User login
Recurrent Painful Nodules Following Synthol Injection to Enhance Bicep Volume
To the Editor:
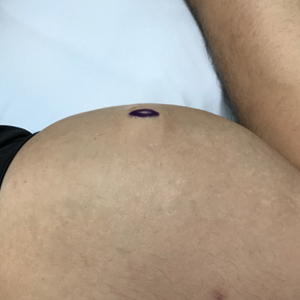
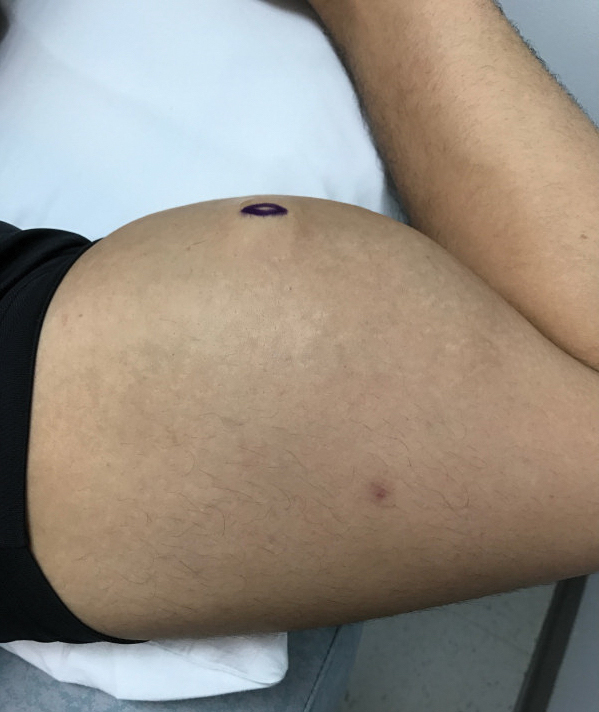
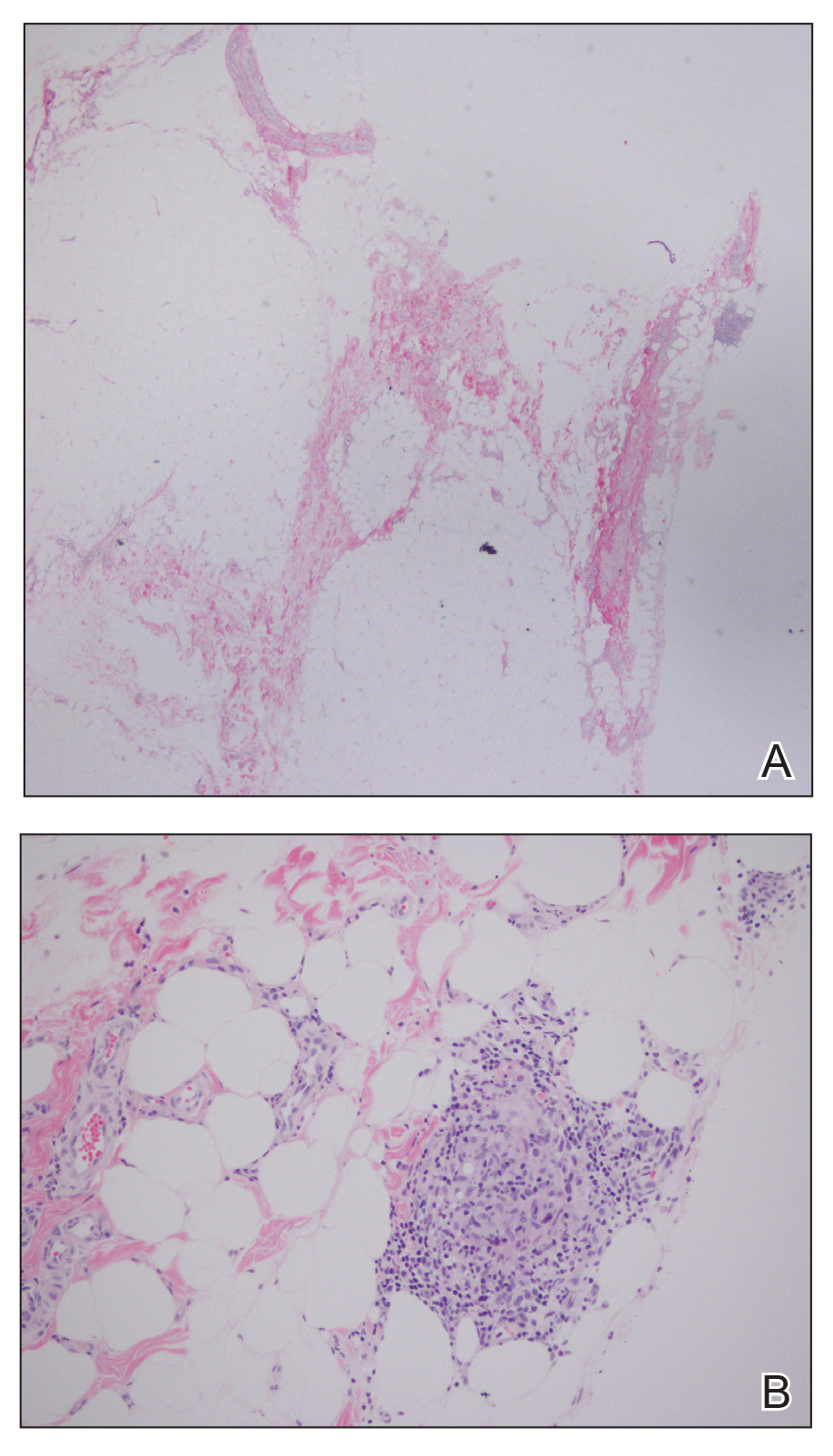
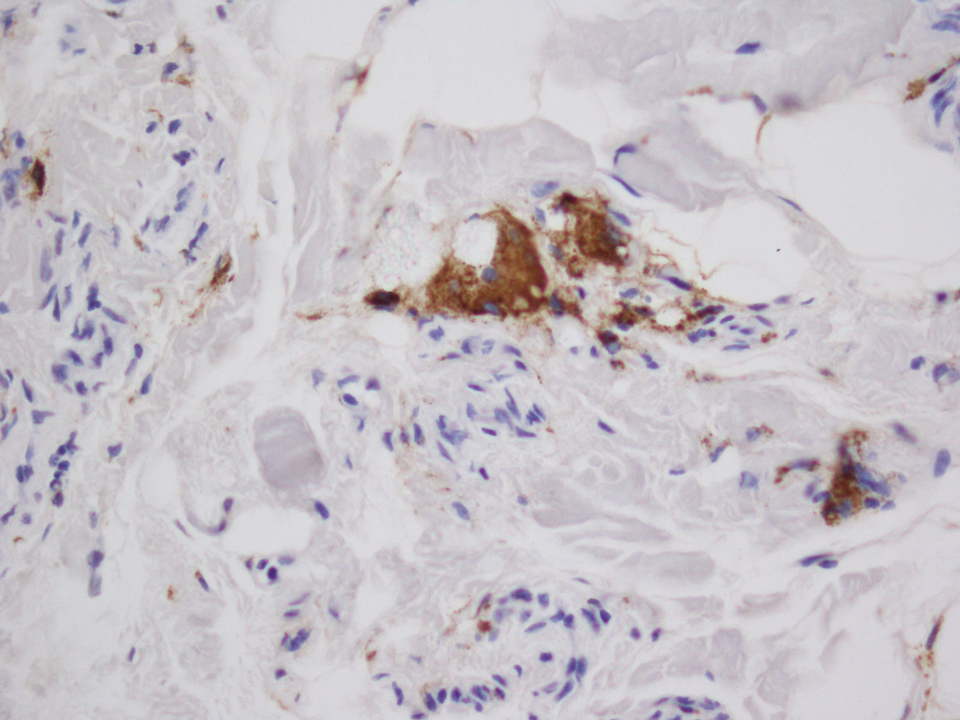
A 28-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with red, tender, swollen nodules on the left arm of 5 days’ duration, which had been a recurrent issue involving both arms. He also experienced intermittent fatigue and mild myalgia but denied associated fevers or chills. Oral clindamycin prescribed by a local emergency department provided some improvement. Upon further questioning, the patient admitted to injecting an unknown substance into the muscles 10 years prior for the purpose of enhancing their volume and appearance. Physical examination revealed large bilateral biceps with firm, mobile, nontender, subcutaneous nodules and mild erythema on the inner aspects of the arms. An incisional biopsy of a left arm nodule was performed with tissue culture (Figure 1). Microscopic evaluation revealed mild dermal sclerosis with edema and sclerosis of fat septae (Figure 2A). The fat lobules contained granulomas with surrounding lymphocytes and clear holes noted within the histiocytic giant cells, indicating a likely foreign substance (Figure 2B). Immunohistochemical staining of the histiocytes with CD68 highlighted the clear vacuoles (Figure 3). Polarization examination, Alcian blue, periodic acid–Schiff, and acid-fast bacilli staining were negative. Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures and staining also were negative. The histologic findings of septal and lobular panniculitis with sclerosis and granulomatous inflammation in the clinical setting were consistent with a foreign body reaction secondary to synthol injection.
The willingness of athletes in competitive sports to undergo procedures or utilize substances for a competitive advantage despite both immediate and long-term consequences is well documented.1,2 In bodybuilding, use of anabolic steroids and intramuscular oil injections has been documented.3 The use of site enhancements in the form of “fillers” such as petroleum jelly and paraffin have been used for more than 100 years.4 The use of oil for volumetric site enhancement began in the 1960s in Italy with formebolone and evolved to the use of synthol in the 1990s.5 Synthol is a substance composed of 85% oil in the form of medium-chain triglycerides, 7.5% alcohol, and 7.5% lidocaine.6 The presumed mechanism of action of injected oils consists of an initial inflammatory response followed by fibrosis and chronic macrophagocytosis, ultimately leading to expanded volume in the subcutaneous tissue.7 These procedures are purely aesthetic with no increase in muscle strength or performance.
There are few cases in the literature of side effects from intramuscular synthol injections. In one report, a 29-year-old man presented with painful muscle fibrosis requiring open surgical excision of massively fibrotic bicep tissue.8 Another report documented a 45-year-old man who presented with spontaneous ulcerations on the biceps that initially were treated with antibiotics and compression therapy but eventually required surgical intervention and skin grafting.9 Complications have been more frequently reported from injections of other oils such as paraffin and sesame.10,11 Given the similar underlying mechanisms of action, injected oils share the local side effects of inflammation, infection, chronic wounds, and ulceration,9,10 as well as a systemic risk for embolization leading to pulmonary emboli, myocardial infarction, and stroke.6 Although no standard of care exists for the management of complications arising from intramuscular oil injections, treatments that have been employed include antibiotics, corticosteroids, wound care, and compression therapy; definitive treatment typically is surgical excision.6,8,9,11,12 Psychiatric evaluation also should be considered to evaluate for the possibility of body dysmorphic disorder and other associated psychiatric conditions.11
Pressure for a particular aesthetic appearance, both within and outside the world of competitive sports, has driven individuals to various methods of muscular enhancement. Volumetric site enhancements have become increasingly popular, in part due to the perceived lack of systemic side effects, such as those associated with anabolic steroids.8 However, most users are unaware of the notable short-term and long-term risks associated with intramuscular oil injections. Synthol is widely available on the Internet and easily can be purchased and injected by anyone.13 Medical providers should be aware of the possibility of aesthetic site enhancement use in their patients and be able to recognize and intervene in these cases to prevent chronic damage to muscle tissue and accompanying complications. Despite extensive commercialization of these products, few reports in the medical literature exist detailing the side effects of intramuscular oil injections, which may be contributing to the trivialization of these procedures by the general public.12
- Baron DA, Martin DM, Abol Magd S. Doping in sports and its spread to at-risk populations: an international review. World Psychiatry. 2007;6:118-123.
- Holt RIG, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Sönksen PH. The history of doping and growth hormone abuse in sport. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009;19:320-326.
- Figueiredo VC, Pedroso da Silva PR. Cosmetic doping—when anabolic-androgenic steroids are not enough. Subst Use Misuse. 2014;49:1163-1167.
- Glicenstein J. The first “fillers,” vaseline and paraffin. from miracle to disaster [in French]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2007;52:157-161.
- Evans NA. Gym and tonic: a profile of 100 male steroid users. Br J Sports Med. 1997;31:54-58.
- Pupka A, Sikora J, Mauricz J, et al. The usage of synthol in the body building [in Polish]. Polim Med. 2009;39:63-65.
- Di Benedetto G, Pierangeli M, Scalise A, et al. Paraffin oil injection in the body: an obsolete and destructive procedure. Ann Plast Surg. 2002;49:391-396.
- Ghandourah S, Hofer MJ, Kiessling A, et al. Painful muscle fibrosis following synthol injections in a bodybuilder: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012;6:248.
- Ikander P, Nielsen AM, Sørensen JA. Injection of synthol in a bodybuilder can cause chronic wounds and ulceration [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2015;177:V12140642.
- Henriksen TF, Løvenwald JB, Matzen SH. Paraffin oil injection in bodybuilders calls for preventive action [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010;172:219-220.
- Darsow U, Bruckbauer H, Worret WI, et al. Subcutaneous oleomas induced by self-injection of sesame seed oil for muscle augmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2, pt 1):292-294.
- Banke IJ, Prodinger PM, Waldt S, et al. Irreversible muscle damage in bodybuilding due to long-term intramuscular oil injection. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33:829-834.
- Hall M, Grogan S, Gough B. Bodybuilders’ accounts of synthol use: the construction of lay expertise online. J Health Psychol. 2016;21:1939-1948.
To the Editor:
A 28-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with red, tender, swollen nodules on the left arm of 5 days’ duration, which had been a recurrent issue involving both arms. He also experienced intermittent fatigue and mild myalgia but denied associated fevers or chills. Oral clindamycin prescribed by a local emergency department provided some improvement. Upon further questioning, the patient admitted to injecting an unknown substance into the muscles 10 years prior for the purpose of enhancing their volume and appearance. Physical examination revealed large bilateral biceps with firm, mobile, nontender, subcutaneous nodules and mild erythema on the inner aspects of the arms. An incisional biopsy of a left arm nodule was performed with tissue culture (Figure 1). Microscopic evaluation revealed mild dermal sclerosis with edema and sclerosis of fat septae (Figure 2A). The fat lobules contained granulomas with surrounding lymphocytes and clear holes noted within the histiocytic giant cells, indicating a likely foreign substance (Figure 2B). Immunohistochemical staining of the histiocytes with CD68 highlighted the clear vacuoles (Figure 3). Polarization examination, Alcian blue, periodic acid–Schiff, and acid-fast bacilli staining were negative. Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures and staining also were negative. The histologic findings of septal and lobular panniculitis with sclerosis and granulomatous inflammation in the clinical setting were consistent with a foreign body reaction secondary to synthol injection.



The willingness of athletes in competitive sports to undergo procedures or utilize substances for a competitive advantage despite both immediate and long-term consequences is well documented.1,2 In bodybuilding, use of anabolic steroids and intramuscular oil injections has been documented.3 The use of site enhancements in the form of “fillers” such as petroleum jelly and paraffin have been used for more than 100 years.4 The use of oil for volumetric site enhancement began in the 1960s in Italy with formebolone and evolved to the use of synthol in the 1990s.5 Synthol is a substance composed of 85% oil in the form of medium-chain triglycerides, 7.5% alcohol, and 7.5% lidocaine.6 The presumed mechanism of action of injected oils consists of an initial inflammatory response followed by fibrosis and chronic macrophagocytosis, ultimately leading to expanded volume in the subcutaneous tissue.7 These procedures are purely aesthetic with no increase in muscle strength or performance.
There are few cases in the literature of side effects from intramuscular synthol injections. In one report, a 29-year-old man presented with painful muscle fibrosis requiring open surgical excision of massively fibrotic bicep tissue.8 Another report documented a 45-year-old man who presented with spontaneous ulcerations on the biceps that initially were treated with antibiotics and compression therapy but eventually required surgical intervention and skin grafting.9 Complications have been more frequently reported from injections of other oils such as paraffin and sesame.10,11 Given the similar underlying mechanisms of action, injected oils share the local side effects of inflammation, infection, chronic wounds, and ulceration,9,10 as well as a systemic risk for embolization leading to pulmonary emboli, myocardial infarction, and stroke.6 Although no standard of care exists for the management of complications arising from intramuscular oil injections, treatments that have been employed include antibiotics, corticosteroids, wound care, and compression therapy; definitive treatment typically is surgical excision.6,8,9,11,12 Psychiatric evaluation also should be considered to evaluate for the possibility of body dysmorphic disorder and other associated psychiatric conditions.11
Pressure for a particular aesthetic appearance, both within and outside the world of competitive sports, has driven individuals to various methods of muscular enhancement. Volumetric site enhancements have become increasingly popular, in part due to the perceived lack of systemic side effects, such as those associated with anabolic steroids.8 However, most users are unaware of the notable short-term and long-term risks associated with intramuscular oil injections. Synthol is widely available on the Internet and easily can be purchased and injected by anyone.13 Medical providers should be aware of the possibility of aesthetic site enhancement use in their patients and be able to recognize and intervene in these cases to prevent chronic damage to muscle tissue and accompanying complications. Despite extensive commercialization of these products, few reports in the medical literature exist detailing the side effects of intramuscular oil injections, which may be contributing to the trivialization of these procedures by the general public.12
To the Editor:
A 28-year-old man presented to the dermatology clinic with red, tender, swollen nodules on the left arm of 5 days’ duration, which had been a recurrent issue involving both arms. He also experienced intermittent fatigue and mild myalgia but denied associated fevers or chills. Oral clindamycin prescribed by a local emergency department provided some improvement. Upon further questioning, the patient admitted to injecting an unknown substance into the muscles 10 years prior for the purpose of enhancing their volume and appearance. Physical examination revealed large bilateral biceps with firm, mobile, nontender, subcutaneous nodules and mild erythema on the inner aspects of the arms. An incisional biopsy of a left arm nodule was performed with tissue culture (Figure 1). Microscopic evaluation revealed mild dermal sclerosis with edema and sclerosis of fat septae (Figure 2A). The fat lobules contained granulomas with surrounding lymphocytes and clear holes noted within the histiocytic giant cells, indicating a likely foreign substance (Figure 2B). Immunohistochemical staining of the histiocytes with CD68 highlighted the clear vacuoles (Figure 3). Polarization examination, Alcian blue, periodic acid–Schiff, and acid-fast bacilli staining were negative. Bacterial, fungal, and mycobacterial tissue cultures and staining also were negative. The histologic findings of septal and lobular panniculitis with sclerosis and granulomatous inflammation in the clinical setting were consistent with a foreign body reaction secondary to synthol injection.



The willingness of athletes in competitive sports to undergo procedures or utilize substances for a competitive advantage despite both immediate and long-term consequences is well documented.1,2 In bodybuilding, use of anabolic steroids and intramuscular oil injections has been documented.3 The use of site enhancements in the form of “fillers” such as petroleum jelly and paraffin have been used for more than 100 years.4 The use of oil for volumetric site enhancement began in the 1960s in Italy with formebolone and evolved to the use of synthol in the 1990s.5 Synthol is a substance composed of 85% oil in the form of medium-chain triglycerides, 7.5% alcohol, and 7.5% lidocaine.6 The presumed mechanism of action of injected oils consists of an initial inflammatory response followed by fibrosis and chronic macrophagocytosis, ultimately leading to expanded volume in the subcutaneous tissue.7 These procedures are purely aesthetic with no increase in muscle strength or performance.
There are few cases in the literature of side effects from intramuscular synthol injections. In one report, a 29-year-old man presented with painful muscle fibrosis requiring open surgical excision of massively fibrotic bicep tissue.8 Another report documented a 45-year-old man who presented with spontaneous ulcerations on the biceps that initially were treated with antibiotics and compression therapy but eventually required surgical intervention and skin grafting.9 Complications have been more frequently reported from injections of other oils such as paraffin and sesame.10,11 Given the similar underlying mechanisms of action, injected oils share the local side effects of inflammation, infection, chronic wounds, and ulceration,9,10 as well as a systemic risk for embolization leading to pulmonary emboli, myocardial infarction, and stroke.6 Although no standard of care exists for the management of complications arising from intramuscular oil injections, treatments that have been employed include antibiotics, corticosteroids, wound care, and compression therapy; definitive treatment typically is surgical excision.6,8,9,11,12 Psychiatric evaluation also should be considered to evaluate for the possibility of body dysmorphic disorder and other associated psychiatric conditions.11
Pressure for a particular aesthetic appearance, both within and outside the world of competitive sports, has driven individuals to various methods of muscular enhancement. Volumetric site enhancements have become increasingly popular, in part due to the perceived lack of systemic side effects, such as those associated with anabolic steroids.8 However, most users are unaware of the notable short-term and long-term risks associated with intramuscular oil injections. Synthol is widely available on the Internet and easily can be purchased and injected by anyone.13 Medical providers should be aware of the possibility of aesthetic site enhancement use in their patients and be able to recognize and intervene in these cases to prevent chronic damage to muscle tissue and accompanying complications. Despite extensive commercialization of these products, few reports in the medical literature exist detailing the side effects of intramuscular oil injections, which may be contributing to the trivialization of these procedures by the general public.12
- Baron DA, Martin DM, Abol Magd S. Doping in sports and its spread to at-risk populations: an international review. World Psychiatry. 2007;6:118-123.
- Holt RIG, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Sönksen PH. The history of doping and growth hormone abuse in sport. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009;19:320-326.
- Figueiredo VC, Pedroso da Silva PR. Cosmetic doping—when anabolic-androgenic steroids are not enough. Subst Use Misuse. 2014;49:1163-1167.
- Glicenstein J. The first “fillers,” vaseline and paraffin. from miracle to disaster [in French]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2007;52:157-161.
- Evans NA. Gym and tonic: a profile of 100 male steroid users. Br J Sports Med. 1997;31:54-58.
- Pupka A, Sikora J, Mauricz J, et al. The usage of synthol in the body building [in Polish]. Polim Med. 2009;39:63-65.
- Di Benedetto G, Pierangeli M, Scalise A, et al. Paraffin oil injection in the body: an obsolete and destructive procedure. Ann Plast Surg. 2002;49:391-396.
- Ghandourah S, Hofer MJ, Kiessling A, et al. Painful muscle fibrosis following synthol injections in a bodybuilder: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012;6:248.
- Ikander P, Nielsen AM, Sørensen JA. Injection of synthol in a bodybuilder can cause chronic wounds and ulceration [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2015;177:V12140642.
- Henriksen TF, Løvenwald JB, Matzen SH. Paraffin oil injection in bodybuilders calls for preventive action [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010;172:219-220.
- Darsow U, Bruckbauer H, Worret WI, et al. Subcutaneous oleomas induced by self-injection of sesame seed oil for muscle augmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2, pt 1):292-294.
- Banke IJ, Prodinger PM, Waldt S, et al. Irreversible muscle damage in bodybuilding due to long-term intramuscular oil injection. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33:829-834.
- Hall M, Grogan S, Gough B. Bodybuilders’ accounts of synthol use: the construction of lay expertise online. J Health Psychol. 2016;21:1939-1948.
- Baron DA, Martin DM, Abol Magd S. Doping in sports and its spread to at-risk populations: an international review. World Psychiatry. 2007;6:118-123.
- Holt RIG, Erotokritou-Mulligan I, Sönksen PH. The history of doping and growth hormone abuse in sport. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2009;19:320-326.
- Figueiredo VC, Pedroso da Silva PR. Cosmetic doping—when anabolic-androgenic steroids are not enough. Subst Use Misuse. 2014;49:1163-1167.
- Glicenstein J. The first “fillers,” vaseline and paraffin. from miracle to disaster [in French]. Ann Chir Plast Esthet. 2007;52:157-161.
- Evans NA. Gym and tonic: a profile of 100 male steroid users. Br J Sports Med. 1997;31:54-58.
- Pupka A, Sikora J, Mauricz J, et al. The usage of synthol in the body building [in Polish]. Polim Med. 2009;39:63-65.
- Di Benedetto G, Pierangeli M, Scalise A, et al. Paraffin oil injection in the body: an obsolete and destructive procedure. Ann Plast Surg. 2002;49:391-396.
- Ghandourah S, Hofer MJ, Kiessling A, et al. Painful muscle fibrosis following synthol injections in a bodybuilder: a case report. J Med Case Rep. 2012;6:248.
- Ikander P, Nielsen AM, Sørensen JA. Injection of synthol in a bodybuilder can cause chronic wounds and ulceration [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2015;177:V12140642.
- Henriksen TF, Løvenwald JB, Matzen SH. Paraffin oil injection in bodybuilders calls for preventive action [in Danish]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2010;172:219-220.
- Darsow U, Bruckbauer H, Worret WI, et al. Subcutaneous oleomas induced by self-injection of sesame seed oil for muscle augmentation. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2000;42(2, pt 1):292-294.
- Banke IJ, Prodinger PM, Waldt S, et al. Irreversible muscle damage in bodybuilding due to long-term intramuscular oil injection. Int J Sports Med. 2012;33:829-834.
- Hall M, Grogan S, Gough B. Bodybuilders’ accounts of synthol use: the construction of lay expertise online. J Health Psychol. 2016;21:1939-1948.
Practice Points
- The use of injectable volumetric site enhancers in the form of oils to improve the aesthetic appearance of muscles has been prevalent for decades despite potentially serious adverse reactions.
- Complications from these procedures are underrecognized in the medical setting, perhaps owing to the trivialization of these procedures by the general public.
Disseminated Vesicles and Necrotic Papules
The Diagnosis: Lues Maligna
Laboratory evaluation demonstrated a total CD4 count of 26 cells/μL (reference range, 443-1471 cells/μL) with a viral load of 1,770,111 copies/mL (reference range, 0 copies/mL), as well as a positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test with a titer of 1:8 (reference range, nonreactive). A reactive treponemal antibody test confirmed a true positive RPR test result. Viral culture as well as direct fluorescence antibodies for varicella-zoster virus and an active vesicle of herpes simplex virus (HSV) were negative. Serum immunoglobulin titers for varicella-zoster virus demonstrated low IgM with a positive IgG demonstrating immunity without recent infection. Blood and lesional skin tissue cultures were negative for additional infectious etiologies including bacterial and fungal elements. A lumbar puncture was not performed.
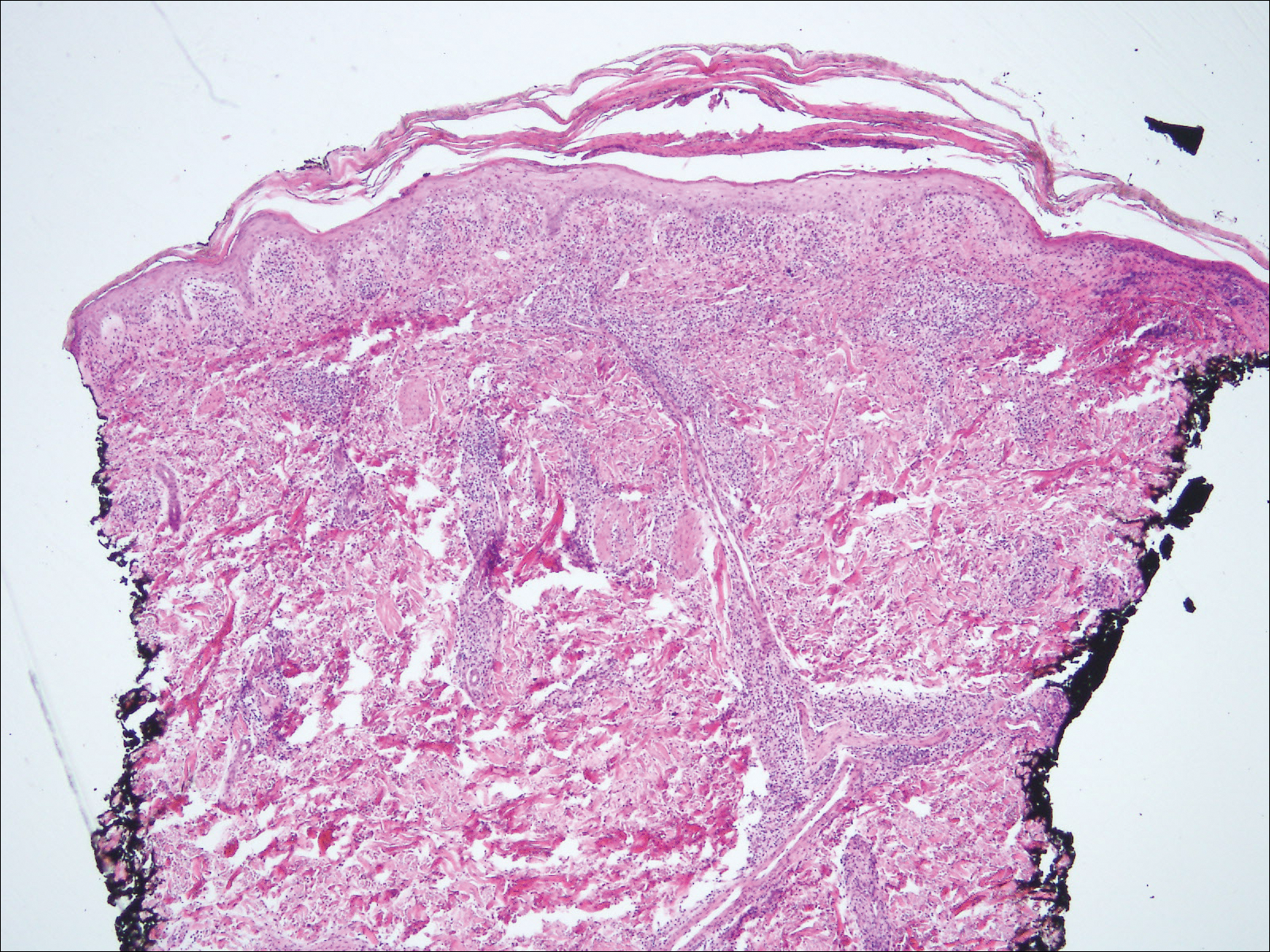
Biopsy of a papulonodule on the left arm demonstrated a lichenoid lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with superficial and deep inflammation (Figure 1). Neutrophils also were noted within a follicle with ballooning and acantholysis within the follicular epithelium. Additional staining for Mycobacterium, HSV-1, HSV-2, and Treponema were negative. In the clinical setting, this histologic pattern was most consistent with secondary syphilis. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta also was included in the histopathologic differential diagnosis by a dermatopathologist (M.C.).
Based on the clinical, microbiologic, and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of lues maligna (cutaneous secondary syphilis) with a vesiculonecrotic presentation was made. The patient's low RPR titer was attributed to profound immunosuppression, while a confirmation of syphilis infection was made with treponemal antibody testing. Histopathologic examination was consistent with lues maligna and did not demonstrate evidence of any other infectious etiologies.
Following 7 days of intravenous penicillin, the patient demonstrated dramatic improvement of all skin lesions and was discharged receiving once-weekly intramuscular penicillin for 4 weeks. In accordance with the diagnosis, the patient demonstrated rapid improvement of the lesions following appropriate antibiotic therapy.
After the diagnosis of lues maligna was made, the patient disclosed a sexual encounter with a male partner 6 weeks prior to the current presentation, after which he developed a self-resolving genital ulcer suspicious for a primary chancre.
Increasing rates of syphilis transmission have been attributed to males aged 15 to 44 years who have sexual encounters with other males.1 Although syphilis commonly is known as the great mimicker, syphilology texts state that lesions are not associated with syphilis if vesicles are part of the cutaneous eruption in an adult.2 However, rare reports of secondary syphilis presenting as vesicles, pustules, bullae, and pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta-like eruptions also have been documented.2-4
Initial screening for suspected syphilis involves sensitive, but not specific, nontreponemal RPR testing reported in the form of a titer. Nontreponemal titers in human immunodeficiency virus-positive individuals can be unusually high or low, fluctuate rapidly, and/or be unresponsive to antibiotic therapy.1
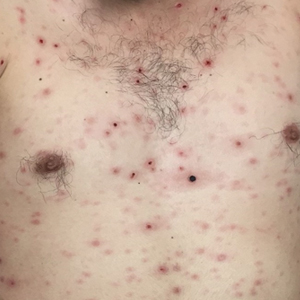
Lues maligna is a rare form of malignant secondary syphilis that most commonly presents in human immunodeficiency virus-positive hosts.5 Although lues maligna often presents with ulceronodular lesions, 2 cases presenting with vesiculonecrotic lesions also have been reported.6 Patients often experience systemic symptoms including fever, fatigue, and joint pain. Rapid plasma reagin titers can range from 1:8 to 1:128 in affected individuals.6 Diagnosis is dependent on serologic and histologic confirmation while ruling out viral, fungal, and bacterial etiologies. Characteristic red-brown lesions of secondary syphilis involving the palms and soles (Figure 2) alsoaid in diagnosis.1 Additionally, identification of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction following treatment and rapid response to antibiotic therapy are helpful diagnostic findings.6,7 While histopathologic examination of lues maligna typically does not reveal evidence of spirochetes, it also is important to rule out other infectious etiologies.7
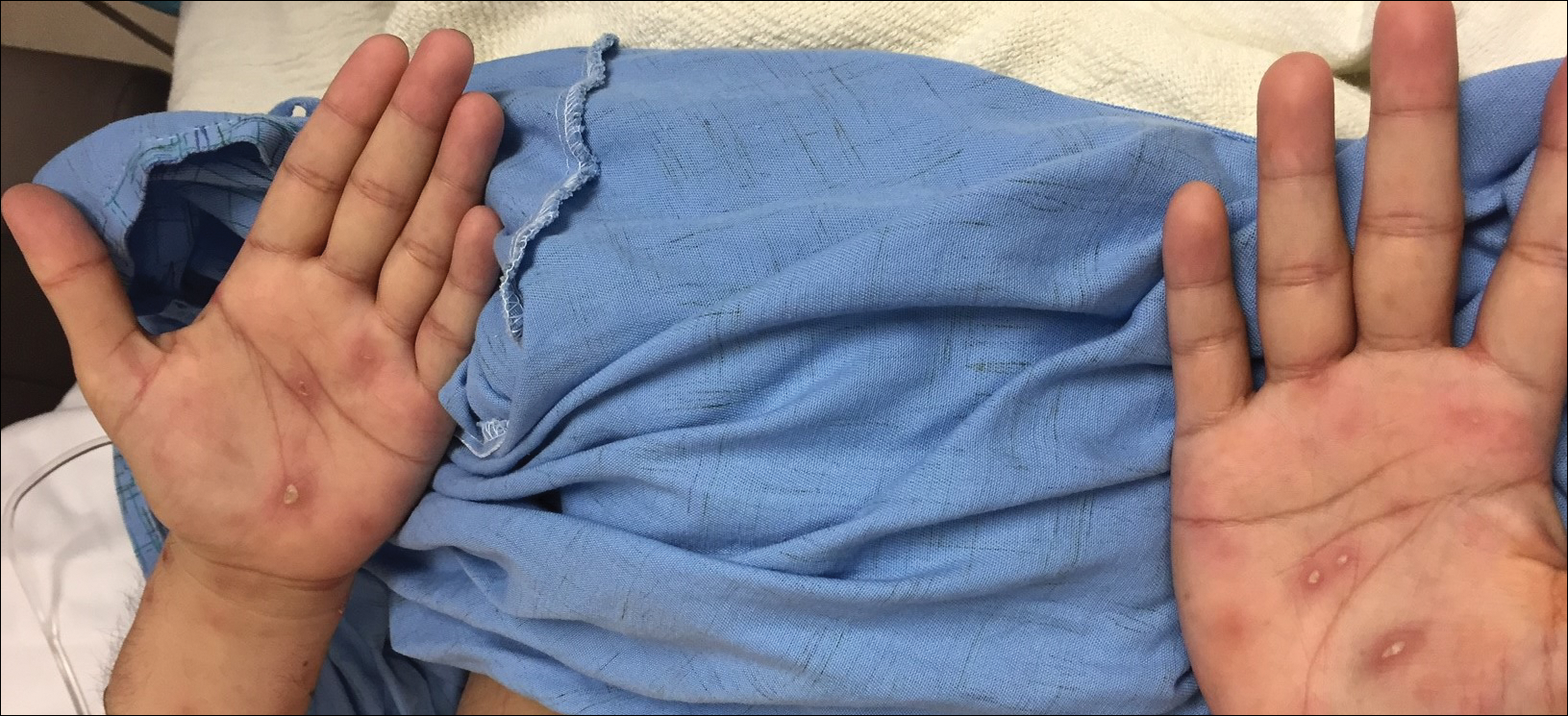

Our case emphasizes the importance of early recognition and treatment of the variable clinical, laboratory, and histologic presentations of lues maligna.
- Syphilis fact sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis.htm. Updated June 13, 2017. Accessed March 22, 2018.
- Lawrence P, Saxe N. Bullous secondary syphilis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:44-46.
- Pastuszczak M, Woz´niak W, Jaworek AK, et al. Pityriasis lichenoides-like secondary syphilis and neurosyphilis in a HIV-infected patient. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013;30:127-130.
- Schnirring-Judge M, Gustaferro C, Terol C. Vesiculobullous syphilis: a case involving an unusual cutaneous manifestation of secondary syphilis [published online November 24, 2010]. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:96-101.
- Pföhler C, Koerner R, von Müller L, et al. Lues maligna in a patient with unknown HIV infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2011. pii: bcr0520114221. doi: 10.1136/bcr.05.2011.4221.
- Don PC, Rubinstein R, Christie S. Malignant syphilis (lues maligna) and concurrent infection with HIV. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:403-407.
- Tucker JD, Shah S, Jarell AD, et al. Lues maligna in early HIV infection case report and review of the literature. Sex Transm Dis. 2009;36:512-514.
The Diagnosis: Lues Maligna
Laboratory evaluation demonstrated a total CD4 count of 26 cells/μL (reference range, 443-1471 cells/μL) with a viral load of 1,770,111 copies/mL (reference range, 0 copies/mL), as well as a positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test with a titer of 1:8 (reference range, nonreactive). A reactive treponemal antibody test confirmed a true positive RPR test result. Viral culture as well as direct fluorescence antibodies for varicella-zoster virus and an active vesicle of herpes simplex virus (HSV) were negative. Serum immunoglobulin titers for varicella-zoster virus demonstrated low IgM with a positive IgG demonstrating immunity without recent infection. Blood and lesional skin tissue cultures were negative for additional infectious etiologies including bacterial and fungal elements. A lumbar puncture was not performed.
Biopsy of a papulonodule on the left arm demonstrated a lichenoid lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with superficial and deep inflammation (Figure 1). Neutrophils also were noted within a follicle with ballooning and acantholysis within the follicular epithelium. Additional staining for Mycobacterium, HSV-1, HSV-2, and Treponema were negative. In the clinical setting, this histologic pattern was most consistent with secondary syphilis. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta also was included in the histopathologic differential diagnosis by a dermatopathologist (M.C.).

Based on the clinical, microbiologic, and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of lues maligna (cutaneous secondary syphilis) with a vesiculonecrotic presentation was made. The patient's low RPR titer was attributed to profound immunosuppression, while a confirmation of syphilis infection was made with treponemal antibody testing. Histopathologic examination was consistent with lues maligna and did not demonstrate evidence of any other infectious etiologies.
Following 7 days of intravenous penicillin, the patient demonstrated dramatic improvement of all skin lesions and was discharged receiving once-weekly intramuscular penicillin for 4 weeks. In accordance with the diagnosis, the patient demonstrated rapid improvement of the lesions following appropriate antibiotic therapy.
After the diagnosis of lues maligna was made, the patient disclosed a sexual encounter with a male partner 6 weeks prior to the current presentation, after which he developed a self-resolving genital ulcer suspicious for a primary chancre.
Increasing rates of syphilis transmission have been attributed to males aged 15 to 44 years who have sexual encounters with other males.1 Although syphilis commonly is known as the great mimicker, syphilology texts state that lesions are not associated with syphilis if vesicles are part of the cutaneous eruption in an adult.2 However, rare reports of secondary syphilis presenting as vesicles, pustules, bullae, and pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta-like eruptions also have been documented.2-4
Initial screening for suspected syphilis involves sensitive, but not specific, nontreponemal RPR testing reported in the form of a titer. Nontreponemal titers in human immunodeficiency virus-positive individuals can be unusually high or low, fluctuate rapidly, and/or be unresponsive to antibiotic therapy.1
Lues maligna is a rare form of malignant secondary syphilis that most commonly presents in human immunodeficiency virus-positive hosts.5 Although lues maligna often presents with ulceronodular lesions, 2 cases presenting with vesiculonecrotic lesions also have been reported.6 Patients often experience systemic symptoms including fever, fatigue, and joint pain. Rapid plasma reagin titers can range from 1:8 to 1:128 in affected individuals.6 Diagnosis is dependent on serologic and histologic confirmation while ruling out viral, fungal, and bacterial etiologies. Characteristic red-brown lesions of secondary syphilis involving the palms and soles (Figure 2) alsoaid in diagnosis.1 Additionally, identification of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction following treatment and rapid response to antibiotic therapy are helpful diagnostic findings.6,7 While histopathologic examination of lues maligna typically does not reveal evidence of spirochetes, it also is important to rule out other infectious etiologies.7

Our case emphasizes the importance of early recognition and treatment of the variable clinical, laboratory, and histologic presentations of lues maligna.
The Diagnosis: Lues Maligna
Laboratory evaluation demonstrated a total CD4 count of 26 cells/μL (reference range, 443-1471 cells/μL) with a viral load of 1,770,111 copies/mL (reference range, 0 copies/mL), as well as a positive rapid plasma reagin (RPR) test with a titer of 1:8 (reference range, nonreactive). A reactive treponemal antibody test confirmed a true positive RPR test result. Viral culture as well as direct fluorescence antibodies for varicella-zoster virus and an active vesicle of herpes simplex virus (HSV) were negative. Serum immunoglobulin titers for varicella-zoster virus demonstrated low IgM with a positive IgG demonstrating immunity without recent infection. Blood and lesional skin tissue cultures were negative for additional infectious etiologies including bacterial and fungal elements. A lumbar puncture was not performed.
Biopsy of a papulonodule on the left arm demonstrated a lichenoid lymphohistiocytic infiltrate with superficial and deep inflammation (Figure 1). Neutrophils also were noted within a follicle with ballooning and acantholysis within the follicular epithelium. Additional staining for Mycobacterium, HSV-1, HSV-2, and Treponema were negative. In the clinical setting, this histologic pattern was most consistent with secondary syphilis. Pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta also was included in the histopathologic differential diagnosis by a dermatopathologist (M.C.).

Based on the clinical, microbiologic, and histopathologic findings, a diagnosis of lues maligna (cutaneous secondary syphilis) with a vesiculonecrotic presentation was made. The patient's low RPR titer was attributed to profound immunosuppression, while a confirmation of syphilis infection was made with treponemal antibody testing. Histopathologic examination was consistent with lues maligna and did not demonstrate evidence of any other infectious etiologies.
Following 7 days of intravenous penicillin, the patient demonstrated dramatic improvement of all skin lesions and was discharged receiving once-weekly intramuscular penicillin for 4 weeks. In accordance with the diagnosis, the patient demonstrated rapid improvement of the lesions following appropriate antibiotic therapy.
After the diagnosis of lues maligna was made, the patient disclosed a sexual encounter with a male partner 6 weeks prior to the current presentation, after which he developed a self-resolving genital ulcer suspicious for a primary chancre.
Increasing rates of syphilis transmission have been attributed to males aged 15 to 44 years who have sexual encounters with other males.1 Although syphilis commonly is known as the great mimicker, syphilology texts state that lesions are not associated with syphilis if vesicles are part of the cutaneous eruption in an adult.2 However, rare reports of secondary syphilis presenting as vesicles, pustules, bullae, and pityriasis lichenoides et varioliformis acuta-like eruptions also have been documented.2-4
Initial screening for suspected syphilis involves sensitive, but not specific, nontreponemal RPR testing reported in the form of a titer. Nontreponemal titers in human immunodeficiency virus-positive individuals can be unusually high or low, fluctuate rapidly, and/or be unresponsive to antibiotic therapy.1
Lues maligna is a rare form of malignant secondary syphilis that most commonly presents in human immunodeficiency virus-positive hosts.5 Although lues maligna often presents with ulceronodular lesions, 2 cases presenting with vesiculonecrotic lesions also have been reported.6 Patients often experience systemic symptoms including fever, fatigue, and joint pain. Rapid plasma reagin titers can range from 1:8 to 1:128 in affected individuals.6 Diagnosis is dependent on serologic and histologic confirmation while ruling out viral, fungal, and bacterial etiologies. Characteristic red-brown lesions of secondary syphilis involving the palms and soles (Figure 2) alsoaid in diagnosis.1 Additionally, identification of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction following treatment and rapid response to antibiotic therapy are helpful diagnostic findings.6,7 While histopathologic examination of lues maligna typically does not reveal evidence of spirochetes, it also is important to rule out other infectious etiologies.7

Our case emphasizes the importance of early recognition and treatment of the variable clinical, laboratory, and histologic presentations of lues maligna.
- Syphilis fact sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis.htm. Updated June 13, 2017. Accessed March 22, 2018.
- Lawrence P, Saxe N. Bullous secondary syphilis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:44-46.
- Pastuszczak M, Woz´niak W, Jaworek AK, et al. Pityriasis lichenoides-like secondary syphilis and neurosyphilis in a HIV-infected patient. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013;30:127-130.
- Schnirring-Judge M, Gustaferro C, Terol C. Vesiculobullous syphilis: a case involving an unusual cutaneous manifestation of secondary syphilis [published online November 24, 2010]. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:96-101.
- Pföhler C, Koerner R, von Müller L, et al. Lues maligna in a patient with unknown HIV infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2011. pii: bcr0520114221. doi: 10.1136/bcr.05.2011.4221.
- Don PC, Rubinstein R, Christie S. Malignant syphilis (lues maligna) and concurrent infection with HIV. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:403-407.
- Tucker JD, Shah S, Jarell AD, et al. Lues maligna in early HIV infection case report and review of the literature. Sex Transm Dis. 2009;36:512-514.
- Syphilis fact sheet. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention website. https://www.cdc.gov/std/syphilis/stdfact-syphilis.htm. Updated June 13, 2017. Accessed March 22, 2018.
- Lawrence P, Saxe N. Bullous secondary syphilis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1992;17:44-46.
- Pastuszczak M, Woz´niak W, Jaworek AK, et al. Pityriasis lichenoides-like secondary syphilis and neurosyphilis in a HIV-infected patient. Postepy Dermatol Alergol. 2013;30:127-130.
- Schnirring-Judge M, Gustaferro C, Terol C. Vesiculobullous syphilis: a case involving an unusual cutaneous manifestation of secondary syphilis [published online November 24, 2010]. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2011;50:96-101.
- Pföhler C, Koerner R, von Müller L, et al. Lues maligna in a patient with unknown HIV infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2011. pii: bcr0520114221. doi: 10.1136/bcr.05.2011.4221.
- Don PC, Rubinstein R, Christie S. Malignant syphilis (lues maligna) and concurrent infection with HIV. Int J Dermatol. 1995;34:403-407.
- Tucker JD, Shah S, Jarell AD, et al. Lues maligna in early HIV infection case report and review of the literature. Sex Transm Dis. 2009;36:512-514.

A 30-year-old man who had contracted human immunodeficiency virus from a male sexual partner 4 years prior presented to the emergency department with fevers, chills, night sweats, and rhinorrhea of 2 weeks' duration. He reported that he had been off highly active antiretroviral therapy for 2 years. Physical examination revealed numerous erythematous, papulonecrotic, crusted lesions on the face, neck, chest, back, arms, and legs that had developed over the past 4 days. Fluid-filled vesicles also were noted on the arms and legs, while erythematous, indurated nodules with overlying scaling were noted on the bilateral palms and soles. The patient reported that he had been vaccinated for varicella-zoster virus as a child without primary infection.