User login
Revisiting our approach to behavioral health referrals
Approximately 1 in 4 people ages 18 years and older and 1 in 3 people ages 18 to 25 years had a mental illness in the past year, according to the 2021 National Survey of Drug Use and Health.1 The survey also found that adults ages 18 to 25 years had the highest rate of serious mental illness but the lowest treatment rate compared to other adult age groups.1 Unfortunately, more than 60% of patients receiving mental health treatment fail to benefit to a clinically meaningful degree.2
However, there is growing evidence that referring patients to behavioral health practitioners (BHPs) with outcome-measured skills that meet the patient’s specific needs can have a dramatic and positive impact. There are 2 main steps to pairing patients with an appropriate BHP: (1) use of measurement-based care data that can be analyzed at the patient and therapist level, and (2) data-driven referrals that pair patients with BHPs based on such routine outcome monitoring data (paired-on outcome data).
Psychotherapy’s slow road toward measurement-based care
Routine outcome monitoring is the systematic measurement of symptoms and functioning during treatment. It serves multiple functions, including program evaluation and benchmarking of patient improvement rates. Moreover, routine outcome monitoring–derived feedback (based on repeated patient outcome measurements) can inform personalized and responsive care decisions throughout treatment.
For all intents and purposes,
- routinely administered symptom/functioning measure, ideally before each clinical encounter,
- practitioner review of these patient-level data,
- patient review of these data with their practitioner, and
- collaborative reevaluation of the person-specific treatment plan informed by these data.
CASE SCENARIO
Violeta W is a 33-year-old woman who presented to her family physician for her annual wellness exam. Prior to the exam, the medical assistant administered a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) to screen for depressive symptoms. Ms. W’s score was 20 out of 27, suggestive of depression. To further assess the severity of depressive symptoms and their effect on daily function, the physician reviewed responses to the questionnaire with her and discussed treatment options. Ms. W was most interested in trying a low-dose selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).
At her follow-up visit 4 weeks later, the medical assistant re-administered the PHQ-9. The physician then reviewed Ms. W’s responses with her and, based on Ms. W’s subjective report and objective symptoms (still a score of 20 out of 27 on the PHQ-9), increased her SSRI dose. At each subsequent visit, Ms. W completed a PHQ-9 and reviewed responses and depressive symptoms with her physician.
The value of measurement-based care in mental health care
A narrative review by Lewis et al3 of 21 randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) across a range of age groups (eg, adolescents, young adults, adults), disorders (eg, anxiety, mood), and settings (eg, outpatient, inpatient) found that in at least 9 review articles, measurement-based care was associated with significantly improved outcomes vs usual care (ie, treatment without routine outcome monitoring plus feedback). The average increase in treatment effect size was about 30% when treatment was accompanied by measurement-based care.3
Continue to: Moreover, a recent within-patient meta-analysis...
Moreover, a recent within-patient meta-analysis by de Jong et al4 shows that measurement-based care yields a small but significant increase in therapeutic outcomes (d = .15). Use of measurement-based care also is associated with improved communication between the patient and therapist.5 In pharmacotherapy practice, measurement-based care has been shown to predict rapid dose increases and changes in medication, when necessary; faster recovery rates; higher response rates to treatment3; and fewer dropouts.4
Perhaps one of the best-studied benefits of measurement-based mental health care is the ability to predict deterioration in care (ie, patients who are off-track in a way that practitioners often miss without the help of routine outcome monitoring data).6,7 Studies show that without a data-informed approach to care, some forms of psychotherapy or therapy with BHPs who are not sufficiently skilled in treating a given diagnosis increase symptoms or create significant harmful and iatrogenic effects.8-10 Conversely, the meta-analysis by de Jong et al4 found a lower percentage of deterioration in patients receiving measurement-based care. The difference in deterioration was significant: An average of 5.4% of patients in control conditions deteriorated compared to an average of 4.6% in feedback (measurement-based care) groups. There were even larger effect sizes when therapists received training in the feedback system.4
Routine outcome monitoring without a dialogue between patient and practitioner about the assessments (eg, ignoring complete measurement-based care requirements) may be inadequate. A recent review by Muir et al6 found no differences in patient outcomes when data were used solely for aggregate quality improvement activities, suggesting the need for practitioners to review results of routine outcome monitoring assessments with patients and use data to alter care when necessary.
Measurement-based care is believed to deliver benefits and reduce harm by enhancing and encouraging active patient involvement, improving patient understanding of symptoms, promoting better communication, and facilitating better care coordination.3 The benefits of measurement-based care can be enhanced with a comprehensive core routine outcome monitoring tool and the level of monitoring-generated information delivered for multiple stakeholders (eg, patient, therapist, clinic).11
A look at multidimensional assessment
The features of routine outcome monitoring tools vary significantly.12 Some measures assess single-symptom or problem domains (eg, PHQ-9 for depression or Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 [GAD-7] scale for anxiety) or multiple dimensions (multidimensional routine outcome monitoring). Multidimensional routine outcome monitoring may have benefits over single-domain measures. Single-domain measures and the subscales or factors of more comprehensive multidimensional routine outcome monitoring assessments should possess adequate specificity and sensitivity.
Continue to: Some recent research findings...
Some recent research findings question the construct validity of brief single-domain measures of common presenting problems, such as depression and anxiety. For example, results from a factor analysis of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scale in patients with traumatic brain injury suggest these tools measure 1 psychological construct that includes depression and the cognitive components of anxiety (eg, worry)13—a finding consistent with those of other tools.14 Similarly, a larger study of 7763 BH patients found that a single factor accounted for most of the variance of the 2 combined measures, with no set of factors meeting the exacting standards used to develop multidimensional routine outcome monitoring.15 These findings suggest that the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 largely overlap and are not measuring different aspects of health as most practitioners believe (eg, depression and anxiety).
In commonly used assessments, multiple-factor analytic studies with high standards have supported the construct validity of domain-specific subscales, indicating that the various questions tap into different constructs of psychological health.14,16,17
Beyond multiple domain–specific indicators, multidimensional routine outcome measurements provide a global total score that minimizes Type I (false-positive conclusion) and Type II (false-negative conclusion) errors in tracking patient improvement or deterioration.18 As one would expect, multidimensional routine outcome monitoring generally includes more items than single-domain measures; however, this comes with a trade-off. If there are specificity and sensitivity concerns with an ultra-brief single-domain measure, an alternative to a core multidimensional routine outcome measurement is to aggregate a series of single-domain measures into a battery of patient self-reports. However, this approach may take longer for patients to complete since they would have to shift among the varying response sets and wording across the unique single-domain measures.
In addition, the standardization/normalization of multidimensional routine outcome monitoring likely makes interpretation easier than referring to norms and clinical severity cutoffs for many distinct measures. Furthermore, increased specificity enhances predictive power and allows BHPs to screen and track other conditions besides depression and anxiety. (It is worth noting that there are no known studies that have looked at the difference in time to administer or ease of interpretation of multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tools vs multiple single-domain measures.)
Two multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tools that cover a comprehensive series of discrete symptom and functional domains are the Treatment Outcome Package12 and Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms.16 These tools, which include subscales beyond general depression and anxiety (eg, sleep, substance misuse, social conflict), take 7 to 10 minutes to complete and provide outcome results across 12 symptom and 8 functional dimensions. As an example, the Treatment Outcome Package has good psychometric qualities (eg, reliability, construct and concurrent validity) for adults,12 children,14,19 and adolescents,19 and can be administered through a secure online data collection portal. The Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms has demonstrated high construct validity and good convergent validity.16 These assessments can be administered in paper or digital (eg, electronic medical record portal, smartphone) format.20
Continue to: CASE SCENARIO
CASE SCENARIO
Ms. W’s physician asked her to go online using her phone and answer the questions in the Treatment Outcome Package. Her results, which she viewed with her physician, were displayed in graph form (FIGURE). Her scores were represented in Z scores normalized to the general population, with “0” representing the general, nontreatment-seeking population average and positive scores representing the number of standard deviations (SDs) more severe than the general population average.
Although this assessment scored Ms. W’s clinically elevated depression as mild, it revealed abnormalities in 3 other domains. Sexual functioning issues represented the most abnormal domain at greater than 3 SDs (more severe than the general population), followed by poor life quality and school/work functioning.
After reviewing Ms. W’s report, her physician decided that pharmacologic management alone (for depression) was not the most appropriate treatment course. Therefore, her physician recommended psychotherapy in addition to the SSRI she was taking. Ms. W agreed to a customized referral for psychotherapy.
Data-driven referrals
When psychotherapy is chosen as a treatment, the individual BHP is an active component of that treatment. Consequently, it is essential to customize referrals to match a patient’s most elevated mental health concerns with a therapist who will most effectively treat those domains. It is rare for a BHP to be skilled in treating every mental health domain.9 Multiple studies have shown that BHPs have identifiable treatment skills in specific domains, which physicians should consider when making referrals.9,21,22 These studies demonstrate the utility of aggregating patient-level routine outcome monitoring data to better understand therapist-level (and ultimately clinic- and system-level) outcomes.
Additionally, recent research has tested this idea prospectively. An RCT funded by the Patient-Centered Outcome Research Institute and published in JAMA Psychiatry showed a significant and positive effect on patient outcomes (ie, reductions in general impairment, impairment involving a patient’s most elevated domain, and global distress) using paired-on outcome data matching vs as-usual matching protocols (eg, therapist self-defined areas of specialty).22 In the RCT, the most effective matching protocol was a combination of eliminating harm and matching the patient on their 3 most problematic domains (the highest match level). These patients ended care as healthy as the general population after 16 weeks of treatment. A random 1-year follow-up assessment from the original RCT showed that most patients who had been matched had maintained their improvement.23
Continue to: Therefore, a multidimensional routine outcome...
Therefore, a multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tool can be used to identify a BHP’s relative strengths and weaknesses across multiple outcome domains. Within a system of care, a sample of BHPs will possess varying outcome-domain profiles. When a new patient is seeking a referral to a BHP, these profiles (or domain-specific outcome track records) can be used to support paired-on outcome data matching. Specifically, a new patient completes the multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tool at pretreatment, and the results reveal the outcome domains on which the patient is most clinically severe. This pattern of domain-specific severity then can be used to pair the new patient with a BHP who has demonstrated success in addressing the same outcome domain(s). This approach matches a new patient to a BHP with established expertise based on routine outcome monitoring.
Retrospective and prospective studies have found that most BHPs have stable performance in their strengths and weaknesses.11,21 One study found that assessing BHP performance with their most recent 30 patients can reliably predict future performance with their next 30 patients.24 This predictability in a practitioner’s outcomes suggests report cards that are updated frequently can be utilized to make case assignments within BH or referrals to a specific BHP from primary care.
Making a paired-on outcome data–matched referral
Making customized BH referrals requires access to information about a practitioner’s previous routine outcome monitoring data per clinical domain (eg, suicidality, violence, quality of life) from their most recent patients. Previous research suggests that follow-up data from a minimum of 15 patients is necessary to make a reliable evaluation of a practitioner’s strengths and weaknesses (ie, effectiveness “report card”) per clinical domain.24
Few, if any, physicians have access to this level of updated outcome data from their referral network. To facilitate widespread use of paired-on outcome data matching, a new Web system (MatchedTherapists.com) will allow the general public and PCPs to access these grades. As a public service option, this site currently allows for a self-assessment using the Treatment Outcome Package. Pending versions will generate paired-on outcome data grades, and users will receive a list of local therapists available for in-person appointments as well as therapists available for virtual appointments. The paired-on outcome data grades are delivered in school-based letter grades. An “A+,” for example, represents the best matching grade. Users also will be able to sort and filter results for other criteria such as telemedicine, insurance, age, gender, and appointment availability. Currently, there are more than 77,000 therapists listed on the site nationwide. A basic listing is free.
CASE SCENARIO
After Ms. W took the multidimensional routine outcome assessment online, she received a list of therapists rank-ordered by paired-on outcome data grade, with the “A+” matches listed first. Three of the best-matched referrals accepted her insurance and were willing to see her through telemedicine. Therapists with available in-person appointments had a “B” grade. After discussing the options with her physician, Ms. W opted for telehealth counseling with the therapist whose profile she liked best. The therapist and PCP tracked her progress through routine outcome monitoring reporting until all her symptoms became subclinical.
Continue to: The future of a "referral bridge"
The future of a “referral bridge”
In this article, we present a solution to a common issue faced by mental health care patients: failure to benefit meaningfully from mental health treatment. Matching patients to specific BHPs based on effectiveness data regarding the therapist’s strengths and skills can improve patient outcomes and reduce harm. In addition, patients appear to value this approach. A Robert Wood Johnson Foundation–funded study demonstrated that patients value seeing practitioners who have a track record of successfully treating previous patients with similar issues.25,26 In many cases, patients indicated they would prioritize this matching process over other factors such as practitioners with a higher number of years of experience or the same demographic characteristics as the patient.25,26
These findings may represent a new area in the science of health care. Over the past century, major advances in diagnosis and treatment—the 2 primary pillars of health care—have turned the art of medicine into a science. However, the art of making referrals has not advanced commensurately, as there has been little attention focused on the “referral bridge” between these 2 pillars. As the studies reviewed in this paper demonstrate, a referral bridge deserves exploration in all fields of medicine.
CORRESPONDENCE
David R. Kraus, PhD, 1 Speen Street, Framingham, MA 01701; [email protected]
1. HHS. 2021 National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) Releases. Accessed March 29, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/release/2021-national-survey-drug-use-and-health-nsduh-releases
2. Barkham M, Lambert, MJ. The efficacy and effectiveness of psychological therapies. In: Barkham M, Lutz W, Castonguay LG, eds. Bergin and Garfield’s Handbook of Psychotherapy and Behavior Change: 50th Anniversary Edition. 7th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2021:135-189.
3. Lewis CC, Boyd M, Puspitasari A, et al. Implementing measurement-based care in behavioral health: a review. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76:324-335. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3329
4. de Jong K, Conijn JM, Gallagher RAV, et al. Using progress feedback to improve outcomes and reduce drop-out, treatment duration, and deterioration: a multilevel meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;85:102002. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102002
5. Carlier IVE, Meuldijk D, Van Vliet IM, et al. Routine outcome monitoring and feedback on physical or mental health status: evidence and theory. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012;18:104-110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2010.01543.x
6. Muir HJ, Coyne AE, Morrison NR, et al. Ethical implications of routine outcomes monitoring for patients, psychotherapists, and mental health care systems. Psychotherapy (Chic). 2019;56:459-469. doi: 10.1037/pst0000246
7. Hannan C, Lambert MJ, Harmon C, et al. A lab test and algorithms for identifying clients at risk for treatment failure. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61:155-163. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20108
8. Castonguay LG, Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, et al. Training implications of harmful effects of psychological treatments. Am Psychol. 2010;65:34-49. doi: 10.1037/a0017330
9. Kraus DR, Castonguay LG, Boswell JF, et al. Therapist effectiveness: implications for accountability and patient care. Psychother Res. 2011;21:267-276. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2011.563249
10. Lilienfeld SO. Psychological treatments that cause harm. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2007;2:53-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6916.2007.00029.x
11. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Kraus DR, et al. The expanding relevance of routinely collected outcome data for mental health care decision making. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43:482-491. doi: 10.1007/s10488-015-0649-6
12. Lyon AR, Lewis CC, Boyd MR, et al. Capabilities and characteristics of digital measurement feedback systems: results from a comprehensive review. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43:441-466. doi: 10.1007/s10488-016-0719-4
13. Teymoori A, Gorbunova A, Haghish FE, et al. Factorial structure and validity of depression (PHQ-9) and anxiety (GAD-7) scales after traumatic brain injury. J Clin Med. 2020;9:873. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030873
14. Kraus DR, Seligman DA, Jordan JR. Validation of a behavioral health treatment outcome and assessment tool designed for naturalistic settings: the Treatment Outcome Package. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61:285‐314. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20084
15. Boothroyd L, Dagnan D, Muncer S. Psychometric analysis of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale and the Patient Health Questionnaire using Mokken scaling and confirmatory factor analysis. Health Prim Care. 2018;2:1-4. doi: 10.15761/HPC.1000145
16. Locke BD, Buzolitz JS, Lei PW, et al. Development of the Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms-62 (CCAPS-62). J Couns Psychol. 2011;58:97-109. doi: 10.1037/a0021282
17. Kraus DR, Boswell JF, Wright AGC, et al. Factor structure of the treatment outcome package for children. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66:627-640. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20675
18. McAleavey AA, Nordberg SS, Kraus D, et al. Errors in treatment outcome monitoring: implications for real-world psychotherapy. Can Psychol. 2010;53:105-114. doi: 10.1037/a0027833
19. Baxter EE, Alexander PC, Kraus DR, et al. Concurrent validation of the Treatment Outcome Package (TOP) for children and adolescents. J Child Fam Stud. 2016;25:2415-2422. doi: 10.1007/s10826-016-0419-4
20. Gual-Montolio P, Martínez-Borba V, Bretón-López JM, et al. How are information and communication technologies supporting routine outcome monitoring and measurement-based care in psychotherapy? A systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:3170. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093170
21. Kraus DR, Bentley JH, Alexander PC, et al. Predicting therapist effectiveness from their own practice-based evidence. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84:473‐483. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000083
22. Constantino MJ, Boswell JF, Coyne AE, et al. Effect of matching therapists to patients vs assignment as usual on adult psychotherapy outcomes. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:960-969. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.1221
23. Constantino MJ, Boswell JF, Kraus DR, et al. Matching patients with therapists to improve mental health care. Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. www.pcori.org/research-results/2015/matching-patients-therapists-improve-mental-health-care
24. Institute of Medicine. Committee on Crossing the Quality Chasm: Adaptation to Mental Health and Addictive Disorders. Improving the Quality of Health Care for Mental and Substance-Use Conditions. National Academies Press; 2006. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/11470/chapter/1
25. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Oswald JM, et al. A multimethod study of mental health care patients’ attitudes toward clinician-level performance information. Psychiatr Serv. 2021;72:452-456. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.202000366
26. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Oswald JM, et al. Mental health care consumers’ relative valuing of clinician performance information. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2018;86:301‐308. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000264
Approximately 1 in 4 people ages 18 years and older and 1 in 3 people ages 18 to 25 years had a mental illness in the past year, according to the 2021 National Survey of Drug Use and Health.1 The survey also found that adults ages 18 to 25 years had the highest rate of serious mental illness but the lowest treatment rate compared to other adult age groups.1 Unfortunately, more than 60% of patients receiving mental health treatment fail to benefit to a clinically meaningful degree.2
However, there is growing evidence that referring patients to behavioral health practitioners (BHPs) with outcome-measured skills that meet the patient’s specific needs can have a dramatic and positive impact. There are 2 main steps to pairing patients with an appropriate BHP: (1) use of measurement-based care data that can be analyzed at the patient and therapist level, and (2) data-driven referrals that pair patients with BHPs based on such routine outcome monitoring data (paired-on outcome data).
Psychotherapy’s slow road toward measurement-based care
Routine outcome monitoring is the systematic measurement of symptoms and functioning during treatment. It serves multiple functions, including program evaluation and benchmarking of patient improvement rates. Moreover, routine outcome monitoring–derived feedback (based on repeated patient outcome measurements) can inform personalized and responsive care decisions throughout treatment.
For all intents and purposes,
- routinely administered symptom/functioning measure, ideally before each clinical encounter,
- practitioner review of these patient-level data,
- patient review of these data with their practitioner, and
- collaborative reevaluation of the person-specific treatment plan informed by these data.
CASE SCENARIO
Violeta W is a 33-year-old woman who presented to her family physician for her annual wellness exam. Prior to the exam, the medical assistant administered a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) to screen for depressive symptoms. Ms. W’s score was 20 out of 27, suggestive of depression. To further assess the severity of depressive symptoms and their effect on daily function, the physician reviewed responses to the questionnaire with her and discussed treatment options. Ms. W was most interested in trying a low-dose selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).
At her follow-up visit 4 weeks later, the medical assistant re-administered the PHQ-9. The physician then reviewed Ms. W’s responses with her and, based on Ms. W’s subjective report and objective symptoms (still a score of 20 out of 27 on the PHQ-9), increased her SSRI dose. At each subsequent visit, Ms. W completed a PHQ-9 and reviewed responses and depressive symptoms with her physician.
The value of measurement-based care in mental health care
A narrative review by Lewis et al3 of 21 randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) across a range of age groups (eg, adolescents, young adults, adults), disorders (eg, anxiety, mood), and settings (eg, outpatient, inpatient) found that in at least 9 review articles, measurement-based care was associated with significantly improved outcomes vs usual care (ie, treatment without routine outcome monitoring plus feedback). The average increase in treatment effect size was about 30% when treatment was accompanied by measurement-based care.3
Continue to: Moreover, a recent within-patient meta-analysis...
Moreover, a recent within-patient meta-analysis by de Jong et al4 shows that measurement-based care yields a small but significant increase in therapeutic outcomes (d = .15). Use of measurement-based care also is associated with improved communication between the patient and therapist.5 In pharmacotherapy practice, measurement-based care has been shown to predict rapid dose increases and changes in medication, when necessary; faster recovery rates; higher response rates to treatment3; and fewer dropouts.4
Perhaps one of the best-studied benefits of measurement-based mental health care is the ability to predict deterioration in care (ie, patients who are off-track in a way that practitioners often miss without the help of routine outcome monitoring data).6,7 Studies show that without a data-informed approach to care, some forms of psychotherapy or therapy with BHPs who are not sufficiently skilled in treating a given diagnosis increase symptoms or create significant harmful and iatrogenic effects.8-10 Conversely, the meta-analysis by de Jong et al4 found a lower percentage of deterioration in patients receiving measurement-based care. The difference in deterioration was significant: An average of 5.4% of patients in control conditions deteriorated compared to an average of 4.6% in feedback (measurement-based care) groups. There were even larger effect sizes when therapists received training in the feedback system.4
Routine outcome monitoring without a dialogue between patient and practitioner about the assessments (eg, ignoring complete measurement-based care requirements) may be inadequate. A recent review by Muir et al6 found no differences in patient outcomes when data were used solely for aggregate quality improvement activities, suggesting the need for practitioners to review results of routine outcome monitoring assessments with patients and use data to alter care when necessary.
Measurement-based care is believed to deliver benefits and reduce harm by enhancing and encouraging active patient involvement, improving patient understanding of symptoms, promoting better communication, and facilitating better care coordination.3 The benefits of measurement-based care can be enhanced with a comprehensive core routine outcome monitoring tool and the level of monitoring-generated information delivered for multiple stakeholders (eg, patient, therapist, clinic).11
A look at multidimensional assessment
The features of routine outcome monitoring tools vary significantly.12 Some measures assess single-symptom or problem domains (eg, PHQ-9 for depression or Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 [GAD-7] scale for anxiety) or multiple dimensions (multidimensional routine outcome monitoring). Multidimensional routine outcome monitoring may have benefits over single-domain measures. Single-domain measures and the subscales or factors of more comprehensive multidimensional routine outcome monitoring assessments should possess adequate specificity and sensitivity.
Continue to: Some recent research findings...
Some recent research findings question the construct validity of brief single-domain measures of common presenting problems, such as depression and anxiety. For example, results from a factor analysis of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scale in patients with traumatic brain injury suggest these tools measure 1 psychological construct that includes depression and the cognitive components of anxiety (eg, worry)13—a finding consistent with those of other tools.14 Similarly, a larger study of 7763 BH patients found that a single factor accounted for most of the variance of the 2 combined measures, with no set of factors meeting the exacting standards used to develop multidimensional routine outcome monitoring.15 These findings suggest that the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 largely overlap and are not measuring different aspects of health as most practitioners believe (eg, depression and anxiety).
In commonly used assessments, multiple-factor analytic studies with high standards have supported the construct validity of domain-specific subscales, indicating that the various questions tap into different constructs of psychological health.14,16,17
Beyond multiple domain–specific indicators, multidimensional routine outcome measurements provide a global total score that minimizes Type I (false-positive conclusion) and Type II (false-negative conclusion) errors in tracking patient improvement or deterioration.18 As one would expect, multidimensional routine outcome monitoring generally includes more items than single-domain measures; however, this comes with a trade-off. If there are specificity and sensitivity concerns with an ultra-brief single-domain measure, an alternative to a core multidimensional routine outcome measurement is to aggregate a series of single-domain measures into a battery of patient self-reports. However, this approach may take longer for patients to complete since they would have to shift among the varying response sets and wording across the unique single-domain measures.
In addition, the standardization/normalization of multidimensional routine outcome monitoring likely makes interpretation easier than referring to norms and clinical severity cutoffs for many distinct measures. Furthermore, increased specificity enhances predictive power and allows BHPs to screen and track other conditions besides depression and anxiety. (It is worth noting that there are no known studies that have looked at the difference in time to administer or ease of interpretation of multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tools vs multiple single-domain measures.)
Two multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tools that cover a comprehensive series of discrete symptom and functional domains are the Treatment Outcome Package12 and Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms.16 These tools, which include subscales beyond general depression and anxiety (eg, sleep, substance misuse, social conflict), take 7 to 10 minutes to complete and provide outcome results across 12 symptom and 8 functional dimensions. As an example, the Treatment Outcome Package has good psychometric qualities (eg, reliability, construct and concurrent validity) for adults,12 children,14,19 and adolescents,19 and can be administered through a secure online data collection portal. The Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms has demonstrated high construct validity and good convergent validity.16 These assessments can be administered in paper or digital (eg, electronic medical record portal, smartphone) format.20
Continue to: CASE SCENARIO
CASE SCENARIO
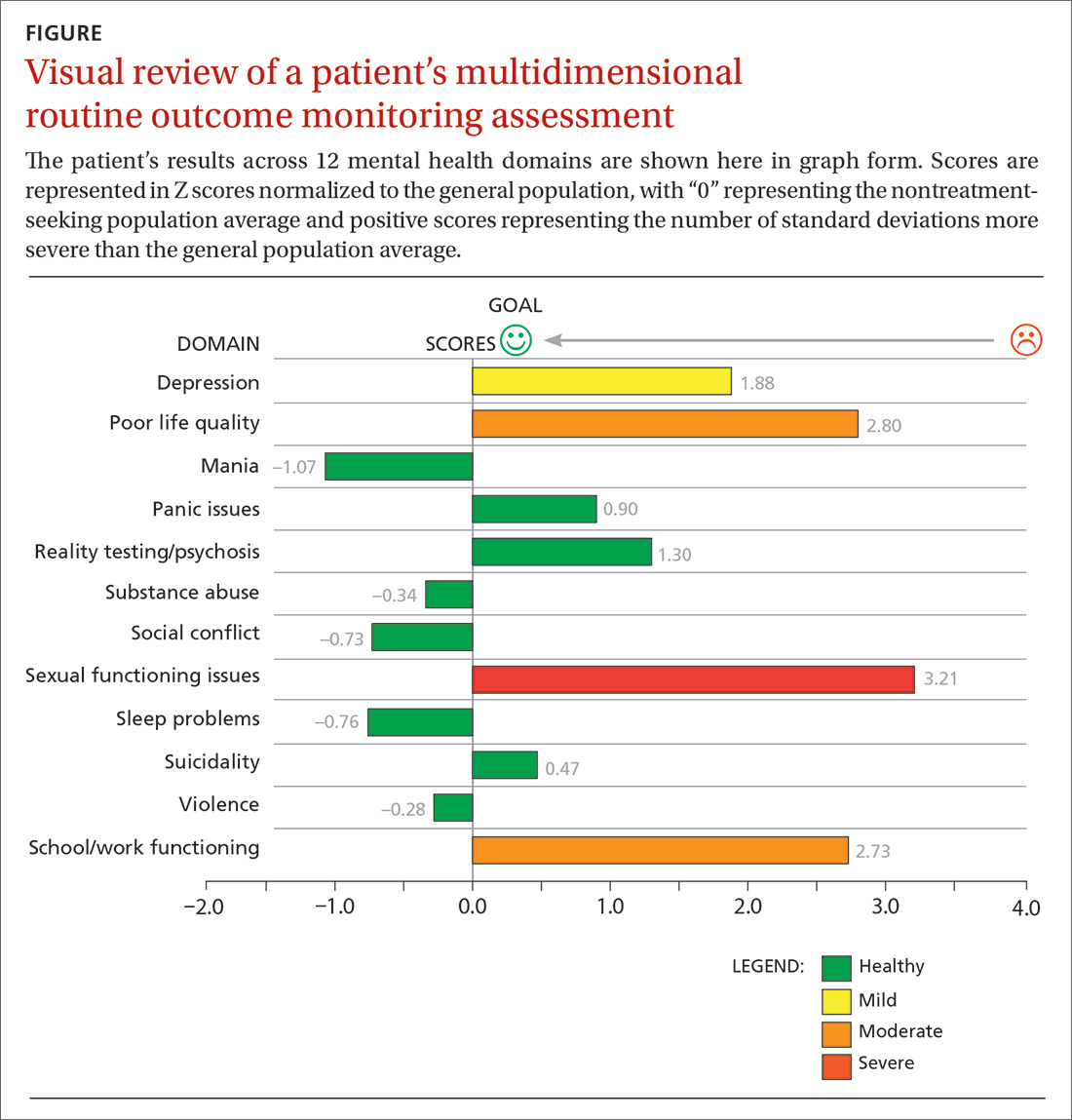
Ms. W’s physician asked her to go online using her phone and answer the questions in the Treatment Outcome Package. Her results, which she viewed with her physician, were displayed in graph form (FIGURE). Her scores were represented in Z scores normalized to the general population, with “0” representing the general, nontreatment-seeking population average and positive scores representing the number of standard deviations (SDs) more severe than the general population average.

Although this assessment scored Ms. W’s clinically elevated depression as mild, it revealed abnormalities in 3 other domains. Sexual functioning issues represented the most abnormal domain at greater than 3 SDs (more severe than the general population), followed by poor life quality and school/work functioning.
After reviewing Ms. W’s report, her physician decided that pharmacologic management alone (for depression) was not the most appropriate treatment course. Therefore, her physician recommended psychotherapy in addition to the SSRI she was taking. Ms. W agreed to a customized referral for psychotherapy.
Data-driven referrals
When psychotherapy is chosen as a treatment, the individual BHP is an active component of that treatment. Consequently, it is essential to customize referrals to match a patient’s most elevated mental health concerns with a therapist who will most effectively treat those domains. It is rare for a BHP to be skilled in treating every mental health domain.9 Multiple studies have shown that BHPs have identifiable treatment skills in specific domains, which physicians should consider when making referrals.9,21,22 These studies demonstrate the utility of aggregating patient-level routine outcome monitoring data to better understand therapist-level (and ultimately clinic- and system-level) outcomes.
Additionally, recent research has tested this idea prospectively. An RCT funded by the Patient-Centered Outcome Research Institute and published in JAMA Psychiatry showed a significant and positive effect on patient outcomes (ie, reductions in general impairment, impairment involving a patient’s most elevated domain, and global distress) using paired-on outcome data matching vs as-usual matching protocols (eg, therapist self-defined areas of specialty).22 In the RCT, the most effective matching protocol was a combination of eliminating harm and matching the patient on their 3 most problematic domains (the highest match level). These patients ended care as healthy as the general population after 16 weeks of treatment. A random 1-year follow-up assessment from the original RCT showed that most patients who had been matched had maintained their improvement.23
Continue to: Therefore, a multidimensional routine outcome...
Therefore, a multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tool can be used to identify a BHP’s relative strengths and weaknesses across multiple outcome domains. Within a system of care, a sample of BHPs will possess varying outcome-domain profiles. When a new patient is seeking a referral to a BHP, these profiles (or domain-specific outcome track records) can be used to support paired-on outcome data matching. Specifically, a new patient completes the multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tool at pretreatment, and the results reveal the outcome domains on which the patient is most clinically severe. This pattern of domain-specific severity then can be used to pair the new patient with a BHP who has demonstrated success in addressing the same outcome domain(s). This approach matches a new patient to a BHP with established expertise based on routine outcome monitoring.
Retrospective and prospective studies have found that most BHPs have stable performance in their strengths and weaknesses.11,21 One study found that assessing BHP performance with their most recent 30 patients can reliably predict future performance with their next 30 patients.24 This predictability in a practitioner’s outcomes suggests report cards that are updated frequently can be utilized to make case assignments within BH or referrals to a specific BHP from primary care.
Making a paired-on outcome data–matched referral
Making customized BH referrals requires access to information about a practitioner’s previous routine outcome monitoring data per clinical domain (eg, suicidality, violence, quality of life) from their most recent patients. Previous research suggests that follow-up data from a minimum of 15 patients is necessary to make a reliable evaluation of a practitioner’s strengths and weaknesses (ie, effectiveness “report card”) per clinical domain.24
Few, if any, physicians have access to this level of updated outcome data from their referral network. To facilitate widespread use of paired-on outcome data matching, a new Web system (MatchedTherapists.com) will allow the general public and PCPs to access these grades. As a public service option, this site currently allows for a self-assessment using the Treatment Outcome Package. Pending versions will generate paired-on outcome data grades, and users will receive a list of local therapists available for in-person appointments as well as therapists available for virtual appointments. The paired-on outcome data grades are delivered in school-based letter grades. An “A+,” for example, represents the best matching grade. Users also will be able to sort and filter results for other criteria such as telemedicine, insurance, age, gender, and appointment availability. Currently, there are more than 77,000 therapists listed on the site nationwide. A basic listing is free.
CASE SCENARIO
After Ms. W took the multidimensional routine outcome assessment online, she received a list of therapists rank-ordered by paired-on outcome data grade, with the “A+” matches listed first. Three of the best-matched referrals accepted her insurance and were willing to see her through telemedicine. Therapists with available in-person appointments had a “B” grade. After discussing the options with her physician, Ms. W opted for telehealth counseling with the therapist whose profile she liked best. The therapist and PCP tracked her progress through routine outcome monitoring reporting until all her symptoms became subclinical.
Continue to: The future of a "referral bridge"
The future of a “referral bridge”
In this article, we present a solution to a common issue faced by mental health care patients: failure to benefit meaningfully from mental health treatment. Matching patients to specific BHPs based on effectiveness data regarding the therapist’s strengths and skills can improve patient outcomes and reduce harm. In addition, patients appear to value this approach. A Robert Wood Johnson Foundation–funded study demonstrated that patients value seeing practitioners who have a track record of successfully treating previous patients with similar issues.25,26 In many cases, patients indicated they would prioritize this matching process over other factors such as practitioners with a higher number of years of experience or the same demographic characteristics as the patient.25,26
These findings may represent a new area in the science of health care. Over the past century, major advances in diagnosis and treatment—the 2 primary pillars of health care—have turned the art of medicine into a science. However, the art of making referrals has not advanced commensurately, as there has been little attention focused on the “referral bridge” between these 2 pillars. As the studies reviewed in this paper demonstrate, a referral bridge deserves exploration in all fields of medicine.
CORRESPONDENCE
David R. Kraus, PhD, 1 Speen Street, Framingham, MA 01701; [email protected]
Approximately 1 in 4 people ages 18 years and older and 1 in 3 people ages 18 to 25 years had a mental illness in the past year, according to the 2021 National Survey of Drug Use and Health.1 The survey also found that adults ages 18 to 25 years had the highest rate of serious mental illness but the lowest treatment rate compared to other adult age groups.1 Unfortunately, more than 60% of patients receiving mental health treatment fail to benefit to a clinically meaningful degree.2
However, there is growing evidence that referring patients to behavioral health practitioners (BHPs) with outcome-measured skills that meet the patient’s specific needs can have a dramatic and positive impact. There are 2 main steps to pairing patients with an appropriate BHP: (1) use of measurement-based care data that can be analyzed at the patient and therapist level, and (2) data-driven referrals that pair patients with BHPs based on such routine outcome monitoring data (paired-on outcome data).
Psychotherapy’s slow road toward measurement-based care
Routine outcome monitoring is the systematic measurement of symptoms and functioning during treatment. It serves multiple functions, including program evaluation and benchmarking of patient improvement rates. Moreover, routine outcome monitoring–derived feedback (based on repeated patient outcome measurements) can inform personalized and responsive care decisions throughout treatment.
For all intents and purposes,
- routinely administered symptom/functioning measure, ideally before each clinical encounter,
- practitioner review of these patient-level data,
- patient review of these data with their practitioner, and
- collaborative reevaluation of the person-specific treatment plan informed by these data.
CASE SCENARIO
Violeta W is a 33-year-old woman who presented to her family physician for her annual wellness exam. Prior to the exam, the medical assistant administered a Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) to screen for depressive symptoms. Ms. W’s score was 20 out of 27, suggestive of depression. To further assess the severity of depressive symptoms and their effect on daily function, the physician reviewed responses to the questionnaire with her and discussed treatment options. Ms. W was most interested in trying a low-dose selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI).
At her follow-up visit 4 weeks later, the medical assistant re-administered the PHQ-9. The physician then reviewed Ms. W’s responses with her and, based on Ms. W’s subjective report and objective symptoms (still a score of 20 out of 27 on the PHQ-9), increased her SSRI dose. At each subsequent visit, Ms. W completed a PHQ-9 and reviewed responses and depressive symptoms with her physician.
The value of measurement-based care in mental health care
A narrative review by Lewis et al3 of 21 randomized controlled clinical trials (RCTs) across a range of age groups (eg, adolescents, young adults, adults), disorders (eg, anxiety, mood), and settings (eg, outpatient, inpatient) found that in at least 9 review articles, measurement-based care was associated with significantly improved outcomes vs usual care (ie, treatment without routine outcome monitoring plus feedback). The average increase in treatment effect size was about 30% when treatment was accompanied by measurement-based care.3
Continue to: Moreover, a recent within-patient meta-analysis...
Moreover, a recent within-patient meta-analysis by de Jong et al4 shows that measurement-based care yields a small but significant increase in therapeutic outcomes (d = .15). Use of measurement-based care also is associated with improved communication between the patient and therapist.5 In pharmacotherapy practice, measurement-based care has been shown to predict rapid dose increases and changes in medication, when necessary; faster recovery rates; higher response rates to treatment3; and fewer dropouts.4
Perhaps one of the best-studied benefits of measurement-based mental health care is the ability to predict deterioration in care (ie, patients who are off-track in a way that practitioners often miss without the help of routine outcome monitoring data).6,7 Studies show that without a data-informed approach to care, some forms of psychotherapy or therapy with BHPs who are not sufficiently skilled in treating a given diagnosis increase symptoms or create significant harmful and iatrogenic effects.8-10 Conversely, the meta-analysis by de Jong et al4 found a lower percentage of deterioration in patients receiving measurement-based care. The difference in deterioration was significant: An average of 5.4% of patients in control conditions deteriorated compared to an average of 4.6% in feedback (measurement-based care) groups. There were even larger effect sizes when therapists received training in the feedback system.4
Routine outcome monitoring without a dialogue between patient and practitioner about the assessments (eg, ignoring complete measurement-based care requirements) may be inadequate. A recent review by Muir et al6 found no differences in patient outcomes when data were used solely for aggregate quality improvement activities, suggesting the need for practitioners to review results of routine outcome monitoring assessments with patients and use data to alter care when necessary.
Measurement-based care is believed to deliver benefits and reduce harm by enhancing and encouraging active patient involvement, improving patient understanding of symptoms, promoting better communication, and facilitating better care coordination.3 The benefits of measurement-based care can be enhanced with a comprehensive core routine outcome monitoring tool and the level of monitoring-generated information delivered for multiple stakeholders (eg, patient, therapist, clinic).11
A look at multidimensional assessment
The features of routine outcome monitoring tools vary significantly.12 Some measures assess single-symptom or problem domains (eg, PHQ-9 for depression or Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 [GAD-7] scale for anxiety) or multiple dimensions (multidimensional routine outcome monitoring). Multidimensional routine outcome monitoring may have benefits over single-domain measures. Single-domain measures and the subscales or factors of more comprehensive multidimensional routine outcome monitoring assessments should possess adequate specificity and sensitivity.
Continue to: Some recent research findings...
Some recent research findings question the construct validity of brief single-domain measures of common presenting problems, such as depression and anxiety. For example, results from a factor analysis of the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 scale in patients with traumatic brain injury suggest these tools measure 1 psychological construct that includes depression and the cognitive components of anxiety (eg, worry)13—a finding consistent with those of other tools.14 Similarly, a larger study of 7763 BH patients found that a single factor accounted for most of the variance of the 2 combined measures, with no set of factors meeting the exacting standards used to develop multidimensional routine outcome monitoring.15 These findings suggest that the PHQ-9 and GAD-7 largely overlap and are not measuring different aspects of health as most practitioners believe (eg, depression and anxiety).
In commonly used assessments, multiple-factor analytic studies with high standards have supported the construct validity of domain-specific subscales, indicating that the various questions tap into different constructs of psychological health.14,16,17
Beyond multiple domain–specific indicators, multidimensional routine outcome measurements provide a global total score that minimizes Type I (false-positive conclusion) and Type II (false-negative conclusion) errors in tracking patient improvement or deterioration.18 As one would expect, multidimensional routine outcome monitoring generally includes more items than single-domain measures; however, this comes with a trade-off. If there are specificity and sensitivity concerns with an ultra-brief single-domain measure, an alternative to a core multidimensional routine outcome measurement is to aggregate a series of single-domain measures into a battery of patient self-reports. However, this approach may take longer for patients to complete since they would have to shift among the varying response sets and wording across the unique single-domain measures.
In addition, the standardization/normalization of multidimensional routine outcome monitoring likely makes interpretation easier than referring to norms and clinical severity cutoffs for many distinct measures. Furthermore, increased specificity enhances predictive power and allows BHPs to screen and track other conditions besides depression and anxiety. (It is worth noting that there are no known studies that have looked at the difference in time to administer or ease of interpretation of multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tools vs multiple single-domain measures.)
Two multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tools that cover a comprehensive series of discrete symptom and functional domains are the Treatment Outcome Package12 and Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms.16 These tools, which include subscales beyond general depression and anxiety (eg, sleep, substance misuse, social conflict), take 7 to 10 minutes to complete and provide outcome results across 12 symptom and 8 functional dimensions. As an example, the Treatment Outcome Package has good psychometric qualities (eg, reliability, construct and concurrent validity) for adults,12 children,14,19 and adolescents,19 and can be administered through a secure online data collection portal. The Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms has demonstrated high construct validity and good convergent validity.16 These assessments can be administered in paper or digital (eg, electronic medical record portal, smartphone) format.20
Continue to: CASE SCENARIO
CASE SCENARIO
Ms. W’s physician asked her to go online using her phone and answer the questions in the Treatment Outcome Package. Her results, which she viewed with her physician, were displayed in graph form (FIGURE). Her scores were represented in Z scores normalized to the general population, with “0” representing the general, nontreatment-seeking population average and positive scores representing the number of standard deviations (SDs) more severe than the general population average.

Although this assessment scored Ms. W’s clinically elevated depression as mild, it revealed abnormalities in 3 other domains. Sexual functioning issues represented the most abnormal domain at greater than 3 SDs (more severe than the general population), followed by poor life quality and school/work functioning.
After reviewing Ms. W’s report, her physician decided that pharmacologic management alone (for depression) was not the most appropriate treatment course. Therefore, her physician recommended psychotherapy in addition to the SSRI she was taking. Ms. W agreed to a customized referral for psychotherapy.
Data-driven referrals
When psychotherapy is chosen as a treatment, the individual BHP is an active component of that treatment. Consequently, it is essential to customize referrals to match a patient’s most elevated mental health concerns with a therapist who will most effectively treat those domains. It is rare for a BHP to be skilled in treating every mental health domain.9 Multiple studies have shown that BHPs have identifiable treatment skills in specific domains, which physicians should consider when making referrals.9,21,22 These studies demonstrate the utility of aggregating patient-level routine outcome monitoring data to better understand therapist-level (and ultimately clinic- and system-level) outcomes.
Additionally, recent research has tested this idea prospectively. An RCT funded by the Patient-Centered Outcome Research Institute and published in JAMA Psychiatry showed a significant and positive effect on patient outcomes (ie, reductions in general impairment, impairment involving a patient’s most elevated domain, and global distress) using paired-on outcome data matching vs as-usual matching protocols (eg, therapist self-defined areas of specialty).22 In the RCT, the most effective matching protocol was a combination of eliminating harm and matching the patient on their 3 most problematic domains (the highest match level). These patients ended care as healthy as the general population after 16 weeks of treatment. A random 1-year follow-up assessment from the original RCT showed that most patients who had been matched had maintained their improvement.23
Continue to: Therefore, a multidimensional routine outcome...
Therefore, a multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tool can be used to identify a BHP’s relative strengths and weaknesses across multiple outcome domains. Within a system of care, a sample of BHPs will possess varying outcome-domain profiles. When a new patient is seeking a referral to a BHP, these profiles (or domain-specific outcome track records) can be used to support paired-on outcome data matching. Specifically, a new patient completes the multidimensional routine outcome monitoring tool at pretreatment, and the results reveal the outcome domains on which the patient is most clinically severe. This pattern of domain-specific severity then can be used to pair the new patient with a BHP who has demonstrated success in addressing the same outcome domain(s). This approach matches a new patient to a BHP with established expertise based on routine outcome monitoring.
Retrospective and prospective studies have found that most BHPs have stable performance in their strengths and weaknesses.11,21 One study found that assessing BHP performance with their most recent 30 patients can reliably predict future performance with their next 30 patients.24 This predictability in a practitioner’s outcomes suggests report cards that are updated frequently can be utilized to make case assignments within BH or referrals to a specific BHP from primary care.
Making a paired-on outcome data–matched referral
Making customized BH referrals requires access to information about a practitioner’s previous routine outcome monitoring data per clinical domain (eg, suicidality, violence, quality of life) from their most recent patients. Previous research suggests that follow-up data from a minimum of 15 patients is necessary to make a reliable evaluation of a practitioner’s strengths and weaknesses (ie, effectiveness “report card”) per clinical domain.24
Few, if any, physicians have access to this level of updated outcome data from their referral network. To facilitate widespread use of paired-on outcome data matching, a new Web system (MatchedTherapists.com) will allow the general public and PCPs to access these grades. As a public service option, this site currently allows for a self-assessment using the Treatment Outcome Package. Pending versions will generate paired-on outcome data grades, and users will receive a list of local therapists available for in-person appointments as well as therapists available for virtual appointments. The paired-on outcome data grades are delivered in school-based letter grades. An “A+,” for example, represents the best matching grade. Users also will be able to sort and filter results for other criteria such as telemedicine, insurance, age, gender, and appointment availability. Currently, there are more than 77,000 therapists listed on the site nationwide. A basic listing is free.
CASE SCENARIO
After Ms. W took the multidimensional routine outcome assessment online, she received a list of therapists rank-ordered by paired-on outcome data grade, with the “A+” matches listed first. Three of the best-matched referrals accepted her insurance and were willing to see her through telemedicine. Therapists with available in-person appointments had a “B” grade. After discussing the options with her physician, Ms. W opted for telehealth counseling with the therapist whose profile she liked best. The therapist and PCP tracked her progress through routine outcome monitoring reporting until all her symptoms became subclinical.
Continue to: The future of a "referral bridge"
The future of a “referral bridge”
In this article, we present a solution to a common issue faced by mental health care patients: failure to benefit meaningfully from mental health treatment. Matching patients to specific BHPs based on effectiveness data regarding the therapist’s strengths and skills can improve patient outcomes and reduce harm. In addition, patients appear to value this approach. A Robert Wood Johnson Foundation–funded study demonstrated that patients value seeing practitioners who have a track record of successfully treating previous patients with similar issues.25,26 In many cases, patients indicated they would prioritize this matching process over other factors such as practitioners with a higher number of years of experience or the same demographic characteristics as the patient.25,26
These findings may represent a new area in the science of health care. Over the past century, major advances in diagnosis and treatment—the 2 primary pillars of health care—have turned the art of medicine into a science. However, the art of making referrals has not advanced commensurately, as there has been little attention focused on the “referral bridge” between these 2 pillars. As the studies reviewed in this paper demonstrate, a referral bridge deserves exploration in all fields of medicine.
CORRESPONDENCE
David R. Kraus, PhD, 1 Speen Street, Framingham, MA 01701; [email protected]
1. HHS. 2021 National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) Releases. Accessed March 29, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/release/2021-national-survey-drug-use-and-health-nsduh-releases
2. Barkham M, Lambert, MJ. The efficacy and effectiveness of psychological therapies. In: Barkham M, Lutz W, Castonguay LG, eds. Bergin and Garfield’s Handbook of Psychotherapy and Behavior Change: 50th Anniversary Edition. 7th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2021:135-189.
3. Lewis CC, Boyd M, Puspitasari A, et al. Implementing measurement-based care in behavioral health: a review. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76:324-335. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3329
4. de Jong K, Conijn JM, Gallagher RAV, et al. Using progress feedback to improve outcomes and reduce drop-out, treatment duration, and deterioration: a multilevel meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;85:102002. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102002
5. Carlier IVE, Meuldijk D, Van Vliet IM, et al. Routine outcome monitoring and feedback on physical or mental health status: evidence and theory. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012;18:104-110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2010.01543.x
6. Muir HJ, Coyne AE, Morrison NR, et al. Ethical implications of routine outcomes monitoring for patients, psychotherapists, and mental health care systems. Psychotherapy (Chic). 2019;56:459-469. doi: 10.1037/pst0000246
7. Hannan C, Lambert MJ, Harmon C, et al. A lab test and algorithms for identifying clients at risk for treatment failure. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61:155-163. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20108
8. Castonguay LG, Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, et al. Training implications of harmful effects of psychological treatments. Am Psychol. 2010;65:34-49. doi: 10.1037/a0017330
9. Kraus DR, Castonguay LG, Boswell JF, et al. Therapist effectiveness: implications for accountability and patient care. Psychother Res. 2011;21:267-276. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2011.563249
10. Lilienfeld SO. Psychological treatments that cause harm. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2007;2:53-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6916.2007.00029.x
11. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Kraus DR, et al. The expanding relevance of routinely collected outcome data for mental health care decision making. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43:482-491. doi: 10.1007/s10488-015-0649-6
12. Lyon AR, Lewis CC, Boyd MR, et al. Capabilities and characteristics of digital measurement feedback systems: results from a comprehensive review. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43:441-466. doi: 10.1007/s10488-016-0719-4
13. Teymoori A, Gorbunova A, Haghish FE, et al. Factorial structure and validity of depression (PHQ-9) and anxiety (GAD-7) scales after traumatic brain injury. J Clin Med. 2020;9:873. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030873
14. Kraus DR, Seligman DA, Jordan JR. Validation of a behavioral health treatment outcome and assessment tool designed for naturalistic settings: the Treatment Outcome Package. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61:285‐314. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20084
15. Boothroyd L, Dagnan D, Muncer S. Psychometric analysis of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale and the Patient Health Questionnaire using Mokken scaling and confirmatory factor analysis. Health Prim Care. 2018;2:1-4. doi: 10.15761/HPC.1000145
16. Locke BD, Buzolitz JS, Lei PW, et al. Development of the Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms-62 (CCAPS-62). J Couns Psychol. 2011;58:97-109. doi: 10.1037/a0021282
17. Kraus DR, Boswell JF, Wright AGC, et al. Factor structure of the treatment outcome package for children. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66:627-640. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20675
18. McAleavey AA, Nordberg SS, Kraus D, et al. Errors in treatment outcome monitoring: implications for real-world psychotherapy. Can Psychol. 2010;53:105-114. doi: 10.1037/a0027833
19. Baxter EE, Alexander PC, Kraus DR, et al. Concurrent validation of the Treatment Outcome Package (TOP) for children and adolescents. J Child Fam Stud. 2016;25:2415-2422. doi: 10.1007/s10826-016-0419-4
20. Gual-Montolio P, Martínez-Borba V, Bretón-López JM, et al. How are information and communication technologies supporting routine outcome monitoring and measurement-based care in psychotherapy? A systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:3170. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093170
21. Kraus DR, Bentley JH, Alexander PC, et al. Predicting therapist effectiveness from their own practice-based evidence. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84:473‐483. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000083
22. Constantino MJ, Boswell JF, Coyne AE, et al. Effect of matching therapists to patients vs assignment as usual on adult psychotherapy outcomes. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:960-969. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.1221
23. Constantino MJ, Boswell JF, Kraus DR, et al. Matching patients with therapists to improve mental health care. Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. www.pcori.org/research-results/2015/matching-patients-therapists-improve-mental-health-care
24. Institute of Medicine. Committee on Crossing the Quality Chasm: Adaptation to Mental Health and Addictive Disorders. Improving the Quality of Health Care for Mental and Substance-Use Conditions. National Academies Press; 2006. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/11470/chapter/1
25. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Oswald JM, et al. A multimethod study of mental health care patients’ attitudes toward clinician-level performance information. Psychiatr Serv. 2021;72:452-456. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.202000366
26. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Oswald JM, et al. Mental health care consumers’ relative valuing of clinician performance information. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2018;86:301‐308. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000264
1. HHS. 2021 National Survey of Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) Releases. Accessed March 29, 2023. www.samhsa.gov/data/release/2021-national-survey-drug-use-and-health-nsduh-releases
2. Barkham M, Lambert, MJ. The efficacy and effectiveness of psychological therapies. In: Barkham M, Lutz W, Castonguay LG, eds. Bergin and Garfield’s Handbook of Psychotherapy and Behavior Change: 50th Anniversary Edition. 7th ed. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2021:135-189.
3. Lewis CC, Boyd M, Puspitasari A, et al. Implementing measurement-based care in behavioral health: a review. JAMA Psychiatry. 2019;76:324-335. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2018.3329
4. de Jong K, Conijn JM, Gallagher RAV, et al. Using progress feedback to improve outcomes and reduce drop-out, treatment duration, and deterioration: a multilevel meta-analysis. Clin Psychol Rev. 2021;85:102002. doi: 10.1016/j.cpr.2021.102002
5. Carlier IVE, Meuldijk D, Van Vliet IM, et al. Routine outcome monitoring and feedback on physical or mental health status: evidence and theory. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012;18:104-110. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2753.2010.01543.x
6. Muir HJ, Coyne AE, Morrison NR, et al. Ethical implications of routine outcomes monitoring for patients, psychotherapists, and mental health care systems. Psychotherapy (Chic). 2019;56:459-469. doi: 10.1037/pst0000246
7. Hannan C, Lambert MJ, Harmon C, et al. A lab test and algorithms for identifying clients at risk for treatment failure. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61:155-163. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20108
8. Castonguay LG, Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, et al. Training implications of harmful effects of psychological treatments. Am Psychol. 2010;65:34-49. doi: 10.1037/a0017330
9. Kraus DR, Castonguay LG, Boswell JF, et al. Therapist effectiveness: implications for accountability and patient care. Psychother Res. 2011;21:267-276. doi: 10.1080/10503307.2011.563249
10. Lilienfeld SO. Psychological treatments that cause harm. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2007;2:53-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-6916.2007.00029.x
11. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Kraus DR, et al. The expanding relevance of routinely collected outcome data for mental health care decision making. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43:482-491. doi: 10.1007/s10488-015-0649-6
12. Lyon AR, Lewis CC, Boyd MR, et al. Capabilities and characteristics of digital measurement feedback systems: results from a comprehensive review. Adm Policy Ment Health. 2016;43:441-466. doi: 10.1007/s10488-016-0719-4
13. Teymoori A, Gorbunova A, Haghish FE, et al. Factorial structure and validity of depression (PHQ-9) and anxiety (GAD-7) scales after traumatic brain injury. J Clin Med. 2020;9:873. doi: 10.3390/jcm9030873
14. Kraus DR, Seligman DA, Jordan JR. Validation of a behavioral health treatment outcome and assessment tool designed for naturalistic settings: the Treatment Outcome Package. J Clin Psychol. 2005;61:285‐314. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20084
15. Boothroyd L, Dagnan D, Muncer S. Psychometric analysis of the Generalized Anxiety Disorder Scale and the Patient Health Questionnaire using Mokken scaling and confirmatory factor analysis. Health Prim Care. 2018;2:1-4. doi: 10.15761/HPC.1000145
16. Locke BD, Buzolitz JS, Lei PW, et al. Development of the Counseling Center Assessment of Psychological Symptoms-62 (CCAPS-62). J Couns Psychol. 2011;58:97-109. doi: 10.1037/a0021282
17. Kraus DR, Boswell JF, Wright AGC, et al. Factor structure of the treatment outcome package for children. J Clin Psychol. 2010;66:627-640. doi: 10.1002/jclp.20675
18. McAleavey AA, Nordberg SS, Kraus D, et al. Errors in treatment outcome monitoring: implications for real-world psychotherapy. Can Psychol. 2010;53:105-114. doi: 10.1037/a0027833
19. Baxter EE, Alexander PC, Kraus DR, et al. Concurrent validation of the Treatment Outcome Package (TOP) for children and adolescents. J Child Fam Stud. 2016;25:2415-2422. doi: 10.1007/s10826-016-0419-4
20. Gual-Montolio P, Martínez-Borba V, Bretón-López JM, et al. How are information and communication technologies supporting routine outcome monitoring and measurement-based care in psychotherapy? A systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17:3170. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093170
21. Kraus DR, Bentley JH, Alexander PC, et al. Predicting therapist effectiveness from their own practice-based evidence. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84:473‐483. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000083
22. Constantino MJ, Boswell JF, Coyne AE, et al. Effect of matching therapists to patients vs assignment as usual on adult psychotherapy outcomes. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2021;78:960-969. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2021.1221
23. Constantino MJ, Boswell JF, Kraus DR, et al. Matching patients with therapists to improve mental health care. Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI). 2021. Accessed March 1, 2023. www.pcori.org/research-results/2015/matching-patients-therapists-improve-mental-health-care
24. Institute of Medicine. Committee on Crossing the Quality Chasm: Adaptation to Mental Health and Addictive Disorders. Improving the Quality of Health Care for Mental and Substance-Use Conditions. National Academies Press; 2006. Accessed February 21, 2023. https://nap.nationalacademies.org/read/11470/chapter/1
25. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Oswald JM, et al. A multimethod study of mental health care patients’ attitudes toward clinician-level performance information. Psychiatr Serv. 2021;72:452-456. doi: 10.1176/appi.ps.202000366
26. Boswell JF, Constantino MJ, Oswald JM, et al. Mental health care consumers’ relative valuing of clinician performance information. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2018;86:301‐308. doi: 10.1037/ccp0000264
Which treatments help women with reduced libido?
SEVERAL TREATMENTS produce modest, but statistically significant, clinical increases in sexual desire and function in women.
The testosterone transdermal patch improves hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in postmenopausal women (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, 2 randomized controlled trials [RCTs]).
Bupropion may be effective for HSDD in premenopausal women (SOR: B, 2 RCTs).
Sildenafil improves HSDD associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) (SOR: B, 1 RCT).
Evidence Summary
Two RCTs examined the effect of testosterone on postmenopausal women with HSDD. One trial randomized 272 women ages 40 to 70 years to a 300-mcg transdermal testosterone patch (TTP; 142 women) or placebo (130 women).1 At 6 months, women using the TTP reported more sexually satisfying episodes (1.69 vs 0.59 episodes in 4 weeks; P=.0089) and a minimal increase in sexual desire scores (12.2 vs 4.56 on a 100-point sexual desire scale; P=.0007) compared with women using placebo.
A second trial randomized 814 postmenopausal women (mean age 54.2 years) to placebo (277 women), a 150-mcg TTP (267 women), or a 300-mcg TTP (270 women).2 At 24 weeks, women taking 300 mcg (but not 150 mcg) of testosterone reported a greater number of satisfying sexual episodes than women taking placebo (2.1 vs 0.7; P<.0001). The 300-mcg TTP caused more unwanted hair growth than placebo (19.9% vs 10.5%; no P value given). The study didn’t continue long enough to assess cardiovascular risks.
Bupropion may improve sexual function in premenopausal women
Two RCTs found benefit from bupropion for premenopausal women with HSDD. In the first, investigators randomized 232 women 20 to 40 years of age to bupropion sustained release (SR) 150 mg daily or placebo. They assessed sexual function at 12 weeks with the Brief Index of Sexual Functioning for Women—a scale with scores ranging from -16 (poor functioning) to +75 (maximum functioning), with a mean value in normal women of 33.6.3 Women taking bupropion reported greater increases in scores than women taking placebo (15.8 to 33.9, vs 15.5 to 16.9; P=.001) and no serious adverse events.
A second RCT randomized 66 premenopausal women (mean age 36.1 years) to take either bupropion SR 150 mg daily, increased to 300 mg daily after one week, or placebo.4 Researchers measured sexual responsiveness (arousal, pleasure, and orgasm) using the Change in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire at baseline and on Days 28, 56, 84, and 112. Women taking bupropion had higher scores by Day 28 than women taking placebo and maintained the difference through Day 112 (P=.05). The authors indicated that the clinical significance of the change is unclear.
Sildenafil increases low sexual desire associated with antidepressants
A double-blind RCT enrolling 98 premenopausal women (mean age 36.7 years) with sexual dysfunction related to SSRIs found that sildenafil (50-100 mg) improved sexual functioning more than placebo using the 7-point Clinical Global Impression score (sildenafil: 1.9 points; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-2.3; placebo: 1.1 points; 95% CI, 0.8-1.5; P=.001).5
The investigators didn’t specify whether the change was clinically significant. However, another RCT that studied 881 pre- and postmenopausal women with HSDD unassociated with SSRIs found no difference between sildenafil (10-100 mg) and placebo.6
Recommendations
The US Food and Drug Administration doesn’t recommend androgens for female sexual dysfunction.
The Endocrine Society says that bupropion may be used for HSDD (although it isn’t licensed for such use) and doesn’t recommend long-term use of testosterone because of inadequate safety studies.7
The North American Menopause Society recommends testosterone therapy for postmenopausal women with HSDD.8
1. Panay N, Al-Azzawi F, Bouchard C, et al. Testosterone treatment of HSDD in naturally menopausal women: the ADORE study. Climacteric. 2010;13:121-131.
2. Davis SR, Moreau M, et al. Testosterone for low libido in women not taking estrogen. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2005-2017.
3. Safarinejad MR, Hosseini SY, Asgari MA, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of bupropion for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in ovulating women. BJU Int. 2010;106:832-839.
4. Segraves RT, Clayton A, Croft H, et al. Buproprion sustained release for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire in premenopausal women. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24:339-342.
5. Nurnberg HG, Hensley PL, Heiman JR, et al. Sildenafil treatment of women with antidepressant-associated sexual dysfunction. JAMA. 2008;300:395-404.
6. Basson R, McInnes R, Smith MD, et al. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil citrate in women with sexual dysfunction associated with female sexual arousal disorder. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2002;11:367-377.
7. Wierman M, Basson R, Davis SR, et al. Androgen therapy in women: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3697-3710.
8. Braunstein GD. The Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline and The North American Menopause Society position statement on androgen therapy in women: another one of Yogi’s forks. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4091-4093.
SEVERAL TREATMENTS produce modest, but statistically significant, clinical increases in sexual desire and function in women.
The testosterone transdermal patch improves hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in postmenopausal women (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, 2 randomized controlled trials [RCTs]).
Bupropion may be effective for HSDD in premenopausal women (SOR: B, 2 RCTs).
Sildenafil improves HSDD associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) (SOR: B, 1 RCT).
Evidence Summary
Two RCTs examined the effect of testosterone on postmenopausal women with HSDD. One trial randomized 272 women ages 40 to 70 years to a 300-mcg transdermal testosterone patch (TTP; 142 women) or placebo (130 women).1 At 6 months, women using the TTP reported more sexually satisfying episodes (1.69 vs 0.59 episodes in 4 weeks; P=.0089) and a minimal increase in sexual desire scores (12.2 vs 4.56 on a 100-point sexual desire scale; P=.0007) compared with women using placebo.
A second trial randomized 814 postmenopausal women (mean age 54.2 years) to placebo (277 women), a 150-mcg TTP (267 women), or a 300-mcg TTP (270 women).2 At 24 weeks, women taking 300 mcg (but not 150 mcg) of testosterone reported a greater number of satisfying sexual episodes than women taking placebo (2.1 vs 0.7; P<.0001). The 300-mcg TTP caused more unwanted hair growth than placebo (19.9% vs 10.5%; no P value given). The study didn’t continue long enough to assess cardiovascular risks.
Bupropion may improve sexual function in premenopausal women
Two RCTs found benefit from bupropion for premenopausal women with HSDD. In the first, investigators randomized 232 women 20 to 40 years of age to bupropion sustained release (SR) 150 mg daily or placebo. They assessed sexual function at 12 weeks with the Brief Index of Sexual Functioning for Women—a scale with scores ranging from -16 (poor functioning) to +75 (maximum functioning), with a mean value in normal women of 33.6.3 Women taking bupropion reported greater increases in scores than women taking placebo (15.8 to 33.9, vs 15.5 to 16.9; P=.001) and no serious adverse events.
A second RCT randomized 66 premenopausal women (mean age 36.1 years) to take either bupropion SR 150 mg daily, increased to 300 mg daily after one week, or placebo.4 Researchers measured sexual responsiveness (arousal, pleasure, and orgasm) using the Change in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire at baseline and on Days 28, 56, 84, and 112. Women taking bupropion had higher scores by Day 28 than women taking placebo and maintained the difference through Day 112 (P=.05). The authors indicated that the clinical significance of the change is unclear.
Sildenafil increases low sexual desire associated with antidepressants
A double-blind RCT enrolling 98 premenopausal women (mean age 36.7 years) with sexual dysfunction related to SSRIs found that sildenafil (50-100 mg) improved sexual functioning more than placebo using the 7-point Clinical Global Impression score (sildenafil: 1.9 points; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-2.3; placebo: 1.1 points; 95% CI, 0.8-1.5; P=.001).5
The investigators didn’t specify whether the change was clinically significant. However, another RCT that studied 881 pre- and postmenopausal women with HSDD unassociated with SSRIs found no difference between sildenafil (10-100 mg) and placebo.6
Recommendations
The US Food and Drug Administration doesn’t recommend androgens for female sexual dysfunction.
The Endocrine Society says that bupropion may be used for HSDD (although it isn’t licensed for such use) and doesn’t recommend long-term use of testosterone because of inadequate safety studies.7
The North American Menopause Society recommends testosterone therapy for postmenopausal women with HSDD.8
SEVERAL TREATMENTS produce modest, but statistically significant, clinical increases in sexual desire and function in women.
The testosterone transdermal patch improves hypoactive sexual desire disorder (HSDD) in postmenopausal women (strength of recommendation [SOR]: A, 2 randomized controlled trials [RCTs]).
Bupropion may be effective for HSDD in premenopausal women (SOR: B, 2 RCTs).
Sildenafil improves HSDD associated with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) (SOR: B, 1 RCT).
Evidence Summary
Two RCTs examined the effect of testosterone on postmenopausal women with HSDD. One trial randomized 272 women ages 40 to 70 years to a 300-mcg transdermal testosterone patch (TTP; 142 women) or placebo (130 women).1 At 6 months, women using the TTP reported more sexually satisfying episodes (1.69 vs 0.59 episodes in 4 weeks; P=.0089) and a minimal increase in sexual desire scores (12.2 vs 4.56 on a 100-point sexual desire scale; P=.0007) compared with women using placebo.
A second trial randomized 814 postmenopausal women (mean age 54.2 years) to placebo (277 women), a 150-mcg TTP (267 women), or a 300-mcg TTP (270 women).2 At 24 weeks, women taking 300 mcg (but not 150 mcg) of testosterone reported a greater number of satisfying sexual episodes than women taking placebo (2.1 vs 0.7; P<.0001). The 300-mcg TTP caused more unwanted hair growth than placebo (19.9% vs 10.5%; no P value given). The study didn’t continue long enough to assess cardiovascular risks.
Bupropion may improve sexual function in premenopausal women
Two RCTs found benefit from bupropion for premenopausal women with HSDD. In the first, investigators randomized 232 women 20 to 40 years of age to bupropion sustained release (SR) 150 mg daily or placebo. They assessed sexual function at 12 weeks with the Brief Index of Sexual Functioning for Women—a scale with scores ranging from -16 (poor functioning) to +75 (maximum functioning), with a mean value in normal women of 33.6.3 Women taking bupropion reported greater increases in scores than women taking placebo (15.8 to 33.9, vs 15.5 to 16.9; P=.001) and no serious adverse events.
A second RCT randomized 66 premenopausal women (mean age 36.1 years) to take either bupropion SR 150 mg daily, increased to 300 mg daily after one week, or placebo.4 Researchers measured sexual responsiveness (arousal, pleasure, and orgasm) using the Change in Sexual Functioning Questionnaire at baseline and on Days 28, 56, 84, and 112. Women taking bupropion had higher scores by Day 28 than women taking placebo and maintained the difference through Day 112 (P=.05). The authors indicated that the clinical significance of the change is unclear.
Sildenafil increases low sexual desire associated with antidepressants
A double-blind RCT enrolling 98 premenopausal women (mean age 36.7 years) with sexual dysfunction related to SSRIs found that sildenafil (50-100 mg) improved sexual functioning more than placebo using the 7-point Clinical Global Impression score (sildenafil: 1.9 points; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-2.3; placebo: 1.1 points; 95% CI, 0.8-1.5; P=.001).5
The investigators didn’t specify whether the change was clinically significant. However, another RCT that studied 881 pre- and postmenopausal women with HSDD unassociated with SSRIs found no difference between sildenafil (10-100 mg) and placebo.6
Recommendations
The US Food and Drug Administration doesn’t recommend androgens for female sexual dysfunction.
The Endocrine Society says that bupropion may be used for HSDD (although it isn’t licensed for such use) and doesn’t recommend long-term use of testosterone because of inadequate safety studies.7
The North American Menopause Society recommends testosterone therapy for postmenopausal women with HSDD.8
1. Panay N, Al-Azzawi F, Bouchard C, et al. Testosterone treatment of HSDD in naturally menopausal women: the ADORE study. Climacteric. 2010;13:121-131.
2. Davis SR, Moreau M, et al. Testosterone for low libido in women not taking estrogen. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2005-2017.
3. Safarinejad MR, Hosseini SY, Asgari MA, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of bupropion for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in ovulating women. BJU Int. 2010;106:832-839.
4. Segraves RT, Clayton A, Croft H, et al. Buproprion sustained release for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire in premenopausal women. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24:339-342.
5. Nurnberg HG, Hensley PL, Heiman JR, et al. Sildenafil treatment of women with antidepressant-associated sexual dysfunction. JAMA. 2008;300:395-404.
6. Basson R, McInnes R, Smith MD, et al. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil citrate in women with sexual dysfunction associated with female sexual arousal disorder. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2002;11:367-377.
7. Wierman M, Basson R, Davis SR, et al. Androgen therapy in women: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3697-3710.
8. Braunstein GD. The Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline and The North American Menopause Society position statement on androgen therapy in women: another one of Yogi’s forks. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4091-4093.
1. Panay N, Al-Azzawi F, Bouchard C, et al. Testosterone treatment of HSDD in naturally menopausal women: the ADORE study. Climacteric. 2010;13:121-131.
2. Davis SR, Moreau M, et al. Testosterone for low libido in women not taking estrogen. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:2005-2017.
3. Safarinejad MR, Hosseini SY, Asgari MA, et al. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the efficacy and safety of bupropion for treating hypoactive sexual desire disorder in ovulating women. BJU Int. 2010;106:832-839.
4. Segraves RT, Clayton A, Croft H, et al. Buproprion sustained release for the treatment of hypoactive sexual desire in premenopausal women. J Clin Psychopharmacol. 2004;24:339-342.
5. Nurnberg HG, Hensley PL, Heiman JR, et al. Sildenafil treatment of women with antidepressant-associated sexual dysfunction. JAMA. 2008;300:395-404.
6. Basson R, McInnes R, Smith MD, et al. Efficacy and safety of sildenafil citrate in women with sexual dysfunction associated with female sexual arousal disorder. J Womens Health Gend Based Med. 2002;11:367-377.
7. Wierman M, Basson R, Davis SR, et al. Androgen therapy in women: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2006;91:3697-3710.
8. Braunstein GD. The Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline and The North American Menopause Society position statement on androgen therapy in women: another one of Yogi’s forks. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:4091-4093.
Evidence-based answers from the Family Physicians Inquiries Network
Consider adding this drug to fight COPD that’s severe
Consider prescribing daily azithromycin for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and a history of exacerbations—but do a careful risk-benefit analysis first.1
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
B: Based on one well-designed double-blind, randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Albert RK, Connett J, Bailey WC, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:689-698.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 65-year-old man with a history of moderate to severe COPD schedules an appointment soon after discharge from the hospital—his second hospitalization for COPD exacerbations in 4 months. The patient uses inhaled glucocorticoids, a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), and a long-acting anticholinergic. Should you add a macrolide to his medication regimen?
Acute exacerbations of COPD—the third highest cause of death in the United States2—have a major effect on quality of life, often resulting in repeat trips to the emergency department (ED) and numerous hospitalizations, office visits, and days lost from work. According to a new study that used 2006 data, there were 1.25 million hospitalizations for COPD exacerbations that year, with health care costs of $11.9 billion.3 Preventing exacerbations and the associated morbidity and mortality is a major challenge that primary care physicians face.
Can a macrolide help?
Corticosteroids, long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs), and the anticholinergic tiotropium are known to reduce COPD exacerbations,4,5 but what about antibiotics? A Cochrane meta-analysis of 9 RCTs that assessed antibiotic use for COPD found that it did not decrease the number of exacerbations. Notably, however, macrolides were not used in any of the studies.6
Macrolides are known to have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory properties that reduce pulmonary exacerbations in other chronic lung diseases. A recent meta-analysis found that patients with cystic fibrosis have fewer pulmonary exacerbations when they take azithromycin 3 times a week.7
Small studies of the effect of macrolides on the frequency of COPD exacerbations have had conflicting results.8,9 The larger study detailed here evaluated the ability of daily azithromycin therapy to reduce COPD exacerbations.
STUDY SUMMARY: Daily dose led to fewer exacerbations
This double-blind RCT included close to 1150 participants from 12 US academic health centers, randomly assigned to receive azithromycin 250 mg daily or placebo, in addition to their usual care. (About 10% of patients in both groups died, withdrew, or were lost to follow-up.)
To be included, patients had to be ≥40 years old and have a clinical diagnosis of COPD, defined as a smoking history of 10 pack-years or more, a decreased forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC) ratio, and a decreased FEV1 after bronchodilation. In addition, participants had to be on long-term oxygen or have used systemic steroids within the previous year or have had an ED visit or hospital admission for COPD during that time frame. Exclusion criteria included a history of asthma, a resting heart rate >100 beats per minute, a prolonged corrected QT interval (QTc) on electrocardiogram or the use of a medication that might prolong QTc, and a documented hearing impairment.
At baseline, participants were similar in basic demographics, COPD severity, smoking history, and medication use: 49% of those in the azithromycin group and 46% of the placebo group were taking a combination of inhaled corticosteroids, LABAs, and a long-acting anticholinergic medication.
The primary outcome was the time to the first COPD exacerbation. This was defined as ≥3 days with 2 or more COPD symptoms—new onset or worsening cough, dyspnea, sputum production, chest tightness, or wheezing—for which antibiotics or steroids were required. Secondary outcomes were quality-of-life measurements on the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) and the Medical Outcomes 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36). Nasopharyngeal swabs were done every 3 months to check for colonization and resistance. Hearing was assessed with audiometry at the time of enrollment, and again at 3 and 12 months. All patients were followed for a year, with monthly telephone calls or clinic visits, to determine if an exacerbation had occurred in the previous month.
The median time to the first exacerbation in the azithromycin group was 266 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 227-313) vs 174 days (95% CI, 143-215) in the placebo group; P<.001. Frequency of acute exacerbations was 1.48 per patient-year for the azithromycin group compared with 1.83 for the placebo group (relative risk=0.83; 95% CI, 0.72–0.95; P=.01). The number needed to treat to prevent one acute exacerbation in a one-year period was 2.86.
There was no significant difference in the SGRQ and SF-36 scores for the azithromycin vs the placebo group. There was a small reduction in unscheduled office visits (0.11 per patient-year; P=.048) in the azithromycin group, and a decrease in hospitalization that was not statistically significant.
Azithromycin group had higher rates of adverse effects
Nasopharyngeal cultures from participants who became colonized during the course of the study found macrolide resistance in 81% of those in the azithromycin group vs 41% of the placebo group (P<.001). Twenty-five percent of patients in the azithromycin group developed measurable hearing loss, compared with 20% of those on placebo (P=0.04; number needed to harm=20).
WHAT’S NEW?: A better understanding of benefits and risks
This study shows that the addition of azithromycin (250 mg/d) to standard COPD treatment decreases the number of exacerbations, but does little to reduce hospital admissions. It also highlights the adverse effect profile of azithromycin and the importance of using the antibiotic only for carefully selected patients.
CAVEATS: Macrolide resistance is a key concern
Twenty-five percent of the azithromycin group had documented hearing loss—an additional one in 20 compared with patients in the placebo group. More importantly, there was an increase in the prevalence of macrolide-resistant respiratory pathogens in patients on daily azithromycin. The long-term impact of daily azithromycin on antibiotic resistance is unknown, both for patients themselves and the community at large.
Physicians will have to assess the benefit of a decrease in COPD exacerbations (approximately one every 3 years) vs the risk of an increase in hearing problems and macrolide resistance. A sensible approach would be to reserve daily use of azithromycin for patients with a history of multiple exacerbations, who potentially have more to gain.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION: There are none
There are no major challenges to implementation aside from the cost, which would be approximately $1200 per year (azithromycin 250 mg [30 tablets] at $98.99 per month).10
Acknowledgement
The PURLs Surveillance System is supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. Albert RK, Connett J, Bailey WC, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:689-698.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Injury prevention & control: data & statistics. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/injury/wisqars/LeadingCauses.html. Accessed April 16, 2012.
3. Perera PN, Armstrong EP, Sherrill DL, et al. Acute exacerbations of COPD in the United States: inpatient burden and predictors of cost and mortality. COPD. 2012;9:131-141.
4. Jenkins CR, Jones PW, Calverley PM, et al. Efficacy of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate by GOLD stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: analysis from the randomised, placebo-controlled TORCH study. Respir Res. 2009;10:59.-
5. Decramer M, Celli B, Kesten S, et al. Effect of tiotropium on outcomes in patients with moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (UPLIFT); a prespecified subgroup analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1171-1178.
6. Black PN, Staykova T, Chacko EE, et al. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for chronic bronchitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD004105.-
7. Southern KW, Barker PM, Solis-Moya A, et al. Macrolide antibiotics for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(12):CD002203.-
8. Seemungal TA, Wilkinson TM, Hurst JR, et al. Long-term erythromycin therapy is associated with decreased chronic obstructive pulmonary exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:1139-1147.
9. Yamaya A, Azuma A, Tanaka H, et al. Inhibitory effects of macrolides on exacerbations and hospitalization in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Japan: a retrospective multicenter analysis. J Am Geriatri Soc. 2008;56:1358-1360.
10. www.Drugstore.com. Accessed March 28, 2012.
Consider prescribing daily azithromycin for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and a history of exacerbations—but do a careful risk-benefit analysis first.1
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
B: Based on one well-designed double-blind, randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Albert RK, Connett J, Bailey WC, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:689-698.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 65-year-old man with a history of moderate to severe COPD schedules an appointment soon after discharge from the hospital—his second hospitalization for COPD exacerbations in 4 months. The patient uses inhaled glucocorticoids, a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), and a long-acting anticholinergic. Should you add a macrolide to his medication regimen?
Acute exacerbations of COPD—the third highest cause of death in the United States2—have a major effect on quality of life, often resulting in repeat trips to the emergency department (ED) and numerous hospitalizations, office visits, and days lost from work. According to a new study that used 2006 data, there were 1.25 million hospitalizations for COPD exacerbations that year, with health care costs of $11.9 billion.3 Preventing exacerbations and the associated morbidity and mortality is a major challenge that primary care physicians face.
Can a macrolide help?
Corticosteroids, long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs), and the anticholinergic tiotropium are known to reduce COPD exacerbations,4,5 but what about antibiotics? A Cochrane meta-analysis of 9 RCTs that assessed antibiotic use for COPD found that it did not decrease the number of exacerbations. Notably, however, macrolides were not used in any of the studies.6
Macrolides are known to have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory properties that reduce pulmonary exacerbations in other chronic lung diseases. A recent meta-analysis found that patients with cystic fibrosis have fewer pulmonary exacerbations when they take azithromycin 3 times a week.7
Small studies of the effect of macrolides on the frequency of COPD exacerbations have had conflicting results.8,9 The larger study detailed here evaluated the ability of daily azithromycin therapy to reduce COPD exacerbations.
STUDY SUMMARY: Daily dose led to fewer exacerbations
This double-blind RCT included close to 1150 participants from 12 US academic health centers, randomly assigned to receive azithromycin 250 mg daily or placebo, in addition to their usual care. (About 10% of patients in both groups died, withdrew, or were lost to follow-up.)
To be included, patients had to be ≥40 years old and have a clinical diagnosis of COPD, defined as a smoking history of 10 pack-years or more, a decreased forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC) ratio, and a decreased FEV1 after bronchodilation. In addition, participants had to be on long-term oxygen or have used systemic steroids within the previous year or have had an ED visit or hospital admission for COPD during that time frame. Exclusion criteria included a history of asthma, a resting heart rate >100 beats per minute, a prolonged corrected QT interval (QTc) on electrocardiogram or the use of a medication that might prolong QTc, and a documented hearing impairment.
At baseline, participants were similar in basic demographics, COPD severity, smoking history, and medication use: 49% of those in the azithromycin group and 46% of the placebo group were taking a combination of inhaled corticosteroids, LABAs, and a long-acting anticholinergic medication.
The primary outcome was the time to the first COPD exacerbation. This was defined as ≥3 days with 2 or more COPD symptoms—new onset or worsening cough, dyspnea, sputum production, chest tightness, or wheezing—for which antibiotics or steroids were required. Secondary outcomes were quality-of-life measurements on the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) and the Medical Outcomes 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36). Nasopharyngeal swabs were done every 3 months to check for colonization and resistance. Hearing was assessed with audiometry at the time of enrollment, and again at 3 and 12 months. All patients were followed for a year, with monthly telephone calls or clinic visits, to determine if an exacerbation had occurred in the previous month.
The median time to the first exacerbation in the azithromycin group was 266 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 227-313) vs 174 days (95% CI, 143-215) in the placebo group; P<.001. Frequency of acute exacerbations was 1.48 per patient-year for the azithromycin group compared with 1.83 for the placebo group (relative risk=0.83; 95% CI, 0.72–0.95; P=.01). The number needed to treat to prevent one acute exacerbation in a one-year period was 2.86.
There was no significant difference in the SGRQ and SF-36 scores for the azithromycin vs the placebo group. There was a small reduction in unscheduled office visits (0.11 per patient-year; P=.048) in the azithromycin group, and a decrease in hospitalization that was not statistically significant.
Azithromycin group had higher rates of adverse effects
Nasopharyngeal cultures from participants who became colonized during the course of the study found macrolide resistance in 81% of those in the azithromycin group vs 41% of the placebo group (P<.001). Twenty-five percent of patients in the azithromycin group developed measurable hearing loss, compared with 20% of those on placebo (P=0.04; number needed to harm=20).
WHAT’S NEW?: A better understanding of benefits and risks
This study shows that the addition of azithromycin (250 mg/d) to standard COPD treatment decreases the number of exacerbations, but does little to reduce hospital admissions. It also highlights the adverse effect profile of azithromycin and the importance of using the antibiotic only for carefully selected patients.
CAVEATS: Macrolide resistance is a key concern
Twenty-five percent of the azithromycin group had documented hearing loss—an additional one in 20 compared with patients in the placebo group. More importantly, there was an increase in the prevalence of macrolide-resistant respiratory pathogens in patients on daily azithromycin. The long-term impact of daily azithromycin on antibiotic resistance is unknown, both for patients themselves and the community at large.
Physicians will have to assess the benefit of a decrease in COPD exacerbations (approximately one every 3 years) vs the risk of an increase in hearing problems and macrolide resistance. A sensible approach would be to reserve daily use of azithromycin for patients with a history of multiple exacerbations, who potentially have more to gain.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION: There are none
There are no major challenges to implementation aside from the cost, which would be approximately $1200 per year (azithromycin 250 mg [30 tablets] at $98.99 per month).10
Acknowledgement
The PURLs Surveillance System is supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
Consider prescribing daily azithromycin for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and a history of exacerbations—but do a careful risk-benefit analysis first.1
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
B: Based on one well-designed double-blind, randomized controlled trial (RCT).
Albert RK, Connett J, Bailey WC, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:689-698.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 65-year-old man with a history of moderate to severe COPD schedules an appointment soon after discharge from the hospital—his second hospitalization for COPD exacerbations in 4 months. The patient uses inhaled glucocorticoids, a long-acting beta-agonist (LABA), and a long-acting anticholinergic. Should you add a macrolide to his medication regimen?
Acute exacerbations of COPD—the third highest cause of death in the United States2—have a major effect on quality of life, often resulting in repeat trips to the emergency department (ED) and numerous hospitalizations, office visits, and days lost from work. According to a new study that used 2006 data, there were 1.25 million hospitalizations for COPD exacerbations that year, with health care costs of $11.9 billion.3 Preventing exacerbations and the associated morbidity and mortality is a major challenge that primary care physicians face.
Can a macrolide help?
Corticosteroids, long-acting beta-agonists (LABAs), and the anticholinergic tiotropium are known to reduce COPD exacerbations,4,5 but what about antibiotics? A Cochrane meta-analysis of 9 RCTs that assessed antibiotic use for COPD found that it did not decrease the number of exacerbations. Notably, however, macrolides were not used in any of the studies.6
Macrolides are known to have anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and immunomodulatory properties that reduce pulmonary exacerbations in other chronic lung diseases. A recent meta-analysis found that patients with cystic fibrosis have fewer pulmonary exacerbations when they take azithromycin 3 times a week.7
Small studies of the effect of macrolides on the frequency of COPD exacerbations have had conflicting results.8,9 The larger study detailed here evaluated the ability of daily azithromycin therapy to reduce COPD exacerbations.
STUDY SUMMARY: Daily dose led to fewer exacerbations
This double-blind RCT included close to 1150 participants from 12 US academic health centers, randomly assigned to receive azithromycin 250 mg daily or placebo, in addition to their usual care. (About 10% of patients in both groups died, withdrew, or were lost to follow-up.)
To be included, patients had to be ≥40 years old and have a clinical diagnosis of COPD, defined as a smoking history of 10 pack-years or more, a decreased forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC) ratio, and a decreased FEV1 after bronchodilation. In addition, participants had to be on long-term oxygen or have used systemic steroids within the previous year or have had an ED visit or hospital admission for COPD during that time frame. Exclusion criteria included a history of asthma, a resting heart rate >100 beats per minute, a prolonged corrected QT interval (QTc) on electrocardiogram or the use of a medication that might prolong QTc, and a documented hearing impairment.
At baseline, participants were similar in basic demographics, COPD severity, smoking history, and medication use: 49% of those in the azithromycin group and 46% of the placebo group were taking a combination of inhaled corticosteroids, LABAs, and a long-acting anticholinergic medication.
The primary outcome was the time to the first COPD exacerbation. This was defined as ≥3 days with 2 or more COPD symptoms—new onset or worsening cough, dyspnea, sputum production, chest tightness, or wheezing—for which antibiotics or steroids were required. Secondary outcomes were quality-of-life measurements on the St. George’s Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) and the Medical Outcomes 36-item Short Form Health Survey (SF-36). Nasopharyngeal swabs were done every 3 months to check for colonization and resistance. Hearing was assessed with audiometry at the time of enrollment, and again at 3 and 12 months. All patients were followed for a year, with monthly telephone calls or clinic visits, to determine if an exacerbation had occurred in the previous month.
The median time to the first exacerbation in the azithromycin group was 266 days (95% confidence interval [CI], 227-313) vs 174 days (95% CI, 143-215) in the placebo group; P<.001. Frequency of acute exacerbations was 1.48 per patient-year for the azithromycin group compared with 1.83 for the placebo group (relative risk=0.83; 95% CI, 0.72–0.95; P=.01). The number needed to treat to prevent one acute exacerbation in a one-year period was 2.86.
There was no significant difference in the SGRQ and SF-36 scores for the azithromycin vs the placebo group. There was a small reduction in unscheduled office visits (0.11 per patient-year; P=.048) in the azithromycin group, and a decrease in hospitalization that was not statistically significant.
Azithromycin group had higher rates of adverse effects
Nasopharyngeal cultures from participants who became colonized during the course of the study found macrolide resistance in 81% of those in the azithromycin group vs 41% of the placebo group (P<.001). Twenty-five percent of patients in the azithromycin group developed measurable hearing loss, compared with 20% of those on placebo (P=0.04; number needed to harm=20).
WHAT’S NEW?: A better understanding of benefits and risks
This study shows that the addition of azithromycin (250 mg/d) to standard COPD treatment decreases the number of exacerbations, but does little to reduce hospital admissions. It also highlights the adverse effect profile of azithromycin and the importance of using the antibiotic only for carefully selected patients.
CAVEATS: Macrolide resistance is a key concern
Twenty-five percent of the azithromycin group had documented hearing loss—an additional one in 20 compared with patients in the placebo group. More importantly, there was an increase in the prevalence of macrolide-resistant respiratory pathogens in patients on daily azithromycin. The long-term impact of daily azithromycin on antibiotic resistance is unknown, both for patients themselves and the community at large.
Physicians will have to assess the benefit of a decrease in COPD exacerbations (approximately one every 3 years) vs the risk of an increase in hearing problems and macrolide resistance. A sensible approach would be to reserve daily use of azithromycin for patients with a history of multiple exacerbations, who potentially have more to gain.
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION: There are none
There are no major challenges to implementation aside from the cost, which would be approximately $1200 per year (azithromycin 250 mg [30 tablets] at $98.99 per month).10
Acknowledgement
The PURLs Surveillance System is supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center for Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. Albert RK, Connett J, Bailey WC, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:689-698.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Injury prevention & control: data & statistics. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/injury/wisqars/LeadingCauses.html. Accessed April 16, 2012.
3. Perera PN, Armstrong EP, Sherrill DL, et al. Acute exacerbations of COPD in the United States: inpatient burden and predictors of cost and mortality. COPD. 2012;9:131-141.
4. Jenkins CR, Jones PW, Calverley PM, et al. Efficacy of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate by GOLD stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: analysis from the randomised, placebo-controlled TORCH study. Respir Res. 2009;10:59.-
5. Decramer M, Celli B, Kesten S, et al. Effect of tiotropium on outcomes in patients with moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (UPLIFT); a prespecified subgroup analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1171-1178.
6. Black PN, Staykova T, Chacko EE, et al. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for chronic bronchitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD004105.-
7. Southern KW, Barker PM, Solis-Moya A, et al. Macrolide antibiotics for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(12):CD002203.-
8. Seemungal TA, Wilkinson TM, Hurst JR, et al. Long-term erythromycin therapy is associated with decreased chronic obstructive pulmonary exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:1139-1147.
9. Yamaya A, Azuma A, Tanaka H, et al. Inhibitory effects of macrolides on exacerbations and hospitalization in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Japan: a retrospective multicenter analysis. J Am Geriatri Soc. 2008;56:1358-1360.
10. www.Drugstore.com. Accessed March 28, 2012.
1. Albert RK, Connett J, Bailey WC, et al. Azithromycin for prevention of exacerbations of COPD. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:689-698.
2. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Injury prevention & control: data & statistics. Available at: http://www.cdc.gov/injury/wisqars/LeadingCauses.html. Accessed April 16, 2012.
3. Perera PN, Armstrong EP, Sherrill DL, et al. Acute exacerbations of COPD in the United States: inpatient burden and predictors of cost and mortality. COPD. 2012;9:131-141.
4. Jenkins CR, Jones PW, Calverley PM, et al. Efficacy of salmeterol/fluticasone propionate by GOLD stage of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: analysis from the randomised, placebo-controlled TORCH study. Respir Res. 2009;10:59.-
5. Decramer M, Celli B, Kesten S, et al. Effect of tiotropium on outcomes in patients with moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (UPLIFT); a prespecified subgroup analysis of a randomized controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374:1171-1178.
6. Black PN, Staykova T, Chacko EE, et al. Prophylactic antibiotic therapy for chronic bronchitis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2003;(1):CD004105.-
7. Southern KW, Barker PM, Solis-Moya A, et al. Macrolide antibiotics for cystic fibrosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011;(12):CD002203.-
8. Seemungal TA, Wilkinson TM, Hurst JR, et al. Long-term erythromycin therapy is associated with decreased chronic obstructive pulmonary exacerbations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:1139-1147.
9. Yamaya A, Azuma A, Tanaka H, et al. Inhibitory effects of macrolides on exacerbations and hospitalization in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease in Japan: a retrospective multicenter analysis. J Am Geriatri Soc. 2008;56:1358-1360.
10. www.Drugstore.com. Accessed March 28, 2012.
Copyright © 2012 The Family Physicians Inquiries Network. All rights reserved.
