User login
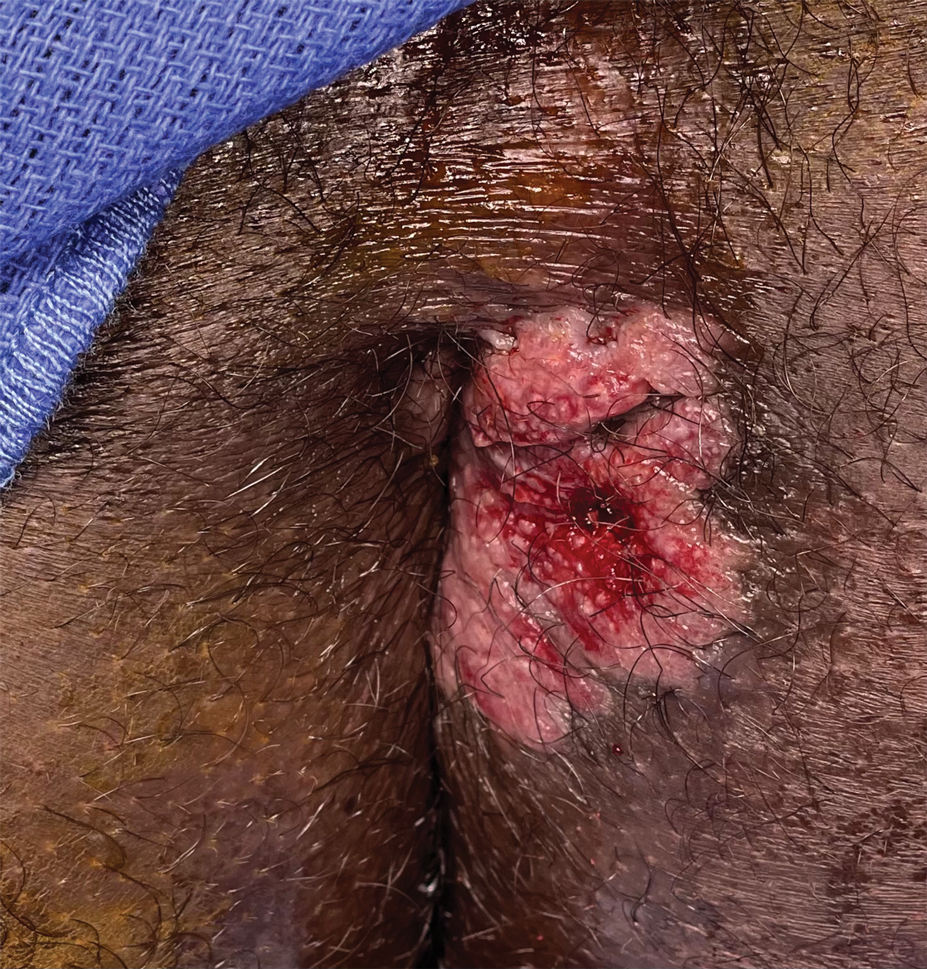
Painful Fungating Perianal Mass
The Diagnosis: Condyloma Latum
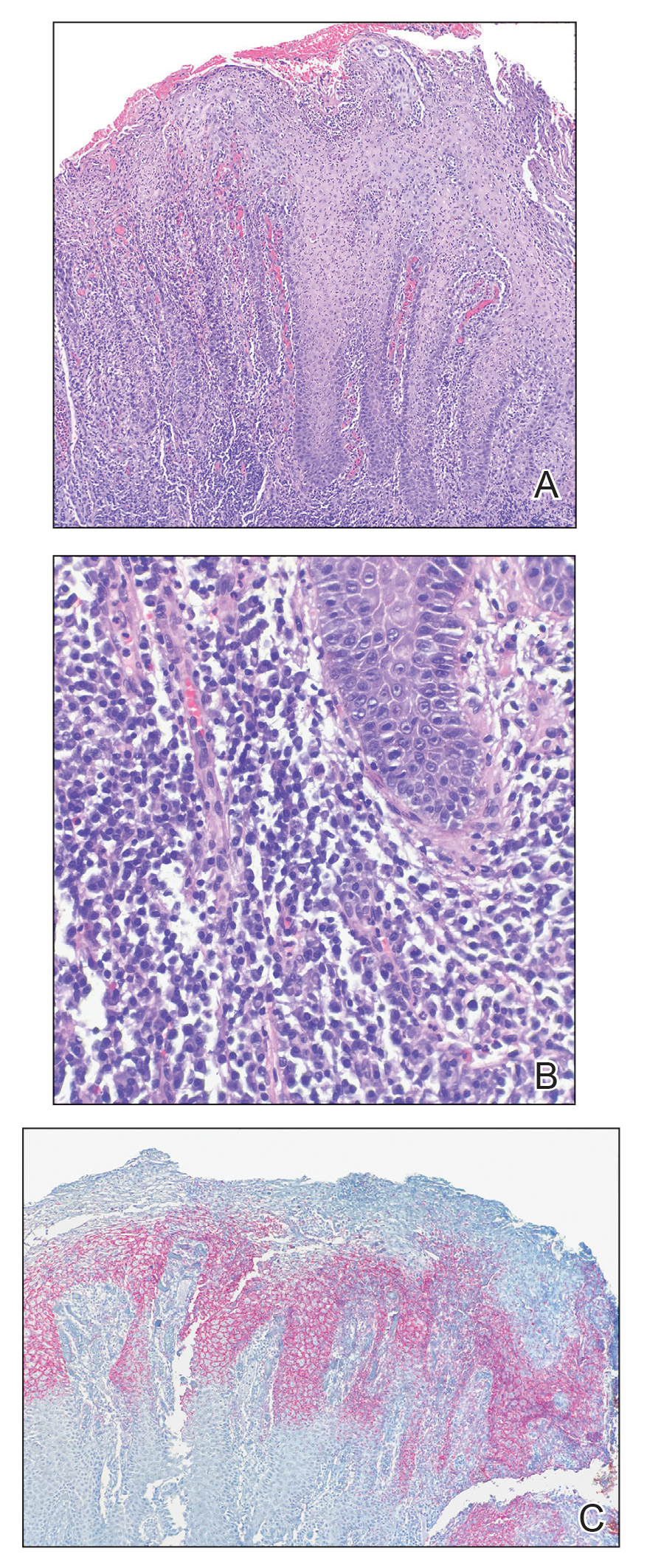
A punch biopsy of the perianal mass revealed epidermal acanthosis with elongated slender rete ridges, scattered intraepidermal neutrophils, and a dense dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure, A) with a prominent plasma cell component (Figure, B). A treponemal immunohistochemical stain revealed numerous coiled spirochetes concentrated in the lower epidermis (Figure, C). Serologic test results including rapid plasma reagin (titer 1:1024) and Treponema pallidum antibody were reactive, confirming the diagnosis of secondary syphilis with condyloma latum. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G with resolution of the lesion 2 weeks later.
Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete T pallidum, reached historically low rates in the United States in the early 2000s due to the widespread use of penicillin and effective public health efforts.1 However, the rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections recently have markedly increased, resulting in the current epidemic of syphilis in the United States and Europe.1,2 Its wide variety of clinical and histopathologic manifestations make recognition challenging and lend it the moniker “the great imitator.”
Secondary syphilis results from the systemic spread of T pallidum and classically is characterized by the triad of a skin rash that frequently involves the palms and soles, mucosal ulceration such as condyloma latum, and lymphadenopathy.2,3 However, condyloma latum may represent the only manifestation of secondary syphilis in a subset of patients,4 as observed in our patient.
In the 2 months prior to diagnosis, our patient was evaluated at multiple emergency departments and primary care clinics, receiving diagnoses of condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes simplex virus, hemorrhoids, and suspicion for malignancy—entities that comprise the differential diagnosis for condyloma latum.2,5 Despite some degree of overlap in patient populations, risk factors, and presentations between these diagnostic considerations, recognition of certain clinical features, in addition to histopathologic evaluation, may facilitate navigation of this differential diagnosis.
Primary and secondary syphilis infections have been predominantly observed in men, mostly men who have sex with men and/or those who are infected with HIV.1 Condyloma acuminata, genital herpes simplex virus, and chancroid also are seen in younger individuals, more commonly in those with multiple sexual partners, but show a more even gender distribution and are not restricted to those partaking in anal intercourse. The clinical presentation of condyloma latum can be differentiated by its painless, flat, smooth, and commonly hypopigmented appearance, often with associated surface erosion and a gray exudate, in contrast to condyloma acuminatum, which typically presents as nontender, flesh-colored or hyperpigmented, exophytic papules that may coalesce into plaques.2,3,6 Genital herpes simplex virus infection presents with multiple small papulovesicular lesions with ulceration, most commonly on the tip or shaft of the penis, though perianal lesions may be seen in men who have sex with men.7 Similarly, chancroid presents with painful necrotizing genital ulcers most commonly on the penis, though perianal lesions also may be seen.8 Hemorrhoids classically are seen in middle-aged adults with a history of constipation, present with rectal bleeding, and may be associated with pain in the setting of thrombosis or ulceration.9 Finally, perianal squamous cell carcinoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically in the sixth decade of life. Verrucous carcinoma most commonly arises in the oropharynx or anogenital region in sites of chronic irritation and presents as a slow-growing exophytic mass. Classic squamous cell carcinoma most commonly occurs in association with human papillomavirus infection and presents with scaly erythematous papules or plaques.10
Our case highlighted the clinical difficulty in recognizing condyloma latum, as this lesion remained undiagnosed for 2 months, and our patient presumptively was treated for multiple perianal pathologies prior to a biopsy being performed. Due to the clinical similarity of various perianal lesions, the diagnosis of condyloma latum should be considered, and serologic studies should be performed in fitting clinical contexts, especially in light of recently rising rates of syphilis infection.1,2
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Tayal S, Shaban F, Dasgupta K, et al. A case of syphilitic anal condylomata lata mimicking malignancy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 17:69-71.
- Aung PP, Wimmer DB, Lester TR, et al. Perianal condylomata lata mimicking carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49:209-214.
- Pourang A, Fung MA, Tartar D, et al. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;10:18-21.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJ, de Vries HJ. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259.
- Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Kumar S. Genital warts. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Groves MJ. Genital herpes: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2016; 93:928-934.
- Irizarry L, Velasquez J, Wray AA. Chancroid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Mounsey AL, Halladay J, Sadiq TS. Hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:204-210.
- Abbass MA, Valente MA. Premalignant and malignant perianal lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32:386-393.
The Diagnosis: Condyloma Latum
A punch biopsy of the perianal mass revealed epidermal acanthosis with elongated slender rete ridges, scattered intraepidermal neutrophils, and a dense dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure, A) with a prominent plasma cell component (Figure, B). A treponemal immunohistochemical stain revealed numerous coiled spirochetes concentrated in the lower epidermis (Figure, C). Serologic test results including rapid plasma reagin (titer 1:1024) and Treponema pallidum antibody were reactive, confirming the diagnosis of secondary syphilis with condyloma latum. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G with resolution of the lesion 2 weeks later.

Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete T pallidum, reached historically low rates in the United States in the early 2000s due to the widespread use of penicillin and effective public health efforts.1 However, the rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections recently have markedly increased, resulting in the current epidemic of syphilis in the United States and Europe.1,2 Its wide variety of clinical and histopathologic manifestations make recognition challenging and lend it the moniker “the great imitator.”
Secondary syphilis results from the systemic spread of T pallidum and classically is characterized by the triad of a skin rash that frequently involves the palms and soles, mucosal ulceration such as condyloma latum, and lymphadenopathy.2,3 However, condyloma latum may represent the only manifestation of secondary syphilis in a subset of patients,4 as observed in our patient.
In the 2 months prior to diagnosis, our patient was evaluated at multiple emergency departments and primary care clinics, receiving diagnoses of condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes simplex virus, hemorrhoids, and suspicion for malignancy—entities that comprise the differential diagnosis for condyloma latum.2,5 Despite some degree of overlap in patient populations, risk factors, and presentations between these diagnostic considerations, recognition of certain clinical features, in addition to histopathologic evaluation, may facilitate navigation of this differential diagnosis.
Primary and secondary syphilis infections have been predominantly observed in men, mostly men who have sex with men and/or those who are infected with HIV.1 Condyloma acuminata, genital herpes simplex virus, and chancroid also are seen in younger individuals, more commonly in those with multiple sexual partners, but show a more even gender distribution and are not restricted to those partaking in anal intercourse. The clinical presentation of condyloma latum can be differentiated by its painless, flat, smooth, and commonly hypopigmented appearance, often with associated surface erosion and a gray exudate, in contrast to condyloma acuminatum, which typically presents as nontender, flesh-colored or hyperpigmented, exophytic papules that may coalesce into plaques.2,3,6 Genital herpes simplex virus infection presents with multiple small papulovesicular lesions with ulceration, most commonly on the tip or shaft of the penis, though perianal lesions may be seen in men who have sex with men.7 Similarly, chancroid presents with painful necrotizing genital ulcers most commonly on the penis, though perianal lesions also may be seen.8 Hemorrhoids classically are seen in middle-aged adults with a history of constipation, present with rectal bleeding, and may be associated with pain in the setting of thrombosis or ulceration.9 Finally, perianal squamous cell carcinoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically in the sixth decade of life. Verrucous carcinoma most commonly arises in the oropharynx or anogenital region in sites of chronic irritation and presents as a slow-growing exophytic mass. Classic squamous cell carcinoma most commonly occurs in association with human papillomavirus infection and presents with scaly erythematous papules or plaques.10
Our case highlighted the clinical difficulty in recognizing condyloma latum, as this lesion remained undiagnosed for 2 months, and our patient presumptively was treated for multiple perianal pathologies prior to a biopsy being performed. Due to the clinical similarity of various perianal lesions, the diagnosis of condyloma latum should be considered, and serologic studies should be performed in fitting clinical contexts, especially in light of recently rising rates of syphilis infection.1,2
The Diagnosis: Condyloma Latum
A punch biopsy of the perianal mass revealed epidermal acanthosis with elongated slender rete ridges, scattered intraepidermal neutrophils, and a dense dermal inflammatory infiltrate (Figure, A) with a prominent plasma cell component (Figure, B). A treponemal immunohistochemical stain revealed numerous coiled spirochetes concentrated in the lower epidermis (Figure, C). Serologic test results including rapid plasma reagin (titer 1:1024) and Treponema pallidum antibody were reactive, confirming the diagnosis of secondary syphilis with condyloma latum. The patient was treated with intramuscular penicillin G with resolution of the lesion 2 weeks later.

Syphilis, a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete T pallidum, reached historically low rates in the United States in the early 2000s due to the widespread use of penicillin and effective public health efforts.1 However, the rates of primary and secondary syphilis infections recently have markedly increased, resulting in the current epidemic of syphilis in the United States and Europe.1,2 Its wide variety of clinical and histopathologic manifestations make recognition challenging and lend it the moniker “the great imitator.”
Secondary syphilis results from the systemic spread of T pallidum and classically is characterized by the triad of a skin rash that frequently involves the palms and soles, mucosal ulceration such as condyloma latum, and lymphadenopathy.2,3 However, condyloma latum may represent the only manifestation of secondary syphilis in a subset of patients,4 as observed in our patient.
In the 2 months prior to diagnosis, our patient was evaluated at multiple emergency departments and primary care clinics, receiving diagnoses of condyloma acuminatum, genital herpes simplex virus, hemorrhoids, and suspicion for malignancy—entities that comprise the differential diagnosis for condyloma latum.2,5 Despite some degree of overlap in patient populations, risk factors, and presentations between these diagnostic considerations, recognition of certain clinical features, in addition to histopathologic evaluation, may facilitate navigation of this differential diagnosis.
Primary and secondary syphilis infections have been predominantly observed in men, mostly men who have sex with men and/or those who are infected with HIV.1 Condyloma acuminata, genital herpes simplex virus, and chancroid also are seen in younger individuals, more commonly in those with multiple sexual partners, but show a more even gender distribution and are not restricted to those partaking in anal intercourse. The clinical presentation of condyloma latum can be differentiated by its painless, flat, smooth, and commonly hypopigmented appearance, often with associated surface erosion and a gray exudate, in contrast to condyloma acuminatum, which typically presents as nontender, flesh-colored or hyperpigmented, exophytic papules that may coalesce into plaques.2,3,6 Genital herpes simplex virus infection presents with multiple small papulovesicular lesions with ulceration, most commonly on the tip or shaft of the penis, though perianal lesions may be seen in men who have sex with men.7 Similarly, chancroid presents with painful necrotizing genital ulcers most commonly on the penis, though perianal lesions also may be seen.8 Hemorrhoids classically are seen in middle-aged adults with a history of constipation, present with rectal bleeding, and may be associated with pain in the setting of thrombosis or ulceration.9 Finally, perianal squamous cell carcinoma primarily occurs in older adults, typically in the sixth decade of life. Verrucous carcinoma most commonly arises in the oropharynx or anogenital region in sites of chronic irritation and presents as a slow-growing exophytic mass. Classic squamous cell carcinoma most commonly occurs in association with human papillomavirus infection and presents with scaly erythematous papules or plaques.10
Our case highlighted the clinical difficulty in recognizing condyloma latum, as this lesion remained undiagnosed for 2 months, and our patient presumptively was treated for multiple perianal pathologies prior to a biopsy being performed. Due to the clinical similarity of various perianal lesions, the diagnosis of condyloma latum should be considered, and serologic studies should be performed in fitting clinical contexts, especially in light of recently rising rates of syphilis infection.1,2
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Tayal S, Shaban F, Dasgupta K, et al. A case of syphilitic anal condylomata lata mimicking malignancy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 17:69-71.
- Aung PP, Wimmer DB, Lester TR, et al. Perianal condylomata lata mimicking carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49:209-214.
- Pourang A, Fung MA, Tartar D, et al. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;10:18-21.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJ, de Vries HJ. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259.
- Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Kumar S. Genital warts. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Groves MJ. Genital herpes: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2016; 93:928-934.
- Irizarry L, Velasquez J, Wray AA. Chancroid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Mounsey AL, Halladay J, Sadiq TS. Hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:204-210.
- Abbass MA, Valente MA. Premalignant and malignant perianal lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32:386-393.
- Ghanem KG, Ram S, Rice PA. The modern epidemic of syphilis. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:845-854.
- Tayal S, Shaban F, Dasgupta K, et al. A case of syphilitic anal condylomata lata mimicking malignancy. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015; 17:69-71.
- Aung PP, Wimmer DB, Lester TR, et al. Perianal condylomata lata mimicking carcinoma. J Cutan Pathol. 2022;49:209-214.
- Pourang A, Fung MA, Tartar D, et al. Condyloma lata in secondary syphilis. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;10:18-21.
- Bruins FG, van Deudekom FJ, de Vries HJ. Syphilitic condylomata lata mimicking anogenital warts. BMJ. 2015;350:h1259.
- Leslie SW, Sajjad H, Kumar S. Genital warts. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2021.
- Groves MJ. Genital herpes: a review. Am Fam Physician. 2016; 93:928-934.
- Irizarry L, Velasquez J, Wray AA. Chancroid. In: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; 2022.
- Mounsey AL, Halladay J, Sadiq TS. Hemorrhoids. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84:204-210.
- Abbass MA, Valente MA. Premalignant and malignant perianal lesions. Clin Colon Rectal Surg. 2019;32:386-393.
A 21-year-old man presented to our clinic with rectal pain of 2 months’ duration that occurred in association with bowel movements and rectal bleeding in the setting of constipation. The patient’s symptoms had persisted despite multiple clinical encounters and treatment with sulfamethoxazole-trimethoprim, clotrimazole, valacyclovir, topical hydrocortisone and pramoxine, topical lidocaine, imiquimod, and psyllium seed. The patient denied engaging in receptive anal intercourse and had no notable medical or surgical history. Physical examination revealed a 6-cm hypopigmented fungating mass on the left gluteal cleft just external to the anal verge; there were no other abnormal findings. The patient denied any other systemic symptoms.