User login
A Prescription for Note Bloat: An Effective Progress Note Template
The widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) has led to significant progress in the modernization of healthcare delivery. Ease of access has improved clinical efficiency, and digital data have allowed for point-of-care decision support tools ranging from predicting the 30-day risk of readmission to providing up-to-date guidelines for the care of various diseases.1,2 Documentation tools such as copy-forward and autopopulation increase the speed of documentation, and typed notes improve legibility and ease of note transmission.3,4
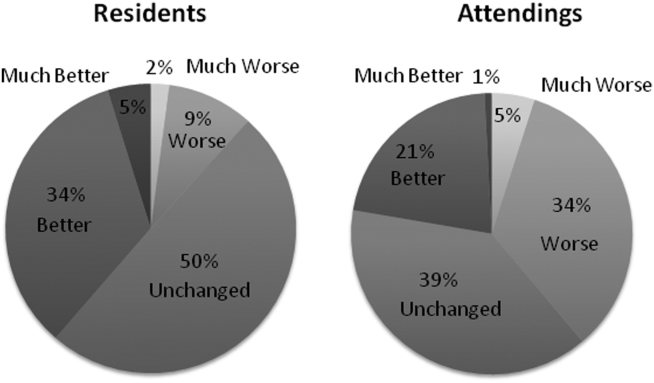
However, all of these benefits come with a potential for harm, particularly with respect to accurate and concise documentation. Many experts have described the perpetuation of false information leading to errors, copying-forward of inconsistent and outdated information, and the phenomenon of “note bloat” — physician notes that contain multiple pages of nonessential information, often leaving key aspects buried or lost.5-7 Providers seem to recognize the hazards of copy-and-paste functionality yet persist in utilizing it. In 1 survey, more than 70% of attendings and residents felt that copy and paste led to inaccurate and outdated information, yet 80% stated they would still use it.8
There is little evidence to guide institutions on ways to improve EHR documentation practices. Recent studies have shown that operative note templates improved documentation and decreased the number of missing components.9,10 In the nonoperative setting, 1 small pilot study of pediatric interns demonstrated that a bundled intervention composed of a note template and classroom teaching resulted in improvement in overall note quality and a decrease in “note clutter.”11 In a larger study of pediatric residents, a standardized and simplified note template resulted in a shorter note, although notes were completed later in the day.12 The present study seeks to build upon these efforts by investigating the effect of didactic teaching and an electronic progress note template on note quality, length, and timeliness across 4 academic internal medicine residency programs.
METHODS
Study Design
This prospective quality improvement study took place across 4 academic institutions: University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), University of California San Francisco (UCSF), University of California San Diego (UCSD), and University of Iowa, all of which use Epic EHR (Epic Corp., Madison, WI). The intervention combined brief educational conferences directed at housestaff and attendings with the implementation of an electronic progress note template. Guided by resident input, a note-writing task force at UCSF and UCLA developed a set of best practice guidelines and an aligned note template for progress notes (supplementary Appendix 1). UCSD and the University of Iowa adopted them at their respective institutions. The template’s design minimized autopopulation while encouraging providers to enter relevant data via free text fields (eg, physical exam), prompts (eg, “I have reviewed all the labs from today. Pertinent labs include…”), and drop-down menus (eg, deep vein thrombosis [DVT] prophylaxis: enoxaparin, heparin subcutaneously, etc; supplementary Appendix 2). Additionally, an inpatient checklist was included at the end of the note to serve as a reminder for key inpatient concerns and quality measures, such as Foley catheter days, discharge planning, and code status. Lectures that focused on issues with documentation in the EHR, the best practice guidelines, and a review of the note template with instructions on how to access it were presented to the housestaff. Each institution tailored the lecture to suit their culture. Housestaff were encouraged but not required to use the note template.
Selection and Grading of Progress Notes
Progress notes were eligible for the study if they were written by an intern on an internal medicine teaching service, from a patient with a hospitalization length of at least 3 days with a progress note selected from hospital day 2 or 3, and written while the patient was on the general medicine wards. The preintervention notes were authored from September 2013 to December 2013 and the postintervention notes from April 2014 to June 2014. One note was selected per patient and no more than 3 notes were selected per intern. Each institution selected the first 50 notes chronologically that met these criteria for both the preintervention and the postintervention periods, for a total of 400 notes. The note-grading tool consisted of the following 3 sections to analyze note quality: (1) a general impression of the note (eg, below average, average, above average); (2) the validated Physician Documentation Quality Instrument, 9-item version (PDQI-9) that evaluates notes on 9 domains (up to date, accurate, thorough, useful, organized, comprehensible, succinct, synthesized, internally consistent) on a Likert scale from 1 (not at all) to 5 (extremely); and (3) a note competency questionnaire based on the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education competency note checklist that asked yes or no questions about best practice elements (eg, is there a relevant and focused physical exam).12
Graders were internal medicine teaching faculty involved in the study and were assigned to review notes from their respective sites by directly utilizing the EHR. Although this introduces potential for bias, it was felt that many of the grading elements required the grader to know details of the patient that would not be captured if the note was removed from the context of the EHR. Additionally, graders documented note length (number of lines of text), the time signed by the housestaff, and whether the template was used. Three different graders independently evaluated each note and submitted ratings by using Research Electronic Data Capture.13
Statistical Analysis
Means for each item on the grading tool were computed across raters for each progress note. These were summarized by institution as well as by pre- and postintervention. Cumulative logit mixed effects models were used to compare item responses between study conditions. The number of lines per note before and after the note template intervention was compared by using a mixed effects negative binomial regression model. The timestamp on each note, representing the time of day the note was signed, was compared pre- and postintervention by using a linear mixed effects model. All models included random note and rater effects, and fixed institution and intervention period effects, as well as their interaction. Inter-rater reliability of the grading tool was assessed by calculating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) using the estimated variance components. Data obtained from the PDQI-9 portion were analyzed by individual components as well as by sum score combining each component. The sum score was used to generate odds ratios to assess the likelihood that postintervention notes that used the template compared to those that did not would increase PDQI-9 sum scores. Both cumulative and site-specific data were analyzed. P values < .05 were considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC).
RESULTS
The mean general impression score significantly improved from 2.0 to 2.3 (on a 1-3 scale in which 2 is average) after the intervention (P < .001). Additionally, note quality significantly improved across each domain of the PDQI-9 (P < .001 for all domains, Table 1). The ICC was 0.245 for the general impression score and 0.143 for the PDQI-9 sum score.
Three of 4 institutions documented the number of lines per note and the time the note was signed by the intern. Mean number of lines per note decreased by 25% (361 lines preintervention, 265 lines postintervention, P < .001). Mean time signed was approximately 1 hour and 15 minutes earlier in the day (3:27
Site-specific data revealed variation between sites. Template use was 92% at UCSF, 90% at UCLA, 79% at Iowa, and 21% at UCSD. The mean general impression score significantly improved at UCSF, UCLA, and UCSD, but not at Iowa. The PDQI-9 score improved across all domains at UCSF and UCLA, 2 domains at UCSD, and 0 domains at Iowa. Documentation of pertinent labs and studies significantly improved at UCSF, UCLA, and Iowa, but not UCSD. Note length decreased at UCSF and UCLA, but not at UCSD. Notes were signed earlier at UCLA and UCSD, but not at UCSF.
When comparing postintervention notes based on template use, notes that used the template were significantly more likely to receive a higher mean impression score (odds ratio [OR] 11.95, P < .001), higher PDQI-9 sum score (OR 3.05, P < .001), be approximately 25% shorter (326 lines vs 239 lines, P < .001), and be completed approximately 1 hour and 20 minutes earlier (3:07
DISCUSSION
A bundled intervention consisting of educational lectures and a best practice progress note template significantly improved the quality, decreased the length, and resulted in earlier completion of inpatient progress notes. These findings are consistent with a prior study that demonstrated that a bundled note template intervention improved total note score and reduced note clutter.11 We saw a broad improvement in progress notes across all 9 domains of the PDQI-9, which corresponded with an improved general impression score. We also found statistically significant improvements in 7 of the 13 categories of the competency questionnaire.
Arguably the greatest impact of the intervention was shortening the documentation of labs and studies. Autopopulation can lead to the appearance of a comprehensive note; however, key data are often lost in a sea of numbers and imaging reports.6,14 Using simple prompts followed by free text such as, “I have reviewed all the labs from today. Pertinent labs include…” reduced autopopulation and reminded housestaff to identify only the key information that affected patient care for that day, resulting in a more streamlined, clear, and high-yield note.
The time spent documenting care is an important consideration for physician workflow and for uptake of any note intervention.14-18 One study from 2016 revealed that internal medicine housestaff spend more than half of an average shift using the computer, with 52% of that time spent on documentation.17 Although functions such as autopopulation and copy-forward were created as efficiency tools, we hypothesize that they may actually prolong note writing time by leading to disorganized, distended notes that are difficult to use the following day. There was concern that limiting these “efficiency functions” might discourage housestaff from using the progress note template. It was encouraging to find that postintervention notes were signed 1.3 hours earlier in the day. This study did not measure the impact of shorter notes and earlier completion time, but in theory, this could allow interns to spend more time in direct patient care and to be at lower risk of duty hour violations.19 Furthermore, while the clinical impact of this is unknown, it is possible that timely note completion may improve patient care by making notes available earlier for consultants and other members of the care team.
We found that adding an “inpatient checklist” to the progress note template facilitated a review of key inpatient concerns and quality measures. Although we did not specifically compare before-and-after documentation of all of the components of the checklist, there appeared to be improvement in the domains measured. Notably, there was a 31% increase (P < .001) in the percentage of notes documenting the “discharge plan, goals of hospitalization, or estimated length of stay.” In the surgical literature, studies have demonstrated that incorporating checklists improves patient safety, the delivery of care, and potentially shortens the length of stay.20-22 Future studies should explore the impact of adding a checklist to the daily progress note, as there may be potential to improve both process and outcome measures.
Institution-specific data provided insightful results. UCSD encountered low template use among their interns; however, they still had evidence of improvement in note quality, though not at the same level of UCLA and UCSF. Some barriers to uptake identified were as follows: (1) interns were accustomed to import labs and studies into their note to use as their rounding report, and (2) the intervention took place late in the year when interns had developed a functional writing system that they were reluctant to change. The University of Iowa did not show significant improvement in their note quality despite a relatively high template uptake. Both of these outcomes raise the possibility that in addition to the template, there were other factors at play. Perhaps because UCSF and UCLA created the best practice guidelines and template, it was a better fit for their culture and they had more institutional buy-in. Or because the educational lectures were similar, but not standardized across institutions, some lectures may have been more effective than others. However, when evaluating the postintervention notes at UCSD and Iowa, templated notes were found to be much more likely to score higher on the PDQI-9 than nontemplated notes, which serves as evidence of the efficacy of the note template.
Some of the strengths of this study include the relatively large sample size spanning 4 institutions and the use of 3 different assessment tools for grading progress note quality (general impression score, PDQI-9, and competency note questionnaire). An additional strength is our unique finding suggesting that note writing may be more efficient by removing, rather than adding, “efficiency functions.” There were several limitations of this study. Pre- and postintervention notes were examined at different points in the same academic year, thus certain domains may have improved as interns progressed in clinical skill and comfort with documentation, independent of our intervention.21 However, our analysis of postintervention notes across the same time period revealed that use of the template was strongly associated with higher quality, shorter notes and earlier completion time arguing that the effect seen was not merely intern experience. The poor interrater reliability is also a limitation. Although the PDQI-9 was previously validated, future use of the grading tool may require more rater training for calibration or more objective wording.23 The study was not blinded, and thus, bias may have falsely elevated postintervention scores; however, we attempted to minimize bias by incorporating a more objective yes/no competency questionnaire and by having each note scored by 3 graders. Other studies have attempted to address this form of bias by printing out notes and blinding the graders. This design, however, isolates the note from all other data in the medical record, making it difficult to assess domains such as accuracy and completeness. Our inclusion of objective outcomes such as note length and time of note completion help to mitigate some of the bias.
Future research can expand on the results of this study by introducing similar progress note interventions at other institutions and/or in nonacademic environments to validate the results and expand generalizability. Longer term follow-up would be useful to determine if these effects are transient or long lasting. Similarly, it would be interesting to determine if such results are sustained even after new interns start suggesting that institutional culture can be changed. Investigators could focus on similar projects to improve other notes that are particularly at a high risk for propagating false information, such as the History and Physical or Discharge Summary. Future research should also focus on outcomes data, including whether a more efficient note can allow housestaff to spend more time with patients, decrease patient length of stay, reduce clinical errors, and improve educational time for trainees. Lastly, we should determine if interventions such as this can mitigate the widespread frustrations with electronic documentation that are associated with physician and provider burnout.15,24 One would hope that the technology could be harnessed to improve provider productivity and be effectively integrated into comprehensive patient care.
Our research makes progress toward recommendations made by the American College of Physicians “to improve accuracy of information recorded and the value of information,” and develop automated tools that “enhance documentation quality without facilitating improper behaviors.”19 Institutions should consider developing internal best practices for clinical documentation and building structured note templates.19 Our research would suggest that, combined with a small educational intervention, such templates can make progress notes more accurate and succinct, make note writing more efficient, and be harnessed to improve quality metrics.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Michael Pfeffer, MD, and Sitaram Vangala, MS, for their contributions to and support of this research study and manuscript.
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
1. Herzig SJ, Guess JR, Feinbloom DB, et al. Improving appropriateness of acid-suppressive medication use via computerized clinical decision support. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(1):41-45. PubMed
2. Nguyen OK, Makam AN, Clark C, et al. Predicting all-cause readmissions using electronic health record data from the entire hospitalization: Model development and comparison. J Hosp Med. 2016;11(7):473-480. PubMed
3. Donati A, Gabbanelli V, Pantanetti S, et al. The impact of a clinical information system in an intensive care unit. J Clin Monit Comput. 2008;22(1):31-36. PubMed
4. Schiff GD, Bates DW. Can electronic clinical documentation help prevent diagnostic errors? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1066-1069. PubMed
5. Hartzband P, Groopman J. Off the record--avoiding the pitfalls of going electronic. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(16):1656-1658. PubMed
6. Hirschtick RE. A piece of my mind. Copy-and-paste. JAMA. 2006;295(20):2335-2336. PubMed
7. Hirschtick RE. A piece of my mind. John Lennon’s elbow. JAMA. 2012;308(5):463-464. PubMed
8. O’Donnell HC, Kaushal R, Barrón Y, Callahan MA, Adelman RD, Siegler EL. Physicians’ attitudes towards copy and pasting in electronic note writing. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(1):63-68. PubMed
9. Mahapatra P, Ieong E. Improving Documentation and Communication Using Operative Note Proformas. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2016;5(1):u209122.w3712. PubMed
10. Thomson DR, Baldwin MJ, Bellini MI, Silva MA. Improving the quality of operative notes for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Assessing the impact of a standardized operation note proforma. Int J Surg. 2016;27:17-20. PubMed
11. Dean SM, Eickhoff JC, Bakel LA. The effectiveness of a bundled intervention to improve resident progress notes in an electronic health record. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(2):104-107. PubMed
12. Aylor M, Campbell EM, Winter C, Phillipi CA. Resident Notes in an Electronic Health Record: A Mixed-Methods Study Using a Standardized Intervention With Qualitative Analysis. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2016;6(3):257-262.
13. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. PubMed
14. Chi J, Kugler J, Chu IM, et al. Medical students and the electronic health record: ‘an epic use of time’. Am J Med. 2014;127(9):891-895. PubMed
15. Martin SA, Sinsky CA. The map is not the territory: medical records and 21st century practice. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2053-2056. PubMed
16. Oxentenko AS, Manohar CU, McCoy CP, et al. Internal medicine residents’ computer use in the inpatient setting. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(4):529-532. PubMed
17. Mamykina L, Vawdrey DK, Hripcsak G. How Do Residents Spend Their Shift Time? A Time and Motion Study With a Particular Focus on the Use of Computers. Acad Med. 2016;91(6):827-832. PubMed
18. Chen L, Guo U, Illipparambil LC, et al. Racing Against the Clock: Internal Medicine Residents’ Time Spent On Electronic Health Records. J Grad Med Educ. 2016;8(1):39-44. PubMed
19. Kuhn T, Basch P, Barr M, Yackel T, Physicians MICotACo. Clinical documentation in the 21st century: executive summary of a policy position paper from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(4):301-303. PubMed
20. Treadwell JR, Lucas S, Tsou AY. Surgical checklists: a systematic review of impacts and implementation. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(4):299-318. PubMed
21. Ko HC, Turner TJ, Finnigan MA. Systematic review of safety checklists for use by medical care teams in acute hospital settings--limited evidence of effectiveness. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:211. PubMed
22. Diaz-Montes TP, Cobb L, Ibeanu OA, Njoku P, Gerardi MA. Introduction of checklists at daily progress notes improves patient care among the gynecological oncology service. J Patient Saf. 2012;8(4):189-193. PubMed
23. Stetson PD, Bakken S, Wrenn JO, Siegler EL. Assessing Electronic Note Quality Using the Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI-9). Appl Clin Inform. 2012;3(2):164-174. PubMed
24. Friedberg MW, Chen PG, Van Busum KR, et al. Factors affecting physician professional satisfaction and their implications for patient care, health systems, and health policy. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation; 2013. PubMed
The widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) has led to significant progress in the modernization of healthcare delivery. Ease of access has improved clinical efficiency, and digital data have allowed for point-of-care decision support tools ranging from predicting the 30-day risk of readmission to providing up-to-date guidelines for the care of various diseases.1,2 Documentation tools such as copy-forward and autopopulation increase the speed of documentation, and typed notes improve legibility and ease of note transmission.3,4
However, all of these benefits come with a potential for harm, particularly with respect to accurate and concise documentation. Many experts have described the perpetuation of false information leading to errors, copying-forward of inconsistent and outdated information, and the phenomenon of “note bloat” — physician notes that contain multiple pages of nonessential information, often leaving key aspects buried or lost.5-7 Providers seem to recognize the hazards of copy-and-paste functionality yet persist in utilizing it. In 1 survey, more than 70% of attendings and residents felt that copy and paste led to inaccurate and outdated information, yet 80% stated they would still use it.8
There is little evidence to guide institutions on ways to improve EHR documentation practices. Recent studies have shown that operative note templates improved documentation and decreased the number of missing components.9,10 In the nonoperative setting, 1 small pilot study of pediatric interns demonstrated that a bundled intervention composed of a note template and classroom teaching resulted in improvement in overall note quality and a decrease in “note clutter.”11 In a larger study of pediatric residents, a standardized and simplified note template resulted in a shorter note, although notes were completed later in the day.12 The present study seeks to build upon these efforts by investigating the effect of didactic teaching and an electronic progress note template on note quality, length, and timeliness across 4 academic internal medicine residency programs.
METHODS
Study Design
This prospective quality improvement study took place across 4 academic institutions: University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), University of California San Francisco (UCSF), University of California San Diego (UCSD), and University of Iowa, all of which use Epic EHR (Epic Corp., Madison, WI). The intervention combined brief educational conferences directed at housestaff and attendings with the implementation of an electronic progress note template. Guided by resident input, a note-writing task force at UCSF and UCLA developed a set of best practice guidelines and an aligned note template for progress notes (supplementary Appendix 1). UCSD and the University of Iowa adopted them at their respective institutions. The template’s design minimized autopopulation while encouraging providers to enter relevant data via free text fields (eg, physical exam), prompts (eg, “I have reviewed all the labs from today. Pertinent labs include…”), and drop-down menus (eg, deep vein thrombosis [DVT] prophylaxis: enoxaparin, heparin subcutaneously, etc; supplementary Appendix 2). Additionally, an inpatient checklist was included at the end of the note to serve as a reminder for key inpatient concerns and quality measures, such as Foley catheter days, discharge planning, and code status. Lectures that focused on issues with documentation in the EHR, the best practice guidelines, and a review of the note template with instructions on how to access it were presented to the housestaff. Each institution tailored the lecture to suit their culture. Housestaff were encouraged but not required to use the note template.
Selection and Grading of Progress Notes
Progress notes were eligible for the study if they were written by an intern on an internal medicine teaching service, from a patient with a hospitalization length of at least 3 days with a progress note selected from hospital day 2 or 3, and written while the patient was on the general medicine wards. The preintervention notes were authored from September 2013 to December 2013 and the postintervention notes from April 2014 to June 2014. One note was selected per patient and no more than 3 notes were selected per intern. Each institution selected the first 50 notes chronologically that met these criteria for both the preintervention and the postintervention periods, for a total of 400 notes. The note-grading tool consisted of the following 3 sections to analyze note quality: (1) a general impression of the note (eg, below average, average, above average); (2) the validated Physician Documentation Quality Instrument, 9-item version (PDQI-9) that evaluates notes on 9 domains (up to date, accurate, thorough, useful, organized, comprehensible, succinct, synthesized, internally consistent) on a Likert scale from 1 (not at all) to 5 (extremely); and (3) a note competency questionnaire based on the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education competency note checklist that asked yes or no questions about best practice elements (eg, is there a relevant and focused physical exam).12
Graders were internal medicine teaching faculty involved in the study and were assigned to review notes from their respective sites by directly utilizing the EHR. Although this introduces potential for bias, it was felt that many of the grading elements required the grader to know details of the patient that would not be captured if the note was removed from the context of the EHR. Additionally, graders documented note length (number of lines of text), the time signed by the housestaff, and whether the template was used. Three different graders independently evaluated each note and submitted ratings by using Research Electronic Data Capture.13
Statistical Analysis
Means for each item on the grading tool were computed across raters for each progress note. These were summarized by institution as well as by pre- and postintervention. Cumulative logit mixed effects models were used to compare item responses between study conditions. The number of lines per note before and after the note template intervention was compared by using a mixed effects negative binomial regression model. The timestamp on each note, representing the time of day the note was signed, was compared pre- and postintervention by using a linear mixed effects model. All models included random note and rater effects, and fixed institution and intervention period effects, as well as their interaction. Inter-rater reliability of the grading tool was assessed by calculating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) using the estimated variance components. Data obtained from the PDQI-9 portion were analyzed by individual components as well as by sum score combining each component. The sum score was used to generate odds ratios to assess the likelihood that postintervention notes that used the template compared to those that did not would increase PDQI-9 sum scores. Both cumulative and site-specific data were analyzed. P values < .05 were considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC).
RESULTS
The mean general impression score significantly improved from 2.0 to 2.3 (on a 1-3 scale in which 2 is average) after the intervention (P < .001). Additionally, note quality significantly improved across each domain of the PDQI-9 (P < .001 for all domains, Table 1). The ICC was 0.245 for the general impression score and 0.143 for the PDQI-9 sum score.
Three of 4 institutions documented the number of lines per note and the time the note was signed by the intern. Mean number of lines per note decreased by 25% (361 lines preintervention, 265 lines postintervention, P < .001). Mean time signed was approximately 1 hour and 15 minutes earlier in the day (3:27
Site-specific data revealed variation between sites. Template use was 92% at UCSF, 90% at UCLA, 79% at Iowa, and 21% at UCSD. The mean general impression score significantly improved at UCSF, UCLA, and UCSD, but not at Iowa. The PDQI-9 score improved across all domains at UCSF and UCLA, 2 domains at UCSD, and 0 domains at Iowa. Documentation of pertinent labs and studies significantly improved at UCSF, UCLA, and Iowa, but not UCSD. Note length decreased at UCSF and UCLA, but not at UCSD. Notes were signed earlier at UCLA and UCSD, but not at UCSF.
When comparing postintervention notes based on template use, notes that used the template were significantly more likely to receive a higher mean impression score (odds ratio [OR] 11.95, P < .001), higher PDQI-9 sum score (OR 3.05, P < .001), be approximately 25% shorter (326 lines vs 239 lines, P < .001), and be completed approximately 1 hour and 20 minutes earlier (3:07
DISCUSSION
A bundled intervention consisting of educational lectures and a best practice progress note template significantly improved the quality, decreased the length, and resulted in earlier completion of inpatient progress notes. These findings are consistent with a prior study that demonstrated that a bundled note template intervention improved total note score and reduced note clutter.11 We saw a broad improvement in progress notes across all 9 domains of the PDQI-9, which corresponded with an improved general impression score. We also found statistically significant improvements in 7 of the 13 categories of the competency questionnaire.
Arguably the greatest impact of the intervention was shortening the documentation of labs and studies. Autopopulation can lead to the appearance of a comprehensive note; however, key data are often lost in a sea of numbers and imaging reports.6,14 Using simple prompts followed by free text such as, “I have reviewed all the labs from today. Pertinent labs include…” reduced autopopulation and reminded housestaff to identify only the key information that affected patient care for that day, resulting in a more streamlined, clear, and high-yield note.
The time spent documenting care is an important consideration for physician workflow and for uptake of any note intervention.14-18 One study from 2016 revealed that internal medicine housestaff spend more than half of an average shift using the computer, with 52% of that time spent on documentation.17 Although functions such as autopopulation and copy-forward were created as efficiency tools, we hypothesize that they may actually prolong note writing time by leading to disorganized, distended notes that are difficult to use the following day. There was concern that limiting these “efficiency functions” might discourage housestaff from using the progress note template. It was encouraging to find that postintervention notes were signed 1.3 hours earlier in the day. This study did not measure the impact of shorter notes and earlier completion time, but in theory, this could allow interns to spend more time in direct patient care and to be at lower risk of duty hour violations.19 Furthermore, while the clinical impact of this is unknown, it is possible that timely note completion may improve patient care by making notes available earlier for consultants and other members of the care team.
We found that adding an “inpatient checklist” to the progress note template facilitated a review of key inpatient concerns and quality measures. Although we did not specifically compare before-and-after documentation of all of the components of the checklist, there appeared to be improvement in the domains measured. Notably, there was a 31% increase (P < .001) in the percentage of notes documenting the “discharge plan, goals of hospitalization, or estimated length of stay.” In the surgical literature, studies have demonstrated that incorporating checklists improves patient safety, the delivery of care, and potentially shortens the length of stay.20-22 Future studies should explore the impact of adding a checklist to the daily progress note, as there may be potential to improve both process and outcome measures.
Institution-specific data provided insightful results. UCSD encountered low template use among their interns; however, they still had evidence of improvement in note quality, though not at the same level of UCLA and UCSF. Some barriers to uptake identified were as follows: (1) interns were accustomed to import labs and studies into their note to use as their rounding report, and (2) the intervention took place late in the year when interns had developed a functional writing system that they were reluctant to change. The University of Iowa did not show significant improvement in their note quality despite a relatively high template uptake. Both of these outcomes raise the possibility that in addition to the template, there were other factors at play. Perhaps because UCSF and UCLA created the best practice guidelines and template, it was a better fit for their culture and they had more institutional buy-in. Or because the educational lectures were similar, but not standardized across institutions, some lectures may have been more effective than others. However, when evaluating the postintervention notes at UCSD and Iowa, templated notes were found to be much more likely to score higher on the PDQI-9 than nontemplated notes, which serves as evidence of the efficacy of the note template.
Some of the strengths of this study include the relatively large sample size spanning 4 institutions and the use of 3 different assessment tools for grading progress note quality (general impression score, PDQI-9, and competency note questionnaire). An additional strength is our unique finding suggesting that note writing may be more efficient by removing, rather than adding, “efficiency functions.” There were several limitations of this study. Pre- and postintervention notes were examined at different points in the same academic year, thus certain domains may have improved as interns progressed in clinical skill and comfort with documentation, independent of our intervention.21 However, our analysis of postintervention notes across the same time period revealed that use of the template was strongly associated with higher quality, shorter notes and earlier completion time arguing that the effect seen was not merely intern experience. The poor interrater reliability is also a limitation. Although the PDQI-9 was previously validated, future use of the grading tool may require more rater training for calibration or more objective wording.23 The study was not blinded, and thus, bias may have falsely elevated postintervention scores; however, we attempted to minimize bias by incorporating a more objective yes/no competency questionnaire and by having each note scored by 3 graders. Other studies have attempted to address this form of bias by printing out notes and blinding the graders. This design, however, isolates the note from all other data in the medical record, making it difficult to assess domains such as accuracy and completeness. Our inclusion of objective outcomes such as note length and time of note completion help to mitigate some of the bias.
Future research can expand on the results of this study by introducing similar progress note interventions at other institutions and/or in nonacademic environments to validate the results and expand generalizability. Longer term follow-up would be useful to determine if these effects are transient or long lasting. Similarly, it would be interesting to determine if such results are sustained even after new interns start suggesting that institutional culture can be changed. Investigators could focus on similar projects to improve other notes that are particularly at a high risk for propagating false information, such as the History and Physical or Discharge Summary. Future research should also focus on outcomes data, including whether a more efficient note can allow housestaff to spend more time with patients, decrease patient length of stay, reduce clinical errors, and improve educational time for trainees. Lastly, we should determine if interventions such as this can mitigate the widespread frustrations with electronic documentation that are associated with physician and provider burnout.15,24 One would hope that the technology could be harnessed to improve provider productivity and be effectively integrated into comprehensive patient care.
Our research makes progress toward recommendations made by the American College of Physicians “to improve accuracy of information recorded and the value of information,” and develop automated tools that “enhance documentation quality without facilitating improper behaviors.”19 Institutions should consider developing internal best practices for clinical documentation and building structured note templates.19 Our research would suggest that, combined with a small educational intervention, such templates can make progress notes more accurate and succinct, make note writing more efficient, and be harnessed to improve quality metrics.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Michael Pfeffer, MD, and Sitaram Vangala, MS, for their contributions to and support of this research study and manuscript.
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
The widespread adoption of electronic health records (EHRs) has led to significant progress in the modernization of healthcare delivery. Ease of access has improved clinical efficiency, and digital data have allowed for point-of-care decision support tools ranging from predicting the 30-day risk of readmission to providing up-to-date guidelines for the care of various diseases.1,2 Documentation tools such as copy-forward and autopopulation increase the speed of documentation, and typed notes improve legibility and ease of note transmission.3,4
However, all of these benefits come with a potential for harm, particularly with respect to accurate and concise documentation. Many experts have described the perpetuation of false information leading to errors, copying-forward of inconsistent and outdated information, and the phenomenon of “note bloat” — physician notes that contain multiple pages of nonessential information, often leaving key aspects buried or lost.5-7 Providers seem to recognize the hazards of copy-and-paste functionality yet persist in utilizing it. In 1 survey, more than 70% of attendings and residents felt that copy and paste led to inaccurate and outdated information, yet 80% stated they would still use it.8
There is little evidence to guide institutions on ways to improve EHR documentation practices. Recent studies have shown that operative note templates improved documentation and decreased the number of missing components.9,10 In the nonoperative setting, 1 small pilot study of pediatric interns demonstrated that a bundled intervention composed of a note template and classroom teaching resulted in improvement in overall note quality and a decrease in “note clutter.”11 In a larger study of pediatric residents, a standardized and simplified note template resulted in a shorter note, although notes were completed later in the day.12 The present study seeks to build upon these efforts by investigating the effect of didactic teaching and an electronic progress note template on note quality, length, and timeliness across 4 academic internal medicine residency programs.
METHODS
Study Design
This prospective quality improvement study took place across 4 academic institutions: University of California Los Angeles (UCLA), University of California San Francisco (UCSF), University of California San Diego (UCSD), and University of Iowa, all of which use Epic EHR (Epic Corp., Madison, WI). The intervention combined brief educational conferences directed at housestaff and attendings with the implementation of an electronic progress note template. Guided by resident input, a note-writing task force at UCSF and UCLA developed a set of best practice guidelines and an aligned note template for progress notes (supplementary Appendix 1). UCSD and the University of Iowa adopted them at their respective institutions. The template’s design minimized autopopulation while encouraging providers to enter relevant data via free text fields (eg, physical exam), prompts (eg, “I have reviewed all the labs from today. Pertinent labs include…”), and drop-down menus (eg, deep vein thrombosis [DVT] prophylaxis: enoxaparin, heparin subcutaneously, etc; supplementary Appendix 2). Additionally, an inpatient checklist was included at the end of the note to serve as a reminder for key inpatient concerns and quality measures, such as Foley catheter days, discharge planning, and code status. Lectures that focused on issues with documentation in the EHR, the best practice guidelines, and a review of the note template with instructions on how to access it were presented to the housestaff. Each institution tailored the lecture to suit their culture. Housestaff were encouraged but not required to use the note template.
Selection and Grading of Progress Notes
Progress notes were eligible for the study if they were written by an intern on an internal medicine teaching service, from a patient with a hospitalization length of at least 3 days with a progress note selected from hospital day 2 or 3, and written while the patient was on the general medicine wards. The preintervention notes were authored from September 2013 to December 2013 and the postintervention notes from April 2014 to June 2014. One note was selected per patient and no more than 3 notes were selected per intern. Each institution selected the first 50 notes chronologically that met these criteria for both the preintervention and the postintervention periods, for a total of 400 notes. The note-grading tool consisted of the following 3 sections to analyze note quality: (1) a general impression of the note (eg, below average, average, above average); (2) the validated Physician Documentation Quality Instrument, 9-item version (PDQI-9) that evaluates notes on 9 domains (up to date, accurate, thorough, useful, organized, comprehensible, succinct, synthesized, internally consistent) on a Likert scale from 1 (not at all) to 5 (extremely); and (3) a note competency questionnaire based on the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education competency note checklist that asked yes or no questions about best practice elements (eg, is there a relevant and focused physical exam).12
Graders were internal medicine teaching faculty involved in the study and were assigned to review notes from their respective sites by directly utilizing the EHR. Although this introduces potential for bias, it was felt that many of the grading elements required the grader to know details of the patient that would not be captured if the note was removed from the context of the EHR. Additionally, graders documented note length (number of lines of text), the time signed by the housestaff, and whether the template was used. Three different graders independently evaluated each note and submitted ratings by using Research Electronic Data Capture.13
Statistical Analysis
Means for each item on the grading tool were computed across raters for each progress note. These were summarized by institution as well as by pre- and postintervention. Cumulative logit mixed effects models were used to compare item responses between study conditions. The number of lines per note before and after the note template intervention was compared by using a mixed effects negative binomial regression model. The timestamp on each note, representing the time of day the note was signed, was compared pre- and postintervention by using a linear mixed effects model. All models included random note and rater effects, and fixed institution and intervention period effects, as well as their interaction. Inter-rater reliability of the grading tool was assessed by calculating the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) using the estimated variance components. Data obtained from the PDQI-9 portion were analyzed by individual components as well as by sum score combining each component. The sum score was used to generate odds ratios to assess the likelihood that postintervention notes that used the template compared to those that did not would increase PDQI-9 sum scores. Both cumulative and site-specific data were analyzed. P values < .05 were considered statistically significant. All analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC).
RESULTS
The mean general impression score significantly improved from 2.0 to 2.3 (on a 1-3 scale in which 2 is average) after the intervention (P < .001). Additionally, note quality significantly improved across each domain of the PDQI-9 (P < .001 for all domains, Table 1). The ICC was 0.245 for the general impression score and 0.143 for the PDQI-9 sum score.
Three of 4 institutions documented the number of lines per note and the time the note was signed by the intern. Mean number of lines per note decreased by 25% (361 lines preintervention, 265 lines postintervention, P < .001). Mean time signed was approximately 1 hour and 15 minutes earlier in the day (3:27
Site-specific data revealed variation between sites. Template use was 92% at UCSF, 90% at UCLA, 79% at Iowa, and 21% at UCSD. The mean general impression score significantly improved at UCSF, UCLA, and UCSD, but not at Iowa. The PDQI-9 score improved across all domains at UCSF and UCLA, 2 domains at UCSD, and 0 domains at Iowa. Documentation of pertinent labs and studies significantly improved at UCSF, UCLA, and Iowa, but not UCSD. Note length decreased at UCSF and UCLA, but not at UCSD. Notes were signed earlier at UCLA and UCSD, but not at UCSF.
When comparing postintervention notes based on template use, notes that used the template were significantly more likely to receive a higher mean impression score (odds ratio [OR] 11.95, P < .001), higher PDQI-9 sum score (OR 3.05, P < .001), be approximately 25% shorter (326 lines vs 239 lines, P < .001), and be completed approximately 1 hour and 20 minutes earlier (3:07
DISCUSSION
A bundled intervention consisting of educational lectures and a best practice progress note template significantly improved the quality, decreased the length, and resulted in earlier completion of inpatient progress notes. These findings are consistent with a prior study that demonstrated that a bundled note template intervention improved total note score and reduced note clutter.11 We saw a broad improvement in progress notes across all 9 domains of the PDQI-9, which corresponded with an improved general impression score. We also found statistically significant improvements in 7 of the 13 categories of the competency questionnaire.
Arguably the greatest impact of the intervention was shortening the documentation of labs and studies. Autopopulation can lead to the appearance of a comprehensive note; however, key data are often lost in a sea of numbers and imaging reports.6,14 Using simple prompts followed by free text such as, “I have reviewed all the labs from today. Pertinent labs include…” reduced autopopulation and reminded housestaff to identify only the key information that affected patient care for that day, resulting in a more streamlined, clear, and high-yield note.
The time spent documenting care is an important consideration for physician workflow and for uptake of any note intervention.14-18 One study from 2016 revealed that internal medicine housestaff spend more than half of an average shift using the computer, with 52% of that time spent on documentation.17 Although functions such as autopopulation and copy-forward were created as efficiency tools, we hypothesize that they may actually prolong note writing time by leading to disorganized, distended notes that are difficult to use the following day. There was concern that limiting these “efficiency functions” might discourage housestaff from using the progress note template. It was encouraging to find that postintervention notes were signed 1.3 hours earlier in the day. This study did not measure the impact of shorter notes and earlier completion time, but in theory, this could allow interns to spend more time in direct patient care and to be at lower risk of duty hour violations.19 Furthermore, while the clinical impact of this is unknown, it is possible that timely note completion may improve patient care by making notes available earlier for consultants and other members of the care team.
We found that adding an “inpatient checklist” to the progress note template facilitated a review of key inpatient concerns and quality measures. Although we did not specifically compare before-and-after documentation of all of the components of the checklist, there appeared to be improvement in the domains measured. Notably, there was a 31% increase (P < .001) in the percentage of notes documenting the “discharge plan, goals of hospitalization, or estimated length of stay.” In the surgical literature, studies have demonstrated that incorporating checklists improves patient safety, the delivery of care, and potentially shortens the length of stay.20-22 Future studies should explore the impact of adding a checklist to the daily progress note, as there may be potential to improve both process and outcome measures.
Institution-specific data provided insightful results. UCSD encountered low template use among their interns; however, they still had evidence of improvement in note quality, though not at the same level of UCLA and UCSF. Some barriers to uptake identified were as follows: (1) interns were accustomed to import labs and studies into their note to use as their rounding report, and (2) the intervention took place late in the year when interns had developed a functional writing system that they were reluctant to change. The University of Iowa did not show significant improvement in their note quality despite a relatively high template uptake. Both of these outcomes raise the possibility that in addition to the template, there were other factors at play. Perhaps because UCSF and UCLA created the best practice guidelines and template, it was a better fit for their culture and they had more institutional buy-in. Or because the educational lectures were similar, but not standardized across institutions, some lectures may have been more effective than others. However, when evaluating the postintervention notes at UCSD and Iowa, templated notes were found to be much more likely to score higher on the PDQI-9 than nontemplated notes, which serves as evidence of the efficacy of the note template.
Some of the strengths of this study include the relatively large sample size spanning 4 institutions and the use of 3 different assessment tools for grading progress note quality (general impression score, PDQI-9, and competency note questionnaire). An additional strength is our unique finding suggesting that note writing may be more efficient by removing, rather than adding, “efficiency functions.” There were several limitations of this study. Pre- and postintervention notes were examined at different points in the same academic year, thus certain domains may have improved as interns progressed in clinical skill and comfort with documentation, independent of our intervention.21 However, our analysis of postintervention notes across the same time period revealed that use of the template was strongly associated with higher quality, shorter notes and earlier completion time arguing that the effect seen was not merely intern experience. The poor interrater reliability is also a limitation. Although the PDQI-9 was previously validated, future use of the grading tool may require more rater training for calibration or more objective wording.23 The study was not blinded, and thus, bias may have falsely elevated postintervention scores; however, we attempted to minimize bias by incorporating a more objective yes/no competency questionnaire and by having each note scored by 3 graders. Other studies have attempted to address this form of bias by printing out notes and blinding the graders. This design, however, isolates the note from all other data in the medical record, making it difficult to assess domains such as accuracy and completeness. Our inclusion of objective outcomes such as note length and time of note completion help to mitigate some of the bias.
Future research can expand on the results of this study by introducing similar progress note interventions at other institutions and/or in nonacademic environments to validate the results and expand generalizability. Longer term follow-up would be useful to determine if these effects are transient or long lasting. Similarly, it would be interesting to determine if such results are sustained even after new interns start suggesting that institutional culture can be changed. Investigators could focus on similar projects to improve other notes that are particularly at a high risk for propagating false information, such as the History and Physical or Discharge Summary. Future research should also focus on outcomes data, including whether a more efficient note can allow housestaff to spend more time with patients, decrease patient length of stay, reduce clinical errors, and improve educational time for trainees. Lastly, we should determine if interventions such as this can mitigate the widespread frustrations with electronic documentation that are associated with physician and provider burnout.15,24 One would hope that the technology could be harnessed to improve provider productivity and be effectively integrated into comprehensive patient care.
Our research makes progress toward recommendations made by the American College of Physicians “to improve accuracy of information recorded and the value of information,” and develop automated tools that “enhance documentation quality without facilitating improper behaviors.”19 Institutions should consider developing internal best practices for clinical documentation and building structured note templates.19 Our research would suggest that, combined with a small educational intervention, such templates can make progress notes more accurate and succinct, make note writing more efficient, and be harnessed to improve quality metrics.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors thank Michael Pfeffer, MD, and Sitaram Vangala, MS, for their contributions to and support of this research study and manuscript.
Disclosure: The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
1. Herzig SJ, Guess JR, Feinbloom DB, et al. Improving appropriateness of acid-suppressive medication use via computerized clinical decision support. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(1):41-45. PubMed
2. Nguyen OK, Makam AN, Clark C, et al. Predicting all-cause readmissions using electronic health record data from the entire hospitalization: Model development and comparison. J Hosp Med. 2016;11(7):473-480. PubMed
3. Donati A, Gabbanelli V, Pantanetti S, et al. The impact of a clinical information system in an intensive care unit. J Clin Monit Comput. 2008;22(1):31-36. PubMed
4. Schiff GD, Bates DW. Can electronic clinical documentation help prevent diagnostic errors? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1066-1069. PubMed
5. Hartzband P, Groopman J. Off the record--avoiding the pitfalls of going electronic. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(16):1656-1658. PubMed
6. Hirschtick RE. A piece of my mind. Copy-and-paste. JAMA. 2006;295(20):2335-2336. PubMed
7. Hirschtick RE. A piece of my mind. John Lennon’s elbow. JAMA. 2012;308(5):463-464. PubMed
8. O’Donnell HC, Kaushal R, Barrón Y, Callahan MA, Adelman RD, Siegler EL. Physicians’ attitudes towards copy and pasting in electronic note writing. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(1):63-68. PubMed
9. Mahapatra P, Ieong E. Improving Documentation and Communication Using Operative Note Proformas. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2016;5(1):u209122.w3712. PubMed
10. Thomson DR, Baldwin MJ, Bellini MI, Silva MA. Improving the quality of operative notes for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Assessing the impact of a standardized operation note proforma. Int J Surg. 2016;27:17-20. PubMed
11. Dean SM, Eickhoff JC, Bakel LA. The effectiveness of a bundled intervention to improve resident progress notes in an electronic health record. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(2):104-107. PubMed
12. Aylor M, Campbell EM, Winter C, Phillipi CA. Resident Notes in an Electronic Health Record: A Mixed-Methods Study Using a Standardized Intervention With Qualitative Analysis. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2016;6(3):257-262.
13. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. PubMed
14. Chi J, Kugler J, Chu IM, et al. Medical students and the electronic health record: ‘an epic use of time’. Am J Med. 2014;127(9):891-895. PubMed
15. Martin SA, Sinsky CA. The map is not the territory: medical records and 21st century practice. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2053-2056. PubMed
16. Oxentenko AS, Manohar CU, McCoy CP, et al. Internal medicine residents’ computer use in the inpatient setting. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(4):529-532. PubMed
17. Mamykina L, Vawdrey DK, Hripcsak G. How Do Residents Spend Their Shift Time? A Time and Motion Study With a Particular Focus on the Use of Computers. Acad Med. 2016;91(6):827-832. PubMed
18. Chen L, Guo U, Illipparambil LC, et al. Racing Against the Clock: Internal Medicine Residents’ Time Spent On Electronic Health Records. J Grad Med Educ. 2016;8(1):39-44. PubMed
19. Kuhn T, Basch P, Barr M, Yackel T, Physicians MICotACo. Clinical documentation in the 21st century: executive summary of a policy position paper from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(4):301-303. PubMed
20. Treadwell JR, Lucas S, Tsou AY. Surgical checklists: a systematic review of impacts and implementation. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(4):299-318. PubMed
21. Ko HC, Turner TJ, Finnigan MA. Systematic review of safety checklists for use by medical care teams in acute hospital settings--limited evidence of effectiveness. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:211. PubMed
22. Diaz-Montes TP, Cobb L, Ibeanu OA, Njoku P, Gerardi MA. Introduction of checklists at daily progress notes improves patient care among the gynecological oncology service. J Patient Saf. 2012;8(4):189-193. PubMed
23. Stetson PD, Bakken S, Wrenn JO, Siegler EL. Assessing Electronic Note Quality Using the Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI-9). Appl Clin Inform. 2012;3(2):164-174. PubMed
24. Friedberg MW, Chen PG, Van Busum KR, et al. Factors affecting physician professional satisfaction and their implications for patient care, health systems, and health policy. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation; 2013. PubMed
1. Herzig SJ, Guess JR, Feinbloom DB, et al. Improving appropriateness of acid-suppressive medication use via computerized clinical decision support. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(1):41-45. PubMed
2. Nguyen OK, Makam AN, Clark C, et al. Predicting all-cause readmissions using electronic health record data from the entire hospitalization: Model development and comparison. J Hosp Med. 2016;11(7):473-480. PubMed
3. Donati A, Gabbanelli V, Pantanetti S, et al. The impact of a clinical information system in an intensive care unit. J Clin Monit Comput. 2008;22(1):31-36. PubMed
4. Schiff GD, Bates DW. Can electronic clinical documentation help prevent diagnostic errors? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1066-1069. PubMed
5. Hartzband P, Groopman J. Off the record--avoiding the pitfalls of going electronic. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(16):1656-1658. PubMed
6. Hirschtick RE. A piece of my mind. Copy-and-paste. JAMA. 2006;295(20):2335-2336. PubMed
7. Hirschtick RE. A piece of my mind. John Lennon’s elbow. JAMA. 2012;308(5):463-464. PubMed
8. O’Donnell HC, Kaushal R, Barrón Y, Callahan MA, Adelman RD, Siegler EL. Physicians’ attitudes towards copy and pasting in electronic note writing. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(1):63-68. PubMed
9. Mahapatra P, Ieong E. Improving Documentation and Communication Using Operative Note Proformas. BMJ Qual Improv Rep. 2016;5(1):u209122.w3712. PubMed
10. Thomson DR, Baldwin MJ, Bellini MI, Silva MA. Improving the quality of operative notes for laparoscopic cholecystectomy: Assessing the impact of a standardized operation note proforma. Int J Surg. 2016;27:17-20. PubMed
11. Dean SM, Eickhoff JC, Bakel LA. The effectiveness of a bundled intervention to improve resident progress notes in an electronic health record. J Hosp Med. 2015;10(2):104-107. PubMed
12. Aylor M, Campbell EM, Winter C, Phillipi CA. Resident Notes in an Electronic Health Record: A Mixed-Methods Study Using a Standardized Intervention With Qualitative Analysis. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2016;6(3):257-262.
13. Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research electronic data capture (REDCap)--a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. PubMed
14. Chi J, Kugler J, Chu IM, et al. Medical students and the electronic health record: ‘an epic use of time’. Am J Med. 2014;127(9):891-895. PubMed
15. Martin SA, Sinsky CA. The map is not the territory: medical records and 21st century practice. Lancet. 2016;388(10055):2053-2056. PubMed
16. Oxentenko AS, Manohar CU, McCoy CP, et al. Internal medicine residents’ computer use in the inpatient setting. J Grad Med Educ. 2012;4(4):529-532. PubMed
17. Mamykina L, Vawdrey DK, Hripcsak G. How Do Residents Spend Their Shift Time? A Time and Motion Study With a Particular Focus on the Use of Computers. Acad Med. 2016;91(6):827-832. PubMed
18. Chen L, Guo U, Illipparambil LC, et al. Racing Against the Clock: Internal Medicine Residents’ Time Spent On Electronic Health Records. J Grad Med Educ. 2016;8(1):39-44. PubMed
19. Kuhn T, Basch P, Barr M, Yackel T, Physicians MICotACo. Clinical documentation in the 21st century: executive summary of a policy position paper from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. 2015;162(4):301-303. PubMed
20. Treadwell JR, Lucas S, Tsou AY. Surgical checklists: a systematic review of impacts and implementation. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(4):299-318. PubMed
21. Ko HC, Turner TJ, Finnigan MA. Systematic review of safety checklists for use by medical care teams in acute hospital settings--limited evidence of effectiveness. BMC Health Serv Res. 2011;11:211. PubMed
22. Diaz-Montes TP, Cobb L, Ibeanu OA, Njoku P, Gerardi MA. Introduction of checklists at daily progress notes improves patient care among the gynecological oncology service. J Patient Saf. 2012;8(4):189-193. PubMed
23. Stetson PD, Bakken S, Wrenn JO, Siegler EL. Assessing Electronic Note Quality Using the Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI-9). Appl Clin Inform. 2012;3(2):164-174. PubMed
24. Friedberg MW, Chen PG, Van Busum KR, et al. Factors affecting physician professional satisfaction and their implications for patient care, health systems, and health policy. Santa Monica, CA: RAND Corporation; 2013. PubMed
© 2018 Society of Hospital Medicine
A Physician With Thigh Pain
Necrotizing soft-tissue infection (NSTI) often is difficult to distinguish from a superficial soft-tissue infection like cellulitis. Both conditions present with pain, edema, and erythema and can be accompanied by fever and malaise. The diagnosis of NSTI must be made quickly because successful treatment requires early surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotics. The following case demonstrates the challenge of diagnosing NSTI.
Case Presentation
A 50-year-old physician developed a sore throat with subjective fevers, night sweats, and chills. After 2 days, his symptoms resolved. The next day he developed right thigh pain while playing tennis and limped off the court. That night he had fevers, chills, and sweats. For the next 3 days, his right thigh pain persisted with waxing and waning fevers.
The patient’s medical history included gastroesophageal reflux disease, vitamin D deficiency, and a positive purified protein derivative test for which he had completed 1 year of isoniazid therapy. The patient was married and in a monogamous relationship with his wife. He had traveled to the Sierra National Forest and Yosemite Park during the preceding winter. He did not swim in a lake or recall a tick bite. He had not consumed raw food, imported meats, or dairy products. He recently started oral fluconazole for tinea corporis.
The patient’s temperature was 39.5°C, heart rate was 115 beats per minute, blood pressure (BP) was 142/88 mm Hg, and respiratory rate was 18 breaths per minute with an oxygen saturation of 95% while breathing ambient air. He was drenched in sweat yet remained comfortable throughout the interview. The oropharyngeal mucosa was moist without lesions or erythema. There was no rash or lymphadenopathy. The lungs were clear to auscultation. The cardiac exam revealed tachycardia. There was point tenderness to deep palpation of the mid-anterior right thigh without crepitus, erythema, or edema.
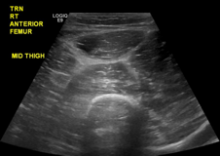
The patient’s sodium level was 129 mmol/L (normal range 135-145 mmol/L), bicarbonate was 20 mmol/L (normal range 22-32 mmol/L), creatinine was 1.1 mg/dL (normal range 0.7-1.2 mg/dL), and glucose was 194 mg/dL. The white blood cell count (WBC) was 12,900 cells/mm3 (normal range 3,400-10,000 cells/mm3) with 96% neutrophils. The hematocrit was 41% (normal range 41-53%), and the platelet count was 347,000 cells/mm3 (normal range 140,000-450,000 cells/mm3). The lactate level was 2.2 mmol/L (normal range 0-2 mmol/L). The creatine kinase level was 347 U/L (normal range 50-388 U/L), and the lactate dehydrogenase level was 254 U/L (normal range 102-199 U/L). A rapid group A streptococcal (GAS) antigen test was negative. A radiograph of the right femur revealed mildly edematous soft tissue. On ultrasound the right quadriceps appeared mildly edematous, but there was no evidence of abscess or discrete fluid collection (eFigure 1).
eFigure 1. Ultrasound of the Right Anterior Thigh Ultrasound revealed heterogeneous, mildly edematous quadriceps muscle. There was no abscess or discrete fluid collection. There was trace fluid along the fascia of the quadriceps muscle.
Four liters of normal saline, acetaminophen, ceftriaxone, and doxycycline were administered to the patient. Overnight he was afebrile, tachycardic, and normotensive. The following morning his BP decreased to 81/53 mm Hg. His WBC count was 33,000 cells/mm3 with 96% neutrophils. A peripheral blood smear showed immature granulocytes. The sodium and creatinine increased to 135 mmol/L and 1.3 mg/dL, respectively. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 20 mm/h (normal range 0-10 mm/h), and the C-reactive protein level was 174 mg/L (normal range < 6.3 mg/L).The right thigh became erythematous and edematous.
Given concern for necrotizing fasciitis, antibiotics were changed to vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and clindamycin. The patient was taken to the operating room (OR). The right quadriceps muscle was markedly edematous with overlying necrotic fibrofatty tissue with easy separation of the fascia from the anterolateral rectus femoris and rectus lateralis muscles. Necrotizing fasciitis was diagnosed.
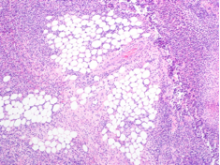
The tissue was debrided, and surgical pathology revealed fibroadipose tissue with extensive necrosis and dense acute inflammation (eFigure 2). After the anterolateral space between the fascia and underlying thigh muscle was drained, a Penrose drain was placed, and the wound was left open with plans for a second-look operation within 24 hours.
eFigure 2. Surgical Pathology of Debrided Right Thigh
Pathology revealed fibroadipose tissue with extensive necrosis and dense acute inflammation.
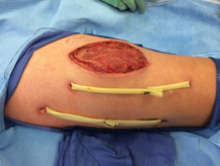
eFigure 3. Right Anterior Thigh
Two Penrose drains inserted after second operation.
In the ensuing hours erythema extended proximal to the operative site. The patient was emergently taken to the OR. The focus of necrotizing fasciitis along the anterolateral aspect of the thigh had extended posteriorly and superiorly. This area was irrigated, all loculations were disrupted, and a second Penrose drain was placed.
The wound was left open for 6 more days. On hospital day 9, operative exploration revealed no necrotizing fasciitis. The fascia and skin wound were then closed (eFigure 3).
Cultures from the fascia grew the GAS bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes (S pyogenes), which was sensitive to penicillin. The blood cultures from admission were sterile. A test for Epstein-Barr virus immunoglobulin M antibody was negative. The patient was discharged after 10 days in the hospital to complete a 2-week course of IV penicillin. Two months later he resumed playing tennis and returned to his clinical duties.
Discussion
In the U.S., there are approximately 3.5 cases of invasive GAS infection per 100,000 persons.1 Type I NSTI is polymicrobial (aerobic and anaerobic organisms). Risk factors include recent surgery, immunocompromised states, drug use, diabetes mellitus, and traumatic wounds.2 Type II NSTI is caused by GAS or other β-hemolytic streptococci either alone or in association with another organism, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus. Type II NSTI is classically found on the extremities and occurs in young, healthy, immunocompetent patients—such as this patient.3
The portal of entry in nearly half of type II NSTI is unknown; minor local trauma is often suspected.4 However, cases have been reported in which the only identifiable source was a preceding sore throat.4 The origin of this patient’s GAS remains unknown, but perhaps his pharyngitis led to transient bacteremia, which then seeded his injured thigh muscle. An in vitro model demonstrated that injured muscles increase surface expression of the cytoskeletal protein vimentin, which binds GAS.5 Exotoxins and endotoxins produced by S pyogenes may lead to microvascular thrombosis, tissue ischemia, liquefactive necrosis, and systemic release of cytokines followed by systemic illness, multiorgan dysfunction, and death.6
The Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) score was developed to aid in early diagnosis of NSTI.7 It was derived from a series of 2,555 patients admitted with cellulitis or abscesses at a single institution. Scores > 8 have a positive predictive value of 93% for NSTI. This patient had a LRINEC score of 9. Radiographs or computed tomography scans may demonstrate soft-tissue air collections but lack sensitivity and are often nondiagnostic.8,9 T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging can delineate the anatomic extent of soft-tissue infections but is time consuming and may delay treatment.10 When the pretest probability is high, proceeding directly to the OR for direct visualization and possible debridement is advisable. Histologic features of necrotizing fasciitis include inflammation with polymorphonuclear cells and necrosis of the subcutaneous fat and fascia with relative sparing of the muscle.11Necrotizing soft-tissue infection requires early surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage. Without surgical debridement, the mortality rate approaches 100%.2 Antibiotics should include activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms. The duration of antibiotic therapy has not been defined and is dependent on the patient’s clinical status. Adjunctive treatment options may include IV immunoglobulin and hyperbaric oxygen therapy, although the data supporting their utility are limited.12,13
Conclusion
Despite the LRINEC scoring systems and advanced imaging, necrotizing fasciitis remains challenging to diagnose in a timely manner. In this case, close monitoring of the patient facilitated timely evaluation and treatment of a fatal disease.
1. O'Loughlin RE, Roberson A, Cieslak PR, et al; Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Team. The epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infection and potential vaccine implications: United States, 2000-2004. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(7):853-857.
2. Anaya DA, Dellinger EP. Necrotizing soft-tissue infection: diagnosis and management. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(5):705-710.
3. Naqvi GA, Malik SA, Jan W. Necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity: a case report and current concept of diagnosis and management. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2009;17:28.
4. Stevens DL. Streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome: spectrum of disease, pathogenesis, and new concepts in treatment. Emerg Infect Dis. 1195;1(3):69-78.
5. Bryant AE, Bayer CR, Huntington JD, Stevens DL. Group A streptococcal myonecrosis: increased vimentin expression after skeletal-muscle injury mediates the binding of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Infect Dis. 2006;193(12):1685-1692.
6. Cainzos M, Gonzalez-Rodriguez FJ. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2007;13(4):433-439.
7. Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(7):1535-1541.
8. Goh T, Goh LG, Ang CH, Wong CH. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Surg. 2014;101(1):119-125.
9. Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Basetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis and management. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(3):560-566.
10. Brothers TE, Tagge DU, Stutley JE, Conway WF, Del Schutte H Jr, Byrne TK. Magnetic resonance imaging differentiates between necrotizing and non-necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;187(4):416-421.
11. Bakleh M, Wold LE, Mandrekar JN, Harmsen WS, Dimashkieh HH, Baddour LM. Correlation of histopathologic findings with clinical outcome in necrotizing fasciitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40(3):410-414.
12. Barry W, Hudgins L, Donta ST, Pesanti EL. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1992;267(24):3315-3316.
13. Wilkinson D, Doolette D. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and survival from necrotizing soft tissue infection. Arch Surg. 2004;139(12):1339-1345.
Necrotizing soft-tissue infection (NSTI) often is difficult to distinguish from a superficial soft-tissue infection like cellulitis. Both conditions present with pain, edema, and erythema and can be accompanied by fever and malaise. The diagnosis of NSTI must be made quickly because successful treatment requires early surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotics. The following case demonstrates the challenge of diagnosing NSTI.
Case Presentation
A 50-year-old physician developed a sore throat with subjective fevers, night sweats, and chills. After 2 days, his symptoms resolved. The next day he developed right thigh pain while playing tennis and limped off the court. That night he had fevers, chills, and sweats. For the next 3 days, his right thigh pain persisted with waxing and waning fevers.
The patient’s medical history included gastroesophageal reflux disease, vitamin D deficiency, and a positive purified protein derivative test for which he had completed 1 year of isoniazid therapy. The patient was married and in a monogamous relationship with his wife. He had traveled to the Sierra National Forest and Yosemite Park during the preceding winter. He did not swim in a lake or recall a tick bite. He had not consumed raw food, imported meats, or dairy products. He recently started oral fluconazole for tinea corporis.
The patient’s temperature was 39.5°C, heart rate was 115 beats per minute, blood pressure (BP) was 142/88 mm Hg, and respiratory rate was 18 breaths per minute with an oxygen saturation of 95% while breathing ambient air. He was drenched in sweat yet remained comfortable throughout the interview. The oropharyngeal mucosa was moist without lesions or erythema. There was no rash or lymphadenopathy. The lungs were clear to auscultation. The cardiac exam revealed tachycardia. There was point tenderness to deep palpation of the mid-anterior right thigh without crepitus, erythema, or edema.
The patient’s sodium level was 129 mmol/L (normal range 135-145 mmol/L), bicarbonate was 20 mmol/L (normal range 22-32 mmol/L), creatinine was 1.1 mg/dL (normal range 0.7-1.2 mg/dL), and glucose was 194 mg/dL. The white blood cell count (WBC) was 12,900 cells/mm3 (normal range 3,400-10,000 cells/mm3) with 96% neutrophils. The hematocrit was 41% (normal range 41-53%), and the platelet count was 347,000 cells/mm3 (normal range 140,000-450,000 cells/mm3). The lactate level was 2.2 mmol/L (normal range 0-2 mmol/L). The creatine kinase level was 347 U/L (normal range 50-388 U/L), and the lactate dehydrogenase level was 254 U/L (normal range 102-199 U/L). A rapid group A streptococcal (GAS) antigen test was negative. A radiograph of the right femur revealed mildly edematous soft tissue. On ultrasound the right quadriceps appeared mildly edematous, but there was no evidence of abscess or discrete fluid collection (eFigure 1).
eFigure 1. Ultrasound of the Right Anterior Thigh Ultrasound revealed heterogeneous, mildly edematous quadriceps muscle. There was no abscess or discrete fluid collection. There was trace fluid along the fascia of the quadriceps muscle.
Four liters of normal saline, acetaminophen, ceftriaxone, and doxycycline were administered to the patient. Overnight he was afebrile, tachycardic, and normotensive. The following morning his BP decreased to 81/53 mm Hg. His WBC count was 33,000 cells/mm3 with 96% neutrophils. A peripheral blood smear showed immature granulocytes. The sodium and creatinine increased to 135 mmol/L and 1.3 mg/dL, respectively. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 20 mm/h (normal range 0-10 mm/h), and the C-reactive protein level was 174 mg/L (normal range < 6.3 mg/L).The right thigh became erythematous and edematous.
Given concern for necrotizing fasciitis, antibiotics were changed to vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and clindamycin. The patient was taken to the operating room (OR). The right quadriceps muscle was markedly edematous with overlying necrotic fibrofatty tissue with easy separation of the fascia from the anterolateral rectus femoris and rectus lateralis muscles. Necrotizing fasciitis was diagnosed.
The tissue was debrided, and surgical pathology revealed fibroadipose tissue with extensive necrosis and dense acute inflammation (eFigure 2). After the anterolateral space between the fascia and underlying thigh muscle was drained, a Penrose drain was placed, and the wound was left open with plans for a second-look operation within 24 hours.
eFigure 2. Surgical Pathology of Debrided Right Thigh
Pathology revealed fibroadipose tissue with extensive necrosis and dense acute inflammation.
eFigure 3. Right Anterior Thigh
Two Penrose drains inserted after second operation.
In the ensuing hours erythema extended proximal to the operative site. The patient was emergently taken to the OR. The focus of necrotizing fasciitis along the anterolateral aspect of the thigh had extended posteriorly and superiorly. This area was irrigated, all loculations were disrupted, and a second Penrose drain was placed.
The wound was left open for 6 more days. On hospital day 9, operative exploration revealed no necrotizing fasciitis. The fascia and skin wound were then closed (eFigure 3).
Cultures from the fascia grew the GAS bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes (S pyogenes), which was sensitive to penicillin. The blood cultures from admission were sterile. A test for Epstein-Barr virus immunoglobulin M antibody was negative. The patient was discharged after 10 days in the hospital to complete a 2-week course of IV penicillin. Two months later he resumed playing tennis and returned to his clinical duties.
Discussion
In the U.S., there are approximately 3.5 cases of invasive GAS infection per 100,000 persons.1 Type I NSTI is polymicrobial (aerobic and anaerobic organisms). Risk factors include recent surgery, immunocompromised states, drug use, diabetes mellitus, and traumatic wounds.2 Type II NSTI is caused by GAS or other β-hemolytic streptococci either alone or in association with another organism, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus. Type II NSTI is classically found on the extremities and occurs in young, healthy, immunocompetent patients—such as this patient.3
The portal of entry in nearly half of type II NSTI is unknown; minor local trauma is often suspected.4 However, cases have been reported in which the only identifiable source was a preceding sore throat.4 The origin of this patient’s GAS remains unknown, but perhaps his pharyngitis led to transient bacteremia, which then seeded his injured thigh muscle. An in vitro model demonstrated that injured muscles increase surface expression of the cytoskeletal protein vimentin, which binds GAS.5 Exotoxins and endotoxins produced by S pyogenes may lead to microvascular thrombosis, tissue ischemia, liquefactive necrosis, and systemic release of cytokines followed by systemic illness, multiorgan dysfunction, and death.6
The Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) score was developed to aid in early diagnosis of NSTI.7 It was derived from a series of 2,555 patients admitted with cellulitis or abscesses at a single institution. Scores > 8 have a positive predictive value of 93% for NSTI. This patient had a LRINEC score of 9. Radiographs or computed tomography scans may demonstrate soft-tissue air collections but lack sensitivity and are often nondiagnostic.8,9 T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging can delineate the anatomic extent of soft-tissue infections but is time consuming and may delay treatment.10 When the pretest probability is high, proceeding directly to the OR for direct visualization and possible debridement is advisable. Histologic features of necrotizing fasciitis include inflammation with polymorphonuclear cells and necrosis of the subcutaneous fat and fascia with relative sparing of the muscle.11Necrotizing soft-tissue infection requires early surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage. Without surgical debridement, the mortality rate approaches 100%.2 Antibiotics should include activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms. The duration of antibiotic therapy has not been defined and is dependent on the patient’s clinical status. Adjunctive treatment options may include IV immunoglobulin and hyperbaric oxygen therapy, although the data supporting their utility are limited.12,13
Conclusion
Despite the LRINEC scoring systems and advanced imaging, necrotizing fasciitis remains challenging to diagnose in a timely manner. In this case, close monitoring of the patient facilitated timely evaluation and treatment of a fatal disease.
Necrotizing soft-tissue infection (NSTI) often is difficult to distinguish from a superficial soft-tissue infection like cellulitis. Both conditions present with pain, edema, and erythema and can be accompanied by fever and malaise. The diagnosis of NSTI must be made quickly because successful treatment requires early surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotics. The following case demonstrates the challenge of diagnosing NSTI.
Case Presentation
A 50-year-old physician developed a sore throat with subjective fevers, night sweats, and chills. After 2 days, his symptoms resolved. The next day he developed right thigh pain while playing tennis and limped off the court. That night he had fevers, chills, and sweats. For the next 3 days, his right thigh pain persisted with waxing and waning fevers.
The patient’s medical history included gastroesophageal reflux disease, vitamin D deficiency, and a positive purified protein derivative test for which he had completed 1 year of isoniazid therapy. The patient was married and in a monogamous relationship with his wife. He had traveled to the Sierra National Forest and Yosemite Park during the preceding winter. He did not swim in a lake or recall a tick bite. He had not consumed raw food, imported meats, or dairy products. He recently started oral fluconazole for tinea corporis.
The patient’s temperature was 39.5°C, heart rate was 115 beats per minute, blood pressure (BP) was 142/88 mm Hg, and respiratory rate was 18 breaths per minute with an oxygen saturation of 95% while breathing ambient air. He was drenched in sweat yet remained comfortable throughout the interview. The oropharyngeal mucosa was moist without lesions or erythema. There was no rash or lymphadenopathy. The lungs were clear to auscultation. The cardiac exam revealed tachycardia. There was point tenderness to deep palpation of the mid-anterior right thigh without crepitus, erythema, or edema.
The patient’s sodium level was 129 mmol/L (normal range 135-145 mmol/L), bicarbonate was 20 mmol/L (normal range 22-32 mmol/L), creatinine was 1.1 mg/dL (normal range 0.7-1.2 mg/dL), and glucose was 194 mg/dL. The white blood cell count (WBC) was 12,900 cells/mm3 (normal range 3,400-10,000 cells/mm3) with 96% neutrophils. The hematocrit was 41% (normal range 41-53%), and the platelet count was 347,000 cells/mm3 (normal range 140,000-450,000 cells/mm3). The lactate level was 2.2 mmol/L (normal range 0-2 mmol/L). The creatine kinase level was 347 U/L (normal range 50-388 U/L), and the lactate dehydrogenase level was 254 U/L (normal range 102-199 U/L). A rapid group A streptococcal (GAS) antigen test was negative. A radiograph of the right femur revealed mildly edematous soft tissue. On ultrasound the right quadriceps appeared mildly edematous, but there was no evidence of abscess or discrete fluid collection (eFigure 1).
eFigure 1. Ultrasound of the Right Anterior Thigh Ultrasound revealed heterogeneous, mildly edematous quadriceps muscle. There was no abscess or discrete fluid collection. There was trace fluid along the fascia of the quadriceps muscle.
Four liters of normal saline, acetaminophen, ceftriaxone, and doxycycline were administered to the patient. Overnight he was afebrile, tachycardic, and normotensive. The following morning his BP decreased to 81/53 mm Hg. His WBC count was 33,000 cells/mm3 with 96% neutrophils. A peripheral blood smear showed immature granulocytes. The sodium and creatinine increased to 135 mmol/L and 1.3 mg/dL, respectively. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate was 20 mm/h (normal range 0-10 mm/h), and the C-reactive protein level was 174 mg/L (normal range < 6.3 mg/L).The right thigh became erythematous and edematous.
Given concern for necrotizing fasciitis, antibiotics were changed to vancomycin, piperacillin-tazobactam, and clindamycin. The patient was taken to the operating room (OR). The right quadriceps muscle was markedly edematous with overlying necrotic fibrofatty tissue with easy separation of the fascia from the anterolateral rectus femoris and rectus lateralis muscles. Necrotizing fasciitis was diagnosed.
The tissue was debrided, and surgical pathology revealed fibroadipose tissue with extensive necrosis and dense acute inflammation (eFigure 2). After the anterolateral space between the fascia and underlying thigh muscle was drained, a Penrose drain was placed, and the wound was left open with plans for a second-look operation within 24 hours.
eFigure 2. Surgical Pathology of Debrided Right Thigh
Pathology revealed fibroadipose tissue with extensive necrosis and dense acute inflammation.
eFigure 3. Right Anterior Thigh
Two Penrose drains inserted after second operation.
In the ensuing hours erythema extended proximal to the operative site. The patient was emergently taken to the OR. The focus of necrotizing fasciitis along the anterolateral aspect of the thigh had extended posteriorly and superiorly. This area was irrigated, all loculations were disrupted, and a second Penrose drain was placed.
The wound was left open for 6 more days. On hospital day 9, operative exploration revealed no necrotizing fasciitis. The fascia and skin wound were then closed (eFigure 3).
Cultures from the fascia grew the GAS bacteria Streptococcus pyogenes (S pyogenes), which was sensitive to penicillin. The blood cultures from admission were sterile. A test for Epstein-Barr virus immunoglobulin M antibody was negative. The patient was discharged after 10 days in the hospital to complete a 2-week course of IV penicillin. Two months later he resumed playing tennis and returned to his clinical duties.
Discussion
In the U.S., there are approximately 3.5 cases of invasive GAS infection per 100,000 persons.1 Type I NSTI is polymicrobial (aerobic and anaerobic organisms). Risk factors include recent surgery, immunocompromised states, drug use, diabetes mellitus, and traumatic wounds.2 Type II NSTI is caused by GAS or other β-hemolytic streptococci either alone or in association with another organism, most commonly Staphylococcus aureus. Type II NSTI is classically found on the extremities and occurs in young, healthy, immunocompetent patients—such as this patient.3
The portal of entry in nearly half of type II NSTI is unknown; minor local trauma is often suspected.4 However, cases have been reported in which the only identifiable source was a preceding sore throat.4 The origin of this patient’s GAS remains unknown, but perhaps his pharyngitis led to transient bacteremia, which then seeded his injured thigh muscle. An in vitro model demonstrated that injured muscles increase surface expression of the cytoskeletal protein vimentin, which binds GAS.5 Exotoxins and endotoxins produced by S pyogenes may lead to microvascular thrombosis, tissue ischemia, liquefactive necrosis, and systemic release of cytokines followed by systemic illness, multiorgan dysfunction, and death.6
The Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis (LRINEC) score was developed to aid in early diagnosis of NSTI.7 It was derived from a series of 2,555 patients admitted with cellulitis or abscesses at a single institution. Scores > 8 have a positive predictive value of 93% for NSTI. This patient had a LRINEC score of 9. Radiographs or computed tomography scans may demonstrate soft-tissue air collections but lack sensitivity and are often nondiagnostic.8,9 T1-weighted magnetic resonance imaging can delineate the anatomic extent of soft-tissue infections but is time consuming and may delay treatment.10 When the pretest probability is high, proceeding directly to the OR for direct visualization and possible debridement is advisable. Histologic features of necrotizing fasciitis include inflammation with polymorphonuclear cells and necrosis of the subcutaneous fat and fascia with relative sparing of the muscle.11Necrotizing soft-tissue infection requires early surgical debridement and broad-spectrum antibiotic coverage. Without surgical debridement, the mortality rate approaches 100%.2 Antibiotics should include activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, and anaerobic organisms. The duration of antibiotic therapy has not been defined and is dependent on the patient’s clinical status. Adjunctive treatment options may include IV immunoglobulin and hyperbaric oxygen therapy, although the data supporting their utility are limited.12,13
Conclusion
Despite the LRINEC scoring systems and advanced imaging, necrotizing fasciitis remains challenging to diagnose in a timely manner. In this case, close monitoring of the patient facilitated timely evaluation and treatment of a fatal disease.
1. O'Loughlin RE, Roberson A, Cieslak PR, et al; Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Team. The epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infection and potential vaccine implications: United States, 2000-2004. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(7):853-857.
2. Anaya DA, Dellinger EP. Necrotizing soft-tissue infection: diagnosis and management. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(5):705-710.
3. Naqvi GA, Malik SA, Jan W. Necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity: a case report and current concept of diagnosis and management. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2009;17:28.
4. Stevens DL. Streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome: spectrum of disease, pathogenesis, and new concepts in treatment. Emerg Infect Dis. 1195;1(3):69-78.
5. Bryant AE, Bayer CR, Huntington JD, Stevens DL. Group A streptococcal myonecrosis: increased vimentin expression after skeletal-muscle injury mediates the binding of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Infect Dis. 2006;193(12):1685-1692.
6. Cainzos M, Gonzalez-Rodriguez FJ. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2007;13(4):433-439.
7. Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(7):1535-1541.
8. Goh T, Goh LG, Ang CH, Wong CH. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Surg. 2014;101(1):119-125.
9. Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Basetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis and management. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(3):560-566.
10. Brothers TE, Tagge DU, Stutley JE, Conway WF, Del Schutte H Jr, Byrne TK. Magnetic resonance imaging differentiates between necrotizing and non-necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;187(4):416-421.
11. Bakleh M, Wold LE, Mandrekar JN, Harmsen WS, Dimashkieh HH, Baddour LM. Correlation of histopathologic findings with clinical outcome in necrotizing fasciitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40(3):410-414.
12. Barry W, Hudgins L, Donta ST, Pesanti EL. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1992;267(24):3315-3316.
13. Wilkinson D, Doolette D. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and survival from necrotizing soft tissue infection. Arch Surg. 2004;139(12):1339-1345.
1. O'Loughlin RE, Roberson A, Cieslak PR, et al; Active Bacterial Core Surveillance Team. The epidemiology of invasive group A streptococcal infection and potential vaccine implications: United States, 2000-2004. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;45(7):853-857.
2. Anaya DA, Dellinger EP. Necrotizing soft-tissue infection: diagnosis and management. Clin Infect Dis. 2007;44(5):705-710.
3. Naqvi GA, Malik SA, Jan W. Necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity: a case report and current concept of diagnosis and management. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 2009;17:28.
4. Stevens DL. Streptococcal toxic-shock syndrome: spectrum of disease, pathogenesis, and new concepts in treatment. Emerg Infect Dis. 1195;1(3):69-78.
5. Bryant AE, Bayer CR, Huntington JD, Stevens DL. Group A streptococcal myonecrosis: increased vimentin expression after skeletal-muscle injury mediates the binding of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Infect Dis. 2006;193(12):1685-1692.
6. Cainzos M, Gonzalez-Rodriguez FJ. Necrotizing soft tissue infections. Curr Opin Crit Care. 2007;13(4):433-439.
7. Wong CH, Khin LW, Heng KS, Tan KC, Low CO. The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score: a tool for distinguishing necrotizing fasciitis from other soft tissue infections. Crit Care Med. 2004;32(7):1535-1541.
8. Goh T, Goh LG, Ang CH, Wong CH. Early diagnosis of necrotizing fasciitis. Br J Surg. 2014;101(1):119-125.
9. Lancerotto L, Tocco I, Salmaso R, Vindigni V, Basetto F. Necrotizing fasciitis: classification, diagnosis and management. J Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2012;72(3):560-566.
10. Brothers TE, Tagge DU, Stutley JE, Conway WF, Del Schutte H Jr, Byrne TK. Magnetic resonance imaging differentiates between necrotizing and non-necrotizing fasciitis of the lower extremity. J Am Coll Surg. 1998;187(4):416-421.
11. Bakleh M, Wold LE, Mandrekar JN, Harmsen WS, Dimashkieh HH, Baddour LM. Correlation of histopathologic findings with clinical outcome in necrotizing fasciitis. Clin Infect Dis. 2005;40(3):410-414.
12. Barry W, Hudgins L, Donta ST, Pesanti EL. Intravenous immunoglobulin therapy for toxic shock syndrome. JAMA. 1992;267(24):3315-3316.
13. Wilkinson D, Doolette D. Hyperbaric oxygen treatment and survival from necrotizing soft tissue infection. Arch Surg. 2004;139(12):1339-1345.
Perceptions of Current Note Quality
The electronic health record (EHR) has revolutionized the practice of medicine. As part of the economic stimulus package in 2009, Congress enacted the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, which included incentives for physicians and hospitals to adopt an EHR by 2015. In the setting of more limited duty hours and demands for increased clinical productivity, EHRs have functions that may improve the quality and efficiency of clinical documentation.[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
The process of note writing and the use of notes for clinical care have changed substantially with EHR implementation. Use of efficiency tools (ie, copy forward functions and autopopulation of data) may increase the speed of documentation.[5] Notes in an EHR are more legible and accessible and may be able to organize data to improve clinical care.[6]
Yet, many have commented on the negative consequences of documentation in an EHR. In a New England Journal of Medicine Perspective article, Drs. Hartzband and Groopman wrote, we have observed the electronic medical record become a powerful vehicle for perpetuating erroneous information, leading to diagnostic errors that gain momentum when passed on electronically.[7] As a result, the copy forward and autopopulation functions have come under significant scrutiny.[8, 9, 10] A survey conducted at 2 academic institutions found that 71% of residents and attendings believed that the copy forward function led to inconsistencies and outdated information.[11] Autopopulation has been criticized for creating lengthy notes full of trivial or redundant data, a phenomenon termed note bloat. Bloated notes may be less effective as a communication tool.[12] Additionally, the process of composing a note often stimulates critical thinking and may lead to changes in care. The act of copying forward a previous note and autopopulating data bypasses that process and in effect may suppress critical thinking.[13] Previous studies have raised numerous concerns regarding copy forward and autopopulation functionality in the EHR. Many have described the duplication of outdated data and the possibility of the introduction and perpetuation of errors.[14, 15, 16] The Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health system evaluated 6322 copy events and found that 1 in 10 electronic patient charts contained an instance of high‐risk copying.[17] In a survey of faculty and residents at a single academic medical center, the majority of users of copy and paste functionality recognized the hazards; they responded that their notes may contain more outdated (66%) and more inconsistent information (69%). Yet, most felt copy forwarding improved the documentation of the entire hospital course (87%), overall physician documentation (69%), and should definitely be continued (91%).[11] Others have complained about the impact of copy forward on the expression of clinical reasoning.[7, 9, 18]
Previous discussions on the topic of overall note quality following EHR implementation have been limited to perspectives or opinion pieces of individual attending providers.[18] We conducted a survey across 4 academic institutions to analyze both housestaff and attendings perceptions of the quality of notes since the implementation of an EHR to better inform the discussion of the impact of an EHR on note quality.
METHODS
Participants
Surveys were administered via email to interns, residents (second‐, third‐, or fourth‐year residents, hereafter referred to as residents) and attendings at 4 academic hospitals that use the Epic EHR (Epic Corp., Madison, WI). The 4 institutions each adopted the Epic EHR, with mandatory faculty and resident training, between 1 and 5 years prior to the survey. Three of the institutions previously used systems with electronic notes, whereas the fourth institution previously used a system with handwritten notes. The study participation emails included a link to an online survey in REDCap.[19] We included interns and residents from the following types of residency programs: internal medicine categorical or primary care, medicine‐pediatrics, or medicine‐psychiatry. For housestaff (the combination of both interns and residents), exclusion criteria included preliminary or transitional year interns, or any interns or residents from other specialties who rotate on the medicine service. For attendings, participants included hospitalists, general internal medicine attendings, chief residents, and subspecialty medicine attendings, each of whom had worked for any amount of time on the inpatient medicine teaching service in the prior 12 months.
Design
We developed 3 unique surveys for interns, residents, and attendings to assess their perception of inpatient progress notes (see Supporting Information, Appendix, in the online version of this article). The surveys incorporated questions from 2 previously published sources, the 9‐item Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI‐9) (see online Appendix), a validated note‐scoring tool, and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education note‐writing competency checklists.[20] Additionally, faculty at the participating institutions developed questions to address practices and attitudes toward autopopulation, copy forward, and the purposes of a progress note. Responses were based on a 5‐point Likert scale. The intern and resident surveys asked for self‐evaluation of their own progress notes and those of their peers, whereas the attending surveys asked for assessment of housestaff notes.
The survey was left open for a total of 55 days and participants were sent reminder emails. The study received a waiver from the institutional review board at all 4 institutions.
Data Analysis
Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).[19] The survey data were analyzed and the figures were created using Microsoft Excel 2008 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA). Mean values for each survey question were calculated. Differences between the means among the groups were assessed using 2‐sample t tests. P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Demographics
We received 99 completed surveys from interns, 155 completed surveys from residents, and 153 completed surveys from attendings across the 4 institutions. The overall response rate for interns was 68%, ranging from 59% at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) to 74% at the University of Iowa. The overall response rate for residents was 49%, ranging from 38% at UCSF to 66% at the University of California, Los Angeles. The overall response rate for attendings was 70%, ranging from 53% at UCSD to 74% at UCSF.
A total of 78% of interns and 72% of residents had used an EHR at a prior institution. Of the residents, 90 were second‐year residents, 64 were third‐year residents, and 2 were fourth‐year residents. A total of 76% of attendings self‐identified as hospitalists.
Overall Assessment of Note Quality
Participants were asked to rate the quality of progress notes on a 5‐point scale (poor, fair, good, very good, excellent). Half of interns and residents rated their own progress notes as very good or excellent. A total of 44% percent of interns and 24% of residents rated their peers notes as very good or excellent, whereas only 15% of attending physicians rated housestaff notes as very good or excellent.
When asked to rate the change in progress note quality since their hospital had adopted the EHR, the majority of residents answered unchanged or better, and the majority of attendings answered unchanged or worse (Figure 1).
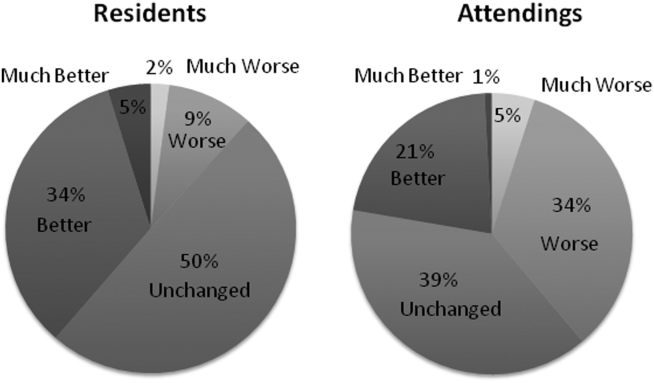
PDQI‐9 Framework
Participants answered each PDQI‐9 question on a 5‐point Likert scale ranging from not at all (1) to extremely (5). In 8 of the 9 PDQI‐9 domains, there were no significant differences between interns and residents. Across each domain, attending perceptions of housestaff notes were significantly lower than housestaff perceptions of their own notes (P<0.001) (Figure 2). Both housestaff and attendings gave the highest ratings to thorough, up to date, and synthesized and the lowest rating to succinct.
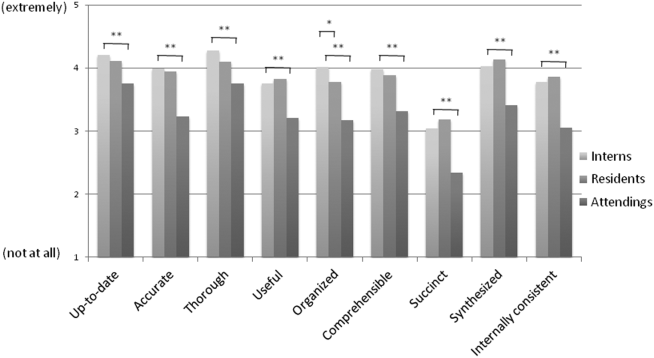
Copy Forward and Autopopulation
Overall, the effect of copy forward and autopopulation on critical thinking, note accuracy, and prioritizing the problem list was thought to be neutral or somewhat positive by interns, neutral by residents, and neutral or somewhat negative by attendings (P<0.001) (Figure 3). In all, 16% of interns, 22% of residents, and 55% of attendings reported that copy forward had a somewhat negative or very negative impact on critical thinking (P<0.001). In all, 16% of interns, 29% of residents and 39% of attendings thought that autopopulation had a somewhat negative or very negative impact on critical thinking (P<0.001).
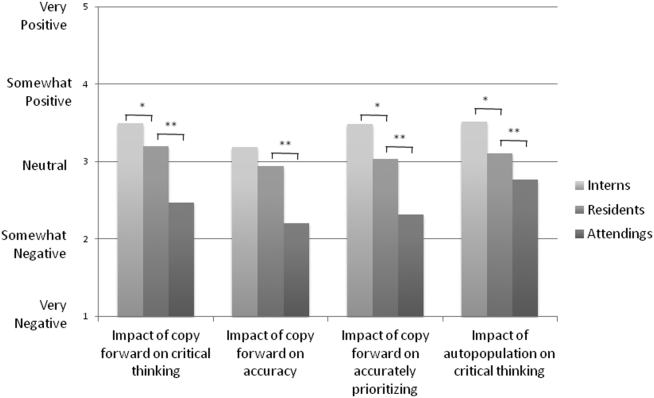
Purpose of Progress Notes
Participants were provided with 7 possible purposes of a progress note and asked to rate the importance of each stated purpose. There was nearly perfect agreement between interns, residents, and attendings in the rank order of the importance of each purpose of a progress note (Table 1). Attendings and housestaff ranked communication with other providers and documenting important events and the plan for the day as the 2 most important purposes of a progress note, and billing and quality improvement as less important.
| Interns | Residents | Attendings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication with other providers | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Documenting important events and the plan for the day | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Prioritizing issues going forward in the patient's care | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Medicolegal | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Stimulate critical thinking | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Billing | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Quality improvement | 7 | 7 | 7 |
DISCUSSION
This is the first large multicenter analysis of both attendings and housestaff perceptions of note quality in the EHR era. The findings provide insight into important differences and similarities in the perceptions of the 2 groups. Most striking is the difference in opinion of overall note quality, with only a small minority of faculty rating current housestaff notes as very good or excellent, whereas a much larger proportion of housestaff rated their own notes and those of their peers to be of high quality. Though participants were not specifically asked why note quality in general was suboptimal, housestaff and faculty rankings of specific domains from the PDQI‐9 may yield an important clue. Specifically, all groups expressed that the weakest attribute of current progress notes is succinct. This finding is consistent with the note bloat phenomenon, which has been maligned as a consequence of EHR implementation.[7, 14, 18, 21, 22]
One interesting finding was that only 5% of interns rated the notes of other housestaff as fair or poor. One possible explanation for this may be the tendency for an individual to enhance or augment the status or performance of the group to which he or she belongs as a mechanism to increase self‐image, known as the social identity theory.[23] Thus, housestaff may not criticize their peers to allow for identification with a group that is not deficient in note writing.
The more positive assessment of overall note quality among housestaff could be related to the different roles of housestaff and attendings on a teaching service. On a teaching service, housestaff are typically the writer, whereas attendings are almost exclusively the reader of progress notes. Housestaff may reap benefits, including efficiency, beyond the finished product. A perception of higher quality may reflect the process of note writing, data gathering, and critical thinking required to build an assessment and plan. The scores on the PDQI‐9 support this notion, as housestaff rated all 9 domains significantly higher than attendings.
Housestaff and attendings held greater differences of opinion with respect to the EHR's impact on note quality. Generally, housestaff perceived the EHR to have improved progress note quality, whereas attendings perceived the opposite. One explanation could be that these results reflect changing stages of development of physicians well described through the RIME framework (reporter, interpreter, manager, educator). Attendings may expect notes to reflect synthesis and analysis, whereas trainees may be satisfied with the data gathering that an EHR facilitates. In our survey, the trend of answers from intern to resident to attending suggests an evolving process of attitudes toward note quality.
The above reasons may also explain why housestaff were generally more positive than attendings about the effect of copy forward and autopopulation functions on critical thinking. Perhaps, as these functions can potentially increase efficiency and decrease time spent at the computer, although data are mixed on this finding, housestaff may have more time to spend with patients or develop a thorough plan and thus rate these functions positively.
Notably, housestaff and attendings had excellent agreement on the purposes of a progress note. They agreed that the 2 most important purposes were communication with other providers and documenting important events and the plan for the day. These are the 2 listed purposes that are most directly related to patient care. If future interventions to improve note quality require housestaff and attendings to significantly change their behavior, a focus on the impact on patient care might yield the best results.
There were several limitations in our study. Any study based on self‐assessment is subject to bias. A previous meta‐analysis and review described poor to moderate correlations between self‐assessed and external measures of performance.[24, 25] The survey data were aggregated from 4 institutions despite somewhat different, though relatively high, response rates between the institutions. There could be a response bias; those who did not respond may have systematically different perceptions of note quality. It should be noted that the general demographics of the respondents reflected those of the housestaff and attendings at 4 academic centers. All 4 of the participating institutions adopted the Epic EHR within the last several years of the survey being administered, and perceptions of note quality may be biased depending on the prior system used (ie, change from handwritten to electronic vs electronic to other electronic system). In addition, the survey results reflect experience with only 1 EHR, and our results may not apply to other EHR vendors or institutions like the VA, which have a long‐standing system in place. Last, we did not explore the impact of perceived note quality on the measured or perceived quality of care. One previous study found no direct correlation between note quality and clinical quality.[26]
There are several future directions for research based on our findings. First, potential differences between housestaff and attending perceptions of note quality could be further teased apart by studying the perceptions of attendings on a nonteaching service who write their own daily progress notes. Second, housestaff perceptions on why copy forward and autopopulation may increase critical thinking could be explored further with more direct questioning. Finally, although our study captured only perceptions of note quality, validated tools could be used to objectively measure note quality; these measurements could then be compared to perception of note quality as well as clinical outcomes.
Given the prevalence and the apparent belief that the benefits of an EHR outweigh the hazards, institutions should embrace these innovations but take steps to mitigate the potential errors and problems associated with copy forward and autopopulation. The results of our study should help inform future interventions.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the contributions of Russell Leslie from the University of Iowa.
Disclosure: Nothing to report.
- , , , et al. Systematic review: impact of health information technology on quality, efficiency, and costs of medical care. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(10):742–752.
- , , , , . Clinical information technologies and inpatient outcomes: a multiple hospital study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(2):108–114.
- , , , et al. Effect of computerized physician order entry and a team intervention on prevention of serious medication errors. JAMA. 1998;280(15):1311–1316.
- , , , . Electronic health records and quality of diabetes care. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(9):825–833.
- , , , et al. The impact of a clinical information system in an intensive care unit. J Clin Monit Comput. 2008;22(1):31–36.
- , . Can electronic clinical documentation help prevent diagnostic errors? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1066–1069.
- , . Off the record—avoiding the pitfalls of going electronic. N Eng J Med. 2008;358(16):1656–1658.
- , , . Copying and pasting of examinations within the electronic medical record. Int J Med Inform. 2007;76(suppl 1):S122–S128.
- , . Copy and paste: a remediable hazard of electronic health records. Am J Med. 2009;122(6):495–496.
- , , . The role of copy‐and‐paste in the hospital electronic health record. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(8):1217–1218.
- , , , , , . Physicians’ attitudes towards copy and pasting in electronic note writing. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(1):63–68.
- , , , , . Medical education in the electronic medical record (EMR) era: benefits, challenges, and future directions. Acad Med. 2013;88(6):748–752.
- , . Educational impact of the electronic medical record. J Surg Educ. 2012;69(1):105–112.
- , , , , , . Direct text entry in electronic progress notes. An evaluation of input errors. Methods Inf Med. 2003;42(1):61–67.
- . The clinical record: a 200‐year‐old 21st‐century challenge. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(10):682–683.
- . Sloppy and paste. Morbidity and Mortality Rounds on the Web. Available at: http://www.webmm.ahrq.gov/case.aspx?caseID=274. Published July 2012. Accessed September 26, 2014.
- , , , . Are electronic medical records trustworthy? Observations on copying, pasting and duplication. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2003:269–273.
- . A piece of my mind. John Lennon's elbow. JAMA. 2012;308(5):463–464.
- , , , , , . Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata‐driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377–381.
- , , . ACGME competency note checklist. Available at: http://www.im.org/p/cm/ld/fid=831. Accessed August 8, 2013.
- , , , . Assessing electronic note quality using the Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI‐9). Appl Clin Inform. 2012;3(2):164–174.
- , , , . Quantifying clinical narrative redundancy in an electronic health record. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(1):49–53.
- , . The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. In: Psychology of Intergroup Relations. 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: Nelson‐Hall Publishers; 1986:7–24.
- , . Student self‐assessment in higher education: a meta‐analysis. Rev Educ Res. 1989;59:395–430.
- . A review of the validity and accuracy of self‐assessments in health professions training. Acad Med. 1991;66:762–769.
- , , , , . Association of note quality and quality of care: a cross‐sectional study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(5):406–413.
The electronic health record (EHR) has revolutionized the practice of medicine. As part of the economic stimulus package in 2009, Congress enacted the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, which included incentives for physicians and hospitals to adopt an EHR by 2015. In the setting of more limited duty hours and demands for increased clinical productivity, EHRs have functions that may improve the quality and efficiency of clinical documentation.[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
The process of note writing and the use of notes for clinical care have changed substantially with EHR implementation. Use of efficiency tools (ie, copy forward functions and autopopulation of data) may increase the speed of documentation.[5] Notes in an EHR are more legible and accessible and may be able to organize data to improve clinical care.[6]
Yet, many have commented on the negative consequences of documentation in an EHR. In a New England Journal of Medicine Perspective article, Drs. Hartzband and Groopman wrote, we have observed the electronic medical record become a powerful vehicle for perpetuating erroneous information, leading to diagnostic errors that gain momentum when passed on electronically.[7] As a result, the copy forward and autopopulation functions have come under significant scrutiny.[8, 9, 10] A survey conducted at 2 academic institutions found that 71% of residents and attendings believed that the copy forward function led to inconsistencies and outdated information.[11] Autopopulation has been criticized for creating lengthy notes full of trivial or redundant data, a phenomenon termed note bloat. Bloated notes may be less effective as a communication tool.[12] Additionally, the process of composing a note often stimulates critical thinking and may lead to changes in care. The act of copying forward a previous note and autopopulating data bypasses that process and in effect may suppress critical thinking.[13] Previous studies have raised numerous concerns regarding copy forward and autopopulation functionality in the EHR. Many have described the duplication of outdated data and the possibility of the introduction and perpetuation of errors.[14, 15, 16] The Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health system evaluated 6322 copy events and found that 1 in 10 electronic patient charts contained an instance of high‐risk copying.[17] In a survey of faculty and residents at a single academic medical center, the majority of users of copy and paste functionality recognized the hazards; they responded that their notes may contain more outdated (66%) and more inconsistent information (69%). Yet, most felt copy forwarding improved the documentation of the entire hospital course (87%), overall physician documentation (69%), and should definitely be continued (91%).[11] Others have complained about the impact of copy forward on the expression of clinical reasoning.[7, 9, 18]
Previous discussions on the topic of overall note quality following EHR implementation have been limited to perspectives or opinion pieces of individual attending providers.[18] We conducted a survey across 4 academic institutions to analyze both housestaff and attendings perceptions of the quality of notes since the implementation of an EHR to better inform the discussion of the impact of an EHR on note quality.
METHODS
Participants
Surveys were administered via email to interns, residents (second‐, third‐, or fourth‐year residents, hereafter referred to as residents) and attendings at 4 academic hospitals that use the Epic EHR (Epic Corp., Madison, WI). The 4 institutions each adopted the Epic EHR, with mandatory faculty and resident training, between 1 and 5 years prior to the survey. Three of the institutions previously used systems with electronic notes, whereas the fourth institution previously used a system with handwritten notes. The study participation emails included a link to an online survey in REDCap.[19] We included interns and residents from the following types of residency programs: internal medicine categorical or primary care, medicine‐pediatrics, or medicine‐psychiatry. For housestaff (the combination of both interns and residents), exclusion criteria included preliminary or transitional year interns, or any interns or residents from other specialties who rotate on the medicine service. For attendings, participants included hospitalists, general internal medicine attendings, chief residents, and subspecialty medicine attendings, each of whom had worked for any amount of time on the inpatient medicine teaching service in the prior 12 months.
Design
We developed 3 unique surveys for interns, residents, and attendings to assess their perception of inpatient progress notes (see Supporting Information, Appendix, in the online version of this article). The surveys incorporated questions from 2 previously published sources, the 9‐item Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI‐9) (see online Appendix), a validated note‐scoring tool, and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education note‐writing competency checklists.[20] Additionally, faculty at the participating institutions developed questions to address practices and attitudes toward autopopulation, copy forward, and the purposes of a progress note. Responses were based on a 5‐point Likert scale. The intern and resident surveys asked for self‐evaluation of their own progress notes and those of their peers, whereas the attending surveys asked for assessment of housestaff notes.
The survey was left open for a total of 55 days and participants were sent reminder emails. The study received a waiver from the institutional review board at all 4 institutions.
Data Analysis
Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).[19] The survey data were analyzed and the figures were created using Microsoft Excel 2008 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA). Mean values for each survey question were calculated. Differences between the means among the groups were assessed using 2‐sample t tests. P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Demographics
We received 99 completed surveys from interns, 155 completed surveys from residents, and 153 completed surveys from attendings across the 4 institutions. The overall response rate for interns was 68%, ranging from 59% at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) to 74% at the University of Iowa. The overall response rate for residents was 49%, ranging from 38% at UCSF to 66% at the University of California, Los Angeles. The overall response rate for attendings was 70%, ranging from 53% at UCSD to 74% at UCSF.
A total of 78% of interns and 72% of residents had used an EHR at a prior institution. Of the residents, 90 were second‐year residents, 64 were third‐year residents, and 2 were fourth‐year residents. A total of 76% of attendings self‐identified as hospitalists.
Overall Assessment of Note Quality
Participants were asked to rate the quality of progress notes on a 5‐point scale (poor, fair, good, very good, excellent). Half of interns and residents rated their own progress notes as very good or excellent. A total of 44% percent of interns and 24% of residents rated their peers notes as very good or excellent, whereas only 15% of attending physicians rated housestaff notes as very good or excellent.
When asked to rate the change in progress note quality since their hospital had adopted the EHR, the majority of residents answered unchanged or better, and the majority of attendings answered unchanged or worse (Figure 1).

PDQI‐9 Framework
Participants answered each PDQI‐9 question on a 5‐point Likert scale ranging from not at all (1) to extremely (5). In 8 of the 9 PDQI‐9 domains, there were no significant differences between interns and residents. Across each domain, attending perceptions of housestaff notes were significantly lower than housestaff perceptions of their own notes (P<0.001) (Figure 2). Both housestaff and attendings gave the highest ratings to thorough, up to date, and synthesized and the lowest rating to succinct.

Copy Forward and Autopopulation
Overall, the effect of copy forward and autopopulation on critical thinking, note accuracy, and prioritizing the problem list was thought to be neutral or somewhat positive by interns, neutral by residents, and neutral or somewhat negative by attendings (P<0.001) (Figure 3). In all, 16% of interns, 22% of residents, and 55% of attendings reported that copy forward had a somewhat negative or very negative impact on critical thinking (P<0.001). In all, 16% of interns, 29% of residents and 39% of attendings thought that autopopulation had a somewhat negative or very negative impact on critical thinking (P<0.001).

Purpose of Progress Notes
Participants were provided with 7 possible purposes of a progress note and asked to rate the importance of each stated purpose. There was nearly perfect agreement between interns, residents, and attendings in the rank order of the importance of each purpose of a progress note (Table 1). Attendings and housestaff ranked communication with other providers and documenting important events and the plan for the day as the 2 most important purposes of a progress note, and billing and quality improvement as less important.
| Interns | Residents | Attendings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication with other providers | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Documenting important events and the plan for the day | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Prioritizing issues going forward in the patient's care | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Medicolegal | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Stimulate critical thinking | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Billing | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Quality improvement | 7 | 7 | 7 |
DISCUSSION
This is the first large multicenter analysis of both attendings and housestaff perceptions of note quality in the EHR era. The findings provide insight into important differences and similarities in the perceptions of the 2 groups. Most striking is the difference in opinion of overall note quality, with only a small minority of faculty rating current housestaff notes as very good or excellent, whereas a much larger proportion of housestaff rated their own notes and those of their peers to be of high quality. Though participants were not specifically asked why note quality in general was suboptimal, housestaff and faculty rankings of specific domains from the PDQI‐9 may yield an important clue. Specifically, all groups expressed that the weakest attribute of current progress notes is succinct. This finding is consistent with the note bloat phenomenon, which has been maligned as a consequence of EHR implementation.[7, 14, 18, 21, 22]
One interesting finding was that only 5% of interns rated the notes of other housestaff as fair or poor. One possible explanation for this may be the tendency for an individual to enhance or augment the status or performance of the group to which he or she belongs as a mechanism to increase self‐image, known as the social identity theory.[23] Thus, housestaff may not criticize their peers to allow for identification with a group that is not deficient in note writing.
The more positive assessment of overall note quality among housestaff could be related to the different roles of housestaff and attendings on a teaching service. On a teaching service, housestaff are typically the writer, whereas attendings are almost exclusively the reader of progress notes. Housestaff may reap benefits, including efficiency, beyond the finished product. A perception of higher quality may reflect the process of note writing, data gathering, and critical thinking required to build an assessment and plan. The scores on the PDQI‐9 support this notion, as housestaff rated all 9 domains significantly higher than attendings.
Housestaff and attendings held greater differences of opinion with respect to the EHR's impact on note quality. Generally, housestaff perceived the EHR to have improved progress note quality, whereas attendings perceived the opposite. One explanation could be that these results reflect changing stages of development of physicians well described through the RIME framework (reporter, interpreter, manager, educator). Attendings may expect notes to reflect synthesis and analysis, whereas trainees may be satisfied with the data gathering that an EHR facilitates. In our survey, the trend of answers from intern to resident to attending suggests an evolving process of attitudes toward note quality.
The above reasons may also explain why housestaff were generally more positive than attendings about the effect of copy forward and autopopulation functions on critical thinking. Perhaps, as these functions can potentially increase efficiency and decrease time spent at the computer, although data are mixed on this finding, housestaff may have more time to spend with patients or develop a thorough plan and thus rate these functions positively.
Notably, housestaff and attendings had excellent agreement on the purposes of a progress note. They agreed that the 2 most important purposes were communication with other providers and documenting important events and the plan for the day. These are the 2 listed purposes that are most directly related to patient care. If future interventions to improve note quality require housestaff and attendings to significantly change their behavior, a focus on the impact on patient care might yield the best results.
There were several limitations in our study. Any study based on self‐assessment is subject to bias. A previous meta‐analysis and review described poor to moderate correlations between self‐assessed and external measures of performance.[24, 25] The survey data were aggregated from 4 institutions despite somewhat different, though relatively high, response rates between the institutions. There could be a response bias; those who did not respond may have systematically different perceptions of note quality. It should be noted that the general demographics of the respondents reflected those of the housestaff and attendings at 4 academic centers. All 4 of the participating institutions adopted the Epic EHR within the last several years of the survey being administered, and perceptions of note quality may be biased depending on the prior system used (ie, change from handwritten to electronic vs electronic to other electronic system). In addition, the survey results reflect experience with only 1 EHR, and our results may not apply to other EHR vendors or institutions like the VA, which have a long‐standing system in place. Last, we did not explore the impact of perceived note quality on the measured or perceived quality of care. One previous study found no direct correlation between note quality and clinical quality.[26]
There are several future directions for research based on our findings. First, potential differences between housestaff and attending perceptions of note quality could be further teased apart by studying the perceptions of attendings on a nonteaching service who write their own daily progress notes. Second, housestaff perceptions on why copy forward and autopopulation may increase critical thinking could be explored further with more direct questioning. Finally, although our study captured only perceptions of note quality, validated tools could be used to objectively measure note quality; these measurements could then be compared to perception of note quality as well as clinical outcomes.
Given the prevalence and the apparent belief that the benefits of an EHR outweigh the hazards, institutions should embrace these innovations but take steps to mitigate the potential errors and problems associated with copy forward and autopopulation. The results of our study should help inform future interventions.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the contributions of Russell Leslie from the University of Iowa.
Disclosure: Nothing to report.
The electronic health record (EHR) has revolutionized the practice of medicine. As part of the economic stimulus package in 2009, Congress enacted the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, which included incentives for physicians and hospitals to adopt an EHR by 2015. In the setting of more limited duty hours and demands for increased clinical productivity, EHRs have functions that may improve the quality and efficiency of clinical documentation.[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
The process of note writing and the use of notes for clinical care have changed substantially with EHR implementation. Use of efficiency tools (ie, copy forward functions and autopopulation of data) may increase the speed of documentation.[5] Notes in an EHR are more legible and accessible and may be able to organize data to improve clinical care.[6]
Yet, many have commented on the negative consequences of documentation in an EHR. In a New England Journal of Medicine Perspective article, Drs. Hartzband and Groopman wrote, we have observed the electronic medical record become a powerful vehicle for perpetuating erroneous information, leading to diagnostic errors that gain momentum when passed on electronically.[7] As a result, the copy forward and autopopulation functions have come under significant scrutiny.[8, 9, 10] A survey conducted at 2 academic institutions found that 71% of residents and attendings believed that the copy forward function led to inconsistencies and outdated information.[11] Autopopulation has been criticized for creating lengthy notes full of trivial or redundant data, a phenomenon termed note bloat. Bloated notes may be less effective as a communication tool.[12] Additionally, the process of composing a note often stimulates critical thinking and may lead to changes in care. The act of copying forward a previous note and autopopulating data bypasses that process and in effect may suppress critical thinking.[13] Previous studies have raised numerous concerns regarding copy forward and autopopulation functionality in the EHR. Many have described the duplication of outdated data and the possibility of the introduction and perpetuation of errors.[14, 15, 16] The Veterans Affairs (VA) Puget Sound Health system evaluated 6322 copy events and found that 1 in 10 electronic patient charts contained an instance of high‐risk copying.[17] In a survey of faculty and residents at a single academic medical center, the majority of users of copy and paste functionality recognized the hazards; they responded that their notes may contain more outdated (66%) and more inconsistent information (69%). Yet, most felt copy forwarding improved the documentation of the entire hospital course (87%), overall physician documentation (69%), and should definitely be continued (91%).[11] Others have complained about the impact of copy forward on the expression of clinical reasoning.[7, 9, 18]
Previous discussions on the topic of overall note quality following EHR implementation have been limited to perspectives or opinion pieces of individual attending providers.[18] We conducted a survey across 4 academic institutions to analyze both housestaff and attendings perceptions of the quality of notes since the implementation of an EHR to better inform the discussion of the impact of an EHR on note quality.
METHODS
Participants
Surveys were administered via email to interns, residents (second‐, third‐, or fourth‐year residents, hereafter referred to as residents) and attendings at 4 academic hospitals that use the Epic EHR (Epic Corp., Madison, WI). The 4 institutions each adopted the Epic EHR, with mandatory faculty and resident training, between 1 and 5 years prior to the survey. Three of the institutions previously used systems with electronic notes, whereas the fourth institution previously used a system with handwritten notes. The study participation emails included a link to an online survey in REDCap.[19] We included interns and residents from the following types of residency programs: internal medicine categorical or primary care, medicine‐pediatrics, or medicine‐psychiatry. For housestaff (the combination of both interns and residents), exclusion criteria included preliminary or transitional year interns, or any interns or residents from other specialties who rotate on the medicine service. For attendings, participants included hospitalists, general internal medicine attendings, chief residents, and subspecialty medicine attendings, each of whom had worked for any amount of time on the inpatient medicine teaching service in the prior 12 months.
Design
We developed 3 unique surveys for interns, residents, and attendings to assess their perception of inpatient progress notes (see Supporting Information, Appendix, in the online version of this article). The surveys incorporated questions from 2 previously published sources, the 9‐item Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI‐9) (see online Appendix), a validated note‐scoring tool, and the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education note‐writing competency checklists.[20] Additionally, faculty at the participating institutions developed questions to address practices and attitudes toward autopopulation, copy forward, and the purposes of a progress note. Responses were based on a 5‐point Likert scale. The intern and resident surveys asked for self‐evaluation of their own progress notes and those of their peers, whereas the attending surveys asked for assessment of housestaff notes.
The survey was left open for a total of 55 days and participants were sent reminder emails. The study received a waiver from the institutional review board at all 4 institutions.
Data Analysis
Study data were collected and managed using REDCap electronic data capture tools hosted at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF).[19] The survey data were analyzed and the figures were created using Microsoft Excel 2008 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA). Mean values for each survey question were calculated. Differences between the means among the groups were assessed using 2‐sample t tests. P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Demographics
We received 99 completed surveys from interns, 155 completed surveys from residents, and 153 completed surveys from attendings across the 4 institutions. The overall response rate for interns was 68%, ranging from 59% at the University of California, San Diego (UCSD) to 74% at the University of Iowa. The overall response rate for residents was 49%, ranging from 38% at UCSF to 66% at the University of California, Los Angeles. The overall response rate for attendings was 70%, ranging from 53% at UCSD to 74% at UCSF.
A total of 78% of interns and 72% of residents had used an EHR at a prior institution. Of the residents, 90 were second‐year residents, 64 were third‐year residents, and 2 were fourth‐year residents. A total of 76% of attendings self‐identified as hospitalists.
Overall Assessment of Note Quality
Participants were asked to rate the quality of progress notes on a 5‐point scale (poor, fair, good, very good, excellent). Half of interns and residents rated their own progress notes as very good or excellent. A total of 44% percent of interns and 24% of residents rated their peers notes as very good or excellent, whereas only 15% of attending physicians rated housestaff notes as very good or excellent.
When asked to rate the change in progress note quality since their hospital had adopted the EHR, the majority of residents answered unchanged or better, and the majority of attendings answered unchanged or worse (Figure 1).

PDQI‐9 Framework
Participants answered each PDQI‐9 question on a 5‐point Likert scale ranging from not at all (1) to extremely (5). In 8 of the 9 PDQI‐9 domains, there were no significant differences between interns and residents. Across each domain, attending perceptions of housestaff notes were significantly lower than housestaff perceptions of their own notes (P<0.001) (Figure 2). Both housestaff and attendings gave the highest ratings to thorough, up to date, and synthesized and the lowest rating to succinct.

Copy Forward and Autopopulation
Overall, the effect of copy forward and autopopulation on critical thinking, note accuracy, and prioritizing the problem list was thought to be neutral or somewhat positive by interns, neutral by residents, and neutral or somewhat negative by attendings (P<0.001) (Figure 3). In all, 16% of interns, 22% of residents, and 55% of attendings reported that copy forward had a somewhat negative or very negative impact on critical thinking (P<0.001). In all, 16% of interns, 29% of residents and 39% of attendings thought that autopopulation had a somewhat negative or very negative impact on critical thinking (P<0.001).

Purpose of Progress Notes
Participants were provided with 7 possible purposes of a progress note and asked to rate the importance of each stated purpose. There was nearly perfect agreement between interns, residents, and attendings in the rank order of the importance of each purpose of a progress note (Table 1). Attendings and housestaff ranked communication with other providers and documenting important events and the plan for the day as the 2 most important purposes of a progress note, and billing and quality improvement as less important.
| Interns | Residents | Attendings | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Communication with other providers | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Documenting important events and the plan for the day | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| Prioritizing issues going forward in the patient's care | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Medicolegal | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| Stimulate critical thinking | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Billing | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| Quality improvement | 7 | 7 | 7 |
DISCUSSION
This is the first large multicenter analysis of both attendings and housestaff perceptions of note quality in the EHR era. The findings provide insight into important differences and similarities in the perceptions of the 2 groups. Most striking is the difference in opinion of overall note quality, with only a small minority of faculty rating current housestaff notes as very good or excellent, whereas a much larger proportion of housestaff rated their own notes and those of their peers to be of high quality. Though participants were not specifically asked why note quality in general was suboptimal, housestaff and faculty rankings of specific domains from the PDQI‐9 may yield an important clue. Specifically, all groups expressed that the weakest attribute of current progress notes is succinct. This finding is consistent with the note bloat phenomenon, which has been maligned as a consequence of EHR implementation.[7, 14, 18, 21, 22]
One interesting finding was that only 5% of interns rated the notes of other housestaff as fair or poor. One possible explanation for this may be the tendency for an individual to enhance or augment the status or performance of the group to which he or she belongs as a mechanism to increase self‐image, known as the social identity theory.[23] Thus, housestaff may not criticize their peers to allow for identification with a group that is not deficient in note writing.
The more positive assessment of overall note quality among housestaff could be related to the different roles of housestaff and attendings on a teaching service. On a teaching service, housestaff are typically the writer, whereas attendings are almost exclusively the reader of progress notes. Housestaff may reap benefits, including efficiency, beyond the finished product. A perception of higher quality may reflect the process of note writing, data gathering, and critical thinking required to build an assessment and plan. The scores on the PDQI‐9 support this notion, as housestaff rated all 9 domains significantly higher than attendings.
Housestaff and attendings held greater differences of opinion with respect to the EHR's impact on note quality. Generally, housestaff perceived the EHR to have improved progress note quality, whereas attendings perceived the opposite. One explanation could be that these results reflect changing stages of development of physicians well described through the RIME framework (reporter, interpreter, manager, educator). Attendings may expect notes to reflect synthesis and analysis, whereas trainees may be satisfied with the data gathering that an EHR facilitates. In our survey, the trend of answers from intern to resident to attending suggests an evolving process of attitudes toward note quality.
The above reasons may also explain why housestaff were generally more positive than attendings about the effect of copy forward and autopopulation functions on critical thinking. Perhaps, as these functions can potentially increase efficiency and decrease time spent at the computer, although data are mixed on this finding, housestaff may have more time to spend with patients or develop a thorough plan and thus rate these functions positively.
Notably, housestaff and attendings had excellent agreement on the purposes of a progress note. They agreed that the 2 most important purposes were communication with other providers and documenting important events and the plan for the day. These are the 2 listed purposes that are most directly related to patient care. If future interventions to improve note quality require housestaff and attendings to significantly change their behavior, a focus on the impact on patient care might yield the best results.
There were several limitations in our study. Any study based on self‐assessment is subject to bias. A previous meta‐analysis and review described poor to moderate correlations between self‐assessed and external measures of performance.[24, 25] The survey data were aggregated from 4 institutions despite somewhat different, though relatively high, response rates between the institutions. There could be a response bias; those who did not respond may have systematically different perceptions of note quality. It should be noted that the general demographics of the respondents reflected those of the housestaff and attendings at 4 academic centers. All 4 of the participating institutions adopted the Epic EHR within the last several years of the survey being administered, and perceptions of note quality may be biased depending on the prior system used (ie, change from handwritten to electronic vs electronic to other electronic system). In addition, the survey results reflect experience with only 1 EHR, and our results may not apply to other EHR vendors or institutions like the VA, which have a long‐standing system in place. Last, we did not explore the impact of perceived note quality on the measured or perceived quality of care. One previous study found no direct correlation between note quality and clinical quality.[26]
There are several future directions for research based on our findings. First, potential differences between housestaff and attending perceptions of note quality could be further teased apart by studying the perceptions of attendings on a nonteaching service who write their own daily progress notes. Second, housestaff perceptions on why copy forward and autopopulation may increase critical thinking could be explored further with more direct questioning. Finally, although our study captured only perceptions of note quality, validated tools could be used to objectively measure note quality; these measurements could then be compared to perception of note quality as well as clinical outcomes.
Given the prevalence and the apparent belief that the benefits of an EHR outweigh the hazards, institutions should embrace these innovations but take steps to mitigate the potential errors and problems associated with copy forward and autopopulation. The results of our study should help inform future interventions.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the contributions of Russell Leslie from the University of Iowa.
Disclosure: Nothing to report.
- , , , et al. Systematic review: impact of health information technology on quality, efficiency, and costs of medical care. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(10):742–752.
- , , , , . Clinical information technologies and inpatient outcomes: a multiple hospital study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(2):108–114.
- , , , et al. Effect of computerized physician order entry and a team intervention on prevention of serious medication errors. JAMA. 1998;280(15):1311–1316.
- , , , . Electronic health records and quality of diabetes care. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(9):825–833.
- , , , et al. The impact of a clinical information system in an intensive care unit. J Clin Monit Comput. 2008;22(1):31–36.
- , . Can electronic clinical documentation help prevent diagnostic errors? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1066–1069.
- , . Off the record—avoiding the pitfalls of going electronic. N Eng J Med. 2008;358(16):1656–1658.
- , , . Copying and pasting of examinations within the electronic medical record. Int J Med Inform. 2007;76(suppl 1):S122–S128.
- , . Copy and paste: a remediable hazard of electronic health records. Am J Med. 2009;122(6):495–496.
- , , . The role of copy‐and‐paste in the hospital electronic health record. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(8):1217–1218.
- , , , , , . Physicians’ attitudes towards copy and pasting in electronic note writing. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(1):63–68.
- , , , , . Medical education in the electronic medical record (EMR) era: benefits, challenges, and future directions. Acad Med. 2013;88(6):748–752.
- , . Educational impact of the electronic medical record. J Surg Educ. 2012;69(1):105–112.
- , , , , , . Direct text entry in electronic progress notes. An evaluation of input errors. Methods Inf Med. 2003;42(1):61–67.
- . The clinical record: a 200‐year‐old 21st‐century challenge. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(10):682–683.
- . Sloppy and paste. Morbidity and Mortality Rounds on the Web. Available at: http://www.webmm.ahrq.gov/case.aspx?caseID=274. Published July 2012. Accessed September 26, 2014.
- , , , . Are electronic medical records trustworthy? Observations on copying, pasting and duplication. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2003:269–273.
- . A piece of my mind. John Lennon's elbow. JAMA. 2012;308(5):463–464.
- , , , , , . Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata‐driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377–381.
- , , . ACGME competency note checklist. Available at: http://www.im.org/p/cm/ld/fid=831. Accessed August 8, 2013.
- , , , . Assessing electronic note quality using the Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI‐9). Appl Clin Inform. 2012;3(2):164–174.
- , , , . Quantifying clinical narrative redundancy in an electronic health record. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(1):49–53.
- , . The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. In: Psychology of Intergroup Relations. 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: Nelson‐Hall Publishers; 1986:7–24.
- , . Student self‐assessment in higher education: a meta‐analysis. Rev Educ Res. 1989;59:395–430.
- . A review of the validity and accuracy of self‐assessments in health professions training. Acad Med. 1991;66:762–769.
- , , , , . Association of note quality and quality of care: a cross‐sectional study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(5):406–413.
- , , , et al. Systematic review: impact of health information technology on quality, efficiency, and costs of medical care. Ann Intern Med. 2006;144(10):742–752.
- , , , , . Clinical information technologies and inpatient outcomes: a multiple hospital study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(2):108–114.
- , , , et al. Effect of computerized physician order entry and a team intervention on prevention of serious medication errors. JAMA. 1998;280(15):1311–1316.
- , , , . Electronic health records and quality of diabetes care. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(9):825–833.
- , , , et al. The impact of a clinical information system in an intensive care unit. J Clin Monit Comput. 2008;22(1):31–36.
- , . Can electronic clinical documentation help prevent diagnostic errors? N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12):1066–1069.
- , . Off the record—avoiding the pitfalls of going electronic. N Eng J Med. 2008;358(16):1656–1658.
- , , . Copying and pasting of examinations within the electronic medical record. Int J Med Inform. 2007;76(suppl 1):S122–S128.
- , . Copy and paste: a remediable hazard of electronic health records. Am J Med. 2009;122(6):495–496.
- , , . The role of copy‐and‐paste in the hospital electronic health record. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174(8):1217–1218.
- , , , , , . Physicians’ attitudes towards copy and pasting in electronic note writing. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(1):63–68.
- , , , , . Medical education in the electronic medical record (EMR) era: benefits, challenges, and future directions. Acad Med. 2013;88(6):748–752.
- , . Educational impact of the electronic medical record. J Surg Educ. 2012;69(1):105–112.
- , , , , , . Direct text entry in electronic progress notes. An evaluation of input errors. Methods Inf Med. 2003;42(1):61–67.
- . The clinical record: a 200‐year‐old 21st‐century challenge. Ann Intern Med. 2010;153(10):682–683.
- . Sloppy and paste. Morbidity and Mortality Rounds on the Web. Available at: http://www.webmm.ahrq.gov/case.aspx?caseID=274. Published July 2012. Accessed September 26, 2014.
- , , , . Are electronic medical records trustworthy? Observations on copying, pasting and duplication. AMIA Annu Symp Proc. 2003:269–273.
- . A piece of my mind. John Lennon's elbow. JAMA. 2012;308(5):463–464.
- , , , , , . Research electronic data capture (REDCap)—a metadata‐driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377–381.
- , , . ACGME competency note checklist. Available at: http://www.im.org/p/cm/ld/fid=831. Accessed August 8, 2013.
- , , , . Assessing electronic note quality using the Physician Documentation Quality Instrument (PDQI‐9). Appl Clin Inform. 2012;3(2):164–174.
- , , , . Quantifying clinical narrative redundancy in an electronic health record. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(1):49–53.
- , . The social identity theory of intergroup behavior. In: Psychology of Intergroup Relations. 2nd ed. Chicago, IL: Nelson‐Hall Publishers; 1986:7–24.
- , . Student self‐assessment in higher education: a meta‐analysis. Rev Educ Res. 1989;59:395–430.
- . A review of the validity and accuracy of self‐assessments in health professions training. Acad Med. 1991;66:762–769.
- , , , , . Association of note quality and quality of care: a cross‐sectional study. BMJ Qual Saf. 2014;23(5):406–413.
© 2015 Society of Hospital Medicine