User login
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
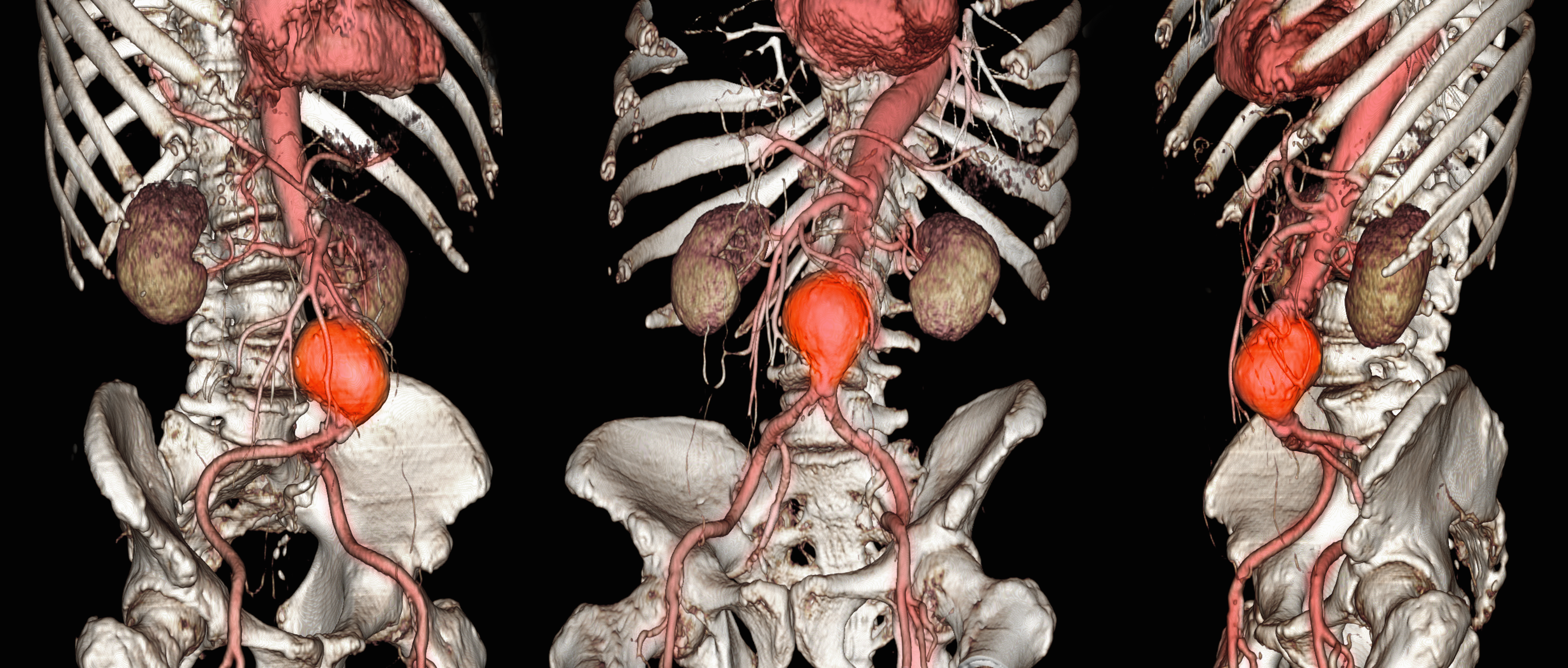
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a public health threat, with a global prevalence of 4.8% and a prevalence in males that increases with age, from 1.3% between ages 45 and 54 years to 12.5% between ages 75 and 84 years.1 AAA is often asymptomatic until it ruptures and can become life-threatening, with mortality rates near 90% in the event of rupture with survival rates of about 50% to 70% for individuals with rupture who require urgent surgical intervention.2,3 Males experience AAA at 4 times the rate of females.4
Previous research has found that the awareness of having an AAA causes anxiety that some have described as “living with a ticking time bomb.”5 Others reported worries and concerns about life’s fragility and mortality due to an AAA diagnosis.6 However, the psychological impact on the individuals’ quality of life (QoL) remains unclear, especially for individuals with a small AAA (< 5.5 cm).7 Factors such as age, male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, carotid artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia have been strongly associated with increased growth rate and the risk of small AAA ruptures.8,9
Most patients with a small AAA enter surveillance awaiting future repair and not only have the anxiety of living with an AAA despite the low risk of rupture, but also a worse QoL than those who have undergone repair.10,11 However, data are sparse regarding the effects on QoL of knowing they have an AAA, whether repaired or not. This study sought to examine the impact an AAA diagnosis had on male QoL at the initial investigation and after 12 months.
Methods
This prospective study was examined and approved by the Veterans Affairs Northern California Health Care System (NCHCS) Institutional Review Board. It was conducted at the Sacramento US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center from January 1, 2019, to February 28, 2022. Patients were identified through the vascular clinic. One hundred sixteen patients with AAA were eligible and agreed to participate. Of these, 91 (78%) completed the survey at baseline and 12 months later. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent was obtained from every patient before completing the survey. This study included only male patients due to their higher prevalence than female patients.4 Patients were also eligible if they were aged > 18 years and had a previously known AAA that was being followed with a recorded clinical imaging study in the NCHCS vascular clinic. Patients were excluded if they were unable to return for their 12-month follow-up investigation, were incapable of giving informed consent, were unable to complete the 12-item short form health survey version 2 (SF-12v2), had a documented history of psychiatric illness, or refused to participate. The SF-12v2, an abbreviated version of the 36-item short form health survey (SF-36), is a generic health-related quality-of-life survey that measures 8 domains of general health status: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and mental health (MH). A higher number on the QoL scale indicates better QoL. The GH, PF, RP, and BP scales yield a physical component score (PCS), and the VT, SF, RE, and MH scales generate a mental component score (MCS). Although SF-12v2 has not been validated for patients with AAA, it has been widely used and validated to measure health-related QoL in cohorts of healthy and chronically ill individuals.12,13
Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including means, SDs, frequency, percentages, 95% CIs, and correlations were calculated. The t test was used to analyze differences in mean scores. For continuous variables, such as SF-12v2 domains, PCS, and MCS, mean, SD, 95% CI, and range were determined. Comparisons were performed using X2 or t test. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical risk factors, including age, race, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and smoking status, were also recorded.
Results
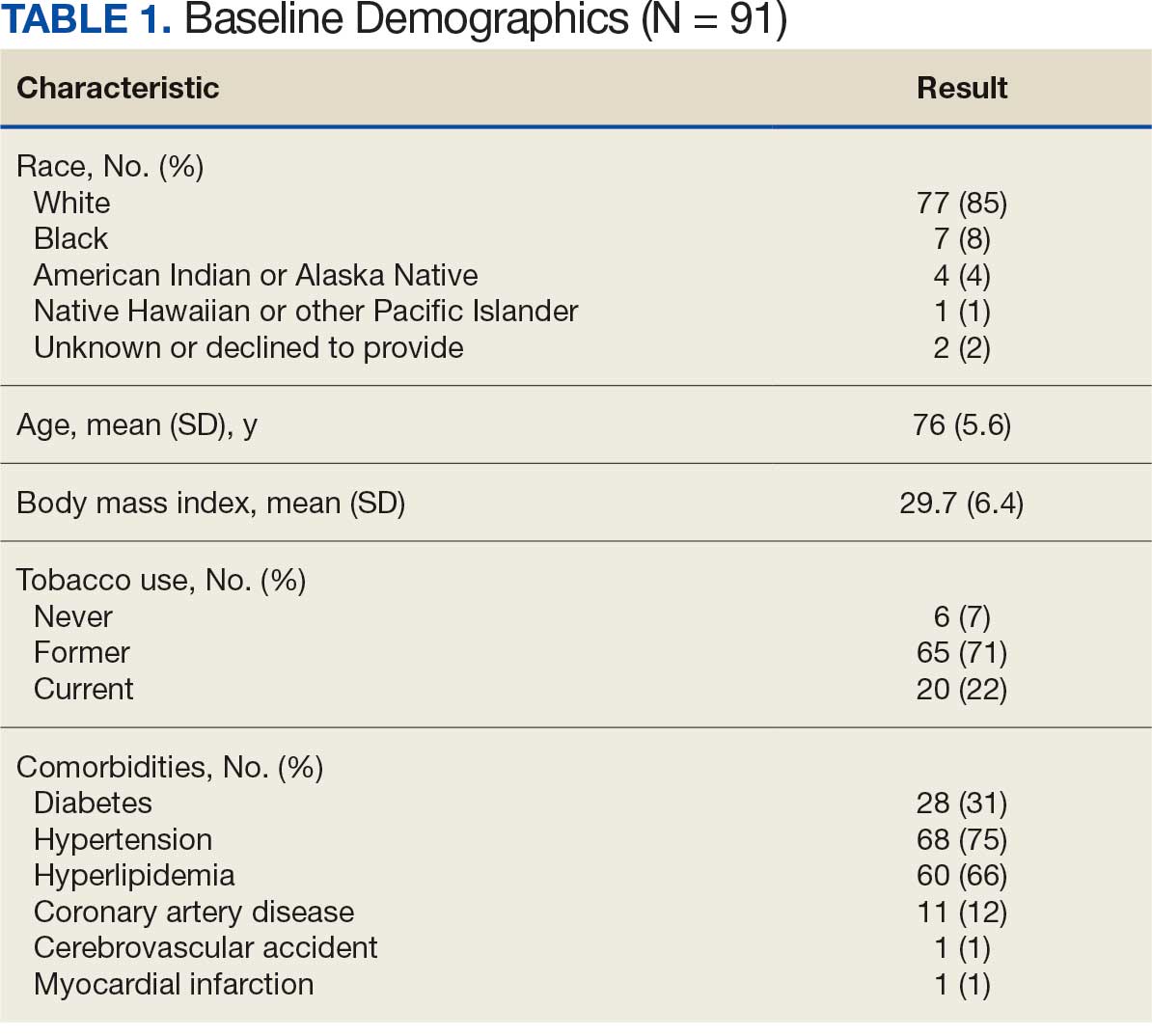
Between January 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, 91 patients were diagnosed with an AAA and completed the survey at the initial and 12-month investigations. Patients had a mean (SD) age of 76.0 (5.6) years (range, 64-93) and BMI of 29.7 (6.4). Comorbid diabetes was present in 31% of patients, hypertension in 75%, hyperlipidemia 66%, and coronary artery disease in 12% (Table 1). Most patients smoked tobacco: 71% indicated previous use and 22% were current users.
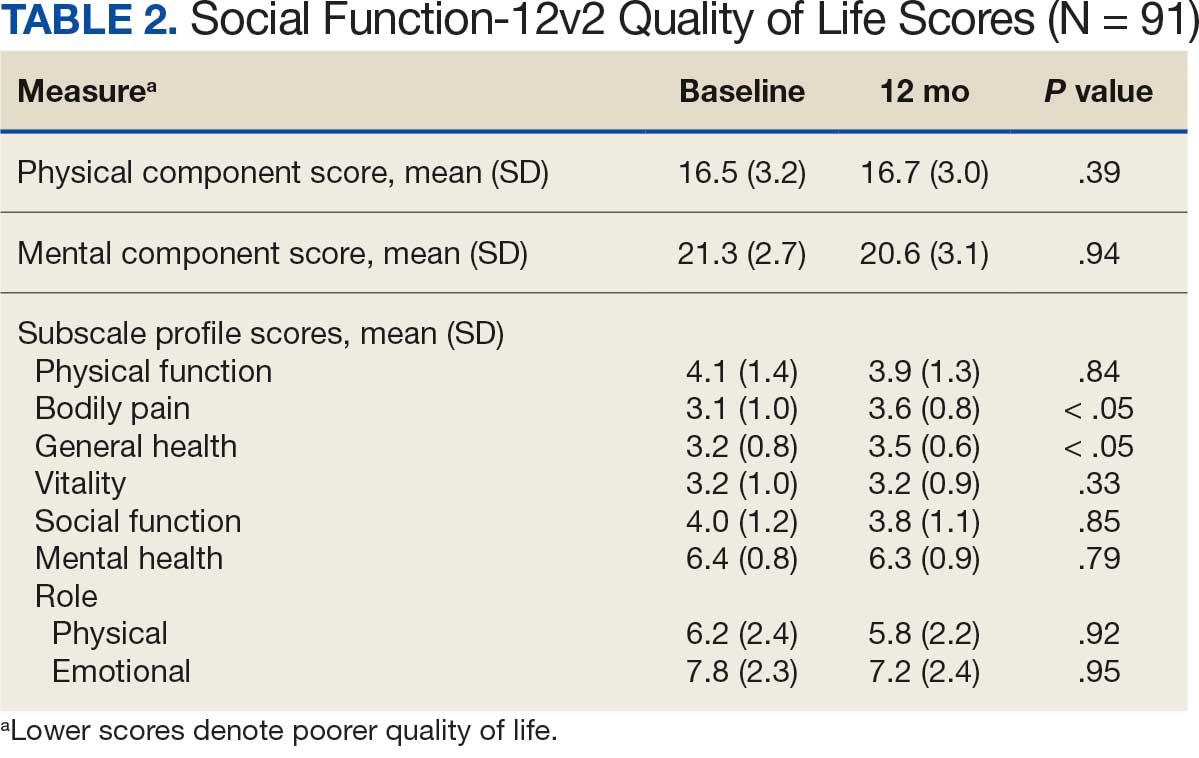
When comparing baseline vs 12-month follow-up, patients indicated a higher QoL in GH (3.2 vs 3.5, respectively; P < .05) and BP (3.1 vs 3.6, respectively; P < .05). No statistically significant difference was seen PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, MH, as well as PCS and MCS between baseline and follow-up with respect to QoL (P < .05). However, the 5 domains of SF-12v2: PF, RP, SF, RE, MH, and PCS had lower QoL scores at the 12-month follow-up when compared with baseline, but with no statistically significant difference between both investigations (Table 2).
Discussion
Previous studies have characterized the results of QoL measures as subjective because they are based on patient perceptions of their physical and psychological condition.14,15 However, SF-36 and SF-12v2 responses provide a multifaceted account that encompasses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of QoL. Despite being the most widely used generic instrument in many fields of medicine, SF-36 is time consuming for clinicians who may prefer simpler and more time-efficient instruments.16-18 The SF-12v2 not only imposes less burden on respondents but also generates accurate summary scores for patients physical and mental health.19
The replicability of SF-12v2 PCS and MCS scores has been demonstrated. In the United Kingdom, Jenkinson and Layte constructed SF-12v2 summary measures from a large scale dataset by sending the SF-36 and other questions on health and lifestyles to 9332 individuals and compared the results of the SF-36 and SF-12v2 across diverse patient groups (eg, Parkinson disease, congestive heart failure, sleep apnea, benign prostatic hypertrophy). Results from SF-36 PCS, SF-36 MCS, and PCS-12v2 (ρ, 0.94; P < .001) and SF-12v2 MCS (ρ, 0.96; P < .001) were found to be highly correlated, and also produced similar results, both in the community sample and across a variety of disease-specific groups.20
The aim of this longitudinal observational study was to measure the QoL of males with an AAA ≥ 3.0 cm at baseline and 12 months later. The mean age of participants was 76 years, which aligns with previous research that found the prevalence of AAAs increased with age.1 Study participants had a mean BMI of 29.7, which also supports previous research that indicated that obesity is independently associated with an AAA.21 Patients with an AAA and a history of smoking (former or current), hypertension, or hyperlipidemia had lower mean scores for 3 of 8 SF-12v2 domains at the 12-month follow-up.
These findings support previous research that indicated smoking is not only a very strong risk factor for the presence of an AAA but also associated with increased rates of expansion and the risk of rupture in patients with an AAA.22 Bath et al found that patients with an AAA compared to patients without an AAA were older (age 72.6 vs 69.8 years; P < .001), had a higher BMI (28.1 vs 27.0; P < .001), were more likely to be a current smoker (15.1% vs 5.2%; P < .001), and were more likely to have diabetes (18.8% vs 10.0%; P < .001), ischemic heart disease (12.2% vs 4.4%; P < .001), high cholesterol (53.2% vs 30.8%; P <. 001), previous stroke (6.1% vs 2.9%; P < .001), and a previous myocardial infarction (21.1% vs 5.8%; P < .001).23 Lesjak et al found that men with AAA reported significantly lower scores in the domains of social functioning, pain, and general health 6 months after ultrasound compared with men without AAA.24
Previous research indicates that patients with an AAA have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and comorbidities that may impact their perceived QoL. In a study assessing cardiovascular risk in 2323 patients with a small AAA, Bath et al found a high prevalence of coronary artery disease (44.9%), myocardial infarction (26.8%), heart failure (4.4%) and cerebrovascular accident (14.0%) which may have contributed to the decreased level of self-perceived QoL in these patients.25
This aligned with a study by Golledge et al, who found that participants diagnosed with an AAA and peripheral artery disease not only had significantly poorer QoL scores in 5 SF-36 domains (PF, RP, GH, VT, and PCS)when compared with participants diagnosed with an AAA alone. They also had significantly poorer QoL scores in 7 domains of the SF-36 (PF, RP, GH, VT, SF, RE, and PCS) when compared with controls without an AAA.26
Our analysis found that males with an AAA had a rise in SF-12v2 QoL scores from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the GH and BP domains. There was no statistically significant difference in QoL in the other 6 domains (PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, and MH) between the initial and 12-month investigations. Bath et al also found that men with an AAA had a transient reduction in mental QoL during the first year after the initial screening but returned to baseline.23
Strengths and Limitations
This study is notable for its sample of patients who previously had a diagnosed AAA that were followed with a recorded clinical imaging study and the use of a validated QoL measure (SF-12v2) that provided virtually identical summary scores (PCS and MCS) as the SF-36.27 However, this study was limited by the brevity of the SF-12v2 instrument which made it difficult to extract sufficient reliable information for the 8 domains.28 Subjective perception of patients is another limitation inherent to any QoL study. QoL scores were not available before the initial investigation. Measuring QoL at baseline and 12 months later does not capture the potential fluctuations and changes in QoL that the patient may experience some months later. Another limitation arises from the fact that the AAA patient population in the study included patients under surveillance and patients who had undergone repair.
Fourteen patients (15%) had received AAA repair: 10 had endovascular reconstruction and 4 had open surgical repair. Including patients with a previous AAA repair may have influenced reported QoL levels. Suckow et al performed a 2-phase study on 1008 patients, 351 (35%) were under surveillance and 657 (65%) had undergone repair. In that study, patients under AAA surveillance had worse emotional impact scores compared with patients with repair (22 vs 13; P < .001).11 Additionally, the size of the abdominal aorta at the time of survey was not addressed in the study, which could constitute explanatory variables.
Conclusions
This study found higher QoL at 12-month follow-up compared to baseline in both the GH and BP domains of the SF-12v2 health survey for male veterans with an AAA. Periodic QoL assessments for patients with an AAA may be helpful in tracking QoL course, minimizing their physical and psychological concerns, and improving overall care and support. However, further research is necessary to assess the QoL of patients with an AAA who are under surveillance compared with those who had an aneurysm repair to accurately measure the impact of an AAA on QoL.
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Profeta VF, et al. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in population- based studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:2805. doi:10.3390/ijerph15122805
- Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
- Kent KC. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
- Harthun NL. Current issues in the treatment of women with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Gend Med. 2008;5:36-43.
- Aoki H. Taking control of the time bomb in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ J. 2016;80:314-315. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-15-1350
- Damhus CS, Siersma V, Hansson A, Bang CW, Brodersen J. Psychosocial consequences of screeningdetected abdominal aortic aneurisms: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2021;39:459-465. doi:10.1080/02813432.2021.2004713
- Ericsson A, Kumlien C, Ching S, Carlson E, Molassiotis A. Impact on quality of life of men with screening-detected abdominal aortic aneurysms attending regular follow ups: a narrative literature review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:589-596. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.012
- Galyfos G, Voulalas G, Stamatatos I, et al. Small abdominal aortic aneurysms: should we wait? Vasc Dis Manag. 2015;12:E152-E159.
- Kristensen KL, Dahl M, Rasmussen LM, et al. Glycated hemoglobin is associated with the growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37:730-736. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308874
- Xiao-Yan L, Yu-Kui M, Li-Hui L. Risk factors for preoperative anxiety and depression in patients scheduled for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Chine Med J. 2018;131:1951-1957. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.238154
- Suckow BD, Schanzer AS, Hoel AW, et al. A novel quality of life instrument for patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:809-815. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.01.018
- Flatz A, Casillas A, Stringhini S, et al. Association between education and quality of diabetes care in Switzerland. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:87-92. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S77139
- Christensen AV, Bjorner JB, Ekholm O, et al. Increased risk of mortality and readmission associated with lower SF-12 scores in cardiac patients: Results from the national DenHeart study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:330-338. doi:10.1177/1474515119885480
- Hamming JF, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94:923-924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
- Urbach DR. Measuring quality of life after surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:161-165. doi:10.1177/ 155335060501200216
- Gandek B, Sinclair SJ, Kosinski M, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the SF-36® health survey in medicare managed care. Health Care Financ Rev. 2004;25:5.
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short form health survey (SF-36). Med Care. 1992;30:473-483. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
- Takayoshi K, Mototsugu T, Tomohiro T, et al. Health-related quality of life prospectively evaluated by the 8-item short form after endovascular repair versus open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:960- 968. doi:10.1007/s00380-017-0956-9
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Penn A, et al. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke. 1999;30:1213-1217. doi:10.1161/01.str.30.6.1213
- Jenkinson C, Layte R. The development and testing of the UK SF-12. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1997;2:14-18. doi:10.1177/135581969700200105
- Golledge J, Clancy P, Jamrozik K, et al. Obesity, adipokines, and abdominal aortic aneurysm: Health in Men study. Circulation. 2007;116:2275-2279. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717926
- Norman PE, Curci JA. Understanding the effects of tobacco smoke on the pathogenesis of aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1473-1477. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300158
- Bath MF, Sidloff D, Saratzis A, et al. Impact of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening on quality of life. BJS. 2018;105:203-208. doi:10.1002/bjs.10721
- Lesjak M, Boreland F, Lyle D, Sidford J, Flecknoe-Brown S, Fletcher J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: does it affect men’s quality of life? Aust J Prim Health. 2012;18:284-288. doi:10.1071/PY11131
- Bath MF, Gokani VJ, Sidloff DA, et al. Systematic review of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death in patients with a small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102:866-872. doi:10.1002/bjs.9837
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Rowbotham SE, et al. Health-related quality of life amongst people diagnosed with abdominal aortic aneurysm and peripheral artery disease and the effect of fenofibrate. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14583. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71454-4
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med. 1997;19:179- 186. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024606
- White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, et al. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1757-1767. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a public health threat, with a global prevalence of 4.8% and a prevalence in males that increases with age, from 1.3% between ages 45 and 54 years to 12.5% between ages 75 and 84 years.1 AAA is often asymptomatic until it ruptures and can become life-threatening, with mortality rates near 90% in the event of rupture with survival rates of about 50% to 70% for individuals with rupture who require urgent surgical intervention.2,3 Males experience AAA at 4 times the rate of females.4
Previous research has found that the awareness of having an AAA causes anxiety that some have described as “living with a ticking time bomb.”5 Others reported worries and concerns about life’s fragility and mortality due to an AAA diagnosis.6 However, the psychological impact on the individuals’ quality of life (QoL) remains unclear, especially for individuals with a small AAA (< 5.5 cm).7 Factors such as age, male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, carotid artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia have been strongly associated with increased growth rate and the risk of small AAA ruptures.8,9
Most patients with a small AAA enter surveillance awaiting future repair and not only have the anxiety of living with an AAA despite the low risk of rupture, but also a worse QoL than those who have undergone repair.10,11 However, data are sparse regarding the effects on QoL of knowing they have an AAA, whether repaired or not. This study sought to examine the impact an AAA diagnosis had on male QoL at the initial investigation and after 12 months.
Methods
This prospective study was examined and approved by the Veterans Affairs Northern California Health Care System (NCHCS) Institutional Review Board. It was conducted at the Sacramento US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center from January 1, 2019, to February 28, 2022. Patients were identified through the vascular clinic. One hundred sixteen patients with AAA were eligible and agreed to participate. Of these, 91 (78%) completed the survey at baseline and 12 months later. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent was obtained from every patient before completing the survey. This study included only male patients due to their higher prevalence than female patients.4 Patients were also eligible if they were aged > 18 years and had a previously known AAA that was being followed with a recorded clinical imaging study in the NCHCS vascular clinic. Patients were excluded if they were unable to return for their 12-month follow-up investigation, were incapable of giving informed consent, were unable to complete the 12-item short form health survey version 2 (SF-12v2), had a documented history of psychiatric illness, or refused to participate. The SF-12v2, an abbreviated version of the 36-item short form health survey (SF-36), is a generic health-related quality-of-life survey that measures 8 domains of general health status: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and mental health (MH). A higher number on the QoL scale indicates better QoL. The GH, PF, RP, and BP scales yield a physical component score (PCS), and the VT, SF, RE, and MH scales generate a mental component score (MCS). Although SF-12v2 has not been validated for patients with AAA, it has been widely used and validated to measure health-related QoL in cohorts of healthy and chronically ill individuals.12,13
Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including means, SDs, frequency, percentages, 95% CIs, and correlations were calculated. The t test was used to analyze differences in mean scores. For continuous variables, such as SF-12v2 domains, PCS, and MCS, mean, SD, 95% CI, and range were determined. Comparisons were performed using X2 or t test. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical risk factors, including age, race, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and smoking status, were also recorded.
Results
Between January 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, 91 patients were diagnosed with an AAA and completed the survey at the initial and 12-month investigations. Patients had a mean (SD) age of 76.0 (5.6) years (range, 64-93) and BMI of 29.7 (6.4). Comorbid diabetes was present in 31% of patients, hypertension in 75%, hyperlipidemia 66%, and coronary artery disease in 12% (Table 1). Most patients smoked tobacco: 71% indicated previous use and 22% were current users.

When comparing baseline vs 12-month follow-up, patients indicated a higher QoL in GH (3.2 vs 3.5, respectively; P < .05) and BP (3.1 vs 3.6, respectively; P < .05). No statistically significant difference was seen PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, MH, as well as PCS and MCS between baseline and follow-up with respect to QoL (P < .05). However, the 5 domains of SF-12v2: PF, RP, SF, RE, MH, and PCS had lower QoL scores at the 12-month follow-up when compared with baseline, but with no statistically significant difference between both investigations (Table 2).

Discussion
Previous studies have characterized the results of QoL measures as subjective because they are based on patient perceptions of their physical and psychological condition.14,15 However, SF-36 and SF-12v2 responses provide a multifaceted account that encompasses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of QoL. Despite being the most widely used generic instrument in many fields of medicine, SF-36 is time consuming for clinicians who may prefer simpler and more time-efficient instruments.16-18 The SF-12v2 not only imposes less burden on respondents but also generates accurate summary scores for patients physical and mental health.19
The replicability of SF-12v2 PCS and MCS scores has been demonstrated. In the United Kingdom, Jenkinson and Layte constructed SF-12v2 summary measures from a large scale dataset by sending the SF-36 and other questions on health and lifestyles to 9332 individuals and compared the results of the SF-36 and SF-12v2 across diverse patient groups (eg, Parkinson disease, congestive heart failure, sleep apnea, benign prostatic hypertrophy). Results from SF-36 PCS, SF-36 MCS, and PCS-12v2 (ρ, 0.94; P < .001) and SF-12v2 MCS (ρ, 0.96; P < .001) were found to be highly correlated, and also produced similar results, both in the community sample and across a variety of disease-specific groups.20
The aim of this longitudinal observational study was to measure the QoL of males with an AAA ≥ 3.0 cm at baseline and 12 months later. The mean age of participants was 76 years, which aligns with previous research that found the prevalence of AAAs increased with age.1 Study participants had a mean BMI of 29.7, which also supports previous research that indicated that obesity is independently associated with an AAA.21 Patients with an AAA and a history of smoking (former or current), hypertension, or hyperlipidemia had lower mean scores for 3 of 8 SF-12v2 domains at the 12-month follow-up.
These findings support previous research that indicated smoking is not only a very strong risk factor for the presence of an AAA but also associated with increased rates of expansion and the risk of rupture in patients with an AAA.22 Bath et al found that patients with an AAA compared to patients without an AAA were older (age 72.6 vs 69.8 years; P < .001), had a higher BMI (28.1 vs 27.0; P < .001), were more likely to be a current smoker (15.1% vs 5.2%; P < .001), and were more likely to have diabetes (18.8% vs 10.0%; P < .001), ischemic heart disease (12.2% vs 4.4%; P < .001), high cholesterol (53.2% vs 30.8%; P <. 001), previous stroke (6.1% vs 2.9%; P < .001), and a previous myocardial infarction (21.1% vs 5.8%; P < .001).23 Lesjak et al found that men with AAA reported significantly lower scores in the domains of social functioning, pain, and general health 6 months after ultrasound compared with men without AAA.24
Previous research indicates that patients with an AAA have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and comorbidities that may impact their perceived QoL. In a study assessing cardiovascular risk in 2323 patients with a small AAA, Bath et al found a high prevalence of coronary artery disease (44.9%), myocardial infarction (26.8%), heart failure (4.4%) and cerebrovascular accident (14.0%) which may have contributed to the decreased level of self-perceived QoL in these patients.25
This aligned with a study by Golledge et al, who found that participants diagnosed with an AAA and peripheral artery disease not only had significantly poorer QoL scores in 5 SF-36 domains (PF, RP, GH, VT, and PCS)when compared with participants diagnosed with an AAA alone. They also had significantly poorer QoL scores in 7 domains of the SF-36 (PF, RP, GH, VT, SF, RE, and PCS) when compared with controls without an AAA.26
Our analysis found that males with an AAA had a rise in SF-12v2 QoL scores from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the GH and BP domains. There was no statistically significant difference in QoL in the other 6 domains (PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, and MH) between the initial and 12-month investigations. Bath et al also found that men with an AAA had a transient reduction in mental QoL during the first year after the initial screening but returned to baseline.23
Strengths and Limitations
This study is notable for its sample of patients who previously had a diagnosed AAA that were followed with a recorded clinical imaging study and the use of a validated QoL measure (SF-12v2) that provided virtually identical summary scores (PCS and MCS) as the SF-36.27 However, this study was limited by the brevity of the SF-12v2 instrument which made it difficult to extract sufficient reliable information for the 8 domains.28 Subjective perception of patients is another limitation inherent to any QoL study. QoL scores were not available before the initial investigation. Measuring QoL at baseline and 12 months later does not capture the potential fluctuations and changes in QoL that the patient may experience some months later. Another limitation arises from the fact that the AAA patient population in the study included patients under surveillance and patients who had undergone repair.
Fourteen patients (15%) had received AAA repair: 10 had endovascular reconstruction and 4 had open surgical repair. Including patients with a previous AAA repair may have influenced reported QoL levels. Suckow et al performed a 2-phase study on 1008 patients, 351 (35%) were under surveillance and 657 (65%) had undergone repair. In that study, patients under AAA surveillance had worse emotional impact scores compared with patients with repair (22 vs 13; P < .001).11 Additionally, the size of the abdominal aorta at the time of survey was not addressed in the study, which could constitute explanatory variables.
Conclusions
This study found higher QoL at 12-month follow-up compared to baseline in both the GH and BP domains of the SF-12v2 health survey for male veterans with an AAA. Periodic QoL assessments for patients with an AAA may be helpful in tracking QoL course, minimizing their physical and psychological concerns, and improving overall care and support. However, further research is necessary to assess the QoL of patients with an AAA who are under surveillance compared with those who had an aneurysm repair to accurately measure the impact of an AAA on QoL.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) is a public health threat, with a global prevalence of 4.8% and a prevalence in males that increases with age, from 1.3% between ages 45 and 54 years to 12.5% between ages 75 and 84 years.1 AAA is often asymptomatic until it ruptures and can become life-threatening, with mortality rates near 90% in the event of rupture with survival rates of about 50% to 70% for individuals with rupture who require urgent surgical intervention.2,3 Males experience AAA at 4 times the rate of females.4
Previous research has found that the awareness of having an AAA causes anxiety that some have described as “living with a ticking time bomb.”5 Others reported worries and concerns about life’s fragility and mortality due to an AAA diagnosis.6 However, the psychological impact on the individuals’ quality of life (QoL) remains unclear, especially for individuals with a small AAA (< 5.5 cm).7 Factors such as age, male sex, smoking, family history, hypertension, carotid artery disease, and hypercholesterolemia have been strongly associated with increased growth rate and the risk of small AAA ruptures.8,9
Most patients with a small AAA enter surveillance awaiting future repair and not only have the anxiety of living with an AAA despite the low risk of rupture, but also a worse QoL than those who have undergone repair.10,11 However, data are sparse regarding the effects on QoL of knowing they have an AAA, whether repaired or not. This study sought to examine the impact an AAA diagnosis had on male QoL at the initial investigation and after 12 months.
Methods
This prospective study was examined and approved by the Veterans Affairs Northern California Health Care System (NCHCS) Institutional Review Board. It was conducted at the Sacramento US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Medical Center from January 1, 2019, to February 28, 2022. Patients were identified through the vascular clinic. One hundred sixteen patients with AAA were eligible and agreed to participate. Of these, 91 (78%) completed the survey at baseline and 12 months later. Participation was voluntary; written informed consent was obtained from every patient before completing the survey. This study included only male patients due to their higher prevalence than female patients.4 Patients were also eligible if they were aged > 18 years and had a previously known AAA that was being followed with a recorded clinical imaging study in the NCHCS vascular clinic. Patients were excluded if they were unable to return for their 12-month follow-up investigation, were incapable of giving informed consent, were unable to complete the 12-item short form health survey version 2 (SF-12v2), had a documented history of psychiatric illness, or refused to participate. The SF-12v2, an abbreviated version of the 36-item short form health survey (SF-36), is a generic health-related quality-of-life survey that measures 8 domains of general health status: general health (GH), physical functioning (PF), role limitations due to physical problems (RP), bodily pain (BP), vitality (VT), social functioning (SF), role emotional (RE), and mental health (MH). A higher number on the QoL scale indicates better QoL. The GH, PF, RP, and BP scales yield a physical component score (PCS), and the VT, SF, RE, and MH scales generate a mental component score (MCS). Although SF-12v2 has not been validated for patients with AAA, it has been widely used and validated to measure health-related QoL in cohorts of healthy and chronically ill individuals.12,13
Analysis
Descriptive statistics, including means, SDs, frequency, percentages, 95% CIs, and correlations were calculated. The t test was used to analyze differences in mean scores. For continuous variables, such as SF-12v2 domains, PCS, and MCS, mean, SD, 95% CI, and range were determined. Comparisons were performed using X2 or t test. P < .05 was considered statistically significant. Clinical risk factors, including age, race, body mass index (BMI), diabetes, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, coronary artery disease, cerebrovascular accident, myocardial infarction, and smoking status, were also recorded.
Results
Between January 1, 2019, and February 28, 2022, 91 patients were diagnosed with an AAA and completed the survey at the initial and 12-month investigations. Patients had a mean (SD) age of 76.0 (5.6) years (range, 64-93) and BMI of 29.7 (6.4). Comorbid diabetes was present in 31% of patients, hypertension in 75%, hyperlipidemia 66%, and coronary artery disease in 12% (Table 1). Most patients smoked tobacco: 71% indicated previous use and 22% were current users.

When comparing baseline vs 12-month follow-up, patients indicated a higher QoL in GH (3.2 vs 3.5, respectively; P < .05) and BP (3.1 vs 3.6, respectively; P < .05). No statistically significant difference was seen PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, MH, as well as PCS and MCS between baseline and follow-up with respect to QoL (P < .05). However, the 5 domains of SF-12v2: PF, RP, SF, RE, MH, and PCS had lower QoL scores at the 12-month follow-up when compared with baseline, but with no statistically significant difference between both investigations (Table 2).

Discussion
Previous studies have characterized the results of QoL measures as subjective because they are based on patient perceptions of their physical and psychological condition.14,15 However, SF-36 and SF-12v2 responses provide a multifaceted account that encompasses the physical, psychological, and social aspects of QoL. Despite being the most widely used generic instrument in many fields of medicine, SF-36 is time consuming for clinicians who may prefer simpler and more time-efficient instruments.16-18 The SF-12v2 not only imposes less burden on respondents but also generates accurate summary scores for patients physical and mental health.19
The replicability of SF-12v2 PCS and MCS scores has been demonstrated. In the United Kingdom, Jenkinson and Layte constructed SF-12v2 summary measures from a large scale dataset by sending the SF-36 and other questions on health and lifestyles to 9332 individuals and compared the results of the SF-36 and SF-12v2 across diverse patient groups (eg, Parkinson disease, congestive heart failure, sleep apnea, benign prostatic hypertrophy). Results from SF-36 PCS, SF-36 MCS, and PCS-12v2 (ρ, 0.94; P < .001) and SF-12v2 MCS (ρ, 0.96; P < .001) were found to be highly correlated, and also produced similar results, both in the community sample and across a variety of disease-specific groups.20
The aim of this longitudinal observational study was to measure the QoL of males with an AAA ≥ 3.0 cm at baseline and 12 months later. The mean age of participants was 76 years, which aligns with previous research that found the prevalence of AAAs increased with age.1 Study participants had a mean BMI of 29.7, which also supports previous research that indicated that obesity is independently associated with an AAA.21 Patients with an AAA and a history of smoking (former or current), hypertension, or hyperlipidemia had lower mean scores for 3 of 8 SF-12v2 domains at the 12-month follow-up.
These findings support previous research that indicated smoking is not only a very strong risk factor for the presence of an AAA but also associated with increased rates of expansion and the risk of rupture in patients with an AAA.22 Bath et al found that patients with an AAA compared to patients without an AAA were older (age 72.6 vs 69.8 years; P < .001), had a higher BMI (28.1 vs 27.0; P < .001), were more likely to be a current smoker (15.1% vs 5.2%; P < .001), and were more likely to have diabetes (18.8% vs 10.0%; P < .001), ischemic heart disease (12.2% vs 4.4%; P < .001), high cholesterol (53.2% vs 30.8%; P <. 001), previous stroke (6.1% vs 2.9%; P < .001), and a previous myocardial infarction (21.1% vs 5.8%; P < .001).23 Lesjak et al found that men with AAA reported significantly lower scores in the domains of social functioning, pain, and general health 6 months after ultrasound compared with men without AAA.24
Previous research indicates that patients with an AAA have a higher risk of cardiovascular diseases and comorbidities that may impact their perceived QoL. In a study assessing cardiovascular risk in 2323 patients with a small AAA, Bath et al found a high prevalence of coronary artery disease (44.9%), myocardial infarction (26.8%), heart failure (4.4%) and cerebrovascular accident (14.0%) which may have contributed to the decreased level of self-perceived QoL in these patients.25
This aligned with a study by Golledge et al, who found that participants diagnosed with an AAA and peripheral artery disease not only had significantly poorer QoL scores in 5 SF-36 domains (PF, RP, GH, VT, and PCS)when compared with participants diagnosed with an AAA alone. They also had significantly poorer QoL scores in 7 domains of the SF-36 (PF, RP, GH, VT, SF, RE, and PCS) when compared with controls without an AAA.26
Our analysis found that males with an AAA had a rise in SF-12v2 QoL scores from baseline to 12-month follow-up in the GH and BP domains. There was no statistically significant difference in QoL in the other 6 domains (PF, RP, VT, SF, RE, and MH) between the initial and 12-month investigations. Bath et al also found that men with an AAA had a transient reduction in mental QoL during the first year after the initial screening but returned to baseline.23
Strengths and Limitations
This study is notable for its sample of patients who previously had a diagnosed AAA that were followed with a recorded clinical imaging study and the use of a validated QoL measure (SF-12v2) that provided virtually identical summary scores (PCS and MCS) as the SF-36.27 However, this study was limited by the brevity of the SF-12v2 instrument which made it difficult to extract sufficient reliable information for the 8 domains.28 Subjective perception of patients is another limitation inherent to any QoL study. QoL scores were not available before the initial investigation. Measuring QoL at baseline and 12 months later does not capture the potential fluctuations and changes in QoL that the patient may experience some months later. Another limitation arises from the fact that the AAA patient population in the study included patients under surveillance and patients who had undergone repair.
Fourteen patients (15%) had received AAA repair: 10 had endovascular reconstruction and 4 had open surgical repair. Including patients with a previous AAA repair may have influenced reported QoL levels. Suckow et al performed a 2-phase study on 1008 patients, 351 (35%) were under surveillance and 657 (65%) had undergone repair. In that study, patients under AAA surveillance had worse emotional impact scores compared with patients with repair (22 vs 13; P < .001).11 Additionally, the size of the abdominal aorta at the time of survey was not addressed in the study, which could constitute explanatory variables.
Conclusions
This study found higher QoL at 12-month follow-up compared to baseline in both the GH and BP domains of the SF-12v2 health survey for male veterans with an AAA. Periodic QoL assessments for patients with an AAA may be helpful in tracking QoL course, minimizing their physical and psychological concerns, and improving overall care and support. However, further research is necessary to assess the QoL of patients with an AAA who are under surveillance compared with those who had an aneurysm repair to accurately measure the impact of an AAA on QoL.
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Profeta VF, et al. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in population- based studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:2805. doi:10.3390/ijerph15122805
- Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
- Kent KC. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
- Harthun NL. Current issues in the treatment of women with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Gend Med. 2008;5:36-43.
- Aoki H. Taking control of the time bomb in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ J. 2016;80:314-315. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-15-1350
- Damhus CS, Siersma V, Hansson A, Bang CW, Brodersen J. Psychosocial consequences of screeningdetected abdominal aortic aneurisms: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2021;39:459-465. doi:10.1080/02813432.2021.2004713
- Ericsson A, Kumlien C, Ching S, Carlson E, Molassiotis A. Impact on quality of life of men with screening-detected abdominal aortic aneurysms attending regular follow ups: a narrative literature review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:589-596. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.012
- Galyfos G, Voulalas G, Stamatatos I, et al. Small abdominal aortic aneurysms: should we wait? Vasc Dis Manag. 2015;12:E152-E159.
- Kristensen KL, Dahl M, Rasmussen LM, et al. Glycated hemoglobin is associated with the growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37:730-736. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308874
- Xiao-Yan L, Yu-Kui M, Li-Hui L. Risk factors for preoperative anxiety and depression in patients scheduled for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Chine Med J. 2018;131:1951-1957. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.238154
- Suckow BD, Schanzer AS, Hoel AW, et al. A novel quality of life instrument for patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:809-815. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.01.018
- Flatz A, Casillas A, Stringhini S, et al. Association between education and quality of diabetes care in Switzerland. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:87-92. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S77139
- Christensen AV, Bjorner JB, Ekholm O, et al. Increased risk of mortality and readmission associated with lower SF-12 scores in cardiac patients: Results from the national DenHeart study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:330-338. doi:10.1177/1474515119885480
- Hamming JF, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94:923-924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
- Urbach DR. Measuring quality of life after surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:161-165. doi:10.1177/ 155335060501200216
- Gandek B, Sinclair SJ, Kosinski M, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the SF-36® health survey in medicare managed care. Health Care Financ Rev. 2004;25:5.
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short form health survey (SF-36). Med Care. 1992;30:473-483. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
- Takayoshi K, Mototsugu T, Tomohiro T, et al. Health-related quality of life prospectively evaluated by the 8-item short form after endovascular repair versus open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:960- 968. doi:10.1007/s00380-017-0956-9
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Penn A, et al. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke. 1999;30:1213-1217. doi:10.1161/01.str.30.6.1213
- Jenkinson C, Layte R. The development and testing of the UK SF-12. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1997;2:14-18. doi:10.1177/135581969700200105
- Golledge J, Clancy P, Jamrozik K, et al. Obesity, adipokines, and abdominal aortic aneurysm: Health in Men study. Circulation. 2007;116:2275-2279. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717926
- Norman PE, Curci JA. Understanding the effects of tobacco smoke on the pathogenesis of aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1473-1477. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300158
- Bath MF, Sidloff D, Saratzis A, et al. Impact of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening on quality of life. BJS. 2018;105:203-208. doi:10.1002/bjs.10721
- Lesjak M, Boreland F, Lyle D, Sidford J, Flecknoe-Brown S, Fletcher J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: does it affect men’s quality of life? Aust J Prim Health. 2012;18:284-288. doi:10.1071/PY11131
- Bath MF, Gokani VJ, Sidloff DA, et al. Systematic review of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death in patients with a small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102:866-872. doi:10.1002/bjs.9837
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Rowbotham SE, et al. Health-related quality of life amongst people diagnosed with abdominal aortic aneurysm and peripheral artery disease and the effect of fenofibrate. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14583. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71454-4
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med. 1997;19:179- 186. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024606
- White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, et al. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1757-1767. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2
- Altobelli E, Rapacchietta L, Profeta VF, et al. Risk factors for abdominal aortic aneurysm in population- based studies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15:2805. doi:10.3390/ijerph15122805
- Chaikof EL, Dalman RL, Eskandari MK, et al. The society for vascular surgery practice guidelines on the care of patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. J Vasc Surg. 2018;67:2-77.e2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2017.10.044
- Kent KC. Abdominal aortic aneurysms. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:2101-2108. doi:10.1056/NEJMcp1401430
- Harthun NL. Current issues in the treatment of women with abdominal aortic aneurysm. Gend Med. 2008;5:36-43.
- Aoki H. Taking control of the time bomb in abdominal aortic aneurysm. Circ J. 2016;80:314-315. doi:10.1253/circj.CJ-15-1350
- Damhus CS, Siersma V, Hansson A, Bang CW, Brodersen J. Psychosocial consequences of screeningdetected abdominal aortic aneurisms: a cross-sectional study. Scand J Prim Health Care. 2021;39:459-465. doi:10.1080/02813432.2021.2004713
- Ericsson A, Kumlien C, Ching S, Carlson E, Molassiotis A. Impact on quality of life of men with screening-detected abdominal aortic aneurysms attending regular follow ups: a narrative literature review. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:589-596. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2018.10.012
- Galyfos G, Voulalas G, Stamatatos I, et al. Small abdominal aortic aneurysms: should we wait? Vasc Dis Manag. 2015;12:E152-E159.
- Kristensen KL, Dahl M, Rasmussen LM, et al. Glycated hemoglobin is associated with the growth rate of abdominal aortic aneurysms. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2017;37:730-736. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308874
- Xiao-Yan L, Yu-Kui M, Li-Hui L. Risk factors for preoperative anxiety and depression in patients scheduled for abdominal aortic aneurysm repair. Chine Med J. 2018;131:1951-1957. doi:10.4103/0366-6999.238154
- Suckow BD, Schanzer AS, Hoel AW, et al. A novel quality of life instrument for patients with an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2019;57:809-815. doi:10.1016/j.ejvs.2019.01.018
- Flatz A, Casillas A, Stringhini S, et al. Association between education and quality of diabetes care in Switzerland. Int J Gen Med. 2015;8:87-92. doi:10.2147/IJGM.S77139
- Christensen AV, Bjorner JB, Ekholm O, et al. Increased risk of mortality and readmission associated with lower SF-12 scores in cardiac patients: Results from the national DenHeart study. Eur J Cardiovasc Nurs. 2020;19:330-338. doi:10.1177/1474515119885480
- Hamming JF, De Vries J. Measuring quality of life. Br J Surg. 2007;94:923-924. doi:10.1002/bjs.5948
- Urbach DR. Measuring quality of life after surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:161-165. doi:10.1177/ 155335060501200216
- Gandek B, Sinclair SJ, Kosinski M, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the SF-36® health survey in medicare managed care. Health Care Financ Rev. 2004;25:5.
- Ware JE, Sherbourne CD. The MOS 36-item short form health survey (SF-36). Med Care. 1992;30:473-483. doi:10.1097/00005650-199206000-00002
- Takayoshi K, Mototsugu T, Tomohiro T, et al. Health-related quality of life prospectively evaluated by the 8-item short form after endovascular repair versus open surgery for abdominal aortic aneurysms. Heart Vessels. 2017;32:960- 968. doi:10.1007/s00380-017-0956-9
- Pickard AS, Johnson JA, Penn A, et al. Replicability of SF-36 summary scores by the SF-12 in stroke patients. Stroke. 1999;30:1213-1217. doi:10.1161/01.str.30.6.1213
- Jenkinson C, Layte R. The development and testing of the UK SF-12. J Health Serv Res Policy. 1997;2:14-18. doi:10.1177/135581969700200105
- Golledge J, Clancy P, Jamrozik K, et al. Obesity, adipokines, and abdominal aortic aneurysm: Health in Men study. Circulation. 2007;116:2275-2279. doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.717926
- Norman PE, Curci JA. Understanding the effects of tobacco smoke on the pathogenesis of aortic aneurysm. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2013;33:1473-1477. doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.112.300158
- Bath MF, Sidloff D, Saratzis A, et al. Impact of abdominal aortic aneurysm screening on quality of life. BJS. 2018;105:203-208. doi:10.1002/bjs.10721
- Lesjak M, Boreland F, Lyle D, Sidford J, Flecknoe-Brown S, Fletcher J. Screening for abdominal aortic aneurysm: does it affect men’s quality of life? Aust J Prim Health. 2012;18:284-288. doi:10.1071/PY11131
- Bath MF, Gokani VJ, Sidloff DA, et al. Systematic review of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular death in patients with a small abdominal aortic aneurysm. Br J Surg. 2015;102:866-872. doi:10.1002/bjs.9837
- Golledge J, Pinchbeck J, Rowbotham SE, et al. Health-related quality of life amongst people diagnosed with abdominal aortic aneurysm and peripheral artery disease and the effect of fenofibrate. Sci Rep. 2020;10:14583. doi:10.1038/s41598-020-71454-4
- Jenkinson C, Layte R, Jenkinson D. A shorter form health survey: can the SF-12 replicate results from the SF-36 in longitudinal studies? J Public Health Med. 1997;19:179- 186. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.pubmed.a024606
- White MK, Maher SM, Rizio AA, et al. A meta-analytic review of measurement equivalence study findings of the SF-36® and SF-12® Health Surveys across electronic modes compared to paper administration. Qual Life Res. 2018;27:1757-1767. doi:10.1007/s11136-018-1851-2
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Quality of Life for Males With Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Task force advocates selective screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms
Men aged 65-75 years with a history of smoking should undergo one-time screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but clinicians can selectively screen men in this age group who don’t smoke, according to updated recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force published in JAMA.
The task force issued a B recommendation for screening men aged 65-75 years with a smoking history and a C recommendation for selectively screening male never smokers in this age group in an update to the previous recommendations issued in 2014.
The task force also recommended against screening for AAA in women with no history of smoking (D recommendation) and cited insufficient evidence to make recommendations about AAA screening for women with a history of smoking or a family history of AAA (I statement).
The current prevalence of AAA in the United States is unclear because of the low rate of screening, but data from countries including the United Kingdom, Sweden, Denmark, and New Zealand have shown a decline in AAA among screened men aged 65 years and older, according to the USPSTF report.
Risk factors for AAA include smoking, male gender, older age, and having a first-degree relative with AAA, the task force noted.
In an evidence review accompanying the recommendations, Janelle M. Guirguis-Blake, MD, of the University of Washington, Tacoma, and colleagues analyzed data from 33 studies. They found a significant reduction in AAA-related mortality over 12-15 years’ follow-up among men aged 65 years and older who underwent AAA screening, compared with unscreened controls (odds ratio, 0.65). In addition, the risk of ruptures related to AAA was significantly lower over 12-15 years among men who underwent screening, compared with unscreened controls (OR, 0.62). However, no significant difference was noted in all-cause mortality over 12-15 years between screened and unscreened groups (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.98-1.00).
Data from four studies of early surgery to treat small aneurysms showed no significant difference in AAA-related mortality or all-cause mortality.
“Screening for AAA entails a simple, noninvasive, and focused ultrasonography examination that costs roughly $50. The only potential harms are the psychologic burden of knowing of the presence of an aneurysm and the risk of elective surgery,” wrote Marc Schermerhorn, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, in an accompanying editorial published in JAMA Surgery (doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.5234).
“The latter can be calculated for each patient, weighed against the risk of rupture, and together with the estimated life expectancy, should be factored into the decision to screen and the decision to operate. We as a country can do better to detect and treat this disease cost effectively for all appropriate patients including women and elderly individuals,” he said.
Dr. Schermerhorn noted that overall the recommendations are reasonable, but he expressed concern for three populations excluded from the guidelines that warrant additional consideration: nonsmokers with equivalent risk factors, patients older than 75 years, and women. “In the meantime, we should work to ensure that patients determined appropriate by the USPSTF are actually screened,” he said.
The USPSTF is supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Schermerhorn disclosed relationships with Abbott, Cook Medical, Endologix, Medtronic, and Philips.
SOURCE: Guirguis-Blake JM et al. JAMA. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17021.
Men aged 65-75 years with a history of smoking should undergo one-time screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but clinicians can selectively screen men in this age group who don’t smoke, according to updated recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force published in JAMA.
The task force issued a B recommendation for screening men aged 65-75 years with a smoking history and a C recommendation for selectively screening male never smokers in this age group in an update to the previous recommendations issued in 2014.
The task force also recommended against screening for AAA in women with no history of smoking (D recommendation) and cited insufficient evidence to make recommendations about AAA screening for women with a history of smoking or a family history of AAA (I statement).
The current prevalence of AAA in the United States is unclear because of the low rate of screening, but data from countries including the United Kingdom, Sweden, Denmark, and New Zealand have shown a decline in AAA among screened men aged 65 years and older, according to the USPSTF report.
Risk factors for AAA include smoking, male gender, older age, and having a first-degree relative with AAA, the task force noted.
In an evidence review accompanying the recommendations, Janelle M. Guirguis-Blake, MD, of the University of Washington, Tacoma, and colleagues analyzed data from 33 studies. They found a significant reduction in AAA-related mortality over 12-15 years’ follow-up among men aged 65 years and older who underwent AAA screening, compared with unscreened controls (odds ratio, 0.65). In addition, the risk of ruptures related to AAA was significantly lower over 12-15 years among men who underwent screening, compared with unscreened controls (OR, 0.62). However, no significant difference was noted in all-cause mortality over 12-15 years between screened and unscreened groups (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.98-1.00).
Data from four studies of early surgery to treat small aneurysms showed no significant difference in AAA-related mortality or all-cause mortality.
“Screening for AAA entails a simple, noninvasive, and focused ultrasonography examination that costs roughly $50. The only potential harms are the psychologic burden of knowing of the presence of an aneurysm and the risk of elective surgery,” wrote Marc Schermerhorn, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, in an accompanying editorial published in JAMA Surgery (doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.5234).
“The latter can be calculated for each patient, weighed against the risk of rupture, and together with the estimated life expectancy, should be factored into the decision to screen and the decision to operate. We as a country can do better to detect and treat this disease cost effectively for all appropriate patients including women and elderly individuals,” he said.
Dr. Schermerhorn noted that overall the recommendations are reasonable, but he expressed concern for three populations excluded from the guidelines that warrant additional consideration: nonsmokers with equivalent risk factors, patients older than 75 years, and women. “In the meantime, we should work to ensure that patients determined appropriate by the USPSTF are actually screened,” he said.
The USPSTF is supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Schermerhorn disclosed relationships with Abbott, Cook Medical, Endologix, Medtronic, and Philips.
SOURCE: Guirguis-Blake JM et al. JAMA. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17021.
Men aged 65-75 years with a history of smoking should undergo one-time screening for abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but clinicians can selectively screen men in this age group who don’t smoke, according to updated recommendations from the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force published in JAMA.
The task force issued a B recommendation for screening men aged 65-75 years with a smoking history and a C recommendation for selectively screening male never smokers in this age group in an update to the previous recommendations issued in 2014.
The task force also recommended against screening for AAA in women with no history of smoking (D recommendation) and cited insufficient evidence to make recommendations about AAA screening for women with a history of smoking or a family history of AAA (I statement).
The current prevalence of AAA in the United States is unclear because of the low rate of screening, but data from countries including the United Kingdom, Sweden, Denmark, and New Zealand have shown a decline in AAA among screened men aged 65 years and older, according to the USPSTF report.
Risk factors for AAA include smoking, male gender, older age, and having a first-degree relative with AAA, the task force noted.
In an evidence review accompanying the recommendations, Janelle M. Guirguis-Blake, MD, of the University of Washington, Tacoma, and colleagues analyzed data from 33 studies. They found a significant reduction in AAA-related mortality over 12-15 years’ follow-up among men aged 65 years and older who underwent AAA screening, compared with unscreened controls (odds ratio, 0.65). In addition, the risk of ruptures related to AAA was significantly lower over 12-15 years among men who underwent screening, compared with unscreened controls (OR, 0.62). However, no significant difference was noted in all-cause mortality over 12-15 years between screened and unscreened groups (relative risk, 0.99; 95% confidence interval, 0.98-1.00).
Data from four studies of early surgery to treat small aneurysms showed no significant difference in AAA-related mortality or all-cause mortality.
“Screening for AAA entails a simple, noninvasive, and focused ultrasonography examination that costs roughly $50. The only potential harms are the psychologic burden of knowing of the presence of an aneurysm and the risk of elective surgery,” wrote Marc Schermerhorn, MD, of Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, in an accompanying editorial published in JAMA Surgery (doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2019.5234).
“The latter can be calculated for each patient, weighed against the risk of rupture, and together with the estimated life expectancy, should be factored into the decision to screen and the decision to operate. We as a country can do better to detect and treat this disease cost effectively for all appropriate patients including women and elderly individuals,” he said.
Dr. Schermerhorn noted that overall the recommendations are reasonable, but he expressed concern for three populations excluded from the guidelines that warrant additional consideration: nonsmokers with equivalent risk factors, patients older than 75 years, and women. “In the meantime, we should work to ensure that patients determined appropriate by the USPSTF are actually screened,” he said.
The USPSTF is supported by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Schermerhorn disclosed relationships with Abbott, Cook Medical, Endologix, Medtronic, and Philips.
SOURCE: Guirguis-Blake JM et al. JAMA. 2019. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17021.
FROM JAMA
What repair is best for juxtarenal aneurysm?
CHICAGO – Outcomes with fenestrated endografts and endograft anchors to repair abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) in the region of the renal artery have improved as the techniques have gained popularity in recent years, but open repair may still achieve better overall results, vascular surgeons on opposite sides of the controversy contended during a debate at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
Fenestrated endovascular aortic repair (FEVAR) “is as safe as open surgery to treat complex aneurysm,” said Carlos Bechara, MD, of Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago. “EndoAnchors [Medtronic] do provide an excellent off-the-shelf solution to treat short, hostile necks with promising short-term results.”
Arguing for open repair was Paul DiMusto, MD, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison. “Open repair has an equal perioperative mortality to FEVAR,” Dr. DiMusto said, adding that the open approach also has a higher long-term branch patency rate, lower secondary-intervention rate, a lower incidence of long-term renal failure, and higher long-term survival. “So putting that all together, open repair is best,” he said.
They staked out their positions by citing a host of published trials.
“The presence of a short neck can create a challenging clinical scenario for an endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,” Dr. Bechara said. However, he noted he was discussing complex aneurysm in which the aortic clamp is placed above the renal arteries, differentiating it from infrarenal AAA in which the clamp is below the renal arteries with no renal ischemia time. He noted a 2011 study that determined a short neck was a predictor of Type 1A endoleak after AAA repair, but that compliance with best practices at the time was poor; more than 44% of EVARs did not follow the manufacturer’s instruction (Circulation. 2011;123:2848-55).
But FEVAR was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012, with an indication for an infrarenal neck length of 4-14 mm, Dr. Bechara noted. Since then, several studies have reported excellent outcomes with the technique. An early small study of 67 patients reported a 100% technical success rate with one patient having a Type 1 endoleak at 3 years (J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1420-8).
This year, a larger study evaluated 6,825 patients in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program who had FEVAR, open AAA repair or standard infrarenal endovascular repair during 2012-2016. “Actually, the fenestrated approach had fewer complications than open repair and the outcomes were comparable to standard EVAR,” Dr. Bechara noted. The trial reported FEVAR had lower rates of perioperative mortality (1.8% vs. 8.8%; P = .001), postoperative renal dysfunction (1.4% vs. 7.7%; P = .002), and overall complications (11% vs. 33%; P less than.001) than did open repair (J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:1670-78).
In regard to the use of endograft anchors for treatment of endoleaks, migrating grafts, and high-risk seal zones, Dr. Bechara noted they are a good “off-the-shelf” choice for complex AAA repair. He cited current results of a cohort of 70 patients with short-neck AAA (J Vasc Surg. 2019;70:732-40). “This study showed a procedural success rate at 97% and a technical success rate at 88.6%,” he said. “They had no stent migration, no increase in sac size or AAA rupture or open conversion.”
He also pointed to just-published results from a randomized trial of 881 patients with up to 14 years of follow-up that found comparable rates of death/secondary procedures, as well as durability, between patients who had endovascular and open repairs (77.7% and 75.5%, respectively, N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126-35). Also, he noted that hospital volume is an important predictor of success with open repair, with high-volume centers reporting lower mortality (3.9%) than low-volume centers (9%; Ann Surg. 2018 Nov 29. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002873). “So not many centers are doing high-volume open aortic surgery,” he said.
To make his case that open surgery for juxtarenal AAAs is superior, Dr. DiMusto cited a number of recent studies, including a three-center trial of 200 patients who had open and FEVAR procedures (J Endovasc Ther. 2019;26:105-12). “There was no difference in perioperative mortality [2.2% for FEVAR, 1.9% in open repair], ” Dr. DiMusto said “There was a higher freedom from reintervention in the open group [96% vs. 78%], and there was higher long-term vessel patency in the open group” (97.5% having target patency for open vs. 93.3% for FEVAR).
He also pointed to a meta-analysis of 2,326 patients that found similar outcomes for mortality and postoperative renal insufficiency between FEVAR and open repair, around 4.1%, but showed significantly higher rates of renal failure in FEVAR, at 19.7% versus 7.7% (J Vasc Surg. 2015;61:242-55). This study also reported significantly more secondary interventions with FEVAR, 12.7% vs. 4.9%, Dr. DiMusto said.
Another study of 3,253 complex AAA repairs, including 887 FEVAR and 2,125 open procedures, showed that FEVAR had a technical success rate of 97%, with no appreciable difference in perioperative mortality between the two procedures (Ann Surg. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003094).
However, Dr. DiMusto said, adjusted 3-year mortality in this study was higher with FEVAR, and further analysis yielded outcomes that favored open repair. “After excluding perioperative deaths, differences remained, with 9% mortality for FEVAR and 5% for open repair [P = .02],” he said. “This corresponded to a 66% higher risk for overall mortality following FEVAR.”
What’s more, Dr. DiMusto said, draft guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom advise against offering complex EVAR to people with an unruptured AAA under two scenarios: if open surgery is an option; and even if they’re unable to have surgery because of anesthetic or medical issues. The final guidelines have yet to be released.
Dr. Bechara disclosed financial relationships with Gore Medical and Cook Medical and equity interest in MOKITA Medical. Dr. DiMusto has no relevant financial disclosures.
CHICAGO – Outcomes with fenestrated endografts and endograft anchors to repair abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) in the region of the renal artery have improved as the techniques have gained popularity in recent years, but open repair may still achieve better overall results, vascular surgeons on opposite sides of the controversy contended during a debate at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
Fenestrated endovascular aortic repair (FEVAR) “is as safe as open surgery to treat complex aneurysm,” said Carlos Bechara, MD, of Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago. “EndoAnchors [Medtronic] do provide an excellent off-the-shelf solution to treat short, hostile necks with promising short-term results.”
Arguing for open repair was Paul DiMusto, MD, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison. “Open repair has an equal perioperative mortality to FEVAR,” Dr. DiMusto said, adding that the open approach also has a higher long-term branch patency rate, lower secondary-intervention rate, a lower incidence of long-term renal failure, and higher long-term survival. “So putting that all together, open repair is best,” he said.
They staked out their positions by citing a host of published trials.
“The presence of a short neck can create a challenging clinical scenario for an endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,” Dr. Bechara said. However, he noted he was discussing complex aneurysm in which the aortic clamp is placed above the renal arteries, differentiating it from infrarenal AAA in which the clamp is below the renal arteries with no renal ischemia time. He noted a 2011 study that determined a short neck was a predictor of Type 1A endoleak after AAA repair, but that compliance with best practices at the time was poor; more than 44% of EVARs did not follow the manufacturer’s instruction (Circulation. 2011;123:2848-55).
But FEVAR was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012, with an indication for an infrarenal neck length of 4-14 mm, Dr. Bechara noted. Since then, several studies have reported excellent outcomes with the technique. An early small study of 67 patients reported a 100% technical success rate with one patient having a Type 1 endoleak at 3 years (J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1420-8).
This year, a larger study evaluated 6,825 patients in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program who had FEVAR, open AAA repair or standard infrarenal endovascular repair during 2012-2016. “Actually, the fenestrated approach had fewer complications than open repair and the outcomes were comparable to standard EVAR,” Dr. Bechara noted. The trial reported FEVAR had lower rates of perioperative mortality (1.8% vs. 8.8%; P = .001), postoperative renal dysfunction (1.4% vs. 7.7%; P = .002), and overall complications (11% vs. 33%; P less than.001) than did open repair (J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:1670-78).
In regard to the use of endograft anchors for treatment of endoleaks, migrating grafts, and high-risk seal zones, Dr. Bechara noted they are a good “off-the-shelf” choice for complex AAA repair. He cited current results of a cohort of 70 patients with short-neck AAA (J Vasc Surg. 2019;70:732-40). “This study showed a procedural success rate at 97% and a technical success rate at 88.6%,” he said. “They had no stent migration, no increase in sac size or AAA rupture or open conversion.”
He also pointed to just-published results from a randomized trial of 881 patients with up to 14 years of follow-up that found comparable rates of death/secondary procedures, as well as durability, between patients who had endovascular and open repairs (77.7% and 75.5%, respectively, N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126-35). Also, he noted that hospital volume is an important predictor of success with open repair, with high-volume centers reporting lower mortality (3.9%) than low-volume centers (9%; Ann Surg. 2018 Nov 29. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002873). “So not many centers are doing high-volume open aortic surgery,” he said.
To make his case that open surgery for juxtarenal AAAs is superior, Dr. DiMusto cited a number of recent studies, including a three-center trial of 200 patients who had open and FEVAR procedures (J Endovasc Ther. 2019;26:105-12). “There was no difference in perioperative mortality [2.2% for FEVAR, 1.9% in open repair], ” Dr. DiMusto said “There was a higher freedom from reintervention in the open group [96% vs. 78%], and there was higher long-term vessel patency in the open group” (97.5% having target patency for open vs. 93.3% for FEVAR).
He also pointed to a meta-analysis of 2,326 patients that found similar outcomes for mortality and postoperative renal insufficiency between FEVAR and open repair, around 4.1%, but showed significantly higher rates of renal failure in FEVAR, at 19.7% versus 7.7% (J Vasc Surg. 2015;61:242-55). This study also reported significantly more secondary interventions with FEVAR, 12.7% vs. 4.9%, Dr. DiMusto said.
Another study of 3,253 complex AAA repairs, including 887 FEVAR and 2,125 open procedures, showed that FEVAR had a technical success rate of 97%, with no appreciable difference in perioperative mortality between the two procedures (Ann Surg. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003094).
However, Dr. DiMusto said, adjusted 3-year mortality in this study was higher with FEVAR, and further analysis yielded outcomes that favored open repair. “After excluding perioperative deaths, differences remained, with 9% mortality for FEVAR and 5% for open repair [P = .02],” he said. “This corresponded to a 66% higher risk for overall mortality following FEVAR.”
What’s more, Dr. DiMusto said, draft guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom advise against offering complex EVAR to people with an unruptured AAA under two scenarios: if open surgery is an option; and even if they’re unable to have surgery because of anesthetic or medical issues. The final guidelines have yet to be released.
Dr. Bechara disclosed financial relationships with Gore Medical and Cook Medical and equity interest in MOKITA Medical. Dr. DiMusto has no relevant financial disclosures.
CHICAGO – Outcomes with fenestrated endografts and endograft anchors to repair abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) in the region of the renal artery have improved as the techniques have gained popularity in recent years, but open repair may still achieve better overall results, vascular surgeons on opposite sides of the controversy contended during a debate at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
Fenestrated endovascular aortic repair (FEVAR) “is as safe as open surgery to treat complex aneurysm,” said Carlos Bechara, MD, of Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago. “EndoAnchors [Medtronic] do provide an excellent off-the-shelf solution to treat short, hostile necks with promising short-term results.”
Arguing for open repair was Paul DiMusto, MD, of the University of Wisconsin–Madison. “Open repair has an equal perioperative mortality to FEVAR,” Dr. DiMusto said, adding that the open approach also has a higher long-term branch patency rate, lower secondary-intervention rate, a lower incidence of long-term renal failure, and higher long-term survival. “So putting that all together, open repair is best,” he said.
They staked out their positions by citing a host of published trials.
“The presence of a short neck can create a challenging clinical scenario for an endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm,” Dr. Bechara said. However, he noted he was discussing complex aneurysm in which the aortic clamp is placed above the renal arteries, differentiating it from infrarenal AAA in which the clamp is below the renal arteries with no renal ischemia time. He noted a 2011 study that determined a short neck was a predictor of Type 1A endoleak after AAA repair, but that compliance with best practices at the time was poor; more than 44% of EVARs did not follow the manufacturer’s instruction (Circulation. 2011;123:2848-55).
But FEVAR was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2012, with an indication for an infrarenal neck length of 4-14 mm, Dr. Bechara noted. Since then, several studies have reported excellent outcomes with the technique. An early small study of 67 patients reported a 100% technical success rate with one patient having a Type 1 endoleak at 3 years (J Vasc Surg. 2014;60:1420-8).
This year, a larger study evaluated 6,825 patients in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program who had FEVAR, open AAA repair or standard infrarenal endovascular repair during 2012-2016. “Actually, the fenestrated approach had fewer complications than open repair and the outcomes were comparable to standard EVAR,” Dr. Bechara noted. The trial reported FEVAR had lower rates of perioperative mortality (1.8% vs. 8.8%; P = .001), postoperative renal dysfunction (1.4% vs. 7.7%; P = .002), and overall complications (11% vs. 33%; P less than.001) than did open repair (J Vasc Surg. 2019;69:1670-78).
In regard to the use of endograft anchors for treatment of endoleaks, migrating grafts, and high-risk seal zones, Dr. Bechara noted they are a good “off-the-shelf” choice for complex AAA repair. He cited current results of a cohort of 70 patients with short-neck AAA (J Vasc Surg. 2019;70:732-40). “This study showed a procedural success rate at 97% and a technical success rate at 88.6%,” he said. “They had no stent migration, no increase in sac size or AAA rupture or open conversion.”
He also pointed to just-published results from a randomized trial of 881 patients with up to 14 years of follow-up that found comparable rates of death/secondary procedures, as well as durability, between patients who had endovascular and open repairs (77.7% and 75.5%, respectively, N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2126-35). Also, he noted that hospital volume is an important predictor of success with open repair, with high-volume centers reporting lower mortality (3.9%) than low-volume centers (9%; Ann Surg. 2018 Nov 29. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002873). “So not many centers are doing high-volume open aortic surgery,” he said.
To make his case that open surgery for juxtarenal AAAs is superior, Dr. DiMusto cited a number of recent studies, including a three-center trial of 200 patients who had open and FEVAR procedures (J Endovasc Ther. 2019;26:105-12). “There was no difference in perioperative mortality [2.2% for FEVAR, 1.9% in open repair], ” Dr. DiMusto said “There was a higher freedom from reintervention in the open group [96% vs. 78%], and there was higher long-term vessel patency in the open group” (97.5% having target patency for open vs. 93.3% for FEVAR).
He also pointed to a meta-analysis of 2,326 patients that found similar outcomes for mortality and postoperative renal insufficiency between FEVAR and open repair, around 4.1%, but showed significantly higher rates of renal failure in FEVAR, at 19.7% versus 7.7% (J Vasc Surg. 2015;61:242-55). This study also reported significantly more secondary interventions with FEVAR, 12.7% vs. 4.9%, Dr. DiMusto said.
Another study of 3,253 complex AAA repairs, including 887 FEVAR and 2,125 open procedures, showed that FEVAR had a technical success rate of 97%, with no appreciable difference in perioperative mortality between the two procedures (Ann Surg. 2019 Feb 1. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000003094).
However, Dr. DiMusto said, adjusted 3-year mortality in this study was higher with FEVAR, and further analysis yielded outcomes that favored open repair. “After excluding perioperative deaths, differences remained, with 9% mortality for FEVAR and 5% for open repair [P = .02],” he said. “This corresponded to a 66% higher risk for overall mortality following FEVAR.”
What’s more, Dr. DiMusto said, draft guidelines from the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom advise against offering complex EVAR to people with an unruptured AAA under two scenarios: if open surgery is an option; and even if they’re unable to have surgery because of anesthetic or medical issues. The final guidelines have yet to be released.
Dr. Bechara disclosed financial relationships with Gore Medical and Cook Medical and equity interest in MOKITA Medical. Dr. DiMusto has no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
Chronic kidney disease may not be deterrent for B-FEVAR
CHICAGO – Although advanced renal dysfunction is a major contraindication for open repair of complex thoracoabdominal aneurysms (TAAA) and pararenal aneurysms (PRA), a single-center study of patients who had branched-fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (B-FEVAR) found that those with severe or moderate dysfunction and those with normal kidney function had similar results, according to a study reported at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“In our series of patients with stage 4 and 5 chronic kidney disease, branched-fenestration aneurysm repair for pararenal and thoracoabdominal aneurysm was associated with acceptable morbidity and mortality,” said Luis C. Cajas-Monson, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Although often a contraindication for open repair, B-FEVAR could be a safe alternative for TAAA patients with poor renal function.”
The study evaluated 231 patients who had B-FEVAR for the following etiologies: 80 for PRA; 89 for Type I to III TAAA; and 62 for type IV TAAA. The patients had at least 1 year of follow-up. A small percentage of patients (4%; n = 9) had stage IV or V chronic kidney disease; the remainder had stage I to III CKD. The study compared results in the lower- and higher-stage CKD groups.
“The frequency of endovascular aortic aneurysm repair continues to increase, and it has advanced to treating more complex aortic pathology,” Dr. Cajas-Monson said. “There appears to be no significant decline in renal function with complex EVAR.” He noted that in open TAAA repair, the more severe the chronic kidney disease state, the worse the outcomes.
The Mayo researchers set out to evaluate the impact of renal function on survival after B-FEVAR for TAAA and PRA. “We hypothesized that renal function is not a significant factor in early and late survival after B-FEVAR,” Dr. Cajas-Monson said. TAAA patients represented 65% of the study population, with 59% having Extent I to III and 41% having Extent IV disease.
Dr. Cajas-Monson noted that demographics were comparable between the higher- and lower-stage CKD groups, with the exception of higher baseline creatinine levels in the CKD 4/5 patients: 3.14 vs. 1.13 (P less than .001). Operative outcomes and length of stay were also similar.
The higher-stage group had a higher overall rate of major adverse events, but given the small sample size this was not found to be significantly different (44% vs. 29%; P = .26). However, there were no events of perioperative death, stroke, paraplegia or estimated blood loss greater than 1 L in the higher-stage patients, while the lower-stage group had low percentages of these events.
Three-year survival was 84% in the lower-stage group and 75% in the higher-stage group.
Dr. Cajas-Monson acknowledged that the small sample size was a limitation of the study. “Further evaluation of patients with renal dysfunction is needed to validate our initial findings,” he said.
This abstract of this study was published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery (2019. 70 [3]:e67).
Dr. Cajas-Monson had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Cajas-Monson LC et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 19.
CHICAGO – Although advanced renal dysfunction is a major contraindication for open repair of complex thoracoabdominal aneurysms (TAAA) and pararenal aneurysms (PRA), a single-center study of patients who had branched-fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (B-FEVAR) found that those with severe or moderate dysfunction and those with normal kidney function had similar results, according to a study reported at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“In our series of patients with stage 4 and 5 chronic kidney disease, branched-fenestration aneurysm repair for pararenal and thoracoabdominal aneurysm was associated with acceptable morbidity and mortality,” said Luis C. Cajas-Monson, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Although often a contraindication for open repair, B-FEVAR could be a safe alternative for TAAA patients with poor renal function.”
The study evaluated 231 patients who had B-FEVAR for the following etiologies: 80 for PRA; 89 for Type I to III TAAA; and 62 for type IV TAAA. The patients had at least 1 year of follow-up. A small percentage of patients (4%; n = 9) had stage IV or V chronic kidney disease; the remainder had stage I to III CKD. The study compared results in the lower- and higher-stage CKD groups.
“The frequency of endovascular aortic aneurysm repair continues to increase, and it has advanced to treating more complex aortic pathology,” Dr. Cajas-Monson said. “There appears to be no significant decline in renal function with complex EVAR.” He noted that in open TAAA repair, the more severe the chronic kidney disease state, the worse the outcomes.
The Mayo researchers set out to evaluate the impact of renal function on survival after B-FEVAR for TAAA and PRA. “We hypothesized that renal function is not a significant factor in early and late survival after B-FEVAR,” Dr. Cajas-Monson said. TAAA patients represented 65% of the study population, with 59% having Extent I to III and 41% having Extent IV disease.
Dr. Cajas-Monson noted that demographics were comparable between the higher- and lower-stage CKD groups, with the exception of higher baseline creatinine levels in the CKD 4/5 patients: 3.14 vs. 1.13 (P less than .001). Operative outcomes and length of stay were also similar.
The higher-stage group had a higher overall rate of major adverse events, but given the small sample size this was not found to be significantly different (44% vs. 29%; P = .26). However, there were no events of perioperative death, stroke, paraplegia or estimated blood loss greater than 1 L in the higher-stage patients, while the lower-stage group had low percentages of these events.
Three-year survival was 84% in the lower-stage group and 75% in the higher-stage group.
Dr. Cajas-Monson acknowledged that the small sample size was a limitation of the study. “Further evaluation of patients with renal dysfunction is needed to validate our initial findings,” he said.
This abstract of this study was published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery (2019. 70 [3]:e67).
Dr. Cajas-Monson had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Cajas-Monson LC et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 19.
CHICAGO – Although advanced renal dysfunction is a major contraindication for open repair of complex thoracoabdominal aneurysms (TAAA) and pararenal aneurysms (PRA), a single-center study of patients who had branched-fenestrated endovascular aneurysm repair (B-FEVAR) found that those with severe or moderate dysfunction and those with normal kidney function had similar results, according to a study reported at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“In our series of patients with stage 4 and 5 chronic kidney disease, branched-fenestration aneurysm repair for pararenal and thoracoabdominal aneurysm was associated with acceptable morbidity and mortality,” said Luis C. Cajas-Monson, MD, of the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn. “Although often a contraindication for open repair, B-FEVAR could be a safe alternative for TAAA patients with poor renal function.”
The study evaluated 231 patients who had B-FEVAR for the following etiologies: 80 for PRA; 89 for Type I to III TAAA; and 62 for type IV TAAA. The patients had at least 1 year of follow-up. A small percentage of patients (4%; n = 9) had stage IV or V chronic kidney disease; the remainder had stage I to III CKD. The study compared results in the lower- and higher-stage CKD groups.
“The frequency of endovascular aortic aneurysm repair continues to increase, and it has advanced to treating more complex aortic pathology,” Dr. Cajas-Monson said. “There appears to be no significant decline in renal function with complex EVAR.” He noted that in open TAAA repair, the more severe the chronic kidney disease state, the worse the outcomes.
The Mayo researchers set out to evaluate the impact of renal function on survival after B-FEVAR for TAAA and PRA. “We hypothesized that renal function is not a significant factor in early and late survival after B-FEVAR,” Dr. Cajas-Monson said. TAAA patients represented 65% of the study population, with 59% having Extent I to III and 41% having Extent IV disease.
Dr. Cajas-Monson noted that demographics were comparable between the higher- and lower-stage CKD groups, with the exception of higher baseline creatinine levels in the CKD 4/5 patients: 3.14 vs. 1.13 (P less than .001). Operative outcomes and length of stay were also similar.
The higher-stage group had a higher overall rate of major adverse events, but given the small sample size this was not found to be significantly different (44% vs. 29%; P = .26). However, there were no events of perioperative death, stroke, paraplegia or estimated blood loss greater than 1 L in the higher-stage patients, while the lower-stage group had low percentages of these events.
Three-year survival was 84% in the lower-stage group and 75% in the higher-stage group.
Dr. Cajas-Monson acknowledged that the small sample size was a limitation of the study. “Further evaluation of patients with renal dysfunction is needed to validate our initial findings,” he said.
This abstract of this study was published in the Journal of Vascular Surgery (2019. 70 [3]:e67).
Dr. Cajas-Monson had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Cajas-Monson LC et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 19.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
F-BEVAR safe in patients with one kidney
CHICAGO – Patients who have one kidney do as well after fenestrated-branched endovascular aneurysm repair (F-BEVAR) of pararenal or thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm as patients with both kidneys, according to a study of almost 300 patients presented at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“Despite the worse baseline renal function associated with single functioning kidney patients, F-BEVAR is safe and effective with nearly identical outcomes in patients with a SFK [single functioning kidney] as compared to patients with two functioning kidneys,” said Keouna Pather of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The study evaluated 287 F-BEVAR patients enrolled in a physician-sponsored investigation device exemption study from November 2013 to October 2018. Thirty of those patients had one kidney, the remaining 257 were the control group. Ms. Pather noted that characteristics were similar between both patient groups with the exception that SFK patients were younger (age 70 vs. 74 years; P = .009) and had larger renal artery diameter (6 vs. 5.7 mm; P = .05). “Patients with a SFK had enlargement of their renal artery in a compensatory fashion,” she said.
Survival at 2 years was 92% for SFK patients and 84% for controls.
“The SFK patients did start at a worse baseline of CKD [chronic kidney disease] stages as compared to controls,” she noted. In the SFK group, 63% (n = 19) had Stage III CKD versus 40% (n = 104) of controls (P = .02). Likewise, rates of Stage IV CKD were 10% (n = 3) and 2% (n = 4), respectively (P = .03).
In terms of outcomes, two patients in the control group died within 30 days but none in the SFK group did, Ms. Pather said. Also, a higher percentage of SFK patients had estimated blood loss greater than 1 L, compared with controls (20% vs. 7%; P = .02). All other outcomes, including rates of acute kidney injury (20% vs. 12%; P = .26), were not statistically different, she said.
“Between the groups, there was no significant difference in CKD progression that needed stenting,” she added, with 27% (n = 8) and 26% (n = 67) of the SFK and controls progressing to CKD Stages III to V.
The study also identified predictors of acute kidney injury in SFK patients: total fluoroscopy time (hours), which raised the risk by 78.5%, and estimated blood loss greater than 1 L, which increased risk by 109%.
Predictors of renal function deterioration in SFK patients were renal artery occlusion or reintervention for branch stenosis or kink, which raised the risk threefold; a Crawford extent II, which more than doubled the risk; and acute kidney injury, which raised chances almost fivefold. “Development of postoperative AKI [acute kidney injury] is the most important predictor for renal function deterioration,” Pather said.
When freedom from renal function deterioration at 2 years was compared between the two groups, again the results were similar because of the small sample size of the SFK group: 100% for the SFK group and 84% for controls.
Ms. Pather had no financial relationships to disclose.
CHICAGO – Patients who have one kidney do as well after fenestrated-branched endovascular aneurysm repair (F-BEVAR) of pararenal or thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm as patients with both kidneys, according to a study of almost 300 patients presented at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“Despite the worse baseline renal function associated with single functioning kidney patients, F-BEVAR is safe and effective with nearly identical outcomes in patients with a SFK [single functioning kidney] as compared to patients with two functioning kidneys,” said Keouna Pather of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The study evaluated 287 F-BEVAR patients enrolled in a physician-sponsored investigation device exemption study from November 2013 to October 2018. Thirty of those patients had one kidney, the remaining 257 were the control group. Ms. Pather noted that characteristics were similar between both patient groups with the exception that SFK patients were younger (age 70 vs. 74 years; P = .009) and had larger renal artery diameter (6 vs. 5.7 mm; P = .05). “Patients with a SFK had enlargement of their renal artery in a compensatory fashion,” she said.
Survival at 2 years was 92% for SFK patients and 84% for controls.
“The SFK patients did start at a worse baseline of CKD [chronic kidney disease] stages as compared to controls,” she noted. In the SFK group, 63% (n = 19) had Stage III CKD versus 40% (n = 104) of controls (P = .02). Likewise, rates of Stage IV CKD were 10% (n = 3) and 2% (n = 4), respectively (P = .03).
In terms of outcomes, two patients in the control group died within 30 days but none in the SFK group did, Ms. Pather said. Also, a higher percentage of SFK patients had estimated blood loss greater than 1 L, compared with controls (20% vs. 7%; P = .02). All other outcomes, including rates of acute kidney injury (20% vs. 12%; P = .26), were not statistically different, she said.
“Between the groups, there was no significant difference in CKD progression that needed stenting,” she added, with 27% (n = 8) and 26% (n = 67) of the SFK and controls progressing to CKD Stages III to V.
The study also identified predictors of acute kidney injury in SFK patients: total fluoroscopy time (hours), which raised the risk by 78.5%, and estimated blood loss greater than 1 L, which increased risk by 109%.
Predictors of renal function deterioration in SFK patients were renal artery occlusion or reintervention for branch stenosis or kink, which raised the risk threefold; a Crawford extent II, which more than doubled the risk; and acute kidney injury, which raised chances almost fivefold. “Development of postoperative AKI [acute kidney injury] is the most important predictor for renal function deterioration,” Pather said.
When freedom from renal function deterioration at 2 years was compared between the two groups, again the results were similar because of the small sample size of the SFK group: 100% for the SFK group and 84% for controls.
Ms. Pather had no financial relationships to disclose.
CHICAGO – Patients who have one kidney do as well after fenestrated-branched endovascular aneurysm repair (F-BEVAR) of pararenal or thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm as patients with both kidneys, according to a study of almost 300 patients presented at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“Despite the worse baseline renal function associated with single functioning kidney patients, F-BEVAR is safe and effective with nearly identical outcomes in patients with a SFK [single functioning kidney] as compared to patients with two functioning kidneys,” said Keouna Pather of Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
The study evaluated 287 F-BEVAR patients enrolled in a physician-sponsored investigation device exemption study from November 2013 to October 2018. Thirty of those patients had one kidney, the remaining 257 were the control group. Ms. Pather noted that characteristics were similar between both patient groups with the exception that SFK patients were younger (age 70 vs. 74 years; P = .009) and had larger renal artery diameter (6 vs. 5.7 mm; P = .05). “Patients with a SFK had enlargement of their renal artery in a compensatory fashion,” she said.
Survival at 2 years was 92% for SFK patients and 84% for controls.
“The SFK patients did start at a worse baseline of CKD [chronic kidney disease] stages as compared to controls,” she noted. In the SFK group, 63% (n = 19) had Stage III CKD versus 40% (n = 104) of controls (P = .02). Likewise, rates of Stage IV CKD were 10% (n = 3) and 2% (n = 4), respectively (P = .03).
In terms of outcomes, two patients in the control group died within 30 days but none in the SFK group did, Ms. Pather said. Also, a higher percentage of SFK patients had estimated blood loss greater than 1 L, compared with controls (20% vs. 7%; P = .02). All other outcomes, including rates of acute kidney injury (20% vs. 12%; P = .26), were not statistically different, she said.
“Between the groups, there was no significant difference in CKD progression that needed stenting,” she added, with 27% (n = 8) and 26% (n = 67) of the SFK and controls progressing to CKD Stages III to V.
The study also identified predictors of acute kidney injury in SFK patients: total fluoroscopy time (hours), which raised the risk by 78.5%, and estimated blood loss greater than 1 L, which increased risk by 109%.
Predictors of renal function deterioration in SFK patients were renal artery occlusion or reintervention for branch stenosis or kink, which raised the risk threefold; a Crawford extent II, which more than doubled the risk; and acute kidney injury, which raised chances almost fivefold. “Development of postoperative AKI [acute kidney injury] is the most important predictor for renal function deterioration,” Pather said.
When freedom from renal function deterioration at 2 years was compared between the two groups, again the results were similar because of the small sample size of the SFK group: 100% for the SFK group and 84% for controls.
Ms. Pather had no financial relationships to disclose.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
Key clinical point: Fenestrated-branched endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm is safe and effective.
Major finding: Two-year survival rates were 92% for one-kidney patients and 84% for those with two kidneys.
Study details: Retrospective review of a prospectively collected database of 287 patients who had F-BEVAR from 2013 to 2018.
Disclosures: Ms. Pather has no financial relationships to disclose.
Source: Pather K et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 2.
Study questions preemptive TEVAR for extended type A dissections
CHICAGO – The need for additional intervention after repair of the ascending aorta in extended type A aortic dissection has been thought to follow the practice for type B dissection and favor preemptive thoracic endovascular aortic repair. However, preemptive TEVAR may, at least in the midterm, provide no benefit in patients with extended type A dissections, according to results reported at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“TEVAR does not appear to be indicated in patients with extended type A dissections after acute aortic repair,” said Amy B. Reed, MD, of the University of Minnesota.
The study’s hypothesis was that growth rates of dissection and the need for additional intervention in the descending thoracic aorta are similar between extended type A (ExTA) and type B aortic dissection after initial repair of the ascending aorta. Dr. Reed noted that investigators from the INSTEAD-XL trial reported that preemptive TEVAR improved outcomes in patients with type B dissections (Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:407-16). “The thinking has been that patients with uncomplicated ExTA would also benefit from early TEVAR,” Dr. Reed said.
The study evaluated 87 consecutive patients from 2011 to 2018, 43 with ExTA and 44 with type B dissections. Characteristics of both groups were similar, except the type B group had a significantly higher rate of coronary artery disease, 16% vs. 0% (P = .01). The distal extent of the dissection was beyond the aortic bifurcation in 75% of the ExTA patients and 52% of the type B group, “so we felt that these groups were really well matched,” Dr. Reed said.
Of the 43 ExTA patients, five had repair and 38 had no intervention. At an average follow-up of 33 months, 23 of the no-intervention patients showed no growth of their dissection, Dr. Reed said. In the type B group, 15 had no repair, and of those nine showed no growth (one patient died early and five did show growth).
“When we look at intervention-free survival, there’s a significant difference between our ExTA patients vs. our type B patients over time, with significantly more type B patients requiring intervention,” she said. At 28 months, 88% of ExTA were intervention free, whereas at 9 months 35% of type B patients were.
“We feel that, following the repair of ascending acute aortic dissection, in those patients with ExTA dissections, there does appear to be a slow progression of distal aortic disease,” Dr. Reed said. “Rarely do these patients develop complications such as dissection needing intervention either in the acute hospital period or delayed.”
Because the findings are based on medium-term follow-up, she said, “We certainly need further follow-up to confirm these midterm findings.”
Dr. Reed had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
CHICAGO – The need for additional intervention after repair of the ascending aorta in extended type A aortic dissection has been thought to follow the practice for type B dissection and favor preemptive thoracic endovascular aortic repair. However, preemptive TEVAR may, at least in the midterm, provide no benefit in patients with extended type A dissections, according to results reported at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“TEVAR does not appear to be indicated in patients with extended type A dissections after acute aortic repair,” said Amy B. Reed, MD, of the University of Minnesota.
The study’s hypothesis was that growth rates of dissection and the need for additional intervention in the descending thoracic aorta are similar between extended type A (ExTA) and type B aortic dissection after initial repair of the ascending aorta. Dr. Reed noted that investigators from the INSTEAD-XL trial reported that preemptive TEVAR improved outcomes in patients with type B dissections (Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:407-16). “The thinking has been that patients with uncomplicated ExTA would also benefit from early TEVAR,” Dr. Reed said.
The study evaluated 87 consecutive patients from 2011 to 2018, 43 with ExTA and 44 with type B dissections. Characteristics of both groups were similar, except the type B group had a significantly higher rate of coronary artery disease, 16% vs. 0% (P = .01). The distal extent of the dissection was beyond the aortic bifurcation in 75% of the ExTA patients and 52% of the type B group, “so we felt that these groups were really well matched,” Dr. Reed said.
Of the 43 ExTA patients, five had repair and 38 had no intervention. At an average follow-up of 33 months, 23 of the no-intervention patients showed no growth of their dissection, Dr. Reed said. In the type B group, 15 had no repair, and of those nine showed no growth (one patient died early and five did show growth).
“When we look at intervention-free survival, there’s a significant difference between our ExTA patients vs. our type B patients over time, with significantly more type B patients requiring intervention,” she said. At 28 months, 88% of ExTA were intervention free, whereas at 9 months 35% of type B patients were.
“We feel that, following the repair of ascending acute aortic dissection, in those patients with ExTA dissections, there does appear to be a slow progression of distal aortic disease,” Dr. Reed said. “Rarely do these patients develop complications such as dissection needing intervention either in the acute hospital period or delayed.”
Because the findings are based on medium-term follow-up, she said, “We certainly need further follow-up to confirm these midterm findings.”
Dr. Reed had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
CHICAGO – The need for additional intervention after repair of the ascending aorta in extended type A aortic dissection has been thought to follow the practice for type B dissection and favor preemptive thoracic endovascular aortic repair. However, preemptive TEVAR may, at least in the midterm, provide no benefit in patients with extended type A dissections, according to results reported at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“TEVAR does not appear to be indicated in patients with extended type A dissections after acute aortic repair,” said Amy B. Reed, MD, of the University of Minnesota.
The study’s hypothesis was that growth rates of dissection and the need for additional intervention in the descending thoracic aorta are similar between extended type A (ExTA) and type B aortic dissection after initial repair of the ascending aorta. Dr. Reed noted that investigators from the INSTEAD-XL trial reported that preemptive TEVAR improved outcomes in patients with type B dissections (Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2013;6:407-16). “The thinking has been that patients with uncomplicated ExTA would also benefit from early TEVAR,” Dr. Reed said.
The study evaluated 87 consecutive patients from 2011 to 2018, 43 with ExTA and 44 with type B dissections. Characteristics of both groups were similar, except the type B group had a significantly higher rate of coronary artery disease, 16% vs. 0% (P = .01). The distal extent of the dissection was beyond the aortic bifurcation in 75% of the ExTA patients and 52% of the type B group, “so we felt that these groups were really well matched,” Dr. Reed said.
Of the 43 ExTA patients, five had repair and 38 had no intervention. At an average follow-up of 33 months, 23 of the no-intervention patients showed no growth of their dissection, Dr. Reed said. In the type B group, 15 had no repair, and of those nine showed no growth (one patient died early and five did show growth).
“When we look at intervention-free survival, there’s a significant difference between our ExTA patients vs. our type B patients over time, with significantly more type B patients requiring intervention,” she said. At 28 months, 88% of ExTA were intervention free, whereas at 9 months 35% of type B patients were.
“We feel that, following the repair of ascending acute aortic dissection, in those patients with ExTA dissections, there does appear to be a slow progression of distal aortic disease,” Dr. Reed said. “Rarely do these patients develop complications such as dissection needing intervention either in the acute hospital period or delayed.”
Because the findings are based on medium-term follow-up, she said, “We certainly need further follow-up to confirm these midterm findings.”
Dr. Reed had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
Trial: Stem cells may reduce AAA inflammation
CHICAGO – Early results of a trial evaluating allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells to target aortic inflammation in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) has reported encouraging early results, according to research presented here at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
Katherin Leckie, MD, an integrated vascular surgery resident in the vascular surgery division, Indiana University, Indianapolis, reported on early results from the ARREST (Aneurysm Repression With Mesenchymal Stem Cells) trial. Twenty-one patients have been enrolled so far, and early results showed that treatment with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) increased levels of a key anti-inflammatory cell type, the Tr1, in proportion to a key proinflammatory cell type, the Th17.
“In AAA, the Tr1:Th17 ratio is decreased,” Dr. Leckie said. AAA serum stimulates MSC secretion of IL-10. Previously, mouse studies have shown MSCs restore the Tr1:Th17 balance and prevent aneurysms, Dr. Leckie noted.
The ARREST trial is evaluating that finding in humans with small AAAs of 35-50 mm in diameter. When the trial is fully enrolled, the 36 patients are to be evenly divided between three treatment groups: placebo; 1 million MSC/kg; and 3 million MSC/kg. The primary endpoint is change in Tr1:Th17 ratio at 14 days. Secondary endpoints are change in AAA inflammation at 2 weeks and change in AAA diameter and volume at 1-5 years.
At 14 days, the high-dose group had already seen a more than 100% change in Tr1:Th17 ratio (P = .03), versus about a 35% change for the low-dose and no change for the placebo groups. At 28 days, the high-dose group’s change increased to greater than 150%, while that of the low-dose group reached around 50%, with no change in the placebo group.
The study also found a possible trend toward changes in AAA diameter among the three groups after 1 year, Dr. Leckie said. In the placebo group, AAA diameter increased 3.5 mm on average. In the low-dose group, AAA diameter increased almost 1.5 mm. However, in the high-dose group, aortic diameter actually decreased about 0.5 mm (P = .189), Dr. Leckie said.
“MSCs have significantly improved the Tr1:Th17 imbalance at 14 days,” Dr. Leckie said. “There’s also a possible trend toward decreased aortic inflammation at 14 days as well as decreased growth of AAA at 12 months.”
Dr. Leckie had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
CHICAGO – Early results of a trial evaluating allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells to target aortic inflammation in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) has reported encouraging early results, according to research presented here at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
Katherin Leckie, MD, an integrated vascular surgery resident in the vascular surgery division, Indiana University, Indianapolis, reported on early results from the ARREST (Aneurysm Repression With Mesenchymal Stem Cells) trial. Twenty-one patients have been enrolled so far, and early results showed that treatment with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) increased levels of a key anti-inflammatory cell type, the Tr1, in proportion to a key proinflammatory cell type, the Th17.
“In AAA, the Tr1:Th17 ratio is decreased,” Dr. Leckie said. AAA serum stimulates MSC secretion of IL-10. Previously, mouse studies have shown MSCs restore the Tr1:Th17 balance and prevent aneurysms, Dr. Leckie noted.
The ARREST trial is evaluating that finding in humans with small AAAs of 35-50 mm in diameter. When the trial is fully enrolled, the 36 patients are to be evenly divided between three treatment groups: placebo; 1 million MSC/kg; and 3 million MSC/kg. The primary endpoint is change in Tr1:Th17 ratio at 14 days. Secondary endpoints are change in AAA inflammation at 2 weeks and change in AAA diameter and volume at 1-5 years.
At 14 days, the high-dose group had already seen a more than 100% change in Tr1:Th17 ratio (P = .03), versus about a 35% change for the low-dose and no change for the placebo groups. At 28 days, the high-dose group’s change increased to greater than 150%, while that of the low-dose group reached around 50%, with no change in the placebo group.
The study also found a possible trend toward changes in AAA diameter among the three groups after 1 year, Dr. Leckie said. In the placebo group, AAA diameter increased 3.5 mm on average. In the low-dose group, AAA diameter increased almost 1.5 mm. However, in the high-dose group, aortic diameter actually decreased about 0.5 mm (P = .189), Dr. Leckie said.
“MSCs have significantly improved the Tr1:Th17 imbalance at 14 days,” Dr. Leckie said. “There’s also a possible trend toward decreased aortic inflammation at 14 days as well as decreased growth of AAA at 12 months.”
Dr. Leckie had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
CHICAGO – Early results of a trial evaluating allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells to target aortic inflammation in patients with small abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) has reported encouraging early results, according to research presented here at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
Katherin Leckie, MD, an integrated vascular surgery resident in the vascular surgery division, Indiana University, Indianapolis, reported on early results from the ARREST (Aneurysm Repression With Mesenchymal Stem Cells) trial. Twenty-one patients have been enrolled so far, and early results showed that treatment with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) increased levels of a key anti-inflammatory cell type, the Tr1, in proportion to a key proinflammatory cell type, the Th17.
“In AAA, the Tr1:Th17 ratio is decreased,” Dr. Leckie said. AAA serum stimulates MSC secretion of IL-10. Previously, mouse studies have shown MSCs restore the Tr1:Th17 balance and prevent aneurysms, Dr. Leckie noted.
The ARREST trial is evaluating that finding in humans with small AAAs of 35-50 mm in diameter. When the trial is fully enrolled, the 36 patients are to be evenly divided between three treatment groups: placebo; 1 million MSC/kg; and 3 million MSC/kg. The primary endpoint is change in Tr1:Th17 ratio at 14 days. Secondary endpoints are change in AAA inflammation at 2 weeks and change in AAA diameter and volume at 1-5 years.
At 14 days, the high-dose group had already seen a more than 100% change in Tr1:Th17 ratio (P = .03), versus about a 35% change for the low-dose and no change for the placebo groups. At 28 days, the high-dose group’s change increased to greater than 150%, while that of the low-dose group reached around 50%, with no change in the placebo group.
The study also found a possible trend toward changes in AAA diameter among the three groups after 1 year, Dr. Leckie said. In the placebo group, AAA diameter increased 3.5 mm on average. In the low-dose group, AAA diameter increased almost 1.5 mm. However, in the high-dose group, aortic diameter actually decreased about 0.5 mm (P = .189), Dr. Leckie said.
“MSCs have significantly improved the Tr1:Th17 imbalance at 14 days,” Dr. Leckie said. “There’s also a possible trend toward decreased aortic inflammation at 14 days as well as decreased growth of AAA at 12 months.”
Dr. Leckie had no relevant financial relationships to disclose.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
Is EVAR for ruptured AAA worth revisiting?
CHICAGO – Numerous studies have shown conflicting results for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but an analysis of 4,000-plus cases from a national registry has found a 41% reduction in mortality with endovascular repair vs. open repair, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“EVAR is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for treatment of AAA,” said Samer Alharthi, MD, MPH, of the University of Toledo in Ohio. “As surgeon experience and endovascular technology have improved, a greater percentage of ruptured AAA are being treated by EVAR.”
Dr. Alharthi reported on a retrospective analysis of 4,133 patients who had repair for ruptured AAA in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2016. Notably, the number of EVAR repairs continue to increase and peaked in 2015, with 53% of ruptured AAA treated by EVAR.
Over the term of the study, the overall mortality rate was 22.6% for EVAR and 33.2% for open repair (P less than .001), Dr. Alharthi said. “After adjusting for cofounders, there was a 41% reduction in the mortality rate with the EVAR approach,” he said.
The only appreciable significant difference in demographics between the two groups was a higher percentage of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease having open repair – 942 (49.2%) vs. 701 (36.2%) – and a higher percentage of patients with end-stage renal disease having EVAR, Dr. Alharthi said. Other comorbidities had no statistically significant difference.
“Complications – pneumonia, reintubation, and acute renal failure – were higher in the open than the EVAR group,” he said. For example, rates of acute renal failure were 15.4% and 8.2% (P less than.001), respectively. Rates of myocardial infarction were similar between the two groups: 6.3% and 6% (P = .74), respectively.
Dr. Alharthi had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Alharthi S et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 13.
CHICAGO – Numerous studies have shown conflicting results for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but an analysis of 4,000-plus cases from a national registry has found a 41% reduction in mortality with endovascular repair vs. open repair, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“EVAR is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for treatment of AAA,” said Samer Alharthi, MD, MPH, of the University of Toledo in Ohio. “As surgeon experience and endovascular technology have improved, a greater percentage of ruptured AAA are being treated by EVAR.”
Dr. Alharthi reported on a retrospective analysis of 4,133 patients who had repair for ruptured AAA in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2016. Notably, the number of EVAR repairs continue to increase and peaked in 2015, with 53% of ruptured AAA treated by EVAR.
Over the term of the study, the overall mortality rate was 22.6% for EVAR and 33.2% for open repair (P less than .001), Dr. Alharthi said. “After adjusting for cofounders, there was a 41% reduction in the mortality rate with the EVAR approach,” he said.
The only appreciable significant difference in demographics between the two groups was a higher percentage of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease having open repair – 942 (49.2%) vs. 701 (36.2%) – and a higher percentage of patients with end-stage renal disease having EVAR, Dr. Alharthi said. Other comorbidities had no statistically significant difference.
“Complications – pneumonia, reintubation, and acute renal failure – were higher in the open than the EVAR group,” he said. For example, rates of acute renal failure were 15.4% and 8.2% (P less than.001), respectively. Rates of myocardial infarction were similar between the two groups: 6.3% and 6% (P = .74), respectively.
Dr. Alharthi had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Alharthi S et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 13.
CHICAGO – Numerous studies have shown conflicting results for endovascular repair in ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA), but an analysis of 4,000-plus cases from a national registry has found a 41% reduction in mortality with endovascular repair vs. open repair, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Midwestern Vascular Surgery Society.
“EVAR is becoming an increasingly popular strategy for treatment of AAA,” said Samer Alharthi, MD, MPH, of the University of Toledo in Ohio. “As surgeon experience and endovascular technology have improved, a greater percentage of ruptured AAA are being treated by EVAR.”
Dr. Alharthi reported on a retrospective analysis of 4,133 patients who had repair for ruptured AAA in the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Improvement Program database from 2010 to 2016. Notably, the number of EVAR repairs continue to increase and peaked in 2015, with 53% of ruptured AAA treated by EVAR.
Over the term of the study, the overall mortality rate was 22.6% for EVAR and 33.2% for open repair (P less than .001), Dr. Alharthi said. “After adjusting for cofounders, there was a 41% reduction in the mortality rate with the EVAR approach,” he said.
The only appreciable significant difference in demographics between the two groups was a higher percentage of smokers with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease having open repair – 942 (49.2%) vs. 701 (36.2%) – and a higher percentage of patients with end-stage renal disease having EVAR, Dr. Alharthi said. Other comorbidities had no statistically significant difference.
“Complications – pneumonia, reintubation, and acute renal failure – were higher in the open than the EVAR group,” he said. For example, rates of acute renal failure were 15.4% and 8.2% (P less than.001), respectively. Rates of myocardial infarction were similar between the two groups: 6.3% and 6% (P = .74), respectively.
Dr. Alharthi had no financial relationships to disclose.
SOURCE: Alharthi S et al. Midwestern Vascular 2019, Abstract 13.
REPORTING FROM MIDWESTERN VASCULAR 2019
In vasculitis, the skin tells the story
MILAN – , Robert Micheletti, MD, said at the World Congress of Dermatology.
In granulomatous vasculitis, histiocytes and giant cells can play a significant role, explained Dr. Micheletti, director of the cutaneous vasculitis clinic at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. The condition may be secondary to an autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus or RA; a granulomatous disease such as Crohn’s disease or sarcoidosis; infections such as tuberculosis, a fungal disease, or herpes or zoster viruses, or lymphoma, Dr. Micheletti said.
However, a primary systemic vasculitis such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA; formerly known as Wegener’s polyangiitis) or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA; also known as Churg-Strauss vasculitis), giant cell arteritis, or Takayasu arteritis may also be responsible, he said. Occasionally, the culprit can also be a drug-induced vasculitis.
The physical examination gives clues to the size of involved vessels, which in turn helps to classify the vasculitis, Dr. Micheletti said.
When vasculitis affects small vessels, the skin findings will be palpable purpura, urticarial papules, vesicles, and petechiae, he said, adding that “The small vessel involvement accounts for the small size of the lesions, and complement cascade and inflammation account for the palpability of the lesions and the symptomatology.” As red blood cells extravasate from the affected vessels, nonblanching purpura develop, and gravity’s effect on the deposition of immune complex material dictates how lesions are distributed.
“Manifestations more typical of medium vessel vasculitis include subcutaneous nodules, livedo reticularis, retiform purpura, larger hemorrhagic bullae, and more significant ulceration and necrosis,” he said. “If such lesions are seen, suspect medium-vessel vasculitis or vasculitis overlapping small and medium vessels.” Cutaneous or systemic polyarteritis nodosa, antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis, and cryoglobulinemic vasculitis are examples, he added.
The particularities of renal manifestations of vasculitis also offer clues to the vessels involved. When a vasculitis patient has glomerulonephritis, suspect small-vessel involvement, Dr. Micheletti said. However, vasculitis affecting medium-sized vessels will cause renovascular hypertension and, potentially renal arterial aneurysms.
Nerves are typically spared in small-vessel vasculitis, while wrist or foot drop can be seen in mononeuritis multiplex.
Recently, the Diagnostic and Classification Criteria in Vasculitis Study (DCVAS) looked at more than 6,800 patients at over 130 sites around the world, proposing new classification criteria for ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and large-vessel vasculitis. The study found that skin findings are common in AAV, with 30%-50% of cases presenting initially with skin lesions. Petechiae and/or purpura are the most common of the skin manifestations, he said. By contrast, for EGPA, allergic and nonspecific findings were the most common findings.
Although skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis in up to 94% of AAV cases, it’s underutilized and performed in less than half (24%-44%) of cases, Dr. Micheletti said. The study’s findings “demonstrate the importance of a good skin exam, as well as its utility for diagnosis” of vasculitis, he said.
An additional finding form the DCVAS study was that skin lesions can give clues to severity of vasculitis: “Among 1,184 patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, those with cutaneous involvement were more likely to have systemic manifestations of disease, more likely to have such severe manifestations as glomerulonephritis, alveolar hemorrhage, and mononeuritis,” said Dr. Micheletti, with a hazard ratio of 2.0 among those individuals who had EGPA or GPA.
“Skin findings have diagnostic and, potentially, prognostic importance,” he said. “Use the physician exam and your clinical acumen to your advantage,” but always confirm vasculitis with a biopsy. “Clinicopathologic correlation is key.” A simple urinalysis will screen for renal involvement, and is of “paramount importance,” he added.
Dr. Micheletti reported that he had no relevant disclosures.
MILAN – , Robert Micheletti, MD, said at the World Congress of Dermatology.
In granulomatous vasculitis, histiocytes and giant cells can play a significant role, explained Dr. Micheletti, director of the cutaneous vasculitis clinic at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. The condition may be secondary to an autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus or RA; a granulomatous disease such as Crohn’s disease or sarcoidosis; infections such as tuberculosis, a fungal disease, or herpes or zoster viruses, or lymphoma, Dr. Micheletti said.
However, a primary systemic vasculitis such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA; formerly known as Wegener’s polyangiitis) or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA; also known as Churg-Strauss vasculitis), giant cell arteritis, or Takayasu arteritis may also be responsible, he said. Occasionally, the culprit can also be a drug-induced vasculitis.
The physical examination gives clues to the size of involved vessels, which in turn helps to classify the vasculitis, Dr. Micheletti said.
When vasculitis affects small vessels, the skin findings will be palpable purpura, urticarial papules, vesicles, and petechiae, he said, adding that “The small vessel involvement accounts for the small size of the lesions, and complement cascade and inflammation account for the palpability of the lesions and the symptomatology.” As red blood cells extravasate from the affected vessels, nonblanching purpura develop, and gravity’s effect on the deposition of immune complex material dictates how lesions are distributed.
“Manifestations more typical of medium vessel vasculitis include subcutaneous nodules, livedo reticularis, retiform purpura, larger hemorrhagic bullae, and more significant ulceration and necrosis,” he said. “If such lesions are seen, suspect medium-vessel vasculitis or vasculitis overlapping small and medium vessels.” Cutaneous or systemic polyarteritis nodosa, antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis, and cryoglobulinemic vasculitis are examples, he added.
The particularities of renal manifestations of vasculitis also offer clues to the vessels involved. When a vasculitis patient has glomerulonephritis, suspect small-vessel involvement, Dr. Micheletti said. However, vasculitis affecting medium-sized vessels will cause renovascular hypertension and, potentially renal arterial aneurysms.
Nerves are typically spared in small-vessel vasculitis, while wrist or foot drop can be seen in mononeuritis multiplex.
Recently, the Diagnostic and Classification Criteria in Vasculitis Study (DCVAS) looked at more than 6,800 patients at over 130 sites around the world, proposing new classification criteria for ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and large-vessel vasculitis. The study found that skin findings are common in AAV, with 30%-50% of cases presenting initially with skin lesions. Petechiae and/or purpura are the most common of the skin manifestations, he said. By contrast, for EGPA, allergic and nonspecific findings were the most common findings.
Although skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis in up to 94% of AAV cases, it’s underutilized and performed in less than half (24%-44%) of cases, Dr. Micheletti said. The study’s findings “demonstrate the importance of a good skin exam, as well as its utility for diagnosis” of vasculitis, he said.
An additional finding form the DCVAS study was that skin lesions can give clues to severity of vasculitis: “Among 1,184 patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, those with cutaneous involvement were more likely to have systemic manifestations of disease, more likely to have such severe manifestations as glomerulonephritis, alveolar hemorrhage, and mononeuritis,” said Dr. Micheletti, with a hazard ratio of 2.0 among those individuals who had EGPA or GPA.
“Skin findings have diagnostic and, potentially, prognostic importance,” he said. “Use the physician exam and your clinical acumen to your advantage,” but always confirm vasculitis with a biopsy. “Clinicopathologic correlation is key.” A simple urinalysis will screen for renal involvement, and is of “paramount importance,” he added.
Dr. Micheletti reported that he had no relevant disclosures.
MILAN – , Robert Micheletti, MD, said at the World Congress of Dermatology.
In granulomatous vasculitis, histiocytes and giant cells can play a significant role, explained Dr. Micheletti, director of the cutaneous vasculitis clinic at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. The condition may be secondary to an autoimmune disease such as lupus erythematosus or RA; a granulomatous disease such as Crohn’s disease or sarcoidosis; infections such as tuberculosis, a fungal disease, or herpes or zoster viruses, or lymphoma, Dr. Micheletti said.
However, a primary systemic vasculitis such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA; formerly known as Wegener’s polyangiitis) or eosinophilic granulomatosis with polyangiitis (EGPA; also known as Churg-Strauss vasculitis), giant cell arteritis, or Takayasu arteritis may also be responsible, he said. Occasionally, the culprit can also be a drug-induced vasculitis.
The physical examination gives clues to the size of involved vessels, which in turn helps to classify the vasculitis, Dr. Micheletti said.
When vasculitis affects small vessels, the skin findings will be palpable purpura, urticarial papules, vesicles, and petechiae, he said, adding that “The small vessel involvement accounts for the small size of the lesions, and complement cascade and inflammation account for the palpability of the lesions and the symptomatology.” As red blood cells extravasate from the affected vessels, nonblanching purpura develop, and gravity’s effect on the deposition of immune complex material dictates how lesions are distributed.
“Manifestations more typical of medium vessel vasculitis include subcutaneous nodules, livedo reticularis, retiform purpura, larger hemorrhagic bullae, and more significant ulceration and necrosis,” he said. “If such lesions are seen, suspect medium-vessel vasculitis or vasculitis overlapping small and medium vessels.” Cutaneous or systemic polyarteritis nodosa, antineutrophilic cytoplasmic autoantibody (ANCA)–associated vasculitis, and cryoglobulinemic vasculitis are examples, he added.
The particularities of renal manifestations of vasculitis also offer clues to the vessels involved. When a vasculitis patient has glomerulonephritis, suspect small-vessel involvement, Dr. Micheletti said. However, vasculitis affecting medium-sized vessels will cause renovascular hypertension and, potentially renal arterial aneurysms.
Nerves are typically spared in small-vessel vasculitis, while wrist or foot drop can be seen in mononeuritis multiplex.
Recently, the Diagnostic and Classification Criteria in Vasculitis Study (DCVAS) looked at more than 6,800 patients at over 130 sites around the world, proposing new classification criteria for ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) and large-vessel vasculitis. The study found that skin findings are common in AAV, with 30%-50% of cases presenting initially with skin lesions. Petechiae and/or purpura are the most common of the skin manifestations, he said. By contrast, for EGPA, allergic and nonspecific findings were the most common findings.
Although skin biopsy can confirm the diagnosis in up to 94% of AAV cases, it’s underutilized and performed in less than half (24%-44%) of cases, Dr. Micheletti said. The study’s findings “demonstrate the importance of a good skin exam, as well as its utility for diagnosis” of vasculitis, he said.
An additional finding form the DCVAS study was that skin lesions can give clues to severity of vasculitis: “Among 1,184 patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis, those with cutaneous involvement were more likely to have systemic manifestations of disease, more likely to have such severe manifestations as glomerulonephritis, alveolar hemorrhage, and mononeuritis,” said Dr. Micheletti, with a hazard ratio of 2.0 among those individuals who had EGPA or GPA.
“Skin findings have diagnostic and, potentially, prognostic importance,” he said. “Use the physician exam and your clinical acumen to your advantage,” but always confirm vasculitis with a biopsy. “Clinicopathologic correlation is key.” A simple urinalysis will screen for renal involvement, and is of “paramount importance,” he added.
Dr. Micheletti reported that he had no relevant disclosures.
AT WCD2019
Is Surveillance Futile for Small AAAs in the Very Elderly?
To determine the necessity of permanent monitoring of small aortic aneurysms in the elderly, Mark Rockley, MD, of the Ottawa Hospital and his colleagues investigated the yield of ultrasound surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) in octogenarians, as compared with a younger population. Their goal was to detect the frequency of AAA growth reaching the threshold size for repair. Secondary objectives included analysis of the incidence of AAA repair, and the cost-effectiveness of surveillance.
In Saturday’s Scientific Session 8, Dr. Rockley will report on their retrospective cohort study performed on all patients undergoing AAA surveillance in Ottawa during 2007-2017. The patients were split into two groups by enrollment age (those younger and those equal to or older than 80 years of age) with cross-over to prevent lead-time bias, and stratification by enrollment AAA size.
The two cohorts were cross-referenced with the Ottawa Surgical Database, leveraging the common health region to assure complete data capture, according to Dr. Rockley.
The threshold size for repair was sex specific (women at 5.0cm, men at 5.5 cm) and the factors influencing AAA growth rate were assessed using multiple linear regression. Analyses with Cox proportional hazards and multiple regression models adjusted for sex and enrollment aneurysm size, and cost-effectiveness were analyzed by referencing Ontario billing codes.
The researchers found that 1,231 patients underwent serial ultrasound surveillance, of which 460 (37.4%) were octogenarians at the time of enrollment. Multiple linear regression demonstrated that old age, male sex, and smaller enrollment aneurysm size were significantly protective against AAA growth.
Overall, 355 (28.8%) subjects reached the AAA size threshold for repair, and 313 (25.4%) underwent AAA repair. Octogenarians were half as likely to reach the AAA threshold size for repair when compared with their younger counterparts, and of the 355 subjects whose AAA reached the threshold size for repair, octogenarians were half as likely to undergo elective AAA repair).
Repair of ruptured AAA was rare (0.94%) and age differences were insignificant. The cost of ultrasound surveillance alone to identify one patient who ultimately received elective AAA repair was more than four times more expensive for octogenarians with 3.0-3.9–cm enrollment aneurysms, when compared with the rest of the study sample ($12,080 vs. $2,915, in Canadian dollars, respectively), said Dr. Rockley.
“Our study showed that octogenarians are half as likely as their younger counterparts to experience aortic growth reaching th.e repair threshold size Furthermore, in the event of reaching the size threshold, octogenarians are half as likely to undergo repair, without a significantly increased risk of requiring repair for AAA rupture. In the context of patient-specific factors and wishes, surveillance of AAA less than 4cm in octogenarians is costly and unlikely to be beneficial.” Dr. Rockley concluded.
Saturday, June 15
8-9:30 a.m.
Gaylord National, Potomac A/B
S8: Scientific Session 8: SS29
To determine the necessity of permanent monitoring of small aortic aneurysms in the elderly, Mark Rockley, MD, of the Ottawa Hospital and his colleagues investigated the yield of ultrasound surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) in octogenarians, as compared with a younger population. Their goal was to detect the frequency of AAA growth reaching the threshold size for repair. Secondary objectives included analysis of the incidence of AAA repair, and the cost-effectiveness of surveillance.
In Saturday’s Scientific Session 8, Dr. Rockley will report on their retrospective cohort study performed on all patients undergoing AAA surveillance in Ottawa during 2007-2017. The patients were split into two groups by enrollment age (those younger and those equal to or older than 80 years of age) with cross-over to prevent lead-time bias, and stratification by enrollment AAA size.
The two cohorts were cross-referenced with the Ottawa Surgical Database, leveraging the common health region to assure complete data capture, according to Dr. Rockley.
The threshold size for repair was sex specific (women at 5.0cm, men at 5.5 cm) and the factors influencing AAA growth rate were assessed using multiple linear regression. Analyses with Cox proportional hazards and multiple regression models adjusted for sex and enrollment aneurysm size, and cost-effectiveness were analyzed by referencing Ontario billing codes.
The researchers found that 1,231 patients underwent serial ultrasound surveillance, of which 460 (37.4%) were octogenarians at the time of enrollment. Multiple linear regression demonstrated that old age, male sex, and smaller enrollment aneurysm size were significantly protective against AAA growth.
Overall, 355 (28.8%) subjects reached the AAA size threshold for repair, and 313 (25.4%) underwent AAA repair. Octogenarians were half as likely to reach the AAA threshold size for repair when compared with their younger counterparts, and of the 355 subjects whose AAA reached the threshold size for repair, octogenarians were half as likely to undergo elective AAA repair).
Repair of ruptured AAA was rare (0.94%) and age differences were insignificant. The cost of ultrasound surveillance alone to identify one patient who ultimately received elective AAA repair was more than four times more expensive for octogenarians with 3.0-3.9–cm enrollment aneurysms, when compared with the rest of the study sample ($12,080 vs. $2,915, in Canadian dollars, respectively), said Dr. Rockley.
“Our study showed that octogenarians are half as likely as their younger counterparts to experience aortic growth reaching th.e repair threshold size Furthermore, in the event of reaching the size threshold, octogenarians are half as likely to undergo repair, without a significantly increased risk of requiring repair for AAA rupture. In the context of patient-specific factors and wishes, surveillance of AAA less than 4cm in octogenarians is costly and unlikely to be beneficial.” Dr. Rockley concluded.
Saturday, June 15
8-9:30 a.m.
Gaylord National, Potomac A/B
S8: Scientific Session 8: SS29
To determine the necessity of permanent monitoring of small aortic aneurysms in the elderly, Mark Rockley, MD, of the Ottawa Hospital and his colleagues investigated the yield of ultrasound surveillance for small abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAAs) in octogenarians, as compared with a younger population. Their goal was to detect the frequency of AAA growth reaching the threshold size for repair. Secondary objectives included analysis of the incidence of AAA repair, and the cost-effectiveness of surveillance.
In Saturday’s Scientific Session 8, Dr. Rockley will report on their retrospective cohort study performed on all patients undergoing AAA surveillance in Ottawa during 2007-2017. The patients were split into two groups by enrollment age (those younger and those equal to or older than 80 years of age) with cross-over to prevent lead-time bias, and stratification by enrollment AAA size.
The two cohorts were cross-referenced with the Ottawa Surgical Database, leveraging the common health region to assure complete data capture, according to Dr. Rockley.
The threshold size for repair was sex specific (women at 5.0cm, men at 5.5 cm) and the factors influencing AAA growth rate were assessed using multiple linear regression. Analyses with Cox proportional hazards and multiple regression models adjusted for sex and enrollment aneurysm size, and cost-effectiveness were analyzed by referencing Ontario billing codes.
The researchers found that 1,231 patients underwent serial ultrasound surveillance, of which 460 (37.4%) were octogenarians at the time of enrollment. Multiple linear regression demonstrated that old age, male sex, and smaller enrollment aneurysm size were significantly protective against AAA growth.
Overall, 355 (28.8%) subjects reached the AAA size threshold for repair, and 313 (25.4%) underwent AAA repair. Octogenarians were half as likely to reach the AAA threshold size for repair when compared with their younger counterparts, and of the 355 subjects whose AAA reached the threshold size for repair, octogenarians were half as likely to undergo elective AAA repair).
Repair of ruptured AAA was rare (0.94%) and age differences were insignificant. The cost of ultrasound surveillance alone to identify one patient who ultimately received elective AAA repair was more than four times more expensive for octogenarians with 3.0-3.9–cm enrollment aneurysms, when compared with the rest of the study sample ($12,080 vs. $2,915, in Canadian dollars, respectively), said Dr. Rockley.
“Our study showed that octogenarians are half as likely as their younger counterparts to experience aortic growth reaching th.e repair threshold size Furthermore, in the event of reaching the size threshold, octogenarians are half as likely to undergo repair, without a significantly increased risk of requiring repair for AAA rupture. In the context of patient-specific factors and wishes, surveillance of AAA less than 4cm in octogenarians is costly and unlikely to be beneficial.” Dr. Rockley concluded.
Saturday, June 15
8-9:30 a.m.
Gaylord National, Potomac A/B
S8: Scientific Session 8: SS29