User login
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
About half of US adults aged ≥ 65 years report arthritis, and of those, 44% have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation.1,2 Arthritis is a significant health issue for veterans, with veterans reporting higher rates of disability compared with the civilian population.3
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis.4 Among individuals aged ≥ 40 years, the incidence of OA is nearly twice as high among veterans compared with civilians and is a leading cause of separation from military service and disability.5,6 OA pain and disability have been shown to be associated with increases in health care and medication use, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and muscle relaxants.7,8 Because OA is chronic and has no cure, safe and effective management strategies—such as exercise— are critical to minimize pain and maintain physical function.9
Exercise can reduce pain and disability associated with OA and is a first-line recommendation in guidelines for the treatment of knee and hip OA.9 Given the limited exercise and high levels of physical inactivity among veterans with OA, there is a need to identify opportunities that support veterans with OA engaging in regular exercise.
Gerofit, an outpatient clinical exercise program available at 30 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) sites, may provide an opportunity for older veterans with arthritis to engage in exercise.10 Gerofit is specifically designed for veterans aged ≥ 65 years. It is not disease-specific and supports older veterans with multiple chronic conditions, including OA. Veterans aged ≥ 65 years with a referral from a VA clinician are eligible for Gerofit. Those who are unable to perform activities of daily living; unable to independently function without assistance; have a history of unstable angina, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, oxygen dependence, volatile behavioral issues, or are unable to work successfully in a group environment/setting; experience active substance abuse, homelessness, or uncontrolled incontinence; and have open wounds that cannot be appropriately dressed are excluded from Gerofit. Exercise sessions are held 3 times per week and last from 60 to 90 minutes. Sessions are supervised by Gerofit staff and include personalized exercise prescriptions based on functional assessments. Exercise prescriptions include aerobic, resistance, and balance/flexibility components and are modified by the Gerofit program staff as needed. Gerofit adopts a functional fitness approach and includes individual progression as appropriate according to evidence-based guidelines, using the Borg ratings of perceived exertion. 11 Assessments are performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter. Clinical staff conduct all assessments, including physical function testing, and record them in a database. Assessments are reviewed with the veteran to chart progress and identify future goals or needs. Veterans perform personalized self-paced exercises in the Gerofit group setting. Exercise prescriptions are continuously modified to meet individualized needs and goals. Veterans may participate continuously with no end date.
Participation in supervised exercise is associated with improved physical function and individuals with arthritis can improve function even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis. 12 In this analysis, we examine the impact of exercise on the status and location of arthritis (upper body, lower body, or both). Lower body arthritis is more common than upper body arthritis and lower extremity function is associated with increased ability to perform activities of daily living, resulting in independence among older adults.13,14 We also include upper body strength measures to capture important functional movements such as reaching and pulling.15 Among those who participate in Gerofit, the greatest gains in physical function occur during the initial 3 months, which tend to be sustained over 12 months.16 For this reason, this study focused on the initial 3 months of the program.
Older adults with arthritis may have pain and functional limitations that exceed those of the general older adult population. Exercise programs for older adults that do not specifically target arthritis but are able to improve physical function among those with arthritis could potentially increase access to exercise for older adults living with arthritis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether change in physical function with participation in Gerofit for 3 months varies by arthritis status, including no arthritis, any arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both upper and lower body arthritis compared with no arthritis.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of previously collected data from 10 VHA Gerofit sites (Ann Arbor, Baltimore, Greater Los Angeles, Canandaigua, Cincinnati, Miami, Honolulu, Denver, Durham, and Pittsburgh) from 2002 to 2019. Implementation data regarding the consistency of the program delivery at Gerofit expansion sites have been previously published.16 Although the delivery of Gerofit transitioned to telehealth due to COVID-19, data for this analysis were collected from in-person exercise sessions prior to the pandemic.17 Data were collected for clinical purposes. This project was part of the Gerofit quality improvement initiative and was reviewed and approved by the Durham Institutional Review Board as quality improvement.
Participants in Gerofit who completed baseline and 3-month assessments were included to analyze the effects of exercise on physical function. At each of the time points, physical functional assessments included: (1) usual gait speed (> 10 meters [m/s], or 10- meter walk test [10MWT]); (2) lower body strength (chair stands [number completed in 30 seconds]); (3) upper body strength (number of arm curls [5-lb for females/8-lb for males] completed in 30 seconds); and (4) 6-minute walk distance [6MWD] in meters to measure aerobic endurance). These measures have been validated in older adults.18-21 Arm curls were added to the physical function assessments after the 10MWT, chair stands, and 6MWD; therefore, fewer participants had data for this measure. Participants self-reported at baseline on 45 common medical conditions, including arthritis or rheumatism (both upper body and lower body were offered as choices). Self-reporting has been shown to be an acceptable method of identifying arthritis in adults.22
Descriptive statistics at baseline were calculated for all participants. One-way analysis of variance and X2 tests were used to determine differences in baseline characteristics across arthritis status. The primary outcomes were changes in physical function measures from baseline to 3 months by arthritis status. Arthritis status was defined as: any arthritis, which includes individuals who reported upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both; and arthritis status individuals reporting either upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both. Categories of arthritis for arthritis status were mutually exclusive. Two separate linear models were constructed for each of the 4 physical function measures, with change from baseline to 3 months as the outcome (dependent variable) and arthritis status, age, and body mass index (BMI) as predictors (independent variables). The first model compared any arthritis with no arthritis and the second model compared arthritis status (both upper and lower body arthritis vs lower body arthritis) with no arthritis. These models were used to obtain mean changes and 95% CIs in physical function and to test for differences in the change in physical function measures by arthritis status. Statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.0.3.
Results
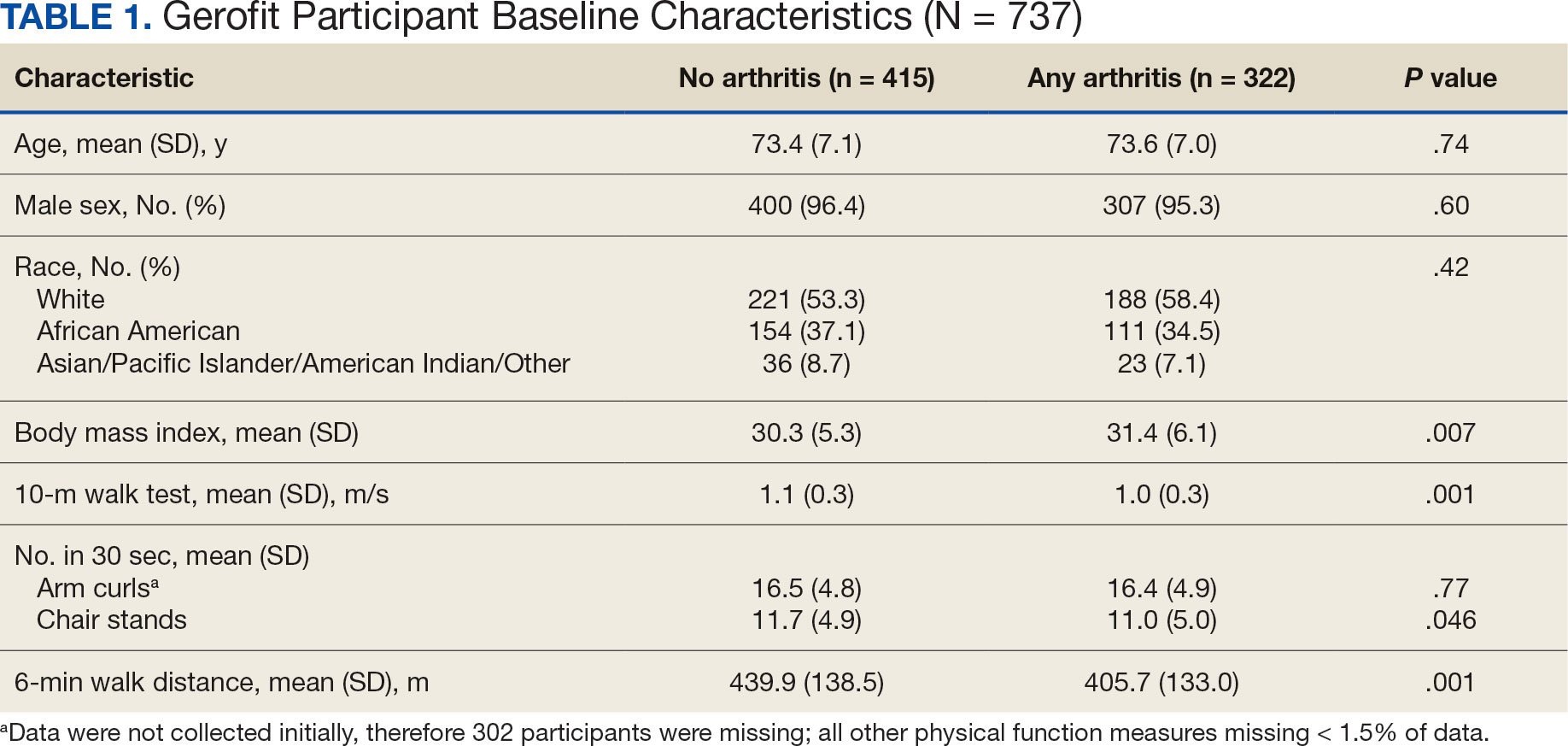
Baseline and 3-month data were available for 737 Gerofit participants and included in the analysis. The mean (SD) age was 73.5 (7.1) years. A total of 707 participants were male (95.9%) and 322 (43.6%) reported some arthritis, with arthritis in both the upper and lower body being reported by 168 participants (52.2%) (Table 1). There were no differences in age, sex, or race for those with any arthritis compared with those with no arthritis, but BMI was significantly higher in those reporting any arthritis compared with no arthritis. For the baseline functional measures, statistically significant differences were observed between those with no arthritis and those reporting any arthritis for the 10MWT (P = .001), chair stands (P = .046), and 6MWD (P = .001), but not for arm curls (P = .77), with those with no arthritis performing better.
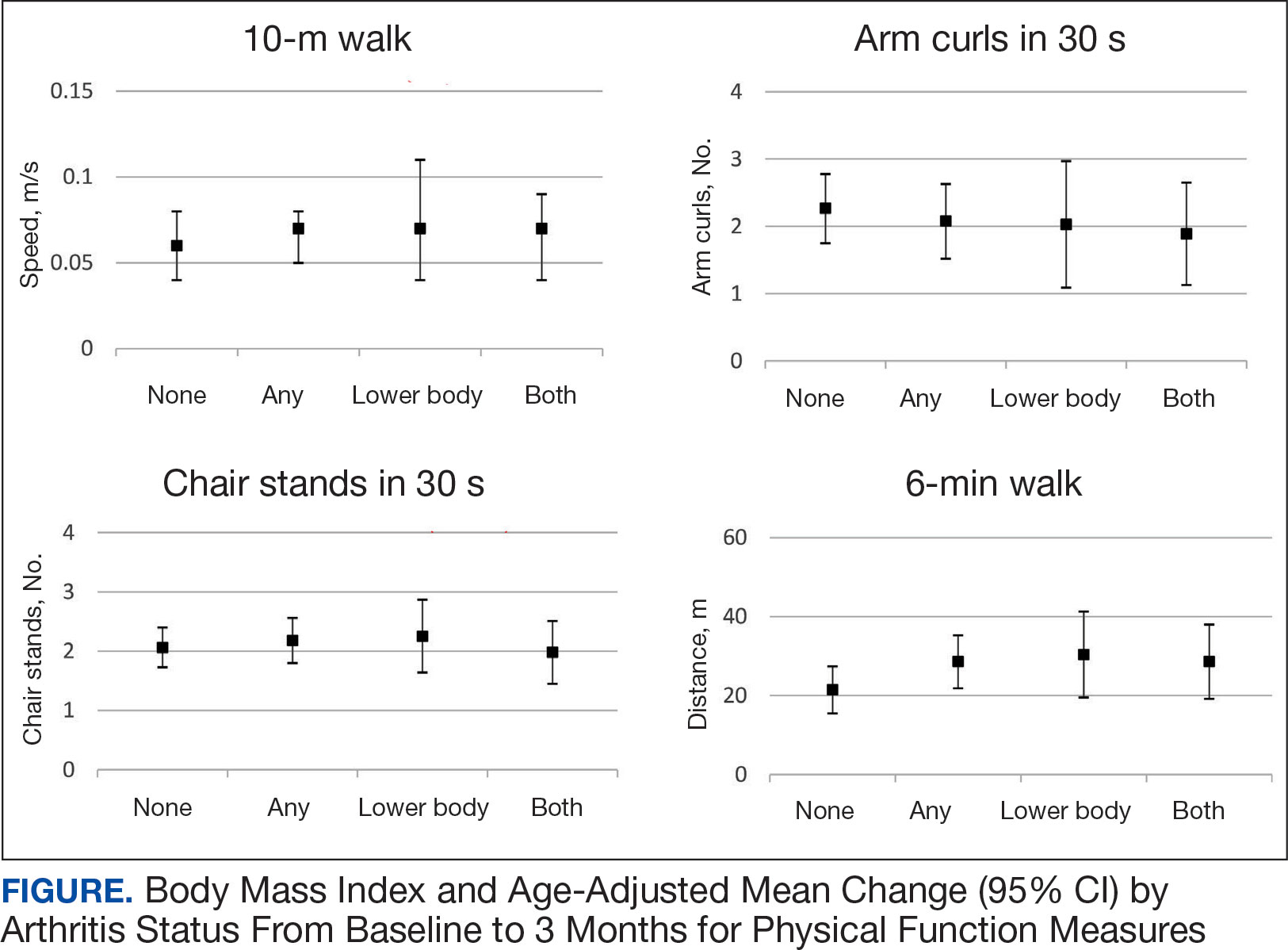
All 4 arthritis status groups showed improvements in each of the physical function measures over 3 months. For the 10MWT the mean change (95% CI) in gait speed (m/s) was 0.06 (0.04-0.08) for patients with no arthritis, 0.07 (0.05- 0.08) for any arthritis, 0.07 (0.04-0.11) for lower body arthritis, and 0.07 (0.04- 0.09) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of arm curls in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.3 (1.8-2.8) for patients with no arthritis, 2.1 (1.5-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.0 (1.1-3.0) for lower body arthritis, and 1.9 (1.1-2.7) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of chair stands in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.1 (1.7-2.4) for patients with no arthritis, 2.2 (1.8-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.3 (1.6-2.9), for lower body arthritis, and 2.0 (1.5-2.5) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the 6MWD distance in meters the mean change (95% CI) was 21.5 (15.5-27.4) for patients with no arthritis, 28.6 (21.9-35.3) for any arthritis, 30.4 (19.5-41.3) for lower body arthritis, and 28.6 (19.2-38.0) for both lower and upper body arthritis (Figure).
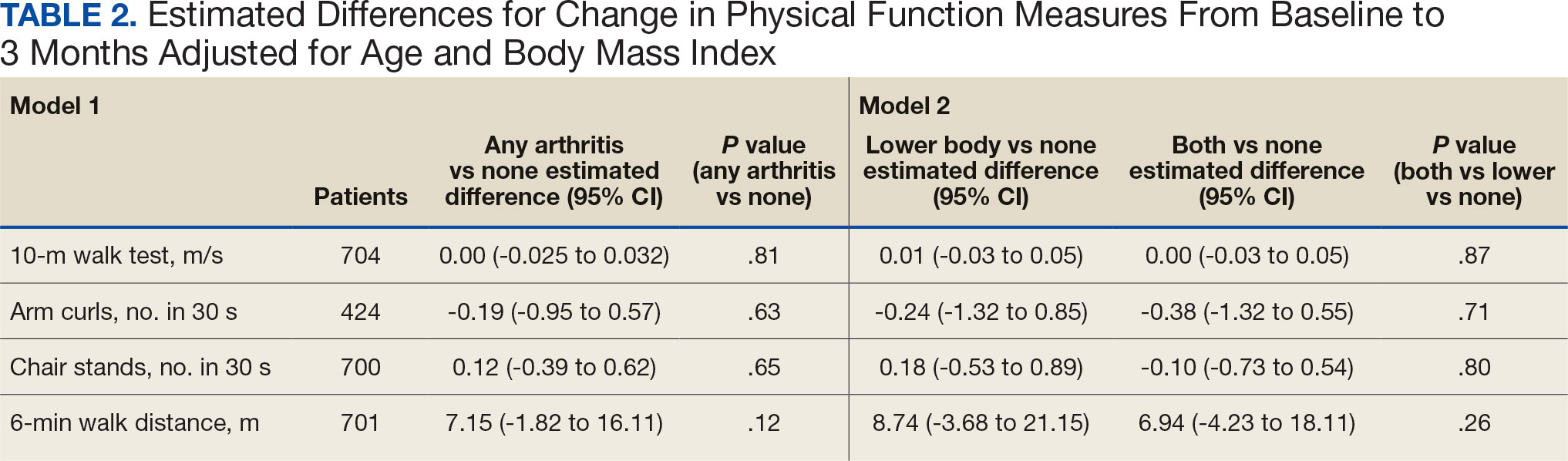
We used 2 models to measure the change from baseline to 3 months for each of the arthritis groups. Model 1 compared any arthritis vs no arthritis and model 2 compared lower body arthritis and both upper and lower body arthritis vs no arthritis for each physical function measure (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-month change in physical function for any of the physical function measures between arthritis groups after adjusting for age and BMI.
Discussion
Participation in Gerofit was associated with functional gains among all participants over 3 months, regardless of arthritis status. Older veterans reporting any arthritis had significantly lower physical function scores upon enrollment into Gerofit compared with those veterans reporting no arthritis. However, compared with individuals who reported no arthritis, individuals who reported arthritis (any arthritis, lower body arthritis only, or both lower and upper body arthritis) experienced similar improvements (ie, no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline to follow-up among those with and without arthritis). This study suggests that progressive, multicomponent exercise programs for older adults may be beneficial for those with arthritis.
Involvement of multiple sites of arthritis is associated with moderate to severe functional limitations as well as lower healthrelated quality of life.23 While it has been found that individuals with arthritis can improve function with supervised exercise, even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis, it was not clear whether individuals with multiple joint involvement also would benefit.12 The results of this study suggest that these individuals can improve across various domains of physical function despite variation in arthritis location and status. As incidence of arthritis increases with age, targeting older adults for exercise programs such as Gerofit may improve functional limitations and health-related quality of life associated with arthritis.2
We evaluated physical function using multiple measures to assess upper (arm curls) and lower (chair stands, 10MWT) extremity physical function and aerobic endurance (6MWD). Participants in this study reached clinically meaningful changes with 3 months of participation in Gerofit for most of the physical function measures. Gerofit participants had a mean gait speed improvement of 0.05 to 0.07 m/s compared with 0.10 to 0.30 m/s, which was reported previously. 24,25 In this study, nearly all groups achieved the clinically important improvements in the chair stand in 30 seconds (2.0 to 2.6) and the 6MWD (21.8 to 59.1 m) that have been reported in the literature.24-26
The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends the chair stand and 6MWD performance-based tests for individuals with hip and knee arthritis because they align with patient-reported outcomes and represent the types of activities relevant to this population.27 The findings of this study suggest that improvement in these physical function measures with participation in exercise align with data from arthritis-specific exercise programs designed for wide implementation. Hughes and colleagues reported improvements in the 6MWD after the 8-week Fit and Strong exercise intervention, which included walking and lower body resistance training.28 The Arthritis Foundation’s Walk With Ease program is a 6-week walking program that has shown improvements in chair stands and gait speed.29 Another Arthritis Foundation program, People with Arthritis Can Exercise, is an 8-week course consisting of a variety of resistance, aerobic, and balance activities. This program has been associated with increases in chair stands but not gait speed or 6MWD.30,31
This study found that participation in a VHA outpatient clinical supervised exercise program results in improvements in physical function that can be realized by older adults regardless of arthritis burden. Gerofit programs typically require 1.5 to 2.0 dedicated full-time equivalent employees to run the program effectively and additional administrative support, depending on size of the program.32 The cost savings generated by the program include reductions in hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, days in hospital, and medication use and provide a compelling argument for the program’s financial viability to health care systems through long-term savings and improved health outcomes for older adults.33-36
While evidenced-based arthritis programs exist, this study illustrates that an exercise program without a focus on arthritis also improves physical function, potentially reducing the risk of disability related to arthritis. The clinical implication for these findings is that arthritis-specific exercise programs may not be needed to achieve functional improvements in individuals with arthritis. This is critical for under-resourced or exercise- limited health care systems or communities. Therefore, if exercise programming is limited, or arthritis-specific programs and interventions are not available, nonspecific exercise programs will also be beneficial to individuals with arthritis. Thus, individuals with arthritis should be encouraged to participate in any available exercise programming to achieve improvements in physical function. In addition, many older adults have multiple comorbidities, most of which improve with participation in exercise. 37 Disease-specific exercise programs can offer tailored exercises and coaching related to common barriers in participation, such as joint pain for arthritis.31 It is unclear whether these additional programmatic components are associated with greater improvements in outcomes, such as physical function. More research is needed to explore the benefits of disease-specific tailored exercise programs compared with general exercise programs.
Strengths and Limitations
This study demonstrated the effect of participation in a clinical, supervised exercise program in a real-world setting. It suggests that even exercise programs not specifically targeted for arthritis populations can improve physical function among those with arthritis.
As a VHA clinical supervised exercise program, Gerofit may not be generalizable to all older adults or other exercise programs. In addition, this analysis only included a veteran population that was > 95% male and may not be generalizable to other populations. Arthritis status was defined by self-report and not verified in the health record. However, this approach has been shown to be acceptable in this setting and the most common type of arthritis in this population (OA) is a painful musculoskeletal condition associated with functional limitations.4,22,38,39 Self-reported arthritis or rheumatism is associated with functional limitations.1 Therefore, it is unlikely that the results would differ for physician-diagnosed or radiographically defined OA. Additionally, the study did not have data on the total number of joints with arthritis or arthritis severity but rather used upper body, lower body, and both upper and lower body arthritis as a proxy for arthritis status. While our models were adjusted for age and BMI, 2 known confounding factors for the association between arthritis and physical function, there are other potential confounding factors that were not included in the models. 40,41 Finally, this study only included individuals with completed baseline and 3-month follow-up assessments, and the individuals who participated for longer or shorter periods may have had different physical function outcomes than individuals included in this study.
Conclusions
Participation in 3 months VHA Gerofit outpatient supervised exercise programs can improve physical function for all older adults, regardless of arthritis status. These programs may increase access to exercise programming that is beneficial for common conditions affecting older adults, such as arthritis.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults- -United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421-426.
- Theis KA, Murphy LB, Guglielmo D, et al. Prevalence of arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1401-1407. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7040a2
- Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Allen KD, et al. Arthritis among veterans—United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:999-1003.
- Park J, Mendy A, Vieira ER. Various types of arthritis in the United States: prevalence and age-related trends from 1999 to 2014. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:256-258.
- Cameron KL, Hsiao MS, Owens BD, Burks R, Svoboda SJ. Incidence of physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis among active duty United States military service members. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2974-2982. doi:10.1002/art.30498
- Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(suppl 1):S23-S30. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-08-S23
- Rivera JC, Amuan ME, Morris RM, Johnson AE, Pugh MJ. Arthritis, comorbidities, and care utilization in veterans of Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:682-687. doi:10.1002/jor.23323
- Singh JA, Nelson DB, Fink HA, Nichol KL. Health-related quality of life predicts future health care utilization and mortality in veterans with self-reported physician-diagnosed arthritis: the Veterans Arthritis Quality of Life Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34:755- 765. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.08.001
- Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.11.012
- Morey MC, Crowley GM, Robbins MS, Cowper PA, Sullivan RJ Jr. The Gerofit Program: a VA innovation. South Med J. 1994;87:S83-S87.
- Chen MJ, Fan X, Moe ST. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:873-899. doi:10.1080/026404102320761787
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Sullivan RJ Jr, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, Robbins MS. Five-year performance trends for older exercisers: a hierarchical model of endurance, strength, and flexibility. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:1226-1231. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01374.x
- Allen KD, Gol ight ly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:276-283. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000161
- den Ouden MEM, Schuurmans MJ, Arts IEMA, van der Schouw YT. Association between physical performance characteristics and independence in activities of daily living in middle-aged and elderly men. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:274-280. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00890.x
- Daly M, Vidt ME, Eggebeen JD, et al. Upper extremity muscle volumes and functional strength after resistance training in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2013;21:186-207. doi:10.1123/japa.21.2.186
- Morey MC, Lee CC, Castle S, et al. Should structured exercise be promoted as a model of care? Dissemination of the Department of Veterans Affairs Gerofit Program. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66:1009-1016. doi:10.1111/jgs.15276
- Jennings SC, Manning KM, Bettger JP, et al. Rapid transition to telehealth group exercise and functional assessments in response to COVID-19. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420980313. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420980313
- Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:314-322. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51104.x
- Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70:113- 119. doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
- Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 1999;7:129-161. doi:10.1123/japa.7.2.129
- Harada ND, Chiu V, Stewart AL. Mobility-related function in older adults: assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:837-841. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
- Peeters GGME, Alshurafa M, Schaap L, de Vet HCW. Diagnostic accuracy of self-reported arthritis in the general adult population is acceptable. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.09.019
- Cuperus N, Vliet Vlieland TPM, Mahler EAM, Kersten CC, Hoogeboom TJ, van den Ende CHM. The clinical burden of generalized osteoarthritis represented by self-reported health-related quality of life and activity limitations: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:871-877. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3149-1
- Coleman G, Dobson F, Hinman RS, Bennell K, White DK. Measures of physical performance. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(suppl 10):452-485. doi:10.1002/acr.24373
- Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:743-749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
- Wright AA, Cook CE, Baxter GD, Dockerty JD, Abbott JH. A comparison of 3 methodological approaches to defining major clinically important improvement of 4 performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41:319-327. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3515
- Dobson F, Hinman R, Roos EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1042- 1052. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002
- Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell R, Pollak N, Huber G, Sharma L. Impact of the fit and strong intervention on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist. 2004;44:217-228. doi:10.1093/geront/44.2.217
- Callahan LF, Shreffler JH, Altpeter M, et al. Evaluation of group and self-directed formats of the Arthritis Foundation's Walk With Ease Program. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:1098-1107. doi:10.1002/acr.20490
- Boutaugh ML. Arthritis Foundation community-based physical activity programs: effectiveness and implementation issues. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:463-470. doi:10.1002/art.11050
- Callahan LF, Mielenz T, Freburger J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the People with Arthritis Can Exercise Program: symptoms, function, physical activity, and psychosocial outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:92-101. doi:10.1002/art.23239
- Hall KS, Jennings SC, Pearson MP. Outpatient care models: the Gerofit model of care for exercise promotion in older adults. In: Malone ML, Boltz M, Macias Tejada J, White H, eds. Geriatrics Models of Care. Springer; 2024:205-213. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-56204-4_21
- Pepin MJ, Valencia WM, Bettger JP, et al. Impact of supervised exercise on one-year medication use in older veterans with multiple morbidities. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420956751. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420956751
- Abbate L, Li J, Veazie P, et al. Does Gerofit exercise reduce veterans’ use of emergency department and inpatient care? Innov Aging. 2020;4(suppl 1):771. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2786
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Crowley GM, Sullivan RJ Jr, Puglisi CM. Exercise adherence and 10-year mortality in chronically ill older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1929-1933. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50602.x
- Manning KM, Hall KS, Sloane R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: the effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell. 2024;23:e13987. doi:10.1111/acel.13987
- Bean JF, Vora A, Frontera WR. Benefits of exercise for community-dwelling older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7 suppl 3):S31-S42; quiz S3-S4. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.010
- Covinsky KE, Lindquist K, Dunlop DD, Yelin E. Pain, functional limitations, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:1556-1561. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02388.x
- Katz JN, Wright EA, Baron JA, Losina E. Development and validation of an index of musculoskeletal functional limitations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:62. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-10-62
- Allen KD, Thoma LM, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:184-195. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.020
- Riebe D, Blissmer BJ, Greaney ML, Ewing Garber C, Lees FD, Clark PG. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J Aging Health. 2009;21:1159-1178. doi:10.1177/0898264309350076
About half of US adults aged ≥ 65 years report arthritis, and of those, 44% have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation.1,2 Arthritis is a significant health issue for veterans, with veterans reporting higher rates of disability compared with the civilian population.3
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis.4 Among individuals aged ≥ 40 years, the incidence of OA is nearly twice as high among veterans compared with civilians and is a leading cause of separation from military service and disability.5,6 OA pain and disability have been shown to be associated with increases in health care and medication use, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and muscle relaxants.7,8 Because OA is chronic and has no cure, safe and effective management strategies—such as exercise— are critical to minimize pain and maintain physical function.9
Exercise can reduce pain and disability associated with OA and is a first-line recommendation in guidelines for the treatment of knee and hip OA.9 Given the limited exercise and high levels of physical inactivity among veterans with OA, there is a need to identify opportunities that support veterans with OA engaging in regular exercise.
Gerofit, an outpatient clinical exercise program available at 30 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) sites, may provide an opportunity for older veterans with arthritis to engage in exercise.10 Gerofit is specifically designed for veterans aged ≥ 65 years. It is not disease-specific and supports older veterans with multiple chronic conditions, including OA. Veterans aged ≥ 65 years with a referral from a VA clinician are eligible for Gerofit. Those who are unable to perform activities of daily living; unable to independently function without assistance; have a history of unstable angina, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, oxygen dependence, volatile behavioral issues, or are unable to work successfully in a group environment/setting; experience active substance abuse, homelessness, or uncontrolled incontinence; and have open wounds that cannot be appropriately dressed are excluded from Gerofit. Exercise sessions are held 3 times per week and last from 60 to 90 minutes. Sessions are supervised by Gerofit staff and include personalized exercise prescriptions based on functional assessments. Exercise prescriptions include aerobic, resistance, and balance/flexibility components and are modified by the Gerofit program staff as needed. Gerofit adopts a functional fitness approach and includes individual progression as appropriate according to evidence-based guidelines, using the Borg ratings of perceived exertion. 11 Assessments are performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter. Clinical staff conduct all assessments, including physical function testing, and record them in a database. Assessments are reviewed with the veteran to chart progress and identify future goals or needs. Veterans perform personalized self-paced exercises in the Gerofit group setting. Exercise prescriptions are continuously modified to meet individualized needs and goals. Veterans may participate continuously with no end date.
Participation in supervised exercise is associated with improved physical function and individuals with arthritis can improve function even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis. 12 In this analysis, we examine the impact of exercise on the status and location of arthritis (upper body, lower body, or both). Lower body arthritis is more common than upper body arthritis and lower extremity function is associated with increased ability to perform activities of daily living, resulting in independence among older adults.13,14 We also include upper body strength measures to capture important functional movements such as reaching and pulling.15 Among those who participate in Gerofit, the greatest gains in physical function occur during the initial 3 months, which tend to be sustained over 12 months.16 For this reason, this study focused on the initial 3 months of the program.
Older adults with arthritis may have pain and functional limitations that exceed those of the general older adult population. Exercise programs for older adults that do not specifically target arthritis but are able to improve physical function among those with arthritis could potentially increase access to exercise for older adults living with arthritis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether change in physical function with participation in Gerofit for 3 months varies by arthritis status, including no arthritis, any arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both upper and lower body arthritis compared with no arthritis.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of previously collected data from 10 VHA Gerofit sites (Ann Arbor, Baltimore, Greater Los Angeles, Canandaigua, Cincinnati, Miami, Honolulu, Denver, Durham, and Pittsburgh) from 2002 to 2019. Implementation data regarding the consistency of the program delivery at Gerofit expansion sites have been previously published.16 Although the delivery of Gerofit transitioned to telehealth due to COVID-19, data for this analysis were collected from in-person exercise sessions prior to the pandemic.17 Data were collected for clinical purposes. This project was part of the Gerofit quality improvement initiative and was reviewed and approved by the Durham Institutional Review Board as quality improvement.
Participants in Gerofit who completed baseline and 3-month assessments were included to analyze the effects of exercise on physical function. At each of the time points, physical functional assessments included: (1) usual gait speed (> 10 meters [m/s], or 10- meter walk test [10MWT]); (2) lower body strength (chair stands [number completed in 30 seconds]); (3) upper body strength (number of arm curls [5-lb for females/8-lb for males] completed in 30 seconds); and (4) 6-minute walk distance [6MWD] in meters to measure aerobic endurance). These measures have been validated in older adults.18-21 Arm curls were added to the physical function assessments after the 10MWT, chair stands, and 6MWD; therefore, fewer participants had data for this measure. Participants self-reported at baseline on 45 common medical conditions, including arthritis or rheumatism (both upper body and lower body were offered as choices). Self-reporting has been shown to be an acceptable method of identifying arthritis in adults.22
Descriptive statistics at baseline were calculated for all participants. One-way analysis of variance and X2 tests were used to determine differences in baseline characteristics across arthritis status. The primary outcomes were changes in physical function measures from baseline to 3 months by arthritis status. Arthritis status was defined as: any arthritis, which includes individuals who reported upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both; and arthritis status individuals reporting either upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both. Categories of arthritis for arthritis status were mutually exclusive. Two separate linear models were constructed for each of the 4 physical function measures, with change from baseline to 3 months as the outcome (dependent variable) and arthritis status, age, and body mass index (BMI) as predictors (independent variables). The first model compared any arthritis with no arthritis and the second model compared arthritis status (both upper and lower body arthritis vs lower body arthritis) with no arthritis. These models were used to obtain mean changes and 95% CIs in physical function and to test for differences in the change in physical function measures by arthritis status. Statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.0.3.
Results
Baseline and 3-month data were available for 737 Gerofit participants and included in the analysis. The mean (SD) age was 73.5 (7.1) years. A total of 707 participants were male (95.9%) and 322 (43.6%) reported some arthritis, with arthritis in both the upper and lower body being reported by 168 participants (52.2%) (Table 1). There were no differences in age, sex, or race for those with any arthritis compared with those with no arthritis, but BMI was significantly higher in those reporting any arthritis compared with no arthritis. For the baseline functional measures, statistically significant differences were observed between those with no arthritis and those reporting any arthritis for the 10MWT (P = .001), chair stands (P = .046), and 6MWD (P = .001), but not for arm curls (P = .77), with those with no arthritis performing better.

All 4 arthritis status groups showed improvements in each of the physical function measures over 3 months. For the 10MWT the mean change (95% CI) in gait speed (m/s) was 0.06 (0.04-0.08) for patients with no arthritis, 0.07 (0.05- 0.08) for any arthritis, 0.07 (0.04-0.11) for lower body arthritis, and 0.07 (0.04- 0.09) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of arm curls in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.3 (1.8-2.8) for patients with no arthritis, 2.1 (1.5-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.0 (1.1-3.0) for lower body arthritis, and 1.9 (1.1-2.7) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of chair stands in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.1 (1.7-2.4) for patients with no arthritis, 2.2 (1.8-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.3 (1.6-2.9), for lower body arthritis, and 2.0 (1.5-2.5) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the 6MWD distance in meters the mean change (95% CI) was 21.5 (15.5-27.4) for patients with no arthritis, 28.6 (21.9-35.3) for any arthritis, 30.4 (19.5-41.3) for lower body arthritis, and 28.6 (19.2-38.0) for both lower and upper body arthritis (Figure).

We used 2 models to measure the change from baseline to 3 months for each of the arthritis groups. Model 1 compared any arthritis vs no arthritis and model 2 compared lower body arthritis and both upper and lower body arthritis vs no arthritis for each physical function measure (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-month change in physical function for any of the physical function measures between arthritis groups after adjusting for age and BMI.

Discussion
Participation in Gerofit was associated with functional gains among all participants over 3 months, regardless of arthritis status. Older veterans reporting any arthritis had significantly lower physical function scores upon enrollment into Gerofit compared with those veterans reporting no arthritis. However, compared with individuals who reported no arthritis, individuals who reported arthritis (any arthritis, lower body arthritis only, or both lower and upper body arthritis) experienced similar improvements (ie, no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline to follow-up among those with and without arthritis). This study suggests that progressive, multicomponent exercise programs for older adults may be beneficial for those with arthritis.
Involvement of multiple sites of arthritis is associated with moderate to severe functional limitations as well as lower healthrelated quality of life.23 While it has been found that individuals with arthritis can improve function with supervised exercise, even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis, it was not clear whether individuals with multiple joint involvement also would benefit.12 The results of this study suggest that these individuals can improve across various domains of physical function despite variation in arthritis location and status. As incidence of arthritis increases with age, targeting older adults for exercise programs such as Gerofit may improve functional limitations and health-related quality of life associated with arthritis.2
We evaluated physical function using multiple measures to assess upper (arm curls) and lower (chair stands, 10MWT) extremity physical function and aerobic endurance (6MWD). Participants in this study reached clinically meaningful changes with 3 months of participation in Gerofit for most of the physical function measures. Gerofit participants had a mean gait speed improvement of 0.05 to 0.07 m/s compared with 0.10 to 0.30 m/s, which was reported previously. 24,25 In this study, nearly all groups achieved the clinically important improvements in the chair stand in 30 seconds (2.0 to 2.6) and the 6MWD (21.8 to 59.1 m) that have been reported in the literature.24-26
The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends the chair stand and 6MWD performance-based tests for individuals with hip and knee arthritis because they align with patient-reported outcomes and represent the types of activities relevant to this population.27 The findings of this study suggest that improvement in these physical function measures with participation in exercise align with data from arthritis-specific exercise programs designed for wide implementation. Hughes and colleagues reported improvements in the 6MWD after the 8-week Fit and Strong exercise intervention, which included walking and lower body resistance training.28 The Arthritis Foundation’s Walk With Ease program is a 6-week walking program that has shown improvements in chair stands and gait speed.29 Another Arthritis Foundation program, People with Arthritis Can Exercise, is an 8-week course consisting of a variety of resistance, aerobic, and balance activities. This program has been associated with increases in chair stands but not gait speed or 6MWD.30,31
This study found that participation in a VHA outpatient clinical supervised exercise program results in improvements in physical function that can be realized by older adults regardless of arthritis burden. Gerofit programs typically require 1.5 to 2.0 dedicated full-time equivalent employees to run the program effectively and additional administrative support, depending on size of the program.32 The cost savings generated by the program include reductions in hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, days in hospital, and medication use and provide a compelling argument for the program’s financial viability to health care systems through long-term savings and improved health outcomes for older adults.33-36
While evidenced-based arthritis programs exist, this study illustrates that an exercise program without a focus on arthritis also improves physical function, potentially reducing the risk of disability related to arthritis. The clinical implication for these findings is that arthritis-specific exercise programs may not be needed to achieve functional improvements in individuals with arthritis. This is critical for under-resourced or exercise- limited health care systems or communities. Therefore, if exercise programming is limited, or arthritis-specific programs and interventions are not available, nonspecific exercise programs will also be beneficial to individuals with arthritis. Thus, individuals with arthritis should be encouraged to participate in any available exercise programming to achieve improvements in physical function. In addition, many older adults have multiple comorbidities, most of which improve with participation in exercise. 37 Disease-specific exercise programs can offer tailored exercises and coaching related to common barriers in participation, such as joint pain for arthritis.31 It is unclear whether these additional programmatic components are associated with greater improvements in outcomes, such as physical function. More research is needed to explore the benefits of disease-specific tailored exercise programs compared with general exercise programs.
Strengths and Limitations
This study demonstrated the effect of participation in a clinical, supervised exercise program in a real-world setting. It suggests that even exercise programs not specifically targeted for arthritis populations can improve physical function among those with arthritis.
As a VHA clinical supervised exercise program, Gerofit may not be generalizable to all older adults or other exercise programs. In addition, this analysis only included a veteran population that was > 95% male and may not be generalizable to other populations. Arthritis status was defined by self-report and not verified in the health record. However, this approach has been shown to be acceptable in this setting and the most common type of arthritis in this population (OA) is a painful musculoskeletal condition associated with functional limitations.4,22,38,39 Self-reported arthritis or rheumatism is associated with functional limitations.1 Therefore, it is unlikely that the results would differ for physician-diagnosed or radiographically defined OA. Additionally, the study did not have data on the total number of joints with arthritis or arthritis severity but rather used upper body, lower body, and both upper and lower body arthritis as a proxy for arthritis status. While our models were adjusted for age and BMI, 2 known confounding factors for the association between arthritis and physical function, there are other potential confounding factors that were not included in the models. 40,41 Finally, this study only included individuals with completed baseline and 3-month follow-up assessments, and the individuals who participated for longer or shorter periods may have had different physical function outcomes than individuals included in this study.
Conclusions
Participation in 3 months VHA Gerofit outpatient supervised exercise programs can improve physical function for all older adults, regardless of arthritis status. These programs may increase access to exercise programming that is beneficial for common conditions affecting older adults, such as arthritis.
About half of US adults aged ≥ 65 years report arthritis, and of those, 44% have an arthritis-attributable activity limitation.1,2 Arthritis is a significant health issue for veterans, with veterans reporting higher rates of disability compared with the civilian population.3
Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common type of arthritis.4 Among individuals aged ≥ 40 years, the incidence of OA is nearly twice as high among veterans compared with civilians and is a leading cause of separation from military service and disability.5,6 OA pain and disability have been shown to be associated with increases in health care and medication use, including opioids, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory medications, and muscle relaxants.7,8 Because OA is chronic and has no cure, safe and effective management strategies—such as exercise— are critical to minimize pain and maintain physical function.9
Exercise can reduce pain and disability associated with OA and is a first-line recommendation in guidelines for the treatment of knee and hip OA.9 Given the limited exercise and high levels of physical inactivity among veterans with OA, there is a need to identify opportunities that support veterans with OA engaging in regular exercise.
Gerofit, an outpatient clinical exercise program available at 30 Veterans Health Administration (VHA) sites, may provide an opportunity for older veterans with arthritis to engage in exercise.10 Gerofit is specifically designed for veterans aged ≥ 65 years. It is not disease-specific and supports older veterans with multiple chronic conditions, including OA. Veterans aged ≥ 65 years with a referral from a VA clinician are eligible for Gerofit. Those who are unable to perform activities of daily living; unable to independently function without assistance; have a history of unstable angina, proliferative diabetic retinopathy, oxygen dependence, volatile behavioral issues, or are unable to work successfully in a group environment/setting; experience active substance abuse, homelessness, or uncontrolled incontinence; and have open wounds that cannot be appropriately dressed are excluded from Gerofit. Exercise sessions are held 3 times per week and last from 60 to 90 minutes. Sessions are supervised by Gerofit staff and include personalized exercise prescriptions based on functional assessments. Exercise prescriptions include aerobic, resistance, and balance/flexibility components and are modified by the Gerofit program staff as needed. Gerofit adopts a functional fitness approach and includes individual progression as appropriate according to evidence-based guidelines, using the Borg ratings of perceived exertion. 11 Assessments are performed at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, and annually thereafter. Clinical staff conduct all assessments, including physical function testing, and record them in a database. Assessments are reviewed with the veteran to chart progress and identify future goals or needs. Veterans perform personalized self-paced exercises in the Gerofit group setting. Exercise prescriptions are continuously modified to meet individualized needs and goals. Veterans may participate continuously with no end date.
Participation in supervised exercise is associated with improved physical function and individuals with arthritis can improve function even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis. 12 In this analysis, we examine the impact of exercise on the status and location of arthritis (upper body, lower body, or both). Lower body arthritis is more common than upper body arthritis and lower extremity function is associated with increased ability to perform activities of daily living, resulting in independence among older adults.13,14 We also include upper body strength measures to capture important functional movements such as reaching and pulling.15 Among those who participate in Gerofit, the greatest gains in physical function occur during the initial 3 months, which tend to be sustained over 12 months.16 For this reason, this study focused on the initial 3 months of the program.
Older adults with arthritis may have pain and functional limitations that exceed those of the general older adult population. Exercise programs for older adults that do not specifically target arthritis but are able to improve physical function among those with arthritis could potentially increase access to exercise for older adults living with arthritis. Therefore, the purpose of this study was to determine whether change in physical function with participation in Gerofit for 3 months varies by arthritis status, including no arthritis, any arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both upper and lower body arthritis compared with no arthritis.
Methods
This is a secondary analysis of previously collected data from 10 VHA Gerofit sites (Ann Arbor, Baltimore, Greater Los Angeles, Canandaigua, Cincinnati, Miami, Honolulu, Denver, Durham, and Pittsburgh) from 2002 to 2019. Implementation data regarding the consistency of the program delivery at Gerofit expansion sites have been previously published.16 Although the delivery of Gerofit transitioned to telehealth due to COVID-19, data for this analysis were collected from in-person exercise sessions prior to the pandemic.17 Data were collected for clinical purposes. This project was part of the Gerofit quality improvement initiative and was reviewed and approved by the Durham Institutional Review Board as quality improvement.
Participants in Gerofit who completed baseline and 3-month assessments were included to analyze the effects of exercise on physical function. At each of the time points, physical functional assessments included: (1) usual gait speed (> 10 meters [m/s], or 10- meter walk test [10MWT]); (2) lower body strength (chair stands [number completed in 30 seconds]); (3) upper body strength (number of arm curls [5-lb for females/8-lb for males] completed in 30 seconds); and (4) 6-minute walk distance [6MWD] in meters to measure aerobic endurance). These measures have been validated in older adults.18-21 Arm curls were added to the physical function assessments after the 10MWT, chair stands, and 6MWD; therefore, fewer participants had data for this measure. Participants self-reported at baseline on 45 common medical conditions, including arthritis or rheumatism (both upper body and lower body were offered as choices). Self-reporting has been shown to be an acceptable method of identifying arthritis in adults.22
Descriptive statistics at baseline were calculated for all participants. One-way analysis of variance and X2 tests were used to determine differences in baseline characteristics across arthritis status. The primary outcomes were changes in physical function measures from baseline to 3 months by arthritis status. Arthritis status was defined as: any arthritis, which includes individuals who reported upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both; and arthritis status individuals reporting either upper body arthritis, lower body arthritis, or both. Categories of arthritis for arthritis status were mutually exclusive. Two separate linear models were constructed for each of the 4 physical function measures, with change from baseline to 3 months as the outcome (dependent variable) and arthritis status, age, and body mass index (BMI) as predictors (independent variables). The first model compared any arthritis with no arthritis and the second model compared arthritis status (both upper and lower body arthritis vs lower body arthritis) with no arthritis. These models were used to obtain mean changes and 95% CIs in physical function and to test for differences in the change in physical function measures by arthritis status. Statistical analyses were performed using R software, version 4.0.3.
Results
Baseline and 3-month data were available for 737 Gerofit participants and included in the analysis. The mean (SD) age was 73.5 (7.1) years. A total of 707 participants were male (95.9%) and 322 (43.6%) reported some arthritis, with arthritis in both the upper and lower body being reported by 168 participants (52.2%) (Table 1). There were no differences in age, sex, or race for those with any arthritis compared with those with no arthritis, but BMI was significantly higher in those reporting any arthritis compared with no arthritis. For the baseline functional measures, statistically significant differences were observed between those with no arthritis and those reporting any arthritis for the 10MWT (P = .001), chair stands (P = .046), and 6MWD (P = .001), but not for arm curls (P = .77), with those with no arthritis performing better.

All 4 arthritis status groups showed improvements in each of the physical function measures over 3 months. For the 10MWT the mean change (95% CI) in gait speed (m/s) was 0.06 (0.04-0.08) for patients with no arthritis, 0.07 (0.05- 0.08) for any arthritis, 0.07 (0.04-0.11) for lower body arthritis, and 0.07 (0.04- 0.09) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of arm curls in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.3 (1.8-2.8) for patients with no arthritis, 2.1 (1.5-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.0 (1.1-3.0) for lower body arthritis, and 1.9 (1.1-2.7) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the number of chair stands in 30 seconds the mean change (95% CI) was 2.1 (1.7-2.4) for patients with no arthritis, 2.2 (1.8-2.6) for any arthritis, 2.3 (1.6-2.9), for lower body arthritis, and 2.0 (1.5-2.5) for both lower and upper body arthritis. For the 6MWD distance in meters the mean change (95% CI) was 21.5 (15.5-27.4) for patients with no arthritis, 28.6 (21.9-35.3) for any arthritis, 30.4 (19.5-41.3) for lower body arthritis, and 28.6 (19.2-38.0) for both lower and upper body arthritis (Figure).

We used 2 models to measure the change from baseline to 3 months for each of the arthritis groups. Model 1 compared any arthritis vs no arthritis and model 2 compared lower body arthritis and both upper and lower body arthritis vs no arthritis for each physical function measure (Table 2). There were no statistically significant differences in 3-month change in physical function for any of the physical function measures between arthritis groups after adjusting for age and BMI.

Discussion
Participation in Gerofit was associated with functional gains among all participants over 3 months, regardless of arthritis status. Older veterans reporting any arthritis had significantly lower physical function scores upon enrollment into Gerofit compared with those veterans reporting no arthritis. However, compared with individuals who reported no arthritis, individuals who reported arthritis (any arthritis, lower body arthritis only, or both lower and upper body arthritis) experienced similar improvements (ie, no statistically significant differences in mean change from baseline to follow-up among those with and without arthritis). This study suggests that progressive, multicomponent exercise programs for older adults may be beneficial for those with arthritis.
Involvement of multiple sites of arthritis is associated with moderate to severe functional limitations as well as lower healthrelated quality of life.23 While it has been found that individuals with arthritis can improve function with supervised exercise, even though their baseline functional status is lower than individuals without arthritis, it was not clear whether individuals with multiple joint involvement also would benefit.12 The results of this study suggest that these individuals can improve across various domains of physical function despite variation in arthritis location and status. As incidence of arthritis increases with age, targeting older adults for exercise programs such as Gerofit may improve functional limitations and health-related quality of life associated with arthritis.2
We evaluated physical function using multiple measures to assess upper (arm curls) and lower (chair stands, 10MWT) extremity physical function and aerobic endurance (6MWD). Participants in this study reached clinically meaningful changes with 3 months of participation in Gerofit for most of the physical function measures. Gerofit participants had a mean gait speed improvement of 0.05 to 0.07 m/s compared with 0.10 to 0.30 m/s, which was reported previously. 24,25 In this study, nearly all groups achieved the clinically important improvements in the chair stand in 30 seconds (2.0 to 2.6) and the 6MWD (21.8 to 59.1 m) that have been reported in the literature.24-26
The Osteoarthritis Research Society International recommends the chair stand and 6MWD performance-based tests for individuals with hip and knee arthritis because they align with patient-reported outcomes and represent the types of activities relevant to this population.27 The findings of this study suggest that improvement in these physical function measures with participation in exercise align with data from arthritis-specific exercise programs designed for wide implementation. Hughes and colleagues reported improvements in the 6MWD after the 8-week Fit and Strong exercise intervention, which included walking and lower body resistance training.28 The Arthritis Foundation’s Walk With Ease program is a 6-week walking program that has shown improvements in chair stands and gait speed.29 Another Arthritis Foundation program, People with Arthritis Can Exercise, is an 8-week course consisting of a variety of resistance, aerobic, and balance activities. This program has been associated with increases in chair stands but not gait speed or 6MWD.30,31
This study found that participation in a VHA outpatient clinical supervised exercise program results in improvements in physical function that can be realized by older adults regardless of arthritis burden. Gerofit programs typically require 1.5 to 2.0 dedicated full-time equivalent employees to run the program effectively and additional administrative support, depending on size of the program.32 The cost savings generated by the program include reductions in hospitalization rates, emergency department visits, days in hospital, and medication use and provide a compelling argument for the program’s financial viability to health care systems through long-term savings and improved health outcomes for older adults.33-36
While evidenced-based arthritis programs exist, this study illustrates that an exercise program without a focus on arthritis also improves physical function, potentially reducing the risk of disability related to arthritis. The clinical implication for these findings is that arthritis-specific exercise programs may not be needed to achieve functional improvements in individuals with arthritis. This is critical for under-resourced or exercise- limited health care systems or communities. Therefore, if exercise programming is limited, or arthritis-specific programs and interventions are not available, nonspecific exercise programs will also be beneficial to individuals with arthritis. Thus, individuals with arthritis should be encouraged to participate in any available exercise programming to achieve improvements in physical function. In addition, many older adults have multiple comorbidities, most of which improve with participation in exercise. 37 Disease-specific exercise programs can offer tailored exercises and coaching related to common barriers in participation, such as joint pain for arthritis.31 It is unclear whether these additional programmatic components are associated with greater improvements in outcomes, such as physical function. More research is needed to explore the benefits of disease-specific tailored exercise programs compared with general exercise programs.
Strengths and Limitations
This study demonstrated the effect of participation in a clinical, supervised exercise program in a real-world setting. It suggests that even exercise programs not specifically targeted for arthritis populations can improve physical function among those with arthritis.
As a VHA clinical supervised exercise program, Gerofit may not be generalizable to all older adults or other exercise programs. In addition, this analysis only included a veteran population that was > 95% male and may not be generalizable to other populations. Arthritis status was defined by self-report and not verified in the health record. However, this approach has been shown to be acceptable in this setting and the most common type of arthritis in this population (OA) is a painful musculoskeletal condition associated with functional limitations.4,22,38,39 Self-reported arthritis or rheumatism is associated with functional limitations.1 Therefore, it is unlikely that the results would differ for physician-diagnosed or radiographically defined OA. Additionally, the study did not have data on the total number of joints with arthritis or arthritis severity but rather used upper body, lower body, and both upper and lower body arthritis as a proxy for arthritis status. While our models were adjusted for age and BMI, 2 known confounding factors for the association between arthritis and physical function, there are other potential confounding factors that were not included in the models. 40,41 Finally, this study only included individuals with completed baseline and 3-month follow-up assessments, and the individuals who participated for longer or shorter periods may have had different physical function outcomes than individuals included in this study.
Conclusions
Participation in 3 months VHA Gerofit outpatient supervised exercise programs can improve physical function for all older adults, regardless of arthritis status. These programs may increase access to exercise programming that is beneficial for common conditions affecting older adults, such as arthritis.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults- -United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421-426.
- Theis KA, Murphy LB, Guglielmo D, et al. Prevalence of arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1401-1407. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7040a2
- Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Allen KD, et al. Arthritis among veterans—United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:999-1003.
- Park J, Mendy A, Vieira ER. Various types of arthritis in the United States: prevalence and age-related trends from 1999 to 2014. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:256-258.
- Cameron KL, Hsiao MS, Owens BD, Burks R, Svoboda SJ. Incidence of physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis among active duty United States military service members. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2974-2982. doi:10.1002/art.30498
- Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(suppl 1):S23-S30. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-08-S23
- Rivera JC, Amuan ME, Morris RM, Johnson AE, Pugh MJ. Arthritis, comorbidities, and care utilization in veterans of Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:682-687. doi:10.1002/jor.23323
- Singh JA, Nelson DB, Fink HA, Nichol KL. Health-related quality of life predicts future health care utilization and mortality in veterans with self-reported physician-diagnosed arthritis: the Veterans Arthritis Quality of Life Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34:755- 765. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.08.001
- Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.11.012
- Morey MC, Crowley GM, Robbins MS, Cowper PA, Sullivan RJ Jr. The Gerofit Program: a VA innovation. South Med J. 1994;87:S83-S87.
- Chen MJ, Fan X, Moe ST. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:873-899. doi:10.1080/026404102320761787
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Sullivan RJ Jr, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, Robbins MS. Five-year performance trends for older exercisers: a hierarchical model of endurance, strength, and flexibility. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:1226-1231. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01374.x
- Allen KD, Gol ight ly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:276-283. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000161
- den Ouden MEM, Schuurmans MJ, Arts IEMA, van der Schouw YT. Association between physical performance characteristics and independence in activities of daily living in middle-aged and elderly men. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:274-280. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00890.x
- Daly M, Vidt ME, Eggebeen JD, et al. Upper extremity muscle volumes and functional strength after resistance training in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2013;21:186-207. doi:10.1123/japa.21.2.186
- Morey MC, Lee CC, Castle S, et al. Should structured exercise be promoted as a model of care? Dissemination of the Department of Veterans Affairs Gerofit Program. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66:1009-1016. doi:10.1111/jgs.15276
- Jennings SC, Manning KM, Bettger JP, et al. Rapid transition to telehealth group exercise and functional assessments in response to COVID-19. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420980313. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420980313
- Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:314-322. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51104.x
- Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70:113- 119. doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
- Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 1999;7:129-161. doi:10.1123/japa.7.2.129
- Harada ND, Chiu V, Stewart AL. Mobility-related function in older adults: assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:837-841. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
- Peeters GGME, Alshurafa M, Schaap L, de Vet HCW. Diagnostic accuracy of self-reported arthritis in the general adult population is acceptable. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.09.019
- Cuperus N, Vliet Vlieland TPM, Mahler EAM, Kersten CC, Hoogeboom TJ, van den Ende CHM. The clinical burden of generalized osteoarthritis represented by self-reported health-related quality of life and activity limitations: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:871-877. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3149-1
- Coleman G, Dobson F, Hinman RS, Bennell K, White DK. Measures of physical performance. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(suppl 10):452-485. doi:10.1002/acr.24373
- Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:743-749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
- Wright AA, Cook CE, Baxter GD, Dockerty JD, Abbott JH. A comparison of 3 methodological approaches to defining major clinically important improvement of 4 performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41:319-327. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3515
- Dobson F, Hinman R, Roos EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1042- 1052. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002
- Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell R, Pollak N, Huber G, Sharma L. Impact of the fit and strong intervention on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist. 2004;44:217-228. doi:10.1093/geront/44.2.217
- Callahan LF, Shreffler JH, Altpeter M, et al. Evaluation of group and self-directed formats of the Arthritis Foundation's Walk With Ease Program. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:1098-1107. doi:10.1002/acr.20490
- Boutaugh ML. Arthritis Foundation community-based physical activity programs: effectiveness and implementation issues. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:463-470. doi:10.1002/art.11050
- Callahan LF, Mielenz T, Freburger J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the People with Arthritis Can Exercise Program: symptoms, function, physical activity, and psychosocial outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:92-101. doi:10.1002/art.23239
- Hall KS, Jennings SC, Pearson MP. Outpatient care models: the Gerofit model of care for exercise promotion in older adults. In: Malone ML, Boltz M, Macias Tejada J, White H, eds. Geriatrics Models of Care. Springer; 2024:205-213. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-56204-4_21
- Pepin MJ, Valencia WM, Bettger JP, et al. Impact of supervised exercise on one-year medication use in older veterans with multiple morbidities. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420956751. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420956751
- Abbate L, Li J, Veazie P, et al. Does Gerofit exercise reduce veterans’ use of emergency department and inpatient care? Innov Aging. 2020;4(suppl 1):771. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2786
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Crowley GM, Sullivan RJ Jr, Puglisi CM. Exercise adherence and 10-year mortality in chronically ill older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1929-1933. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50602.x
- Manning KM, Hall KS, Sloane R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: the effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell. 2024;23:e13987. doi:10.1111/acel.13987
- Bean JF, Vora A, Frontera WR. Benefits of exercise for community-dwelling older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7 suppl 3):S31-S42; quiz S3-S4. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.010
- Covinsky KE, Lindquist K, Dunlop DD, Yelin E. Pain, functional limitations, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:1556-1561. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02388.x
- Katz JN, Wright EA, Baron JA, Losina E. Development and validation of an index of musculoskeletal functional limitations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:62. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-10-62
- Allen KD, Thoma LM, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:184-195. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.020
- Riebe D, Blissmer BJ, Greaney ML, Ewing Garber C, Lees FD, Clark PG. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J Aging Health. 2009;21:1159-1178. doi:10.1177/0898264309350076
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Prevalence and most common causes of disability among adults- -United States, 2005. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2009;58:421-426.
- Theis KA, Murphy LB, Guglielmo D, et al. Prevalence of arthritis and arthritis-attributable activity limitation—United States, 2016–2018. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2021;70:1401-1407. doi:10.15585/mmwr.mm7040a2
- Murphy LB, Helmick CG, Allen KD, et al. Arthritis among veterans—United States, 2011–2013. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2014;63:999-1003.
- Park J, Mendy A, Vieira ER. Various types of arthritis in the United States: prevalence and age-related trends from 1999 to 2014. Am J Public Health. 2018;108:256-258.
- Cameron KL, Hsiao MS, Owens BD, Burks R, Svoboda SJ. Incidence of physician-diagnosed osteoarthritis among active duty United States military service members. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:2974-2982. doi:10.1002/art.30498
- Patzkowski JC, Rivera JC, Ficke JR, Wenke JC. The changing face of disability in the US Army: the Operation Enduring Freedom and Operation Iraqi Freedom effect. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2012;20(suppl 1):S23-S30. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-20-08-S23
- Rivera JC, Amuan ME, Morris RM, Johnson AE, Pugh MJ. Arthritis, comorbidities, and care utilization in veterans of Operations Enduring and Iraqi Freedom. J Orthop Res. 2017;35:682-687. doi:10.1002/jor.23323
- Singh JA, Nelson DB, Fink HA, Nichol KL. Health-related quality of life predicts future health care utilization and mortality in veterans with self-reported physician-diagnosed arthritis: the Veterans Arthritis Quality of Life Study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005;34:755- 765. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2004.08.001
- Nelson AE, Allen KD, Golightly YM, Goode AP, Jordan JM. A systematic review of recommendations and guidelines for the management of osteoarthritis: the Chronic Osteoarthritis Management Initiative of the U.S. Bone and Joint Initiative. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2014;43:701-712. doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2013.11.012
- Morey MC, Crowley GM, Robbins MS, Cowper PA, Sullivan RJ Jr. The Gerofit Program: a VA innovation. South Med J. 1994;87:S83-S87.
- Chen MJ, Fan X, Moe ST. Criterion-related validity of the Borg ratings of perceived exertion scale in healthy individuals: a meta-analysis. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:873-899. doi:10.1080/026404102320761787
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Sullivan RJ Jr, Crowley GM, Cowper PA, Robbins MS. Five-year performance trends for older exercisers: a hierarchical model of endurance, strength, and flexibility. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1996;44:1226-1231. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.1996.tb01374.x
- Allen KD, Gol ight ly YM. State of the evidence. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2015;27:276-283. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000161
- den Ouden MEM, Schuurmans MJ, Arts IEMA, van der Schouw YT. Association between physical performance characteristics and independence in activities of daily living in middle-aged and elderly men. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2013;13:274-280. doi:10.1111/j.1447-0594.2012.00890.x
- Daly M, Vidt ME, Eggebeen JD, et al. Upper extremity muscle volumes and functional strength after resistance training in older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 2013;21:186-207. doi:10.1123/japa.21.2.186
- Morey MC, Lee CC, Castle S, et al. Should structured exercise be promoted as a model of care? Dissemination of the Department of Veterans Affairs Gerofit Program. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2018;66:1009-1016. doi:10.1111/jgs.15276
- Jennings SC, Manning KM, Bettger JP, et al. Rapid transition to telehealth group exercise and functional assessments in response to COVID-19. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420980313. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420980313
- Studenski S, Perera S, Wallace D, et al. Physical performance measures in the clinical setting. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2003;51:314-322. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51104.x
- Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC. A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community residing older adults. Res Q Exerc Sport. 1999;70:113- 119. doi:10.1080/02701367.1999.10608028
- Rikli RE, Jones CJ. Development and validation of a functional fitness test for community-residing older adults. J Aging Phys Act. 1999;7:129-161. doi:10.1123/japa.7.2.129
- Harada ND, Chiu V, Stewart AL. Mobility-related function in older adults: assessment with a 6-minute walk test. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1999;80:837-841. doi:10.1016/s0003-9993(99)90236-8
- Peeters GGME, Alshurafa M, Schaap L, de Vet HCW. Diagnostic accuracy of self-reported arthritis in the general adult population is acceptable. J Clin Epidemiol. 2015;68:452-459. doi:10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.09.019
- Cuperus N, Vliet Vlieland TPM, Mahler EAM, Kersten CC, Hoogeboom TJ, van den Ende CHM. The clinical burden of generalized osteoarthritis represented by self-reported health-related quality of life and activity limitations: a cross-sectional study. Rheumatol Int. 2015;35:871-877. doi:10.1007/s00296-014-3149-1
- Coleman G, Dobson F, Hinman RS, Bennell K, White DK. Measures of physical performance. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2020;72(suppl 10):452-485. doi:10.1002/acr.24373
- Perera S, Mody SH, Woodman RC, Studenski SA. Meaningful change and responsiveness in common physical performance measures in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:743-749. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2006.00701.x
- Wright AA, Cook CE, Baxter GD, Dockerty JD, Abbott JH. A comparison of 3 methodological approaches to defining major clinically important improvement of 4 performance measures in patients with hip osteoarthritis. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2011;41:319-327. doi:10.2519/jospt.2011.3515
- Dobson F, Hinman R, Roos EM, et al. OARSI recommended performance-based tests to assess physical function in people diagnosed with hip or knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21:1042- 1052. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2013.05.002
- Hughes SL, Seymour RB, Campbell R, Pollak N, Huber G, Sharma L. Impact of the fit and strong intervention on older adults with osteoarthritis. Gerontologist. 2004;44:217-228. doi:10.1093/geront/44.2.217
- Callahan LF, Shreffler JH, Altpeter M, et al. Evaluation of group and self-directed formats of the Arthritis Foundation's Walk With Ease Program. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2011;63:1098-1107. doi:10.1002/acr.20490
- Boutaugh ML. Arthritis Foundation community-based physical activity programs: effectiveness and implementation issues. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;49:463-470. doi:10.1002/art.11050
- Callahan LF, Mielenz T, Freburger J, et al. A randomized controlled trial of the People with Arthritis Can Exercise Program: symptoms, function, physical activity, and psychosocial outcomes. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;59:92-101. doi:10.1002/art.23239
- Hall KS, Jennings SC, Pearson MP. Outpatient care models: the Gerofit model of care for exercise promotion in older adults. In: Malone ML, Boltz M, Macias Tejada J, White H, eds. Geriatrics Models of Care. Springer; 2024:205-213. doi:10.1007/978-3-031-56204-4_21
- Pepin MJ, Valencia WM, Bettger JP, et al. Impact of supervised exercise on one-year medication use in older veterans with multiple morbidities. Gerontol Geriatr Med. 2020;6:2333721420956751. doi:10.1177/ 2333721420956751
- Abbate L, Li J, Veazie P, et al. Does Gerofit exercise reduce veterans’ use of emergency department and inpatient care? Innov Aging. 2020;4(suppl 1):771. doi:10.1093/geroni/igaa057.2786
- Morey MC, Pieper CF, Crowley GM, Sullivan RJ Jr, Puglisi CM. Exercise adherence and 10-year mortality in chronically ill older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2002;50:1929-1933. doi:10.1046/j.1532-5415.2002.50602.x
- Manning KM, Hall KS, Sloane R, et al. Longitudinal analysis of physical function in older adults: the effects of physical inactivity and exercise training. Aging Cell. 2024;23:e13987. doi:10.1111/acel.13987
- Bean JF, Vora A, Frontera WR. Benefits of exercise for community-dwelling older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2004;85(7 suppl 3):S31-S42; quiz S3-S4. doi:10.1016/j.apmr.2004.03.010
- Covinsky KE, Lindquist K, Dunlop DD, Yelin E. Pain, functional limitations, and aging. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:1556-1561. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2009.02388.x
- Katz JN, Wright EA, Baron JA, Losina E. Development and validation of an index of musculoskeletal functional limitations. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2009;10:62. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-10-62
- Allen KD, Thoma LM, Golightly YM. Epidemiology of osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30:184-195. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.020
- Riebe D, Blissmer BJ, Greaney ML, Ewing Garber C, Lees FD, Clark PG. The relationship between obesity, physical activity, and physical function in older adults. J Aging Health. 2009;21:1159-1178. doi:10.1177/0898264309350076
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
Impact of 3 Months of Supervised Exercise on Function by Arthritis Status
Around 5% of US Population Diagnosed With Autoimmune Disease
TOPLINE:
In 2022, autoimmune diseases affected over 15 million individuals in the United States, with women nearly twice as likely to be affected as men and more than one third of affected individuals having more than one autoimmune condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used electronic health record (EHR) data from six healthcare systems in the United States between 2011 and 2022 to estimate the prevalence of autoimmune diseases according to sex and age.
- They selected 105 autoimmune diseases from the textbook The Autoimmune Diseases and estimated their prevalence in more than 10 million individuals from these healthcare systems; these statistics were subsequently extrapolated to an estimated US population of 333.3 million.
- An individual was considered to have a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease if they had at least two diagnosis codes for the condition, with the codes being at least 30 days apart.
- A software program was developed to compute the prevalence of autoimmune diseases alone and in aggregate, enabling other researchers to replicate or modify the analysis over time.
TAKEAWAY:
- More than 15 million people, accounting for 4.6% of the US population, were diagnosed with at least one autoimmune disease from January 2011 to June 2022; 34% were diagnosed with more than one autoimmune disease.
- Sex-stratified analysis revealed that 63% of patients diagnosed with autoimmune disease were women, and only 37% were men, establishing a female-to-male ratio of 1.7:1; age-stratified analysis revealed increasing prevalence of autoimmune conditions with age, peaking in individuals aged ≥ 65 years.
- Among individuals with autoimmune diseases, 65% of patients had one condition, whereas 24% had two, 8% had three, and 2% had four or more autoimmune diseases (does not add to 100% due to rounding).
- Rheumatoid arthritis emerged as the most prevalent autoimmune disease, followed by psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, Grave’s disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis; 19 of the top 20 most prevalent autoimmune diseases occurred more frequently in women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Accurate data on the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as a category of disease and for individual autoimmune diseases are needed to further clinical and basic research to improve diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapies for these diseases, which significantly impact the US population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron H. Abend, Autoimmune Registry, Guilford, Connecticut, and was published online in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data presented several challenges, including potential inaccuracies in diagnosis codes and the possibility of missing patients with single diagnosis codes because of the two-code requirement. Certain autoimmune diseases evolve over time and involve nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms that can mimic other diseases, potentially resulting in underdiagnosis. Moreover, rare diseases lacking specific diagnosis codes may have been underrepresented.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from Autoimmune Registry; the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and other sources. Information on potential conflicts of interest was not disclosed.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In 2022, autoimmune diseases affected over 15 million individuals in the United States, with women nearly twice as likely to be affected as men and more than one third of affected individuals having more than one autoimmune condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used electronic health record (EHR) data from six healthcare systems in the United States between 2011 and 2022 to estimate the prevalence of autoimmune diseases according to sex and age.
- They selected 105 autoimmune diseases from the textbook The Autoimmune Diseases and estimated their prevalence in more than 10 million individuals from these healthcare systems; these statistics were subsequently extrapolated to an estimated US population of 333.3 million.
- An individual was considered to have a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease if they had at least two diagnosis codes for the condition, with the codes being at least 30 days apart.
- A software program was developed to compute the prevalence of autoimmune diseases alone and in aggregate, enabling other researchers to replicate or modify the analysis over time.
TAKEAWAY:
- More than 15 million people, accounting for 4.6% of the US population, were diagnosed with at least one autoimmune disease from January 2011 to June 2022; 34% were diagnosed with more than one autoimmune disease.
- Sex-stratified analysis revealed that 63% of patients diagnosed with autoimmune disease were women, and only 37% were men, establishing a female-to-male ratio of 1.7:1; age-stratified analysis revealed increasing prevalence of autoimmune conditions with age, peaking in individuals aged ≥ 65 years.
- Among individuals with autoimmune diseases, 65% of patients had one condition, whereas 24% had two, 8% had three, and 2% had four or more autoimmune diseases (does not add to 100% due to rounding).
- Rheumatoid arthritis emerged as the most prevalent autoimmune disease, followed by psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, Grave’s disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis; 19 of the top 20 most prevalent autoimmune diseases occurred more frequently in women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Accurate data on the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as a category of disease and for individual autoimmune diseases are needed to further clinical and basic research to improve diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapies for these diseases, which significantly impact the US population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron H. Abend, Autoimmune Registry, Guilford, Connecticut, and was published online in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data presented several challenges, including potential inaccuracies in diagnosis codes and the possibility of missing patients with single diagnosis codes because of the two-code requirement. Certain autoimmune diseases evolve over time and involve nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms that can mimic other diseases, potentially resulting in underdiagnosis. Moreover, rare diseases lacking specific diagnosis codes may have been underrepresented.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from Autoimmune Registry; the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and other sources. Information on potential conflicts of interest was not disclosed.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
In 2022, autoimmune diseases affected over 15 million individuals in the United States, with women nearly twice as likely to be affected as men and more than one third of affected individuals having more than one autoimmune condition.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers used electronic health record (EHR) data from six healthcare systems in the United States between 2011 and 2022 to estimate the prevalence of autoimmune diseases according to sex and age.
- They selected 105 autoimmune diseases from the textbook The Autoimmune Diseases and estimated their prevalence in more than 10 million individuals from these healthcare systems; these statistics were subsequently extrapolated to an estimated US population of 333.3 million.
- An individual was considered to have a diagnosis of an autoimmune disease if they had at least two diagnosis codes for the condition, with the codes being at least 30 days apart.
- A software program was developed to compute the prevalence of autoimmune diseases alone and in aggregate, enabling other researchers to replicate or modify the analysis over time.
TAKEAWAY:
- More than 15 million people, accounting for 4.6% of the US population, were diagnosed with at least one autoimmune disease from January 2011 to June 2022; 34% were diagnosed with more than one autoimmune disease.
- Sex-stratified analysis revealed that 63% of patients diagnosed with autoimmune disease were women, and only 37% were men, establishing a female-to-male ratio of 1.7:1; age-stratified analysis revealed increasing prevalence of autoimmune conditions with age, peaking in individuals aged ≥ 65 years.
- Among individuals with autoimmune diseases, 65% of patients had one condition, whereas 24% had two, 8% had three, and 2% had four or more autoimmune diseases (does not add to 100% due to rounding).
- Rheumatoid arthritis emerged as the most prevalent autoimmune disease, followed by psoriasis, type 1 diabetes, Grave’s disease, and autoimmune thyroiditis; 19 of the top 20 most prevalent autoimmune diseases occurred more frequently in women.
IN PRACTICE:
“Accurate data on the prevalence of autoimmune diseases as a category of disease and for individual autoimmune diseases are needed to further clinical and basic research to improve diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapies for these diseases, which significantly impact the US population,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Aaron H. Abend, Autoimmune Registry, Guilford, Connecticut, and was published online in The Journal of Clinical Investigation.
LIMITATIONS:
The use of EHR data presented several challenges, including potential inaccuracies in diagnosis codes and the possibility of missing patients with single diagnosis codes because of the two-code requirement. Certain autoimmune diseases evolve over time and involve nonspecific clinical signs and symptoms that can mimic other diseases, potentially resulting in underdiagnosis. Moreover, rare diseases lacking specific diagnosis codes may have been underrepresented.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received support from Autoimmune Registry; the National Institutes of Health National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences; the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and other sources. Information on potential conflicts of interest was not disclosed.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TNF Inhibitors Show Comparable Safety With Non-TNF Inhibitors in US Veterans With RA-ILD
TOPLINE:
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors led to no significant difference in survival or respiratory-related hospitalizations, compared with non-TNF inhibitors, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
METHODOLOGY:
- Guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the American College of Chest Physicians conditionally advise against the use of TNF inhibitors for treating ILD in patients with RA-ILD, with persisting uncertainty about the safety of TNF inhibitors.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, with a focus on comparing outcomes in patients with RA-ILD who initiated TNF or non-TNF inhibitors between 2006 and 2018.
- A total of 1047 US veterans with RA-ILD were included, with 237 who initiated TNF inhibitors propensity matched in a 1:1 ratio with 237 who initiated non-TNF inhibitors (mean age, 68 years; 92% men).
- The primary composite outcome was time to death or respiratory-related hospitalization over a follow-up period of up to 3 years.
- The secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, respiratory-related mortality, and respiratory-related hospitalization, with additional assessments over a 1-year period.
TAKEAWAY:
- No significant difference was observed in the composite outcome of death or respiratory-related hospitalization between the TNF and non-TNF inhibitor groups (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.92-1.58).
- No significant differences in the risk for respiratory-related hospitalization and all-cause or respiratory-related mortality were found between the TNF and non-TNF inhibitor groups. Similar findings were observed for all the outcomes during 1 year of follow-up.
- The mean duration of medication use prior to discontinuation, the time to discontinuation, and the mean predicted forced vital capacity percentage were similar for both groups.
- In a subgroup analysis of patients aged ≥ 65 years, those treated with non-TNF inhibitors had a higher risk for the composite outcome and all-cause and respiratory-related mortality than those treated with TNF inhibitors. No significant differences in outcomes were observed between the two treatment groups among patients aged < 65 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results do not suggest that systematic avoidance of TNF inhibitors is required in all patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated ILD. However, given disease heterogeneity and imprecision of our estimates, some subpopulations of patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated ILD might benefit from specific biological or targeted synthetic DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] treatment strategies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Bryant R. England, MD, PhD, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha It was published online on January 7, 2025, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Administrative algorithms were used for identifying RA-ILD, potentially leading to misclassification and limiting phenotyping accuracy. Even with the use of propensity score methods, there might still be residual selection bias or unmeasured confounding. The study lacked comprehensive measures of posttreatment forced vital capacity and other indicators of ILD severity. The study population, predominantly men and those with a smoking history, may limit the generalizability of the findings to other groups.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was primarily funded by the US Department of Veterans Affairs. Some authors reported having financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors led to no significant difference in survival or respiratory-related hospitalizations, compared with non-TNF inhibitors, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
METHODOLOGY:
- Guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the American College of Chest Physicians conditionally advise against the use of TNF inhibitors for treating ILD in patients with RA-ILD, with persisting uncertainty about the safety of TNF inhibitors.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, with a focus on comparing outcomes in patients with RA-ILD who initiated TNF or non-TNF inhibitors between 2006 and 2018.
- A total of 1047 US veterans with RA-ILD were included, with 237 who initiated TNF inhibitors propensity matched in a 1:1 ratio with 237 who initiated non-TNF inhibitors (mean age, 68 years; 92% men).
- The primary composite outcome was time to death or respiratory-related hospitalization over a follow-up period of up to 3 years.
- The secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, respiratory-related mortality, and respiratory-related hospitalization, with additional assessments over a 1-year period.
TAKEAWAY:
- No significant difference was observed in the composite outcome of death or respiratory-related hospitalization between the TNF and non-TNF inhibitor groups (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.92-1.58).
- No significant differences in the risk for respiratory-related hospitalization and all-cause or respiratory-related mortality were found between the TNF and non-TNF inhibitor groups. Similar findings were observed for all the outcomes during 1 year of follow-up.
- The mean duration of medication use prior to discontinuation, the time to discontinuation, and the mean predicted forced vital capacity percentage were similar for both groups.
- In a subgroup analysis of patients aged ≥ 65 years, those treated with non-TNF inhibitors had a higher risk for the composite outcome and all-cause and respiratory-related mortality than those treated with TNF inhibitors. No significant differences in outcomes were observed between the two treatment groups among patients aged < 65 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results do not suggest that systematic avoidance of TNF inhibitors is required in all patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated ILD. However, given disease heterogeneity and imprecision of our estimates, some subpopulations of patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated ILD might benefit from specific biological or targeted synthetic DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] treatment strategies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Bryant R. England, MD, PhD, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha It was published online on January 7, 2025, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Administrative algorithms were used for identifying RA-ILD, potentially leading to misclassification and limiting phenotyping accuracy. Even with the use of propensity score methods, there might still be residual selection bias or unmeasured confounding. The study lacked comprehensive measures of posttreatment forced vital capacity and other indicators of ILD severity. The study population, predominantly men and those with a smoking history, may limit the generalizability of the findings to other groups.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was primarily funded by the US Department of Veterans Affairs. Some authors reported having financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors led to no significant difference in survival or respiratory-related hospitalizations, compared with non-TNF inhibitors, in patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD).
METHODOLOGY:
- Guidelines from the American College of Rheumatology and the American College of Chest Physicians conditionally advise against the use of TNF inhibitors for treating ILD in patients with RA-ILD, with persisting uncertainty about the safety of TNF inhibitors.
- Researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the US Department of Veterans Affairs, with a focus on comparing outcomes in patients with RA-ILD who initiated TNF or non-TNF inhibitors between 2006 and 2018.
- A total of 1047 US veterans with RA-ILD were included, with 237 who initiated TNF inhibitors propensity matched in a 1:1 ratio with 237 who initiated non-TNF inhibitors (mean age, 68 years; 92% men).
- The primary composite outcome was time to death or respiratory-related hospitalization over a follow-up period of up to 3 years.
- The secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, respiratory-related mortality, and respiratory-related hospitalization, with additional assessments over a 1-year period.
TAKEAWAY:
- No significant difference was observed in the composite outcome of death or respiratory-related hospitalization between the TNF and non-TNF inhibitor groups (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.92-1.58).
- No significant differences in the risk for respiratory-related hospitalization and all-cause or respiratory-related mortality were found between the TNF and non-TNF inhibitor groups. Similar findings were observed for all the outcomes during 1 year of follow-up.
- The mean duration of medication use prior to discontinuation, the time to discontinuation, and the mean predicted forced vital capacity percentage were similar for both groups.
- In a subgroup analysis of patients aged ≥ 65 years, those treated with non-TNF inhibitors had a higher risk for the composite outcome and all-cause and respiratory-related mortality than those treated with TNF inhibitors. No significant differences in outcomes were observed between the two treatment groups among patients aged < 65 years.
IN PRACTICE:
“Our results do not suggest that systematic avoidance of TNF inhibitors is required in all patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated ILD. However, given disease heterogeneity and imprecision of our estimates, some subpopulations of patients with rheumatoid arthritis–associated ILD might benefit from specific biological or targeted synthetic DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] treatment strategies,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Bryant R. England, MD, PhD, University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha It was published online on January 7, 2025, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Administrative algorithms were used for identifying RA-ILD, potentially leading to misclassification and limiting phenotyping accuracy. Even with the use of propensity score methods, there might still be residual selection bias or unmeasured confounding. The study lacked comprehensive measures of posttreatment forced vital capacity and other indicators of ILD severity. The study population, predominantly men and those with a smoking history, may limit the generalizability of the findings to other groups.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was primarily funded by the US Department of Veterans Affairs. Some authors reported having financial relationships with pharmaceutical companies unrelated to the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Show Higher Risk for Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction
TOPLINE:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) face a higher risk for heart failure (HF) than those without the condition, with the elevated risk primarily driven by HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Mass General Brigham Biobank to investigate the risk for overall HF and its subtypes, particularly HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) and HFpEF, in patients with RA.
- They included 1445 patients newly diagnosed with RA (mean age, 51.4 years; 78.7% women) and 4335 matched comparators without RA.
- Patients with RA were identified using diagnosis codes and RA-related natural language processing concepts.
- HFpEF and HFrEF were defined as HF with an EF ≥ 50% and ≤ 40%, respectively; incidences for overall HF, HFpEF, and HFrEF were calculated per 1000 person-years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study identified 92 incident HF cases in the RA cohort and 157 in the non-RA cohort over a median follow-up of 10.3 years per patient.
- HFpEF was the predominant HF subtype in both cohorts, with a higher incidence in patients with RA than in those without the condition (4.33 vs 2.11 per 1000 person-years).
- Patients with RA showed a 79% higher risk for HF than those without the condition (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.79; 95% CI, 1.38-2.32).
- Among the HF subtypes, patients with RA had a significantly increased risk for HFpEF (aHR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.43-2.77) but not for HFrEF.
IN PRACTICE:
“RA can be considered a human model for inflammation, and findings from this study support the notion that chronic inflammation increases risk for HFpEF,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yumeko Kawano, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was conducted within an academic tertiary hospital system and involved participants from a biobank, which may have introduced selection bias and limited generalizability. The study did not account for post-baseline variables that could mediate the observed associations, such as the chronic use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, or specific disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. The study relied on the availability of clinically performed cardiology studies for HF subtyping, possibly introducing misclassification of HF.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. One author received support from the Ruth L. Kirschstein Institutional National Research Service Award, National Institutes of Health.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) face a higher risk for heart failure (HF) than those without the condition, with the elevated risk primarily driven by HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Mass General Brigham Biobank to investigate the risk for overall HF and its subtypes, particularly HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) and HFpEF, in patients with RA.
- They included 1445 patients newly diagnosed with RA (mean age, 51.4 years; 78.7% women) and 4335 matched comparators without RA.
- Patients with RA were identified using diagnosis codes and RA-related natural language processing concepts.
- HFpEF and HFrEF were defined as HF with an EF ≥ 50% and ≤ 40%, respectively; incidences for overall HF, HFpEF, and HFrEF were calculated per 1000 person-years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study identified 92 incident HF cases in the RA cohort and 157 in the non-RA cohort over a median follow-up of 10.3 years per patient.
- HFpEF was the predominant HF subtype in both cohorts, with a higher incidence in patients with RA than in those without the condition (4.33 vs 2.11 per 1000 person-years).
- Patients with RA showed a 79% higher risk for HF than those without the condition (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.79; 95% CI, 1.38-2.32).
- Among the HF subtypes, patients with RA had a significantly increased risk for HFpEF (aHR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.43-2.77) but not for HFrEF.
IN PRACTICE:
“RA can be considered a human model for inflammation, and findings from this study support the notion that chronic inflammation increases risk for HFpEF,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yumeko Kawano, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was conducted within an academic tertiary hospital system and involved participants from a biobank, which may have introduced selection bias and limited generalizability. The study did not account for post-baseline variables that could mediate the observed associations, such as the chronic use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, or specific disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. The study relied on the availability of clinically performed cardiology studies for HF subtyping, possibly introducing misclassification of HF.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. One author received support from the Ruth L. Kirschstein Institutional National Research Service Award, National Institutes of Health.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) face a higher risk for heart failure (HF) than those without the condition, with the elevated risk primarily driven by HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study using data from the Mass General Brigham Biobank to investigate the risk for overall HF and its subtypes, particularly HF with reduced EF (HFrEF) and HFpEF, in patients with RA.
- They included 1445 patients newly diagnosed with RA (mean age, 51.4 years; 78.7% women) and 4335 matched comparators without RA.
- Patients with RA were identified using diagnosis codes and RA-related natural language processing concepts.
- HFpEF and HFrEF were defined as HF with an EF ≥ 50% and ≤ 40%, respectively; incidences for overall HF, HFpEF, and HFrEF were calculated per 1000 person-years.
TAKEAWAY:
- The study identified 92 incident HF cases in the RA cohort and 157 in the non-RA cohort over a median follow-up of 10.3 years per patient.
- HFpEF was the predominant HF subtype in both cohorts, with a higher incidence in patients with RA than in those without the condition (4.33 vs 2.11 per 1000 person-years).
- Patients with RA showed a 79% higher risk for HF than those without the condition (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.79; 95% CI, 1.38-2.32).
- Among the HF subtypes, patients with RA had a significantly increased risk for HFpEF (aHR, 1.99; 95% CI, 1.43-2.77) but not for HFrEF.
IN PRACTICE:
“RA can be considered a human model for inflammation, and findings from this study support the notion that chronic inflammation increases risk for HFpEF,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Yumeko Kawano, MD, Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts, and was published online in Arthritis Care & Research.
LIMITATIONS:
This study was conducted within an academic tertiary hospital system and involved participants from a biobank, which may have introduced selection bias and limited generalizability. The study did not account for post-baseline variables that could mediate the observed associations, such as the chronic use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids, or specific disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. The study relied on the availability of clinically performed cardiology studies for HF subtyping, possibly introducing misclassification of HF.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. One author received support from the Ruth L. Kirschstein Institutional National Research Service Award, National Institutes of Health.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Need for Biologic in Early RA Signals Lower Likelihood of Achieving Drug-Free Remission
TOPLINE:
Patients who require biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for severe RA are less likely to achieve sustained DMARD-free remission than those not needing the medication.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with early RA from the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic (EAC; n = 627) and the Rotterdam Early Arthritis Cohort (tREACH) trial (n = 425) were followed for 5 years and 3 years, respectively.
- Most patients in both the EAC (86%) and tREACH (64%) cohorts had never used a biologic DMARD during the follow-up period.
- The primary outcome measure was sustained DMARD-free remission, defined as the absence of clinical synovitis after discontinuation of DMARDs for at least 1 year.
TAKEAWAY:
- None of the EAC patients using a biologic DMARD achieved sustained DMARD-free remission, but 37% of those who never used the drug reached remission at 5 years (hazard ratio [HR], 0.02; P < .0001).
- No tREACH patients using a biologic DMARD reached sustained DMARD-free remission, but 15% of those who never used the drug achieved remission at 3 years (HR, 0.03; P < .0001).
- Sustained DMARD-free remission was higher in EAC patients who were negative for anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) than in those who were ACPA-positive at 5 years (56% vs 14%; P < .0001).
- During follow-up, some patients in both the EAC (9%) and tREACH (14%) cohorts experienced late flares after more than 1 year of discontinuing DMARDs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Sustained DMARD-free remission is unlikely in patients needing a biologic DMARD,” the authors said.
SOURCE:
Judith W. Heutz, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the study, published online on December 20, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Because both cohorts were defined during follow-up rather than at baseline, outcomes related to the use of DMARDs and remission status could have been misinterpreted. Although the study adjusted for ACPA status, other factors such as disease activity were not corrected, which could have potentially led to residual confounding. Sparse data bias was present, especially in the biologic DMARD user group, in which none of the patients reached sustained DMARD-free remission.
DISCLOSURES:
The EAC received funding from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation and the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. The tREACH trial was supported by an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients who require biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for severe RA are less likely to achieve sustained DMARD-free remission than those not needing the medication.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with early RA from the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic (EAC; n = 627) and the Rotterdam Early Arthritis Cohort (tREACH) trial (n = 425) were followed for 5 years and 3 years, respectively.
- Most patients in both the EAC (86%) and tREACH (64%) cohorts had never used a biologic DMARD during the follow-up period.
- The primary outcome measure was sustained DMARD-free remission, defined as the absence of clinical synovitis after discontinuation of DMARDs for at least 1 year.
TAKEAWAY:
- None of the EAC patients using a biologic DMARD achieved sustained DMARD-free remission, but 37% of those who never used the drug reached remission at 5 years (hazard ratio [HR], 0.02; P < .0001).
- No tREACH patients using a biologic DMARD reached sustained DMARD-free remission, but 15% of those who never used the drug achieved remission at 3 years (HR, 0.03; P < .0001).
- Sustained DMARD-free remission was higher in EAC patients who were negative for anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) than in those who were ACPA-positive at 5 years (56% vs 14%; P < .0001).
- During follow-up, some patients in both the EAC (9%) and tREACH (14%) cohorts experienced late flares after more than 1 year of discontinuing DMARDs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Sustained DMARD-free remission is unlikely in patients needing a biologic DMARD,” the authors said.
SOURCE:
Judith W. Heutz, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the study, published online on December 20, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Because both cohorts were defined during follow-up rather than at baseline, outcomes related to the use of DMARDs and remission status could have been misinterpreted. Although the study adjusted for ACPA status, other factors such as disease activity were not corrected, which could have potentially led to residual confounding. Sparse data bias was present, especially in the biologic DMARD user group, in which none of the patients reached sustained DMARD-free remission.
DISCLOSURES:
The EAC received funding from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation and the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. The tREACH trial was supported by an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Patients who require biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) for severe RA are less likely to achieve sustained DMARD-free remission than those not needing the medication.
METHODOLOGY:
- Patients with early RA from the Leiden Early Arthritis Clinic (EAC; n = 627) and the Rotterdam Early Arthritis Cohort (tREACH) trial (n = 425) were followed for 5 years and 3 years, respectively.
- Most patients in both the EAC (86%) and tREACH (64%) cohorts had never used a biologic DMARD during the follow-up period.
- The primary outcome measure was sustained DMARD-free remission, defined as the absence of clinical synovitis after discontinuation of DMARDs for at least 1 year.
TAKEAWAY:
- None of the EAC patients using a biologic DMARD achieved sustained DMARD-free remission, but 37% of those who never used the drug reached remission at 5 years (hazard ratio [HR], 0.02; P < .0001).
- No tREACH patients using a biologic DMARD reached sustained DMARD-free remission, but 15% of those who never used the drug achieved remission at 3 years (HR, 0.03; P < .0001).
- Sustained DMARD-free remission was higher in EAC patients who were negative for anti-citrullinated protein antibody (ACPA) than in those who were ACPA-positive at 5 years (56% vs 14%; P < .0001).
- During follow-up, some patients in both the EAC (9%) and tREACH (14%) cohorts experienced late flares after more than 1 year of discontinuing DMARDs.
IN PRACTICE:
“Sustained DMARD-free remission is unlikely in patients needing a biologic DMARD,” the authors said.
SOURCE:
Judith W. Heutz, MD, Erasmus Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, led the study, published online on December 20, 2024, in The Lancet Rheumatology.
LIMITATIONS:
Because both cohorts were defined during follow-up rather than at baseline, outcomes related to the use of DMARDs and remission status could have been misinterpreted. Although the study adjusted for ACPA status, other factors such as disease activity were not corrected, which could have potentially led to residual confounding. Sparse data bias was present, especially in the biologic DMARD user group, in which none of the patients reached sustained DMARD-free remission.
DISCLOSURES:
The EAC received funding from the Dutch Arthritis Foundation and the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation program. The tREACH trial was supported by an unrestricted grant from Pfizer. The authors declared no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Novel JAK1 Inhibitor Effective for RA in Phase 3 Study
TOPLINE:
(RA) who have an inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs).
METHODOLOGY:
- This phase 3 trial, conducted across 59 sites in China, evaluated the efficacy and safety of ivarmacitinib in patients with moderate to severe active RA despite treatment with one or more csDMARDs.
- The patients were randomly assigned to receive either placebo (n = 188; mean age, 50.9 years; 85.6% women) or 4 mg ivarmacitinib (n = 189; mean age, 49.7 years; 91% women) or 8 mg ivarmacitinib (n = 189; mean age, 49.8 years; 83.6% women) once daily for 24 weeks, alongside background csDMARDs.
- After 24 weeks, the patients receiving placebo were switched to receive 4 mg ivarmacitinib for the additional 28-week extension period, whereas those receiving ivarmacitinib continued their initial dosage.
- Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50/70 responses and, Disease Activity Score 28-joint count C-reactive protein (DAS28(CRP)) score < 2.6 or ≤ 3.2, as well as measures of other patient-reported outcomes such as pain, physical function, and quality of life at 24 and 52 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 24 weeks, the proportion of patients achieving a 20% improvement in the ACR20 response — the primary endpoint — was higher among those receiving 4 mg ivarmacitinib (70.4%) or 8 mg ivarmacitinib (75.1%) than among those receiving placebo (40.4%; P < .0001 for both comparisons), with the efficacy either maintained or improved through 52 weeks.
- The proportion of patients achieving ACR50/70 responses or a DAS28(CRP) score < 2.6 or ≤ 3.2 was higher in the ivarmacitinib groups than in the placebo group (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
- Compared with the placebo group, both the ivarmacitinib groups showed improvements in patient-reported outcomes such as pain, physical function, quality of life, and duration and severity of morning stiffness.
- The overall rates of treatment discontinuation caused by adverse events were low across all the groups, with no deaths, tuberculosis or gastrointestinal perforations reported throughout the 52 weeks.
IN PRACTICE:
“Based on these findings, ivarmacitinib with background csDMARDs allowed, could be considered a treatment option in patients with moderate to severe active RA who have an inadequate response to csDMARDs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jinjing Liu and Xiaofeng Zeng, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China. It was published online on November 27, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
As the study was conducted in a Chinese population, the findings may have limited applicability across diverse global populations. Additionally, as the placebo-controlled period was limited to 24 weeks because of ethical concerns, comparisons between placebo and ivarmacitinib beyond that period were restricted. Lastly, this study was not powered to compare efficacy and safety between the two active dose regimens.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals. Two authors declared being employees of the company. The other authors reported no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
(RA) who have an inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs).
METHODOLOGY:
- This phase 3 trial, conducted across 59 sites in China, evaluated the efficacy and safety of ivarmacitinib in patients with moderate to severe active RA despite treatment with one or more csDMARDs.
- The patients were randomly assigned to receive either placebo (n = 188; mean age, 50.9 years; 85.6% women) or 4 mg ivarmacitinib (n = 189; mean age, 49.7 years; 91% women) or 8 mg ivarmacitinib (n = 189; mean age, 49.8 years; 83.6% women) once daily for 24 weeks, alongside background csDMARDs.
- After 24 weeks, the patients receiving placebo were switched to receive 4 mg ivarmacitinib for the additional 28-week extension period, whereas those receiving ivarmacitinib continued their initial dosage.
- Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50/70 responses and, Disease Activity Score 28-joint count C-reactive protein (DAS28(CRP)) score < 2.6 or ≤ 3.2, as well as measures of other patient-reported outcomes such as pain, physical function, and quality of life at 24 and 52 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 24 weeks, the proportion of patients achieving a 20% improvement in the ACR20 response — the primary endpoint — was higher among those receiving 4 mg ivarmacitinib (70.4%) or 8 mg ivarmacitinib (75.1%) than among those receiving placebo (40.4%; P < .0001 for both comparisons), with the efficacy either maintained or improved through 52 weeks.
- The proportion of patients achieving ACR50/70 responses or a DAS28(CRP) score < 2.6 or ≤ 3.2 was higher in the ivarmacitinib groups than in the placebo group (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
- Compared with the placebo group, both the ivarmacitinib groups showed improvements in patient-reported outcomes such as pain, physical function, quality of life, and duration and severity of morning stiffness.
- The overall rates of treatment discontinuation caused by adverse events were low across all the groups, with no deaths, tuberculosis or gastrointestinal perforations reported throughout the 52 weeks.
IN PRACTICE:
“Based on these findings, ivarmacitinib with background csDMARDs allowed, could be considered a treatment option in patients with moderate to severe active RA who have an inadequate response to csDMARDs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jinjing Liu and Xiaofeng Zeng, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China. It was published online on November 27, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
As the study was conducted in a Chinese population, the findings may have limited applicability across diverse global populations. Additionally, as the placebo-controlled period was limited to 24 weeks because of ethical concerns, comparisons between placebo and ivarmacitinib beyond that period were restricted. Lastly, this study was not powered to compare efficacy and safety between the two active dose regimens.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals. Two authors declared being employees of the company. The other authors reported no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
(RA) who have an inadequate response to conventional synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (csDMARDs).
METHODOLOGY:
- This phase 3 trial, conducted across 59 sites in China, evaluated the efficacy and safety of ivarmacitinib in patients with moderate to severe active RA despite treatment with one or more csDMARDs.
- The patients were randomly assigned to receive either placebo (n = 188; mean age, 50.9 years; 85.6% women) or 4 mg ivarmacitinib (n = 189; mean age, 49.7 years; 91% women) or 8 mg ivarmacitinib (n = 189; mean age, 49.8 years; 83.6% women) once daily for 24 weeks, alongside background csDMARDs.
- After 24 weeks, the patients receiving placebo were switched to receive 4 mg ivarmacitinib for the additional 28-week extension period, whereas those receiving ivarmacitinib continued their initial dosage.
- Secondary endpoints included the proportion of patients achieving American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 50/70 responses and, Disease Activity Score 28-joint count C-reactive protein (DAS28(CRP)) score < 2.6 or ≤ 3.2, as well as measures of other patient-reported outcomes such as pain, physical function, and quality of life at 24 and 52 weeks.
TAKEAWAY:
- At 24 weeks, the proportion of patients achieving a 20% improvement in the ACR20 response — the primary endpoint — was higher among those receiving 4 mg ivarmacitinib (70.4%) or 8 mg ivarmacitinib (75.1%) than among those receiving placebo (40.4%; P < .0001 for both comparisons), with the efficacy either maintained or improved through 52 weeks.
- The proportion of patients achieving ACR50/70 responses or a DAS28(CRP) score < 2.6 or ≤ 3.2 was higher in the ivarmacitinib groups than in the placebo group (P < .0001 for all comparisons).
- Compared with the placebo group, both the ivarmacitinib groups showed improvements in patient-reported outcomes such as pain, physical function, quality of life, and duration and severity of morning stiffness.
- The overall rates of treatment discontinuation caused by adverse events were low across all the groups, with no deaths, tuberculosis or gastrointestinal perforations reported throughout the 52 weeks.
IN PRACTICE:
“Based on these findings, ivarmacitinib with background csDMARDs allowed, could be considered a treatment option in patients with moderate to severe active RA who have an inadequate response to csDMARDs,” the authors wrote.
SOURCE:
This study was led by Jinjing Liu and Xiaofeng Zeng, Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Peking Union Medical College Hospital, Beijing, China. It was published online on November 27, 2024, in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
LIMITATIONS:
As the study was conducted in a Chinese population, the findings may have limited applicability across diverse global populations. Additionally, as the placebo-controlled period was limited to 24 weeks because of ethical concerns, comparisons between placebo and ivarmacitinib beyond that period were restricted. Lastly, this study was not powered to compare efficacy and safety between the two active dose regimens.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was funded by Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceuticals. Two authors declared being employees of the company. The other authors reported no competing interests.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic Markers May Predict TNF Inhibitor Response in Rheumatoid Arthritis
TOPLINE:
Genetic markers, specifically tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 2 (TNFR2) gene polymorphisms, may predict response to TNF inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This approach could optimize treatment and improve patient outcomes.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study aimed to determine if TNFR2 gene polymorphisms could serve as biomarkers for treatment responsiveness to TNF inhibitors.
- It included 52 adult patients with RA (average age, 57.4 years; mean body mass index, 31.4; 65% women; 80% White) who had a mean disease duration of 8.9 years and started treatment with a single TNF inhibitor (infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, or certolizumab pegol).
- TNFR2-M (methionine) and TNFR2-R(arginine) gene polymorphisms were identified using genomic DNA isolated from patients’ blood samples to determine M/M, M/R, or R/R genotypes.
- The primary outcome was nonresponse to TNF inhibitors, defined as discontinuation of medication in < 3 months.
- The relationship between TNF inhibitor responsiveness and TNFR2 gene polymorphisms was analyzed using univariable logistic regression.
TAKEAWAY:
- Genomic DNA analysis revealed that 28 patients were homozygous for methionine, 22 were heterozygous, and two were homozygous for arginine.
- Of these, 96.4% of patients with the M/M genotype were responders to TNF inhibitors, whereas 75% of those with the M/R genotype and 50% with the R/R genotype were responders.
- Patients with the M/M genotype had approximately 10 times higher odds of responding to TNF inhibitors than those with the M/R and R/R genotypes (odds ratio, 10.12; P = .04).
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying predictors for nonresponsiveness to TNF antagonists based on TNFR2 gene polymorphisms may become a valuable tool for personalized medicine, allowing for a more specific TNF [inhibitor] therapy in RA patients,” the authors wrote. “Given that TNF [inhibitor] therapy is used for many autoimmune conditions beyond RA, this genotyping could potentially serve as a useful framework for personalized treatment strategies in other autoimmune diseases to delay or reduce disease progression overall.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Elaine Husni, MD, MPH, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic in Ohio. It was published online on November 7, 2024, in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism and presented as a poster at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2024 Annual Meeting.
LIMITATIONS:
This study’s sample size was relatively small.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Arthritis Foundation and in part by the National Institutes of Health. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Genetic markers, specifically tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 2 (TNFR2) gene polymorphisms, may predict response to TNF inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This approach could optimize treatment and improve patient outcomes.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study aimed to determine if TNFR2 gene polymorphisms could serve as biomarkers for treatment responsiveness to TNF inhibitors.
- It included 52 adult patients with RA (average age, 57.4 years; mean body mass index, 31.4; 65% women; 80% White) who had a mean disease duration of 8.9 years and started treatment with a single TNF inhibitor (infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, or certolizumab pegol).
- TNFR2-M (methionine) and TNFR2-R(arginine) gene polymorphisms were identified using genomic DNA isolated from patients’ blood samples to determine M/M, M/R, or R/R genotypes.
- The primary outcome was nonresponse to TNF inhibitors, defined as discontinuation of medication in < 3 months.
- The relationship between TNF inhibitor responsiveness and TNFR2 gene polymorphisms was analyzed using univariable logistic regression.
TAKEAWAY:
- Genomic DNA analysis revealed that 28 patients were homozygous for methionine, 22 were heterozygous, and two were homozygous for arginine.
- Of these, 96.4% of patients with the M/M genotype were responders to TNF inhibitors, whereas 75% of those with the M/R genotype and 50% with the R/R genotype were responders.
- Patients with the M/M genotype had approximately 10 times higher odds of responding to TNF inhibitors than those with the M/R and R/R genotypes (odds ratio, 10.12; P = .04).
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying predictors for nonresponsiveness to TNF antagonists based on TNFR2 gene polymorphisms may become a valuable tool for personalized medicine, allowing for a more specific TNF [inhibitor] therapy in RA patients,” the authors wrote. “Given that TNF [inhibitor] therapy is used for many autoimmune conditions beyond RA, this genotyping could potentially serve as a useful framework for personalized treatment strategies in other autoimmune diseases to delay or reduce disease progression overall.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Elaine Husni, MD, MPH, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic in Ohio. It was published online on November 7, 2024, in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism and presented as a poster at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2024 Annual Meeting.
LIMITATIONS:
This study’s sample size was relatively small.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Arthritis Foundation and in part by the National Institutes of Health. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Genetic markers, specifically tumor necrosis factor alpha receptor 2 (TNFR2) gene polymorphisms, may predict response to TNF inhibitor therapy in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This approach could optimize treatment and improve patient outcomes.
METHODOLOGY:
- The study aimed to determine if TNFR2 gene polymorphisms could serve as biomarkers for treatment responsiveness to TNF inhibitors.
- It included 52 adult patients with RA (average age, 57.4 years; mean body mass index, 31.4; 65% women; 80% White) who had a mean disease duration of 8.9 years and started treatment with a single TNF inhibitor (infliximab, adalimumab, etanercept, golimumab, or certolizumab pegol).
- TNFR2-M (methionine) and TNFR2-R(arginine) gene polymorphisms were identified using genomic DNA isolated from patients’ blood samples to determine M/M, M/R, or R/R genotypes.
- The primary outcome was nonresponse to TNF inhibitors, defined as discontinuation of medication in < 3 months.
- The relationship between TNF inhibitor responsiveness and TNFR2 gene polymorphisms was analyzed using univariable logistic regression.
TAKEAWAY:
- Genomic DNA analysis revealed that 28 patients were homozygous for methionine, 22 were heterozygous, and two were homozygous for arginine.
- Of these, 96.4% of patients with the M/M genotype were responders to TNF inhibitors, whereas 75% of those with the M/R genotype and 50% with the R/R genotype were responders.
- Patients with the M/M genotype had approximately 10 times higher odds of responding to TNF inhibitors than those with the M/R and R/R genotypes (odds ratio, 10.12; P = .04).
IN PRACTICE:
“Identifying predictors for nonresponsiveness to TNF antagonists based on TNFR2 gene polymorphisms may become a valuable tool for personalized medicine, allowing for a more specific TNF [inhibitor] therapy in RA patients,” the authors wrote. “Given that TNF [inhibitor] therapy is used for many autoimmune conditions beyond RA, this genotyping could potentially serve as a useful framework for personalized treatment strategies in other autoimmune diseases to delay or reduce disease progression overall.”
SOURCE:
This study was led by Elaine Husni, MD, MPH, Lerner Research Institute, Cleveland Clinic in Ohio. It was published online on November 7, 2024, in Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism and presented as a poster at the American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 2024 Annual Meeting.
LIMITATIONS:
This study’s sample size was relatively small.
DISCLOSURES:
This study was supported by the Arthritis Foundation and in part by the National Institutes of Health. No relevant conflicts of interest were disclosed by the authors.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
New Test’s Utility in Distinguishing OA From Inflammatory Arthritis Questioned
A new diagnostic test can accurately distinguish osteoarthritis (OA) from inflammatory arthritis using two synovial fluid biomarkers, according to research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research on December 18, 2024.
However, experts question whether such a test would be useful.
“The need would seem to be fairly limited, mostly those with single joint involvement and a lack of other systemic features to specify a diagnosis, which is not that common, at least in rheumatology, where there are usually features in the history and physical that can clarify the diagnosis,” said Amanda E. Nelson, MD, MSCR, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She was not involved with the research.
The test uses an algorithm that incorporates concentrations of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and interleukin 8 (IL-8) in synovial fluid. The researchers hypothesized that a ratio of the two biomarkers could distinguish between primary OA and other inflammatory arthritic diagnoses.
“Primary OA is unlikely when either COMP concentration or COMP/IL‐8 ratio in the synovial fluid is low since these conditions indicate either lack of cartilage degradation or presence of high inflammation,” wrote Daniel Keter and coauthors at CD Diagnostics, Claymont, Delaware, and CD Laboratories, Towson, Maryland. “In contrast, a high COMP concentration result in combination with high COMP/IL‐8 ratio would be suggestive of low inflammation in the setting of cartilage deterioration, which is indicative of primary OA.”
In patients with OA, synovial fluid can be difficult to aspirate in sufficient amounts for testing, Nelson said.
“If synovial fluid is present and able to be aspirated, it is unclear if this test has any benefit over a simple, standard cell count and crystal assessment, which can also distinguish between osteoarthritis and more inflammatory arthritides,” she said.
Differentiating OA
To test this potential diagnostic algorithm, researchers obtained 171 knee synovial fluid samples from approved clinical remnant sample sources and a biovendor. All samples were annotated with an existing arthritic diagnosis, including 54 with primary OA, 57 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 30 with crystal arthritis (CA), and 30 with native septic arthritis (NSA).
Researchers assigned a CA diagnosis based on the presence of monosodium urate or calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate crystals in the synovial fluid, and NSA was determined via the Synovasure Alpha Defensin test. OA was confirmed via radiograph as Kellgren‐Lawrence grades 2‐4 with no other arthritic diagnoses. RA samples were purchased via a biovendor, and researchers were not provided with diagnosis‐confirming data.
All samples were randomized and blinded before testing, and researchers used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests for both COMP and IL-8 biomarkers.
Of the 54 OA samples, 47 tested positive for OA using the COMP + COMP/IL-8 ratio algorithm. Of the 117 samples with inflammatory arthritis, 13 tested positive for OA. Overall, the diagnostic algorithm demonstrated a clinical sensitivity of 87.0% and specificity of 88.9%. The positive predictive value was 78.3%, while the negative predictive value was 93.7%.
Unclear Clinical Need
Nelson noted that while this test aims to differentiate between arthritic diagnoses, patients can also have multiple conditions.
“Many individuals with rheumatoid arthritis will develop osteoarthritis, but they can have both, so a yes/no test is of unclear utility,” she said. OA and calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease can often occur together, “but the driver is really the OA, and the CPPD is present but not actively inflammatory,” she continued. “Septic arthritis should be readily distinguishable by cell count alone [and again, can coexist with any of the other conditions], and a thorough history and physical should be able to differentiate in most cases.”
While these results from this study are “reasonably impressive,” more clinical information is needed to interpret these results, added C. Kent Kwoh, MD, director of the University of Arizona Arthritis Center and professor of medicine and medical imaging at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, Arizona.
Because the study is retrospective in nature and researchers obtained specimens from different sources, it was not clear if these patients were being treated when these samples were taken and if their various conditions were controlled or flaring.
“I would say this is a reasonable first step,” Kwoh said. “We would need prospective studies, more clinical characterization, and potentially longitudinal studies to understand when this test may be useful.”
This research was internally funded by Zimmer Biomet. All authors were employees of CD Diagnostics or CD Laboratories, both of which are subsidiaries of Zimmer Biomet. Kwoh reported receiving grants or contracts with AbbVie, Artiva, Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cumberland, Pfizer, GSK, and Galapagos, and consulting fees from TrialSpark/Formation Bio, Express Scripts, GSK, TLC BioSciences, and AposHealth. He participates on Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards of Moebius Medical, Sun Pharma, Novartis, Xalud, and Kolon TissueGene. Nelson reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new diagnostic test can accurately distinguish osteoarthritis (OA) from inflammatory arthritis using two synovial fluid biomarkers, according to research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research on December 18, 2024.
However, experts question whether such a test would be useful.
“The need would seem to be fairly limited, mostly those with single joint involvement and a lack of other systemic features to specify a diagnosis, which is not that common, at least in rheumatology, where there are usually features in the history and physical that can clarify the diagnosis,” said Amanda E. Nelson, MD, MSCR, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She was not involved with the research.
The test uses an algorithm that incorporates concentrations of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and interleukin 8 (IL-8) in synovial fluid. The researchers hypothesized that a ratio of the two biomarkers could distinguish between primary OA and other inflammatory arthritic diagnoses.
“Primary OA is unlikely when either COMP concentration or COMP/IL‐8 ratio in the synovial fluid is low since these conditions indicate either lack of cartilage degradation or presence of high inflammation,” wrote Daniel Keter and coauthors at CD Diagnostics, Claymont, Delaware, and CD Laboratories, Towson, Maryland. “In contrast, a high COMP concentration result in combination with high COMP/IL‐8 ratio would be suggestive of low inflammation in the setting of cartilage deterioration, which is indicative of primary OA.”
In patients with OA, synovial fluid can be difficult to aspirate in sufficient amounts for testing, Nelson said.
“If synovial fluid is present and able to be aspirated, it is unclear if this test has any benefit over a simple, standard cell count and crystal assessment, which can also distinguish between osteoarthritis and more inflammatory arthritides,” she said.
Differentiating OA
To test this potential diagnostic algorithm, researchers obtained 171 knee synovial fluid samples from approved clinical remnant sample sources and a biovendor. All samples were annotated with an existing arthritic diagnosis, including 54 with primary OA, 57 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 30 with crystal arthritis (CA), and 30 with native septic arthritis (NSA).
Researchers assigned a CA diagnosis based on the presence of monosodium urate or calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate crystals in the synovial fluid, and NSA was determined via the Synovasure Alpha Defensin test. OA was confirmed via radiograph as Kellgren‐Lawrence grades 2‐4 with no other arthritic diagnoses. RA samples were purchased via a biovendor, and researchers were not provided with diagnosis‐confirming data.
All samples were randomized and blinded before testing, and researchers used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests for both COMP and IL-8 biomarkers.
Of the 54 OA samples, 47 tested positive for OA using the COMP + COMP/IL-8 ratio algorithm. Of the 117 samples with inflammatory arthritis, 13 tested positive for OA. Overall, the diagnostic algorithm demonstrated a clinical sensitivity of 87.0% and specificity of 88.9%. The positive predictive value was 78.3%, while the negative predictive value was 93.7%.
Unclear Clinical Need
Nelson noted that while this test aims to differentiate between arthritic diagnoses, patients can also have multiple conditions.
“Many individuals with rheumatoid arthritis will develop osteoarthritis, but they can have both, so a yes/no test is of unclear utility,” she said. OA and calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease can often occur together, “but the driver is really the OA, and the CPPD is present but not actively inflammatory,” she continued. “Septic arthritis should be readily distinguishable by cell count alone [and again, can coexist with any of the other conditions], and a thorough history and physical should be able to differentiate in most cases.”
While these results from this study are “reasonably impressive,” more clinical information is needed to interpret these results, added C. Kent Kwoh, MD, director of the University of Arizona Arthritis Center and professor of medicine and medical imaging at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, Arizona.
Because the study is retrospective in nature and researchers obtained specimens from different sources, it was not clear if these patients were being treated when these samples were taken and if their various conditions were controlled or flaring.
“I would say this is a reasonable first step,” Kwoh said. “We would need prospective studies, more clinical characterization, and potentially longitudinal studies to understand when this test may be useful.”
This research was internally funded by Zimmer Biomet. All authors were employees of CD Diagnostics or CD Laboratories, both of which are subsidiaries of Zimmer Biomet. Kwoh reported receiving grants or contracts with AbbVie, Artiva, Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cumberland, Pfizer, GSK, and Galapagos, and consulting fees from TrialSpark/Formation Bio, Express Scripts, GSK, TLC BioSciences, and AposHealth. He participates on Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards of Moebius Medical, Sun Pharma, Novartis, Xalud, and Kolon TissueGene. Nelson reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
A new diagnostic test can accurately distinguish osteoarthritis (OA) from inflammatory arthritis using two synovial fluid biomarkers, according to research published in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research on December 18, 2024.
However, experts question whether such a test would be useful.
“The need would seem to be fairly limited, mostly those with single joint involvement and a lack of other systemic features to specify a diagnosis, which is not that common, at least in rheumatology, where there are usually features in the history and physical that can clarify the diagnosis,” said Amanda E. Nelson, MD, MSCR, professor of medicine in the Division of Rheumatology, Allergy, and Immunology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. She was not involved with the research.
The test uses an algorithm that incorporates concentrations of cartilage oligomeric matrix protein (COMP) and interleukin 8 (IL-8) in synovial fluid. The researchers hypothesized that a ratio of the two biomarkers could distinguish between primary OA and other inflammatory arthritic diagnoses.
“Primary OA is unlikely when either COMP concentration or COMP/IL‐8 ratio in the synovial fluid is low since these conditions indicate either lack of cartilage degradation or presence of high inflammation,” wrote Daniel Keter and coauthors at CD Diagnostics, Claymont, Delaware, and CD Laboratories, Towson, Maryland. “In contrast, a high COMP concentration result in combination with high COMP/IL‐8 ratio would be suggestive of low inflammation in the setting of cartilage deterioration, which is indicative of primary OA.”
In patients with OA, synovial fluid can be difficult to aspirate in sufficient amounts for testing, Nelson said.
“If synovial fluid is present and able to be aspirated, it is unclear if this test has any benefit over a simple, standard cell count and crystal assessment, which can also distinguish between osteoarthritis and more inflammatory arthritides,” she said.
Differentiating OA
To test this potential diagnostic algorithm, researchers obtained 171 knee synovial fluid samples from approved clinical remnant sample sources and a biovendor. All samples were annotated with an existing arthritic diagnosis, including 54 with primary OA, 57 with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), 30 with crystal arthritis (CA), and 30 with native septic arthritis (NSA).
Researchers assigned a CA diagnosis based on the presence of monosodium urate or calcium pyrophosphate dehydrate crystals in the synovial fluid, and NSA was determined via the Synovasure Alpha Defensin test. OA was confirmed via radiograph as Kellgren‐Lawrence grades 2‐4 with no other arthritic diagnoses. RA samples were purchased via a biovendor, and researchers were not provided with diagnosis‐confirming data.
All samples were randomized and blinded before testing, and researchers used enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay tests for both COMP and IL-8 biomarkers.
Of the 54 OA samples, 47 tested positive for OA using the COMP + COMP/IL-8 ratio algorithm. Of the 117 samples with inflammatory arthritis, 13 tested positive for OA. Overall, the diagnostic algorithm demonstrated a clinical sensitivity of 87.0% and specificity of 88.9%. The positive predictive value was 78.3%, while the negative predictive value was 93.7%.
Unclear Clinical Need
Nelson noted that while this test aims to differentiate between arthritic diagnoses, patients can also have multiple conditions.
“Many individuals with rheumatoid arthritis will develop osteoarthritis, but they can have both, so a yes/no test is of unclear utility,” she said. OA and calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) disease can often occur together, “but the driver is really the OA, and the CPPD is present but not actively inflammatory,” she continued. “Septic arthritis should be readily distinguishable by cell count alone [and again, can coexist with any of the other conditions], and a thorough history and physical should be able to differentiate in most cases.”
While these results from this study are “reasonably impressive,” more clinical information is needed to interpret these results, added C. Kent Kwoh, MD, director of the University of Arizona Arthritis Center and professor of medicine and medical imaging at the University of Arizona College of Medicine, Tucson, Arizona.
Because the study is retrospective in nature and researchers obtained specimens from different sources, it was not clear if these patients were being treated when these samples were taken and if their various conditions were controlled or flaring.
“I would say this is a reasonable first step,” Kwoh said. “We would need prospective studies, more clinical characterization, and potentially longitudinal studies to understand when this test may be useful.”
This research was internally funded by Zimmer Biomet. All authors were employees of CD Diagnostics or CD Laboratories, both of which are subsidiaries of Zimmer Biomet. Kwoh reported receiving grants or contracts with AbbVie, Artiva, Eli Lilly and Company, Bristol Myers Squibb, Cumberland, Pfizer, GSK, and Galapagos, and consulting fees from TrialSpark/Formation Bio, Express Scripts, GSK, TLC BioSciences, and AposHealth. He participates on Data Safety Monitoring or Advisory Boards of Moebius Medical, Sun Pharma, Novartis, Xalud, and Kolon TissueGene. Nelson reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF ORTHOPAEDIC RESEARCH
Health Impacts of Micro- and Nanoplastics
In preparation for a future international treaty aimed at reducing plastic pollution, the French Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices presented the conclusions of a public hearing on the impact of plastics on various aspects of human health.
Increased Global Plastic Production
Philippe Bolo, a member of the French Democratic Party and the rapporteur for the public mission on the health impacts of plastics, spoke about the latest round of treaty negotiations, held from November 25 to December 1 in South Korea, attended by leading French and global experts about the impact of plastics on human health.
The hearing highlighted a sharp increase in plastic production. “It has doubled in the last 20 years and is expected to exceed 500 million tons in 2024,” Bolo said. This is about 60 kg per person. According to projections from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, on its current trajectory, plastic production will reach 750 million tons by 2040 and surpass 1 billion tons before 2050, he said.
Minimal Plastic Waste Recycling
Around one third (32%) of plastics are used for packaging. “Therefore, most plastic production is still intended for single-use purposes,” he said. Plastic waste follows a similar growth trajectory, with volumes expected to rise from 360 million tons in 2020 to 617 million tons by 2040 unless action is taken. Very little of this waste is recycled, even in the most countries that are most advanced in terms of collection, sorting, and processing.
In France, for example, in 2018, only 0.6 million tons of the 3.6 million tons of plastic waste produced was truly recycled. This is less than one fifth (17%). Globally, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled. In 2020, plastic waste that ended up in the environment represented 81 million tons, or 22% of the total. “Beyond waste, this leads to pollution by microplastics and nanoplastics, resulting from their fragmentation. All environments are affected: Seas, rivers, soils, air, and even living organisms,” Bolo said.
Methodological Challenges
However, measuring the impact of plastics on health faces methodological difficulties due to the wide variety of composition, size, and shape of plastics. Nevertheless, the French Standardization Association (Association Française de Normalisation) has conducted work to establish a characterization standard for microplastics in water, which serves as an international reference.
“It is also very difficult to know what we are ingesting,” Bolo said. “A study conducted in 2019 estimated that the average human absorbs 5 grams of plastics per week, the equivalent of a credit card.» Since then, other studies have revised this estimate downward, but no consensus has been reached.
A recent study across 109 countries, both industrialized and developing, found significant exposure, estimated at 500 mg/d, particularly in Southeast Asian countries, where it was due mainly to seafood consumption.
A study concluded that plastic water bottles contain 240,000 particles per liter, 90% of which are nanoplastics. These nanoparticles can pass through the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream and reach several organs including the heart, brain, and placenta, as well as the fetus.
Changes to the Microbiome
Microplastics also accumulate in organs. Thus, the amount of plastic in the lungs increases with age, suggesting that particles may persist in the body without being eliminated. The health consequences of this are still poorly understood, but exposure to plastics appears to cause changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Pathobionts (commensal bacteria with harmful potential) have been found in both adults and children, which could contribute to dysbiosis of the gut microbiome. Furthermore, a decrease in butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid beneficial to health, has been observed in children’s intestines.
Inhaled nanoplastics may disrupt the mucociliary clearance mechanisms of the respiratory system. The toxicity of inhaled plastic particles was demonstrated as early as the 1970s among workers in the flocking industry. Some developed lung function impairments, shortness of breath, inflammation, fibrosis, and even lung cancer. Similar symptoms have been observed in workers in the textile and polyvinyl chloride industries.
A study published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine measured the amount of microplastics collected from carotid plaque of more than 300 patients who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. It found a 4.53 times higher risk for the primary endpoint, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and all-cause mortality, among individuals with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque compared with those without.
Health Affects High
The danger of plastics is also directly linked to the chemical substances they contain. A general scientific review looked at the health impacts of three chemicals used almost exclusively in plastics: Polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs), used as flame retardants in textiles or electronics; bisphenol A (BPA), used in the lining of cans and bottles; and phthalates, particularly diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), used to make plastics more flexible.
The review highlighted strong epidemiological evidence linking fetal exposure to PBDEs during pregnancy to low birth weight and later exposure to delayed or impaired cognitive development in children and even a loss of IQ. Statistically significant evidence of disruption of thyroid function in adults was also found.
BPA is linked to genital malformations in female newborns exposed to BPA in utero, type 2 diabetes in adults, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women. BPA exposure also increases the risk for obesity and hypertension in both children and adults, as well as the risk for cardiovascular disease in adults.
Finally, the review established links between exposure to DEHP and miscarriages, genital malformations in male newborns, delayed or impaired cognitive development in children, loss of IQ, delayed psychomotor development, early puberty in young girls, and endometriosis in young women. DEHP exposure also has multiple effects on cardiometabolic health, including insulin resistance, obesity, and elevated blood pressure.
The economic costs associated with the health impacts of these three substances have been estimated at $675 billion in the United States.
Bolo said that the solution to this plastic pollution is necessarily international. “We need an ambitious and legally binding treaty to reduce plastic production,” he said. “The damage is already done; we need to act to protect human health,” he concluded. The parliamentary office has made nine recommendations to the treaty negotiators.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In preparation for a future international treaty aimed at reducing plastic pollution, the French Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices presented the conclusions of a public hearing on the impact of plastics on various aspects of human health.
Increased Global Plastic Production
Philippe Bolo, a member of the French Democratic Party and the rapporteur for the public mission on the health impacts of plastics, spoke about the latest round of treaty negotiations, held from November 25 to December 1 in South Korea, attended by leading French and global experts about the impact of plastics on human health.
The hearing highlighted a sharp increase in plastic production. “It has doubled in the last 20 years and is expected to exceed 500 million tons in 2024,” Bolo said. This is about 60 kg per person. According to projections from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, on its current trajectory, plastic production will reach 750 million tons by 2040 and surpass 1 billion tons before 2050, he said.
Minimal Plastic Waste Recycling
Around one third (32%) of plastics are used for packaging. “Therefore, most plastic production is still intended for single-use purposes,” he said. Plastic waste follows a similar growth trajectory, with volumes expected to rise from 360 million tons in 2020 to 617 million tons by 2040 unless action is taken. Very little of this waste is recycled, even in the most countries that are most advanced in terms of collection, sorting, and processing.
In France, for example, in 2018, only 0.6 million tons of the 3.6 million tons of plastic waste produced was truly recycled. This is less than one fifth (17%). Globally, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled. In 2020, plastic waste that ended up in the environment represented 81 million tons, or 22% of the total. “Beyond waste, this leads to pollution by microplastics and nanoplastics, resulting from their fragmentation. All environments are affected: Seas, rivers, soils, air, and even living organisms,” Bolo said.
Methodological Challenges
However, measuring the impact of plastics on health faces methodological difficulties due to the wide variety of composition, size, and shape of plastics. Nevertheless, the French Standardization Association (Association Française de Normalisation) has conducted work to establish a characterization standard for microplastics in water, which serves as an international reference.
“It is also very difficult to know what we are ingesting,” Bolo said. “A study conducted in 2019 estimated that the average human absorbs 5 grams of plastics per week, the equivalent of a credit card.» Since then, other studies have revised this estimate downward, but no consensus has been reached.
A recent study across 109 countries, both industrialized and developing, found significant exposure, estimated at 500 mg/d, particularly in Southeast Asian countries, where it was due mainly to seafood consumption.
A study concluded that plastic water bottles contain 240,000 particles per liter, 90% of which are nanoplastics. These nanoparticles can pass through the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream and reach several organs including the heart, brain, and placenta, as well as the fetus.
Changes to the Microbiome
Microplastics also accumulate in organs. Thus, the amount of plastic in the lungs increases with age, suggesting that particles may persist in the body without being eliminated. The health consequences of this are still poorly understood, but exposure to plastics appears to cause changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Pathobionts (commensal bacteria with harmful potential) have been found in both adults and children, which could contribute to dysbiosis of the gut microbiome. Furthermore, a decrease in butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid beneficial to health, has been observed in children’s intestines.
Inhaled nanoplastics may disrupt the mucociliary clearance mechanisms of the respiratory system. The toxicity of inhaled plastic particles was demonstrated as early as the 1970s among workers in the flocking industry. Some developed lung function impairments, shortness of breath, inflammation, fibrosis, and even lung cancer. Similar symptoms have been observed in workers in the textile and polyvinyl chloride industries.
A study published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine measured the amount of microplastics collected from carotid plaque of more than 300 patients who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. It found a 4.53 times higher risk for the primary endpoint, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and all-cause mortality, among individuals with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque compared with those without.
Health Affects High
The danger of plastics is also directly linked to the chemical substances they contain. A general scientific review looked at the health impacts of three chemicals used almost exclusively in plastics: Polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs), used as flame retardants in textiles or electronics; bisphenol A (BPA), used in the lining of cans and bottles; and phthalates, particularly diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), used to make plastics more flexible.
The review highlighted strong epidemiological evidence linking fetal exposure to PBDEs during pregnancy to low birth weight and later exposure to delayed or impaired cognitive development in children and even a loss of IQ. Statistically significant evidence of disruption of thyroid function in adults was also found.
BPA is linked to genital malformations in female newborns exposed to BPA in utero, type 2 diabetes in adults, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women. BPA exposure also increases the risk for obesity and hypertension in both children and adults, as well as the risk for cardiovascular disease in adults.
Finally, the review established links between exposure to DEHP and miscarriages, genital malformations in male newborns, delayed or impaired cognitive development in children, loss of IQ, delayed psychomotor development, early puberty in young girls, and endometriosis in young women. DEHP exposure also has multiple effects on cardiometabolic health, including insulin resistance, obesity, and elevated blood pressure.
The economic costs associated with the health impacts of these three substances have been estimated at $675 billion in the United States.
Bolo said that the solution to this plastic pollution is necessarily international. “We need an ambitious and legally binding treaty to reduce plastic production,” he said. “The damage is already done; we need to act to protect human health,” he concluded. The parliamentary office has made nine recommendations to the treaty negotiators.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In preparation for a future international treaty aimed at reducing plastic pollution, the French Parliamentary Office for the Evaluation of Scientific and Technological Choices presented the conclusions of a public hearing on the impact of plastics on various aspects of human health.
Increased Global Plastic Production
Philippe Bolo, a member of the French Democratic Party and the rapporteur for the public mission on the health impacts of plastics, spoke about the latest round of treaty negotiations, held from November 25 to December 1 in South Korea, attended by leading French and global experts about the impact of plastics on human health.
The hearing highlighted a sharp increase in plastic production. “It has doubled in the last 20 years and is expected to exceed 500 million tons in 2024,” Bolo said. This is about 60 kg per person. According to projections from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development, on its current trajectory, plastic production will reach 750 million tons by 2040 and surpass 1 billion tons before 2050, he said.
Minimal Plastic Waste Recycling
Around one third (32%) of plastics are used for packaging. “Therefore, most plastic production is still intended for single-use purposes,” he said. Plastic waste follows a similar growth trajectory, with volumes expected to rise from 360 million tons in 2020 to 617 million tons by 2040 unless action is taken. Very little of this waste is recycled, even in the most countries that are most advanced in terms of collection, sorting, and processing.
In France, for example, in 2018, only 0.6 million tons of the 3.6 million tons of plastic waste produced was truly recycled. This is less than one fifth (17%). Globally, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled. In 2020, plastic waste that ended up in the environment represented 81 million tons, or 22% of the total. “Beyond waste, this leads to pollution by microplastics and nanoplastics, resulting from their fragmentation. All environments are affected: Seas, rivers, soils, air, and even living organisms,” Bolo said.
Methodological Challenges
However, measuring the impact of plastics on health faces methodological difficulties due to the wide variety of composition, size, and shape of plastics. Nevertheless, the French Standardization Association (Association Française de Normalisation) has conducted work to establish a characterization standard for microplastics in water, which serves as an international reference.
“It is also very difficult to know what we are ingesting,” Bolo said. “A study conducted in 2019 estimated that the average human absorbs 5 grams of plastics per week, the equivalent of a credit card.» Since then, other studies have revised this estimate downward, but no consensus has been reached.
A recent study across 109 countries, both industrialized and developing, found significant exposure, estimated at 500 mg/d, particularly in Southeast Asian countries, where it was due mainly to seafood consumption.
A study concluded that plastic water bottles contain 240,000 particles per liter, 90% of which are nanoplastics. These nanoparticles can pass through the intestinal barrier to enter the bloodstream and reach several organs including the heart, brain, and placenta, as well as the fetus.
Changes to the Microbiome
Microplastics also accumulate in organs. Thus, the amount of plastic in the lungs increases with age, suggesting that particles may persist in the body without being eliminated. The health consequences of this are still poorly understood, but exposure to plastics appears to cause changes in the composition of the intestinal microbiota. Pathobionts (commensal bacteria with harmful potential) have been found in both adults and children, which could contribute to dysbiosis of the gut microbiome. Furthermore, a decrease in butyrate, a short-chain fatty acid beneficial to health, has been observed in children’s intestines.
Inhaled nanoplastics may disrupt the mucociliary clearance mechanisms of the respiratory system. The toxicity of inhaled plastic particles was demonstrated as early as the 1970s among workers in the flocking industry. Some developed lung function impairments, shortness of breath, inflammation, fibrosis, and even lung cancer. Similar symptoms have been observed in workers in the textile and polyvinyl chloride industries.
A study published recently in The New England Journal of Medicine measured the amount of microplastics collected from carotid plaque of more than 300 patients who had undergone carotid endarterectomy for asymptomatic carotid artery disease. It found a 4.53 times higher risk for the primary endpoint, a composite of myocardial infarction, stroke, and all-cause mortality, among individuals with microplastics and nanoplastics in plaque compared with those without.
Health Affects High
The danger of plastics is also directly linked to the chemical substances they contain. A general scientific review looked at the health impacts of three chemicals used almost exclusively in plastics: Polybromodiphenyl ethers (PBDEs), used as flame retardants in textiles or electronics; bisphenol A (BPA), used in the lining of cans and bottles; and phthalates, particularly diethylhexyl phthalate (DEHP), used to make plastics more flexible.
The review highlighted strong epidemiological evidence linking fetal exposure to PBDEs during pregnancy to low birth weight and later exposure to delayed or impaired cognitive development in children and even a loss of IQ. Statistically significant evidence of disruption of thyroid function in adults was also found.
BPA is linked to genital malformations in female newborns exposed to BPA in utero, type 2 diabetes in adults, insulin resistance, and polycystic ovary syndrome in women. BPA exposure also increases the risk for obesity and hypertension in both children and adults, as well as the risk for cardiovascular disease in adults.
Finally, the review established links between exposure to DEHP and miscarriages, genital malformations in male newborns, delayed or impaired cognitive development in children, loss of IQ, delayed psychomotor development, early puberty in young girls, and endometriosis in young women. DEHP exposure also has multiple effects on cardiometabolic health, including insulin resistance, obesity, and elevated blood pressure.
The economic costs associated with the health impacts of these three substances have been estimated at $675 billion in the United States.
Bolo said that the solution to this plastic pollution is necessarily international. “We need an ambitious and legally binding treaty to reduce plastic production,” he said. “The damage is already done; we need to act to protect human health,” he concluded. The parliamentary office has made nine recommendations to the treaty negotiators.
This story was translated from Medscape’s French edition using several editorial tools, including AI, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Which Biologics May Contribute to Cancer Risk in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis?
TOPLINE:
The initiation of biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs), particularly rituximab and abatacept, is associated with an increased risk for incident cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) within 2 years of starting treatment.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess the safety of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, non-TNF inhibitors, and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in patients with RA using US administrative claims data from the Merative Marketscan Research Databases from November 2012 to December 2021.
- A total of 25,305 patients with RA (median age, 50 years; 79% women; 49% from the southern United States) were identified using diagnostic codes on or before treatment initiation.
- Treatment exposures, including the initiation of TNF inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, and infliximab), non-TNF inhibitors (abatacept, interleukin 6 [IL-6] inhibitors, and rituximab), and JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib), were compared.
- The primary outcome was any incident cancer (excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer) occurring after a minimum of 90 days and within 2 years of treatment initiation.
- Sensitivity analyses used 1:1 propensity matching to compare cancer rates between populations treated with rituximab, IL-6 inhibitors, abatacept, or JAK inhibitors and matched reference populations treated with TNF inhibitors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rituximab (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.17-3.14) and abatacept (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.03-2.11) were significantly associated with an increased risk for incident cancer, compared with TNF inhibitors.
- In the propensity-matched analysis, a statistically significant increase in risk was observed in patients treated with rituximab (aHR, 4.37; 95% CI, 1.48-12.93) and abatacept (aHR, 3.12; 95%CI, 1.52-6.44).
- IL-6 inhibitors showed no significant association with cancer in the primary analysis, but a significantly increased risk was observed in the propensity-matched analysis (HR, 5.65; 95% CI, 1.11-28.79).
- JAK inhibitors were not associated with a significant increase in the risk for cancer, compared with TNF inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given the limitations of using private insurance claims data and confounding by indication, it is likely that these patients may have a higher disease burden, resulting in channeling bias,” the authors wrote. “To understand these associations, larger studies with longer follow-up and more granular collection of data, including medication indications and RA disease activity measures, would be needed for better comparison of incident cancer risk among these drugs,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Xavier Sendaydiego, MD, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
A relatively small number of cancer outcomes may have affected the ability to adjust for confounders. The follow-up period was limited to 2 years, potentially missing long-term cancer risks. The use of US-specific administrative claims data, including only patients aged 18-64 years, may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the claims data lacked direct measures of disease activity or severity of RA, and information on treatment adherence was unavailable, leading to potential misclassification.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and the National Institute on Aging. Some authors reported receiving personal fees, nonfinancial support, and grants from various pharmaceutical companies or government sources. One author reported having a pending patent and another author reported receiving a fellowship, travel reimbursement, and royalties outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The initiation of biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs), particularly rituximab and abatacept, is associated with an increased risk for incident cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) within 2 years of starting treatment.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess the safety of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, non-TNF inhibitors, and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in patients with RA using US administrative claims data from the Merative Marketscan Research Databases from November 2012 to December 2021.
- A total of 25,305 patients with RA (median age, 50 years; 79% women; 49% from the southern United States) were identified using diagnostic codes on or before treatment initiation.
- Treatment exposures, including the initiation of TNF inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, and infliximab), non-TNF inhibitors (abatacept, interleukin 6 [IL-6] inhibitors, and rituximab), and JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib), were compared.
- The primary outcome was any incident cancer (excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer) occurring after a minimum of 90 days and within 2 years of treatment initiation.
- Sensitivity analyses used 1:1 propensity matching to compare cancer rates between populations treated with rituximab, IL-6 inhibitors, abatacept, or JAK inhibitors and matched reference populations treated with TNF inhibitors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rituximab (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.17-3.14) and abatacept (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.03-2.11) were significantly associated with an increased risk for incident cancer, compared with TNF inhibitors.
- In the propensity-matched analysis, a statistically significant increase in risk was observed in patients treated with rituximab (aHR, 4.37; 95% CI, 1.48-12.93) and abatacept (aHR, 3.12; 95%CI, 1.52-6.44).
- IL-6 inhibitors showed no significant association with cancer in the primary analysis, but a significantly increased risk was observed in the propensity-matched analysis (HR, 5.65; 95% CI, 1.11-28.79).
- JAK inhibitors were not associated with a significant increase in the risk for cancer, compared with TNF inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given the limitations of using private insurance claims data and confounding by indication, it is likely that these patients may have a higher disease burden, resulting in channeling bias,” the authors wrote. “To understand these associations, larger studies with longer follow-up and more granular collection of data, including medication indications and RA disease activity measures, would be needed for better comparison of incident cancer risk among these drugs,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Xavier Sendaydiego, MD, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
A relatively small number of cancer outcomes may have affected the ability to adjust for confounders. The follow-up period was limited to 2 years, potentially missing long-term cancer risks. The use of US-specific administrative claims data, including only patients aged 18-64 years, may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the claims data lacked direct measures of disease activity or severity of RA, and information on treatment adherence was unavailable, leading to potential misclassification.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and the National Institute on Aging. Some authors reported receiving personal fees, nonfinancial support, and grants from various pharmaceutical companies or government sources. One author reported having a pending patent and another author reported receiving a fellowship, travel reimbursement, and royalties outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The initiation of biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (b/tsDMARDs), particularly rituximab and abatacept, is associated with an increased risk for incident cancer in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) within 2 years of starting treatment.
METHODOLOGY:
- The researchers conducted a retrospective cohort study to assess the safety of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors, non-TNF inhibitors, and Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors in patients with RA using US administrative claims data from the Merative Marketscan Research Databases from November 2012 to December 2021.
- A total of 25,305 patients with RA (median age, 50 years; 79% women; 49% from the southern United States) were identified using diagnostic codes on or before treatment initiation.
- Treatment exposures, including the initiation of TNF inhibitors (adalimumab, etanercept, certolizumab pegol, golimumab, and infliximab), non-TNF inhibitors (abatacept, interleukin 6 [IL-6] inhibitors, and rituximab), and JAK inhibitors (tofacitinib, baricitinib, and upadacitinib), were compared.
- The primary outcome was any incident cancer (excluding nonmelanoma skin cancer) occurring after a minimum of 90 days and within 2 years of treatment initiation.
- Sensitivity analyses used 1:1 propensity matching to compare cancer rates between populations treated with rituximab, IL-6 inhibitors, abatacept, or JAK inhibitors and matched reference populations treated with TNF inhibitors.
TAKEAWAY:
- Rituximab (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.91; 95% CI, 1.17-3.14) and abatacept (aHR, 1.47; 95% CI, 1.03-2.11) were significantly associated with an increased risk for incident cancer, compared with TNF inhibitors.
- In the propensity-matched analysis, a statistically significant increase in risk was observed in patients treated with rituximab (aHR, 4.37; 95% CI, 1.48-12.93) and abatacept (aHR, 3.12; 95%CI, 1.52-6.44).
- IL-6 inhibitors showed no significant association with cancer in the primary analysis, but a significantly increased risk was observed in the propensity-matched analysis (HR, 5.65; 95% CI, 1.11-28.79).
- JAK inhibitors were not associated with a significant increase in the risk for cancer, compared with TNF inhibitors.
IN PRACTICE:
“Given the limitations of using private insurance claims data and confounding by indication, it is likely that these patients may have a higher disease burden, resulting in channeling bias,” the authors wrote. “To understand these associations, larger studies with longer follow-up and more granular collection of data, including medication indications and RA disease activity measures, would be needed for better comparison of incident cancer risk among these drugs,” they added.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Xavier Sendaydiego, MD, University of Washington, Seattle. It was published online in JAMA Network Open.
LIMITATIONS:
A relatively small number of cancer outcomes may have affected the ability to adjust for confounders. The follow-up period was limited to 2 years, potentially missing long-term cancer risks. The use of US-specific administrative claims data, including only patients aged 18-64 years, may limit the generalizability of the findings. Additionally, the claims data lacked direct measures of disease activity or severity of RA, and information on treatment adherence was unavailable, leading to potential misclassification.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by grants from the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases and the National Institute on Aging. Some authors reported receiving personal fees, nonfinancial support, and grants from various pharmaceutical companies or government sources. One author reported having a pending patent and another author reported receiving a fellowship, travel reimbursement, and royalties outside the submitted work.
This article was created using several editorial tools, including artificial intelligence, as part of the process. Human editors reviewed this content before publication. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.


