User login
Flu increase may be slowing
A bit of revisionist history has outpatient influenza activity at a lower level than was reported last week, even though it hasn’t dropped.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Feb. 10 was 7.5%, according to the Centers for Disease Control. That is lower than the 7.7% previously reported for the week ending Feb. 3, which would seem to be a drop, but the CDC also has revised that earlier number to 7.5%, so there is no change. (This is not the first time an earlier ILI level has been retroactively lowered: The figure reported for the week ending Jan. 13 was revised in the following report from 6.3% down to 6.0%.)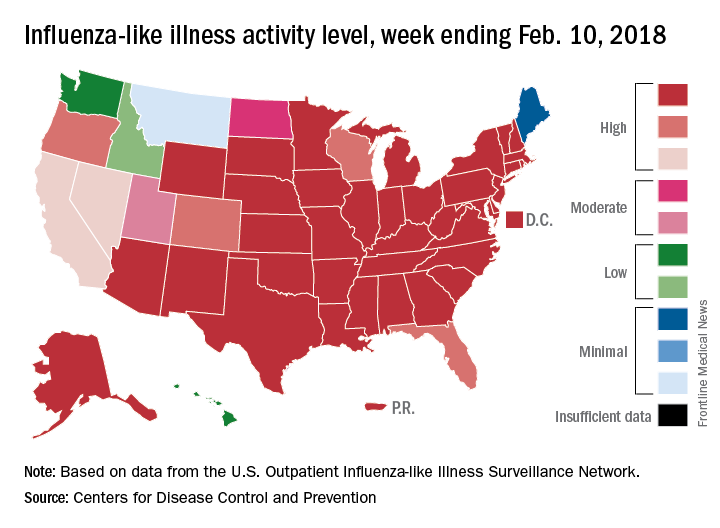
Hospital visits, however, continue to rise at record levels. The cumulative rate for the week ending Feb. 10 was 67.9 visits per 100,000 population, which is higher than the same week for the 2014-2015 (52.9 per 100,000) when flu hospitalizations for the season hit a high of 710,000. Flu-related pediatric deaths also went up, with 22 new reports; this brings the total to 84 for the 2017-2018 season.
A bit of revisionist history has outpatient influenza activity at a lower level than was reported last week, even though it hasn’t dropped.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Feb. 10 was 7.5%, according to the Centers for Disease Control. That is lower than the 7.7% previously reported for the week ending Feb. 3, which would seem to be a drop, but the CDC also has revised that earlier number to 7.5%, so there is no change. (This is not the first time an earlier ILI level has been retroactively lowered: The figure reported for the week ending Jan. 13 was revised in the following report from 6.3% down to 6.0%.)
Hospital visits, however, continue to rise at record levels. The cumulative rate for the week ending Feb. 10 was 67.9 visits per 100,000 population, which is higher than the same week for the 2014-2015 (52.9 per 100,000) when flu hospitalizations for the season hit a high of 710,000. Flu-related pediatric deaths also went up, with 22 new reports; this brings the total to 84 for the 2017-2018 season.
A bit of revisionist history has outpatient influenza activity at a lower level than was reported last week, even though it hasn’t dropped.
The proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) for the week ending Feb. 10 was 7.5%, according to the Centers for Disease Control. That is lower than the 7.7% previously reported for the week ending Feb. 3, which would seem to be a drop, but the CDC also has revised that earlier number to 7.5%, so there is no change. (This is not the first time an earlier ILI level has been retroactively lowered: The figure reported for the week ending Jan. 13 was revised in the following report from 6.3% down to 6.0%.)
Hospital visits, however, continue to rise at record levels. The cumulative rate for the week ending Feb. 10 was 67.9 visits per 100,000 population, which is higher than the same week for the 2014-2015 (52.9 per 100,000) when flu hospitalizations for the season hit a high of 710,000. Flu-related pediatric deaths also went up, with 22 new reports; this brings the total to 84 for the 2017-2018 season.
FROM THE CDC WEEKLY U.S. INFLUENZA SURVEILLANCE REPORT
MMWR: Current flu vaccine does not protect elderly
, according to the Feb. 16 issue of Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The elderly are not among them. Although the vaccine was somewhat protective in children and adults up to 49 years old, “no statistically significant protection was observed in other age groups,” including people 65 years and older, reported investigators led by Brendan Flannery, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention influenza division.
They also reported that the cumulative hospitalization rate attributed to laboratory-confirmed influenza for the week ending Feb. 3, 2018 (59.9/100,000), exceeded the rate for the same week in 2014-2015 (50.9/100,000), an A(H3N2) virus–predominant season, and is the highest rate observed for this week since the system expanded to include adults during the 2005-2006 season.
This year’s overall effectiveness rating was in contrast to the 2016-2017 seasonal effectiveness of 48% (MMWR. 2017 Feb 17;66[6];167-71).
The CDC noted that influenza is going to be active for several more weeks, so “vaccination is still recommended,” but “treatment with influenza antiviral medications, where appropriate, is especially important this season.” Meanwhile, “influenza vaccines with improved effectiveness are needed,” the CDC said.
The estimates are based on 4,562 patients 6 months to over 65 years old presenting with acute respiratory illness in 2018 from Nov. 2 to Feb. 3 at five outpatient medical clinics scattered across the United States. Nasal and oropharyngeal swabs were tested with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for the presence of influenza viruses; 413 subjects were 65 years or older.
Vaccine effectiveness against the less common virus A(H1N1)pdm09 was 67%, and 42% against the even rarer influenza B viruses. Estimates were adjusted for a range of confounders, including study site, age, general health, and week of illness. Vaccination rates ranged from 45% to 59% across the study sites; 38% of the subjects tested positive for influenza, most for type A viruses. The shot didn’t work too well: 43% of the influenza cases had gotten it.
The 25% effectiveness against A(H3N2) is a bit higher than recent reports of 17% from Canada and 10% from Australia, but similar to the 32% efficacy reported in the United States for the 2016-2017 season.
“These interim estimates reflect ongoing challenges with the A(H3N2) vaccine component since the 2011-12 season,” the investigators wrote. “Multiple factors might be contributing to the reported [vaccine effectiveness] against A(H3N2) viruses this season. … Genetic changes in the vaccine virus hemagglutinin protein that arise during passage in eggs might result in a vaccine immune response that is less effective against circulating viruses.”
On a related note, on Feb. 18, Senators Edward J. Markey (D-Mass.), Richard Blumenthal (D-Conn.), and Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.) held a press conference to announce they were introducing the Flu Vaccine Bill to dedicate $1 billion over a 5-year period in order to develop a flu vaccine that could provide lifetime protection.
The investigators had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Flannery B. et al. MMWR. 2018 Feb 16;67(6):180-5; Budd A. et al. MMWR. 2018 Feb 16;67(6):169-79.
, according to the Feb. 16 issue of Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The elderly are not among them. Although the vaccine was somewhat protective in children and adults up to 49 years old, “no statistically significant protection was observed in other age groups,” including people 65 years and older, reported investigators led by Brendan Flannery, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention influenza division.
They also reported that the cumulative hospitalization rate attributed to laboratory-confirmed influenza for the week ending Feb. 3, 2018 (59.9/100,000), exceeded the rate for the same week in 2014-2015 (50.9/100,000), an A(H3N2) virus–predominant season, and is the highest rate observed for this week since the system expanded to include adults during the 2005-2006 season.
This year’s overall effectiveness rating was in contrast to the 2016-2017 seasonal effectiveness of 48% (MMWR. 2017 Feb 17;66[6];167-71).
The CDC noted that influenza is going to be active for several more weeks, so “vaccination is still recommended,” but “treatment with influenza antiviral medications, where appropriate, is especially important this season.” Meanwhile, “influenza vaccines with improved effectiveness are needed,” the CDC said.
The estimates are based on 4,562 patients 6 months to over 65 years old presenting with acute respiratory illness in 2018 from Nov. 2 to Feb. 3 at five outpatient medical clinics scattered across the United States. Nasal and oropharyngeal swabs were tested with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for the presence of influenza viruses; 413 subjects were 65 years or older.
Vaccine effectiveness against the less common virus A(H1N1)pdm09 was 67%, and 42% against the even rarer influenza B viruses. Estimates were adjusted for a range of confounders, including study site, age, general health, and week of illness. Vaccination rates ranged from 45% to 59% across the study sites; 38% of the subjects tested positive for influenza, most for type A viruses. The shot didn’t work too well: 43% of the influenza cases had gotten it.
The 25% effectiveness against A(H3N2) is a bit higher than recent reports of 17% from Canada and 10% from Australia, but similar to the 32% efficacy reported in the United States for the 2016-2017 season.
“These interim estimates reflect ongoing challenges with the A(H3N2) vaccine component since the 2011-12 season,” the investigators wrote. “Multiple factors might be contributing to the reported [vaccine effectiveness] against A(H3N2) viruses this season. … Genetic changes in the vaccine virus hemagglutinin protein that arise during passage in eggs might result in a vaccine immune response that is less effective against circulating viruses.”
On a related note, on Feb. 18, Senators Edward J. Markey (D-Mass.), Richard Blumenthal (D-Conn.), and Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.) held a press conference to announce they were introducing the Flu Vaccine Bill to dedicate $1 billion over a 5-year period in order to develop a flu vaccine that could provide lifetime protection.
The investigators had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Flannery B. et al. MMWR. 2018 Feb 16;67(6):180-5; Budd A. et al. MMWR. 2018 Feb 16;67(6):169-79.
, according to the Feb. 16 issue of Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
The elderly are not among them. Although the vaccine was somewhat protective in children and adults up to 49 years old, “no statistically significant protection was observed in other age groups,” including people 65 years and older, reported investigators led by Brendan Flannery, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention influenza division.
They also reported that the cumulative hospitalization rate attributed to laboratory-confirmed influenza for the week ending Feb. 3, 2018 (59.9/100,000), exceeded the rate for the same week in 2014-2015 (50.9/100,000), an A(H3N2) virus–predominant season, and is the highest rate observed for this week since the system expanded to include adults during the 2005-2006 season.
This year’s overall effectiveness rating was in contrast to the 2016-2017 seasonal effectiveness of 48% (MMWR. 2017 Feb 17;66[6];167-71).
The CDC noted that influenza is going to be active for several more weeks, so “vaccination is still recommended,” but “treatment with influenza antiviral medications, where appropriate, is especially important this season.” Meanwhile, “influenza vaccines with improved effectiveness are needed,” the CDC said.
The estimates are based on 4,562 patients 6 months to over 65 years old presenting with acute respiratory illness in 2018 from Nov. 2 to Feb. 3 at five outpatient medical clinics scattered across the United States. Nasal and oropharyngeal swabs were tested with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction for the presence of influenza viruses; 413 subjects were 65 years or older.
Vaccine effectiveness against the less common virus A(H1N1)pdm09 was 67%, and 42% against the even rarer influenza B viruses. Estimates were adjusted for a range of confounders, including study site, age, general health, and week of illness. Vaccination rates ranged from 45% to 59% across the study sites; 38% of the subjects tested positive for influenza, most for type A viruses. The shot didn’t work too well: 43% of the influenza cases had gotten it.
The 25% effectiveness against A(H3N2) is a bit higher than recent reports of 17% from Canada and 10% from Australia, but similar to the 32% efficacy reported in the United States for the 2016-2017 season.
“These interim estimates reflect ongoing challenges with the A(H3N2) vaccine component since the 2011-12 season,” the investigators wrote. “Multiple factors might be contributing to the reported [vaccine effectiveness] against A(H3N2) viruses this season. … Genetic changes in the vaccine virus hemagglutinin protein that arise during passage in eggs might result in a vaccine immune response that is less effective against circulating viruses.”
On a related note, on Feb. 18, Senators Edward J. Markey (D-Mass.), Richard Blumenthal (D-Conn.), and Amy Klobuchar (D-Minn.) held a press conference to announce they were introducing the Flu Vaccine Bill to dedicate $1 billion over a 5-year period in order to develop a flu vaccine that could provide lifetime protection.
The investigators had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Flannery B. et al. MMWR. 2018 Feb 16;67(6):180-5; Budd A. et al. MMWR. 2018 Feb 16;67(6):169-79.
FROM MORBIDITY AND MORTALITY WEEKLY REPORT
This is what a flu pandemic looks like
For the week ending Feb. 3, 2018, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 7.7%, which would appear to equal the mark of 7.7% set in October of 2009. The earlier 7.7%, however, is rounded down from 7.715%, while the current mark is rounded up from 7.653%, data from the CDC’s Fluview website show.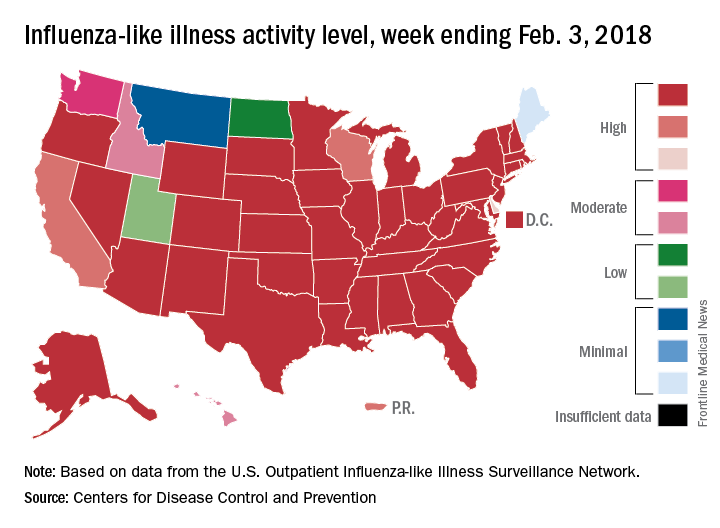
Deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were above the epidemic threshold set by the National Center for Health Statistics Mortality Surveillance system, acting CDC director Anne Schuchat, MD, said in a teleconference sponsored by the agency.
ILI activity was at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale in 41 states, compared with 34 the week before, and was categorized in the “high” range (levels 8-10) in another 3 states and Puerto Rico, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network. In California, which was noted as a possible bright spot last week by Dr. Schuchat because activity there had been decreasing, the ILI level went back up to level 9 after being at 7 the week before.
Flu-related hospitalizations are continuing to rise at a record clip, with the cumulative rate for the week of Feb. 3 at 59.9 per 100,000 population, the CDC reported. A total of 1 in 10 hospital-based deaths last week were related to influenza. At this point in the 2014-2015 flu season – which has the highest number of hospitalizations at 710,000 – the hospitalization rate was only 50.9 per 100,000 population.
There were 10 pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Feb. 3, although 9 occurred in previous weeks. There have been 63 flu-related deaths among children so far during the 2017-2018 season.
Dr. Schuchat continued to recommend members of the public to get a flu shot and to stay home if they are feeling sick.
“What could be mild symptoms for you could be deadly for someone else,” Dr. Schuchat said, adding that antiviral medications remain important. “Physicians do not have to wait for confirmatory flu testing. They should begin treatment with antiviral drugs immediately in they suspect they have a severely ill or a high risk patient.”
“Flu vaccines often have lower effectiveness against H3N1 viruses. However, some protection is better than none. The vaccine’s effectiveness against other flu viruses, like B and H1N1, is better. Because of the ongoing intensity of the flu season and the increasing circulation of influenza B and h1n1, we do continue to recommend vaccination even this late in the season.”
Dr. Schuchat stressed the importance of the pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. “Flu can make people more vulnerable to secondary infections like bacterial pneumonia. We recommend people aged 65 and over get a pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine,” she said.
For the week ending Feb. 3, 2018, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 7.7%, which would appear to equal the mark of 7.7% set in October of 2009. The earlier 7.7%, however, is rounded down from 7.715%, while the current mark is rounded up from 7.653%, data from the CDC’s Fluview website show.
Deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were above the epidemic threshold set by the National Center for Health Statistics Mortality Surveillance system, acting CDC director Anne Schuchat, MD, said in a teleconference sponsored by the agency.
ILI activity was at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale in 41 states, compared with 34 the week before, and was categorized in the “high” range (levels 8-10) in another 3 states and Puerto Rico, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network. In California, which was noted as a possible bright spot last week by Dr. Schuchat because activity there had been decreasing, the ILI level went back up to level 9 after being at 7 the week before.
Flu-related hospitalizations are continuing to rise at a record clip, with the cumulative rate for the week of Feb. 3 at 59.9 per 100,000 population, the CDC reported. A total of 1 in 10 hospital-based deaths last week were related to influenza. At this point in the 2014-2015 flu season – which has the highest number of hospitalizations at 710,000 – the hospitalization rate was only 50.9 per 100,000 population.
There were 10 pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Feb. 3, although 9 occurred in previous weeks. There have been 63 flu-related deaths among children so far during the 2017-2018 season.
Dr. Schuchat continued to recommend members of the public to get a flu shot and to stay home if they are feeling sick.
“What could be mild symptoms for you could be deadly for someone else,” Dr. Schuchat said, adding that antiviral medications remain important. “Physicians do not have to wait for confirmatory flu testing. They should begin treatment with antiviral drugs immediately in they suspect they have a severely ill or a high risk patient.”
“Flu vaccines often have lower effectiveness against H3N1 viruses. However, some protection is better than none. The vaccine’s effectiveness against other flu viruses, like B and H1N1, is better. Because of the ongoing intensity of the flu season and the increasing circulation of influenza B and h1n1, we do continue to recommend vaccination even this late in the season.”
Dr. Schuchat stressed the importance of the pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. “Flu can make people more vulnerable to secondary infections like bacterial pneumonia. We recommend people aged 65 and over get a pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine,” she said.
For the week ending Feb. 3, 2018, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) was 7.7%, which would appear to equal the mark of 7.7% set in October of 2009. The earlier 7.7%, however, is rounded down from 7.715%, while the current mark is rounded up from 7.653%, data from the CDC’s Fluview website show.
Deaths attributed to pneumonia and influenza were above the epidemic threshold set by the National Center for Health Statistics Mortality Surveillance system, acting CDC director Anne Schuchat, MD, said in a teleconference sponsored by the agency.
ILI activity was at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale in 41 states, compared with 34 the week before, and was categorized in the “high” range (levels 8-10) in another 3 states and Puerto Rico, according to data from the CDC’s Outpatient Influenza-like Illness Surveillance Network. In California, which was noted as a possible bright spot last week by Dr. Schuchat because activity there had been decreasing, the ILI level went back up to level 9 after being at 7 the week before.
Flu-related hospitalizations are continuing to rise at a record clip, with the cumulative rate for the week of Feb. 3 at 59.9 per 100,000 population, the CDC reported. A total of 1 in 10 hospital-based deaths last week were related to influenza. At this point in the 2014-2015 flu season – which has the highest number of hospitalizations at 710,000 – the hospitalization rate was only 50.9 per 100,000 population.
There were 10 pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Feb. 3, although 9 occurred in previous weeks. There have been 63 flu-related deaths among children so far during the 2017-2018 season.
Dr. Schuchat continued to recommend members of the public to get a flu shot and to stay home if they are feeling sick.
“What could be mild symptoms for you could be deadly for someone else,” Dr. Schuchat said, adding that antiviral medications remain important. “Physicians do not have to wait for confirmatory flu testing. They should begin treatment with antiviral drugs immediately in they suspect they have a severely ill or a high risk patient.”
“Flu vaccines often have lower effectiveness against H3N1 viruses. However, some protection is better than none. The vaccine’s effectiveness against other flu viruses, like B and H1N1, is better. Because of the ongoing intensity of the flu season and the increasing circulation of influenza B and h1n1, we do continue to recommend vaccination even this late in the season.”
Dr. Schuchat stressed the importance of the pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine. “Flu can make people more vulnerable to secondary infections like bacterial pneumonia. We recommend people aged 65 and over get a pneumococcal pneumonia vaccine,” she said.
FROM A CDC TELECONFERENCE
Hospitals filling as flu season worsens
Through the last full week of January, the cumulative “hospitalization rate is the highest we’ve seen,” acting Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Anne Schuchat, MD, said. For the current season so far, the hospitalization rate stands at 51.4 per 100,000 population, putting it on pace to top the total of 710,000 flu-related admissions that occurred during the 2014-2015 season, she said in a weekly briefing Feb. 2.
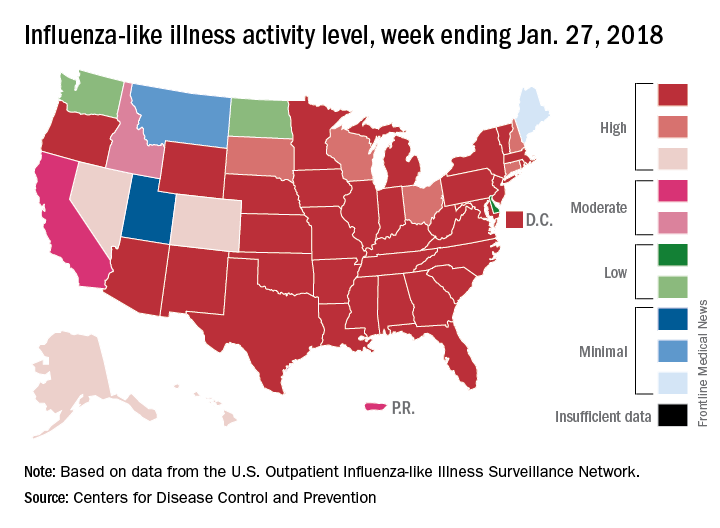
Flu-related pediatric deaths also took a big jump for the week as another 16 were reported, which brings the total for the season to 53. Of the children who have died so far, only 20% were vaccinated, said Dan Jernigan, MD, MPH, director of the influenza division at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta. He also noted that half of the children who have been hospitalized did not had an underlying condition.
The one bit of good news for the week was that activity in the West seems to be easing up, Dr. Schuchat said. The geographic spread of ILI was reported as widespread in 48 states, which is down from 49 the previous week because Oregon dropped off the list. To go along with that, the ILI activity level in California has dropped 2 weeks in a row and now stands at level 7, the CDC data show.
Through the last full week of January, the cumulative “hospitalization rate is the highest we’ve seen,” acting Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Anne Schuchat, MD, said. For the current season so far, the hospitalization rate stands at 51.4 per 100,000 population, putting it on pace to top the total of 710,000 flu-related admissions that occurred during the 2014-2015 season, she said in a weekly briefing Feb. 2.

Flu-related pediatric deaths also took a big jump for the week as another 16 were reported, which brings the total for the season to 53. Of the children who have died so far, only 20% were vaccinated, said Dan Jernigan, MD, MPH, director of the influenza division at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta. He also noted that half of the children who have been hospitalized did not had an underlying condition.
The one bit of good news for the week was that activity in the West seems to be easing up, Dr. Schuchat said. The geographic spread of ILI was reported as widespread in 48 states, which is down from 49 the previous week because Oregon dropped off the list. To go along with that, the ILI activity level in California has dropped 2 weeks in a row and now stands at level 7, the CDC data show.
Through the last full week of January, the cumulative “hospitalization rate is the highest we’ve seen,” acting Centers for Disease Control and Prevention director Anne Schuchat, MD, said. For the current season so far, the hospitalization rate stands at 51.4 per 100,000 population, putting it on pace to top the total of 710,000 flu-related admissions that occurred during the 2014-2015 season, she said in a weekly briefing Feb. 2.

Flu-related pediatric deaths also took a big jump for the week as another 16 were reported, which brings the total for the season to 53. Of the children who have died so far, only 20% were vaccinated, said Dan Jernigan, MD, MPH, director of the influenza division at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta. He also noted that half of the children who have been hospitalized did not had an underlying condition.
The one bit of good news for the week was that activity in the West seems to be easing up, Dr. Schuchat said. The geographic spread of ILI was reported as widespread in 48 states, which is down from 49 the previous week because Oregon dropped off the list. To go along with that, the ILI activity level in California has dropped 2 weeks in a row and now stands at level 7, the CDC data show.
Birth cohort affected 2015-2016 flu vaccine effectiveness
The influenza vaccine introduced in 2009 showed reduced effectiveness during the 2015-2016 influenza season, but only in adults born between 1958 and 1979, according to an analysis published online in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Using the Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network, researchers analyzed data from 2,115 patients with medically attended acute respiratory illness who tested positive for A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza virus, and 14,696 patients who tested negative for the influenza virus, from 2010-2011 to 2015-2016 (excluding the 2014-2015 influenza season).
Overall, 48% of the influenza virus–negative patients and 28% of the virus-positive patients had received at least one dose of the seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine more than 2 weeks before they fell ill.
However, the vaccine, which was based on the A/California/07/2009 strain of the A(H1N1)pdm09 virus, was only 47% effective during the 2015-2016 season, compared with 61% effectiveness during the 2010-2011 season through to the 2013-2014 season.
When researchers looked at vaccine effectiveness by birth cohort, they found that one particular cohort – individuals born between 1958 and 1979 – showed a significantly reduced vaccine effectiveness (22%) during the 2015-2016 season. By comparison, vaccine effectiveness in this cohort was 61% during the 2010-2013 seasons, and 56% during the 2013-2014 season.
When this birth cohort was excluded from analysis of the 2015-2016 season, the overall vaccine effectiveness for that season was 61%.
While the vaccine was based on an early reference strain of A(H1N1)pdm09, the virus itself later acquired mutations in the hemagglutinin gene, leading to the emergence of new genetic clades, including 6B, which dominated in the 2013-2014 influenza season, and 6B.1, which dominated in 2015-2016.
“Limited serologic data suggest that some adults born during 1958-1979 (age range in 2015-2016, 36-57 years) have decreased antibody titers against A(H1N1)pdm09 group 6B and 6B.1 viruses,” wrote Brendan Flannery, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and his coauthors.
They suggested that individuals in this cohort may have been immunologically primed with A/USSR/90/1977-like viruses, which were the first group of A(H1N1) viruses that this cohort would have been exposed to. A(H1N1) strains didn’t circulate between 1958 and 1977. Vaccination with A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses may have induced antibodies against shared antigenic components found on early versions of A(H1N1)pdm09.
If these shared antigenic epitopes were then altered in the later 6B and 6B.1 viruses, that might account for decreased antibody titers in this age group.
“Replacement of the A/California/07/2009(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine reference strain with A/Michigan/45/2015 (group 6B.1) should lead to improved [vaccine effectiveness] against circulating A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the investigators noted.
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Eight authors declared funding, grants, and consultancies with the pharmaceutical industry, with five also declaring funding from the CDC.
SOURCE: Flannery B et al. J Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix634.
This study proposes that influenza virus strains encountered early in life focus the immune response to later infection or vaccination on shared epitopes between the early and later strains. Supporting this hypothesis is evidence from other studies showing that 60% of the serological response to inactivated influenza vaccines is the result of boosting pre-existing antibodies, rather than the creation of new, vaccine-induced antibodies.
However there are also some flaws to this argument, and we should be careful to avoid confirmation bias. For example, the reduction in effectiveness of vaccines against A(H1N1) has been observed in North America, where this study is located, but to a lesser extent in studies conducted in other regions. Reductions in vaccine effectiveness have also been observed in other birth cohorts and during other influenza seasons.
That aside, accumulating evidence suggests that the vaccine strain be updated from A/California/7/2009 to A/Michigan/45/2015 (a clade 6B.1 strain) for the 2016-2017 influenza seasons.
Allen C. Cheng, PhD, is from the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine at Monash University, Melbourne, and Kanta Subbarao, MBBS, is from the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Influenza and the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, Australia. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (J Infect Dis. 2018, Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix635). The authors declared support from the Australian Department of Health and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
This study proposes that influenza virus strains encountered early in life focus the immune response to later infection or vaccination on shared epitopes between the early and later strains. Supporting this hypothesis is evidence from other studies showing that 60% of the serological response to inactivated influenza vaccines is the result of boosting pre-existing antibodies, rather than the creation of new, vaccine-induced antibodies.
However there are also some flaws to this argument, and we should be careful to avoid confirmation bias. For example, the reduction in effectiveness of vaccines against A(H1N1) has been observed in North America, where this study is located, but to a lesser extent in studies conducted in other regions. Reductions in vaccine effectiveness have also been observed in other birth cohorts and during other influenza seasons.
That aside, accumulating evidence suggests that the vaccine strain be updated from A/California/7/2009 to A/Michigan/45/2015 (a clade 6B.1 strain) for the 2016-2017 influenza seasons.
Allen C. Cheng, PhD, is from the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine at Monash University, Melbourne, and Kanta Subbarao, MBBS, is from the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Influenza and the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, Australia. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (J Infect Dis. 2018, Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix635). The authors declared support from the Australian Department of Health and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
This study proposes that influenza virus strains encountered early in life focus the immune response to later infection or vaccination on shared epitopes between the early and later strains. Supporting this hypothesis is evidence from other studies showing that 60% of the serological response to inactivated influenza vaccines is the result of boosting pre-existing antibodies, rather than the creation of new, vaccine-induced antibodies.
However there are also some flaws to this argument, and we should be careful to avoid confirmation bias. For example, the reduction in effectiveness of vaccines against A(H1N1) has been observed in North America, where this study is located, but to a lesser extent in studies conducted in other regions. Reductions in vaccine effectiveness have also been observed in other birth cohorts and during other influenza seasons.
That aside, accumulating evidence suggests that the vaccine strain be updated from A/California/7/2009 to A/Michigan/45/2015 (a clade 6B.1 strain) for the 2016-2017 influenza seasons.
Allen C. Cheng, PhD, is from the School of Public Health and Preventive Medicine at Monash University, Melbourne, and Kanta Subbarao, MBBS, is from the World Health Organization Collaborating Centre for Reference and Research on Influenza and the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity, Australia. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (J Infect Dis. 2018, Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix635). The authors declared support from the Australian Department of Health and the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council. No conflicts of interest were declared.
The influenza vaccine introduced in 2009 showed reduced effectiveness during the 2015-2016 influenza season, but only in adults born between 1958 and 1979, according to an analysis published online in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Using the Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network, researchers analyzed data from 2,115 patients with medically attended acute respiratory illness who tested positive for A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza virus, and 14,696 patients who tested negative for the influenza virus, from 2010-2011 to 2015-2016 (excluding the 2014-2015 influenza season).
Overall, 48% of the influenza virus–negative patients and 28% of the virus-positive patients had received at least one dose of the seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine more than 2 weeks before they fell ill.
However, the vaccine, which was based on the A/California/07/2009 strain of the A(H1N1)pdm09 virus, was only 47% effective during the 2015-2016 season, compared with 61% effectiveness during the 2010-2011 season through to the 2013-2014 season.
When researchers looked at vaccine effectiveness by birth cohort, they found that one particular cohort – individuals born between 1958 and 1979 – showed a significantly reduced vaccine effectiveness (22%) during the 2015-2016 season. By comparison, vaccine effectiveness in this cohort was 61% during the 2010-2013 seasons, and 56% during the 2013-2014 season.
When this birth cohort was excluded from analysis of the 2015-2016 season, the overall vaccine effectiveness for that season was 61%.
While the vaccine was based on an early reference strain of A(H1N1)pdm09, the virus itself later acquired mutations in the hemagglutinin gene, leading to the emergence of new genetic clades, including 6B, which dominated in the 2013-2014 influenza season, and 6B.1, which dominated in 2015-2016.
“Limited serologic data suggest that some adults born during 1958-1979 (age range in 2015-2016, 36-57 years) have decreased antibody titers against A(H1N1)pdm09 group 6B and 6B.1 viruses,” wrote Brendan Flannery, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and his coauthors.
They suggested that individuals in this cohort may have been immunologically primed with A/USSR/90/1977-like viruses, which were the first group of A(H1N1) viruses that this cohort would have been exposed to. A(H1N1) strains didn’t circulate between 1958 and 1977. Vaccination with A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses may have induced antibodies against shared antigenic components found on early versions of A(H1N1)pdm09.
If these shared antigenic epitopes were then altered in the later 6B and 6B.1 viruses, that might account for decreased antibody titers in this age group.
“Replacement of the A/California/07/2009(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine reference strain with A/Michigan/45/2015 (group 6B.1) should lead to improved [vaccine effectiveness] against circulating A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the investigators noted.
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Eight authors declared funding, grants, and consultancies with the pharmaceutical industry, with five also declaring funding from the CDC.
SOURCE: Flannery B et al. J Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix634.
The influenza vaccine introduced in 2009 showed reduced effectiveness during the 2015-2016 influenza season, but only in adults born between 1958 and 1979, according to an analysis published online in the Journal of Infectious Diseases.
Using the Influenza Vaccine Effectiveness Network, researchers analyzed data from 2,115 patients with medically attended acute respiratory illness who tested positive for A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza virus, and 14,696 patients who tested negative for the influenza virus, from 2010-2011 to 2015-2016 (excluding the 2014-2015 influenza season).
Overall, 48% of the influenza virus–negative patients and 28% of the virus-positive patients had received at least one dose of the seasonal inactivated influenza vaccine more than 2 weeks before they fell ill.
However, the vaccine, which was based on the A/California/07/2009 strain of the A(H1N1)pdm09 virus, was only 47% effective during the 2015-2016 season, compared with 61% effectiveness during the 2010-2011 season through to the 2013-2014 season.
When researchers looked at vaccine effectiveness by birth cohort, they found that one particular cohort – individuals born between 1958 and 1979 – showed a significantly reduced vaccine effectiveness (22%) during the 2015-2016 season. By comparison, vaccine effectiveness in this cohort was 61% during the 2010-2013 seasons, and 56% during the 2013-2014 season.
When this birth cohort was excluded from analysis of the 2015-2016 season, the overall vaccine effectiveness for that season was 61%.
While the vaccine was based on an early reference strain of A(H1N1)pdm09, the virus itself later acquired mutations in the hemagglutinin gene, leading to the emergence of new genetic clades, including 6B, which dominated in the 2013-2014 influenza season, and 6B.1, which dominated in 2015-2016.
“Limited serologic data suggest that some adults born during 1958-1979 (age range in 2015-2016, 36-57 years) have decreased antibody titers against A(H1N1)pdm09 group 6B and 6B.1 viruses,” wrote Brendan Flannery, PhD, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and his coauthors.
They suggested that individuals in this cohort may have been immunologically primed with A/USSR/90/1977-like viruses, which were the first group of A(H1N1) viruses that this cohort would have been exposed to. A(H1N1) strains didn’t circulate between 1958 and 1977. Vaccination with A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses may have induced antibodies against shared antigenic components found on early versions of A(H1N1)pdm09.
If these shared antigenic epitopes were then altered in the later 6B and 6B.1 viruses, that might account for decreased antibody titers in this age group.
“Replacement of the A/California/07/2009(H1N1)pdm09 vaccine reference strain with A/Michigan/45/2015 (group 6B.1) should lead to improved [vaccine effectiveness] against circulating A(H1N1)pdm09 viruses,” the investigators noted.
The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Eight authors declared funding, grants, and consultancies with the pharmaceutical industry, with five also declaring funding from the CDC.
SOURCE: Flannery B et al. J Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix634.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The influenza vaccine effectiveness during the 2015-2016 season was just 22% in individuals born between 1958 and 1979.
Data source: A retrospective case-control study of 2,115 patients who tested positive for A(H1N1)pdm09 influenza virus, and 14,696 negative controls.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the National Institutes of Health, and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Eight authors declared funding, grants, and consultancies with the pharmaceutical industry, with five also declaring funding from the CDC.
Source: Flannery B et al. J Infect Dis. 2018 Jan 18. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jix634.
CDC: Flu levels highest since pandemic year 2009
according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That season was dominated by influenza A (H3N2), and the 2017-2018 season seems to be going down that same path. For the week ending Jan. 20, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness increased to 6.6%, which is, for the second consecutive week, the highest level reported since October of – you guessed it – 2009, when it hit 7.7%, the CDC said in its weekly flu surveillance report.
The level reported last week, 6.3%, has been revised downward and now stands at an even 6%.
It turns out that 2018 is something of a milestone for the H3N2 virus. The virus first emerged in 1968, so it has reached its 50th anniversary, Dan Jernigan, MD, director of the influenza division at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said on Jan. 26 in a weekly briefing.
H3N2 must not be happy about hitting the big 5-0, however, because the map of influenza-like illness activity looks pretty red and angry. For the week ending Jan. 20, there were 30 states at the highest level of flu activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, with another nine in the “high” range at levels 8 and 9.
Dr. Jernigan did suggest that activity may have peaked in some areas of the country, with California among them.
There were seven pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Jan. 20, although six occurred in previous weeks. There have been 37 flu-related deaths among children so far during the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said.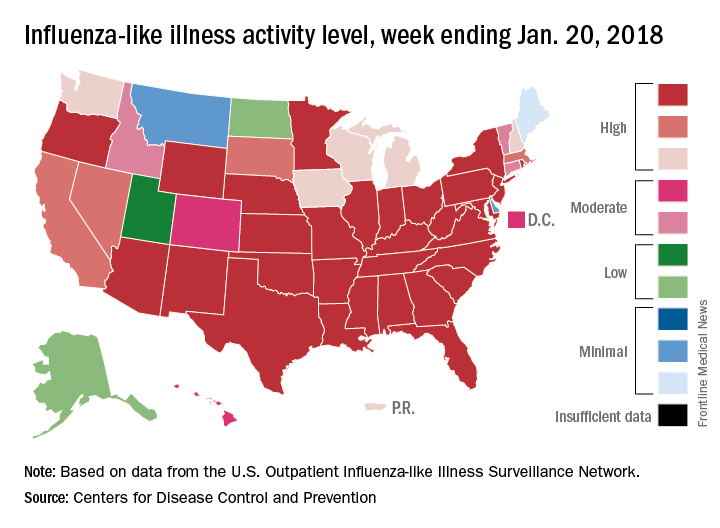
according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That season was dominated by influenza A (H3N2), and the 2017-2018 season seems to be going down that same path. For the week ending Jan. 20, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness increased to 6.6%, which is, for the second consecutive week, the highest level reported since October of – you guessed it – 2009, when it hit 7.7%, the CDC said in its weekly flu surveillance report.
The level reported last week, 6.3%, has been revised downward and now stands at an even 6%.
It turns out that 2018 is something of a milestone for the H3N2 virus. The virus first emerged in 1968, so it has reached its 50th anniversary, Dan Jernigan, MD, director of the influenza division at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said on Jan. 26 in a weekly briefing.
H3N2 must not be happy about hitting the big 5-0, however, because the map of influenza-like illness activity looks pretty red and angry. For the week ending Jan. 20, there were 30 states at the highest level of flu activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, with another nine in the “high” range at levels 8 and 9.
Dr. Jernigan did suggest that activity may have peaked in some areas of the country, with California among them.
There were seven pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Jan. 20, although six occurred in previous weeks. There have been 37 flu-related deaths among children so far during the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said.
according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
That season was dominated by influenza A (H3N2), and the 2017-2018 season seems to be going down that same path. For the week ending Jan. 20, the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness increased to 6.6%, which is, for the second consecutive week, the highest level reported since October of – you guessed it – 2009, when it hit 7.7%, the CDC said in its weekly flu surveillance report.
The level reported last week, 6.3%, has been revised downward and now stands at an even 6%.
It turns out that 2018 is something of a milestone for the H3N2 virus. The virus first emerged in 1968, so it has reached its 50th anniversary, Dan Jernigan, MD, director of the influenza division at the CDC’s National Center for Immunization and Respiratory Diseases, Atlanta, said on Jan. 26 in a weekly briefing.
H3N2 must not be happy about hitting the big 5-0, however, because the map of influenza-like illness activity looks pretty red and angry. For the week ending Jan. 20, there were 30 states at the highest level of flu activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, with another nine in the “high” range at levels 8 and 9.
Dr. Jernigan did suggest that activity may have peaked in some areas of the country, with California among them.
There were seven pediatric deaths reported for the week ending Jan. 20, although six occurred in previous weeks. There have been 37 flu-related deaths among children so far during the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said.
Influenza: All that and MI too
Myocardial infarction admissions were six times more likely to occur in the week after a positive test for influenza than in the year before or the 51 weeks after the infection, according to analysis of a Canadian cohort that links laboratories with administrative databases.
The investigators used this cohort data to define definitions of “risk interval” – the first 7 days after flu detection – and a combined “control interval” – 52 weeks before the flu detection and 51 weeks after the end of the risk interval.
Among the total of 364 hospital admissions for MI in patients with confirmed influenza, 20 occurred during the defined 1-week risk interval (20 admissions/week) and 344 occurred during the control interval (3.3 admissions/week), giving an incidence ratio (IR) of 6.05, Jeffrey C. Kwong, MD, of the University of Toronto and his associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
There was little difference between days 1 and 3 after flu confirmation (IR, 6.3) and days 4-7 (IR, 5.8), but risk dropped off quickly after that, with IRs of 0.6 at days 8-14 and 0.75 at days 15-28. Risk was increased for older adults, those with influenza B infection, and those who had their first MI, the investigators said.
MI incidence also was elevated after infection with noninfluenza respiratory viruses, although to a lesser extent than with influenza, which suggests that “influenza is illustrative of the role that acute respiratory infections have in precipitating acute myocardial infarction,” Dr. Kwong and his associates wrote.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, by Public Health Ontario, and by the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Kwong reported grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research during the conduct of the study, as well as grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research and University of Toronto.
SOURCE: Kwong JC et al. N Engl J Med. 2018. 378(4):345-53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1702090.
Myocardial infarction admissions were six times more likely to occur in the week after a positive test for influenza than in the year before or the 51 weeks after the infection, according to analysis of a Canadian cohort that links laboratories with administrative databases.
The investigators used this cohort data to define definitions of “risk interval” – the first 7 days after flu detection – and a combined “control interval” – 52 weeks before the flu detection and 51 weeks after the end of the risk interval.
Among the total of 364 hospital admissions for MI in patients with confirmed influenza, 20 occurred during the defined 1-week risk interval (20 admissions/week) and 344 occurred during the control interval (3.3 admissions/week), giving an incidence ratio (IR) of 6.05, Jeffrey C. Kwong, MD, of the University of Toronto and his associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
There was little difference between days 1 and 3 after flu confirmation (IR, 6.3) and days 4-7 (IR, 5.8), but risk dropped off quickly after that, with IRs of 0.6 at days 8-14 and 0.75 at days 15-28. Risk was increased for older adults, those with influenza B infection, and those who had their first MI, the investigators said.
MI incidence also was elevated after infection with noninfluenza respiratory viruses, although to a lesser extent than with influenza, which suggests that “influenza is illustrative of the role that acute respiratory infections have in precipitating acute myocardial infarction,” Dr. Kwong and his associates wrote.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, by Public Health Ontario, and by the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Kwong reported grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research during the conduct of the study, as well as grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research and University of Toronto.
SOURCE: Kwong JC et al. N Engl J Med. 2018. 378(4):345-53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1702090.
Myocardial infarction admissions were six times more likely to occur in the week after a positive test for influenza than in the year before or the 51 weeks after the infection, according to analysis of a Canadian cohort that links laboratories with administrative databases.
The investigators used this cohort data to define definitions of “risk interval” – the first 7 days after flu detection – and a combined “control interval” – 52 weeks before the flu detection and 51 weeks after the end of the risk interval.
Among the total of 364 hospital admissions for MI in patients with confirmed influenza, 20 occurred during the defined 1-week risk interval (20 admissions/week) and 344 occurred during the control interval (3.3 admissions/week), giving an incidence ratio (IR) of 6.05, Jeffrey C. Kwong, MD, of the University of Toronto and his associates reported in the New England Journal of Medicine.
There was little difference between days 1 and 3 after flu confirmation (IR, 6.3) and days 4-7 (IR, 5.8), but risk dropped off quickly after that, with IRs of 0.6 at days 8-14 and 0.75 at days 15-28. Risk was increased for older adults, those with influenza B infection, and those who had their first MI, the investigators said.
MI incidence also was elevated after infection with noninfluenza respiratory viruses, although to a lesser extent than with influenza, which suggests that “influenza is illustrative of the role that acute respiratory infections have in precipitating acute myocardial infarction,” Dr. Kwong and his associates wrote.
The study was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, by Public Health Ontario, and by the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences. Dr. Kwong reported grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research during the conduct of the study, as well as grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research and University of Toronto.
SOURCE: Kwong JC et al. N Engl J Med. 2018. 378(4):345-53. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1702090.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Flu season takes another turn for the worse
By one measure at least – the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) – this flu season is now the worst in almost a decade, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
which hit an early peak of 7.7% in October of 2009. The slight pause that occurred in the first week of January as the rate only rose from 5.7% to 5.8% now looks more like the earlier trend from December, when the level of outpatient visits more than doubled over a 3-week period, data from the CDC FluView website show.
“The geographic spread of influenza in Puerto Rico and 49 states was reported as widespread” for the week ending Jan. 13, and 24 states had the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, the CDC influenza division reported Jan 19.
There were 10 flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, with two occurring in the week ending Jan. 13. A total of 30 deaths in children have been associated with influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said.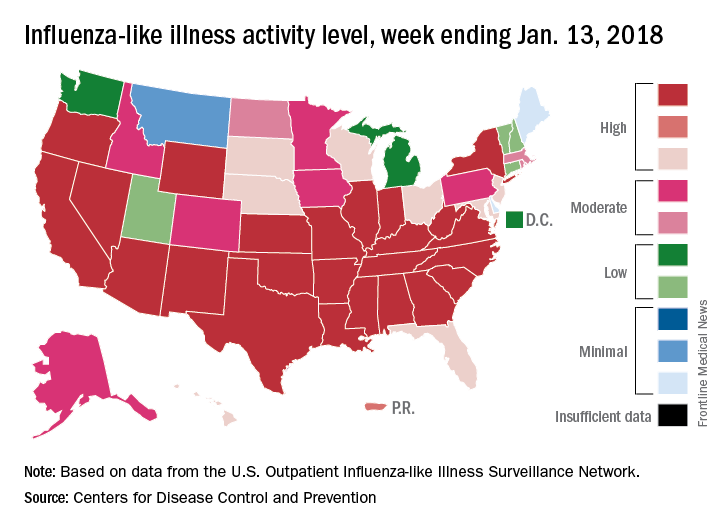
By one measure at least – the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) – this flu season is now the worst in almost a decade, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
which hit an early peak of 7.7% in October of 2009. The slight pause that occurred in the first week of January as the rate only rose from 5.7% to 5.8% now looks more like the earlier trend from December, when the level of outpatient visits more than doubled over a 3-week period, data from the CDC FluView website show.
“The geographic spread of influenza in Puerto Rico and 49 states was reported as widespread” for the week ending Jan. 13, and 24 states had the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, the CDC influenza division reported Jan 19.
There were 10 flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, with two occurring in the week ending Jan. 13. A total of 30 deaths in children have been associated with influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said.
By one measure at least – the proportion of outpatient visits for influenza-like illness (ILI) – this flu season is now the worst in almost a decade, according to data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
which hit an early peak of 7.7% in October of 2009. The slight pause that occurred in the first week of January as the rate only rose from 5.7% to 5.8% now looks more like the earlier trend from December, when the level of outpatient visits more than doubled over a 3-week period, data from the CDC FluView website show.
“The geographic spread of influenza in Puerto Rico and 49 states was reported as widespread” for the week ending Jan. 13, and 24 states had the highest level of ILI activity on the CDC’s 1-10 scale, the CDC influenza division reported Jan 19.
There were 10 flu-related pediatric deaths reported during the week, with two occurring in the week ending Jan. 13. A total of 30 deaths in children have been associated with influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said.
U.S. influenza activity widespread to start 2018
As far as the influenza virus is concerned, the new year started in the same way as the old one ended: with almost half of the states at the highest level of flu activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Jan. 6, 2018, there were 23 states – including California, Illinois, and Texas – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, which was up from 22 for the last full week of 2017. Joining the 23 states in the “high” range were New Jersey and Ohio at level 9 and Colorado at level 8, the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 12.
Seven flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week ending Jan. 6, although one occurred during the week ending Dec. 16 and two were during the week ending Dec. 23. There have been a total of 20 pediatric deaths related to influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said. In 2016-2017, there were 110 pediatric deaths from the flu.
As far as the influenza virus is concerned, the new year started in the same way as the old one ended: with almost half of the states at the highest level of flu activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Jan. 6, 2018, there were 23 states – including California, Illinois, and Texas – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, which was up from 22 for the last full week of 2017. Joining the 23 states in the “high” range were New Jersey and Ohio at level 9 and Colorado at level 8, the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 12.
Seven flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week ending Jan. 6, although one occurred during the week ending Dec. 16 and two were during the week ending Dec. 23. There have been a total of 20 pediatric deaths related to influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said. In 2016-2017, there were 110 pediatric deaths from the flu.
As far as the influenza virus is concerned, the new year started in the same way as the old one ended: with almost half of the states at the highest level of flu activity, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
For the week ending Jan. 6, 2018, there were 23 states – including California, Illinois, and Texas – at level 10 on the CDC’s 1-10 scale for influenza-like illness (ILI) activity, which was up from 22 for the last full week of 2017. Joining the 23 states in the “high” range were New Jersey and Ohio at level 9 and Colorado at level 8, the CDC’s influenza division reported Jan. 12.
Seven flu-related pediatric deaths were reported during the week ending Jan. 6, although one occurred during the week ending Dec. 16 and two were during the week ending Dec. 23. There have been a total of 20 pediatric deaths related to influenza so far for the 2017-2018 season, the CDC said. In 2016-2017, there were 110 pediatric deaths from the flu.
Don’t give up on influenza vaccine
I suspect most health care providers have heard the complaint, “The vaccine doesn’t work. One year I got the vaccine, and I still came down with the flu.”
Over the years, I’ve polished my responses to vaccine naysayers.
Influenza vaccine doesn’t protect you against every virus that can cause cold and flu symptoms. It only prevents influenza. It’s possible you had a different virus, such as adenovirus, coronavirus, parainfluenza virus, or respiratory syncytial virus.
Some years, the vaccine works better than others because there is a mismatch between the viruses chosen for the vaccine, and the viruses that end up circulating. Even when it doesn’t prevent flu, the vaccine can potentially reduce the severity of illness.
The discussion became a little more complicated in 2016 when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices withdrew its support for the live attenuated influenza virus vaccine (LAIV4) because of concerns about effectiveness. During the 2015-2016 influenza season, LAIV4 demonstrated no statistically significant effectiveness in children 2-17 years of age against H1N1pdm09, the predominant influenza strain. Fortunately, inactivated injectable vaccine did offer protection. An estimated 41.8 million children aged 6 months to 17 years ultimately received this vaccine during the 2016-2017 influenza season.
Now with the 2017-2018 influenza season in full swing, some media reports are proclaiming the influenza vaccine is only 10% effective this year. This claim is based on an interim analysis of data from the most recent flu season in Australia and the effectiveness of the vaccine against the circulating H3N2 virus strain. News from the U.S. CDC is more encouraging. The H3N2 virus contained in this year’s vaccine is the same as that used last year, and so far, circulating H3N2 viruses in the United States are similar to the vaccine virus. Public health officials suggest that we can hope that the vaccine works as well as it did last year, when overall vaccine effectiveness against all circulating flu viruses was 39%, and effectiveness against the H3N2 virus specifically was 32%.
I’m upping my game when talking to parents about flu vaccine. I mention one study conducted between 2010 and 2012 in which influenza immunization reduced a child’s risk of being admitted to an intensive care unit with flu by 74% (J Infect Dis. 2014 Sep 1;210[5]:674-83). I emphasize that flu vaccine reduces the chance that a child will die from flu. According to a study published in 2017, influenza vaccine reduced the risk of death from flu by 65% in healthy children and 51% in children with high-risk medical conditions (Pediatrics. 2017 May. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-4244).
When I’m talking to trainees, I no longer just focus on the match between circulating strains of flu and vaccine strains. I mention that viruses used to produce most seasonal flu vaccines are grown in eggs, a process that can result in minor antigenic changes in the hemagglutinin protein, especially in H3N2 viruses. These “egg-adapted changes” may result in a vaccine that stimulates a less effective immune response, even with a good match between circulating strains and vaccine strains. For example, Zost et al. found that the H3N2 virus that emerged during the 2014-2015 season possessed a new hemagglutinin-associated glycosylation site (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 21;114[47]:12578-83). Although this virus was represented in the 2016-2017 influenza vaccine, the egg-adapted version lost the glycosylation site, resulting in decreased vaccine immunogenicity and less protection against H3N2 viruses circulating in the community.
The real take-home message here is that we need better flu vaccines. In the short term, cell-based flu vaccines that use virus grown in animal cells are a potential alternative to egg-based vaccines. In the long term, we need a universal flu vaccine. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is prioritizing work on a vaccine that could provide long-lasting protection against multiple subtypes of the virus. According to a report on the National Institutes of Health website, such a vaccine could “eliminate the need to update and administer the seasonal flu vaccine each year and could provide protection against newly emerging flu strains,” including those with the potential to cause a pandemic. The NIH researchers acknowledge, however, that achieving this goal will require “a broad range of expertise and substantial resources.”
Until new vaccines are available, we need to do a better job of using available, albeit imperfect, flu vaccines. During the 2016-2017 season, only 59% of children 6 months to 17 years were immunized, and there were 110 influenza-associated deaths in children, according to the CDC. It’s likely that some of these were preventable.
The total magnitude of suffering associated with flu is more difficult to quantify, but anecdotes can be illuminating. A friend recently diagnosed with influenza shared her experience via Facebook. “Rough night. I’m seconds away from a meltdown. My body aches so bad that I can’t get comfortable on the couch or my bed. Can’t breathe, and I cough until I vomit. My head is about to burst along with my ears. Just took a hot bath hoping that would help. I don’t know what else to do. The flu really sucks.”
Indeed. Even a 1 in 10 chance of preventing the flu is better than no chance at all.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
I suspect most health care providers have heard the complaint, “The vaccine doesn’t work. One year I got the vaccine, and I still came down with the flu.”
Over the years, I’ve polished my responses to vaccine naysayers.
Influenza vaccine doesn’t protect you against every virus that can cause cold and flu symptoms. It only prevents influenza. It’s possible you had a different virus, such as adenovirus, coronavirus, parainfluenza virus, or respiratory syncytial virus.
Some years, the vaccine works better than others because there is a mismatch between the viruses chosen for the vaccine, and the viruses that end up circulating. Even when it doesn’t prevent flu, the vaccine can potentially reduce the severity of illness.
The discussion became a little more complicated in 2016 when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices withdrew its support for the live attenuated influenza virus vaccine (LAIV4) because of concerns about effectiveness. During the 2015-2016 influenza season, LAIV4 demonstrated no statistically significant effectiveness in children 2-17 years of age against H1N1pdm09, the predominant influenza strain. Fortunately, inactivated injectable vaccine did offer protection. An estimated 41.8 million children aged 6 months to 17 years ultimately received this vaccine during the 2016-2017 influenza season.
Now with the 2017-2018 influenza season in full swing, some media reports are proclaiming the influenza vaccine is only 10% effective this year. This claim is based on an interim analysis of data from the most recent flu season in Australia and the effectiveness of the vaccine against the circulating H3N2 virus strain. News from the U.S. CDC is more encouraging. The H3N2 virus contained in this year’s vaccine is the same as that used last year, and so far, circulating H3N2 viruses in the United States are similar to the vaccine virus. Public health officials suggest that we can hope that the vaccine works as well as it did last year, when overall vaccine effectiveness against all circulating flu viruses was 39%, and effectiveness against the H3N2 virus specifically was 32%.
I’m upping my game when talking to parents about flu vaccine. I mention one study conducted between 2010 and 2012 in which influenza immunization reduced a child’s risk of being admitted to an intensive care unit with flu by 74% (J Infect Dis. 2014 Sep 1;210[5]:674-83). I emphasize that flu vaccine reduces the chance that a child will die from flu. According to a study published in 2017, influenza vaccine reduced the risk of death from flu by 65% in healthy children and 51% in children with high-risk medical conditions (Pediatrics. 2017 May. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-4244).
When I’m talking to trainees, I no longer just focus on the match between circulating strains of flu and vaccine strains. I mention that viruses used to produce most seasonal flu vaccines are grown in eggs, a process that can result in minor antigenic changes in the hemagglutinin protein, especially in H3N2 viruses. These “egg-adapted changes” may result in a vaccine that stimulates a less effective immune response, even with a good match between circulating strains and vaccine strains. For example, Zost et al. found that the H3N2 virus that emerged during the 2014-2015 season possessed a new hemagglutinin-associated glycosylation site (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 21;114[47]:12578-83). Although this virus was represented in the 2016-2017 influenza vaccine, the egg-adapted version lost the glycosylation site, resulting in decreased vaccine immunogenicity and less protection against H3N2 viruses circulating in the community.
The real take-home message here is that we need better flu vaccines. In the short term, cell-based flu vaccines that use virus grown in animal cells are a potential alternative to egg-based vaccines. In the long term, we need a universal flu vaccine. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is prioritizing work on a vaccine that could provide long-lasting protection against multiple subtypes of the virus. According to a report on the National Institutes of Health website, such a vaccine could “eliminate the need to update and administer the seasonal flu vaccine each year and could provide protection against newly emerging flu strains,” including those with the potential to cause a pandemic. The NIH researchers acknowledge, however, that achieving this goal will require “a broad range of expertise and substantial resources.”
Until new vaccines are available, we need to do a better job of using available, albeit imperfect, flu vaccines. During the 2016-2017 season, only 59% of children 6 months to 17 years were immunized, and there were 110 influenza-associated deaths in children, according to the CDC. It’s likely that some of these were preventable.
The total magnitude of suffering associated with flu is more difficult to quantify, but anecdotes can be illuminating. A friend recently diagnosed with influenza shared her experience via Facebook. “Rough night. I’m seconds away from a meltdown. My body aches so bad that I can’t get comfortable on the couch or my bed. Can’t breathe, and I cough until I vomit. My head is about to burst along with my ears. Just took a hot bath hoping that would help. I don’t know what else to do. The flu really sucks.”
Indeed. Even a 1 in 10 chance of preventing the flu is better than no chance at all.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].
I suspect most health care providers have heard the complaint, “The vaccine doesn’t work. One year I got the vaccine, and I still came down with the flu.”
Over the years, I’ve polished my responses to vaccine naysayers.
Influenza vaccine doesn’t protect you against every virus that can cause cold and flu symptoms. It only prevents influenza. It’s possible you had a different virus, such as adenovirus, coronavirus, parainfluenza virus, or respiratory syncytial virus.
Some years, the vaccine works better than others because there is a mismatch between the viruses chosen for the vaccine, and the viruses that end up circulating. Even when it doesn’t prevent flu, the vaccine can potentially reduce the severity of illness.
The discussion became a little more complicated in 2016 when the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices withdrew its support for the live attenuated influenza virus vaccine (LAIV4) because of concerns about effectiveness. During the 2015-2016 influenza season, LAIV4 demonstrated no statistically significant effectiveness in children 2-17 years of age against H1N1pdm09, the predominant influenza strain. Fortunately, inactivated injectable vaccine did offer protection. An estimated 41.8 million children aged 6 months to 17 years ultimately received this vaccine during the 2016-2017 influenza season.
Now with the 2017-2018 influenza season in full swing, some media reports are proclaiming the influenza vaccine is only 10% effective this year. This claim is based on an interim analysis of data from the most recent flu season in Australia and the effectiveness of the vaccine against the circulating H3N2 virus strain. News from the U.S. CDC is more encouraging. The H3N2 virus contained in this year’s vaccine is the same as that used last year, and so far, circulating H3N2 viruses in the United States are similar to the vaccine virus. Public health officials suggest that we can hope that the vaccine works as well as it did last year, when overall vaccine effectiveness against all circulating flu viruses was 39%, and effectiveness against the H3N2 virus specifically was 32%.
I’m upping my game when talking to parents about flu vaccine. I mention one study conducted between 2010 and 2012 in which influenza immunization reduced a child’s risk of being admitted to an intensive care unit with flu by 74% (J Infect Dis. 2014 Sep 1;210[5]:674-83). I emphasize that flu vaccine reduces the chance that a child will die from flu. According to a study published in 2017, influenza vaccine reduced the risk of death from flu by 65% in healthy children and 51% in children with high-risk medical conditions (Pediatrics. 2017 May. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-4244).
When I’m talking to trainees, I no longer just focus on the match between circulating strains of flu and vaccine strains. I mention that viruses used to produce most seasonal flu vaccines are grown in eggs, a process that can result in minor antigenic changes in the hemagglutinin protein, especially in H3N2 viruses. These “egg-adapted changes” may result in a vaccine that stimulates a less effective immune response, even with a good match between circulating strains and vaccine strains. For example, Zost et al. found that the H3N2 virus that emerged during the 2014-2015 season possessed a new hemagglutinin-associated glycosylation site (Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017 Nov 21;114[47]:12578-83). Although this virus was represented in the 2016-2017 influenza vaccine, the egg-adapted version lost the glycosylation site, resulting in decreased vaccine immunogenicity and less protection against H3N2 viruses circulating in the community.
The real take-home message here is that we need better flu vaccines. In the short term, cell-based flu vaccines that use virus grown in animal cells are a potential alternative to egg-based vaccines. In the long term, we need a universal flu vaccine. The National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases is prioritizing work on a vaccine that could provide long-lasting protection against multiple subtypes of the virus. According to a report on the National Institutes of Health website, such a vaccine could “eliminate the need to update and administer the seasonal flu vaccine each year and could provide protection against newly emerging flu strains,” including those with the potential to cause a pandemic. The NIH researchers acknowledge, however, that achieving this goal will require “a broad range of expertise and substantial resources.”
Until new vaccines are available, we need to do a better job of using available, albeit imperfect, flu vaccines. During the 2016-2017 season, only 59% of children 6 months to 17 years were immunized, and there were 110 influenza-associated deaths in children, according to the CDC. It’s likely that some of these were preventable.
The total magnitude of suffering associated with flu is more difficult to quantify, but anecdotes can be illuminating. A friend recently diagnosed with influenza shared her experience via Facebook. “Rough night. I’m seconds away from a meltdown. My body aches so bad that I can’t get comfortable on the couch or my bed. Can’t breathe, and I cough until I vomit. My head is about to burst along with my ears. Just took a hot bath hoping that would help. I don’t know what else to do. The flu really sucks.”
Indeed. Even a 1 in 10 chance of preventing the flu is better than no chance at all.
Dr. Bryant is a pediatrician specializing in infectious diseases at the University of Louisville (Ky.) and Norton Children’s Hospital in Louisville. She said she had no relevant financial disclosures. Email her at [email protected].