User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
Boston Scientific bails on Lotus Edge aortic valve system
Boston Scientific said it is voluntarily recalling all unused inventory of the Lotus Edge transcatheter aortic valve replacement system effective immediately.
In making the announcement today, Boston Scientific chair and CEO Mike Mahoney said the company has been increasingly challenged by the intricacies of the delivery system required to allow physicians to fully reposition and recapture the valve – key features of the system.
“The complexity of the delivery system, manufacturing challenges, the continued need for further technical enhancements, and current market adoption rates led us to the difficult decision to stop investing in the Lotus Edge platform,” Mr. Mahoney said.
Instead, the company will focus on the ACURATE neo2 aortic valve system, the Sentinel cerebral embolic protection device, and other high-growth areas, he noted.
The decision is expected to result in a $225 million to $300 million pretax charge, with $100 million to $150 million of these charges to impact the company’s adjusted results.
The Lotus device was approved in the United States in April 2019 for use in patients with severe aortic stenosis at high surgical risk based on the REPRISE 3 trial.
The Lotus Edge valve was approved in Europe in 2016, but final testing and rollout of the valve in the United States were delayed following a 2017 global recall of all Lotus valves because of reports of premature release of a pin connecting the valve to the delivery system.
Issues with the delivery system led to other Lotus valve recalls in both 2016 and 2014.
“Given the additional time and investment required to develop and reintroduce an enhanced delivery system, the company has chosen to retire the entire Lotus product platform immediately. All related commercial, clinical, research & development and manufacturing activities will also cease,” the statement said.
There is no safety issue for patients who currently have an implanted Lotus Edge valve, the company said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Boston Scientific said it is voluntarily recalling all unused inventory of the Lotus Edge transcatheter aortic valve replacement system effective immediately.
In making the announcement today, Boston Scientific chair and CEO Mike Mahoney said the company has been increasingly challenged by the intricacies of the delivery system required to allow physicians to fully reposition and recapture the valve – key features of the system.
“The complexity of the delivery system, manufacturing challenges, the continued need for further technical enhancements, and current market adoption rates led us to the difficult decision to stop investing in the Lotus Edge platform,” Mr. Mahoney said.
Instead, the company will focus on the ACURATE neo2 aortic valve system, the Sentinel cerebral embolic protection device, and other high-growth areas, he noted.
The decision is expected to result in a $225 million to $300 million pretax charge, with $100 million to $150 million of these charges to impact the company’s adjusted results.
The Lotus device was approved in the United States in April 2019 for use in patients with severe aortic stenosis at high surgical risk based on the REPRISE 3 trial.
The Lotus Edge valve was approved in Europe in 2016, but final testing and rollout of the valve in the United States were delayed following a 2017 global recall of all Lotus valves because of reports of premature release of a pin connecting the valve to the delivery system.
Issues with the delivery system led to other Lotus valve recalls in both 2016 and 2014.
“Given the additional time and investment required to develop and reintroduce an enhanced delivery system, the company has chosen to retire the entire Lotus product platform immediately. All related commercial, clinical, research & development and manufacturing activities will also cease,” the statement said.
There is no safety issue for patients who currently have an implanted Lotus Edge valve, the company said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Boston Scientific said it is voluntarily recalling all unused inventory of the Lotus Edge transcatheter aortic valve replacement system effective immediately.
In making the announcement today, Boston Scientific chair and CEO Mike Mahoney said the company has been increasingly challenged by the intricacies of the delivery system required to allow physicians to fully reposition and recapture the valve – key features of the system.
“The complexity of the delivery system, manufacturing challenges, the continued need for further technical enhancements, and current market adoption rates led us to the difficult decision to stop investing in the Lotus Edge platform,” Mr. Mahoney said.
Instead, the company will focus on the ACURATE neo2 aortic valve system, the Sentinel cerebral embolic protection device, and other high-growth areas, he noted.
The decision is expected to result in a $225 million to $300 million pretax charge, with $100 million to $150 million of these charges to impact the company’s adjusted results.
The Lotus device was approved in the United States in April 2019 for use in patients with severe aortic stenosis at high surgical risk based on the REPRISE 3 trial.
The Lotus Edge valve was approved in Europe in 2016, but final testing and rollout of the valve in the United States were delayed following a 2017 global recall of all Lotus valves because of reports of premature release of a pin connecting the valve to the delivery system.
Issues with the delivery system led to other Lotus valve recalls in both 2016 and 2014.
“Given the additional time and investment required to develop and reintroduce an enhanced delivery system, the company has chosen to retire the entire Lotus product platform immediately. All related commercial, clinical, research & development and manufacturing activities will also cease,” the statement said.
There is no safety issue for patients who currently have an implanted Lotus Edge valve, the company said.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 burdens follow patients after discharge
COVID-19 patients who survive their hospitalization don’t leave the disease behind upon discharge, as a significant percentage died within 60 days of discharge, with an ICU admission heightening the risk, according to an observational study of 38 Michigan hospitals. What’s more, many of them were burdened with health and emotional challenges ranging from hospital readmission to job loss and financial problems.
“These data confirm that the toll of COVID-19 extends well beyond hospitalization, a finding consistent with long-term sequelae from sepsis and other severe respiratory viral illnesses,” wrote lead author Vineet Chopra, MBBS, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues (Ann Intern Med. 2020 Nov 11: doi: 10.7326/M20-5661)
The researchers found that 29.2% of all patients hospitalized for COVID-19 from March 16 to July 1 died. The observational cohort study included 1,648 COVID-19 patients hospitalized at 38 Michigan hospitals participating in a statewide collaborative.
The bulk of those deaths occurred during hospitalization: 24.2% of patients (n = 398). Of the 1,250 patients discharged, 78% (n = 975) went home and 12.6% (n = 158) went to a skilled nursing facility, with the remainder unaccounted for. Within 60 days of discharge, 6.7% (n = 84) of hospitalized survivors had died and 15.2% (n = 189) were readmitted. The researchers gathered 60-day postdischarge data via a telephone survey, contacting 41.8% (n = 488) of discharged patients.
Outcomes were even worse for discharged patients who spent time in the ICU. The death rate among this group was 10.4% (17 of 165) after discharge. That resulted in an overall study death rate of 63.5% (n = 257) for the 405 patients who were in the ICU.
While the study data were in the first wave of the novel coronavirus, the findings have relevance today, said Mary Jo Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP, directory of pulmonary hypertension services at Baystate Health in Springfield, Mass.
“This is the best information we have to date,” she said. “We have to continue to have an open mind and expect that this information may change as the virus possibly mutates as it spreads, and we should continue doing these types of outcomes studies at 90 days, 120 days, etc.”
The median age of study patients was 62, with a range of 50-72. The three leading comorbidities among discharged patients were hypertension (n = 800, 64%), diabetes (34.9%, n = 436), and cardiovascular disease (24.1%, n = 301).
Poor postdischarge outcomes weren’t limited to mortality and readmission. Almost 19% (n = 92) reported new or worsening cardiopulmonary symptoms such as cough and dyspnea, 13.3% had a persistent loss of taste or smell, and 12% (n = 58) reported more difficulty with daily living tasks.
The after-effects were not only physical. Nearly half of discharged patients (48.7%, n = 238) reported emotional effects and almost 6% (n = 28) sought mental health care. Among the 40% (n = 195) employed before they were hospitalized, 36% (n = 78) couldn’t return to work because of health issues or layoffs. Sixty percent (n = 117) of the pre-employed discharged patients did return to work, but 25% (n = 30) did so with reduced hours or modified job duties because of health problems.
Financial problems were also a burden. More than a third, 36.7% (n = 179), reported some financial impact from their hospitalization. About 10% (n = 47) said they used most or all of their savings, and 7% (n = 35) said they resorted to rationing necessities such as food or medications.
The researchers noted that one in five patients had no primary care follow-up at 2 months post discharge. “Collectively, these findings suggest that better models to support COVID-19 survivors are necessary,” said Dr. Chopra and colleagues.
The postdischarge course for patients involves two humps, said Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP a pulmonary and critical care specialist at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif.: Getting over the hospitalization itself and the recovery phase. “As you look at the median age of the survivors, elderly patients who survive a hospital stay are still going to have a period of recovery, and like any viral illness that leads to someone being hospitalized, when you have an elderly patient with comorbidities, not all of them can make it over that final hump.”
He echoed the study authors’ call for better postdischarge support for COVID-19 patients. “There’s typically, although not at every hospital, a one-size-fits-all discharge planning process,” Dr. Gupta said. “For older patients, particularly with comorbid conditions, close follow-up after discharge is important.”
Dr. Farmer noted that one challenge in discharge support may be a matter of personnel. “The providers of this care might be fearful of patients who have had COVID-19 – Do the patients remain contagious? What if symptoms of COVID-19 return such as dry cough, fever? – and of contracting the disease themselves,” she said.
The findings regarding the emotional status of discharged patients should factor into discharge planning, she added. “Providers of posthospital care need to be educated in the emotional impact of this disease (e.g., the patients may feel ostracized or that no one wants to be around them) to assist in their recovery.”
Dr. Chopra and Dr. Farmer have no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Gupta is an employee and shareholder of Genentech.
SOURCE: Chopra V et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Nov 11. doi: 10.7326/M20-5661.
COVID-19 patients who survive their hospitalization don’t leave the disease behind upon discharge, as a significant percentage died within 60 days of discharge, with an ICU admission heightening the risk, according to an observational study of 38 Michigan hospitals. What’s more, many of them were burdened with health and emotional challenges ranging from hospital readmission to job loss and financial problems.
“These data confirm that the toll of COVID-19 extends well beyond hospitalization, a finding consistent with long-term sequelae from sepsis and other severe respiratory viral illnesses,” wrote lead author Vineet Chopra, MBBS, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues (Ann Intern Med. 2020 Nov 11: doi: 10.7326/M20-5661)
The researchers found that 29.2% of all patients hospitalized for COVID-19 from March 16 to July 1 died. The observational cohort study included 1,648 COVID-19 patients hospitalized at 38 Michigan hospitals participating in a statewide collaborative.
The bulk of those deaths occurred during hospitalization: 24.2% of patients (n = 398). Of the 1,250 patients discharged, 78% (n = 975) went home and 12.6% (n = 158) went to a skilled nursing facility, with the remainder unaccounted for. Within 60 days of discharge, 6.7% (n = 84) of hospitalized survivors had died and 15.2% (n = 189) were readmitted. The researchers gathered 60-day postdischarge data via a telephone survey, contacting 41.8% (n = 488) of discharged patients.
Outcomes were even worse for discharged patients who spent time in the ICU. The death rate among this group was 10.4% (17 of 165) after discharge. That resulted in an overall study death rate of 63.5% (n = 257) for the 405 patients who were in the ICU.
While the study data were in the first wave of the novel coronavirus, the findings have relevance today, said Mary Jo Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP, directory of pulmonary hypertension services at Baystate Health in Springfield, Mass.
“This is the best information we have to date,” she said. “We have to continue to have an open mind and expect that this information may change as the virus possibly mutates as it spreads, and we should continue doing these types of outcomes studies at 90 days, 120 days, etc.”
The median age of study patients was 62, with a range of 50-72. The three leading comorbidities among discharged patients were hypertension (n = 800, 64%), diabetes (34.9%, n = 436), and cardiovascular disease (24.1%, n = 301).
Poor postdischarge outcomes weren’t limited to mortality and readmission. Almost 19% (n = 92) reported new or worsening cardiopulmonary symptoms such as cough and dyspnea, 13.3% had a persistent loss of taste or smell, and 12% (n = 58) reported more difficulty with daily living tasks.
The after-effects were not only physical. Nearly half of discharged patients (48.7%, n = 238) reported emotional effects and almost 6% (n = 28) sought mental health care. Among the 40% (n = 195) employed before they were hospitalized, 36% (n = 78) couldn’t return to work because of health issues or layoffs. Sixty percent (n = 117) of the pre-employed discharged patients did return to work, but 25% (n = 30) did so with reduced hours or modified job duties because of health problems.
Financial problems were also a burden. More than a third, 36.7% (n = 179), reported some financial impact from their hospitalization. About 10% (n = 47) said they used most or all of their savings, and 7% (n = 35) said they resorted to rationing necessities such as food or medications.
The researchers noted that one in five patients had no primary care follow-up at 2 months post discharge. “Collectively, these findings suggest that better models to support COVID-19 survivors are necessary,” said Dr. Chopra and colleagues.
The postdischarge course for patients involves two humps, said Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP a pulmonary and critical care specialist at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif.: Getting over the hospitalization itself and the recovery phase. “As you look at the median age of the survivors, elderly patients who survive a hospital stay are still going to have a period of recovery, and like any viral illness that leads to someone being hospitalized, when you have an elderly patient with comorbidities, not all of them can make it over that final hump.”
He echoed the study authors’ call for better postdischarge support for COVID-19 patients. “There’s typically, although not at every hospital, a one-size-fits-all discharge planning process,” Dr. Gupta said. “For older patients, particularly with comorbid conditions, close follow-up after discharge is important.”
Dr. Farmer noted that one challenge in discharge support may be a matter of personnel. “The providers of this care might be fearful of patients who have had COVID-19 – Do the patients remain contagious? What if symptoms of COVID-19 return such as dry cough, fever? – and of contracting the disease themselves,” she said.
The findings regarding the emotional status of discharged patients should factor into discharge planning, she added. “Providers of posthospital care need to be educated in the emotional impact of this disease (e.g., the patients may feel ostracized or that no one wants to be around them) to assist in their recovery.”
Dr. Chopra and Dr. Farmer have no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Gupta is an employee and shareholder of Genentech.
SOURCE: Chopra V et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Nov 11. doi: 10.7326/M20-5661.
COVID-19 patients who survive their hospitalization don’t leave the disease behind upon discharge, as a significant percentage died within 60 days of discharge, with an ICU admission heightening the risk, according to an observational study of 38 Michigan hospitals. What’s more, many of them were burdened with health and emotional challenges ranging from hospital readmission to job loss and financial problems.
“These data confirm that the toll of COVID-19 extends well beyond hospitalization, a finding consistent with long-term sequelae from sepsis and other severe respiratory viral illnesses,” wrote lead author Vineet Chopra, MBBS, of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues (Ann Intern Med. 2020 Nov 11: doi: 10.7326/M20-5661)
The researchers found that 29.2% of all patients hospitalized for COVID-19 from March 16 to July 1 died. The observational cohort study included 1,648 COVID-19 patients hospitalized at 38 Michigan hospitals participating in a statewide collaborative.
The bulk of those deaths occurred during hospitalization: 24.2% of patients (n = 398). Of the 1,250 patients discharged, 78% (n = 975) went home and 12.6% (n = 158) went to a skilled nursing facility, with the remainder unaccounted for. Within 60 days of discharge, 6.7% (n = 84) of hospitalized survivors had died and 15.2% (n = 189) were readmitted. The researchers gathered 60-day postdischarge data via a telephone survey, contacting 41.8% (n = 488) of discharged patients.
Outcomes were even worse for discharged patients who spent time in the ICU. The death rate among this group was 10.4% (17 of 165) after discharge. That resulted in an overall study death rate of 63.5% (n = 257) for the 405 patients who were in the ICU.
While the study data were in the first wave of the novel coronavirus, the findings have relevance today, said Mary Jo Farmer, MD, PhD, FCCP, directory of pulmonary hypertension services at Baystate Health in Springfield, Mass.
“This is the best information we have to date,” she said. “We have to continue to have an open mind and expect that this information may change as the virus possibly mutates as it spreads, and we should continue doing these types of outcomes studies at 90 days, 120 days, etc.”
The median age of study patients was 62, with a range of 50-72. The three leading comorbidities among discharged patients were hypertension (n = 800, 64%), diabetes (34.9%, n = 436), and cardiovascular disease (24.1%, n = 301).
Poor postdischarge outcomes weren’t limited to mortality and readmission. Almost 19% (n = 92) reported new or worsening cardiopulmonary symptoms such as cough and dyspnea, 13.3% had a persistent loss of taste or smell, and 12% (n = 58) reported more difficulty with daily living tasks.
The after-effects were not only physical. Nearly half of discharged patients (48.7%, n = 238) reported emotional effects and almost 6% (n = 28) sought mental health care. Among the 40% (n = 195) employed before they were hospitalized, 36% (n = 78) couldn’t return to work because of health issues or layoffs. Sixty percent (n = 117) of the pre-employed discharged patients did return to work, but 25% (n = 30) did so with reduced hours or modified job duties because of health problems.
Financial problems were also a burden. More than a third, 36.7% (n = 179), reported some financial impact from their hospitalization. About 10% (n = 47) said they used most or all of their savings, and 7% (n = 35) said they resorted to rationing necessities such as food or medications.
The researchers noted that one in five patients had no primary care follow-up at 2 months post discharge. “Collectively, these findings suggest that better models to support COVID-19 survivors are necessary,” said Dr. Chopra and colleagues.
The postdischarge course for patients involves two humps, said Sachin Gupta, MD, FCCP a pulmonary and critical care specialist at Alameda Health System in Oakland, Calif.: Getting over the hospitalization itself and the recovery phase. “As you look at the median age of the survivors, elderly patients who survive a hospital stay are still going to have a period of recovery, and like any viral illness that leads to someone being hospitalized, when you have an elderly patient with comorbidities, not all of them can make it over that final hump.”
He echoed the study authors’ call for better postdischarge support for COVID-19 patients. “There’s typically, although not at every hospital, a one-size-fits-all discharge planning process,” Dr. Gupta said. “For older patients, particularly with comorbid conditions, close follow-up after discharge is important.”
Dr. Farmer noted that one challenge in discharge support may be a matter of personnel. “The providers of this care might be fearful of patients who have had COVID-19 – Do the patients remain contagious? What if symptoms of COVID-19 return such as dry cough, fever? – and of contracting the disease themselves,” she said.
The findings regarding the emotional status of discharged patients should factor into discharge planning, she added. “Providers of posthospital care need to be educated in the emotional impact of this disease (e.g., the patients may feel ostracized or that no one wants to be around them) to assist in their recovery.”
Dr. Chopra and Dr. Farmer have no financial relationships to disclose. Dr. Gupta is an employee and shareholder of Genentech.
SOURCE: Chopra V et al. Ann Intern Med. 2020 Nov 11. doi: 10.7326/M20-5661.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
First SGLT1/2 inhibitor shows ‘spectacular’ phase 3 safety and efficacy in T2D
Sotagliflozin, a novel type of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor, showed the diverse benefits this drug class provides along some new twists in a pair of international pivotal trials that together enrolled nearly 12,000 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Unprecedented benefits were seen for the first time with a drug, sotagliflozin (Zynquista) that produces both sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition as well as SGLT1 inhibition.
They included a big reduction in both MIs and strokes; an ability to meaningfully reduce hyperglycemia in patients with severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2; an ability to safely and effectively start in patients still hospitalized (but stable) for an acute heart failure episode; and a striking 37% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalizations, or an urgent outpatient visit for heart failure in 739 of the patients enrolled in both trials who had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
These studies produced for the first time evidence from controlled, prospective, randomized trials that a drug could improve the outcome of HFpEF patients.
All these novel outcomes came on top of the usual benefits clinicians have generally seen across the SGLT2 inhibitors already on the U.S. market: reductions in cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations among all patients with type 2 diabetes, preservation of renal function, and hemoglobin A1c lowering among T2D patients with eGFR levels of at least 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“The data look spectacular,” summed up Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who presented the results from the two trials, SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED, in talks at the virtual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
“I think sotagliflozin has the potential to be the best in class” based on the several added attributes shown in the two trials, he said in an interview. “We’ve shown that it is very safe, well tolerated, and effective.”
The primary results were a significant 33% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in the rate of total cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations for heart failure, or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure during just over 9 months of median follow-up among patients with T2D recently hospitalized for heart failure in SOLOIST-WFH. And a significant 26% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin for the same endpoint after a median follow-up of just over 14 months in SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
“Sotagliflozin adds to the SGLT2 inhibitor story,” and the SOLOIST-WHF results “may shift our focus to vulnerable, acute heart failure patients with an opportunity to treat during the transition phase,” when these patients leave the hospital, commented Jane E. Wilcox, MD, the study’s designated discussant and a heart failure cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
A dual SGLT inhibitor
What sets sotagliflozin apart from the SGLT2 inhibitors is that it not only inhibits that protein but also SGTL1, which primarily resides in the gastrointestinal tract and is the main route for gut absorption of glucose. Dr. Bhatt said that he was unaware of any other SGLT1/2 inhibitors currently in advanced clinical testing.
The activity of sotagliflozin against the SGLT1 protein likely explains its ability to cut A1c levels in patients with severe renal dysfunction, a condition that stymies glucose lowering by SGLT2 inhibitors. In SCORED, which randomized 10,584 patients with T2D at 750 study sites in 44 countries, 813 patients (8%) had an eGFR of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2 at enrollment. Sotagliflozin treatment led to an average 0.6% cut in A1c in this subgroup, and by the same average amount among the patients with GFRs of 30-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“This is a huge finding for endocrinologists and primary care physicians” who treat patients with T2D who have severe renal dysfunction, said Dr. Bhatt, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “It’s a good enough reason by itself to approve this drug.”
The same mechanism may also be behind another unexpected finding in SCORED. Treatment with sotagliflozin cut the rate of total episodes of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke by an absolute 1.6%, compared with placebo, and by a relative 23%. This benefit was largely driven by a 32% relative risk reduction total in MIs, and a 34% relative risk reduction in total stroke, both significant differences.
“No SGLT2 inhibitor has shown a reduction in stroke, and the MI signals have been mixed. The sizable MI and stroke effects are unique to sotagliflozin,” compared with the SGLT2 inhibitors, and likely reflect one or more mechanisms that result from blocked gut SGLT1 and a cut in GI glucose uptake, said Dr. Bhatt. “Probably some novel mechanism we don’t fully understand.”
First-ever HFpEF benefit
In contrast to these two benefits that are probably unique to drugs that inhibit the SGLT1 protein, sotagliflozin showed two other notable and unprecedented benefits that are likely generalizable to the SGLT2 inhibitors.
First is the striking benefit for HFpEF. Neither SOLOIST, which enrolled 1,222 patients with T2D and just hospitalized for worsening heart failure, nor SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease based exclusively on an eGFR of 25-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, excluded patients with HFpEF, defined as heart failure patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 50%. The two studies together included a total of 739 of these patients, and they split fairly evenly between treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo.
The combined analysis showed that the incidence rate for the primary endpoint in both SOLOIST and SCORED was 59% with placebo and 39% with sotagliflozin, an absolute event reduction of 11.6 events/100 patient-years, and a significant 37% relative risk reduction, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 event per year event of 9.
Although this observation comes from a nonprespecified combined analysis, “to me this result seems real, and I think it’s a class effect that I’m willing to extrapolate to the SGLT2 inhibitors,” Dr. Bhatt said. “It will change my practice,” he added, by spurring him to more aggressively prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor to a patient with T2D and HFpEF.
“I think there has been some hesitation to use SGLT2 inhibitors in T2D patients with HFpEF” because of the paucity of data in this population, even though labeling and society recommendations do not rule it out. “I hope this finding will move that needle, and also generally improve SGLT2 inhibitor uptake, which has been low,” he said.
Also safe soon after acute heart failure decompensation
The other finding likely generalizable to SGLT2 inhibitors stems from the design of SOLOIST-WHF, which tested the efficacy and safety of starting sotagliflozin in patients with T2D as soon as they were stable after hospitalization for acute heart failure decompensation.
“Showing safety and efficacy when started in the hospital is pretty meaningful, because its tells patients that this drug is important and they should stay on it,” which should improve adherence, predicted Dr. Bhatt, who is also executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “That’s the ultimate treatment path to prevent patients from falling through the cracks” and failing to receive an SGLT2 inhibitor.
SOLOIST-WHF enrolled patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure who also required intravenous diuretic treatment but had become stable enough to transition to an oral diuretic and come off oxygen. During a median follow-up of just over 9 months (both SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED ended sooner than planned because of a change in drug company sponsorship), treatment with sotagliflozin cut the primary endpoint by a relative 33%, compared with placebo, and with an absolute reduction of 25 events per 100 patient-years for a number needed to treat of 4. Sotagliflozin produced a strikingly high level of treatment efficiency driven by the high event rate in these recently decompensated patients. The benefit also appeared quickly, with a significant cut in events discernible within 28 days.
Extrapolating this finding to the SGLT2 inhibitors is “not a huge leap of faith,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“There is a role for sotagliflozin in acute heart failure. It showed benefit in these high-risk, transition-phase patients,” said Dr. Wilcox.
Simultaneously with Dr. Bhatt’s presentation, results of SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trials were sponsored initially by Sanofi, and more recently by Lexicon. Dr. Bhatt has received research funding from both companies, and also from several other companies. He also is an adviser to several companies. Dr. Wilcox has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic.
Sotagliflozin, a novel type of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor, showed the diverse benefits this drug class provides along some new twists in a pair of international pivotal trials that together enrolled nearly 12,000 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Unprecedented benefits were seen for the first time with a drug, sotagliflozin (Zynquista) that produces both sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition as well as SGLT1 inhibition.
They included a big reduction in both MIs and strokes; an ability to meaningfully reduce hyperglycemia in patients with severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2; an ability to safely and effectively start in patients still hospitalized (but stable) for an acute heart failure episode; and a striking 37% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalizations, or an urgent outpatient visit for heart failure in 739 of the patients enrolled in both trials who had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
These studies produced for the first time evidence from controlled, prospective, randomized trials that a drug could improve the outcome of HFpEF patients.
All these novel outcomes came on top of the usual benefits clinicians have generally seen across the SGLT2 inhibitors already on the U.S. market: reductions in cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations among all patients with type 2 diabetes, preservation of renal function, and hemoglobin A1c lowering among T2D patients with eGFR levels of at least 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“The data look spectacular,” summed up Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who presented the results from the two trials, SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED, in talks at the virtual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
“I think sotagliflozin has the potential to be the best in class” based on the several added attributes shown in the two trials, he said in an interview. “We’ve shown that it is very safe, well tolerated, and effective.”
The primary results were a significant 33% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in the rate of total cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations for heart failure, or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure during just over 9 months of median follow-up among patients with T2D recently hospitalized for heart failure in SOLOIST-WFH. And a significant 26% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin for the same endpoint after a median follow-up of just over 14 months in SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
“Sotagliflozin adds to the SGLT2 inhibitor story,” and the SOLOIST-WHF results “may shift our focus to vulnerable, acute heart failure patients with an opportunity to treat during the transition phase,” when these patients leave the hospital, commented Jane E. Wilcox, MD, the study’s designated discussant and a heart failure cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
A dual SGLT inhibitor
What sets sotagliflozin apart from the SGLT2 inhibitors is that it not only inhibits that protein but also SGTL1, which primarily resides in the gastrointestinal tract and is the main route for gut absorption of glucose. Dr. Bhatt said that he was unaware of any other SGLT1/2 inhibitors currently in advanced clinical testing.
The activity of sotagliflozin against the SGLT1 protein likely explains its ability to cut A1c levels in patients with severe renal dysfunction, a condition that stymies glucose lowering by SGLT2 inhibitors. In SCORED, which randomized 10,584 patients with T2D at 750 study sites in 44 countries, 813 patients (8%) had an eGFR of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2 at enrollment. Sotagliflozin treatment led to an average 0.6% cut in A1c in this subgroup, and by the same average amount among the patients with GFRs of 30-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“This is a huge finding for endocrinologists and primary care physicians” who treat patients with T2D who have severe renal dysfunction, said Dr. Bhatt, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “It’s a good enough reason by itself to approve this drug.”
The same mechanism may also be behind another unexpected finding in SCORED. Treatment with sotagliflozin cut the rate of total episodes of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke by an absolute 1.6%, compared with placebo, and by a relative 23%. This benefit was largely driven by a 32% relative risk reduction total in MIs, and a 34% relative risk reduction in total stroke, both significant differences.
“No SGLT2 inhibitor has shown a reduction in stroke, and the MI signals have been mixed. The sizable MI and stroke effects are unique to sotagliflozin,” compared with the SGLT2 inhibitors, and likely reflect one or more mechanisms that result from blocked gut SGLT1 and a cut in GI glucose uptake, said Dr. Bhatt. “Probably some novel mechanism we don’t fully understand.”
First-ever HFpEF benefit
In contrast to these two benefits that are probably unique to drugs that inhibit the SGLT1 protein, sotagliflozin showed two other notable and unprecedented benefits that are likely generalizable to the SGLT2 inhibitors.
First is the striking benefit for HFpEF. Neither SOLOIST, which enrolled 1,222 patients with T2D and just hospitalized for worsening heart failure, nor SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease based exclusively on an eGFR of 25-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, excluded patients with HFpEF, defined as heart failure patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 50%. The two studies together included a total of 739 of these patients, and they split fairly evenly between treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo.
The combined analysis showed that the incidence rate for the primary endpoint in both SOLOIST and SCORED was 59% with placebo and 39% with sotagliflozin, an absolute event reduction of 11.6 events/100 patient-years, and a significant 37% relative risk reduction, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 event per year event of 9.
Although this observation comes from a nonprespecified combined analysis, “to me this result seems real, and I think it’s a class effect that I’m willing to extrapolate to the SGLT2 inhibitors,” Dr. Bhatt said. “It will change my practice,” he added, by spurring him to more aggressively prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor to a patient with T2D and HFpEF.
“I think there has been some hesitation to use SGLT2 inhibitors in T2D patients with HFpEF” because of the paucity of data in this population, even though labeling and society recommendations do not rule it out. “I hope this finding will move that needle, and also generally improve SGLT2 inhibitor uptake, which has been low,” he said.
Also safe soon after acute heart failure decompensation
The other finding likely generalizable to SGLT2 inhibitors stems from the design of SOLOIST-WHF, which tested the efficacy and safety of starting sotagliflozin in patients with T2D as soon as they were stable after hospitalization for acute heart failure decompensation.
“Showing safety and efficacy when started in the hospital is pretty meaningful, because its tells patients that this drug is important and they should stay on it,” which should improve adherence, predicted Dr. Bhatt, who is also executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “That’s the ultimate treatment path to prevent patients from falling through the cracks” and failing to receive an SGLT2 inhibitor.
SOLOIST-WHF enrolled patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure who also required intravenous diuretic treatment but had become stable enough to transition to an oral diuretic and come off oxygen. During a median follow-up of just over 9 months (both SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED ended sooner than planned because of a change in drug company sponsorship), treatment with sotagliflozin cut the primary endpoint by a relative 33%, compared with placebo, and with an absolute reduction of 25 events per 100 patient-years for a number needed to treat of 4. Sotagliflozin produced a strikingly high level of treatment efficiency driven by the high event rate in these recently decompensated patients. The benefit also appeared quickly, with a significant cut in events discernible within 28 days.
Extrapolating this finding to the SGLT2 inhibitors is “not a huge leap of faith,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“There is a role for sotagliflozin in acute heart failure. It showed benefit in these high-risk, transition-phase patients,” said Dr. Wilcox.
Simultaneously with Dr. Bhatt’s presentation, results of SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trials were sponsored initially by Sanofi, and more recently by Lexicon. Dr. Bhatt has received research funding from both companies, and also from several other companies. He also is an adviser to several companies. Dr. Wilcox has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic.
Sotagliflozin, a novel type of sodium-glucose cotransporter inhibitor, showed the diverse benefits this drug class provides along some new twists in a pair of international pivotal trials that together enrolled nearly 12,000 patients with type 2 diabetes.
Unprecedented benefits were seen for the first time with a drug, sotagliflozin (Zynquista) that produces both sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition as well as SGLT1 inhibition.
They included a big reduction in both MIs and strokes; an ability to meaningfully reduce hyperglycemia in patients with severe renal dysfunction with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2; an ability to safely and effectively start in patients still hospitalized (but stable) for an acute heart failure episode; and a striking 37% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death, heart failure hospitalizations, or an urgent outpatient visit for heart failure in 739 of the patients enrolled in both trials who had heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
These studies produced for the first time evidence from controlled, prospective, randomized trials that a drug could improve the outcome of HFpEF patients.
All these novel outcomes came on top of the usual benefits clinicians have generally seen across the SGLT2 inhibitors already on the U.S. market: reductions in cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalizations among all patients with type 2 diabetes, preservation of renal function, and hemoglobin A1c lowering among T2D patients with eGFR levels of at least 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“The data look spectacular,” summed up Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, who presented the results from the two trials, SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED, in talks at the virtual scientific sessions of the American Heart Association.
“I think sotagliflozin has the potential to be the best in class” based on the several added attributes shown in the two trials, he said in an interview. “We’ve shown that it is very safe, well tolerated, and effective.”
The primary results were a significant 33% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin treatment, compared with placebo in the rate of total cardiovascular deaths, hospitalizations for heart failure, or urgent outpatient visits for heart failure during just over 9 months of median follow-up among patients with T2D recently hospitalized for heart failure in SOLOIST-WFH. And a significant 26% relative risk reduction with sotagliflozin for the same endpoint after a median follow-up of just over 14 months in SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease.
“Sotagliflozin adds to the SGLT2 inhibitor story,” and the SOLOIST-WHF results “may shift our focus to vulnerable, acute heart failure patients with an opportunity to treat during the transition phase,” when these patients leave the hospital, commented Jane E. Wilcox, MD, the study’s designated discussant and a heart failure cardiologist at Northwestern Medicine in Chicago.
A dual SGLT inhibitor
What sets sotagliflozin apart from the SGLT2 inhibitors is that it not only inhibits that protein but also SGTL1, which primarily resides in the gastrointestinal tract and is the main route for gut absorption of glucose. Dr. Bhatt said that he was unaware of any other SGLT1/2 inhibitors currently in advanced clinical testing.
The activity of sotagliflozin against the SGLT1 protein likely explains its ability to cut A1c levels in patients with severe renal dysfunction, a condition that stymies glucose lowering by SGLT2 inhibitors. In SCORED, which randomized 10,584 patients with T2D at 750 study sites in 44 countries, 813 patients (8%) had an eGFR of 25-29 mL/min per 1.73 m2 at enrollment. Sotagliflozin treatment led to an average 0.6% cut in A1c in this subgroup, and by the same average amount among the patients with GFRs of 30-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2.
“This is a huge finding for endocrinologists and primary care physicians” who treat patients with T2D who have severe renal dysfunction, said Dr. Bhatt, a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School in Boston. “It’s a good enough reason by itself to approve this drug.”
The same mechanism may also be behind another unexpected finding in SCORED. Treatment with sotagliflozin cut the rate of total episodes of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke by an absolute 1.6%, compared with placebo, and by a relative 23%. This benefit was largely driven by a 32% relative risk reduction total in MIs, and a 34% relative risk reduction in total stroke, both significant differences.
“No SGLT2 inhibitor has shown a reduction in stroke, and the MI signals have been mixed. The sizable MI and stroke effects are unique to sotagliflozin,” compared with the SGLT2 inhibitors, and likely reflect one or more mechanisms that result from blocked gut SGLT1 and a cut in GI glucose uptake, said Dr. Bhatt. “Probably some novel mechanism we don’t fully understand.”
First-ever HFpEF benefit
In contrast to these two benefits that are probably unique to drugs that inhibit the SGLT1 protein, sotagliflozin showed two other notable and unprecedented benefits that are likely generalizable to the SGLT2 inhibitors.
First is the striking benefit for HFpEF. Neither SOLOIST, which enrolled 1,222 patients with T2D and just hospitalized for worsening heart failure, nor SCORED, which enrolled patients with T2D and chronic kidney disease based exclusively on an eGFR of 25-60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, excluded patients with HFpEF, defined as heart failure patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 50%. The two studies together included a total of 739 of these patients, and they split fairly evenly between treatment with sotagliflozin or placebo.
The combined analysis showed that the incidence rate for the primary endpoint in both SOLOIST and SCORED was 59% with placebo and 39% with sotagliflozin, an absolute event reduction of 11.6 events/100 patient-years, and a significant 37% relative risk reduction, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 event per year event of 9.
Although this observation comes from a nonprespecified combined analysis, “to me this result seems real, and I think it’s a class effect that I’m willing to extrapolate to the SGLT2 inhibitors,” Dr. Bhatt said. “It will change my practice,” he added, by spurring him to more aggressively prescribe an SGLT2 inhibitor to a patient with T2D and HFpEF.
“I think there has been some hesitation to use SGLT2 inhibitors in T2D patients with HFpEF” because of the paucity of data in this population, even though labeling and society recommendations do not rule it out. “I hope this finding will move that needle, and also generally improve SGLT2 inhibitor uptake, which has been low,” he said.
Also safe soon after acute heart failure decompensation
The other finding likely generalizable to SGLT2 inhibitors stems from the design of SOLOIST-WHF, which tested the efficacy and safety of starting sotagliflozin in patients with T2D as soon as they were stable after hospitalization for acute heart failure decompensation.
“Showing safety and efficacy when started in the hospital is pretty meaningful, because its tells patients that this drug is important and they should stay on it,” which should improve adherence, predicted Dr. Bhatt, who is also executive director of Interventional Cardiovascular Programs at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. “That’s the ultimate treatment path to prevent patients from falling through the cracks” and failing to receive an SGLT2 inhibitor.
SOLOIST-WHF enrolled patients hospitalized for worsening heart failure who also required intravenous diuretic treatment but had become stable enough to transition to an oral diuretic and come off oxygen. During a median follow-up of just over 9 months (both SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED ended sooner than planned because of a change in drug company sponsorship), treatment with sotagliflozin cut the primary endpoint by a relative 33%, compared with placebo, and with an absolute reduction of 25 events per 100 patient-years for a number needed to treat of 4. Sotagliflozin produced a strikingly high level of treatment efficiency driven by the high event rate in these recently decompensated patients. The benefit also appeared quickly, with a significant cut in events discernible within 28 days.
Extrapolating this finding to the SGLT2 inhibitors is “not a huge leap of faith,” Dr. Bhatt said.
“There is a role for sotagliflozin in acute heart failure. It showed benefit in these high-risk, transition-phase patients,” said Dr. Wilcox.
Simultaneously with Dr. Bhatt’s presentation, results of SOLOIST-WHF and SCORED were published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The trials were sponsored initially by Sanofi, and more recently by Lexicon. Dr. Bhatt has received research funding from both companies, and also from several other companies. He also is an adviser to several companies. Dr. Wilcox has been a consultant to Boehringer Ingelheim and Medtronic.
FROM AHA 2020
Factor XI inhibitor–based anticoagulation strategies gain ground
according to Jeffrey I. Weitz, MD.
These strategies could pick up where direct-acting oral anticoagulants leave off, he suggested during a presentation at the biennial summit of the Thrombosis & Hemostasis Societies of North America.
“We all know that the direct oral anticoagulants – the DOACs – are an advance over vitamin K antagonists,” said Dr. Weitz, professor of medicine and biochemistry at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario.
Not only are DOACs at least as effective as vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation or for treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), but they also reduce intracranial bleeding and major bleeding risk in those settings, respectively, and they are more convenient to administer because they can be delivered using fixed doses without the need for coagulation monitoring, he added.
Still, new targets are needed, he said, explaining that, although DOACs moved closer to the goal of attenuating thrombosis without increasing the risk of bleeding, annual rates of major bleeding remain at 2%-3% in the atrial fibrillation population, and rates of major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding are about 10%.
“The fear of bleeding leads to underuse of anticoagulants for eligible patients with atrial fibrillation and inappropriate use of low-dose [non–vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant] regimens, which can leave patients unprotected from thrombotic complications,” he said.
Factor XI
That’s where Factor XI (FXI) may come in, Dr. Weitz said.
Current anticoagulants target enzymes, including FXa or thrombin, in the common pathway of coagulation, but the intrinsic pathway at the level of FXI and FXII has attracted attention in recent years.
The intrinsic pathway is activated when blood comes into contact with medical devices like stents, mechanical heart valves, or central venous catheters, but evidence also suggests that it plays a role in clot stabilization and growth, he explained, noting additional evidence of attenuation of thrombosis in mice deficient in FXI or FXII and in animals with FXI or FXII inhibitors.
“There is no bleeding with congenital FXII deficiency, and patients with FXI deficiency rarely have spontaneous bleeding, although they can bleed with surgery or trauma,” he noted. “Therefore, the promise of contact pathway inhibition is that we can attenuate thrombosis with little or no disruption of hemostasis.”
The initiators of the intrinsic pathway are naturally occurring polyphosphates that can activate FXI and FXII, promote platelet activation, and lead to thrombosis. A number of agents are being investigated to target these enzymes – particularly FXI, for which the strongest epidemiological and other evidence of its link with thrombosis exists. He noted that FXI deficiency appears protective against deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) and ischemic stroke, whereas high levels are linked with an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis.
Investigative strategies include the use of antisense oligonucleotides to reduce hepatic synthesis of FXI, aptamers to bind FXI and block its activity, antibodies to bind FXI and block its activation or activity, and small molecules to bind reversibly to the active site of FXI and block its activity “much like the DOACs block the activity of FXa or thrombin.”
“We have to remember that the DOACs have taken over from vitamin K antagonists, like warfarin, for many indications, and as they go generic their uptake will increase even further,” Dr. Weitz said. “When we compare the FXI inhibitors with existing anticoagulants, we don’t necessarily want to go up against the DOACs – we’re looking for indications where [DOACs] have yet to be tested or may be unsafe.”
Potential indications include the following:
Prevention of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with end-stage renal disease with or without atrial fibrillation.
Provision of a safer platform for antiplatelet therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Secondary stroke prevention.
Prevention or treatment of cancer-associated VTE.
Prevention of thrombosis associated with central venous catheters, left ventricular assist devices, or mechanical heart valves.
Agents in development
Of the FXI inhibitors in development, ISIS-FXIRx, an antisense oligonucleotide against FXI, is furthest along. In a study published in Blood, ISIS-FXIRx produced a dose-dependent and sustained reduction in FXI levels in healthy volunteers, and in a later randomized study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, it significantly reduced the incidence of DVT in patients undergoing voluntary total knee arthroplasty (30.4% with enoxaparin vs. 4.2% with ISIS-FXIRx at a dose of 300 mg). Bleeding rates were 8.3% and 2.6%, respectively.
The findings showed the potential for reducing thrombosis without increasing bleeding by targeting FXI, Dr. Weitz said, adding that ISIS-FXIRx was also evaluated in a small study of patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis and was shown to produce a dose-dependent reduction in FXI levels and to reduce the incidence of category 3 and 4 clotting in the air trap and dialyzer, compared with placebo, when given in addition to heparin.
This suggests that FXI knockdown can attenuate device-associated clotting to a greater extent than heparin alone, Dr. Weitz said.
The FXIa-directed inhibitory antibody osocimab has also been evaluated in both healthy volunteers and in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. In a 2019 study of healthy volunteers, a single IV injection showed a dose-dependent pharmacokinetic profile and produced FXI inhibition for about 1 month, and in the FOXTROT trial published in January in JAMA by Dr. Weitz and colleagues, osocimab was shown to reduce the incidence of symptomatic VTE, asymptomatic DVT, and VTE-related death up to day 10-13 after total knee arthroplasty.
Osocimab at doses ranging from 0.3-1.8 mg/kg given postoperatively or preoperatively were noninferior to enoxaparin (rates of 15.7%-23.7% vs. 26.3%), and osocimab at a preoperative dose of 1.8 mg/kg was superior to both enoxaparin and apixaban (11.5% vs. 26.3% and 14.5%, respectively), he said.
Bleeding rates ranged from 0%-5% with osocimab, compared with 6% with enoxaparin and 2% with apixaban
Ongoing studies
Currently ongoing studies of FXI-directed anticoagulation strategies include a study comparing ISIS-FXIRx with placebo in 200 patients with end-stage renal disease, a study comparing osocimab with placebo in 600 patients with end-stage renal disease, and a study comparing abelacimab – an antibody that binds to FXI and prevents its activation by either FXIIa or thrombin, with enoxaparin in 700 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty, Dr. Weitz said.
Additionally, there is “considerable activity” with small molecule inhibitors of FXIa, including a phase 2, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study looking at the novel JNG-7003/BMS-986177 agent for secondary stroke/transient ischemic attack prevention in 2,500 patients and a phase 2 study comparing it with enoxaparin for postoperative thromboprophylaxis in 1,200 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.
Parallel phase 2 studies are also underway to compare the novel BAY-2433334 small molecule inhibitor with placebo for stroke/transient ischemic attack prevention, with apixaban for atrial fibrillation, and for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute MI.
These ongoing trials will help determine the risk-benefit profile of FXI inhibitors he said.
Session comoderator Anne Rose, PharmD, pharmacy coordinator at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, noted that these types of agents have been discussed “for quite some time” and asked whether they will be available for use in clinical practice in the near future.
Dr. Weitz predicted it will be at least a few years. The studies are just now moving to phase 2b and will still need to be evaluated in phase 3 trials and for appropriate new indications, he said.
Dr. Weitz reported research support from Canadian Institutes of Health research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, and Canadian Fund for Innovation, and he is a consultant and/or scientific advisory board member for Anthos, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Portola, Servier , and Thetherex.
according to Jeffrey I. Weitz, MD.
These strategies could pick up where direct-acting oral anticoagulants leave off, he suggested during a presentation at the biennial summit of the Thrombosis & Hemostasis Societies of North America.
“We all know that the direct oral anticoagulants – the DOACs – are an advance over vitamin K antagonists,” said Dr. Weitz, professor of medicine and biochemistry at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario.
Not only are DOACs at least as effective as vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation or for treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), but they also reduce intracranial bleeding and major bleeding risk in those settings, respectively, and they are more convenient to administer because they can be delivered using fixed doses without the need for coagulation monitoring, he added.
Still, new targets are needed, he said, explaining that, although DOACs moved closer to the goal of attenuating thrombosis without increasing the risk of bleeding, annual rates of major bleeding remain at 2%-3% in the atrial fibrillation population, and rates of major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding are about 10%.
“The fear of bleeding leads to underuse of anticoagulants for eligible patients with atrial fibrillation and inappropriate use of low-dose [non–vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant] regimens, which can leave patients unprotected from thrombotic complications,” he said.
Factor XI
That’s where Factor XI (FXI) may come in, Dr. Weitz said.
Current anticoagulants target enzymes, including FXa or thrombin, in the common pathway of coagulation, but the intrinsic pathway at the level of FXI and FXII has attracted attention in recent years.
The intrinsic pathway is activated when blood comes into contact with medical devices like stents, mechanical heart valves, or central venous catheters, but evidence also suggests that it plays a role in clot stabilization and growth, he explained, noting additional evidence of attenuation of thrombosis in mice deficient in FXI or FXII and in animals with FXI or FXII inhibitors.
“There is no bleeding with congenital FXII deficiency, and patients with FXI deficiency rarely have spontaneous bleeding, although they can bleed with surgery or trauma,” he noted. “Therefore, the promise of contact pathway inhibition is that we can attenuate thrombosis with little or no disruption of hemostasis.”
The initiators of the intrinsic pathway are naturally occurring polyphosphates that can activate FXI and FXII, promote platelet activation, and lead to thrombosis. A number of agents are being investigated to target these enzymes – particularly FXI, for which the strongest epidemiological and other evidence of its link with thrombosis exists. He noted that FXI deficiency appears protective against deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) and ischemic stroke, whereas high levels are linked with an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis.
Investigative strategies include the use of antisense oligonucleotides to reduce hepatic synthesis of FXI, aptamers to bind FXI and block its activity, antibodies to bind FXI and block its activation or activity, and small molecules to bind reversibly to the active site of FXI and block its activity “much like the DOACs block the activity of FXa or thrombin.”
“We have to remember that the DOACs have taken over from vitamin K antagonists, like warfarin, for many indications, and as they go generic their uptake will increase even further,” Dr. Weitz said. “When we compare the FXI inhibitors with existing anticoagulants, we don’t necessarily want to go up against the DOACs – we’re looking for indications where [DOACs] have yet to be tested or may be unsafe.”
Potential indications include the following:
Prevention of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with end-stage renal disease with or without atrial fibrillation.
Provision of a safer platform for antiplatelet therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Secondary stroke prevention.
Prevention or treatment of cancer-associated VTE.
Prevention of thrombosis associated with central venous catheters, left ventricular assist devices, or mechanical heart valves.
Agents in development
Of the FXI inhibitors in development, ISIS-FXIRx, an antisense oligonucleotide against FXI, is furthest along. In a study published in Blood, ISIS-FXIRx produced a dose-dependent and sustained reduction in FXI levels in healthy volunteers, and in a later randomized study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, it significantly reduced the incidence of DVT in patients undergoing voluntary total knee arthroplasty (30.4% with enoxaparin vs. 4.2% with ISIS-FXIRx at a dose of 300 mg). Bleeding rates were 8.3% and 2.6%, respectively.
The findings showed the potential for reducing thrombosis without increasing bleeding by targeting FXI, Dr. Weitz said, adding that ISIS-FXIRx was also evaluated in a small study of patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis and was shown to produce a dose-dependent reduction in FXI levels and to reduce the incidence of category 3 and 4 clotting in the air trap and dialyzer, compared with placebo, when given in addition to heparin.
This suggests that FXI knockdown can attenuate device-associated clotting to a greater extent than heparin alone, Dr. Weitz said.
The FXIa-directed inhibitory antibody osocimab has also been evaluated in both healthy volunteers and in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. In a 2019 study of healthy volunteers, a single IV injection showed a dose-dependent pharmacokinetic profile and produced FXI inhibition for about 1 month, and in the FOXTROT trial published in January in JAMA by Dr. Weitz and colleagues, osocimab was shown to reduce the incidence of symptomatic VTE, asymptomatic DVT, and VTE-related death up to day 10-13 after total knee arthroplasty.
Osocimab at doses ranging from 0.3-1.8 mg/kg given postoperatively or preoperatively were noninferior to enoxaparin (rates of 15.7%-23.7% vs. 26.3%), and osocimab at a preoperative dose of 1.8 mg/kg was superior to both enoxaparin and apixaban (11.5% vs. 26.3% and 14.5%, respectively), he said.
Bleeding rates ranged from 0%-5% with osocimab, compared with 6% with enoxaparin and 2% with apixaban
Ongoing studies
Currently ongoing studies of FXI-directed anticoagulation strategies include a study comparing ISIS-FXIRx with placebo in 200 patients with end-stage renal disease, a study comparing osocimab with placebo in 600 patients with end-stage renal disease, and a study comparing abelacimab – an antibody that binds to FXI and prevents its activation by either FXIIa or thrombin, with enoxaparin in 700 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty, Dr. Weitz said.
Additionally, there is “considerable activity” with small molecule inhibitors of FXIa, including a phase 2, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study looking at the novel JNG-7003/BMS-986177 agent for secondary stroke/transient ischemic attack prevention in 2,500 patients and a phase 2 study comparing it with enoxaparin for postoperative thromboprophylaxis in 1,200 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.
Parallel phase 2 studies are also underway to compare the novel BAY-2433334 small molecule inhibitor with placebo for stroke/transient ischemic attack prevention, with apixaban for atrial fibrillation, and for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute MI.
These ongoing trials will help determine the risk-benefit profile of FXI inhibitors he said.
Session comoderator Anne Rose, PharmD, pharmacy coordinator at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, noted that these types of agents have been discussed “for quite some time” and asked whether they will be available for use in clinical practice in the near future.
Dr. Weitz predicted it will be at least a few years. The studies are just now moving to phase 2b and will still need to be evaluated in phase 3 trials and for appropriate new indications, he said.
Dr. Weitz reported research support from Canadian Institutes of Health research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, and Canadian Fund for Innovation, and he is a consultant and/or scientific advisory board member for Anthos, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Portola, Servier , and Thetherex.
according to Jeffrey I. Weitz, MD.
These strategies could pick up where direct-acting oral anticoagulants leave off, he suggested during a presentation at the biennial summit of the Thrombosis & Hemostasis Societies of North America.
“We all know that the direct oral anticoagulants – the DOACs – are an advance over vitamin K antagonists,” said Dr. Weitz, professor of medicine and biochemistry at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontario.
Not only are DOACs at least as effective as vitamin K antagonists such as warfarin for stroke prevention in atrial fibrillation or for treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), but they also reduce intracranial bleeding and major bleeding risk in those settings, respectively, and they are more convenient to administer because they can be delivered using fixed doses without the need for coagulation monitoring, he added.
Still, new targets are needed, he said, explaining that, although DOACs moved closer to the goal of attenuating thrombosis without increasing the risk of bleeding, annual rates of major bleeding remain at 2%-3% in the atrial fibrillation population, and rates of major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding are about 10%.
“The fear of bleeding leads to underuse of anticoagulants for eligible patients with atrial fibrillation and inappropriate use of low-dose [non–vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulant] regimens, which can leave patients unprotected from thrombotic complications,” he said.
Factor XI
That’s where Factor XI (FXI) may come in, Dr. Weitz said.
Current anticoagulants target enzymes, including FXa or thrombin, in the common pathway of coagulation, but the intrinsic pathway at the level of FXI and FXII has attracted attention in recent years.
The intrinsic pathway is activated when blood comes into contact with medical devices like stents, mechanical heart valves, or central venous catheters, but evidence also suggests that it plays a role in clot stabilization and growth, he explained, noting additional evidence of attenuation of thrombosis in mice deficient in FXI or FXII and in animals with FXI or FXII inhibitors.
“There is no bleeding with congenital FXII deficiency, and patients with FXI deficiency rarely have spontaneous bleeding, although they can bleed with surgery or trauma,” he noted. “Therefore, the promise of contact pathway inhibition is that we can attenuate thrombosis with little or no disruption of hemostasis.”
The initiators of the intrinsic pathway are naturally occurring polyphosphates that can activate FXI and FXII, promote platelet activation, and lead to thrombosis. A number of agents are being investigated to target these enzymes – particularly FXI, for which the strongest epidemiological and other evidence of its link with thrombosis exists. He noted that FXI deficiency appears protective against deep-vein thrombosis (DVT) and ischemic stroke, whereas high levels are linked with an increased risk of venous and arterial thrombosis.
Investigative strategies include the use of antisense oligonucleotides to reduce hepatic synthesis of FXI, aptamers to bind FXI and block its activity, antibodies to bind FXI and block its activation or activity, and small molecules to bind reversibly to the active site of FXI and block its activity “much like the DOACs block the activity of FXa or thrombin.”
“We have to remember that the DOACs have taken over from vitamin K antagonists, like warfarin, for many indications, and as they go generic their uptake will increase even further,” Dr. Weitz said. “When we compare the FXI inhibitors with existing anticoagulants, we don’t necessarily want to go up against the DOACs – we’re looking for indications where [DOACs] have yet to be tested or may be unsafe.”
Potential indications include the following:
Prevention of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with end-stage renal disease with or without atrial fibrillation.
Provision of a safer platform for antiplatelet therapy in patients with acute coronary syndrome.
Secondary stroke prevention.
Prevention or treatment of cancer-associated VTE.
Prevention of thrombosis associated with central venous catheters, left ventricular assist devices, or mechanical heart valves.
Agents in development
Of the FXI inhibitors in development, ISIS-FXIRx, an antisense oligonucleotide against FXI, is furthest along. In a study published in Blood, ISIS-FXIRx produced a dose-dependent and sustained reduction in FXI levels in healthy volunteers, and in a later randomized study published in The New England Journal of Medicine, it significantly reduced the incidence of DVT in patients undergoing voluntary total knee arthroplasty (30.4% with enoxaparin vs. 4.2% with ISIS-FXIRx at a dose of 300 mg). Bleeding rates were 8.3% and 2.6%, respectively.
The findings showed the potential for reducing thrombosis without increasing bleeding by targeting FXI, Dr. Weitz said, adding that ISIS-FXIRx was also evaluated in a small study of patients with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis and was shown to produce a dose-dependent reduction in FXI levels and to reduce the incidence of category 3 and 4 clotting in the air trap and dialyzer, compared with placebo, when given in addition to heparin.
This suggests that FXI knockdown can attenuate device-associated clotting to a greater extent than heparin alone, Dr. Weitz said.
The FXIa-directed inhibitory antibody osocimab has also been evaluated in both healthy volunteers and in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. In a 2019 study of healthy volunteers, a single IV injection showed a dose-dependent pharmacokinetic profile and produced FXI inhibition for about 1 month, and in the FOXTROT trial published in January in JAMA by Dr. Weitz and colleagues, osocimab was shown to reduce the incidence of symptomatic VTE, asymptomatic DVT, and VTE-related death up to day 10-13 after total knee arthroplasty.
Osocimab at doses ranging from 0.3-1.8 mg/kg given postoperatively or preoperatively were noninferior to enoxaparin (rates of 15.7%-23.7% vs. 26.3%), and osocimab at a preoperative dose of 1.8 mg/kg was superior to both enoxaparin and apixaban (11.5% vs. 26.3% and 14.5%, respectively), he said.
Bleeding rates ranged from 0%-5% with osocimab, compared with 6% with enoxaparin and 2% with apixaban
Ongoing studies
Currently ongoing studies of FXI-directed anticoagulation strategies include a study comparing ISIS-FXIRx with placebo in 200 patients with end-stage renal disease, a study comparing osocimab with placebo in 600 patients with end-stage renal disease, and a study comparing abelacimab – an antibody that binds to FXI and prevents its activation by either FXIIa or thrombin, with enoxaparin in 700 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty, Dr. Weitz said.
Additionally, there is “considerable activity” with small molecule inhibitors of FXIa, including a phase 2, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging study looking at the novel JNG-7003/BMS-986177 agent for secondary stroke/transient ischemic attack prevention in 2,500 patients and a phase 2 study comparing it with enoxaparin for postoperative thromboprophylaxis in 1,200 patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty.
Parallel phase 2 studies are also underway to compare the novel BAY-2433334 small molecule inhibitor with placebo for stroke/transient ischemic attack prevention, with apixaban for atrial fibrillation, and for prevention of major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with acute MI.
These ongoing trials will help determine the risk-benefit profile of FXI inhibitors he said.
Session comoderator Anne Rose, PharmD, pharmacy coordinator at the University of Wisconsin, Madison, noted that these types of agents have been discussed “for quite some time” and asked whether they will be available for use in clinical practice in the near future.
Dr. Weitz predicted it will be at least a few years. The studies are just now moving to phase 2b and will still need to be evaluated in phase 3 trials and for appropriate new indications, he said.
Dr. Weitz reported research support from Canadian Institutes of Health research, Heart and Stroke Foundation, and Canadian Fund for Innovation, and he is a consultant and/or scientific advisory board member for Anthos, Bayer, Boehringer-Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi-Sankyo, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Janssen, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Portola, Servier , and Thetherex.
FROM THE THSNA BIENNIAL SUMMIT
Osteoporosis drugs don’t worsen COVID-19 risk, may help
New observational data are the first to support recommendations to continue osteoporosis medications during the COVID-19 pandemic, and even suggest that some agents may protect against the virus.
Findings from the cross-sectional study of 2,102 patients with osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and/or fibromyalgia – so-called noninflammatory rheumatic conditions – during March 1 to May 3, 2020, were recently published in Aging by Josep Blanch-Rubió, MD, scientific clinical director of the Rheumatology Service, Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, and colleagues.
Patients taking denosumab, zoledronate, and calcium showed trends toward lower incidence of developing symptomatic presumed COVID-19 (polymerase chain reaction tests weren’t widely available at the time), as did those taking the antidepressant serotonin/norepinephrine inhibitor duloxetine.
Some analgesics, particularly pregabalin and most other antidepressants, were associated with higher incidences of COVID-19, while oral bisphosphonates, vitamin D, thiazide diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, and chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs had no effect on COVID-19 incidence.
These data are the first to support guidance issued in May 2020 by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research and four other professional societies advising continuation of osteoporosis medications during the pandemic. That statement’s authors acknowledged that, lacking data, their recommendations were based primarily on expert opinion.
“There were guidelines without any scientific base. ... This is the first scientific evidence showing that indeed you should continue your osteoporosis treatment if you have COVID-19. This is the first study to provide scientific support for the guidelines,” study coauthor Rafael Maldonado, MD, PhD, of the Laboratory of Neuropharmacology, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, said in an interview.
And while the data don’t offer proof of benefit for any drug – all of the 95% confidence intervals crossed 1.0 – they do show trends that deserve further study, Dr. Maldonado said.
“What we observed is that there is no harm. Treatments should be continued.”
“But we obtained very interesting results with denosumab, zoledronate, calcium, and duloxetine. ... There is a clear tendency, and the message is we should promote studies to see if these four treatments provide benefit.”
Different mechanisms for each?
Asked to comment on the findings, Matthew T. Drake, MD, PhD, said in an interview, “I would agree that there’s no reason any of these medications should be stopped or discontinued since there’s no evidence that they make the risk for infection worse.”
“But how [some of them may] improve or reduce the infection risk in my mind is somewhat unclear. ... It’s hard to come up with a unifying explanation” because those mentioned as potentially beneficial “are fairly different,” he noted.
Dr. Drake, associate professor of medicine in the department of endocrinology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said he agreed with the study authors that denosumab’s targeting of the RANK/RANKL system is a possible anti-COVID-19 mechanism for that drug because that system is involved in immune response.
Regarding zoledronate/zoledronic acid, both the Spanish authors and Dr. Drake pointed to a landmark study linking the intravenous drug to longer survival in patients with hip fracture. The study authors note that there could be several mechanisms for an overall survival benefit, but additionally, “zoledronate may make dendritic cells and their precursors less susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, which could explain the beneficial effects here ... on COVID-19 incidence.”
And, the authors hypothesized, the reason for the lack of benefit with oral bisphosphonates might relate to the higher potency of the intravenous zoledronate. Dr. Drake added that its higher bioavailability may also play a role.
As for calcium, the authors suggest that the beneficial effect against COVID-19 could relate to its action in generating two immune cell types – T follicular helper cells and T follicular regulatory cells – which promote an appropriate immune response against infectious agents, including viruses.
Data supporting the guidelines
Of the 2,102 patients in the study by Blanch-Rubió and colleagues, 80.5% were women, and their mean age was 66.4 years. Overall, 63.7% had osteoarthritis, 43.5% had osteoporosis, and 27.2% had fibromyalgia. Treatments included vitamin D in 62%, calcium in 23.3%, denosumab in 12.6%, and intravenous zoledronate in 8.5%. Over half were taking analgesics and nearly a third antidepressants, with 9.9% taking duloxetine.
During the study period, 5.2%, or 109 individuals, were diagnosed with COVID-19 based on presenting for medical care with hallmark symptoms.
After adjustments for sex, age, diabetes, pulmonary disease, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and active cancer or treatment, the relative risks for COVID-19 were 0.58 for denosumab, 0.62 for intravenous zoledronate, and 0.64 for calcium, all nonsignificant trends. No associations were found between COVID-19 and oral bisphosphonates, vitamin D, or thiazide diuretics. Increased but nonsignificant relative risks for COVID-19 were seen with analgesics, particularly pregabalin (1.55), gabapentin (1.39), and opioids (1.25).
Among antidepressants, there was a relative risk of 1.54 for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, 1.38 for amitriptyline, and 1.22 for all dual-action antidepressants together. In contrast, there was a negative association with the dual-action antidepressant duloxetine, with an adjusted relative risk of 0.68.
“The good news,” Dr. Drake said, “is that none of it appears bad.”
Dr. Blanch-Rubió has received grants or consulting fees from Amgen, Laboratorio Stada, Gedeon-Rhicter Ibérica, Lilly España, Pfizer, Gebro Pharma, and UCB Pharma. Dr. Maldonado has received research grants or consulting fees from Aelis, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, BrainCo, Esteve, Ferrer, GlaxoSmithKline, Grünenthal, GW Pharmaceuticals, Janus, Lundbeck, Pharmaleads, Phytoplant, Rhodes, Sanofi, Spherium, Union de Pharmacologie Scientifique Appliquée, Upjohn, and Uriach. Dr. Drake has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New observational data are the first to support recommendations to continue osteoporosis medications during the COVID-19 pandemic, and even suggest that some agents may protect against the virus.
Findings from the cross-sectional study of 2,102 patients with osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and/or fibromyalgia – so-called noninflammatory rheumatic conditions – during March 1 to May 3, 2020, were recently published in Aging by Josep Blanch-Rubió, MD, scientific clinical director of the Rheumatology Service, Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, and colleagues.
Patients taking denosumab, zoledronate, and calcium showed trends toward lower incidence of developing symptomatic presumed COVID-19 (polymerase chain reaction tests weren’t widely available at the time), as did those taking the antidepressant serotonin/norepinephrine inhibitor duloxetine.
Some analgesics, particularly pregabalin and most other antidepressants, were associated with higher incidences of COVID-19, while oral bisphosphonates, vitamin D, thiazide diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, and chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs had no effect on COVID-19 incidence.
These data are the first to support guidance issued in May 2020 by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research and four other professional societies advising continuation of osteoporosis medications during the pandemic. That statement’s authors acknowledged that, lacking data, their recommendations were based primarily on expert opinion.
“There were guidelines without any scientific base. ... This is the first scientific evidence showing that indeed you should continue your osteoporosis treatment if you have COVID-19. This is the first study to provide scientific support for the guidelines,” study coauthor Rafael Maldonado, MD, PhD, of the Laboratory of Neuropharmacology, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, said in an interview.
And while the data don’t offer proof of benefit for any drug – all of the 95% confidence intervals crossed 1.0 – they do show trends that deserve further study, Dr. Maldonado said.
“What we observed is that there is no harm. Treatments should be continued.”
“But we obtained very interesting results with denosumab, zoledronate, calcium, and duloxetine. ... There is a clear tendency, and the message is we should promote studies to see if these four treatments provide benefit.”
Different mechanisms for each?
Asked to comment on the findings, Matthew T. Drake, MD, PhD, said in an interview, “I would agree that there’s no reason any of these medications should be stopped or discontinued since there’s no evidence that they make the risk for infection worse.”
“But how [some of them may] improve or reduce the infection risk in my mind is somewhat unclear. ... It’s hard to come up with a unifying explanation” because those mentioned as potentially beneficial “are fairly different,” he noted.
Dr. Drake, associate professor of medicine in the department of endocrinology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said he agreed with the study authors that denosumab’s targeting of the RANK/RANKL system is a possible anti-COVID-19 mechanism for that drug because that system is involved in immune response.
Regarding zoledronate/zoledronic acid, both the Spanish authors and Dr. Drake pointed to a landmark study linking the intravenous drug to longer survival in patients with hip fracture. The study authors note that there could be several mechanisms for an overall survival benefit, but additionally, “zoledronate may make dendritic cells and their precursors less susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, which could explain the beneficial effects here ... on COVID-19 incidence.”
And, the authors hypothesized, the reason for the lack of benefit with oral bisphosphonates might relate to the higher potency of the intravenous zoledronate. Dr. Drake added that its higher bioavailability may also play a role.
As for calcium, the authors suggest that the beneficial effect against COVID-19 could relate to its action in generating two immune cell types – T follicular helper cells and T follicular regulatory cells – which promote an appropriate immune response against infectious agents, including viruses.
Data supporting the guidelines
Of the 2,102 patients in the study by Blanch-Rubió and colleagues, 80.5% were women, and their mean age was 66.4 years. Overall, 63.7% had osteoarthritis, 43.5% had osteoporosis, and 27.2% had fibromyalgia. Treatments included vitamin D in 62%, calcium in 23.3%, denosumab in 12.6%, and intravenous zoledronate in 8.5%. Over half were taking analgesics and nearly a third antidepressants, with 9.9% taking duloxetine.
During the study period, 5.2%, or 109 individuals, were diagnosed with COVID-19 based on presenting for medical care with hallmark symptoms.
After adjustments for sex, age, diabetes, pulmonary disease, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and active cancer or treatment, the relative risks for COVID-19 were 0.58 for denosumab, 0.62 for intravenous zoledronate, and 0.64 for calcium, all nonsignificant trends. No associations were found between COVID-19 and oral bisphosphonates, vitamin D, or thiazide diuretics. Increased but nonsignificant relative risks for COVID-19 were seen with analgesics, particularly pregabalin (1.55), gabapentin (1.39), and opioids (1.25).
Among antidepressants, there was a relative risk of 1.54 for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, 1.38 for amitriptyline, and 1.22 for all dual-action antidepressants together. In contrast, there was a negative association with the dual-action antidepressant duloxetine, with an adjusted relative risk of 0.68.
“The good news,” Dr. Drake said, “is that none of it appears bad.”
Dr. Blanch-Rubió has received grants or consulting fees from Amgen, Laboratorio Stada, Gedeon-Rhicter Ibérica, Lilly España, Pfizer, Gebro Pharma, and UCB Pharma. Dr. Maldonado has received research grants or consulting fees from Aelis, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, BrainCo, Esteve, Ferrer, GlaxoSmithKline, Grünenthal, GW Pharmaceuticals, Janus, Lundbeck, Pharmaleads, Phytoplant, Rhodes, Sanofi, Spherium, Union de Pharmacologie Scientifique Appliquée, Upjohn, and Uriach. Dr. Drake has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
New observational data are the first to support recommendations to continue osteoporosis medications during the COVID-19 pandemic, and even suggest that some agents may protect against the virus.
Findings from the cross-sectional study of 2,102 patients with osteoporosis, osteoarthritis, and/or fibromyalgia – so-called noninflammatory rheumatic conditions – during March 1 to May 3, 2020, were recently published in Aging by Josep Blanch-Rubió, MD, scientific clinical director of the Rheumatology Service, Hospital del Mar, Barcelona, and colleagues.
Patients taking denosumab, zoledronate, and calcium showed trends toward lower incidence of developing symptomatic presumed COVID-19 (polymerase chain reaction tests weren’t widely available at the time), as did those taking the antidepressant serotonin/norepinephrine inhibitor duloxetine.
Some analgesics, particularly pregabalin and most other antidepressants, were associated with higher incidences of COVID-19, while oral bisphosphonates, vitamin D, thiazide diuretics, antihypertensive drugs, and chronic nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs had no effect on COVID-19 incidence.
These data are the first to support guidance issued in May 2020 by the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research and four other professional societies advising continuation of osteoporosis medications during the pandemic. That statement’s authors acknowledged that, lacking data, their recommendations were based primarily on expert opinion.
“There were guidelines without any scientific base. ... This is the first scientific evidence showing that indeed you should continue your osteoporosis treatment if you have COVID-19. This is the first study to provide scientific support for the guidelines,” study coauthor Rafael Maldonado, MD, PhD, of the Laboratory of Neuropharmacology, Universitat Pompeu Fabra, Barcelona, said in an interview.
And while the data don’t offer proof of benefit for any drug – all of the 95% confidence intervals crossed 1.0 – they do show trends that deserve further study, Dr. Maldonado said.
“What we observed is that there is no harm. Treatments should be continued.”
“But we obtained very interesting results with denosumab, zoledronate, calcium, and duloxetine. ... There is a clear tendency, and the message is we should promote studies to see if these four treatments provide benefit.”
Different mechanisms for each?
Asked to comment on the findings, Matthew T. Drake, MD, PhD, said in an interview, “I would agree that there’s no reason any of these medications should be stopped or discontinued since there’s no evidence that they make the risk for infection worse.”
“But how [some of them may] improve or reduce the infection risk in my mind is somewhat unclear. ... It’s hard to come up with a unifying explanation” because those mentioned as potentially beneficial “are fairly different,” he noted.
Dr. Drake, associate professor of medicine in the department of endocrinology at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said he agreed with the study authors that denosumab’s targeting of the RANK/RANKL system is a possible anti-COVID-19 mechanism for that drug because that system is involved in immune response.
Regarding zoledronate/zoledronic acid, both the Spanish authors and Dr. Drake pointed to a landmark study linking the intravenous drug to longer survival in patients with hip fracture. The study authors note that there could be several mechanisms for an overall survival benefit, but additionally, “zoledronate may make dendritic cells and their precursors less susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, which could explain the beneficial effects here ... on COVID-19 incidence.”
And, the authors hypothesized, the reason for the lack of benefit with oral bisphosphonates might relate to the higher potency of the intravenous zoledronate. Dr. Drake added that its higher bioavailability may also play a role.
As for calcium, the authors suggest that the beneficial effect against COVID-19 could relate to its action in generating two immune cell types – T follicular helper cells and T follicular regulatory cells – which promote an appropriate immune response against infectious agents, including viruses.
Data supporting the guidelines
Of the 2,102 patients in the study by Blanch-Rubió and colleagues, 80.5% were women, and their mean age was 66.4 years. Overall, 63.7% had osteoarthritis, 43.5% had osteoporosis, and 27.2% had fibromyalgia. Treatments included vitamin D in 62%, calcium in 23.3%, denosumab in 12.6%, and intravenous zoledronate in 8.5%. Over half were taking analgesics and nearly a third antidepressants, with 9.9% taking duloxetine.
During the study period, 5.2%, or 109 individuals, were diagnosed with COVID-19 based on presenting for medical care with hallmark symptoms.
After adjustments for sex, age, diabetes, pulmonary disease, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and active cancer or treatment, the relative risks for COVID-19 were 0.58 for denosumab, 0.62 for intravenous zoledronate, and 0.64 for calcium, all nonsignificant trends. No associations were found between COVID-19 and oral bisphosphonates, vitamin D, or thiazide diuretics. Increased but nonsignificant relative risks for COVID-19 were seen with analgesics, particularly pregabalin (1.55), gabapentin (1.39), and opioids (1.25).
Among antidepressants, there was a relative risk of 1.54 for selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, 1.38 for amitriptyline, and 1.22 for all dual-action antidepressants together. In contrast, there was a negative association with the dual-action antidepressant duloxetine, with an adjusted relative risk of 0.68.
“The good news,” Dr. Drake said, “is that none of it appears bad.”
Dr. Blanch-Rubió has received grants or consulting fees from Amgen, Laboratorio Stada, Gedeon-Rhicter Ibérica, Lilly España, Pfizer, Gebro Pharma, and UCB Pharma. Dr. Maldonado has received research grants or consulting fees from Aelis, Almirall, Boehringer Ingelheim, BrainCo, Esteve, Ferrer, GlaxoSmithKline, Grünenthal, GW Pharmaceuticals, Janus, Lundbeck, Pharmaleads, Phytoplant, Rhodes, Sanofi, Spherium, Union de Pharmacologie Scientifique Appliquée, Upjohn, and Uriach. Dr. Drake has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiac arrest in COVID-19 pandemic: ‘Survival is possible’
In the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, rates of sustained return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were lower throughout the country, compared with a year earlier, in one study.
A second study of that period showed that patients with COVID-19 had rates that were better than previously reported of surviving in-hospital cardiac arrest.
Paul S. Chan, MD, presented the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest research, and Oscar J. Mitchell, MD, presented the in-hospital cardiac arrest findings in a late-breaking resuscitation science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The former study was also simultaneously published online Nov. 14 in JAMA Cardiology.
Importantly, “the survival rates were not zero in either setting,” said Dr. Chan, commenting on the implications of both studies taken together.
“The survival rates – either return of circulation or survival to discharge – were not futile,” Dr. Chan, from Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“And I think that’s an overall important message – that we can’t write off patients who have a cardiac arrest at this point,” he stressed. “They deserve a response. Although the outcomes might not be as good as we had seen in years prior, we are seeing patients making it out of the hospital and surviving.”
Dr. Mitchell, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, echoed this message in an interview.
“I think that the key finding here is that survival is possible after patients with COVID-19 suffer an in-hospital cardiac arrest,” Dr. Mitchell said. “We hope that the information from our study will be of use to frontline providers who are treating patients with COVID-19.”
“In coming weeks, there will likely be increased hospital strain and enormous challenges to providing COVID-19 care,” added Benjamin S. Abella, MD, the senior author of the in-hospital study. Dr. Abella is also from the University of Pennsylvania and was cochair of the Resuscitation Science symposium during the AHA meeting.
“It is crucial that hospital leaders prepare now for how they will manage COVID-19 resuscitation efforts,” Dr. Abella said. “Emergency medicine and critical care leaders must be mindful that many COVID-19 patients with arrest could survive to return to their families.”
“It is important to note both studies demonstrated variations in outcome and that those differences were associated with the differential COVID prevalence and mortality,” session comoderator Cindy H. Hsu, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, said in an interview.
“Future studies,” she said, “should address knowledge gaps including associated comorbidities and affected resuscitation process variables during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, March 2019 vs. March 2020
Compared with 2019, in 2020, the reported rates of return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest fell from 25% to 10.6% in New York and from 13.5% to 5.0% in northern Italy – two areas that were severely affected, Dr. Chan noted.
In this study, the researchers aimed to examine whether out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes would be similar throughout the United States, including areas that were less severely affected, in the first weeks of the pandemic.
They linked data from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), which covers an area with about 152 million U.S. residents, with COVID-19 disease mortality data.
There were 9,863 out-of-hospital arrests from March 16 to April 30, 2020, compared with 9,440 cases during this time in 2019.
The patients in both years had a similar age (mean, 62 years) and sex (62% male), but there were more Black patients in 2020 (28% vs. 23%).
Overall, in communities with low to high rates of death from COVID-19, the rate of return of spontaneous circulation was 18% lower in that early pandemic period than in the same time in the previous year (23% vs. 29.8%; adjusted rate ratio, 0.82).
The rates of return of spontaneous circulation were also lower in communities with a low rate of COVID-19 mortality, but to a lesser extent (11%-15% lower in 2020 vs. 2019).
In the subset of emergency medical agencies with complete data on hospital survival, overall rates of survival to discharge were 17% lower during the studied pandemic period versus the same time a year earlier (6.6% vs. 9.8%; adjusted RR, 0.83).
This drop in survival was greater in communities with moderate to high COVID-19 mortality.
These outcomes were not explained by differences in emergency medical services arrival or treatment times, rates of bystander CPR, or initial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest rhythm.
Dr. Chan was a coauthor of an interim guidance issued April 9, 2020, by the AHA and several other medical societies for ways to protect frontline workers from contracting COVID-19 while they were performing CPR.
Communities that were not heavily affected by COVID-19 could have also been following the recommendations, which might have affected outcomes, he speculated.
For example, “when we pause chest compressions it can potentially worsen survival even if it’s for a short period of time. That might explain the lower rates of return of circulation.”
“That guidance was really meant for heavily affected communities,” Dr. Chan added. “Of course, as we speak, the pandemic is pretty much everywhere in the United States. It’s not just in the northeast; it’s not just in Arizona, Florida, California, Texas like it was in the summer. You are seeing surges in 46 of the 50 states.
“If your community is heavily affected by COVID-19 in terms of deaths at this time, paramedics will need to take caution to also help protect themselves, and the guidance may apply at that point,” he said.
In-hospital cardiac arrest, March Through May 2020
The early studies of in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19 showed “concerningly low rates” of return of spontaneous circulation and survival, said Dr. Mitchell.
“The first was a study from Wuhan, which demonstrated a 2.9% 30-day survival and the second was a small cohort from NYC with 0% survival to hospital discharge,” he said. “This raised concerns that offering CPR to patients who had a cardiac arrest from COVID-19 might only hold a low probability of success.”
To investigate this, the researchers formed a COVID study group comprising two hospitals in New York and nine hospitals in the Northeast and West Coast.
They identified 260 hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 who had in-hospital cardiac arrest between March 1 and May 31, 2020. The patients had a median age of 69 years, and 72% were male. Most had preexisting comorbidities. Most of the cardiac arrests were in the ICU (64%), and almost all were witnessed (91%).
Return of spontaneous circulation occurred in 22% of the patients, and 12% had survived 30 days later. Of the 260 cardiac arrests, most (204) occurred in the New York hospitals.
There was a huge variation in outcomes. The rate of sustained return of spontaneous circulation was much lower in the two hospitals in New York compared with elsewhere (11% vs. 64%), as was 30-day survival (6% vs. 36%).
“Variation in outcomes from [in-hospital cardiac arrest] has been well described prior to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Mitchell, “and is felt to be due to a range of factors, including variation in detection and prevention of cardiac arrest, management of patients during the cardiac arrest, and differences in postarrest care – including targeted temperature management and neuroprognostication.”
“We hypothesize that the strains of the COVID-19 pandemic may have amplified these variations (although we were unable to compare hospital performance before and after the pandemic),” he said.
Nevertheless, “in contrast to [earlier] studies, we have found that survival with a good neurological status is possible after in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19, which is certainly reassuring for those of us on the front line.”
Dr. Chan has received research support from the American Heart Association (which helps fund CARES); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Optum Rx. Dr. Abella has received honoraria from NeuroproteXeon, Becton Dickinson, and Physio-Control, and research grants from Medtronic, PCORI, Physio-Control, Stryker, and TerSera. Dr. Mitchell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, rates of sustained return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were lower throughout the country, compared with a year earlier, in one study.
A second study of that period showed that patients with COVID-19 had rates that were better than previously reported of surviving in-hospital cardiac arrest.
Paul S. Chan, MD, presented the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest research, and Oscar J. Mitchell, MD, presented the in-hospital cardiac arrest findings in a late-breaking resuscitation science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The former study was also simultaneously published online Nov. 14 in JAMA Cardiology.
Importantly, “the survival rates were not zero in either setting,” said Dr. Chan, commenting on the implications of both studies taken together.
“The survival rates – either return of circulation or survival to discharge – were not futile,” Dr. Chan, from Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“And I think that’s an overall important message – that we can’t write off patients who have a cardiac arrest at this point,” he stressed. “They deserve a response. Although the outcomes might not be as good as we had seen in years prior, we are seeing patients making it out of the hospital and surviving.”
Dr. Mitchell, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, echoed this message in an interview.
“I think that the key finding here is that survival is possible after patients with COVID-19 suffer an in-hospital cardiac arrest,” Dr. Mitchell said. “We hope that the information from our study will be of use to frontline providers who are treating patients with COVID-19.”
“In coming weeks, there will likely be increased hospital strain and enormous challenges to providing COVID-19 care,” added Benjamin S. Abella, MD, the senior author of the in-hospital study. Dr. Abella is also from the University of Pennsylvania and was cochair of the Resuscitation Science symposium during the AHA meeting.
“It is crucial that hospital leaders prepare now for how they will manage COVID-19 resuscitation efforts,” Dr. Abella said. “Emergency medicine and critical care leaders must be mindful that many COVID-19 patients with arrest could survive to return to their families.”
“It is important to note both studies demonstrated variations in outcome and that those differences were associated with the differential COVID prevalence and mortality,” session comoderator Cindy H. Hsu, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, said in an interview.
“Future studies,” she said, “should address knowledge gaps including associated comorbidities and affected resuscitation process variables during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, March 2019 vs. March 2020
Compared with 2019, in 2020, the reported rates of return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest fell from 25% to 10.6% in New York and from 13.5% to 5.0% in northern Italy – two areas that were severely affected, Dr. Chan noted.
In this study, the researchers aimed to examine whether out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes would be similar throughout the United States, including areas that were less severely affected, in the first weeks of the pandemic.
They linked data from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), which covers an area with about 152 million U.S. residents, with COVID-19 disease mortality data.
There were 9,863 out-of-hospital arrests from March 16 to April 30, 2020, compared with 9,440 cases during this time in 2019.
The patients in both years had a similar age (mean, 62 years) and sex (62% male), but there were more Black patients in 2020 (28% vs. 23%).
Overall, in communities with low to high rates of death from COVID-19, the rate of return of spontaneous circulation was 18% lower in that early pandemic period than in the same time in the previous year (23% vs. 29.8%; adjusted rate ratio, 0.82).
The rates of return of spontaneous circulation were also lower in communities with a low rate of COVID-19 mortality, but to a lesser extent (11%-15% lower in 2020 vs. 2019).
In the subset of emergency medical agencies with complete data on hospital survival, overall rates of survival to discharge were 17% lower during the studied pandemic period versus the same time a year earlier (6.6% vs. 9.8%; adjusted RR, 0.83).
This drop in survival was greater in communities with moderate to high COVID-19 mortality.
These outcomes were not explained by differences in emergency medical services arrival or treatment times, rates of bystander CPR, or initial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest rhythm.
Dr. Chan was a coauthor of an interim guidance issued April 9, 2020, by the AHA and several other medical societies for ways to protect frontline workers from contracting COVID-19 while they were performing CPR.
Communities that were not heavily affected by COVID-19 could have also been following the recommendations, which might have affected outcomes, he speculated.
For example, “when we pause chest compressions it can potentially worsen survival even if it’s for a short period of time. That might explain the lower rates of return of circulation.”
“That guidance was really meant for heavily affected communities,” Dr. Chan added. “Of course, as we speak, the pandemic is pretty much everywhere in the United States. It’s not just in the northeast; it’s not just in Arizona, Florida, California, Texas like it was in the summer. You are seeing surges in 46 of the 50 states.
“If your community is heavily affected by COVID-19 in terms of deaths at this time, paramedics will need to take caution to also help protect themselves, and the guidance may apply at that point,” he said.
In-hospital cardiac arrest, March Through May 2020
The early studies of in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19 showed “concerningly low rates” of return of spontaneous circulation and survival, said Dr. Mitchell.
“The first was a study from Wuhan, which demonstrated a 2.9% 30-day survival and the second was a small cohort from NYC with 0% survival to hospital discharge,” he said. “This raised concerns that offering CPR to patients who had a cardiac arrest from COVID-19 might only hold a low probability of success.”
To investigate this, the researchers formed a COVID study group comprising two hospitals in New York and nine hospitals in the Northeast and West Coast.
They identified 260 hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 who had in-hospital cardiac arrest between March 1 and May 31, 2020. The patients had a median age of 69 years, and 72% were male. Most had preexisting comorbidities. Most of the cardiac arrests were in the ICU (64%), and almost all were witnessed (91%).
Return of spontaneous circulation occurred in 22% of the patients, and 12% had survived 30 days later. Of the 260 cardiac arrests, most (204) occurred in the New York hospitals.
There was a huge variation in outcomes. The rate of sustained return of spontaneous circulation was much lower in the two hospitals in New York compared with elsewhere (11% vs. 64%), as was 30-day survival (6% vs. 36%).
“Variation in outcomes from [in-hospital cardiac arrest] has been well described prior to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Mitchell, “and is felt to be due to a range of factors, including variation in detection and prevention of cardiac arrest, management of patients during the cardiac arrest, and differences in postarrest care – including targeted temperature management and neuroprognostication.”
“We hypothesize that the strains of the COVID-19 pandemic may have amplified these variations (although we were unable to compare hospital performance before and after the pandemic),” he said.
Nevertheless, “in contrast to [earlier] studies, we have found that survival with a good neurological status is possible after in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19, which is certainly reassuring for those of us on the front line.”
Dr. Chan has received research support from the American Heart Association (which helps fund CARES); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Optum Rx. Dr. Abella has received honoraria from NeuroproteXeon, Becton Dickinson, and Physio-Control, and research grants from Medtronic, PCORI, Physio-Control, Stryker, and TerSera. Dr. Mitchell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the early weeks of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, rates of sustained return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest were lower throughout the country, compared with a year earlier, in one study.
A second study of that period showed that patients with COVID-19 had rates that were better than previously reported of surviving in-hospital cardiac arrest.
Paul S. Chan, MD, presented the out-of-hospital cardiac arrest research, and Oscar J. Mitchell, MD, presented the in-hospital cardiac arrest findings in a late-breaking resuscitation science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions. The former study was also simultaneously published online Nov. 14 in JAMA Cardiology.
Importantly, “the survival rates were not zero in either setting,” said Dr. Chan, commenting on the implications of both studies taken together.
“The survival rates – either return of circulation or survival to discharge – were not futile,” Dr. Chan, from Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview.
“And I think that’s an overall important message – that we can’t write off patients who have a cardiac arrest at this point,” he stressed. “They deserve a response. Although the outcomes might not be as good as we had seen in years prior, we are seeing patients making it out of the hospital and surviving.”
Dr. Mitchell, from the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia, echoed this message in an interview.
“I think that the key finding here is that survival is possible after patients with COVID-19 suffer an in-hospital cardiac arrest,” Dr. Mitchell said. “We hope that the information from our study will be of use to frontline providers who are treating patients with COVID-19.”
“In coming weeks, there will likely be increased hospital strain and enormous challenges to providing COVID-19 care,” added Benjamin S. Abella, MD, the senior author of the in-hospital study. Dr. Abella is also from the University of Pennsylvania and was cochair of the Resuscitation Science symposium during the AHA meeting.
“It is crucial that hospital leaders prepare now for how they will manage COVID-19 resuscitation efforts,” Dr. Abella said. “Emergency medicine and critical care leaders must be mindful that many COVID-19 patients with arrest could survive to return to their families.”
“It is important to note both studies demonstrated variations in outcome and that those differences were associated with the differential COVID prevalence and mortality,” session comoderator Cindy H. Hsu, MD, PhD, University of Michigan, said in an interview.
“Future studies,” she said, “should address knowledge gaps including associated comorbidities and affected resuscitation process variables during the COVID-19 pandemic.”
Out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, March 2019 vs. March 2020
Compared with 2019, in 2020, the reported rates of return of spontaneous circulation after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest fell from 25% to 10.6% in New York and from 13.5% to 5.0% in northern Italy – two areas that were severely affected, Dr. Chan noted.
In this study, the researchers aimed to examine whether out-of-hospital cardiac arrest outcomes would be similar throughout the United States, including areas that were less severely affected, in the first weeks of the pandemic.
They linked data from the Cardiac Arrest Registry to Enhance Survival (CARES), which covers an area with about 152 million U.S. residents, with COVID-19 disease mortality data.
There were 9,863 out-of-hospital arrests from March 16 to April 30, 2020, compared with 9,440 cases during this time in 2019.
The patients in both years had a similar age (mean, 62 years) and sex (62% male), but there were more Black patients in 2020 (28% vs. 23%).
Overall, in communities with low to high rates of death from COVID-19, the rate of return of spontaneous circulation was 18% lower in that early pandemic period than in the same time in the previous year (23% vs. 29.8%; adjusted rate ratio, 0.82).
The rates of return of spontaneous circulation were also lower in communities with a low rate of COVID-19 mortality, but to a lesser extent (11%-15% lower in 2020 vs. 2019).
In the subset of emergency medical agencies with complete data on hospital survival, overall rates of survival to discharge were 17% lower during the studied pandemic period versus the same time a year earlier (6.6% vs. 9.8%; adjusted RR, 0.83).
This drop in survival was greater in communities with moderate to high COVID-19 mortality.
These outcomes were not explained by differences in emergency medical services arrival or treatment times, rates of bystander CPR, or initial out-of-hospital cardiac arrest rhythm.
Dr. Chan was a coauthor of an interim guidance issued April 9, 2020, by the AHA and several other medical societies for ways to protect frontline workers from contracting COVID-19 while they were performing CPR.
Communities that were not heavily affected by COVID-19 could have also been following the recommendations, which might have affected outcomes, he speculated.
For example, “when we pause chest compressions it can potentially worsen survival even if it’s for a short period of time. That might explain the lower rates of return of circulation.”
“That guidance was really meant for heavily affected communities,” Dr. Chan added. “Of course, as we speak, the pandemic is pretty much everywhere in the United States. It’s not just in the northeast; it’s not just in Arizona, Florida, California, Texas like it was in the summer. You are seeing surges in 46 of the 50 states.
“If your community is heavily affected by COVID-19 in terms of deaths at this time, paramedics will need to take caution to also help protect themselves, and the guidance may apply at that point,” he said.
In-hospital cardiac arrest, March Through May 2020
The early studies of in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19 showed “concerningly low rates” of return of spontaneous circulation and survival, said Dr. Mitchell.
“The first was a study from Wuhan, which demonstrated a 2.9% 30-day survival and the second was a small cohort from NYC with 0% survival to hospital discharge,” he said. “This raised concerns that offering CPR to patients who had a cardiac arrest from COVID-19 might only hold a low probability of success.”
To investigate this, the researchers formed a COVID study group comprising two hospitals in New York and nine hospitals in the Northeast and West Coast.
They identified 260 hospitalized adult patients with COVID-19 who had in-hospital cardiac arrest between March 1 and May 31, 2020. The patients had a median age of 69 years, and 72% were male. Most had preexisting comorbidities. Most of the cardiac arrests were in the ICU (64%), and almost all were witnessed (91%).
Return of spontaneous circulation occurred in 22% of the patients, and 12% had survived 30 days later. Of the 260 cardiac arrests, most (204) occurred in the New York hospitals.
There was a huge variation in outcomes. The rate of sustained return of spontaneous circulation was much lower in the two hospitals in New York compared with elsewhere (11% vs. 64%), as was 30-day survival (6% vs. 36%).
“Variation in outcomes from [in-hospital cardiac arrest] has been well described prior to the COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Mitchell, “and is felt to be due to a range of factors, including variation in detection and prevention of cardiac arrest, management of patients during the cardiac arrest, and differences in postarrest care – including targeted temperature management and neuroprognostication.”
“We hypothesize that the strains of the COVID-19 pandemic may have amplified these variations (although we were unable to compare hospital performance before and after the pandemic),” he said.
Nevertheless, “in contrast to [earlier] studies, we have found that survival with a good neurological status is possible after in-hospital cardiac arrest in patients with COVID-19, which is certainly reassuring for those of us on the front line.”
Dr. Chan has received research support from the American Heart Association (which helps fund CARES); the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; and Optum Rx. Dr. Abella has received honoraria from NeuroproteXeon, Becton Dickinson, and Physio-Control, and research grants from Medtronic, PCORI, Physio-Control, Stryker, and TerSera. Dr. Mitchell has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2020
In those with obesity, will losing weight cut COVID-19 severity?
As study after study piles up showing that those with obesity who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 are more likely to have severe disease, several experts gave advice for clinicians and patients during the virtual ObesityWeek Interactive 2020 meeting.
Pichamol Jirapinyo, MD, MPH, associate director of bariatric endoscopy at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, presented a study on those with obesity from New England hospitals which adds to the evidence that this is “a vulnerable population for COVID-19, like elderly or immunocompromised people,” Dr. Jirapinyo said in an interview.
These findings reinforce the need for clinicians to be “more aware of complications of obesity and refer earlier for treatment,” she added.
One audience member wanted to know if there are data showing whether people with a body mass index (BMI) above 35 kg/m2 who successfully lose weight subsequently have lower rates of hospitalization, ICU admission, and death if they become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Dr. Jirapinyo said she is not aware of any such studies, but anecdotally, two of her patients who had endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty last fall (whose BMI dropped from about 38 to 30) and later became infected with COVID-19 had mild symptoms.
But David A. Kass, MD, director, Institute of CardioScience at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, cautioned that
“Whether this gets reversed by weight loss is an attractive hypothesis, but at this point, it’s still a hypothesis,” he stressed.
Changes to immunity, inflammatory signaling in obesity
“There must be north of 600 or more studies by now with this message that obesity – particularly severe obesity with a BMI of 35 and higher – is a strong independent risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcome,” Dr. Kass emphasized.
“[COVID-19] revealed to the public in a somewhat dramatic fashion that being very obese does put one at higher risk of this disease being more debilitating and even fatal,” he added.
“Before this pandemic, many viewed obesity as only a problem if you have the other associated diseases – hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, atherosclerosis, obstructive sleep apnea, etc.”
“What was not as appreciated is that marked obesity changes the body in various ways all by itself – altering metabolism, inflammatory signaling, immune surveillance, and responsiveness (including a less robust response to vaccines that has been written about as well).”
“This is a bit like having a genetic abnormality that makes you at higher risk for getting, say, cancer,” he explained.
“It is there, it is real, it has an impact – but it still does take other stresses to reveal the risk potential. COVID-19 did that with obesity,” he said.
Latest study on effect of obesity, diabetes on COVID-19 severity
The study presented by Dr. Jirapinyo and colleagues identified 1,680 patients with COVID-19 at six hospitals in March 2020. Patients were a mean age of 51 years, had a mean BMI of 29.4, and 39% had obesity. Patients who required hospitalization were more likely to have obesity (46% vs. 35%; P < .0001).
Obesity was a significant risk factor for hospitalization (odds ratio, 1.7), ICU admission (OR, 1.8), and intubation (OR, 1.8; all P < .001), after controlling for age, sex, cardiovascular, pulmonary, liver, and kidney disease, and cancer.
Compared with having a normal weight, having severe obesity was also associated with roughly threefold higher risks of ICU admission and intubation – after controlling for major comorbidities.
Pandemic focuses minds on obesity prevention, treatment
Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, said in an interview that these latest findings are “highly consistent with other studies that point to excess adiposity as a potential modifiable risk factor for more severe COVID-19.”
It “also strongly suggests that if people are worried about their risk for COVID-19 and want to improve their chances of a milder outcome, then it is reasonable to encourage them to make sustainable lifestyle changes that may lessen weight and improve their fitness levels,” said Dr. Sattar, professor of metabolic medicine, University of Glasgow.
“But of course, the big worry,” he added, “is that many are putting on weight due to lockdowns, less commuting to work, anxiety, and overeating and drinking, etc., so that many are struggling, and especially those at highest risk, such as those living in more overcrowded housing, etc. By contrast, more advantaged folk may have an easier time to improve lifestyles.”
The pandemic highlights that “we need a concerted effort on obesity prevention and treatment,” according to Dr. Sattar.
“For years we have realized links between obesity and chronic cardiometabolic conditions,” he said, “but to think excess weight may also be detrimental to acute effects of a novel virus running amok in the world has focused minds on obesity in a manner not seen before.
“Whether these new painful learnings lead to a more determined effort in countries to improve the obesogenic environment or to place more resources into prevention and management of obesity remains to be seen,” he said.
Increased inquiries about bariatric surgery following COVID-19
Meanwhile, Matthew M. Hutter, MD, MPH, president, American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, said in an interview that “COVID-19 and studies like this are now making many aware that obesity is not just a lifestyle choice or a cosmetic issue, but “a disease that needs to be taken seriously” and treated.
“Metabolic and bariatric surgery is a very safe and effective treatment for persons with obesity with a BMI >40 kg/m2 or BMI >35 kg/m2 and related diseases like diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, reflux, back pain, and many others,” added Dr. Hutter, who is also professor of surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“Recently, some metabolic and bariatric centers have seen an increase in patients considering surgery,” he said. “Some say that COVID-19 has made them realize they need to do something to be healthier.”
“Currently, less than 1% of those who could benefit from surgery are actually having” it each year, Dr. Hutter noted, “and I think there are many who should seriously consider surgery to be healthier, live longer, and live better.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As study after study piles up showing that those with obesity who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 are more likely to have severe disease, several experts gave advice for clinicians and patients during the virtual ObesityWeek Interactive 2020 meeting.
Pichamol Jirapinyo, MD, MPH, associate director of bariatric endoscopy at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, presented a study on those with obesity from New England hospitals which adds to the evidence that this is “a vulnerable population for COVID-19, like elderly or immunocompromised people,” Dr. Jirapinyo said in an interview.
These findings reinforce the need for clinicians to be “more aware of complications of obesity and refer earlier for treatment,” she added.
One audience member wanted to know if there are data showing whether people with a body mass index (BMI) above 35 kg/m2 who successfully lose weight subsequently have lower rates of hospitalization, ICU admission, and death if they become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Dr. Jirapinyo said she is not aware of any such studies, but anecdotally, two of her patients who had endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty last fall (whose BMI dropped from about 38 to 30) and later became infected with COVID-19 had mild symptoms.
But David A. Kass, MD, director, Institute of CardioScience at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, cautioned that
“Whether this gets reversed by weight loss is an attractive hypothesis, but at this point, it’s still a hypothesis,” he stressed.
Changes to immunity, inflammatory signaling in obesity
“There must be north of 600 or more studies by now with this message that obesity – particularly severe obesity with a BMI of 35 and higher – is a strong independent risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcome,” Dr. Kass emphasized.
“[COVID-19] revealed to the public in a somewhat dramatic fashion that being very obese does put one at higher risk of this disease being more debilitating and even fatal,” he added.
“Before this pandemic, many viewed obesity as only a problem if you have the other associated diseases – hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, atherosclerosis, obstructive sleep apnea, etc.”
“What was not as appreciated is that marked obesity changes the body in various ways all by itself – altering metabolism, inflammatory signaling, immune surveillance, and responsiveness (including a less robust response to vaccines that has been written about as well).”
“This is a bit like having a genetic abnormality that makes you at higher risk for getting, say, cancer,” he explained.
“It is there, it is real, it has an impact – but it still does take other stresses to reveal the risk potential. COVID-19 did that with obesity,” he said.
Latest study on effect of obesity, diabetes on COVID-19 severity
The study presented by Dr. Jirapinyo and colleagues identified 1,680 patients with COVID-19 at six hospitals in March 2020. Patients were a mean age of 51 years, had a mean BMI of 29.4, and 39% had obesity. Patients who required hospitalization were more likely to have obesity (46% vs. 35%; P < .0001).
Obesity was a significant risk factor for hospitalization (odds ratio, 1.7), ICU admission (OR, 1.8), and intubation (OR, 1.8; all P < .001), after controlling for age, sex, cardiovascular, pulmonary, liver, and kidney disease, and cancer.
Compared with having a normal weight, having severe obesity was also associated with roughly threefold higher risks of ICU admission and intubation – after controlling for major comorbidities.
Pandemic focuses minds on obesity prevention, treatment
Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, said in an interview that these latest findings are “highly consistent with other studies that point to excess adiposity as a potential modifiable risk factor for more severe COVID-19.”
It “also strongly suggests that if people are worried about their risk for COVID-19 and want to improve their chances of a milder outcome, then it is reasonable to encourage them to make sustainable lifestyle changes that may lessen weight and improve their fitness levels,” said Dr. Sattar, professor of metabolic medicine, University of Glasgow.
“But of course, the big worry,” he added, “is that many are putting on weight due to lockdowns, less commuting to work, anxiety, and overeating and drinking, etc., so that many are struggling, and especially those at highest risk, such as those living in more overcrowded housing, etc. By contrast, more advantaged folk may have an easier time to improve lifestyles.”
The pandemic highlights that “we need a concerted effort on obesity prevention and treatment,” according to Dr. Sattar.
“For years we have realized links between obesity and chronic cardiometabolic conditions,” he said, “but to think excess weight may also be detrimental to acute effects of a novel virus running amok in the world has focused minds on obesity in a manner not seen before.
“Whether these new painful learnings lead to a more determined effort in countries to improve the obesogenic environment or to place more resources into prevention and management of obesity remains to be seen,” he said.
Increased inquiries about bariatric surgery following COVID-19
Meanwhile, Matthew M. Hutter, MD, MPH, president, American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, said in an interview that “COVID-19 and studies like this are now making many aware that obesity is not just a lifestyle choice or a cosmetic issue, but “a disease that needs to be taken seriously” and treated.
“Metabolic and bariatric surgery is a very safe and effective treatment for persons with obesity with a BMI >40 kg/m2 or BMI >35 kg/m2 and related diseases like diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, reflux, back pain, and many others,” added Dr. Hutter, who is also professor of surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“Recently, some metabolic and bariatric centers have seen an increase in patients considering surgery,” he said. “Some say that COVID-19 has made them realize they need to do something to be healthier.”
“Currently, less than 1% of those who could benefit from surgery are actually having” it each year, Dr. Hutter noted, “and I think there are many who should seriously consider surgery to be healthier, live longer, and live better.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As study after study piles up showing that those with obesity who become infected with SARS-CoV-2 are more likely to have severe disease, several experts gave advice for clinicians and patients during the virtual ObesityWeek Interactive 2020 meeting.
Pichamol Jirapinyo, MD, MPH, associate director of bariatric endoscopy at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, presented a study on those with obesity from New England hospitals which adds to the evidence that this is “a vulnerable population for COVID-19, like elderly or immunocompromised people,” Dr. Jirapinyo said in an interview.
These findings reinforce the need for clinicians to be “more aware of complications of obesity and refer earlier for treatment,” she added.
One audience member wanted to know if there are data showing whether people with a body mass index (BMI) above 35 kg/m2 who successfully lose weight subsequently have lower rates of hospitalization, ICU admission, and death if they become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Dr. Jirapinyo said she is not aware of any such studies, but anecdotally, two of her patients who had endoscopic sleeve gastroplasty last fall (whose BMI dropped from about 38 to 30) and later became infected with COVID-19 had mild symptoms.
But David A. Kass, MD, director, Institute of CardioScience at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, cautioned that
“Whether this gets reversed by weight loss is an attractive hypothesis, but at this point, it’s still a hypothesis,” he stressed.
Changes to immunity, inflammatory signaling in obesity
“There must be north of 600 or more studies by now with this message that obesity – particularly severe obesity with a BMI of 35 and higher – is a strong independent risk factor for worse COVID-19 outcome,” Dr. Kass emphasized.
“[COVID-19] revealed to the public in a somewhat dramatic fashion that being very obese does put one at higher risk of this disease being more debilitating and even fatal,” he added.
“Before this pandemic, many viewed obesity as only a problem if you have the other associated diseases – hypertension, diabetes, heart disease, atherosclerosis, obstructive sleep apnea, etc.”
“What was not as appreciated is that marked obesity changes the body in various ways all by itself – altering metabolism, inflammatory signaling, immune surveillance, and responsiveness (including a less robust response to vaccines that has been written about as well).”
“This is a bit like having a genetic abnormality that makes you at higher risk for getting, say, cancer,” he explained.
“It is there, it is real, it has an impact – but it still does take other stresses to reveal the risk potential. COVID-19 did that with obesity,” he said.
Latest study on effect of obesity, diabetes on COVID-19 severity
The study presented by Dr. Jirapinyo and colleagues identified 1,680 patients with COVID-19 at six hospitals in March 2020. Patients were a mean age of 51 years, had a mean BMI of 29.4, and 39% had obesity. Patients who required hospitalization were more likely to have obesity (46% vs. 35%; P < .0001).
Obesity was a significant risk factor for hospitalization (odds ratio, 1.7), ICU admission (OR, 1.8), and intubation (OR, 1.8; all P < .001), after controlling for age, sex, cardiovascular, pulmonary, liver, and kidney disease, and cancer.
Compared with having a normal weight, having severe obesity was also associated with roughly threefold higher risks of ICU admission and intubation – after controlling for major comorbidities.
Pandemic focuses minds on obesity prevention, treatment
Naveed Sattar, MD, PhD, said in an interview that these latest findings are “highly consistent with other studies that point to excess adiposity as a potential modifiable risk factor for more severe COVID-19.”
It “also strongly suggests that if people are worried about their risk for COVID-19 and want to improve their chances of a milder outcome, then it is reasonable to encourage them to make sustainable lifestyle changes that may lessen weight and improve their fitness levels,” said Dr. Sattar, professor of metabolic medicine, University of Glasgow.
“But of course, the big worry,” he added, “is that many are putting on weight due to lockdowns, less commuting to work, anxiety, and overeating and drinking, etc., so that many are struggling, and especially those at highest risk, such as those living in more overcrowded housing, etc. By contrast, more advantaged folk may have an easier time to improve lifestyles.”
The pandemic highlights that “we need a concerted effort on obesity prevention and treatment,” according to Dr. Sattar.
“For years we have realized links between obesity and chronic cardiometabolic conditions,” he said, “but to think excess weight may also be detrimental to acute effects of a novel virus running amok in the world has focused minds on obesity in a manner not seen before.
“Whether these new painful learnings lead to a more determined effort in countries to improve the obesogenic environment or to place more resources into prevention and management of obesity remains to be seen,” he said.
Increased inquiries about bariatric surgery following COVID-19
Meanwhile, Matthew M. Hutter, MD, MPH, president, American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery, said in an interview that “COVID-19 and studies like this are now making many aware that obesity is not just a lifestyle choice or a cosmetic issue, but “a disease that needs to be taken seriously” and treated.
“Metabolic and bariatric surgery is a very safe and effective treatment for persons with obesity with a BMI >40 kg/m2 or BMI >35 kg/m2 and related diseases like diabetes, hypertension, sleep apnea, reflux, back pain, and many others,” added Dr. Hutter, who is also professor of surgery, Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“Recently, some metabolic and bariatric centers have seen an increase in patients considering surgery,” he said. “Some say that COVID-19 has made them realize they need to do something to be healthier.”
“Currently, less than 1% of those who could benefit from surgery are actually having” it each year, Dr. Hutter noted, “and I think there are many who should seriously consider surgery to be healthier, live longer, and live better.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New-onset AFib common but unrecognized in the month after cardiac surgery
One in five patients at elevated stroke risk who underwent cardiac surgery with no history of atrial fibrillation preoperatively or at discharge developed postoperative AFib documented on a continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring device within the first 30 days after leaving the hospital in the randomized SEARCH-AF trial.
“Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery is not confined to the hospitalization period per se. We believe that these data should help inform on clinical practice guidelines on monitoring for postoperative atrial fibrillation in such patients,” said Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, reporting the results at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“Guidelines provide little or no direction on optimal monitoring post cardiac surgery, particularly if patients are in sinus rhythm at discharge,” the surgeon noted.
SEARCH-AF was an open-label, multicenter study that included 336 patients at elevated stroke risk with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, no history of preoperative AFib, and none more than briefly with resolution during hospitalization. They were randomized to 30 days of postdischarge continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring with Medtronic’s SEEQ device, to Icentia’s CardioSTAT device, or to usual care, with Holter monitoring at the discretion of the treating physicians.
The primary result was a cumulative duration of AFib or atrial flutter of 6 minutes or longer during that 30-day period. This outcome occurred in 19.6% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and 1.7% of usual-care controls. Thus, there is an ongoing persistent occult risk of AFib that typically goes unrecognized. This 10-fold difference in the incidence of postoperative AFib translated into an absolute 17.9% between-group difference and a number-needed-to-treat of 6.
The secondary outcome of a cumulative atrial fib/flutter burden of 6 hours or more during 30 days occurred in 8.6% of the continuously monitored group and none of the controls. A cumulative AFib/flutter burden of 24 hours or greater occurred in 3.1% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and zero controls. These are AFib burdens that in other studies have been linked to increased risks of stroke and death, said Dr. Verma, professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Toronto.
“From a clinical standpoint, what this trial tells me is for my patients being discharged home tomorrow from the hospital, where they haven’t had AFib and I haven’t initiated anticoagulation, I have a low threshold to monitor these patients and to watch for periods of sustained unrecognized atrial fibrillation,” the surgeon added.
Experts: Results won’t change guidelines
Discussant Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has stated that there are insufficient data available to recommend ECG screening for AFib to prevent stroke. Before the task force can be convinced to recommend it and for payers to cover it, a number of key questions need to be answered. And the SEARCH-AF trial doesn’t provide those answers, said Dr. Freedman, professor of cardiology and deputy director of the Heart Research Institute at the University of Sydney.
First off, it’ll be necessary to know if the risk posed by screen-detected AFib, including postoperative AFib, is similar to that of clinical AFib. Next, it must be shown that this screen-detected postoperative AFib is actionable; that is, that a screening strategy to detect postoperative AFib arising after discharge and then treat with oral anticoagulants will actually prevent more strokes than with usual care. There are large studies underway addressing that question, including HEARTLINE, STROKESTOP, and SAFERGUARD-AF, he observed.
In an interview, Rod S. Passman, MD, who gave a state-of-the-art talk on AFib detection at the meeting and wasn’t involved in SEARCH-AF, said he doesn’t consider the results practice-changing.
“It’s not guideline-changing because you’ve only shown that more intensive monitoring finds more AFib. Guideline-changing would be that finding that AFib and doing something about it impacts hard outcomes, and we don’t have that data yet,” said Dr. Passman, an electrophysiologist who is director of the Center for Arrhythmia Research and professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The SEARCH-AF trial was funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Verma reported having received speaker’s fees and/or research support from those and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Freedman disclosed having no financial conflicts.
One in five patients at elevated stroke risk who underwent cardiac surgery with no history of atrial fibrillation preoperatively or at discharge developed postoperative AFib documented on a continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring device within the first 30 days after leaving the hospital in the randomized SEARCH-AF trial.
“Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery is not confined to the hospitalization period per se. We believe that these data should help inform on clinical practice guidelines on monitoring for postoperative atrial fibrillation in such patients,” said Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, reporting the results at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“Guidelines provide little or no direction on optimal monitoring post cardiac surgery, particularly if patients are in sinus rhythm at discharge,” the surgeon noted.
SEARCH-AF was an open-label, multicenter study that included 336 patients at elevated stroke risk with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, no history of preoperative AFib, and none more than briefly with resolution during hospitalization. They were randomized to 30 days of postdischarge continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring with Medtronic’s SEEQ device, to Icentia’s CardioSTAT device, or to usual care, with Holter monitoring at the discretion of the treating physicians.
The primary result was a cumulative duration of AFib or atrial flutter of 6 minutes or longer during that 30-day period. This outcome occurred in 19.6% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and 1.7% of usual-care controls. Thus, there is an ongoing persistent occult risk of AFib that typically goes unrecognized. This 10-fold difference in the incidence of postoperative AFib translated into an absolute 17.9% between-group difference and a number-needed-to-treat of 6.
The secondary outcome of a cumulative atrial fib/flutter burden of 6 hours or more during 30 days occurred in 8.6% of the continuously monitored group and none of the controls. A cumulative AFib/flutter burden of 24 hours or greater occurred in 3.1% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and zero controls. These are AFib burdens that in other studies have been linked to increased risks of stroke and death, said Dr. Verma, professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Toronto.
“From a clinical standpoint, what this trial tells me is for my patients being discharged home tomorrow from the hospital, where they haven’t had AFib and I haven’t initiated anticoagulation, I have a low threshold to monitor these patients and to watch for periods of sustained unrecognized atrial fibrillation,” the surgeon added.
Experts: Results won’t change guidelines
Discussant Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has stated that there are insufficient data available to recommend ECG screening for AFib to prevent stroke. Before the task force can be convinced to recommend it and for payers to cover it, a number of key questions need to be answered. And the SEARCH-AF trial doesn’t provide those answers, said Dr. Freedman, professor of cardiology and deputy director of the Heart Research Institute at the University of Sydney.
First off, it’ll be necessary to know if the risk posed by screen-detected AFib, including postoperative AFib, is similar to that of clinical AFib. Next, it must be shown that this screen-detected postoperative AFib is actionable; that is, that a screening strategy to detect postoperative AFib arising after discharge and then treat with oral anticoagulants will actually prevent more strokes than with usual care. There are large studies underway addressing that question, including HEARTLINE, STROKESTOP, and SAFERGUARD-AF, he observed.
In an interview, Rod S. Passman, MD, who gave a state-of-the-art talk on AFib detection at the meeting and wasn’t involved in SEARCH-AF, said he doesn’t consider the results practice-changing.
“It’s not guideline-changing because you’ve only shown that more intensive monitoring finds more AFib. Guideline-changing would be that finding that AFib and doing something about it impacts hard outcomes, and we don’t have that data yet,” said Dr. Passman, an electrophysiologist who is director of the Center for Arrhythmia Research and professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The SEARCH-AF trial was funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Verma reported having received speaker’s fees and/or research support from those and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Freedman disclosed having no financial conflicts.
One in five patients at elevated stroke risk who underwent cardiac surgery with no history of atrial fibrillation preoperatively or at discharge developed postoperative AFib documented on a continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring device within the first 30 days after leaving the hospital in the randomized SEARCH-AF trial.
“Postoperative atrial fibrillation after cardiac surgery is not confined to the hospitalization period per se. We believe that these data should help inform on clinical practice guidelines on monitoring for postoperative atrial fibrillation in such patients,” said Subodh Verma, MD, PhD, reporting the results at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“Guidelines provide little or no direction on optimal monitoring post cardiac surgery, particularly if patients are in sinus rhythm at discharge,” the surgeon noted.
SEARCH-AF was an open-label, multicenter study that included 336 patients at elevated stroke risk with an average CHA2DS2-VASc score of 4, no history of preoperative AFib, and none more than briefly with resolution during hospitalization. They were randomized to 30 days of postdischarge continuous cardiac rhythm monitoring with Medtronic’s SEEQ device, to Icentia’s CardioSTAT device, or to usual care, with Holter monitoring at the discretion of the treating physicians.
The primary result was a cumulative duration of AFib or atrial flutter of 6 minutes or longer during that 30-day period. This outcome occurred in 19.6% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and 1.7% of usual-care controls. Thus, there is an ongoing persistent occult risk of AFib that typically goes unrecognized. This 10-fold difference in the incidence of postoperative AFib translated into an absolute 17.9% between-group difference and a number-needed-to-treat of 6.
The secondary outcome of a cumulative atrial fib/flutter burden of 6 hours or more during 30 days occurred in 8.6% of the continuously monitored group and none of the controls. A cumulative AFib/flutter burden of 24 hours or greater occurred in 3.1% of the enhanced cardiac monitoring group and zero controls. These are AFib burdens that in other studies have been linked to increased risks of stroke and death, said Dr. Verma, professor of cardiovascular surgery at the University of Toronto.
“From a clinical standpoint, what this trial tells me is for my patients being discharged home tomorrow from the hospital, where they haven’t had AFib and I haven’t initiated anticoagulation, I have a low threshold to monitor these patients and to watch for periods of sustained unrecognized atrial fibrillation,” the surgeon added.
Experts: Results won’t change guidelines
Discussant Ben Freedman, MBBS, PhD, noted that the U.S. Preventive Services Task Force has stated that there are insufficient data available to recommend ECG screening for AFib to prevent stroke. Before the task force can be convinced to recommend it and for payers to cover it, a number of key questions need to be answered. And the SEARCH-AF trial doesn’t provide those answers, said Dr. Freedman, professor of cardiology and deputy director of the Heart Research Institute at the University of Sydney.
First off, it’ll be necessary to know if the risk posed by screen-detected AFib, including postoperative AFib, is similar to that of clinical AFib. Next, it must be shown that this screen-detected postoperative AFib is actionable; that is, that a screening strategy to detect postoperative AFib arising after discharge and then treat with oral anticoagulants will actually prevent more strokes than with usual care. There are large studies underway addressing that question, including HEARTLINE, STROKESTOP, and SAFERGUARD-AF, he observed.
In an interview, Rod S. Passman, MD, who gave a state-of-the-art talk on AFib detection at the meeting and wasn’t involved in SEARCH-AF, said he doesn’t consider the results practice-changing.
“It’s not guideline-changing because you’ve only shown that more intensive monitoring finds more AFib. Guideline-changing would be that finding that AFib and doing something about it impacts hard outcomes, and we don’t have that data yet,” said Dr. Passman, an electrophysiologist who is director of the Center for Arrhythmia Research and professor of medicine and preventive medicine at Northwestern University, Chicago.
The SEARCH-AF trial was funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Verma reported having received speaker’s fees and/or research support from those and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Freedman disclosed having no financial conflicts.
FROM AHA 2020
VTEs tied to immune checkpoint inhibitor cancer treatment
Cancer patients who receive an immune checkpoint inhibitor have more than a doubled rate of venous thromboembolism during the subsequent 2 years, compared with their rate during the 2 years before treatment, according to a retrospective analysis of more than 2,800 patients treated at a single U.S. center.
The study focused on cancer patients treated with an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. It showed that during the 2 years prior to treatment with any type of ICI, the incidence of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) was 4.85/100 patient-years that then jumped to 11.75/100 patient-years during the 2 years following treatment. This translated into an incidence rate ratio of 2.43 during posttreatment follow-up, compared with pretreatment, Jingyi Gong, MD, said at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The increased VTE rate resulted from rises in both the rate of deep vein thrombosis, which had an IRR of 3.23 during the posttreatment period, and for pulmonary embolism, which showed an IRR of 2.24, said Dr. Gong, a physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. She hypothesized that this effect may result from a procoagulant effect of the immune activation and inflammation triggered by ICIs.
Hypothesis-generating results
Cardiologists cautioned that these findings should only be considered hypothesis generating, but raise an important alert for clinicians to have heightened awareness of the potential for VTE following ICI treatment.
“A clear message is to be aware that there is this signal, and be vigilant for patients who might present with VTE following ICI treatment,” commented Richard J. Kovacs, MD, a cardiologist and professor at Indiana University, Indianapolis. The data that Dr. Gong reported are “moderately convincing,” he added in an interview.
“Awareness that patients who receive ICI may be at increased VTE risk is very important,” agreed Umberto Campia, MD, a cardiologist, vascular specialist, and member of the cardio-oncology group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who was not involved in the new study.
The potential impact of ICI treatment on VTE risk is slowly emerging, added Dr. Campia. Until recently, the literature primarily was case reports, but recently another retrospective, single-center study came out that reported a 13% incidence of VTE in cancer patients following ICI treatment. On the other hand, a recently published meta-analysis of more than 20,000 patients from 68 ICI studies failed to find a suggestion of increased VTE incidence following ICI interventions.
Attempting to assess the impact of treatment on VTE risk in cancer patients is challenging because cancer itself boosts the risk. Recommendations on the use of VTE prophylaxis in cancer patients most recently came out in 2014 from the American Society of Clinical Oncology, which said that VTE prophylaxis for ambulatory cancer patients “may be considered for highly select high-risk patients.” The impact of cancer therapy on VTE risk and the need for prophylaxis is usually assessed by applying the Khorana score, Dr. Campia said in an interview.
VTE spikes acutely after ICI treatment
Dr. Gong analyzed VTE incidence rates by time during the total 4-year period studied, and found that the rate gradually and steadily rose with time throughout the 2 years preceding treatment, spiked immediately following ICI treatment, and then gradually and steadily fell back to roughly the rate seen just before treatment, reaching that level about a year after treatment. She ran a sensitivity analysis that excluded patients who died during the first year following their ICI treatment, and in this calculation an acute spike in VTE following ICI treatment still occurred but with reduced magnitude.
She also reported the results of several subgroup analyses. The IRRs remained consistent among women and men, among patients who were aged over or under 65 years, and regardless of cancer type or treatment with corticosteroids. But the subgroup analyses identified two parameters that seemed to clearly split VTE rates.
Among patients on treatment with an anticoagulant agent at the time of their ICI treatment, roughly 10% of the patients, the IRR was 0.56, compared with a ratio of 3.86 among the other patients, suggesting possible protection. A second factor that seemed linked with VTE incidence was the number of ICI treatment cycles a patient received. Those who received more than five cycles had a risk ratio of 3.95, while those who received five or fewer cycles had a RR of 1.66.
Her analysis included 2,842 cancer patients who received treatment with an ICI at Massachusetts General Hospital. Patients averaged 64 years of age, slightly more than half were men, and 13% had a prior history of VTE. Patients received an average of 5 ICI treatment cycles, but a quarter of the patients received more than 10 cycles.
During the 2-year follow-up, 244 patients (9%) developed VTE. The patients who developed VTE were significantly younger than those who did not, with an average age of 63 years, compared with 65. And the patients who eventually developed VTE had a significantly higher prevalence of prior VTE at 18%, compared with 12% among the patients who stayed VTE free.
The cancer types patients had were non–small cell lung, 29%; melanoma, 28%; head and neck, 12%; renal genitourinary, 6%; and other, 25%. ICIs have been available for routine U.S. practice since 2011. The class includes agents such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and durvalumab (Imfinzi).
Researchers would need to perform a prospective, randomized study to determine whether anticoagulant prophylaxis is clearly beneficial for patients receiving ICI treatment, Dr. Gong said. But both Dr. Kovacs and Dr. Campia said that more data on this topic are first needed.
“We need to confirm that treatment with ICI is associated with VTEs. Retrospective data are not definitive,” said Dr. Campia. “We would need to prospectively assess the impact of ICI,” which will not be easy, as it’s quickly become a cornerstone for treating many cancers. “We need to become more familiar with the adverse effects of these drugs. We are still learning about their toxicities.”
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Gong, Dr. Kovacs, and Dr. Campia had no disclosures.
Cancer patients who receive an immune checkpoint inhibitor have more than a doubled rate of venous thromboembolism during the subsequent 2 years, compared with their rate during the 2 years before treatment, according to a retrospective analysis of more than 2,800 patients treated at a single U.S. center.
The study focused on cancer patients treated with an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. It showed that during the 2 years prior to treatment with any type of ICI, the incidence of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) was 4.85/100 patient-years that then jumped to 11.75/100 patient-years during the 2 years following treatment. This translated into an incidence rate ratio of 2.43 during posttreatment follow-up, compared with pretreatment, Jingyi Gong, MD, said at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The increased VTE rate resulted from rises in both the rate of deep vein thrombosis, which had an IRR of 3.23 during the posttreatment period, and for pulmonary embolism, which showed an IRR of 2.24, said Dr. Gong, a physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. She hypothesized that this effect may result from a procoagulant effect of the immune activation and inflammation triggered by ICIs.
Hypothesis-generating results
Cardiologists cautioned that these findings should only be considered hypothesis generating, but raise an important alert for clinicians to have heightened awareness of the potential for VTE following ICI treatment.
“A clear message is to be aware that there is this signal, and be vigilant for patients who might present with VTE following ICI treatment,” commented Richard J. Kovacs, MD, a cardiologist and professor at Indiana University, Indianapolis. The data that Dr. Gong reported are “moderately convincing,” he added in an interview.
“Awareness that patients who receive ICI may be at increased VTE risk is very important,” agreed Umberto Campia, MD, a cardiologist, vascular specialist, and member of the cardio-oncology group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who was not involved in the new study.
The potential impact of ICI treatment on VTE risk is slowly emerging, added Dr. Campia. Until recently, the literature primarily was case reports, but recently another retrospective, single-center study came out that reported a 13% incidence of VTE in cancer patients following ICI treatment. On the other hand, a recently published meta-analysis of more than 20,000 patients from 68 ICI studies failed to find a suggestion of increased VTE incidence following ICI interventions.
Attempting to assess the impact of treatment on VTE risk in cancer patients is challenging because cancer itself boosts the risk. Recommendations on the use of VTE prophylaxis in cancer patients most recently came out in 2014 from the American Society of Clinical Oncology, which said that VTE prophylaxis for ambulatory cancer patients “may be considered for highly select high-risk patients.” The impact of cancer therapy on VTE risk and the need for prophylaxis is usually assessed by applying the Khorana score, Dr. Campia said in an interview.
VTE spikes acutely after ICI treatment
Dr. Gong analyzed VTE incidence rates by time during the total 4-year period studied, and found that the rate gradually and steadily rose with time throughout the 2 years preceding treatment, spiked immediately following ICI treatment, and then gradually and steadily fell back to roughly the rate seen just before treatment, reaching that level about a year after treatment. She ran a sensitivity analysis that excluded patients who died during the first year following their ICI treatment, and in this calculation an acute spike in VTE following ICI treatment still occurred but with reduced magnitude.
She also reported the results of several subgroup analyses. The IRRs remained consistent among women and men, among patients who were aged over or under 65 years, and regardless of cancer type or treatment with corticosteroids. But the subgroup analyses identified two parameters that seemed to clearly split VTE rates.
Among patients on treatment with an anticoagulant agent at the time of their ICI treatment, roughly 10% of the patients, the IRR was 0.56, compared with a ratio of 3.86 among the other patients, suggesting possible protection. A second factor that seemed linked with VTE incidence was the number of ICI treatment cycles a patient received. Those who received more than five cycles had a risk ratio of 3.95, while those who received five or fewer cycles had a RR of 1.66.
Her analysis included 2,842 cancer patients who received treatment with an ICI at Massachusetts General Hospital. Patients averaged 64 years of age, slightly more than half were men, and 13% had a prior history of VTE. Patients received an average of 5 ICI treatment cycles, but a quarter of the patients received more than 10 cycles.
During the 2-year follow-up, 244 patients (9%) developed VTE. The patients who developed VTE were significantly younger than those who did not, with an average age of 63 years, compared with 65. And the patients who eventually developed VTE had a significantly higher prevalence of prior VTE at 18%, compared with 12% among the patients who stayed VTE free.
The cancer types patients had were non–small cell lung, 29%; melanoma, 28%; head and neck, 12%; renal genitourinary, 6%; and other, 25%. ICIs have been available for routine U.S. practice since 2011. The class includes agents such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and durvalumab (Imfinzi).
Researchers would need to perform a prospective, randomized study to determine whether anticoagulant prophylaxis is clearly beneficial for patients receiving ICI treatment, Dr. Gong said. But both Dr. Kovacs and Dr. Campia said that more data on this topic are first needed.
“We need to confirm that treatment with ICI is associated with VTEs. Retrospective data are not definitive,” said Dr. Campia. “We would need to prospectively assess the impact of ICI,” which will not be easy, as it’s quickly become a cornerstone for treating many cancers. “We need to become more familiar with the adverse effects of these drugs. We are still learning about their toxicities.”
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Gong, Dr. Kovacs, and Dr. Campia had no disclosures.
Cancer patients who receive an immune checkpoint inhibitor have more than a doubled rate of venous thromboembolism during the subsequent 2 years, compared with their rate during the 2 years before treatment, according to a retrospective analysis of more than 2,800 patients treated at a single U.S. center.
The study focused on cancer patients treated with an immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) at Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston. It showed that during the 2 years prior to treatment with any type of ICI, the incidence of venous thromboembolic events (VTE) was 4.85/100 patient-years that then jumped to 11.75/100 patient-years during the 2 years following treatment. This translated into an incidence rate ratio of 2.43 during posttreatment follow-up, compared with pretreatment, Jingyi Gong, MD, said at the virtual American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The increased VTE rate resulted from rises in both the rate of deep vein thrombosis, which had an IRR of 3.23 during the posttreatment period, and for pulmonary embolism, which showed an IRR of 2.24, said Dr. Gong, a physician at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston. She hypothesized that this effect may result from a procoagulant effect of the immune activation and inflammation triggered by ICIs.
Hypothesis-generating results
Cardiologists cautioned that these findings should only be considered hypothesis generating, but raise an important alert for clinicians to have heightened awareness of the potential for VTE following ICI treatment.
“A clear message is to be aware that there is this signal, and be vigilant for patients who might present with VTE following ICI treatment,” commented Richard J. Kovacs, MD, a cardiologist and professor at Indiana University, Indianapolis. The data that Dr. Gong reported are “moderately convincing,” he added in an interview.
“Awareness that patients who receive ICI may be at increased VTE risk is very important,” agreed Umberto Campia, MD, a cardiologist, vascular specialist, and member of the cardio-oncology group at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, who was not involved in the new study.
The potential impact of ICI treatment on VTE risk is slowly emerging, added Dr. Campia. Until recently, the literature primarily was case reports, but recently another retrospective, single-center study came out that reported a 13% incidence of VTE in cancer patients following ICI treatment. On the other hand, a recently published meta-analysis of more than 20,000 patients from 68 ICI studies failed to find a suggestion of increased VTE incidence following ICI interventions.
Attempting to assess the impact of treatment on VTE risk in cancer patients is challenging because cancer itself boosts the risk. Recommendations on the use of VTE prophylaxis in cancer patients most recently came out in 2014 from the American Society of Clinical Oncology, which said that VTE prophylaxis for ambulatory cancer patients “may be considered for highly select high-risk patients.” The impact of cancer therapy on VTE risk and the need for prophylaxis is usually assessed by applying the Khorana score, Dr. Campia said in an interview.
VTE spikes acutely after ICI treatment
Dr. Gong analyzed VTE incidence rates by time during the total 4-year period studied, and found that the rate gradually and steadily rose with time throughout the 2 years preceding treatment, spiked immediately following ICI treatment, and then gradually and steadily fell back to roughly the rate seen just before treatment, reaching that level about a year after treatment. She ran a sensitivity analysis that excluded patients who died during the first year following their ICI treatment, and in this calculation an acute spike in VTE following ICI treatment still occurred but with reduced magnitude.
She also reported the results of several subgroup analyses. The IRRs remained consistent among women and men, among patients who were aged over or under 65 years, and regardless of cancer type or treatment with corticosteroids. But the subgroup analyses identified two parameters that seemed to clearly split VTE rates.
Among patients on treatment with an anticoagulant agent at the time of their ICI treatment, roughly 10% of the patients, the IRR was 0.56, compared with a ratio of 3.86 among the other patients, suggesting possible protection. A second factor that seemed linked with VTE incidence was the number of ICI treatment cycles a patient received. Those who received more than five cycles had a risk ratio of 3.95, while those who received five or fewer cycles had a RR of 1.66.
Her analysis included 2,842 cancer patients who received treatment with an ICI at Massachusetts General Hospital. Patients averaged 64 years of age, slightly more than half were men, and 13% had a prior history of VTE. Patients received an average of 5 ICI treatment cycles, but a quarter of the patients received more than 10 cycles.
During the 2-year follow-up, 244 patients (9%) developed VTE. The patients who developed VTE were significantly younger than those who did not, with an average age of 63 years, compared with 65. And the patients who eventually developed VTE had a significantly higher prevalence of prior VTE at 18%, compared with 12% among the patients who stayed VTE free.
The cancer types patients had were non–small cell lung, 29%; melanoma, 28%; head and neck, 12%; renal genitourinary, 6%; and other, 25%. ICIs have been available for routine U.S. practice since 2011. The class includes agents such as pembrolizumab (Keytruda) and durvalumab (Imfinzi).
Researchers would need to perform a prospective, randomized study to determine whether anticoagulant prophylaxis is clearly beneficial for patients receiving ICI treatment, Dr. Gong said. But both Dr. Kovacs and Dr. Campia said that more data on this topic are first needed.
“We need to confirm that treatment with ICI is associated with VTEs. Retrospective data are not definitive,” said Dr. Campia. “We would need to prospectively assess the impact of ICI,” which will not be easy, as it’s quickly become a cornerstone for treating many cancers. “We need to become more familiar with the adverse effects of these drugs. We are still learning about their toxicities.”
The study had no commercial funding. Dr. Gong, Dr. Kovacs, and Dr. Campia had no disclosures.
FROM AHA 2020
Open enrollment 2021: A big start for HealthCare.gov
Over 818,000 plans were selected for the 2021 coverage year during the first week, Nov.1-7, of this year’s open enrollment on the federal health insurance exchange, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.
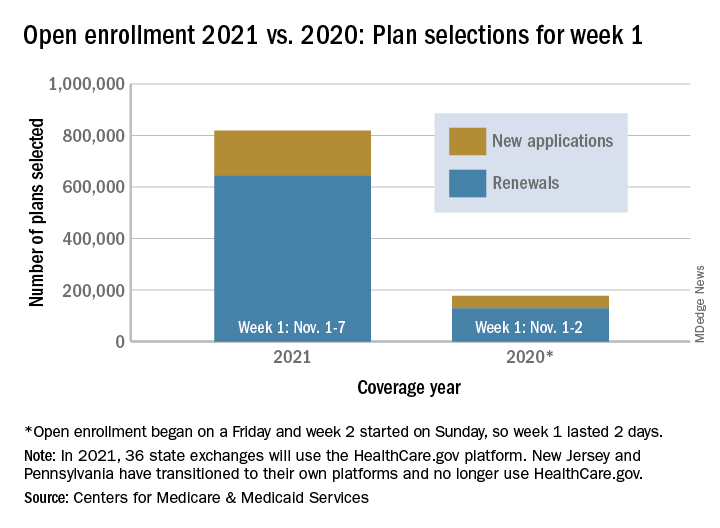
The bulk of those plans, nearly 79%, were renewals by consumers who had coverage through the federal exchange this year. The balance covers new plans selected by individuals who were not covered through HealthCare.gov this year, the CMS noted in a written statement.
The total enrollment for week 1 marks a considerable increase over last year’s first week of open enrollment, which saw approximately 177,000 plans selected, but Nov. 1 fell on a Friday in 2019, so that total represents only 2 days since weeks are tracked as running from Sunday to Saturday, the CMS explained.
For the 2021 benefit year, the HealthCare.gov platform covers 36 states, down from 38 for the 2020 benefit year, because New Jersey and Pennsylvania have “transitioned to their own state-based exchange platforms,” the CMS noted, adding that the two accounted for 7% of all plans selected last year.
“The final number of plan selections associated with enrollment activity during a reporting period may change due to plan modifications or cancellations,” CMS said, and its weekly snapshot “does not report the number of consumers who have paid premiums to effectuate their enrollment.”
This year’s open-enrollment period on HealthCare.gov is scheduled to conclude Dec. 15.
Over 818,000 plans were selected for the 2021 coverage year during the first week, Nov.1-7, of this year’s open enrollment on the federal health insurance exchange, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

The bulk of those plans, nearly 79%, were renewals by consumers who had coverage through the federal exchange this year. The balance covers new plans selected by individuals who were not covered through HealthCare.gov this year, the CMS noted in a written statement.
The total enrollment for week 1 marks a considerable increase over last year’s first week of open enrollment, which saw approximately 177,000 plans selected, but Nov. 1 fell on a Friday in 2019, so that total represents only 2 days since weeks are tracked as running from Sunday to Saturday, the CMS explained.
For the 2021 benefit year, the HealthCare.gov platform covers 36 states, down from 38 for the 2020 benefit year, because New Jersey and Pennsylvania have “transitioned to their own state-based exchange platforms,” the CMS noted, adding that the two accounted for 7% of all plans selected last year.
“The final number of plan selections associated with enrollment activity during a reporting period may change due to plan modifications or cancellations,” CMS said, and its weekly snapshot “does not report the number of consumers who have paid premiums to effectuate their enrollment.”
This year’s open-enrollment period on HealthCare.gov is scheduled to conclude Dec. 15.
Over 818,000 plans were selected for the 2021 coverage year during the first week, Nov.1-7, of this year’s open enrollment on the federal health insurance exchange, according to the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services.

The bulk of those plans, nearly 79%, were renewals by consumers who had coverage through the federal exchange this year. The balance covers new plans selected by individuals who were not covered through HealthCare.gov this year, the CMS noted in a written statement.
The total enrollment for week 1 marks a considerable increase over last year’s first week of open enrollment, which saw approximately 177,000 plans selected, but Nov. 1 fell on a Friday in 2019, so that total represents only 2 days since weeks are tracked as running from Sunday to Saturday, the CMS explained.
For the 2021 benefit year, the HealthCare.gov platform covers 36 states, down from 38 for the 2020 benefit year, because New Jersey and Pennsylvania have “transitioned to their own state-based exchange platforms,” the CMS noted, adding that the two accounted for 7% of all plans selected last year.
“The final number of plan selections associated with enrollment activity during a reporting period may change due to plan modifications or cancellations,” CMS said, and its weekly snapshot “does not report the number of consumers who have paid premiums to effectuate their enrollment.”
This year’s open-enrollment period on HealthCare.gov is scheduled to conclude Dec. 15.