User login
according to the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research.
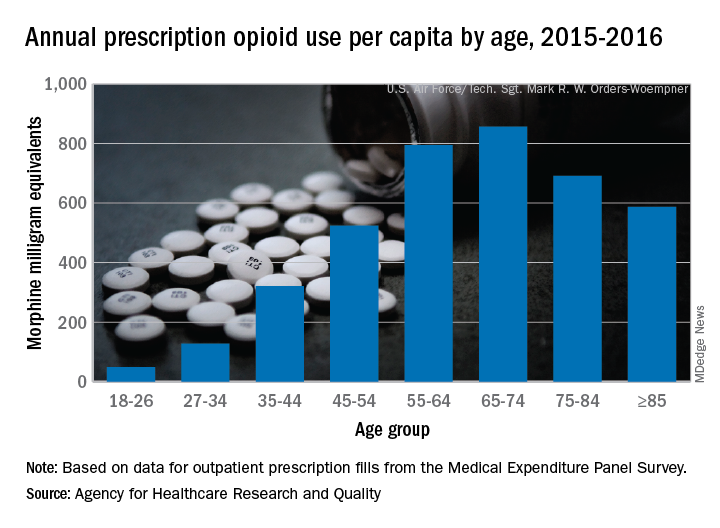
Elderly adults with chronic and acute pain obtained an average of 774 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) of prescription opioids annually during 2015-2016 from outpatient clinicians, compared with 376 MMEs a year for nonelderly adults, said Asako S. Moriya, PhD, and G. Edward Miller, PhD, of the AHRQ.
Narrowing the age groups shows that opioid MMEs increased with age, starting at 49 MMEs for 18- to 26-year-olds and rising to a high of 856 MMEs in the 65- to 74-year-old group, before dropping off in the oldest adults, the investigators said in a Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) research findings report.
The analysis included “all opioid medications that are commonly used to treat pain” and excluded respiratory agents, antitussives, and drugs used for medication-assisted treatment, they noted. The MEPS data cover prescriptions purchased or obtained in outpatient settings but not those administered in inpatient settings or in clinics or physician offices.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research.

Elderly adults with chronic and acute pain obtained an average of 774 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) of prescription opioids annually during 2015-2016 from outpatient clinicians, compared with 376 MMEs a year for nonelderly adults, said Asako S. Moriya, PhD, and G. Edward Miller, PhD, of the AHRQ.
Narrowing the age groups shows that opioid MMEs increased with age, starting at 49 MMEs for 18- to 26-year-olds and rising to a high of 856 MMEs in the 65- to 74-year-old group, before dropping off in the oldest adults, the investigators said in a Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) research findings report.
The analysis included “all opioid medications that are commonly used to treat pain” and excluded respiratory agents, antitussives, and drugs used for medication-assisted treatment, they noted. The MEPS data cover prescriptions purchased or obtained in outpatient settings but not those administered in inpatient settings or in clinics or physician offices.
according to the Agency for Healthcare Quality and Research.

Elderly adults with chronic and acute pain obtained an average of 774 morphine milligram equivalents (MMEs) of prescription opioids annually during 2015-2016 from outpatient clinicians, compared with 376 MMEs a year for nonelderly adults, said Asako S. Moriya, PhD, and G. Edward Miller, PhD, of the AHRQ.
Narrowing the age groups shows that opioid MMEs increased with age, starting at 49 MMEs for 18- to 26-year-olds and rising to a high of 856 MMEs in the 65- to 74-year-old group, before dropping off in the oldest adults, the investigators said in a Medical Expenditure Panel Survey (MEPS) research findings report.
The analysis included “all opioid medications that are commonly used to treat pain” and excluded respiratory agents, antitussives, and drugs used for medication-assisted treatment, they noted. The MEPS data cover prescriptions purchased or obtained in outpatient settings but not those administered in inpatient settings or in clinics or physician offices.