User login
Reactive Angioendotheliomatosis Following Ad26.COV2.S Vaccination
To the Editor:
Reactive angioendotheliomatosis (RAE) is a rare self-limited cutaneous vascular proliferation of endothelial cells within blood vessels that manifests clinically as infiltrated red-blue patches and plaques with purpura that can progress to occlude vascular lumina. The etiology of RAE is mostly idiopathic; however, the disorder typically occurs in association with a range of systemic diseases, including infection, cryoglobulinemia, leukemia, antiphospholipid syndrome, peripheral vascular disease, and arteriovenous fistula. Histopathologic examination of these lesions shows marked proliferation of endothelial cells, including occlusion of the lumen of blood vessels over wide areas.
After ruling out malignancy, treatment of RAE focuses on targeting the underlying cause or disease, if any is present; 75% of reported cases occur in association with systemic disease.1 Onset can occur at any age without predilection for sex. Reactive angioendotheliomatosis commonly manifests on the extremities but may occur on the head and neck in rare instances.2
The rarity of the condition and its poorly defined clinical characteristics make it difficult to develop a treatment plan. There are no standardized treatment guidelines for the reactive form of angiomatosis. We report a case of RAE that developed 2 weeks after vaccination with the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine (Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine [formerly Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson]) that improved following 2 weeks of treatment with a topical corticosteroid and an oral antihistamine.
A 58-year-old man presented to an outpatient dermatology clinic with pruritus and occasional paresthesia associated with a rash over the left arm of 1 month’s duration. The patient suspected that the rash may have formed secondary to the bite of oak mites on the arms and chest while he was carrying milled wood. Further inquiry into the patient’s history revealed that he received the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine 2 weeks prior to the appearance of the rash. He denied mechanical trauma. His medical history included hypercholesterolemia and a mild COVID-19 infection 8 months prior to the appearance of the rash that did not require hospitalization. He denied fever or chills during the 2 weeks following vaccination. The pruritus was minimally relieved for short periods with over-the-counter calamine lotion. The patient’s medication regimen included daily pravastatin and loratadine at the time of the initial visit. He used acetaminophen as needed for knee pain.
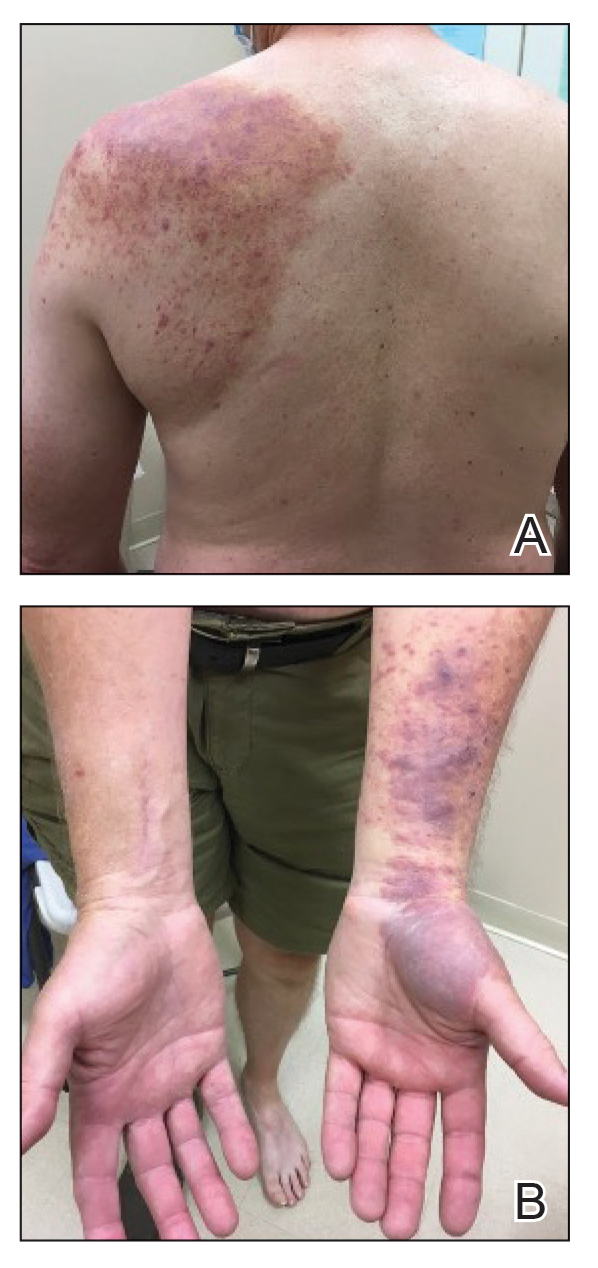
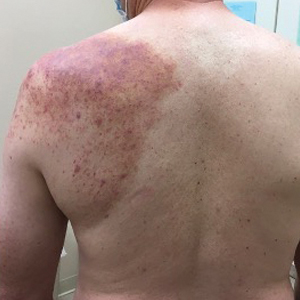
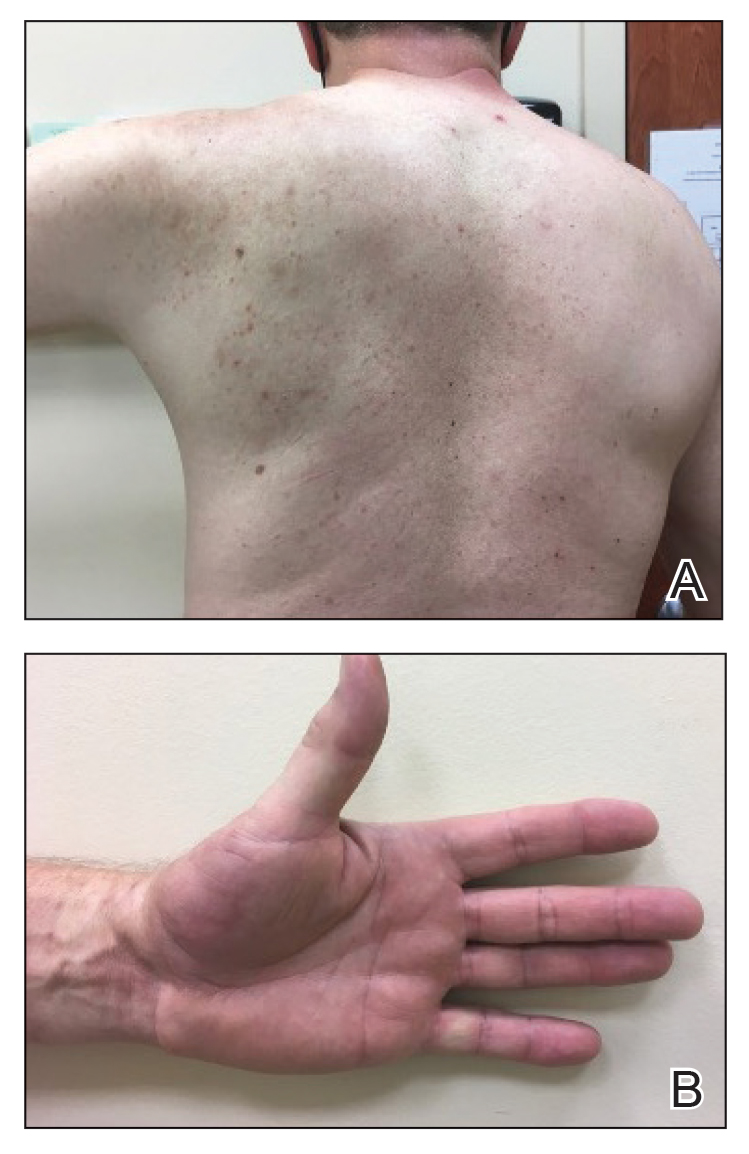
Physical examination revealed palpable purpura in a dermatomal distribution with nonpitting edema over the left scapula (Figure 1A), left anterolateral shoulder, left lateral volar forearm, and thenar eminence of the left hand (Figure 1B). Notably, the entire right arm, conjunctivae, tongue, lips, and bilateral fingernails were clear. Three 4-mm punch biopsies were performed at the initial presentation: 1 perilesional biopsy for direct immunofluorescence testing and 2 lesional biopsies for routine histologic evaluation. An extensive serologic workup failed to reveal abnormalities. An activated partial thromboplastin time, dilute Russell viper venom time, serum protein electrophoresis, and levels of rheumatoid factor and angiotensin-converting enzyme were within reference range. Anticardiolipin antibodies IgA, IgM, and IgG were negative. A cryoglobulin test was negative.
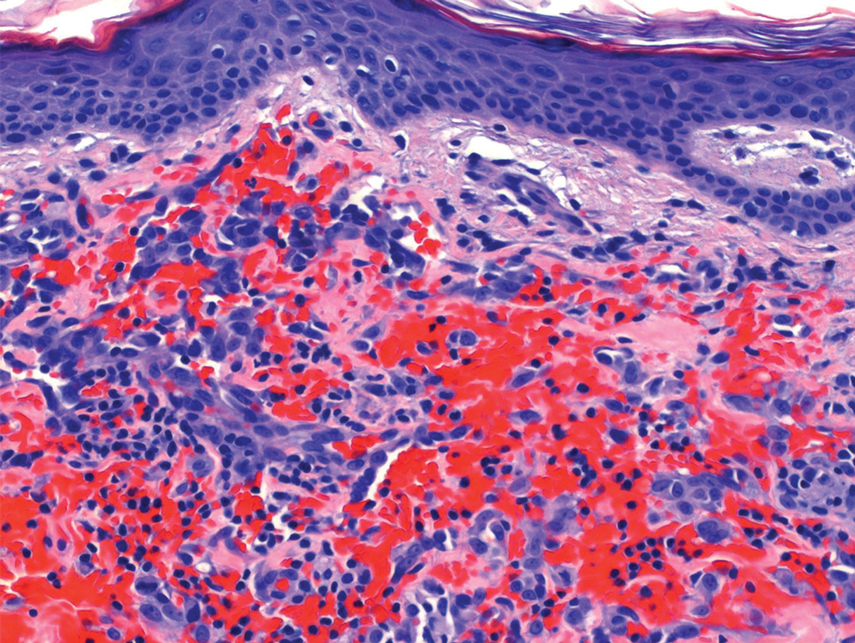
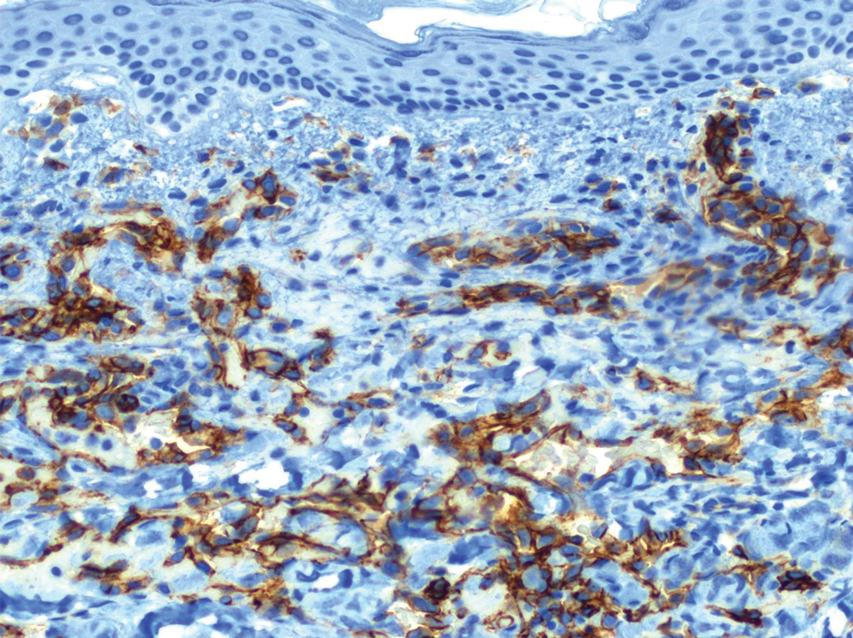
Histopathology revealed a proliferation of irregularly shaped vascular spaces with plump endothelium in the papillary dermis (Figure 2). Scattered leukocyte common antigen-positive lymphocytes were noted within lesions. The epidermis appeared normal, without evidence of spongiosis or alteration of the stratum corneum. Immunohistochemical studies of the perilesional skin biopsy revealed positivity for CD31 and D2-40 (Figure 3). Specimens were negative for CD20 and human herpesvirus 8. Direct immunofluorescence of the perilesional biopsy was negative.
A diagnosis of RAE was made based on clinical and histologic findings. Treatment with triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily and oral cetirizine 10 mg twice daily was initiated. Re-evaluation 2 weeks later revealed notable improvement in the affected areas, including decreased edema, improvement of the purpura, and absence of pruritus. The patient noted no further spread or blister formation while the active areas were being treated with the topical steroid. The treatment regimen was modified to triamcinolone ointment 0.1% once daily, and cetirizine was discontinued. At 3-month follow-up, active areas had completely resolved (Figure 4) and triamcinolone was discontinued. To date, the patient has not had recurrence of symptoms and remains healthy.
Gottron and Nikolowski3 reported the first case of RAE in an adult patient who presented with purpuric patches secondary to skin infarction. Current definitions use the umbrella term cutaneous reactive angiomatosis to cover 3 major subtypes: reactive angioendotheliomatosis, diffuse dermal angioendotheliomatosis, and acroangiodermatitis (pseudo-Kaposi sarcoma [KS]). The manifestation of these subgroups is clinically similar, and they must be differentiated through histologic evaluation.4
Reactive angioendotheliomatosis has an unknown pathogenesis and is poorly defined clinically. The exact pathophysiology is unknown but likely is linked to vaso-occlusion and hypoxia.1 A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE, as well as a review of Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library, using the terms reactive angioendotheliomatosis, COVID, vaccine, Ad26.COV2.S, and RAE in any combination revealed no prior cases of RAE in association with Ad26.COV2.S vaccination.
By the late 1980s, systemic angioendotheliomatosis was segregated into 2 distinct entities: malignant and reactive.4 The differential diagnosis of malignant systemic angioendotheliomatosis includes KS and angiosarcoma; nonmalignant causes are the variants of cutaneous reactive angiomatosis. It is important to rule out KS because of its malignant and deceptive nature. It is unknown if KS originates in blood vessels or lymphatic endothelial cells; however, evidence is strongly in favor of blood vessel origin using CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers.5 CD34 positivity is more reliable than CD31 in diagnosing KS, but the absence of both markers does not offer enough evidence to rule out KS on its own.6
In our patient, histopathology revealed cells positive for CD31 and D2-40; the latter is a lymphatic endothelial cell marker that stains the endothelium of lymphatic channels but not blood vessels.7 Positive D2-40 can be indicative of KS and non-KS lesions, each with a distinct staining pattern. D2-40 staining on non-KS lesions is confined to lymphatic vessels, as it was in our patient; in contrast, spindle-shaped cells also will be stained in KS lesions.8
Another cell marker, CD20, is a B cell–specific protein that can be measured to help diagnose malignant diseases such as B-cell lymphoma and leukemia. Human herpesvirus 8 (also known as KS-associated herpesvirus) is the infectious cause of KS and traditionally has been detected using methods such as the polymerase chain reaction.9,10
Most cases of RAE are idiopathic and occur in association with systemic disease, which was not the case in our patient. We speculated that his reaction was most likely triggered by vascular transfection of endothelial cells secondary to Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. Alternatively, vaccination may have caused vascular occlusion, though the lack of cyanosis, nail changes, and route of inoculant make this less likely.
All approved COVID-19 vaccines are designed solely for intramuscular injection. In comparison to other types of tissue, muscles have superior vascularity, allowing for enhanced mobilization of compounds, which results in faster systemic circulation.11 Alternative methods of injection, including intravascular, subcutaneous, and intradermal, may lead to decreased efficacy or adverse events, or both.
Prior cases of RAE have been treated with laser therapy, topical or systemic corticosteroids, excisional removal, or topical β-blockers, such as timolol.12 β-Blocking agents act on β-adrenergic receptors on endothelial cells to inhibit angiogenesis by reducing release of blood vessel growth-signaling molecules and triggering apoptosis. In this patient, topical steroids and oral antihistamines were sufficient treatment.
Vaccine-related adverse events have been reported but remain rare. The benefits of Ad26.COV2.S vaccination for protection against COVID-19 outweigh the extremely low risk for adverse events.13 For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a booster for individuals who are eligible to maximize protection. Intramuscular injection of Ad26.COV2.S resulted in a lower incidence of moderate to severe COVID-19 cases in all age groups vs the placebo group. Hypersensitivity adverse events were reported in 0.4% of Ad26.COV2.S-vaccinated patients vs 0.4% of patients who received a placebo; the more common reactions were nonanaphylactic.13
There have been 12 reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, which sparked nationwide controversy over the safety of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.14 After further investigation into those reports, the US Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concluded that the benefits of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine outweigh the low risk for associated thrombosis.15
Although adverse reactions are rare, it is important that health care providers take proper safety measures before and while administering any COVID-19 vaccine. Patients should be screened for contraindications to the COVID-19 vaccine to mitigate adverse effects seen in the small percentage of patients who may need to take alternative precautions.
The broad tissue tropism and high transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 are the main contributors to its infection having reached pandemic scale. The spike (S) protein on SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, the most thoroughly studied SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which is found in a range of tissues, including arterial endothelial cells, leading to its transfection. Several studies have proposed that expression of the S protein causes endothelial dysfunction through cytokine release, activation of complement, and ultimately microvascular occlusion.16
Recent developments in the use of viral-like particles, such as vesicular stomatitis virus, may mitigate future cases of RAE that are associated with endothelial cell transfection. Vesicular stomatitis virus is a popular model virus for research applications due to its glycoprotein and matrix protein contributing to its broad tropism. Recent efforts to alter these proteins have successfully limited the broad tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus.17
The SARS-CoV-2 virus must be handled in a Biosafety Level 3 laboratory. Conversely, pseudoviruses can be handled in lower containment facilities due to their safe and efficacious nature, offering an avenue to expedite vaccine development against many viral outbreaks, including SARS-CoV-2.18
An increasing number of cutaneous manifestations have been associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis, a rare self-limiting exanthem, has been reported in association with COVID-19 vaccination.19 Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis manifests as erythematous blanchable papules that resemble angiomas, typically in a widespread distribution. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis has striking similarities to RAE histologically; both manifest as dilated dermal blood vessels with plump endothelial cells.
Our case is unique because of the vasculitic palpable nature of the lesions, which were localized to the left arm. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis formation after COVID-19 infection or SARS-CoV-2 vaccination may suggest alteration of ACE2 by binding of S protein.20 Such alteration of the ACE2 pathway would lead to inflammation of angiotensin II, causing proliferation of endothelial cells in the formation of angiomalike lesions. This hypothesis suggests a paraviral eruption secondary to an immunologic reaction, not a classical virtual eruption from direct contact of the virus on blood vessels. Although EPA and RAE are harmless and self-limiting, these reports will spread awareness of the increasing number of skin manifestations related to COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccination.
Acknowledgment—Thoughtful insights and comments on this manuscript were provided by Christine J. Ko, MD (New Haven, Connecticut); Christine L. Egan, MD (Glen Mills, Pennsylvania); Howard A. Bueller, MD (Delray Beach, Florida); and Juan Pablo Robles, PhD (Juriquilla, Mexico).
- McMenamin ME, Fletcher CDM. Reactive angioendotheliomatosis: a study of 15 cases demonstrating a wide clinicopathologic spectrum. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:686-697. doi:10.1097/00000478-200206000-00001
- Khan S, Pujani M, Jetley S, et al. Angiomatosis: a rare vascular proliferation of head and neck region. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2015;8:108-110. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.158448
- Gottron HA, Nikolowski W. Extrarenal Lohlein focal nephritis of the skin in endocarditis. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1958;207:156-176.
- Cooper PH. Angioendotheliomatosis: two separate diseases. J Cutan Pathol. 1988;15:259. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1988.tb00556.x
- Cancian L, Hansen A, Boshoff C. Cellular origin of Kaposi’s sarcoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced cell reprogramming. Trends Cell Biol. Sep 2013;23:421-32. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.001
- Russell Jones R, Orchard G, Zelger B, et al. Immunostaining for CD31 and CD34 in Kaposi sarcoma. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:1011-1016. doi:10.1136/jcp.48.11.1011
- Kahn HJ, Bailey D, Marks A. Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi’s sarcoma and a subset of angiosarcomas. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:434-440. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880543
- Genedy RM, Hamza AM, Abdel Latef AA, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of D2-40 in differentiating Kaposi sarcoma from its mimickers. J Egyptian Womens Dermatolog Soc. 2021;18:67-74. doi:10.4103/jewd.jewd_61_20
- Mesri EA, Cesarman E, Boshoff C. Kaposi’s sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:707-719. doi:10.1038/nrc2888
- Patel RM, Goldblum JR, Hsi ED. Immunohistochemical detection of human herpes virus-8 latent nuclear antigen-1 is useful in the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:456-460. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800061
- Zuckerman JN. The importance of injecting vaccines into muscle. Different patients need different needle sizes. BMJ. 2000;321:1237-1238. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7271.1237
- Bhatia R, Hazarika N, Chandrasekaran D, et al. Treatment of posttraumatic reactive angioendotheliomatosis with topical timolol maleate. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1002-1004. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1770
- Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, et al; ENSEMBLE Study Group. Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:2187-2201. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2101544
- See I, Su JR, Lale A, et al. US case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, March 2 to April 21, 2021. JAMA. 2021;325:2448-2456. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7517
- Berry CT, Eliliwi M, Gallagher S, et al. Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis following single-dose Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;15:11-14. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.07.002
- Flaumenhaft R, Enjyoji K, Schmaier AA. Vasculopathy in COVID-19. Blood. 2022;140:222-235. doi:10.1182/blood.2021012250
- Hastie E, Cataldi M, Marriott I, et al. Understanding and altering cell tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virus Res. 2013;176:16-32. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2013.06.003
- Xiong H-L, Wu Y-T, Cao J-L, et al. Robust neutralization assay based on SARS-CoV-2 S-protein-bearing vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) pseudovirus and ACE2-overexpressing BHK21 cells. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:2105-2113. doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1815589
- Mohta A, Jain SK, Mehta RD, et al. Development of eruptive pseudoangiomatosis following COVID-19 immunization – apropos of 5 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:e722-e725. doi:10.1111/jdv.17499
- Angeli F, Spanevello A, Reboldi G, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: lights and shadows. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;88:1-8. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.04.019
To the Editor:
Reactive angioendotheliomatosis (RAE) is a rare self-limited cutaneous vascular proliferation of endothelial cells within blood vessels that manifests clinically as infiltrated red-blue patches and plaques with purpura that can progress to occlude vascular lumina. The etiology of RAE is mostly idiopathic; however, the disorder typically occurs in association with a range of systemic diseases, including infection, cryoglobulinemia, leukemia, antiphospholipid syndrome, peripheral vascular disease, and arteriovenous fistula. Histopathologic examination of these lesions shows marked proliferation of endothelial cells, including occlusion of the lumen of blood vessels over wide areas.
After ruling out malignancy, treatment of RAE focuses on targeting the underlying cause or disease, if any is present; 75% of reported cases occur in association with systemic disease.1 Onset can occur at any age without predilection for sex. Reactive angioendotheliomatosis commonly manifests on the extremities but may occur on the head and neck in rare instances.2
The rarity of the condition and its poorly defined clinical characteristics make it difficult to develop a treatment plan. There are no standardized treatment guidelines for the reactive form of angiomatosis. We report a case of RAE that developed 2 weeks after vaccination with the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine (Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine [formerly Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson]) that improved following 2 weeks of treatment with a topical corticosteroid and an oral antihistamine.
A 58-year-old man presented to an outpatient dermatology clinic with pruritus and occasional paresthesia associated with a rash over the left arm of 1 month’s duration. The patient suspected that the rash may have formed secondary to the bite of oak mites on the arms and chest while he was carrying milled wood. Further inquiry into the patient’s history revealed that he received the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine 2 weeks prior to the appearance of the rash. He denied mechanical trauma. His medical history included hypercholesterolemia and a mild COVID-19 infection 8 months prior to the appearance of the rash that did not require hospitalization. He denied fever or chills during the 2 weeks following vaccination. The pruritus was minimally relieved for short periods with over-the-counter calamine lotion. The patient’s medication regimen included daily pravastatin and loratadine at the time of the initial visit. He used acetaminophen as needed for knee pain.

Physical examination revealed palpable purpura in a dermatomal distribution with nonpitting edema over the left scapula (Figure 1A), left anterolateral shoulder, left lateral volar forearm, and thenar eminence of the left hand (Figure 1B). Notably, the entire right arm, conjunctivae, tongue, lips, and bilateral fingernails were clear. Three 4-mm punch biopsies were performed at the initial presentation: 1 perilesional biopsy for direct immunofluorescence testing and 2 lesional biopsies for routine histologic evaluation. An extensive serologic workup failed to reveal abnormalities. An activated partial thromboplastin time, dilute Russell viper venom time, serum protein electrophoresis, and levels of rheumatoid factor and angiotensin-converting enzyme were within reference range. Anticardiolipin antibodies IgA, IgM, and IgG were negative. A cryoglobulin test was negative.

Histopathology revealed a proliferation of irregularly shaped vascular spaces with plump endothelium in the papillary dermis (Figure 2). Scattered leukocyte common antigen-positive lymphocytes were noted within lesions. The epidermis appeared normal, without evidence of spongiosis or alteration of the stratum corneum. Immunohistochemical studies of the perilesional skin biopsy revealed positivity for CD31 and D2-40 (Figure 3). Specimens were negative for CD20 and human herpesvirus 8. Direct immunofluorescence of the perilesional biopsy was negative.

A diagnosis of RAE was made based on clinical and histologic findings. Treatment with triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily and oral cetirizine 10 mg twice daily was initiated. Re-evaluation 2 weeks later revealed notable improvement in the affected areas, including decreased edema, improvement of the purpura, and absence of pruritus. The patient noted no further spread or blister formation while the active areas were being treated with the topical steroid. The treatment regimen was modified to triamcinolone ointment 0.1% once daily, and cetirizine was discontinued. At 3-month follow-up, active areas had completely resolved (Figure 4) and triamcinolone was discontinued. To date, the patient has not had recurrence of symptoms and remains healthy.

Gottron and Nikolowski3 reported the first case of RAE in an adult patient who presented with purpuric patches secondary to skin infarction. Current definitions use the umbrella term cutaneous reactive angiomatosis to cover 3 major subtypes: reactive angioendotheliomatosis, diffuse dermal angioendotheliomatosis, and acroangiodermatitis (pseudo-Kaposi sarcoma [KS]). The manifestation of these subgroups is clinically similar, and they must be differentiated through histologic evaluation.4
Reactive angioendotheliomatosis has an unknown pathogenesis and is poorly defined clinically. The exact pathophysiology is unknown but likely is linked to vaso-occlusion and hypoxia.1 A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE, as well as a review of Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library, using the terms reactive angioendotheliomatosis, COVID, vaccine, Ad26.COV2.S, and RAE in any combination revealed no prior cases of RAE in association with Ad26.COV2.S vaccination.
By the late 1980s, systemic angioendotheliomatosis was segregated into 2 distinct entities: malignant and reactive.4 The differential diagnosis of malignant systemic angioendotheliomatosis includes KS and angiosarcoma; nonmalignant causes are the variants of cutaneous reactive angiomatosis. It is important to rule out KS because of its malignant and deceptive nature. It is unknown if KS originates in blood vessels or lymphatic endothelial cells; however, evidence is strongly in favor of blood vessel origin using CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers.5 CD34 positivity is more reliable than CD31 in diagnosing KS, but the absence of both markers does not offer enough evidence to rule out KS on its own.6
In our patient, histopathology revealed cells positive for CD31 and D2-40; the latter is a lymphatic endothelial cell marker that stains the endothelium of lymphatic channels but not blood vessels.7 Positive D2-40 can be indicative of KS and non-KS lesions, each with a distinct staining pattern. D2-40 staining on non-KS lesions is confined to lymphatic vessels, as it was in our patient; in contrast, spindle-shaped cells also will be stained in KS lesions.8
Another cell marker, CD20, is a B cell–specific protein that can be measured to help diagnose malignant diseases such as B-cell lymphoma and leukemia. Human herpesvirus 8 (also known as KS-associated herpesvirus) is the infectious cause of KS and traditionally has been detected using methods such as the polymerase chain reaction.9,10
Most cases of RAE are idiopathic and occur in association with systemic disease, which was not the case in our patient. We speculated that his reaction was most likely triggered by vascular transfection of endothelial cells secondary to Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. Alternatively, vaccination may have caused vascular occlusion, though the lack of cyanosis, nail changes, and route of inoculant make this less likely.
All approved COVID-19 vaccines are designed solely for intramuscular injection. In comparison to other types of tissue, muscles have superior vascularity, allowing for enhanced mobilization of compounds, which results in faster systemic circulation.11 Alternative methods of injection, including intravascular, subcutaneous, and intradermal, may lead to decreased efficacy or adverse events, or both.
Prior cases of RAE have been treated with laser therapy, topical or systemic corticosteroids, excisional removal, or topical β-blockers, such as timolol.12 β-Blocking agents act on β-adrenergic receptors on endothelial cells to inhibit angiogenesis by reducing release of blood vessel growth-signaling molecules and triggering apoptosis. In this patient, topical steroids and oral antihistamines were sufficient treatment.
Vaccine-related adverse events have been reported but remain rare. The benefits of Ad26.COV2.S vaccination for protection against COVID-19 outweigh the extremely low risk for adverse events.13 For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a booster for individuals who are eligible to maximize protection. Intramuscular injection of Ad26.COV2.S resulted in a lower incidence of moderate to severe COVID-19 cases in all age groups vs the placebo group. Hypersensitivity adverse events were reported in 0.4% of Ad26.COV2.S-vaccinated patients vs 0.4% of patients who received a placebo; the more common reactions were nonanaphylactic.13
There have been 12 reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, which sparked nationwide controversy over the safety of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.14 After further investigation into those reports, the US Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concluded that the benefits of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine outweigh the low risk for associated thrombosis.15
Although adverse reactions are rare, it is important that health care providers take proper safety measures before and while administering any COVID-19 vaccine. Patients should be screened for contraindications to the COVID-19 vaccine to mitigate adverse effects seen in the small percentage of patients who may need to take alternative precautions.
The broad tissue tropism and high transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 are the main contributors to its infection having reached pandemic scale. The spike (S) protein on SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, the most thoroughly studied SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which is found in a range of tissues, including arterial endothelial cells, leading to its transfection. Several studies have proposed that expression of the S protein causes endothelial dysfunction through cytokine release, activation of complement, and ultimately microvascular occlusion.16
Recent developments in the use of viral-like particles, such as vesicular stomatitis virus, may mitigate future cases of RAE that are associated with endothelial cell transfection. Vesicular stomatitis virus is a popular model virus for research applications due to its glycoprotein and matrix protein contributing to its broad tropism. Recent efforts to alter these proteins have successfully limited the broad tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus.17
The SARS-CoV-2 virus must be handled in a Biosafety Level 3 laboratory. Conversely, pseudoviruses can be handled in lower containment facilities due to their safe and efficacious nature, offering an avenue to expedite vaccine development against many viral outbreaks, including SARS-CoV-2.18
An increasing number of cutaneous manifestations have been associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis, a rare self-limiting exanthem, has been reported in association with COVID-19 vaccination.19 Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis manifests as erythematous blanchable papules that resemble angiomas, typically in a widespread distribution. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis has striking similarities to RAE histologically; both manifest as dilated dermal blood vessels with plump endothelial cells.
Our case is unique because of the vasculitic palpable nature of the lesions, which were localized to the left arm. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis formation after COVID-19 infection or SARS-CoV-2 vaccination may suggest alteration of ACE2 by binding of S protein.20 Such alteration of the ACE2 pathway would lead to inflammation of angiotensin II, causing proliferation of endothelial cells in the formation of angiomalike lesions. This hypothesis suggests a paraviral eruption secondary to an immunologic reaction, not a classical virtual eruption from direct contact of the virus on blood vessels. Although EPA and RAE are harmless and self-limiting, these reports will spread awareness of the increasing number of skin manifestations related to COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccination.
Acknowledgment—Thoughtful insights and comments on this manuscript were provided by Christine J. Ko, MD (New Haven, Connecticut); Christine L. Egan, MD (Glen Mills, Pennsylvania); Howard A. Bueller, MD (Delray Beach, Florida); and Juan Pablo Robles, PhD (Juriquilla, Mexico).
To the Editor:
Reactive angioendotheliomatosis (RAE) is a rare self-limited cutaneous vascular proliferation of endothelial cells within blood vessels that manifests clinically as infiltrated red-blue patches and plaques with purpura that can progress to occlude vascular lumina. The etiology of RAE is mostly idiopathic; however, the disorder typically occurs in association with a range of systemic diseases, including infection, cryoglobulinemia, leukemia, antiphospholipid syndrome, peripheral vascular disease, and arteriovenous fistula. Histopathologic examination of these lesions shows marked proliferation of endothelial cells, including occlusion of the lumen of blood vessels over wide areas.
After ruling out malignancy, treatment of RAE focuses on targeting the underlying cause or disease, if any is present; 75% of reported cases occur in association with systemic disease.1 Onset can occur at any age without predilection for sex. Reactive angioendotheliomatosis commonly manifests on the extremities but may occur on the head and neck in rare instances.2
The rarity of the condition and its poorly defined clinical characteristics make it difficult to develop a treatment plan. There are no standardized treatment guidelines for the reactive form of angiomatosis. We report a case of RAE that developed 2 weeks after vaccination with the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine (Johnson & Johnson Innovative Medicine [formerly Janssen Pharmaceutical Companies of Johnson & Johnson]) that improved following 2 weeks of treatment with a topical corticosteroid and an oral antihistamine.
A 58-year-old man presented to an outpatient dermatology clinic with pruritus and occasional paresthesia associated with a rash over the left arm of 1 month’s duration. The patient suspected that the rash may have formed secondary to the bite of oak mites on the arms and chest while he was carrying milled wood. Further inquiry into the patient’s history revealed that he received the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine 2 weeks prior to the appearance of the rash. He denied mechanical trauma. His medical history included hypercholesterolemia and a mild COVID-19 infection 8 months prior to the appearance of the rash that did not require hospitalization. He denied fever or chills during the 2 weeks following vaccination. The pruritus was minimally relieved for short periods with over-the-counter calamine lotion. The patient’s medication regimen included daily pravastatin and loratadine at the time of the initial visit. He used acetaminophen as needed for knee pain.

Physical examination revealed palpable purpura in a dermatomal distribution with nonpitting edema over the left scapula (Figure 1A), left anterolateral shoulder, left lateral volar forearm, and thenar eminence of the left hand (Figure 1B). Notably, the entire right arm, conjunctivae, tongue, lips, and bilateral fingernails were clear. Three 4-mm punch biopsies were performed at the initial presentation: 1 perilesional biopsy for direct immunofluorescence testing and 2 lesional biopsies for routine histologic evaluation. An extensive serologic workup failed to reveal abnormalities. An activated partial thromboplastin time, dilute Russell viper venom time, serum protein electrophoresis, and levels of rheumatoid factor and angiotensin-converting enzyme were within reference range. Anticardiolipin antibodies IgA, IgM, and IgG were negative. A cryoglobulin test was negative.

Histopathology revealed a proliferation of irregularly shaped vascular spaces with plump endothelium in the papillary dermis (Figure 2). Scattered leukocyte common antigen-positive lymphocytes were noted within lesions. The epidermis appeared normal, without evidence of spongiosis or alteration of the stratum corneum. Immunohistochemical studies of the perilesional skin biopsy revealed positivity for CD31 and D2-40 (Figure 3). Specimens were negative for CD20 and human herpesvirus 8. Direct immunofluorescence of the perilesional biopsy was negative.

A diagnosis of RAE was made based on clinical and histologic findings. Treatment with triamcinolone ointment 0.1% twice daily and oral cetirizine 10 mg twice daily was initiated. Re-evaluation 2 weeks later revealed notable improvement in the affected areas, including decreased edema, improvement of the purpura, and absence of pruritus. The patient noted no further spread or blister formation while the active areas were being treated with the topical steroid. The treatment regimen was modified to triamcinolone ointment 0.1% once daily, and cetirizine was discontinued. At 3-month follow-up, active areas had completely resolved (Figure 4) and triamcinolone was discontinued. To date, the patient has not had recurrence of symptoms and remains healthy.

Gottron and Nikolowski3 reported the first case of RAE in an adult patient who presented with purpuric patches secondary to skin infarction. Current definitions use the umbrella term cutaneous reactive angiomatosis to cover 3 major subtypes: reactive angioendotheliomatosis, diffuse dermal angioendotheliomatosis, and acroangiodermatitis (pseudo-Kaposi sarcoma [KS]). The manifestation of these subgroups is clinically similar, and they must be differentiated through histologic evaluation.4
Reactive angioendotheliomatosis has an unknown pathogenesis and is poorly defined clinically. The exact pathophysiology is unknown but likely is linked to vaso-occlusion and hypoxia.1 A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE, as well as a review of Science Direct, Google Scholar, and Cochrane Library, using the terms reactive angioendotheliomatosis, COVID, vaccine, Ad26.COV2.S, and RAE in any combination revealed no prior cases of RAE in association with Ad26.COV2.S vaccination.
By the late 1980s, systemic angioendotheliomatosis was segregated into 2 distinct entities: malignant and reactive.4 The differential diagnosis of malignant systemic angioendotheliomatosis includes KS and angiosarcoma; nonmalignant causes are the variants of cutaneous reactive angiomatosis. It is important to rule out KS because of its malignant and deceptive nature. It is unknown if KS originates in blood vessels or lymphatic endothelial cells; however, evidence is strongly in favor of blood vessel origin using CD31 and CD34 endothelial markers.5 CD34 positivity is more reliable than CD31 in diagnosing KS, but the absence of both markers does not offer enough evidence to rule out KS on its own.6
In our patient, histopathology revealed cells positive for CD31 and D2-40; the latter is a lymphatic endothelial cell marker that stains the endothelium of lymphatic channels but not blood vessels.7 Positive D2-40 can be indicative of KS and non-KS lesions, each with a distinct staining pattern. D2-40 staining on non-KS lesions is confined to lymphatic vessels, as it was in our patient; in contrast, spindle-shaped cells also will be stained in KS lesions.8
Another cell marker, CD20, is a B cell–specific protein that can be measured to help diagnose malignant diseases such as B-cell lymphoma and leukemia. Human herpesvirus 8 (also known as KS-associated herpesvirus) is the infectious cause of KS and traditionally has been detected using methods such as the polymerase chain reaction.9,10
Most cases of RAE are idiopathic and occur in association with systemic disease, which was not the case in our patient. We speculated that his reaction was most likely triggered by vascular transfection of endothelial cells secondary to Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. Alternatively, vaccination may have caused vascular occlusion, though the lack of cyanosis, nail changes, and route of inoculant make this less likely.
All approved COVID-19 vaccines are designed solely for intramuscular injection. In comparison to other types of tissue, muscles have superior vascularity, allowing for enhanced mobilization of compounds, which results in faster systemic circulation.11 Alternative methods of injection, including intravascular, subcutaneous, and intradermal, may lead to decreased efficacy or adverse events, or both.
Prior cases of RAE have been treated with laser therapy, topical or systemic corticosteroids, excisional removal, or topical β-blockers, such as timolol.12 β-Blocking agents act on β-adrenergic receptors on endothelial cells to inhibit angiogenesis by reducing release of blood vessel growth-signaling molecules and triggering apoptosis. In this patient, topical steroids and oral antihistamines were sufficient treatment.
Vaccine-related adverse events have been reported but remain rare. The benefits of Ad26.COV2.S vaccination for protection against COVID-19 outweigh the extremely low risk for adverse events.13 For that reason, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a booster for individuals who are eligible to maximize protection. Intramuscular injection of Ad26.COV2.S resulted in a lower incidence of moderate to severe COVID-19 cases in all age groups vs the placebo group. Hypersensitivity adverse events were reported in 0.4% of Ad26.COV2.S-vaccinated patients vs 0.4% of patients who received a placebo; the more common reactions were nonanaphylactic.13
There have been 12 reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, which sparked nationwide controversy over the safety of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine.14 After further investigation into those reports, the US Food and Drug Administration and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention concluded that the benefits of the Ad26.COV2.S vaccine outweigh the low risk for associated thrombosis.15
Although adverse reactions are rare, it is important that health care providers take proper safety measures before and while administering any COVID-19 vaccine. Patients should be screened for contraindications to the COVID-19 vaccine to mitigate adverse effects seen in the small percentage of patients who may need to take alternative precautions.
The broad tissue tropism and high transmissibility of SARS-CoV-2 are the main contributors to its infection having reached pandemic scale. The spike (S) protein on SARS-CoV-2 binds to ACE2, the most thoroughly studied SARS-CoV-2 receptor, which is found in a range of tissues, including arterial endothelial cells, leading to its transfection. Several studies have proposed that expression of the S protein causes endothelial dysfunction through cytokine release, activation of complement, and ultimately microvascular occlusion.16
Recent developments in the use of viral-like particles, such as vesicular stomatitis virus, may mitigate future cases of RAE that are associated with endothelial cell transfection. Vesicular stomatitis virus is a popular model virus for research applications due to its glycoprotein and matrix protein contributing to its broad tropism. Recent efforts to alter these proteins have successfully limited the broad tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus.17
The SARS-CoV-2 virus must be handled in a Biosafety Level 3 laboratory. Conversely, pseudoviruses can be handled in lower containment facilities due to their safe and efficacious nature, offering an avenue to expedite vaccine development against many viral outbreaks, including SARS-CoV-2.18
An increasing number of cutaneous manifestations have been associated with COVID-19 infection and vaccination. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis, a rare self-limiting exanthem, has been reported in association with COVID-19 vaccination.19 Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis manifests as erythematous blanchable papules that resemble angiomas, typically in a widespread distribution. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis has striking similarities to RAE histologically; both manifest as dilated dermal blood vessels with plump endothelial cells.
Our case is unique because of the vasculitic palpable nature of the lesions, which were localized to the left arm. Eruptive pseudoangiomatosis formation after COVID-19 infection or SARS-CoV-2 vaccination may suggest alteration of ACE2 by binding of S protein.20 Such alteration of the ACE2 pathway would lead to inflammation of angiotensin II, causing proliferation of endothelial cells in the formation of angiomalike lesions. This hypothesis suggests a paraviral eruption secondary to an immunologic reaction, not a classical virtual eruption from direct contact of the virus on blood vessels. Although EPA and RAE are harmless and self-limiting, these reports will spread awareness of the increasing number of skin manifestations related to COVID-19 and SARS-CoV-2 virus vaccination.
Acknowledgment—Thoughtful insights and comments on this manuscript were provided by Christine J. Ko, MD (New Haven, Connecticut); Christine L. Egan, MD (Glen Mills, Pennsylvania); Howard A. Bueller, MD (Delray Beach, Florida); and Juan Pablo Robles, PhD (Juriquilla, Mexico).
- McMenamin ME, Fletcher CDM. Reactive angioendotheliomatosis: a study of 15 cases demonstrating a wide clinicopathologic spectrum. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:686-697. doi:10.1097/00000478-200206000-00001
- Khan S, Pujani M, Jetley S, et al. Angiomatosis: a rare vascular proliferation of head and neck region. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2015;8:108-110. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.158448
- Gottron HA, Nikolowski W. Extrarenal Lohlein focal nephritis of the skin in endocarditis. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1958;207:156-176.
- Cooper PH. Angioendotheliomatosis: two separate diseases. J Cutan Pathol. 1988;15:259. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1988.tb00556.x
- Cancian L, Hansen A, Boshoff C. Cellular origin of Kaposi’s sarcoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced cell reprogramming. Trends Cell Biol. Sep 2013;23:421-32. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.001
- Russell Jones R, Orchard G, Zelger B, et al. Immunostaining for CD31 and CD34 in Kaposi sarcoma. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:1011-1016. doi:10.1136/jcp.48.11.1011
- Kahn HJ, Bailey D, Marks A. Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi’s sarcoma and a subset of angiosarcomas. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:434-440. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880543
- Genedy RM, Hamza AM, Abdel Latef AA, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of D2-40 in differentiating Kaposi sarcoma from its mimickers. J Egyptian Womens Dermatolog Soc. 2021;18:67-74. doi:10.4103/jewd.jewd_61_20
- Mesri EA, Cesarman E, Boshoff C. Kaposi’s sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:707-719. doi:10.1038/nrc2888
- Patel RM, Goldblum JR, Hsi ED. Immunohistochemical detection of human herpes virus-8 latent nuclear antigen-1 is useful in the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:456-460. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800061
- Zuckerman JN. The importance of injecting vaccines into muscle. Different patients need different needle sizes. BMJ. 2000;321:1237-1238. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7271.1237
- Bhatia R, Hazarika N, Chandrasekaran D, et al. Treatment of posttraumatic reactive angioendotheliomatosis with topical timolol maleate. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1002-1004. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1770
- Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, et al; ENSEMBLE Study Group. Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:2187-2201. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2101544
- See I, Su JR, Lale A, et al. US case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, March 2 to April 21, 2021. JAMA. 2021;325:2448-2456. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7517
- Berry CT, Eliliwi M, Gallagher S, et al. Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis following single-dose Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;15:11-14. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.07.002
- Flaumenhaft R, Enjyoji K, Schmaier AA. Vasculopathy in COVID-19. Blood. 2022;140:222-235. doi:10.1182/blood.2021012250
- Hastie E, Cataldi M, Marriott I, et al. Understanding and altering cell tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virus Res. 2013;176:16-32. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2013.06.003
- Xiong H-L, Wu Y-T, Cao J-L, et al. Robust neutralization assay based on SARS-CoV-2 S-protein-bearing vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) pseudovirus and ACE2-overexpressing BHK21 cells. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:2105-2113. doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1815589
- Mohta A, Jain SK, Mehta RD, et al. Development of eruptive pseudoangiomatosis following COVID-19 immunization – apropos of 5 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:e722-e725. doi:10.1111/jdv.17499
- Angeli F, Spanevello A, Reboldi G, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: lights and shadows. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;88:1-8. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.04.019
- McMenamin ME, Fletcher CDM. Reactive angioendotheliomatosis: a study of 15 cases demonstrating a wide clinicopathologic spectrum. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:686-697. doi:10.1097/00000478-200206000-00001
- Khan S, Pujani M, Jetley S, et al. Angiomatosis: a rare vascular proliferation of head and neck region. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2015;8:108-110. doi:10.4103/0974-2077.158448
- Gottron HA, Nikolowski W. Extrarenal Lohlein focal nephritis of the skin in endocarditis. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1958;207:156-176.
- Cooper PH. Angioendotheliomatosis: two separate diseases. J Cutan Pathol. 1988;15:259. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1988.tb00556.x
- Cancian L, Hansen A, Boshoff C. Cellular origin of Kaposi’s sarcoma and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-induced cell reprogramming. Trends Cell Biol. Sep 2013;23:421-32. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2013.04.001
- Russell Jones R, Orchard G, Zelger B, et al. Immunostaining for CD31 and CD34 in Kaposi sarcoma. J Clin Pathol. 1995;48:1011-1016. doi:10.1136/jcp.48.11.1011
- Kahn HJ, Bailey D, Marks A. Monoclonal antibody D2-40, a new marker of lymphatic endothelium, reacts with Kaposi’s sarcoma and a subset of angiosarcomas. Mod Pathol. 2002;15:434-440. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3880543
- Genedy RM, Hamza AM, Abdel Latef AA, et al. Sensitivity and specificity of D2-40 in differentiating Kaposi sarcoma from its mimickers. J Egyptian Womens Dermatolog Soc. 2021;18:67-74. doi:10.4103/jewd.jewd_61_20
- Mesri EA, Cesarman E, Boshoff C. Kaposi’s sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:707-719. doi:10.1038/nrc2888
- Patel RM, Goldblum JR, Hsi ED. Immunohistochemical detection of human herpes virus-8 latent nuclear antigen-1 is useful in the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma. Mod Pathol. 2004;17:456-460. doi:10.1038/modpathol.3800061
- Zuckerman JN. The importance of injecting vaccines into muscle. Different patients need different needle sizes. BMJ. 2000;321:1237-1238. doi:10.1136/bmj.321.7271.1237
- Bhatia R, Hazarika N, Chandrasekaran D, et al. Treatment of posttraumatic reactive angioendotheliomatosis with topical timolol maleate. JAMA Dermatol. 2021;157:1002-1004. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2021.1770
- Sadoff J, Gray G, Vandebosch A, et al; ENSEMBLE Study Group. Safety and efficacy of single-dose Ad26.COV2.S vaccine against Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2021;384:2187-2201. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2101544
- See I, Su JR, Lale A, et al. US case reports of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis with thrombocytopenia after Ad26.COV2.S vaccination, March 2 to April 21, 2021. JAMA. 2021;325:2448-2456. doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7517
- Berry CT, Eliliwi M, Gallagher S, et al. Cutaneous small vessel vasculitis following single-dose Janssen Ad26.COV2.S vaccination. JAAD Case Rep. 2021;15:11-14. doi:10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.07.002
- Flaumenhaft R, Enjyoji K, Schmaier AA. Vasculopathy in COVID-19. Blood. 2022;140:222-235. doi:10.1182/blood.2021012250
- Hastie E, Cataldi M, Marriott I, et al. Understanding and altering cell tropism of vesicular stomatitis virus. Virus Res. 2013;176:16-32. doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2013.06.003
- Xiong H-L, Wu Y-T, Cao J-L, et al. Robust neutralization assay based on SARS-CoV-2 S-protein-bearing vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) pseudovirus and ACE2-overexpressing BHK21 cells. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9:2105-2113. doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1815589
- Mohta A, Jain SK, Mehta RD, et al. Development of eruptive pseudoangiomatosis following COVID-19 immunization – apropos of 5 cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2021;35:e722-e725. doi:10.1111/jdv.17499
- Angeli F, Spanevello A, Reboldi G, et al. SARS-CoV-2 vaccines: lights and shadows. Eur J Intern Med. 2021;88:1-8. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2021.04.019
Practice points
- Reactive angioendotheliomatosis (RAE) is a rare benign vascular proliferation of endothelial cells lining blood vessels that clinically appears similar to Kaposi sarcoma and must be differentiated by microscopic evaluation.
- An increasing number of reports link SARS-CoV-2 viral infection or vaccination against this virus with various cutaneous manifestations. Our case offers a link between RAE and Ad26.COV2.S vaccination.