User login
Oral Transmission of Chagas Disease Has Severe Effects
Thanks to decades of successful vector control strategies, vector-borne transmission of Chagas disease has significantly decreased in many regions. Oral ingestion of Trypanosoma cruzi through contaminated food and beverages, however, is increasing. Unlike vector transmission, oral transmission of Chagas disease entails high lethality in pediatric and adult populations.
“The oral transmission of Chagas disease is becoming a much more recognized route, and it is crucial to understand that people can die from this type of transmission,” Norman L. Beatty, MD, assistant professor of infectious diseases and global medicine at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, Florida, told this news organization. Dr. Beatty is the lead author of a recent article on the subject.
In regions where the parasite circulates in the environment, people are consuming foods, fruit juices, and possibly wild animal meat that may be contaminated. “As we experience changes in our environment and in the way we consume food, it is crucial to consider how food preparation is carried out in areas where T cruzi transmission occurs in the environment,” said Dr. Beatty. “And as organic farming methods without insecticides become increasingly common, more research is needed in these areas, both in Latin America and in the United States, to understand if oral transmission of T cruzi is occurring.”
In the Amazon basin, foodborne transmission is already the leading cause of acute Chagas disease. It has been described in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
Dr. Beatty’s colleagues recently treated a Brazilian patient at the hospital in Florida. “He came to our hospital very ill, with acute myocarditis after consuming contaminated açaí.” Clarifying that there is widespread awareness about oral transmission in Brazil, he stated, “We are concerned that it may not be recognized in other areas of Latin America.”
Mexico and regions of Central America have little to no information on oral transmission, but it is likely occurring, and cases may be going undetected in the region, said Dr. Beatty.
He investigated the issue in Colombia as part of an international collaboration involving the University of Antioquia, aiming to find ways to mitigate oral transmission and create a model that can be used throughout Latin America and the United States. For the Colombia study, they reviewed all cases reported to the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, and oral transmission turned out to be more common than the research group expected. “Still, I imagine that in certain areas with limited resources…there are many more cases that are not being reported.
“A myth I would like to dispel is that Chagas disease is not being transmitted in the United States,” Dr. Beatty added. He mentioned that at least 30 American states have vectors, and in Florida, it was documented that triatomines invaded homes and bit residents. In addition, 30% of these insects are infected with T cruzi. Research is underway to determine whether Floridians are becoming infected and if they are also at risk of contracting Chagas disease orally, said Dr. Beatty. “In the United States, we know very little about how many people are infected and what the infection routes are. Much more research is needed.”
Roberto Chuit, MD, PhD, a doctor in public health and an external consultant for the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), agreed that this route of food contamination, which occurs because of vector-borne parasites, was until recently masked or hidden by the predominance of vector presence. Just as it began to gain importance as other transmission routes were controlled, “it now has extremely high importance in the Americas, as does vertical transmission,” he said.
In 2023, more than 50 years after the first description of oral transmission, the PAHO expert meeting proposed to alert health services and the broader community about the severity and potential lethality of oral Chagas disease outbreaks to elicit immediate responses and mitigation measures. The body also proposed conducting studies to provide detailed information on the contamination source and the wild vectors present in oral transmission foci.
Unique Clinical Manifestations
The exacerbated signs and symptoms of oral infection (see sidebar) are attributed to the high parasite loads in contaminated food and beverages. A single crushed triatomine along with a food or beverage harboring T cruzi can contain an estimated 600,000 metacyclic trypomastigotes, compared with 3000-4000 per µL when infection occurs by triatomine fecal matter. The robust systemic immune response observed in patients with acute oral Chagas disease is thought to result from more efficient transmission after penetration through the oral, pharyngeal, and gastric mucosae.
Seven Things to Know About Orally Transmitted Chagas Disease
1. It presents with exacerbated symptoms and rapid disease progression in immunocompetent individuals. This presentation is not common in vector-borne, congenital, or transfusion-related transmission. It can cause fulminant myocarditis and heart failure, meningoencephalitis, or potentially fatal shock due to parasitemia.
2. Most patients (71%-100%) with acute oral Chagas present with fever.
3. Electrocardiographic abnormalities, specifically ventricular depolarization alterations and pericardial involvement, are observed in most patients.
4. Facial edema, which typically affects the entire face and parts of the lips, is present in 57%-100% of patients with acute oral Chagas disease. In those with acute symptoms from vector transmission, unilateral periorbital swelling (Romaña’s sign) is more common.
5. Other notable systemic symptoms include edema of the lower extremities, myalgia, generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal discomfort, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, headache, chest pain, cutaneous erythematous rash, jaundice, arthralgia, epistaxis, hematemesis, melena, and palpitations.
6. The incubation period after oral ingestion of products contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi is approximately 3-22 days, in contrast to 4-15 days for vector-borne transmission and 8-160 days for transfusion and transplant-related transmission.
7. Patients need antiparasitic drugs immediately.
Thinking Epidemiologically
Dr. Chuit recalled that suspicion of food contamination should be based on epidemiology, especially in outbreaks affecting several people and in regions where Chagas vectors have been described. Sometimes, however, a single careless tourist consumes contaminated products.
“The difficulty is that many times it is not considered, and if it is not considered, the search for the parasite is not requested,” said Dr. Chuit. He added that it is common for the professional to consider Chagas disease only if viral and bacterial isolation tests are negative. Clinicians sometimes consider Chagas disease because the patient has not responded to regular treatments for other causes, such as antibiotics and hydration.
Epidemiology is important, especially when Chagas disease is diagnosed in groups or a family, because they are usually not isolated cases but outbreaks of 3-40 cases, according to Dr. Chuit. “Under these conditions, it must be quickly considered…that this parasite may be involved.”
One of the difficulties is that the source of these oral transmissions is not recognized most of the time. In general, the sources are usually foods that are more likely to be contaminated by insects or insect feces, such as orange juice or sugarcane. But in fact, any food or beverage left unattended could be contaminated by vectors or possible secretions from infected marsupial odoriferous glands.
An analysis of 32 outbreaks from 1965 to 2022 showed that the main foods involved in oral transmission were homemade fruit juices. But different vector species were identified, and the reservoirs were mainly dogs, rodents, and large American opossums (Didelphis).
The largest oral Chagas outbreak was linked to the consumption of contaminated guava juice in a primary school in Caracas, Venezuela. Nonindustrially produced açaí is a common source of orally acquired Chagas disease in Brazil. In Colombia, Chagas disease has been associated with the consumption of palm wine, sugar cane, and tangerine juice. Other oral transmission routes include consuming meat from wild animals and ingesting blood from infected armadillos, which is related to a traditional medicine practice.
Deadly Yet Easily Treatable
In the outbreak of 119 confirmed and suspected cases in Venezuela, 20.3% required hospitalization, and a 5-year-old child died of acute myocarditis. These percentages differ from those reported in vector transmission, which is asymptomatic in the acute phase for 95%-99% of cases or will only develop a mild febrile illness that resolves on its own.
“Not all cases will present as severe, because depending on the inoculum, there may be individuals with subclinical situations. But any food poisoning that occurs in endemic areas, where food is not properly controlled, and these street foods are associated with processes in jungle areas, raises the possibility that T cruzi is involved and should be considered as a differential diagnosis,» noted Dr. Chuit. “The treatment is highly effective, and people recover quickly.”
“The most important thing about oral transmission of Chagas is that someone infected in this way needs antiparasitic drugs immediately. We can cure them if we treat them immediately,” said Dr. Beatty, adding that treatment is sometimes delayed due to lack of access to appropriate antiparasitic drugs. “Here in the United States and in Latin America, it is quite common for healthcare professionals not to understand the differences between vector, vertical, and oral transmission. By not treating these patients, they become ill quickly.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Chuit declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to decades of successful vector control strategies, vector-borne transmission of Chagas disease has significantly decreased in many regions. Oral ingestion of Trypanosoma cruzi through contaminated food and beverages, however, is increasing. Unlike vector transmission, oral transmission of Chagas disease entails high lethality in pediatric and adult populations.
“The oral transmission of Chagas disease is becoming a much more recognized route, and it is crucial to understand that people can die from this type of transmission,” Norman L. Beatty, MD, assistant professor of infectious diseases and global medicine at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, Florida, told this news organization. Dr. Beatty is the lead author of a recent article on the subject.
In regions where the parasite circulates in the environment, people are consuming foods, fruit juices, and possibly wild animal meat that may be contaminated. “As we experience changes in our environment and in the way we consume food, it is crucial to consider how food preparation is carried out in areas where T cruzi transmission occurs in the environment,” said Dr. Beatty. “And as organic farming methods without insecticides become increasingly common, more research is needed in these areas, both in Latin America and in the United States, to understand if oral transmission of T cruzi is occurring.”
In the Amazon basin, foodborne transmission is already the leading cause of acute Chagas disease. It has been described in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
Dr. Beatty’s colleagues recently treated a Brazilian patient at the hospital in Florida. “He came to our hospital very ill, with acute myocarditis after consuming contaminated açaí.” Clarifying that there is widespread awareness about oral transmission in Brazil, he stated, “We are concerned that it may not be recognized in other areas of Latin America.”
Mexico and regions of Central America have little to no information on oral transmission, but it is likely occurring, and cases may be going undetected in the region, said Dr. Beatty.
He investigated the issue in Colombia as part of an international collaboration involving the University of Antioquia, aiming to find ways to mitigate oral transmission and create a model that can be used throughout Latin America and the United States. For the Colombia study, they reviewed all cases reported to the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, and oral transmission turned out to be more common than the research group expected. “Still, I imagine that in certain areas with limited resources…there are many more cases that are not being reported.
“A myth I would like to dispel is that Chagas disease is not being transmitted in the United States,” Dr. Beatty added. He mentioned that at least 30 American states have vectors, and in Florida, it was documented that triatomines invaded homes and bit residents. In addition, 30% of these insects are infected with T cruzi. Research is underway to determine whether Floridians are becoming infected and if they are also at risk of contracting Chagas disease orally, said Dr. Beatty. “In the United States, we know very little about how many people are infected and what the infection routes are. Much more research is needed.”
Roberto Chuit, MD, PhD, a doctor in public health and an external consultant for the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), agreed that this route of food contamination, which occurs because of vector-borne parasites, was until recently masked or hidden by the predominance of vector presence. Just as it began to gain importance as other transmission routes were controlled, “it now has extremely high importance in the Americas, as does vertical transmission,” he said.
In 2023, more than 50 years after the first description of oral transmission, the PAHO expert meeting proposed to alert health services and the broader community about the severity and potential lethality of oral Chagas disease outbreaks to elicit immediate responses and mitigation measures. The body also proposed conducting studies to provide detailed information on the contamination source and the wild vectors present in oral transmission foci.
Unique Clinical Manifestations
The exacerbated signs and symptoms of oral infection (see sidebar) are attributed to the high parasite loads in contaminated food and beverages. A single crushed triatomine along with a food or beverage harboring T cruzi can contain an estimated 600,000 metacyclic trypomastigotes, compared with 3000-4000 per µL when infection occurs by triatomine fecal matter. The robust systemic immune response observed in patients with acute oral Chagas disease is thought to result from more efficient transmission after penetration through the oral, pharyngeal, and gastric mucosae.
Seven Things to Know About Orally Transmitted Chagas Disease
1. It presents with exacerbated symptoms and rapid disease progression in immunocompetent individuals. This presentation is not common in vector-borne, congenital, or transfusion-related transmission. It can cause fulminant myocarditis and heart failure, meningoencephalitis, or potentially fatal shock due to parasitemia.
2. Most patients (71%-100%) with acute oral Chagas present with fever.
3. Electrocardiographic abnormalities, specifically ventricular depolarization alterations and pericardial involvement, are observed in most patients.
4. Facial edema, which typically affects the entire face and parts of the lips, is present in 57%-100% of patients with acute oral Chagas disease. In those with acute symptoms from vector transmission, unilateral periorbital swelling (Romaña’s sign) is more common.
5. Other notable systemic symptoms include edema of the lower extremities, myalgia, generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal discomfort, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, headache, chest pain, cutaneous erythematous rash, jaundice, arthralgia, epistaxis, hematemesis, melena, and palpitations.
6. The incubation period after oral ingestion of products contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi is approximately 3-22 days, in contrast to 4-15 days for vector-borne transmission and 8-160 days for transfusion and transplant-related transmission.
7. Patients need antiparasitic drugs immediately.
Thinking Epidemiologically
Dr. Chuit recalled that suspicion of food contamination should be based on epidemiology, especially in outbreaks affecting several people and in regions where Chagas vectors have been described. Sometimes, however, a single careless tourist consumes contaminated products.
“The difficulty is that many times it is not considered, and if it is not considered, the search for the parasite is not requested,” said Dr. Chuit. He added that it is common for the professional to consider Chagas disease only if viral and bacterial isolation tests are negative. Clinicians sometimes consider Chagas disease because the patient has not responded to regular treatments for other causes, such as antibiotics and hydration.
Epidemiology is important, especially when Chagas disease is diagnosed in groups or a family, because they are usually not isolated cases but outbreaks of 3-40 cases, according to Dr. Chuit. “Under these conditions, it must be quickly considered…that this parasite may be involved.”
One of the difficulties is that the source of these oral transmissions is not recognized most of the time. In general, the sources are usually foods that are more likely to be contaminated by insects or insect feces, such as orange juice or sugarcane. But in fact, any food or beverage left unattended could be contaminated by vectors or possible secretions from infected marsupial odoriferous glands.
An analysis of 32 outbreaks from 1965 to 2022 showed that the main foods involved in oral transmission were homemade fruit juices. But different vector species were identified, and the reservoirs were mainly dogs, rodents, and large American opossums (Didelphis).
The largest oral Chagas outbreak was linked to the consumption of contaminated guava juice in a primary school in Caracas, Venezuela. Nonindustrially produced açaí is a common source of orally acquired Chagas disease in Brazil. In Colombia, Chagas disease has been associated with the consumption of palm wine, sugar cane, and tangerine juice. Other oral transmission routes include consuming meat from wild animals and ingesting blood from infected armadillos, which is related to a traditional medicine practice.
Deadly Yet Easily Treatable
In the outbreak of 119 confirmed and suspected cases in Venezuela, 20.3% required hospitalization, and a 5-year-old child died of acute myocarditis. These percentages differ from those reported in vector transmission, which is asymptomatic in the acute phase for 95%-99% of cases or will only develop a mild febrile illness that resolves on its own.
“Not all cases will present as severe, because depending on the inoculum, there may be individuals with subclinical situations. But any food poisoning that occurs in endemic areas, where food is not properly controlled, and these street foods are associated with processes in jungle areas, raises the possibility that T cruzi is involved and should be considered as a differential diagnosis,» noted Dr. Chuit. “The treatment is highly effective, and people recover quickly.”
“The most important thing about oral transmission of Chagas is that someone infected in this way needs antiparasitic drugs immediately. We can cure them if we treat them immediately,” said Dr. Beatty, adding that treatment is sometimes delayed due to lack of access to appropriate antiparasitic drugs. “Here in the United States and in Latin America, it is quite common for healthcare professionals not to understand the differences between vector, vertical, and oral transmission. By not treating these patients, they become ill quickly.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Chuit declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Thanks to decades of successful vector control strategies, vector-borne transmission of Chagas disease has significantly decreased in many regions. Oral ingestion of Trypanosoma cruzi through contaminated food and beverages, however, is increasing. Unlike vector transmission, oral transmission of Chagas disease entails high lethality in pediatric and adult populations.
“The oral transmission of Chagas disease is becoming a much more recognized route, and it is crucial to understand that people can die from this type of transmission,” Norman L. Beatty, MD, assistant professor of infectious diseases and global medicine at the University of Florida College of Medicine in Gainesville, Florida, told this news organization. Dr. Beatty is the lead author of a recent article on the subject.
In regions where the parasite circulates in the environment, people are consuming foods, fruit juices, and possibly wild animal meat that may be contaminated. “As we experience changes in our environment and in the way we consume food, it is crucial to consider how food preparation is carried out in areas where T cruzi transmission occurs in the environment,” said Dr. Beatty. “And as organic farming methods without insecticides become increasingly common, more research is needed in these areas, both in Latin America and in the United States, to understand if oral transmission of T cruzi is occurring.”
In the Amazon basin, foodborne transmission is already the leading cause of acute Chagas disease. It has been described in Argentina, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, French Guiana, and Venezuela.
Dr. Beatty’s colleagues recently treated a Brazilian patient at the hospital in Florida. “He came to our hospital very ill, with acute myocarditis after consuming contaminated açaí.” Clarifying that there is widespread awareness about oral transmission in Brazil, he stated, “We are concerned that it may not be recognized in other areas of Latin America.”
Mexico and regions of Central America have little to no information on oral transmission, but it is likely occurring, and cases may be going undetected in the region, said Dr. Beatty.
He investigated the issue in Colombia as part of an international collaboration involving the University of Antioquia, aiming to find ways to mitigate oral transmission and create a model that can be used throughout Latin America and the United States. For the Colombia study, they reviewed all cases reported to the Ministry of Health and Social Protection, and oral transmission turned out to be more common than the research group expected. “Still, I imagine that in certain areas with limited resources…there are many more cases that are not being reported.
“A myth I would like to dispel is that Chagas disease is not being transmitted in the United States,” Dr. Beatty added. He mentioned that at least 30 American states have vectors, and in Florida, it was documented that triatomines invaded homes and bit residents. In addition, 30% of these insects are infected with T cruzi. Research is underway to determine whether Floridians are becoming infected and if they are also at risk of contracting Chagas disease orally, said Dr. Beatty. “In the United States, we know very little about how many people are infected and what the infection routes are. Much more research is needed.”
Roberto Chuit, MD, PhD, a doctor in public health and an external consultant for the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO), agreed that this route of food contamination, which occurs because of vector-borne parasites, was until recently masked or hidden by the predominance of vector presence. Just as it began to gain importance as other transmission routes were controlled, “it now has extremely high importance in the Americas, as does vertical transmission,” he said.
In 2023, more than 50 years after the first description of oral transmission, the PAHO expert meeting proposed to alert health services and the broader community about the severity and potential lethality of oral Chagas disease outbreaks to elicit immediate responses and mitigation measures. The body also proposed conducting studies to provide detailed information on the contamination source and the wild vectors present in oral transmission foci.
Unique Clinical Manifestations
The exacerbated signs and symptoms of oral infection (see sidebar) are attributed to the high parasite loads in contaminated food and beverages. A single crushed triatomine along with a food or beverage harboring T cruzi can contain an estimated 600,000 metacyclic trypomastigotes, compared with 3000-4000 per µL when infection occurs by triatomine fecal matter. The robust systemic immune response observed in patients with acute oral Chagas disease is thought to result from more efficient transmission after penetration through the oral, pharyngeal, and gastric mucosae.
Seven Things to Know About Orally Transmitted Chagas Disease
1. It presents with exacerbated symptoms and rapid disease progression in immunocompetent individuals. This presentation is not common in vector-borne, congenital, or transfusion-related transmission. It can cause fulminant myocarditis and heart failure, meningoencephalitis, or potentially fatal shock due to parasitemia.
2. Most patients (71%-100%) with acute oral Chagas present with fever.
3. Electrocardiographic abnormalities, specifically ventricular depolarization alterations and pericardial involvement, are observed in most patients.
4. Facial edema, which typically affects the entire face and parts of the lips, is present in 57%-100% of patients with acute oral Chagas disease. In those with acute symptoms from vector transmission, unilateral periorbital swelling (Romaña’s sign) is more common.
5. Other notable systemic symptoms include edema of the lower extremities, myalgia, generalized lymphadenopathy, abdominal discomfort, dyspnea, vomiting, diarrhea, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly, headache, chest pain, cutaneous erythematous rash, jaundice, arthralgia, epistaxis, hematemesis, melena, and palpitations.
6. The incubation period after oral ingestion of products contaminated with Trypanosoma cruzi is approximately 3-22 days, in contrast to 4-15 days for vector-borne transmission and 8-160 days for transfusion and transplant-related transmission.
7. Patients need antiparasitic drugs immediately.
Thinking Epidemiologically
Dr. Chuit recalled that suspicion of food contamination should be based on epidemiology, especially in outbreaks affecting several people and in regions where Chagas vectors have been described. Sometimes, however, a single careless tourist consumes contaminated products.
“The difficulty is that many times it is not considered, and if it is not considered, the search for the parasite is not requested,” said Dr. Chuit. He added that it is common for the professional to consider Chagas disease only if viral and bacterial isolation tests are negative. Clinicians sometimes consider Chagas disease because the patient has not responded to regular treatments for other causes, such as antibiotics and hydration.
Epidemiology is important, especially when Chagas disease is diagnosed in groups or a family, because they are usually not isolated cases but outbreaks of 3-40 cases, according to Dr. Chuit. “Under these conditions, it must be quickly considered…that this parasite may be involved.”
One of the difficulties is that the source of these oral transmissions is not recognized most of the time. In general, the sources are usually foods that are more likely to be contaminated by insects or insect feces, such as orange juice or sugarcane. But in fact, any food or beverage left unattended could be contaminated by vectors or possible secretions from infected marsupial odoriferous glands.
An analysis of 32 outbreaks from 1965 to 2022 showed that the main foods involved in oral transmission were homemade fruit juices. But different vector species were identified, and the reservoirs were mainly dogs, rodents, and large American opossums (Didelphis).
The largest oral Chagas outbreak was linked to the consumption of contaminated guava juice in a primary school in Caracas, Venezuela. Nonindustrially produced açaí is a common source of orally acquired Chagas disease in Brazil. In Colombia, Chagas disease has been associated with the consumption of palm wine, sugar cane, and tangerine juice. Other oral transmission routes include consuming meat from wild animals and ingesting blood from infected armadillos, which is related to a traditional medicine practice.
Deadly Yet Easily Treatable
In the outbreak of 119 confirmed and suspected cases in Venezuela, 20.3% required hospitalization, and a 5-year-old child died of acute myocarditis. These percentages differ from those reported in vector transmission, which is asymptomatic in the acute phase for 95%-99% of cases or will only develop a mild febrile illness that resolves on its own.
“Not all cases will present as severe, because depending on the inoculum, there may be individuals with subclinical situations. But any food poisoning that occurs in endemic areas, where food is not properly controlled, and these street foods are associated with processes in jungle areas, raises the possibility that T cruzi is involved and should be considered as a differential diagnosis,» noted Dr. Chuit. “The treatment is highly effective, and people recover quickly.”
“The most important thing about oral transmission of Chagas is that someone infected in this way needs antiparasitic drugs immediately. We can cure them if we treat them immediately,” said Dr. Beatty, adding that treatment is sometimes delayed due to lack of access to appropriate antiparasitic drugs. “Here in the United States and in Latin America, it is quite common for healthcare professionals not to understand the differences between vector, vertical, and oral transmission. By not treating these patients, they become ill quickly.”
Dr. Beatty and Dr. Chuit declared no relevant financial conflicts of interest.
This story was translated from the Medscape Spanish edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA Clears Medical Grade Over-the-Counter Pulse Oximeter
The MightySat Medical, an over-the-counter medical fingertip pulse oximeter, has received clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use without a prescription, according to a press release from manufacturer Masimo.
The device is the first medical fingertip pulse oximeter available directly to consumers without a prescription that includes the same technology used by many hospitals, according to the company.
According to the FDA, home pulse oximeters are currently generally of two classes: hospital-grade prescription devices which have been vetted for accuracy through clinical trials, and over-the-counter devices which are sold direct to consumers but often estimate oxygen saturation. FDA communication on pulse oximeter accuracy states "OTC oximeters that are sold as either general wellness or sporting/aviation products are not intended for medical purposes, so they do not undergo FDA review."
Pulse oximeter use is important for patients diagnosed with breathing problems or lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, flu, pneumonia, or COVID-19 to collect accurate data on arterial blood oxygen saturation that they can share with their healthcare providers, according to the company. Patients with cardiac conditions, including pulmonary hypertension and heart failure may also benefit from pulse oximeter monitoring.
However, challenges of pulse oximeter use include measuring accuracy when patients are moving, measuring patients with poor circulation, and measuring patients with cool, thick, or darker skin. The MightySat Medical is designed to provide reliable measures of oxygen saturation and pulse rate across all patient groups, the manufacturers wrote in the press release.
Asked for additional comment, Diego J. Maselli, MD, FCCP, Professor and Chief in the division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care at UT Health at San Antonio, noted, "Over the past decades, there has been an increased interest in home monitoring of medical conditions, particulrly with the development of more portable and accessible technology."
"This was heightended by the COVID-19 pandemic where telemedicine was frequently required as a means of delivering care," Dr. Maselli continued. "One of the important characteristics to monitor was the oxgen saturation in patients that had an active COVID-19 infection as it would dictate management and was part of the protocol for monitoring the clinical course of infection. Because of this need, many companies developed portable pulse oximeters for home use. This resulted in widespread use of pulse oximeters at home and other places outside clinic or hospital."
Other over-the-counter pulse oximeters that are not cleared by the FDA may create confusion among patients about the accuracy of their measurements, according to the company.
Dr. Maselli also commented that pulse oximeters' value can vary. "Unfortunately, these devices vary in quality and reliability and patients may not be fully aware of this. Most recently, the FDA approved a hospital-grade pulse oximeter that requires no prescription. This device may provide a more accurate reading in a wide range of clinical situations outside the healthcare setting. Patients should be aware that there are different grades of pulse oximeter before selecting one for home use. In addition, patients should work closely with their providers to better select the monitoring modaility that best fits their clinical situation," he said.
MightySat Medical is indicated for individuals aged 18 years and older who are well or poorly perfused under no motion conditions and is not intended as a diagnostic or screening tool for lung disease, according to the release. Treatment decisions based on data from the device should be made only in consultation with a healthcare provider, the company said. Dr. Maselli serves as a member of the CHEST Physician editorial board.
The FDA’s website offers further guidance related to at-home pulse oximeter use, with recommendations and limitations, as well as information on initiatives to ensure accurate and equitable pulse oximetry for all patients.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The MightySat Medical, an over-the-counter medical fingertip pulse oximeter, has received clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use without a prescription, according to a press release from manufacturer Masimo.
The device is the first medical fingertip pulse oximeter available directly to consumers without a prescription that includes the same technology used by many hospitals, according to the company.
According to the FDA, home pulse oximeters are currently generally of two classes: hospital-grade prescription devices which have been vetted for accuracy through clinical trials, and over-the-counter devices which are sold direct to consumers but often estimate oxygen saturation. FDA communication on pulse oximeter accuracy states "OTC oximeters that are sold as either general wellness or sporting/aviation products are not intended for medical purposes, so they do not undergo FDA review."
Pulse oximeter use is important for patients diagnosed with breathing problems or lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, flu, pneumonia, or COVID-19 to collect accurate data on arterial blood oxygen saturation that they can share with their healthcare providers, according to the company. Patients with cardiac conditions, including pulmonary hypertension and heart failure may also benefit from pulse oximeter monitoring.
However, challenges of pulse oximeter use include measuring accuracy when patients are moving, measuring patients with poor circulation, and measuring patients with cool, thick, or darker skin. The MightySat Medical is designed to provide reliable measures of oxygen saturation and pulse rate across all patient groups, the manufacturers wrote in the press release.
Asked for additional comment, Diego J. Maselli, MD, FCCP, Professor and Chief in the division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care at UT Health at San Antonio, noted, "Over the past decades, there has been an increased interest in home monitoring of medical conditions, particulrly with the development of more portable and accessible technology."
"This was heightended by the COVID-19 pandemic where telemedicine was frequently required as a means of delivering care," Dr. Maselli continued. "One of the important characteristics to monitor was the oxgen saturation in patients that had an active COVID-19 infection as it would dictate management and was part of the protocol for monitoring the clinical course of infection. Because of this need, many companies developed portable pulse oximeters for home use. This resulted in widespread use of pulse oximeters at home and other places outside clinic or hospital."
Other over-the-counter pulse oximeters that are not cleared by the FDA may create confusion among patients about the accuracy of their measurements, according to the company.
Dr. Maselli also commented that pulse oximeters' value can vary. "Unfortunately, these devices vary in quality and reliability and patients may not be fully aware of this. Most recently, the FDA approved a hospital-grade pulse oximeter that requires no prescription. This device may provide a more accurate reading in a wide range of clinical situations outside the healthcare setting. Patients should be aware that there are different grades of pulse oximeter before selecting one for home use. In addition, patients should work closely with their providers to better select the monitoring modaility that best fits their clinical situation," he said.
MightySat Medical is indicated for individuals aged 18 years and older who are well or poorly perfused under no motion conditions and is not intended as a diagnostic or screening tool for lung disease, according to the release. Treatment decisions based on data from the device should be made only in consultation with a healthcare provider, the company said. Dr. Maselli serves as a member of the CHEST Physician editorial board.
The FDA’s website offers further guidance related to at-home pulse oximeter use, with recommendations and limitations, as well as information on initiatives to ensure accurate and equitable pulse oximetry for all patients.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The MightySat Medical, an over-the-counter medical fingertip pulse oximeter, has received clearance from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use without a prescription, according to a press release from manufacturer Masimo.
The device is the first medical fingertip pulse oximeter available directly to consumers without a prescription that includes the same technology used by many hospitals, according to the company.
According to the FDA, home pulse oximeters are currently generally of two classes: hospital-grade prescription devices which have been vetted for accuracy through clinical trials, and over-the-counter devices which are sold direct to consumers but often estimate oxygen saturation. FDA communication on pulse oximeter accuracy states "OTC oximeters that are sold as either general wellness or sporting/aviation products are not intended for medical purposes, so they do not undergo FDA review."
Pulse oximeter use is important for patients diagnosed with breathing problems or lung diseases such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary fibrosis, lung cancer, flu, pneumonia, or COVID-19 to collect accurate data on arterial blood oxygen saturation that they can share with their healthcare providers, according to the company. Patients with cardiac conditions, including pulmonary hypertension and heart failure may also benefit from pulse oximeter monitoring.
However, challenges of pulse oximeter use include measuring accuracy when patients are moving, measuring patients with poor circulation, and measuring patients with cool, thick, or darker skin. The MightySat Medical is designed to provide reliable measures of oxygen saturation and pulse rate across all patient groups, the manufacturers wrote in the press release.
Asked for additional comment, Diego J. Maselli, MD, FCCP, Professor and Chief in the division of Pulmonary Diseases and Critical Care at UT Health at San Antonio, noted, "Over the past decades, there has been an increased interest in home monitoring of medical conditions, particulrly with the development of more portable and accessible technology."
"This was heightended by the COVID-19 pandemic where telemedicine was frequently required as a means of delivering care," Dr. Maselli continued. "One of the important characteristics to monitor was the oxgen saturation in patients that had an active COVID-19 infection as it would dictate management and was part of the protocol for monitoring the clinical course of infection. Because of this need, many companies developed portable pulse oximeters for home use. This resulted in widespread use of pulse oximeters at home and other places outside clinic or hospital."
Other over-the-counter pulse oximeters that are not cleared by the FDA may create confusion among patients about the accuracy of their measurements, according to the company.
Dr. Maselli also commented that pulse oximeters' value can vary. "Unfortunately, these devices vary in quality and reliability and patients may not be fully aware of this. Most recently, the FDA approved a hospital-grade pulse oximeter that requires no prescription. This device may provide a more accurate reading in a wide range of clinical situations outside the healthcare setting. Patients should be aware that there are different grades of pulse oximeter before selecting one for home use. In addition, patients should work closely with their providers to better select the monitoring modaility that best fits their clinical situation," he said.
MightySat Medical is indicated for individuals aged 18 years and older who are well or poorly perfused under no motion conditions and is not intended as a diagnostic or screening tool for lung disease, according to the release. Treatment decisions based on data from the device should be made only in consultation with a healthcare provider, the company said. Dr. Maselli serves as a member of the CHEST Physician editorial board.
The FDA’s website offers further guidance related to at-home pulse oximeter use, with recommendations and limitations, as well as information on initiatives to ensure accurate and equitable pulse oximetry for all patients.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Gout Increases the Risk for a Wide Range of Cardiovascular Diseases
People with gout are 58% more likely to develop cardiovascular disease (CVD), according to a new analysis. This increased risk was observed across 12 different cardiovascular conditions, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and valve diseases.
“These findings suggest that the organ damage associated with gout is likely to be much broader than originally thought,” Nathalie Conrad, PhD, senior author of the research and cardiovascular epidemiologist at KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, said in an email. This could be useful for future research on underlying biological mechanisms driving CVD risk in gout, she added.
While previous research has tied gout to increased cardiovascular risk, these studies “largely focused on coronary heart disease, stroke, and thromboembolic outcomes,” she explained, and have been smaller in size.
This new study included more than 862,000 individuals, which permitted researchers to investigate rarer CVD outcomes such as myocarditis and pericarditis.
For the study, researchers used electronic health records from the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink, a primary care database that contains anonymized health data for about 22 million individuals. Using these data, they identified more than 152,600 individuals with gout. Patients included in the analysis were diagnosed between 2000 and 2017, younger than 80 years at diagnosis, and free of CVD for at least 12 months after their gout diagnosis.
Patients with gout were compared with nearly 710,000 controls, matched on demographic factors such as age, sex, and geographic region.
Researchers then investigated the incidence of 12 CVDs, including atherosclerotic diseases, degenerative and thromboembolic diseases, and arrythmias, between the two groups from January 1, 2000, to June 30, 2019.
The findings were published in the March 2024 issue of The Lancet Rheumatology. Overall, patients with gout were 58% more likely to develop any CVD than their matched comparators without gout. There was a higher disease incidence among patients with gout for each of the 12 conditions. This association was more pronounced in women (hazard ratio [HR], 1.88) than in men (HR, 1.49), and gout amplified the risk for CVD in younger individuals to a greater extent.
Individuals younger than 45 years with gout were more than twice as likely to develop CVD compared with similarly aged individuals without gout. For comparison, individuals aged 45-54 years with gout were 84% more likely to develop CVD, and individuals aged 55-64 years were 57% more likely to develop CVD than matched controls.
Conduction system disease had the highest incident risk (HR, 1.88), followed by heart failure and valve disease (HR, 1.85 for both).
Individuals with gout had higher rates of comorbidities than the controls, including hypertension, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Overall, CVD risk was slightly attenuated after adjustment for traditional CVD risk factors such as smoking, blood pressure, and body mass index but still significant: Patients with gout had a 31% higher risk for CVD than comparators.
This shows “that known CVD risk factors only explain part of the CVD risks seen in patients with gout,” Dr. Conrad said. Other factors such as inflammation and other disease activity factors could be at play, she explained, which would need to be explored in future research.
The study “shows the whole landscape” of CVD and gout, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, said in an interview. He was not involved with the research.
“Every possible cardiovascular disease that they could think of was something that gout patients had more of than the non-gout patients,” he added. “I think this is going to be a paper that gets cited a lot, at minimum when describing the background of risk when we look at gout patients.”
The study had some limitations, including that researchers were unable to account for how medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, colchicine, or allopurinol may have affected the association between gout and CVD.
“This is because analyses of nonrandomized treatment can be confounded by indication, wherein it is difficult to differentiate the effects of the treatment from underlying disease severity,” the authors wrote.
There was also a large amount of missing data on blood pressure, body mass index, smoking status, and other health information relevant to cardiovascular risk, so sensitivity analyses adjusting for these factors “should be interpreted with caution,” they added.
Dr. Pillinger also noted that the rates of comorbidities in the gout study population were lower than what have been found in US study populations. For example, about 40% of patients with gout in the analysis had hypertension, while other studies have suggested higher rates of 60%-70%, he said. However, it’s not clear if these differences could have affected outcomes. He added that these limitations do not “in any way weaken [the authors’] conclusion.”
The findings call for better strategies to reduce CVD risk in patients with gout, Dr. Conrad noted.
“Further improvements could come from better recognition and intervention on CVD risk factors (eg, through lifestyle changes or drug therapies where they are indicated), as well as proactive screening for heart disease in patients with gout, which could allow early diagnosis and interventions to delay more severe outcomes,” she added.
This study was funded by Research Foundation Flanders. Dr. Conrad was funded by a personal fellowship from the Research Foundation Flanders and a European Society of Cardiology research grant. She received royalties from Oxford University Innovation. Four of Dr. Conrad’s eight coauthors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Pillinger served as a consultant to Amgen, Federation Bio, Fortress Biotech, and Scilex, and he holds an investigator-initiated grant from Hikma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
People with gout are 58% more likely to develop cardiovascular disease (CVD), according to a new analysis. This increased risk was observed across 12 different cardiovascular conditions, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and valve diseases.
“These findings suggest that the organ damage associated with gout is likely to be much broader than originally thought,” Nathalie Conrad, PhD, senior author of the research and cardiovascular epidemiologist at KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, said in an email. This could be useful for future research on underlying biological mechanisms driving CVD risk in gout, she added.
While previous research has tied gout to increased cardiovascular risk, these studies “largely focused on coronary heart disease, stroke, and thromboembolic outcomes,” she explained, and have been smaller in size.
This new study included more than 862,000 individuals, which permitted researchers to investigate rarer CVD outcomes such as myocarditis and pericarditis.
For the study, researchers used electronic health records from the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink, a primary care database that contains anonymized health data for about 22 million individuals. Using these data, they identified more than 152,600 individuals with gout. Patients included in the analysis were diagnosed between 2000 and 2017, younger than 80 years at diagnosis, and free of CVD for at least 12 months after their gout diagnosis.
Patients with gout were compared with nearly 710,000 controls, matched on demographic factors such as age, sex, and geographic region.
Researchers then investigated the incidence of 12 CVDs, including atherosclerotic diseases, degenerative and thromboembolic diseases, and arrythmias, between the two groups from January 1, 2000, to June 30, 2019.
The findings were published in the March 2024 issue of The Lancet Rheumatology. Overall, patients with gout were 58% more likely to develop any CVD than their matched comparators without gout. There was a higher disease incidence among patients with gout for each of the 12 conditions. This association was more pronounced in women (hazard ratio [HR], 1.88) than in men (HR, 1.49), and gout amplified the risk for CVD in younger individuals to a greater extent.
Individuals younger than 45 years with gout were more than twice as likely to develop CVD compared with similarly aged individuals without gout. For comparison, individuals aged 45-54 years with gout were 84% more likely to develop CVD, and individuals aged 55-64 years were 57% more likely to develop CVD than matched controls.
Conduction system disease had the highest incident risk (HR, 1.88), followed by heart failure and valve disease (HR, 1.85 for both).
Individuals with gout had higher rates of comorbidities than the controls, including hypertension, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Overall, CVD risk was slightly attenuated after adjustment for traditional CVD risk factors such as smoking, blood pressure, and body mass index but still significant: Patients with gout had a 31% higher risk for CVD than comparators.
This shows “that known CVD risk factors only explain part of the CVD risks seen in patients with gout,” Dr. Conrad said. Other factors such as inflammation and other disease activity factors could be at play, she explained, which would need to be explored in future research.
The study “shows the whole landscape” of CVD and gout, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, said in an interview. He was not involved with the research.
“Every possible cardiovascular disease that they could think of was something that gout patients had more of than the non-gout patients,” he added. “I think this is going to be a paper that gets cited a lot, at minimum when describing the background of risk when we look at gout patients.”
The study had some limitations, including that researchers were unable to account for how medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, colchicine, or allopurinol may have affected the association between gout and CVD.
“This is because analyses of nonrandomized treatment can be confounded by indication, wherein it is difficult to differentiate the effects of the treatment from underlying disease severity,” the authors wrote.
There was also a large amount of missing data on blood pressure, body mass index, smoking status, and other health information relevant to cardiovascular risk, so sensitivity analyses adjusting for these factors “should be interpreted with caution,” they added.
Dr. Pillinger also noted that the rates of comorbidities in the gout study population were lower than what have been found in US study populations. For example, about 40% of patients with gout in the analysis had hypertension, while other studies have suggested higher rates of 60%-70%, he said. However, it’s not clear if these differences could have affected outcomes. He added that these limitations do not “in any way weaken [the authors’] conclusion.”
The findings call for better strategies to reduce CVD risk in patients with gout, Dr. Conrad noted.
“Further improvements could come from better recognition and intervention on CVD risk factors (eg, through lifestyle changes or drug therapies where they are indicated), as well as proactive screening for heart disease in patients with gout, which could allow early diagnosis and interventions to delay more severe outcomes,” she added.
This study was funded by Research Foundation Flanders. Dr. Conrad was funded by a personal fellowship from the Research Foundation Flanders and a European Society of Cardiology research grant. She received royalties from Oxford University Innovation. Four of Dr. Conrad’s eight coauthors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Pillinger served as a consultant to Amgen, Federation Bio, Fortress Biotech, and Scilex, and he holds an investigator-initiated grant from Hikma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
People with gout are 58% more likely to develop cardiovascular disease (CVD), according to a new analysis. This increased risk was observed across 12 different cardiovascular conditions, including heart failure, arrhythmias, and valve diseases.
“These findings suggest that the organ damage associated with gout is likely to be much broader than originally thought,” Nathalie Conrad, PhD, senior author of the research and cardiovascular epidemiologist at KU Leuven, Leuven, Belgium, said in an email. This could be useful for future research on underlying biological mechanisms driving CVD risk in gout, she added.
While previous research has tied gout to increased cardiovascular risk, these studies “largely focused on coronary heart disease, stroke, and thromboembolic outcomes,” she explained, and have been smaller in size.
This new study included more than 862,000 individuals, which permitted researchers to investigate rarer CVD outcomes such as myocarditis and pericarditis.
For the study, researchers used electronic health records from the UK Clinical Practice Research Datalink, a primary care database that contains anonymized health data for about 22 million individuals. Using these data, they identified more than 152,600 individuals with gout. Patients included in the analysis were diagnosed between 2000 and 2017, younger than 80 years at diagnosis, and free of CVD for at least 12 months after their gout diagnosis.
Patients with gout were compared with nearly 710,000 controls, matched on demographic factors such as age, sex, and geographic region.
Researchers then investigated the incidence of 12 CVDs, including atherosclerotic diseases, degenerative and thromboembolic diseases, and arrythmias, between the two groups from January 1, 2000, to June 30, 2019.
The findings were published in the March 2024 issue of The Lancet Rheumatology. Overall, patients with gout were 58% more likely to develop any CVD than their matched comparators without gout. There was a higher disease incidence among patients with gout for each of the 12 conditions. This association was more pronounced in women (hazard ratio [HR], 1.88) than in men (HR, 1.49), and gout amplified the risk for CVD in younger individuals to a greater extent.
Individuals younger than 45 years with gout were more than twice as likely to develop CVD compared with similarly aged individuals without gout. For comparison, individuals aged 45-54 years with gout were 84% more likely to develop CVD, and individuals aged 55-64 years were 57% more likely to develop CVD than matched controls.
Conduction system disease had the highest incident risk (HR, 1.88), followed by heart failure and valve disease (HR, 1.85 for both).
Individuals with gout had higher rates of comorbidities than the controls, including hypertension, obesity, and dyslipidemia. Overall, CVD risk was slightly attenuated after adjustment for traditional CVD risk factors such as smoking, blood pressure, and body mass index but still significant: Patients with gout had a 31% higher risk for CVD than comparators.
This shows “that known CVD risk factors only explain part of the CVD risks seen in patients with gout,” Dr. Conrad said. Other factors such as inflammation and other disease activity factors could be at play, she explained, which would need to be explored in future research.
The study “shows the whole landscape” of CVD and gout, Michael H. Pillinger, MD, rheumatologist and professor of medicine, biochemistry, and molecular pharmacology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine in New York City, said in an interview. He was not involved with the research.
“Every possible cardiovascular disease that they could think of was something that gout patients had more of than the non-gout patients,” he added. “I think this is going to be a paper that gets cited a lot, at minimum when describing the background of risk when we look at gout patients.”
The study had some limitations, including that researchers were unable to account for how medications such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, corticosteroids, colchicine, or allopurinol may have affected the association between gout and CVD.
“This is because analyses of nonrandomized treatment can be confounded by indication, wherein it is difficult to differentiate the effects of the treatment from underlying disease severity,” the authors wrote.
There was also a large amount of missing data on blood pressure, body mass index, smoking status, and other health information relevant to cardiovascular risk, so sensitivity analyses adjusting for these factors “should be interpreted with caution,” they added.
Dr. Pillinger also noted that the rates of comorbidities in the gout study population were lower than what have been found in US study populations. For example, about 40% of patients with gout in the analysis had hypertension, while other studies have suggested higher rates of 60%-70%, he said. However, it’s not clear if these differences could have affected outcomes. He added that these limitations do not “in any way weaken [the authors’] conclusion.”
The findings call for better strategies to reduce CVD risk in patients with gout, Dr. Conrad noted.
“Further improvements could come from better recognition and intervention on CVD risk factors (eg, through lifestyle changes or drug therapies where they are indicated), as well as proactive screening for heart disease in patients with gout, which could allow early diagnosis and interventions to delay more severe outcomes,” she added.
This study was funded by Research Foundation Flanders. Dr. Conrad was funded by a personal fellowship from the Research Foundation Flanders and a European Society of Cardiology research grant. She received royalties from Oxford University Innovation. Four of Dr. Conrad’s eight coauthors also reported financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Pillinger served as a consultant to Amgen, Federation Bio, Fortress Biotech, and Scilex, and he holds an investigator-initiated grant from Hikma.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Spinal Cord Injury Tied to Greater Risk for Heart Disease
TOPLINE:
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is associated with a significantly greater risk for heart disease than that of the general non-SCI population, especially among those with severe disability, new observational data suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service on 5083 patients with cervical, thoracic, or lumbar SCI (mean age, 58; 75% men) and 1:3 age- and sex-matched non-SCI controls.
- The study endpoint was new-onset myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure (HF), or atrial fibrillation (AF) during a mean follow-up of 4.3 years.
- Covariates included low income, living in an urban or rural area, alcohol consumption, smoking status, physical activity engagement, body mass index, and blood pressure; comorbidities included hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 169 MI events (7.3 per 1000 person-years), 426 HF events (18.8 per 1000 person-years), and 158 AF events (6.8 per 1000 person-years) occurred among SCI survivors.
- After adjustment, SCI survivors had a higher risk for MI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.41), HF (aHR, 2.24), and AF (aHR, 1.84) than that of controls.
- Cervical and lumbar SCI survivors had an increased risk for heart disease compared with controls regardless of disability, and the risk was slightly higher for those with a disability; for cervical SCI survivors with a disability, aHRs for MI, HF, and AF, respectively, were 2.30, 2.05, and 1.73; for lumbar SCI survivors with a disability, aHRs were 2.79, 2.35, and 2.47.
- Thoracic SCI survivors with disability had a higher risk for MI (aHR, 5.62) and HF (aHR, 3.31) than controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“[T]he recognition and treatment of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors must be reinforced in the SCI population, [and] proper rehabilitation and education should be considered to prevent autonomic dysreflexia or orthostatic hypotension,” the authors wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher R. West, PhD, and Jacquelyn J. Cragg, PhD, both of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, noted that clinical guidelines for cardiovascular and cardiometabolic disease after SCI don’t include approaches to help mitigate the risk for cardiac events such as those reported in the study; therefore, they wrote, the findings “should act as ‘call-to-arms’ to researchers and clinicians to shift gears from tradition and begin studying the clinical efficacy of neuraxial therapies that could help restore autonomic balance [in SCI], such as targeted neuromodulation.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jung Eun Yoo, MD, PhD of Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and published online on February 12 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The database was not designed for the SCI population, so data are incomplete. The incidence of thoracic SCI was particularly low. Because SCI survivors may have impaired perception of chest pain in ischemic heart disease, those with asymptomatic or silent heart disease may not have been captured during follow-up. All study participants were Korean, so the findings may not be generalizable to other ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was partially supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, South Korea. The study authors and the editorialists had no relevant relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is associated with a significantly greater risk for heart disease than that of the general non-SCI population, especially among those with severe disability, new observational data suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service on 5083 patients with cervical, thoracic, or lumbar SCI (mean age, 58; 75% men) and 1:3 age- and sex-matched non-SCI controls.
- The study endpoint was new-onset myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure (HF), or atrial fibrillation (AF) during a mean follow-up of 4.3 years.
- Covariates included low income, living in an urban or rural area, alcohol consumption, smoking status, physical activity engagement, body mass index, and blood pressure; comorbidities included hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 169 MI events (7.3 per 1000 person-years), 426 HF events (18.8 per 1000 person-years), and 158 AF events (6.8 per 1000 person-years) occurred among SCI survivors.
- After adjustment, SCI survivors had a higher risk for MI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.41), HF (aHR, 2.24), and AF (aHR, 1.84) than that of controls.
- Cervical and lumbar SCI survivors had an increased risk for heart disease compared with controls regardless of disability, and the risk was slightly higher for those with a disability; for cervical SCI survivors with a disability, aHRs for MI, HF, and AF, respectively, were 2.30, 2.05, and 1.73; for lumbar SCI survivors with a disability, aHRs were 2.79, 2.35, and 2.47.
- Thoracic SCI survivors with disability had a higher risk for MI (aHR, 5.62) and HF (aHR, 3.31) than controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“[T]he recognition and treatment of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors must be reinforced in the SCI population, [and] proper rehabilitation and education should be considered to prevent autonomic dysreflexia or orthostatic hypotension,” the authors wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher R. West, PhD, and Jacquelyn J. Cragg, PhD, both of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, noted that clinical guidelines for cardiovascular and cardiometabolic disease after SCI don’t include approaches to help mitigate the risk for cardiac events such as those reported in the study; therefore, they wrote, the findings “should act as ‘call-to-arms’ to researchers and clinicians to shift gears from tradition and begin studying the clinical efficacy of neuraxial therapies that could help restore autonomic balance [in SCI], such as targeted neuromodulation.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jung Eun Yoo, MD, PhD of Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and published online on February 12 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The database was not designed for the SCI population, so data are incomplete. The incidence of thoracic SCI was particularly low. Because SCI survivors may have impaired perception of chest pain in ischemic heart disease, those with asymptomatic or silent heart disease may not have been captured during follow-up. All study participants were Korean, so the findings may not be generalizable to other ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was partially supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, South Korea. The study authors and the editorialists had no relevant relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is associated with a significantly greater risk for heart disease than that of the general non-SCI population, especially among those with severe disability, new observational data suggest.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers analyzed data from Korea’s National Health Insurance Service on 5083 patients with cervical, thoracic, or lumbar SCI (mean age, 58; 75% men) and 1:3 age- and sex-matched non-SCI controls.
- The study endpoint was new-onset myocardial infarction (MI), heart failure (HF), or atrial fibrillation (AF) during a mean follow-up of 4.3 years.
- Covariates included low income, living in an urban or rural area, alcohol consumption, smoking status, physical activity engagement, body mass index, and blood pressure; comorbidities included hypertension, type 2 diabetes, and dyslipidemia.
TAKEAWAY:
- A total of 169 MI events (7.3 per 1000 person-years), 426 HF events (18.8 per 1000 person-years), and 158 AF events (6.8 per 1000 person-years) occurred among SCI survivors.
- After adjustment, SCI survivors had a higher risk for MI (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 2.41), HF (aHR, 2.24), and AF (aHR, 1.84) than that of controls.
- Cervical and lumbar SCI survivors had an increased risk for heart disease compared with controls regardless of disability, and the risk was slightly higher for those with a disability; for cervical SCI survivors with a disability, aHRs for MI, HF, and AF, respectively, were 2.30, 2.05, and 1.73; for lumbar SCI survivors with a disability, aHRs were 2.79, 2.35, and 2.47.
- Thoracic SCI survivors with disability had a higher risk for MI (aHR, 5.62) and HF (aHR, 3.31) than controls.
IN PRACTICE:
“[T]he recognition and treatment of modifiable cardiovascular risk factors must be reinforced in the SCI population, [and] proper rehabilitation and education should be considered to prevent autonomic dysreflexia or orthostatic hypotension,” the authors wrote.
In an accompanying editorial, Christopher R. West, PhD, and Jacquelyn J. Cragg, PhD, both of the University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, noted that clinical guidelines for cardiovascular and cardiometabolic disease after SCI don’t include approaches to help mitigate the risk for cardiac events such as those reported in the study; therefore, they wrote, the findings “should act as ‘call-to-arms’ to researchers and clinicians to shift gears from tradition and begin studying the clinical efficacy of neuraxial therapies that could help restore autonomic balance [in SCI], such as targeted neuromodulation.”
SOURCE:
The study was led by Jung Eun Yoo, MD, PhD of Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and published online on February 12 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
The database was not designed for the SCI population, so data are incomplete. The incidence of thoracic SCI was particularly low. Because SCI survivors may have impaired perception of chest pain in ischemic heart disease, those with asymptomatic or silent heart disease may not have been captured during follow-up. All study participants were Korean, so the findings may not be generalizable to other ethnicities.
DISCLOSURES:
This research was partially supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, South Korea. The study authors and the editorialists had no relevant relationships to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Colchicine May Benefit Patients With Diabetes and Recent MI
TOPLINE:
A daily low dose of colchicine significantly reduces ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and a recent myocardial infarction (MI).
METHODOLOGY:
- After an MI, patients with vs without T2D have a higher risk for another cardiovascular event.
- The Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial (COLCOT), a randomized, double-blinded trial, found a lower risk for ischemic cardiovascular events with 0.5 mg colchicine taken daily vs placebo, initiated within 30 days of an MI.
- Researchers conducted a prespecified subgroup analysis of 959 adult patients with T2D (mean age, 62.4 years; 22.2% women) in COLCOT (462 patients in colchicine and 497 patients in placebo groups).
- The primary efficacy endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent hospitalization for angina requiring coronary revascularization within a median 23 months.
- The patients were taking a variety of appropriate medications, including aspirin and another antiplatelet agent and a statin (98%-99%) and metformin (75%-76%).
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for the primary endpoint was reduced by 35% in patients with T2D who received colchicine than in those who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.65; P = .03).
- The primary endpoint event rate per 100 patient-months was significantly lower in the colchicine group than in the placebo group (rate ratio, 0.53; P = .01).
- The frequencies of adverse events were similar in both the treatment and placebo groups (14.6% and 12.8%, respectively; P = .41), with gastrointestinal adverse events being the most common.
- In COLCOT, patients with T2D had a 1.86-fold higher risk for a primary endpoint cardiovascular event, but there was no significant difference in the primary endpoint between those with and without T2D on colchicine.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with both T2D and a recent MI derive a large benefit from inflammation-reducing therapy with colchicine,” the authors noted.
SOURCE:
This study, led by François Roubille, University Hospital of Montpellier, France, was published online on January 5, 2024, in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Patients were not stratified at inclusion for the presence of diabetes. Also, the study did not evaluate the role of glycated hemoglobin and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, as well as the effects of different glucose-lowering medications or possible hypoglycemic episodes.
DISCLOSURES:
The COLCOT study was funded by the Government of Quebec, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and philanthropic foundations. Coauthors Jean-Claude Tardif and Wolfgang Koenig declared receiving research grants, honoraria, advisory board fees, and lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies, as well as having other ties with various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A daily low dose of colchicine significantly reduces ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and a recent myocardial infarction (MI).
METHODOLOGY:
- After an MI, patients with vs without T2D have a higher risk for another cardiovascular event.
- The Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial (COLCOT), a randomized, double-blinded trial, found a lower risk for ischemic cardiovascular events with 0.5 mg colchicine taken daily vs placebo, initiated within 30 days of an MI.
- Researchers conducted a prespecified subgroup analysis of 959 adult patients with T2D (mean age, 62.4 years; 22.2% women) in COLCOT (462 patients in colchicine and 497 patients in placebo groups).
- The primary efficacy endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent hospitalization for angina requiring coronary revascularization within a median 23 months.
- The patients were taking a variety of appropriate medications, including aspirin and another antiplatelet agent and a statin (98%-99%) and metformin (75%-76%).
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for the primary endpoint was reduced by 35% in patients with T2D who received colchicine than in those who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.65; P = .03).
- The primary endpoint event rate per 100 patient-months was significantly lower in the colchicine group than in the placebo group (rate ratio, 0.53; P = .01).
- The frequencies of adverse events were similar in both the treatment and placebo groups (14.6% and 12.8%, respectively; P = .41), with gastrointestinal adverse events being the most common.
- In COLCOT, patients with T2D had a 1.86-fold higher risk for a primary endpoint cardiovascular event, but there was no significant difference in the primary endpoint between those with and without T2D on colchicine.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with both T2D and a recent MI derive a large benefit from inflammation-reducing therapy with colchicine,” the authors noted.
SOURCE:
This study, led by François Roubille, University Hospital of Montpellier, France, was published online on January 5, 2024, in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Patients were not stratified at inclusion for the presence of diabetes. Also, the study did not evaluate the role of glycated hemoglobin and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, as well as the effects of different glucose-lowering medications or possible hypoglycemic episodes.
DISCLOSURES:
The COLCOT study was funded by the Government of Quebec, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and philanthropic foundations. Coauthors Jean-Claude Tardif and Wolfgang Koenig declared receiving research grants, honoraria, advisory board fees, and lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies, as well as having other ties with various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A daily low dose of colchicine significantly reduces ischemic cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and a recent myocardial infarction (MI).
METHODOLOGY:
- After an MI, patients with vs without T2D have a higher risk for another cardiovascular event.
- The Colchicine Cardiovascular Outcomes Trial (COLCOT), a randomized, double-blinded trial, found a lower risk for ischemic cardiovascular events with 0.5 mg colchicine taken daily vs placebo, initiated within 30 days of an MI.
- Researchers conducted a prespecified subgroup analysis of 959 adult patients with T2D (mean age, 62.4 years; 22.2% women) in COLCOT (462 patients in colchicine and 497 patients in placebo groups).
- The primary efficacy endpoint was a composite of cardiovascular death, resuscitated cardiac arrest, MI, stroke, or urgent hospitalization for angina requiring coronary revascularization within a median 23 months.
- The patients were taking a variety of appropriate medications, including aspirin and another antiplatelet agent and a statin (98%-99%) and metformin (75%-76%).
TAKEAWAY:
- The risk for the primary endpoint was reduced by 35% in patients with T2D who received colchicine than in those who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.65; P = .03).
- The primary endpoint event rate per 100 patient-months was significantly lower in the colchicine group than in the placebo group (rate ratio, 0.53; P = .01).
- The frequencies of adverse events were similar in both the treatment and placebo groups (14.6% and 12.8%, respectively; P = .41), with gastrointestinal adverse events being the most common.
- In COLCOT, patients with T2D had a 1.86-fold higher risk for a primary endpoint cardiovascular event, but there was no significant difference in the primary endpoint between those with and without T2D on colchicine.
IN PRACTICE:
“Patients with both T2D and a recent MI derive a large benefit from inflammation-reducing therapy with colchicine,” the authors noted.
SOURCE:
This study, led by François Roubille, University Hospital of Montpellier, France, was published online on January 5, 2024, in Diabetes Care.
LIMITATIONS:
Patients were not stratified at inclusion for the presence of diabetes. Also, the study did not evaluate the role of glycated hemoglobin and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, as well as the effects of different glucose-lowering medications or possible hypoglycemic episodes.
DISCLOSURES:
The COLCOT study was funded by the Government of Quebec, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, and philanthropic foundations. Coauthors Jean-Claude Tardif and Wolfgang Koenig declared receiving research grants, honoraria, advisory board fees, and lecture fees from pharmaceutical companies, as well as having other ties with various sources.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Continued Caution Needed Combining Nitrates With ED Drugs
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.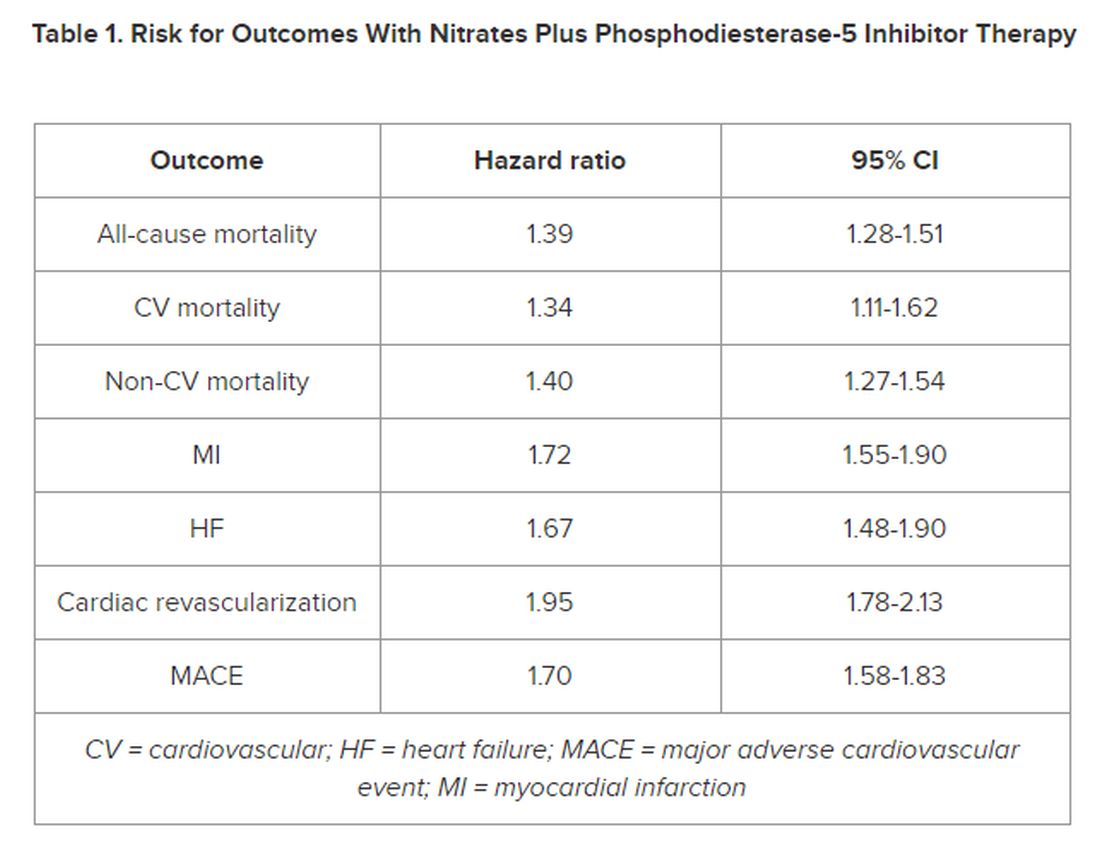
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New research supports continued caution in prescribing a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor (PDE5i) to treat erectile dysfunction (ED) in men with heart disease using nitrate medications.
In a large Swedish population study of men with stable coronary artery disease (CAD), the combined use of a PDE5i and nitrates was associated with a higher risk for cardiovascular (CV) morbidity and mortality.
“According to current recommendations, PDE5i are contraindicated in patients taking organic nitrates; however, in clinical practice, both are commonly prescribed, and concomitant use has increased,” first author Ylva Trolle Lagerros, MD, PhD, with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, told this news organization.
and weigh the benefits of the medication against the possible increased risk for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality given by this combination,” Dr. Lagerros said.
The study was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The researchers used the Swedish Patient Register and the Prescribed Drug Register to assess the association between PDE5i treatment and CV outcomes in men with stable CAD treated with nitrate medication.
Among 55,777 men with a history of previous myocardial infarction (MI) or coronary revascularization who had filled at least two nitrate prescriptions (sublingual, oral, or both), 5710 also had at least two filled prescriptions of a PDE5i.
In multivariate-adjusted analysis, the combined use of PDE5i treatment with nitrates was associated with an increased relative risk for all studied outcomes, including all-cause mortality, CV and non-CV mortality, MI, heart failure, cardiac revascularization (hazard ratio), and major adverse cardiovascular events.
However, the number of events 28 days following a PDE5i prescription fill was “few, with lower incidence rates than in subjects taking nitrates only, indicating a low immediate risk for any event,” the authors noted in their article.
‘Common Bedfellows’
In a JACC editorial, Glenn N. Levine, MD, with Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas, noted that, “ED and CAD are unfortunate, and all too common, bedfellows. But, as with most relationships, assuming proper precautions and care, they can coexist together for many years, perhaps even a lifetime.”
Dr. Levine noted that PDE5is are “reasonably safe” in most patients with stable CAD and only mild angina if not on chronic nitrate therapy. For those on chronic oral nitrate therapy, the use of PDE5is should continue to be regarded as “ill-advised at best and generally contraindicated.”
In some patients on oral nitrate therapy who want to use a PDE5i, particularly those who have undergone revascularization and have minimal or no angina, Dr. Levine said it may be reasonable to initiate a several-week trial of the nitrate therapy (or on a different class of antianginal therapy) and assess if the patient remains relatively angina-free.
In those patients with just rare exertional angina at generally higher levels of activity or those prescribed sublingual nitroglycerin “just in case,” it may be reasonable to prescribe PDE5i after a “clear and detailed” discussion with the patient of the risks for temporarily combining PDE5i and sublingual nitroglycerin.
Dr. Levine said these patients should be instructed not to take nitroglycerin within 24 hours of using a shorter-acting PDE5i and within 48 hours of using the longer-acting PDE5i tadalafil.
They should also be told to call 9-1-1 if angina develops during sexual intercourse and does not resolve upon cessation of such sexual activity, as well as to make medical personnel aware that they have recently used a PDE5i.
The study was funded by Region Stockholm, the Center for Innovative Medicine, and Karolinska Institutet. The researchers and editorial writer had declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Insights Into Mortality in Takotsubo Syndrome
TOPLINE:
Mortality in patients with takotsubo syndrome (TTS), sometimes called broken heart syndrome or stress-induced cardiomyopathy is substantially higher than that in the general population and comparable with that in patients having myocardial infarction (MI), results of a new case-control study showed. The rates of medication use are similar for TTS and MI, despite no current clinical trials or recommendations to guide such therapies, the authors noted.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 620 Scottish patients (mean age, 66 years; 91% women) with TTS, a potentially fatal condition that mimics MI, predominantly affects middle-aged women, and is often triggered by stress.
- The analysis also included two age-, sex-, and geographically matched control groups: Representative participants from the general Scottish population (1:4) and patients with acute MI (1:1).
- Using comprehensive national data sets, researchers extracted information for all three cohorts on prescribing of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular medications, including the duration of dispensing and causes of death, and clustered the major causes of death into 17 major groups.
- At a median follow-up of 5.5 years, there were 722 deaths (153 in patients with TTS, 195 in those with MI, and 374 in the general population cohort).
TAKEAWAY:
- and slightly lower than that in patients having MI (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.62-0.94; P = .012), with cardiovascular causes, particularly heart failure, being the most strongly associated with TTS (HR, 2.47; 95% CI, 1.81-3.39; P < .0001 vs general population), followed by pulmonary causes. Noncardiovascular mortality was similar in TTS and MI.
- Prescription rates of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular medications were similar between patients with TTS and MI.
- The only cardiovascular therapy associated with lower mortality in patients with TTS was angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy (P = .0056); in contrast, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents, and statins were all associated with improved survival in patients with MI.
- Diuretics were associated with worse outcomes in both patients with TTS and MI, as was psychotropic therapy.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings may help to lay the foundations for further exploration of potential mechanisms and treatments” for TTS, an “increasingly recognized and potentially fatal condition,” the authors concluded.
In an accompanying comment, Rodolfo Citro, MD, PHD, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Department, San Giovanni di Dio e Ruggi d’ Aragona University Hospital, Salerno, Italy, and colleagues said the authors should be commended for providing data on cardiovascular mortality “during one of the longest available follow-ups in TTS,” adding the study “suggests the importance of further research for more appropriate management of patients with acute and long-term TTS.”
SOURCE:
The research was led by Amelia E. Rudd, MSC, Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre, University of Aberdeen and NHS Grampian, Aberdeen, Scotland. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Complete alignment of all variables related to clinical characteristics of patients with TTS and MI wasn’t feasible. During the study, TTS was still relatively unfamiliar to clinicians and underdiagnosed. As the study used a national data set of routinely collected data, not all desirable information was available, including indications of why drugs were prescribed or discontinued, which could have led to imprecise results. As the study used nonrandomized data, causality can’t be assumed.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Rudd had no relevant conflicts of interest. Study author Dana K. Dawson, Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre, University of Aberdeen, Scotland, declared receiving the Chief Scientist Office Scotland award CGA-16-4 and the BHF Research Training Fellowship. Commentary authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mortality in patients with takotsubo syndrome (TTS), sometimes called broken heart syndrome or stress-induced cardiomyopathy is substantially higher than that in the general population and comparable with that in patients having myocardial infarction (MI), results of a new case-control study showed. The rates of medication use are similar for TTS and MI, despite no current clinical trials or recommendations to guide such therapies, the authors noted.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 620 Scottish patients (mean age, 66 years; 91% women) with TTS, a potentially fatal condition that mimics MI, predominantly affects middle-aged women, and is often triggered by stress.
- The analysis also included two age-, sex-, and geographically matched control groups: Representative participants from the general Scottish population (1:4) and patients with acute MI (1:1).
- Using comprehensive national data sets, researchers extracted information for all three cohorts on prescribing of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular medications, including the duration of dispensing and causes of death, and clustered the major causes of death into 17 major groups.
- At a median follow-up of 5.5 years, there were 722 deaths (153 in patients with TTS, 195 in those with MI, and 374 in the general population cohort).
TAKEAWAY:
- and slightly lower than that in patients having MI (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.62-0.94; P = .012), with cardiovascular causes, particularly heart failure, being the most strongly associated with TTS (HR, 2.47; 95% CI, 1.81-3.39; P < .0001 vs general population), followed by pulmonary causes. Noncardiovascular mortality was similar in TTS and MI.
- Prescription rates of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular medications were similar between patients with TTS and MI.
- The only cardiovascular therapy associated with lower mortality in patients with TTS was angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy (P = .0056); in contrast, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents, and statins were all associated with improved survival in patients with MI.
- Diuretics were associated with worse outcomes in both patients with TTS and MI, as was psychotropic therapy.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings may help to lay the foundations for further exploration of potential mechanisms and treatments” for TTS, an “increasingly recognized and potentially fatal condition,” the authors concluded.
In an accompanying comment, Rodolfo Citro, MD, PHD, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Department, San Giovanni di Dio e Ruggi d’ Aragona University Hospital, Salerno, Italy, and colleagues said the authors should be commended for providing data on cardiovascular mortality “during one of the longest available follow-ups in TTS,” adding the study “suggests the importance of further research for more appropriate management of patients with acute and long-term TTS.”
SOURCE:
The research was led by Amelia E. Rudd, MSC, Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre, University of Aberdeen and NHS Grampian, Aberdeen, Scotland. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Complete alignment of all variables related to clinical characteristics of patients with TTS and MI wasn’t feasible. During the study, TTS was still relatively unfamiliar to clinicians and underdiagnosed. As the study used a national data set of routinely collected data, not all desirable information was available, including indications of why drugs were prescribed or discontinued, which could have led to imprecise results. As the study used nonrandomized data, causality can’t be assumed.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Rudd had no relevant conflicts of interest. Study author Dana K. Dawson, Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre, University of Aberdeen, Scotland, declared receiving the Chief Scientist Office Scotland award CGA-16-4 and the BHF Research Training Fellowship. Commentary authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Mortality in patients with takotsubo syndrome (TTS), sometimes called broken heart syndrome or stress-induced cardiomyopathy is substantially higher than that in the general population and comparable with that in patients having myocardial infarction (MI), results of a new case-control study showed. The rates of medication use are similar for TTS and MI, despite no current clinical trials or recommendations to guide such therapies, the authors noted.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study included 620 Scottish patients (mean age, 66 years; 91% women) with TTS, a potentially fatal condition that mimics MI, predominantly affects middle-aged women, and is often triggered by stress.
- The analysis also included two age-, sex-, and geographically matched control groups: Representative participants from the general Scottish population (1:4) and patients with acute MI (1:1).
- Using comprehensive national data sets, researchers extracted information for all three cohorts on prescribing of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular medications, including the duration of dispensing and causes of death, and clustered the major causes of death into 17 major groups.
- At a median follow-up of 5.5 years, there were 722 deaths (153 in patients with TTS, 195 in those with MI, and 374 in the general population cohort).
TAKEAWAY:
- and slightly lower than that in patients having MI (HR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.62-0.94; P = .012), with cardiovascular causes, particularly heart failure, being the most strongly associated with TTS (HR, 2.47; 95% CI, 1.81-3.39; P < .0001 vs general population), followed by pulmonary causes. Noncardiovascular mortality was similar in TTS and MI.
- Prescription rates of cardiovascular and noncardiovascular medications were similar between patients with TTS and MI.
- The only cardiovascular therapy associated with lower mortality in patients with TTS was angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker therapy (P = .0056); in contrast, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, beta-blockers, antiplatelet agents, and statins were all associated with improved survival in patients with MI.
- Diuretics were associated with worse outcomes in both patients with TTS and MI, as was psychotropic therapy.
IN PRACTICE:
“These findings may help to lay the foundations for further exploration of potential mechanisms and treatments” for TTS, an “increasingly recognized and potentially fatal condition,” the authors concluded.
In an accompanying comment, Rodolfo Citro, MD, PHD, Cardiovascular and Thoracic Department, San Giovanni di Dio e Ruggi d’ Aragona University Hospital, Salerno, Italy, and colleagues said the authors should be commended for providing data on cardiovascular mortality “during one of the longest available follow-ups in TTS,” adding the study “suggests the importance of further research for more appropriate management of patients with acute and long-term TTS.”
SOURCE:
The research was led by Amelia E. Rudd, MSC, Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre, University of Aberdeen and NHS Grampian, Aberdeen, Scotland. It was published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
LIMITATIONS:
Complete alignment of all variables related to clinical characteristics of patients with TTS and MI wasn’t feasible. During the study, TTS was still relatively unfamiliar to clinicians and underdiagnosed. As the study used a national data set of routinely collected data, not all desirable information was available, including indications of why drugs were prescribed or discontinued, which could have led to imprecise results. As the study used nonrandomized data, causality can’t be assumed.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Rudd had no relevant conflicts of interest. Study author Dana K. Dawson, Aberdeen Cardiovascular and Diabetes Centre, University of Aberdeen, Scotland, declared receiving the Chief Scientist Office Scotland award CGA-16-4 and the BHF Research Training Fellowship. Commentary authors had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Sudden Cardiac Deaths Down Among NCAA Athletes
TOPLINE:
A new study shows sudden cardiac deaths among collegiate athletes decreased over a recent 20-year period, but risks are still elevated among males, Black players, and basketball players, suggesting more intensive screening among these groups is needed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study examined incidence and surrounding circumstances of sudden cardiac death (SCD) among student athletes who competed in at least one varsity sport at National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I, II, or III institutions in the 20 years from July 1, 2002, to June 30, 2022.
- Researchers determined causes of death and gathered demographic characteristics using multiple methods, including review of autopsy and other official documents, Internet searches, and contacts to next of kin, coaches, athletic trainers, coroners, medical examiners, scholarship foundations, and physicians involved in the case.
- SCD was defined as sudden unexpected death attributable to a cardiac cause, or a sudden death in a structurally normal heart with no other explanation for death and a history consistent with cardiac-related death that occurred within an hour of symptom onset, or an unwitnessed death occurring within 24 hours of the person being alive.
- Researchers calculated incidence rates over a typical 4-year collegiate career and reported these as athlete-years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of SCD, which accounted for 13% of the 1102 total deaths during the study period, decreased over time, with a 5-year incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 0.71 (95% CI, 0.61-0.82), while noncardiovascular deaths remained stable.
- IRR for males versus females was 3.79 (95% CI, 2.45-5.88) and for Black versus White athletes was 2.79 (95% CI, 1.98-3.94).
- Basketball and football players were at increased risk of SCD; for example, the incidence rate among Division I Black male basketball athletes was 1:1924 per 4-year athlete-years.
- The most common postmortem finding was autopsy-negative sudden unexplained death, at 19%, followed by idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy/possible cardiomyopathy (17%) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (13%), with no cases of death attributable to COVID-19 myocarditis.
IN PRACTICE:
Although the reason for the decrease in SCD is unknown, “our data suggest that strategies to reduce SCD among competing athletes may be having a positive effect,” wrote the authors. More intensive screening strategies among groups with high SCD incidence may be warranted, they added.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Bradley J. Petek, MD, Sports Cardiology Program, Knight Cardiovascular Institute, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. It was published online November 13 in Circulation and presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions (abstract 479).
LIMITATIONS:
Some cases of SCD may have been missed as there is no mandatory reporting system in the United States. Approaches to cardiac autopsy and reporting varied significantly. The cause of death was unknown in 16 cases, and postmortem genetic testing was available for only 3% of athletes. As the study didn’t have data on resuscitated sudden cardiac arrest or preparticipation cardiovascular screening practices and findings, definitive conclusions couldn’t be drawn regarding causal factors underlying the decreased incidence of SCD.
DISCLOSURES:
There was no outside funding source. Dr. Petek has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A new study shows sudden cardiac deaths among collegiate athletes decreased over a recent 20-year period, but risks are still elevated among males, Black players, and basketball players, suggesting more intensive screening among these groups is needed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study examined incidence and surrounding circumstances of sudden cardiac death (SCD) among student athletes who competed in at least one varsity sport at National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I, II, or III institutions in the 20 years from July 1, 2002, to June 30, 2022.
- Researchers determined causes of death and gathered demographic characteristics using multiple methods, including review of autopsy and other official documents, Internet searches, and contacts to next of kin, coaches, athletic trainers, coroners, medical examiners, scholarship foundations, and physicians involved in the case.
- SCD was defined as sudden unexpected death attributable to a cardiac cause, or a sudden death in a structurally normal heart with no other explanation for death and a history consistent with cardiac-related death that occurred within an hour of symptom onset, or an unwitnessed death occurring within 24 hours of the person being alive.
- Researchers calculated incidence rates over a typical 4-year collegiate career and reported these as athlete-years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of SCD, which accounted for 13% of the 1102 total deaths during the study period, decreased over time, with a 5-year incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 0.71 (95% CI, 0.61-0.82), while noncardiovascular deaths remained stable.
- IRR for males versus females was 3.79 (95% CI, 2.45-5.88) and for Black versus White athletes was 2.79 (95% CI, 1.98-3.94).
- Basketball and football players were at increased risk of SCD; for example, the incidence rate among Division I Black male basketball athletes was 1:1924 per 4-year athlete-years.
- The most common postmortem finding was autopsy-negative sudden unexplained death, at 19%, followed by idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy/possible cardiomyopathy (17%) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (13%), with no cases of death attributable to COVID-19 myocarditis.
IN PRACTICE:
Although the reason for the decrease in SCD is unknown, “our data suggest that strategies to reduce SCD among competing athletes may be having a positive effect,” wrote the authors. More intensive screening strategies among groups with high SCD incidence may be warranted, they added.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Bradley J. Petek, MD, Sports Cardiology Program, Knight Cardiovascular Institute, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. It was published online November 13 in Circulation and presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions (abstract 479).
LIMITATIONS:
Some cases of SCD may have been missed as there is no mandatory reporting system in the United States. Approaches to cardiac autopsy and reporting varied significantly. The cause of death was unknown in 16 cases, and postmortem genetic testing was available for only 3% of athletes. As the study didn’t have data on resuscitated sudden cardiac arrest or preparticipation cardiovascular screening practices and findings, definitive conclusions couldn’t be drawn regarding causal factors underlying the decreased incidence of SCD.
DISCLOSURES:
There was no outside funding source. Dr. Petek has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
A new study shows sudden cardiac deaths among collegiate athletes decreased over a recent 20-year period, but risks are still elevated among males, Black players, and basketball players, suggesting more intensive screening among these groups is needed.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study examined incidence and surrounding circumstances of sudden cardiac death (SCD) among student athletes who competed in at least one varsity sport at National Collegiate Athletic Association (NCAA) Division I, II, or III institutions in the 20 years from July 1, 2002, to June 30, 2022.
- Researchers determined causes of death and gathered demographic characteristics using multiple methods, including review of autopsy and other official documents, Internet searches, and contacts to next of kin, coaches, athletic trainers, coroners, medical examiners, scholarship foundations, and physicians involved in the case.
- SCD was defined as sudden unexpected death attributable to a cardiac cause, or a sudden death in a structurally normal heart with no other explanation for death and a history consistent with cardiac-related death that occurred within an hour of symptom onset, or an unwitnessed death occurring within 24 hours of the person being alive.
- Researchers calculated incidence rates over a typical 4-year collegiate career and reported these as athlete-years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The incidence of SCD, which accounted for 13% of the 1102 total deaths during the study period, decreased over time, with a 5-year incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 0.71 (95% CI, 0.61-0.82), while noncardiovascular deaths remained stable.
- IRR for males versus females was 3.79 (95% CI, 2.45-5.88) and for Black versus White athletes was 2.79 (95% CI, 1.98-3.94).
- Basketball and football players were at increased risk of SCD; for example, the incidence rate among Division I Black male basketball athletes was 1:1924 per 4-year athlete-years.
- The most common postmortem finding was autopsy-negative sudden unexplained death, at 19%, followed by idiopathic left ventricular hypertrophy/possible cardiomyopathy (17%) and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (13%), with no cases of death attributable to COVID-19 myocarditis.
IN PRACTICE:
Although the reason for the decrease in SCD is unknown, “our data suggest that strategies to reduce SCD among competing athletes may be having a positive effect,” wrote the authors. More intensive screening strategies among groups with high SCD incidence may be warranted, they added.
SOURCE:
The study was conducted by Bradley J. Petek, MD, Sports Cardiology Program, Knight Cardiovascular Institute, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. It was published online November 13 in Circulation and presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions (abstract 479).
LIMITATIONS:
Some cases of SCD may have been missed as there is no mandatory reporting system in the United States. Approaches to cardiac autopsy and reporting varied significantly. The cause of death was unknown in 16 cases, and postmortem genetic testing was available for only 3% of athletes. As the study didn’t have data on resuscitated sudden cardiac arrest or preparticipation cardiovascular screening practices and findings, definitive conclusions couldn’t be drawn regarding causal factors underlying the decreased incidence of SCD.
DISCLOSURES:
There was no outside funding source. Dr. Petek has reported no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the other authors are listed with the article.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Anticoagulants Safe With Enzyme-Inducing Meds for Epilepsy
ORLANDO — Combining an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC) does not significantly increase the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with epilepsy, preliminary results of a new study show.
These new data are important, “particularly when we’re talking about a more global perspective, given the vital role of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications in epilepsy care across many middle- and low-income countries where they may be the only readily available treatment options,” said study investigator Emily K. Acton, PhD candidate in epidemiology and a medical student, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago.
The findings also suggest that use of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with DOACs may be associated with a reduction in major bleeding events, although Ms. Acton stressed this requires more research.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting.
Important Implications
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may induce key drug metabolizing enzymes that result in wide-ranging interactions, Ms. Acton told this news organization. “But, in many cases, the clinical significance of these pharmacokinetic interactions is not completely understood.”
This has important implications for managing anticoagulation, said Ms. Acton. “The ease of DOAC use, and growing evidence of the drugs’ safety and efficacy compared to vitamin K antagonists, has led to widespread shifts in clinical practice towards DOACs.”
Due to the relative novelty of DOACs, their interaction profiles have been less than complete, she explained. Evidence that enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may reduce absorption and accelerate metabolism of DOACs, potentially lowering DOAC levels and elevating thromboembolism risk, comes mainly from in vitro and animal studies.
“Research in humans is lacking and complicated in interpretation by inconsistent findings and methodological limitations,” she said.
The investigators wanted to address the “clinical uncertainty” surrounding the real-world relevance of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications and DOAC interactions but conducting a randomized trial “would be neither feasible nor ethical,” said Ms. Acton.
Using healthcare claims data from October 2010 to September 2021, the researchers conducted an active comparator, new-user cohort study among a nationally representative sample of adults with epilepsy who had been co-prescribed these drugs.
They compared thromboembolic and major bleeding event rates between exposure to DOACs with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications vs exposure to DOACs with non-enzyme inducing antiseizure medications.
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included in the study were carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and topiramate. Non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and pregabalin.
The researchers used data-adaptive high-dimensional propensity score matching to control for “hundreds and hundreds” of observed confounders, and proxies for unobserved confounders, said Ms. Acton. They identified outcomes based on validated diagnostic coding algorithms for thromboembolic and major bleeding events and estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) using Cox proportional hazard models with robust variance estimators to account for clustering within matched pairs.
Reduced Risk of Major Bleeding
Outcomes were analyzed in three separate cohorts. These included patients on DOACs for any indication (indication-agnostic); those on DOACs for atrial fibrillation (AF); and those taking DOACs for deep vein thrombus/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE).
In the indication-agnostic analysis, the investigators examined thromboembolic events among 5989 episodes in patients taking both DOACs and enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications, compared witha reference group of 14,671 episodes in patients taking DOACs and non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications.
The reference group was generally older and had a greater prevalence of a number of major comorbidities compared with the exposed group, noted Ms. Acton.
For the indication-agnostic analysis, the aHR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.89-1.39). Results were similar for the AF indication (aHR 1.10; 95% CI 0.82-1.46) and for the DVT/PE indication (aHR 1.11; 95% CI 0.81-1.51).
“This research provides large-scale, real-world evidence enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication use alongside DOACs does not significantly elevate risk of thromboembolic events among a nationally representative epilepsy population,” said Ms. Acton.
However, “it’s always important to consider risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events at the level of the individual patient,” she added.
With respect to major bleeding events, there was a slightly reduced risk in the exposed group, specifically in the analysis of subjects with atrial fibrillation, where the aHR was 0.63 (95% CI 0.44-0.89).
“A potential explanation may be pharmacokinetic interaction with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications occurring to a degree that lowers DOAC levels without necessarily negating therapeutic effects,” said Ms. Acton.
However, she cautioned that more research is needed.
As for the differential potency among the various enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications studied, Ms. Acton said results from a secondary analysis in the atrial fibrillation assessment that removed the potentially less potent enzyme inducers, oxcarbazepine and topiramate, didn’t significantly change the study results.
‘Really Great News’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, epilepsy expert Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Neurology, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said the finding of no meaningful difference between DOAC plus enzyme-inducing medications vs DOACs plus non-enzyme-inducing medications is encouraging.
“This study asks a very important question at the population level and appropriately tries to control for present and hidden factors using a propensity matching approach,” he said.
The fact that the data support no difference in terms of thromboembolic events “is really great news” for patients taking an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication who need to use a DOAC, he said.
While some patients or clinicians might consider transitioning off an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication, this can lead to new side effects and potentially higher drug costs. “Knowing that a transition may be unnecessary is exciting,” said Dr. Goldenholz.
However, he’s concerned the 1.5-year observation period may not be long enough to see a true effect of these drug combinations.
He also noted that due to the “theoretical higher risk,” patients combining DOACs with enzyme-inducing drugs typically need extra monitoring, which may be less practical outside the US. This suggests “the result may not necessarily generalize outside high-income countries,” he said.
Dr. Goldenholz emphasized that the data are preliminary. “As always, I look forward to a full peer-reviewed study before forming final conclusions.”
The study was supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services’ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Ms. Acton and Dr. Goldenholz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO — Combining an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC) does not significantly increase the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with epilepsy, preliminary results of a new study show.
These new data are important, “particularly when we’re talking about a more global perspective, given the vital role of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications in epilepsy care across many middle- and low-income countries where they may be the only readily available treatment options,” said study investigator Emily K. Acton, PhD candidate in epidemiology and a medical student, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago.
The findings also suggest that use of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with DOACs may be associated with a reduction in major bleeding events, although Ms. Acton stressed this requires more research.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting.
Important Implications
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may induce key drug metabolizing enzymes that result in wide-ranging interactions, Ms. Acton told this news organization. “But, in many cases, the clinical significance of these pharmacokinetic interactions is not completely understood.”
This has important implications for managing anticoagulation, said Ms. Acton. “The ease of DOAC use, and growing evidence of the drugs’ safety and efficacy compared to vitamin K antagonists, has led to widespread shifts in clinical practice towards DOACs.”
Due to the relative novelty of DOACs, their interaction profiles have been less than complete, she explained. Evidence that enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may reduce absorption and accelerate metabolism of DOACs, potentially lowering DOAC levels and elevating thromboembolism risk, comes mainly from in vitro and animal studies.
“Research in humans is lacking and complicated in interpretation by inconsistent findings and methodological limitations,” she said.
The investigators wanted to address the “clinical uncertainty” surrounding the real-world relevance of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications and DOAC interactions but conducting a randomized trial “would be neither feasible nor ethical,” said Ms. Acton.
Using healthcare claims data from October 2010 to September 2021, the researchers conducted an active comparator, new-user cohort study among a nationally representative sample of adults with epilepsy who had been co-prescribed these drugs.
They compared thromboembolic and major bleeding event rates between exposure to DOACs with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications vs exposure to DOACs with non-enzyme inducing antiseizure medications.
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included in the study were carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and topiramate. Non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and pregabalin.
The researchers used data-adaptive high-dimensional propensity score matching to control for “hundreds and hundreds” of observed confounders, and proxies for unobserved confounders, said Ms. Acton. They identified outcomes based on validated diagnostic coding algorithms for thromboembolic and major bleeding events and estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) using Cox proportional hazard models with robust variance estimators to account for clustering within matched pairs.
Reduced Risk of Major Bleeding
Outcomes were analyzed in three separate cohorts. These included patients on DOACs for any indication (indication-agnostic); those on DOACs for atrial fibrillation (AF); and those taking DOACs for deep vein thrombus/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE).
In the indication-agnostic analysis, the investigators examined thromboembolic events among 5989 episodes in patients taking both DOACs and enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications, compared witha reference group of 14,671 episodes in patients taking DOACs and non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications.
The reference group was generally older and had a greater prevalence of a number of major comorbidities compared with the exposed group, noted Ms. Acton.
For the indication-agnostic analysis, the aHR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.89-1.39). Results were similar for the AF indication (aHR 1.10; 95% CI 0.82-1.46) and for the DVT/PE indication (aHR 1.11; 95% CI 0.81-1.51).
“This research provides large-scale, real-world evidence enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication use alongside DOACs does not significantly elevate risk of thromboembolic events among a nationally representative epilepsy population,” said Ms. Acton.
However, “it’s always important to consider risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events at the level of the individual patient,” she added.
With respect to major bleeding events, there was a slightly reduced risk in the exposed group, specifically in the analysis of subjects with atrial fibrillation, where the aHR was 0.63 (95% CI 0.44-0.89).
“A potential explanation may be pharmacokinetic interaction with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications occurring to a degree that lowers DOAC levels without necessarily negating therapeutic effects,” said Ms. Acton.
However, she cautioned that more research is needed.
As for the differential potency among the various enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications studied, Ms. Acton said results from a secondary analysis in the atrial fibrillation assessment that removed the potentially less potent enzyme inducers, oxcarbazepine and topiramate, didn’t significantly change the study results.
‘Really Great News’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, epilepsy expert Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Neurology, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said the finding of no meaningful difference between DOAC plus enzyme-inducing medications vs DOACs plus non-enzyme-inducing medications is encouraging.
“This study asks a very important question at the population level and appropriately tries to control for present and hidden factors using a propensity matching approach,” he said.
The fact that the data support no difference in terms of thromboembolic events “is really great news” for patients taking an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication who need to use a DOAC, he said.
While some patients or clinicians might consider transitioning off an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication, this can lead to new side effects and potentially higher drug costs. “Knowing that a transition may be unnecessary is exciting,” said Dr. Goldenholz.
However, he’s concerned the 1.5-year observation period may not be long enough to see a true effect of these drug combinations.
He also noted that due to the “theoretical higher risk,” patients combining DOACs with enzyme-inducing drugs typically need extra monitoring, which may be less practical outside the US. This suggests “the result may not necessarily generalize outside high-income countries,” he said.
Dr. Goldenholz emphasized that the data are preliminary. “As always, I look forward to a full peer-reviewed study before forming final conclusions.”
The study was supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services’ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Ms. Acton and Dr. Goldenholz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
ORLANDO — Combining an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with a direct-acting oral anticoagulant (DOAC) does not significantly increase the risk of thromboembolic events in patients with epilepsy, preliminary results of a new study show.
These new data are important, “particularly when we’re talking about a more global perspective, given the vital role of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications in epilepsy care across many middle- and low-income countries where they may be the only readily available treatment options,” said study investigator Emily K. Acton, PhD candidate in epidemiology and a medical student, University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, and University of Illinois College of Medicine, Chicago.
The findings also suggest that use of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication with DOACs may be associated with a reduction in major bleeding events, although Ms. Acton stressed this requires more research.
The findings were presented at the American Epilepsy Society annual meeting.
Important Implications
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may induce key drug metabolizing enzymes that result in wide-ranging interactions, Ms. Acton told this news organization. “But, in many cases, the clinical significance of these pharmacokinetic interactions is not completely understood.”
This has important implications for managing anticoagulation, said Ms. Acton. “The ease of DOAC use, and growing evidence of the drugs’ safety and efficacy compared to vitamin K antagonists, has led to widespread shifts in clinical practice towards DOACs.”
Due to the relative novelty of DOACs, their interaction profiles have been less than complete, she explained. Evidence that enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications may reduce absorption and accelerate metabolism of DOACs, potentially lowering DOAC levels and elevating thromboembolism risk, comes mainly from in vitro and animal studies.
“Research in humans is lacking and complicated in interpretation by inconsistent findings and methodological limitations,” she said.
The investigators wanted to address the “clinical uncertainty” surrounding the real-world relevance of enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications and DOAC interactions but conducting a randomized trial “would be neither feasible nor ethical,” said Ms. Acton.
Using healthcare claims data from October 2010 to September 2021, the researchers conducted an active comparator, new-user cohort study among a nationally representative sample of adults with epilepsy who had been co-prescribed these drugs.
They compared thromboembolic and major bleeding event rates between exposure to DOACs with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications vs exposure to DOACs with non-enzyme inducing antiseizure medications.
Enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included in the study were carbamazepine, oxcarbazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone, and topiramate. Non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications included gabapentin, lacosamide, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, and pregabalin.
The researchers used data-adaptive high-dimensional propensity score matching to control for “hundreds and hundreds” of observed confounders, and proxies for unobserved confounders, said Ms. Acton. They identified outcomes based on validated diagnostic coding algorithms for thromboembolic and major bleeding events and estimated adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) using Cox proportional hazard models with robust variance estimators to account for clustering within matched pairs.
Reduced Risk of Major Bleeding
Outcomes were analyzed in three separate cohorts. These included patients on DOACs for any indication (indication-agnostic); those on DOACs for atrial fibrillation (AF); and those taking DOACs for deep vein thrombus/pulmonary embolism (DVT/PE).
In the indication-agnostic analysis, the investigators examined thromboembolic events among 5989 episodes in patients taking both DOACs and enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications, compared witha reference group of 14,671 episodes in patients taking DOACs and non-enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications.
The reference group was generally older and had a greater prevalence of a number of major comorbidities compared with the exposed group, noted Ms. Acton.
For the indication-agnostic analysis, the aHR was 1.11 (95% CI 0.89-1.39). Results were similar for the AF indication (aHR 1.10; 95% CI 0.82-1.46) and for the DVT/PE indication (aHR 1.11; 95% CI 0.81-1.51).
“This research provides large-scale, real-world evidence enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication use alongside DOACs does not significantly elevate risk of thromboembolic events among a nationally representative epilepsy population,” said Ms. Acton.
However, “it’s always important to consider risk factors for thromboembolic and bleeding events at the level of the individual patient,” she added.
With respect to major bleeding events, there was a slightly reduced risk in the exposed group, specifically in the analysis of subjects with atrial fibrillation, where the aHR was 0.63 (95% CI 0.44-0.89).
“A potential explanation may be pharmacokinetic interaction with enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications occurring to a degree that lowers DOAC levels without necessarily negating therapeutic effects,” said Ms. Acton.
However, she cautioned that more research is needed.
As for the differential potency among the various enzyme-inducing antiseizure medications studied, Ms. Acton said results from a secondary analysis in the atrial fibrillation assessment that removed the potentially less potent enzyme inducers, oxcarbazepine and topiramate, didn’t significantly change the study results.
‘Really Great News’
Commenting on the findings for this news organization, epilepsy expert Daniel M. Goldenholz, MD, PhD, assistant professor of Neurology, Harvard Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, Massachusetts, said the finding of no meaningful difference between DOAC plus enzyme-inducing medications vs DOACs plus non-enzyme-inducing medications is encouraging.
“This study asks a very important question at the population level and appropriately tries to control for present and hidden factors using a propensity matching approach,” he said.
The fact that the data support no difference in terms of thromboembolic events “is really great news” for patients taking an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication who need to use a DOAC, he said.
While some patients or clinicians might consider transitioning off an enzyme-inducing antiseizure medication, this can lead to new side effects and potentially higher drug costs. “Knowing that a transition may be unnecessary is exciting,” said Dr. Goldenholz.
However, he’s concerned the 1.5-year observation period may not be long enough to see a true effect of these drug combinations.
He also noted that due to the “theoretical higher risk,” patients combining DOACs with enzyme-inducing drugs typically need extra monitoring, which may be less practical outside the US. This suggests “the result may not necessarily generalize outside high-income countries,” he said.
Dr. Goldenholz emphasized that the data are preliminary. “As always, I look forward to a full peer-reviewed study before forming final conclusions.”
The study was supported by the US Department of Health and Human Services’ National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke.
Ms. Acton and Dr. Goldenholz report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AES 2023
Newborn Recipient of Partial Heart Transplant Doing Well
, researchers said.
The surgery was performed on the 18th day of life of a 5-pound newborn boy diagnosed prenatally with persistent truncus arteriosus and severe truncal valve dysfunction. The procedure involved transplantation of the part of the heart containing the aorta and pulmonary valves from an infant donor upon cardiac death.
The standard of care for neonatal heart valve implants are cadaver grafts. But these grafts are not viable and can’t grow or self-repair. Therefore, recipient neonates need to undergo repeated implant-exchange surgeries until an adult-sized heart valve can fit. Clinical outcomes generally are poor.
“We have learned that these partial heart transplant valves, when procured fresh and the [recipient] baby is placed on low-dose antirejection medicine, can grow with the child and function completely normally,” Joseph W. Turek, MD, PhD, MBA of Duke University Medical Center in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization.
“This represents a new field in heart surgery that could dramatically change the way we care for children with poorly functioning heart valves by allowing valve implants that grow with them.”
A case report describing the novel intervention was published online on January 2, 2024, in JAMA.
‘Expected to Last a Lifetime’
The donor was a 2-day-old female weighing 8 pounds. Delivery had been complicated by hypoxic ischemic brain injury, but echocardiography showed structurally normal, functioning outflow heart valves. The heart was donated after cardiac death and procured using standard surgical techniques.
The recipient infant’s operation involved sternotomy, cardiopulmonary bypass, and cardioplegic arrest of the heart. The pulmonary artery ostia and coronary artery buttons were dissected, and the infant’s irreparable truncal valve was excised.
The donor aortic root was transplanted first, using donor tissue to close the ventricular septal defect. Then, the coronary artery buttons were reimplanted; the right ventricular outflow tract was enlarged; and the pulmonary root was transplanted. Postoperative immunosuppression followed.
On the follow-up at age 14 months, the transplanted valves showed no obstruction or insufficiency on echocardiography. Now, almost 21 months later, the recipient is doing well, Dr. Turek said. “His family has shared his many milestones with me, including eating his first birthday cake, videos of his first steps, and his newfound oral appetite (he was largely g-tube fed for a while).”
“The rationale for partial heart transplant is that pediatric heart transplants grow,” Dr. Turek and coauthors wrote. “Moreover, failure of heart transplant outflow valves is exceedingly rare. While heart transplant long-term outcomes are limited by inevitable ventricular dysfunction, partial heart transplants spare the native ventricles and are therefore expected to last a lifetime.”
‘Domino Hearts’
“While this particular baby had truncus arteriosus, this operation should prove to be beneficial for a host of congenital heart conditions with valves that are either too small or poorly functioning,” Dr. Turek said. “We have performed subsequent partial heart operations for babies with aortic stenosis, tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia, and biventricular outflow tract obstruction.”
The challenge is organ availability, he noted. “While this procedure does make use of hearts that would be otherwise unusable for full heart transplant, such as hearts with poor ventricular function or hearts removed from recipients of full heart transplants (aka domino hearts), the availability is still low compared to the need.”
With domino hearts, “you could potentially double the number of hearts that are used for the benefit of children with heart disease,” Dr. Turek said in a Duke communication released with the paper. In a domino heart procedure, a patient who has healthy valves but needs stronger heart muscle receives a full heart transplant, and the healthy valves are then donated to another patient in need, creating a domino effect.
Since this breakthrough procedure in 2022, partial heart transplants have been performed 13 times at four centers, including nine at Duke, three of which used the domino technique.
For now, Dr. Turek told this news organization, “we are hoping to receive funds for a clinical trial that will evaluate these partial heart transplant valves on a larger basis and determine an optimal antirejection dose necessary to maintain viability.”
Preclinical research leading to this case report was supported by the Brett Boyer Foundation. Dr. Turek reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, researchers said.
The surgery was performed on the 18th day of life of a 5-pound newborn boy diagnosed prenatally with persistent truncus arteriosus and severe truncal valve dysfunction. The procedure involved transplantation of the part of the heart containing the aorta and pulmonary valves from an infant donor upon cardiac death.
The standard of care for neonatal heart valve implants are cadaver grafts. But these grafts are not viable and can’t grow or self-repair. Therefore, recipient neonates need to undergo repeated implant-exchange surgeries until an adult-sized heart valve can fit. Clinical outcomes generally are poor.
“We have learned that these partial heart transplant valves, when procured fresh and the [recipient] baby is placed on low-dose antirejection medicine, can grow with the child and function completely normally,” Joseph W. Turek, MD, PhD, MBA of Duke University Medical Center in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization.
“This represents a new field in heart surgery that could dramatically change the way we care for children with poorly functioning heart valves by allowing valve implants that grow with them.”
A case report describing the novel intervention was published online on January 2, 2024, in JAMA.
‘Expected to Last a Lifetime’
The donor was a 2-day-old female weighing 8 pounds. Delivery had been complicated by hypoxic ischemic brain injury, but echocardiography showed structurally normal, functioning outflow heart valves. The heart was donated after cardiac death and procured using standard surgical techniques.
The recipient infant’s operation involved sternotomy, cardiopulmonary bypass, and cardioplegic arrest of the heart. The pulmonary artery ostia and coronary artery buttons were dissected, and the infant’s irreparable truncal valve was excised.
The donor aortic root was transplanted first, using donor tissue to close the ventricular septal defect. Then, the coronary artery buttons were reimplanted; the right ventricular outflow tract was enlarged; and the pulmonary root was transplanted. Postoperative immunosuppression followed.
On the follow-up at age 14 months, the transplanted valves showed no obstruction or insufficiency on echocardiography. Now, almost 21 months later, the recipient is doing well, Dr. Turek said. “His family has shared his many milestones with me, including eating his first birthday cake, videos of his first steps, and his newfound oral appetite (he was largely g-tube fed for a while).”
“The rationale for partial heart transplant is that pediatric heart transplants grow,” Dr. Turek and coauthors wrote. “Moreover, failure of heart transplant outflow valves is exceedingly rare. While heart transplant long-term outcomes are limited by inevitable ventricular dysfunction, partial heart transplants spare the native ventricles and are therefore expected to last a lifetime.”
‘Domino Hearts’
“While this particular baby had truncus arteriosus, this operation should prove to be beneficial for a host of congenital heart conditions with valves that are either too small or poorly functioning,” Dr. Turek said. “We have performed subsequent partial heart operations for babies with aortic stenosis, tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia, and biventricular outflow tract obstruction.”
The challenge is organ availability, he noted. “While this procedure does make use of hearts that would be otherwise unusable for full heart transplant, such as hearts with poor ventricular function or hearts removed from recipients of full heart transplants (aka domino hearts), the availability is still low compared to the need.”
With domino hearts, “you could potentially double the number of hearts that are used for the benefit of children with heart disease,” Dr. Turek said in a Duke communication released with the paper. In a domino heart procedure, a patient who has healthy valves but needs stronger heart muscle receives a full heart transplant, and the healthy valves are then donated to another patient in need, creating a domino effect.
Since this breakthrough procedure in 2022, partial heart transplants have been performed 13 times at four centers, including nine at Duke, three of which used the domino technique.
For now, Dr. Turek told this news organization, “we are hoping to receive funds for a clinical trial that will evaluate these partial heart transplant valves on a larger basis and determine an optimal antirejection dose necessary to maintain viability.”
Preclinical research leading to this case report was supported by the Brett Boyer Foundation. Dr. Turek reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, researchers said.
The surgery was performed on the 18th day of life of a 5-pound newborn boy diagnosed prenatally with persistent truncus arteriosus and severe truncal valve dysfunction. The procedure involved transplantation of the part of the heart containing the aorta and pulmonary valves from an infant donor upon cardiac death.
The standard of care for neonatal heart valve implants are cadaver grafts. But these grafts are not viable and can’t grow or self-repair. Therefore, recipient neonates need to undergo repeated implant-exchange surgeries until an adult-sized heart valve can fit. Clinical outcomes generally are poor.
“We have learned that these partial heart transplant valves, when procured fresh and the [recipient] baby is placed on low-dose antirejection medicine, can grow with the child and function completely normally,” Joseph W. Turek, MD, PhD, MBA of Duke University Medical Center in Durham, North Carolina, told this news organization.
“This represents a new field in heart surgery that could dramatically change the way we care for children with poorly functioning heart valves by allowing valve implants that grow with them.”
A case report describing the novel intervention was published online on January 2, 2024, in JAMA.
‘Expected to Last a Lifetime’
The donor was a 2-day-old female weighing 8 pounds. Delivery had been complicated by hypoxic ischemic brain injury, but echocardiography showed structurally normal, functioning outflow heart valves. The heart was donated after cardiac death and procured using standard surgical techniques.
The recipient infant’s operation involved sternotomy, cardiopulmonary bypass, and cardioplegic arrest of the heart. The pulmonary artery ostia and coronary artery buttons were dissected, and the infant’s irreparable truncal valve was excised.
The donor aortic root was transplanted first, using donor tissue to close the ventricular septal defect. Then, the coronary artery buttons were reimplanted; the right ventricular outflow tract was enlarged; and the pulmonary root was transplanted. Postoperative immunosuppression followed.
On the follow-up at age 14 months, the transplanted valves showed no obstruction or insufficiency on echocardiography. Now, almost 21 months later, the recipient is doing well, Dr. Turek said. “His family has shared his many milestones with me, including eating his first birthday cake, videos of his first steps, and his newfound oral appetite (he was largely g-tube fed for a while).”
“The rationale for partial heart transplant is that pediatric heart transplants grow,” Dr. Turek and coauthors wrote. “Moreover, failure of heart transplant outflow valves is exceedingly rare. While heart transplant long-term outcomes are limited by inevitable ventricular dysfunction, partial heart transplants spare the native ventricles and are therefore expected to last a lifetime.”
‘Domino Hearts’
“While this particular baby had truncus arteriosus, this operation should prove to be beneficial for a host of congenital heart conditions with valves that are either too small or poorly functioning,” Dr. Turek said. “We have performed subsequent partial heart operations for babies with aortic stenosis, tetralogy of Fallot with pulmonary atresia, and biventricular outflow tract obstruction.”
The challenge is organ availability, he noted. “While this procedure does make use of hearts that would be otherwise unusable for full heart transplant, such as hearts with poor ventricular function or hearts removed from recipients of full heart transplants (aka domino hearts), the availability is still low compared to the need.”
With domino hearts, “you could potentially double the number of hearts that are used for the benefit of children with heart disease,” Dr. Turek said in a Duke communication released with the paper. In a domino heart procedure, a patient who has healthy valves but needs stronger heart muscle receives a full heart transplant, and the healthy valves are then donated to another patient in need, creating a domino effect.
Since this breakthrough procedure in 2022, partial heart transplants have been performed 13 times at four centers, including nine at Duke, three of which used the domino technique.
For now, Dr. Turek told this news organization, “we are hoping to receive funds for a clinical trial that will evaluate these partial heart transplant valves on a larger basis and determine an optimal antirejection dose necessary to maintain viability.”
Preclinical research leading to this case report was supported by the Brett Boyer Foundation. Dr. Turek reported no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.