User login
Mothers’ diabetes linked to ADHD in their children
Children born to women who develop diabetes either before or during their pregnancy could be at risk for developing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, data from a large multinational cohort study appear to show.
Considering more than 4.5 million mother-child pairs, it was found that children whose mothers had diabetes around the time of their pregnancy were 16% more likely to have ADHD diagnosed than were those whose mothers did not.
An increased risk was seen regardless of the type of diabetes, and regardless of whether or not the diabetes was present before or appeared during the pregnancy.
“We found a small increased risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes, including pregestational diabetes and gestational diabetes,” Carolyn Cesta, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Cesta, a postdoctoral researcher in the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm noted that the effect sizes seen were lower than had been reported previously.
“This may be because we adjusted for a large number of covariates, including maternal ADHD and psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Cesta said.
ADHD and diabetes
“Previous studies have reported an increase in the risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes,” explained Dr. Cesta.
However, “these studies have been limited by the use of self-reported data, small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for important confounders, and they’re often limited to [White] populations,” she added. “There’s a lot of heterogeneity between these studies,” she said.
To try to iron out the differences seen in the prior studies, Dr. Cesta and associates looked at data from several databases based in Hong Kong (Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System), four Nordic countries (Population Health Registers for Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden), and Taiwan (National Health Insurance Database).
To create the matched mother-child pairs, the databases were searched to find women who had children born between 2001 and 2018, and who had follow-up data available up to 2020 on not only their diabetes status and child’s ADHD status, but also other parameters, such as other maternal diagnoses, maternal medications, and a host of sociodemographic factors.
More than 24 potentially confounding or covariates were considered in the analysis, which used Cox proportional hazard regression modeling and propensity score analysis to calculate hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
“We looked at whether [mothers] had a diagnosis of ADHD themselves, or other psychiatric disorders, because there is high heritability for these disorders,” Dr. Cesta said, indicating that all bases had endeavored to be covered.
Main findings
Results showed some differences in the prevalence of diabetes and ADHD between the three cohorts used in the analysis. The prevalence of any maternal diabetes ranged from 8.8% in the Hong Kong cohort to 3.3% in the Taiwan cohort, with a prevalence of 6.8% for the Nordic cohort.
Rates of pregestational diabetes were lowest in the Taiwan and Hong Kong cohorts, at 0.2% and 0.5%, respectively, and 2.2% in the Nordic cohort. Gestational diabetes rates were a respective 3.1%, 7.8%, and 4.6%.
The highest rate of ADHD in children was seen in the Taiwan cohort, at 9.6%, followed by 4.2% for the Hong Kong cohort, and 2.6% for the Nordic cohort.
The hazard ratio for having childhood ADHD was 1.16 when comparing any maternal diabetes to no maternal diabetes, 1.40 comparing mothers with and without pregestational diabetes, and a respective 1.36 and 1.37 comparing those with and without type 1 diabetes, and those with and without type 2 diabetes.
The HR for childhood ADHD comparing mothers with and without gestational diabetes was 1.13.
“Within the analysis for gestational diabetes, we had enough numbers to look at siblings that are discordant for maternal gestational diabetes,” Dr. Cesta said. Essentially “we’re comparing two siblings from the same mother, one that was exposed to gestational diabetes, one that wasn’t,” she explained.
Interestingly there was no association between ADHD and maternal gestational diabetes in the sibling analysis (HR, 1.0).
“When it comes to gestational diabetes, the evidence from our sibling analysis indicate that the association may actually be confounded by shared genetics and environmental factors,” said Dr. Cesta.
“So, future studies should explore the role of specific genetic factors in glycemic control during pregnancy and the relationship between maternal diabetes and ADHD.”
Answering long-standing questions
These data will help a lot in answering questions that clinicians have been asking themselves a long time, commented Jardena Puder, MD, who chaired the session.
“It still remains a bit puzzling that genetic and environmental factors could be responsible, if you see the same effect in type 1 [diabetes], and in type 2 [diabetes], and gestational diabetes,” said Dr. Puder, who is an endocrinologist and diabetologist at the woman-mother-child department at the Vaud University Hospital Center, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Type 1 and type 2 are “very distinct” in terms of the genetic and environmental factors involved, “so, the fact that you see [the effect] in both remains a bit puzzling,” said Dr. Puder.
“I wish we had the numbers to be able to do the sibling analysis for type 1 and type 2, just to see if we could tease anything out,” said Dr. Cesta.
“I do think this is part of the bigger question of what the relationship is between, like, metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders, because even outside of pregnancy, we see that there’s often a comorbidity with them. So, it’s a good point.”
The next step is to look at the role of treatment and what effects glycemic control might have on the small, but still apparent, association between maternal diabetes and ADHD.
The study had multiple funders including the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, NordForsk, the Research Council of Norway, the Norwegian ADHD Research Network, the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, and European Horizon 2020.
Dr. Cesta had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Puder chaired the session in which the findings were presented and made no specific disclosures.
Children born to women who develop diabetes either before or during their pregnancy could be at risk for developing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, data from a large multinational cohort study appear to show.
Considering more than 4.5 million mother-child pairs, it was found that children whose mothers had diabetes around the time of their pregnancy were 16% more likely to have ADHD diagnosed than were those whose mothers did not.
An increased risk was seen regardless of the type of diabetes, and regardless of whether or not the diabetes was present before or appeared during the pregnancy.
“We found a small increased risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes, including pregestational diabetes and gestational diabetes,” Carolyn Cesta, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Cesta, a postdoctoral researcher in the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm noted that the effect sizes seen were lower than had been reported previously.
“This may be because we adjusted for a large number of covariates, including maternal ADHD and psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Cesta said.
ADHD and diabetes
“Previous studies have reported an increase in the risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes,” explained Dr. Cesta.
However, “these studies have been limited by the use of self-reported data, small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for important confounders, and they’re often limited to [White] populations,” she added. “There’s a lot of heterogeneity between these studies,” she said.
To try to iron out the differences seen in the prior studies, Dr. Cesta and associates looked at data from several databases based in Hong Kong (Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System), four Nordic countries (Population Health Registers for Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden), and Taiwan (National Health Insurance Database).
To create the matched mother-child pairs, the databases were searched to find women who had children born between 2001 and 2018, and who had follow-up data available up to 2020 on not only their diabetes status and child’s ADHD status, but also other parameters, such as other maternal diagnoses, maternal medications, and a host of sociodemographic factors.
More than 24 potentially confounding or covariates were considered in the analysis, which used Cox proportional hazard regression modeling and propensity score analysis to calculate hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
“We looked at whether [mothers] had a diagnosis of ADHD themselves, or other psychiatric disorders, because there is high heritability for these disorders,” Dr. Cesta said, indicating that all bases had endeavored to be covered.
Main findings
Results showed some differences in the prevalence of diabetes and ADHD between the three cohorts used in the analysis. The prevalence of any maternal diabetes ranged from 8.8% in the Hong Kong cohort to 3.3% in the Taiwan cohort, with a prevalence of 6.8% for the Nordic cohort.
Rates of pregestational diabetes were lowest in the Taiwan and Hong Kong cohorts, at 0.2% and 0.5%, respectively, and 2.2% in the Nordic cohort. Gestational diabetes rates were a respective 3.1%, 7.8%, and 4.6%.
The highest rate of ADHD in children was seen in the Taiwan cohort, at 9.6%, followed by 4.2% for the Hong Kong cohort, and 2.6% for the Nordic cohort.
The hazard ratio for having childhood ADHD was 1.16 when comparing any maternal diabetes to no maternal diabetes, 1.40 comparing mothers with and without pregestational diabetes, and a respective 1.36 and 1.37 comparing those with and without type 1 diabetes, and those with and without type 2 diabetes.
The HR for childhood ADHD comparing mothers with and without gestational diabetes was 1.13.
“Within the analysis for gestational diabetes, we had enough numbers to look at siblings that are discordant for maternal gestational diabetes,” Dr. Cesta said. Essentially “we’re comparing two siblings from the same mother, one that was exposed to gestational diabetes, one that wasn’t,” she explained.
Interestingly there was no association between ADHD and maternal gestational diabetes in the sibling analysis (HR, 1.0).
“When it comes to gestational diabetes, the evidence from our sibling analysis indicate that the association may actually be confounded by shared genetics and environmental factors,” said Dr. Cesta.
“So, future studies should explore the role of specific genetic factors in glycemic control during pregnancy and the relationship between maternal diabetes and ADHD.”
Answering long-standing questions
These data will help a lot in answering questions that clinicians have been asking themselves a long time, commented Jardena Puder, MD, who chaired the session.
“It still remains a bit puzzling that genetic and environmental factors could be responsible, if you see the same effect in type 1 [diabetes], and in type 2 [diabetes], and gestational diabetes,” said Dr. Puder, who is an endocrinologist and diabetologist at the woman-mother-child department at the Vaud University Hospital Center, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Type 1 and type 2 are “very distinct” in terms of the genetic and environmental factors involved, “so, the fact that you see [the effect] in both remains a bit puzzling,” said Dr. Puder.
“I wish we had the numbers to be able to do the sibling analysis for type 1 and type 2, just to see if we could tease anything out,” said Dr. Cesta.
“I do think this is part of the bigger question of what the relationship is between, like, metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders, because even outside of pregnancy, we see that there’s often a comorbidity with them. So, it’s a good point.”
The next step is to look at the role of treatment and what effects glycemic control might have on the small, but still apparent, association between maternal diabetes and ADHD.
The study had multiple funders including the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, NordForsk, the Research Council of Norway, the Norwegian ADHD Research Network, the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, and European Horizon 2020.
Dr. Cesta had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Puder chaired the session in which the findings were presented and made no specific disclosures.
Children born to women who develop diabetes either before or during their pregnancy could be at risk for developing attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, data from a large multinational cohort study appear to show.
Considering more than 4.5 million mother-child pairs, it was found that children whose mothers had diabetes around the time of their pregnancy were 16% more likely to have ADHD diagnosed than were those whose mothers did not.
An increased risk was seen regardless of the type of diabetes, and regardless of whether or not the diabetes was present before or appeared during the pregnancy.
“We found a small increased risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes, including pregestational diabetes and gestational diabetes,” Carolyn Cesta, PhD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Dr. Cesta, a postdoctoral researcher in the Centre for Pharmacoepidemiology at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm noted that the effect sizes seen were lower than had been reported previously.
“This may be because we adjusted for a large number of covariates, including maternal ADHD and psychiatric disorders,” Dr. Cesta said.
ADHD and diabetes
“Previous studies have reported an increase in the risk of ADHD in children born to mothers with diabetes,” explained Dr. Cesta.
However, “these studies have been limited by the use of self-reported data, small sample sizes, lack of adjustment for important confounders, and they’re often limited to [White] populations,” she added. “There’s a lot of heterogeneity between these studies,” she said.
To try to iron out the differences seen in the prior studies, Dr. Cesta and associates looked at data from several databases based in Hong Kong (Clinical Data Analysis and Reporting System), four Nordic countries (Population Health Registers for Finland, Iceland, Norway, and Sweden), and Taiwan (National Health Insurance Database).
To create the matched mother-child pairs, the databases were searched to find women who had children born between 2001 and 2018, and who had follow-up data available up to 2020 on not only their diabetes status and child’s ADHD status, but also other parameters, such as other maternal diagnoses, maternal medications, and a host of sociodemographic factors.
More than 24 potentially confounding or covariates were considered in the analysis, which used Cox proportional hazard regression modeling and propensity score analysis to calculate hazard ratios with 95% confidence intervals.
“We looked at whether [mothers] had a diagnosis of ADHD themselves, or other psychiatric disorders, because there is high heritability for these disorders,” Dr. Cesta said, indicating that all bases had endeavored to be covered.
Main findings
Results showed some differences in the prevalence of diabetes and ADHD between the three cohorts used in the analysis. The prevalence of any maternal diabetes ranged from 8.8% in the Hong Kong cohort to 3.3% in the Taiwan cohort, with a prevalence of 6.8% for the Nordic cohort.
Rates of pregestational diabetes were lowest in the Taiwan and Hong Kong cohorts, at 0.2% and 0.5%, respectively, and 2.2% in the Nordic cohort. Gestational diabetes rates were a respective 3.1%, 7.8%, and 4.6%.
The highest rate of ADHD in children was seen in the Taiwan cohort, at 9.6%, followed by 4.2% for the Hong Kong cohort, and 2.6% for the Nordic cohort.
The hazard ratio for having childhood ADHD was 1.16 when comparing any maternal diabetes to no maternal diabetes, 1.40 comparing mothers with and without pregestational diabetes, and a respective 1.36 and 1.37 comparing those with and without type 1 diabetes, and those with and without type 2 diabetes.
The HR for childhood ADHD comparing mothers with and without gestational diabetes was 1.13.
“Within the analysis for gestational diabetes, we had enough numbers to look at siblings that are discordant for maternal gestational diabetes,” Dr. Cesta said. Essentially “we’re comparing two siblings from the same mother, one that was exposed to gestational diabetes, one that wasn’t,” she explained.
Interestingly there was no association between ADHD and maternal gestational diabetes in the sibling analysis (HR, 1.0).
“When it comes to gestational diabetes, the evidence from our sibling analysis indicate that the association may actually be confounded by shared genetics and environmental factors,” said Dr. Cesta.
“So, future studies should explore the role of specific genetic factors in glycemic control during pregnancy and the relationship between maternal diabetes and ADHD.”
Answering long-standing questions
These data will help a lot in answering questions that clinicians have been asking themselves a long time, commented Jardena Puder, MD, who chaired the session.
“It still remains a bit puzzling that genetic and environmental factors could be responsible, if you see the same effect in type 1 [diabetes], and in type 2 [diabetes], and gestational diabetes,” said Dr. Puder, who is an endocrinologist and diabetologist at the woman-mother-child department at the Vaud University Hospital Center, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Type 1 and type 2 are “very distinct” in terms of the genetic and environmental factors involved, “so, the fact that you see [the effect] in both remains a bit puzzling,” said Dr. Puder.
“I wish we had the numbers to be able to do the sibling analysis for type 1 and type 2, just to see if we could tease anything out,” said Dr. Cesta.
“I do think this is part of the bigger question of what the relationship is between, like, metabolic disorders and psychiatric disorders, because even outside of pregnancy, we see that there’s often a comorbidity with them. So, it’s a good point.”
The next step is to look at the role of treatment and what effects glycemic control might have on the small, but still apparent, association between maternal diabetes and ADHD.
The study had multiple funders including the Hong Kong Research Grant Council, NordForsk, the Research Council of Norway, the Norwegian ADHD Research Network, the Hong Kong Innovation and Technology Commission, and European Horizon 2020.
Dr. Cesta had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. Puder chaired the session in which the findings were presented and made no specific disclosures.
FROM EASD 2022
Triple threat: Novel agent shows potent T2D weight loss in phase 1
STOCKHOLM – First came the GLP-1 receptor agonists as treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes, then came tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which added a second incretin agonism for the receptor to the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Now coming onto the clinical scene is a molecule with triple agonism to the GLP-1 receptor, the GIP receptor, and to the glucagon receptor.
That molecule, LY3437943, showed reasonable safety and tolerability and an apparent incremental uptick in weight loss compared with the approved incretin-based agents for people with type 2 diabetes in a 12-week, dose-ranging study involving a 52 patients with type 2 diabetes who received the new agent.
The 12 people who uptitrated for a total of 12 weeks and reached the highest tested dose of LY3437943, 12 mg, injected once weekly during the final 4 weeks, showed an average weight loss of 8.65 kg, while the 11 patients who maxed out at a weekly dose of 6 mg of LY3437943 had an average 12-week weight loss of 7.52 kg, Zvonko Milicevic, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Fifteen more participants received placebo and five received a comparator GLP-1 receptor agonist. All 72 patients in the study were also already on treatment with metformin when they entered, and they were maintained on metformin throughout the study period.
The new agent showed “greater weight loss efficacy than currently approved medications,” said Dr. Milicevic, a staff researcher who works in Vienna for Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943.
‘Really impressive’ weight loss
Martin Haluzik, MD, who chaired the session where Dr. Milicevic spoke, agreed. “The data, especially for weight reduction, were really impressive,” Dr. Haluzik said in an interview. “It looks stronger than the best we have at the moment,” the dual incretin agonist tirzepatide, he added.
Cross-study comparisons are very unreliable, but to put the weight loss seen with LY3437943 in perspective, the 12-week weight reduction that occurred with the highest dose of tirzepatide tested (15 mg/weekly) in the pivotal SURPASS-2 trial with 1,879 randomized patients with type 2 diabetes was an average of roughly 5 kg, while the comparator of 1 mg weekly of semaglutide (Ozempic) tested in the same study produced an average weight loss of about 4 kg.
Other notable efficacy results for LY3437943 after 12 weeks on treatment included an average reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline of 1.90%, achieved in the group that received 6 mg weekly as their maximum dose for 8 weeks after a 4-week run-in at a lower dose; a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 7.99 mm Hg on the 6-mg maximum weekly dose and of 12.06 mm Hg on the maximum 12-mg weekly dose; and “robust” reductions in lipids including cuts from baseline of about 40% for both triglycerides and very-LDL cholesterol, Dr. Milicevic reported.
Adverse effects resemble approved incretin-based agents
The study, which ran at four U.S. sites, had a primary objective of safety assessment, and Dr. Milicevic said the results showed acceptable safety and tolerability consistent with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and tirzepatide. Like those agents, LY3437943 caused primarily mild gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Of the 52 patients in the study who received the triple agonist, 4 discontinued treatment because of a treatment-emergent adverse effect, including 1 patient in the subgroup who received the maximum dose.
The only concerning adverse effect noted by Dr. Haluzik was the average increase in heart rate from baseline of 10.26 beats/min in the subgroup that received the maximum dose, roughly twice the increase seen with tirzepatide and semaglutide in SURPASS-2. The average heart rate increase was about half that, 5.30 beats/min compared with baseline, in the subgroup that received a maximum weekly dose of 6 mg.
Overall, the results showed “no major adverse effects that might hamper use,” said Dr. Haluzik, an endocrinologist and professor at Charles University in Prague.
Two phase 2 studies of LY3437943 are underway and are scheduled to finish before the end of 2022. They include a study of about 300 people with type 2 diabetes that’s running at 43 U.S. sites, and a second study of about 500 people with overweight or obesity running at 28 U.S. sites.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943. Dr. Milicevic is an employee of and stockholder of Eli Lilly. Dr. Haluzik has been an adviser to, consultant to, and received honoraria and research support from Eli Lilly. He has had similar relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
STOCKHOLM – First came the GLP-1 receptor agonists as treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes, then came tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which added a second incretin agonism for the receptor to the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Now coming onto the clinical scene is a molecule with triple agonism to the GLP-1 receptor, the GIP receptor, and to the glucagon receptor.
That molecule, LY3437943, showed reasonable safety and tolerability and an apparent incremental uptick in weight loss compared with the approved incretin-based agents for people with type 2 diabetes in a 12-week, dose-ranging study involving a 52 patients with type 2 diabetes who received the new agent.
The 12 people who uptitrated for a total of 12 weeks and reached the highest tested dose of LY3437943, 12 mg, injected once weekly during the final 4 weeks, showed an average weight loss of 8.65 kg, while the 11 patients who maxed out at a weekly dose of 6 mg of LY3437943 had an average 12-week weight loss of 7.52 kg, Zvonko Milicevic, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Fifteen more participants received placebo and five received a comparator GLP-1 receptor agonist. All 72 patients in the study were also already on treatment with metformin when they entered, and they were maintained on metformin throughout the study period.
The new agent showed “greater weight loss efficacy than currently approved medications,” said Dr. Milicevic, a staff researcher who works in Vienna for Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943.
‘Really impressive’ weight loss
Martin Haluzik, MD, who chaired the session where Dr. Milicevic spoke, agreed. “The data, especially for weight reduction, were really impressive,” Dr. Haluzik said in an interview. “It looks stronger than the best we have at the moment,” the dual incretin agonist tirzepatide, he added.
Cross-study comparisons are very unreliable, but to put the weight loss seen with LY3437943 in perspective, the 12-week weight reduction that occurred with the highest dose of tirzepatide tested (15 mg/weekly) in the pivotal SURPASS-2 trial with 1,879 randomized patients with type 2 diabetes was an average of roughly 5 kg, while the comparator of 1 mg weekly of semaglutide (Ozempic) tested in the same study produced an average weight loss of about 4 kg.
Other notable efficacy results for LY3437943 after 12 weeks on treatment included an average reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline of 1.90%, achieved in the group that received 6 mg weekly as their maximum dose for 8 weeks after a 4-week run-in at a lower dose; a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 7.99 mm Hg on the 6-mg maximum weekly dose and of 12.06 mm Hg on the maximum 12-mg weekly dose; and “robust” reductions in lipids including cuts from baseline of about 40% for both triglycerides and very-LDL cholesterol, Dr. Milicevic reported.
Adverse effects resemble approved incretin-based agents
The study, which ran at four U.S. sites, had a primary objective of safety assessment, and Dr. Milicevic said the results showed acceptable safety and tolerability consistent with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and tirzepatide. Like those agents, LY3437943 caused primarily mild gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Of the 52 patients in the study who received the triple agonist, 4 discontinued treatment because of a treatment-emergent adverse effect, including 1 patient in the subgroup who received the maximum dose.
The only concerning adverse effect noted by Dr. Haluzik was the average increase in heart rate from baseline of 10.26 beats/min in the subgroup that received the maximum dose, roughly twice the increase seen with tirzepatide and semaglutide in SURPASS-2. The average heart rate increase was about half that, 5.30 beats/min compared with baseline, in the subgroup that received a maximum weekly dose of 6 mg.
Overall, the results showed “no major adverse effects that might hamper use,” said Dr. Haluzik, an endocrinologist and professor at Charles University in Prague.
Two phase 2 studies of LY3437943 are underway and are scheduled to finish before the end of 2022. They include a study of about 300 people with type 2 diabetes that’s running at 43 U.S. sites, and a second study of about 500 people with overweight or obesity running at 28 U.S. sites.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943. Dr. Milicevic is an employee of and stockholder of Eli Lilly. Dr. Haluzik has been an adviser to, consultant to, and received honoraria and research support from Eli Lilly. He has had similar relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
STOCKHOLM – First came the GLP-1 receptor agonists as treatments for patients with type 2 diabetes, then came tirzepatide (Mounjaro) which added a second incretin agonism for the receptor to the glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP). Now coming onto the clinical scene is a molecule with triple agonism to the GLP-1 receptor, the GIP receptor, and to the glucagon receptor.
That molecule, LY3437943, showed reasonable safety and tolerability and an apparent incremental uptick in weight loss compared with the approved incretin-based agents for people with type 2 diabetes in a 12-week, dose-ranging study involving a 52 patients with type 2 diabetes who received the new agent.
The 12 people who uptitrated for a total of 12 weeks and reached the highest tested dose of LY3437943, 12 mg, injected once weekly during the final 4 weeks, showed an average weight loss of 8.65 kg, while the 11 patients who maxed out at a weekly dose of 6 mg of LY3437943 had an average 12-week weight loss of 7.52 kg, Zvonko Milicevic, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Fifteen more participants received placebo and five received a comparator GLP-1 receptor agonist. All 72 patients in the study were also already on treatment with metformin when they entered, and they were maintained on metformin throughout the study period.
The new agent showed “greater weight loss efficacy than currently approved medications,” said Dr. Milicevic, a staff researcher who works in Vienna for Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943.
‘Really impressive’ weight loss
Martin Haluzik, MD, who chaired the session where Dr. Milicevic spoke, agreed. “The data, especially for weight reduction, were really impressive,” Dr. Haluzik said in an interview. “It looks stronger than the best we have at the moment,” the dual incretin agonist tirzepatide, he added.
Cross-study comparisons are very unreliable, but to put the weight loss seen with LY3437943 in perspective, the 12-week weight reduction that occurred with the highest dose of tirzepatide tested (15 mg/weekly) in the pivotal SURPASS-2 trial with 1,879 randomized patients with type 2 diabetes was an average of roughly 5 kg, while the comparator of 1 mg weekly of semaglutide (Ozempic) tested in the same study produced an average weight loss of about 4 kg.
Other notable efficacy results for LY3437943 after 12 weeks on treatment included an average reduction in hemoglobin A1c from baseline of 1.90%, achieved in the group that received 6 mg weekly as their maximum dose for 8 weeks after a 4-week run-in at a lower dose; a reduction in systolic blood pressure of 7.99 mm Hg on the 6-mg maximum weekly dose and of 12.06 mm Hg on the maximum 12-mg weekly dose; and “robust” reductions in lipids including cuts from baseline of about 40% for both triglycerides and very-LDL cholesterol, Dr. Milicevic reported.
Adverse effects resemble approved incretin-based agents
The study, which ran at four U.S. sites, had a primary objective of safety assessment, and Dr. Milicevic said the results showed acceptable safety and tolerability consistent with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonists and tirzepatide. Like those agents, LY3437943 caused primarily mild gastrointestinal adverse effects such as nausea and diarrhea. Of the 52 patients in the study who received the triple agonist, 4 discontinued treatment because of a treatment-emergent adverse effect, including 1 patient in the subgroup who received the maximum dose.
The only concerning adverse effect noted by Dr. Haluzik was the average increase in heart rate from baseline of 10.26 beats/min in the subgroup that received the maximum dose, roughly twice the increase seen with tirzepatide and semaglutide in SURPASS-2. The average heart rate increase was about half that, 5.30 beats/min compared with baseline, in the subgroup that received a maximum weekly dose of 6 mg.
Overall, the results showed “no major adverse effects that might hamper use,” said Dr. Haluzik, an endocrinologist and professor at Charles University in Prague.
Two phase 2 studies of LY3437943 are underway and are scheduled to finish before the end of 2022. They include a study of about 300 people with type 2 diabetes that’s running at 43 U.S. sites, and a second study of about 500 people with overweight or obesity running at 28 U.S. sites.
The study was sponsored by Eli Lilly, the company developing LY3437943. Dr. Milicevic is an employee of and stockholder of Eli Lilly. Dr. Haluzik has been an adviser to, consultant to, and received honoraria and research support from Eli Lilly. He has had similar relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, BristolMyersSquibb, Janssen, Johnson & Johnson, Mundipharma, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
AT EASD 2022
‘Amazing’ data for cheap beta-blocker gel for diabetic foot ulcers
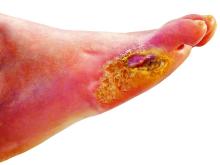
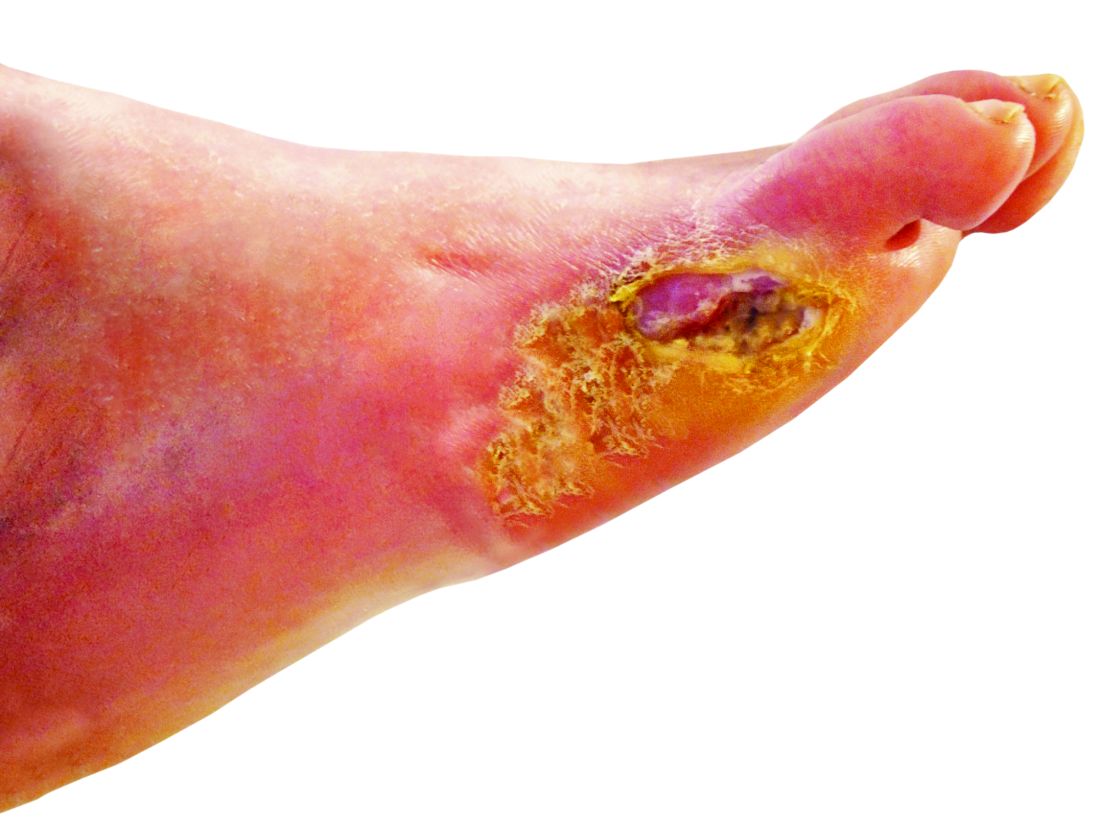
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Esmolol hydrochloride gel (Galnobax, NovoLead) appears to be a safe and effective novel topical treatment option for diabetic foot ulcers, according to results from a new trial of the drug, which is widely available as a generic and is inexpensive.
Of note, the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure at 12 weeks with esmolol (plus standard of care) was around 60% compared with just over 40% in patients who received standard of care alone.
Presenting the findings at this year’s annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes was Ashu Rastogi, MD, a professor of endocrinology at the Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research in Chandigarh, India.
“Esmolol can be given topically as a 14% gel and is a novel treatment option in diabetic foot ulcer,” said Dr. Rastogi.
Esmolol, a short-acting beta-adrenergic blocker, is currently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for cardiac indications only, such as short-term use for controlling supraventricular tachycardia. Beta-blockers are also used to treat hypertension.
However, esmolol has also been repurposed and formulated as a topical gel for the treatment of hard-to-heal diabetic foot ulcers (mainly neuropathic grade 1).
Audience member Ketan Dhatariya, MBBS, MD, PhD, a National Health Service consultant in diabetes, endocrinology, and general medicine and honorary senior lecturer at Norfolk and Norwich University Hospitals, England, enthused about the findings.
“This is an amazing study. I’m part of a working group looking at the updating of a guideline for the International Working Group of the Diabetic Foot, reviewing all the studies on wound healing, specifically pharmacological interventions. This is way beyond anything shown to date in terms of medical intervention. [The authors] should be congratulated; this is really astounding,” he told this news organization.
“Right now, there is very little out there in terms of pharmacological interventions that have shown benefit,” he added. “Once this study has been peer-reviewed and is published properly, it is potentially game-changing because it is a generic, worldwide, cheap, and freely available medication.”
Study across 27 sites in India
Prior phase 1/2 data have shown that 60% of ulcers completely closed with esmolol (14% gel) compared with 39% with standard of care. Encouraged by these findings, a phase 3 randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study was conducted across 27 sites in India.
Patients were a mean age of 56 years, and had a body mass index (BMI) of 25-26 kg/m2 and mean hemoglobin A1c of 8.4%-8.7%. Around 70% of participants were men. Mean ulcer area was approximately 460-500 mm2, two-thirds of the ulcers were plantar, and mean ulcer duration was 40-50 weeks.
After screening and discontinuations (39 participants), a 12-week treatment phase began with patients randomized to one of three groups: esmolol (14% gel) along with standard of care administered twice daily (57 completers); standard of care only (63 completers); or vehicle gel (placebo) along with standard of care administered twice daily (17 completers).
Standard of care comprised wound cleaning, debridement, maintenance of moist wound environment, twice-daily fresh bandages, and off-loading footwear as needed, and was provided to all participants irrespective of study group.
The 12-week treatment period was followed by an observation period of 12 weeks up to the 24-week study endpoint.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure (100% re-epithelialization without drainage or dressing requirement) within the 12-week treatment phase.
Secondary endpoints included time to target ulcer closure during the 12-week treatment phase and proportion of participants achieving target ulcer closure by 24 weeks (end of study). Investigators were blinded throughout.
Subanalyses were conducted based on ulcer location, size, and age, as well as estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 90 mL/min and ankle-brachial index under 0.9 but greater than 0.7.
50% more patients on esmolol had complete ulcer closure
The proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure at 12 weeks was 60.3% in the esmolol plus standard of care group, compared with 41.7% with standard of care only, a difference of 18.6% (odds ratio, 2.13; P = .0276).
“The 24-week end-of-study data show what happened in the 12 weeks following end of treatment,” said Dr. Rastogi, turning to results showing that by 24 weeks the proportion of participants with complete ulcer closure was 77.2% versus 55.6%, respectively, with a difference of 21.6% (OR, 2.71; P = .013).
Time to ulcer closure (a secondary endpoint) was similar between the esmolol plus standard of care vs. standard of care groups (74.3 vs. 72.5 days).
The impact of ulcer location on complete ulcer closure, a subanalysis, showed a higher proportion of patients experienced complete ulcer closure with esmolol plus standard of care versus standard of care. For example, in plantar-based ulcers, esmolol led to complete closure in 58.7% vs. 43.1%, while for nonplantar ulcers, complete closure was found in 63.6% vs. 38.1%.
In wounds less than 5 cm2, the proportion of complete closures was 66.0% vs. 50.0% for esmolol compared with standard of care alone, while in wounds over 5 cm2, these proportions were 47.6% vs. 26.9%.
Subanalyses also showed that esmolol was substantially better in patients with BMI greater than 25, ulcer duration over 12 weeks, and A1c above 8%.
Also, a subanalysis stratified by “real-life” situations favored esmolol, showing a 50.9% difference in the proportion of patients with diabetic foot ulcer healing in those with a history of hypertension and a 31.8% difference favoring esmolol in those with an abnormal electrocardiogram.
Overall, the proportions of patients who had an adverse event were 13.2%, 18.4%, and 37.5% in the esmolol plus standard of care, standard of care alone, and vehicle plus standard of care groups, respectively, and the vast majority were unrelated to study drug. There were no serious adverse events in the esmolol plus standard of care group.
A class effect of beta blockers?
The proposed mechanism of action of esmolol relates to a sequence of reducing inflammation (via vasodilation, fibroblast migration, and cytokine reduction); proliferation by beta-blockade (improves keratinocyte migration and epithelialization); and remodeling (increases collagen turnover).
Asked by an audience member if the observations were a class effect and systemic effect of beta-blockers, Dr. Rastogi said he could not say for sure that it was a class effect, but they deliberately used a beta-1 adrenergic receptor antagonist.
“It may not be a systemic effect because we have some patients who use beta-blockers systemically and they still have diabetic foot ulcers,” he said.
Dr. Rastogi and Dr. Dhatariya have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EASD 2022
Eat more dairy, less red meat to prevent type 2 diabetes
STOCKHOLM – Among animal protein foods, low-fat dairy consumption may minimize the risk of developing type 2 diabetes while red meat raises that risk, a new analysis finds.
“A plant-based dietary pattern with limited intake of meat, moderate intake of fish, eggs, and full-fat dairy, and habitual consumption of yogurt, milk, or low-fat dairy, might represent the most feasible, sustainable, and successful population strategy to optimize the prevention of type 2 diabetes,” lead author Annalisa Giosuè, MD, of the University of Naples (Italy) Federico II, told this news organization.
She presented the findings from an umbrella review of 13 dose-response meta-analyses of prospective cohort studies at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The study is believed to be the first comprehensive overview of the available evidence from all published meta-analyses on the relationship between well-defined amounts of animal-origin foods and the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Dr. Giosuè and colleagues focused on animal-based foods because they represent a gap in most guidelines for type 2 diabetes prevention, she explained.
“The existing evidence and dietary recommendations for type 2 diabetes prevention are mainly based on the appropriate consumption of plant foods: high amounts of the fiber-rich ones and low consumption of the refined ones as well as those rich in free sugars. And also on the adequate choice among fat sources – reduction of saturated fat sources like butter and cream and replacement with plant-based poly- and monounsaturated fat sources like nontropical vegetable oils. But not on the most suitable choices among different animal foods for the prevention of type 2 diabetes,” she explained.
The new findings are in line with the Mediterranean diet in that, while plant based, it also limits red-meat consumption, but not all animal-based foods, and has consistently been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Vegetarian diets have also been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, but far less evidence is available for that, she said.
Asked for comment, session moderator Matthias Schulze, MD, head of the department of molecular epidemiology at the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Berlin, said: “Decreasing intake of red and processed meat is already a strong recommendation, and these data support that. You have to make choices for and against [certain] foods. So, if you decide to eat less red meat, then the question is what do you eat instead? This study shows that specifically other animal products, like dairy and ... fish or white meat sources ... are healthy among the animal-based foods. But you could also obviously look at plant-based foods as protein sources as well.”
And Dr. Schulze noted that the data suggest another dimension to type 2 diabetes prevention beyond simply focusing on weight loss.
“You can achieve weight loss with very different diets. Diet quality plays an important role. These data support that if you look at diabetes prevention, then you would focus on people with high intakes of specific animal-based foods, besides looking at overweight and obesity. Then you could intervene to reduce this intake, with potential substitutions with other animal foods like fish or white meat, or plant-based sources of proteins.”
Red meat damages, dairy protects
The 13 meta-analyses included 175 summary risk ratios for type 2 diabetes incidence for the consumption of total meat, red meat, white meat, processed meats, fish, total dairy, full-fat dairy, low-fat dairy, milk, cheese, yogurt, or eggs.
Significant increases in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes were found for consumption of 100 g/day of total meat (SRR, 1.20; 20% increase) and red meat (SRR, 1.22, 22% increase) and with 50 g/day of processed meats (SRR, 1.30; 30% increase). A borderline increased risk was also seen for 50 g/day of white meat (SRR, 1.04; 4% increase).
The opposite was found for dairy foods. Inverse associations for type 2 diabetes development were found for an intake of 200 g/day of total dairy (SRR, 0.95; 5% reduction), low-fat dairy (SRR, 0.96; 4% reduction), milk (SRR, 0.90; 10% reduction), and for 100 g/day of yogurt (SRR, 0.94, 6% reduction).
Neutral (nonsignificant) effects were found for 200 g/day of full-fat dairy (SRR, 0.98) and for 30 g/day of cheese (SRR, 0.97). Fish consumption also had a neutral association with type 2 diabetes risk (SRR, 1.04 for 100 g/day) as did one egg per day (SRR, 1.07), but evidence quality was low.
And, Dr. Giosuè noted during her presentation, these relationships could change with alterations in the amounts consumed.
Dr. Schulze commented: “Fish is more clearly related to reduced cardiovascular risk than for preventing type 2 diabetes, where we’ve had mixed results. They might not always be the same.”
What are the mechanisms?
The reasons for these positive and negative associations aren’t entirely clear, but Dr. Giosuè noted that dairy products contain several nutrients, vitamins, and other components, such as calcium and vitamin D, that have potential beneficial effects on glucose metabolism.
In particular, she said, “Whey proteins in milk have a well-known beneficial effect on the regulation of the rise of glucose levels in the blood after meals, and also on the control of appetite and body weight.”
Moreover, probiotics found in yogurt have been linked to protective effects against weight gain and obesity, which “may in part [explain] the beneficial role of yogurt in type 2 diabetes prevention.”
Meat, in contrast, is full of cholesterol, saturated fatty acids, and heme iron, which can promote subclinical inflammation and oxidative stress, which may in turn, affect insulin sensitivity, Dr. Giosuè explained. What’s more, “processed meats also contain nitrates, nitrites, and sodium that can contribute to pancreatic cell damage and vascular dysfunction, thus affecting insulin sensitivity.”
And white meat (poultry) has a lower fat content than red meats such as beef, lamb, and pork, as well as a more favorable fatty acid profile and a lower heme-iron content, she said in an interview.
What about vegan diets? The devil is in the details
Asked about the relative health benefits of diets that completely eliminate animal-based foods, Dr. Giosuè replied: “What is important to keep in mind when hearing about the potential of vegan diets to prevent, or manage, or induce the remission of type 2 diabetes, is that the inclusion in the diet of solely foods of plant origin does not mean ‘automatically’ to eat only foods that are good for diabetes prevention.”
“Just like the exclusion of all foods of animal origin is not equivalent to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes ... Solid evidence has demonstrated that plant foods which are refined and/or rich in free sugars like white bread, biscuits, and sweetened beverages are as harmful as red and processed meats for diabetes incidence and progression.”
Dr. Giosuè and Dr. Schulze have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Among animal protein foods, low-fat dairy consumption may minimize the risk of developing type 2 diabetes while red meat raises that risk, a new analysis finds.
“A plant-based dietary pattern with limited intake of meat, moderate intake of fish, eggs, and full-fat dairy, and habitual consumption of yogurt, milk, or low-fat dairy, might represent the most feasible, sustainable, and successful population strategy to optimize the prevention of type 2 diabetes,” lead author Annalisa Giosuè, MD, of the University of Naples (Italy) Federico II, told this news organization.
She presented the findings from an umbrella review of 13 dose-response meta-analyses of prospective cohort studies at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The study is believed to be the first comprehensive overview of the available evidence from all published meta-analyses on the relationship between well-defined amounts of animal-origin foods and the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Dr. Giosuè and colleagues focused on animal-based foods because they represent a gap in most guidelines for type 2 diabetes prevention, she explained.
“The existing evidence and dietary recommendations for type 2 diabetes prevention are mainly based on the appropriate consumption of plant foods: high amounts of the fiber-rich ones and low consumption of the refined ones as well as those rich in free sugars. And also on the adequate choice among fat sources – reduction of saturated fat sources like butter and cream and replacement with plant-based poly- and monounsaturated fat sources like nontropical vegetable oils. But not on the most suitable choices among different animal foods for the prevention of type 2 diabetes,” she explained.
The new findings are in line with the Mediterranean diet in that, while plant based, it also limits red-meat consumption, but not all animal-based foods, and has consistently been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Vegetarian diets have also been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, but far less evidence is available for that, she said.
Asked for comment, session moderator Matthias Schulze, MD, head of the department of molecular epidemiology at the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Berlin, said: “Decreasing intake of red and processed meat is already a strong recommendation, and these data support that. You have to make choices for and against [certain] foods. So, if you decide to eat less red meat, then the question is what do you eat instead? This study shows that specifically other animal products, like dairy and ... fish or white meat sources ... are healthy among the animal-based foods. But you could also obviously look at plant-based foods as protein sources as well.”
And Dr. Schulze noted that the data suggest another dimension to type 2 diabetes prevention beyond simply focusing on weight loss.
“You can achieve weight loss with very different diets. Diet quality plays an important role. These data support that if you look at diabetes prevention, then you would focus on people with high intakes of specific animal-based foods, besides looking at overweight and obesity. Then you could intervene to reduce this intake, with potential substitutions with other animal foods like fish or white meat, or plant-based sources of proteins.”
Red meat damages, dairy protects
The 13 meta-analyses included 175 summary risk ratios for type 2 diabetes incidence for the consumption of total meat, red meat, white meat, processed meats, fish, total dairy, full-fat dairy, low-fat dairy, milk, cheese, yogurt, or eggs.
Significant increases in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes were found for consumption of 100 g/day of total meat (SRR, 1.20; 20% increase) and red meat (SRR, 1.22, 22% increase) and with 50 g/day of processed meats (SRR, 1.30; 30% increase). A borderline increased risk was also seen for 50 g/day of white meat (SRR, 1.04; 4% increase).
The opposite was found for dairy foods. Inverse associations for type 2 diabetes development were found for an intake of 200 g/day of total dairy (SRR, 0.95; 5% reduction), low-fat dairy (SRR, 0.96; 4% reduction), milk (SRR, 0.90; 10% reduction), and for 100 g/day of yogurt (SRR, 0.94, 6% reduction).
Neutral (nonsignificant) effects were found for 200 g/day of full-fat dairy (SRR, 0.98) and for 30 g/day of cheese (SRR, 0.97). Fish consumption also had a neutral association with type 2 diabetes risk (SRR, 1.04 for 100 g/day) as did one egg per day (SRR, 1.07), but evidence quality was low.
And, Dr. Giosuè noted during her presentation, these relationships could change with alterations in the amounts consumed.
Dr. Schulze commented: “Fish is more clearly related to reduced cardiovascular risk than for preventing type 2 diabetes, where we’ve had mixed results. They might not always be the same.”
What are the mechanisms?
The reasons for these positive and negative associations aren’t entirely clear, but Dr. Giosuè noted that dairy products contain several nutrients, vitamins, and other components, such as calcium and vitamin D, that have potential beneficial effects on glucose metabolism.
In particular, she said, “Whey proteins in milk have a well-known beneficial effect on the regulation of the rise of glucose levels in the blood after meals, and also on the control of appetite and body weight.”
Moreover, probiotics found in yogurt have been linked to protective effects against weight gain and obesity, which “may in part [explain] the beneficial role of yogurt in type 2 diabetes prevention.”
Meat, in contrast, is full of cholesterol, saturated fatty acids, and heme iron, which can promote subclinical inflammation and oxidative stress, which may in turn, affect insulin sensitivity, Dr. Giosuè explained. What’s more, “processed meats also contain nitrates, nitrites, and sodium that can contribute to pancreatic cell damage and vascular dysfunction, thus affecting insulin sensitivity.”
And white meat (poultry) has a lower fat content than red meats such as beef, lamb, and pork, as well as a more favorable fatty acid profile and a lower heme-iron content, she said in an interview.
What about vegan diets? The devil is in the details
Asked about the relative health benefits of diets that completely eliminate animal-based foods, Dr. Giosuè replied: “What is important to keep in mind when hearing about the potential of vegan diets to prevent, or manage, or induce the remission of type 2 diabetes, is that the inclusion in the diet of solely foods of plant origin does not mean ‘automatically’ to eat only foods that are good for diabetes prevention.”
“Just like the exclusion of all foods of animal origin is not equivalent to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes ... Solid evidence has demonstrated that plant foods which are refined and/or rich in free sugars like white bread, biscuits, and sweetened beverages are as harmful as red and processed meats for diabetes incidence and progression.”
Dr. Giosuè and Dr. Schulze have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Among animal protein foods, low-fat dairy consumption may minimize the risk of developing type 2 diabetes while red meat raises that risk, a new analysis finds.
“A plant-based dietary pattern with limited intake of meat, moderate intake of fish, eggs, and full-fat dairy, and habitual consumption of yogurt, milk, or low-fat dairy, might represent the most feasible, sustainable, and successful population strategy to optimize the prevention of type 2 diabetes,” lead author Annalisa Giosuè, MD, of the University of Naples (Italy) Federico II, told this news organization.
She presented the findings from an umbrella review of 13 dose-response meta-analyses of prospective cohort studies at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The study is believed to be the first comprehensive overview of the available evidence from all published meta-analyses on the relationship between well-defined amounts of animal-origin foods and the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Dr. Giosuè and colleagues focused on animal-based foods because they represent a gap in most guidelines for type 2 diabetes prevention, she explained.
“The existing evidence and dietary recommendations for type 2 diabetes prevention are mainly based on the appropriate consumption of plant foods: high amounts of the fiber-rich ones and low consumption of the refined ones as well as those rich in free sugars. And also on the adequate choice among fat sources – reduction of saturated fat sources like butter and cream and replacement with plant-based poly- and monounsaturated fat sources like nontropical vegetable oils. But not on the most suitable choices among different animal foods for the prevention of type 2 diabetes,” she explained.
The new findings are in line with the Mediterranean diet in that, while plant based, it also limits red-meat consumption, but not all animal-based foods, and has consistently been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. Vegetarian diets have also been associated with a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, but far less evidence is available for that, she said.
Asked for comment, session moderator Matthias Schulze, MD, head of the department of molecular epidemiology at the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Berlin, said: “Decreasing intake of red and processed meat is already a strong recommendation, and these data support that. You have to make choices for and against [certain] foods. So, if you decide to eat less red meat, then the question is what do you eat instead? This study shows that specifically other animal products, like dairy and ... fish or white meat sources ... are healthy among the animal-based foods. But you could also obviously look at plant-based foods as protein sources as well.”
And Dr. Schulze noted that the data suggest another dimension to type 2 diabetes prevention beyond simply focusing on weight loss.
“You can achieve weight loss with very different diets. Diet quality plays an important role. These data support that if you look at diabetes prevention, then you would focus on people with high intakes of specific animal-based foods, besides looking at overweight and obesity. Then you could intervene to reduce this intake, with potential substitutions with other animal foods like fish or white meat, or plant-based sources of proteins.”
Red meat damages, dairy protects
The 13 meta-analyses included 175 summary risk ratios for type 2 diabetes incidence for the consumption of total meat, red meat, white meat, processed meats, fish, total dairy, full-fat dairy, low-fat dairy, milk, cheese, yogurt, or eggs.
Significant increases in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes were found for consumption of 100 g/day of total meat (SRR, 1.20; 20% increase) and red meat (SRR, 1.22, 22% increase) and with 50 g/day of processed meats (SRR, 1.30; 30% increase). A borderline increased risk was also seen for 50 g/day of white meat (SRR, 1.04; 4% increase).
The opposite was found for dairy foods. Inverse associations for type 2 diabetes development were found for an intake of 200 g/day of total dairy (SRR, 0.95; 5% reduction), low-fat dairy (SRR, 0.96; 4% reduction), milk (SRR, 0.90; 10% reduction), and for 100 g/day of yogurt (SRR, 0.94, 6% reduction).
Neutral (nonsignificant) effects were found for 200 g/day of full-fat dairy (SRR, 0.98) and for 30 g/day of cheese (SRR, 0.97). Fish consumption also had a neutral association with type 2 diabetes risk (SRR, 1.04 for 100 g/day) as did one egg per day (SRR, 1.07), but evidence quality was low.
And, Dr. Giosuè noted during her presentation, these relationships could change with alterations in the amounts consumed.
Dr. Schulze commented: “Fish is more clearly related to reduced cardiovascular risk than for preventing type 2 diabetes, where we’ve had mixed results. They might not always be the same.”
What are the mechanisms?
The reasons for these positive and negative associations aren’t entirely clear, but Dr. Giosuè noted that dairy products contain several nutrients, vitamins, and other components, such as calcium and vitamin D, that have potential beneficial effects on glucose metabolism.
In particular, she said, “Whey proteins in milk have a well-known beneficial effect on the regulation of the rise of glucose levels in the blood after meals, and also on the control of appetite and body weight.”
Moreover, probiotics found in yogurt have been linked to protective effects against weight gain and obesity, which “may in part [explain] the beneficial role of yogurt in type 2 diabetes prevention.”
Meat, in contrast, is full of cholesterol, saturated fatty acids, and heme iron, which can promote subclinical inflammation and oxidative stress, which may in turn, affect insulin sensitivity, Dr. Giosuè explained. What’s more, “processed meats also contain nitrates, nitrites, and sodium that can contribute to pancreatic cell damage and vascular dysfunction, thus affecting insulin sensitivity.”
And white meat (poultry) has a lower fat content than red meats such as beef, lamb, and pork, as well as a more favorable fatty acid profile and a lower heme-iron content, she said in an interview.
What about vegan diets? The devil is in the details
Asked about the relative health benefits of diets that completely eliminate animal-based foods, Dr. Giosuè replied: “What is important to keep in mind when hearing about the potential of vegan diets to prevent, or manage, or induce the remission of type 2 diabetes, is that the inclusion in the diet of solely foods of plant origin does not mean ‘automatically’ to eat only foods that are good for diabetes prevention.”
“Just like the exclusion of all foods of animal origin is not equivalent to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes ... Solid evidence has demonstrated that plant foods which are refined and/or rich in free sugars like white bread, biscuits, and sweetened beverages are as harmful as red and processed meats for diabetes incidence and progression.”
Dr. Giosuè and Dr. Schulze have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2022
Whole grains may improve survival in people with type 2 diabetes
STOCKHOLM – Higher consumption of whole grains, fish, fiber, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces deaths from all causes in people with type 2 diabetes, show new data.
Results from the systematic review and meta-analysis were presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes by lead author Janett Barbaresko, PhD, a researcher from the German Diabetes Center in Düsseldorf.
Adding just one serving (around 20 g/day) of whole grains from foods such as brown bread, brown rice, or breakfast cereals was associated with about a 16% reduction in all-cause mortality, and each portion of fish consumed per week was associated with a 5% lower risk of all-cause mortality. In addition, eating 5 g/day of fiber was associated with a 14% reduction in all-cause mortality, and 0.1 g/day of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with a 13% reduction.
Diet also has role in improving survival in those with type 2 diabetes
Dr. Barbaresko explained that most dietary recommendations for people with type 2 diabetes are not evidence based or are derived from studies of the general population, and that the degree to which different components of diet are associated with all-cause mortality, or indeed the prevention of morbidity and mortality, remains unknown.
By way of example, she noted the American Diabetes Association 2022 guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes complications advises limited intake of saturated and trans fatty acids, higher intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids, and following the Mediterranean or DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diets.
“Our findings show that dietary factors not only play a role in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, but also seem to be relevant for improving survival in people with diagnosed diabetes,” she said, adding that, “in particular, we found some key aspects of a healthy diet such as higher intakes of whole grains, fiber, fish, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may improve survival of individuals with type 2 diabetes.”
She noted that individuals with type 2 diabetes are known to be more prone to circulatory diseases, dementia, cancer, and bone fractures, and that lifestyle modifications, including diet – with or without medications – underpin most management strategies.
“For the first time, we have provided a summary of all published studies on any dietary factor in association to all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Barbaresko. “Moreover, the certainty of evidence has been evaluated for the first time.”
Matthias Schulze, MD, head of the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Berlin, moderated the session.
The new work “summarizes the available evidence, providing important dietary advice for patients with diabetes, for example, recommending whole grains,” he remarked. “However, the study also points to gaps in knowledge, so for many diet factors, we have either no or few studies, or study quality considered to be low, which calls for more research to fill the gap.”
High versus low intake of various dietary factors
The researchers performed meta-analyses based on published studies of all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes aged 18 years and over, as associated with dietary patterns, macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fat), micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), secondary plant compounds (for example, polyphenols), and supplements.
Studies were conducted mainly in the United States and Europe with a mean follow-up of 10 years. Low and high intake were compared, and a dose-response relationship between different dietary factors and all-cause mortality was explored to generate summary risk ratios. The researchers also explored how the certainty of evidence was determined.
Decreased mortality from any cause was found for a higher intake of fish (SRR per serving/week, 0.95; over six studies); whole grain (SRR per 20 g/day, 0.84; two studies); fiber (SRR per 5 g/day, 0.86; three studies), and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (SRR per 0.1 g/day, 0.87; two studies).
A low certainty of evidence was found for an inverse association between all-cause mortality and vegetable consumption (SRR per 100 g/day, 0.88; two studies) and plant protein intake (SRR per 10 g/day, 0.91; three studies).
Eggs were associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (SRR per 10 g/day, 1.05; seven studies), as was dietary cholesterol (SRR per 300 mg/day, 1.19; two studies).
Regarding other dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet and low-carbohydrate diet, either no association was found and/or the evidence was very uncertain. Likewise, evidence was uncertain for foods including nuts, dairy, meat, sugar and sweets; macronutrients, including carbohydrates; and micronutrients, such as caffeine and vitamin D.
“With the Mediterranean diet, we saw an inverse association [with all-cause mortality] comparing high adherence with low adherence to the Mediterranean diet, but the certainty of evidence was very low, indicating a really uncertain meta-evidence,” remarked Dr. Barbaresko.
She concluded that a greater number of studies is needed to investigate the association of dietary factors with all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes to strengthen the evidence for several other dietary factors. She also cautioned that meta-analyses are affected by unmeasured and residual confounding.
Dr. Barbaresko and Dr. Schulze reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Higher consumption of whole grains, fish, fiber, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces deaths from all causes in people with type 2 diabetes, show new data.
Results from the systematic review and meta-analysis were presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes by lead author Janett Barbaresko, PhD, a researcher from the German Diabetes Center in Düsseldorf.
Adding just one serving (around 20 g/day) of whole grains from foods such as brown bread, brown rice, or breakfast cereals was associated with about a 16% reduction in all-cause mortality, and each portion of fish consumed per week was associated with a 5% lower risk of all-cause mortality. In addition, eating 5 g/day of fiber was associated with a 14% reduction in all-cause mortality, and 0.1 g/day of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with a 13% reduction.
Diet also has role in improving survival in those with type 2 diabetes
Dr. Barbaresko explained that most dietary recommendations for people with type 2 diabetes are not evidence based or are derived from studies of the general population, and that the degree to which different components of diet are associated with all-cause mortality, or indeed the prevention of morbidity and mortality, remains unknown.
By way of example, she noted the American Diabetes Association 2022 guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes complications advises limited intake of saturated and trans fatty acids, higher intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids, and following the Mediterranean or DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diets.
“Our findings show that dietary factors not only play a role in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, but also seem to be relevant for improving survival in people with diagnosed diabetes,” she said, adding that, “in particular, we found some key aspects of a healthy diet such as higher intakes of whole grains, fiber, fish, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may improve survival of individuals with type 2 diabetes.”
She noted that individuals with type 2 diabetes are known to be more prone to circulatory diseases, dementia, cancer, and bone fractures, and that lifestyle modifications, including diet – with or without medications – underpin most management strategies.
“For the first time, we have provided a summary of all published studies on any dietary factor in association to all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Barbaresko. “Moreover, the certainty of evidence has been evaluated for the first time.”
Matthias Schulze, MD, head of the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Berlin, moderated the session.
The new work “summarizes the available evidence, providing important dietary advice for patients with diabetes, for example, recommending whole grains,” he remarked. “However, the study also points to gaps in knowledge, so for many diet factors, we have either no or few studies, or study quality considered to be low, which calls for more research to fill the gap.”
High versus low intake of various dietary factors
The researchers performed meta-analyses based on published studies of all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes aged 18 years and over, as associated with dietary patterns, macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fat), micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), secondary plant compounds (for example, polyphenols), and supplements.
Studies were conducted mainly in the United States and Europe with a mean follow-up of 10 years. Low and high intake were compared, and a dose-response relationship between different dietary factors and all-cause mortality was explored to generate summary risk ratios. The researchers also explored how the certainty of evidence was determined.
Decreased mortality from any cause was found for a higher intake of fish (SRR per serving/week, 0.95; over six studies); whole grain (SRR per 20 g/day, 0.84; two studies); fiber (SRR per 5 g/day, 0.86; three studies), and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (SRR per 0.1 g/day, 0.87; two studies).
A low certainty of evidence was found for an inverse association between all-cause mortality and vegetable consumption (SRR per 100 g/day, 0.88; two studies) and plant protein intake (SRR per 10 g/day, 0.91; three studies).
Eggs were associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (SRR per 10 g/day, 1.05; seven studies), as was dietary cholesterol (SRR per 300 mg/day, 1.19; two studies).
Regarding other dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet and low-carbohydrate diet, either no association was found and/or the evidence was very uncertain. Likewise, evidence was uncertain for foods including nuts, dairy, meat, sugar and sweets; macronutrients, including carbohydrates; and micronutrients, such as caffeine and vitamin D.
“With the Mediterranean diet, we saw an inverse association [with all-cause mortality] comparing high adherence with low adherence to the Mediterranean diet, but the certainty of evidence was very low, indicating a really uncertain meta-evidence,” remarked Dr. Barbaresko.
She concluded that a greater number of studies is needed to investigate the association of dietary factors with all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes to strengthen the evidence for several other dietary factors. She also cautioned that meta-analyses are affected by unmeasured and residual confounding.
Dr. Barbaresko and Dr. Schulze reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
STOCKHOLM – Higher consumption of whole grains, fish, fiber, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids reduces deaths from all causes in people with type 2 diabetes, show new data.
Results from the systematic review and meta-analysis were presented at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes by lead author Janett Barbaresko, PhD, a researcher from the German Diabetes Center in Düsseldorf.
Adding just one serving (around 20 g/day) of whole grains from foods such as brown bread, brown rice, or breakfast cereals was associated with about a 16% reduction in all-cause mortality, and each portion of fish consumed per week was associated with a 5% lower risk of all-cause mortality. In addition, eating 5 g/day of fiber was associated with a 14% reduction in all-cause mortality, and 0.1 g/day of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids with a 13% reduction.
Diet also has role in improving survival in those with type 2 diabetes
Dr. Barbaresko explained that most dietary recommendations for people with type 2 diabetes are not evidence based or are derived from studies of the general population, and that the degree to which different components of diet are associated with all-cause mortality, or indeed the prevention of morbidity and mortality, remains unknown.
By way of example, she noted the American Diabetes Association 2022 guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes complications advises limited intake of saturated and trans fatty acids, higher intake of polyunsaturated fatty acids, and following the Mediterranean or DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diets.
“Our findings show that dietary factors not only play a role in the prevention of type 2 diabetes, but also seem to be relevant for improving survival in people with diagnosed diabetes,” she said, adding that, “in particular, we found some key aspects of a healthy diet such as higher intakes of whole grains, fiber, fish, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids may improve survival of individuals with type 2 diabetes.”
She noted that individuals with type 2 diabetes are known to be more prone to circulatory diseases, dementia, cancer, and bone fractures, and that lifestyle modifications, including diet – with or without medications – underpin most management strategies.
“For the first time, we have provided a summary of all published studies on any dietary factor in association to all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes,” said Dr. Barbaresko. “Moreover, the certainty of evidence has been evaluated for the first time.”
Matthias Schulze, MD, head of the German Institute of Human Nutrition, Berlin, moderated the session.
The new work “summarizes the available evidence, providing important dietary advice for patients with diabetes, for example, recommending whole grains,” he remarked. “However, the study also points to gaps in knowledge, so for many diet factors, we have either no or few studies, or study quality considered to be low, which calls for more research to fill the gap.”
High versus low intake of various dietary factors
The researchers performed meta-analyses based on published studies of all-cause mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes aged 18 years and over, as associated with dietary patterns, macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, fat), micronutrients (vitamins and minerals), secondary plant compounds (for example, polyphenols), and supplements.
Studies were conducted mainly in the United States and Europe with a mean follow-up of 10 years. Low and high intake were compared, and a dose-response relationship between different dietary factors and all-cause mortality was explored to generate summary risk ratios. The researchers also explored how the certainty of evidence was determined.
Decreased mortality from any cause was found for a higher intake of fish (SRR per serving/week, 0.95; over six studies); whole grain (SRR per 20 g/day, 0.84; two studies); fiber (SRR per 5 g/day, 0.86; three studies), and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (SRR per 0.1 g/day, 0.87; two studies).
A low certainty of evidence was found for an inverse association between all-cause mortality and vegetable consumption (SRR per 100 g/day, 0.88; two studies) and plant protein intake (SRR per 10 g/day, 0.91; three studies).
Eggs were associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (SRR per 10 g/day, 1.05; seven studies), as was dietary cholesterol (SRR per 300 mg/day, 1.19; two studies).
Regarding other dietary patterns, including the Mediterranean diet and low-carbohydrate diet, either no association was found and/or the evidence was very uncertain. Likewise, evidence was uncertain for foods including nuts, dairy, meat, sugar and sweets; macronutrients, including carbohydrates; and micronutrients, such as caffeine and vitamin D.
“With the Mediterranean diet, we saw an inverse association [with all-cause mortality] comparing high adherence with low adherence to the Mediterranean diet, but the certainty of evidence was very low, indicating a really uncertain meta-evidence,” remarked Dr. Barbaresko.
She concluded that a greater number of studies is needed to investigate the association of dietary factors with all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes to strengthen the evidence for several other dietary factors. She also cautioned that meta-analyses are affected by unmeasured and residual confounding.
Dr. Barbaresko and Dr. Schulze reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT EASD 2022
Waist-hip ratio beats BMI for predicting obesity’s mortality risk
STOCKHOLM – New evidence continues to show that alternative measures of adiposity than body mass index, such as waist-to-hip ratio, work better for predicting the risk a person with overweight or obesity faces from their excess weight.
A direct comparison of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), body mass index (BMI), and fat mass index (FMI) in a total of more than 380,000 United Kingdom residents included in the UK Biobank showed that WHR had the strongest and most consistent relationship to all-cause death, compared with the other two measures, indicating that clinicians should pay more attention to adiposity distribution than they do to BMI when prioritizing obesity interventions, Irfan Khan said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Although it’s likely “way too early” to fully replace BMI as a measure of adiposity, because it is so established in guidelines and in practice, it is now time to “use WHR as an adjunct to BMI” suggested Mr. Khan in an interview.
“A lot of work still needs to be done to translate WHR into practice, but I think it’s getting closer,” said Mr. Khan, a medical student at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who performed his analyses in collaboration with a research team based primarily at McMaster.
Moving away from BMI-centric obesity
“This is a timely topic, because guidelines for treating people with obesity have depended so much on BMI. We want to go from a BMI-centric view to a view of obesity that depends more on disease burden,” commented Matthias Blüher, MD, professor of molecular endocrinology and head of the Obesity Outpatient Clinic for Adults at the University of Leipzig (Germany).
For example, the 2016 obesity management guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology called for a “complications-centric” approach to assessing and intervening in people with obesity rather than a “BMI-centric” approach.
But Dr. Blüher went a step further in an interview, adding that “waist-to-hip ratio is now outdated,” with adjusted measures of WHR such as waist-to-height ratio “considered a better proxy for all-cause death.” He also gave high marks to the Edmonton Obesity Staging System, which independently added to BMI as well as to a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome for predicting mortality in a sample from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The Edmonton System also surpassed BMI for disease-severity staging using data from more than 23,000 Canadians with a BMI that denoted obesity.
1 standard deviation increase in WHR linked with a 41% increased mortality
The study reported by Mr. Khan used both epidemiologic and Mendelian randomization analyses on data collected from more than 380,000 U.K. residents included in the UK Biobank database to examine the statistical associations between BMI, FMI, and WHR and all-cause death. This showed that while BMI and FMI both had significant, independent associations with all-cause mortality, with hazard ratios of 1.14 for each 1 standard deviation increase in BMI and of 1.17 for each standard deviation increase in FMI, the link was a stronger 1.41 per standard deviation increase in WHR, he said.
Another analysis that divided the entire UK Biobank study cohort into 20 roughly similar subgroups by their BMI showed that WHR had the most consistent association across the BMI spectrum.
Further analyses showed that WHR also strongly and significantly linked with cardiovascular disease death and with other causes of death that were not cardiovascular, cancer-related, or associated with respiratory diseases. And the WHR link to all-cause mortality was strongest in men, and much less robust in women, likely because visceral adiposity is much more common among men, even compared with the postmenopausal women who predominate in the UK Biobank cohort.
One more feature of WHR that makes it an attractive metric is its relative ease of measurement, about as easy as BMI, Mr. Khan said.
The study received no commercial funding, and Mr. Khan had no disclosures. Dr. Blüher has been a consultant to or speaker on behalf of Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
STOCKHOLM – New evidence continues to show that alternative measures of adiposity than body mass index, such as waist-to-hip ratio, work better for predicting the risk a person with overweight or obesity faces from their excess weight.
A direct comparison of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), body mass index (BMI), and fat mass index (FMI) in a total of more than 380,000 United Kingdom residents included in the UK Biobank showed that WHR had the strongest and most consistent relationship to all-cause death, compared with the other two measures, indicating that clinicians should pay more attention to adiposity distribution than they do to BMI when prioritizing obesity interventions, Irfan Khan said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Although it’s likely “way too early” to fully replace BMI as a measure of adiposity, because it is so established in guidelines and in practice, it is now time to “use WHR as an adjunct to BMI” suggested Mr. Khan in an interview.
“A lot of work still needs to be done to translate WHR into practice, but I think it’s getting closer,” said Mr. Khan, a medical student at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who performed his analyses in collaboration with a research team based primarily at McMaster.
Moving away from BMI-centric obesity
“This is a timely topic, because guidelines for treating people with obesity have depended so much on BMI. We want to go from a BMI-centric view to a view of obesity that depends more on disease burden,” commented Matthias Blüher, MD, professor of molecular endocrinology and head of the Obesity Outpatient Clinic for Adults at the University of Leipzig (Germany).
For example, the 2016 obesity management guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology called for a “complications-centric” approach to assessing and intervening in people with obesity rather than a “BMI-centric” approach.
But Dr. Blüher went a step further in an interview, adding that “waist-to-hip ratio is now outdated,” with adjusted measures of WHR such as waist-to-height ratio “considered a better proxy for all-cause death.” He also gave high marks to the Edmonton Obesity Staging System, which independently added to BMI as well as to a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome for predicting mortality in a sample from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The Edmonton System also surpassed BMI for disease-severity staging using data from more than 23,000 Canadians with a BMI that denoted obesity.
1 standard deviation increase in WHR linked with a 41% increased mortality
The study reported by Mr. Khan used both epidemiologic and Mendelian randomization analyses on data collected from more than 380,000 U.K. residents included in the UK Biobank database to examine the statistical associations between BMI, FMI, and WHR and all-cause death. This showed that while BMI and FMI both had significant, independent associations with all-cause mortality, with hazard ratios of 1.14 for each 1 standard deviation increase in BMI and of 1.17 for each standard deviation increase in FMI, the link was a stronger 1.41 per standard deviation increase in WHR, he said.
Another analysis that divided the entire UK Biobank study cohort into 20 roughly similar subgroups by their BMI showed that WHR had the most consistent association across the BMI spectrum.
Further analyses showed that WHR also strongly and significantly linked with cardiovascular disease death and with other causes of death that were not cardiovascular, cancer-related, or associated with respiratory diseases. And the WHR link to all-cause mortality was strongest in men, and much less robust in women, likely because visceral adiposity is much more common among men, even compared with the postmenopausal women who predominate in the UK Biobank cohort.
One more feature of WHR that makes it an attractive metric is its relative ease of measurement, about as easy as BMI, Mr. Khan said.
The study received no commercial funding, and Mr. Khan had no disclosures. Dr. Blüher has been a consultant to or speaker on behalf of Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
STOCKHOLM – New evidence continues to show that alternative measures of adiposity than body mass index, such as waist-to-hip ratio, work better for predicting the risk a person with overweight or obesity faces from their excess weight.
A direct comparison of waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), body mass index (BMI), and fat mass index (FMI) in a total of more than 380,000 United Kingdom residents included in the UK Biobank showed that WHR had the strongest and most consistent relationship to all-cause death, compared with the other two measures, indicating that clinicians should pay more attention to adiposity distribution than they do to BMI when prioritizing obesity interventions, Irfan Khan said at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Although it’s likely “way too early” to fully replace BMI as a measure of adiposity, because it is so established in guidelines and in practice, it is now time to “use WHR as an adjunct to BMI” suggested Mr. Khan in an interview.
“A lot of work still needs to be done to translate WHR into practice, but I think it’s getting closer,” said Mr. Khan, a medical student at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., who performed his analyses in collaboration with a research team based primarily at McMaster.
Moving away from BMI-centric obesity
“This is a timely topic, because guidelines for treating people with obesity have depended so much on BMI. We want to go from a BMI-centric view to a view of obesity that depends more on disease burden,” commented Matthias Blüher, MD, professor of molecular endocrinology and head of the Obesity Outpatient Clinic for Adults at the University of Leipzig (Germany).
For example, the 2016 obesity management guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology called for a “complications-centric” approach to assessing and intervening in people with obesity rather than a “BMI-centric” approach.
But Dr. Blüher went a step further in an interview, adding that “waist-to-hip ratio is now outdated,” with adjusted measures of WHR such as waist-to-height ratio “considered a better proxy for all-cause death.” He also gave high marks to the Edmonton Obesity Staging System, which independently added to BMI as well as to a diagnosis of metabolic syndrome for predicting mortality in a sample from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES). The Edmonton System also surpassed BMI for disease-severity staging using data from more than 23,000 Canadians with a BMI that denoted obesity.
1 standard deviation increase in WHR linked with a 41% increased mortality
The study reported by Mr. Khan used both epidemiologic and Mendelian randomization analyses on data collected from more than 380,000 U.K. residents included in the UK Biobank database to examine the statistical associations between BMI, FMI, and WHR and all-cause death. This showed that while BMI and FMI both had significant, independent associations with all-cause mortality, with hazard ratios of 1.14 for each 1 standard deviation increase in BMI and of 1.17 for each standard deviation increase in FMI, the link was a stronger 1.41 per standard deviation increase in WHR, he said.
Another analysis that divided the entire UK Biobank study cohort into 20 roughly similar subgroups by their BMI showed that WHR had the most consistent association across the BMI spectrum.
Further analyses showed that WHR also strongly and significantly linked with cardiovascular disease death and with other causes of death that were not cardiovascular, cancer-related, or associated with respiratory diseases. And the WHR link to all-cause mortality was strongest in men, and much less robust in women, likely because visceral adiposity is much more common among men, even compared with the postmenopausal women who predominate in the UK Biobank cohort.
One more feature of WHR that makes it an attractive metric is its relative ease of measurement, about as easy as BMI, Mr. Khan said.
The study received no commercial funding, and Mr. Khan had no disclosures. Dr. Blüher has been a consultant to or speaker on behalf of Amgen, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Sanofi.
AT EASD 2022
‘Game changer’ semaglutide halves diabetes risk from obesity
Treatment of people with obesity but without diabetes with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide (Wegovy) – hailed at its approval in 2021 as a “game changer” for the treatment of obesity – led to beneficial changes in body mass index (BMI), glycemic control, and other clinical measures.
This collectively cut the calculated risk for possible future development of type 2 diabetes in study participants by more than half, based on post-hoc analysis of data from two pivotal trials that compared semaglutide with placebo.
The findings “suggest that semaglutide could help prevent type 2 diabetes in people with overweight or obesity,” said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Asked to comment, Rodolfo J. Galindo, MD, said: “We devote a significant amount of effort to treating people with diabetes but very little effort for diabetes prevention. We hope that further scientific findings showing the benefits of weight loss, as illustrated by [Dr.] Garvey [and colleagues], for diabetes prevention will change the pandemic of adiposity-based chronic disease.”
GLP-1 agonists as complication-reducing agents
Finding a link between treatment with semaglutide and a reduced future risk of developing type 2 diabetes is important because it shows that this regimen is not just a BMI-centric approach to treating people with obesity but is also a way to potentially reduce complications of obesity such as diabetes onset, explained Dr. Garvey, a professor and director of the Diabetes Research Center at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Recent obesity-management recommendations have focused on interventions aimed at avoiding complications, as in 2016 guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology, he noted.
Having evidence that treatment with a GLP-1 agonist such as semaglutide can reduce the incidence of diabetes in people with obesity might also help convince payers to more uniformly reimburse for this type of obesity intervention, which up to now has commonly faced coverage limitations, especially in the United States, he said in an interview.
Dr. Garvey added that evidence for a reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular disease complications such as myocardial infarction and stroke may need to join diabetes prevention as proven effects from obesity intervention before coverage decisions change.
He cited the SELECT trial, which is testing the hypothesis that semaglutide treatment of people with overweight or obesity can reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events in about 17,500 participants and with expected completion toward the end of 2023.
“A complication-centric approach to management of people with obesity needs prediction tools that allow a focus on prevention strategies for people with obesity who are at increased risk of developing diabetes,” commented Dr. Galindo, an endocrinologist at Emory University, Atlanta, in an interview.
Combined analysis of STEP 1 and STEP 4 data
The analysis conducted by Dr. Garvey and colleagues used data from the STEP 1 trial, which compared semaglutide 2.4 mg subcutaneous once weekly with placebo for weight loss in more than 1,500 people predominantly with obesity (about 6% were overweight) and showed that after 68 weeks semaglutide cut the calculated risk of developing type 2 diabetes over the subsequent 10 years from 18% at baseline to 7%, compared with a drop from 18% at baseline to 16% among those who received placebo.
A second, similar analysis of data from people predominantly with obesity in the STEP 4 trial – which treated around 800 people with semaglutide 2.4 mg for 20 weeks and then randomized them to placebo or continued semaglutide treatment – showed that semaglutide treatment cut their calculated 10-year risk for incident type 2 diabetes from 20% at baseline to about 11% after 20 weeks. The risk rebounded in the study participants who then switched from semaglutide to placebo. Among those randomized to remain on semaglutide for a total of 68 weeks, the 10-year risk fell further to 8%.
Dr. Garvey and associates used a validated prognostic formula, the cardiometabolic disease staging (CMDS) tool, they had previously developed and reported to calculate 10-year risk for development of type 2 diabetes based on three unmodifiable factors (age, sex, and race) and five modifiable factors (BMI, blood pressure, glucose level, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides). They applied the analysis to data from 1,561 of the STEP 1 participants and 766 participants in the STEP 4 study.
“There is no better tool I know of to predict diabetes incidence,” commented Michael A. Nauck, MD, professor and chief of clinical research, diabetes division, St. Josef Hospital, Bochum, Germany.
In his opinion, the CMDS tool is appropriate for estimating the risk of developing incident type 2 diabetes in populations but not in specific individuals.
The new analyses also showed that, in STEP 1, the impact of semaglutide on reducing future risk of developing type 2 diabetes was roughly the same regardless of whether participants entered the study with prediabetes or were normoglycemic at entry.
Blood glucose changes confer the biggest effect
The biggest contributor among the five modifiable components of the CMDS tool for altering the predicted risk for incident diabetes was the reduction in blood glucose produced by semaglutide treatment, which influenced just under half of the change in predicted risk, Dr. Garvey said. The four other modifiable components had roughly similar individual effects on predicted risk, with change in BMI influencing about 15% of the observed effect.
“Our analysis shows that semaglutide treatment is preventing diabetes via several mechanisms. It’s not just a reduction in glucose,” Dr. Garvey said.
Dr. Nauck cautioned, however, that it is hard to judge the efficacy of an intervention like semaglutide for preventing incident diabetes when one of its effects is to dampen down hyperglycemia, the signal indicator of diabetes onset.
Indeed, semaglutide was first approved as a treatment for type 2 diabetes (known as Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) at slightly lower doses than it is approved for obesity. It is also available as an oral agent to treat diabetes (Rybelsus).
Dr. Nauck also noted that the results from at least one previously reported study had already shown the same relationship between treatment with the GLP-1 agonist liraglutide as an anti-obesity agent (3.0 mg dose daily, known as Saxenda) and a reduced subsequent incidence of type 2 diabetes but using actual clinical outcomes during 3 years of follow-up rather than a calculated projection of diabetes likelihood.
The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial randomized 2,254 people with prediabetes and overweight or obesity to weekly treatment with 3.0 mg of liraglutide or placebo. After 160 weeks on treatment, the cumulative incidence of type 2 diabetes was 2% in those who received liraglutide and 6% among those on placebo, with a significant hazard ratio reduction of 79% in the incidence of diabetes on liraglutide treatment.
The STEP 1 and STEP 4 trials were sponsored by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Garvey has reported serving as an advisor without compensation to Novo Nordisk as well as Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Jazz, and Pfizer. He is also a site principal investigator for multicentered clinical trials sponsored by the University of Alabama at Birmingham and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, and Pfizer. Dr .Galindo has reported being a consultant or advisor for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Weight Watchers and receiving research funding from Dexcom, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Nauck has reported being an advisor or consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Menarini/Berlin Chemie, MSD, Regor, and ShouTi/Gasherbrum, receiving research funding from MSD, being a member of a data monitoring and safety board for Inventiva, and being a speaker on behalf of Novo Nordisk as well as for Eli Lilly, Menarini/Berlin Chemie, MSD, and Sun Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment of people with obesity but without diabetes with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide (Wegovy) – hailed at its approval in 2021 as a “game changer” for the treatment of obesity – led to beneficial changes in body mass index (BMI), glycemic control, and other clinical measures.
This collectively cut the calculated risk for possible future development of type 2 diabetes in study participants by more than half, based on post-hoc analysis of data from two pivotal trials that compared semaglutide with placebo.
The findings “suggest that semaglutide could help prevent type 2 diabetes in people with overweight or obesity,” said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Asked to comment, Rodolfo J. Galindo, MD, said: “We devote a significant amount of effort to treating people with diabetes but very little effort for diabetes prevention. We hope that further scientific findings showing the benefits of weight loss, as illustrated by [Dr.] Garvey [and colleagues], for diabetes prevention will change the pandemic of adiposity-based chronic disease.”
GLP-1 agonists as complication-reducing agents
Finding a link between treatment with semaglutide and a reduced future risk of developing type 2 diabetes is important because it shows that this regimen is not just a BMI-centric approach to treating people with obesity but is also a way to potentially reduce complications of obesity such as diabetes onset, explained Dr. Garvey, a professor and director of the Diabetes Research Center at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Recent obesity-management recommendations have focused on interventions aimed at avoiding complications, as in 2016 guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology, he noted.
Having evidence that treatment with a GLP-1 agonist such as semaglutide can reduce the incidence of diabetes in people with obesity might also help convince payers to more uniformly reimburse for this type of obesity intervention, which up to now has commonly faced coverage limitations, especially in the United States, he said in an interview.
Dr. Garvey added that evidence for a reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular disease complications such as myocardial infarction and stroke may need to join diabetes prevention as proven effects from obesity intervention before coverage decisions change.
He cited the SELECT trial, which is testing the hypothesis that semaglutide treatment of people with overweight or obesity can reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events in about 17,500 participants and with expected completion toward the end of 2023.
“A complication-centric approach to management of people with obesity needs prediction tools that allow a focus on prevention strategies for people with obesity who are at increased risk of developing diabetes,” commented Dr. Galindo, an endocrinologist at Emory University, Atlanta, in an interview.
Combined analysis of STEP 1 and STEP 4 data
The analysis conducted by Dr. Garvey and colleagues used data from the STEP 1 trial, which compared semaglutide 2.4 mg subcutaneous once weekly with placebo for weight loss in more than 1,500 people predominantly with obesity (about 6% were overweight) and showed that after 68 weeks semaglutide cut the calculated risk of developing type 2 diabetes over the subsequent 10 years from 18% at baseline to 7%, compared with a drop from 18% at baseline to 16% among those who received placebo.
A second, similar analysis of data from people predominantly with obesity in the STEP 4 trial – which treated around 800 people with semaglutide 2.4 mg for 20 weeks and then randomized them to placebo or continued semaglutide treatment – showed that semaglutide treatment cut their calculated 10-year risk for incident type 2 diabetes from 20% at baseline to about 11% after 20 weeks. The risk rebounded in the study participants who then switched from semaglutide to placebo. Among those randomized to remain on semaglutide for a total of 68 weeks, the 10-year risk fell further to 8%.
Dr. Garvey and associates used a validated prognostic formula, the cardiometabolic disease staging (CMDS) tool, they had previously developed and reported to calculate 10-year risk for development of type 2 diabetes based on three unmodifiable factors (age, sex, and race) and five modifiable factors (BMI, blood pressure, glucose level, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides). They applied the analysis to data from 1,561 of the STEP 1 participants and 766 participants in the STEP 4 study.
“There is no better tool I know of to predict diabetes incidence,” commented Michael A. Nauck, MD, professor and chief of clinical research, diabetes division, St. Josef Hospital, Bochum, Germany.
In his opinion, the CMDS tool is appropriate for estimating the risk of developing incident type 2 diabetes in populations but not in specific individuals.
The new analyses also showed that, in STEP 1, the impact of semaglutide on reducing future risk of developing type 2 diabetes was roughly the same regardless of whether participants entered the study with prediabetes or were normoglycemic at entry.
Blood glucose changes confer the biggest effect
The biggest contributor among the five modifiable components of the CMDS tool for altering the predicted risk for incident diabetes was the reduction in blood glucose produced by semaglutide treatment, which influenced just under half of the change in predicted risk, Dr. Garvey said. The four other modifiable components had roughly similar individual effects on predicted risk, with change in BMI influencing about 15% of the observed effect.
“Our analysis shows that semaglutide treatment is preventing diabetes via several mechanisms. It’s not just a reduction in glucose,” Dr. Garvey said.
Dr. Nauck cautioned, however, that it is hard to judge the efficacy of an intervention like semaglutide for preventing incident diabetes when one of its effects is to dampen down hyperglycemia, the signal indicator of diabetes onset.
Indeed, semaglutide was first approved as a treatment for type 2 diabetes (known as Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) at slightly lower doses than it is approved for obesity. It is also available as an oral agent to treat diabetes (Rybelsus).
Dr. Nauck also noted that the results from at least one previously reported study had already shown the same relationship between treatment with the GLP-1 agonist liraglutide as an anti-obesity agent (3.0 mg dose daily, known as Saxenda) and a reduced subsequent incidence of type 2 diabetes but using actual clinical outcomes during 3 years of follow-up rather than a calculated projection of diabetes likelihood.
The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial randomized 2,254 people with prediabetes and overweight or obesity to weekly treatment with 3.0 mg of liraglutide or placebo. After 160 weeks on treatment, the cumulative incidence of type 2 diabetes was 2% in those who received liraglutide and 6% among those on placebo, with a significant hazard ratio reduction of 79% in the incidence of diabetes on liraglutide treatment.
The STEP 1 and STEP 4 trials were sponsored by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Garvey has reported serving as an advisor without compensation to Novo Nordisk as well as Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Jazz, and Pfizer. He is also a site principal investigator for multicentered clinical trials sponsored by the University of Alabama at Birmingham and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, and Pfizer. Dr .Galindo has reported being a consultant or advisor for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Weight Watchers and receiving research funding from Dexcom, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Nauck has reported being an advisor or consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Menarini/Berlin Chemie, MSD, Regor, and ShouTi/Gasherbrum, receiving research funding from MSD, being a member of a data monitoring and safety board for Inventiva, and being a speaker on behalf of Novo Nordisk as well as for Eli Lilly, Menarini/Berlin Chemie, MSD, and Sun Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treatment of people with obesity but without diabetes with the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist semaglutide (Wegovy) – hailed at its approval in 2021 as a “game changer” for the treatment of obesity – led to beneficial changes in body mass index (BMI), glycemic control, and other clinical measures.
This collectively cut the calculated risk for possible future development of type 2 diabetes in study participants by more than half, based on post-hoc analysis of data from two pivotal trials that compared semaglutide with placebo.
The findings “suggest that semaglutide could help prevent type 2 diabetes in people with overweight or obesity,” said W. Timothy Garvey, MD, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
Asked to comment, Rodolfo J. Galindo, MD, said: “We devote a significant amount of effort to treating people with diabetes but very little effort for diabetes prevention. We hope that further scientific findings showing the benefits of weight loss, as illustrated by [Dr.] Garvey [and colleagues], for diabetes prevention will change the pandemic of adiposity-based chronic disease.”
GLP-1 agonists as complication-reducing agents
Finding a link between treatment with semaglutide and a reduced future risk of developing type 2 diabetes is important because it shows that this regimen is not just a BMI-centric approach to treating people with obesity but is also a way to potentially reduce complications of obesity such as diabetes onset, explained Dr. Garvey, a professor and director of the Diabetes Research Center at the University of Alabama at Birmingham.
Recent obesity-management recommendations have focused on interventions aimed at avoiding complications, as in 2016 guidelines from the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and the American College of Endocrinology, he noted.
Having evidence that treatment with a GLP-1 agonist such as semaglutide can reduce the incidence of diabetes in people with obesity might also help convince payers to more uniformly reimburse for this type of obesity intervention, which up to now has commonly faced coverage limitations, especially in the United States, he said in an interview.
Dr. Garvey added that evidence for a reduction in the incidence of cardiovascular disease complications such as myocardial infarction and stroke may need to join diabetes prevention as proven effects from obesity intervention before coverage decisions change.
He cited the SELECT trial, which is testing the hypothesis that semaglutide treatment of people with overweight or obesity can reduce the incidence of cardiovascular events in about 17,500 participants and with expected completion toward the end of 2023.
“A complication-centric approach to management of people with obesity needs prediction tools that allow a focus on prevention strategies for people with obesity who are at increased risk of developing diabetes,” commented Dr. Galindo, an endocrinologist at Emory University, Atlanta, in an interview.
Combined analysis of STEP 1 and STEP 4 data
The analysis conducted by Dr. Garvey and colleagues used data from the STEP 1 trial, which compared semaglutide 2.4 mg subcutaneous once weekly with placebo for weight loss in more than 1,500 people predominantly with obesity (about 6% were overweight) and showed that after 68 weeks semaglutide cut the calculated risk of developing type 2 diabetes over the subsequent 10 years from 18% at baseline to 7%, compared with a drop from 18% at baseline to 16% among those who received placebo.
A second, similar analysis of data from people predominantly with obesity in the STEP 4 trial – which treated around 800 people with semaglutide 2.4 mg for 20 weeks and then randomized them to placebo or continued semaglutide treatment – showed that semaglutide treatment cut their calculated 10-year risk for incident type 2 diabetes from 20% at baseline to about 11% after 20 weeks. The risk rebounded in the study participants who then switched from semaglutide to placebo. Among those randomized to remain on semaglutide for a total of 68 weeks, the 10-year risk fell further to 8%.
Dr. Garvey and associates used a validated prognostic formula, the cardiometabolic disease staging (CMDS) tool, they had previously developed and reported to calculate 10-year risk for development of type 2 diabetes based on three unmodifiable factors (age, sex, and race) and five modifiable factors (BMI, blood pressure, glucose level, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides). They applied the analysis to data from 1,561 of the STEP 1 participants and 766 participants in the STEP 4 study.
“There is no better tool I know of to predict diabetes incidence,” commented Michael A. Nauck, MD, professor and chief of clinical research, diabetes division, St. Josef Hospital, Bochum, Germany.
In his opinion, the CMDS tool is appropriate for estimating the risk of developing incident type 2 diabetes in populations but not in specific individuals.
The new analyses also showed that, in STEP 1, the impact of semaglutide on reducing future risk of developing type 2 diabetes was roughly the same regardless of whether participants entered the study with prediabetes or were normoglycemic at entry.
Blood glucose changes confer the biggest effect
The biggest contributor among the five modifiable components of the CMDS tool for altering the predicted risk for incident diabetes was the reduction in blood glucose produced by semaglutide treatment, which influenced just under half of the change in predicted risk, Dr. Garvey said. The four other modifiable components had roughly similar individual effects on predicted risk, with change in BMI influencing about 15% of the observed effect.
“Our analysis shows that semaglutide treatment is preventing diabetes via several mechanisms. It’s not just a reduction in glucose,” Dr. Garvey said.
Dr. Nauck cautioned, however, that it is hard to judge the efficacy of an intervention like semaglutide for preventing incident diabetes when one of its effects is to dampen down hyperglycemia, the signal indicator of diabetes onset.
Indeed, semaglutide was first approved as a treatment for type 2 diabetes (known as Ozempic, Novo Nordisk) at slightly lower doses than it is approved for obesity. It is also available as an oral agent to treat diabetes (Rybelsus).
Dr. Nauck also noted that the results from at least one previously reported study had already shown the same relationship between treatment with the GLP-1 agonist liraglutide as an anti-obesity agent (3.0 mg dose daily, known as Saxenda) and a reduced subsequent incidence of type 2 diabetes but using actual clinical outcomes during 3 years of follow-up rather than a calculated projection of diabetes likelihood.
The SCALE Obesity and Prediabetes trial randomized 2,254 people with prediabetes and overweight or obesity to weekly treatment with 3.0 mg of liraglutide or placebo. After 160 weeks on treatment, the cumulative incidence of type 2 diabetes was 2% in those who received liraglutide and 6% among those on placebo, with a significant hazard ratio reduction of 79% in the incidence of diabetes on liraglutide treatment.
The STEP 1 and STEP 4 trials were sponsored by Novo Nordisk, the company that markets semaglutide (Wegovy). Dr. Garvey has reported serving as an advisor without compensation to Novo Nordisk as well as Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Jazz, and Pfizer. He is also a site principal investigator for multicentered clinical trials sponsored by the University of Alabama at Birmingham and funded by Novo Nordisk, Eli Lilly, Epitomee, and Pfizer. Dr .Galindo has reported being a consultant or advisor for Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Pfizer, Sanofi, and Weight Watchers and receiving research funding from Dexcom, Eli Lilly, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Nauck has reported being an advisor or consultant to Novo Nordisk as well as to Boehringer Ingelheim, Eli Lilly, Menarini/Berlin Chemie, MSD, Regor, and ShouTi/Gasherbrum, receiving research funding from MSD, being a member of a data monitoring and safety board for Inventiva, and being a speaker on behalf of Novo Nordisk as well as for Eli Lilly, Menarini/Berlin Chemie, MSD, and Sun Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Experts express caution over type 2 diabetes/tea-drinking claim
type 2 diabetes/tea-drinking claim
A claim that drinking tea might protect people against developing type 2 diabetes has been met with caution from multiple experts ahead of the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The claim is that people who drink four or more cups of tea every day – specifically green, Oolong, or black tea – are 17% less likely to develop type 2 diabetes than those who do not drink tea. Drinking fewer cups of tea per day was not found to confer any benefit.
“Our results are exciting because they suggest that people can do something as simple as drinking four cups of tea a day to potentially lessen their risk of developing type 2 diabetes,” Xiaying Li of Wuhan (China) University of Science and Technology is quoted as saying in an official EASD press release.
“It is possible that particular components in tea, such as polyphenols, may reduce blood glucose levels, but a sufficient amount of these bioactive compounds may be needed to be effective,” Dr. Li added.
“The words ‘suggest’ and ‘potentially’ are crucial here,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, MSc, MBA, emeritus professor of applied statistics at The Open University, said in a separate statement to the press that reeled in Dr. Li’s enthusiasm.
“Tea drinking would only be useful for reducing diabetes risk if the tea drinking causes reductions in risk, that is, if the risk is reduced if you drink the tea and not if you don’t – and this study simply can’t show whether it does this or not,” Dr. Conway stressed.
Naveed Sattar, FMedSci FRCPath FRCPGlas FRSE, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, was also cautiously critical. “There is no good trial evidence whatsoever that the chemicals in tea prevent diabetes,” he observed separately.
“So, I suspect its more about tea being healthier (less calorific) than many alternative drinks or tea drinkers leading healthier lives more generally.”
Dr. Sattar added that it could be that people who drink tea might also be avoiding drinking more harmful sugary drinks and have other health behaviors that might lead them to have a lower risk for type 2 diabetes.
Time for tea?
Dr. Li will present the findings of two analyses on Sept. 21 at the EASD meeting: the first a large observational cohort study and the second an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.
For the cohort study, Dr. Li and her coauthors took data on more than 5,100 adults who had participated in the long-running and ongoing China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). Information on tea drinking behavior was extracted from questionnaires that had been filled out at two time points – 1997 and 2009 – and they determined whether people had developed type 2 diabetes according to American Diabetes Association criteria.
Nearly half, 45.8%, were found to be tea drinkers, and 10% of the population they sampled had developed type 2 diabetes. No association between tea drinking and type 2 diabetes development was found, however, with the hazard ratio comparing tea drinkers and non–tea drinkers sitting firmly at 1.02. Moreover, a sensitivity analysis that excluded participants who had developed type 2 diabetes in the first 3 years of follow-up did not change the result.
Things were slightly different when Dr. Li and associates performed their meta-analysis that involved analyzing data on more than 1 million participants in 19 studies conducted in eight countries that had been published up to September 2021.
Here, they found there was a significant (P < .003) linear association between tea consumption and having type 2 diabetes, with the relative risk of developing type 2 diabetes decreasing by 0.986 for every additional cup of tea that was drunk.
HRs for the development of type 2 diabetes in tea drinkers versus non–tea drinkers were 1.00 for those who drank less than one cup per day, 0.96 for those who had one to two cups, and 0.84 for those who drank four or more cups.
“While more research needs to be done to determine the exact dosage and mechanisms behind these observations, our findings suggest that drinking tea is beneficial in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, but only at high doses (at least 4 cups a day)”, said Dr. Li.
Perhaps, “we did not find an association between tea drinking and type 2 diabetes in our cohort study because we did not look at higher tea consumption,” she added.
Tempest in a teacup
“This is large, observational data. It’s not a randomized controlled trial so there’s plenty of room for data to be misunderstood,” warned Matt Sydes, MSc, professor of clinical trials & methodology at the MRC Clinical Trials Unit, University College London.
“Everyone drinks fluids. If there is an effect here (and that’s a big if), it might be not about the tea they drink, but about what they don’t drink. One can’t tell at the moment. It seems unlikely that a large randomized controlled trial could be done to disambiguate” added Dr. Sydes
“Being only a conference abstract, it is difficult to assess the quality of this research,” Baptiste Leurent, PhD, a medical statistician also working at University College London, said. Not only was the cohort study observational, so were all the other studies included in the meta-analysis, he pointed out.
“Therefore, no cause-effect conclusions can be drawn. The association could simply be due to other factors, such as those drinking more tea having a healthier lifestyle. It does not seem that the authors tried to control for confounders, which is usually difficult in meta-analysis,” Dr. Leurent said.
“There is reason to be a bit skeptical at this point; we really need to have the full details to assess it properly,” said Jonathan Cook of the Centre for Statistics in Medicine at the University of Oxford (England). “It’s a fair attempt to look at this, but not cutting edge, [using] fairly standard approaches.”
Similar studies have shown a reduced risk associated with coffee drinking, noted Duane Mellor, PhD, a registered dietitian and senior teaching fellow at Aston University in Birmingham.
“The important take-home message is that lifestyle is important in managing risk of developing type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Mellor said.
“That includes choosing low-calorie drinks including mainly water as well as unsweetened tea and coffee as your drinks of choice as part of a healthy lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the Young Talents Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, the Science and Technology Research Key Project of Education Department of Hubei Province, the Sanuo Diabetes Charity Foundation, and the Xiangyang Science and Technology Plan Project, all based in China. Dr. Li had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. McConway is a Trustee and on the advisory committee of The Science Media Centre. Dr. Sattar has consulted for many companies that make diabetes and cardiovascular drugs and has been involved in multiple trials of lifestyle approaches for the prevention and remission of diabetes. Dr. Sydes, Dr. Leurent, Dr. Cook, and Dr. Mellor had no conflicts of interest to report.
A claim that drinking tea might protect people against developing type 2 diabetes has been met with caution from multiple experts ahead of the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The claim is that people who drink four or more cups of tea every day – specifically green, Oolong, or black tea – are 17% less likely to develop type 2 diabetes than those who do not drink tea. Drinking fewer cups of tea per day was not found to confer any benefit.
“Our results are exciting because they suggest that people can do something as simple as drinking four cups of tea a day to potentially lessen their risk of developing type 2 diabetes,” Xiaying Li of Wuhan (China) University of Science and Technology is quoted as saying in an official EASD press release.
“It is possible that particular components in tea, such as polyphenols, may reduce blood glucose levels, but a sufficient amount of these bioactive compounds may be needed to be effective,” Dr. Li added.
“The words ‘suggest’ and ‘potentially’ are crucial here,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, MSc, MBA, emeritus professor of applied statistics at The Open University, said in a separate statement to the press that reeled in Dr. Li’s enthusiasm.
“Tea drinking would only be useful for reducing diabetes risk if the tea drinking causes reductions in risk, that is, if the risk is reduced if you drink the tea and not if you don’t – and this study simply can’t show whether it does this or not,” Dr. Conway stressed.
Naveed Sattar, FMedSci FRCPath FRCPGlas FRSE, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, was also cautiously critical. “There is no good trial evidence whatsoever that the chemicals in tea prevent diabetes,” he observed separately.
“So, I suspect its more about tea being healthier (less calorific) than many alternative drinks or tea drinkers leading healthier lives more generally.”
Dr. Sattar added that it could be that people who drink tea might also be avoiding drinking more harmful sugary drinks and have other health behaviors that might lead them to have a lower risk for type 2 diabetes.
Time for tea?
Dr. Li will present the findings of two analyses on Sept. 21 at the EASD meeting: the first a large observational cohort study and the second an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.
For the cohort study, Dr. Li and her coauthors took data on more than 5,100 adults who had participated in the long-running and ongoing China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). Information on tea drinking behavior was extracted from questionnaires that had been filled out at two time points – 1997 and 2009 – and they determined whether people had developed type 2 diabetes according to American Diabetes Association criteria.
Nearly half, 45.8%, were found to be tea drinkers, and 10% of the population they sampled had developed type 2 diabetes. No association between tea drinking and type 2 diabetes development was found, however, with the hazard ratio comparing tea drinkers and non–tea drinkers sitting firmly at 1.02. Moreover, a sensitivity analysis that excluded participants who had developed type 2 diabetes in the first 3 years of follow-up did not change the result.
Things were slightly different when Dr. Li and associates performed their meta-analysis that involved analyzing data on more than 1 million participants in 19 studies conducted in eight countries that had been published up to September 2021.
Here, they found there was a significant (P < .003) linear association between tea consumption and having type 2 diabetes, with the relative risk of developing type 2 diabetes decreasing by 0.986 for every additional cup of tea that was drunk.
HRs for the development of type 2 diabetes in tea drinkers versus non–tea drinkers were 1.00 for those who drank less than one cup per day, 0.96 for those who had one to two cups, and 0.84 for those who drank four or more cups.
“While more research needs to be done to determine the exact dosage and mechanisms behind these observations, our findings suggest that drinking tea is beneficial in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, but only at high doses (at least 4 cups a day)”, said Dr. Li.
Perhaps, “we did not find an association between tea drinking and type 2 diabetes in our cohort study because we did not look at higher tea consumption,” she added.
Tempest in a teacup
“This is large, observational data. It’s not a randomized controlled trial so there’s plenty of room for data to be misunderstood,” warned Matt Sydes, MSc, professor of clinical trials & methodology at the MRC Clinical Trials Unit, University College London.
“Everyone drinks fluids. If there is an effect here (and that’s a big if), it might be not about the tea they drink, but about what they don’t drink. One can’t tell at the moment. It seems unlikely that a large randomized controlled trial could be done to disambiguate” added Dr. Sydes
“Being only a conference abstract, it is difficult to assess the quality of this research,” Baptiste Leurent, PhD, a medical statistician also working at University College London, said. Not only was the cohort study observational, so were all the other studies included in the meta-analysis, he pointed out.
“Therefore, no cause-effect conclusions can be drawn. The association could simply be due to other factors, such as those drinking more tea having a healthier lifestyle. It does not seem that the authors tried to control for confounders, which is usually difficult in meta-analysis,” Dr. Leurent said.
“There is reason to be a bit skeptical at this point; we really need to have the full details to assess it properly,” said Jonathan Cook of the Centre for Statistics in Medicine at the University of Oxford (England). “It’s a fair attempt to look at this, but not cutting edge, [using] fairly standard approaches.”
Similar studies have shown a reduced risk associated with coffee drinking, noted Duane Mellor, PhD, a registered dietitian and senior teaching fellow at Aston University in Birmingham.
“The important take-home message is that lifestyle is important in managing risk of developing type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Mellor said.
“That includes choosing low-calorie drinks including mainly water as well as unsweetened tea and coffee as your drinks of choice as part of a healthy lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the Young Talents Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, the Science and Technology Research Key Project of Education Department of Hubei Province, the Sanuo Diabetes Charity Foundation, and the Xiangyang Science and Technology Plan Project, all based in China. Dr. Li had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. McConway is a Trustee and on the advisory committee of The Science Media Centre. Dr. Sattar has consulted for many companies that make diabetes and cardiovascular drugs and has been involved in multiple trials of lifestyle approaches for the prevention and remission of diabetes. Dr. Sydes, Dr. Leurent, Dr. Cook, and Dr. Mellor had no conflicts of interest to report.
A claim that drinking tea might protect people against developing type 2 diabetes has been met with caution from multiple experts ahead of the annual meeting of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes.
The claim is that people who drink four or more cups of tea every day – specifically green, Oolong, or black tea – are 17% less likely to develop type 2 diabetes than those who do not drink tea. Drinking fewer cups of tea per day was not found to confer any benefit.
“Our results are exciting because they suggest that people can do something as simple as drinking four cups of tea a day to potentially lessen their risk of developing type 2 diabetes,” Xiaying Li of Wuhan (China) University of Science and Technology is quoted as saying in an official EASD press release.
“It is possible that particular components in tea, such as polyphenols, may reduce blood glucose levels, but a sufficient amount of these bioactive compounds may be needed to be effective,” Dr. Li added.
“The words ‘suggest’ and ‘potentially’ are crucial here,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, MSc, MBA, emeritus professor of applied statistics at The Open University, said in a separate statement to the press that reeled in Dr. Li’s enthusiasm.
“Tea drinking would only be useful for reducing diabetes risk if the tea drinking causes reductions in risk, that is, if the risk is reduced if you drink the tea and not if you don’t – and this study simply can’t show whether it does this or not,” Dr. Conway stressed.
Naveed Sattar, FMedSci FRCPath FRCPGlas FRSE, professor of metabolic medicine at the University of Glasgow, was also cautiously critical. “There is no good trial evidence whatsoever that the chemicals in tea prevent diabetes,” he observed separately.
“So, I suspect its more about tea being healthier (less calorific) than many alternative drinks or tea drinkers leading healthier lives more generally.”
Dr. Sattar added that it could be that people who drink tea might also be avoiding drinking more harmful sugary drinks and have other health behaviors that might lead them to have a lower risk for type 2 diabetes.
Time for tea?
Dr. Li will present the findings of two analyses on Sept. 21 at the EASD meeting: the first a large observational cohort study and the second an updated systematic review and meta-analysis.
For the cohort study, Dr. Li and her coauthors took data on more than 5,100 adults who had participated in the long-running and ongoing China Health and Nutrition Survey (CHNS). Information on tea drinking behavior was extracted from questionnaires that had been filled out at two time points – 1997 and 2009 – and they determined whether people had developed type 2 diabetes according to American Diabetes Association criteria.
Nearly half, 45.8%, were found to be tea drinkers, and 10% of the population they sampled had developed type 2 diabetes. No association between tea drinking and type 2 diabetes development was found, however, with the hazard ratio comparing tea drinkers and non–tea drinkers sitting firmly at 1.02. Moreover, a sensitivity analysis that excluded participants who had developed type 2 diabetes in the first 3 years of follow-up did not change the result.
Things were slightly different when Dr. Li and associates performed their meta-analysis that involved analyzing data on more than 1 million participants in 19 studies conducted in eight countries that had been published up to September 2021.
Here, they found there was a significant (P < .003) linear association between tea consumption and having type 2 diabetes, with the relative risk of developing type 2 diabetes decreasing by 0.986 for every additional cup of tea that was drunk.
HRs for the development of type 2 diabetes in tea drinkers versus non–tea drinkers were 1.00 for those who drank less than one cup per day, 0.96 for those who had one to two cups, and 0.84 for those who drank four or more cups.
“While more research needs to be done to determine the exact dosage and mechanisms behind these observations, our findings suggest that drinking tea is beneficial in reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes, but only at high doses (at least 4 cups a day)”, said Dr. Li.
Perhaps, “we did not find an association between tea drinking and type 2 diabetes in our cohort study because we did not look at higher tea consumption,” she added.
Tempest in a teacup
“This is large, observational data. It’s not a randomized controlled trial so there’s plenty of room for data to be misunderstood,” warned Matt Sydes, MSc, professor of clinical trials & methodology at the MRC Clinical Trials Unit, University College London.
“Everyone drinks fluids. If there is an effect here (and that’s a big if), it might be not about the tea they drink, but about what they don’t drink. One can’t tell at the moment. It seems unlikely that a large randomized controlled trial could be done to disambiguate” added Dr. Sydes
“Being only a conference abstract, it is difficult to assess the quality of this research,” Baptiste Leurent, PhD, a medical statistician also working at University College London, said. Not only was the cohort study observational, so were all the other studies included in the meta-analysis, he pointed out.
“Therefore, no cause-effect conclusions can be drawn. The association could simply be due to other factors, such as those drinking more tea having a healthier lifestyle. It does not seem that the authors tried to control for confounders, which is usually difficult in meta-analysis,” Dr. Leurent said.
“There is reason to be a bit skeptical at this point; we really need to have the full details to assess it properly,” said Jonathan Cook of the Centre for Statistics in Medicine at the University of Oxford (England). “It’s a fair attempt to look at this, but not cutting edge, [using] fairly standard approaches.”
Similar studies have shown a reduced risk associated with coffee drinking, noted Duane Mellor, PhD, a registered dietitian and senior teaching fellow at Aston University in Birmingham.
“The important take-home message is that lifestyle is important in managing risk of developing type 2 diabetes,” Dr. Mellor said.
“That includes choosing low-calorie drinks including mainly water as well as unsweetened tea and coffee as your drinks of choice as part of a healthy lifestyle.”
The study was funded by the Young Talents Project of Hubei Provincial Health Commission, the Science and Technology Research Key Project of Education Department of Hubei Province, the Sanuo Diabetes Charity Foundation, and the Xiangyang Science and Technology Plan Project, all based in China. Dr. Li had no conflicts of interest to disclose. Dr. McConway is a Trustee and on the advisory committee of The Science Media Centre. Dr. Sattar has consulted for many companies that make diabetes and cardiovascular drugs and has been involved in multiple trials of lifestyle approaches for the prevention and remission of diabetes. Dr. Sydes, Dr. Leurent, Dr. Cook, and Dr. Mellor had no conflicts of interest to report.
type 2 diabetes/tea-drinking claim
type 2 diabetes/tea-drinking claim
FROM EASD 2022
Mean A1c and A1c variability independently predict diabetes-related complications in T2D
Key clinical point: Increased mean glycated hemoglobin (A1c) level and A1c variability were associated with a significantly higher risk for diabetes-related complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Major finding: Elevated mean A1c level was associated with a significantly higher risk for urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio [UACR] of >300 mg/g (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.308; P < .001), any retinopathy (aHR 1.274; P < .001), and advanced retinopathy (aHR 1.237; P = .036); similarly, increased standard deviation of A1c was associated with an increased risk for UACR of >300 mg/g (aHR 1.478; P < .001), doubling of serum creatinine (aHR 2.133; P < .001), and all-cause (aHR 1.880; P < .001) and cardiovascular (aHR 1.431; P = .016) mortality.
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 1869 patients with T2D who were followed-up for a median of 9.5 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants from the Taipei Veterans General Hospital. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Wu TE et al. Mean HbA1c and HbA1c variability are associated with differing diabetes-related complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 (Sep 2). Doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110069
Key clinical point: Increased mean glycated hemoglobin (A1c) level and A1c variability were associated with a significantly higher risk for diabetes-related complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Major finding: Elevated mean A1c level was associated with a significantly higher risk for urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio [UACR] of >300 mg/g (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.308; P < .001), any retinopathy (aHR 1.274; P < .001), and advanced retinopathy (aHR 1.237; P = .036); similarly, increased standard deviation of A1c was associated with an increased risk for UACR of >300 mg/g (aHR 1.478; P < .001), doubling of serum creatinine (aHR 2.133; P < .001), and all-cause (aHR 1.880; P < .001) and cardiovascular (aHR 1.431; P = .016) mortality.
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 1869 patients with T2D who were followed-up for a median of 9.5 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants from the Taipei Veterans General Hospital. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Wu TE et al. Mean HbA1c and HbA1c variability are associated with differing diabetes-related complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 (Sep 2). Doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110069
Key clinical point: Increased mean glycated hemoglobin (A1c) level and A1c variability were associated with a significantly higher risk for diabetes-related complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Major finding: Elevated mean A1c level was associated with a significantly higher risk for urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio [UACR] of >300 mg/g (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.308; P < .001), any retinopathy (aHR 1.274; P < .001), and advanced retinopathy (aHR 1.237; P = .036); similarly, increased standard deviation of A1c was associated with an increased risk for UACR of >300 mg/g (aHR 1.478; P < .001), doubling of serum creatinine (aHR 2.133; P < .001), and all-cause (aHR 1.880; P < .001) and cardiovascular (aHR 1.431; P = .016) mortality.
Study details: Findings are from a prospective study including 1869 patients with T2D who were followed-up for a median of 9.5 years.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants from the Taipei Veterans General Hospital. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Wu TE et al. Mean HbA1c and HbA1c variability are associated with differing diabetes-related complications in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2022 (Sep 2). Doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2022.110069
Long-term SGLT2 inhibitor use may lower new-onset stroke risk in T2D
Key clinical point: Use vs no use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors was associated with a lower risk for new-onset stroke (NOS) among patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), with risk reductions being greater among those receiving concurrent statins, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA).
Major finding: The risk for NOS was significantly lower among SGLT2 inhibitor users vs nonusers (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.85; 95% CI 0.82-0.88), with similar results being reported in patients receiving statins (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.81-0.86), biguanides (aHR 0.77; 95% CI 0.75-0.79), thiazolidinediones (aHR 0.89; 95% CI 0.85-0.93), and GLP-1 RA (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.71-0.98).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective population-based cohort study including 232,101 patients with T2D using an SGLT2 inhibitor who were matched with 464,202 patients with T2D not using an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants from Chung Shan Medical University Hospital. The authors declared no competing interests.
Source: Lin TK et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors reduce the risk of new-onset stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:966708 (Aug 9). Doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.966708
Key clinical point: Use vs no use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors was associated with a lower risk for new-onset stroke (NOS) among patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), with risk reductions being greater among those receiving concurrent statins, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA).
Major finding: The risk for NOS was significantly lower among SGLT2 inhibitor users vs nonusers (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.85; 95% CI 0.82-0.88), with similar results being reported in patients receiving statins (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.81-0.86), biguanides (aHR 0.77; 95% CI 0.75-0.79), thiazolidinediones (aHR 0.89; 95% CI 0.85-0.93), and GLP-1 RA (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.71-0.98).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective population-based cohort study including 232,101 patients with T2D using an SGLT2 inhibitor who were matched with 464,202 patients with T2D not using an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants from Chung Shan Medical University Hospital. The authors declared no competing interests.
Source: Lin TK et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors reduce the risk of new-onset stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:966708 (Aug 9). Doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.966708
Key clinical point: Use vs no use of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors was associated with a lower risk for new-onset stroke (NOS) among patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D), with risk reductions being greater among those receiving concurrent statins, biguanides, thiazolidinediones, and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA).
Major finding: The risk for NOS was significantly lower among SGLT2 inhibitor users vs nonusers (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.85; 95% CI 0.82-0.88), with similar results being reported in patients receiving statins (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.81-0.86), biguanides (aHR 0.77; 95% CI 0.75-0.79), thiazolidinediones (aHR 0.89; 95% CI 0.85-0.93), and GLP-1 RA (aHR 0.84; 95% CI 0.71-0.98).
Study details: The data come from a retrospective population-based cohort study including 232,101 patients with T2D using an SGLT2 inhibitor who were matched with 464,202 patients with T2D not using an SGLT2 inhibitor.
Disclosures: This study was supported by grants from Chung Shan Medical University Hospital. The authors declared no competing interests.
Source: Lin TK et al. Sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors reduce the risk of new-onset stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022;9:966708 (Aug 9). Doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.966708