User login
Tender Annular Plaque on the Thigh
The Diagnosis: Ecthyma Gangrenosum
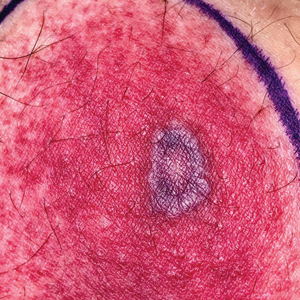
Histopathology revealed basophilic bacterial rods around necrotic vessels with thrombosis and edema (Figure). Blood and tissue cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of P aeruginosa–associated ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) was made. The patient’s symptoms resolved with intravenous cefepime, and he later was transitioned to oral levofloxacin for outpatient treatment.

Ecthyma gangrenosum is an uncommon cutaneous manifestation of bacteremia that most commonly occurs secondary to P aeruginosa in immunocompromised patients, particularly patients with severe neutropenia in the setting of recent chemotherapy.1,2 Ecthyma gangrenosum can occur anywhere on the body, predominantly in moist areas such as the axillae and groin; the arms and legs, such as in our patient, as well as the trunk and face also may be involved.3 Other causes of EG skin lesions include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, fungi such as Candida, and viruses such as herpes simplex virus.2,4-6 Common predisposing conditions associated with EG include neutropenia, leukemia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, extensive burn wounds, and a history of immunosuppressive medications. It also has been known to occur in otherwise healthy, immunocompetent individuals with no difference in clinical manifestation.2
The diagnosis is clinicopathologic, with initial evaluation including blood and wound cultures as well as a complete blood cell count once EG is suspected. An excisional or punch biopsy is performed for confirmation, showing many gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria in cases of pseudomonal EG.7 Histopathology is characterized by bacterial perivascular invasion that then leads to secondary arteriole thrombosis, tissue edema, and separation of the epidermis.7,8 Resultant ischemic necrosis results in the classic macroscopic appearance of an erythematous macule that rapidly progresses into a central necrotic lesion surrounded by an erythematous or violaceous halo after undergoing a hemorrhagic bullous stage.1,9 A Wood lamp can be used to expedite the diagnosis, as Pseudomonas bacteria excretes a pigment (pyoverdine) that fluoresces yellowish green.10
Ecthyma gangrenosum can be classified as a primary skin lesion that may or may not be followed by bacteremia or as a lesion secondary to pseudomonal bacteremia.11 Bacteremia has been reported in half of cases, with hematogenous metastasis of the infection, likely in manifestations with multiple bilateral lesions.2 Our patient’s presentation of a single lesion revealed a positive blood culture result. Lesions also can develop by direct inoculation of the epidermis causing local destruction of the surrounding tissue. The nonbacteremic form of EG has been associated with a lower mortality rate of around 15% compared to patients with bacteremia ranging from 38% to 96%.12 The presence of neutropenia is the most important prognostic factor for mortality at the time of diagnosis.13
Prompt empiric therapy should be initiated after obtaining wound and blood cultures in those with infection until the causative organism and its susceptibility are identified. Pseudomonal infections account for 4% of all cases of hospital-acquired bacteremia and are the third leading cause of gram-negative bloodstream infection.7 Initial broad-spectrum antibiotics include antipseudomonal β-lactams (piperacillin-tazobactam), cephalosporins (cefepime), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), and carbapenems (imipenem).1,7 Medical therapy alone may be sufficient without requiring extensive surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue in some patients. Surgical debridement usually is warranted for lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter.3 Our patient was treated with intravenous cefepime with resolution and was followed with outpatient oral levofloxacin as appropriate. A high index of suspicion should be maintained for relapsing pseudomonal EG infection among patients with AIDS, as the reported recurrence rate is 57%.14
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of EG presenting in immunocompromised patients or individuals with underlying malignancy includes pyoderma gangrenosum, papulonecrotic tuberculid, and leukemia cutis. An erythematous rash with central necrosis presenting in a patient with systemic symptoms is pathognomonic for erythema migrans and should be considered as a diagnostic possibility in areas endemic for Lyme disease in the United States, including the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and north-central regions.15 A thorough history, physical examination, basic laboratory studies, and histopathology are critical to differentiate between these entities with similar macroscopic features. Pyoderma gangrenosum histologically manifests as a noninfectious, deep, suppurative folliculitis with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in 40% of cases.16 Although papulonecrotic tuberculid can present with dermal necrosis resulting from a hypersensitivity reaction to antigenic components of mycobacteria, there typically are granulomatous infiltrates present and a lack of observed organisms on histopathology.17 Although leukemia cutis infrequently occurs in patients diagnosed with leukemia, its salient features on pathology are nodular or diffuse infiltrates of leukemic cells in the dermis and subcutis with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, often with prominent nucleoli.18 Lyme disease can present in various ways; however, cutaneous involvement in the primary lesion is histologically characterized by a perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate containing plasma cells at the periphery of the expanding annular lesion and eosinophils present at the center.19
- Abdou A, Hassam B. Ecthyma gangrenosum [in French]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;30:95. doi:10.11604/pamj.2018.30.95.6244
- Vaiman M, Lazarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum and ecthyma-like lesions: review article. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:633-639. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2277-6
- Vaiman M, Lasarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum versus ecthyma-like lesions: should we separate these conditions? Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:69-72. doi:10.15570 /actaapa.2015.18
- Reich HL, Williams Fadeyi D, Naik NS, et al. Nonpseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl): S114-S117. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.09.019
- Hawkley T, Chang D, Pollard W, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum caused by Citrobacter freundii [published online July 27, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220996
- Santhaseelan RG, Muralidhar V. Non-pseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a chronic alcoholic patient [published online August 3, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220983m
- Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, et al. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections [published online May 29, 2018]. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi:10.7573/dic.212527
- Llamas-Velasco M, Alegría V, Santos-Briz Á, et al. Occlusive nonvasculitic vasculopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:637-662. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000766
- Sarkar S, Patra AK, Mondal M. Ecthyma gangrenosum in the periorbital region in a previously healthy immunocompetent woman without bacteremia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:36-39. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.174326
- Ponka D, Baddar F. Wood lamp examination. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:976.
- Van den Broek PJ, Van der Meer JWM, Kunst MW. The pathogenesis of ecthyma gangrenosum. J Infect. 1979;1:263-267. doi:10.1016 /S0163-4453(79)91329-X
- Downey DM, O’Bryan MC, Burdette SD, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:198-202. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E31802CA481
- Martínez-Longoria CA, Rosales-Solis GM, Ocampo-Garza J, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum: a report of eight cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:698-700. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175580
- Khan MO, Montecalvo MA, Davis I, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cutis. 2000;66:121-123.
- Nadelman RB, Wormser GP. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 1998; 352:557-565.
- Su WP, Schroeter AL, Perry HO, et al. Histopathologic and immunopathologic study of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:323-330. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00466.x
- Tirumalae R, Yeliur IK, Antony M, et al. Papulonecrotic tuberculidclinicopathologic and molecular features of 12 Indian patients. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:17-22. doi:10.5826/dpc.0402a03
- Obiozor C, Ganguly S, Fraga GR. Leukemia cutis with lymphoglandular bodies: a clue to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cutis [published online August 15, 2015]. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6m18g35f
- Vasudevan B, Chatterjee M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:167-174. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110822
The Diagnosis: Ecthyma Gangrenosum
Histopathology revealed basophilic bacterial rods around necrotic vessels with thrombosis and edema (Figure). Blood and tissue cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of P aeruginosa–associated ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) was made. The patient’s symptoms resolved with intravenous cefepime, and he later was transitioned to oral levofloxacin for outpatient treatment.

Ecthyma gangrenosum is an uncommon cutaneous manifestation of bacteremia that most commonly occurs secondary to P aeruginosa in immunocompromised patients, particularly patients with severe neutropenia in the setting of recent chemotherapy.1,2 Ecthyma gangrenosum can occur anywhere on the body, predominantly in moist areas such as the axillae and groin; the arms and legs, such as in our patient, as well as the trunk and face also may be involved.3 Other causes of EG skin lesions include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, fungi such as Candida, and viruses such as herpes simplex virus.2,4-6 Common predisposing conditions associated with EG include neutropenia, leukemia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, extensive burn wounds, and a history of immunosuppressive medications. It also has been known to occur in otherwise healthy, immunocompetent individuals with no difference in clinical manifestation.2
The diagnosis is clinicopathologic, with initial evaluation including blood and wound cultures as well as a complete blood cell count once EG is suspected. An excisional or punch biopsy is performed for confirmation, showing many gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria in cases of pseudomonal EG.7 Histopathology is characterized by bacterial perivascular invasion that then leads to secondary arteriole thrombosis, tissue edema, and separation of the epidermis.7,8 Resultant ischemic necrosis results in the classic macroscopic appearance of an erythematous macule that rapidly progresses into a central necrotic lesion surrounded by an erythematous or violaceous halo after undergoing a hemorrhagic bullous stage.1,9 A Wood lamp can be used to expedite the diagnosis, as Pseudomonas bacteria excretes a pigment (pyoverdine) that fluoresces yellowish green.10
Ecthyma gangrenosum can be classified as a primary skin lesion that may or may not be followed by bacteremia or as a lesion secondary to pseudomonal bacteremia.11 Bacteremia has been reported in half of cases, with hematogenous metastasis of the infection, likely in manifestations with multiple bilateral lesions.2 Our patient’s presentation of a single lesion revealed a positive blood culture result. Lesions also can develop by direct inoculation of the epidermis causing local destruction of the surrounding tissue. The nonbacteremic form of EG has been associated with a lower mortality rate of around 15% compared to patients with bacteremia ranging from 38% to 96%.12 The presence of neutropenia is the most important prognostic factor for mortality at the time of diagnosis.13
Prompt empiric therapy should be initiated after obtaining wound and blood cultures in those with infection until the causative organism and its susceptibility are identified. Pseudomonal infections account for 4% of all cases of hospital-acquired bacteremia and are the third leading cause of gram-negative bloodstream infection.7 Initial broad-spectrum antibiotics include antipseudomonal β-lactams (piperacillin-tazobactam), cephalosporins (cefepime), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), and carbapenems (imipenem).1,7 Medical therapy alone may be sufficient without requiring extensive surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue in some patients. Surgical debridement usually is warranted for lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter.3 Our patient was treated with intravenous cefepime with resolution and was followed with outpatient oral levofloxacin as appropriate. A high index of suspicion should be maintained for relapsing pseudomonal EG infection among patients with AIDS, as the reported recurrence rate is 57%.14
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of EG presenting in immunocompromised patients or individuals with underlying malignancy includes pyoderma gangrenosum, papulonecrotic tuberculid, and leukemia cutis. An erythematous rash with central necrosis presenting in a patient with systemic symptoms is pathognomonic for erythema migrans and should be considered as a diagnostic possibility in areas endemic for Lyme disease in the United States, including the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and north-central regions.15 A thorough history, physical examination, basic laboratory studies, and histopathology are critical to differentiate between these entities with similar macroscopic features. Pyoderma gangrenosum histologically manifests as a noninfectious, deep, suppurative folliculitis with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in 40% of cases.16 Although papulonecrotic tuberculid can present with dermal necrosis resulting from a hypersensitivity reaction to antigenic components of mycobacteria, there typically are granulomatous infiltrates present and a lack of observed organisms on histopathology.17 Although leukemia cutis infrequently occurs in patients diagnosed with leukemia, its salient features on pathology are nodular or diffuse infiltrates of leukemic cells in the dermis and subcutis with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, often with prominent nucleoli.18 Lyme disease can present in various ways; however, cutaneous involvement in the primary lesion is histologically characterized by a perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate containing plasma cells at the periphery of the expanding annular lesion and eosinophils present at the center.19
The Diagnosis: Ecthyma Gangrenosum
Histopathology revealed basophilic bacterial rods around necrotic vessels with thrombosis and edema (Figure). Blood and tissue cultures grew Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Based on the histopathology and clinical presentation, a diagnosis of P aeruginosa–associated ecthyma gangrenosum (EG) was made. The patient’s symptoms resolved with intravenous cefepime, and he later was transitioned to oral levofloxacin for outpatient treatment.

Ecthyma gangrenosum is an uncommon cutaneous manifestation of bacteremia that most commonly occurs secondary to P aeruginosa in immunocompromised patients, particularly patients with severe neutropenia in the setting of recent chemotherapy.1,2 Ecthyma gangrenosum can occur anywhere on the body, predominantly in moist areas such as the axillae and groin; the arms and legs, such as in our patient, as well as the trunk and face also may be involved.3 Other causes of EG skin lesions include methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, Citrobacter freundii, Escherichia coli, fungi such as Candida, and viruses such as herpes simplex virus.2,4-6 Common predisposing conditions associated with EG include neutropenia, leukemia, HIV, diabetes mellitus, extensive burn wounds, and a history of immunosuppressive medications. It also has been known to occur in otherwise healthy, immunocompetent individuals with no difference in clinical manifestation.2
The diagnosis is clinicopathologic, with initial evaluation including blood and wound cultures as well as a complete blood cell count once EG is suspected. An excisional or punch biopsy is performed for confirmation, showing many gram-negative, rod-shaped bacteria in cases of pseudomonal EG.7 Histopathology is characterized by bacterial perivascular invasion that then leads to secondary arteriole thrombosis, tissue edema, and separation of the epidermis.7,8 Resultant ischemic necrosis results in the classic macroscopic appearance of an erythematous macule that rapidly progresses into a central necrotic lesion surrounded by an erythematous or violaceous halo after undergoing a hemorrhagic bullous stage.1,9 A Wood lamp can be used to expedite the diagnosis, as Pseudomonas bacteria excretes a pigment (pyoverdine) that fluoresces yellowish green.10
Ecthyma gangrenosum can be classified as a primary skin lesion that may or may not be followed by bacteremia or as a lesion secondary to pseudomonal bacteremia.11 Bacteremia has been reported in half of cases, with hematogenous metastasis of the infection, likely in manifestations with multiple bilateral lesions.2 Our patient’s presentation of a single lesion revealed a positive blood culture result. Lesions also can develop by direct inoculation of the epidermis causing local destruction of the surrounding tissue. The nonbacteremic form of EG has been associated with a lower mortality rate of around 15% compared to patients with bacteremia ranging from 38% to 96%.12 The presence of neutropenia is the most important prognostic factor for mortality at the time of diagnosis.13
Prompt empiric therapy should be initiated after obtaining wound and blood cultures in those with infection until the causative organism and its susceptibility are identified. Pseudomonal infections account for 4% of all cases of hospital-acquired bacteremia and are the third leading cause of gram-negative bloodstream infection.7 Initial broad-spectrum antibiotics include antipseudomonal β-lactams (piperacillin-tazobactam), cephalosporins (cefepime), fluoroquinolones (levofloxacin), and carbapenems (imipenem).1,7 Medical therapy alone may be sufficient without requiring extensive surgical debridement to remove necrotic tissue in some patients. Surgical debridement usually is warranted for lesions larger than 10 cm in diameter.3 Our patient was treated with intravenous cefepime with resolution and was followed with outpatient oral levofloxacin as appropriate. A high index of suspicion should be maintained for relapsing pseudomonal EG infection among patients with AIDS, as the reported recurrence rate is 57%.14
Clinically, the differential diagnosis of EG presenting in immunocompromised patients or individuals with underlying malignancy includes pyoderma gangrenosum, papulonecrotic tuberculid, and leukemia cutis. An erythematous rash with central necrosis presenting in a patient with systemic symptoms is pathognomonic for erythema migrans and should be considered as a diagnostic possibility in areas endemic for Lyme disease in the United States, including the northeastern, mid-Atlantic, and north-central regions.15 A thorough history, physical examination, basic laboratory studies, and histopathology are critical to differentiate between these entities with similar macroscopic features. Pyoderma gangrenosum histologically manifests as a noninfectious, deep, suppurative folliculitis with leukocytoclastic vasculitis in 40% of cases.16 Although papulonecrotic tuberculid can present with dermal necrosis resulting from a hypersensitivity reaction to antigenic components of mycobacteria, there typically are granulomatous infiltrates present and a lack of observed organisms on histopathology.17 Although leukemia cutis infrequently occurs in patients diagnosed with leukemia, its salient features on pathology are nodular or diffuse infiltrates of leukemic cells in the dermis and subcutis with a high nuclear-to-cytoplasmic ratio, often with prominent nucleoli.18 Lyme disease can present in various ways; however, cutaneous involvement in the primary lesion is histologically characterized by a perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate containing plasma cells at the periphery of the expanding annular lesion and eosinophils present at the center.19
- Abdou A, Hassam B. Ecthyma gangrenosum [in French]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;30:95. doi:10.11604/pamj.2018.30.95.6244
- Vaiman M, Lazarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum and ecthyma-like lesions: review article. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:633-639. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2277-6
- Vaiman M, Lasarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum versus ecthyma-like lesions: should we separate these conditions? Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:69-72. doi:10.15570 /actaapa.2015.18
- Reich HL, Williams Fadeyi D, Naik NS, et al. Nonpseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl): S114-S117. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.09.019
- Hawkley T, Chang D, Pollard W, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum caused by Citrobacter freundii [published online July 27, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220996
- Santhaseelan RG, Muralidhar V. Non-pseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a chronic alcoholic patient [published online August 3, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220983m
- Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, et al. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections [published online May 29, 2018]. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi:10.7573/dic.212527
- Llamas-Velasco M, Alegría V, Santos-Briz Á, et al. Occlusive nonvasculitic vasculopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:637-662. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000766
- Sarkar S, Patra AK, Mondal M. Ecthyma gangrenosum in the periorbital region in a previously healthy immunocompetent woman without bacteremia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:36-39. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.174326
- Ponka D, Baddar F. Wood lamp examination. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:976.
- Van den Broek PJ, Van der Meer JWM, Kunst MW. The pathogenesis of ecthyma gangrenosum. J Infect. 1979;1:263-267. doi:10.1016 /S0163-4453(79)91329-X
- Downey DM, O’Bryan MC, Burdette SD, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:198-202. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E31802CA481
- Martínez-Longoria CA, Rosales-Solis GM, Ocampo-Garza J, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum: a report of eight cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:698-700. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175580
- Khan MO, Montecalvo MA, Davis I, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cutis. 2000;66:121-123.
- Nadelman RB, Wormser GP. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 1998; 352:557-565.
- Su WP, Schroeter AL, Perry HO, et al. Histopathologic and immunopathologic study of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:323-330. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00466.x
- Tirumalae R, Yeliur IK, Antony M, et al. Papulonecrotic tuberculidclinicopathologic and molecular features of 12 Indian patients. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:17-22. doi:10.5826/dpc.0402a03
- Obiozor C, Ganguly S, Fraga GR. Leukemia cutis with lymphoglandular bodies: a clue to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cutis [published online August 15, 2015]. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6m18g35f
- Vasudevan B, Chatterjee M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:167-174. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110822
- Abdou A, Hassam B. Ecthyma gangrenosum [in French]. Pan Afr Med J. 2018;30:95. doi:10.11604/pamj.2018.30.95.6244
- Vaiman M, Lazarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum and ecthyma-like lesions: review article. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2015;34:633-639. doi:10.1007/s10096-014-2277-6
- Vaiman M, Lasarovitch T, Heller L, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum versus ecthyma-like lesions: should we separate these conditions? Acta Dermatovenerol Alp Pannonica Adriat. 2015;24:69-72. doi:10.15570 /actaapa.2015.18
- Reich HL, Williams Fadeyi D, Naik NS, et al. Nonpseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004;50(5 suppl): S114-S117. doi:10.1016/j.jaad.2003.09.019
- Hawkley T, Chang D, Pollard W, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum caused by Citrobacter freundii [published online July 27, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220996
- Santhaseelan RG, Muralidhar V. Non-pseudomonal ecthyma gangrenosum caused by methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in a chronic alcoholic patient [published online August 3, 2017]. BMJ Case Rep. doi:10.1136/bcr-2017-220983m
- Bassetti M, Vena A, Croxatto A, et al. How to manage Pseudomonas aeruginosa infections [published online May 29, 2018]. Drugs Context. 2018;7:212527. doi:10.7573/dic.212527
- Llamas-Velasco M, Alegría V, Santos-Briz Á, et al. Occlusive nonvasculitic vasculopathy. Am J Dermatopathol. 2017;39:637-662. doi:10.1097/DAD.0000000000000766
- Sarkar S, Patra AK, Mondal M. Ecthyma gangrenosum in the periorbital region in a previously healthy immunocompetent woman without bacteremia. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2016;7:36-39. doi:10.4103/2229-5178.174326
- Ponka D, Baddar F. Wood lamp examination. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58:976.
- Van den Broek PJ, Van der Meer JWM, Kunst MW. The pathogenesis of ecthyma gangrenosum. J Infect. 1979;1:263-267. doi:10.1016 /S0163-4453(79)91329-X
- Downey DM, O’Bryan MC, Burdette SD, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in a patient with toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Burn Care Res. 2007;28:198-202. doi:10.1097/BCR.0B013E31802CA481
- Martínez-Longoria CA, Rosales-Solis GM, Ocampo-Garza J, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum: a report of eight cases. An Bras Dermatol. 2017;92:698-700. doi:10.1590/abd1806-4841.20175580
- Khan MO, Montecalvo MA, Davis I, et al. Ecthyma gangrenosum in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Cutis. 2000;66:121-123.
- Nadelman RB, Wormser GP. Lyme borreliosis. Lancet. 1998; 352:557-565.
- Su WP, Schroeter AL, Perry HO, et al. Histopathologic and immunopathologic study of pyoderma gangrenosum. J Cutan Pathol. 1986;13:323-330. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0560.1986.tb00466.x
- Tirumalae R, Yeliur IK, Antony M, et al. Papulonecrotic tuberculidclinicopathologic and molecular features of 12 Indian patients. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2014;4:17-22. doi:10.5826/dpc.0402a03
- Obiozor C, Ganguly S, Fraga GR. Leukemia cutis with lymphoglandular bodies: a clue to acute lymphoblastic leukemia cutis [published online August 15, 2015]. Dermatol Online J. 2015;21:13030/qt6m18g35f
- Vasudevan B, Chatterjee M. Lyme borreliosis and skin. Indian J Dermatol. 2013;58:167-174. doi:10.4103/0019-5154.110822
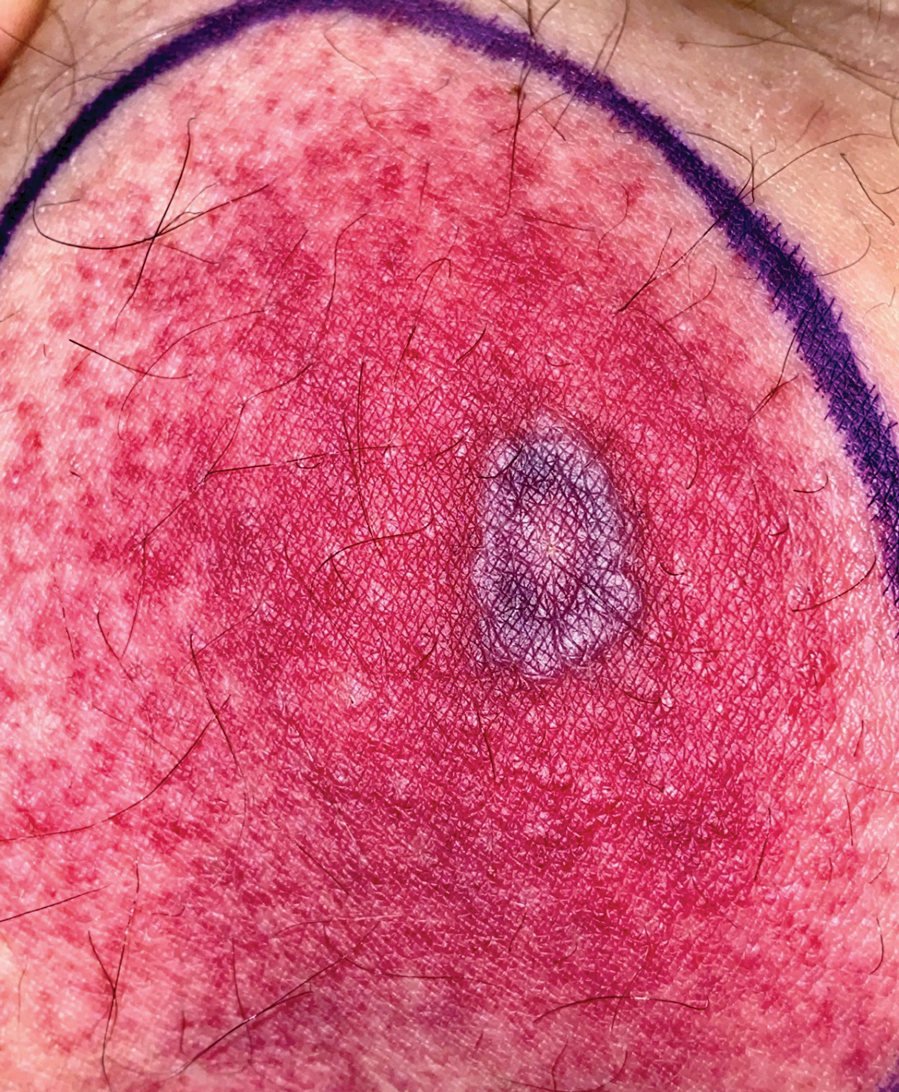
A 58-year-old man who was receiving gilteritinib therapy for relapsed acute myeloid leukemia presented to the emergency department with a painful, rapidly enlarging lesion on the right medial thigh of 2 days’ duration that was accompanied by fever (temperature, 39.2 °C) and body aches. Physical examination revealed a tender annular plaque with a dark violaceous halo overlying a larger area of erythema and induration. Laboratory evaluation revealed a white blood cell count of 600/μL (reference range, 4500–11,000/μL) and an absolute neutrophil count of 200/μL (reference range, 1800–7000/μL). A biopsy was performed.
Progressive Axillary Hyperpigmentation
The Diagnosis: Dowling-Degos Disease
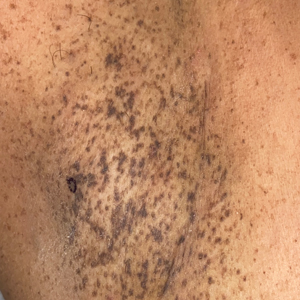
Histopathology demonstrated elongation of the epidermal rete ridges with increased basal pigmentation, suprapapillary epithelial thinning, dermal melanophages, and a mild lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure). Given the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of Dowling-Degos disease (DDD) was made. The patient was counseled on the increased risk for her children developing DDD. Treatment with the erbium:YAG (Er:YAG) laser subsequently was initiated.

Dowling-Degos disease (also known as reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures) is an uncommon autosomal-dominant condition characterized by reticular hyperpigmentation involving the flexural and intertriginous sites. Classic DDD commonly is caused by lossof-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene, KRT51; however, DDD also may result from loss-of-function mutations in the protein O-fucosyltransferase 1, POFUT1, and protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, POGLUT1, genes.2
Rare cases of DDD associated with hidradenitis suppurativa are caused by mutations in the presenilin enhancer protein 2 gene, PSENEN.3
Of note, a missense mutation in KRT5 is implicated in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation. Onset of DDD typically occurs during the third to fourth decades of life. Reticulated hyperpigmented macules initially occur in the axillae and groin and progressively increase over time to involve the neck, inframammary folds, trunk, and flexural surfaces of the arms and thighs. Patients additionally may present with pitted perioral scars, comedolike lesions on the back and neck, epidermoid cysts, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma rarely have been reported in association with classic DDD.4,5
Dowling-Degos disease usually is asymptomatic, though pruritus seldom may occur in the affected flexural areas. Histologically, the epidermal rete ridges are elongated in a filiform or antlerlike pattern with increased pigmentation of the basal layer and thinning of the suprapapillary epithelium. Dermal melanosis and a mild perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate also are present with no increase in the number of melanocytes.6,7 Galli-Galli disease is a variant of DDD that shares similar clinical and histologic features of DDD but is distinguished from DDD by suprabasilar nondyskeratotic acantholysis on histology.8
Regarding other differential diagnoses for our patient, acanthosis nigricans may be distinguished clinically by the presence of velvety and/or verrucous plaques, commonly in the neck folds and axillae. Histologically, acanthosis nigricans is distinct from DDD and involves hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and epidermal papillomatosis. Our patient had no history of diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance. Granular parakeratosis presents with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques classically confined to the axillary region; however, the involvement of other intertriginous areas may occur. Histologically, granular parakeratosis demonstrates compact parakeratosis with small bluish keratohyalin granules within the stratum corneum. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis presents with red-brown keratotic papules that initially appear in the intermammary region and spread laterally forming a reticulated pattern. Histology is similar to acanthosis nigricans and demonstrates hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis. Inverse psoriasis presents with symmetric and sharply demarcated, erythematous, nonscaly plaques in the intertriginous areas. The plaques of inverse psoriasis may be pruritic and/or sore and occasionally may become macerated. Inverse psoriasis shares similar histologic findings compared to classic plaque psoriasis but may have less confluent parakeratosis.
Treatment of DDD essentially is reserved for cosmetic reasons. Topical hydroquinone, tretinoin, and corticosteroids have been used with limited to no success.5,9 Beneficial results after treatment with the Er:YAG laser have been reported.10
- Betz RC, Planko L, Eigelshoven S, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene lead to Dowling-Degos disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;78:510-519.
- Basmanav FB, Oprisoreanu AM, Pasternack SM, et al. Mutations in POGLUT1, encoding protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, cause autosomaldominant Dowling-Degos disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94:135-143.
- Pavlovsky M, Sarig O, Eskin-Schwartz M, et al. A phenotype combining hidradenitis suppurativa with Dowling-Degos disease caused by a founder mutation in PSENEN. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:502-508.
- Ujihara M, Kamakura T, Ikeda M, et al. Dowling-Degos disease associated with squamous cell carcinomas on the dappled pigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:568-571.
- Weber LA, Kantor GR, Bergfeld WF. Reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures (Dowling-Degos disease): a case report associated with hidradenitis suppurativa and squamous cell carcinoma. Cutis. 1990;45:446-450.
- Jones EW, Grice K. Reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures. Dowing Degos disease, a new genodermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1150-1157.
- Kim YC, Davis MD, Schanbacher CF, et al. Dowling-Degos disease (reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures): a clinical and histopathologic study of 6 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999; 40:462-467.
- Reisenauer AK, Wordingham SV, York J, et al. Heterozygous frameshift mutation in keratin 5 in a family with Galli-Galli disease. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:1362-1365.
- Oppolzer G, Schwarz T, Duschet P, et al. Dowling-Degos disease: unsuccessful therapeutic trial with retinoids [in German]. Hautarzt. 1987;38:615-618.
- Wenzel G, Petrow W, Tappe K, et al. Treatment of Dowling-Degos disease with Er:YAG-laser: results after 2.5 years. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:1161-1162.
The Diagnosis: Dowling-Degos Disease
Histopathology demonstrated elongation of the epidermal rete ridges with increased basal pigmentation, suprapapillary epithelial thinning, dermal melanophages, and a mild lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure). Given the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of Dowling-Degos disease (DDD) was made. The patient was counseled on the increased risk for her children developing DDD. Treatment with the erbium:YAG (Er:YAG) laser subsequently was initiated.

Dowling-Degos disease (also known as reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures) is an uncommon autosomal-dominant condition characterized by reticular hyperpigmentation involving the flexural and intertriginous sites. Classic DDD commonly is caused by lossof-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene, KRT51; however, DDD also may result from loss-of-function mutations in the protein O-fucosyltransferase 1, POFUT1, and protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, POGLUT1, genes.2
Rare cases of DDD associated with hidradenitis suppurativa are caused by mutations in the presenilin enhancer protein 2 gene, PSENEN.3
Of note, a missense mutation in KRT5 is implicated in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation. Onset of DDD typically occurs during the third to fourth decades of life. Reticulated hyperpigmented macules initially occur in the axillae and groin and progressively increase over time to involve the neck, inframammary folds, trunk, and flexural surfaces of the arms and thighs. Patients additionally may present with pitted perioral scars, comedolike lesions on the back and neck, epidermoid cysts, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma rarely have been reported in association with classic DDD.4,5
Dowling-Degos disease usually is asymptomatic, though pruritus seldom may occur in the affected flexural areas. Histologically, the epidermal rete ridges are elongated in a filiform or antlerlike pattern with increased pigmentation of the basal layer and thinning of the suprapapillary epithelium. Dermal melanosis and a mild perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate also are present with no increase in the number of melanocytes.6,7 Galli-Galli disease is a variant of DDD that shares similar clinical and histologic features of DDD but is distinguished from DDD by suprabasilar nondyskeratotic acantholysis on histology.8
Regarding other differential diagnoses for our patient, acanthosis nigricans may be distinguished clinically by the presence of velvety and/or verrucous plaques, commonly in the neck folds and axillae. Histologically, acanthosis nigricans is distinct from DDD and involves hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and epidermal papillomatosis. Our patient had no history of diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance. Granular parakeratosis presents with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques classically confined to the axillary region; however, the involvement of other intertriginous areas may occur. Histologically, granular parakeratosis demonstrates compact parakeratosis with small bluish keratohyalin granules within the stratum corneum. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis presents with red-brown keratotic papules that initially appear in the intermammary region and spread laterally forming a reticulated pattern. Histology is similar to acanthosis nigricans and demonstrates hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis. Inverse psoriasis presents with symmetric and sharply demarcated, erythematous, nonscaly plaques in the intertriginous areas. The plaques of inverse psoriasis may be pruritic and/or sore and occasionally may become macerated. Inverse psoriasis shares similar histologic findings compared to classic plaque psoriasis but may have less confluent parakeratosis.
Treatment of DDD essentially is reserved for cosmetic reasons. Topical hydroquinone, tretinoin, and corticosteroids have been used with limited to no success.5,9 Beneficial results after treatment with the Er:YAG laser have been reported.10
The Diagnosis: Dowling-Degos Disease
Histopathology demonstrated elongation of the epidermal rete ridges with increased basal pigmentation, suprapapillary epithelial thinning, dermal melanophages, and a mild lymphocytic infiltrate (Figure). Given the clinical and histologic findings, a diagnosis of Dowling-Degos disease (DDD) was made. The patient was counseled on the increased risk for her children developing DDD. Treatment with the erbium:YAG (Er:YAG) laser subsequently was initiated.

Dowling-Degos disease (also known as reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures) is an uncommon autosomal-dominant condition characterized by reticular hyperpigmentation involving the flexural and intertriginous sites. Classic DDD commonly is caused by lossof-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene, KRT51; however, DDD also may result from loss-of-function mutations in the protein O-fucosyltransferase 1, POFUT1, and protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, POGLUT1, genes.2
Rare cases of DDD associated with hidradenitis suppurativa are caused by mutations in the presenilin enhancer protein 2 gene, PSENEN.3
Of note, a missense mutation in KRT5 is implicated in epidermolysis bullosa simplex with mottled pigmentation. Onset of DDD typically occurs during the third to fourth decades of life. Reticulated hyperpigmented macules initially occur in the axillae and groin and progressively increase over time to involve the neck, inframammary folds, trunk, and flexural surfaces of the arms and thighs. Patients additionally may present with pitted perioral scars, comedolike lesions on the back and neck, epidermoid cysts, and hidradenitis suppurativa. Keratoacanthoma and squamous cell carcinoma rarely have been reported in association with classic DDD.4,5
Dowling-Degos disease usually is asymptomatic, though pruritus seldom may occur in the affected flexural areas. Histologically, the epidermal rete ridges are elongated in a filiform or antlerlike pattern with increased pigmentation of the basal layer and thinning of the suprapapillary epithelium. Dermal melanosis and a mild perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltrate also are present with no increase in the number of melanocytes.6,7 Galli-Galli disease is a variant of DDD that shares similar clinical and histologic features of DDD but is distinguished from DDD by suprabasilar nondyskeratotic acantholysis on histology.8
Regarding other differential diagnoses for our patient, acanthosis nigricans may be distinguished clinically by the presence of velvety and/or verrucous plaques, commonly in the neck folds and axillae. Histologically, acanthosis nigricans is distinct from DDD and involves hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and epidermal papillomatosis. Our patient had no history of diabetes mellitus or insulin resistance. Granular parakeratosis presents with hyperpigmented hyperkeratotic papules and plaques classically confined to the axillary region; however, the involvement of other intertriginous areas may occur. Histologically, granular parakeratosis demonstrates compact parakeratosis with small bluish keratohyalin granules within the stratum corneum. Confluent and reticulated papillomatosis presents with red-brown keratotic papules that initially appear in the intermammary region and spread laterally forming a reticulated pattern. Histology is similar to acanthosis nigricans and demonstrates hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, and papillomatosis. Inverse psoriasis presents with symmetric and sharply demarcated, erythematous, nonscaly plaques in the intertriginous areas. The plaques of inverse psoriasis may be pruritic and/or sore and occasionally may become macerated. Inverse psoriasis shares similar histologic findings compared to classic plaque psoriasis but may have less confluent parakeratosis.
Treatment of DDD essentially is reserved for cosmetic reasons. Topical hydroquinone, tretinoin, and corticosteroids have been used with limited to no success.5,9 Beneficial results after treatment with the Er:YAG laser have been reported.10
- Betz RC, Planko L, Eigelshoven S, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene lead to Dowling-Degos disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;78:510-519.
- Basmanav FB, Oprisoreanu AM, Pasternack SM, et al. Mutations in POGLUT1, encoding protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, cause autosomaldominant Dowling-Degos disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94:135-143.
- Pavlovsky M, Sarig O, Eskin-Schwartz M, et al. A phenotype combining hidradenitis suppurativa with Dowling-Degos disease caused by a founder mutation in PSENEN. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:502-508.
- Ujihara M, Kamakura T, Ikeda M, et al. Dowling-Degos disease associated with squamous cell carcinomas on the dappled pigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:568-571.
- Weber LA, Kantor GR, Bergfeld WF. Reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures (Dowling-Degos disease): a case report associated with hidradenitis suppurativa and squamous cell carcinoma. Cutis. 1990;45:446-450.
- Jones EW, Grice K. Reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures. Dowing Degos disease, a new genodermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1150-1157.
- Kim YC, Davis MD, Schanbacher CF, et al. Dowling-Degos disease (reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures): a clinical and histopathologic study of 6 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999; 40:462-467.
- Reisenauer AK, Wordingham SV, York J, et al. Heterozygous frameshift mutation in keratin 5 in a family with Galli-Galli disease. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:1362-1365.
- Oppolzer G, Schwarz T, Duschet P, et al. Dowling-Degos disease: unsuccessful therapeutic trial with retinoids [in German]. Hautarzt. 1987;38:615-618.
- Wenzel G, Petrow W, Tappe K, et al. Treatment of Dowling-Degos disease with Er:YAG-laser: results after 2.5 years. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:1161-1162.
- Betz RC, Planko L, Eigelshoven S, et al. Loss-of-function mutations in the keratin 5 gene lead to Dowling-Degos disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2006;78:510-519.
- Basmanav FB, Oprisoreanu AM, Pasternack SM, et al. Mutations in POGLUT1, encoding protein O-glucosyltransferase 1, cause autosomaldominant Dowling-Degos disease. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94:135-143.
- Pavlovsky M, Sarig O, Eskin-Schwartz M, et al. A phenotype combining hidradenitis suppurativa with Dowling-Degos disease caused by a founder mutation in PSENEN. Br J Dermatol. 2018;178:502-508.
- Ujihara M, Kamakura T, Ikeda M, et al. Dowling-Degos disease associated with squamous cell carcinomas on the dappled pigmentation. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:568-571.
- Weber LA, Kantor GR, Bergfeld WF. Reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures (Dowling-Degos disease): a case report associated with hidradenitis suppurativa and squamous cell carcinoma. Cutis. 1990;45:446-450.
- Jones EW, Grice K. Reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures. Dowing Degos disease, a new genodermatosis. Arch Dermatol. 1978;114:1150-1157.
- Kim YC, Davis MD, Schanbacher CF, et al. Dowling-Degos disease (reticulate pigmented anomaly of the flexures): a clinical and histopathologic study of 6 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999; 40:462-467.
- Reisenauer AK, Wordingham SV, York J, et al. Heterozygous frameshift mutation in keratin 5 in a family with Galli-Galli disease. Br J Dermatol. 2014;170:1362-1365.
- Oppolzer G, Schwarz T, Duschet P, et al. Dowling-Degos disease: unsuccessful therapeutic trial with retinoids [in German]. Hautarzt. 1987;38:615-618.
- Wenzel G, Petrow W, Tappe K, et al. Treatment of Dowling-Degos disease with Er:YAG-laser: results after 2.5 years. Dermatol Surg. 2003;29:1161-1162.

A 50-year-old Hispanic woman presented with asymptomatic, progressive, brown hyperpigmentation involving the axillae, neck, upper back, and inframammary areas of 5 years’ duration. She had no other notable medical history; family history was unremarkable. She had been treated with topical hydroquinone and tretinoin by an outside physician without improvement. Physical examination revealed reticulated hyperpigmented macules and patches involving the inverse regions of the neck, axillae, and inframammary regions. Additionally, acneform pitted scars involving the perioral region were seen. A 4.0-mm punch biopsy of the right axilla was performed.
Hyperpigmentation on the Head and Neck
The Diagnosis: Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Overlapping With Lichen Planus Pigmentosus
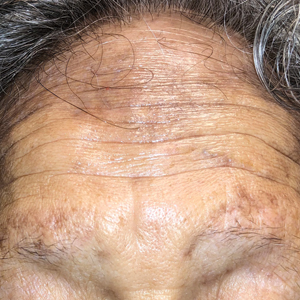
Microscopic examination revealed focal dermal pigmentation, papillary fibrosis, and epidermal atrophy. These clinical and histologic findings indicated a diagnosis of fully developed lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) overlapping with frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). Other cases have demonstrated an association between LPP and FFA.1,2
Lichen planus pigmentosus is considered an uncommon variant of lichen planus, as it has similar histopathologic findings and occasional coexistence.3,4 It is characterized by hyperpigmented macules primarily located in sun-exposed and flexural areas of the skin. First described in India,5 this disease has a predilection for darker skin (Fitzpatrick skin types III-V),6,7 and it has been reported in other racial and ethnic groups including Latin Americans, Middle Eastern populations, Japanese, and Koreans.4,8 Typically, lesions initially appear as ill-defined, blue-grey, round to oval macules that coalesce into hyperpigmented patches. Involvement most commonly begins at the forehead and temples, which are affected in nearly all patients. Infrequently, LPP can be generalized or affect the oral mucosa; involvement of the palms, soles, and nails does not occur. Patients may be asymptomatic, but some experience mild pruritus and burning. The disease course is chronic and insidious, with new lesions appearing over time and old lesions progressively darkening and expanding.6,7,9
Although the pathogenesis of LPP is unknown, several exposures have been implicated, such as amla oil, mustard oil, henna, hair dye, and environmental pollutants.7 Because lesions characteristically occur in sun-exposed areas, UV light also may be involved. In addition, studies have suggested that LPP is associated with endocrinopathies such as diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemias, as in our patient, as well as autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo and systemic lupus erythematosus.10,11
Histopathologic findings are characterized by vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer in the epidermis as well as perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltration and the presence of melanophages in the dermis.3,9 Lichen planus pigmentosus is difficult to treat, as no consistently effective modality has been established. Topical tacrolimus, topical corticosteroids, oral retinoids, lasers, and sun protection have been implemented with underwhelming results.12
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a variant of lichen planopilaris that predominantly affects postmenopausal women and presents with frontotemporal hair loss in a bandlike distribution.5,13 Both terminal and vellus hairs are affected. Involvement of multiple hair-bearing sites of the skin have been reported, including the entire scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Affected areas may display hypopigmentation and be accompanied by pruritus and trichodynia.14,15 The pathogenesis currently is under investigation, with studies demonstrating autoimmune, genetic, and possibly even endocrine predispositions.16-18 Biopsies of lesions are indistinguishable from lichen planopilaris, which shows follicular lymphocytic infiltration, perifollicular fibrosis, interface dermatitis of the follicular infundibulum and isthmus, and vertical fibrous tracks.5 Patients with FFA have demonstrated variable responses to treatments, with one study showing improvement with oral finasteride or dutasteride.14 Topical and intralesional corticosteroids have yielded suboptimal effects. Other modalities include hydroxychloroquine and mycophenolate mofetil.15,19
Co-occurrence of LPP and FFA primarily is seen in postmenopausal women with darker skin,14,15 as in our patient, though premenopausal cases have been reported. Lichen planus pigmentosus may serve as a harbinger in most patients.1,2 In a similar fashion, our patient presented with hyperpigmented macular lesions prior to the onset of frontotemporal hair loss.
Our patient was started on finasteride 2.5 mg daily, minoxidil foam 5%, clobetasol solution 0.05%, triamcinolone ointment 0.1%, and hydrocortisone ointment 2.5%. She was instructed to commence treatment and follow up in 6 months.
The differential diagnosis includes dermatologic conditions that mimic both LPP and FFA. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and fixed drug reaction were unlikely based on the patient's history. The lesions of ashy dermatosis are characteristically gray erythematous macules on the trunk and limbs. Riehl melanosis is a rare pigmented contact dermatitis that is associated with a history of repeated contact with sensitizing allergens. Although Hori nevus is characterized by small, blue-gray or brown macules on the face, lesions predominantly occur on the bony prominences of the cheeks. Melasma also presents with dark to gray macules that affect the face and less commonly the neck, as in our patient.2
Early discoid lupus erythematosus presents with round erythematous plaques with overlying scale extending into the hair follicles. In pseudopalade of Brocq, an idiopathic cicatricial alopecia, lesions typically are flesh colored. Biopsy also shows epidermal atrophy with additional dermal sclerosis and fibrosis. Folliculitis decalvans is a scarring form of alopecia associated with erythema and pustules, findings that were not present in our patient. Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans is a rare, X-linked inherited ichthyosis manifesting as scarring alopecia with follicular depressions and papules on the scalp in younger males. Photophobia and other manifestations may be present. Alopecia mucinosa is a nonscarring alopecia with grouped follicular erythematous patches or plaques. Mucin sometimes can be squeezed from affected areas, and histopathologic examination shows mucin accumulation.4
- Dlova NC. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus: is there a link? Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:439-442.
- Pirmez R, Duque-Estrada B, Donati A, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic features of lichen planus pigmentosus in 37 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1387-1390.
- Rieder E, Kaplan J, Kamino H, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:20713.
- Kashima A, Tajiri A, Yamashita A, et al. Two Japanese cases of lichen planus pigmentosus-inversus. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:740-742.
- Bhutani L, Bedi T, Pandhi R. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatologica. 1974;149:43-50.
- Ross EK, Tan E, Shapiro J. Update on primary cicatricial alopecias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1-37.
- Kanwa AJ, Dogra S, Handa S, et al. A study of 124 Indian patients with lichen planus pigmentosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:481-485.
- Al-Mutairi N, El-Khalawany M. Clinicopathological characteristics of lichen planus pigmentosus and its response to tacrolimus ointment: an open label, non-randomized, prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:535-540.
- Vega ME, Waxtein L, Arenas R, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: a clinicopathologic study of 31 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31:90-94.
- Robles-Méndez JC, Rizo-Frías P, Herz-Ruelas ME, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus and its variants: review and update. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:505-514.
- Torres J, Guadalupe A, Reyes E, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus in patients with endocrinopathies and hepatitis C. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:AB139.
- Kim JE, Won CH, Chang S, et al. Linear lichen planus pigmentosus of the forehead treated by neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser and topical tacrolimus. J Dermatol. 2012;39:189-191.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774.
- Vano-Galvan S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Serrano-Falcon C, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicenter review of 355 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:670-678.
- MacDonald A, Clark C, Holmes S. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a review of 60 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:955-961.
- Harries MJ, Meyer K, Chaudhry I, et al. Lichen planopilaris is characterized by immune privilege collapse of the hair follicle's epithelial stem cell niche. J Pathol. 2013;231:236-247.
- Karnik P, Tekeste Z, McCormick TS, et al. Hair follicle stem cell-specific PPARgamma deletion causes scarring alopecia. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:1243-1257.
- Rodriguez-Bayona B, Ruchaud S, Rodriguez C, et al. Autoantibodies against the chromosomal passenger protein INCENP found in a patient with Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007;4:1.
- Rácz E, Gho C, Moorman PW, et al. Treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planopilaris: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:1461-1470.
The Diagnosis: Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Overlapping With Lichen Planus Pigmentosus
Microscopic examination revealed focal dermal pigmentation, papillary fibrosis, and epidermal atrophy. These clinical and histologic findings indicated a diagnosis of fully developed lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) overlapping with frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). Other cases have demonstrated an association between LPP and FFA.1,2
Lichen planus pigmentosus is considered an uncommon variant of lichen planus, as it has similar histopathologic findings and occasional coexistence.3,4 It is characterized by hyperpigmented macules primarily located in sun-exposed and flexural areas of the skin. First described in India,5 this disease has a predilection for darker skin (Fitzpatrick skin types III-V),6,7 and it has been reported in other racial and ethnic groups including Latin Americans, Middle Eastern populations, Japanese, and Koreans.4,8 Typically, lesions initially appear as ill-defined, blue-grey, round to oval macules that coalesce into hyperpigmented patches. Involvement most commonly begins at the forehead and temples, which are affected in nearly all patients. Infrequently, LPP can be generalized or affect the oral mucosa; involvement of the palms, soles, and nails does not occur. Patients may be asymptomatic, but some experience mild pruritus and burning. The disease course is chronic and insidious, with new lesions appearing over time and old lesions progressively darkening and expanding.6,7,9
Although the pathogenesis of LPP is unknown, several exposures have been implicated, such as amla oil, mustard oil, henna, hair dye, and environmental pollutants.7 Because lesions characteristically occur in sun-exposed areas, UV light also may be involved. In addition, studies have suggested that LPP is associated with endocrinopathies such as diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemias, as in our patient, as well as autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo and systemic lupus erythematosus.10,11
Histopathologic findings are characterized by vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer in the epidermis as well as perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltration and the presence of melanophages in the dermis.3,9 Lichen planus pigmentosus is difficult to treat, as no consistently effective modality has been established. Topical tacrolimus, topical corticosteroids, oral retinoids, lasers, and sun protection have been implemented with underwhelming results.12
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a variant of lichen planopilaris that predominantly affects postmenopausal women and presents with frontotemporal hair loss in a bandlike distribution.5,13 Both terminal and vellus hairs are affected. Involvement of multiple hair-bearing sites of the skin have been reported, including the entire scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Affected areas may display hypopigmentation and be accompanied by pruritus and trichodynia.14,15 The pathogenesis currently is under investigation, with studies demonstrating autoimmune, genetic, and possibly even endocrine predispositions.16-18 Biopsies of lesions are indistinguishable from lichen planopilaris, which shows follicular lymphocytic infiltration, perifollicular fibrosis, interface dermatitis of the follicular infundibulum and isthmus, and vertical fibrous tracks.5 Patients with FFA have demonstrated variable responses to treatments, with one study showing improvement with oral finasteride or dutasteride.14 Topical and intralesional corticosteroids have yielded suboptimal effects. Other modalities include hydroxychloroquine and mycophenolate mofetil.15,19
Co-occurrence of LPP and FFA primarily is seen in postmenopausal women with darker skin,14,15 as in our patient, though premenopausal cases have been reported. Lichen planus pigmentosus may serve as a harbinger in most patients.1,2 In a similar fashion, our patient presented with hyperpigmented macular lesions prior to the onset of frontotemporal hair loss.
Our patient was started on finasteride 2.5 mg daily, minoxidil foam 5%, clobetasol solution 0.05%, triamcinolone ointment 0.1%, and hydrocortisone ointment 2.5%. She was instructed to commence treatment and follow up in 6 months.
The differential diagnosis includes dermatologic conditions that mimic both LPP and FFA. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and fixed drug reaction were unlikely based on the patient's history. The lesions of ashy dermatosis are characteristically gray erythematous macules on the trunk and limbs. Riehl melanosis is a rare pigmented contact dermatitis that is associated with a history of repeated contact with sensitizing allergens. Although Hori nevus is characterized by small, blue-gray or brown macules on the face, lesions predominantly occur on the bony prominences of the cheeks. Melasma also presents with dark to gray macules that affect the face and less commonly the neck, as in our patient.2
Early discoid lupus erythematosus presents with round erythematous plaques with overlying scale extending into the hair follicles. In pseudopalade of Brocq, an idiopathic cicatricial alopecia, lesions typically are flesh colored. Biopsy also shows epidermal atrophy with additional dermal sclerosis and fibrosis. Folliculitis decalvans is a scarring form of alopecia associated with erythema and pustules, findings that were not present in our patient. Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans is a rare, X-linked inherited ichthyosis manifesting as scarring alopecia with follicular depressions and papules on the scalp in younger males. Photophobia and other manifestations may be present. Alopecia mucinosa is a nonscarring alopecia with grouped follicular erythematous patches or plaques. Mucin sometimes can be squeezed from affected areas, and histopathologic examination shows mucin accumulation.4
The Diagnosis: Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia Overlapping With Lichen Planus Pigmentosus
Microscopic examination revealed focal dermal pigmentation, papillary fibrosis, and epidermal atrophy. These clinical and histologic findings indicated a diagnosis of fully developed lichen planus pigmentosus (LPP) overlapping with frontal fibrosing alopecia (FFA). Other cases have demonstrated an association between LPP and FFA.1,2
Lichen planus pigmentosus is considered an uncommon variant of lichen planus, as it has similar histopathologic findings and occasional coexistence.3,4 It is characterized by hyperpigmented macules primarily located in sun-exposed and flexural areas of the skin. First described in India,5 this disease has a predilection for darker skin (Fitzpatrick skin types III-V),6,7 and it has been reported in other racial and ethnic groups including Latin Americans, Middle Eastern populations, Japanese, and Koreans.4,8 Typically, lesions initially appear as ill-defined, blue-grey, round to oval macules that coalesce into hyperpigmented patches. Involvement most commonly begins at the forehead and temples, which are affected in nearly all patients. Infrequently, LPP can be generalized or affect the oral mucosa; involvement of the palms, soles, and nails does not occur. Patients may be asymptomatic, but some experience mild pruritus and burning. The disease course is chronic and insidious, with new lesions appearing over time and old lesions progressively darkening and expanding.6,7,9
Although the pathogenesis of LPP is unknown, several exposures have been implicated, such as amla oil, mustard oil, henna, hair dye, and environmental pollutants.7 Because lesions characteristically occur in sun-exposed areas, UV light also may be involved. In addition, studies have suggested that LPP is associated with endocrinopathies such as diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemias, as in our patient, as well as autoimmune conditions such as vitiligo and systemic lupus erythematosus.10,11
Histopathologic findings are characterized by vacuolar degeneration of the basal layer in the epidermis as well as perivascular lymphohistiocytic infiltration and the presence of melanophages in the dermis.3,9 Lichen planus pigmentosus is difficult to treat, as no consistently effective modality has been established. Topical tacrolimus, topical corticosteroids, oral retinoids, lasers, and sun protection have been implemented with underwhelming results.12
Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a variant of lichen planopilaris that predominantly affects postmenopausal women and presents with frontotemporal hair loss in a bandlike distribution.5,13 Both terminal and vellus hairs are affected. Involvement of multiple hair-bearing sites of the skin have been reported, including the entire scalp, eyebrows, and eyelashes. Affected areas may display hypopigmentation and be accompanied by pruritus and trichodynia.14,15 The pathogenesis currently is under investigation, with studies demonstrating autoimmune, genetic, and possibly even endocrine predispositions.16-18 Biopsies of lesions are indistinguishable from lichen planopilaris, which shows follicular lymphocytic infiltration, perifollicular fibrosis, interface dermatitis of the follicular infundibulum and isthmus, and vertical fibrous tracks.5 Patients with FFA have demonstrated variable responses to treatments, with one study showing improvement with oral finasteride or dutasteride.14 Topical and intralesional corticosteroids have yielded suboptimal effects. Other modalities include hydroxychloroquine and mycophenolate mofetil.15,19
Co-occurrence of LPP and FFA primarily is seen in postmenopausal women with darker skin,14,15 as in our patient, though premenopausal cases have been reported. Lichen planus pigmentosus may serve as a harbinger in most patients.1,2 In a similar fashion, our patient presented with hyperpigmented macular lesions prior to the onset of frontotemporal hair loss.
Our patient was started on finasteride 2.5 mg daily, minoxidil foam 5%, clobetasol solution 0.05%, triamcinolone ointment 0.1%, and hydrocortisone ointment 2.5%. She was instructed to commence treatment and follow up in 6 months.
The differential diagnosis includes dermatologic conditions that mimic both LPP and FFA. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and fixed drug reaction were unlikely based on the patient's history. The lesions of ashy dermatosis are characteristically gray erythematous macules on the trunk and limbs. Riehl melanosis is a rare pigmented contact dermatitis that is associated with a history of repeated contact with sensitizing allergens. Although Hori nevus is characterized by small, blue-gray or brown macules on the face, lesions predominantly occur on the bony prominences of the cheeks. Melasma also presents with dark to gray macules that affect the face and less commonly the neck, as in our patient.2
Early discoid lupus erythematosus presents with round erythematous plaques with overlying scale extending into the hair follicles. In pseudopalade of Brocq, an idiopathic cicatricial alopecia, lesions typically are flesh colored. Biopsy also shows epidermal atrophy with additional dermal sclerosis and fibrosis. Folliculitis decalvans is a scarring form of alopecia associated with erythema and pustules, findings that were not present in our patient. Keratosis follicularis spinulosa decalvans is a rare, X-linked inherited ichthyosis manifesting as scarring alopecia with follicular depressions and papules on the scalp in younger males. Photophobia and other manifestations may be present. Alopecia mucinosa is a nonscarring alopecia with grouped follicular erythematous patches or plaques. Mucin sometimes can be squeezed from affected areas, and histopathologic examination shows mucin accumulation.4
- Dlova NC. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus: is there a link? Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:439-442.
- Pirmez R, Duque-Estrada B, Donati A, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic features of lichen planus pigmentosus in 37 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1387-1390.
- Rieder E, Kaplan J, Kamino H, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:20713.
- Kashima A, Tajiri A, Yamashita A, et al. Two Japanese cases of lichen planus pigmentosus-inversus. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:740-742.
- Bhutani L, Bedi T, Pandhi R. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatologica. 1974;149:43-50.
- Ross EK, Tan E, Shapiro J. Update on primary cicatricial alopecias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1-37.
- Kanwa AJ, Dogra S, Handa S, et al. A study of 124 Indian patients with lichen planus pigmentosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:481-485.
- Al-Mutairi N, El-Khalawany M. Clinicopathological characteristics of lichen planus pigmentosus and its response to tacrolimus ointment: an open label, non-randomized, prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:535-540.
- Vega ME, Waxtein L, Arenas R, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: a clinicopathologic study of 31 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31:90-94.
- Robles-Méndez JC, Rizo-Frías P, Herz-Ruelas ME, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus and its variants: review and update. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:505-514.
- Torres J, Guadalupe A, Reyes E, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus in patients with endocrinopathies and hepatitis C. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:AB139.
- Kim JE, Won CH, Chang S, et al. Linear lichen planus pigmentosus of the forehead treated by neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser and topical tacrolimus. J Dermatol. 2012;39:189-191.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774.
- Vano-Galvan S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Serrano-Falcon C, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicenter review of 355 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:670-678.
- MacDonald A, Clark C, Holmes S. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a review of 60 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:955-961.
- Harries MJ, Meyer K, Chaudhry I, et al. Lichen planopilaris is characterized by immune privilege collapse of the hair follicle's epithelial stem cell niche. J Pathol. 2013;231:236-247.
- Karnik P, Tekeste Z, McCormick TS, et al. Hair follicle stem cell-specific PPARgamma deletion causes scarring alopecia. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:1243-1257.
- Rodriguez-Bayona B, Ruchaud S, Rodriguez C, et al. Autoantibodies against the chromosomal passenger protein INCENP found in a patient with Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007;4:1.
- Rácz E, Gho C, Moorman PW, et al. Treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planopilaris: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:1461-1470.
- Dlova NC. Frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planus pigmentosus: is there a link? Br J Dermatol. 2013;168:439-442.
- Pirmez R, Duque-Estrada B, Donati A, et al. Clinical and dermoscopic features of lichen planus pigmentosus in 37 patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia. Br J Dermatol. 2016;175:1387-1390.
- Rieder E, Kaplan J, Kamino H, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatol Online J. 2013;19:20713.
- Kashima A, Tajiri A, Yamashita A, et al. Two Japanese cases of lichen planus pigmentosus-inversus. Int J Dermatol. 2007;46:740-742.
- Bhutani L, Bedi T, Pandhi R. Lichen planus pigmentosus. Dermatologica. 1974;149:43-50.
- Ross EK, Tan E, Shapiro J. Update on primary cicatricial alopecias. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2005;53:1-37.
- Kanwa AJ, Dogra S, Handa S, et al. A study of 124 Indian patients with lichen planus pigmentosus. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2003;28:481-485.
- Al-Mutairi N, El-Khalawany M. Clinicopathological characteristics of lichen planus pigmentosus and its response to tacrolimus ointment: an open label, non-randomized, prospective study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2010;24:535-540.
- Vega ME, Waxtein L, Arenas R, et al. Ashy dermatosis and lichen planus pigmentosus: a clinicopathologic study of 31 cases. Int J Dermatol. 1992;31:90-94.
- Robles-Méndez JC, Rizo-Frías P, Herz-Ruelas ME, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus and its variants: review and update. Int J Dermatol. 2018;57:505-514.
- Torres J, Guadalupe A, Reyes E, et al. Lichen planus pigmentosus in patients with endocrinopathies and hepatitis C. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2013;68:AB139.
- Kim JE, Won CH, Chang S, et al. Linear lichen planus pigmentosus of the forehead treated by neodymium:yttrium-aluminum-garnet laser and topical tacrolimus. J Dermatol. 2012;39:189-191.
- Kossard S. Postmenopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia: scarring alopecia in a pattern distribution. Arch Dermatol. 1994;130:770-774.
- Vano-Galvan S, Molina-Ruiz AM, Serrano-Falcon C, et al. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a multicenter review of 355 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014;70:670-678.
- MacDonald A, Clark C, Holmes S. Frontal fibrosing alopecia: a review of 60 cases. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;67:955-961.
- Harries MJ, Meyer K, Chaudhry I, et al. Lichen planopilaris is characterized by immune privilege collapse of the hair follicle's epithelial stem cell niche. J Pathol. 2013;231:236-247.
- Karnik P, Tekeste Z, McCormick TS, et al. Hair follicle stem cell-specific PPARgamma deletion causes scarring alopecia. J Invest Dermatol. 2009;129:1243-1257.
- Rodriguez-Bayona B, Ruchaud S, Rodriguez C, et al. Autoantibodies against the chromosomal passenger protein INCENP found in a patient with Graham Little-Piccardi-Lassueur syndrome. J Autoimmune Dis. 2007;4:1.
- Rácz E, Gho C, Moorman PW, et al. Treatment of frontal fibrosing alopecia and lichen planopilaris: a systematic review. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2013;27:1461-1470.
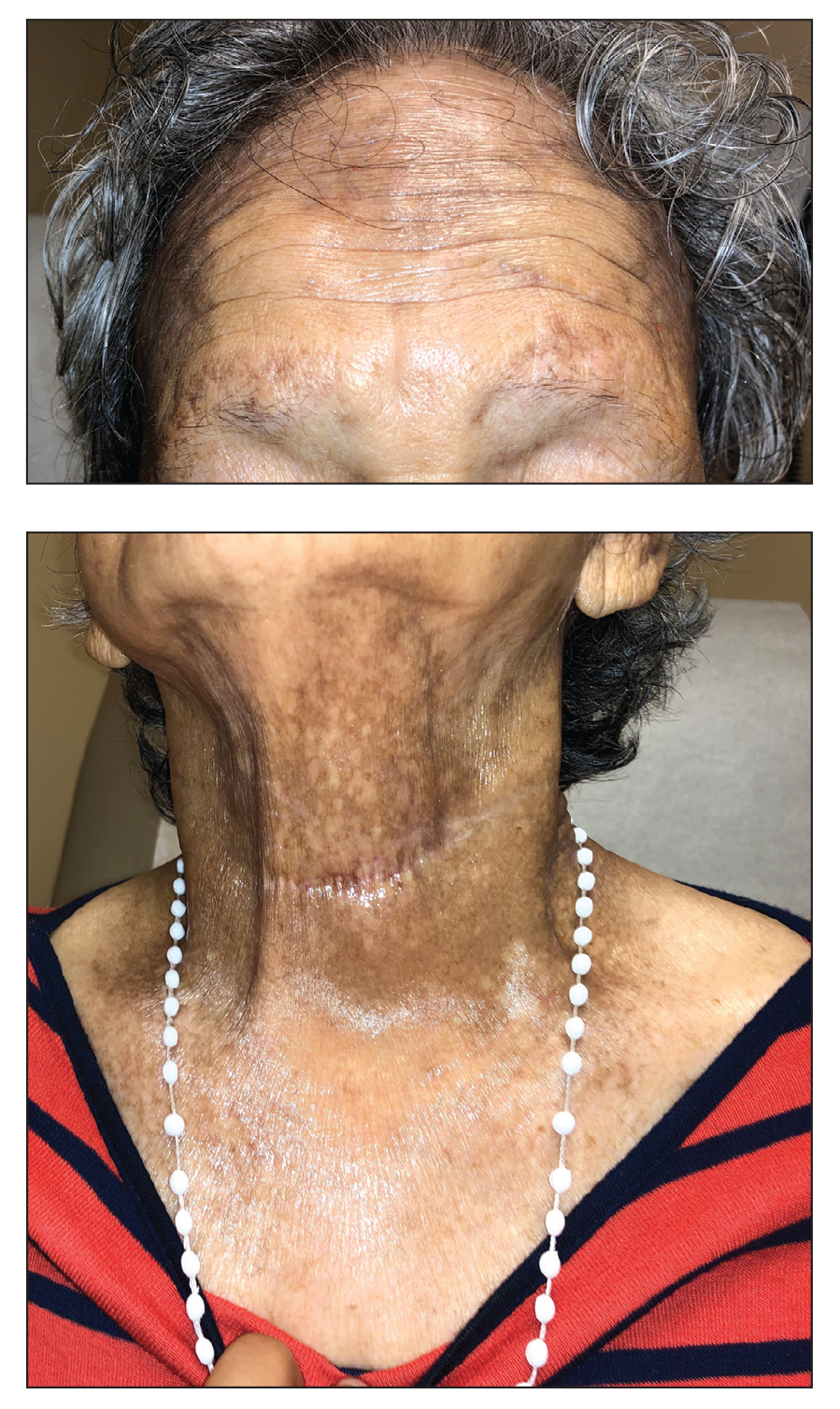
A 78-year-old Asian woman presented to the dermatology clinic with progressively worsening dark spots on the forehead and neck of 3 months’ duration. She noted mild pruritis and hair loss involving the eyebrows and anterior scalp. Her medical history was notable for type 2 diabetes mellitus. She denied any new medical conditions or medications and had no prior history of similar symptoms. Physical examination showed hyperpigmented brown macules and patches on the forehead (top) and anterior neck (bottom) with sparing of the posterior neck and lower face. Alopecia with areas of perifollicular erythema and hyperpigmentation with reduced follicular openings were present on the eyebrows and anterior forehead. Two punch biopsies of head and neck lesions were performed.