User login
Ascending Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms: A ‘Silver Lining’?
Often known as a “silent killer,” ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms (ATAAs) may grow asymptomatically until they rupture, at which point, mortality is over 90%.
But and by extension, for those who have one, a significantly reduced risk for coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction (MI).
“We noticed in the operating room that many patients we worked on who had an ATAA had pristine arteries, like a teenager’s,” said John Elefteriades, MD, William W.L. Glenn Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery and former chief of cardiothoracic surgery at Yale University and Yale New Haven Hospital, New Haven, Connecticut. “The same was true of the femoral artery, which we use to hook up to the heart-lung machine.”
Elefteriades and colleagues have been investigating the implications of this association for more than two decades. Many of their studies are highlighted in a recent review of the evidence supporting the protective relationship between ATAAs and the development of atherosclerosis and the possible mechanisms driving the relationship.
“We see four different layers of protection,” said Sandip Mukherjee, MD, medical director of the Aortic Institute at Yale New Haven Hospital and a senior editor of the journal AORTA. Mukherjee collaborated with Elefteriades on many of the studies.
The first layer of protection is lower intima-media thickness, specifically, 0.131 mm lower than in individuals without an ATAA. “It may not seem like very much, but one point can actually translate into a 13%-15% decline in the rate of myocardial infarction or stroke,” Dr. Mukherjee said.
The second layer is lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Lower LDL cholesterol levels (75 mg/dL) were associated with increased odds of ATAAs (odds ratio [OR], 1.21), whereas elevated levels (150 mg/dL and 200 mg/dL) were associated with decreased odds of ATAAs (OR, 0.62 and 0.29, respectively).
Lower calcification scores for the coronary arteries are the third layer of protection (6.73 vs 9.36 in one study).
The fourth protective layer is a significantly reduced prevalence of coronary artery disease. A study of individuals with ATAA compared to controls found 61 of those with ATAA had coronary artery disease vs 140 of controls, and 11 vs 83 had experienced an MI. Of note, patients with ATAAs were protected despite having higher body mass indices than controls.
Other MI risk factors such as age increased the risk even among those with an ATAA but, again, much less so than among controls; a multivariable binary logistic regression of data in the team’s review showed that patients with ATAAs were 298, 250, and 232 times less likely to have an MI than if they had a family history of MI, dyslipidemia, or hypertension, respectively.
Why the Protection?
The ligamentum arteriosum separates the ascending from the descending (thoracoabdominal) aorta. ATAAs, located above the ligamentum, tend to be pro-aneurysmal but anti-atherosclerotic. In the descending aorta, below the ligamentum, atherosclerotic aneurysms develop.
The differences between the two sections of the aorta originate in the germ layer in the embryo, Dr. Elefteriades said. “The fundamental difference in tissue of origin translates into marked differences in the character of aneurysms in the different aortic segments.”
What specifically underlies the reduced cardiovascular risk? “We don’t really know, but we think that there may be two possible etiologies,” Dr. Mukherjee said. One hypothesis involves transforming growth factor–beta (TGF-beta), which is overexpressed in patients with ATAA and seems to increase their vulnerability to aneurysms while also conferring protection from coronary disease risk.
Some studies have shown differences in cellular responses to TGF-beta between the thoracic and abdominal aorta, including collagen production and contractility. Others have shown that some patients who have had an MI have polymorphisms that decrease their levels of TGF-beta.
Furthermore, TGF-beta plays a key role in the development of the intimal layer, which could underpin the lack of intimal thickening in patients with ATAA.
But overall, studies have been mixed and challenging to interpret, Dr. Elefteriades and Dr. Mukherjee agreed. TGF-beta has multiple remodeling roles in the body, and it is difficult at this point to isolate its exact role in aortic disease.
Another hypothesis involves matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are dysregulated in patients with ATAA and may confer some protection, Mukherjee said. Several studies have shown higher plasma levels of certain MMPs in patients with ATAAs. MMPs also were found to be elevated in the thoracic aortic walls of patients with ATAA who had an aortic dissection, as well as in the aortic smooth muscle cells in the intima and media.
In addition, some studies have shown increased levels of MMP-2 in the aortas of patients with ATAAs compared with patients with coronary artery disease.
Adding to the mix of possibilities, “We recently found a gene that’s dysregulated in our aneurysm patients that is very intimately related to atherosclerosis,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “But the work is too preliminary to say anything more at this point.”
“It would be fabulous to prove what it is causing this protection,” Dr. Mukherjee added. “But the truth is we don’t know. These are hypotheses.”
“The most important message from our work is that most clinicians need to dissociate an ATAA from the concept of atherosclerosis,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “The ascending aorta is not an atherosclerotic phenomenon.”
How to Manage Patients With ATAA
What does the distinct character of ATAAs mean for patient management? “Finding a drug to treat ATAAs — to prevent growth, rupture, or dissection — has been like a search for the Holy Grail,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “Statins are not necessary, as this is a non-atherosclerotic process. Although sporadic studies have reported beneficial effects from beta-blockers or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), this has often been based on ‘soft’ evidence, requiring a combination of outcome measures to achieve significance.”
That said, he noted, “The mainstay, common sense treatment is to keep blood pressure controlled. This is usually achieved by a beta-blocker and an ARB, even if the benefit is not via a direct biologic effect on the aneurysmal degenerative process, but via simple hemodynamics — discouraging rupture by keeping pressure in the aorta low.”
Dr. Mukherjee suggested that these patients should be referred to a specialty aneurysm center where their genes will be evaluated, and then the aneurysm will be followed very closely.
“If the aneurysm is larger than 4.5 cm, we screen the patient every single year, and if they have chest pain, we treat them the same way as we treat other aneurysms,” he said. “As a rule of thumb, if the aneurysm reaches 5 cm, it should come out, although the size at which this should happen may differ between 4.5 cm and 5.5 cm, depending on the patient’s body size.”
As for lifestyle management, Dr. Elefteriades said, “Protection from atherosclerosis and MI won’t go away after the aneurysm is removed. We think it’s in the body’s chemistry. But even though it’s very hard for those patients to have a heart attack, we don’t recommend they eat roast beef every night — although I do think they’d be protected from such lifestyle aberrations.”
For now, he added, “Our team is on a hunt to find a drug to treat ascending disease directly and effectively. We have ongoing laboratory experiments with two drugs undergoing investigation at some level. We hope to embark soon on clinical trials.”
‘A Milestone’
James Hamilton Black III, MD, vice chair of the writing committee for the 2022 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Aortic Disease Guideline and chief of Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, commented on the review and the concept of ATAA’s atherosclerotic protection.
“The association of ascending aortic aneurysms with a lower risk for MI is an interesting one, but it’s probably influenced, at least in part, by the patient population.” That population is at least partially curated since people are coming to an academic center. In addition, Dr. Black noted, “the patients with ATAAs are younger, and so age may be a confounding factor in the analyses. We wouldn’t expect them to have the same burden of atherosclerosis” as older patients.
Nevertheless, he said, “the findings speak to an emerging body of literature suggesting that although the aorta is a single organ, there are certainly different areas, and these would respond quite differently to environmental or genetic or heritable stressors. This isn’t surprising, and there probably are a lot of factors involved.”
Overall, he said, the findings underscore “the precision medicine approaches we need to take with patients with aortic diseases.”
In a commentary on the team’s review article, published in 2022, John G.T. Augoustides, MD, professor of anesthesiology and critical care at the Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, suggested that ATAA’s “silver lining” could advance the understanding of thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) management, be integrated with the expanding horizons in hereditary thoracic aortic disease, and might be explored in the context of bicuspid aortic valve disease.
Highlighting the “relative absence” of atherosclerosis in ascending aortic aneurysms and its importance is a “milestone in our understanding,” he concluded. “It is likely that future advances in TAAs will be significantly influenced by this observation.”
Dr. Elefteriades, Dr. Mukherjee, and Dr. Black have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Often known as a “silent killer,” ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms (ATAAs) may grow asymptomatically until they rupture, at which point, mortality is over 90%.
But and by extension, for those who have one, a significantly reduced risk for coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction (MI).
“We noticed in the operating room that many patients we worked on who had an ATAA had pristine arteries, like a teenager’s,” said John Elefteriades, MD, William W.L. Glenn Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery and former chief of cardiothoracic surgery at Yale University and Yale New Haven Hospital, New Haven, Connecticut. “The same was true of the femoral artery, which we use to hook up to the heart-lung machine.”
Elefteriades and colleagues have been investigating the implications of this association for more than two decades. Many of their studies are highlighted in a recent review of the evidence supporting the protective relationship between ATAAs and the development of atherosclerosis and the possible mechanisms driving the relationship.
“We see four different layers of protection,” said Sandip Mukherjee, MD, medical director of the Aortic Institute at Yale New Haven Hospital and a senior editor of the journal AORTA. Mukherjee collaborated with Elefteriades on many of the studies.
The first layer of protection is lower intima-media thickness, specifically, 0.131 mm lower than in individuals without an ATAA. “It may not seem like very much, but one point can actually translate into a 13%-15% decline in the rate of myocardial infarction or stroke,” Dr. Mukherjee said.
The second layer is lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Lower LDL cholesterol levels (75 mg/dL) were associated with increased odds of ATAAs (odds ratio [OR], 1.21), whereas elevated levels (150 mg/dL and 200 mg/dL) were associated with decreased odds of ATAAs (OR, 0.62 and 0.29, respectively).
Lower calcification scores for the coronary arteries are the third layer of protection (6.73 vs 9.36 in one study).
The fourth protective layer is a significantly reduced prevalence of coronary artery disease. A study of individuals with ATAA compared to controls found 61 of those with ATAA had coronary artery disease vs 140 of controls, and 11 vs 83 had experienced an MI. Of note, patients with ATAAs were protected despite having higher body mass indices than controls.
Other MI risk factors such as age increased the risk even among those with an ATAA but, again, much less so than among controls; a multivariable binary logistic regression of data in the team’s review showed that patients with ATAAs were 298, 250, and 232 times less likely to have an MI than if they had a family history of MI, dyslipidemia, or hypertension, respectively.
Why the Protection?
The ligamentum arteriosum separates the ascending from the descending (thoracoabdominal) aorta. ATAAs, located above the ligamentum, tend to be pro-aneurysmal but anti-atherosclerotic. In the descending aorta, below the ligamentum, atherosclerotic aneurysms develop.
The differences between the two sections of the aorta originate in the germ layer in the embryo, Dr. Elefteriades said. “The fundamental difference in tissue of origin translates into marked differences in the character of aneurysms in the different aortic segments.”
What specifically underlies the reduced cardiovascular risk? “We don’t really know, but we think that there may be two possible etiologies,” Dr. Mukherjee said. One hypothesis involves transforming growth factor–beta (TGF-beta), which is overexpressed in patients with ATAA and seems to increase their vulnerability to aneurysms while also conferring protection from coronary disease risk.
Some studies have shown differences in cellular responses to TGF-beta between the thoracic and abdominal aorta, including collagen production and contractility. Others have shown that some patients who have had an MI have polymorphisms that decrease their levels of TGF-beta.
Furthermore, TGF-beta plays a key role in the development of the intimal layer, which could underpin the lack of intimal thickening in patients with ATAA.
But overall, studies have been mixed and challenging to interpret, Dr. Elefteriades and Dr. Mukherjee agreed. TGF-beta has multiple remodeling roles in the body, and it is difficult at this point to isolate its exact role in aortic disease.
Another hypothesis involves matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are dysregulated in patients with ATAA and may confer some protection, Mukherjee said. Several studies have shown higher plasma levels of certain MMPs in patients with ATAAs. MMPs also were found to be elevated in the thoracic aortic walls of patients with ATAA who had an aortic dissection, as well as in the aortic smooth muscle cells in the intima and media.
In addition, some studies have shown increased levels of MMP-2 in the aortas of patients with ATAAs compared with patients with coronary artery disease.
Adding to the mix of possibilities, “We recently found a gene that’s dysregulated in our aneurysm patients that is very intimately related to atherosclerosis,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “But the work is too preliminary to say anything more at this point.”
“It would be fabulous to prove what it is causing this protection,” Dr. Mukherjee added. “But the truth is we don’t know. These are hypotheses.”
“The most important message from our work is that most clinicians need to dissociate an ATAA from the concept of atherosclerosis,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “The ascending aorta is not an atherosclerotic phenomenon.”
How to Manage Patients With ATAA
What does the distinct character of ATAAs mean for patient management? “Finding a drug to treat ATAAs — to prevent growth, rupture, or dissection — has been like a search for the Holy Grail,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “Statins are not necessary, as this is a non-atherosclerotic process. Although sporadic studies have reported beneficial effects from beta-blockers or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), this has often been based on ‘soft’ evidence, requiring a combination of outcome measures to achieve significance.”
That said, he noted, “The mainstay, common sense treatment is to keep blood pressure controlled. This is usually achieved by a beta-blocker and an ARB, even if the benefit is not via a direct biologic effect on the aneurysmal degenerative process, but via simple hemodynamics — discouraging rupture by keeping pressure in the aorta low.”
Dr. Mukherjee suggested that these patients should be referred to a specialty aneurysm center where their genes will be evaluated, and then the aneurysm will be followed very closely.
“If the aneurysm is larger than 4.5 cm, we screen the patient every single year, and if they have chest pain, we treat them the same way as we treat other aneurysms,” he said. “As a rule of thumb, if the aneurysm reaches 5 cm, it should come out, although the size at which this should happen may differ between 4.5 cm and 5.5 cm, depending on the patient’s body size.”
As for lifestyle management, Dr. Elefteriades said, “Protection from atherosclerosis and MI won’t go away after the aneurysm is removed. We think it’s in the body’s chemistry. But even though it’s very hard for those patients to have a heart attack, we don’t recommend they eat roast beef every night — although I do think they’d be protected from such lifestyle aberrations.”
For now, he added, “Our team is on a hunt to find a drug to treat ascending disease directly and effectively. We have ongoing laboratory experiments with two drugs undergoing investigation at some level. We hope to embark soon on clinical trials.”
‘A Milestone’
James Hamilton Black III, MD, vice chair of the writing committee for the 2022 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Aortic Disease Guideline and chief of Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, commented on the review and the concept of ATAA’s atherosclerotic protection.
“The association of ascending aortic aneurysms with a lower risk for MI is an interesting one, but it’s probably influenced, at least in part, by the patient population.” That population is at least partially curated since people are coming to an academic center. In addition, Dr. Black noted, “the patients with ATAAs are younger, and so age may be a confounding factor in the analyses. We wouldn’t expect them to have the same burden of atherosclerosis” as older patients.
Nevertheless, he said, “the findings speak to an emerging body of literature suggesting that although the aorta is a single organ, there are certainly different areas, and these would respond quite differently to environmental or genetic or heritable stressors. This isn’t surprising, and there probably are a lot of factors involved.”
Overall, he said, the findings underscore “the precision medicine approaches we need to take with patients with aortic diseases.”
In a commentary on the team’s review article, published in 2022, John G.T. Augoustides, MD, professor of anesthesiology and critical care at the Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, suggested that ATAA’s “silver lining” could advance the understanding of thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) management, be integrated with the expanding horizons in hereditary thoracic aortic disease, and might be explored in the context of bicuspid aortic valve disease.
Highlighting the “relative absence” of atherosclerosis in ascending aortic aneurysms and its importance is a “milestone in our understanding,” he concluded. “It is likely that future advances in TAAs will be significantly influenced by this observation.”
Dr. Elefteriades, Dr. Mukherjee, and Dr. Black have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Often known as a “silent killer,” ascending thoracic aortic aneurysms (ATAAs) may grow asymptomatically until they rupture, at which point, mortality is over 90%.
But and by extension, for those who have one, a significantly reduced risk for coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction (MI).
“We noticed in the operating room that many patients we worked on who had an ATAA had pristine arteries, like a teenager’s,” said John Elefteriades, MD, William W.L. Glenn Professor of Cardiothoracic Surgery and former chief of cardiothoracic surgery at Yale University and Yale New Haven Hospital, New Haven, Connecticut. “The same was true of the femoral artery, which we use to hook up to the heart-lung machine.”
Elefteriades and colleagues have been investigating the implications of this association for more than two decades. Many of their studies are highlighted in a recent review of the evidence supporting the protective relationship between ATAAs and the development of atherosclerosis and the possible mechanisms driving the relationship.
“We see four different layers of protection,” said Sandip Mukherjee, MD, medical director of the Aortic Institute at Yale New Haven Hospital and a senior editor of the journal AORTA. Mukherjee collaborated with Elefteriades on many of the studies.
The first layer of protection is lower intima-media thickness, specifically, 0.131 mm lower than in individuals without an ATAA. “It may not seem like very much, but one point can actually translate into a 13%-15% decline in the rate of myocardial infarction or stroke,” Dr. Mukherjee said.
The second layer is lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol. Lower LDL cholesterol levels (75 mg/dL) were associated with increased odds of ATAAs (odds ratio [OR], 1.21), whereas elevated levels (150 mg/dL and 200 mg/dL) were associated with decreased odds of ATAAs (OR, 0.62 and 0.29, respectively).
Lower calcification scores for the coronary arteries are the third layer of protection (6.73 vs 9.36 in one study).
The fourth protective layer is a significantly reduced prevalence of coronary artery disease. A study of individuals with ATAA compared to controls found 61 of those with ATAA had coronary artery disease vs 140 of controls, and 11 vs 83 had experienced an MI. Of note, patients with ATAAs were protected despite having higher body mass indices than controls.
Other MI risk factors such as age increased the risk even among those with an ATAA but, again, much less so than among controls; a multivariable binary logistic regression of data in the team’s review showed that patients with ATAAs were 298, 250, and 232 times less likely to have an MI than if they had a family history of MI, dyslipidemia, or hypertension, respectively.
Why the Protection?
The ligamentum arteriosum separates the ascending from the descending (thoracoabdominal) aorta. ATAAs, located above the ligamentum, tend to be pro-aneurysmal but anti-atherosclerotic. In the descending aorta, below the ligamentum, atherosclerotic aneurysms develop.
The differences between the two sections of the aorta originate in the germ layer in the embryo, Dr. Elefteriades said. “The fundamental difference in tissue of origin translates into marked differences in the character of aneurysms in the different aortic segments.”
What specifically underlies the reduced cardiovascular risk? “We don’t really know, but we think that there may be two possible etiologies,” Dr. Mukherjee said. One hypothesis involves transforming growth factor–beta (TGF-beta), which is overexpressed in patients with ATAA and seems to increase their vulnerability to aneurysms while also conferring protection from coronary disease risk.
Some studies have shown differences in cellular responses to TGF-beta between the thoracic and abdominal aorta, including collagen production and contractility. Others have shown that some patients who have had an MI have polymorphisms that decrease their levels of TGF-beta.
Furthermore, TGF-beta plays a key role in the development of the intimal layer, which could underpin the lack of intimal thickening in patients with ATAA.
But overall, studies have been mixed and challenging to interpret, Dr. Elefteriades and Dr. Mukherjee agreed. TGF-beta has multiple remodeling roles in the body, and it is difficult at this point to isolate its exact role in aortic disease.
Another hypothesis involves matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are dysregulated in patients with ATAA and may confer some protection, Mukherjee said. Several studies have shown higher plasma levels of certain MMPs in patients with ATAAs. MMPs also were found to be elevated in the thoracic aortic walls of patients with ATAA who had an aortic dissection, as well as in the aortic smooth muscle cells in the intima and media.
In addition, some studies have shown increased levels of MMP-2 in the aortas of patients with ATAAs compared with patients with coronary artery disease.
Adding to the mix of possibilities, “We recently found a gene that’s dysregulated in our aneurysm patients that is very intimately related to atherosclerosis,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “But the work is too preliminary to say anything more at this point.”
“It would be fabulous to prove what it is causing this protection,” Dr. Mukherjee added. “But the truth is we don’t know. These are hypotheses.”
“The most important message from our work is that most clinicians need to dissociate an ATAA from the concept of atherosclerosis,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “The ascending aorta is not an atherosclerotic phenomenon.”
How to Manage Patients With ATAA
What does the distinct character of ATAAs mean for patient management? “Finding a drug to treat ATAAs — to prevent growth, rupture, or dissection — has been like a search for the Holy Grail,” Dr. Elefteriades said. “Statins are not necessary, as this is a non-atherosclerotic process. Although sporadic studies have reported beneficial effects from beta-blockers or angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), this has often been based on ‘soft’ evidence, requiring a combination of outcome measures to achieve significance.”
That said, he noted, “The mainstay, common sense treatment is to keep blood pressure controlled. This is usually achieved by a beta-blocker and an ARB, even if the benefit is not via a direct biologic effect on the aneurysmal degenerative process, but via simple hemodynamics — discouraging rupture by keeping pressure in the aorta low.”
Dr. Mukherjee suggested that these patients should be referred to a specialty aneurysm center where their genes will be evaluated, and then the aneurysm will be followed very closely.
“If the aneurysm is larger than 4.5 cm, we screen the patient every single year, and if they have chest pain, we treat them the same way as we treat other aneurysms,” he said. “As a rule of thumb, if the aneurysm reaches 5 cm, it should come out, although the size at which this should happen may differ between 4.5 cm and 5.5 cm, depending on the patient’s body size.”
As for lifestyle management, Dr. Elefteriades said, “Protection from atherosclerosis and MI won’t go away after the aneurysm is removed. We think it’s in the body’s chemistry. But even though it’s very hard for those patients to have a heart attack, we don’t recommend they eat roast beef every night — although I do think they’d be protected from such lifestyle aberrations.”
For now, he added, “Our team is on a hunt to find a drug to treat ascending disease directly and effectively. We have ongoing laboratory experiments with two drugs undergoing investigation at some level. We hope to embark soon on clinical trials.”
‘A Milestone’
James Hamilton Black III, MD, vice chair of the writing committee for the 2022 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Aortic Disease Guideline and chief of Division of Vascular Surgery and Endovascular Therapy at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, commented on the review and the concept of ATAA’s atherosclerotic protection.
“The association of ascending aortic aneurysms with a lower risk for MI is an interesting one, but it’s probably influenced, at least in part, by the patient population.” That population is at least partially curated since people are coming to an academic center. In addition, Dr. Black noted, “the patients with ATAAs are younger, and so age may be a confounding factor in the analyses. We wouldn’t expect them to have the same burden of atherosclerosis” as older patients.
Nevertheless, he said, “the findings speak to an emerging body of literature suggesting that although the aorta is a single organ, there are certainly different areas, and these would respond quite differently to environmental or genetic or heritable stressors. This isn’t surprising, and there probably are a lot of factors involved.”
Overall, he said, the findings underscore “the precision medicine approaches we need to take with patients with aortic diseases.”
In a commentary on the team’s review article, published in 2022, John G.T. Augoustides, MD, professor of anesthesiology and critical care at the Perelman School of Medicine in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, suggested that ATAA’s “silver lining” could advance the understanding of thoracic aortic aneurysm (TAA) management, be integrated with the expanding horizons in hereditary thoracic aortic disease, and might be explored in the context of bicuspid aortic valve disease.
Highlighting the “relative absence” of atherosclerosis in ascending aortic aneurysms and its importance is a “milestone in our understanding,” he concluded. “It is likely that future advances in TAAs will be significantly influenced by this observation.”
Dr. Elefteriades, Dr. Mukherjee, and Dr. Black have no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Death Risk Takes Decades to Revert to Normal in Ex-Smokers
For smokers, deaths with a cardiovascular or cancer-related cause, or ones that can be attributed to a respiratory disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are significantly more common than for nonsmokers. It is widely recognized that stopping smoking leads to a reduction in mortality risk. To make reliable statements on the timeline of this reduction, researchers analyzed interview data and death rates from 438,015 adult US citizens from 1997 to the end of 2019.
The analyses show that . Blake Thomson, PhD, and Fahrad Islami, MD, PhD, both members of the Department of Surveillance and Health Equity Science of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, Georgia, published their results as a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
After Smoking Cessation
Overall, 11,860 cardiovascular, 10,935 cancer-related, and 2,060 respiratory-related deaths were considered from over 5 million patient years. Taken from these figures, the mortality risks of continuous smokers were 2.3 times (cardiovascular), 3.4 times (cancer-related), and 13.3 times (respiratory-related) higher than those of continuous nonsmokers.
Within 10 years of stopping smoking, the following occurred:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.47 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 36% compared with smokers).
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 2.13 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 47% compared with smokers).
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 6.35 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 43% compared with smokers).
In the second decade after stopping smoking, the risk dropped even further. The researchers observed the following trends:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.26 times.
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 1.59 times.
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 3.63 times — each time compared with nonsmokers.
During the third decade after stopping smoking, the risk continued to decrease. The trends were as follows:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.07 times.
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 1.34 times.
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 2.34 times, compared with nonsmokers.
30 Years Later
Only after more than 30 years of not smoking was the cardiovascular-related mortality risk 0.96 and, therefore, no longer significant. Compared with nonsmokers, the cancer-related mortality risk was 1.16, and the respiratory-related mortality risk was 1.31.
Therefore, former smokers can reduce their cardiovascular mortality risk by 100%, the cancer-related by 93%, and the respiratory-related mortality risk by 97%.
The result reinforces earlier analyses on the reduction in mortality risks by stopping smoking, with fewer participants. Smokers, therefore, benefit more the longer that they can refrain from using tobacco. “The earlier in life that smoking is given up, the better,” the authors wrote. But even in the first 10 years, the mortality risks examined decreased by a statistically significant 36% (cardiovascular) to 47% (cancer-related).
An Underestimation?
One disadvantage of the study is that the participants’ data were collected using personal questionnaires. For this reason, participants may have reported their tobacco consumption as being lower than it was, particularly because these questionnaires are often answered in hindsight, the authors pointed out.
In addition, some of the participants who reported stopping smoking completely may have only reduced their consumption. However, both circumstances would cause the results of the analysis to be even clearer, compared with reality, and therefore better.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For smokers, deaths with a cardiovascular or cancer-related cause, or ones that can be attributed to a respiratory disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are significantly more common than for nonsmokers. It is widely recognized that stopping smoking leads to a reduction in mortality risk. To make reliable statements on the timeline of this reduction, researchers analyzed interview data and death rates from 438,015 adult US citizens from 1997 to the end of 2019.
The analyses show that . Blake Thomson, PhD, and Fahrad Islami, MD, PhD, both members of the Department of Surveillance and Health Equity Science of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, Georgia, published their results as a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
After Smoking Cessation
Overall, 11,860 cardiovascular, 10,935 cancer-related, and 2,060 respiratory-related deaths were considered from over 5 million patient years. Taken from these figures, the mortality risks of continuous smokers were 2.3 times (cardiovascular), 3.4 times (cancer-related), and 13.3 times (respiratory-related) higher than those of continuous nonsmokers.
Within 10 years of stopping smoking, the following occurred:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.47 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 36% compared with smokers).
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 2.13 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 47% compared with smokers).
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 6.35 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 43% compared with smokers).
In the second decade after stopping smoking, the risk dropped even further. The researchers observed the following trends:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.26 times.
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 1.59 times.
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 3.63 times — each time compared with nonsmokers.
During the third decade after stopping smoking, the risk continued to decrease. The trends were as follows:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.07 times.
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 1.34 times.
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 2.34 times, compared with nonsmokers.
30 Years Later
Only after more than 30 years of not smoking was the cardiovascular-related mortality risk 0.96 and, therefore, no longer significant. Compared with nonsmokers, the cancer-related mortality risk was 1.16, and the respiratory-related mortality risk was 1.31.
Therefore, former smokers can reduce their cardiovascular mortality risk by 100%, the cancer-related by 93%, and the respiratory-related mortality risk by 97%.
The result reinforces earlier analyses on the reduction in mortality risks by stopping smoking, with fewer participants. Smokers, therefore, benefit more the longer that they can refrain from using tobacco. “The earlier in life that smoking is given up, the better,” the authors wrote. But even in the first 10 years, the mortality risks examined decreased by a statistically significant 36% (cardiovascular) to 47% (cancer-related).
An Underestimation?
One disadvantage of the study is that the participants’ data were collected using personal questionnaires. For this reason, participants may have reported their tobacco consumption as being lower than it was, particularly because these questionnaires are often answered in hindsight, the authors pointed out.
In addition, some of the participants who reported stopping smoking completely may have only reduced their consumption. However, both circumstances would cause the results of the analysis to be even clearer, compared with reality, and therefore better.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
For smokers, deaths with a cardiovascular or cancer-related cause, or ones that can be attributed to a respiratory disease such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are significantly more common than for nonsmokers. It is widely recognized that stopping smoking leads to a reduction in mortality risk. To make reliable statements on the timeline of this reduction, researchers analyzed interview data and death rates from 438,015 adult US citizens from 1997 to the end of 2019.
The analyses show that . Blake Thomson, PhD, and Fahrad Islami, MD, PhD, both members of the Department of Surveillance and Health Equity Science of the American Cancer Society in Atlanta, Georgia, published their results as a research letter in JAMA Internal Medicine.
After Smoking Cessation
Overall, 11,860 cardiovascular, 10,935 cancer-related, and 2,060 respiratory-related deaths were considered from over 5 million patient years. Taken from these figures, the mortality risks of continuous smokers were 2.3 times (cardiovascular), 3.4 times (cancer-related), and 13.3 times (respiratory-related) higher than those of continuous nonsmokers.
Within 10 years of stopping smoking, the following occurred:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.47 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 36% compared with smokers).
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 2.13 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 47% compared with smokers).
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 6.35 times, compared with nonsmokers (by 43% compared with smokers).
In the second decade after stopping smoking, the risk dropped even further. The researchers observed the following trends:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.26 times.
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 1.59 times.
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 3.63 times — each time compared with nonsmokers.
During the third decade after stopping smoking, the risk continued to decrease. The trends were as follows:
- The cardiovascular mortality risk fell by 1.07 times.
- The cancer-related mortality risk fell by 1.34 times.
- The respiratory-related mortality risk fell by 2.34 times, compared with nonsmokers.
30 Years Later
Only after more than 30 years of not smoking was the cardiovascular-related mortality risk 0.96 and, therefore, no longer significant. Compared with nonsmokers, the cancer-related mortality risk was 1.16, and the respiratory-related mortality risk was 1.31.
Therefore, former smokers can reduce their cardiovascular mortality risk by 100%, the cancer-related by 93%, and the respiratory-related mortality risk by 97%.
The result reinforces earlier analyses on the reduction in mortality risks by stopping smoking, with fewer participants. Smokers, therefore, benefit more the longer that they can refrain from using tobacco. “The earlier in life that smoking is given up, the better,” the authors wrote. But even in the first 10 years, the mortality risks examined decreased by a statistically significant 36% (cardiovascular) to 47% (cancer-related).
An Underestimation?
One disadvantage of the study is that the participants’ data were collected using personal questionnaires. For this reason, participants may have reported their tobacco consumption as being lower than it was, particularly because these questionnaires are often answered in hindsight, the authors pointed out.
In addition, some of the participants who reported stopping smoking completely may have only reduced their consumption. However, both circumstances would cause the results of the analysis to be even clearer, compared with reality, and therefore better.
This article was translated from the Medscape German edition.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA INTERNAL MEDICINE
How to Reduce Cardiovascular Morbidity and Mortality in Psoriasis and PsA
Patients with psoriatic disease have significantly higher risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality than does the general population, yet research consistently paints what dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, calls an “abysmal” picture: Only a minority of patients with psoriatic disease know about their increased risks, only a minority of dermatologists and rheumatologists screen for cardiovascular risk factors like lipid levels and blood pressure, and only a minority of patients diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.
In the literature and at medical meetings, Dr. Gelfand and others who have studied cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidity and physician practices have been urging dermatologists and rheumatologists to play a more consistent and active role in primary cardiovascular prevention for patients with psoriatic disease, who are up to 50% more likely than patients without it to develop CVD and who tend to have atherosclerosis at earlier ages.
According to the 2019 joint American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for managing psoriasis “with awareness and attention to comorbidities,” this means not only ensuring that all patients with psoriasis receive standard CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia), but also recognizing that patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy — or who have psoriasis involving > 10% of body surface area — may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
CV risk and premature mortality rises with the severity of skin disease, and patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are believed to have risk levels similar to patients with moderate-severe psoriasis, cardiologist Michael S. Garshick, MD, director of the cardio-rheumatology program at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
In a recent survey study of 100 patients seen at NYU Langone Health’s psoriasis specialty clinic, only one-third indicated they had been advised by their physicians to be screened for CV risk factors, and only one-third reported having been told of the connection between psoriasis and CVD risk. Dr. Garshick shared the unpublished findings at the annual research symposium of the NPF in October.
Similarly, data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey shows that just 16% of psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers from 2007 to 2016 involved screening for CV risk factors. Screening rates were 11% for body mass index, 7.4% for blood pressure, 2.9% for cholesterol, and 1.7% for glucose, Dr. Gelfand and coauthors reported in 2023. .
Such findings are concerning because research shows that fewer than a quarter of patients with psoriasis have a primary care visit within a year of establishing care with their physicians, and that, overall, fewer than half of commercially insured adults under age 65 visit a primary care physician each year, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He included these findings when reporting in 2022 on a survey study on CVD screening.
In many cases, dermatologists and rheumatologists may be the primary providers for patients with psoriatic disease. So, “the question is, how can the dermatologist or rheumatologist use their interactions as a touchpoint to improve the patient’s well-being?” Dr. Barbieri said in an interview.
For the dermatologist, educating patients about the higher CVD risk fits well into conversations about “how there may be inflammation inside the body as well as in the skin,” he said. “Talk about cardiovascular risk just as you talk about PsA risk.” Both specialists, he added, can incorporate blood pressure readings and look for opportunities to measure lipid levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These labs can easily be integrated into a biologic work-up.
“The hard part — and this needs to be individualized — is how do you want to handle [abnormal readings]? Do you want to take on a lot of the ownership and calculate [10-year CVD] risk scores and then counsel patients accordingly?” Dr. Barbieri said. “Or do you want to try to refer, and encourage them to work with their PCP? There a high-touch version and a low-touch version of how you can turn screening into action, into a care plan.”
Beyond traditional risk elevation, the primary care hand-off
Rheumatologists “in general may be more apt to screen for cardiovascular disease” as a result of their internal medicine residency training, and “we’re generally more comfortable prescribing ... if we need to,” said Alexis R. Ogdie, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and director of the Penn Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
Referral to a preventive cardiologist for management of abnormal lab results or ongoing monitoring and prevention is ideal, but when hand-offs to primary care physicians are made — the more common scenario — education is important. “A common problem is that there is underrecognition of the cardiovascular risk being elevated in our patients,” she said, above and beyond risk posed by traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, all of which have been shown to occur more frequently in patients with psoriatic disease than in the general population.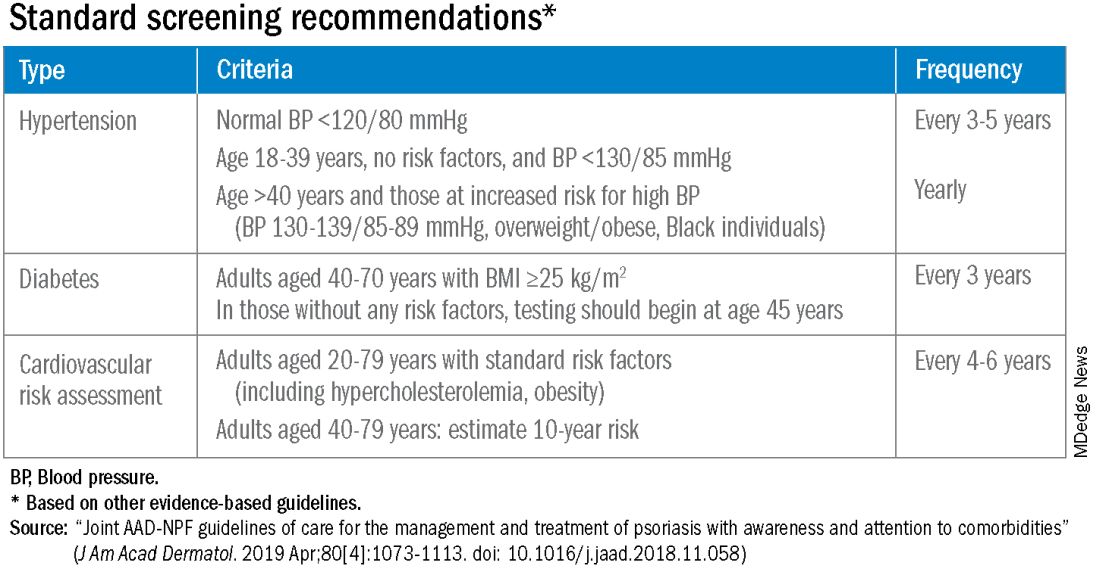
Risk stratification guides CVD prevention in the general population, and “if you use typical scores for cardiovascular risk, they may underestimate risk for our patients with PsA,” said Dr. Ogdie, who has reported on CV risk in patients with PsA. “Relative to what the patient’s perceived risk is, they may be treated similarly (to the general population). But relative to their actual risk, they’re undertreated.”
The 2019 AAD-NPF psoriasis guidelines recommend utilizing a 1.5 multiplication factor in risk score models, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) Risk Estimator, when the patient has a body surface area >10% or is a candidate for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Similarly, the 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)-ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol defines psoriasis, along with RA, metabolic syndrome, HIV, and other diseases, as a “cardiovascular risk enhancer” that should be factored into assessments of ASCVD risk. (The guideline does not specify a psoriasis severity threshold.)
“It’s the first time the specialty [of cardiology] has said, ‘pay attention to a skin disease,’ ” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting.
Using the 1.5 multiplication factor, a patient who otherwise would be classified in the AHA/ACC guideline as “borderline risk,” with a 10-year ASCVD risk of 5% to <7.5%, would instead have an “intermediate” 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥7.5% to <20%. Application of the AHA-ACC “risk enhancer” would have a similar effect.
For management, the main impact of psoriasis being considered a risk enhancer is that “it lowers the threshold for treatment with standard cardiovascular prevention medications such as statins.”
In general, “we should be taking a more aggressive approach to the management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors” in patients with psoriatic disease, he said. Instead of telling a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure, ‘I’ll see you in a year or two,’ or a patient entering a prediabetic stage to “watch what you eat, and I’ll see you in a couple of years,” clinicians need to be more vigilant.
“It’s about recognizing that these traditional cardiometabolic risk factors, synergistically with psoriasis, can start enhancing CV risk at an earlier age than we might expect,” said Dr. Garshick, whose 2021 review of CV risk in psoriasis describes how the inflammatory milieu in psoriasis is linked to atherosclerosis development.
Cardiologists are aware of this, but “many primary care physicians are not. It takes time for medical knowledge to diffuse,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Tell the PCP, in notes or in a form letter, that there is a higher risk of CV disease, and reference the AHA/ACC guidelines,” he advised. “You don’t want your patient to go to their doctor and the doctor to [be uninformed].”
‘Patients trust us’
Dr. Gelfand has been at the forefront of research on psoriasis and heart disease. A study he coauthored in 2006, for instance, documented an independent risk of MI, with adjusted relative risks of 1.29 and 3.10 for a 30-year-old patient with mild or severe disease, respectively, and higher risks for a 60-year-old. In 2010, he and coinvestigators found that severe psoriasis was an independent risk factor for CV mortality (HR, 1.57) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Today, along with Dr. Barbieri, Dr. Ogdie, and others, he is studying the feasibility and efficacy of a proposed national, “centralized care coordinator” model of care whereby dermatologists and rheumatologists would educate the patient, order lipid and HbA1c measurements as medically appropriate, and then refer patients as needed to a care coordinator. The care coordinator would calculate a 10-year CVD risk score and counsel the patient on possible next steps.
In a pilot study of 85 patients at four sites, 92% of patients followed through on their physician’s recommendations to have labs drawn, and 86% indicated the model was acceptable and feasible. A total of 27% of patients had “newly identified, previously undiagnosed, elevated cardiovascular disease risk,” and exploratory effectiveness results indicated a successful reduction in predicted CVD risk in patients who started statins, Dr. Gelfand reported at the NPF meeting.
With funding from the NPF, a larger, single-arm, pragmatic “CP3” trial (NCT05908240) is enrolling 525 patients with psoriasis at 10-20 academic and nonacademic dermatology sites across the United States to further test the model. The primary endpoint will be the change in LDL cholesterol measured at 6 months among people with a 10-year risk ≥5%. Secondary endpoints will cover improvement in disease severity and quality of life, behavior modification, patient experience, and other issues.
“We have only 10-15 minutes [with patients] ... a care coordinator who is empathetic and understanding and [informed] could make a big difference,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. If findings are positive, the model would be tested in rheumatology sites as well. The hope, he said, is that the NPF would be able to fund an in-house care coordinator(s) for the long-term.
Notably, a patient survey conducted as part of exploratory research leading up to the care coordinator project showed that patients trust their dermatologist or rheumatologist for CVD education and screening. Among 160 patients with psoriasis and 162 patients with PsA, 76% and 90% agreed that “I would like it if my dermatologist/rheumatologist educated me about my risk of heart disease,” and 60% and 75%, respectively, agree that “it would be convenient for me to have my cholesterol checked by my dermatologist/rheumatologist.”
“Patients trust us,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. “And the pilot study shows us that patients are motivated.”
Taking an individualized, holistic, longitudinal approach
“Sometimes you do have to triage bit,” Dr. Gelfand said in an interview. “For a young person with normal body weight who doesn’t smoke and has mild psoriasis, one could just educate and advise that they see their primary care physician” for monitoring.
“But for the same patient who is obese, maybe smokes, and doesn’t have a primary care physician, I’d order labs,” he said. “You don’t want a patient walking out the door with an [undiagnosed] LDL of 160 or hypertension.”
Age is also an important consideration, as excess CVD risk associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis rises with age, Dr. Gelfand said during a seminar on psoriasis and PsA held at NYU Langone in December. For a young person, typically, “I need to focus on education and lifestyle … setting them on a healthy lifestyle trajectory,” he said. “Once they get to 40, from 40 to 75 or so, that’s a sweet spot for medical intervention to lower cardiovascular risk.”
Even at older ages, however, lipid management is not the be-all and end-all, he said in the interview. “We have to be holistic.”
One advantage of having highly successful therapies for psoriasis, and to a lesser extent PsA, is the time that becomes available during follow-up visits — once disease is under control — to “focus on other things,” he said. Waiting until disease is under control to discuss diet, exercise, or smoking, for instance, makes sense anyway, he said. “You don’t want to overwhelm patients with too much to do at once.”
Indeed, said dermatologist Robert E. Kalb, MD, of the Buffalo Medical Group in Buffalo, NY, “patients have an open mind [about discussing cardiovascular disease risk], but it is not high on their radar. Most of them just want to get their skin clear.” (Dr. Kalb participated in the care coordinator pilot study, and said in an interview that since its completion, he has been more routinely ordering relevant labs.)
Rheumatologists are less fortunate with highly successful therapies, but “over the continuum of care, we do have time in office visits” to discuss issues like smoking, exercise, and lifestyle, Dr. Ogdie said. “I think of each of those pieces as part of our job.”
In the future, as researchers learn more about the impact of psoriasis and PsA treatments on CVD risk, it may be possible to tailor treatments or to prescribe treatments knowing that the therapies could reduce risk. Observational and epidemiologic data suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy over 3 years reduces the risk of MI, and that patients whose psoriasis is treated have reduced aortic inflammation, improved myocardial strain, and reduced coronary plaque burden, Dr. Garshick said at the NPF meeting.
“But when we look at the randomized controlled trials, they’re actually inconclusive that targeting inflammation in psoriatic disease reduces surrogates of cardiovascular disease,” he said. Dr. Garshick’s own research focuses on platelet and endothelial biology in psoriasis.
Dr. Barbieri reported he had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Garshick reported consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kiniksa, Horizon Therapeutics, and Agepha. Dr. Ogdie reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies.
Patients with psoriatic disease have significantly higher risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality than does the general population, yet research consistently paints what dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, calls an “abysmal” picture: Only a minority of patients with psoriatic disease know about their increased risks, only a minority of dermatologists and rheumatologists screen for cardiovascular risk factors like lipid levels and blood pressure, and only a minority of patients diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.
In the literature and at medical meetings, Dr. Gelfand and others who have studied cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidity and physician practices have been urging dermatologists and rheumatologists to play a more consistent and active role in primary cardiovascular prevention for patients with psoriatic disease, who are up to 50% more likely than patients without it to develop CVD and who tend to have atherosclerosis at earlier ages.
According to the 2019 joint American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for managing psoriasis “with awareness and attention to comorbidities,” this means not only ensuring that all patients with psoriasis receive standard CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia), but also recognizing that patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy — or who have psoriasis involving > 10% of body surface area — may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
CV risk and premature mortality rises with the severity of skin disease, and patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are believed to have risk levels similar to patients with moderate-severe psoriasis, cardiologist Michael S. Garshick, MD, director of the cardio-rheumatology program at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
In a recent survey study of 100 patients seen at NYU Langone Health’s psoriasis specialty clinic, only one-third indicated they had been advised by their physicians to be screened for CV risk factors, and only one-third reported having been told of the connection between psoriasis and CVD risk. Dr. Garshick shared the unpublished findings at the annual research symposium of the NPF in October.
Similarly, data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey shows that just 16% of psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers from 2007 to 2016 involved screening for CV risk factors. Screening rates were 11% for body mass index, 7.4% for blood pressure, 2.9% for cholesterol, and 1.7% for glucose, Dr. Gelfand and coauthors reported in 2023. .
Such findings are concerning because research shows that fewer than a quarter of patients with psoriasis have a primary care visit within a year of establishing care with their physicians, and that, overall, fewer than half of commercially insured adults under age 65 visit a primary care physician each year, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He included these findings when reporting in 2022 on a survey study on CVD screening.
In many cases, dermatologists and rheumatologists may be the primary providers for patients with psoriatic disease. So, “the question is, how can the dermatologist or rheumatologist use their interactions as a touchpoint to improve the patient’s well-being?” Dr. Barbieri said in an interview.
For the dermatologist, educating patients about the higher CVD risk fits well into conversations about “how there may be inflammation inside the body as well as in the skin,” he said. “Talk about cardiovascular risk just as you talk about PsA risk.” Both specialists, he added, can incorporate blood pressure readings and look for opportunities to measure lipid levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These labs can easily be integrated into a biologic work-up.
“The hard part — and this needs to be individualized — is how do you want to handle [abnormal readings]? Do you want to take on a lot of the ownership and calculate [10-year CVD] risk scores and then counsel patients accordingly?” Dr. Barbieri said. “Or do you want to try to refer, and encourage them to work with their PCP? There a high-touch version and a low-touch version of how you can turn screening into action, into a care plan.”
Beyond traditional risk elevation, the primary care hand-off
Rheumatologists “in general may be more apt to screen for cardiovascular disease” as a result of their internal medicine residency training, and “we’re generally more comfortable prescribing ... if we need to,” said Alexis R. Ogdie, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and director of the Penn Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
Referral to a preventive cardiologist for management of abnormal lab results or ongoing monitoring and prevention is ideal, but when hand-offs to primary care physicians are made — the more common scenario — education is important. “A common problem is that there is underrecognition of the cardiovascular risk being elevated in our patients,” she said, above and beyond risk posed by traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, all of which have been shown to occur more frequently in patients with psoriatic disease than in the general population.
Risk stratification guides CVD prevention in the general population, and “if you use typical scores for cardiovascular risk, they may underestimate risk for our patients with PsA,” said Dr. Ogdie, who has reported on CV risk in patients with PsA. “Relative to what the patient’s perceived risk is, they may be treated similarly (to the general population). But relative to their actual risk, they’re undertreated.”
The 2019 AAD-NPF psoriasis guidelines recommend utilizing a 1.5 multiplication factor in risk score models, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) Risk Estimator, when the patient has a body surface area >10% or is a candidate for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Similarly, the 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)-ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol defines psoriasis, along with RA, metabolic syndrome, HIV, and other diseases, as a “cardiovascular risk enhancer” that should be factored into assessments of ASCVD risk. (The guideline does not specify a psoriasis severity threshold.)
“It’s the first time the specialty [of cardiology] has said, ‘pay attention to a skin disease,’ ” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting.
Using the 1.5 multiplication factor, a patient who otherwise would be classified in the AHA/ACC guideline as “borderline risk,” with a 10-year ASCVD risk of 5% to <7.5%, would instead have an “intermediate” 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥7.5% to <20%. Application of the AHA-ACC “risk enhancer” would have a similar effect.
For management, the main impact of psoriasis being considered a risk enhancer is that “it lowers the threshold for treatment with standard cardiovascular prevention medications such as statins.”
In general, “we should be taking a more aggressive approach to the management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors” in patients with psoriatic disease, he said. Instead of telling a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure, ‘I’ll see you in a year or two,’ or a patient entering a prediabetic stage to “watch what you eat, and I’ll see you in a couple of years,” clinicians need to be more vigilant.
“It’s about recognizing that these traditional cardiometabolic risk factors, synergistically with psoriasis, can start enhancing CV risk at an earlier age than we might expect,” said Dr. Garshick, whose 2021 review of CV risk in psoriasis describes how the inflammatory milieu in psoriasis is linked to atherosclerosis development.
Cardiologists are aware of this, but “many primary care physicians are not. It takes time for medical knowledge to diffuse,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Tell the PCP, in notes or in a form letter, that there is a higher risk of CV disease, and reference the AHA/ACC guidelines,” he advised. “You don’t want your patient to go to their doctor and the doctor to [be uninformed].”
‘Patients trust us’
Dr. Gelfand has been at the forefront of research on psoriasis and heart disease. A study he coauthored in 2006, for instance, documented an independent risk of MI, with adjusted relative risks of 1.29 and 3.10 for a 30-year-old patient with mild or severe disease, respectively, and higher risks for a 60-year-old. In 2010, he and coinvestigators found that severe psoriasis was an independent risk factor for CV mortality (HR, 1.57) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Today, along with Dr. Barbieri, Dr. Ogdie, and others, he is studying the feasibility and efficacy of a proposed national, “centralized care coordinator” model of care whereby dermatologists and rheumatologists would educate the patient, order lipid and HbA1c measurements as medically appropriate, and then refer patients as needed to a care coordinator. The care coordinator would calculate a 10-year CVD risk score and counsel the patient on possible next steps.
In a pilot study of 85 patients at four sites, 92% of patients followed through on their physician’s recommendations to have labs drawn, and 86% indicated the model was acceptable and feasible. A total of 27% of patients had “newly identified, previously undiagnosed, elevated cardiovascular disease risk,” and exploratory effectiveness results indicated a successful reduction in predicted CVD risk in patients who started statins, Dr. Gelfand reported at the NPF meeting.
With funding from the NPF, a larger, single-arm, pragmatic “CP3” trial (NCT05908240) is enrolling 525 patients with psoriasis at 10-20 academic and nonacademic dermatology sites across the United States to further test the model. The primary endpoint will be the change in LDL cholesterol measured at 6 months among people with a 10-year risk ≥5%. Secondary endpoints will cover improvement in disease severity and quality of life, behavior modification, patient experience, and other issues.
“We have only 10-15 minutes [with patients] ... a care coordinator who is empathetic and understanding and [informed] could make a big difference,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. If findings are positive, the model would be tested in rheumatology sites as well. The hope, he said, is that the NPF would be able to fund an in-house care coordinator(s) for the long-term.
Notably, a patient survey conducted as part of exploratory research leading up to the care coordinator project showed that patients trust their dermatologist or rheumatologist for CVD education and screening. Among 160 patients with psoriasis and 162 patients with PsA, 76% and 90% agreed that “I would like it if my dermatologist/rheumatologist educated me about my risk of heart disease,” and 60% and 75%, respectively, agree that “it would be convenient for me to have my cholesterol checked by my dermatologist/rheumatologist.”
“Patients trust us,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. “And the pilot study shows us that patients are motivated.”
Taking an individualized, holistic, longitudinal approach
“Sometimes you do have to triage bit,” Dr. Gelfand said in an interview. “For a young person with normal body weight who doesn’t smoke and has mild psoriasis, one could just educate and advise that they see their primary care physician” for monitoring.
“But for the same patient who is obese, maybe smokes, and doesn’t have a primary care physician, I’d order labs,” he said. “You don’t want a patient walking out the door with an [undiagnosed] LDL of 160 or hypertension.”
Age is also an important consideration, as excess CVD risk associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis rises with age, Dr. Gelfand said during a seminar on psoriasis and PsA held at NYU Langone in December. For a young person, typically, “I need to focus on education and lifestyle … setting them on a healthy lifestyle trajectory,” he said. “Once they get to 40, from 40 to 75 or so, that’s a sweet spot for medical intervention to lower cardiovascular risk.”
Even at older ages, however, lipid management is not the be-all and end-all, he said in the interview. “We have to be holistic.”
One advantage of having highly successful therapies for psoriasis, and to a lesser extent PsA, is the time that becomes available during follow-up visits — once disease is under control — to “focus on other things,” he said. Waiting until disease is under control to discuss diet, exercise, or smoking, for instance, makes sense anyway, he said. “You don’t want to overwhelm patients with too much to do at once.”
Indeed, said dermatologist Robert E. Kalb, MD, of the Buffalo Medical Group in Buffalo, NY, “patients have an open mind [about discussing cardiovascular disease risk], but it is not high on their radar. Most of them just want to get their skin clear.” (Dr. Kalb participated in the care coordinator pilot study, and said in an interview that since its completion, he has been more routinely ordering relevant labs.)
Rheumatologists are less fortunate with highly successful therapies, but “over the continuum of care, we do have time in office visits” to discuss issues like smoking, exercise, and lifestyle, Dr. Ogdie said. “I think of each of those pieces as part of our job.”
In the future, as researchers learn more about the impact of psoriasis and PsA treatments on CVD risk, it may be possible to tailor treatments or to prescribe treatments knowing that the therapies could reduce risk. Observational and epidemiologic data suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy over 3 years reduces the risk of MI, and that patients whose psoriasis is treated have reduced aortic inflammation, improved myocardial strain, and reduced coronary plaque burden, Dr. Garshick said at the NPF meeting.
“But when we look at the randomized controlled trials, they’re actually inconclusive that targeting inflammation in psoriatic disease reduces surrogates of cardiovascular disease,” he said. Dr. Garshick’s own research focuses on platelet and endothelial biology in psoriasis.
Dr. Barbieri reported he had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Garshick reported consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kiniksa, Horizon Therapeutics, and Agepha. Dr. Ogdie reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies.
Patients with psoriatic disease have significantly higher risks of myocardial infarction, stroke, and cardiovascular mortality than does the general population, yet research consistently paints what dermatologist Joel M. Gelfand, MD, calls an “abysmal” picture: Only a minority of patients with psoriatic disease know about their increased risks, only a minority of dermatologists and rheumatologists screen for cardiovascular risk factors like lipid levels and blood pressure, and only a minority of patients diagnosed with hyperlipidemia are adequately treated with statin therapy.
In the literature and at medical meetings, Dr. Gelfand and others who have studied cardiovascular disease (CVD) comorbidity and physician practices have been urging dermatologists and rheumatologists to play a more consistent and active role in primary cardiovascular prevention for patients with psoriatic disease, who are up to 50% more likely than patients without it to develop CVD and who tend to have atherosclerosis at earlier ages.
According to the 2019 joint American Academy of Dermatology (AAD)–National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) guidelines for managing psoriasis “with awareness and attention to comorbidities,” this means not only ensuring that all patients with psoriasis receive standard CV risk assessment (screening for hypertension, diabetes, and hyperlipidemia), but also recognizing that patients who are candidates for systemic therapy or phototherapy — or who have psoriasis involving > 10% of body surface area — may benefit from earlier and more frequent screening.
CV risk and premature mortality rises with the severity of skin disease, and patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) are believed to have risk levels similar to patients with moderate-severe psoriasis, cardiologist Michael S. Garshick, MD, director of the cardio-rheumatology program at New York University Langone Health, said in an interview.
In a recent survey study of 100 patients seen at NYU Langone Health’s psoriasis specialty clinic, only one-third indicated they had been advised by their physicians to be screened for CV risk factors, and only one-third reported having been told of the connection between psoriasis and CVD risk. Dr. Garshick shared the unpublished findings at the annual research symposium of the NPF in October.
Similarly, data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey shows that just 16% of psoriasis-related visits to dermatology providers from 2007 to 2016 involved screening for CV risk factors. Screening rates were 11% for body mass index, 7.4% for blood pressure, 2.9% for cholesterol, and 1.7% for glucose, Dr. Gelfand and coauthors reported in 2023. .
Such findings are concerning because research shows that fewer than a quarter of patients with psoriasis have a primary care visit within a year of establishing care with their physicians, and that, overall, fewer than half of commercially insured adults under age 65 visit a primary care physician each year, according to John S. Barbieri, MD, of the department of dermatology at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. He included these findings when reporting in 2022 on a survey study on CVD screening.
In many cases, dermatologists and rheumatologists may be the primary providers for patients with psoriatic disease. So, “the question is, how can the dermatologist or rheumatologist use their interactions as a touchpoint to improve the patient’s well-being?” Dr. Barbieri said in an interview.
For the dermatologist, educating patients about the higher CVD risk fits well into conversations about “how there may be inflammation inside the body as well as in the skin,” he said. “Talk about cardiovascular risk just as you talk about PsA risk.” Both specialists, he added, can incorporate blood pressure readings and look for opportunities to measure lipid levels and hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c). These labs can easily be integrated into a biologic work-up.
“The hard part — and this needs to be individualized — is how do you want to handle [abnormal readings]? Do you want to take on a lot of the ownership and calculate [10-year CVD] risk scores and then counsel patients accordingly?” Dr. Barbieri said. “Or do you want to try to refer, and encourage them to work with their PCP? There a high-touch version and a low-touch version of how you can turn screening into action, into a care plan.”
Beyond traditional risk elevation, the primary care hand-off
Rheumatologists “in general may be more apt to screen for cardiovascular disease” as a result of their internal medicine residency training, and “we’re generally more comfortable prescribing ... if we need to,” said Alexis R. Ogdie, MD, a rheumatologist at the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, and director of the Penn Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic.
Referral to a preventive cardiologist for management of abnormal lab results or ongoing monitoring and prevention is ideal, but when hand-offs to primary care physicians are made — the more common scenario — education is important. “A common problem is that there is underrecognition of the cardiovascular risk being elevated in our patients,” she said, above and beyond risk posed by traditional risk factors such as dyslipidemia, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and obesity, all of which have been shown to occur more frequently in patients with psoriatic disease than in the general population.
Risk stratification guides CVD prevention in the general population, and “if you use typical scores for cardiovascular risk, they may underestimate risk for our patients with PsA,” said Dr. Ogdie, who has reported on CV risk in patients with PsA. “Relative to what the patient’s perceived risk is, they may be treated similarly (to the general population). But relative to their actual risk, they’re undertreated.”
The 2019 AAD-NPF psoriasis guidelines recommend utilizing a 1.5 multiplication factor in risk score models, such as the American College of Cardiology’s Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease (ASCVD) Risk Estimator, when the patient has a body surface area >10% or is a candidate for systemic therapy or phototherapy.
Similarly, the 2018 American Heart Association (AHA)-ACC Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol defines psoriasis, along with RA, metabolic syndrome, HIV, and other diseases, as a “cardiovascular risk enhancer” that should be factored into assessments of ASCVD risk. (The guideline does not specify a psoriasis severity threshold.)
“It’s the first time the specialty [of cardiology] has said, ‘pay attention to a skin disease,’ ” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting.
Using the 1.5 multiplication factor, a patient who otherwise would be classified in the AHA/ACC guideline as “borderline risk,” with a 10-year ASCVD risk of 5% to <7.5%, would instead have an “intermediate” 10-year ASCVD risk of ≥7.5% to <20%. Application of the AHA-ACC “risk enhancer” would have a similar effect.
For management, the main impact of psoriasis being considered a risk enhancer is that “it lowers the threshold for treatment with standard cardiovascular prevention medications such as statins.”
In general, “we should be taking a more aggressive approach to the management of traditional cardiovascular risk factors” in patients with psoriatic disease, he said. Instead of telling a patient with mildly elevated blood pressure, ‘I’ll see you in a year or two,’ or a patient entering a prediabetic stage to “watch what you eat, and I’ll see you in a couple of years,” clinicians need to be more vigilant.
“It’s about recognizing that these traditional cardiometabolic risk factors, synergistically with psoriasis, can start enhancing CV risk at an earlier age than we might expect,” said Dr. Garshick, whose 2021 review of CV risk in psoriasis describes how the inflammatory milieu in psoriasis is linked to atherosclerosis development.
Cardiologists are aware of this, but “many primary care physicians are not. It takes time for medical knowledge to diffuse,” Dr. Gelfand said. “Tell the PCP, in notes or in a form letter, that there is a higher risk of CV disease, and reference the AHA/ACC guidelines,” he advised. “You don’t want your patient to go to their doctor and the doctor to [be uninformed].”
‘Patients trust us’
Dr. Gelfand has been at the forefront of research on psoriasis and heart disease. A study he coauthored in 2006, for instance, documented an independent risk of MI, with adjusted relative risks of 1.29 and 3.10 for a 30-year-old patient with mild or severe disease, respectively, and higher risks for a 60-year-old. In 2010, he and coinvestigators found that severe psoriasis was an independent risk factor for CV mortality (HR, 1.57) after adjusting for age, sex, smoking, diabetes, hypertension, and hyperlipidemia.
Today, along with Dr. Barbieri, Dr. Ogdie, and others, he is studying the feasibility and efficacy of a proposed national, “centralized care coordinator” model of care whereby dermatologists and rheumatologists would educate the patient, order lipid and HbA1c measurements as medically appropriate, and then refer patients as needed to a care coordinator. The care coordinator would calculate a 10-year CVD risk score and counsel the patient on possible next steps.
In a pilot study of 85 patients at four sites, 92% of patients followed through on their physician’s recommendations to have labs drawn, and 86% indicated the model was acceptable and feasible. A total of 27% of patients had “newly identified, previously undiagnosed, elevated cardiovascular disease risk,” and exploratory effectiveness results indicated a successful reduction in predicted CVD risk in patients who started statins, Dr. Gelfand reported at the NPF meeting.
With funding from the NPF, a larger, single-arm, pragmatic “CP3” trial (NCT05908240) is enrolling 525 patients with psoriasis at 10-20 academic and nonacademic dermatology sites across the United States to further test the model. The primary endpoint will be the change in LDL cholesterol measured at 6 months among people with a 10-year risk ≥5%. Secondary endpoints will cover improvement in disease severity and quality of life, behavior modification, patient experience, and other issues.
“We have only 10-15 minutes [with patients] ... a care coordinator who is empathetic and understanding and [informed] could make a big difference,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. If findings are positive, the model would be tested in rheumatology sites as well. The hope, he said, is that the NPF would be able to fund an in-house care coordinator(s) for the long-term.
Notably, a patient survey conducted as part of exploratory research leading up to the care coordinator project showed that patients trust their dermatologist or rheumatologist for CVD education and screening. Among 160 patients with psoriasis and 162 patients with PsA, 76% and 90% agreed that “I would like it if my dermatologist/rheumatologist educated me about my risk of heart disease,” and 60% and 75%, respectively, agree that “it would be convenient for me to have my cholesterol checked by my dermatologist/rheumatologist.”
“Patients trust us,” Dr. Gelfand said at the NPF meeting. “And the pilot study shows us that patients are motivated.”
Taking an individualized, holistic, longitudinal approach
“Sometimes you do have to triage bit,” Dr. Gelfand said in an interview. “For a young person with normal body weight who doesn’t smoke and has mild psoriasis, one could just educate and advise that they see their primary care physician” for monitoring.
“But for the same patient who is obese, maybe smokes, and doesn’t have a primary care physician, I’d order labs,” he said. “You don’t want a patient walking out the door with an [undiagnosed] LDL of 160 or hypertension.”
Age is also an important consideration, as excess CVD risk associated with autoimmune diseases like psoriasis rises with age, Dr. Gelfand said during a seminar on psoriasis and PsA held at NYU Langone in December. For a young person, typically, “I need to focus on education and lifestyle … setting them on a healthy lifestyle trajectory,” he said. “Once they get to 40, from 40 to 75 or so, that’s a sweet spot for medical intervention to lower cardiovascular risk.”
Even at older ages, however, lipid management is not the be-all and end-all, he said in the interview. “We have to be holistic.”
One advantage of having highly successful therapies for psoriasis, and to a lesser extent PsA, is the time that becomes available during follow-up visits — once disease is under control — to “focus on other things,” he said. Waiting until disease is under control to discuss diet, exercise, or smoking, for instance, makes sense anyway, he said. “You don’t want to overwhelm patients with too much to do at once.”
Indeed, said dermatologist Robert E. Kalb, MD, of the Buffalo Medical Group in Buffalo, NY, “patients have an open mind [about discussing cardiovascular disease risk], but it is not high on their radar. Most of them just want to get their skin clear.” (Dr. Kalb participated in the care coordinator pilot study, and said in an interview that since its completion, he has been more routinely ordering relevant labs.)
Rheumatologists are less fortunate with highly successful therapies, but “over the continuum of care, we do have time in office visits” to discuss issues like smoking, exercise, and lifestyle, Dr. Ogdie said. “I think of each of those pieces as part of our job.”
In the future, as researchers learn more about the impact of psoriasis and PsA treatments on CVD risk, it may be possible to tailor treatments or to prescribe treatments knowing that the therapies could reduce risk. Observational and epidemiologic data suggest that tumor necrosis factor-alpha inhibitor therapy over 3 years reduces the risk of MI, and that patients whose psoriasis is treated have reduced aortic inflammation, improved myocardial strain, and reduced coronary plaque burden, Dr. Garshick said at the NPF meeting.
“But when we look at the randomized controlled trials, they’re actually inconclusive that targeting inflammation in psoriatic disease reduces surrogates of cardiovascular disease,” he said. Dr. Garshick’s own research focuses on platelet and endothelial biology in psoriasis.
Dr. Barbieri reported he had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Garshick reported consulting fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Kiniksa, Horizon Therapeutics, and Agepha. Dr. Ogdie reported financial relationships with AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Celgene, Eli Lilly, Gilead, GlaxoSmithKline, Janssen, Novartis, Pfizer, Takeda, and UCB. Dr. Gelfand reported serving as a consultant for AbbVie, Artax, Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, and other companies.
Antihypertensives show similar long-term mortality rates
Long-term data showed negligible differences in mortality among hypertensive adults treated with thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in a review of nearly 33,000 individuals published in JAMA Network Open.
The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) study was designed to compare initial antihypertensive treatments with a calcium channel blocker (CCB; amlodipine), an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (lisinopril) or an alpha-blocker (doxazosin), and a thiazide-type diuretic (chlorthalidone).
The composite primary outcome was fatal coronary heart disease (CHD) or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), but long-term data were lacking, wrote Jose-Miguel Yamal, PhD, of University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and colleagues. A previous study with 8-13 years of follow-up showed no significant differences in mortality between the treatment groups, the researchers noted.
In the current study, a prespecified secondary analysis of ALLHAT, the researchers added 11 more years of data for a total of 19-24 years of follow-up after randomization.
In the original ALLHAT, 32,804 adults aged 55 years and older with a diagnosis of hypertension and at least one additional coronary heart disease risk factor were followed for 4-8 years for all-cause mortality. A subgroup of 22,754 were followed for fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular disease (CVD) for a mean of 13.7 years, with a maximum of 23.9 years.
The study occurred from Feb. 23, 1994, to Dec. 31, 2017. The participants were randomized to receive a thiazide-type diuretic (15,002 patients), a CCB (8,898 patients), or an ACE inhibitor (8,904 patients).
The primary outcome was CVD mortality; secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, combined fatal and nonfatal CVD (CVD morbidity), and both morbidity and mortality for coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, end-stage renal disease, and cancer.
At 23 years, CVD mortality rates per 100 persons were 23.7, 21.6, and 23.8 in the diuretic, CCB, and ACE inhibitor groups, respectively. The adjusted hazard ratios were 0.97 for CCB vs. diuretics and 1.06 for ACE inhibitors vs. diuretics.
Although the risk of stroke mortality and of combined fatal and nonfatal hospitalized stroke was higher in the ACE inhibitor group compared with the diuretic group (adjusted hazard ratios 1.19 and 1.11, respectively), this increase was no longer significant after adjustment for multiple comparisons. “In contrast to the in-trial and 8-year to 13-year analyses, we now observed that the lisinopril group had an increased risk of kidney disease mortality that emerged after approximately 13 years after randomization, but this effect was attenuated after adjustment for baseline variables,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential effect of unblinding if participants stopped the randomized drug, and by the lack of morbidity and mortality data on Canadian participants, Veterans Affairs participants, and those with no Medicare number, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on posttrial medication use, blood pressure, and laboratory findings, they said.
However, the results over the follow-up period of up to 23 years supported those of the larger ALLHAT study, with similar outcomes among the drugs, and with 11 years of passive follow-up, “the results for lisinopril vs. chlorthalidone for stroke and stroke mortality are almost the same,” they concluded.
Findings support current practice, but new drug data are needed
The current study was important to determine whether there was a significant difference in long-term morbidity and mortality between patients treated with thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors, Noel Deep, MD, said in an interview.
“Previously reported data had indicated no significant differences between patients randomized to one of these three classes of antihypertensive medications during the trial period or at 8-13 years post trial,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc., who was not involved in the study. Dr. Deep is chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
“This study reinforces the previously noted benefits of the three classes of antihypertensive medications, as well as the higher rates of cardiovascular disease and stroke in the ACE inhibitor arm,” he said.
In clinical practice, the results suggest that thiazide diuretics should be considered first-line agents for management of hypertension based on their noninferiority compared with ACE inhibitors and CCBs, and lower risk of stroke compared with ACE inhibitors, Dr. Deep said in an interview. “All three classes of antihypertensive medications are equally efficacious in blood pressure control and preventing all-cause mortality,” he said.
More research is needed in the wake of the introduction of other classes of antihypertensives since the original ALLHAT trial, Dr. Deep said. “It would be beneficial to assess the relative benefit/risks of those medications compared to the thiazide diuretics, and I would also look at studies comparing beta blockers to the thiazide diuretics,” he said. The question remains as to whether outcomes were affected by patients’ use of other classes of antihypertensives after the trial period, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Long-term data showed negligible differences in mortality among hypertensive adults treated with thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in a review of nearly 33,000 individuals published in JAMA Network Open.
The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) study was designed to compare initial antihypertensive treatments with a calcium channel blocker (CCB; amlodipine), an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (lisinopril) or an alpha-blocker (doxazosin), and a thiazide-type diuretic (chlorthalidone).
The composite primary outcome was fatal coronary heart disease (CHD) or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), but long-term data were lacking, wrote Jose-Miguel Yamal, PhD, of University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and colleagues. A previous study with 8-13 years of follow-up showed no significant differences in mortality between the treatment groups, the researchers noted.
In the current study, a prespecified secondary analysis of ALLHAT, the researchers added 11 more years of data for a total of 19-24 years of follow-up after randomization.
In the original ALLHAT, 32,804 adults aged 55 years and older with a diagnosis of hypertension and at least one additional coronary heart disease risk factor were followed for 4-8 years for all-cause mortality. A subgroup of 22,754 were followed for fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular disease (CVD) for a mean of 13.7 years, with a maximum of 23.9 years.
The study occurred from Feb. 23, 1994, to Dec. 31, 2017. The participants were randomized to receive a thiazide-type diuretic (15,002 patients), a CCB (8,898 patients), or an ACE inhibitor (8,904 patients).
The primary outcome was CVD mortality; secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, combined fatal and nonfatal CVD (CVD morbidity), and both morbidity and mortality for coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, end-stage renal disease, and cancer.
At 23 years, CVD mortality rates per 100 persons were 23.7, 21.6, and 23.8 in the diuretic, CCB, and ACE inhibitor groups, respectively. The adjusted hazard ratios were 0.97 for CCB vs. diuretics and 1.06 for ACE inhibitors vs. diuretics.
Although the risk of stroke mortality and of combined fatal and nonfatal hospitalized stroke was higher in the ACE inhibitor group compared with the diuretic group (adjusted hazard ratios 1.19 and 1.11, respectively), this increase was no longer significant after adjustment for multiple comparisons. “In contrast to the in-trial and 8-year to 13-year analyses, we now observed that the lisinopril group had an increased risk of kidney disease mortality that emerged after approximately 13 years after randomization, but this effect was attenuated after adjustment for baseline variables,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential effect of unblinding if participants stopped the randomized drug, and by the lack of morbidity and mortality data on Canadian participants, Veterans Affairs participants, and those with no Medicare number, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on posttrial medication use, blood pressure, and laboratory findings, they said.
However, the results over the follow-up period of up to 23 years supported those of the larger ALLHAT study, with similar outcomes among the drugs, and with 11 years of passive follow-up, “the results for lisinopril vs. chlorthalidone for stroke and stroke mortality are almost the same,” they concluded.
Findings support current practice, but new drug data are needed
The current study was important to determine whether there was a significant difference in long-term morbidity and mortality between patients treated with thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors, Noel Deep, MD, said in an interview.
“Previously reported data had indicated no significant differences between patients randomized to one of these three classes of antihypertensive medications during the trial period or at 8-13 years post trial,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc., who was not involved in the study. Dr. Deep is chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
“This study reinforces the previously noted benefits of the three classes of antihypertensive medications, as well as the higher rates of cardiovascular disease and stroke in the ACE inhibitor arm,” he said.
In clinical practice, the results suggest that thiazide diuretics should be considered first-line agents for management of hypertension based on their noninferiority compared with ACE inhibitors and CCBs, and lower risk of stroke compared with ACE inhibitors, Dr. Deep said in an interview. “All three classes of antihypertensive medications are equally efficacious in blood pressure control and preventing all-cause mortality,” he said.
More research is needed in the wake of the introduction of other classes of antihypertensives since the original ALLHAT trial, Dr. Deep said. “It would be beneficial to assess the relative benefit/risks of those medications compared to the thiazide diuretics, and I would also look at studies comparing beta blockers to the thiazide diuretics,” he said. The question remains as to whether outcomes were affected by patients’ use of other classes of antihypertensives after the trial period, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
Long-term data showed negligible differences in mortality among hypertensive adults treated with thiazide-type diuretics, calcium channel blockers, or angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in a review of nearly 33,000 individuals published in JAMA Network Open.
The Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT) study was designed to compare initial antihypertensive treatments with a calcium channel blocker (CCB; amlodipine), an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor (lisinopril) or an alpha-blocker (doxazosin), and a thiazide-type diuretic (chlorthalidone).
The composite primary outcome was fatal coronary heart disease (CHD) or nonfatal myocardial infarction (MI), but long-term data were lacking, wrote Jose-Miguel Yamal, PhD, of University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston, and colleagues. A previous study with 8-13 years of follow-up showed no significant differences in mortality between the treatment groups, the researchers noted.
In the current study, a prespecified secondary analysis of ALLHAT, the researchers added 11 more years of data for a total of 19-24 years of follow-up after randomization.
In the original ALLHAT, 32,804 adults aged 55 years and older with a diagnosis of hypertension and at least one additional coronary heart disease risk factor were followed for 4-8 years for all-cause mortality. A subgroup of 22,754 were followed for fatal or nonfatal cardiovascular disease (CVD) for a mean of 13.7 years, with a maximum of 23.9 years.
The study occurred from Feb. 23, 1994, to Dec. 31, 2017. The participants were randomized to receive a thiazide-type diuretic (15,002 patients), a CCB (8,898 patients), or an ACE inhibitor (8,904 patients).
The primary outcome was CVD mortality; secondary outcomes included all-cause mortality, combined fatal and nonfatal CVD (CVD morbidity), and both morbidity and mortality for coronary heart disease, stroke, heart failure, end-stage renal disease, and cancer.
At 23 years, CVD mortality rates per 100 persons were 23.7, 21.6, and 23.8 in the diuretic, CCB, and ACE inhibitor groups, respectively. The adjusted hazard ratios were 0.97 for CCB vs. diuretics and 1.06 for ACE inhibitors vs. diuretics.
Although the risk of stroke mortality and of combined fatal and nonfatal hospitalized stroke was higher in the ACE inhibitor group compared with the diuretic group (adjusted hazard ratios 1.19 and 1.11, respectively), this increase was no longer significant after adjustment for multiple comparisons. “In contrast to the in-trial and 8-year to 13-year analyses, we now observed that the lisinopril group had an increased risk of kidney disease mortality that emerged after approximately 13 years after randomization, but this effect was attenuated after adjustment for baseline variables,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The findings were limited by several factors including the potential effect of unblinding if participants stopped the randomized drug, and by the lack of morbidity and mortality data on Canadian participants, Veterans Affairs participants, and those with no Medicare number, the researchers noted. Other limitations included the lack of data on posttrial medication use, blood pressure, and laboratory findings, they said.
However, the results over the follow-up period of up to 23 years supported those of the larger ALLHAT study, with similar outcomes among the drugs, and with 11 years of passive follow-up, “the results for lisinopril vs. chlorthalidone for stroke and stroke mortality are almost the same,” they concluded.
Findings support current practice, but new drug data are needed
The current study was important to determine whether there was a significant difference in long-term morbidity and mortality between patients treated with thiazide diuretics, calcium channel blockers and ACE inhibitors, Noel Deep, MD, said in an interview.
“Previously reported data had indicated no significant differences between patients randomized to one of these three classes of antihypertensive medications during the trial period or at 8-13 years post trial,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc., who was not involved in the study. Dr. Deep is chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
“This study reinforces the previously noted benefits of the three classes of antihypertensive medications, as well as the higher rates of cardiovascular disease and stroke in the ACE inhibitor arm,” he said.
In clinical practice, the results suggest that thiazide diuretics should be considered first-line agents for management of hypertension based on their noninferiority compared with ACE inhibitors and CCBs, and lower risk of stroke compared with ACE inhibitors, Dr. Deep said in an interview. “All three classes of antihypertensive medications are equally efficacious in blood pressure control and preventing all-cause mortality,” he said.
More research is needed in the wake of the introduction of other classes of antihypertensives since the original ALLHAT trial, Dr. Deep said. “It would be beneficial to assess the relative benefit/risks of those medications compared to the thiazide diuretics, and I would also look at studies comparing beta blockers to the thiazide diuretics,” he said. The question remains as to whether outcomes were affected by patients’ use of other classes of antihypertensives after the trial period, he said.
The study was supported by the National Institute on Aging of the National Institutes of Health. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose and serves on the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Smoking alters salivary microbiota in potential path to disease risk
TOPLINE:
Salivary microbiota changes caused by cigarette smoking may affect metabolic pathways and increase disease risk.
METHODOLOGY:
The researchers analyzed health information and data on the composition of salivary microbiota from 1601 adult participants in the Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) microbiome study (CHRISMB); CHRIS is an ongoing study in Italy.
The average age of the study population was 45 years; 53% were female, and 45% were current or former smokers.
The researchers hypothesized that changes in salivary microbial composition would be associated with smoking, with more nitrate-reducing bacteria present, and that nitrate reduction pathways would be reduced in smokers.
TAKEAWAY:
The researchers identified 44 genera that differed in the salivary microbiota of current smokers and nonsmokers. In smokers, seven genera in the phylum Proteobacteria were decreased and six in the phylum Actinobacteria were increased compared with nonsmokers; these phyla contain primarily aerobic and anaerobic taxa, respectively.
Some microbiota changes were significantly associated with daily smoking intensity; genera from the classes Betaproteobacteria (Lautropia or Neisseria), Gammaproteobacteria (Cardiobacterium), and Flavobacteriia (Capnocytophaga) decreased significantly with increased grams of tobacco smoked per day, measured in 5-g increments.
Smoking was associated with changes in the salivary microbiota; the nitrate reduction pathway was significantly lower in smokers compared with nonsmokers, and these decreases were consistent with previous studies of decreased cardiovascular events in former smokers.
However, the salivary microbiota of smokers who had quit for at least 5 years resembled that of individuals who had never smoked.
IN PRACTICE:
“Decreased microbial nitrate reduction pathway abundance in smokers may provide an additional explanation for the effect of smoking on cardiovascular and periodontal diseases risk, a hypothesis which should be tested in future studies,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author of the study was Giacomo Antonello, MD, of Eurac Research, Affiliated Institute of the University of Lübeck, Bolzano, Italy. The study was published online in Scientific Reports (a Nature journal) on November 2, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design and lack of professional assessment of tooth and gum health were limiting factors, as were potential confounding factors including medication use, diet, and alcohol intake.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Department of Innovation, Research and University of the Autonomous Province of Bolzano-South Tyrol and by the European Regional Development Fund. The CHRISMB microbiota data generation was funded by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Salivary microbiota changes caused by cigarette smoking may affect metabolic pathways and increase disease risk.
METHODOLOGY:
The researchers analyzed health information and data on the composition of salivary microbiota from 1601 adult participants in the Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) microbiome study (CHRISMB); CHRIS is an ongoing study in Italy.
The average age of the study population was 45 years; 53% were female, and 45% were current or former smokers.
The researchers hypothesized that changes in salivary microbial composition would be associated with smoking, with more nitrate-reducing bacteria present, and that nitrate reduction pathways would be reduced in smokers.
TAKEAWAY:
The researchers identified 44 genera that differed in the salivary microbiota of current smokers and nonsmokers. In smokers, seven genera in the phylum Proteobacteria were decreased and six in the phylum Actinobacteria were increased compared with nonsmokers; these phyla contain primarily aerobic and anaerobic taxa, respectively.
Some microbiota changes were significantly associated with daily smoking intensity; genera from the classes Betaproteobacteria (Lautropia or Neisseria), Gammaproteobacteria (Cardiobacterium), and Flavobacteriia (Capnocytophaga) decreased significantly with increased grams of tobacco smoked per day, measured in 5-g increments.
Smoking was associated with changes in the salivary microbiota; the nitrate reduction pathway was significantly lower in smokers compared with nonsmokers, and these decreases were consistent with previous studies of decreased cardiovascular events in former smokers.
However, the salivary microbiota of smokers who had quit for at least 5 years resembled that of individuals who had never smoked.
IN PRACTICE:
“Decreased microbial nitrate reduction pathway abundance in smokers may provide an additional explanation for the effect of smoking on cardiovascular and periodontal diseases risk, a hypothesis which should be tested in future studies,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author of the study was Giacomo Antonello, MD, of Eurac Research, Affiliated Institute of the University of Lübeck, Bolzano, Italy. The study was published online in Scientific Reports (a Nature journal) on November 2, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design and lack of professional assessment of tooth and gum health were limiting factors, as were potential confounding factors including medication use, diet, and alcohol intake.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Department of Innovation, Research and University of the Autonomous Province of Bolzano-South Tyrol and by the European Regional Development Fund. The CHRISMB microbiota data generation was funded by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Salivary microbiota changes caused by cigarette smoking may affect metabolic pathways and increase disease risk.
METHODOLOGY:
The researchers analyzed health information and data on the composition of salivary microbiota from 1601 adult participants in the Cooperative Health Research in South Tyrol (CHRIS) microbiome study (CHRISMB); CHRIS is an ongoing study in Italy.
The average age of the study population was 45 years; 53% were female, and 45% were current or former smokers.
The researchers hypothesized that changes in salivary microbial composition would be associated with smoking, with more nitrate-reducing bacteria present, and that nitrate reduction pathways would be reduced in smokers.
TAKEAWAY:
The researchers identified 44 genera that differed in the salivary microbiota of current smokers and nonsmokers. In smokers, seven genera in the phylum Proteobacteria were decreased and six in the phylum Actinobacteria were increased compared with nonsmokers; these phyla contain primarily aerobic and anaerobic taxa, respectively.
Some microbiota changes were significantly associated with daily smoking intensity; genera from the classes Betaproteobacteria (Lautropia or Neisseria), Gammaproteobacteria (Cardiobacterium), and Flavobacteriia (Capnocytophaga) decreased significantly with increased grams of tobacco smoked per day, measured in 5-g increments.
Smoking was associated with changes in the salivary microbiota; the nitrate reduction pathway was significantly lower in smokers compared with nonsmokers, and these decreases were consistent with previous studies of decreased cardiovascular events in former smokers.
However, the salivary microbiota of smokers who had quit for at least 5 years resembled that of individuals who had never smoked.
IN PRACTICE:
“Decreased microbial nitrate reduction pathway abundance in smokers may provide an additional explanation for the effect of smoking on cardiovascular and periodontal diseases risk, a hypothesis which should be tested in future studies,” the researchers wrote.
SOURCE:
The lead author of the study was Giacomo Antonello, MD, of Eurac Research, Affiliated Institute of the University of Lübeck, Bolzano, Italy. The study was published online in Scientific Reports (a Nature journal) on November 2, 2023.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design and lack of professional assessment of tooth and gum health were limiting factors, as were potential confounding factors including medication use, diet, and alcohol intake.
DISCLOSURES:
The study was supported by the Department of Innovation, Research and University of the Autonomous Province of Bolzano-South Tyrol and by the European Regional Development Fund. The CHRISMB microbiota data generation was funded by the National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bariatric surgery still best option for some with obesity
Bariatric surgery continues to play a major role in obesity management despite the emergence of potent new weight-loss medications, according to two experts who spoke at an Endocrine Society science writers briefing.
“Bariatric surgery is safe, effective, and unfortunately underutilized for treating obesity and its complications,” said Jaime Almandoz, MD, medical director of the Weight Wellness Program at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
Added Dr. Almandoz, who is triple board-certified in internal medicine, endocrinology, and obesity medicine, “Sometimes this gets presented in a linear fashion. ‘We’ll try lifestyle first, and if that doesn’t work, we’ll try medications, and if that doesn’t work, we’ll try surgery.’ But sometimes we might need to go straight to surgery instead of going through medications first, because it may be the most effective and evidence-based treatment for the person in the office in front of you.”
Moreover, he pointed out that currently, Medicare and many private insurers don’t cover antiobesity medications but do cover bariatric surgery.
Indeed, Srividya Kidambi, MD, professor and chief of endocrinology and molecular medicine at the Medical College of Wisconsin/Froedtert Hospital, Milwaukee, said there are certain types of patients for whom she might consider bariatric surgery first. One would be a person with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 40 kg/m2 or with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and severe comorbidities.
Another, she said, would be young, relatively healthy people with obesity who have no comorbid conditions. “We know that if we stop the medication, the weight comes back. So, if I see a 20- to 25-year-old, am I really to commit them to lifelong therapy, or is bariatric surgery a better option in these cases? These drugs have not been around that long ... so I tend to recommend bariatric surgery in some patients.”
During the recent briefing, Dr. Almandoz summarized the evidence base for the benefits of bariatric surgery beyond weight loss, which include remission of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease, reduction of the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer, and increased life expectancy.
“Everyone seems to be talking about GLP-1s for facilitating weight loss and treating obesity. ... What I want to do is provide a counterpoint to accessible therapies that are covered by more insurance plans and that may, in fact, have a better evidence base for treating obesity and its related complications,” he said in his introduction.
Bariatric surgery has been used for decades, and many centers of excellence perform it, with greatly reduced complication rates seen today than in the past. “It’s comparable to having a gallbladder surgery in terms of perioperative risk,” he noted.
Medicare and private insurers generally cover bariatric surgery for people with BMI greater than 40 kg/m2 or 35-39 kg/m2 and at least one weight-related comorbidity, including type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, atherosclerotic disease, hyperlipidemia, and fatty liver disease.
Data suggest that weight reduction of about 3% can lead to meaningful reductions in blood glucose and triglyceride levels, but weight loss of 15% or greater is associated with reductions in cardiovascular events and type 2 diabetes remission. Lifestyle modification typically produces about 5% weight loss, compared with 20%-35% with bariatric surgery with sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass.
Older weight loss medications produced weight loss of 5%-10%; only the newer medications, semaglutide 2.4 mg and tirzepatide, come close to that. Weight loss with semaglutide is about 15%, while tirzepatide can produce weight loss of up to 22%. But, there are still issues with affordability, access, and lack of coverage, Dr. Almandoz noted.
One recent randomized trial of more than 400 individuals showed that bariatric surgery was more effective than lifestyle and medical therapies for treating metabolic-associated steatohepatitis without worsening of fibrosis.
Another showed that the surgery was associated with fewer major adverse liver outcomes among people who already had MASH. That same study showed a 70% reduction in cardiovascular events with bariatric surgery.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, numerous trials have demonstrated long-term remission and reduced A1c at 5 years and 10 years post surgery, along with reductions in microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Other data suggest that a shorter history of type 2 diabetes is among the factors predicting remission with bariatric surgery. “Oftentimes, both patients and providers will wait until the diabetes is quite advanced before they even have the conversation about weight loss or even bariatric surgery. This suggests that if we intervene earlier in the course of disease, when it is less severe and less advanced, we have a higher rate of causing remission in the diabetes,” Dr. Almandoz said.
The American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Care incorporate bariatric surgery as either “recommended” or “may be considered” to treat type 2 diabetes, depending on BMI level, for those who don’t achieve durable weight loss with nonsurgical methods, he noted.
A retrospective cohort study showed significant reductions in cardiovascular outcomes with bariatric surgery among people with baseline cardiovascular disease. “This is not just about bariatric surgery to cause weight loss. This is about the multitude of effects that happen when we treat obesity as a disease with highly effective therapies such as surgery,” he said.
Even cancer risk and cancer-related mortality were significantly reduced with bariatric surgery, another study found.
And in the long-term Swedish Obese Subjects Study, among people with obesity, bariatric surgery was associated with a 3-year increase in life expectancy, compared with not undergoing surgery.
However, Dr. Almandoz also pointed out that some patients may benefit from both weight-loss medication and bariatric surgery. “Once someone has undergone pharmacotherapy, there may still be a role for bariatric procedures in helping to optimize body weight and control body weight long term. And likewise for those who have undergone bariatric surgery, there’s also a role for pharmacotherapy in terms of treating insufficient weight loss or weight recurrence after bariatric surgery. ... So I think there’s clearly a role for integration of therapies.”
Dr. Almandoz serves as consultant/advisory board member for Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Kidambi is director of TOPS Center for Metabolic Research and is medical editor of TOPS Magazine, for which her institution receives an honorarium.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bariatric surgery continues to play a major role in obesity management despite the emergence of potent new weight-loss medications, according to two experts who spoke at an Endocrine Society science writers briefing.
“Bariatric surgery is safe, effective, and unfortunately underutilized for treating obesity and its complications,” said Jaime Almandoz, MD, medical director of the Weight Wellness Program at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
Added Dr. Almandoz, who is triple board-certified in internal medicine, endocrinology, and obesity medicine, “Sometimes this gets presented in a linear fashion. ‘We’ll try lifestyle first, and if that doesn’t work, we’ll try medications, and if that doesn’t work, we’ll try surgery.’ But sometimes we might need to go straight to surgery instead of going through medications first, because it may be the most effective and evidence-based treatment for the person in the office in front of you.”
Moreover, he pointed out that currently, Medicare and many private insurers don’t cover antiobesity medications but do cover bariatric surgery.
Indeed, Srividya Kidambi, MD, professor and chief of endocrinology and molecular medicine at the Medical College of Wisconsin/Froedtert Hospital, Milwaukee, said there are certain types of patients for whom she might consider bariatric surgery first. One would be a person with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 40 kg/m2 or with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and severe comorbidities.
Another, she said, would be young, relatively healthy people with obesity who have no comorbid conditions. “We know that if we stop the medication, the weight comes back. So, if I see a 20- to 25-year-old, am I really to commit them to lifelong therapy, or is bariatric surgery a better option in these cases? These drugs have not been around that long ... so I tend to recommend bariatric surgery in some patients.”
During the recent briefing, Dr. Almandoz summarized the evidence base for the benefits of bariatric surgery beyond weight loss, which include remission of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease, reduction of the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer, and increased life expectancy.
“Everyone seems to be talking about GLP-1s for facilitating weight loss and treating obesity. ... What I want to do is provide a counterpoint to accessible therapies that are covered by more insurance plans and that may, in fact, have a better evidence base for treating obesity and its related complications,” he said in his introduction.
Bariatric surgery has been used for decades, and many centers of excellence perform it, with greatly reduced complication rates seen today than in the past. “It’s comparable to having a gallbladder surgery in terms of perioperative risk,” he noted.
Medicare and private insurers generally cover bariatric surgery for people with BMI greater than 40 kg/m2 or 35-39 kg/m2 and at least one weight-related comorbidity, including type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, atherosclerotic disease, hyperlipidemia, and fatty liver disease.
Data suggest that weight reduction of about 3% can lead to meaningful reductions in blood glucose and triglyceride levels, but weight loss of 15% or greater is associated with reductions in cardiovascular events and type 2 diabetes remission. Lifestyle modification typically produces about 5% weight loss, compared with 20%-35% with bariatric surgery with sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass.
Older weight loss medications produced weight loss of 5%-10%; only the newer medications, semaglutide 2.4 mg and tirzepatide, come close to that. Weight loss with semaglutide is about 15%, while tirzepatide can produce weight loss of up to 22%. But, there are still issues with affordability, access, and lack of coverage, Dr. Almandoz noted.
One recent randomized trial of more than 400 individuals showed that bariatric surgery was more effective than lifestyle and medical therapies for treating metabolic-associated steatohepatitis without worsening of fibrosis.
Another showed that the surgery was associated with fewer major adverse liver outcomes among people who already had MASH. That same study showed a 70% reduction in cardiovascular events with bariatric surgery.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, numerous trials have demonstrated long-term remission and reduced A1c at 5 years and 10 years post surgery, along with reductions in microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Other data suggest that a shorter history of type 2 diabetes is among the factors predicting remission with bariatric surgery. “Oftentimes, both patients and providers will wait until the diabetes is quite advanced before they even have the conversation about weight loss or even bariatric surgery. This suggests that if we intervene earlier in the course of disease, when it is less severe and less advanced, we have a higher rate of causing remission in the diabetes,” Dr. Almandoz said.
The American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Care incorporate bariatric surgery as either “recommended” or “may be considered” to treat type 2 diabetes, depending on BMI level, for those who don’t achieve durable weight loss with nonsurgical methods, he noted.
A retrospective cohort study showed significant reductions in cardiovascular outcomes with bariatric surgery among people with baseline cardiovascular disease. “This is not just about bariatric surgery to cause weight loss. This is about the multitude of effects that happen when we treat obesity as a disease with highly effective therapies such as surgery,” he said.
Even cancer risk and cancer-related mortality were significantly reduced with bariatric surgery, another study found.
And in the long-term Swedish Obese Subjects Study, among people with obesity, bariatric surgery was associated with a 3-year increase in life expectancy, compared with not undergoing surgery.
However, Dr. Almandoz also pointed out that some patients may benefit from both weight-loss medication and bariatric surgery. “Once someone has undergone pharmacotherapy, there may still be a role for bariatric procedures in helping to optimize body weight and control body weight long term. And likewise for those who have undergone bariatric surgery, there’s also a role for pharmacotherapy in terms of treating insufficient weight loss or weight recurrence after bariatric surgery. ... So I think there’s clearly a role for integration of therapies.”
Dr. Almandoz serves as consultant/advisory board member for Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Kidambi is director of TOPS Center for Metabolic Research and is medical editor of TOPS Magazine, for which her institution receives an honorarium.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bariatric surgery continues to play a major role in obesity management despite the emergence of potent new weight-loss medications, according to two experts who spoke at an Endocrine Society science writers briefing.
“Bariatric surgery is safe, effective, and unfortunately underutilized for treating obesity and its complications,” said Jaime Almandoz, MD, medical director of the Weight Wellness Program at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas.
Added Dr. Almandoz, who is triple board-certified in internal medicine, endocrinology, and obesity medicine, “Sometimes this gets presented in a linear fashion. ‘We’ll try lifestyle first, and if that doesn’t work, we’ll try medications, and if that doesn’t work, we’ll try surgery.’ But sometimes we might need to go straight to surgery instead of going through medications first, because it may be the most effective and evidence-based treatment for the person in the office in front of you.”
Moreover, he pointed out that currently, Medicare and many private insurers don’t cover antiobesity medications but do cover bariatric surgery.
Indeed, Srividya Kidambi, MD, professor and chief of endocrinology and molecular medicine at the Medical College of Wisconsin/Froedtert Hospital, Milwaukee, said there are certain types of patients for whom she might consider bariatric surgery first. One would be a person with a body mass index (BMI) greater than 40 kg/m2 or with a BMI greater than 35 kg/m2 and severe comorbidities.
Another, she said, would be young, relatively healthy people with obesity who have no comorbid conditions. “We know that if we stop the medication, the weight comes back. So, if I see a 20- to 25-year-old, am I really to commit them to lifelong therapy, or is bariatric surgery a better option in these cases? These drugs have not been around that long ... so I tend to recommend bariatric surgery in some patients.”
During the recent briefing, Dr. Almandoz summarized the evidence base for the benefits of bariatric surgery beyond weight loss, which include remission of type 2 diabetes and fatty liver disease, reduction of the risks of cardiovascular disease and cancer, and increased life expectancy.
“Everyone seems to be talking about GLP-1s for facilitating weight loss and treating obesity. ... What I want to do is provide a counterpoint to accessible therapies that are covered by more insurance plans and that may, in fact, have a better evidence base for treating obesity and its related complications,” he said in his introduction.
Bariatric surgery has been used for decades, and many centers of excellence perform it, with greatly reduced complication rates seen today than in the past. “It’s comparable to having a gallbladder surgery in terms of perioperative risk,” he noted.
Medicare and private insurers generally cover bariatric surgery for people with BMI greater than 40 kg/m2 or 35-39 kg/m2 and at least one weight-related comorbidity, including type 2 diabetes, obstructive sleep apnea, hypertension, atherosclerotic disease, hyperlipidemia, and fatty liver disease.
Data suggest that weight reduction of about 3% can lead to meaningful reductions in blood glucose and triglyceride levels, but weight loss of 15% or greater is associated with reductions in cardiovascular events and type 2 diabetes remission. Lifestyle modification typically produces about 5% weight loss, compared with 20%-35% with bariatric surgery with sleeve gastrectomy or gastric bypass.
Older weight loss medications produced weight loss of 5%-10%; only the newer medications, semaglutide 2.4 mg and tirzepatide, come close to that. Weight loss with semaglutide is about 15%, while tirzepatide can produce weight loss of up to 22%. But, there are still issues with affordability, access, and lack of coverage, Dr. Almandoz noted.
One recent randomized trial of more than 400 individuals showed that bariatric surgery was more effective than lifestyle and medical therapies for treating metabolic-associated steatohepatitis without worsening of fibrosis.
Another showed that the surgery was associated with fewer major adverse liver outcomes among people who already had MASH. That same study showed a 70% reduction in cardiovascular events with bariatric surgery.
For patients with type 2 diabetes, numerous trials have demonstrated long-term remission and reduced A1c at 5 years and 10 years post surgery, along with reductions in microvascular and macrovascular complications.
Other data suggest that a shorter history of type 2 diabetes is among the factors predicting remission with bariatric surgery. “Oftentimes, both patients and providers will wait until the diabetes is quite advanced before they even have the conversation about weight loss or even bariatric surgery. This suggests that if we intervene earlier in the course of disease, when it is less severe and less advanced, we have a higher rate of causing remission in the diabetes,” Dr. Almandoz said.
The American Diabetes Association’s Standards of Care incorporate bariatric surgery as either “recommended” or “may be considered” to treat type 2 diabetes, depending on BMI level, for those who don’t achieve durable weight loss with nonsurgical methods, he noted.
A retrospective cohort study showed significant reductions in cardiovascular outcomes with bariatric surgery among people with baseline cardiovascular disease. “This is not just about bariatric surgery to cause weight loss. This is about the multitude of effects that happen when we treat obesity as a disease with highly effective therapies such as surgery,” he said.
Even cancer risk and cancer-related mortality were significantly reduced with bariatric surgery, another study found.
And in the long-term Swedish Obese Subjects Study, among people with obesity, bariatric surgery was associated with a 3-year increase in life expectancy, compared with not undergoing surgery.
However, Dr. Almandoz also pointed out that some patients may benefit from both weight-loss medication and bariatric surgery. “Once someone has undergone pharmacotherapy, there may still be a role for bariatric procedures in helping to optimize body weight and control body weight long term. And likewise for those who have undergone bariatric surgery, there’s also a role for pharmacotherapy in terms of treating insufficient weight loss or weight recurrence after bariatric surgery. ... So I think there’s clearly a role for integration of therapies.”
Dr. Almandoz serves as consultant/advisory board member for Novo Nordisk, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Kidambi is director of TOPS Center for Metabolic Research and is medical editor of TOPS Magazine, for which her institution receives an honorarium.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AI-ECG gets STEMI patients to cath lab sooner
PHILADELPHIA – An artificial intelligence platform that sends alerts based on electrocardiography results enabled cardiologists and emergency department physicians at a major hospital in Taiwan to move patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) into the catheterization laboratory 9 minutes sooner than the conventional protocol that did not use AI.
“This is the first randomized clinical trial to demonstrate the reduction of electrocardiography to coronary cath lab activation time" from 52.3 to 43.3 minutes (P = .003), Chin Sheng Lin, MD, PhD, director of cardiology at the National Defense Medical Center Tri-Service General Hospital in Taipei City, said in presenting the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Lin reported results from the Artificial Intelligence Enabled Rapid Identify of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Using Electrocardiogram (ARISE) trial. The trial included 43,994 patients who came to the hospital’s emergency and inpatient departments with at least one ECG but no history of coronary angiography (CAG) in the previous 3 days between May 2022 and April 2023.
They were randomly assigned by date to either AI-ECG for rapid identification and triage of STEMI or standard care. Overall, 145 patients were finally diagnosed with STEMI based on CAG, 77 in the intervention group and 68 in the control group. All patients were seen by one of 20 cardiologists who participated in the study.
Dr. Lin and his group developed an AI algorithm that captures the ECG readout in the emergency department, analyzes the data and then sends a high-risk alarm to the front-line physician and on-duty cardiologist to activate the primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Trial results
The differentiation between groups was even more pronounced in ED patients during regular working hours, Dr. Lin said, at 61.6 minutes for the intervention group vs. 33.1 minutes for controls (P = .001).*
He noted that the AI group showed a trend towards fewer cases of clinically suspected STEMI but not getting CAG, 6.5% vs. 15.8%, for an odds ratio of 0.37 (95% confidence interval, 0.14-0.94).
The AI-ECG model also demonstrated a high diagnostic accuracy. “With this AI-ECG system, because it has a very high accuracy and a high positive predictive variable that reach 88%, we can send a message to the on-duty cardiologists and also the emergency room physician and they can send the patients to receive the operation or the PCI as soon as possible,” Dr. Lin said in an interview.
The time differential is critical, Dr. Lin said. “For the patient with acute myocardial infarction, 1 minute is critical, because the patients can die within minutes,” he said. “If we can save 9 minutes I think we can save more lives, but it needs a larger study to evaluate that.”
Dr. Lin acknowledged a few limitations with the trial, among them its single-center nature, relatively small sample size of STEMI patients and the short-term of follow-up. Future study should involve multiple centers along with a prehospital, emergency medical services AI-ECG model.
‘Novel’ for an AI trial
“This is an incredible application of an AI technology in a real-world problem,” said Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH, an interventional cardiologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who did not participate in the study. “What I really love about this study is it’s actually a clinical problem that has large implications, particularly for under-resourced areas.”
Using a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the AI platform is “very, very novel,” he said, and called the time improvement “enormous.” Referencing Dr. Lin’s next steps for studying the AI-ECG platform, Dr. Nallamothu said, “if we could push this up even earlier to paramedics and EMTs and prehospital systems, there would be a lot of excitement there.”
He noted the sensitivity analysis resulted in a rate of 88.8% along with the positive predictive value of 88%. “Missing 1 out of 10 ST-elevation MIs in my eyes can still be considered a big deal, so we need to know if this is happening in particular types of patients, for example women versus men, or other groups.”
However, some investigations reported false activation rates as high as 33%, he said. “So, to say that, the positive predictive value is at 88% is really exciting and I think it can make a real inroads,” Dr. Nallamothu said.
Dr. Lin and Dr. Nallamothu have no relevant disclosures.
*Correction, 11/20/23: An earlier version of this article misstated in both trial arms the time to coronary catheterization lab activation.
PHILADELPHIA – An artificial intelligence platform that sends alerts based on electrocardiography results enabled cardiologists and emergency department physicians at a major hospital in Taiwan to move patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) into the catheterization laboratory 9 minutes sooner than the conventional protocol that did not use AI.
“This is the first randomized clinical trial to demonstrate the reduction of electrocardiography to coronary cath lab activation time" from 52.3 to 43.3 minutes (P = .003), Chin Sheng Lin, MD, PhD, director of cardiology at the National Defense Medical Center Tri-Service General Hospital in Taipei City, said in presenting the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Lin reported results from the Artificial Intelligence Enabled Rapid Identify of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Using Electrocardiogram (ARISE) trial. The trial included 43,994 patients who came to the hospital’s emergency and inpatient departments with at least one ECG but no history of coronary angiography (CAG) in the previous 3 days between May 2022 and April 2023.
They were randomly assigned by date to either AI-ECG for rapid identification and triage of STEMI or standard care. Overall, 145 patients were finally diagnosed with STEMI based on CAG, 77 in the intervention group and 68 in the control group. All patients were seen by one of 20 cardiologists who participated in the study.
Dr. Lin and his group developed an AI algorithm that captures the ECG readout in the emergency department, analyzes the data and then sends a high-risk alarm to the front-line physician and on-duty cardiologist to activate the primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Trial results
The differentiation between groups was even more pronounced in ED patients during regular working hours, Dr. Lin said, at 61.6 minutes for the intervention group vs. 33.1 minutes for controls (P = .001).*
He noted that the AI group showed a trend towards fewer cases of clinically suspected STEMI but not getting CAG, 6.5% vs. 15.8%, for an odds ratio of 0.37 (95% confidence interval, 0.14-0.94).
The AI-ECG model also demonstrated a high diagnostic accuracy. “With this AI-ECG system, because it has a very high accuracy and a high positive predictive variable that reach 88%, we can send a message to the on-duty cardiologists and also the emergency room physician and they can send the patients to receive the operation or the PCI as soon as possible,” Dr. Lin said in an interview.
The time differential is critical, Dr. Lin said. “For the patient with acute myocardial infarction, 1 minute is critical, because the patients can die within minutes,” he said. “If we can save 9 minutes I think we can save more lives, but it needs a larger study to evaluate that.”
Dr. Lin acknowledged a few limitations with the trial, among them its single-center nature, relatively small sample size of STEMI patients and the short-term of follow-up. Future study should involve multiple centers along with a prehospital, emergency medical services AI-ECG model.
‘Novel’ for an AI trial
“This is an incredible application of an AI technology in a real-world problem,” said Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH, an interventional cardiologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who did not participate in the study. “What I really love about this study is it’s actually a clinical problem that has large implications, particularly for under-resourced areas.”
Using a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the AI platform is “very, very novel,” he said, and called the time improvement “enormous.” Referencing Dr. Lin’s next steps for studying the AI-ECG platform, Dr. Nallamothu said, “if we could push this up even earlier to paramedics and EMTs and prehospital systems, there would be a lot of excitement there.”
He noted the sensitivity analysis resulted in a rate of 88.8% along with the positive predictive value of 88%. “Missing 1 out of 10 ST-elevation MIs in my eyes can still be considered a big deal, so we need to know if this is happening in particular types of patients, for example women versus men, or other groups.”
However, some investigations reported false activation rates as high as 33%, he said. “So, to say that, the positive predictive value is at 88% is really exciting and I think it can make a real inroads,” Dr. Nallamothu said.
Dr. Lin and Dr. Nallamothu have no relevant disclosures.
*Correction, 11/20/23: An earlier version of this article misstated in both trial arms the time to coronary catheterization lab activation.
PHILADELPHIA – An artificial intelligence platform that sends alerts based on electrocardiography results enabled cardiologists and emergency department physicians at a major hospital in Taiwan to move patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) into the catheterization laboratory 9 minutes sooner than the conventional protocol that did not use AI.
“This is the first randomized clinical trial to demonstrate the reduction of electrocardiography to coronary cath lab activation time" from 52.3 to 43.3 minutes (P = .003), Chin Sheng Lin, MD, PhD, director of cardiology at the National Defense Medical Center Tri-Service General Hospital in Taipei City, said in presenting the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Lin reported results from the Artificial Intelligence Enabled Rapid Identify of ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction Using Electrocardiogram (ARISE) trial. The trial included 43,994 patients who came to the hospital’s emergency and inpatient departments with at least one ECG but no history of coronary angiography (CAG) in the previous 3 days between May 2022 and April 2023.
They were randomly assigned by date to either AI-ECG for rapid identification and triage of STEMI or standard care. Overall, 145 patients were finally diagnosed with STEMI based on CAG, 77 in the intervention group and 68 in the control group. All patients were seen by one of 20 cardiologists who participated in the study.
Dr. Lin and his group developed an AI algorithm that captures the ECG readout in the emergency department, analyzes the data and then sends a high-risk alarm to the front-line physician and on-duty cardiologist to activate the primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
Trial results
The differentiation between groups was even more pronounced in ED patients during regular working hours, Dr. Lin said, at 61.6 minutes for the intervention group vs. 33.1 minutes for controls (P = .001).*
He noted that the AI group showed a trend towards fewer cases of clinically suspected STEMI but not getting CAG, 6.5% vs. 15.8%, for an odds ratio of 0.37 (95% confidence interval, 0.14-0.94).
The AI-ECG model also demonstrated a high diagnostic accuracy. “With this AI-ECG system, because it has a very high accuracy and a high positive predictive variable that reach 88%, we can send a message to the on-duty cardiologists and also the emergency room physician and they can send the patients to receive the operation or the PCI as soon as possible,” Dr. Lin said in an interview.
The time differential is critical, Dr. Lin said. “For the patient with acute myocardial infarction, 1 minute is critical, because the patients can die within minutes,” he said. “If we can save 9 minutes I think we can save more lives, but it needs a larger study to evaluate that.”
Dr. Lin acknowledged a few limitations with the trial, among them its single-center nature, relatively small sample size of STEMI patients and the short-term of follow-up. Future study should involve multiple centers along with a prehospital, emergency medical services AI-ECG model.
‘Novel’ for an AI trial
“This is an incredible application of an AI technology in a real-world problem,” said Brahmajee K. Nallamothu, MD, MPH, an interventional cardiologist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, who did not participate in the study. “What I really love about this study is it’s actually a clinical problem that has large implications, particularly for under-resourced areas.”
Using a randomized clinical trial to evaluate the AI platform is “very, very novel,” he said, and called the time improvement “enormous.” Referencing Dr. Lin’s next steps for studying the AI-ECG platform, Dr. Nallamothu said, “if we could push this up even earlier to paramedics and EMTs and prehospital systems, there would be a lot of excitement there.”
He noted the sensitivity analysis resulted in a rate of 88.8% along with the positive predictive value of 88%. “Missing 1 out of 10 ST-elevation MIs in my eyes can still be considered a big deal, so we need to know if this is happening in particular types of patients, for example women versus men, or other groups.”
However, some investigations reported false activation rates as high as 33%, he said. “So, to say that, the positive predictive value is at 88% is really exciting and I think it can make a real inroads,” Dr. Nallamothu said.
Dr. Lin and Dr. Nallamothu have no relevant disclosures.
*Correction, 11/20/23: An earlier version of this article misstated in both trial arms the time to coronary catheterization lab activation.
AT AHA 2023
‘Love more’: Why doctors should promote social connection
Those who embrace lifestyle medicine are familiar with the slogan Dean Ornish, MD, likes to use: Eat well, move more, stress less, love more.
That last one, love, was the renowned physician and author’s focus at the recent American College of Lifestyle Medicine Conference in Denver. That’s because love – essentially the support, connectedness, and caring that patients feel when they join a lifestyle-change program – is “where healing occurs at the deepest level.”
Indeed, social connectedness is emerging as a vital pillar in the burgeoning field of lifestyle medicine, a specialty that uses lifestyle interventions to treat chronic conditions. About 300 lifestyle medicine programs are now integrated into residencies in medical schools across the country, up from a handful just 5 years ago, said Meagan Grega, MD, the conference chair.
“The energy and growth in American lifestyle medicine is unparalleled by anything else I see in the health care world right now,” said Dr. Grega, a family physician for 25 years in eastern Pennsylvania.
The field applies volumes of research, from the 1990s to today, demonstrating the healing effects of lifestyle changes. Dr. Ornish’s Preventive Medicine Research Institute has published research on small changes (like pomegranate juice helping blood flow in the heart) and huge ones: Coronary heart patients reversed the narrowing of arteries without lipid-lowering drugs after 1 year of lifestyle changes, including a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management, and group support.
Ranking alongside bedrocks such as healthy diet, sleep, exercise, and stress management is positive social connection. That part, the “love more” part, often draws skepticism but is vital, said Dr. Ornish, who is sometimes referred to as the father of lifestyle medicine.
It’s “invariably the part that’s the most meaningful – that sense of connection to community that can come when you bring total strangers together,” Dr. Ornish said. “The ‘love more’ part, in many ways, is not only as important, but in some ways even more because everything really flows from that.”
Patients in a support group, who can “let down their emotional defenses and talk openly and authentically,” are much more likely to make and maintain healthy changes, Dr. Ornish said.
Love as medicine
Mounting evidence links loneliness and isolation with a range of health issues, from mood disorders such as depression to chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease. What’s more, data suggest that loneliness and social isolation in the United States are on the rise, and the COVID pandemic made that more clear. In May 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, called loneliness, isolation, and lack of connection in the United States a “public health crisis.”
“Good relationships keep us happier and healthier,” said Robert Waldinger, MD, a psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dr. Waldinger, who was not affiliated with the conference, is head of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, one of the longest studies of adult life. Beginning in 1938, the study has tracked 724 people plus more than 1,300 of their descendants and found that embracing community and close relationships helps us live longer and be happier.
In the study, the people who were most satisfied with their relationships at age 50 years were the healthiest at age 80 years. Knowing you have someone to rely on protects the brain: “Those people’s memories stay sharper longer,” Dr. Waldinger said.
He draws a distinction between connection and love. “Love is, I think, more of a feeling,” Dr. Waldinger noted. “Connection is a feeling, but it’s also an activity.”
One in five Americans say they’re lonely, he said, “and loneliness is a stressor.” People who are isolated don’t sleep as well, he added. Their health declines earlier in midlife, brain function slips sooner, and their lives are shorter.
“You don’t have anyone to complain to,” he said. If you do, “you can feel your body start to calm down.” Those without social connections may stay in a low-level “fight-or-flight mode.”
“What we think happens is that you have low levels of inflammation chronically, and those can gradually break down body systems.” Moreover, higher rates of cardiac reactivity, for instance, a racing heartbeat when upset, can lead to high blood pressure and lower immune function.
In his talk, Dr. Ornish said, “Anger is that one emotion that has consistently been shown to make heart disease worse.”
Helping people in those straits is gratifying, Dr. Ornish said. “If we can work with people as lifestyle medicine practitioners when they’re suffering, there’s an opportunity for transformation.”
Future
Of course, that can be easier said than done. Dr. Ornish relayed a patient’s typical reaction to a lifestyle program: “This is kind of weird stuff. Like, I get diet. But a plant-based diet, really? Meditation? Loving more? Really?”
He told the conference, “Part of our job as lifestyle medicine practitioners is to spend a little extra time with them. It doesn’t even take that much time. And to really help them understand what brings them a sense of hope and meaning and purpose.”
The results can be motivating. “Most people feel so much better so quickly,” Dr. Ornish said. “It reframes the reason for change from fear of dying to joy of living.”
Dr. Grega, for one, is optimistic for the future, citing survey results showing that 95% of medical students think that they›d be better counselors with lifestyle training. ‘They passionately want this type of thing,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Those who embrace lifestyle medicine are familiar with the slogan Dean Ornish, MD, likes to use: Eat well, move more, stress less, love more.
That last one, love, was the renowned physician and author’s focus at the recent American College of Lifestyle Medicine Conference in Denver. That’s because love – essentially the support, connectedness, and caring that patients feel when they join a lifestyle-change program – is “where healing occurs at the deepest level.”
Indeed, social connectedness is emerging as a vital pillar in the burgeoning field of lifestyle medicine, a specialty that uses lifestyle interventions to treat chronic conditions. About 300 lifestyle medicine programs are now integrated into residencies in medical schools across the country, up from a handful just 5 years ago, said Meagan Grega, MD, the conference chair.
“The energy and growth in American lifestyle medicine is unparalleled by anything else I see in the health care world right now,” said Dr. Grega, a family physician for 25 years in eastern Pennsylvania.
The field applies volumes of research, from the 1990s to today, demonstrating the healing effects of lifestyle changes. Dr. Ornish’s Preventive Medicine Research Institute has published research on small changes (like pomegranate juice helping blood flow in the heart) and huge ones: Coronary heart patients reversed the narrowing of arteries without lipid-lowering drugs after 1 year of lifestyle changes, including a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management, and group support.
Ranking alongside bedrocks such as healthy diet, sleep, exercise, and stress management is positive social connection. That part, the “love more” part, often draws skepticism but is vital, said Dr. Ornish, who is sometimes referred to as the father of lifestyle medicine.
It’s “invariably the part that’s the most meaningful – that sense of connection to community that can come when you bring total strangers together,” Dr. Ornish said. “The ‘love more’ part, in many ways, is not only as important, but in some ways even more because everything really flows from that.”
Patients in a support group, who can “let down their emotional defenses and talk openly and authentically,” are much more likely to make and maintain healthy changes, Dr. Ornish said.
Love as medicine
Mounting evidence links loneliness and isolation with a range of health issues, from mood disorders such as depression to chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease. What’s more, data suggest that loneliness and social isolation in the United States are on the rise, and the COVID pandemic made that more clear. In May 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, called loneliness, isolation, and lack of connection in the United States a “public health crisis.”
“Good relationships keep us happier and healthier,” said Robert Waldinger, MD, a psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dr. Waldinger, who was not affiliated with the conference, is head of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, one of the longest studies of adult life. Beginning in 1938, the study has tracked 724 people plus more than 1,300 of their descendants and found that embracing community and close relationships helps us live longer and be happier.
In the study, the people who were most satisfied with their relationships at age 50 years were the healthiest at age 80 years. Knowing you have someone to rely on protects the brain: “Those people’s memories stay sharper longer,” Dr. Waldinger said.
He draws a distinction between connection and love. “Love is, I think, more of a feeling,” Dr. Waldinger noted. “Connection is a feeling, but it’s also an activity.”
One in five Americans say they’re lonely, he said, “and loneliness is a stressor.” People who are isolated don’t sleep as well, he added. Their health declines earlier in midlife, brain function slips sooner, and their lives are shorter.
“You don’t have anyone to complain to,” he said. If you do, “you can feel your body start to calm down.” Those without social connections may stay in a low-level “fight-or-flight mode.”
“What we think happens is that you have low levels of inflammation chronically, and those can gradually break down body systems.” Moreover, higher rates of cardiac reactivity, for instance, a racing heartbeat when upset, can lead to high blood pressure and lower immune function.
In his talk, Dr. Ornish said, “Anger is that one emotion that has consistently been shown to make heart disease worse.”
Helping people in those straits is gratifying, Dr. Ornish said. “If we can work with people as lifestyle medicine practitioners when they’re suffering, there’s an opportunity for transformation.”
Future
Of course, that can be easier said than done. Dr. Ornish relayed a patient’s typical reaction to a lifestyle program: “This is kind of weird stuff. Like, I get diet. But a plant-based diet, really? Meditation? Loving more? Really?”
He told the conference, “Part of our job as lifestyle medicine practitioners is to spend a little extra time with them. It doesn’t even take that much time. And to really help them understand what brings them a sense of hope and meaning and purpose.”
The results can be motivating. “Most people feel so much better so quickly,” Dr. Ornish said. “It reframes the reason for change from fear of dying to joy of living.”
Dr. Grega, for one, is optimistic for the future, citing survey results showing that 95% of medical students think that they›d be better counselors with lifestyle training. ‘They passionately want this type of thing,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Those who embrace lifestyle medicine are familiar with the slogan Dean Ornish, MD, likes to use: Eat well, move more, stress less, love more.
That last one, love, was the renowned physician and author’s focus at the recent American College of Lifestyle Medicine Conference in Denver. That’s because love – essentially the support, connectedness, and caring that patients feel when they join a lifestyle-change program – is “where healing occurs at the deepest level.”
Indeed, social connectedness is emerging as a vital pillar in the burgeoning field of lifestyle medicine, a specialty that uses lifestyle interventions to treat chronic conditions. About 300 lifestyle medicine programs are now integrated into residencies in medical schools across the country, up from a handful just 5 years ago, said Meagan Grega, MD, the conference chair.
“The energy and growth in American lifestyle medicine is unparalleled by anything else I see in the health care world right now,” said Dr. Grega, a family physician for 25 years in eastern Pennsylvania.
The field applies volumes of research, from the 1990s to today, demonstrating the healing effects of lifestyle changes. Dr. Ornish’s Preventive Medicine Research Institute has published research on small changes (like pomegranate juice helping blood flow in the heart) and huge ones: Coronary heart patients reversed the narrowing of arteries without lipid-lowering drugs after 1 year of lifestyle changes, including a vegetarian diet, aerobic exercise, stress management, and group support.
Ranking alongside bedrocks such as healthy diet, sleep, exercise, and stress management is positive social connection. That part, the “love more” part, often draws skepticism but is vital, said Dr. Ornish, who is sometimes referred to as the father of lifestyle medicine.
It’s “invariably the part that’s the most meaningful – that sense of connection to community that can come when you bring total strangers together,” Dr. Ornish said. “The ‘love more’ part, in many ways, is not only as important, but in some ways even more because everything really flows from that.”
Patients in a support group, who can “let down their emotional defenses and talk openly and authentically,” are much more likely to make and maintain healthy changes, Dr. Ornish said.
Love as medicine
Mounting evidence links loneliness and isolation with a range of health issues, from mood disorders such as depression to chronic conditions such as cardiovascular disease. What’s more, data suggest that loneliness and social isolation in the United States are on the rise, and the COVID pandemic made that more clear. In May 2023, Surgeon General Vivek Murthy, MD, called loneliness, isolation, and lack of connection in the United States a “public health crisis.”
“Good relationships keep us happier and healthier,” said Robert Waldinger, MD, a psychiatrist at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston.
Dr. Waldinger, who was not affiliated with the conference, is head of the Harvard Study of Adult Development, one of the longest studies of adult life. Beginning in 1938, the study has tracked 724 people plus more than 1,300 of their descendants and found that embracing community and close relationships helps us live longer and be happier.
In the study, the people who were most satisfied with their relationships at age 50 years were the healthiest at age 80 years. Knowing you have someone to rely on protects the brain: “Those people’s memories stay sharper longer,” Dr. Waldinger said.
He draws a distinction between connection and love. “Love is, I think, more of a feeling,” Dr. Waldinger noted. “Connection is a feeling, but it’s also an activity.”
One in five Americans say they’re lonely, he said, “and loneliness is a stressor.” People who are isolated don’t sleep as well, he added. Their health declines earlier in midlife, brain function slips sooner, and their lives are shorter.
“You don’t have anyone to complain to,” he said. If you do, “you can feel your body start to calm down.” Those without social connections may stay in a low-level “fight-or-flight mode.”
“What we think happens is that you have low levels of inflammation chronically, and those can gradually break down body systems.” Moreover, higher rates of cardiac reactivity, for instance, a racing heartbeat when upset, can lead to high blood pressure and lower immune function.
In his talk, Dr. Ornish said, “Anger is that one emotion that has consistently been shown to make heart disease worse.”
Helping people in those straits is gratifying, Dr. Ornish said. “If we can work with people as lifestyle medicine practitioners when they’re suffering, there’s an opportunity for transformation.”
Future
Of course, that can be easier said than done. Dr. Ornish relayed a patient’s typical reaction to a lifestyle program: “This is kind of weird stuff. Like, I get diet. But a plant-based diet, really? Meditation? Loving more? Really?”
He told the conference, “Part of our job as lifestyle medicine practitioners is to spend a little extra time with them. It doesn’t even take that much time. And to really help them understand what brings them a sense of hope and meaning and purpose.”
The results can be motivating. “Most people feel so much better so quickly,” Dr. Ornish said. “It reframes the reason for change from fear of dying to joy of living.”
Dr. Grega, for one, is optimistic for the future, citing survey results showing that 95% of medical students think that they›d be better counselors with lifestyle training. ‘They passionately want this type of thing,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study takes fine-grained look at MACE risk with glucocorticoids in RA
SAN DIEGO – Even when taken at low doses and over short periods, glucocorticoids (GCs) were linked to a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) over the long term in a Veterans Affairs population of older, mostly male patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a new retrospective cohort study has found.
The analysis of nearly 19,000 patients, presented by rheumatologist Beth Wallace, MD, MSc, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed that the level of risk for MACE rose with the dose, duration, and recency of GC use, in which risk increased significantly at prednisone-equivalent doses as low as 5 mg/day, durations as short as 30 days, and with last use as long as 1 year before MACE.
“Up to half of RA patients in the United States use long-term glucocorticoids despite previous work suggesting they increase MACE in a dose-dependent way,” said Dr. Wallace, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a rheumatologist at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare Center. “Our group previously presented work suggesting that less than 14 days of glucocorticoid use in a 6-month period is associated with a two-thirds increase in odds of MACE over the following 6 months, with 90 days of use associated with more than twofold increase.”
In recent years, researchers such as Dr. Wallace have focused attention on the risks of GCs in RA. The American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology emphasize avoiding long-term use of GCs in RA and keeping doses as small and over the shortest amount of time as possible.
When Dr. Wallace and colleagues looked at the clinical pattern of GC use for patients with RA during the past 2 years, those who took 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg daily doses for 30 days and had stopped at least a year before had risk for MACE that rose significantly by 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, compared with those who didn’t take GCs in the past 2 years.
While those increases were small, risk for MACE rose even more for those who took the same daily doses for 90 days, increasing 10%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. Researchers linked current ongoing use of GCs for the past 90 days to a 13%, 19%, and 27% higher risk for MACE at those respective doses.
The findings “add to the literature suggesting that there is some risk even with low-dose steroids,” said Michael George, MD, assistant professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who did not take part in the research but is familiar with the findings.
“We can see that even glucocorticoids taken several years ago may affect cardiovascular risk but that recent use has a bigger effect on risk,” Dr. George said in an interview. “This study also suggests that very low-dose use affects risk.”
For the new study, Dr. Wallace and colleagues examined a Veterans Affairs database and identified 18,882 patients with RA (mean age, 62.5 years; 84% male; 66% GC users) who met the criteria of being > 40 and < 90 years old. The subjects had an initial VA rheumatology visit during 2010-2018 and were excluded if they had a non-RA rheumatologic disorder, prior MACE, or heart failure. MACE was defined as MI, stroke/TIA, cardiac arrest, coronary revascularization, or death from CV cause.
A total of 16% of the cohort had the largest exposure to GCs, defined as use for 90 days or more; 23% had exposure of 14-89 days, and 14% had exposure of 1-13 days.
The median 5-year MACE risk at baseline was 5.3%, and 3,754 patients (19.9%) had high baseline MACE risk. Incident MACE occurred in 4.1% of patients, and the median time to MACE was 2.67 years (interquartile ratio, 1.26-4.45 years).
Covariates included factors such as age, race, sex, body mass index, smoking status, adjusted Elixhauser index, VA risk score for cardiovascular disease, cancer, hospitalization for infection, number of rheumatology clinic visits, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, opioids, methotrexate, biologics, and hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Wallace noted limitations including the possibility of residual confounding and the influence of background cardiovascular risk. The study didn’t examine the clinical value of taking GCs or compare that to the potential risk. Nor did it examine cost or the risks and benefits of alternative therapeutic options.
A study released earlier this year suggested that patients taking daily prednisolone doses under 5 mg do not have a higher risk of MACE. Previous studies had reached conflicting results.
“Glucocorticoids can provide major benefits to patients, but these benefits must be balanced with the potential risks,” Dr. George said. At low doses, these risks may be small, but they are present. In many cases, escalating DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] therapy may be safer than continuing glucocorticoids.”
He added that the risks of GCs may be especially high in older patients and in those who have cardiovascular risk factors: “Often biologics are avoided in these higher-risk patients. But in fact, in many cases biologics may be the safer choice.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Wallace reported no relevant financial relationships, and some of the other authors reported various ties with industry. Dr. George reported research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen and consulting fees from AbbVie.
SAN DIEGO – Even when taken at low doses and over short periods, glucocorticoids (GCs) were linked to a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) over the long term in a Veterans Affairs population of older, mostly male patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a new retrospective cohort study has found.
The analysis of nearly 19,000 patients, presented by rheumatologist Beth Wallace, MD, MSc, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed that the level of risk for MACE rose with the dose, duration, and recency of GC use, in which risk increased significantly at prednisone-equivalent doses as low as 5 mg/day, durations as short as 30 days, and with last use as long as 1 year before MACE.
“Up to half of RA patients in the United States use long-term glucocorticoids despite previous work suggesting they increase MACE in a dose-dependent way,” said Dr. Wallace, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a rheumatologist at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare Center. “Our group previously presented work suggesting that less than 14 days of glucocorticoid use in a 6-month period is associated with a two-thirds increase in odds of MACE over the following 6 months, with 90 days of use associated with more than twofold increase.”
In recent years, researchers such as Dr. Wallace have focused attention on the risks of GCs in RA. The American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology emphasize avoiding long-term use of GCs in RA and keeping doses as small and over the shortest amount of time as possible.
When Dr. Wallace and colleagues looked at the clinical pattern of GC use for patients with RA during the past 2 years, those who took 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg daily doses for 30 days and had stopped at least a year before had risk for MACE that rose significantly by 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, compared with those who didn’t take GCs in the past 2 years.
While those increases were small, risk for MACE rose even more for those who took the same daily doses for 90 days, increasing 10%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. Researchers linked current ongoing use of GCs for the past 90 days to a 13%, 19%, and 27% higher risk for MACE at those respective doses.
The findings “add to the literature suggesting that there is some risk even with low-dose steroids,” said Michael George, MD, assistant professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who did not take part in the research but is familiar with the findings.
“We can see that even glucocorticoids taken several years ago may affect cardiovascular risk but that recent use has a bigger effect on risk,” Dr. George said in an interview. “This study also suggests that very low-dose use affects risk.”
For the new study, Dr. Wallace and colleagues examined a Veterans Affairs database and identified 18,882 patients with RA (mean age, 62.5 years; 84% male; 66% GC users) who met the criteria of being > 40 and < 90 years old. The subjects had an initial VA rheumatology visit during 2010-2018 and were excluded if they had a non-RA rheumatologic disorder, prior MACE, or heart failure. MACE was defined as MI, stroke/TIA, cardiac arrest, coronary revascularization, or death from CV cause.
A total of 16% of the cohort had the largest exposure to GCs, defined as use for 90 days or more; 23% had exposure of 14-89 days, and 14% had exposure of 1-13 days.
The median 5-year MACE risk at baseline was 5.3%, and 3,754 patients (19.9%) had high baseline MACE risk. Incident MACE occurred in 4.1% of patients, and the median time to MACE was 2.67 years (interquartile ratio, 1.26-4.45 years).
Covariates included factors such as age, race, sex, body mass index, smoking status, adjusted Elixhauser index, VA risk score for cardiovascular disease, cancer, hospitalization for infection, number of rheumatology clinic visits, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, opioids, methotrexate, biologics, and hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Wallace noted limitations including the possibility of residual confounding and the influence of background cardiovascular risk. The study didn’t examine the clinical value of taking GCs or compare that to the potential risk. Nor did it examine cost or the risks and benefits of alternative therapeutic options.
A study released earlier this year suggested that patients taking daily prednisolone doses under 5 mg do not have a higher risk of MACE. Previous studies had reached conflicting results.
“Glucocorticoids can provide major benefits to patients, but these benefits must be balanced with the potential risks,” Dr. George said. At low doses, these risks may be small, but they are present. In many cases, escalating DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] therapy may be safer than continuing glucocorticoids.”
He added that the risks of GCs may be especially high in older patients and in those who have cardiovascular risk factors: “Often biologics are avoided in these higher-risk patients. But in fact, in many cases biologics may be the safer choice.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Wallace reported no relevant financial relationships, and some of the other authors reported various ties with industry. Dr. George reported research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen and consulting fees from AbbVie.
SAN DIEGO – Even when taken at low doses and over short periods, glucocorticoids (GCs) were linked to a higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) over the long term in a Veterans Affairs population of older, mostly male patients with rheumatoid arthritis, a new retrospective cohort study has found.
The analysis of nearly 19,000 patients, presented by rheumatologist Beth Wallace, MD, MSc, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology, showed that the level of risk for MACE rose with the dose, duration, and recency of GC use, in which risk increased significantly at prednisone-equivalent doses as low as 5 mg/day, durations as short as 30 days, and with last use as long as 1 year before MACE.
“Up to half of RA patients in the United States use long-term glucocorticoids despite previous work suggesting they increase MACE in a dose-dependent way,” said Dr. Wallace, assistant professor of medicine at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and a rheumatologist at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare Center. “Our group previously presented work suggesting that less than 14 days of glucocorticoid use in a 6-month period is associated with a two-thirds increase in odds of MACE over the following 6 months, with 90 days of use associated with more than twofold increase.”
In recent years, researchers such as Dr. Wallace have focused attention on the risks of GCs in RA. The American College of Rheumatology and the European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology emphasize avoiding long-term use of GCs in RA and keeping doses as small and over the shortest amount of time as possible.
When Dr. Wallace and colleagues looked at the clinical pattern of GC use for patients with RA during the past 2 years, those who took 5 mg, 7.5 mg, and 10 mg daily doses for 30 days and had stopped at least a year before had risk for MACE that rose significantly by 3%, 5%, and 7%, respectively, compared with those who didn’t take GCs in the past 2 years.
While those increases were small, risk for MACE rose even more for those who took the same daily doses for 90 days, increasing 10%, 15%, and 21%, respectively. Researchers linked current ongoing use of GCs for the past 90 days to a 13%, 19%, and 27% higher risk for MACE at those respective doses.
The findings “add to the literature suggesting that there is some risk even with low-dose steroids,” said Michael George, MD, assistant professor of rheumatology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, who did not take part in the research but is familiar with the findings.
“We can see that even glucocorticoids taken several years ago may affect cardiovascular risk but that recent use has a bigger effect on risk,” Dr. George said in an interview. “This study also suggests that very low-dose use affects risk.”
For the new study, Dr. Wallace and colleagues examined a Veterans Affairs database and identified 18,882 patients with RA (mean age, 62.5 years; 84% male; 66% GC users) who met the criteria of being > 40 and < 90 years old. The subjects had an initial VA rheumatology visit during 2010-2018 and were excluded if they had a non-RA rheumatologic disorder, prior MACE, or heart failure. MACE was defined as MI, stroke/TIA, cardiac arrest, coronary revascularization, or death from CV cause.
A total of 16% of the cohort had the largest exposure to GCs, defined as use for 90 days or more; 23% had exposure of 14-89 days, and 14% had exposure of 1-13 days.
The median 5-year MACE risk at baseline was 5.3%, and 3,754 patients (19.9%) had high baseline MACE risk. Incident MACE occurred in 4.1% of patients, and the median time to MACE was 2.67 years (interquartile ratio, 1.26-4.45 years).
Covariates included factors such as age, race, sex, body mass index, smoking status, adjusted Elixhauser index, VA risk score for cardiovascular disease, cancer, hospitalization for infection, number of rheumatology clinic visits, and use of lipid-lowering drugs, opioids, methotrexate, biologics, and hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Wallace noted limitations including the possibility of residual confounding and the influence of background cardiovascular risk. The study didn’t examine the clinical value of taking GCs or compare that to the potential risk. Nor did it examine cost or the risks and benefits of alternative therapeutic options.
A study released earlier this year suggested that patients taking daily prednisolone doses under 5 mg do not have a higher risk of MACE. Previous studies had reached conflicting results.
“Glucocorticoids can provide major benefits to patients, but these benefits must be balanced with the potential risks,” Dr. George said. At low doses, these risks may be small, but they are present. In many cases, escalating DMARD [disease-modifying antirheumatic drug] therapy may be safer than continuing glucocorticoids.”
He added that the risks of GCs may be especially high in older patients and in those who have cardiovascular risk factors: “Often biologics are avoided in these higher-risk patients. But in fact, in many cases biologics may be the safer choice.”
No study funding was reported. Dr. Wallace reported no relevant financial relationships, and some of the other authors reported various ties with industry. Dr. George reported research funding from GlaxoSmithKline and Janssen and consulting fees from AbbVie.
AT ACR 2023
Classification identifies four stages of heart attack
Relying on more than 50 years of data on acute MI with reperfusion therapy, the society has identified the following four stages of progressively worsening myocardial tissue injury:
- Aborted MI (no or minimal myocardial necrosis).
- MI with significant cardiomyocyte necrosis but without microvascular injury.
- Cardiomyocyte necrosis and microvascular dysfunction leading to microvascular obstruction (that is, “no reflow”).
- Cardiomyocyte and microvascular necrosis leading to reperfusion hemorrhage.
The classification is described in an expert consensus statement that was published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
The new classification will allow for better risk stratification and more appropriate treatment and provide refined endpoints for clinical trials and translational research, according to the authors.
Currently, all patients with acute MI receive the same treatment, even though they may have different levels of tissue injury severity, statement author Andreas Kumar, MD, chair of the writing group and associate professor of medicine at Northern Ontario School of Medicine University, Sudbury, said in an interview.
“In some cases, treatment for a mild stage 1 acute MI may be deadly for someone with stage 4 hemorrhagic MI,” said Dr. Kumar.
Technological advances
The classification is based on decades of data. “The initial data were obtained with pathology studies in the 1970s. When cardiac MRI came around, around the year 2000, suddenly there was a noninvasive imaging method where we could investigate patients in vivo,” said Dr. Kumar. “We learned a lot about tissue changes in acute MI. And especially in the last 2 to 5 years, we have learned a lot about hemorrhagic MI. So, this then gave us enough knowledge to come up with this new classification.”
The idea of classifying acute MI came to Dr. Kumar and senior author Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, executive director of the Krannert Cardiovascular Research Center at Indiana University, Indianapolis, when both were at the University of Toronto.
“This work has been years in the making,” Dr. Dharmakumar said in an interview. “We’ve been thinking about this for a long time, but we needed to get substantial layers of evidence to support the classification. We had a feeling about these stages for a long time, but that feeling needed to be substantiated.”
In 2022, Dr. Dharmakumar and Dr. Kumar observed that damage to the heart from MI was not only a result of ischemia caused by a blocked artery, but also a result of bleeding in the myocardium after the artery had been opened. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The author of an accompanying editorial lauded the investigators “for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.”
“Hemorrhagic MI is a very dangerous injury because hemorrhage itself causes a lot of problems,” said Dr. Kumar. “We reported that there is infarct expansion after reperfusion, so once you open up the vessel, the heart attack actually gets larger. We also showed that the remodeling of these hearts is worse. These patients take a second hit with hemorrhage occurring in the myocardium.”
Classification and staging
“The standard guideline therapy for somebody who comes into the hospital is to put in a stent, open the artery, have the patient stay in the hospital for 48-72 hours, and then be released home,” said Dr. Dharmukumar. “But here’s the problem. These two patients who are going back home have different levels of injury, yet they are taking the same medications. Even inside the hospital, we have heterogeneity in mortality risk. But we are not paying attention to one patient differently than the other, even though we should, because their injuries are very different.”
The CCS classification may provide endpoints and outcome measures beyond the commonly used clinical markers, which could lead to improved treatments to help patients recover from their cardiac events.
“We have this issue of rampant heart failure in acute MI survivors. We’ve gotten really good at saving patients from immediate death, but now we are just postponing some of the serious problems survivors are going to face, said Dr. Dharmukumar. “What are we doing for these patients who are really at risk? We’ve been treating every single patient the same way and we have not been paying attention to the very different stages of injury.”
In an accompanying editorial, Prakriti Gaba, MD, a clinical fellow in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, wrote: “There is no doubt that the classification system proposed by the investigators is important and timely, as acute MI continues to account for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide.”
Imaging and staging could be useful in guiding appropriate therapy, Bhatt said in an interview. “The authors’ hope, which I think is a very laudable one, is that more finely characterizing exactly what the extent of damage is and what the mechanism of damage is in a heart attack will make it possible to develop therapies that are particularly targeted to each of the stages,” he said.
“It is quite common to have the ability to do cardiac MRI at experienced cardiovascular centers, although this may not be true for smaller community hospitals,” Dr. Bhatt added. “But at least at larger hospitals, this will allow for much finer evaluation and assessment of exactly what is going on in that particular patient and how extensive the heart muscle damage is. Eventually, this will facilitate the development of therapies that are specifically targeted to treat each stage.”
Dr. Kumar is partly supported by a research grant from the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association. Dr. Dharmakumar was funded in part by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dharmakumar has an ownership interest in Cardio-Theranostics. Dr. Bhatt has served on advisory boards for Angiowave, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, High Enroll, Janssen, Level Ex, McKinsey, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, NirvaMed, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Stasys. He is a member of the board of directors of or holds stock in Angiowave, Boston VA Research Institute, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DRS.LINQ, High Enroll, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft. He has worked as a consultant for Broadview Ventures, and Hims. He has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology, Arnold and Porter law firm, Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Belvoir Publications, Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group, Cowen and Company, Duke Clinical Research Institute, HMP Global, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD, MJH Life Sciences, Oakstone CME, Piper Sandler, Population Health Research Institute, Slack Publications, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, WebMD, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Relying on more than 50 years of data on acute MI with reperfusion therapy, the society has identified the following four stages of progressively worsening myocardial tissue injury:
- Aborted MI (no or minimal myocardial necrosis).
- MI with significant cardiomyocyte necrosis but without microvascular injury.
- Cardiomyocyte necrosis and microvascular dysfunction leading to microvascular obstruction (that is, “no reflow”).
- Cardiomyocyte and microvascular necrosis leading to reperfusion hemorrhage.
The classification is described in an expert consensus statement that was published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
The new classification will allow for better risk stratification and more appropriate treatment and provide refined endpoints for clinical trials and translational research, according to the authors.
Currently, all patients with acute MI receive the same treatment, even though they may have different levels of tissue injury severity, statement author Andreas Kumar, MD, chair of the writing group and associate professor of medicine at Northern Ontario School of Medicine University, Sudbury, said in an interview.
“In some cases, treatment for a mild stage 1 acute MI may be deadly for someone with stage 4 hemorrhagic MI,” said Dr. Kumar.
Technological advances
The classification is based on decades of data. “The initial data were obtained with pathology studies in the 1970s. When cardiac MRI came around, around the year 2000, suddenly there was a noninvasive imaging method where we could investigate patients in vivo,” said Dr. Kumar. “We learned a lot about tissue changes in acute MI. And especially in the last 2 to 5 years, we have learned a lot about hemorrhagic MI. So, this then gave us enough knowledge to come up with this new classification.”
The idea of classifying acute MI came to Dr. Kumar and senior author Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, executive director of the Krannert Cardiovascular Research Center at Indiana University, Indianapolis, when both were at the University of Toronto.
“This work has been years in the making,” Dr. Dharmakumar said in an interview. “We’ve been thinking about this for a long time, but we needed to get substantial layers of evidence to support the classification. We had a feeling about these stages for a long time, but that feeling needed to be substantiated.”
In 2022, Dr. Dharmakumar and Dr. Kumar observed that damage to the heart from MI was not only a result of ischemia caused by a blocked artery, but also a result of bleeding in the myocardium after the artery had been opened. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The author of an accompanying editorial lauded the investigators “for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.”
“Hemorrhagic MI is a very dangerous injury because hemorrhage itself causes a lot of problems,” said Dr. Kumar. “We reported that there is infarct expansion after reperfusion, so once you open up the vessel, the heart attack actually gets larger. We also showed that the remodeling of these hearts is worse. These patients take a second hit with hemorrhage occurring in the myocardium.”
Classification and staging
“The standard guideline therapy for somebody who comes into the hospital is to put in a stent, open the artery, have the patient stay in the hospital for 48-72 hours, and then be released home,” said Dr. Dharmukumar. “But here’s the problem. These two patients who are going back home have different levels of injury, yet they are taking the same medications. Even inside the hospital, we have heterogeneity in mortality risk. But we are not paying attention to one patient differently than the other, even though we should, because their injuries are very different.”
The CCS classification may provide endpoints and outcome measures beyond the commonly used clinical markers, which could lead to improved treatments to help patients recover from their cardiac events.
“We have this issue of rampant heart failure in acute MI survivors. We’ve gotten really good at saving patients from immediate death, but now we are just postponing some of the serious problems survivors are going to face, said Dr. Dharmukumar. “What are we doing for these patients who are really at risk? We’ve been treating every single patient the same way and we have not been paying attention to the very different stages of injury.”
In an accompanying editorial, Prakriti Gaba, MD, a clinical fellow in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, wrote: “There is no doubt that the classification system proposed by the investigators is important and timely, as acute MI continues to account for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide.”
Imaging and staging could be useful in guiding appropriate therapy, Bhatt said in an interview. “The authors’ hope, which I think is a very laudable one, is that more finely characterizing exactly what the extent of damage is and what the mechanism of damage is in a heart attack will make it possible to develop therapies that are particularly targeted to each of the stages,” he said.
“It is quite common to have the ability to do cardiac MRI at experienced cardiovascular centers, although this may not be true for smaller community hospitals,” Dr. Bhatt added. “But at least at larger hospitals, this will allow for much finer evaluation and assessment of exactly what is going on in that particular patient and how extensive the heart muscle damage is. Eventually, this will facilitate the development of therapies that are specifically targeted to treat each stage.”
Dr. Kumar is partly supported by a research grant from the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association. Dr. Dharmakumar was funded in part by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dharmakumar has an ownership interest in Cardio-Theranostics. Dr. Bhatt has served on advisory boards for Angiowave, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, High Enroll, Janssen, Level Ex, McKinsey, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, NirvaMed, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Stasys. He is a member of the board of directors of or holds stock in Angiowave, Boston VA Research Institute, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DRS.LINQ, High Enroll, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft. He has worked as a consultant for Broadview Ventures, and Hims. He has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology, Arnold and Porter law firm, Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Belvoir Publications, Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group, Cowen and Company, Duke Clinical Research Institute, HMP Global, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD, MJH Life Sciences, Oakstone CME, Piper Sandler, Population Health Research Institute, Slack Publications, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, WebMD, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Relying on more than 50 years of data on acute MI with reperfusion therapy, the society has identified the following four stages of progressively worsening myocardial tissue injury:
- Aborted MI (no or minimal myocardial necrosis).
- MI with significant cardiomyocyte necrosis but without microvascular injury.
- Cardiomyocyte necrosis and microvascular dysfunction leading to microvascular obstruction (that is, “no reflow”).
- Cardiomyocyte and microvascular necrosis leading to reperfusion hemorrhage.
The classification is described in an expert consensus statement that was published in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology.
The new classification will allow for better risk stratification and more appropriate treatment and provide refined endpoints for clinical trials and translational research, according to the authors.
Currently, all patients with acute MI receive the same treatment, even though they may have different levels of tissue injury severity, statement author Andreas Kumar, MD, chair of the writing group and associate professor of medicine at Northern Ontario School of Medicine University, Sudbury, said in an interview.
“In some cases, treatment for a mild stage 1 acute MI may be deadly for someone with stage 4 hemorrhagic MI,” said Dr. Kumar.
Technological advances
The classification is based on decades of data. “The initial data were obtained with pathology studies in the 1970s. When cardiac MRI came around, around the year 2000, suddenly there was a noninvasive imaging method where we could investigate patients in vivo,” said Dr. Kumar. “We learned a lot about tissue changes in acute MI. And especially in the last 2 to 5 years, we have learned a lot about hemorrhagic MI. So, this then gave us enough knowledge to come up with this new classification.”
The idea of classifying acute MI came to Dr. Kumar and senior author Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, executive director of the Krannert Cardiovascular Research Center at Indiana University, Indianapolis, when both were at the University of Toronto.
“This work has been years in the making,” Dr. Dharmakumar said in an interview. “We’ve been thinking about this for a long time, but we needed to get substantial layers of evidence to support the classification. We had a feeling about these stages for a long time, but that feeling needed to be substantiated.”
In 2022, Dr. Dharmakumar and Dr. Kumar observed that damage to the heart from MI was not only a result of ischemia caused by a blocked artery, but also a result of bleeding in the myocardium after the artery had been opened. Their findings were published in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The author of an accompanying editorial lauded the investigators “for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.”
“Hemorrhagic MI is a very dangerous injury because hemorrhage itself causes a lot of problems,” said Dr. Kumar. “We reported that there is infarct expansion after reperfusion, so once you open up the vessel, the heart attack actually gets larger. We also showed that the remodeling of these hearts is worse. These patients take a second hit with hemorrhage occurring in the myocardium.”
Classification and staging
“The standard guideline therapy for somebody who comes into the hospital is to put in a stent, open the artery, have the patient stay in the hospital for 48-72 hours, and then be released home,” said Dr. Dharmukumar. “But here’s the problem. These two patients who are going back home have different levels of injury, yet they are taking the same medications. Even inside the hospital, we have heterogeneity in mortality risk. But we are not paying attention to one patient differently than the other, even though we should, because their injuries are very different.”
The CCS classification may provide endpoints and outcome measures beyond the commonly used clinical markers, which could lead to improved treatments to help patients recover from their cardiac events.
“We have this issue of rampant heart failure in acute MI survivors. We’ve gotten really good at saving patients from immediate death, but now we are just postponing some of the serious problems survivors are going to face, said Dr. Dharmukumar. “What are we doing for these patients who are really at risk? We’ve been treating every single patient the same way and we have not been paying attention to the very different stages of injury.”
In an accompanying editorial, Prakriti Gaba, MD, a clinical fellow in medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, and Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, MPH, director of the Mount Sinai Fuster Heart Hospital, New York, wrote: “There is no doubt that the classification system proposed by the investigators is important and timely, as acute MI continues to account for substantial morbidity and mortality worldwide.”
Imaging and staging could be useful in guiding appropriate therapy, Bhatt said in an interview. “The authors’ hope, which I think is a very laudable one, is that more finely characterizing exactly what the extent of damage is and what the mechanism of damage is in a heart attack will make it possible to develop therapies that are particularly targeted to each of the stages,” he said.
“It is quite common to have the ability to do cardiac MRI at experienced cardiovascular centers, although this may not be true for smaller community hospitals,” Dr. Bhatt added. “But at least at larger hospitals, this will allow for much finer evaluation and assessment of exactly what is going on in that particular patient and how extensive the heart muscle damage is. Eventually, this will facilitate the development of therapies that are specifically targeted to treat each stage.”
Dr. Kumar is partly supported by a research grant from the Northern Ontario Academic Medicine Association. Dr. Dharmakumar was funded in part by grants from the U.S. National Institutes of Health. Dr. Dharmakumar has an ownership interest in Cardio-Theranostics. Dr. Bhatt has served on advisory boards for Angiowave, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cardax, CellProthera, Cereno Scientific, Elsevier Practice Update Cardiology, High Enroll, Janssen, Level Ex, McKinsey, Medscape Cardiology, Merck, MyoKardia, NirvaMed, Novo Nordisk, PhaseBio, PLx Pharma, Regado Biosciences, and Stasys. He is a member of the board of directors of or holds stock in Angiowave, Boston VA Research Institute, Bristol-Myers Squibb, DRS.LINQ, High Enroll, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, and TobeSoft. He has worked as a consultant for Broadview Ventures, and Hims. He has received honoraria from the American College of Cardiology, Arnold and Porter law firm, Baim Institute for Clinical Research, Belvoir Publications, Canadian Medical and Surgical Knowledge Translation Research Group, Cowen and Company, Duke Clinical Research Institute, HMP Global, Journal of the American College of Cardiology, K2P, Level Ex, Medtelligence/ReachMD, MJH Life Sciences, Oakstone CME, Piper Sandler, Population Health Research Institute, Slack Publications, Society of Cardiovascular Patient Care, WebMD, and Wiley.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN JOURNAL OF CARDIOLOGY










