User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Taking cardiac pacing from boring to super cool
For the past 2 decades, catheter ablation stole most of the excitement in electrophysiology. Cardiac pacing was seen as necessary but boring. His-bundle pacing earned only modest attention.
But at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society, cardiac pacing consolidated its comeback and entered the super-cool category.
Not one but three late-breaking clinical trials considered the role of pacing the heart’s conduction system for both preventive and therapeutic purposes. Conduction system pacing, or CSP as we call it, includes pacing the His bundle or the left bundle branch. Left bundle–branch pacing has now largely replaced His-bundle pacing.
Before I tell you about the studies, let’s review why CSP disrupts the status quo.
The core idea goes back to basic physiology: After the impulse leaves the atrioventricular node, the heart’s specialized conduction system allows rapid and synchronous conduction to both the right and left ventricles.
Standard cardiac pacing means fixing a pacing lead into the muscle of the right ventricle. From that spot, conduction spreads via slower muscle-to-muscle conduction, which leads to a wide QRS complex and the right ventricle contracts before the left ventricle.
While such dyssynchronous contraction is better than no contraction, this approach leads to a pacing-induced cardiomyopathy in a substantial number of cases. (The incidence reported in many studies varies widely.)
The most disruptive effect of conduction system pacing is that it is a form of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). And that is nifty because, until recently, resynchronizing the ventricles required placing two ventricular leads: one in the right ventricle and the other in the coronary sinus to pace the left ventricle.
Left bundle-branch pacing vs. biventricular pacing
The first of the three HRS studies is the LBBP-RESYNC randomized controlled trial led by Jiangang Zou, MD, PhD, and performed in multiple centers in China. It compared the efficacy of left bundle–branch pacing (LBBP) with that of conventional biventricular pacing in 40 patients with heart failure who were eligible for CRT. The primary endpoint was the change in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) from baseline to 6-month follow-up.
The results favored LBBP. Although both pacing techniques improved LVEF from baseline, the between-group difference in LVEF was greater in the LBBP arm than the biventricular pacing arm by a statistically significant 5.6% (95% confidence interval, 0.3%-10.9%). Secondary endpoints, such as reductions in left ventricular end-systolic volume, N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, and QRS duration, also favored LBBP.
Conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing
A second late-breaking study, from the Geisinger group, led by Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, was simultaneously published in Heart Rhythm.
This nonrandomized observational study compared nearly 500 patients eligible for CRT treated at two health systems. One group favors conduction system pacing and the other does traditional biventricular pacing, which set up a two-armed comparison.
CSP was accomplished by LBBP (65%) and His-bundle pacing (35%).
The primary endpoint of death or first hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 28.3% of patients in the CSP arm versus 38.4% of the biventricular arm (hazard ratio, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.08-2.09). QRS duration and LVEF also improved from baseline in both groups.
LBB area pacing as a bailout for failed CRT
The Geisinger group also presented and published an international multicenter study that assessed the feasibility of LBBP as a bailout when standard biventricular pacing did not work – because of inadequate coronary sinus anatomy or CRT nonresponse, defined as lack of clinical or echocardiographic improvement.
This series included 212 patients in whom CRT failed and who underwent attempted LBBP pacing. The bailout was successful in 200 patients (91%). The primary endpoint was defined as an increase in LVEF above 5% on echocardiography.
During 12-month follow-up, 61% of patients had an improvement in LVEF above 5% and nearly 30% had a “super-response,” defined as a 20% or greater increase or normalization of LVEF. Similar to the previous studies, LBBP resulted in shorter QRS duration and improved echocardiography parameters.
Am I persuaded?
I was an early adopter of His-bundle pacing. When successful, it delivered both aesthetically pleasing QRS complexes and clinical efficacy. But there were many challenges: it is technically difficult, and capture thresholds are often high at implant and get higher over time, which leads to shorter battery life.
Pacing the left bundle branch mitigates these challenges. Here, the operator approaches from the right side and screws the lead a few millimeters into the septum, so the tip of the lead can capture the left bundle or one of its branches. This allows activation of the heart’s specialized conduction system and thus synchronizes right and left ventricle contraction.
Although there is a learning curve, LBBP is technically easier than His-bundle pacing and ultimately results in far better pacing and sensing parameters. What’s more, the preferred lead for LBBP has a stellar efficacy record – over years.
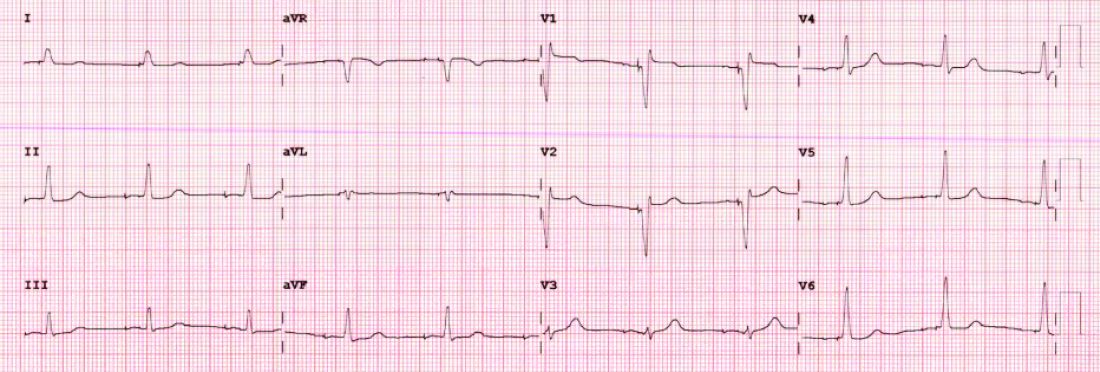
I have become enthralled by the gorgeous QRS complexes from LBBP. The ability to pace the heart without creating dyssynchrony infuses me with joy. I chose cardiology largely because of the beauty of the ECG.
But as a medical conservative who is cautious about unproven therapies, I have questions. How is LBBP defined? Is left septal pacing good enough, or do you need actual left bundle capture? What about long-term performance of a lead in the septum?
Biventricular pacing has set a high bar because it has been proven effective for reducing hard clinical outcomes in large randomized controlled trials.
The studies at HRS begin to answer these questions. The randomized controlled trial from China supports the notion that effective LBBP (the investigators rigorously defined left bundle capture) leads to favorable effects on cardiac contraction. The two observational studies reported similarly encouraging findings on cardiac function.
The three studies therefore tentatively support the notion that LBBP actually produces favorable cardiac performance.
Whether LBBP leads to better clinical outcomes remains uncertain. The nonrandomized comparison study, which found better hard outcomes in the CSP arm, cannot be used to infer causality. There is too much risk for selection bias.
But the LBBP bailout study does suggest that this strategy is reasonable when coronary sinus leads fail – especially since the alternative is surgical placement of an epicardial lead on the left ventricle.
At minimum, the HRS studies persuade me that LBBP will likely prevent pacing-induced cardiomyopathy. If I or a family member required a pacemaker, I’d surely want the operator to be skilled at placing a left bundle lead.
While I am confident that conduction system pacing will become a transformative advance in cardiac pacing, aesthetically pleasing ECG patterns are not enough. There remains much to learn with this nascent approach.
The barriers to getting more CSP trials
The challenge going forward will be funding new trials. CSP stands to prevent pacing-induced cardiomyopathy and offer less costly alternatives to standard biventricular pacing for CRT. This is great for patients, but it would mean that fewer higher-cost CRT devices will be sold.
Heart rhythm research is largely industry-funded because in most cases better therapies for patients mean more profits for industry. In the case of CSP, there is no such confluence of interests.
Conduction system pacing has come about because of the efforts of a few tireless champions who not only published extensively but were also skilled at using social media to spread the excitement. Trials have been small and often self-funded.
The data presented at HRS provides enough equipoise to support a large outcomes-based randomized controlled trial. Imagine if our CSP champions were able to find public-funding sources for such future trials.
Now that would be super cool.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky., and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He participates in clinical research and writes often about the state of medical evidence. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For the past 2 decades, catheter ablation stole most of the excitement in electrophysiology. Cardiac pacing was seen as necessary but boring. His-bundle pacing earned only modest attention.
But at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society, cardiac pacing consolidated its comeback and entered the super-cool category.
Not one but three late-breaking clinical trials considered the role of pacing the heart’s conduction system for both preventive and therapeutic purposes. Conduction system pacing, or CSP as we call it, includes pacing the His bundle or the left bundle branch. Left bundle–branch pacing has now largely replaced His-bundle pacing.
Before I tell you about the studies, let’s review why CSP disrupts the status quo.
The core idea goes back to basic physiology: After the impulse leaves the atrioventricular node, the heart’s specialized conduction system allows rapid and synchronous conduction to both the right and left ventricles.
Standard cardiac pacing means fixing a pacing lead into the muscle of the right ventricle. From that spot, conduction spreads via slower muscle-to-muscle conduction, which leads to a wide QRS complex and the right ventricle contracts before the left ventricle.
While such dyssynchronous contraction is better than no contraction, this approach leads to a pacing-induced cardiomyopathy in a substantial number of cases. (The incidence reported in many studies varies widely.)
The most disruptive effect of conduction system pacing is that it is a form of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). And that is nifty because, until recently, resynchronizing the ventricles required placing two ventricular leads: one in the right ventricle and the other in the coronary sinus to pace the left ventricle.
Left bundle-branch pacing vs. biventricular pacing
The first of the three HRS studies is the LBBP-RESYNC randomized controlled trial led by Jiangang Zou, MD, PhD, and performed in multiple centers in China. It compared the efficacy of left bundle–branch pacing (LBBP) with that of conventional biventricular pacing in 40 patients with heart failure who were eligible for CRT. The primary endpoint was the change in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) from baseline to 6-month follow-up.
The results favored LBBP. Although both pacing techniques improved LVEF from baseline, the between-group difference in LVEF was greater in the LBBP arm than the biventricular pacing arm by a statistically significant 5.6% (95% confidence interval, 0.3%-10.9%). Secondary endpoints, such as reductions in left ventricular end-systolic volume, N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, and QRS duration, also favored LBBP.
Conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing
A second late-breaking study, from the Geisinger group, led by Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, was simultaneously published in Heart Rhythm.
This nonrandomized observational study compared nearly 500 patients eligible for CRT treated at two health systems. One group favors conduction system pacing and the other does traditional biventricular pacing, which set up a two-armed comparison.
CSP was accomplished by LBBP (65%) and His-bundle pacing (35%).
The primary endpoint of death or first hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 28.3% of patients in the CSP arm versus 38.4% of the biventricular arm (hazard ratio, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.08-2.09). QRS duration and LVEF also improved from baseline in both groups.
LBB area pacing as a bailout for failed CRT
The Geisinger group also presented and published an international multicenter study that assessed the feasibility of LBBP as a bailout when standard biventricular pacing did not work – because of inadequate coronary sinus anatomy or CRT nonresponse, defined as lack of clinical or echocardiographic improvement.
This series included 212 patients in whom CRT failed and who underwent attempted LBBP pacing. The bailout was successful in 200 patients (91%). The primary endpoint was defined as an increase in LVEF above 5% on echocardiography.
During 12-month follow-up, 61% of patients had an improvement in LVEF above 5% and nearly 30% had a “super-response,” defined as a 20% or greater increase or normalization of LVEF. Similar to the previous studies, LBBP resulted in shorter QRS duration and improved echocardiography parameters.
Am I persuaded?
I was an early adopter of His-bundle pacing. When successful, it delivered both aesthetically pleasing QRS complexes and clinical efficacy. But there were many challenges: it is technically difficult, and capture thresholds are often high at implant and get higher over time, which leads to shorter battery life.
Pacing the left bundle branch mitigates these challenges. Here, the operator approaches from the right side and screws the lead a few millimeters into the septum, so the tip of the lead can capture the left bundle or one of its branches. This allows activation of the heart’s specialized conduction system and thus synchronizes right and left ventricle contraction.
Although there is a learning curve, LBBP is technically easier than His-bundle pacing and ultimately results in far better pacing and sensing parameters. What’s more, the preferred lead for LBBP has a stellar efficacy record – over years.

I have become enthralled by the gorgeous QRS complexes from LBBP. The ability to pace the heart without creating dyssynchrony infuses me with joy. I chose cardiology largely because of the beauty of the ECG.
But as a medical conservative who is cautious about unproven therapies, I have questions. How is LBBP defined? Is left septal pacing good enough, or do you need actual left bundle capture? What about long-term performance of a lead in the septum?
Biventricular pacing has set a high bar because it has been proven effective for reducing hard clinical outcomes in large randomized controlled trials.
The studies at HRS begin to answer these questions. The randomized controlled trial from China supports the notion that effective LBBP (the investigators rigorously defined left bundle capture) leads to favorable effects on cardiac contraction. The two observational studies reported similarly encouraging findings on cardiac function.
The three studies therefore tentatively support the notion that LBBP actually produces favorable cardiac performance.
Whether LBBP leads to better clinical outcomes remains uncertain. The nonrandomized comparison study, which found better hard outcomes in the CSP arm, cannot be used to infer causality. There is too much risk for selection bias.
But the LBBP bailout study does suggest that this strategy is reasonable when coronary sinus leads fail – especially since the alternative is surgical placement of an epicardial lead on the left ventricle.
At minimum, the HRS studies persuade me that LBBP will likely prevent pacing-induced cardiomyopathy. If I or a family member required a pacemaker, I’d surely want the operator to be skilled at placing a left bundle lead.
While I am confident that conduction system pacing will become a transformative advance in cardiac pacing, aesthetically pleasing ECG patterns are not enough. There remains much to learn with this nascent approach.
The barriers to getting more CSP trials
The challenge going forward will be funding new trials. CSP stands to prevent pacing-induced cardiomyopathy and offer less costly alternatives to standard biventricular pacing for CRT. This is great for patients, but it would mean that fewer higher-cost CRT devices will be sold.
Heart rhythm research is largely industry-funded because in most cases better therapies for patients mean more profits for industry. In the case of CSP, there is no such confluence of interests.
Conduction system pacing has come about because of the efforts of a few tireless champions who not only published extensively but were also skilled at using social media to spread the excitement. Trials have been small and often self-funded.
The data presented at HRS provides enough equipoise to support a large outcomes-based randomized controlled trial. Imagine if our CSP champions were able to find public-funding sources for such future trials.
Now that would be super cool.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky., and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He participates in clinical research and writes often about the state of medical evidence. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
For the past 2 decades, catheter ablation stole most of the excitement in electrophysiology. Cardiac pacing was seen as necessary but boring. His-bundle pacing earned only modest attention.
But at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society, cardiac pacing consolidated its comeback and entered the super-cool category.
Not one but three late-breaking clinical trials considered the role of pacing the heart’s conduction system for both preventive and therapeutic purposes. Conduction system pacing, or CSP as we call it, includes pacing the His bundle or the left bundle branch. Left bundle–branch pacing has now largely replaced His-bundle pacing.
Before I tell you about the studies, let’s review why CSP disrupts the status quo.
The core idea goes back to basic physiology: After the impulse leaves the atrioventricular node, the heart’s specialized conduction system allows rapid and synchronous conduction to both the right and left ventricles.
Standard cardiac pacing means fixing a pacing lead into the muscle of the right ventricle. From that spot, conduction spreads via slower muscle-to-muscle conduction, which leads to a wide QRS complex and the right ventricle contracts before the left ventricle.
While such dyssynchronous contraction is better than no contraction, this approach leads to a pacing-induced cardiomyopathy in a substantial number of cases. (The incidence reported in many studies varies widely.)
The most disruptive effect of conduction system pacing is that it is a form of cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT). And that is nifty because, until recently, resynchronizing the ventricles required placing two ventricular leads: one in the right ventricle and the other in the coronary sinus to pace the left ventricle.
Left bundle-branch pacing vs. biventricular pacing
The first of the three HRS studies is the LBBP-RESYNC randomized controlled trial led by Jiangang Zou, MD, PhD, and performed in multiple centers in China. It compared the efficacy of left bundle–branch pacing (LBBP) with that of conventional biventricular pacing in 40 patients with heart failure who were eligible for CRT. The primary endpoint was the change in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) from baseline to 6-month follow-up.
The results favored LBBP. Although both pacing techniques improved LVEF from baseline, the between-group difference in LVEF was greater in the LBBP arm than the biventricular pacing arm by a statistically significant 5.6% (95% confidence interval, 0.3%-10.9%). Secondary endpoints, such as reductions in left ventricular end-systolic volume, N-terminal of the prohormone brain natriuretic peptide, and QRS duration, also favored LBBP.
Conduction system pacing vs. biventricular pacing
A second late-breaking study, from the Geisinger group, led by Pugazhendhi Vijayaraman, MD, was simultaneously published in Heart Rhythm.
This nonrandomized observational study compared nearly 500 patients eligible for CRT treated at two health systems. One group favors conduction system pacing and the other does traditional biventricular pacing, which set up a two-armed comparison.
CSP was accomplished by LBBP (65%) and His-bundle pacing (35%).
The primary endpoint of death or first hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 28.3% of patients in the CSP arm versus 38.4% of the biventricular arm (hazard ratio, 1.52; 95% CI, 1.08-2.09). QRS duration and LVEF also improved from baseline in both groups.
LBB area pacing as a bailout for failed CRT
The Geisinger group also presented and published an international multicenter study that assessed the feasibility of LBBP as a bailout when standard biventricular pacing did not work – because of inadequate coronary sinus anatomy or CRT nonresponse, defined as lack of clinical or echocardiographic improvement.
This series included 212 patients in whom CRT failed and who underwent attempted LBBP pacing. The bailout was successful in 200 patients (91%). The primary endpoint was defined as an increase in LVEF above 5% on echocardiography.
During 12-month follow-up, 61% of patients had an improvement in LVEF above 5% and nearly 30% had a “super-response,” defined as a 20% or greater increase or normalization of LVEF. Similar to the previous studies, LBBP resulted in shorter QRS duration and improved echocardiography parameters.
Am I persuaded?
I was an early adopter of His-bundle pacing. When successful, it delivered both aesthetically pleasing QRS complexes and clinical efficacy. But there were many challenges: it is technically difficult, and capture thresholds are often high at implant and get higher over time, which leads to shorter battery life.
Pacing the left bundle branch mitigates these challenges. Here, the operator approaches from the right side and screws the lead a few millimeters into the septum, so the tip of the lead can capture the left bundle or one of its branches. This allows activation of the heart’s specialized conduction system and thus synchronizes right and left ventricle contraction.
Although there is a learning curve, LBBP is technically easier than His-bundle pacing and ultimately results in far better pacing and sensing parameters. What’s more, the preferred lead for LBBP has a stellar efficacy record – over years.

I have become enthralled by the gorgeous QRS complexes from LBBP. The ability to pace the heart without creating dyssynchrony infuses me with joy. I chose cardiology largely because of the beauty of the ECG.
But as a medical conservative who is cautious about unproven therapies, I have questions. How is LBBP defined? Is left septal pacing good enough, or do you need actual left bundle capture? What about long-term performance of a lead in the septum?
Biventricular pacing has set a high bar because it has been proven effective for reducing hard clinical outcomes in large randomized controlled trials.
The studies at HRS begin to answer these questions. The randomized controlled trial from China supports the notion that effective LBBP (the investigators rigorously defined left bundle capture) leads to favorable effects on cardiac contraction. The two observational studies reported similarly encouraging findings on cardiac function.
The three studies therefore tentatively support the notion that LBBP actually produces favorable cardiac performance.
Whether LBBP leads to better clinical outcomes remains uncertain. The nonrandomized comparison study, which found better hard outcomes in the CSP arm, cannot be used to infer causality. There is too much risk for selection bias.
But the LBBP bailout study does suggest that this strategy is reasonable when coronary sinus leads fail – especially since the alternative is surgical placement of an epicardial lead on the left ventricle.
At minimum, the HRS studies persuade me that LBBP will likely prevent pacing-induced cardiomyopathy. If I or a family member required a pacemaker, I’d surely want the operator to be skilled at placing a left bundle lead.
While I am confident that conduction system pacing will become a transformative advance in cardiac pacing, aesthetically pleasing ECG patterns are not enough. There remains much to learn with this nascent approach.
The barriers to getting more CSP trials
The challenge going forward will be funding new trials. CSP stands to prevent pacing-induced cardiomyopathy and offer less costly alternatives to standard biventricular pacing for CRT. This is great for patients, but it would mean that fewer higher-cost CRT devices will be sold.
Heart rhythm research is largely industry-funded because in most cases better therapies for patients mean more profits for industry. In the case of CSP, there is no such confluence of interests.
Conduction system pacing has come about because of the efforts of a few tireless champions who not only published extensively but were also skilled at using social media to spread the excitement. Trials have been small and often self-funded.
The data presented at HRS provides enough equipoise to support a large outcomes-based randomized controlled trial. Imagine if our CSP champions were able to find public-funding sources for such future trials.
Now that would be super cool.
Dr. Mandrola practices cardiac electrophysiology in Louisville, Ky., and is a writer and podcaster for Medscape. He participates in clinical research and writes often about the state of medical evidence. He has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TikTok challenge hits Taco Bell right in its ‘Stuft Nacho’
Losing weight for TikTok: Taco Bell edition
There are many reasons why a person would want to lose weight. Too numerous to list. Losing weight to improve your health, however, doesn’t bring in a few hundred thousand TikTok subscribers. Losing weight to convince Taco Bell to bring back an obscure menu item, on the other hand ...
Chris Sandberg, a 37-year-old man from San Francisco, has struggled with his weight for years, losing and gaining hundreds of pounds in an endless cycle of feast and famine. In an unrelated development, at the start of the pandemic he also started making videos on TikTok. As the pandemic wore on, he realized that his excess weight put him at increased risk for severe COVID, as well as other chronic diseases, and he resolved to lose weight. He decided to turn his weight-loss journey into a TikTok challenge but, as we said, losing weight for its own sake isn’t enough for the almighty algorithm. He needed a different goal, preferably something offbeat and a little silly.
Back in 2013, Taco Bell introduced the Grilled Stuft Nacho, “a flour tortilla, shaped like a nacho, stuffed with beef, cheesy jalapeño sauce, sour cream and crunchy red strips,” according to its website. Mr. Sandberg discovered the item in 2015 and instantly fell in love, purchasing one every day for a week. After that first week, however, he discovered, to his horror, that the Grilled Stuft Nacho had been discontinued.
That loss haunted him for years, until inspiration struck in 2021. He pledged to work out every day on TikTok until Taco Bell brought back the Grilled Stuft Nacho. A bit incongruous, exercising for notoriously unhealthy fast food, but that’s kind of the point. He began the challenge on Jan. 4, 2021, and has continued it every day since, nearly 500 days. Over that time, he’s lost 87 pounds (from 275 at the start to under 190) and currently has 450,000 TikTok subscribers.
A year into the challenge, a local Taco Bell made Mr. Sandberg his beloved Grilled Stuft Nacho, but since the challenge was to exercise until Taco Bell brings the item back to all its restaurants, not just for him, the great journey continues. And we admire him for it. In fact, he’s inspired us: We will write a LOTME every week until it receives a Pulitzer Prize. This is important journalism we do here. Don’t deny it!
Episode XIX: COVID strikes back
So what’s next for COVID? Is Disney going to turn it into a series? Can it support a spin-off? Did James Cameron really buy the movie rights? Can it compete against the NFL in the all-important 18-34 demographic? When are Star Wars characters going to get involved?
COVID’s motivations and negotiations are pretty much a mystery to us, but we can answer that last question. They already are involved. Well, one of them anyway.
The Chinese government has been enforcing a COVID lockdown in Shanghai for over a month now, but authorities had started letting people out of their homes for short periods of time. A recent push to bring down transmission, however, has made residents increasingly frustrated and argumentative, according to Reuters.
A now-unavailable video, which Reuters could not verify, surfaced on Chinese social media showing police in hazmat suits arguing with people who were being told that they were going to be quarantined because a neighbor had tested positive.
That’s when the Force kicks in, and this next bit comes directly from the Reuters report: “This is so that we can thoroughly remove any positive cases,” one of the officers is heard saying. “Stop asking me why, there is no why.”
There is no why? Does that remind you of someone? Someone short and green, with an odd syntax? That’s right. Clearly, Yoda it is. Yoda is alive and working for the Chinese government in Shanghai. You read it here first.
Your coffee may be guilty of sexual discrimination
How do you take your coffee? Espresso, drip, instant, or brewed from a regular old coffee machine? Well, a recent study published in Open Heart suggests that gender and brewing method can alter your coffee’s effect on cholesterol levels.
Besides caffeine, coffee beans have naturally occurring chemicals such as diterpenes, cafestol, and kahweol that raise cholesterol levels in the blood. And then there are the various brewing methods, which are going to release different amounts of chemicals from the beans. According to Consumer Reports, an ounce of espresso has 63 mg of caffeine and an ounce of regular coffee has 12-16 mg. That’s a bit deceiving, though, since no one ever drinks an ounce of regular coffee, so figure 96-128 mg of caffeine for an 8-ounce cup. That’s enough to make anyone’s heart race.
Data from 21,083 participants in the seventh survey of the Tromsø Study who were aged 40 and older showed that women drank a mean of 3.8 cups per day while men drank 4.9 cups. Drinking six or more cups of plunger-brewed coffee was associated with increased cholesterol in both genders, but drinking three to five cups of espresso was significantly associated with high cholesterol in men only. Having six or more cups of filtered coffee daily raised cholesterol in women, but instant coffee increased cholesterol levels in both genders, regardless of how many cups they drank.
People all over the planet drink coffee, some of us like our lives depend on it. Since “coffee is the most frequently consumed central stimulant worldwide,” the investigators said, “even small health effects can have considerable health consequences.”
We’ll drink to that.
Have you ever dreamed of having a clone?
When will science grace us with the ability to clone ourselves? It sounds like a dream come true. Our clones can do the stuff that we don’t want to do, like sit in on that 3-hour meeting or do our grocery shopping – really just all the boring stuff we don’t want to do.
In 1996, when a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal cloned successfully, people thought it was the start of an amazing cloning era, but, alas, we haven’t made it to cloning humans yet, as LiveScience discovered when it took a look at the subject.
The idea of cloning was quite exciting for science, as people looked forward to eradicating genetic diseases and birth defects. Research done in 1999, however, countered those hopes by suggesting that cloning might increase birth defects.
So why do you think we haven’t advanced to truly cloning humans? Ethics? Time and effort? Technological barriers? “Human cloning is a particularly dramatic action, and was one of the topics that helped launch American bioethics,” Hank Greely, professor of law and genetics at Stanford (Calif.) University, told LiveScience.
What if the clones turned evil and were bent on destroying the world?
We might imagine a clone of ourselves being completely identical to us in our thoughts, actions, and physical looks. However, that’s not necessarily true; a clone would be its own person even if it looks exactly like you.
So what do the professionals think? Is it worth giving human cloning a shot? Are there benefits? Mr. Greely said that “there are none that we should be willing to consider.”
The dream of having a clone to help your son with his math homework may have gone down the drain, but maybe it’s best not to open doors that could lead to drastic changes in our world.
Losing weight for TikTok: Taco Bell edition
There are many reasons why a person would want to lose weight. Too numerous to list. Losing weight to improve your health, however, doesn’t bring in a few hundred thousand TikTok subscribers. Losing weight to convince Taco Bell to bring back an obscure menu item, on the other hand ...
Chris Sandberg, a 37-year-old man from San Francisco, has struggled with his weight for years, losing and gaining hundreds of pounds in an endless cycle of feast and famine. In an unrelated development, at the start of the pandemic he also started making videos on TikTok. As the pandemic wore on, he realized that his excess weight put him at increased risk for severe COVID, as well as other chronic diseases, and he resolved to lose weight. He decided to turn his weight-loss journey into a TikTok challenge but, as we said, losing weight for its own sake isn’t enough for the almighty algorithm. He needed a different goal, preferably something offbeat and a little silly.
Back in 2013, Taco Bell introduced the Grilled Stuft Nacho, “a flour tortilla, shaped like a nacho, stuffed with beef, cheesy jalapeño sauce, sour cream and crunchy red strips,” according to its website. Mr. Sandberg discovered the item in 2015 and instantly fell in love, purchasing one every day for a week. After that first week, however, he discovered, to his horror, that the Grilled Stuft Nacho had been discontinued.
That loss haunted him for years, until inspiration struck in 2021. He pledged to work out every day on TikTok until Taco Bell brought back the Grilled Stuft Nacho. A bit incongruous, exercising for notoriously unhealthy fast food, but that’s kind of the point. He began the challenge on Jan. 4, 2021, and has continued it every day since, nearly 500 days. Over that time, he’s lost 87 pounds (from 275 at the start to under 190) and currently has 450,000 TikTok subscribers.
A year into the challenge, a local Taco Bell made Mr. Sandberg his beloved Grilled Stuft Nacho, but since the challenge was to exercise until Taco Bell brings the item back to all its restaurants, not just for him, the great journey continues. And we admire him for it. In fact, he’s inspired us: We will write a LOTME every week until it receives a Pulitzer Prize. This is important journalism we do here. Don’t deny it!
Episode XIX: COVID strikes back
So what’s next for COVID? Is Disney going to turn it into a series? Can it support a spin-off? Did James Cameron really buy the movie rights? Can it compete against the NFL in the all-important 18-34 demographic? When are Star Wars characters going to get involved?
COVID’s motivations and negotiations are pretty much a mystery to us, but we can answer that last question. They already are involved. Well, one of them anyway.
The Chinese government has been enforcing a COVID lockdown in Shanghai for over a month now, but authorities had started letting people out of their homes for short periods of time. A recent push to bring down transmission, however, has made residents increasingly frustrated and argumentative, according to Reuters.
A now-unavailable video, which Reuters could not verify, surfaced on Chinese social media showing police in hazmat suits arguing with people who were being told that they were going to be quarantined because a neighbor had tested positive.
That’s when the Force kicks in, and this next bit comes directly from the Reuters report: “This is so that we can thoroughly remove any positive cases,” one of the officers is heard saying. “Stop asking me why, there is no why.”
There is no why? Does that remind you of someone? Someone short and green, with an odd syntax? That’s right. Clearly, Yoda it is. Yoda is alive and working for the Chinese government in Shanghai. You read it here first.
Your coffee may be guilty of sexual discrimination
How do you take your coffee? Espresso, drip, instant, or brewed from a regular old coffee machine? Well, a recent study published in Open Heart suggests that gender and brewing method can alter your coffee’s effect on cholesterol levels.
Besides caffeine, coffee beans have naturally occurring chemicals such as diterpenes, cafestol, and kahweol that raise cholesterol levels in the blood. And then there are the various brewing methods, which are going to release different amounts of chemicals from the beans. According to Consumer Reports, an ounce of espresso has 63 mg of caffeine and an ounce of regular coffee has 12-16 mg. That’s a bit deceiving, though, since no one ever drinks an ounce of regular coffee, so figure 96-128 mg of caffeine for an 8-ounce cup. That’s enough to make anyone’s heart race.
Data from 21,083 participants in the seventh survey of the Tromsø Study who were aged 40 and older showed that women drank a mean of 3.8 cups per day while men drank 4.9 cups. Drinking six or more cups of plunger-brewed coffee was associated with increased cholesterol in both genders, but drinking three to five cups of espresso was significantly associated with high cholesterol in men only. Having six or more cups of filtered coffee daily raised cholesterol in women, but instant coffee increased cholesterol levels in both genders, regardless of how many cups they drank.
People all over the planet drink coffee, some of us like our lives depend on it. Since “coffee is the most frequently consumed central stimulant worldwide,” the investigators said, “even small health effects can have considerable health consequences.”
We’ll drink to that.
Have you ever dreamed of having a clone?
When will science grace us with the ability to clone ourselves? It sounds like a dream come true. Our clones can do the stuff that we don’t want to do, like sit in on that 3-hour meeting or do our grocery shopping – really just all the boring stuff we don’t want to do.
In 1996, when a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal cloned successfully, people thought it was the start of an amazing cloning era, but, alas, we haven’t made it to cloning humans yet, as LiveScience discovered when it took a look at the subject.
The idea of cloning was quite exciting for science, as people looked forward to eradicating genetic diseases and birth defects. Research done in 1999, however, countered those hopes by suggesting that cloning might increase birth defects.
So why do you think we haven’t advanced to truly cloning humans? Ethics? Time and effort? Technological barriers? “Human cloning is a particularly dramatic action, and was one of the topics that helped launch American bioethics,” Hank Greely, professor of law and genetics at Stanford (Calif.) University, told LiveScience.
What if the clones turned evil and were bent on destroying the world?
We might imagine a clone of ourselves being completely identical to us in our thoughts, actions, and physical looks. However, that’s not necessarily true; a clone would be its own person even if it looks exactly like you.
So what do the professionals think? Is it worth giving human cloning a shot? Are there benefits? Mr. Greely said that “there are none that we should be willing to consider.”
The dream of having a clone to help your son with his math homework may have gone down the drain, but maybe it’s best not to open doors that could lead to drastic changes in our world.
Losing weight for TikTok: Taco Bell edition
There are many reasons why a person would want to lose weight. Too numerous to list. Losing weight to improve your health, however, doesn’t bring in a few hundred thousand TikTok subscribers. Losing weight to convince Taco Bell to bring back an obscure menu item, on the other hand ...
Chris Sandberg, a 37-year-old man from San Francisco, has struggled with his weight for years, losing and gaining hundreds of pounds in an endless cycle of feast and famine. In an unrelated development, at the start of the pandemic he also started making videos on TikTok. As the pandemic wore on, he realized that his excess weight put him at increased risk for severe COVID, as well as other chronic diseases, and he resolved to lose weight. He decided to turn his weight-loss journey into a TikTok challenge but, as we said, losing weight for its own sake isn’t enough for the almighty algorithm. He needed a different goal, preferably something offbeat and a little silly.
Back in 2013, Taco Bell introduced the Grilled Stuft Nacho, “a flour tortilla, shaped like a nacho, stuffed with beef, cheesy jalapeño sauce, sour cream and crunchy red strips,” according to its website. Mr. Sandberg discovered the item in 2015 and instantly fell in love, purchasing one every day for a week. After that first week, however, he discovered, to his horror, that the Grilled Stuft Nacho had been discontinued.
That loss haunted him for years, until inspiration struck in 2021. He pledged to work out every day on TikTok until Taco Bell brought back the Grilled Stuft Nacho. A bit incongruous, exercising for notoriously unhealthy fast food, but that’s kind of the point. He began the challenge on Jan. 4, 2021, and has continued it every day since, nearly 500 days. Over that time, he’s lost 87 pounds (from 275 at the start to under 190) and currently has 450,000 TikTok subscribers.
A year into the challenge, a local Taco Bell made Mr. Sandberg his beloved Grilled Stuft Nacho, but since the challenge was to exercise until Taco Bell brings the item back to all its restaurants, not just for him, the great journey continues. And we admire him for it. In fact, he’s inspired us: We will write a LOTME every week until it receives a Pulitzer Prize. This is important journalism we do here. Don’t deny it!
Episode XIX: COVID strikes back
So what’s next for COVID? Is Disney going to turn it into a series? Can it support a spin-off? Did James Cameron really buy the movie rights? Can it compete against the NFL in the all-important 18-34 demographic? When are Star Wars characters going to get involved?
COVID’s motivations and negotiations are pretty much a mystery to us, but we can answer that last question. They already are involved. Well, one of them anyway.
The Chinese government has been enforcing a COVID lockdown in Shanghai for over a month now, but authorities had started letting people out of their homes for short periods of time. A recent push to bring down transmission, however, has made residents increasingly frustrated and argumentative, according to Reuters.
A now-unavailable video, which Reuters could not verify, surfaced on Chinese social media showing police in hazmat suits arguing with people who were being told that they were going to be quarantined because a neighbor had tested positive.
That’s when the Force kicks in, and this next bit comes directly from the Reuters report: “This is so that we can thoroughly remove any positive cases,” one of the officers is heard saying. “Stop asking me why, there is no why.”
There is no why? Does that remind you of someone? Someone short and green, with an odd syntax? That’s right. Clearly, Yoda it is. Yoda is alive and working for the Chinese government in Shanghai. You read it here first.
Your coffee may be guilty of sexual discrimination
How do you take your coffee? Espresso, drip, instant, or brewed from a regular old coffee machine? Well, a recent study published in Open Heart suggests that gender and brewing method can alter your coffee’s effect on cholesterol levels.
Besides caffeine, coffee beans have naturally occurring chemicals such as diterpenes, cafestol, and kahweol that raise cholesterol levels in the blood. And then there are the various brewing methods, which are going to release different amounts of chemicals from the beans. According to Consumer Reports, an ounce of espresso has 63 mg of caffeine and an ounce of regular coffee has 12-16 mg. That’s a bit deceiving, though, since no one ever drinks an ounce of regular coffee, so figure 96-128 mg of caffeine for an 8-ounce cup. That’s enough to make anyone’s heart race.
Data from 21,083 participants in the seventh survey of the Tromsø Study who were aged 40 and older showed that women drank a mean of 3.8 cups per day while men drank 4.9 cups. Drinking six or more cups of plunger-brewed coffee was associated with increased cholesterol in both genders, but drinking three to five cups of espresso was significantly associated with high cholesterol in men only. Having six or more cups of filtered coffee daily raised cholesterol in women, but instant coffee increased cholesterol levels in both genders, regardless of how many cups they drank.
People all over the planet drink coffee, some of us like our lives depend on it. Since “coffee is the most frequently consumed central stimulant worldwide,” the investigators said, “even small health effects can have considerable health consequences.”
We’ll drink to that.
Have you ever dreamed of having a clone?
When will science grace us with the ability to clone ourselves? It sounds like a dream come true. Our clones can do the stuff that we don’t want to do, like sit in on that 3-hour meeting or do our grocery shopping – really just all the boring stuff we don’t want to do.
In 1996, when a sheep named Dolly became the first mammal cloned successfully, people thought it was the start of an amazing cloning era, but, alas, we haven’t made it to cloning humans yet, as LiveScience discovered when it took a look at the subject.
The idea of cloning was quite exciting for science, as people looked forward to eradicating genetic diseases and birth defects. Research done in 1999, however, countered those hopes by suggesting that cloning might increase birth defects.
So why do you think we haven’t advanced to truly cloning humans? Ethics? Time and effort? Technological barriers? “Human cloning is a particularly dramatic action, and was one of the topics that helped launch American bioethics,” Hank Greely, professor of law and genetics at Stanford (Calif.) University, told LiveScience.
What if the clones turned evil and were bent on destroying the world?
We might imagine a clone of ourselves being completely identical to us in our thoughts, actions, and physical looks. However, that’s not necessarily true; a clone would be its own person even if it looks exactly like you.
So what do the professionals think? Is it worth giving human cloning a shot? Are there benefits? Mr. Greely said that “there are none that we should be willing to consider.”
The dream of having a clone to help your son with his math homework may have gone down the drain, but maybe it’s best not to open doors that could lead to drastic changes in our world.
Recommendations for improving federal diabetes programs: How primary care clinicians can help with implementation
Recently the National Clinical Care Commission provided recommendations to Congress for improving federal diabetes programs in a report. This commission was put together after Congress passed the National Clinical Care Commission Act in 2017.
The report provides a wide range of recommendations that look to combat and prevent diabetes at many levels. An exciting aspect of the recommendations is that they consider how all agencies, including those that are not specifically health care, can fight diabetes.
The report acknowledges that many recent advances in diabetes treatments have made huge differences for clinicians and patients alike. Unfortunately, they have not been translated quickly into practice and when they have been, there have been disparities in the rollouts.
The document also states that many other factors, including housing, health care access, and food access, greatly affect the prevention and control of diabetes, according to a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. These factors have led to significant disparities in the population impacted by diabetes.
The topic areas of the recommendations include federal programs and policies; population-level programs to prevent diabetes, facilitate treatments, and promote health equity; type 2 diabetes prevention; insurance coverage; diabetes care delivery; and diabetes research.
Supporting recommendations in clinics
Family physicians, internists, and pediatricians can directly support many of the recommendations in their clinics. For those recommendations that are not directed at primary care clinics specifically, physicians should provide advocacy for their implementation.
If implemented, some of these recommendations will allow primary care physicians to improve at providing treatments to their patients for diabetes prevention and treatment of the disease. For example, the recommendations call for requirements of insurance companies to cover screening for prediabetes with the use of hemoglobin A1c and the participation in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recognized diabetes prevention programs.
The recommendations also call for the requirement of high-value diabetes services and treatment to be covered predeductible by insurers. If more consistently covered by insurers, it would be easier for us to implement these opportunities including educational groups in our practices. Additionally, if they were available predeductible, we could recommend these to our patients with less worry about cost.
Within care delivery recommendations, they also highlight the importance of an adequate and sustainable team to enhance care for patients with diabetes. Many of us know that it takes more than just the medications, but also significant counseling on diet, exercise and other lifestyle aspects – which need to be tailored to each patient for both prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The recommendations also call for the education and treatment modalities to be able to be provided and covered via virtual methods, while potentially increasing physicians’ ability to provide and patients’ ability to access. Ensuring both the workforce is available and that insurance provides coverage would make these programs accessible to so many more physician offices and ultimately patients.
Importance of social factors
As stated earlier, one of the great aspects of this report is its acknowledgment of the importance of social factors on the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The report recommends expanding housing opportunities for low-income individuals as individuals cannot focus on their health when worried about housing. It also recommends increasing assistance with programs focused on food security. Primary care physicians should advocate for the adoption of these and other recommendations, because of the potentially meaningful impact these changes could have.
Ensuring adequate housing and access to healthy food would go a long way in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. If there are increases in these resources, team members within primary care physician offices would be wonderful allies to help direct patients to these resources. As these concerns may be top of mind for some patients, linking patients to these resources in the physician’s office may reinforce for patients that physicians understand our patients’ biggest concerns.
Ultimately, if the sweeping recommendations in this report are adopted and enforced, it could mean significant improvements for many patients at risk for and living with diabetes. They would provide payment for these resources making them more accessible for patients and physicians alike.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Recently the National Clinical Care Commission provided recommendations to Congress for improving federal diabetes programs in a report. This commission was put together after Congress passed the National Clinical Care Commission Act in 2017.
The report provides a wide range of recommendations that look to combat and prevent diabetes at many levels. An exciting aspect of the recommendations is that they consider how all agencies, including those that are not specifically health care, can fight diabetes.
The report acknowledges that many recent advances in diabetes treatments have made huge differences for clinicians and patients alike. Unfortunately, they have not been translated quickly into practice and when they have been, there have been disparities in the rollouts.
The document also states that many other factors, including housing, health care access, and food access, greatly affect the prevention and control of diabetes, according to a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. These factors have led to significant disparities in the population impacted by diabetes.
The topic areas of the recommendations include federal programs and policies; population-level programs to prevent diabetes, facilitate treatments, and promote health equity; type 2 diabetes prevention; insurance coverage; diabetes care delivery; and diabetes research.
Supporting recommendations in clinics
Family physicians, internists, and pediatricians can directly support many of the recommendations in their clinics. For those recommendations that are not directed at primary care clinics specifically, physicians should provide advocacy for their implementation.
If implemented, some of these recommendations will allow primary care physicians to improve at providing treatments to their patients for diabetes prevention and treatment of the disease. For example, the recommendations call for requirements of insurance companies to cover screening for prediabetes with the use of hemoglobin A1c and the participation in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recognized diabetes prevention programs.
The recommendations also call for the requirement of high-value diabetes services and treatment to be covered predeductible by insurers. If more consistently covered by insurers, it would be easier for us to implement these opportunities including educational groups in our practices. Additionally, if they were available predeductible, we could recommend these to our patients with less worry about cost.
Within care delivery recommendations, they also highlight the importance of an adequate and sustainable team to enhance care for patients with diabetes. Many of us know that it takes more than just the medications, but also significant counseling on diet, exercise and other lifestyle aspects – which need to be tailored to each patient for both prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The recommendations also call for the education and treatment modalities to be able to be provided and covered via virtual methods, while potentially increasing physicians’ ability to provide and patients’ ability to access. Ensuring both the workforce is available and that insurance provides coverage would make these programs accessible to so many more physician offices and ultimately patients.
Importance of social factors
As stated earlier, one of the great aspects of this report is its acknowledgment of the importance of social factors on the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The report recommends expanding housing opportunities for low-income individuals as individuals cannot focus on their health when worried about housing. It also recommends increasing assistance with programs focused on food security. Primary care physicians should advocate for the adoption of these and other recommendations, because of the potentially meaningful impact these changes could have.
Ensuring adequate housing and access to healthy food would go a long way in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. If there are increases in these resources, team members within primary care physician offices would be wonderful allies to help direct patients to these resources. As these concerns may be top of mind for some patients, linking patients to these resources in the physician’s office may reinforce for patients that physicians understand our patients’ biggest concerns.
Ultimately, if the sweeping recommendations in this report are adopted and enforced, it could mean significant improvements for many patients at risk for and living with diabetes. They would provide payment for these resources making them more accessible for patients and physicians alike.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Recently the National Clinical Care Commission provided recommendations to Congress for improving federal diabetes programs in a report. This commission was put together after Congress passed the National Clinical Care Commission Act in 2017.
The report provides a wide range of recommendations that look to combat and prevent diabetes at many levels. An exciting aspect of the recommendations is that they consider how all agencies, including those that are not specifically health care, can fight diabetes.
The report acknowledges that many recent advances in diabetes treatments have made huge differences for clinicians and patients alike. Unfortunately, they have not been translated quickly into practice and when they have been, there have been disparities in the rollouts.
The document also states that many other factors, including housing, health care access, and food access, greatly affect the prevention and control of diabetes, according to a paper published in Annals of Internal Medicine. These factors have led to significant disparities in the population impacted by diabetes.
The topic areas of the recommendations include federal programs and policies; population-level programs to prevent diabetes, facilitate treatments, and promote health equity; type 2 diabetes prevention; insurance coverage; diabetes care delivery; and diabetes research.
Supporting recommendations in clinics
Family physicians, internists, and pediatricians can directly support many of the recommendations in their clinics. For those recommendations that are not directed at primary care clinics specifically, physicians should provide advocacy for their implementation.
If implemented, some of these recommendations will allow primary care physicians to improve at providing treatments to their patients for diabetes prevention and treatment of the disease. For example, the recommendations call for requirements of insurance companies to cover screening for prediabetes with the use of hemoglobin A1c and the participation in Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recognized diabetes prevention programs.
The recommendations also call for the requirement of high-value diabetes services and treatment to be covered predeductible by insurers. If more consistently covered by insurers, it would be easier for us to implement these opportunities including educational groups in our practices. Additionally, if they were available predeductible, we could recommend these to our patients with less worry about cost.
Within care delivery recommendations, they also highlight the importance of an adequate and sustainable team to enhance care for patients with diabetes. Many of us know that it takes more than just the medications, but also significant counseling on diet, exercise and other lifestyle aspects – which need to be tailored to each patient for both prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The recommendations also call for the education and treatment modalities to be able to be provided and covered via virtual methods, while potentially increasing physicians’ ability to provide and patients’ ability to access. Ensuring both the workforce is available and that insurance provides coverage would make these programs accessible to so many more physician offices and ultimately patients.
Importance of social factors
As stated earlier, one of the great aspects of this report is its acknowledgment of the importance of social factors on the prevention and treatment of diabetes.
The report recommends expanding housing opportunities for low-income individuals as individuals cannot focus on their health when worried about housing. It also recommends increasing assistance with programs focused on food security. Primary care physicians should advocate for the adoption of these and other recommendations, because of the potentially meaningful impact these changes could have.
Ensuring adequate housing and access to healthy food would go a long way in the prevention and treatment of diabetes. If there are increases in these resources, team members within primary care physician offices would be wonderful allies to help direct patients to these resources. As these concerns may be top of mind for some patients, linking patients to these resources in the physician’s office may reinforce for patients that physicians understand our patients’ biggest concerns.
Ultimately, if the sweeping recommendations in this report are adopted and enforced, it could mean significant improvements for many patients at risk for and living with diabetes. They would provide payment for these resources making them more accessible for patients and physicians alike.
Dr. Wheat is a family physician at Erie Family Health Center and program director of Northwestern University’s McGaw Family Medicine residency program, both in Chicago. Dr. Wheat serves on the editorial advisory board of Family Practice News. You can contact her at [email protected].
Medical education programs tell how climate change affects health
Ms. Manivannan, copresident of Emory Medical Students for Climate Action, was in the first class of Emory’s medical students to experience the birth of a refined curriculum – lobbied for and partially created by students themselves. The new course of study addresses the myriad ways climate affects health: from air pollution and its effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system to heat-related kidney disease.
“We have known that climate has affected health for decades,” Ms. Manivannan said in a recent interview. “The narrative used to be that icebergs were melting and in 2050 polar bears would be extinct. The piece that’s different now is people are linking climate to increases in asthma and various diseases. We have a way to directly communicate that it’s not a far-off thing. It’s happening to your friends and family right now.”
Hospitals, medical schools, and public health programs are stepping up to educate the next generation of doctors as well as veteran medical workers on one of the most widespread, insidious health threats of our time – climate change – and specific ways it could affect their patients.
Although climate change may seem to many Americans like a distant threat, Marilyn Howarth, MD, a pediatrician in Philadelphia, is trying to make sure physicians are better prepared to treat a growing number of health problems associated with global warming.
“There isn’t a lot of education for pediatricians and internists on environmental health issues. It has not been a standard part of education in medical school or residency training,” Dr. Howarth, deputy director of the new Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, said. “With increasing attention on our climate, we really recognize there’s a real gap in physician knowledge, both in pediatric and adult care.”
Scientists have found that climate change can alter just about every system within the human body. Studies show that more extreme weather events, such as heat waves, thunderstorms, and floods, can worsen asthma and produce more pollen and mold, triggering debilitating respiratory problems.
According to the American Lung Association, ultrafine particles of air pollution can be inhaled and then travel throughout the bloodstream, wreaking havoc on organs and increasing risk of heart attack and stroke. Various types of air pollution also cause changes to the climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which leads to problems such as rising sea levels and extreme weather. Plus, in a new study published in Nature, scientists warn that warming climates are forcing animals to migrate to different areas, raising the risk that new infectious diseases will hop from animals – such as bats – to humans, a process called “zoonotic spillover” that many researchers believe is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health
One of the latest initiatives aimed at disseminating information about children’s health to health care providers is the Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, part of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine. CHOP and Penn Medicine are jointly funding this center’s work, which will include educating health care providers on how to better screen for climate-caused health risks and treat related conditions, such as lead poisoning and asthma.
Outreach will focus on providers who treat patients with illnesses that researchers have linked to climate change, Dr. Howarth said. The center will offer clinicians access to seminars and webinars, along with online resources to help doctors treat environmental illnesses. For example, doctors at CHOP’s Poison Control Center are developing a toolkit for physicians to treat patients with elevated levels of lead in the blood. Scientists have linked extreme weather events related to climate change to flooding that pushes metals away from river banks where they were previously contained, allowing them to more easily contaminate homes, soils, and yards.
The initiative builds on CHOP’s Community Asthma Prevention Program (CAPP), which was launched in 1997 by Tyra Bryant-Stephens, MD, its current medical director. CAPP deploys community health workers into homes armed with supplies and tips for managing asthma. The new center will use similar tactics to provide education and resources to patients. The goal is to reach as many at-risk local children as possible.
Future generation of doctors fuel growth in climate change education
Lisa Doggett, MD, cofounder and president of the board of directors of Texas Physicians for Social Responsibility, announced in March that the University of Texas at Austin, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas have all decided to begin offering a course on environmental threats. Emory’s new curriculum has become more comprehensive every year since its start – thanks in part to the input of students like Ms. Manivannan. Faculty members tasked her with approving the new additions to the curriculum on how climate affects health, which in 2019 had consisted of a few slides about issues such as extreme heat exposure and air pollution and their effects on childbirth outcomes.
Material on climate change has now been woven into 13 courses. It is discussed at length in relation to pulmonology, cardiology, and gastropulmonology, for example, said Rebecca Philipsborn, MD, MPA, FAAP, faculty lead for the environmental and health curriculum at Emory.
The curriculum has only been incorporated into Emory’s program for the past 2 years. Dr. Philipsborn said the school plans to expand it to the clinical years to help trainees learn to treat conditions such as pediatric asthma.
“In the past few years, there has been so much momentum, and part of that is a testament to already seeing effects of climate change and how they affect delivery of health care,” she said.
At least one medical journal has recently ramped up its efforts to educate physicians on the links between health issues and climate change. Editors of Family Practice, from Oxford University Press, have announced that they plan to publish a special Climate Crisis and Primary Health Care issue in September.
Of course, not all climate initiatives in medicine are new. A select few have existed for decades.
But only now are physicians widely seeing the links between health and environment, according to Aaron Bernstein, MD, MPH, interim director of the Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE) at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
C-CHANGE, founded in 1996, was the first center in the world to focus on the health effects of environmental change.
“It’s taken 20 years, but what we’re seeing, I think, is the fruits of education,” Dr. Bernstein said. “There’s clearly a wave building here, and I think it really started with education and people younger than the people in charge calling them into account.”
Like the Philadelphia center, Harvard’s program conducts research on climate and health and educates people from high schoolers to health care veterans. Dr. Bernstein helps lead Climate MD, a program that aims to prepare health care workers for climate crises. The Climate MD team has published several articles in peer-reviewed journals on how to better treat patients struggling with environmental health problems. For example, an article on mapping patients in hurricane zones helped shed light on how systems can identify climate-vulnerable patients using public data.
They also developed a tool to help pediatricians provide “climate-informed primary care” – guidance on how to assess whether children are at risk of any harmful environmental exposures, a feature that is not part of standard pediatric visits.
Like the other programs, Climate MD uses community outreach to treat as many local patients as possible. Staff work with providers at more than 100 health clinics, particularly in areas where climate change disproportionately affects residents.
The next major step is to bring some of this into clinical practice, Dr. Bernstein said. In February 2020, C-CHANGE held its first symposium to address that issue.
“The key is to understand climate issues from a provider’s perspective,” he said. “Then those issues can really be brought to the bedside.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Manivannan, copresident of Emory Medical Students for Climate Action, was in the first class of Emory’s medical students to experience the birth of a refined curriculum – lobbied for and partially created by students themselves. The new course of study addresses the myriad ways climate affects health: from air pollution and its effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system to heat-related kidney disease.
“We have known that climate has affected health for decades,” Ms. Manivannan said in a recent interview. “The narrative used to be that icebergs were melting and in 2050 polar bears would be extinct. The piece that’s different now is people are linking climate to increases in asthma and various diseases. We have a way to directly communicate that it’s not a far-off thing. It’s happening to your friends and family right now.”
Hospitals, medical schools, and public health programs are stepping up to educate the next generation of doctors as well as veteran medical workers on one of the most widespread, insidious health threats of our time – climate change – and specific ways it could affect their patients.
Although climate change may seem to many Americans like a distant threat, Marilyn Howarth, MD, a pediatrician in Philadelphia, is trying to make sure physicians are better prepared to treat a growing number of health problems associated with global warming.
“There isn’t a lot of education for pediatricians and internists on environmental health issues. It has not been a standard part of education in medical school or residency training,” Dr. Howarth, deputy director of the new Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, said. “With increasing attention on our climate, we really recognize there’s a real gap in physician knowledge, both in pediatric and adult care.”
Scientists have found that climate change can alter just about every system within the human body. Studies show that more extreme weather events, such as heat waves, thunderstorms, and floods, can worsen asthma and produce more pollen and mold, triggering debilitating respiratory problems.
According to the American Lung Association, ultrafine particles of air pollution can be inhaled and then travel throughout the bloodstream, wreaking havoc on organs and increasing risk of heart attack and stroke. Various types of air pollution also cause changes to the climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which leads to problems such as rising sea levels and extreme weather. Plus, in a new study published in Nature, scientists warn that warming climates are forcing animals to migrate to different areas, raising the risk that new infectious diseases will hop from animals – such as bats – to humans, a process called “zoonotic spillover” that many researchers believe is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health
One of the latest initiatives aimed at disseminating information about children’s health to health care providers is the Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, part of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine. CHOP and Penn Medicine are jointly funding this center’s work, which will include educating health care providers on how to better screen for climate-caused health risks and treat related conditions, such as lead poisoning and asthma.
Outreach will focus on providers who treat patients with illnesses that researchers have linked to climate change, Dr. Howarth said. The center will offer clinicians access to seminars and webinars, along with online resources to help doctors treat environmental illnesses. For example, doctors at CHOP’s Poison Control Center are developing a toolkit for physicians to treat patients with elevated levels of lead in the blood. Scientists have linked extreme weather events related to climate change to flooding that pushes metals away from river banks where they were previously contained, allowing them to more easily contaminate homes, soils, and yards.
The initiative builds on CHOP’s Community Asthma Prevention Program (CAPP), which was launched in 1997 by Tyra Bryant-Stephens, MD, its current medical director. CAPP deploys community health workers into homes armed with supplies and tips for managing asthma. The new center will use similar tactics to provide education and resources to patients. The goal is to reach as many at-risk local children as possible.
Future generation of doctors fuel growth in climate change education
Lisa Doggett, MD, cofounder and president of the board of directors of Texas Physicians for Social Responsibility, announced in March that the University of Texas at Austin, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas have all decided to begin offering a course on environmental threats. Emory’s new curriculum has become more comprehensive every year since its start – thanks in part to the input of students like Ms. Manivannan. Faculty members tasked her with approving the new additions to the curriculum on how climate affects health, which in 2019 had consisted of a few slides about issues such as extreme heat exposure and air pollution and their effects on childbirth outcomes.
Material on climate change has now been woven into 13 courses. It is discussed at length in relation to pulmonology, cardiology, and gastropulmonology, for example, said Rebecca Philipsborn, MD, MPA, FAAP, faculty lead for the environmental and health curriculum at Emory.
The curriculum has only been incorporated into Emory’s program for the past 2 years. Dr. Philipsborn said the school plans to expand it to the clinical years to help trainees learn to treat conditions such as pediatric asthma.
“In the past few years, there has been so much momentum, and part of that is a testament to already seeing effects of climate change and how they affect delivery of health care,” she said.
At least one medical journal has recently ramped up its efforts to educate physicians on the links between health issues and climate change. Editors of Family Practice, from Oxford University Press, have announced that they plan to publish a special Climate Crisis and Primary Health Care issue in September.
Of course, not all climate initiatives in medicine are new. A select few have existed for decades.
But only now are physicians widely seeing the links between health and environment, according to Aaron Bernstein, MD, MPH, interim director of the Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE) at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
C-CHANGE, founded in 1996, was the first center in the world to focus on the health effects of environmental change.
“It’s taken 20 years, but what we’re seeing, I think, is the fruits of education,” Dr. Bernstein said. “There’s clearly a wave building here, and I think it really started with education and people younger than the people in charge calling them into account.”
Like the Philadelphia center, Harvard’s program conducts research on climate and health and educates people from high schoolers to health care veterans. Dr. Bernstein helps lead Climate MD, a program that aims to prepare health care workers for climate crises. The Climate MD team has published several articles in peer-reviewed journals on how to better treat patients struggling with environmental health problems. For example, an article on mapping patients in hurricane zones helped shed light on how systems can identify climate-vulnerable patients using public data.
They also developed a tool to help pediatricians provide “climate-informed primary care” – guidance on how to assess whether children are at risk of any harmful environmental exposures, a feature that is not part of standard pediatric visits.
Like the other programs, Climate MD uses community outreach to treat as many local patients as possible. Staff work with providers at more than 100 health clinics, particularly in areas where climate change disproportionately affects residents.
The next major step is to bring some of this into clinical practice, Dr. Bernstein said. In February 2020, C-CHANGE held its first symposium to address that issue.
“The key is to understand climate issues from a provider’s perspective,” he said. “Then those issues can really be brought to the bedside.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ms. Manivannan, copresident of Emory Medical Students for Climate Action, was in the first class of Emory’s medical students to experience the birth of a refined curriculum – lobbied for and partially created by students themselves. The new course of study addresses the myriad ways climate affects health: from air pollution and its effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system to heat-related kidney disease.
“We have known that climate has affected health for decades,” Ms. Manivannan said in a recent interview. “The narrative used to be that icebergs were melting and in 2050 polar bears would be extinct. The piece that’s different now is people are linking climate to increases in asthma and various diseases. We have a way to directly communicate that it’s not a far-off thing. It’s happening to your friends and family right now.”
Hospitals, medical schools, and public health programs are stepping up to educate the next generation of doctors as well as veteran medical workers on one of the most widespread, insidious health threats of our time – climate change – and specific ways it could affect their patients.
Although climate change may seem to many Americans like a distant threat, Marilyn Howarth, MD, a pediatrician in Philadelphia, is trying to make sure physicians are better prepared to treat a growing number of health problems associated with global warming.
“There isn’t a lot of education for pediatricians and internists on environmental health issues. It has not been a standard part of education in medical school or residency training,” Dr. Howarth, deputy director of the new Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, said. “With increasing attention on our climate, we really recognize there’s a real gap in physician knowledge, both in pediatric and adult care.”
Scientists have found that climate change can alter just about every system within the human body. Studies show that more extreme weather events, such as heat waves, thunderstorms, and floods, can worsen asthma and produce more pollen and mold, triggering debilitating respiratory problems.
According to the American Lung Association, ultrafine particles of air pollution can be inhaled and then travel throughout the bloodstream, wreaking havoc on organs and increasing risk of heart attack and stroke. Various types of air pollution also cause changes to the climate by trapping heat in the atmosphere, which leads to problems such as rising sea levels and extreme weather. Plus, in a new study published in Nature, scientists warn that warming climates are forcing animals to migrate to different areas, raising the risk that new infectious diseases will hop from animals – such as bats – to humans, a process called “zoonotic spillover” that many researchers believe is responsible for the COVID-19 pandemic.
The Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health
One of the latest initiatives aimed at disseminating information about children’s health to health care providers is the Philadelphia Regional Center for Children’s Environmental Health, part of Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia and Penn Medicine. CHOP and Penn Medicine are jointly funding this center’s work, which will include educating health care providers on how to better screen for climate-caused health risks and treat related conditions, such as lead poisoning and asthma.
Outreach will focus on providers who treat patients with illnesses that researchers have linked to climate change, Dr. Howarth said. The center will offer clinicians access to seminars and webinars, along with online resources to help doctors treat environmental illnesses. For example, doctors at CHOP’s Poison Control Center are developing a toolkit for physicians to treat patients with elevated levels of lead in the blood. Scientists have linked extreme weather events related to climate change to flooding that pushes metals away from river banks where they were previously contained, allowing them to more easily contaminate homes, soils, and yards.
The initiative builds on CHOP’s Community Asthma Prevention Program (CAPP), which was launched in 1997 by Tyra Bryant-Stephens, MD, its current medical director. CAPP deploys community health workers into homes armed with supplies and tips for managing asthma. The new center will use similar tactics to provide education and resources to patients. The goal is to reach as many at-risk local children as possible.
Future generation of doctors fuel growth in climate change education
Lisa Doggett, MD, cofounder and president of the board of directors of Texas Physicians for Social Responsibility, announced in March that the University of Texas at Austin, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, and the University of Texas Southwestern in Dallas have all decided to begin offering a course on environmental threats. Emory’s new curriculum has become more comprehensive every year since its start – thanks in part to the input of students like Ms. Manivannan. Faculty members tasked her with approving the new additions to the curriculum on how climate affects health, which in 2019 had consisted of a few slides about issues such as extreme heat exposure and air pollution and their effects on childbirth outcomes.
Material on climate change has now been woven into 13 courses. It is discussed at length in relation to pulmonology, cardiology, and gastropulmonology, for example, said Rebecca Philipsborn, MD, MPA, FAAP, faculty lead for the environmental and health curriculum at Emory.
The curriculum has only been incorporated into Emory’s program for the past 2 years. Dr. Philipsborn said the school plans to expand it to the clinical years to help trainees learn to treat conditions such as pediatric asthma.
“In the past few years, there has been so much momentum, and part of that is a testament to already seeing effects of climate change and how they affect delivery of health care,” she said.
At least one medical journal has recently ramped up its efforts to educate physicians on the links between health issues and climate change. Editors of Family Practice, from Oxford University Press, have announced that they plan to publish a special Climate Crisis and Primary Health Care issue in September.
Of course, not all climate initiatives in medicine are new. A select few have existed for decades.
But only now are physicians widely seeing the links between health and environment, according to Aaron Bernstein, MD, MPH, interim director of the Center for Climate, Health, and the Global Environment (C-CHANGE) at Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
C-CHANGE, founded in 1996, was the first center in the world to focus on the health effects of environmental change.
“It’s taken 20 years, but what we’re seeing, I think, is the fruits of education,” Dr. Bernstein said. “There’s clearly a wave building here, and I think it really started with education and people younger than the people in charge calling them into account.”
Like the Philadelphia center, Harvard’s program conducts research on climate and health and educates people from high schoolers to health care veterans. Dr. Bernstein helps lead Climate MD, a program that aims to prepare health care workers for climate crises. The Climate MD team has published several articles in peer-reviewed journals on how to better treat patients struggling with environmental health problems. For example, an article on mapping patients in hurricane zones helped shed light on how systems can identify climate-vulnerable patients using public data.
They also developed a tool to help pediatricians provide “climate-informed primary care” – guidance on how to assess whether children are at risk of any harmful environmental exposures, a feature that is not part of standard pediatric visits.
Like the other programs, Climate MD uses community outreach to treat as many local patients as possible. Staff work with providers at more than 100 health clinics, particularly in areas where climate change disproportionately affects residents.
The next major step is to bring some of this into clinical practice, Dr. Bernstein said. In February 2020, C-CHANGE held its first symposium to address that issue.
“The key is to understand climate issues from a provider’s perspective,” he said. “Then those issues can really be brought to the bedside.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
My choice? Unvaccinated pose outsize risk to vaccinated
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a mathematical modeling study.
The study, which simulated patterns of infection among vaccinated and unvaccinated populations, showed that, as the populations mixed less, attack rates decreased among vaccinated people (from 15% to 10%) and increased among unvaccinated people (from 62% to 79%). The unvaccinated increasingly became the source of infection, however.
“When the vaccinated and unvaccinated mix, indirect protection is conferred upon the unvaccinated by the buffering effect of vaccinated individuals, and by contrast, risk in the vaccinated goes up,” lead author David Fisman, MD, professor of epidemiology at the University of Toronto, told this news organization.
As the groups mix less and less, the size of the epidemic increases among the unvaccinated and decreases among the vaccinated. “But the impact of the unvaccinated on risk in the vaccinated is disproportionate to the numbers of contacts between the two groups,” said Dr. Fisman.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Relative contributions to risk
The researchers used a model of a respiratory viral disease “similar to SARS-CoV-2 infection with Delta variant.” They included reproduction values to capture the dynamics of the Omicron variant, which was emerging at the time. In the study, vaccines ranged in effectiveness from 40% to 80%. The study incorporated various levels of mixing between a partially vaccinated and an unvaccinated population. The mixing ranged from random mixing to like-with-like mixing (“assortativity”). There were three possible “compartments” of people in the model: those considered susceptible to infection, those considered infected and infectious, and those considered immune because of recovery.
The model showed that, as mixing between the vaccinated and the unvaccinated populations increased, case numbers rose, “with cases in the unvaccinated subpopulation accounting for a substantial proportion of infections.” However, as mixing between the populations decreased, the final attack rate decreased among vaccinated people, but the relative “contribution of risk to vaccinated people caused by infection acquired from contact with unvaccinated people ... increased.”
When the vaccination rate was increased in the model, case numbers among the vaccinated declined “as expected, owing to indirect protective effects,” the researchers noted. But this also “further increased the relative contribution to risk in vaccinated people by those who were unvaccinated.”
Self-regarding risk?
The findings show that “choices made by people who forgo vaccination contribute disproportionately to risk among those who do get vaccinated,” the researchers wrote. “Although risk associated with avoiding vaccination during a virulent pandemic accrues chiefly to those who are unvaccinated, the choice of some individuals to refuse vaccination is likely to affect the health and safety of vaccinated people in a manner disproportionate to the fraction of unvaccinated people in the population.”
The fact that like-with-like mixing cannot mitigate the risk to vaccinated people “undermines the assertion that vaccine choice is best left to the individual and supports strong public actions aimed at enhancing vaccine uptake and limiting access to public spaces for unvaccinated people,” they wrote.
Mandates and passports
“Our model provides support for vaccine mandates and passports during epidemics, such that vaccination is required for people to take part in nonessential activities,” said Dr. Fisman. The choice to not be vaccinated against COVID-19 should not be considered “self-regarding,” he added. “Risk is self-regarding when it only impacts the person engaging in the activity. Something like smoking cigarettes (alone, without others around) creates a lot of risk over time, but if nobody is breathing your secondhand smoke, you’re only creating risk for yourself. By contrast, we regulate, in Ontario, your right to smoke in public indoor spaces such as restaurants, because once other people are around, the risk isn’t self-regarding anymore. You’re creating risk for others.”
The authors also noted that the risks created by the unvaccinated extend beyond those of infection by “creating a risk that those around them may not be able to obtain the care they need.” They recommended that considerations of equity and justice for people who do choose to be vaccinated, as well as those who choose not to be, need to be included in formulating vaccination policy.
Illuminating the discussion
Asked to comment on the study, Matthew Oughton, MD, assistant professor of medicine at McGill University, Montreal, said: “It is easy to dismiss a mathematical model as a series of assumptions that leads to an implausible conclusion. ... However, they can serve to illustrate and, to an extent, quantify the results of complex interactions, and this study does just that.” Dr. Oughton was not involved in the research.
During the past 2 years, the scientific press and the general press have often discussed the individual and collective effects of disease-prevention methods, including nonpharmaceutical interventions. “Models like this can help illuminate those discussions by highlighting important consequences of preventive measures,” said Dr. Oughton, who also works in the division of infectious diseases at the Jewish General Hospital, Montreal.
It’s worth noting that the authors modeled vaccine effectiveness against all infection, “rather than the generally greater and more durable effects we have seen for vaccines in prevention of severe infection,” said Dr. Oughton. He added that the authors did not include the effect of vaccination in reducing forward transmission. “Inclusion of this effect would presumably have reduced overall infectious burden in mixed populations and increased the difference between groups at lower levels of mixing between populations.”
The research was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Fisman has served on advisory boards related to influenza and SARS-CoV-2 vaccines for Seqirus, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, and Sanofi-Pasteur Vaccines and has served as a legal expert on issues related to COVID-19 epidemiology for the Elementary Teachers Federation of Ontario and the Registered Nurses Association of Ontario. Dr. Oughton disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
CDC predicts a rise in COVID-19 hospitalizations and deaths in coming weeks
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to a national forecast used by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
The national model also predicts that about 5,000 deaths will occur over the next two weeks, with Ohio, New Jersey, and New York projected to see the largest totals of daily deaths in upcoming weeks.
The numbers follow several weeks of steady increases in infections across the country. More than 67,000 new cases are being reported daily, according to the data tracker from The New York Times, marking a 59% increase in the past two weeks.
In the Northeast, infection rates have risen by nearly 65%. In the New York and New Jersey region, infection rates are up about 55% in the past two weeks.
Hospitalizations have already begun to climb as well, with about 19,000 COVID-19 patients hospitalized nationwide and 1,725 in intensive care, according to the latest data from the Department of Health and Human Services. In the last week, hospital admissions have jumped by 20%, and emergency department visits are up by 18%.
The CDC forecast shows that 42 states and territories will see increases in hospital admissions during the next two weeks. Florida, Minnesota, New York, and Wisconsin will see some of the largest increases.
On average, more than 2,200 COVID-19 patients are entering the hospital each day, which has increased about 20% in the last week, according to ABC News. This also marks the highest number of COVID-19 patients needing hospital care since mid-March.
Public health officials have cited several factors for the increase in cases, such as states lifting mask mandates and other safety restrictions, ABC News reported. Highly contagious Omicron subvariants, such as BA.2 and BA.2.12.1, continue to spread in the United States and escape immunity from previous infections.
The BA.2 subvariant accounts for 62% of new national cases, according to the latest CDC data. The BA.2.12.1 subvariant makes up about 36% of new cases across the United States but 62% in the New York area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Screening for diabetes at normal BMIs could cut racial disparities
Use of race-based diabetes screening thresholds could reduce the disparity that arises from current screening guidelines in the United States, new research suggests.
In August 2021, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) lowered the recommended age for type 2 diabetes screening from 40 to 35 years among people with a body mass index of 25 kg/m2 or greater.
However, the diabetes rate among ethnic minorities aged 35-70 years in the United States is not just higher overall but, in certain populations, also occurs more frequently at a younger age and at lower BMIs, the new study indicates.
Among people with a BMI below 25 kg/m2, the diabetes prevalence is two to four times higher among Asian, Black, and Hispanic Americans than among the U.S. White population.
And the authors of the new study, led by Rahul Aggarwal, MD, predict that if screening begins at age 35 years, the BMI cut-off equivalent to 25 kg/m2 for White Americans would be 18.5 kg/m2 for Hispanic and Black Americans and 20 kg/m2 for Asian Americans.
“While diabetes has often been thought of as a disease that primarily affects adults with overweight or [obesity], our findings suggest that normal-weight adults in minority groups have surprisingly high rates of diabetes,” Dr. Aggarwal, senior resident physician in internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
“Assessing diabetes risks in certain racial/ethnic groups will be necessary, even if these adults do not have overweight or [obesity],” he added.
Not screening in this way “is a missed opportunity for early intervention,” he noted.
And both the authors and an editorialist stress that the issue isn’t just theoretical.
“USPSTF recommendations influence what payers choose to cover, which in turn determines access to preventative services ... Addressing the staggering inequities in diabetes outcomes will require substantial investments in diabetes prevention and treatment, but making screening more equitable is a good place to start,” said senior author Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, of the Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology and director of the Cardiac Critical Care Unit at Beth Israel, Boston.
Screen minorities at a younger age if current BMI threshold kept
In their study, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for 2011-2018, Dr. Aggarwal and colleagues also calculated that, if the BMI threshold is kept at 25 kg/m2, then the equivalent age cut-offs for Asian, Black, and Hispanic Americans would be 23, 21, and 25 years, respectively, compared with 35 years for White Americans.
The findings were published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The prevalence of diabetes in those aged 35-70 years in the NHANES population was 17.3% for Asian Americans and 12.5% for those who were White (odds ratio, 1.51 vs. Whites). Among Black Americans and Mexican Americans, the prevalence was 20.7% and 20.6%, respectively, almost twice the prevalence in Whites (OR, 1.85 and 1.80). For other Hispanic Americans, the prevalence was 16.4% (OR, 1.37 vs. Whites). All of those differences were significant, compared with White Americans.
Undiagnosed diabetes was also significantly more common among minority populations, at 27.6%, 22.8%, 21.2%, and 23.5% for Asian, Black, Mexican, and other Hispanic Americans, respectively, versus 12.5% for White Americans.
‘The time has come for USPSTF to offer more concrete guidance’
“While there is more work to be done on carefully examining the long-term risk–benefit trade-off of various diabetes screening, I believe the time has come for USPSTF to offer more concrete guidance on the use of lower thresholds for screening higher-risk individuals,” Dr. Kazi told this news organization.
The author of an accompanying editorial agrees, noting that in a recent commentary the USPSTF, itself, “acknowledged the persistent inequalities across the screening-to-treatment continuum that result in racial/ethnic health disparities in the United States.”
And the USPSTF “emphasized the need to improve systems of care to ensure equitable and consistent delivery of high-quality preventive and treatment services, with special attention to racial/ethnic groups who may experience worse health outcomes,” continues Quyen Ngo-Metzger, MD, Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Pasadena, California.
For other conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and infectious disease, the USPSTF already recommends risk-based preventive services.
“To address the current inequity in diabetes screening, the USPSTF should apply the same consideration to its diabetes screening recommendation,” she notes.
‘Implementation will require an eye for pragmatism’
Asked about how this recommendation might be carried out in the real world, Dr. Aggarwal said in an interview that, because all three minority groups with normal weight had similar diabetes risk profiles to White adults with overweight, “one way for clinicians to easily implement these findings is by screening all Asian, Black, and Hispanic adults ages 35-70 years with normal weight for diabetes, similarly to how all White adults ages 35-70 years with overweight are currently recommended for screening.”
Dr. Kazi said: “I believe that implementation will require an eye for pragmatism,” noting that another option would be to have screening algorithms embedded in the electronic health record to flag individuals who qualify.
In any case, “the simplicity of the current one-size-fits-all approach is alluring, but it is profoundly inequitable. The more I look at the empiric evidence on diabetes burden in our communities, the more the status quo becomes untenable.”
However, Dr. Kazi also noted, “the benefit of any screening program relates to what we do with the information. The key is to ensure that folks identified as having diabetes – or better still prediabetes – receive timely lifestyle and pharmacological interventions to avert its long-term complications.”
This study was supported by institutional funds from the Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology. Dr. Aggarwal, Dr. Kazi, and Dr. Ngo-Metzger have reported no relevant relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of race-based diabetes screening thresholds could reduce the disparity that arises from current screening guidelines in the United States, new research suggests.
In August 2021, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) lowered the recommended age for type 2 diabetes screening from 40 to 35 years among people with a body mass index of 25 kg/m2 or greater.
However, the diabetes rate among ethnic minorities aged 35-70 years in the United States is not just higher overall but, in certain populations, also occurs more frequently at a younger age and at lower BMIs, the new study indicates.
Among people with a BMI below 25 kg/m2, the diabetes prevalence is two to four times higher among Asian, Black, and Hispanic Americans than among the U.S. White population.
And the authors of the new study, led by Rahul Aggarwal, MD, predict that if screening begins at age 35 years, the BMI cut-off equivalent to 25 kg/m2 for White Americans would be 18.5 kg/m2 for Hispanic and Black Americans and 20 kg/m2 for Asian Americans.
“While diabetes has often been thought of as a disease that primarily affects adults with overweight or [obesity], our findings suggest that normal-weight adults in minority groups have surprisingly high rates of diabetes,” Dr. Aggarwal, senior resident physician in internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
“Assessing diabetes risks in certain racial/ethnic groups will be necessary, even if these adults do not have overweight or [obesity],” he added.
Not screening in this way “is a missed opportunity for early intervention,” he noted.
And both the authors and an editorialist stress that the issue isn’t just theoretical.
“USPSTF recommendations influence what payers choose to cover, which in turn determines access to preventative services ... Addressing the staggering inequities in diabetes outcomes will require substantial investments in diabetes prevention and treatment, but making screening more equitable is a good place to start,” said senior author Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, of the Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology and director of the Cardiac Critical Care Unit at Beth Israel, Boston.
Screen minorities at a younger age if current BMI threshold kept
In their study, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for 2011-2018, Dr. Aggarwal and colleagues also calculated that, if the BMI threshold is kept at 25 kg/m2, then the equivalent age cut-offs for Asian, Black, and Hispanic Americans would be 23, 21, and 25 years, respectively, compared with 35 years for White Americans.
The findings were published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The prevalence of diabetes in those aged 35-70 years in the NHANES population was 17.3% for Asian Americans and 12.5% for those who were White (odds ratio, 1.51 vs. Whites). Among Black Americans and Mexican Americans, the prevalence was 20.7% and 20.6%, respectively, almost twice the prevalence in Whites (OR, 1.85 and 1.80). For other Hispanic Americans, the prevalence was 16.4% (OR, 1.37 vs. Whites). All of those differences were significant, compared with White Americans.
Undiagnosed diabetes was also significantly more common among minority populations, at 27.6%, 22.8%, 21.2%, and 23.5% for Asian, Black, Mexican, and other Hispanic Americans, respectively, versus 12.5% for White Americans.
‘The time has come for USPSTF to offer more concrete guidance’
“While there is more work to be done on carefully examining the long-term risk–benefit trade-off of various diabetes screening, I believe the time has come for USPSTF to offer more concrete guidance on the use of lower thresholds for screening higher-risk individuals,” Dr. Kazi told this news organization.
The author of an accompanying editorial agrees, noting that in a recent commentary the USPSTF, itself, “acknowledged the persistent inequalities across the screening-to-treatment continuum that result in racial/ethnic health disparities in the United States.”
And the USPSTF “emphasized the need to improve systems of care to ensure equitable and consistent delivery of high-quality preventive and treatment services, with special attention to racial/ethnic groups who may experience worse health outcomes,” continues Quyen Ngo-Metzger, MD, Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Pasadena, California.
For other conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and infectious disease, the USPSTF already recommends risk-based preventive services.
“To address the current inequity in diabetes screening, the USPSTF should apply the same consideration to its diabetes screening recommendation,” she notes.
‘Implementation will require an eye for pragmatism’
Asked about how this recommendation might be carried out in the real world, Dr. Aggarwal said in an interview that, because all three minority groups with normal weight had similar diabetes risk profiles to White adults with overweight, “one way for clinicians to easily implement these findings is by screening all Asian, Black, and Hispanic adults ages 35-70 years with normal weight for diabetes, similarly to how all White adults ages 35-70 years with overweight are currently recommended for screening.”
Dr. Kazi said: “I believe that implementation will require an eye for pragmatism,” noting that another option would be to have screening algorithms embedded in the electronic health record to flag individuals who qualify.
In any case, “the simplicity of the current one-size-fits-all approach is alluring, but it is profoundly inequitable. The more I look at the empiric evidence on diabetes burden in our communities, the more the status quo becomes untenable.”
However, Dr. Kazi also noted, “the benefit of any screening program relates to what we do with the information. The key is to ensure that folks identified as having diabetes – or better still prediabetes – receive timely lifestyle and pharmacological interventions to avert its long-term complications.”
This study was supported by institutional funds from the Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology. Dr. Aggarwal, Dr. Kazi, and Dr. Ngo-Metzger have reported no relevant relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of race-based diabetes screening thresholds could reduce the disparity that arises from current screening guidelines in the United States, new research suggests.
In August 2021, the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) lowered the recommended age for type 2 diabetes screening from 40 to 35 years among people with a body mass index of 25 kg/m2 or greater.
However, the diabetes rate among ethnic minorities aged 35-70 years in the United States is not just higher overall but, in certain populations, also occurs more frequently at a younger age and at lower BMIs, the new study indicates.
Among people with a BMI below 25 kg/m2, the diabetes prevalence is two to four times higher among Asian, Black, and Hispanic Americans than among the U.S. White population.
And the authors of the new study, led by Rahul Aggarwal, MD, predict that if screening begins at age 35 years, the BMI cut-off equivalent to 25 kg/m2 for White Americans would be 18.5 kg/m2 for Hispanic and Black Americans and 20 kg/m2 for Asian Americans.
“While diabetes has often been thought of as a disease that primarily affects adults with overweight or [obesity], our findings suggest that normal-weight adults in minority groups have surprisingly high rates of diabetes,” Dr. Aggarwal, senior resident physician in internal medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston, told this news organization.
“Assessing diabetes risks in certain racial/ethnic groups will be necessary, even if these adults do not have overweight or [obesity],” he added.
Not screening in this way “is a missed opportunity for early intervention,” he noted.
And both the authors and an editorialist stress that the issue isn’t just theoretical.
“USPSTF recommendations influence what payers choose to cover, which in turn determines access to preventative services ... Addressing the staggering inequities in diabetes outcomes will require substantial investments in diabetes prevention and treatment, but making screening more equitable is a good place to start,” said senior author Dhruv S. Kazi, MD, of the Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology and director of the Cardiac Critical Care Unit at Beth Israel, Boston.
Screen minorities at a younger age if current BMI threshold kept
In their study, based on data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for 2011-2018, Dr. Aggarwal and colleagues also calculated that, if the BMI threshold is kept at 25 kg/m2, then the equivalent age cut-offs for Asian, Black, and Hispanic Americans would be 23, 21, and 25 years, respectively, compared with 35 years for White Americans.
The findings were published online in the Annals of Internal Medicine.
The prevalence of diabetes in those aged 35-70 years in the NHANES population was 17.3% for Asian Americans and 12.5% for those who were White (odds ratio, 1.51 vs. Whites). Among Black Americans and Mexican Americans, the prevalence was 20.7% and 20.6%, respectively, almost twice the prevalence in Whites (OR, 1.85 and 1.80). For other Hispanic Americans, the prevalence was 16.4% (OR, 1.37 vs. Whites). All of those differences were significant, compared with White Americans.
Undiagnosed diabetes was also significantly more common among minority populations, at 27.6%, 22.8%, 21.2%, and 23.5% for Asian, Black, Mexican, and other Hispanic Americans, respectively, versus 12.5% for White Americans.
‘The time has come for USPSTF to offer more concrete guidance’
“While there is more work to be done on carefully examining the long-term risk–benefit trade-off of various diabetes screening, I believe the time has come for USPSTF to offer more concrete guidance on the use of lower thresholds for screening higher-risk individuals,” Dr. Kazi told this news organization.
The author of an accompanying editorial agrees, noting that in a recent commentary the USPSTF, itself, “acknowledged the persistent inequalities across the screening-to-treatment continuum that result in racial/ethnic health disparities in the United States.”
And the USPSTF “emphasized the need to improve systems of care to ensure equitable and consistent delivery of high-quality preventive and treatment services, with special attention to racial/ethnic groups who may experience worse health outcomes,” continues Quyen Ngo-Metzger, MD, Kaiser Permanente Bernard J. Tyson School of Medicine, Pasadena, California.
For other conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular disease, and infectious disease, the USPSTF already recommends risk-based preventive services.
“To address the current inequity in diabetes screening, the USPSTF should apply the same consideration to its diabetes screening recommendation,” she notes.
‘Implementation will require an eye for pragmatism’
Asked about how this recommendation might be carried out in the real world, Dr. Aggarwal said in an interview that, because all three minority groups with normal weight had similar diabetes risk profiles to White adults with overweight, “one way for clinicians to easily implement these findings is by screening all Asian, Black, and Hispanic adults ages 35-70 years with normal weight for diabetes, similarly to how all White adults ages 35-70 years with overweight are currently recommended for screening.”
Dr. Kazi said: “I believe that implementation will require an eye for pragmatism,” noting that another option would be to have screening algorithms embedded in the electronic health record to flag individuals who qualify.
In any case, “the simplicity of the current one-size-fits-all approach is alluring, but it is profoundly inequitable. The more I look at the empiric evidence on diabetes burden in our communities, the more the status quo becomes untenable.”
However, Dr. Kazi also noted, “the benefit of any screening program relates to what we do with the information. The key is to ensure that folks identified as having diabetes – or better still prediabetes – receive timely lifestyle and pharmacological interventions to avert its long-term complications.”
This study was supported by institutional funds from the Richard A. and Susan F. Smith Center for Outcomes Research in Cardiology. Dr. Aggarwal, Dr. Kazi, and Dr. Ngo-Metzger have reported no relevant relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Endovascular benefit finally confirmed for basilar artery stroke
The benefit of endovascular therapy in the treatment of stroke caused by an occlusion of the basilar artery has finally been confirmed in the ATTENTION randomized trial.
The study, conducted in China, showed that endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion is associated with higher rates of favorable and independent outcomes, as well as lower overall disability and lower mortality at 90 days, than best medical management alone.
The results were presented by Raul Nogueira, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2022, where they were greeted with applause from the audience.
“We can finally say that we have conquered the basilar artery territory. It is about time. We can finally confirm that the benefit of endovascular therapy persists in the posterior circulation,” Dr. Nogueira said.
“The disability reduction benefit of endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion appears to be within the same range as that observed in the anterior circulation. However, in contrast to most anterior circulation endovascular trials, the ATTENTION trial also demonstrated a potential benefit in terms of mortality,” he added.
Dr. Nogueira explained that the first series of endovascular treatment for stroke in the modern era was published in 1988, and this was in the basilar artery occlusion territory, but almost 35 years later, although there has been overwhelming proof of benefit of endovascular treatment in the antiterror circulation, it remains unknown whether endovascular treatment is beneficial to treat acute basilar artery occlusion. This is despite efforts in conducting two trials – the BEST and BASICS trials – which showed a direction of benefit but failed to show real significance.
“Having said that, these trials paved the way for the current trial, specifically by demonstrating the importance of consecutive recruitment, fast enrollment, and the minimalization of crossover. They also confirmed the ideal target population for this procedure in an individual patient level meta-analysis of these two trials,” he said.
In addition, there have also been two large Chinese registries suggesting significant benefits.
The ATTENTION trial was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that endovascular therapy is superior to best medical management alone in achieving more favorable outcomes (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days in subjects presenting with acute basilar artery stroke within 12 hours of the estimated time of onset.
The study enrolled 342 patients at 36 comprehensive stroke centers in China. All patients had occlusion of the basilar artery confirmed on vascular imaging within 12 hours of stroke onset, and they had severe symptoms at presentation, with an NIHSS score of at least 10. They were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to endovascular treatment or best medical management alone.
“It took us less than a year to enroll 342 patients,” Dr. Nogueira noted. “To put this into perspective, it took the BASICS trial over 8 years to enroll 300 patients, so these are very high-volume centers.”
He reported that two patients withdrew consent, and there were three patient crossovers on each side, comparing favorably with BASICS, leaving 226 patients in the intervention group and 114 in the control group.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups: median age was 67 years, median NIHSS score was 24, about 25% received thrombolysis, and median time from stroke onset to randomization was 5 hours.
Results showed that the primary outcome – a favorable functional outcome (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days – was achieved in 22.8% of the control group and in 46% of the endovascular group, giving an adjusted risk ratio of 2.1 (P < .001).
The number needed to treat was just four.
“There were no surprises with secondary endpoints; everything was highly statistically significant,” Dr. Nogueira said.
Specifically, there was a lower rate of overall disability in the shift analysis, with a common odds ratio of 2.8 favoring the intervention.
Safety results showed an increased risk for symptomatic ICH in the endovascular group (5.3% vs. 0.0%) but, despite that, 90-day mortality was significantly lower in the endovascular group (36.7% vs. 55.3%).
Dr. Nogueira noted a limitation of the study was that it was conducted in China.
“This was a Chinese study and, as Asians are known to have higher rates of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the overall degree of generalizability of our findings to Western countries needs to be considered,” he commented.
However, subgroup analysis showed no treatment effect modification based on the presence of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, he noted.
Also, the proportion of comorbidities in the ATTENTION trial was similar to that in the BASICS trial, with the same degree of diabetes and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Nogueira concluded that, in contrast to previous randomized trials of endovascular treatment for basilar artery occlusion, the ATTENTION trial was able to reinforce consecutive enrollment, resulting in a fast recruitment while minimizing crossovers.
Furthermore, he pointed out that the overall results are consistent with modern era observational studies, large registries, and meta-analysis.
Commenting on the study, Joanna Wardlaw, MD, professor of applied neuroimaging at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland), and chair of the ESOC Planning Group, said: “This is a very important result, since it provides confirmation beyond doubt the benefit of thrombectomy versus medical therapy for basilar artery occlusion stroke up to 12 hours after onset.”
Dr. Wardlaw added: “The trial was large enough to provide clear results and to enable subgroup analyses; no subgroup did not benefit from thrombectomy.”
In a discussion after the presentation, Urs Fischer, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University Hospital Basel, Switzerland, said he was not surprised by the results of the ATTENTION trial.
“We have been doing thrombectomy in patients with basilar artery occlusion now for 20 years, although trials are extremely important to answer these questions, so now we have some clear evidence,” Dr. Fischer said. “Nevertheless, there are some caveats, as this is an Asian population, but this is a proof of concept, and it is going in the right direction.”
The ATTENTION trial was sponsored by the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefit of endovascular therapy in the treatment of stroke caused by an occlusion of the basilar artery has finally been confirmed in the ATTENTION randomized trial.
The study, conducted in China, showed that endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion is associated with higher rates of favorable and independent outcomes, as well as lower overall disability and lower mortality at 90 days, than best medical management alone.
The results were presented by Raul Nogueira, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2022, where they were greeted with applause from the audience.
“We can finally say that we have conquered the basilar artery territory. It is about time. We can finally confirm that the benefit of endovascular therapy persists in the posterior circulation,” Dr. Nogueira said.
“The disability reduction benefit of endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion appears to be within the same range as that observed in the anterior circulation. However, in contrast to most anterior circulation endovascular trials, the ATTENTION trial also demonstrated a potential benefit in terms of mortality,” he added.
Dr. Nogueira explained that the first series of endovascular treatment for stroke in the modern era was published in 1988, and this was in the basilar artery occlusion territory, but almost 35 years later, although there has been overwhelming proof of benefit of endovascular treatment in the antiterror circulation, it remains unknown whether endovascular treatment is beneficial to treat acute basilar artery occlusion. This is despite efforts in conducting two trials – the BEST and BASICS trials – which showed a direction of benefit but failed to show real significance.
“Having said that, these trials paved the way for the current trial, specifically by demonstrating the importance of consecutive recruitment, fast enrollment, and the minimalization of crossover. They also confirmed the ideal target population for this procedure in an individual patient level meta-analysis of these two trials,” he said.
In addition, there have also been two large Chinese registries suggesting significant benefits.
The ATTENTION trial was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that endovascular therapy is superior to best medical management alone in achieving more favorable outcomes (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days in subjects presenting with acute basilar artery stroke within 12 hours of the estimated time of onset.
The study enrolled 342 patients at 36 comprehensive stroke centers in China. All patients had occlusion of the basilar artery confirmed on vascular imaging within 12 hours of stroke onset, and they had severe symptoms at presentation, with an NIHSS score of at least 10. They were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to endovascular treatment or best medical management alone.
“It took us less than a year to enroll 342 patients,” Dr. Nogueira noted. “To put this into perspective, it took the BASICS trial over 8 years to enroll 300 patients, so these are very high-volume centers.”
He reported that two patients withdrew consent, and there were three patient crossovers on each side, comparing favorably with BASICS, leaving 226 patients in the intervention group and 114 in the control group.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups: median age was 67 years, median NIHSS score was 24, about 25% received thrombolysis, and median time from stroke onset to randomization was 5 hours.
Results showed that the primary outcome – a favorable functional outcome (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days – was achieved in 22.8% of the control group and in 46% of the endovascular group, giving an adjusted risk ratio of 2.1 (P < .001).
The number needed to treat was just four.
“There were no surprises with secondary endpoints; everything was highly statistically significant,” Dr. Nogueira said.
Specifically, there was a lower rate of overall disability in the shift analysis, with a common odds ratio of 2.8 favoring the intervention.
Safety results showed an increased risk for symptomatic ICH in the endovascular group (5.3% vs. 0.0%) but, despite that, 90-day mortality was significantly lower in the endovascular group (36.7% vs. 55.3%).
Dr. Nogueira noted a limitation of the study was that it was conducted in China.
“This was a Chinese study and, as Asians are known to have higher rates of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the overall degree of generalizability of our findings to Western countries needs to be considered,” he commented.
However, subgroup analysis showed no treatment effect modification based on the presence of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, he noted.
Also, the proportion of comorbidities in the ATTENTION trial was similar to that in the BASICS trial, with the same degree of diabetes and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Nogueira concluded that, in contrast to previous randomized trials of endovascular treatment for basilar artery occlusion, the ATTENTION trial was able to reinforce consecutive enrollment, resulting in a fast recruitment while minimizing crossovers.
Furthermore, he pointed out that the overall results are consistent with modern era observational studies, large registries, and meta-analysis.
Commenting on the study, Joanna Wardlaw, MD, professor of applied neuroimaging at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland), and chair of the ESOC Planning Group, said: “This is a very important result, since it provides confirmation beyond doubt the benefit of thrombectomy versus medical therapy for basilar artery occlusion stroke up to 12 hours after onset.”
Dr. Wardlaw added: “The trial was large enough to provide clear results and to enable subgroup analyses; no subgroup did not benefit from thrombectomy.”
In a discussion after the presentation, Urs Fischer, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University Hospital Basel, Switzerland, said he was not surprised by the results of the ATTENTION trial.
“We have been doing thrombectomy in patients with basilar artery occlusion now for 20 years, although trials are extremely important to answer these questions, so now we have some clear evidence,” Dr. Fischer said. “Nevertheless, there are some caveats, as this is an Asian population, but this is a proof of concept, and it is going in the right direction.”
The ATTENTION trial was sponsored by the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The benefit of endovascular therapy in the treatment of stroke caused by an occlusion of the basilar artery has finally been confirmed in the ATTENTION randomized trial.
The study, conducted in China, showed that endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion is associated with higher rates of favorable and independent outcomes, as well as lower overall disability and lower mortality at 90 days, than best medical management alone.
The results were presented by Raul Nogueira, MD, professor of neurology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) 2022, where they were greeted with applause from the audience.
“We can finally say that we have conquered the basilar artery territory. It is about time. We can finally confirm that the benefit of endovascular therapy persists in the posterior circulation,” Dr. Nogueira said.
“The disability reduction benefit of endovascular therapy for basilar artery occlusion appears to be within the same range as that observed in the anterior circulation. However, in contrast to most anterior circulation endovascular trials, the ATTENTION trial also demonstrated a potential benefit in terms of mortality,” he added.
Dr. Nogueira explained that the first series of endovascular treatment for stroke in the modern era was published in 1988, and this was in the basilar artery occlusion territory, but almost 35 years later, although there has been overwhelming proof of benefit of endovascular treatment in the antiterror circulation, it remains unknown whether endovascular treatment is beneficial to treat acute basilar artery occlusion. This is despite efforts in conducting two trials – the BEST and BASICS trials – which showed a direction of benefit but failed to show real significance.
“Having said that, these trials paved the way for the current trial, specifically by demonstrating the importance of consecutive recruitment, fast enrollment, and the minimalization of crossover. They also confirmed the ideal target population for this procedure in an individual patient level meta-analysis of these two trials,” he said.
In addition, there have also been two large Chinese registries suggesting significant benefits.
The ATTENTION trial was conducted to evaluate the hypothesis that endovascular therapy is superior to best medical management alone in achieving more favorable outcomes (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days in subjects presenting with acute basilar artery stroke within 12 hours of the estimated time of onset.
The study enrolled 342 patients at 36 comprehensive stroke centers in China. All patients had occlusion of the basilar artery confirmed on vascular imaging within 12 hours of stroke onset, and they had severe symptoms at presentation, with an NIHSS score of at least 10. They were randomized in a 2:1 ratio to endovascular treatment or best medical management alone.
“It took us less than a year to enroll 342 patients,” Dr. Nogueira noted. “To put this into perspective, it took the BASICS trial over 8 years to enroll 300 patients, so these are very high-volume centers.”
He reported that two patients withdrew consent, and there were three patient crossovers on each side, comparing favorably with BASICS, leaving 226 patients in the intervention group and 114 in the control group.
Baseline characteristics were similar between the two groups: median age was 67 years, median NIHSS score was 24, about 25% received thrombolysis, and median time from stroke onset to randomization was 5 hours.
Results showed that the primary outcome – a favorable functional outcome (mRS, 0-3) at 90 days – was achieved in 22.8% of the control group and in 46% of the endovascular group, giving an adjusted risk ratio of 2.1 (P < .001).
The number needed to treat was just four.
“There were no surprises with secondary endpoints; everything was highly statistically significant,” Dr. Nogueira said.
Specifically, there was a lower rate of overall disability in the shift analysis, with a common odds ratio of 2.8 favoring the intervention.
Safety results showed an increased risk for symptomatic ICH in the endovascular group (5.3% vs. 0.0%) but, despite that, 90-day mortality was significantly lower in the endovascular group (36.7% vs. 55.3%).
Dr. Nogueira noted a limitation of the study was that it was conducted in China.
“This was a Chinese study and, as Asians are known to have higher rates of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, the overall degree of generalizability of our findings to Western countries needs to be considered,” he commented.
However, subgroup analysis showed no treatment effect modification based on the presence of intracranial atherosclerotic disease, he noted.
Also, the proportion of comorbidities in the ATTENTION trial was similar to that in the BASICS trial, with the same degree of diabetes and atrial fibrillation.
Dr. Nogueira concluded that, in contrast to previous randomized trials of endovascular treatment for basilar artery occlusion, the ATTENTION trial was able to reinforce consecutive enrollment, resulting in a fast recruitment while minimizing crossovers.
Furthermore, he pointed out that the overall results are consistent with modern era observational studies, large registries, and meta-analysis.
Commenting on the study, Joanna Wardlaw, MD, professor of applied neuroimaging at the University of Edinburgh (Scotland), and chair of the ESOC Planning Group, said: “This is a very important result, since it provides confirmation beyond doubt the benefit of thrombectomy versus medical therapy for basilar artery occlusion stroke up to 12 hours after onset.”
Dr. Wardlaw added: “The trial was large enough to provide clear results and to enable subgroup analyses; no subgroup did not benefit from thrombectomy.”
In a discussion after the presentation, Urs Fischer, MD, chair of the department of neurology at the University Hospital Basel, Switzerland, said he was not surprised by the results of the ATTENTION trial.
“We have been doing thrombectomy in patients with basilar artery occlusion now for 20 years, although trials are extremely important to answer these questions, so now we have some clear evidence,” Dr. Fischer said. “Nevertheless, there are some caveats, as this is an Asian population, but this is a proof of concept, and it is going in the right direction.”
The ATTENTION trial was sponsored by the First Affiliated Hospital of University of Science and Technology of China.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antithrombotic therapies shifting for Watchman LAA occlusion
A new study finds clinicians are shifting away from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved combination of warfarin and aspirin after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device and that adverse events, particularly bleeding, are lower when aspirin is dropped.
Of 31,994 patients successfully implanted with the Watchman 2.5 device in the 3 years after its March 2015 approval, only 1 in 10 received the full postprocedure protocol studied in pivotal trials and codified into the FDA-device approval.
The protocol consisted of aspirin (81-325 mg) indefinitely and warfarin for 45 days. Following transesophageal echocardiography, patients were then maintained on warfarin and aspirin if there was a peridevice leak greater than 5 mm or switched to clopidogrel 75 mg for 6 months if a peridevice leak was ruled out or was 5 mm or less.
Based on the results, drawn from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry, the most common discharge medications were warfarin and aspirin in 36.9% of patients, followed by a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and aspirin (20.8%), warfarin alone (13.5%), DOAC only (12.3%), and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (5%).
“There’s a little bit of practice leading the science in this space,” lead author James V. Freeman, MD, MPH, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., told this news organization.
Patients who couldn’t tolerate long-term anticoagulation were excluded from the pivotal trials but are now the patients in whom the device is most often used, because of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement mandate for a relative or absolute contraindication to long-term anticoagulation, he noted.
Not surprisingly, 70% of patients in the registry had history of clinically relevant bleeding, the mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.6, and mean HAS-BLED score was 3. At an average age of 76, they were also older, by years, than those in the clinical trials.
Secular trends at the time also saw the ascendancy of the DOACs relative to warfarin, observed Dr. Freeman. “So I think it’s pretty reasonable for physicians to be considering DOACs rather than warfarin in this context.”
Aspirin takes another hit
Results, published May 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed that any adverse event occurred at 45 days in 5.7% of patients discharged on warfarin and aspirin, 4% on warfarin alone, 5.2% on DOAC and aspirin, 3.8% on DOAC only, and 5.5% on DAPT.
Rates of any major adverse event were 4.4%, 3.3%, 4.3%, 3.1%, and 4.2% respectively, and for major bleeding were 3%, 1.8%, 2.8%, 1.7%, and 2.2% respectively. Although patients were similar across treatment groups, those treated with DAPT were slightly older and had more comorbidities, Dr. Freeman said.
In Cox frailty regression, the adjusted risk of any adverse event at 45 days was significantly lower when patients were discharged on warfarin alone (hazard ratio, 0.692; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.84) and a DOAC alone (HR, 0.731; 95% CI, 0.57-0.93), compared with warfarin and aspirin. There were no differences among the other groups.
The risk of any major adverse event was also significantly lower with warfarin alone (HR, 0.658; 95% CI, 0.53-0.80) and DOAC alone (HR, 0.767; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98).
At 6 months, rates of any adverse event (HR, 0.814; 95% CI, 0.72-0.93) and any major adverse event (HR, 0.840; 95% CI, 0.73-0.95) were significantly lower only in patients treated with warfarin alone.
“I think if there’s a take-home [message] here, it’s that for a lot of patients there’s good data now to suggest getting rid of the aspirin is a very reasonable thing to do,” Dr. Freeman said.
Further studies are needed in the space, but the results are consistent with those from transcatheter aortic valve replacement studies showing discharge on warfarin or DOAC anticoagulation alone reduces major adverse events without increasing thrombotic events, he said.
“I do think if there’s a strong indication for aspirin – someone has terrible coronary disease – there may be a role for using it,” Dr. Freeman said. But for a lot of these patients, anticoagulation alone without aspirin “may present a big opportunity to mitigate morbidity associated with this procedure.”
Dr. Freeman said he doesn’t expect the findings would be dramatically different with the second-generation Watchman FLX device but noted that randomized data will be forthcoming, as Boston Scientific changed the CHAMPION-AF trial protocol to include DOAC alone without aspirin.
Commenting for this news organization, Domenico Della Rocca, MD, Texas Cardiac Arrhythmia Institute at St. David’s Medical Center, Austin, said the study is a useful overview of post-LAAO therapies in a large population – but not surprising.
“Practice has changed over the years. More and more we are adopting and trusting the DOACs,” he said. “And, we are realizing that dual antiplatelet therapy is so aggressive and antiplatelet therapy alone maybe is not the best choice based on data on activation of coagulation.”
Commenting further, he said “I think it’s too early to suggest being too keen to completely drop aspirin,” noting that 20%-25% of patients have clopidogrel resistance and that the combination of two antiplatelets may be too aggressive a strategy for others.
Dr. Della Rocca and colleagues recently reported favorable long-term results with half-dose DOAC therapy after Watchman implantation and said the team is launching a randomized trial in more than 500 LAAO patients in the United States and Europe later this year. The trial will be comparing a DOAC-based strategy with low-dose apixaban long-term versus clopidogrel and aspirin initially and then switching to 100 mg aspirin long-term.
“We hope that in the next 2-3 years we will have some better answers, but at this point I would say that clopidogrel is kind of an obsolete strategy for appendage closure,” Dr. Della Rocca said.
In an accompanying editorial, David R. Holmes Jr., MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., says “the cornucopia of these specific strategies can be expected to change as practices evolve, as instructions for use broaden and, hopefully, with the results of well-done, scientifically performed trials. This current LAAO Registry report, however, serves as a useful benchmark.”
He cautioned that this is an observational cohort study and that unmeasured imbalances still may affect the ability to identify an unbiased treatment signal. The use of DAPT was also infrequent during the study and “conclusions based on this information are soft.”
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants. Dr. Freeman has received salary support from the ACC NCDR and the NHLBI and has received consulting/advisory board fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Biosense Webster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study finds clinicians are shifting away from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved combination of warfarin and aspirin after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device and that adverse events, particularly bleeding, are lower when aspirin is dropped.
Of 31,994 patients successfully implanted with the Watchman 2.5 device in the 3 years after its March 2015 approval, only 1 in 10 received the full postprocedure protocol studied in pivotal trials and codified into the FDA-device approval.
The protocol consisted of aspirin (81-325 mg) indefinitely and warfarin for 45 days. Following transesophageal echocardiography, patients were then maintained on warfarin and aspirin if there was a peridevice leak greater than 5 mm or switched to clopidogrel 75 mg for 6 months if a peridevice leak was ruled out or was 5 mm or less.
Based on the results, drawn from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry, the most common discharge medications were warfarin and aspirin in 36.9% of patients, followed by a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and aspirin (20.8%), warfarin alone (13.5%), DOAC only (12.3%), and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (5%).
“There’s a little bit of practice leading the science in this space,” lead author James V. Freeman, MD, MPH, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., told this news organization.
Patients who couldn’t tolerate long-term anticoagulation were excluded from the pivotal trials but are now the patients in whom the device is most often used, because of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement mandate for a relative or absolute contraindication to long-term anticoagulation, he noted.
Not surprisingly, 70% of patients in the registry had history of clinically relevant bleeding, the mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.6, and mean HAS-BLED score was 3. At an average age of 76, they were also older, by years, than those in the clinical trials.
Secular trends at the time also saw the ascendancy of the DOACs relative to warfarin, observed Dr. Freeman. “So I think it’s pretty reasonable for physicians to be considering DOACs rather than warfarin in this context.”
Aspirin takes another hit
Results, published May 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed that any adverse event occurred at 45 days in 5.7% of patients discharged on warfarin and aspirin, 4% on warfarin alone, 5.2% on DOAC and aspirin, 3.8% on DOAC only, and 5.5% on DAPT.
Rates of any major adverse event were 4.4%, 3.3%, 4.3%, 3.1%, and 4.2% respectively, and for major bleeding were 3%, 1.8%, 2.8%, 1.7%, and 2.2% respectively. Although patients were similar across treatment groups, those treated with DAPT were slightly older and had more comorbidities, Dr. Freeman said.
In Cox frailty regression, the adjusted risk of any adverse event at 45 days was significantly lower when patients were discharged on warfarin alone (hazard ratio, 0.692; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.84) and a DOAC alone (HR, 0.731; 95% CI, 0.57-0.93), compared with warfarin and aspirin. There were no differences among the other groups.
The risk of any major adverse event was also significantly lower with warfarin alone (HR, 0.658; 95% CI, 0.53-0.80) and DOAC alone (HR, 0.767; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98).
At 6 months, rates of any adverse event (HR, 0.814; 95% CI, 0.72-0.93) and any major adverse event (HR, 0.840; 95% CI, 0.73-0.95) were significantly lower only in patients treated with warfarin alone.
“I think if there’s a take-home [message] here, it’s that for a lot of patients there’s good data now to suggest getting rid of the aspirin is a very reasonable thing to do,” Dr. Freeman said.
Further studies are needed in the space, but the results are consistent with those from transcatheter aortic valve replacement studies showing discharge on warfarin or DOAC anticoagulation alone reduces major adverse events without increasing thrombotic events, he said.
“I do think if there’s a strong indication for aspirin – someone has terrible coronary disease – there may be a role for using it,” Dr. Freeman said. But for a lot of these patients, anticoagulation alone without aspirin “may present a big opportunity to mitigate morbidity associated with this procedure.”
Dr. Freeman said he doesn’t expect the findings would be dramatically different with the second-generation Watchman FLX device but noted that randomized data will be forthcoming, as Boston Scientific changed the CHAMPION-AF trial protocol to include DOAC alone without aspirin.
Commenting for this news organization, Domenico Della Rocca, MD, Texas Cardiac Arrhythmia Institute at St. David’s Medical Center, Austin, said the study is a useful overview of post-LAAO therapies in a large population – but not surprising.
“Practice has changed over the years. More and more we are adopting and trusting the DOACs,” he said. “And, we are realizing that dual antiplatelet therapy is so aggressive and antiplatelet therapy alone maybe is not the best choice based on data on activation of coagulation.”
Commenting further, he said “I think it’s too early to suggest being too keen to completely drop aspirin,” noting that 20%-25% of patients have clopidogrel resistance and that the combination of two antiplatelets may be too aggressive a strategy for others.
Dr. Della Rocca and colleagues recently reported favorable long-term results with half-dose DOAC therapy after Watchman implantation and said the team is launching a randomized trial in more than 500 LAAO patients in the United States and Europe later this year. The trial will be comparing a DOAC-based strategy with low-dose apixaban long-term versus clopidogrel and aspirin initially and then switching to 100 mg aspirin long-term.
“We hope that in the next 2-3 years we will have some better answers, but at this point I would say that clopidogrel is kind of an obsolete strategy for appendage closure,” Dr. Della Rocca said.
In an accompanying editorial, David R. Holmes Jr., MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., says “the cornucopia of these specific strategies can be expected to change as practices evolve, as instructions for use broaden and, hopefully, with the results of well-done, scientifically performed trials. This current LAAO Registry report, however, serves as a useful benchmark.”
He cautioned that this is an observational cohort study and that unmeasured imbalances still may affect the ability to identify an unbiased treatment signal. The use of DAPT was also infrequent during the study and “conclusions based on this information are soft.”
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants. Dr. Freeman has received salary support from the ACC NCDR and the NHLBI and has received consulting/advisory board fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Biosense Webster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study finds clinicians are shifting away from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration–approved combination of warfarin and aspirin after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device and that adverse events, particularly bleeding, are lower when aspirin is dropped.
Of 31,994 patients successfully implanted with the Watchman 2.5 device in the 3 years after its March 2015 approval, only 1 in 10 received the full postprocedure protocol studied in pivotal trials and codified into the FDA-device approval.
The protocol consisted of aspirin (81-325 mg) indefinitely and warfarin for 45 days. Following transesophageal echocardiography, patients were then maintained on warfarin and aspirin if there was a peridevice leak greater than 5 mm or switched to clopidogrel 75 mg for 6 months if a peridevice leak was ruled out or was 5 mm or less.
Based on the results, drawn from the National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry, the most common discharge medications were warfarin and aspirin in 36.9% of patients, followed by a direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) and aspirin (20.8%), warfarin alone (13.5%), DOAC only (12.3%), and dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) with aspirin and a P2Y12 inhibitor (5%).
“There’s a little bit of practice leading the science in this space,” lead author James V. Freeman, MD, MPH, Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Conn., told this news organization.
Patients who couldn’t tolerate long-term anticoagulation were excluded from the pivotal trials but are now the patients in whom the device is most often used, because of the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid reimbursement mandate for a relative or absolute contraindication to long-term anticoagulation, he noted.
Not surprisingly, 70% of patients in the registry had history of clinically relevant bleeding, the mean CHA2DS2-VASc score was 4.6, and mean HAS-BLED score was 3. At an average age of 76, they were also older, by years, than those in the clinical trials.
Secular trends at the time also saw the ascendancy of the DOACs relative to warfarin, observed Dr. Freeman. “So I think it’s pretty reasonable for physicians to be considering DOACs rather than warfarin in this context.”
Aspirin takes another hit
Results, published May 2 in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, showed that any adverse event occurred at 45 days in 5.7% of patients discharged on warfarin and aspirin, 4% on warfarin alone, 5.2% on DOAC and aspirin, 3.8% on DOAC only, and 5.5% on DAPT.
Rates of any major adverse event were 4.4%, 3.3%, 4.3%, 3.1%, and 4.2% respectively, and for major bleeding were 3%, 1.8%, 2.8%, 1.7%, and 2.2% respectively. Although patients were similar across treatment groups, those treated with DAPT were slightly older and had more comorbidities, Dr. Freeman said.
In Cox frailty regression, the adjusted risk of any adverse event at 45 days was significantly lower when patients were discharged on warfarin alone (hazard ratio, 0.692; 95% confidence interval, 0.56-0.84) and a DOAC alone (HR, 0.731; 95% CI, 0.57-0.93), compared with warfarin and aspirin. There were no differences among the other groups.
The risk of any major adverse event was also significantly lower with warfarin alone (HR, 0.658; 95% CI, 0.53-0.80) and DOAC alone (HR, 0.767; 95% CI, 0.59-0.98).
At 6 months, rates of any adverse event (HR, 0.814; 95% CI, 0.72-0.93) and any major adverse event (HR, 0.840; 95% CI, 0.73-0.95) were significantly lower only in patients treated with warfarin alone.
“I think if there’s a take-home [message] here, it’s that for a lot of patients there’s good data now to suggest getting rid of the aspirin is a very reasonable thing to do,” Dr. Freeman said.
Further studies are needed in the space, but the results are consistent with those from transcatheter aortic valve replacement studies showing discharge on warfarin or DOAC anticoagulation alone reduces major adverse events without increasing thrombotic events, he said.
“I do think if there’s a strong indication for aspirin – someone has terrible coronary disease – there may be a role for using it,” Dr. Freeman said. But for a lot of these patients, anticoagulation alone without aspirin “may present a big opportunity to mitigate morbidity associated with this procedure.”
Dr. Freeman said he doesn’t expect the findings would be dramatically different with the second-generation Watchman FLX device but noted that randomized data will be forthcoming, as Boston Scientific changed the CHAMPION-AF trial protocol to include DOAC alone without aspirin.
Commenting for this news organization, Domenico Della Rocca, MD, Texas Cardiac Arrhythmia Institute at St. David’s Medical Center, Austin, said the study is a useful overview of post-LAAO therapies in a large population – but not surprising.
“Practice has changed over the years. More and more we are adopting and trusting the DOACs,” he said. “And, we are realizing that dual antiplatelet therapy is so aggressive and antiplatelet therapy alone maybe is not the best choice based on data on activation of coagulation.”
Commenting further, he said “I think it’s too early to suggest being too keen to completely drop aspirin,” noting that 20%-25% of patients have clopidogrel resistance and that the combination of two antiplatelets may be too aggressive a strategy for others.
Dr. Della Rocca and colleagues recently reported favorable long-term results with half-dose DOAC therapy after Watchman implantation and said the team is launching a randomized trial in more than 500 LAAO patients in the United States and Europe later this year. The trial will be comparing a DOAC-based strategy with low-dose apixaban long-term versus clopidogrel and aspirin initially and then switching to 100 mg aspirin long-term.
“We hope that in the next 2-3 years we will have some better answers, but at this point I would say that clopidogrel is kind of an obsolete strategy for appendage closure,” Dr. Della Rocca said.
In an accompanying editorial, David R. Holmes Jr., MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., says “the cornucopia of these specific strategies can be expected to change as practices evolve, as instructions for use broaden and, hopefully, with the results of well-done, scientifically performed trials. This current LAAO Registry report, however, serves as a useful benchmark.”
He cautioned that this is an observational cohort study and that unmeasured imbalances still may affect the ability to identify an unbiased treatment signal. The use of DAPT was also infrequent during the study and “conclusions based on this information are soft.”
The study was funded by the American College of Cardiology National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR), and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) grants. Dr. Freeman has received salary support from the ACC NCDR and the NHLBI and has received consulting/advisory board fees from Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, and Biosense Webster.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Screening for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy is often incomplete
Nearly three-quarters of clinicians reported screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, but only one-quarter comprehensively identified cardiovascular risk, based on survey data from approximately 1,500 clinicians in the United States.
Rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been on the rise in the United States for the past decade, and women with a history of these disorders require cardiovascular risk monitoring during the postpartum period and beyond, wrote Nicole D. Ford, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues. Specifically, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends cardiovascular risk evaluation and lifestyle modification for these individuals, the researchers said.
The most effective management of women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy will likely involve a team effort by primary care, ob.gyns., and cardiologists, but data on clinician screening and referrals are limited, they added.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from a cross-sectional, web-based survey of clinicians practicing in the United States (Fall DocStyles 2020). The study population of 1,502 respondents with complete surveys included 1,000 primary care physicians, 251 ob.gyns., and 251 nurse practitioners or physician assistants. Approximately 60% of the respondents were male, and approximately 65% had been in practice for at least 10 years.
Overall, 73.6% of clinicians reported screening patients for a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The screening rates were highest among ob.gyns. (94.8%).
However, although 93.9% of clinicians overall correctly identified at least one potential risk associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, only 24.8% correctly identified all cardiovascular risks associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy listed in the survey, the researchers noted.
Screening rates ranged from 49% to 91% for pregnant women, 34%-75% for postpartum women, 26%-61% for nonpregnant reproductive-age women, 20%-45% for perimenopausal or menopausal women, and 1%-4% for others outside of these categories.
The most often–cited barriers to referral were lack of patient follow-through (51.5%) and patient refusal (33.6%). To improve and facilitate referrals, respondents’ most frequent resource request was for more referral options (42.9%), followed by patient education materials (36.2%), and professional guidelines (34.1%).
In a multivariate analysis, primary care physicians were more than five times as likely to report not screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (adjusted prevalence ratio, 5.54); nurse practitioners and physician assistants were more than seven times as likely (adjusted prevalence ratio, 7.42).
The researchers also found that clinicians who saw fewer than 80 patients per week were almost twice as likely not to screen for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy than those who saw 110 or more patients per week (adjusted prevalence ratio, 1.81).
“Beyond the immediate postpartum period, there is a lack of clear guidance on CVD [cardiovascular disease] evaluation and ongoing monitoring in women with history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Recognizing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy as a risk factor for CVD may allow clinicians to identify women requiring early evaluation and intervention,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potentially biased estimates of screening practices, and the potential for selection bias because of the convenience sample used to recruit survey participants, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the inclusion of data from several clinician types and the relatively large sample size, and are consistent with those of previous studies, they said. Based on the findings, addressing barriers at both the patient and clinician level and increasing both patient and clinician education about the long-term risks of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy might increase cardiovascular screening and subsequent referrals, they concluded.
More education, improved screening tools needed
“Unfortunately, most CVD risk stratification scores such as the Framingham score do not include pregnancy complications, despite excellent evidence that pregnancy complications increase risk of CVD,” said Catherine M. Albright, MD, MS, of the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview. “This is likely because these scores were developed primarily to screen for CVD risk in men. Given the rising incidence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the clear evidence that this is a risk factor for future CVD, more studies like this one are needed in order to help guide patient and provider education,” said Dr. Albright, who was not involved in the study.
“It is generally well reported within the ob.gyn. literature about the increased lifetime CVD risk related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and we, as ob.gyns., always ask about pregnancy history because of our specialty, which gives us the opportunity to counsel about future risks,” she said.
“Women’s health [including during pregnancy] has been undervalued and underresearched for a long time,” with limited focus on pregnancy-related issues until recently, Dr. Albright noted. “This is clear in the attitudes and education of the primary care providers in this study,” she said.
A major barrier to screening in clinical practice has been that the standard screening guidelines for CVD (for example, those published by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce) have not included pregnancy history, said Dr. Albright. “Subsequently, these questions are not asked during routine annual visits,” she said. Ideally, “we should be able to leverage the electronic medical record to prompt providers to view a previously recorded pregnancy history or to ask about pregnancy history as a routine part of CVD risk assessment, and, of course, additional education outside of ob.gyn. and cardiology is needed,” she said.
The clinical takeaway from the current study is that “every annual visit with a person who has been pregnant is an opportunity to ask about and document pregnancy history,” Dr. Albright said. “After the completion of childbearing, many patients no longer see an ob.gyn., so other providers need to feel comfortable asking about and counseling about risks related to pregnancy complications,” she added.
“It is clear that adverse pregnancy outcomes pose lifetime health risks,” said Dr. Albright. “We will continue to look into the mechanisms of this through research. However, right now the additional research that is needed is to determine the optimal screening and follow-up for patients with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, as well as to examine how existing CVD-screening algorithms can be modified to include adverse pregnancy outcomes,” she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Albright had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Nearly three-quarters of clinicians reported screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, but only one-quarter comprehensively identified cardiovascular risk, based on survey data from approximately 1,500 clinicians in the United States.
Rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been on the rise in the United States for the past decade, and women with a history of these disorders require cardiovascular risk monitoring during the postpartum period and beyond, wrote Nicole D. Ford, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues. Specifically, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends cardiovascular risk evaluation and lifestyle modification for these individuals, the researchers said.
The most effective management of women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy will likely involve a team effort by primary care, ob.gyns., and cardiologists, but data on clinician screening and referrals are limited, they added.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from a cross-sectional, web-based survey of clinicians practicing in the United States (Fall DocStyles 2020). The study population of 1,502 respondents with complete surveys included 1,000 primary care physicians, 251 ob.gyns., and 251 nurse practitioners or physician assistants. Approximately 60% of the respondents were male, and approximately 65% had been in practice for at least 10 years.
Overall, 73.6% of clinicians reported screening patients for a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The screening rates were highest among ob.gyns. (94.8%).
However, although 93.9% of clinicians overall correctly identified at least one potential risk associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, only 24.8% correctly identified all cardiovascular risks associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy listed in the survey, the researchers noted.
Screening rates ranged from 49% to 91% for pregnant women, 34%-75% for postpartum women, 26%-61% for nonpregnant reproductive-age women, 20%-45% for perimenopausal or menopausal women, and 1%-4% for others outside of these categories.
The most often–cited barriers to referral were lack of patient follow-through (51.5%) and patient refusal (33.6%). To improve and facilitate referrals, respondents’ most frequent resource request was for more referral options (42.9%), followed by patient education materials (36.2%), and professional guidelines (34.1%).
In a multivariate analysis, primary care physicians were more than five times as likely to report not screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (adjusted prevalence ratio, 5.54); nurse practitioners and physician assistants were more than seven times as likely (adjusted prevalence ratio, 7.42).
The researchers also found that clinicians who saw fewer than 80 patients per week were almost twice as likely not to screen for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy than those who saw 110 or more patients per week (adjusted prevalence ratio, 1.81).
“Beyond the immediate postpartum period, there is a lack of clear guidance on CVD [cardiovascular disease] evaluation and ongoing monitoring in women with history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Recognizing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy as a risk factor for CVD may allow clinicians to identify women requiring early evaluation and intervention,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potentially biased estimates of screening practices, and the potential for selection bias because of the convenience sample used to recruit survey participants, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the inclusion of data from several clinician types and the relatively large sample size, and are consistent with those of previous studies, they said. Based on the findings, addressing barriers at both the patient and clinician level and increasing both patient and clinician education about the long-term risks of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy might increase cardiovascular screening and subsequent referrals, they concluded.
More education, improved screening tools needed
“Unfortunately, most CVD risk stratification scores such as the Framingham score do not include pregnancy complications, despite excellent evidence that pregnancy complications increase risk of CVD,” said Catherine M. Albright, MD, MS, of the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview. “This is likely because these scores were developed primarily to screen for CVD risk in men. Given the rising incidence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the clear evidence that this is a risk factor for future CVD, more studies like this one are needed in order to help guide patient and provider education,” said Dr. Albright, who was not involved in the study.
“It is generally well reported within the ob.gyn. literature about the increased lifetime CVD risk related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and we, as ob.gyns., always ask about pregnancy history because of our specialty, which gives us the opportunity to counsel about future risks,” she said.
“Women’s health [including during pregnancy] has been undervalued and underresearched for a long time,” with limited focus on pregnancy-related issues until recently, Dr. Albright noted. “This is clear in the attitudes and education of the primary care providers in this study,” she said.
A major barrier to screening in clinical practice has been that the standard screening guidelines for CVD (for example, those published by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce) have not included pregnancy history, said Dr. Albright. “Subsequently, these questions are not asked during routine annual visits,” she said. Ideally, “we should be able to leverage the electronic medical record to prompt providers to view a previously recorded pregnancy history or to ask about pregnancy history as a routine part of CVD risk assessment, and, of course, additional education outside of ob.gyn. and cardiology is needed,” she said.
The clinical takeaway from the current study is that “every annual visit with a person who has been pregnant is an opportunity to ask about and document pregnancy history,” Dr. Albright said. “After the completion of childbearing, many patients no longer see an ob.gyn., so other providers need to feel comfortable asking about and counseling about risks related to pregnancy complications,” she added.
“It is clear that adverse pregnancy outcomes pose lifetime health risks,” said Dr. Albright. “We will continue to look into the mechanisms of this through research. However, right now the additional research that is needed is to determine the optimal screening and follow-up for patients with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, as well as to examine how existing CVD-screening algorithms can be modified to include adverse pregnancy outcomes,” she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Albright had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Nearly three-quarters of clinicians reported screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, but only one-quarter comprehensively identified cardiovascular risk, based on survey data from approximately 1,500 clinicians in the United States.
Rates of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy have been on the rise in the United States for the past decade, and women with a history of these disorders require cardiovascular risk monitoring during the postpartum period and beyond, wrote Nicole D. Ford, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, and colleagues. Specifically, the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends cardiovascular risk evaluation and lifestyle modification for these individuals, the researchers said.
The most effective management of women with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy will likely involve a team effort by primary care, ob.gyns., and cardiologists, but data on clinician screening and referrals are limited, they added.
In a study published in Obstetrics & Gynecology, the researchers reviewed data from a cross-sectional, web-based survey of clinicians practicing in the United States (Fall DocStyles 2020). The study population of 1,502 respondents with complete surveys included 1,000 primary care physicians, 251 ob.gyns., and 251 nurse practitioners or physician assistants. Approximately 60% of the respondents were male, and approximately 65% had been in practice for at least 10 years.
Overall, 73.6% of clinicians reported screening patients for a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. The screening rates were highest among ob.gyns. (94.8%).
However, although 93.9% of clinicians overall correctly identified at least one potential risk associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, only 24.8% correctly identified all cardiovascular risks associated with hypertensive disorders of pregnancy listed in the survey, the researchers noted.
Screening rates ranged from 49% to 91% for pregnant women, 34%-75% for postpartum women, 26%-61% for nonpregnant reproductive-age women, 20%-45% for perimenopausal or menopausal women, and 1%-4% for others outside of these categories.
The most often–cited barriers to referral were lack of patient follow-through (51.5%) and patient refusal (33.6%). To improve and facilitate referrals, respondents’ most frequent resource request was for more referral options (42.9%), followed by patient education materials (36.2%), and professional guidelines (34.1%).
In a multivariate analysis, primary care physicians were more than five times as likely to report not screening patients for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy (adjusted prevalence ratio, 5.54); nurse practitioners and physician assistants were more than seven times as likely (adjusted prevalence ratio, 7.42).
The researchers also found that clinicians who saw fewer than 80 patients per week were almost twice as likely not to screen for hypertensive disorders of pregnancy than those who saw 110 or more patients per week (adjusted prevalence ratio, 1.81).
“Beyond the immediate postpartum period, there is a lack of clear guidance on CVD [cardiovascular disease] evaluation and ongoing monitoring in women with history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Recognizing hypertensive disorders of pregnancy as a risk factor for CVD may allow clinicians to identify women requiring early evaluation and intervention,” they said.
The study findings were limited by several factors including potentially biased estimates of screening practices, and the potential for selection bias because of the convenience sample used to recruit survey participants, the researchers noted.
However, the results were strengthened by the inclusion of data from several clinician types and the relatively large sample size, and are consistent with those of previous studies, they said. Based on the findings, addressing barriers at both the patient and clinician level and increasing both patient and clinician education about the long-term risks of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy might increase cardiovascular screening and subsequent referrals, they concluded.
More education, improved screening tools needed
“Unfortunately, most CVD risk stratification scores such as the Framingham score do not include pregnancy complications, despite excellent evidence that pregnancy complications increase risk of CVD,” said Catherine M. Albright, MD, MS, of the University of Washington, Seattle, in an interview. “This is likely because these scores were developed primarily to screen for CVD risk in men. Given the rising incidence of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and the clear evidence that this is a risk factor for future CVD, more studies like this one are needed in order to help guide patient and provider education,” said Dr. Albright, who was not involved in the study.
“It is generally well reported within the ob.gyn. literature about the increased lifetime CVD risk related to hypertensive disorders of pregnancy and we, as ob.gyns., always ask about pregnancy history because of our specialty, which gives us the opportunity to counsel about future risks,” she said.
“Women’s health [including during pregnancy] has been undervalued and underresearched for a long time,” with limited focus on pregnancy-related issues until recently, Dr. Albright noted. “This is clear in the attitudes and education of the primary care providers in this study,” she said.
A major barrier to screening in clinical practice has been that the standard screening guidelines for CVD (for example, those published by the United States Preventive Services Taskforce) have not included pregnancy history, said Dr. Albright. “Subsequently, these questions are not asked during routine annual visits,” she said. Ideally, “we should be able to leverage the electronic medical record to prompt providers to view a previously recorded pregnancy history or to ask about pregnancy history as a routine part of CVD risk assessment, and, of course, additional education outside of ob.gyn. and cardiology is needed,” she said.
The clinical takeaway from the current study is that “every annual visit with a person who has been pregnant is an opportunity to ask about and document pregnancy history,” Dr. Albright said. “After the completion of childbearing, many patients no longer see an ob.gyn., so other providers need to feel comfortable asking about and counseling about risks related to pregnancy complications,” she added.
“It is clear that adverse pregnancy outcomes pose lifetime health risks,” said Dr. Albright. “We will continue to look into the mechanisms of this through research. However, right now the additional research that is needed is to determine the optimal screening and follow-up for patients with a history of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, as well as to examine how existing CVD-screening algorithms can be modified to include adverse pregnancy outcomes,” she emphasized.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Albright had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM OBSTETRICS & GYNECOLOGY












