measures on time to antibiotics for patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Ann Emerg Med. 2007 Nov;50(5):510-6.
5. Pines JM and Hollander JE. Emergency department crowding is associated with poor care for patients with severe pain. Ann Emerg Med. 2008 Jan;51(1):1-5.
6. Chalfin DB et al. Impact of delayed transfer of critically ill patients from the emergency department to the intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2007 Jun;35(6):1477-83.
7. Pines JM et al. The financial consequences of lost demand and reducing boarding in hospital emergency departments. Ann Emerg Med. 2011 Oct;58(4):331-40.
8. Natafgi N et al. Using tele-emergency to avoid patient transfers in rural emergency. J Telemed Telecare. 2018 Apri;24(3):193-201.
9. Providence.org/telehealthhospitalistcasestudy.
10. Woodruff Health Sciences Center. CMS report: eICU program reduced hospital stays, saved millions, eased provider shortage. 2017 Apr 5.
11. Lilly CM et al. ICU telemedicine program financial outcomes. Chest. 2017 Feb;151(2):286-97.
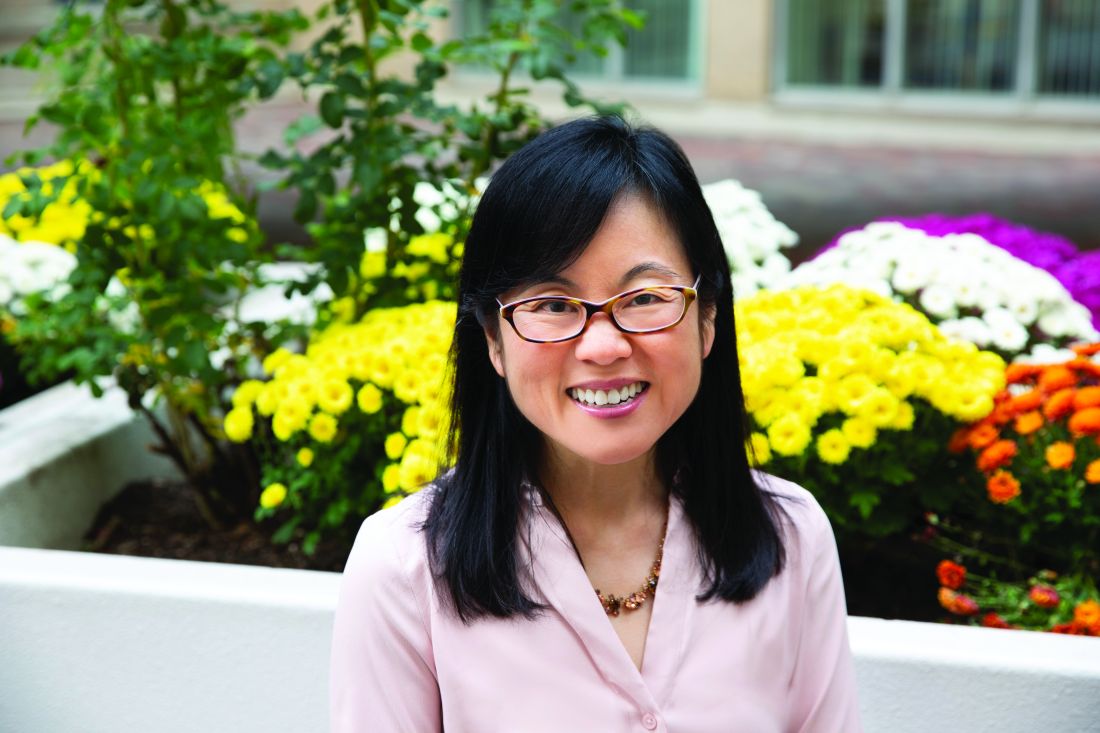
A ‘hospitalist plus’: Grace C. Huang, MD
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Grace C. Huang, MD, is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Dr. Huang currently serves as vice chair for career development and mentoring in the department of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess as well as director of the Office of Academic Careers and Faculty Development, and codirector of the Beth Israel Deaconess Academy of Medical Educators. She is also director of the Rabkin Fellowship in Medical Education, a program for Harvard Medical School faculty designed to help develop the skills needed to launch or advance academic careers in medical education or academic leadership.
Additionally, Dr. Huang is the editor in chief of MedEdPORTAL, a MEDLINE-indexed, open-access journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
At what point in your training did you decide to practice hospital medicine, and what about it appealed to you?
I trained at a point in time where it was rare for people to aspire to go in to hospital medicine. It just wasn’t that common, and there were so few examples of what a career trajectory in hospital medicine would look like. So I don’t know that I actively chose to go into hospital medicine; I chose it because it was what I knew how to do, based on my residency experience.
But it is really easy and authentic for me now to share about what makes hospital medicine such a vibrant career choice. I’m doing a lot of things in my job other than hospital medicine, but when I am on service, it reminds me acutely what it means to stay connected to why I became a doctor. The practice of hospital medicine means to be there at the most intense time of many people’s lives, to shoulder the responsibility of knowing that what I say to my patients will be remembered forever, and to be challenged by some of medicine’s hardest problems.
Hospital medicine has a way of putting you at the nexus of individual, family, society, government, and planet. But it also means that, even while I am witness to disease, suffering, broken relationships, social injustice, and environmental issues, I get a privileged look at what it means to comfort, to identify what really matters to people, to understand what gives us dignity as human beings. Lastly, I always come back to the fact that working as a team has made my clinical job so much more enriching; it’s not trench warfare, but you do create bonds quickly with learners, colleagues, and other health professionals in such an intense, fast-paced environment.
What is your current role at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center?
At Beth Israel Deaconess, I’m holding four different jobs. It’s sometimes hard for me to keep track of them, but they all center on career and faculty development. I’m a vice chair for career development within the department of medicine, and I also have an institutional role for faculty development for clinicians, educators, and researchers. I provide academic promotion support for the faculty, provide ad hoc mentorship, and run professional development programming. I also direct a year-long medical education fellowship. On the side, I am the editor in chief for a medical education journal.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice and research?
Being a generalist means I love a lot of areas of clinical practice. I’m not sure there’s a particular area that I enjoy more than others. I love teaching specific topics – antibiotics, pharmacology, direct oral anticoagulants, the microbiology of common infections. I love thinking about how the heart and kidney battle for dominance each day and being the mediator. I have a particular interest in high-value care and lab ordering (or the fact that we should do much less of it). I love complex diagnostic problems and mapping them out on paper for my team.
The research that I’ve been doing over the past 20 years has focused on how we train internists and internists-to-be to do bedside procedures. It stemmed from my own ineptitude in doing procedures, and it caused me to question the age-old approach we took in sticking needles into patients without standardized training, supervision, or safety measures.
I’ve been proud of the small role I’ve been able to play in influencing how residents are taught to do procedures, and now I’m working with others to focus on how we should teach procedures to hospitalists, who don’t do procedures on a regular basis, and aren’t under the same expectations for ongoing skill development.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine, and what are the most rewarding?
The intensity is probably what’s hardest for me about hospital medicine. At this point in my career, if I’m on service for a week, it takes me just as long to recover. It’s the cognitive load of needing to keep track of details that can make a big difference, the rapidity at which patients can deteriorate, the need to change course in an instant because of new information, and wanting to be mentally present and available for my patients and my learners.
It’s also hard to see suffering up close and personal and to leave feeling helpless to change the course of severe illness or to optimize care within the constraints of the health care system. This is why I do – and have to – extract satisfaction from the smallest of wins and brief moments of connection. Like seeing a patient turn the corner after being on the brink. Or gaining trust from an initially upset family member. Getting a copy of the eulogy from the daughter of my patient. A phone call from a patient I cared for 18 months ago, thanking me for my care. Visiting patients in the hospital socially that I had gotten to know over the years.
How has COVID-19 impacted hospitalist practice, and what changes will outlast the pandemic?
What you read in the lay press has put a spotlight on hospital-based work. What has been shared resonates with my own experience – the loss of connection from visitor restrictions, the isolation patients experience when everyone is wearing personal protective equipment, the worsening of everything that was already hard to begin with, like health care disparities, mental health, access to community supports, financial challenges, the disproportionate burden on unpaid caregivers, etc.
After the pandemic is “over,” I hope that we will retain a sense of intentionality how we address limited resources, the importance of social connection, the structural racism that has disadvantaged patients and physicians of color.
How will hospital medicine as a field change in the next decade or 2?
The hospitalist model has already influenced other specialties, like ob.gyn., neurology, and cardiology, and I expect that to continue. Hospitalists have already become leaders at the highest levels, and we will see them in higher numbers throughout health care leadership.
Are there any particular mentors who have been influential in your journey as a hospitalist?
Because I’m one of the older hospitalists in my group, there were fewer mentors, other than my boss, Joe Li, MD, SFHM, [section chief in hospital medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess], who has been an amazing role model. I think also of my colleagues as peer mentors, who continue to push me to be a better doctor. Whether it means remaining curious during the physical exam, or inspiring me with their excitement about clinical cases.
Do you have any advice for students and residents interested in hospital medicine?
When I talk to trainees about career development as a hospitalist, I encourage them to think about what will make them a “Hospitalist Plus.” Whether that Plus is teaching, research, or leadership, being a hospitalist gives you an opportunity to extend your impact as a physician into related realm.
I look around at our hospital medicine group, and every person has their Plus. We have educators, quality improvement leaders, a health services researcher, a health policy expert, a textbook editor – everyone brings special expertise to the group. My Plus now is much bigger than my footprint as a hospitalist, but I would never have gotten here had I not chosen a career path that would allow me to explore the farthest reaches of my potential as a physician.
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Grace C. Huang, MD, is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Dr. Huang currently serves as vice chair for career development and mentoring in the department of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess as well as director of the Office of Academic Careers and Faculty Development, and codirector of the Beth Israel Deaconess Academy of Medical Educators. She is also director of the Rabkin Fellowship in Medical Education, a program for Harvard Medical School faculty designed to help develop the skills needed to launch or advance academic careers in medical education or academic leadership.
Additionally, Dr. Huang is the editor in chief of MedEdPORTAL, a MEDLINE-indexed, open-access journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
At what point in your training did you decide to practice hospital medicine, and what about it appealed to you?
I trained at a point in time where it was rare for people to aspire to go in to hospital medicine. It just wasn’t that common, and there were so few examples of what a career trajectory in hospital medicine would look like. So I don’t know that I actively chose to go into hospital medicine; I chose it because it was what I knew how to do, based on my residency experience.
But it is really easy and authentic for me now to share about what makes hospital medicine such a vibrant career choice. I’m doing a lot of things in my job other than hospital medicine, but when I am on service, it reminds me acutely what it means to stay connected to why I became a doctor. The practice of hospital medicine means to be there at the most intense time of many people’s lives, to shoulder the responsibility of knowing that what I say to my patients will be remembered forever, and to be challenged by some of medicine’s hardest problems.
Hospital medicine has a way of putting you at the nexus of individual, family, society, government, and planet. But it also means that, even while I am witness to disease, suffering, broken relationships, social injustice, and environmental issues, I get a privileged look at what it means to comfort, to identify what really matters to people, to understand what gives us dignity as human beings. Lastly, I always come back to the fact that working as a team has made my clinical job so much more enriching; it’s not trench warfare, but you do create bonds quickly with learners, colleagues, and other health professionals in such an intense, fast-paced environment.
What is your current role at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center?
At Beth Israel Deaconess, I’m holding four different jobs. It’s sometimes hard for me to keep track of them, but they all center on career and faculty development. I’m a vice chair for career development within the department of medicine, and I also have an institutional role for faculty development for clinicians, educators, and researchers. I provide academic promotion support for the faculty, provide ad hoc mentorship, and run professional development programming. I also direct a year-long medical education fellowship. On the side, I am the editor in chief for a medical education journal.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice and research?
Being a generalist means I love a lot of areas of clinical practice. I’m not sure there’s a particular area that I enjoy more than others. I love teaching specific topics – antibiotics, pharmacology, direct oral anticoagulants, the microbiology of common infections. I love thinking about how the heart and kidney battle for dominance each day and being the mediator. I have a particular interest in high-value care and lab ordering (or the fact that we should do much less of it). I love complex diagnostic problems and mapping them out on paper for my team.
The research that I’ve been doing over the past 20 years has focused on how we train internists and internists-to-be to do bedside procedures. It stemmed from my own ineptitude in doing procedures, and it caused me to question the age-old approach we took in sticking needles into patients without standardized training, supervision, or safety measures.
I’ve been proud of the small role I’ve been able to play in influencing how residents are taught to do procedures, and now I’m working with others to focus on how we should teach procedures to hospitalists, who don’t do procedures on a regular basis, and aren’t under the same expectations for ongoing skill development.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine, and what are the most rewarding?
The intensity is probably what’s hardest for me about hospital medicine. At this point in my career, if I’m on service for a week, it takes me just as long to recover. It’s the cognitive load of needing to keep track of details that can make a big difference, the rapidity at which patients can deteriorate, the need to change course in an instant because of new information, and wanting to be mentally present and available for my patients and my learners.
It’s also hard to see suffering up close and personal and to leave feeling helpless to change the course of severe illness or to optimize care within the constraints of the health care system. This is why I do – and have to – extract satisfaction from the smallest of wins and brief moments of connection. Like seeing a patient turn the corner after being on the brink. Or gaining trust from an initially upset family member. Getting a copy of the eulogy from the daughter of my patient. A phone call from a patient I cared for 18 months ago, thanking me for my care. Visiting patients in the hospital socially that I had gotten to know over the years.
How has COVID-19 impacted hospitalist practice, and what changes will outlast the pandemic?
What you read in the lay press has put a spotlight on hospital-based work. What has been shared resonates with my own experience – the loss of connection from visitor restrictions, the isolation patients experience when everyone is wearing personal protective equipment, the worsening of everything that was already hard to begin with, like health care disparities, mental health, access to community supports, financial challenges, the disproportionate burden on unpaid caregivers, etc.
After the pandemic is “over,” I hope that we will retain a sense of intentionality how we address limited resources, the importance of social connection, the structural racism that has disadvantaged patients and physicians of color.
How will hospital medicine as a field change in the next decade or 2?
The hospitalist model has already influenced other specialties, like ob.gyn., neurology, and cardiology, and I expect that to continue. Hospitalists have already become leaders at the highest levels, and we will see them in higher numbers throughout health care leadership.
Are there any particular mentors who have been influential in your journey as a hospitalist?
Because I’m one of the older hospitalists in my group, there were fewer mentors, other than my boss, Joe Li, MD, SFHM, [section chief in hospital medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess], who has been an amazing role model. I think also of my colleagues as peer mentors, who continue to push me to be a better doctor. Whether it means remaining curious during the physical exam, or inspiring me with their excitement about clinical cases.
Do you have any advice for students and residents interested in hospital medicine?
When I talk to trainees about career development as a hospitalist, I encourage them to think about what will make them a “Hospitalist Plus.” Whether that Plus is teaching, research, or leadership, being a hospitalist gives you an opportunity to extend your impact as a physician into related realm.
I look around at our hospital medicine group, and every person has their Plus. We have educators, quality improvement leaders, a health services researcher, a health policy expert, a textbook editor – everyone brings special expertise to the group. My Plus now is much bigger than my footprint as a hospitalist, but I would never have gotten here had I not chosen a career path that would allow me to explore the farthest reaches of my potential as a physician.
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
Grace C. Huang, MD, is a hospitalist at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and an associate professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
Dr. Huang currently serves as vice chair for career development and mentoring in the department of medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess as well as director of the Office of Academic Careers and Faculty Development, and codirector of the Beth Israel Deaconess Academy of Medical Educators. She is also director of the Rabkin Fellowship in Medical Education, a program for Harvard Medical School faculty designed to help develop the skills needed to launch or advance academic careers in medical education or academic leadership.
Additionally, Dr. Huang is the editor in chief of MedEdPORTAL, a MEDLINE-indexed, open-access journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges.
At what point in your training did you decide to practice hospital medicine, and what about it appealed to you?
I trained at a point in time where it was rare for people to aspire to go in to hospital medicine. It just wasn’t that common, and there were so few examples of what a career trajectory in hospital medicine would look like. So I don’t know that I actively chose to go into hospital medicine; I chose it because it was what I knew how to do, based on my residency experience.
But it is really easy and authentic for me now to share about what makes hospital medicine such a vibrant career choice. I’m doing a lot of things in my job other than hospital medicine, but when I am on service, it reminds me acutely what it means to stay connected to why I became a doctor. The practice of hospital medicine means to be there at the most intense time of many people’s lives, to shoulder the responsibility of knowing that what I say to my patients will be remembered forever, and to be challenged by some of medicine’s hardest problems.
Hospital medicine has a way of putting you at the nexus of individual, family, society, government, and planet. But it also means that, even while I am witness to disease, suffering, broken relationships, social injustice, and environmental issues, I get a privileged look at what it means to comfort, to identify what really matters to people, to understand what gives us dignity as human beings. Lastly, I always come back to the fact that working as a team has made my clinical job so much more enriching; it’s not trench warfare, but you do create bonds quickly with learners, colleagues, and other health professionals in such an intense, fast-paced environment.
What is your current role at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center?
At Beth Israel Deaconess, I’m holding four different jobs. It’s sometimes hard for me to keep track of them, but they all center on career and faculty development. I’m a vice chair for career development within the department of medicine, and I also have an institutional role for faculty development for clinicians, educators, and researchers. I provide academic promotion support for the faculty, provide ad hoc mentorship, and run professional development programming. I also direct a year-long medical education fellowship. On the side, I am the editor in chief for a medical education journal.
What are your favorite areas of clinical practice and research?
Being a generalist means I love a lot of areas of clinical practice. I’m not sure there’s a particular area that I enjoy more than others. I love teaching specific topics – antibiotics, pharmacology, direct oral anticoagulants, the microbiology of common infections. I love thinking about how the heart and kidney battle for dominance each day and being the mediator. I have a particular interest in high-value care and lab ordering (or the fact that we should do much less of it). I love complex diagnostic problems and mapping them out on paper for my team.
The research that I’ve been doing over the past 20 years has focused on how we train internists and internists-to-be to do bedside procedures. It stemmed from my own ineptitude in doing procedures, and it caused me to question the age-old approach we took in sticking needles into patients without standardized training, supervision, or safety measures.
I’ve been proud of the small role I’ve been able to play in influencing how residents are taught to do procedures, and now I’m working with others to focus on how we should teach procedures to hospitalists, who don’t do procedures on a regular basis, and aren’t under the same expectations for ongoing skill development.
What are the most challenging aspects of practicing hospital medicine, and what are the most rewarding?
The intensity is probably what’s hardest for me about hospital medicine. At this point in my career, if I’m on service for a week, it takes me just as long to recover. It’s the cognitive load of needing to keep track of details that can make a big difference, the rapidity at which patients can deteriorate, the need to change course in an instant because of new information, and wanting to be mentally present and available for my patients and my learners.
It’s also hard to see suffering up close and personal and to leave feeling helpless to change the course of severe illness or to optimize care within the constraints of the health care system. This is why I do – and have to – extract satisfaction from the smallest of wins and brief moments of connection. Like seeing a patient turn the corner after being on the brink. Or gaining trust from an initially upset family member. Getting a copy of the eulogy from the daughter of my patient. A phone call from a patient I cared for 18 months ago, thanking me for my care. Visiting patients in the hospital socially that I had gotten to know over the years.
How has COVID-19 impacted hospitalist practice, and what changes will outlast the pandemic?
What you read in the lay press has put a spotlight on hospital-based work. What has been shared resonates with my own experience – the loss of connection from visitor restrictions, the isolation patients experience when everyone is wearing personal protective equipment, the worsening of everything that was already hard to begin with, like health care disparities, mental health, access to community supports, financial challenges, the disproportionate burden on unpaid caregivers, etc.
After the pandemic is “over,” I hope that we will retain a sense of intentionality how we address limited resources, the importance of social connection, the structural racism that has disadvantaged patients and physicians of color.
How will hospital medicine as a field change in the next decade or 2?
The hospitalist model has already influenced other specialties, like ob.gyn., neurology, and cardiology, and I expect that to continue. Hospitalists have already become leaders at the highest levels, and we will see them in higher numbers throughout health care leadership.
Are there any particular mentors who have been influential in your journey as a hospitalist?
Because I’m one of the older hospitalists in my group, there were fewer mentors, other than my boss, Joe Li, MD, SFHM, [section chief in hospital medicine at Beth Israel Deaconess], who has been an amazing role model. I think also of my colleagues as peer mentors, who continue to push me to be a better doctor. Whether it means remaining curious during the physical exam, or inspiring me with their excitement about clinical cases.
Do you have any advice for students and residents interested in hospital medicine?
When I talk to trainees about career development as a hospitalist, I encourage them to think about what will make them a “Hospitalist Plus.” Whether that Plus is teaching, research, or leadership, being a hospitalist gives you an opportunity to extend your impact as a physician into related realm.
I look around at our hospital medicine group, and every person has their Plus. We have educators, quality improvement leaders, a health services researcher, a health policy expert, a textbook editor – everyone brings special expertise to the group. My Plus now is much bigger than my footprint as a hospitalist, but I would never have gotten here had I not chosen a career path that would allow me to explore the farthest reaches of my potential as a physician.
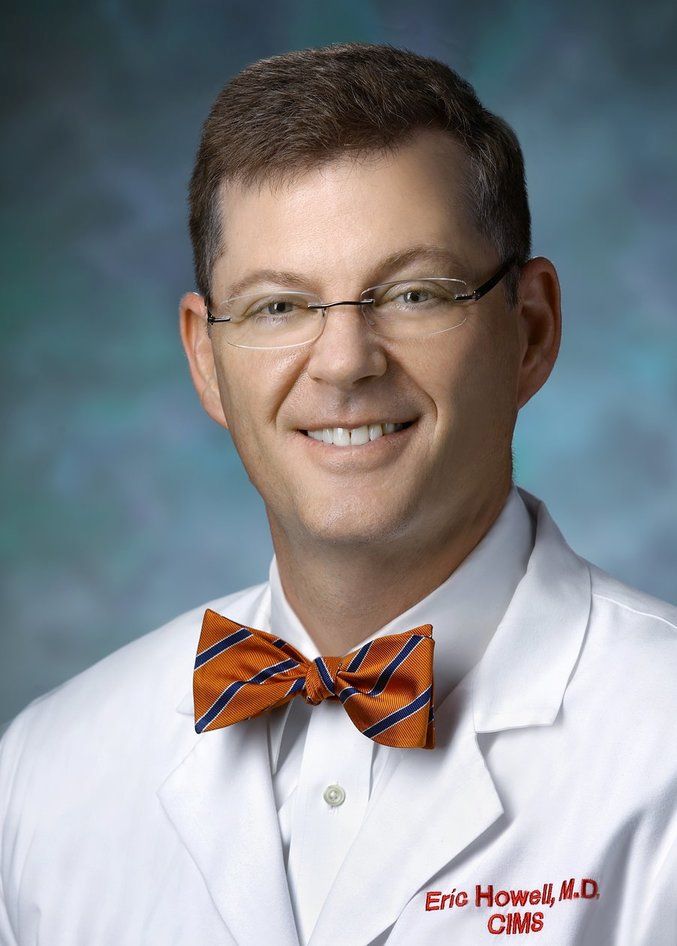
SHM CEO Eric Howell likes to fix things
Engineering provided a foundation for hospital medicine
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
For Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, CEO since July 2020 for the Society of Hospital Medicine, an undergraduate degree in electrical engineering and a lifelong proclivity for figuring out puzzles, solving problems, and taking things apart to see how they fit back together were building blocks for an exemplary career as a hospitalist, group administrator, and medical educator.
When he was growing up in historic Annapolis, Md., near the shores of Chesapeake Bay, things to put back together included remote control airplanes, small boat engines, and cars. As a hospitalist, his interest in solving problems and facility with numbers and systems led him to become an expert on quality improvement, transitions of care, and conflict management.
“One thing about engineering, you’re always having to fix things. It helps you learn to assess complex situations,” said Dr. Howell, who is 52. “It was helpful for me to bring an engineering approach into the hospital. One of my earliest successes was reengineering admissions processes to dramatically reduce the amount of time patients were spending in the emergency room before they could be admitted to the hospital.”
But his career path in hospital medicine came about by a lucky chance, following residency and a year as chief resident at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore. “One of my duties as chief resident was taking care of hospitalized patients. I didn’t know it but I was becoming a de facto hospitalist,” he recalled.
At the time, he thought he might end up choosing to specialize in something like cardiology or critical care medicine, but in 2000 he was invited to join the new “non-house-staff” medical service at Bayview. Also called a general medicine inpatient service, it eventually evolved into the hospitalist service.
His residency program director, Roy Ziegelstein, MD, a cardiologist and now the vice dean of education at Johns Hopkins, created a job for him.
“I was one of the first four doctors hired. I thought I’d just do it for a year, but I loved inpatient work, so I stayed,” Dr. Howell said. “Roy mentored me for the next 20 years and helped me to become an above average hospitalist.”
Early on, Dr. Howell’s department chair, David Hellman, MD, who had worked at the University of California–San Francisco with hospital medicine pioneer Robert Wachter, MD, MHM, sent Dr. Howell to San Francisco to be mentored by Dr. Wachter, since there were few hospital mentors on the East Coast at that time.
“What I took away from that experience was how important it was to professionalize hospital medicine – in order to develop specialized expertise,” Dr. Howell recalled. “Dr. Wachter taught me that hospitalists need to have a professional focus. Quality improvement, systems-based improvement, and value all became part of that,” he said.
“Many people thought to be a hospitalist all you had to know was basic medicine. But it turns out medicine in the hospital is just as specialized as any other specialty. The hospital itself requires specialized knowledge that didn’t even exist 20 years ago.” Because of complicated disease states and clinical systems, hospitalists have to be better at navigating the software of today’s hospital.
New job opportunities
Dr. Howell describes his career path as a new job focus opening up every 5 years or so, redefining what he does and trying something new and exciting with better pay. His first was a focus on clinical hospital medicine and learning how to be a better doctor. Then in 2005 he began work as a teacher at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. There he mastered the teaching of medical trainees, winning awards as an instructor, including SHM’s award for excellence in teaching.
In 2010 he again changed his focus to program building, leading the expansion of the hospitalist service for Bayview and three other hospitals in the Johns Hopkins system. Dr. Howell helped grow the service to nearly 200 clinicians while becoming skilled at operational and program development.
His fourth job incarnation, starting in 2015, was the obsessive pursuit of quality improvement, marshaling data to measure and improve clinical and other outcomes on the quality dashboard – mortality, length of stay, readmissions, rates of adverse events – and putting quality improvement strategies in place.
“Our mortality rates at Bayview were well below national standards. We came up with an amazing program. A lot of hospital medicine programs pursue improvement, but we really measured it. We benchmarked ourselves against other programs at Hopkins,” he said. “I set up a dedicated conference room, as many QI programs do. We called it True North, and each wall had a different QI focus, with updates on the reported metrics. Every other week we met there to talk about the metrics,” he said.
That experience led to working with SHM, which he had joined as a member early in his career and for which he had previously served as president. He became SHM’s quality improvement liaison and a co-principal investigator on Project BOOST (Better Outcomes for Older adults through Safe Transitions), SHM’s pioneering, national mentored-implementation model aimed at improving transitions of care from participating hospitals to reduce readmissions. “BOOST really established SHM’s reputation as a quality improvement-oriented organization. It was a stake in the ground for quality and led to SHM receiving the Joint Commission’s 2011 John M. Eisenberg Award for Innovation in Patient Safety and Quality,” he said.
Dr. Howell’s fifth career phase, medical society management, emerged when he was recruited to apply for the SHM chief executive position – held since its inception by retiring CEO Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM. Dr. Howell started work at SHM in the midst of the pandemic, spending much of his time working from home – especially when Philadelphia implemented stricter COVID-19 restrictions. Once pandemic restrictions are loosened, he expects to do a lot of traveling. But for now, the external-facing part of his job is mainly on Zoom.
Making the world a better place
Dr. Howell said he has held fast to three mottos in life, which have guided his career path as well as his personal life: (1) to make the world a better place; (2) to be ethical and transparent; and (3) to invest in people. His wife of 19 years, Heather Howell, an Annapolis realtor, says making the world a better place is what they taught their children, Mason, 18, who starts college at Rice University in fall 2021 with an interest in premed, and Anna, 16, a competitive sailor. “We always had a poster hanging in our house extolling that message,” Ms. Howell said.
Dr. Howell grew up in a nautical family, with many of his relatives working in the maritime business. His kids grew up on the water, learning to pilot a powerboat before driving a car, as he did. “We boat all the time on the bay” in his lobster boat, which he often works on to keep it seaworthy, Ms. Howell said.
“There’s nothing like taking care of hospitalized patients to make you feel you’re making the world a better place,” Dr. Howell observed. “Very often you can make a huge difference for the patients you do care for, and that is incredibly rewarding.” Although the demands of his SHM leadership position required relinquishing most of his responsibilities at Johns Hopkins, he continues to see patients and teach residents there 2-4 weeks a year on a teaching service.
“Why do I still see patients? I find it so rewarding. And I get to teach, which I love,” he said. “To be honest, I don’t think you truly need to see patients to be head of a professional medical society like SHM. Maybe someday I’ll give that up. But only if it’s necessary to make the society more successful.”
Half of Dr. Howell’s Society work now is planned and half is “putting out fires” – while learning members’ needs in real time. “Right now, we’re worried about burnout and PTSD, because frankly it’s stressful to take care of COVID patients. It’s scary for a lot of clinicians. I’m working with our members to make sure they have what they need to be clinically prepared, including resources to be more resilient professionally.”
Every step of his career, Dr. Howell said, has seemed like the best job he ever had. “Making the world a better place is still important to me. I tell SHM members that it’s important to know they are making a difference. What they’re doing is really important, especially with COVID, and it needs to be sustainable,” he said.
“SHM has such a powerful mission – it’s about making patient care better, and making hospitalists better clinicians. I know the Society is having a powerful impact, and that’s good enough for me. I’m into teams. Hospital medicine is a team sport, but so is SHM, interacting with its members, staff, and board.”
Initiating another new program
One of Dr. Howell’s last major projects for Hopkins was to launch and be chief medical officer for the Joint Commission–accredited Baltimore Civic Center Field Hospital for COVID-19 patients, opened in March 2020.
With a surge capacity of 250 beds, and a negative pressure ward set up in the center’s exhibit hall, it is jointly operated by the University of Maryland Medical System and Johns Hopkins Hospital. The field hospital’s mission has since expanded to include viral tests, infusions of monoclonal antibodies, and COVID-19 vaccinations.
Planning for a smooth transition, Dr. Howell brought Melinda E. Kantsiper, MD, director of clinical operations, Division of Hospital Medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview, on board as associate medical officer, to eventually replace him as CMO after a few months working alongside him. “Eric brings that logical engineering eye to problem solving,” Dr. Kantsiper said.
“We wanted to build a very safe, high-quality hospital setting but had to do it very quickly. Watching him once again do what he does best, initiating a new program, building things carefully and thoughtfully, without being overly cautious, I could see his years of experience and good judgment about how hospitals run. He’s very logical but very caring. He’s also good at spotting young leaders and their talents.”
Some people have a knack for solving problems, added Dr. Ziegelstein, Dr. Howell’s mentor from his early days at Bayview. “Eric is different. He’s someone who’s able to identify gaps, problem areas, and vulnerabilities within an organization and then come up with a potential menu of solutions, think about which would be most likely to succeed, implement it, and assess the outcome. That’s the difference between a skilled manager and a true leader, and I’d say Eric had that ability while still in training,” Dr. Ziegelstein said.
“Eric understood early on not only what the field of hospital medicine could offer, he also understood how to catalyze change, without taking on too much change at one time,” Dr. Ziegelstein said. “He understood people’s sensibilities and concerns about this new service, and he catalyzed its growth through incremental change.”
Engineering provided a foundation for hospital medicine
Engineering provided a foundation for hospital medicine
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
For Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, CEO since July 2020 for the Society of Hospital Medicine, an undergraduate degree in electrical engineering and a lifelong proclivity for figuring out puzzles, solving problems, and taking things apart to see how they fit back together were building blocks for an exemplary career as a hospitalist, group administrator, and medical educator.
When he was growing up in historic Annapolis, Md., near the shores of Chesapeake Bay, things to put back together included remote control airplanes, small boat engines, and cars. As a hospitalist, his interest in solving problems and facility with numbers and systems led him to become an expert on quality improvement, transitions of care, and conflict management.
“One thing about engineering, you’re always having to fix things. It helps you learn to assess complex situations,” said Dr. Howell, who is 52. “It was helpful for me to bring an engineering approach into the hospital. One of my earliest successes was reengineering admissions processes to dramatically reduce the amount of time patients were spending in the emergency room before they could be admitted to the hospital.”
But his career path in hospital medicine came about by a lucky chance, following residency and a year as chief resident at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore. “One of my duties as chief resident was taking care of hospitalized patients. I didn’t know it but I was becoming a de facto hospitalist,” he recalled.
At the time, he thought he might end up choosing to specialize in something like cardiology or critical care medicine, but in 2000 he was invited to join the new “non-house-staff” medical service at Bayview. Also called a general medicine inpatient service, it eventually evolved into the hospitalist service.
His residency program director, Roy Ziegelstein, MD, a cardiologist and now the vice dean of education at Johns Hopkins, created a job for him.
“I was one of the first four doctors hired. I thought I’d just do it for a year, but I loved inpatient work, so I stayed,” Dr. Howell said. “Roy mentored me for the next 20 years and helped me to become an above average hospitalist.”
Early on, Dr. Howell’s department chair, David Hellman, MD, who had worked at the University of California–San Francisco with hospital medicine pioneer Robert Wachter, MD, MHM, sent Dr. Howell to San Francisco to be mentored by Dr. Wachter, since there were few hospital mentors on the East Coast at that time.
“What I took away from that experience was how important it was to professionalize hospital medicine – in order to develop specialized expertise,” Dr. Howell recalled. “Dr. Wachter taught me that hospitalists need to have a professional focus. Quality improvement, systems-based improvement, and value all became part of that,” he said.
“Many people thought to be a hospitalist all you had to know was basic medicine. But it turns out medicine in the hospital is just as specialized as any other specialty. The hospital itself requires specialized knowledge that didn’t even exist 20 years ago.” Because of complicated disease states and clinical systems, hospitalists have to be better at navigating the software of today’s hospital.
New job opportunities
Dr. Howell describes his career path as a new job focus opening up every 5 years or so, redefining what he does and trying something new and exciting with better pay. His first was a focus on clinical hospital medicine and learning how to be a better doctor. Then in 2005 he began work as a teacher at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. There he mastered the teaching of medical trainees, winning awards as an instructor, including SHM’s award for excellence in teaching.
In 2010 he again changed his focus to program building, leading the expansion of the hospitalist service for Bayview and three other hospitals in the Johns Hopkins system. Dr. Howell helped grow the service to nearly 200 clinicians while becoming skilled at operational and program development.
His fourth job incarnation, starting in 2015, was the obsessive pursuit of quality improvement, marshaling data to measure and improve clinical and other outcomes on the quality dashboard – mortality, length of stay, readmissions, rates of adverse events – and putting quality improvement strategies in place.
“Our mortality rates at Bayview were well below national standards. We came up with an amazing program. A lot of hospital medicine programs pursue improvement, but we really measured it. We benchmarked ourselves against other programs at Hopkins,” he said. “I set up a dedicated conference room, as many QI programs do. We called it True North, and each wall had a different QI focus, with updates on the reported metrics. Every other week we met there to talk about the metrics,” he said.
That experience led to working with SHM, which he had joined as a member early in his career and for which he had previously served as president. He became SHM’s quality improvement liaison and a co-principal investigator on Project BOOST (Better Outcomes for Older adults through Safe Transitions), SHM’s pioneering, national mentored-implementation model aimed at improving transitions of care from participating hospitals to reduce readmissions. “BOOST really established SHM’s reputation as a quality improvement-oriented organization. It was a stake in the ground for quality and led to SHM receiving the Joint Commission’s 2011 John M. Eisenberg Award for Innovation in Patient Safety and Quality,” he said.
Dr. Howell’s fifth career phase, medical society management, emerged when he was recruited to apply for the SHM chief executive position – held since its inception by retiring CEO Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM. Dr. Howell started work at SHM in the midst of the pandemic, spending much of his time working from home – especially when Philadelphia implemented stricter COVID-19 restrictions. Once pandemic restrictions are loosened, he expects to do a lot of traveling. But for now, the external-facing part of his job is mainly on Zoom.
Making the world a better place
Dr. Howell said he has held fast to three mottos in life, which have guided his career path as well as his personal life: (1) to make the world a better place; (2) to be ethical and transparent; and (3) to invest in people. His wife of 19 years, Heather Howell, an Annapolis realtor, says making the world a better place is what they taught their children, Mason, 18, who starts college at Rice University in fall 2021 with an interest in premed, and Anna, 16, a competitive sailor. “We always had a poster hanging in our house extolling that message,” Ms. Howell said.
Dr. Howell grew up in a nautical family, with many of his relatives working in the maritime business. His kids grew up on the water, learning to pilot a powerboat before driving a car, as he did. “We boat all the time on the bay” in his lobster boat, which he often works on to keep it seaworthy, Ms. Howell said.
“There’s nothing like taking care of hospitalized patients to make you feel you’re making the world a better place,” Dr. Howell observed. “Very often you can make a huge difference for the patients you do care for, and that is incredibly rewarding.” Although the demands of his SHM leadership position required relinquishing most of his responsibilities at Johns Hopkins, he continues to see patients and teach residents there 2-4 weeks a year on a teaching service.
“Why do I still see patients? I find it so rewarding. And I get to teach, which I love,” he said. “To be honest, I don’t think you truly need to see patients to be head of a professional medical society like SHM. Maybe someday I’ll give that up. But only if it’s necessary to make the society more successful.”
Half of Dr. Howell’s Society work now is planned and half is “putting out fires” – while learning members’ needs in real time. “Right now, we’re worried about burnout and PTSD, because frankly it’s stressful to take care of COVID patients. It’s scary for a lot of clinicians. I’m working with our members to make sure they have what they need to be clinically prepared, including resources to be more resilient professionally.”
Every step of his career, Dr. Howell said, has seemed like the best job he ever had. “Making the world a better place is still important to me. I tell SHM members that it’s important to know they are making a difference. What they’re doing is really important, especially with COVID, and it needs to be sustainable,” he said.
“SHM has such a powerful mission – it’s about making patient care better, and making hospitalists better clinicians. I know the Society is having a powerful impact, and that’s good enough for me. I’m into teams. Hospital medicine is a team sport, but so is SHM, interacting with its members, staff, and board.”
Initiating another new program
One of Dr. Howell’s last major projects for Hopkins was to launch and be chief medical officer for the Joint Commission–accredited Baltimore Civic Center Field Hospital for COVID-19 patients, opened in March 2020.
With a surge capacity of 250 beds, and a negative pressure ward set up in the center’s exhibit hall, it is jointly operated by the University of Maryland Medical System and Johns Hopkins Hospital. The field hospital’s mission has since expanded to include viral tests, infusions of monoclonal antibodies, and COVID-19 vaccinations.
Planning for a smooth transition, Dr. Howell brought Melinda E. Kantsiper, MD, director of clinical operations, Division of Hospital Medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview, on board as associate medical officer, to eventually replace him as CMO after a few months working alongside him. “Eric brings that logical engineering eye to problem solving,” Dr. Kantsiper said.
“We wanted to build a very safe, high-quality hospital setting but had to do it very quickly. Watching him once again do what he does best, initiating a new program, building things carefully and thoughtfully, without being overly cautious, I could see his years of experience and good judgment about how hospitals run. He’s very logical but very caring. He’s also good at spotting young leaders and their talents.”
Some people have a knack for solving problems, added Dr. Ziegelstein, Dr. Howell’s mentor from his early days at Bayview. “Eric is different. He’s someone who’s able to identify gaps, problem areas, and vulnerabilities within an organization and then come up with a potential menu of solutions, think about which would be most likely to succeed, implement it, and assess the outcome. That’s the difference between a skilled manager and a true leader, and I’d say Eric had that ability while still in training,” Dr. Ziegelstein said.
“Eric understood early on not only what the field of hospital medicine could offer, he also understood how to catalyze change, without taking on too much change at one time,” Dr. Ziegelstein said. “He understood people’s sensibilities and concerns about this new service, and he catalyzed its growth through incremental change.”
Editor’s note: This profile is part of SHM’s celebration of National Hospitalist Day on March 4. National Hospitalist Day occurs the first Thursday in March annually, and celebrates the fastest growing specialty in modern medicine and hospitalists’ enduring contributions to the evolving health care landscape.
For Eric E. Howell, MD, MHM, CEO since July 2020 for the Society of Hospital Medicine, an undergraduate degree in electrical engineering and a lifelong proclivity for figuring out puzzles, solving problems, and taking things apart to see how they fit back together were building blocks for an exemplary career as a hospitalist, group administrator, and medical educator.
When he was growing up in historic Annapolis, Md., near the shores of Chesapeake Bay, things to put back together included remote control airplanes, small boat engines, and cars. As a hospitalist, his interest in solving problems and facility with numbers and systems led him to become an expert on quality improvement, transitions of care, and conflict management.
“One thing about engineering, you’re always having to fix things. It helps you learn to assess complex situations,” said Dr. Howell, who is 52. “It was helpful for me to bring an engineering approach into the hospital. One of my earliest successes was reengineering admissions processes to dramatically reduce the amount of time patients were spending in the emergency room before they could be admitted to the hospital.”
But his career path in hospital medicine came about by a lucky chance, following residency and a year as chief resident at Johns Hopkins Bayview Medical Center in Baltimore. “One of my duties as chief resident was taking care of hospitalized patients. I didn’t know it but I was becoming a de facto hospitalist,” he recalled.
At the time, he thought he might end up choosing to specialize in something like cardiology or critical care medicine, but in 2000 he was invited to join the new “non-house-staff” medical service at Bayview. Also called a general medicine inpatient service, it eventually evolved into the hospitalist service.
His residency program director, Roy Ziegelstein, MD, a cardiologist and now the vice dean of education at Johns Hopkins, created a job for him.
“I was one of the first four doctors hired. I thought I’d just do it for a year, but I loved inpatient work, so I stayed,” Dr. Howell said. “Roy mentored me for the next 20 years and helped me to become an above average hospitalist.”
Early on, Dr. Howell’s department chair, David Hellman, MD, who had worked at the University of California–San Francisco with hospital medicine pioneer Robert Wachter, MD, MHM, sent Dr. Howell to San Francisco to be mentored by Dr. Wachter, since there were few hospital mentors on the East Coast at that time.
“What I took away from that experience was how important it was to professionalize hospital medicine – in order to develop specialized expertise,” Dr. Howell recalled. “Dr. Wachter taught me that hospitalists need to have a professional focus. Quality improvement, systems-based improvement, and value all became part of that,” he said.
“Many people thought to be a hospitalist all you had to know was basic medicine. But it turns out medicine in the hospital is just as specialized as any other specialty. The hospital itself requires specialized knowledge that didn’t even exist 20 years ago.” Because of complicated disease states and clinical systems, hospitalists have to be better at navigating the software of today’s hospital.
New job opportunities
Dr. Howell describes his career path as a new job focus opening up every 5 years or so, redefining what he does and trying something new and exciting with better pay. His first was a focus on clinical hospital medicine and learning how to be a better doctor. Then in 2005 he began work as a teacher at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine. There he mastered the teaching of medical trainees, winning awards as an instructor, including SHM’s award for excellence in teaching.
In 2010 he again changed his focus to program building, leading the expansion of the hospitalist service for Bayview and three other hospitals in the Johns Hopkins system. Dr. Howell helped grow the service to nearly 200 clinicians while becoming skilled at operational and program development.
His fourth job incarnation, starting in 2015, was the obsessive pursuit of quality improvement, marshaling data to measure and improve clinical and other outcomes on the quality dashboard – mortality, length of stay, readmissions, rates of adverse events – and putting quality improvement strategies in place.
“Our mortality rates at Bayview were well below national standards. We came up with an amazing program. A lot of hospital medicine programs pursue improvement, but we really measured it. We benchmarked ourselves against other programs at Hopkins,” he said. “I set up a dedicated conference room, as many QI programs do. We called it True North, and each wall had a different QI focus, with updates on the reported metrics. Every other week we met there to talk about the metrics,” he said.
That experience led to working with SHM, which he had joined as a member early in his career and for which he had previously served as president. He became SHM’s quality improvement liaison and a co-principal investigator on Project BOOST (Better Outcomes for Older adults through Safe Transitions), SHM’s pioneering, national mentored-implementation model aimed at improving transitions of care from participating hospitals to reduce readmissions. “BOOST really established SHM’s reputation as a quality improvement-oriented organization. It was a stake in the ground for quality and led to SHM receiving the Joint Commission’s 2011 John M. Eisenberg Award for Innovation in Patient Safety and Quality,” he said.
Dr. Howell’s fifth career phase, medical society management, emerged when he was recruited to apply for the SHM chief executive position – held since its inception by retiring CEO Larry Wellikson, MD, MHM. Dr. Howell started work at SHM in the midst of the pandemic, spending much of his time working from home – especially when Philadelphia implemented stricter COVID-19 restrictions. Once pandemic restrictions are loosened, he expects to do a lot of traveling. But for now, the external-facing part of his job is mainly on Zoom.
Making the world a better place
Dr. Howell said he has held fast to three mottos in life, which have guided his career path as well as his personal life: (1) to make the world a better place; (2) to be ethical and transparent; and (3) to invest in people. His wife of 19 years, Heather Howell, an Annapolis realtor, says making the world a better place is what they taught their children, Mason, 18, who starts college at Rice University in fall 2021 with an interest in premed, and Anna, 16, a competitive sailor. “We always had a poster hanging in our house extolling that message,” Ms. Howell said.
Dr. Howell grew up in a nautical family, with many of his relatives working in the maritime business. His kids grew up on the water, learning to pilot a powerboat before driving a car, as he did. “We boat all the time on the bay” in his lobster boat, which he often works on to keep it seaworthy, Ms. Howell said.
“There’s nothing like taking care of hospitalized patients to make you feel you’re making the world a better place,” Dr. Howell observed. “Very often you can make a huge difference for the patients you do care for, and that is incredibly rewarding.” Although the demands of his SHM leadership position required relinquishing most of his responsibilities at Johns Hopkins, he continues to see patients and teach residents there 2-4 weeks a year on a teaching service.
“Why do I still see patients? I find it so rewarding. And I get to teach, which I love,” he said. “To be honest, I don’t think you truly need to see patients to be head of a professional medical society like SHM. Maybe someday I’ll give that up. But only if it’s necessary to make the society more successful.”
Half of Dr. Howell’s Society work now is planned and half is “putting out fires” – while learning members’ needs in real time. “Right now, we’re worried about burnout and PTSD, because frankly it’s stressful to take care of COVID patients. It’s scary for a lot of clinicians. I’m working with our members to make sure they have what they need to be clinically prepared, including resources to be more resilient professionally.”
Every step of his career, Dr. Howell said, has seemed like the best job he ever had. “Making the world a better place is still important to me. I tell SHM members that it’s important to know they are making a difference. What they’re doing is really important, especially with COVID, and it needs to be sustainable,” he said.
“SHM has such a powerful mission – it’s about making patient care better, and making hospitalists better clinicians. I know the Society is having a powerful impact, and that’s good enough for me. I’m into teams. Hospital medicine is a team sport, but so is SHM, interacting with its members, staff, and board.”
Initiating another new program
One of Dr. Howell’s last major projects for Hopkins was to launch and be chief medical officer for the Joint Commission–accredited Baltimore Civic Center Field Hospital for COVID-19 patients, opened in March 2020.
With a surge capacity of 250 beds, and a negative pressure ward set up in the center’s exhibit hall, it is jointly operated by the University of Maryland Medical System and Johns Hopkins Hospital. The field hospital’s mission has since expanded to include viral tests, infusions of monoclonal antibodies, and COVID-19 vaccinations.
Planning for a smooth transition, Dr. Howell brought Melinda E. Kantsiper, MD, director of clinical operations, Division of Hospital Medicine at Johns Hopkins Bayview, on board as associate medical officer, to eventually replace him as CMO after a few months working alongside him. “Eric brings that logical engineering eye to problem solving,” Dr. Kantsiper said.
“We wanted to build a very safe, high-quality hospital setting but had to do it very quickly. Watching him once again do what he does best, initiating a new program, building things carefully and thoughtfully, without being overly cautious, I could see his years of experience and good judgment about how hospitals run. He’s very logical but very caring. He’s also good at spotting young leaders and their talents.”
Some people have a knack for solving problems, added Dr. Ziegelstein, Dr. Howell’s mentor from his early days at Bayview. “Eric is different. He’s someone who’s able to identify gaps, problem areas, and vulnerabilities within an organization and then come up with a potential menu of solutions, think about which would be most likely to succeed, implement it, and assess the outcome. That’s the difference between a skilled manager and a true leader, and I’d say Eric had that ability while still in training,” Dr. Ziegelstein said.
“Eric understood early on not only what the field of hospital medicine could offer, he also understood how to catalyze change, without taking on too much change at one time,” Dr. Ziegelstein said. “He understood people’s sensibilities and concerns about this new service, and he catalyzed its growth through incremental change.”
Education and networking are driving forces behind Converge platform
As Jade Myers set out to help create the virtual platform for SHM Converge, she was aware, through surveys and other communication, that the top wish of members of the Society of Hospital Medicine was an extensive and interactive educational experience.
“People really wanted to get back to the in-person conference,” said Ms. Myers, SHM’s director of meetings. “While we couldn’t do that, we can provide the same caliber and as robust an experience from an educational perspective as we would for an in-person activity.”
That has required significant revamping of the virtual platform compared to the platform for last year’s annual conference. In 2020, there was only one session running live at a time. This year, there will be 12 sessions running at the same time. There will also be more opportunities for networking, as well as other features for enjoyment and a sense of calm.
Here are some features of the SHM Converge platform:
- A host segment to kick-start each day, with an introduction of the day’s sessions and events.
- Nine didactic educational sessions at any given time. These sessions will include a live chat for peer-to-peer engagement, as well as questions and answers throughout the session to continue the discussion between speakers and participants.
- Three workshops at any given time. These sessions – on topics such as communication, gender equity, and clinical guidelines – will provide an opportunity for dynamic small-group discussion.
- A scientific abstract poster competition and reception, with an e-gallery of about 700 posters, providing a networking opportunity and highlighting emerging scientific and clinical cases.
- Special Interest Forums, in the form of live, interactive Zoom conferences. There will be 25 forums, which are designed to build community and facilitate collaboration.
- A variety of games, including trivia and a word scramble.
- Personalized profiles with information such as “Hospitalist in Training,” or “Committee Member.” These will be visible to other attendees to make it easier for people to connect when they have something in common.
- Early- and Mid-Career Speed Mentorship, in which a mentor and mentee can interact one-on-one, with each mentee able to meet with two mentors, with pairings designed for the best mentorship experience.
- Sessions on wellness and resilience.
“People are kind of Zoom fatigued,” Ms. Myers said, “so we’re trying to meet their needs while also offering an opportunity for respite, because our attendees are on the front lines right now, and they’re dealing with all types of fatigue and challenging times.”
The annual conference was on target for a banner year in 2020 before the COVID-19 pandemic forced the cancellation of the in-person conference in San Diego, and SHM Converge is a product of planning that began then, as organizers started considering a virtual event.
“In 2020, we were slated to have the largest conference in person that we have ever had,” said Hayleigh Scott, SHM’s meeting projects manager. “San Diego was going to be our really big year.”
But attendance at last year’s virtual conference was a fraction of what was expected at the in-person conference. This year, that seems poised to improve. There will be many more offerings, with more than 125 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™ and 45 Maintenance of Certification points possible, Ms. Myers said. Because attendees won’t have to worry about being in two places at once, it will be possible to secure more CME credits at SHM Converge than at any previous SHM annual conference, she said.
The volume of content will be a heavy load on SHM personnel. Last year, three society staff members were on hand at each session to make sure it ran smoothly and to answer questions. With 12 sessions running simultaneously this year, many more staff members will need to be involved. But that is not unfamiliar for the society during meeting week, Ms. Myers said.
“We’re going to need to pull from pretty much our entire staff in order to make this conference happen, which is exciting and daunting,” she said. “It’s always been an all-hands-on-deck program and this is going to be more similar to an in-person conference in that way.”
As Jade Myers set out to help create the virtual platform for SHM Converge, she was aware, through surveys and other communication, that the top wish of members of the Society of Hospital Medicine was an extensive and interactive educational experience.
“People really wanted to get back to the in-person conference,” said Ms. Myers, SHM’s director of meetings. “While we couldn’t do that, we can provide the same caliber and as robust an experience from an educational perspective as we would for an in-person activity.”
That has required significant revamping of the virtual platform compared to the platform for last year’s annual conference. In 2020, there was only one session running live at a time. This year, there will be 12 sessions running at the same time. There will also be more opportunities for networking, as well as other features for enjoyment and a sense of calm.
Here are some features of the SHM Converge platform:
- A host segment to kick-start each day, with an introduction of the day’s sessions and events.
- Nine didactic educational sessions at any given time. These sessions will include a live chat for peer-to-peer engagement, as well as questions and answers throughout the session to continue the discussion between speakers and participants.
- Three workshops at any given time. These sessions – on topics such as communication, gender equity, and clinical guidelines – will provide an opportunity for dynamic small-group discussion.
- A scientific abstract poster competition and reception, with an e-gallery of about 700 posters, providing a networking opportunity and highlighting emerging scientific and clinical cases.
- Special Interest Forums, in the form of live, interactive Zoom conferences. There will be 25 forums, which are designed to build community and facilitate collaboration.
- A variety of games, including trivia and a word scramble.
- Personalized profiles with information such as “Hospitalist in Training,” or “Committee Member.” These will be visible to other attendees to make it easier for people to connect when they have something in common.
- Early- and Mid-Career Speed Mentorship, in which a mentor and mentee can interact one-on-one, with each mentee able to meet with two mentors, with pairings designed for the best mentorship experience.
- Sessions on wellness and resilience.
“People are kind of Zoom fatigued,” Ms. Myers said, “so we’re trying to meet their needs while also offering an opportunity for respite, because our attendees are on the front lines right now, and they’re dealing with all types of fatigue and challenging times.”
The annual conference was on target for a banner year in 2020 before the COVID-19 pandemic forced the cancellation of the in-person conference in San Diego, and SHM Converge is a product of planning that began then, as organizers started considering a virtual event.
“In 2020, we were slated to have the largest conference in person that we have ever had,” said Hayleigh Scott, SHM’s meeting projects manager. “San Diego was going to be our really big year.”
But attendance at last year’s virtual conference was a fraction of what was expected at the in-person conference. This year, that seems poised to improve. There will be many more offerings, with more than 125 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™ and 45 Maintenance of Certification points possible, Ms. Myers said. Because attendees won’t have to worry about being in two places at once, it will be possible to secure more CME credits at SHM Converge than at any previous SHM annual conference, she said.
The volume of content will be a heavy load on SHM personnel. Last year, three society staff members were on hand at each session to make sure it ran smoothly and to answer questions. With 12 sessions running simultaneously this year, many more staff members will need to be involved. But that is not unfamiliar for the society during meeting week, Ms. Myers said.
“We’re going to need to pull from pretty much our entire staff in order to make this conference happen, which is exciting and daunting,” she said. “It’s always been an all-hands-on-deck program and this is going to be more similar to an in-person conference in that way.”
As Jade Myers set out to help create the virtual platform for SHM Converge, she was aware, through surveys and other communication, that the top wish of members of the Society of Hospital Medicine was an extensive and interactive educational experience.
“People really wanted to get back to the in-person conference,” said Ms. Myers, SHM’s director of meetings. “While we couldn’t do that, we can provide the same caliber and as robust an experience from an educational perspective as we would for an in-person activity.”
That has required significant revamping of the virtual platform compared to the platform for last year’s annual conference. In 2020, there was only one session running live at a time. This year, there will be 12 sessions running at the same time. There will also be more opportunities for networking, as well as other features for enjoyment and a sense of calm.
Here are some features of the SHM Converge platform:
- A host segment to kick-start each day, with an introduction of the day’s sessions and events.
- Nine didactic educational sessions at any given time. These sessions will include a live chat for peer-to-peer engagement, as well as questions and answers throughout the session to continue the discussion between speakers and participants.
- Three workshops at any given time. These sessions – on topics such as communication, gender equity, and clinical guidelines – will provide an opportunity for dynamic small-group discussion.
- A scientific abstract poster competition and reception, with an e-gallery of about 700 posters, providing a networking opportunity and highlighting emerging scientific and clinical cases.
- Special Interest Forums, in the form of live, interactive Zoom conferences. There will be 25 forums, which are designed to build community and facilitate collaboration.
- A variety of games, including trivia and a word scramble.
- Personalized profiles with information such as “Hospitalist in Training,” or “Committee Member.” These will be visible to other attendees to make it easier for people to connect when they have something in common.
- Early- and Mid-Career Speed Mentorship, in which a mentor and mentee can interact one-on-one, with each mentee able to meet with two mentors, with pairings designed for the best mentorship experience.
- Sessions on wellness and resilience.
“People are kind of Zoom fatigued,” Ms. Myers said, “so we’re trying to meet their needs while also offering an opportunity for respite, because our attendees are on the front lines right now, and they’re dealing with all types of fatigue and challenging times.”
The annual conference was on target for a banner year in 2020 before the COVID-19 pandemic forced the cancellation of the in-person conference in San Diego, and SHM Converge is a product of planning that began then, as organizers started considering a virtual event.
“In 2020, we were slated to have the largest conference in person that we have ever had,” said Hayleigh Scott, SHM’s meeting projects manager. “San Diego was going to be our really big year.”
But attendance at last year’s virtual conference was a fraction of what was expected at the in-person conference. This year, that seems poised to improve. There will be many more offerings, with more than 125 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits™ and 45 Maintenance of Certification points possible, Ms. Myers said. Because attendees won’t have to worry about being in two places at once, it will be possible to secure more CME credits at SHM Converge than at any previous SHM annual conference, she said.
The volume of content will be a heavy load on SHM personnel. Last year, three society staff members were on hand at each session to make sure it ran smoothly and to answer questions. With 12 sessions running simultaneously this year, many more staff members will need to be involved. But that is not unfamiliar for the society during meeting week, Ms. Myers said.
“We’re going to need to pull from pretty much our entire staff in order to make this conference happen, which is exciting and daunting,” she said. “It’s always been an all-hands-on-deck program and this is going to be more similar to an in-person conference in that way.”
Hospitalist advisory board picks ‘must-see’ Converge sessions
With dozens and dozens of sessions on the SHM Converge program, picking what to go to can feel virtually impossible.
The editorial board of The Hospitalist is here to help. With knowledge in an array of subspecialties – and experience in attending many SHM annual conferences, they have pointed out sessions they consider “must see,” whether based on the importance of the topic, the entertainment aspect, or the dynamic qualities of the speakers.
Here are their selections:
Ilaria Gadalla, DMSc, PA-C, physician assistant department chair, South University, West Palm Beach, Fla.
What You Say, What They Hear: Conversations with Your Hospital C-suite (Tuesday, May 4, 1:40 p.m. to 2:40 p.m.)
“As a department leader, developing my communication skills is always an area I seek to improve,” Dr. Gadalla said. “Tips to help with interpreting the audience and tailoring presentations for receptive feedback are invaluable tools.”
Hiring the Right Hospitalist: The Other Kind of Choosing Wisely (Wednesday, May 5, 2 p.m. to 3 p.m.)
“[This] is also an interesting session – selection criteria in the age of virtual interviewing is challenging,” she said. “I look forward to benefiting from my colleagues’ experience to enhance my leadership style.”
Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, FAAFP, MBA, hospitalist at Ballad Health, Johnson City, Tenn.
Understanding High-Value Care: Cost, Rationing, Overuse, and Underuse: Workshop (Tuesday May 4, 1:40 p.m. to 2:40 p.m.)
“Health care in the U.S. is expensive, and we have to pay utmost attention to the cost while providing the highest-quality medical care and service to sustain the health care,” Dr. Odeti said. “I am excited about this workshop organized by Dr. Justin Glasgow, Dr. Sarah Baron, Dr. Mona Krouss, and Dr. Harry Cho. I have known these leaders in the health care quality and patient safety arena over several years and their immense contributions to their organizations and the quality improvement special interest group of SHM. This workshop will help us understand how to define value in health care, implement high-value care, and eliminate low-value care.”
Hospitalists Piloting the Twin Engines of the Mid-Revenue Cycle Ship: A Primer on Utilization Management and Clinical Documentation Improvement (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:30 p.m.)
“The business of running hospitals carries with it many financial challenges,” Dr. Odeti said. “The intersection of tremendous fixed overhead and the vagaries of payer behavior is the cause. The COVID-19 pandemic and its devastating impact have compounded the problem. Hospitalists are natural institution leaders who are fundamental in overcoming this impasse through taking command and piloting the twin-engine ship of utilization management and clinical documentation improvement. These two domains working in synergy with experienced pilots are critical to attaining both high-quality care and the long-term viability of our health care systems. Dr. Aziz Ansari has been an expert in this domain and a highly sought-after speaker at SHM annual conferences. His sessions are incredibly captivating and educational.”
Harry Cho, MD, FACP, SFHM, chief value officer at NYC Health+ Hospitals
Medical Jeopardy (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:10 p.m.)
“[I am] always looking forward to a fun-filled session for medical learning with this fantastic group of facilitators,” Dr. Cho said.
Back to the Future - Things I Wish I Knew Earlier in my Career (Wednesday, May 5, 3:50 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“Listening to Brad Sharpe brings me back to the days in training, eagerly absorbing every pearl of wisdom from mentors,” he said.
Marina Farah, MD, MHA, performance improvement consultant, FarahMD Consulting, Corvallis, Ore.
“I am excited to learn more about best practices and lessons learned from adopting telehealth in the hospital setting,” Dr. Farah said.
The Biden Administration, the 117th Congress, and What We Might See in Healthcare (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:10 p.m.)
“I am looking forward to learning more about upcoming legislation and policy changes that impact U.S. health care delivery and provider reimbursement,” she said.
James Kim, MD, associate professor of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta
Health Equity and Disparities in Hospitalized Patients (Tuesday, May 4, 3:30 p.m. to 4:10 p.m. )
“[Kimberly Manning, MD] is an amazing speaker, and I know that this is a topic that she can speak about both eloquently and passionately,” Dr. Kim said. “She has been advocating for her patients at Grady for years and so this is something that she has first-hand experience about.”
Top 5 Clinical Practice Guidelines Every Hospitalist Needs to Know: Workshop (Wednesday, May 5, 3:50 p.m. to 4:50 p.m. )
“This sounds like a high-yield session,” he said. “For busy clinicians, being able to know what guidelines should affect your daily practice is extremely important.”
Lonika Sood, MD, MHPE, FACP, FHM, clinical education director of internal medicine, Washington State University, Spokane
“This is an important conversation that has surfaced with the pandemic, and likely has caused a lot of confusion amongst frontline clinicians and patients,” Dr. Sood said. “I look forward to hearing about some strategies from the presenters.”
Behind the Curtain: How a Journal Works (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“The Journal of Hospital Medicine is on the forefront of providing high-quality scientific information relevant to hospital medicine, and it would be helpful to hear of the presenters’ successes and challenges.”
Anika Kumar, MD, FAAP, FHM, assistant professor of pediatrics, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Fireside Chat: Story-telling and the Nocturnist in Pediatrics (Tuesday, May 4, 3:30 p.m. to 4:50 p.m.)
“I look forward to their discussion about storytelling and the role narrative medicine plays in patient care, especially pediatrics,” Dr. Kumar said.
Febrile Infant Update (Thursday, May 6, 3:10 p.m. to 3:50 p.m.)
“This clinical update session with Dr. Russell McCulloh will be exciting, as caring for febrile infants is bread-and-butter pediatric hospital medicine,” she said. “And this update will help review new research in this diagnosis.”
Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, FACP, CHCQM-PHYADV, director of clinical operations, quality, and patient experience, Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C.
Any session in the “Clinical Updates” and “Quality” tracks
“I would recommend ‘Clinical Updates’ and ‘Quality’ sessions, as they are so close to my practice and I look forward to those sessions,” Dr. Sitammagari said. “Clinical Updates provide the latest updates in clinical practice which is very useful for everyday patient management for hospitalists. Quality sessions discuss innovative ways to improve the quality of hospitalist practice.”
Raman Palabindala, MD, SFHM, medical director of utilization management, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson
Medical Jeopardy (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:10 p.m.)
“I will always promote my fun event, Medical Jeopardy (Dr. Palabindala is a moderator). It is going to be a challenge between three great attendings from three great organizations across the country to win the national Jeopardy competition. Not only will you learn a lot, but you also will have a lot of fun. I am sure it is going to be more entertaining this time, given virtual play.”
LAMA’s DRAMA: Left AMA – Documentation & Rules of AMA (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“I also recommend the talk by Dr. Medarametla not just for the title LAMA DRAMA (for ‘left against medical advice’),” he said. “We all need to learn this one to the core and I am sure he will deliver the most engaging presentation.”
With dozens and dozens of sessions on the SHM Converge program, picking what to go to can feel virtually impossible.
The editorial board of The Hospitalist is here to help. With knowledge in an array of subspecialties – and experience in attending many SHM annual conferences, they have pointed out sessions they consider “must see,” whether based on the importance of the topic, the entertainment aspect, or the dynamic qualities of the speakers.
Here are their selections:
Ilaria Gadalla, DMSc, PA-C, physician assistant department chair, South University, West Palm Beach, Fla.
What You Say, What They Hear: Conversations with Your Hospital C-suite (Tuesday, May 4, 1:40 p.m. to 2:40 p.m.)
“As a department leader, developing my communication skills is always an area I seek to improve,” Dr. Gadalla said. “Tips to help with interpreting the audience and tailoring presentations for receptive feedback are invaluable tools.”
Hiring the Right Hospitalist: The Other Kind of Choosing Wisely (Wednesday, May 5, 2 p.m. to 3 p.m.)
“[This] is also an interesting session – selection criteria in the age of virtual interviewing is challenging,” she said. “I look forward to benefiting from my colleagues’ experience to enhance my leadership style.”
Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, FAAFP, MBA, hospitalist at Ballad Health, Johnson City, Tenn.
Understanding High-Value Care: Cost, Rationing, Overuse, and Underuse: Workshop (Tuesday May 4, 1:40 p.m. to 2:40 p.m.)
“Health care in the U.S. is expensive, and we have to pay utmost attention to the cost while providing the highest-quality medical care and service to sustain the health care,” Dr. Odeti said. “I am excited about this workshop organized by Dr. Justin Glasgow, Dr. Sarah Baron, Dr. Mona Krouss, and Dr. Harry Cho. I have known these leaders in the health care quality and patient safety arena over several years and their immense contributions to their organizations and the quality improvement special interest group of SHM. This workshop will help us understand how to define value in health care, implement high-value care, and eliminate low-value care.”
Hospitalists Piloting the Twin Engines of the Mid-Revenue Cycle Ship: A Primer on Utilization Management and Clinical Documentation Improvement (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:30 p.m.)
“The business of running hospitals carries with it many financial challenges,” Dr. Odeti said. “The intersection of tremendous fixed overhead and the vagaries of payer behavior is the cause. The COVID-19 pandemic and its devastating impact have compounded the problem. Hospitalists are natural institution leaders who are fundamental in overcoming this impasse through taking command and piloting the twin-engine ship of utilization management and clinical documentation improvement. These two domains working in synergy with experienced pilots are critical to attaining both high-quality care and the long-term viability of our health care systems. Dr. Aziz Ansari has been an expert in this domain and a highly sought-after speaker at SHM annual conferences. His sessions are incredibly captivating and educational.”
Harry Cho, MD, FACP, SFHM, chief value officer at NYC Health+ Hospitals
Medical Jeopardy (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:10 p.m.)
“[I am] always looking forward to a fun-filled session for medical learning with this fantastic group of facilitators,” Dr. Cho said.
Back to the Future - Things I Wish I Knew Earlier in my Career (Wednesday, May 5, 3:50 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“Listening to Brad Sharpe brings me back to the days in training, eagerly absorbing every pearl of wisdom from mentors,” he said.
Marina Farah, MD, MHA, performance improvement consultant, FarahMD Consulting, Corvallis, Ore.
“I am excited to learn more about best practices and lessons learned from adopting telehealth in the hospital setting,” Dr. Farah said.
The Biden Administration, the 117th Congress, and What We Might See in Healthcare (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:10 p.m.)
“I am looking forward to learning more about upcoming legislation and policy changes that impact U.S. health care delivery and provider reimbursement,” she said.
James Kim, MD, associate professor of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta
Health Equity and Disparities in Hospitalized Patients (Tuesday, May 4, 3:30 p.m. to 4:10 p.m. )
“[Kimberly Manning, MD] is an amazing speaker, and I know that this is a topic that she can speak about both eloquently and passionately,” Dr. Kim said. “She has been advocating for her patients at Grady for years and so this is something that she has first-hand experience about.”
Top 5 Clinical Practice Guidelines Every Hospitalist Needs to Know: Workshop (Wednesday, May 5, 3:50 p.m. to 4:50 p.m. )
“This sounds like a high-yield session,” he said. “For busy clinicians, being able to know what guidelines should affect your daily practice is extremely important.”
Lonika Sood, MD, MHPE, FACP, FHM, clinical education director of internal medicine, Washington State University, Spokane
“This is an important conversation that has surfaced with the pandemic, and likely has caused a lot of confusion amongst frontline clinicians and patients,” Dr. Sood said. “I look forward to hearing about some strategies from the presenters.”
Behind the Curtain: How a Journal Works (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“The Journal of Hospital Medicine is on the forefront of providing high-quality scientific information relevant to hospital medicine, and it would be helpful to hear of the presenters’ successes and challenges.”
Anika Kumar, MD, FAAP, FHM, assistant professor of pediatrics, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Fireside Chat: Story-telling and the Nocturnist in Pediatrics (Tuesday, May 4, 3:30 p.m. to 4:50 p.m.)
“I look forward to their discussion about storytelling and the role narrative medicine plays in patient care, especially pediatrics,” Dr. Kumar said.
Febrile Infant Update (Thursday, May 6, 3:10 p.m. to 3:50 p.m.)
“This clinical update session with Dr. Russell McCulloh will be exciting, as caring for febrile infants is bread-and-butter pediatric hospital medicine,” she said. “And this update will help review new research in this diagnosis.”
Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, FACP, CHCQM-PHYADV, director of clinical operations, quality, and patient experience, Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C.
Any session in the “Clinical Updates” and “Quality” tracks
“I would recommend ‘Clinical Updates’ and ‘Quality’ sessions, as they are so close to my practice and I look forward to those sessions,” Dr. Sitammagari said. “Clinical Updates provide the latest updates in clinical practice which is very useful for everyday patient management for hospitalists. Quality sessions discuss innovative ways to improve the quality of hospitalist practice.”
Raman Palabindala, MD, SFHM, medical director of utilization management, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson
Medical Jeopardy (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:10 p.m.)
“I will always promote my fun event, Medical Jeopardy (Dr. Palabindala is a moderator). It is going to be a challenge between three great attendings from three great organizations across the country to win the national Jeopardy competition. Not only will you learn a lot, but you also will have a lot of fun. I am sure it is going to be more entertaining this time, given virtual play.”
LAMA’s DRAMA: Left AMA – Documentation & Rules of AMA (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“I also recommend the talk by Dr. Medarametla not just for the title LAMA DRAMA (for ‘left against medical advice’),” he said. “We all need to learn this one to the core and I am sure he will deliver the most engaging presentation.”
With dozens and dozens of sessions on the SHM Converge program, picking what to go to can feel virtually impossible.
The editorial board of The Hospitalist is here to help. With knowledge in an array of subspecialties – and experience in attending many SHM annual conferences, they have pointed out sessions they consider “must see,” whether based on the importance of the topic, the entertainment aspect, or the dynamic qualities of the speakers.
Here are their selections:
Ilaria Gadalla, DMSc, PA-C, physician assistant department chair, South University, West Palm Beach, Fla.
What You Say, What They Hear: Conversations with Your Hospital C-suite (Tuesday, May 4, 1:40 p.m. to 2:40 p.m.)
“As a department leader, developing my communication skills is always an area I seek to improve,” Dr. Gadalla said. “Tips to help with interpreting the audience and tailoring presentations for receptive feedback are invaluable tools.”
Hiring the Right Hospitalist: The Other Kind of Choosing Wisely (Wednesday, May 5, 2 p.m. to 3 p.m.)
“[This] is also an interesting session – selection criteria in the age of virtual interviewing is challenging,” she said. “I look forward to benefiting from my colleagues’ experience to enhance my leadership style.”
Shyam Odeti, MD, SFHM, FAAFP, MBA, hospitalist at Ballad Health, Johnson City, Tenn.
Understanding High-Value Care: Cost, Rationing, Overuse, and Underuse: Workshop (Tuesday May 4, 1:40 p.m. to 2:40 p.m.)
“Health care in the U.S. is expensive, and we have to pay utmost attention to the cost while providing the highest-quality medical care and service to sustain the health care,” Dr. Odeti said. “I am excited about this workshop organized by Dr. Justin Glasgow, Dr. Sarah Baron, Dr. Mona Krouss, and Dr. Harry Cho. I have known these leaders in the health care quality and patient safety arena over several years and their immense contributions to their organizations and the quality improvement special interest group of SHM. This workshop will help us understand how to define value in health care, implement high-value care, and eliminate low-value care.”
Hospitalists Piloting the Twin Engines of the Mid-Revenue Cycle Ship: A Primer on Utilization Management and Clinical Documentation Improvement (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:30 p.m.)
“The business of running hospitals carries with it many financial challenges,” Dr. Odeti said. “The intersection of tremendous fixed overhead and the vagaries of payer behavior is the cause. The COVID-19 pandemic and its devastating impact have compounded the problem. Hospitalists are natural institution leaders who are fundamental in overcoming this impasse through taking command and piloting the twin-engine ship of utilization management and clinical documentation improvement. These two domains working in synergy with experienced pilots are critical to attaining both high-quality care and the long-term viability of our health care systems. Dr. Aziz Ansari has been an expert in this domain and a highly sought-after speaker at SHM annual conferences. His sessions are incredibly captivating and educational.”
Harry Cho, MD, FACP, SFHM, chief value officer at NYC Health+ Hospitals
Medical Jeopardy (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:10 p.m.)
“[I am] always looking forward to a fun-filled session for medical learning with this fantastic group of facilitators,” Dr. Cho said.
Back to the Future - Things I Wish I Knew Earlier in my Career (Wednesday, May 5, 3:50 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“Listening to Brad Sharpe brings me back to the days in training, eagerly absorbing every pearl of wisdom from mentors,” he said.
Marina Farah, MD, MHA, performance improvement consultant, FarahMD Consulting, Corvallis, Ore.
“I am excited to learn more about best practices and lessons learned from adopting telehealth in the hospital setting,” Dr. Farah said.
The Biden Administration, the 117th Congress, and What We Might See in Healthcare (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:10 p.m.)
“I am looking forward to learning more about upcoming legislation and policy changes that impact U.S. health care delivery and provider reimbursement,” she said.
James Kim, MD, associate professor of medicine, Emory University, Atlanta
Health Equity and Disparities in Hospitalized Patients (Tuesday, May 4, 3:30 p.m. to 4:10 p.m. )
“[Kimberly Manning, MD] is an amazing speaker, and I know that this is a topic that she can speak about both eloquently and passionately,” Dr. Kim said. “She has been advocating for her patients at Grady for years and so this is something that she has first-hand experience about.”
Top 5 Clinical Practice Guidelines Every Hospitalist Needs to Know: Workshop (Wednesday, May 5, 3:50 p.m. to 4:50 p.m. )
“This sounds like a high-yield session,” he said. “For busy clinicians, being able to know what guidelines should affect your daily practice is extremely important.”
Lonika Sood, MD, MHPE, FACP, FHM, clinical education director of internal medicine, Washington State University, Spokane
“This is an important conversation that has surfaced with the pandemic, and likely has caused a lot of confusion amongst frontline clinicians and patients,” Dr. Sood said. “I look forward to hearing about some strategies from the presenters.”
Behind the Curtain: How a Journal Works (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“The Journal of Hospital Medicine is on the forefront of providing high-quality scientific information relevant to hospital medicine, and it would be helpful to hear of the presenters’ successes and challenges.”
Anika Kumar, MD, FAAP, FHM, assistant professor of pediatrics, Cleveland Clinic Lerner College of Medicine
Fireside Chat: Story-telling and the Nocturnist in Pediatrics (Tuesday, May 4, 3:30 p.m. to 4:50 p.m.)
“I look forward to their discussion about storytelling and the role narrative medicine plays in patient care, especially pediatrics,” Dr. Kumar said.
Febrile Infant Update (Thursday, May 6, 3:10 p.m. to 3:50 p.m.)
“This clinical update session with Dr. Russell McCulloh will be exciting, as caring for febrile infants is bread-and-butter pediatric hospital medicine,” she said. “And this update will help review new research in this diagnosis.”
Kranthi Sitammagari, MD, FACP, CHCQM-PHYADV, director of clinical operations, quality, and patient experience, Atrium Health Hospitalist Group, Monroe, N.C.
Any session in the “Clinical Updates” and “Quality” tracks
“I would recommend ‘Clinical Updates’ and ‘Quality’ sessions, as they are so close to my practice and I look forward to those sessions,” Dr. Sitammagari said. “Clinical Updates provide the latest updates in clinical practice which is very useful for everyday patient management for hospitalists. Quality sessions discuss innovative ways to improve the quality of hospitalist practice.”
Raman Palabindala, MD, SFHM, medical director of utilization management, University of Mississippi Medical Center, Jackson
Medical Jeopardy (Thursday, May 6, 2:30 p.m. to 3:10 p.m.)
“I will always promote my fun event, Medical Jeopardy (Dr. Palabindala is a moderator). It is going to be a challenge between three great attendings from three great organizations across the country to win the national Jeopardy competition. Not only will you learn a lot, but you also will have a lot of fun. I am sure it is going to be more entertaining this time, given virtual play.”
LAMA’s DRAMA: Left AMA – Documentation & Rules of AMA (Friday, May 7, 3:30 p.m. to 4:30 p.m.)
“I also recommend the talk by Dr. Medarametla not just for the title LAMA DRAMA (for ‘left against medical advice’),” he said. “We all need to learn this one to the core and I am sure he will deliver the most engaging presentation.”
Immigrant hospitalists to share diverse experiences
Ingrid Pinzon, MD, FACP, was working as a medical assistant to a physician a decade ago when she heard the doctor prescribe ibuprofen to a woman who was in the latter stages of pregnancy. Dr. Pinzon was a doctor, having received her education and training in Colombia, but because she had emigrated to the United States and hadn’t yet completed her certification and training here, she was not recognized yet as an American physician.
But she knew that ibuprofen was not recommended during late-term pregnancy, and she was alarmed. She informed the physician of the mistake. The doctor headed to Google, Dr. Pinzon said, and called the patient to rescind the ibuprofen prescription. But she soon fired Dr. Pinzon, seemingly for having had the courage to speak up.
Dr. Pinzon, now medical director of care coordination at Emory Johns Creek Hospital in Atlanta, will describe her experience as an immigrant physician in the Society of Hospital Medicine Converge session: “A Walk in Our Shoes: Immigrant Physicians Sharing Their Stories.” She will be joined by Patricia O’Brien, MD, PhD, FAAP, a pediatric hospitalist in Tampa; Manpreet Malik, MD, a hospitalist at Emory University; and Benji Mathews, MD, SFHM, FACP, chief of hospital medicine at HealthPartners and associate professor at the University of Minnesota.
They will describe their struggles to find their way in the United States, along with the satisfaction of having hard work pay off with better lives for themselves and their families. And together, they’ll provide a variety of narratives that will show, contrary to how many Americans view immigrants, how the experiences of immigrants don’t follow the same path, but each one carves out a path of his or her own.
“The thrust of this is really storytelling, along with putting into context what we can do to help our hospitalist brothers and sisters who are immigrants, and shining the light on it,” Dr. O’Brien said.
Dr. Pinzon was working as a doctor for the Colombian government when she began receiving threats from soldiers in a guerrilla army, which didn’t agree with her alignment with the government. One day, a guerrilla soldier threatened her and her two daughters – aged 5 and 11 at the time – and accurately described her daughters’ whereabouts.
Less than a week later, she and her daughters flew from Bogota to the United States, never to return to Colombia.
“I dropped everything I had when I came here,” she said. An immigration attorney initially recommended that she marry an American man in order to stay in the United States. When Dr. Pinzon declined, they pursued political asylum, and she received it less than a year later.
For 3 years, she worked jobs as assistants in medical offices and in other jobs, well below her education level, as she guided her daughters through school and went through the U.S. medical certification process. She was besieged by doubt constantly, she said.
“I cried for 3 years in a row,” she said. “I wanted to go back to my country. I didn’t want to stay here.”
Finally, she did her medical residency between 2011 and 2014, and got a job with Emory. Her daughters are grown, and one is a doctor in general surgery residency. Dr. Pinzon said she is happy to care for patients, particularly those who are Spanish-speaking and struggle as she did. But she often encounters patients who don’t hide that they dislike her accent.
“I will mute the TV and I will say: ‘I have a strong accent and so I want to make sure communication is clear,’ ” she said. “We have to prove ourselves all of the time. I feel like I have to prove myself to my patients that I’m a good doctor all of the time.” American-born doctors, she added, “shouldn’t take for granted what they already have.”
Dr. O’Brien grew up in Ireland, but in the late 1980s, the country was in a serious recession, with unemployment close to 20%, and her father applied for residency in Canada and the United States. They were accepted in Canada first, and moved there in 1988. A few years later, her parents moved them to Florida.
“They knew in order for us to do well, we had to go abroad,” she said. Dr. O’Brien went to college, medical school and graduate school in Florida, and completed residency in Cincinnati. Feeling the tug of her birthplace, she moved back to Ireland and worked there for a couple years.
“I never really wanted to leave because it was my home,” she said. While there, she came to a new-found appreciation for the U.S. health care system. It’s true that, in Ireland, everyone is insured, but there long wait times – for example, up to 2 years for a sedated nonurgent MRI for a child. She once had to send a patient to Dublin in a taxi with a nurse because an ambulance was unavailable.
“After going back to Ireland, where – I honestly thought I was going to go back and settle there – I realized how visionary my parents were in moving us,” Dr. O’Brien said. “This system in the U.S., there are lot of things broken about it, but we have all the resources.”
She moved back to the United States in August 2016, during a period of anti-immigrant rhetoric.
Nonetheless, Dr. O’Brien said she is happy to be here despite the lack of tolerance she sees in a minority of the U.S. population.
“Have a bit of sensitivity toward your provider. Maybe they speak with an accent. Maybe they don’t speak English perfectly. Maybe they have a different skin color. But their intention is good and it’s to help you and improve your health,” she said.
Ingrid Pinzon, MD, FACP, was working as a medical assistant to a physician a decade ago when she heard the doctor prescribe ibuprofen to a woman who was in the latter stages of pregnancy. Dr. Pinzon was a doctor, having received her education and training in Colombia, but because she had emigrated to the United States and hadn’t yet completed her certification and training here, she was not recognized yet as an American physician.
But she knew that ibuprofen was not recommended during late-term pregnancy, and she was alarmed. She informed the physician of the mistake. The doctor headed to Google, Dr. Pinzon said, and called the patient to rescind the ibuprofen prescription. But she soon fired Dr. Pinzon, seemingly for having had the courage to speak up.
Dr. Pinzon, now medical director of care coordination at Emory Johns Creek Hospital in Atlanta, will describe her experience as an immigrant physician in the Society of Hospital Medicine Converge session: “A Walk in Our Shoes: Immigrant Physicians Sharing Their Stories.” She will be joined by Patricia O’Brien, MD, PhD, FAAP, a pediatric hospitalist in Tampa; Manpreet Malik, MD, a hospitalist at Emory University; and Benji Mathews, MD, SFHM, FACP, chief of hospital medicine at HealthPartners and associate professor at the University of Minnesota.
They will describe their struggles to find their way in the United States, along with the satisfaction of having hard work pay off with better lives for themselves and their families. And together, they’ll provide a variety of narratives that will show, contrary to how many Americans view immigrants, how the experiences of immigrants don’t follow the same path, but each one carves out a path of his or her own.
“The thrust of this is really storytelling, along with putting into context what we can do to help our hospitalist brothers and sisters who are immigrants, and shining the light on it,” Dr. O’Brien said.
Dr. Pinzon was working as a doctor for the Colombian government when she began receiving threats from soldiers in a guerrilla army, which didn’t agree with her alignment with the government. One day, a guerrilla soldier threatened her and her two daughters – aged 5 and 11 at the time – and accurately described her daughters’ whereabouts.
Less than a week later, she and her daughters flew from Bogota to the United States, never to return to Colombia.
“I dropped everything I had when I came here,” she said. An immigration attorney initially recommended that she marry an American man in order to stay in the United States. When Dr. Pinzon declined, they pursued political asylum, and she received it less than a year later.
For 3 years, she worked jobs as assistants in medical offices and in other jobs, well below her education level, as she guided her daughters through school and went through the U.S. medical certification process. She was besieged by doubt constantly, she said.
“I cried for 3 years in a row,” she said. “I wanted to go back to my country. I didn’t want to stay here.”
Finally, she did her medical residency between 2011 and 2014, and got a job with Emory. Her daughters are grown, and one is a doctor in general surgery residency. Dr. Pinzon said she is happy to care for patients, particularly those who are Spanish-speaking and struggle as she did. But she often encounters patients who don’t hide that they dislike her accent.
“I will mute the TV and I will say: ‘I have a strong accent and so I want to make sure communication is clear,’ ” she said. “We have to prove ourselves all of the time. I feel like I have to prove myself to my patients that I’m a good doctor all of the time.” American-born doctors, she added, “shouldn’t take for granted what they already have.”
Dr. O’Brien grew up in Ireland, but in the late 1980s, the country was in a serious recession, with unemployment close to 20%, and her father applied for residency in Canada and the United States. They were accepted in Canada first, and moved there in 1988. A few years later, her parents moved them to Florida.
“They knew in order for us to do well, we had to go abroad,” she said. Dr. O’Brien went to college, medical school and graduate school in Florida, and completed residency in Cincinnati. Feeling the tug of her birthplace, she moved back to Ireland and worked there for a couple years.
“I never really wanted to leave because it was my home,” she said. While there, she came to a new-found appreciation for the U.S. health care system. It’s true that, in Ireland, everyone is insured, but there long wait times – for example, up to 2 years for a sedated nonurgent MRI for a child. She once had to send a patient to Dublin in a taxi with a nurse because an ambulance was unavailable.
“After going back to Ireland, where – I honestly thought I was going to go back and settle there – I realized how visionary my parents were in moving us,” Dr. O’Brien said. “This system in the U.S., there are lot of things broken about it, but we have all the resources.”
She moved back to the United States in August 2016, during a period of anti-immigrant rhetoric.
Nonetheless, Dr. O’Brien said she is happy to be here despite the lack of tolerance she sees in a minority of the U.S. population.
“Have a bit of sensitivity toward your provider. Maybe they speak with an accent. Maybe they don’t speak English perfectly. Maybe they have a different skin color. But their intention is good and it’s to help you and improve your health,” she said.
Ingrid Pinzon, MD, FACP, was working as a medical assistant to a physician a decade ago when she heard the doctor prescribe ibuprofen to a woman who was in the latter stages of pregnancy. Dr. Pinzon was a doctor, having received her education and training in Colombia, but because she had emigrated to the United States and hadn’t yet completed her certification and training here, she was not recognized yet as an American physician.
But she knew that ibuprofen was not recommended during late-term pregnancy, and she was alarmed. She informed the physician of the mistake. The doctor headed to Google, Dr. Pinzon said, and called the patient to rescind the ibuprofen prescription. But she soon fired Dr. Pinzon, seemingly for having had the courage to speak up.
Dr. Pinzon, now medical director of care coordination at Emory Johns Creek Hospital in Atlanta, will describe her experience as an immigrant physician in the Society of Hospital Medicine Converge session: “A Walk in Our Shoes: Immigrant Physicians Sharing Their Stories.” She will be joined by Patricia O’Brien, MD, PhD, FAAP, a pediatric hospitalist in Tampa; Manpreet Malik, MD, a hospitalist at Emory University; and Benji Mathews, MD, SFHM, FACP, chief of hospital medicine at HealthPartners and associate professor at the University of Minnesota.
They will describe their struggles to find their way in the United States, along with the satisfaction of having hard work pay off with better lives for themselves and their families. And together, they’ll provide a variety of narratives that will show, contrary to how many Americans view immigrants, how the experiences of immigrants don’t follow the same path, but each one carves out a path of his or her own.
“The thrust of this is really storytelling, along with putting into context what we can do to help our hospitalist brothers and sisters who are immigrants, and shining the light on it,” Dr. O’Brien said.
Dr. Pinzon was working as a doctor for the Colombian government when she began receiving threats from soldiers in a guerrilla army, which didn’t agree with her alignment with the government. One day, a guerrilla soldier threatened her and her two daughters – aged 5 and 11 at the time – and accurately described her daughters’ whereabouts.
Less than a week later, she and her daughters flew from Bogota to the United States, never to return to Colombia.
“I dropped everything I had when I came here,” she said. An immigration attorney initially recommended that she marry an American man in order to stay in the United States. When Dr. Pinzon declined, they pursued political asylum, and she received it less than a year later.
For 3 years, she worked jobs as assistants in medical offices and in other jobs, well below her education level, as she guided her daughters through school and went through the U.S. medical certification process. She was besieged by doubt constantly, she said.
“I cried for 3 years in a row,” she said. “I wanted to go back to my country. I didn’t want to stay here.”
Finally, she did her medical residency between 2011 and 2014, and got a job with Emory. Her daughters are grown, and one is a doctor in general surgery residency. Dr. Pinzon said she is happy to care for patients, particularly those who are Spanish-speaking and struggle as she did. But she often encounters patients who don’t hide that they dislike her accent.
“I will mute the TV and I will say: ‘I have a strong accent and so I want to make sure communication is clear,’ ” she said. “We have to prove ourselves all of the time. I feel like I have to prove myself to my patients that I’m a good doctor all of the time.” American-born doctors, she added, “shouldn’t take for granted what they already have.”
Dr. O’Brien grew up in Ireland, but in the late 1980s, the country was in a serious recession, with unemployment close to 20%, and her father applied for residency in Canada and the United States. They were accepted in Canada first, and moved there in 1988. A few years later, her parents moved them to Florida.
“They knew in order for us to do well, we had to go abroad,” she said. Dr. O’Brien went to college, medical school and graduate school in Florida, and completed residency in Cincinnati. Feeling the tug of her birthplace, she moved back to Ireland and worked there for a couple years.
“I never really wanted to leave because it was my home,” she said. While there, she came to a new-found appreciation for the U.S. health care system. It’s true that, in Ireland, everyone is insured, but there long wait times – for example, up to 2 years for a sedated nonurgent MRI for a child. She once had to send a patient to Dublin in a taxi with a nurse because an ambulance was unavailable.
“After going back to Ireland, where – I honestly thought I was going to go back and settle there – I realized how visionary my parents were in moving us,” Dr. O’Brien said. “This system in the U.S., there are lot of things broken about it, but we have all the resources.”
She moved back to the United States in August 2016, during a period of anti-immigrant rhetoric.
Nonetheless, Dr. O’Brien said she is happy to be here despite the lack of tolerance she sees in a minority of the U.S. population.
“Have a bit of sensitivity toward your provider. Maybe they speak with an accent. Maybe they don’t speak English perfectly. Maybe they have a different skin color. But their intention is good and it’s to help you and improve your health,” she said.
Pulmonary and critical care session highlights new advances and research
An overview of five important advances in pulmonary and critical care medicine are on the agenda for the “Update in Pulmonary and Critical Care” session on Tuesday, May 4, at the virtual 2021 SHM Converge conference.
“I hope this session gives attendees a nice, broad look at advances both in the intensive care unit and in general pulmonary medicine,” said James Walter, MD, of Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, who serves as director of the session.
On the critical care medicine side, Dr. Walter will review the latest research on the efficacy of ascorbic acid in treating patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. “There was a lot of excitement and some skepticism about early results promising a really large treatment effect in giving critically ill patients with sepsis large doses of vitamin C,” Dr. Walter said. The last year has produced some high-quality randomized trials that have contributed to a better understanding of the potential effects ascorbic acid in sepsis can have, he noted.
Dr. Walter, who is also medical director of the Northwestern Lung Rescue Program, intends to discuss what he believes is a definitive trial regarding the benefit of preemptively starting critically ill patients with acute kidney injury on renal replacement therapy instead of waiting until there are specific clinical signs. “This has been another area of uncertainty in critical care and I think we finally have a very definitive answer with this high quality, randomized, controlled trial that I plan to review,” he said.
Though he said there have been a number of important advances in pulmonary medicine over the past year, Dr. Walter will highlight just two.
Up until recently, the antifibrotics nintedanib and pirfenidone have mostly been used in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. However, recent research suggests there may be a potential benefit to using these drugs in patients with fibrotic lung disease outside of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. “I think this is an important advance for hospital medicine providers to be aware of,” said Dr. Walter.
He will also go over some large randomized controlled trials of the use of triple therapy – a combination of a long-acting beta agonist (LABA), a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid in one inhaler – in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The trials looked at whether triple inhaler therapy was beneficial compared to the typical therapies used for COPD.
The session wouldn’t be complete without a nod to COVID-19, which Dr. Walter said has significantly changed the landscape for hospital medicine providers. He plans to discuss what he considers the most impactful study – the RECOVERY trial. This study looked at the role of dexamethasone in patients with more severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2.
“From the incredible amount of data that’s come out in the last year about COVID, I think this is probably the trial that’s changed practice the most and shown the largest therapeutic benefit of all the pharmacotherapies,” Dr. Walter said. “It’s an important one for providers to be aware of in terms of what the trial shows and how it informs which patients are most likely to benefit from dexamethasone therapy.”
Dr. Walter hopes clinicians who participate in the session will leave with these takeaways:
- Be able to summarize recent trials of ascorbic acid in sepsis and think about how to incorporate – or not – the use of vitamin C in critically ill sepsis patients.
- A thorough understanding of when renal replacement therapy should be offered to critically ill patients with acute kidney dysfunction.
- Be able to discuss the impact of antifibrotic therapy in interstitial lung diseases outside of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- An understanding of the role of triple inhaler combinations in COPD.
- Be able to explain when dexamethasone is most likely to benefit hypoxemic patients with COVID-19.
An overview of five important advances in pulmonary and critical care medicine are on the agenda for the “Update in Pulmonary and Critical Care” session on Tuesday, May 4, at the virtual 2021 SHM Converge conference.
“I hope this session gives attendees a nice, broad look at advances both in the intensive care unit and in general pulmonary medicine,” said James Walter, MD, of Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, who serves as director of the session.
On the critical care medicine side, Dr. Walter will review the latest research on the efficacy of ascorbic acid in treating patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. “There was a lot of excitement and some skepticism about early results promising a really large treatment effect in giving critically ill patients with sepsis large doses of vitamin C,” Dr. Walter said. The last year has produced some high-quality randomized trials that have contributed to a better understanding of the potential effects ascorbic acid in sepsis can have, he noted.
Dr. Walter, who is also medical director of the Northwestern Lung Rescue Program, intends to discuss what he believes is a definitive trial regarding the benefit of preemptively starting critically ill patients with acute kidney injury on renal replacement therapy instead of waiting until there are specific clinical signs. “This has been another area of uncertainty in critical care and I think we finally have a very definitive answer with this high quality, randomized, controlled trial that I plan to review,” he said.
Though he said there have been a number of important advances in pulmonary medicine over the past year, Dr. Walter will highlight just two.
Up until recently, the antifibrotics nintedanib and pirfenidone have mostly been used in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. However, recent research suggests there may be a potential benefit to using these drugs in patients with fibrotic lung disease outside of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. “I think this is an important advance for hospital medicine providers to be aware of,” said Dr. Walter.
He will also go over some large randomized controlled trials of the use of triple therapy – a combination of a long-acting beta agonist (LABA), a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid in one inhaler – in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The trials looked at whether triple inhaler therapy was beneficial compared to the typical therapies used for COPD.
The session wouldn’t be complete without a nod to COVID-19, which Dr. Walter said has significantly changed the landscape for hospital medicine providers. He plans to discuss what he considers the most impactful study – the RECOVERY trial. This study looked at the role of dexamethasone in patients with more severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2.
“From the incredible amount of data that’s come out in the last year about COVID, I think this is probably the trial that’s changed practice the most and shown the largest therapeutic benefit of all the pharmacotherapies,” Dr. Walter said. “It’s an important one for providers to be aware of in terms of what the trial shows and how it informs which patients are most likely to benefit from dexamethasone therapy.”
Dr. Walter hopes clinicians who participate in the session will leave with these takeaways:
- Be able to summarize recent trials of ascorbic acid in sepsis and think about how to incorporate – or not – the use of vitamin C in critically ill sepsis patients.
- A thorough understanding of when renal replacement therapy should be offered to critically ill patients with acute kidney dysfunction.
- Be able to discuss the impact of antifibrotic therapy in interstitial lung diseases outside of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- An understanding of the role of triple inhaler combinations in COPD.
- Be able to explain when dexamethasone is most likely to benefit hypoxemic patients with COVID-19.
An overview of five important advances in pulmonary and critical care medicine are on the agenda for the “Update in Pulmonary and Critical Care” session on Tuesday, May 4, at the virtual 2021 SHM Converge conference.
“I hope this session gives attendees a nice, broad look at advances both in the intensive care unit and in general pulmonary medicine,” said James Walter, MD, of Northwestern Medicine in Chicago, who serves as director of the session.
On the critical care medicine side, Dr. Walter will review the latest research on the efficacy of ascorbic acid in treating patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. “There was a lot of excitement and some skepticism about early results promising a really large treatment effect in giving critically ill patients with sepsis large doses of vitamin C,” Dr. Walter said. The last year has produced some high-quality randomized trials that have contributed to a better understanding of the potential effects ascorbic acid in sepsis can have, he noted.
Dr. Walter, who is also medical director of the Northwestern Lung Rescue Program, intends to discuss what he believes is a definitive trial regarding the benefit of preemptively starting critically ill patients with acute kidney injury on renal replacement therapy instead of waiting until there are specific clinical signs. “This has been another area of uncertainty in critical care and I think we finally have a very definitive answer with this high quality, randomized, controlled trial that I plan to review,” he said.
Though he said there have been a number of important advances in pulmonary medicine over the past year, Dr. Walter will highlight just two.
Up until recently, the antifibrotics nintedanib and pirfenidone have mostly been used in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. However, recent research suggests there may be a potential benefit to using these drugs in patients with fibrotic lung disease outside of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. “I think this is an important advance for hospital medicine providers to be aware of,” said Dr. Walter.
He will also go over some large randomized controlled trials of the use of triple therapy – a combination of a long-acting beta agonist (LABA), a long-acting muscarinic antagonist (LAMA), and an inhaled corticosteroid in one inhaler – in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. The trials looked at whether triple inhaler therapy was beneficial compared to the typical therapies used for COPD.
The session wouldn’t be complete without a nod to COVID-19, which Dr. Walter said has significantly changed the landscape for hospital medicine providers. He plans to discuss what he considers the most impactful study – the RECOVERY trial. This study looked at the role of dexamethasone in patients with more severe manifestations of SARS-CoV-2.
“From the incredible amount of data that’s come out in the last year about COVID, I think this is probably the trial that’s changed practice the most and shown the largest therapeutic benefit of all the pharmacotherapies,” Dr. Walter said. “It’s an important one for providers to be aware of in terms of what the trial shows and how it informs which patients are most likely to benefit from dexamethasone therapy.”
Dr. Walter hopes clinicians who participate in the session will leave with these takeaways:
- Be able to summarize recent trials of ascorbic acid in sepsis and think about how to incorporate – or not – the use of vitamin C in critically ill sepsis patients.
- A thorough understanding of when renal replacement therapy should be offered to critically ill patients with acute kidney dysfunction.
- Be able to discuss the impact of antifibrotic therapy in interstitial lung diseases outside of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
- An understanding of the role of triple inhaler combinations in COPD.
- Be able to explain when dexamethasone is most likely to benefit hypoxemic patients with COVID-19.
SHM Converge to be an ‘intellectual feast’
Course director Dr. Daniel Steinberg highlights top content
The weeks leading up to our Annual Conference always trigger certain rituals for me.
Deciding which sessions to attend feels like planning an intellectual feast mixed with an exercise in compromise, as I realize there is just no way to attend every session that I want to. Scheduling all my plans to connect over dinner and drinks with current and former colleagues is a logistical challenge I undertake with anticipation and some stress, especially when I’m the one tasked with making restaurant reservations. Thinking about how to pay for it all means digging out the rules around my CME faculty allowance, after first figuring out if I still even have a CME allowance, of course.
In the years that I am presenting, there are the last-minute emails with my co-presenters to arrange a time to run through our slides together on site. The prospect of seeing cherished colleagues and friends from SHM mixes with the fact that I know I will miss my wife and young son while I am away. Overall though, I am filled with a tremendous sense of excitement, a feeling that I enjoy in a sustained way for weeks before the meeting.
My excitement for SHM Converge is just as strong, but different in some great and important ways. The availability of on-demand content means I won’t have to choose one session over another this year – I can have my cake and eat it, too. Without the need to travel, expenses will be considerably less, and I won’t need to be away from my family.
But what I am most thrilled about when I think about SHM Converge is the content. A year of planning by our outstanding SHM staff, leadership, and Annual Conference Committee has produced a lineup of world-class speakers. Our virtual platform will offer a rich interactive and networking experience. Perennial favorite sessions, such as the Great Debate, Rapid Fire, and Update sessions will provide attendees the chance to update their core clinical knowledge across the breadth of hospital medicine.
Many aspects of health equity will be explored. Over 15 sessions and four special-interest forums covering topics such as racial and gender inequities, implicit bias, vulnerable populations, and ethics will help attendees not only understand the issues but also will show them how they can take action to make a difference.
Clinical and operational aspects of COVID-19 will also be covered at SHM Converge as speakers share the tremendous innovation, triumphs, and challenges that have taken place over the past year. Wellness and resilience are, of course, as relevant as ever, and sessions on balancing parenthood and work, learning from personal failures, and how to handle uncertainty and be resilient are among the topics that will be covered.
The essence of what we will do at SHM Converge in May is captured in our new meeting logo, an animation of nodes connecting with each other through lines that travel short and long, and intersect along the way. It’s a great representation of the togetherness, community, and mutual support that is at the core of who we are as SHM – now, more than ever. Thank you for joining us!
Dr. Steinberg is chief patient safety officer at Mount Sinai Downtown, and associate dean for quality/patient safety in GME, Mount Sinai Health System, New York. He is professor of medicine and medical education at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and course director of SHM Converge.
Course director Dr. Daniel Steinberg highlights top content
Course director Dr. Daniel Steinberg highlights top content
The weeks leading up to our Annual Conference always trigger certain rituals for me.
Deciding which sessions to attend feels like planning an intellectual feast mixed with an exercise in compromise, as I realize there is just no way to attend every session that I want to. Scheduling all my plans to connect over dinner and drinks with current and former colleagues is a logistical challenge I undertake with anticipation and some stress, especially when I’m the one tasked with making restaurant reservations. Thinking about how to pay for it all means digging out the rules around my CME faculty allowance, after first figuring out if I still even have a CME allowance, of course.
In the years that I am presenting, there are the last-minute emails with my co-presenters to arrange a time to run through our slides together on site. The prospect of seeing cherished colleagues and friends from SHM mixes with the fact that I know I will miss my wife and young son while I am away. Overall though, I am filled with a tremendous sense of excitement, a feeling that I enjoy in a sustained way for weeks before the meeting.
My excitement for SHM Converge is just as strong, but different in some great and important ways. The availability of on-demand content means I won’t have to choose one session over another this year – I can have my cake and eat it, too. Without the need to travel, expenses will be considerably less, and I won’t need to be away from my family.
But what I am most thrilled about when I think about SHM Converge is the content. A year of planning by our outstanding SHM staff, leadership, and Annual Conference Committee has produced a lineup of world-class speakers. Our virtual platform will offer a rich interactive and networking experience. Perennial favorite sessions, such as the Great Debate, Rapid Fire, and Update sessions will provide attendees the chance to update their core clinical knowledge across the breadth of hospital medicine.
Many aspects of health equity will be explored. Over 15 sessions and four special-interest forums covering topics such as racial and gender inequities, implicit bias, vulnerable populations, and ethics will help attendees not only understand the issues but also will show them how they can take action to make a difference.
Clinical and operational aspects of COVID-19 will also be covered at SHM Converge as speakers share the tremendous innovation, triumphs, and challenges that have taken place over the past year. Wellness and resilience are, of course, as relevant as ever, and sessions on balancing parenthood and work, learning from personal failures, and how to handle uncertainty and be resilient are among the topics that will be covered.
The essence of what we will do at SHM Converge in May is captured in our new meeting logo, an animation of nodes connecting with each other through lines that travel short and long, and intersect along the way. It’s a great representation of the togetherness, community, and mutual support that is at the core of who we are as SHM – now, more than ever. Thank you for joining us!
Dr. Steinberg is chief patient safety officer at Mount Sinai Downtown, and associate dean for quality/patient safety in GME, Mount Sinai Health System, New York. He is professor of medicine and medical education at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and course director of SHM Converge.
The weeks leading up to our Annual Conference always trigger certain rituals for me.
Deciding which sessions to attend feels like planning an intellectual feast mixed with an exercise in compromise, as I realize there is just no way to attend every session that I want to. Scheduling all my plans to connect over dinner and drinks with current and former colleagues is a logistical challenge I undertake with anticipation and some stress, especially when I’m the one tasked with making restaurant reservations. Thinking about how to pay for it all means digging out the rules around my CME faculty allowance, after first figuring out if I still even have a CME allowance, of course.
In the years that I am presenting, there are the last-minute emails with my co-presenters to arrange a time to run through our slides together on site. The prospect of seeing cherished colleagues and friends from SHM mixes with the fact that I know I will miss my wife and young son while I am away. Overall though, I am filled with a tremendous sense of excitement, a feeling that I enjoy in a sustained way for weeks before the meeting.
My excitement for SHM Converge is just as strong, but different in some great and important ways. The availability of on-demand content means I won’t have to choose one session over another this year – I can have my cake and eat it, too. Without the need to travel, expenses will be considerably less, and I won’t need to be away from my family.
But what I am most thrilled about when I think about SHM Converge is the content. A year of planning by our outstanding SHM staff, leadership, and Annual Conference Committee has produced a lineup of world-class speakers. Our virtual platform will offer a rich interactive and networking experience. Perennial favorite sessions, such as the Great Debate, Rapid Fire, and Update sessions will provide attendees the chance to update their core clinical knowledge across the breadth of hospital medicine.
Many aspects of health equity will be explored. Over 15 sessions and four special-interest forums covering topics such as racial and gender inequities, implicit bias, vulnerable populations, and ethics will help attendees not only understand the issues but also will show them how they can take action to make a difference.
Clinical and operational aspects of COVID-19 will also be covered at SHM Converge as speakers share the tremendous innovation, triumphs, and challenges that have taken place over the past year. Wellness and resilience are, of course, as relevant as ever, and sessions on balancing parenthood and work, learning from personal failures, and how to handle uncertainty and be resilient are among the topics that will be covered.
The essence of what we will do at SHM Converge in May is captured in our new meeting logo, an animation of nodes connecting with each other through lines that travel short and long, and intersect along the way. It’s a great representation of the togetherness, community, and mutual support that is at the core of who we are as SHM – now, more than ever. Thank you for joining us!
Dr. Steinberg is chief patient safety officer at Mount Sinai Downtown, and associate dean for quality/patient safety in GME, Mount Sinai Health System, New York. He is professor of medicine and medical education at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, and course director of SHM Converge.
Seeking the next generation of antibiotics
Crispr drugs can be effective
Globally, some 700,000 people die from antibiotic-resistant infections ever year; by 2050, that number could be 10 million, according to the United Nations. To find new ways to fight pathogenic microorganisms, scientists are looking to Crispr, the gene-editing tool, according to the New York Times.
“Crispr is a specialized region of DNA that creates what amount to genetic scissors – enzymes that allow the cell (or a scientist) to precisely edit other DNA or its sister molecule, RNA…Crispr was originally discovered in bacteria, where it helps keep track of past injury. When a virus attacks, the bacterium stores small chunks of the viral genome within its own DNA. This helps the bacterium recognize viral infections when they occur again. Then, using Crispr-associated enzymes, it can disarm the virus and prevent the infection from spreading…today researchers are looking to Crispr to edit bacteria and viruses that infect humans and create new treatments.”
In a recent study, researchers successfully used a Crispr-associated enzyme called Cas9 to eliminate a species of Salmonella. They programmed the Cas9 to view the bacterium as the enemy and forced Salmonella to make lethal cuts to its own genome.
Some companies are now exploring Crispr-based antibiotics that might be delivered through viruses engineered so that they cannot reproduce or cause infections themselves, to name just one approach.
“Now researchers face the challenge of demonstrating that Crispr antibacterial and antiviral drugs are effective in living animals and in humans, not just in the lab, and that they will be cheaper than conventional therapies.”
Reference
1. Sheikh K. Is Crispr the Next Antibiotic? The New York Times. Oct 28, 2019.
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/28/health/crispr-genetics-antibiotic-resistance.html. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
Crispr drugs can be effective
Crispr drugs can be effective
Globally, some 700,000 people die from antibiotic-resistant infections ever year; by 2050, that number could be 10 million, according to the United Nations. To find new ways to fight pathogenic microorganisms, scientists are looking to Crispr, the gene-editing tool, according to the New York Times.
“Crispr is a specialized region of DNA that creates what amount to genetic scissors – enzymes that allow the cell (or a scientist) to precisely edit other DNA or its sister molecule, RNA…Crispr was originally discovered in bacteria, where it helps keep track of past injury. When a virus attacks, the bacterium stores small chunks of the viral genome within its own DNA. This helps the bacterium recognize viral infections when they occur again. Then, using Crispr-associated enzymes, it can disarm the virus and prevent the infection from spreading…today researchers are looking to Crispr to edit bacteria and viruses that infect humans and create new treatments.”
In a recent study, researchers successfully used a Crispr-associated enzyme called Cas9 to eliminate a species of Salmonella. They programmed the Cas9 to view the bacterium as the enemy and forced Salmonella to make lethal cuts to its own genome.
Some companies are now exploring Crispr-based antibiotics that might be delivered through viruses engineered so that they cannot reproduce or cause infections themselves, to name just one approach.
“Now researchers face the challenge of demonstrating that Crispr antibacterial and antiviral drugs are effective in living animals and in humans, not just in the lab, and that they will be cheaper than conventional therapies.”
Reference
1. Sheikh K. Is Crispr the Next Antibiotic? The New York Times. Oct 28, 2019.
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/28/health/crispr-genetics-antibiotic-resistance.html. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.
Globally, some 700,000 people die from antibiotic-resistant infections ever year; by 2050, that number could be 10 million, according to the United Nations. To find new ways to fight pathogenic microorganisms, scientists are looking to Crispr, the gene-editing tool, according to the New York Times.
“Crispr is a specialized region of DNA that creates what amount to genetic scissors – enzymes that allow the cell (or a scientist) to precisely edit other DNA or its sister molecule, RNA…Crispr was originally discovered in bacteria, where it helps keep track of past injury. When a virus attacks, the bacterium stores small chunks of the viral genome within its own DNA. This helps the bacterium recognize viral infections when they occur again. Then, using Crispr-associated enzymes, it can disarm the virus and prevent the infection from spreading…today researchers are looking to Crispr to edit bacteria and viruses that infect humans and create new treatments.”
In a recent study, researchers successfully used a Crispr-associated enzyme called Cas9 to eliminate a species of Salmonella. They programmed the Cas9 to view the bacterium as the enemy and forced Salmonella to make lethal cuts to its own genome.
Some companies are now exploring Crispr-based antibiotics that might be delivered through viruses engineered so that they cannot reproduce or cause infections themselves, to name just one approach.
“Now researchers face the challenge of demonstrating that Crispr antibacterial and antiviral drugs are effective in living animals and in humans, not just in the lab, and that they will be cheaper than conventional therapies.”
Reference
1. Sheikh K. Is Crispr the Next Antibiotic? The New York Times. Oct 28, 2019.
https://www.nytimes.com/2019/10/28/health/crispr-genetics-antibiotic-resistance.html. Accessed Dec 3, 2019.


























