User login
Formerly Skin & Allergy News
ass lick
assault rifle
balls
ballsac
black jack
bleach
Boko Haram
bondage
causas
cheap
child abuse
cocaine
compulsive behaviors
cost of miracles
cunt
Daech
display network stats
drug paraphernalia
explosion
fart
fda and death
fda AND warn
fda AND warning
fda AND warns
feom
fuck
gambling
gfc
gun
human trafficking
humira AND expensive
illegal
ISIL
ISIS
Islamic caliphate
Islamic state
madvocate
masturbation
mixed martial arts
MMA
molestation
national rifle association
NRA
nsfw
nuccitelli
pedophile
pedophilia
poker
porn
porn
pornography
psychedelic drug
recreational drug
sex slave rings
shit
slot machine
snort
substance abuse
terrorism
terrorist
texarkana
Texas hold 'em
UFC
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden active')]
The leading independent newspaper covering dermatology news and commentary.
Stop blaming the unvaccinated
As politicians battle over masks and mandates, heated rhetoric has been used to describe the fourth heartbreaking surge in COVID as a “pandemic of the unvaccinated.”
While it may serve to further divide red and blue states, I disagree with the assertion that the current surge in cases is driven simply by the unvaccinated. Why? First, the premise would assume complete efficacy with our vaccinated population, which is statistically incorrect (at least 15 million of the U.S. population never completed a second round of injections), which means they were not considered “fully vaccinated.”
Alternately, we need to examine what has occurred in nations with significantly higher vaccination rates than ours (the United Kingdom and Israel) to realize that variants have overrun the dramatic success achieved in those countries as well. Israel, once considered to be the most vaccinated country in the world, is facing a brutal fourth wave of COVID that has sent the country spiraling into another heartbreaking lockdown.
The unvaccinated could hardly be blamed for what is happening in either of these highly vaccinated countries.
The concept of blame
So why use blame? It defeats the purpose of encouraging those who are hesitant or possibly misinformed or disenfranchised to move forward. It lacks compassion. It does not encompass the art and science of nursing (for example, the University of Southern Indiana), such as those that hospitals have used to frame optimal nursing care. I abhor the idea of labeling because it denies the prospect of future comprehension.
Labeling reminds me of one of the saddest cases in my career.
An unfortunate case
I was the nurse caring for a man from a motor vehicular accident where an entire family was brutally killed. My patient was alleged to be the cause, with a blood alcohol level of 0.40%+ post hydration, intubated and ventilated, with a flailed chest and multiple orthopedic injuries as well as blunt head trauma. He was secured to the bed with handcuffs, although that was unnecessary. Multiple times I was asked how I could possibly care for such an individual, by the police and even a few colleagues. But it was not my place to judge the man.
He was in pain, and he was dying. I comforted him for the 2 weeks it took his battered body to pass into the next realm. No one visited him except the police, eagerly waiting for the man to wake up to explain the tragic events that occurred. It was my job to ease what pain I could and protect him from labels. Did he deserve the labels? Who knew? I did not care. I cared about his writhing and his physical anguish.
The comparison
Blame did not help the situation then, nor does it help us move forward now. As nurses, we seek to work within a framework of understanding. As we tire of caring for thousands of COVID patients, we do not stop to ask if they “deserve” care or if they have taken precautions and lived reasonably prior to seeking assistance for disease. We would not be nurses if we did this.
Think about Gov. Greg Abbott, who has asked that Texans not be allowed to mandate masks for children returning to school. He has recently been diagnosed with COVID, despite assuring the public he is fully vaccinated. Politically, his diagnosis could be visualized as a fiasco for a purple state where he has been adamant in denying the efficacy of masks for children.
Yet, his diagnosis should not be fodder for the press. The first concern should be his health and well-being, similar for any man of his age and potential comorbidity.
Conclusion
We should be people first, human beings that remain interconnected by our need for care and survival, not conservatives, independents, or liberals, not “vaccinated or unvaccinated,” not seen as “breakthrough” infections, or the immunosuppressed possibly unable to mount a robust response to COVID.
Labels do not define the ability to effectively defeat coronavirus or variants, as highly vaccinated countries have demonstrated in recent months. We are in the midst of a global pandemic, and the battle is raging onward.
In fact, the longer this pandemic continues, the more likely it is we will need to live with this as an endemic disease, so we should stop blaming those who become ill and need support.
It could be any of us.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As politicians battle over masks and mandates, heated rhetoric has been used to describe the fourth heartbreaking surge in COVID as a “pandemic of the unvaccinated.”
While it may serve to further divide red and blue states, I disagree with the assertion that the current surge in cases is driven simply by the unvaccinated. Why? First, the premise would assume complete efficacy with our vaccinated population, which is statistically incorrect (at least 15 million of the U.S. population never completed a second round of injections), which means they were not considered “fully vaccinated.”
Alternately, we need to examine what has occurred in nations with significantly higher vaccination rates than ours (the United Kingdom and Israel) to realize that variants have overrun the dramatic success achieved in those countries as well. Israel, once considered to be the most vaccinated country in the world, is facing a brutal fourth wave of COVID that has sent the country spiraling into another heartbreaking lockdown.
The unvaccinated could hardly be blamed for what is happening in either of these highly vaccinated countries.
The concept of blame
So why use blame? It defeats the purpose of encouraging those who are hesitant or possibly misinformed or disenfranchised to move forward. It lacks compassion. It does not encompass the art and science of nursing (for example, the University of Southern Indiana), such as those that hospitals have used to frame optimal nursing care. I abhor the idea of labeling because it denies the prospect of future comprehension.
Labeling reminds me of one of the saddest cases in my career.
An unfortunate case
I was the nurse caring for a man from a motor vehicular accident where an entire family was brutally killed. My patient was alleged to be the cause, with a blood alcohol level of 0.40%+ post hydration, intubated and ventilated, with a flailed chest and multiple orthopedic injuries as well as blunt head trauma. He was secured to the bed with handcuffs, although that was unnecessary. Multiple times I was asked how I could possibly care for such an individual, by the police and even a few colleagues. But it was not my place to judge the man.
He was in pain, and he was dying. I comforted him for the 2 weeks it took his battered body to pass into the next realm. No one visited him except the police, eagerly waiting for the man to wake up to explain the tragic events that occurred. It was my job to ease what pain I could and protect him from labels. Did he deserve the labels? Who knew? I did not care. I cared about his writhing and his physical anguish.
The comparison
Blame did not help the situation then, nor does it help us move forward now. As nurses, we seek to work within a framework of understanding. As we tire of caring for thousands of COVID patients, we do not stop to ask if they “deserve” care or if they have taken precautions and lived reasonably prior to seeking assistance for disease. We would not be nurses if we did this.
Think about Gov. Greg Abbott, who has asked that Texans not be allowed to mandate masks for children returning to school. He has recently been diagnosed with COVID, despite assuring the public he is fully vaccinated. Politically, his diagnosis could be visualized as a fiasco for a purple state where he has been adamant in denying the efficacy of masks for children.
Yet, his diagnosis should not be fodder for the press. The first concern should be his health and well-being, similar for any man of his age and potential comorbidity.
Conclusion
We should be people first, human beings that remain interconnected by our need for care and survival, not conservatives, independents, or liberals, not “vaccinated or unvaccinated,” not seen as “breakthrough” infections, or the immunosuppressed possibly unable to mount a robust response to COVID.
Labels do not define the ability to effectively defeat coronavirus or variants, as highly vaccinated countries have demonstrated in recent months. We are in the midst of a global pandemic, and the battle is raging onward.
In fact, the longer this pandemic continues, the more likely it is we will need to live with this as an endemic disease, so we should stop blaming those who become ill and need support.
It could be any of us.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As politicians battle over masks and mandates, heated rhetoric has been used to describe the fourth heartbreaking surge in COVID as a “pandemic of the unvaccinated.”
While it may serve to further divide red and blue states, I disagree with the assertion that the current surge in cases is driven simply by the unvaccinated. Why? First, the premise would assume complete efficacy with our vaccinated population, which is statistically incorrect (at least 15 million of the U.S. population never completed a second round of injections), which means they were not considered “fully vaccinated.”
Alternately, we need to examine what has occurred in nations with significantly higher vaccination rates than ours (the United Kingdom and Israel) to realize that variants have overrun the dramatic success achieved in those countries as well. Israel, once considered to be the most vaccinated country in the world, is facing a brutal fourth wave of COVID that has sent the country spiraling into another heartbreaking lockdown.
The unvaccinated could hardly be blamed for what is happening in either of these highly vaccinated countries.
The concept of blame
So why use blame? It defeats the purpose of encouraging those who are hesitant or possibly misinformed or disenfranchised to move forward. It lacks compassion. It does not encompass the art and science of nursing (for example, the University of Southern Indiana), such as those that hospitals have used to frame optimal nursing care. I abhor the idea of labeling because it denies the prospect of future comprehension.
Labeling reminds me of one of the saddest cases in my career.
An unfortunate case
I was the nurse caring for a man from a motor vehicular accident where an entire family was brutally killed. My patient was alleged to be the cause, with a blood alcohol level of 0.40%+ post hydration, intubated and ventilated, with a flailed chest and multiple orthopedic injuries as well as blunt head trauma. He was secured to the bed with handcuffs, although that was unnecessary. Multiple times I was asked how I could possibly care for such an individual, by the police and even a few colleagues. But it was not my place to judge the man.
He was in pain, and he was dying. I comforted him for the 2 weeks it took his battered body to pass into the next realm. No one visited him except the police, eagerly waiting for the man to wake up to explain the tragic events that occurred. It was my job to ease what pain I could and protect him from labels. Did he deserve the labels? Who knew? I did not care. I cared about his writhing and his physical anguish.
The comparison
Blame did not help the situation then, nor does it help us move forward now. As nurses, we seek to work within a framework of understanding. As we tire of caring for thousands of COVID patients, we do not stop to ask if they “deserve” care or if they have taken precautions and lived reasonably prior to seeking assistance for disease. We would not be nurses if we did this.
Think about Gov. Greg Abbott, who has asked that Texans not be allowed to mandate masks for children returning to school. He has recently been diagnosed with COVID, despite assuring the public he is fully vaccinated. Politically, his diagnosis could be visualized as a fiasco for a purple state where he has been adamant in denying the efficacy of masks for children.
Yet, his diagnosis should not be fodder for the press. The first concern should be his health and well-being, similar for any man of his age and potential comorbidity.
Conclusion
We should be people first, human beings that remain interconnected by our need for care and survival, not conservatives, independents, or liberals, not “vaccinated or unvaccinated,” not seen as “breakthrough” infections, or the immunosuppressed possibly unable to mount a robust response to COVID.
Labels do not define the ability to effectively defeat coronavirus or variants, as highly vaccinated countries have demonstrated in recent months. We are in the midst of a global pandemic, and the battle is raging onward.
In fact, the longer this pandemic continues, the more likely it is we will need to live with this as an endemic disease, so we should stop blaming those who become ill and need support.
It could be any of us.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A hot dog a day takes 36 minutes away
The death ‘dog’
Imagine you’re out in your backyard managing the grill for a big family barbecue. You’ve got a dazzling assortment of meat assorted on your fancy new propane grill, all charring nicely. Naturally, the hot dogs finish first, and as you pull them off, you figure you’ll help yourself to one now. After all, you are the chef, you deserve a reward. But, as you bite into your smoking hot sandwich, a cold, bony finger taps you on the shoulder. You turn and come face to face with the Grim Reaper. “YOU JUST LOST 36 MINUTES,” Death says. “ALSO, MAY I HAVE ONE OF THOSE? THEY LOOK DELICIOUS.”
Nonplussed and moving automatically, you scoop up another hot dog and place it in a bun. “WITH KETCHUP PLEASE,” Death says. “I NEVER CARED FOR MUSTARD.”
“I don’t understand,” you say. “Surely I won’t die at a family barbecue.”
“DO NOT CALL ME SHIRLEY,” Death says. “AND YOU WILL NOT. IT’S PART OF MY NEW CONTRACT.”
A new study, published in Nature Food, found that a person may lose up to 36 minutes for every hot dog consumed. Researchers from the University of Michigan analyzed nearly 6,000 different foods using a new nutritional index to quantify their health effects in minutes of healthy life lost or gained. Eating a serving of nuts adds an extra 26 minutes of life. The researchers determined that replacing just 10% of daily caloric intake from beef and processed foods with fruits, vegetables, and nuts can add 48 minutes per day. It would also reduce the daily carbon footprint by 33%.
“So you go around to everyone eating bad food and tell them how much life they’ve lost?” you ask when the Grim Reaper finishes his story. “Sounds like a drag.”
“IT IS. WE’VE HAD TO HIRE NEW BLOOD.” Death chuckles at its own bad pun. “NOW IF YOU’LL EXCUSE ME, I MUST CHASTISE A MAN IN FLORIDA FOR EATING A WELL-DONE STEAK.”
More stress, less sex
As the world becomes a more stressful place, the human population could face a 50% drop by the end of the century.
Think of stress as a one-two punch to the libido and human fertility. The more people are stressed out, the less likely they are to have quality interactions with others. Many of us would rather be alone with our wine and cheese to watch our favorite show.
Researchers have found that high stress levels have been known to drop sperm count, ovulation, and sexual activity. Guess what? There has been a 50% decrease in sperm counts over the last 50 years. That’s the second punch. But let’s not forget, the times are changing.
“Changes in reproductive behavior that contribute to the population drop include more young couples choosing to be ‘child-free,’ people having fewer children, and couples waiting longer to start families,” said Alexander Suvorov, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, the paper’s author.
Let’s summarize: The more stress we’re dealing with, the less people want to deal with each other.
Who would have thought the future would be less fun?
‘You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.’
WARNING: The following descriptions of COVID-19–related insanity may be offensive to some readers.
Greetings, ladies and gentlemen! Welcome to the first round of Pandemic Pandemonium. Let’s get right to the action.
This week’s preshow match-off involves face mask woes. The first comes to us from Alabama, where a woman wore a space helmet to a school board meeting to protest mask mandates. The second comes from Australia, in the form of mischievous magpies. We will explain.
It is not uncommon for magpies to attack those who come too close to their nests in the spring, or “swooping season,” as it’s affectionately called. The magpies are smart enough to recognize the faces of people they see regularly and not attack; however, it’s feared that mask wearing will change this.
While you’re chewing on that exciting appetizer, let’s take a look at our main course, which has a distinct governmental flavor. Jeff Landry is the attorney general of Louisiana, and, like our space-helmet wearer, he’s not a fan of mask mandates. According to Business Insider, Mr. Landry “drafted and distributed sample letters intended to help parents evade mask-wearing ordinances and COVID-19 vaccination requirements for their children in schools.”
Up against him is the Food and Drug Administration’s Twitter account. In an unrelated matter, the agency tweeted, “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” This was in response to people using the nonhuman forms of ivermectin to treat very human COVID-19.
Well, there you have it. Who will win tonight’s exciting edition of Pandemic Pandemonium? The first reader to contact us gets to decide the fate of these worthy contestants.
From venomous poison to heart drug
It’s not likely that anyone who sees a giant, venomous spider is thinking, “Hey! That thing could save my life!” It’s usually quite the opposite. Honestly, we would run away from just about any spider. But what if one of the deadliest spiders in the world could also save you from dying of a heart attack?
You probably don’t believe us, right? That’s fair, but the deadly Fraser Island (K’gari) funnel web spider, might also be the most helpful. Investigators from the University of Queensland in Australia have found a way to extract a molecule from the spider’s venom that might help stop damage from heart attacks and may even preserve hearts being used for transplants. “The Hi1a protein from spider venom blocks acid-sensing ion channels in the heart, so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” Nathan Palpant, PhD, of the university, noted in a written statement.
No one has ever developed a drug to stop the “death signal,” so maybe it’s time to befriend spiders instead of running away from them in horror. Just leave the venom extraction to the professionals.
The death ‘dog’
Imagine you’re out in your backyard managing the grill for a big family barbecue. You’ve got a dazzling assortment of meat assorted on your fancy new propane grill, all charring nicely. Naturally, the hot dogs finish first, and as you pull them off, you figure you’ll help yourself to one now. After all, you are the chef, you deserve a reward. But, as you bite into your smoking hot sandwich, a cold, bony finger taps you on the shoulder. You turn and come face to face with the Grim Reaper. “YOU JUST LOST 36 MINUTES,” Death says. “ALSO, MAY I HAVE ONE OF THOSE? THEY LOOK DELICIOUS.”
Nonplussed and moving automatically, you scoop up another hot dog and place it in a bun. “WITH KETCHUP PLEASE,” Death says. “I NEVER CARED FOR MUSTARD.”
“I don’t understand,” you say. “Surely I won’t die at a family barbecue.”
“DO NOT CALL ME SHIRLEY,” Death says. “AND YOU WILL NOT. IT’S PART OF MY NEW CONTRACT.”
A new study, published in Nature Food, found that a person may lose up to 36 minutes for every hot dog consumed. Researchers from the University of Michigan analyzed nearly 6,000 different foods using a new nutritional index to quantify their health effects in minutes of healthy life lost or gained. Eating a serving of nuts adds an extra 26 minutes of life. The researchers determined that replacing just 10% of daily caloric intake from beef and processed foods with fruits, vegetables, and nuts can add 48 minutes per day. It would also reduce the daily carbon footprint by 33%.
“So you go around to everyone eating bad food and tell them how much life they’ve lost?” you ask when the Grim Reaper finishes his story. “Sounds like a drag.”
“IT IS. WE’VE HAD TO HIRE NEW BLOOD.” Death chuckles at its own bad pun. “NOW IF YOU’LL EXCUSE ME, I MUST CHASTISE A MAN IN FLORIDA FOR EATING A WELL-DONE STEAK.”
More stress, less sex
As the world becomes a more stressful place, the human population could face a 50% drop by the end of the century.
Think of stress as a one-two punch to the libido and human fertility. The more people are stressed out, the less likely they are to have quality interactions with others. Many of us would rather be alone with our wine and cheese to watch our favorite show.
Researchers have found that high stress levels have been known to drop sperm count, ovulation, and sexual activity. Guess what? There has been a 50% decrease in sperm counts over the last 50 years. That’s the second punch. But let’s not forget, the times are changing.
“Changes in reproductive behavior that contribute to the population drop include more young couples choosing to be ‘child-free,’ people having fewer children, and couples waiting longer to start families,” said Alexander Suvorov, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, the paper’s author.
Let’s summarize: The more stress we’re dealing with, the less people want to deal with each other.
Who would have thought the future would be less fun?
‘You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.’
WARNING: The following descriptions of COVID-19–related insanity may be offensive to some readers.
Greetings, ladies and gentlemen! Welcome to the first round of Pandemic Pandemonium. Let’s get right to the action.
This week’s preshow match-off involves face mask woes. The first comes to us from Alabama, where a woman wore a space helmet to a school board meeting to protest mask mandates. The second comes from Australia, in the form of mischievous magpies. We will explain.
It is not uncommon for magpies to attack those who come too close to their nests in the spring, or “swooping season,” as it’s affectionately called. The magpies are smart enough to recognize the faces of people they see regularly and not attack; however, it’s feared that mask wearing will change this.
While you’re chewing on that exciting appetizer, let’s take a look at our main course, which has a distinct governmental flavor. Jeff Landry is the attorney general of Louisiana, and, like our space-helmet wearer, he’s not a fan of mask mandates. According to Business Insider, Mr. Landry “drafted and distributed sample letters intended to help parents evade mask-wearing ordinances and COVID-19 vaccination requirements for their children in schools.”
Up against him is the Food and Drug Administration’s Twitter account. In an unrelated matter, the agency tweeted, “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” This was in response to people using the nonhuman forms of ivermectin to treat very human COVID-19.
Well, there you have it. Who will win tonight’s exciting edition of Pandemic Pandemonium? The first reader to contact us gets to decide the fate of these worthy contestants.
From venomous poison to heart drug
It’s not likely that anyone who sees a giant, venomous spider is thinking, “Hey! That thing could save my life!” It’s usually quite the opposite. Honestly, we would run away from just about any spider. But what if one of the deadliest spiders in the world could also save you from dying of a heart attack?
You probably don’t believe us, right? That’s fair, but the deadly Fraser Island (K’gari) funnel web spider, might also be the most helpful. Investigators from the University of Queensland in Australia have found a way to extract a molecule from the spider’s venom that might help stop damage from heart attacks and may even preserve hearts being used for transplants. “The Hi1a protein from spider venom blocks acid-sensing ion channels in the heart, so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” Nathan Palpant, PhD, of the university, noted in a written statement.
No one has ever developed a drug to stop the “death signal,” so maybe it’s time to befriend spiders instead of running away from them in horror. Just leave the venom extraction to the professionals.
The death ‘dog’
Imagine you’re out in your backyard managing the grill for a big family barbecue. You’ve got a dazzling assortment of meat assorted on your fancy new propane grill, all charring nicely. Naturally, the hot dogs finish first, and as you pull them off, you figure you’ll help yourself to one now. After all, you are the chef, you deserve a reward. But, as you bite into your smoking hot sandwich, a cold, bony finger taps you on the shoulder. You turn and come face to face with the Grim Reaper. “YOU JUST LOST 36 MINUTES,” Death says. “ALSO, MAY I HAVE ONE OF THOSE? THEY LOOK DELICIOUS.”
Nonplussed and moving automatically, you scoop up another hot dog and place it in a bun. “WITH KETCHUP PLEASE,” Death says. “I NEVER CARED FOR MUSTARD.”
“I don’t understand,” you say. “Surely I won’t die at a family barbecue.”
“DO NOT CALL ME SHIRLEY,” Death says. “AND YOU WILL NOT. IT’S PART OF MY NEW CONTRACT.”
A new study, published in Nature Food, found that a person may lose up to 36 minutes for every hot dog consumed. Researchers from the University of Michigan analyzed nearly 6,000 different foods using a new nutritional index to quantify their health effects in minutes of healthy life lost or gained. Eating a serving of nuts adds an extra 26 minutes of life. The researchers determined that replacing just 10% of daily caloric intake from beef and processed foods with fruits, vegetables, and nuts can add 48 minutes per day. It would also reduce the daily carbon footprint by 33%.
“So you go around to everyone eating bad food and tell them how much life they’ve lost?” you ask when the Grim Reaper finishes his story. “Sounds like a drag.”
“IT IS. WE’VE HAD TO HIRE NEW BLOOD.” Death chuckles at its own bad pun. “NOW IF YOU’LL EXCUSE ME, I MUST CHASTISE A MAN IN FLORIDA FOR EATING A WELL-DONE STEAK.”
More stress, less sex
As the world becomes a more stressful place, the human population could face a 50% drop by the end of the century.
Think of stress as a one-two punch to the libido and human fertility. The more people are stressed out, the less likely they are to have quality interactions with others. Many of us would rather be alone with our wine and cheese to watch our favorite show.
Researchers have found that high stress levels have been known to drop sperm count, ovulation, and sexual activity. Guess what? There has been a 50% decrease in sperm counts over the last 50 years. That’s the second punch. But let’s not forget, the times are changing.
“Changes in reproductive behavior that contribute to the population drop include more young couples choosing to be ‘child-free,’ people having fewer children, and couples waiting longer to start families,” said Alexander Suvorov, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, the paper’s author.
Let’s summarize: The more stress we’re dealing with, the less people want to deal with each other.
Who would have thought the future would be less fun?
‘You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.’
WARNING: The following descriptions of COVID-19–related insanity may be offensive to some readers.
Greetings, ladies and gentlemen! Welcome to the first round of Pandemic Pandemonium. Let’s get right to the action.
This week’s preshow match-off involves face mask woes. The first comes to us from Alabama, where a woman wore a space helmet to a school board meeting to protest mask mandates. The second comes from Australia, in the form of mischievous magpies. We will explain.
It is not uncommon for magpies to attack those who come too close to their nests in the spring, or “swooping season,” as it’s affectionately called. The magpies are smart enough to recognize the faces of people they see regularly and not attack; however, it’s feared that mask wearing will change this.
While you’re chewing on that exciting appetizer, let’s take a look at our main course, which has a distinct governmental flavor. Jeff Landry is the attorney general of Louisiana, and, like our space-helmet wearer, he’s not a fan of mask mandates. According to Business Insider, Mr. Landry “drafted and distributed sample letters intended to help parents evade mask-wearing ordinances and COVID-19 vaccination requirements for their children in schools.”
Up against him is the Food and Drug Administration’s Twitter account. In an unrelated matter, the agency tweeted, “You are not a horse. You are not a cow. Seriously, y’all. Stop it.” This was in response to people using the nonhuman forms of ivermectin to treat very human COVID-19.
Well, there you have it. Who will win tonight’s exciting edition of Pandemic Pandemonium? The first reader to contact us gets to decide the fate of these worthy contestants.
From venomous poison to heart drug
It’s not likely that anyone who sees a giant, venomous spider is thinking, “Hey! That thing could save my life!” It’s usually quite the opposite. Honestly, we would run away from just about any spider. But what if one of the deadliest spiders in the world could also save you from dying of a heart attack?
You probably don’t believe us, right? That’s fair, but the deadly Fraser Island (K’gari) funnel web spider, might also be the most helpful. Investigators from the University of Queensland in Australia have found a way to extract a molecule from the spider’s venom that might help stop damage from heart attacks and may even preserve hearts being used for transplants. “The Hi1a protein from spider venom blocks acid-sensing ion channels in the heart, so the death message is blocked, cell death is reduced, and we see improved heart cell survival,” Nathan Palpant, PhD, of the university, noted in a written statement.
No one has ever developed a drug to stop the “death signal,” so maybe it’s time to befriend spiders instead of running away from them in horror. Just leave the venom extraction to the professionals.
Bimekizumab approved in Europe for psoriasis treatment
, according to a statement from the manufacturer.
Bimekizumab (Bimzelx), a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, is the first approved treatment for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)–17A and IL-17F, the statement from UCB said.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration is expected to make a decision on approval of bimekizumab for treating psoriasis on Oct. 15.
Approval in the EU was based on data from three phase 3 trials including a total of 1,480 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, which found that those treated with bimekizumab experienced significantly greater skin clearance, compared with placebo, ustekinumab, and adalimumab, with a favorable safety profile, according to the company.
In all three studies (BE VIVID, BE READY, and BE SURE), more than 80% of patients treated with bimekizumab showed improved skin clearance after 16 weeks, significantly more than those treated with ustekinumab, placebo, or adalimumab, based on an improvement of at least 90% in the Psoriasis Area & Severity Index (PASI 90) and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) response of clear or almost clear skin (IGA 0/1). In all three studies, these clinical responses persisted after 1 year.
The recommended dose of bimekizumab is 320 mg, given in two subcutaneous injections every 4 weeks to week 16, then every 8 weeks. However, for “some patients” weighing 120 kg or more who have not achieved complete skin clearance at 16 weeks, 320 mg every 4 weeks after that time may improve response to treatment, according to the company statement.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in the studies were upper respiratory tract infections (a majority of which were nasopharyngitis), reported by 14.5% of patients, followed by oral candidiasis, reported by 7.3%.
Results of BE READY and BE VIVID were published in The Lancet. Results of the BE SURE study were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Bimekizumab is contraindicated for individuals with clinically important active infections such as tuberculosis, and for individuals with any hypersensitivity to the active substance. More details on bimekizumab are available on the website of the European Medicines Agency.
, according to a statement from the manufacturer.
Bimekizumab (Bimzelx), a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, is the first approved treatment for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)–17A and IL-17F, the statement from UCB said.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration is expected to make a decision on approval of bimekizumab for treating psoriasis on Oct. 15.
Approval in the EU was based on data from three phase 3 trials including a total of 1,480 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, which found that those treated with bimekizumab experienced significantly greater skin clearance, compared with placebo, ustekinumab, and adalimumab, with a favorable safety profile, according to the company.
In all three studies (BE VIVID, BE READY, and BE SURE), more than 80% of patients treated with bimekizumab showed improved skin clearance after 16 weeks, significantly more than those treated with ustekinumab, placebo, or adalimumab, based on an improvement of at least 90% in the Psoriasis Area & Severity Index (PASI 90) and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) response of clear or almost clear skin (IGA 0/1). In all three studies, these clinical responses persisted after 1 year.
The recommended dose of bimekizumab is 320 mg, given in two subcutaneous injections every 4 weeks to week 16, then every 8 weeks. However, for “some patients” weighing 120 kg or more who have not achieved complete skin clearance at 16 weeks, 320 mg every 4 weeks after that time may improve response to treatment, according to the company statement.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in the studies were upper respiratory tract infections (a majority of which were nasopharyngitis), reported by 14.5% of patients, followed by oral candidiasis, reported by 7.3%.
Results of BE READY and BE VIVID were published in The Lancet. Results of the BE SURE study were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Bimekizumab is contraindicated for individuals with clinically important active infections such as tuberculosis, and for individuals with any hypersensitivity to the active substance. More details on bimekizumab are available on the website of the European Medicines Agency.
, according to a statement from the manufacturer.
Bimekizumab (Bimzelx), a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody, is the first approved treatment for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis that selectively inhibits interleukin (IL)–17A and IL-17F, the statement from UCB said.
In the United States, the Food and Drug Administration is expected to make a decision on approval of bimekizumab for treating psoriasis on Oct. 15.
Approval in the EU was based on data from three phase 3 trials including a total of 1,480 adult patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, which found that those treated with bimekizumab experienced significantly greater skin clearance, compared with placebo, ustekinumab, and adalimumab, with a favorable safety profile, according to the company.
In all three studies (BE VIVID, BE READY, and BE SURE), more than 80% of patients treated with bimekizumab showed improved skin clearance after 16 weeks, significantly more than those treated with ustekinumab, placebo, or adalimumab, based on an improvement of at least 90% in the Psoriasis Area & Severity Index (PASI 90) and an Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) response of clear or almost clear skin (IGA 0/1). In all three studies, these clinical responses persisted after 1 year.
The recommended dose of bimekizumab is 320 mg, given in two subcutaneous injections every 4 weeks to week 16, then every 8 weeks. However, for “some patients” weighing 120 kg or more who have not achieved complete skin clearance at 16 weeks, 320 mg every 4 weeks after that time may improve response to treatment, according to the company statement.
The most common treatment-related adverse events in the studies were upper respiratory tract infections (a majority of which were nasopharyngitis), reported by 14.5% of patients, followed by oral candidiasis, reported by 7.3%.
Results of BE READY and BE VIVID were published in The Lancet. Results of the BE SURE study were published in The New England Journal of Medicine.
Bimekizumab is contraindicated for individuals with clinically important active infections such as tuberculosis, and for individuals with any hypersensitivity to the active substance. More details on bimekizumab are available on the website of the European Medicines Agency.
Psoriatic arthritis health care costs continue to rise over time
Annual health care costs for patients with psoriatic arthritis rose over recent 5-year periods across all categories of resource use to a significantly greater extent than among patients with psoriasis only or those without any psoriatic disease diagnoses, according to commercial insurance claims data.
Using an IBM MarketScan Commercial Database, researchers examined claims data for 208,434 patients with psoriasis, 47,274 with PsA, and 255,708 controls who had neither psoriasis nor PsA. Controls were matched for age and sex. Those with RA, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis were excluded.
The investigators examined data for 2009-2020, following patients for 5 years within that period. They looked at hospitalizations, outpatient and pharmacy services, lab services, and office visits, Steven Peterson, director of market access for rheumatology at Janssen Pharmaceuticals, said in his presentation of the data at the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology 2021 annual meeting, held recently as a virtual event.
The research was also published online May 2, 2021, in Clinical Rheumatology.
Big differences between the groups were seen in the first year, when the average health care costs for the PsA group were $28,322, about half of which was outpatient drug costs. That compared with $12,039 for the psoriasis group and $6,672 for the control group.
The differences tended to widen over time. By the fifth year, average costs for the PsA group were $34,290, nearly 60% of which were drug costs. That compared with $12,877 for the psoriasis group and $8,569 for the control group. In each year examined, outpatient drug costs accounted for less than half of the expenses for the psoriasis group and about a quarter for the control group.
Researchers found that the PsA group needed 28.7 prescriptions per person per year, compared with 17.0 and 12.7 in the psoriasis and control groups, respectively, Mr. Peterson said. He also noted that patients with PsA and psoriasis tended to have higher rates of hypertension, depression, and anxiety.
“The cost and resource utilization disparity between these patient groups demonstrates the high remaining unmet medical need for patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis,” Mr. Peterson said during the virtual proceedings.
Do findings reflect treatment advances?
Elaine Husni, MD, MPH, director of the Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Center at the Cleveland Clinic, where she studies health outcomes in PsA, said the findings are helpful in pointing to a trend across a large sample. But she added it’s important to remember that the increasing costs could reflect recent advances in PsA treatment, which include costly biologic drugs.
“There’s a ton more treatments for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis than there were even just 5 years ago,” she said in an interview. She was not involved in the research.
Dr. Husni would like to see a more detailed look at the costs, from the categories of expenses to the patients who are incurring the highest costs.
“Is it just a couple of percent of really sick patients that are driving the psoriatic arthritis group?” she wondered.
She also pointed out that PsA is going to be more expensive by its very nature. PsA tends to develop 3-10 years after psoriasis, adding to the costs for someone who already has psoriasis and at a time when they are older and likely have higher health care costs because of comorbidities that develop with age.
Dr. Husni said she does think about treatment costs, in that a less expensive first-line drug might be more appropriate than going straight to a more expensive biologic, especially because they also tend to be safer. She said it’s not just a simple question of curbing costs.
“Is there a way that we can personalize medicine?” she asked. “Is there a way that we can be more accurate about which people may need the more expensive drugs, and which patients may need the less expensive drugs? Are we getting better at monitoring so we can avoid high-cost events?”
Mr. Peterson is an employee of Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Husni reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB, Novartis, Lilly, and Pfizer.
* Update, 9/28/21: The headline and parts of this story were updated to better reflect the study on which it reports.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Annual health care costs for patients with psoriatic arthritis rose over recent 5-year periods across all categories of resource use to a significantly greater extent than among patients with psoriasis only or those without any psoriatic disease diagnoses, according to commercial insurance claims data.
Using an IBM MarketScan Commercial Database, researchers examined claims data for 208,434 patients with psoriasis, 47,274 with PsA, and 255,708 controls who had neither psoriasis nor PsA. Controls were matched for age and sex. Those with RA, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis were excluded.
The investigators examined data for 2009-2020, following patients for 5 years within that period. They looked at hospitalizations, outpatient and pharmacy services, lab services, and office visits, Steven Peterson, director of market access for rheumatology at Janssen Pharmaceuticals, said in his presentation of the data at the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology 2021 annual meeting, held recently as a virtual event.
The research was also published online May 2, 2021, in Clinical Rheumatology.
Big differences between the groups were seen in the first year, when the average health care costs for the PsA group were $28,322, about half of which was outpatient drug costs. That compared with $12,039 for the psoriasis group and $6,672 for the control group.
The differences tended to widen over time. By the fifth year, average costs for the PsA group were $34,290, nearly 60% of which were drug costs. That compared with $12,877 for the psoriasis group and $8,569 for the control group. In each year examined, outpatient drug costs accounted for less than half of the expenses for the psoriasis group and about a quarter for the control group.
Researchers found that the PsA group needed 28.7 prescriptions per person per year, compared with 17.0 and 12.7 in the psoriasis and control groups, respectively, Mr. Peterson said. He also noted that patients with PsA and psoriasis tended to have higher rates of hypertension, depression, and anxiety.
“The cost and resource utilization disparity between these patient groups demonstrates the high remaining unmet medical need for patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis,” Mr. Peterson said during the virtual proceedings.
Do findings reflect treatment advances?
Elaine Husni, MD, MPH, director of the Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Center at the Cleveland Clinic, where she studies health outcomes in PsA, said the findings are helpful in pointing to a trend across a large sample. But she added it’s important to remember that the increasing costs could reflect recent advances in PsA treatment, which include costly biologic drugs.
“There’s a ton more treatments for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis than there were even just 5 years ago,” she said in an interview. She was not involved in the research.
Dr. Husni would like to see a more detailed look at the costs, from the categories of expenses to the patients who are incurring the highest costs.
“Is it just a couple of percent of really sick patients that are driving the psoriatic arthritis group?” she wondered.
She also pointed out that PsA is going to be more expensive by its very nature. PsA tends to develop 3-10 years after psoriasis, adding to the costs for someone who already has psoriasis and at a time when they are older and likely have higher health care costs because of comorbidities that develop with age.
Dr. Husni said she does think about treatment costs, in that a less expensive first-line drug might be more appropriate than going straight to a more expensive biologic, especially because they also tend to be safer. She said it’s not just a simple question of curbing costs.
“Is there a way that we can personalize medicine?” she asked. “Is there a way that we can be more accurate about which people may need the more expensive drugs, and which patients may need the less expensive drugs? Are we getting better at monitoring so we can avoid high-cost events?”
Mr. Peterson is an employee of Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Husni reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB, Novartis, Lilly, and Pfizer.
* Update, 9/28/21: The headline and parts of this story were updated to better reflect the study on which it reports.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Annual health care costs for patients with psoriatic arthritis rose over recent 5-year periods across all categories of resource use to a significantly greater extent than among patients with psoriasis only or those without any psoriatic disease diagnoses, according to commercial insurance claims data.
Using an IBM MarketScan Commercial Database, researchers examined claims data for 208,434 patients with psoriasis, 47,274 with PsA, and 255,708 controls who had neither psoriasis nor PsA. Controls were matched for age and sex. Those with RA, ankylosing spondylitis, Crohn’s disease, or ulcerative colitis were excluded.
The investigators examined data for 2009-2020, following patients for 5 years within that period. They looked at hospitalizations, outpatient and pharmacy services, lab services, and office visits, Steven Peterson, director of market access for rheumatology at Janssen Pharmaceuticals, said in his presentation of the data at the Pan American League of Associations for Rheumatology 2021 annual meeting, held recently as a virtual event.
The research was also published online May 2, 2021, in Clinical Rheumatology.
Big differences between the groups were seen in the first year, when the average health care costs for the PsA group were $28,322, about half of which was outpatient drug costs. That compared with $12,039 for the psoriasis group and $6,672 for the control group.
The differences tended to widen over time. By the fifth year, average costs for the PsA group were $34,290, nearly 60% of which were drug costs. That compared with $12,877 for the psoriasis group and $8,569 for the control group. In each year examined, outpatient drug costs accounted for less than half of the expenses for the psoriasis group and about a quarter for the control group.
Researchers found that the PsA group needed 28.7 prescriptions per person per year, compared with 17.0 and 12.7 in the psoriasis and control groups, respectively, Mr. Peterson said. He also noted that patients with PsA and psoriasis tended to have higher rates of hypertension, depression, and anxiety.
“The cost and resource utilization disparity between these patient groups demonstrates the high remaining unmet medical need for patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis,” Mr. Peterson said during the virtual proceedings.
Do findings reflect treatment advances?
Elaine Husni, MD, MPH, director of the Arthritis and Musculoskeletal Center at the Cleveland Clinic, where she studies health outcomes in PsA, said the findings are helpful in pointing to a trend across a large sample. But she added it’s important to remember that the increasing costs could reflect recent advances in PsA treatment, which include costly biologic drugs.
“There’s a ton more treatments for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis than there were even just 5 years ago,” she said in an interview. She was not involved in the research.
Dr. Husni would like to see a more detailed look at the costs, from the categories of expenses to the patients who are incurring the highest costs.
“Is it just a couple of percent of really sick patients that are driving the psoriatic arthritis group?” she wondered.
She also pointed out that PsA is going to be more expensive by its very nature. PsA tends to develop 3-10 years after psoriasis, adding to the costs for someone who already has psoriasis and at a time when they are older and likely have higher health care costs because of comorbidities that develop with age.
Dr. Husni said she does think about treatment costs, in that a less expensive first-line drug might be more appropriate than going straight to a more expensive biologic, especially because they also tend to be safer. She said it’s not just a simple question of curbing costs.
“Is there a way that we can personalize medicine?” she asked. “Is there a way that we can be more accurate about which people may need the more expensive drugs, and which patients may need the less expensive drugs? Are we getting better at monitoring so we can avoid high-cost events?”
Mr. Peterson is an employee of Janssen Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Husni reported serving as a consultant to AbbVie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, UCB, Novartis, Lilly, and Pfizer.
* Update, 9/28/21: The headline and parts of this story were updated to better reflect the study on which it reports.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Review eyes nail unit toxicities secondary to targeted cancer therapy
while damage to other nail unit anatomic areas can be wide-ranging.
Those are key findings from an evidence-based literature review published on July 21, 2021, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, as a letter to the editor. “Dermatologic toxicities are often the earliest-presenting and highest-incidence adverse events due to targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies,” corresponding author Anisha B. Patel, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues wrote. “Nail unit toxicities due to immunotherapy are caused by nonspecific immune activation. Targeted therapies, particularly mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibitors, lead to epidermal thinning of the nail folds and periungual tissue, increasing susceptibility to trauma and penetration by nail plate fragments. Although cutaneous toxicities have been well described, further characterization of nail unit toxicities is needed.”
The researchers searched the PubMed database using the terms nail, nail toxicity, nail dystrophy, paronychia, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, onychopathy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and reviewed relevant articles for clinical presentation, diagnosis, incidence, outcomes, and references. They also proposed treatment algorithms for this patient population based on the existing literature and the authors’ collective clinical experience.
Dr. Patel and colleagues found that paronychia and periungual pyogenic granulomas were the most common nail unit toxicities caused by targeted therapy. “Damage to other nail unit anatomic areas includes drug induced or exacerbated lichen planus and psoriasis as well as pigmentary and neoplastic changes,” they wrote. “Onycholysis, onychoschizia, paronychia, psoriasis, lichen planus, and dermatomyositis have been reported with immune checkpoint inhibitors,” with the time of onset during the first week of treatment to several months after treatment has started.
According to National Cancer Institute criteria, nail adverse events associated with medical treatment include nail changes, discoloration, ridging, paronychia, and infection. The severity of nail loss, paronychia, and infection can be graded up to 3 (defined as “severe or medically significant but not life threatening”), while the remainder of nail toxicities may be categorized only as grade 1 (defined as “mild,” with “intervention not indicated”). “High-grade toxicities have been reported, especially with pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors,” the authors wrote, referring to a previous study.
The review includes treatment algorithms for paronychia, periungual pyogenic granuloma, nail lichen planus, and psoriasis. “Long-acting and nonselective immunosuppressants are reserved for dose-limiting toxicities, given their unknown effects on already-immunosuppressed patients with cancer and on cancer therapy,” the authors wrote. “A discussion with the oncology department is essential before starting an immunomodulator or immunosuppressant.”
To manage onycholysis, Dr. Patel and colleagues recommended trimming the onycholytic nail plate to its attachment point. “Partial avulsion is used to treat a refractory abscess or painful hemorrhage,” they wrote. “A Pseudomonas superinfection is treated twice daily with a topical antibiotic solution. Brittle nail syndrome is managed with emollients or the application of polyureaurethane, a 16% nail solution, or a hydrosoluble nail lacquer,” they wrote, adding that biotin supplementation is not recommended.
Jonathan Leventhal, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that nail toxicity from targeted cancer therapy is one of the most common reasons for consultation in his role as director of the Yale University oncodermatology program at Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, Conn. “When severe, these reactions frequently impact patients’ quality of life,” he said.
“This study is helpful for all dermatologists caring for cancer patients,” with strengths that include “succinctly summarizing the most prevalent conditions and providing a clear and practical algorithm for approaching these nail toxicities,” he said. In addition to targeted agents and immunotherapy, “we commonly see nail toxicities from cytotoxic chemotherapy, which was not reviewed in this paper. Multidisciplinary evaluation and dermatologic involvement is certainly beneficial to make accurate diagnoses and promptly manage these conditions, helping patients stay on their oncologic therapies.”
The researchers reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Leventhal disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Regeneron, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and La Roche–Posay. He has also received research funding from Azitra and OnQuality.
while damage to other nail unit anatomic areas can be wide-ranging.
Those are key findings from an evidence-based literature review published on July 21, 2021, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, as a letter to the editor. “Dermatologic toxicities are often the earliest-presenting and highest-incidence adverse events due to targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies,” corresponding author Anisha B. Patel, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues wrote. “Nail unit toxicities due to immunotherapy are caused by nonspecific immune activation. Targeted therapies, particularly mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibitors, lead to epidermal thinning of the nail folds and periungual tissue, increasing susceptibility to trauma and penetration by nail plate fragments. Although cutaneous toxicities have been well described, further characterization of nail unit toxicities is needed.”
The researchers searched the PubMed database using the terms nail, nail toxicity, nail dystrophy, paronychia, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, onychopathy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and reviewed relevant articles for clinical presentation, diagnosis, incidence, outcomes, and references. They also proposed treatment algorithms for this patient population based on the existing literature and the authors’ collective clinical experience.
Dr. Patel and colleagues found that paronychia and periungual pyogenic granulomas were the most common nail unit toxicities caused by targeted therapy. “Damage to other nail unit anatomic areas includes drug induced or exacerbated lichen planus and psoriasis as well as pigmentary and neoplastic changes,” they wrote. “Onycholysis, onychoschizia, paronychia, psoriasis, lichen planus, and dermatomyositis have been reported with immune checkpoint inhibitors,” with the time of onset during the first week of treatment to several months after treatment has started.
According to National Cancer Institute criteria, nail adverse events associated with medical treatment include nail changes, discoloration, ridging, paronychia, and infection. The severity of nail loss, paronychia, and infection can be graded up to 3 (defined as “severe or medically significant but not life threatening”), while the remainder of nail toxicities may be categorized only as grade 1 (defined as “mild,” with “intervention not indicated”). “High-grade toxicities have been reported, especially with pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors,” the authors wrote, referring to a previous study.
The review includes treatment algorithms for paronychia, periungual pyogenic granuloma, nail lichen planus, and psoriasis. “Long-acting and nonselective immunosuppressants are reserved for dose-limiting toxicities, given their unknown effects on already-immunosuppressed patients with cancer and on cancer therapy,” the authors wrote. “A discussion with the oncology department is essential before starting an immunomodulator or immunosuppressant.”
To manage onycholysis, Dr. Patel and colleagues recommended trimming the onycholytic nail plate to its attachment point. “Partial avulsion is used to treat a refractory abscess or painful hemorrhage,” they wrote. “A Pseudomonas superinfection is treated twice daily with a topical antibiotic solution. Brittle nail syndrome is managed with emollients or the application of polyureaurethane, a 16% nail solution, or a hydrosoluble nail lacquer,” they wrote, adding that biotin supplementation is not recommended.
Jonathan Leventhal, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that nail toxicity from targeted cancer therapy is one of the most common reasons for consultation in his role as director of the Yale University oncodermatology program at Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, Conn. “When severe, these reactions frequently impact patients’ quality of life,” he said.
“This study is helpful for all dermatologists caring for cancer patients,” with strengths that include “succinctly summarizing the most prevalent conditions and providing a clear and practical algorithm for approaching these nail toxicities,” he said. In addition to targeted agents and immunotherapy, “we commonly see nail toxicities from cytotoxic chemotherapy, which was not reviewed in this paper. Multidisciplinary evaluation and dermatologic involvement is certainly beneficial to make accurate diagnoses and promptly manage these conditions, helping patients stay on their oncologic therapies.”
The researchers reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Leventhal disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Regeneron, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and La Roche–Posay. He has also received research funding from Azitra and OnQuality.
while damage to other nail unit anatomic areas can be wide-ranging.
Those are key findings from an evidence-based literature review published on July 21, 2021, in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, as a letter to the editor. “Dermatologic toxicities are often the earliest-presenting and highest-incidence adverse events due to targeted anticancer therapies and immunotherapies,” corresponding author Anisha B. Patel, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues wrote. “Nail unit toxicities due to immunotherapy are caused by nonspecific immune activation. Targeted therapies, particularly mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway inhibitors, lead to epidermal thinning of the nail folds and periungual tissue, increasing susceptibility to trauma and penetration by nail plate fragments. Although cutaneous toxicities have been well described, further characterization of nail unit toxicities is needed.”
The researchers searched the PubMed database using the terms nail, nail toxicity, nail dystrophy, paronychia, onycholysis, pyogenic granuloma, onychopathy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy, and reviewed relevant articles for clinical presentation, diagnosis, incidence, outcomes, and references. They also proposed treatment algorithms for this patient population based on the existing literature and the authors’ collective clinical experience.
Dr. Patel and colleagues found that paronychia and periungual pyogenic granulomas were the most common nail unit toxicities caused by targeted therapy. “Damage to other nail unit anatomic areas includes drug induced or exacerbated lichen planus and psoriasis as well as pigmentary and neoplastic changes,” they wrote. “Onycholysis, onychoschizia, paronychia, psoriasis, lichen planus, and dermatomyositis have been reported with immune checkpoint inhibitors,” with the time of onset during the first week of treatment to several months after treatment has started.
According to National Cancer Institute criteria, nail adverse events associated with medical treatment include nail changes, discoloration, ridging, paronychia, and infection. The severity of nail loss, paronychia, and infection can be graded up to 3 (defined as “severe or medically significant but not life threatening”), while the remainder of nail toxicities may be categorized only as grade 1 (defined as “mild,” with “intervention not indicated”). “High-grade toxicities have been reported, especially with pan-fibroblast growth factor receptor inhibitors,” the authors wrote, referring to a previous study.
The review includes treatment algorithms for paronychia, periungual pyogenic granuloma, nail lichen planus, and psoriasis. “Long-acting and nonselective immunosuppressants are reserved for dose-limiting toxicities, given their unknown effects on already-immunosuppressed patients with cancer and on cancer therapy,” the authors wrote. “A discussion with the oncology department is essential before starting an immunomodulator or immunosuppressant.”
To manage onycholysis, Dr. Patel and colleagues recommended trimming the onycholytic nail plate to its attachment point. “Partial avulsion is used to treat a refractory abscess or painful hemorrhage,” they wrote. “A Pseudomonas superinfection is treated twice daily with a topical antibiotic solution. Brittle nail syndrome is managed with emollients or the application of polyureaurethane, a 16% nail solution, or a hydrosoluble nail lacquer,” they wrote, adding that biotin supplementation is not recommended.
Jonathan Leventhal, MD, who was asked to comment on the study, said that nail toxicity from targeted cancer therapy is one of the most common reasons for consultation in his role as director of the Yale University oncodermatology program at Smilow Cancer Hospital, New Haven, Conn. “When severe, these reactions frequently impact patients’ quality of life,” he said.
“This study is helpful for all dermatologists caring for cancer patients,” with strengths that include “succinctly summarizing the most prevalent conditions and providing a clear and practical algorithm for approaching these nail toxicities,” he said. In addition to targeted agents and immunotherapy, “we commonly see nail toxicities from cytotoxic chemotherapy, which was not reviewed in this paper. Multidisciplinary evaluation and dermatologic involvement is certainly beneficial to make accurate diagnoses and promptly manage these conditions, helping patients stay on their oncologic therapies.”
The researchers reported no financial disclosures. Dr. Leventhal disclosed that he is a member of the advisory board for Regeneron, Sanofi, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and La Roche–Posay. He has also received research funding from Azitra and OnQuality.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Health care workers eager for COVID booster shots
As COVID vaccine boosters move closer to reality, most physicians and nurses are ready and willing to get another shot in the arm, according to a new Medscape survey.
Altogether, 93% of physicians and 87% of nurses/advanced practice nurses (APNs) said they wanted to get a booster, although the timing of when they wanted the shots differed somewhat between the two groups surveyed Aug. 4-15.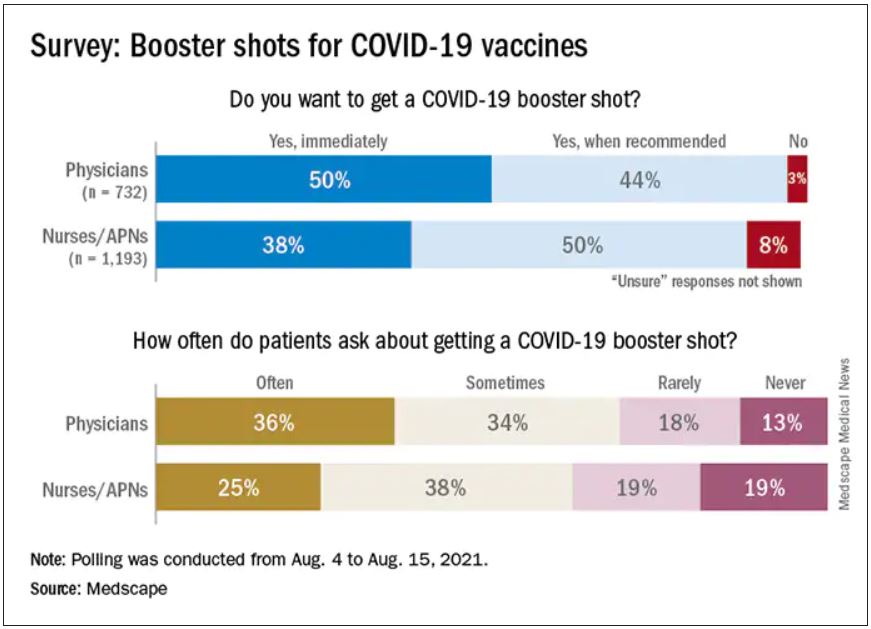
Among the 732 physicians polled, 50% wanted to get their shot immediately, compared with 38% of the 1,193 nurses/APNs who responded, while 44% of physicians and 50% of nurses/APNs said that they would wait until the vaccine booster was authorized and recommended.
At this point in time, almost all of the health care workers surveyed – 98% of physicians and 94% of nurses/APNs – have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. A small proportion of each group, however, received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (1% of physicians and 3% of nurses) and are not included in the current plan for booster shots.
The Medscape survey sample did include one group that is already eligible for a third dose: About 20% of physicians and 26% of nurses/ANPs said they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system.
Respondents’ experiences with patient requests for boosters suggest a somewhat lower level of interest. About two-thirds of the health care workers (69% of physicians and 63% of nurses) said that patients frequently or sometimes asked about COVID boosters, compared with 13% (physicians) and 19% (nurses) who said their patients had never asked.
Interest lower among general population
In a separate survey conducted by WebMD, 82% of those who have been at least partially vaccinated said they want to get a COVID vaccine booster (14% immediately and 68% after authorization and recommendation). Of the remaining vaccinees, 7% said they do not want to get a booster and 11% were unsure.
The full sample of 592 respondents surveyed Aug. 5-10, however, included 19% who do not plan to get vaccinated and 6% who are planning to be vaccinated but have not yet done so.
The proportion of immunocompromised individuals in the two survey groups was similar, with about 25% of those in the WebMD survey reporting they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system. Those respondents were more than twice as likely to want to get a booster immediately, compared to those with an uncompromised immune system (24% vs. 11%).
The distribution of vaccines received by brand was also comparable between the two groups surveyed. Of health care workers and readers, over half of each group received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (59% vs. 54%), followed by Moderna (38% vs. 40%) and Johnson & Johnson (3% vs. 5%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID vaccine boosters move closer to reality, most physicians and nurses are ready and willing to get another shot in the arm, according to a new Medscape survey.
Altogether, 93% of physicians and 87% of nurses/advanced practice nurses (APNs) said they wanted to get a booster, although the timing of when they wanted the shots differed somewhat between the two groups surveyed Aug. 4-15.
Among the 732 physicians polled, 50% wanted to get their shot immediately, compared with 38% of the 1,193 nurses/APNs who responded, while 44% of physicians and 50% of nurses/APNs said that they would wait until the vaccine booster was authorized and recommended.
At this point in time, almost all of the health care workers surveyed – 98% of physicians and 94% of nurses/APNs – have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. A small proportion of each group, however, received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (1% of physicians and 3% of nurses) and are not included in the current plan for booster shots.
The Medscape survey sample did include one group that is already eligible for a third dose: About 20% of physicians and 26% of nurses/ANPs said they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system.
Respondents’ experiences with patient requests for boosters suggest a somewhat lower level of interest. About two-thirds of the health care workers (69% of physicians and 63% of nurses) said that patients frequently or sometimes asked about COVID boosters, compared with 13% (physicians) and 19% (nurses) who said their patients had never asked.
Interest lower among general population
In a separate survey conducted by WebMD, 82% of those who have been at least partially vaccinated said they want to get a COVID vaccine booster (14% immediately and 68% after authorization and recommendation). Of the remaining vaccinees, 7% said they do not want to get a booster and 11% were unsure.
The full sample of 592 respondents surveyed Aug. 5-10, however, included 19% who do not plan to get vaccinated and 6% who are planning to be vaccinated but have not yet done so.
The proportion of immunocompromised individuals in the two survey groups was similar, with about 25% of those in the WebMD survey reporting they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system. Those respondents were more than twice as likely to want to get a booster immediately, compared to those with an uncompromised immune system (24% vs. 11%).
The distribution of vaccines received by brand was also comparable between the two groups surveyed. Of health care workers and readers, over half of each group received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (59% vs. 54%), followed by Moderna (38% vs. 40%) and Johnson & Johnson (3% vs. 5%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID vaccine boosters move closer to reality, most physicians and nurses are ready and willing to get another shot in the arm, according to a new Medscape survey.
Altogether, 93% of physicians and 87% of nurses/advanced practice nurses (APNs) said they wanted to get a booster, although the timing of when they wanted the shots differed somewhat between the two groups surveyed Aug. 4-15.
Among the 732 physicians polled, 50% wanted to get their shot immediately, compared with 38% of the 1,193 nurses/APNs who responded, while 44% of physicians and 50% of nurses/APNs said that they would wait until the vaccine booster was authorized and recommended.
At this point in time, almost all of the health care workers surveyed – 98% of physicians and 94% of nurses/APNs – have been fully vaccinated against COVID-19. A small proportion of each group, however, received the Johnson & Johnson vaccine (1% of physicians and 3% of nurses) and are not included in the current plan for booster shots.
The Medscape survey sample did include one group that is already eligible for a third dose: About 20% of physicians and 26% of nurses/ANPs said they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system.
Respondents’ experiences with patient requests for boosters suggest a somewhat lower level of interest. About two-thirds of the health care workers (69% of physicians and 63% of nurses) said that patients frequently or sometimes asked about COVID boosters, compared with 13% (physicians) and 19% (nurses) who said their patients had never asked.
Interest lower among general population
In a separate survey conducted by WebMD, 82% of those who have been at least partially vaccinated said they want to get a COVID vaccine booster (14% immediately and 68% after authorization and recommendation). Of the remaining vaccinees, 7% said they do not want to get a booster and 11% were unsure.
The full sample of 592 respondents surveyed Aug. 5-10, however, included 19% who do not plan to get vaccinated and 6% who are planning to be vaccinated but have not yet done so.
The proportion of immunocompromised individuals in the two survey groups was similar, with about 25% of those in the WebMD survey reporting they have a condition or take a medication that compromises their immune system. Those respondents were more than twice as likely to want to get a booster immediately, compared to those with an uncompromised immune system (24% vs. 11%).
The distribution of vaccines received by brand was also comparable between the two groups surveyed. Of health care workers and readers, over half of each group received the Pfizer/BioNTech vaccine (59% vs. 54%), followed by Moderna (38% vs. 40%) and Johnson & Johnson (3% vs. 5%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Plastic barriers may not stop COVID-19 spread, experts say
Plastic barriers that separate people in stores, restaurants, and classrooms may not be as effective at stopping the spread of COVID-19 as originally thought, according to The New York Times.
Scientists who study air flow, ventilation, and aerosol droplets say the barriers may not help, and in fact, could make the situation worse by blocking normal air flow, the newspaper reported.
Typically, as people interact and breathe in a room, currents and ventilation systems recirculate the air and disperse the exhaled particles. With plastic barriers, however, particles could get trapped in “dead zones” and build up.
“If you have a forest of barriers in a classroom, it’s going to interfere with proper ventilation of that room,” Linsey Marr, professor of civil and environmental engineering at Virginia Tech, told the newspaper.
“Everybody’s aerosols are going to be trapped and stuck there and building up, and they will end up spreading beyond your own desk,” she said.
Several variables factor into the efficacy of plastic barriers, The New York Times reported. Shields may stop big respiratory droplets from coughs and sneezes, for instance, but they may not do much to prevent small aerosol particles from viruses such as COVID-19 from spreading.
“We have shown this effect of blocking larger particles, but also that the smaller aerosols travel over the screen and become mixed in the room air within about 5 minutes,” Catherine Noakes, professor of environment engineering at the University of Leeds, told the newspaper.
“This means if people are interacting for more than a few minutes, they would likely be exposed to the virus regardless of the screen,” she said.
The effectiveness of plastic barriers likely also depends on the location and setup, the newspaper reported. A bus driver with a large barrier, for instance, may be able to avoid inhaling the particles that passengers are exhaling. A bank cashier or store clerk behind a large barrier may also be partly protected.
Even still, scientists say more research is needed. For instance, taller barriers are more likely to be effective. However, a large number of barriers in one room could likely block air flow.
Researchers have recommended that schools and offices focus on ventilation, masks, and vaccines to slow the spread of the coronavirus.
“Air flow in rooms is pretty complicated,” Richard Corsi, dean of engineering at the University of California at Davis, told the newspaper.
“Every room is different in terms of the arrangement of furniture, the height of the walls and ceilings, the vents, where the bookshelves are,” he said. “All of these things have a huge impact on the actual flow and air distribution in a room.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Plastic barriers that separate people in stores, restaurants, and classrooms may not be as effective at stopping the spread of COVID-19 as originally thought, according to The New York Times.
Scientists who study air flow, ventilation, and aerosol droplets say the barriers may not help, and in fact, could make the situation worse by blocking normal air flow, the newspaper reported.
Typically, as people interact and breathe in a room, currents and ventilation systems recirculate the air and disperse the exhaled particles. With plastic barriers, however, particles could get trapped in “dead zones” and build up.
“If you have a forest of barriers in a classroom, it’s going to interfere with proper ventilation of that room,” Linsey Marr, professor of civil and environmental engineering at Virginia Tech, told the newspaper.
“Everybody’s aerosols are going to be trapped and stuck there and building up, and they will end up spreading beyond your own desk,” she said.
Several variables factor into the efficacy of plastic barriers, The New York Times reported. Shields may stop big respiratory droplets from coughs and sneezes, for instance, but they may not do much to prevent small aerosol particles from viruses such as COVID-19 from spreading.
“We have shown this effect of blocking larger particles, but also that the smaller aerosols travel over the screen and become mixed in the room air within about 5 minutes,” Catherine Noakes, professor of environment engineering at the University of Leeds, told the newspaper.
“This means if people are interacting for more than a few minutes, they would likely be exposed to the virus regardless of the screen,” she said.
The effectiveness of plastic barriers likely also depends on the location and setup, the newspaper reported. A bus driver with a large barrier, for instance, may be able to avoid inhaling the particles that passengers are exhaling. A bank cashier or store clerk behind a large barrier may also be partly protected.
Even still, scientists say more research is needed. For instance, taller barriers are more likely to be effective. However, a large number of barriers in one room could likely block air flow.
Researchers have recommended that schools and offices focus on ventilation, masks, and vaccines to slow the spread of the coronavirus.
“Air flow in rooms is pretty complicated,” Richard Corsi, dean of engineering at the University of California at Davis, told the newspaper.
“Every room is different in terms of the arrangement of furniture, the height of the walls and ceilings, the vents, where the bookshelves are,” he said. “All of these things have a huge impact on the actual flow and air distribution in a room.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Plastic barriers that separate people in stores, restaurants, and classrooms may not be as effective at stopping the spread of COVID-19 as originally thought, according to The New York Times.
Scientists who study air flow, ventilation, and aerosol droplets say the barriers may not help, and in fact, could make the situation worse by blocking normal air flow, the newspaper reported.
Typically, as people interact and breathe in a room, currents and ventilation systems recirculate the air and disperse the exhaled particles. With plastic barriers, however, particles could get trapped in “dead zones” and build up.
“If you have a forest of barriers in a classroom, it’s going to interfere with proper ventilation of that room,” Linsey Marr, professor of civil and environmental engineering at Virginia Tech, told the newspaper.
“Everybody’s aerosols are going to be trapped and stuck there and building up, and they will end up spreading beyond your own desk,” she said.
Several variables factor into the efficacy of plastic barriers, The New York Times reported. Shields may stop big respiratory droplets from coughs and sneezes, for instance, but they may not do much to prevent small aerosol particles from viruses such as COVID-19 from spreading.
“We have shown this effect of blocking larger particles, but also that the smaller aerosols travel over the screen and become mixed in the room air within about 5 minutes,” Catherine Noakes, professor of environment engineering at the University of Leeds, told the newspaper.
“This means if people are interacting for more than a few minutes, they would likely be exposed to the virus regardless of the screen,” she said.
The effectiveness of plastic barriers likely also depends on the location and setup, the newspaper reported. A bus driver with a large barrier, for instance, may be able to avoid inhaling the particles that passengers are exhaling. A bank cashier or store clerk behind a large barrier may also be partly protected.
Even still, scientists say more research is needed. For instance, taller barriers are more likely to be effective. However, a large number of barriers in one room could likely block air flow.
Researchers have recommended that schools and offices focus on ventilation, masks, and vaccines to slow the spread of the coronavirus.
“Air flow in rooms is pretty complicated,” Richard Corsi, dean of engineering at the University of California at Davis, told the newspaper.
“Every room is different in terms of the arrangement of furniture, the height of the walls and ceilings, the vents, where the bookshelves are,” he said. “All of these things have a huge impact on the actual flow and air distribution in a room.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FDA fully approves Pfizer COVID-19 vaccine
The Food and Drug Administration has granted a biological license application, more commonly known as “full approval,” to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
It is the first COVID-19 vaccine to be fully licensed in the United States. It will be marketed under the trade name Comirnaty.
The approval applies to individuals ages 16 years and older. The vaccine is still available for emergency use for those ages 12-15.
The FDA’s stamp of approval is somewhat anticlimactic, following months of real-world use and millions of doses doled out to the general population. It comes after months of scrutiny by the agency of the clinical trial data.
Still, the approval puts the vaccines on firmer legal footing and is expected to spur a raft of new vaccination requirements by employers, schools, and universities.
“The FDA approval is the gold standard,” President Joe Biden said from the White House. “Those who have been waiting for full approval should go and get your shot now.”
“It could save your life or the lives of those you love,” he said.
Biden also called on businesses to mandate COVID vaccines for their employees.
Indeed, soon after the approval was announced, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said the vaccines would be required for all 1.4 million active duty service members.
Public health advocates have seen full approval as an important tool to increase U.S. vaccination rates and had criticized the FDA for taking so long to grant the license.
In a news briefing on the approval, Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had not dragged its feet.
Marks noted that his team had reviewed tens of thousands of pages of clinical trial data -- down to the level of individual patients. They also inspected clinical trial sites and manufacturing facilities, and reviewed information gathered after the vaccines were authorized for use.
“It’s been 97 days since Pfizer completed the role of its [application for approval] and the clock started, which means that we completed this in about 40% of the normal clock time for a submission of this magnitude,” he said. “People worked day and night.”
The agency resisted pressure to speed up its process, saying a thorough review was necessary to ensure public confidence.
“While millions of people have already safely received COVID-19 vaccines, we recognize that for some, the FDA approval of a vaccine may now instill additional confidence to get vaccinated. Today’s milestone puts us one step closer to altering the course of this pandemic in the U.S.,” acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock said in a FDA news release.
Experts agreed the move would increase public confidence.
“I don't expect a big line outside of vaccination sites this afternoon or tomorrow morning, but it will persuade some,” said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
A recent Kaiser Family Foundation poll found that 3 in 10 unvaccinated adults said they would be more likely to get vaccinated if the vaccines were given full approval.
More importantly, Schaffner said, the FDA’s approval would lay the groundwork for vaccine mandates. “I think those kinds of mandates are going to be necessary to get us up over 80% vaccinated.”
In granting the approval, the agency reviewed a record amount of data from more than 40,000 people who took part in clinical trials. About 12,000 recipients have been followed for at least 6 months, the agency said.
The FDA also reviewed safety data collected since it issued its emergency use authorization for the shots in December.
Based on the results from the clinical trials, the vaccine was 91% effective at preventing COVID-19 disease. But that estimate came from data collected before the Delta variant became widespread.
The most commonly reported side effects in the clinical trials were pain, redness and swelling at the injection site, fatigue, headache, muscle or joint pain, chills, and fever.
The FDA said the vaccine is effective in preventing COVID-19 and potentially serious outcomes, including hospitalization and death.
Based on safety data reviewed since the two-dose vaccine was approved, the FDA said the data demonstrates a higher risk for heart inflammation -- clinically known as myocarditis or pericarditis -- especially within 7 days after the second dose of the shots. The risk is highest for men under age 40, compared to women and older men.
The prescription information includes warnings about these risks. The FDA said the drugmakers must continue to study the risks and long-term effects on people who have myocarditis after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated on 8/24/21.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted a biological license application, more commonly known as “full approval,” to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
It is the first COVID-19 vaccine to be fully licensed in the United States. It will be marketed under the trade name Comirnaty.
The approval applies to individuals ages 16 years and older. The vaccine is still available for emergency use for those ages 12-15.
The FDA’s stamp of approval is somewhat anticlimactic, following months of real-world use and millions of doses doled out to the general population. It comes after months of scrutiny by the agency of the clinical trial data.
Still, the approval puts the vaccines on firmer legal footing and is expected to spur a raft of new vaccination requirements by employers, schools, and universities.
“The FDA approval is the gold standard,” President Joe Biden said from the White House. “Those who have been waiting for full approval should go and get your shot now.”
“It could save your life or the lives of those you love,” he said.
Biden also called on businesses to mandate COVID vaccines for their employees.
Indeed, soon after the approval was announced, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said the vaccines would be required for all 1.4 million active duty service members.
Public health advocates have seen full approval as an important tool to increase U.S. vaccination rates and had criticized the FDA for taking so long to grant the license.
In a news briefing on the approval, Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had not dragged its feet.
Marks noted that his team had reviewed tens of thousands of pages of clinical trial data -- down to the level of individual patients. They also inspected clinical trial sites and manufacturing facilities, and reviewed information gathered after the vaccines were authorized for use.
“It’s been 97 days since Pfizer completed the role of its [application for approval] and the clock started, which means that we completed this in about 40% of the normal clock time for a submission of this magnitude,” he said. “People worked day and night.”
The agency resisted pressure to speed up its process, saying a thorough review was necessary to ensure public confidence.
“While millions of people have already safely received COVID-19 vaccines, we recognize that for some, the FDA approval of a vaccine may now instill additional confidence to get vaccinated. Today’s milestone puts us one step closer to altering the course of this pandemic in the U.S.,” acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock said in a FDA news release.
Experts agreed the move would increase public confidence.
“I don't expect a big line outside of vaccination sites this afternoon or tomorrow morning, but it will persuade some,” said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
A recent Kaiser Family Foundation poll found that 3 in 10 unvaccinated adults said they would be more likely to get vaccinated if the vaccines were given full approval.
More importantly, Schaffner said, the FDA’s approval would lay the groundwork for vaccine mandates. “I think those kinds of mandates are going to be necessary to get us up over 80% vaccinated.”
In granting the approval, the agency reviewed a record amount of data from more than 40,000 people who took part in clinical trials. About 12,000 recipients have been followed for at least 6 months, the agency said.
The FDA also reviewed safety data collected since it issued its emergency use authorization for the shots in December.
Based on the results from the clinical trials, the vaccine was 91% effective at preventing COVID-19 disease. But that estimate came from data collected before the Delta variant became widespread.
The most commonly reported side effects in the clinical trials were pain, redness and swelling at the injection site, fatigue, headache, muscle or joint pain, chills, and fever.
The FDA said the vaccine is effective in preventing COVID-19 and potentially serious outcomes, including hospitalization and death.
Based on safety data reviewed since the two-dose vaccine was approved, the FDA said the data demonstrates a higher risk for heart inflammation -- clinically known as myocarditis or pericarditis -- especially within 7 days after the second dose of the shots. The risk is highest for men under age 40, compared to women and older men.
The prescription information includes warnings about these risks. The FDA said the drugmakers must continue to study the risks and long-term effects on people who have myocarditis after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated on 8/24/21.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted a biological license application, more commonly known as “full approval,” to the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.
It is the first COVID-19 vaccine to be fully licensed in the United States. It will be marketed under the trade name Comirnaty.
The approval applies to individuals ages 16 years and older. The vaccine is still available for emergency use for those ages 12-15.
The FDA’s stamp of approval is somewhat anticlimactic, following months of real-world use and millions of doses doled out to the general population. It comes after months of scrutiny by the agency of the clinical trial data.
Still, the approval puts the vaccines on firmer legal footing and is expected to spur a raft of new vaccination requirements by employers, schools, and universities.
“The FDA approval is the gold standard,” President Joe Biden said from the White House. “Those who have been waiting for full approval should go and get your shot now.”
“It could save your life or the lives of those you love,” he said.
Biden also called on businesses to mandate COVID vaccines for their employees.
Indeed, soon after the approval was announced, Defense Secretary Lloyd Austin said the vaccines would be required for all 1.4 million active duty service members.
Public health advocates have seen full approval as an important tool to increase U.S. vaccination rates and had criticized the FDA for taking so long to grant the license.
In a news briefing on the approval, Peter Marks, MD, director of the FDA’s Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research, said the agency had not dragged its feet.
Marks noted that his team had reviewed tens of thousands of pages of clinical trial data -- down to the level of individual patients. They also inspected clinical trial sites and manufacturing facilities, and reviewed information gathered after the vaccines were authorized for use.
“It’s been 97 days since Pfizer completed the role of its [application for approval] and the clock started, which means that we completed this in about 40% of the normal clock time for a submission of this magnitude,” he said. “People worked day and night.”
The agency resisted pressure to speed up its process, saying a thorough review was necessary to ensure public confidence.
“While millions of people have already safely received COVID-19 vaccines, we recognize that for some, the FDA approval of a vaccine may now instill additional confidence to get vaccinated. Today’s milestone puts us one step closer to altering the course of this pandemic in the U.S.,” acting FDA Commissioner Janet Woodcock said in a FDA news release.
Experts agreed the move would increase public confidence.
“I don't expect a big line outside of vaccination sites this afternoon or tomorrow morning, but it will persuade some,” said William Schaffner, MD, a professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University in Nashville.
A recent Kaiser Family Foundation poll found that 3 in 10 unvaccinated adults said they would be more likely to get vaccinated if the vaccines were given full approval.
More importantly, Schaffner said, the FDA’s approval would lay the groundwork for vaccine mandates. “I think those kinds of mandates are going to be necessary to get us up over 80% vaccinated.”
In granting the approval, the agency reviewed a record amount of data from more than 40,000 people who took part in clinical trials. About 12,000 recipients have been followed for at least 6 months, the agency said.
The FDA also reviewed safety data collected since it issued its emergency use authorization for the shots in December.
Based on the results from the clinical trials, the vaccine was 91% effective at preventing COVID-19 disease. But that estimate came from data collected before the Delta variant became widespread.
The most commonly reported side effects in the clinical trials were pain, redness and swelling at the injection site, fatigue, headache, muscle or joint pain, chills, and fever.
The FDA said the vaccine is effective in preventing COVID-19 and potentially serious outcomes, including hospitalization and death.
Based on safety data reviewed since the two-dose vaccine was approved, the FDA said the data demonstrates a higher risk for heart inflammation -- clinically known as myocarditis or pericarditis -- especially within 7 days after the second dose of the shots. The risk is highest for men under age 40, compared to women and older men.
The prescription information includes warnings about these risks. The FDA said the drugmakers must continue to study the risks and long-term effects on people who have myocarditis after vaccination.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was updated on 8/24/21.
Shouldn’t docs who spread false COVID-19 info lose their licenses?
A tall, distinguished-looking physician in shirtsleeves and suspenders walked to the microphone at the Mt. Vernon, Ind., school board meeting on a Friday evening in early August. He launched into an impassioned, 7-minute attack on the public health establishment’s medical guidelines for COVID-19.
“The Center for Disease Control and the Indiana State [Department] of Health are giving you very bad scientific guidance,” said Daniel Stock, MD, a primary care physician with a concierge practice in Noblesville, Ind., He described himself as a “functional family medicine physician,” though he is not board certified in family medicine.
Dr. Stock told the school board members that COVID-19 vaccines are counterproductive because they make coronavirus infections worse. He claimed his treatment of “over 15” COVID-19 patients with vitamin D, ivermectin, and zinc has kept them out of the hospital, and that those treatments reduce mortality risk from the disease by 75%. (A study released in mid-August found that ivermectin is ineffective in treating COVID-19).
In response to Dr. Stock’s remarks, the state health department quickly issued a statement reaffirming that COVID-19 vaccines “are highly effective at preventing hospitalizations and deaths.” But by then, the YouTube video of Dr. Stock’s comments had garnered nearly 600,000 views as of Aug. 12 and had been shared over 10,000 times on Facebook. Opponents of COVID-19 vaccines and masking policies across the country have been citing his comments.
Across the country, state medical licensing boards and state and national medical associations are struggling with how to respond to scientifically baseless public statements about COVID-19 by some physicians such as Dr. Stock. They fear such statements are increasing public confusion and are heightening political conflict. Physicians accused of spreading false information include public officials such as Scott Atlas, MD, who served as President Donald Trump’s COVID-19 advisor, and Kentucky Sen. Rand Paul, an ophthalmologist, whose YouTube account was temporarily suspended in August after he posted a video disputing the effectiveness of masking in stopping the spread of COVID-19.
“That’s the problem – those types of viral videos of someone somewhere who thinks they know something the rest of us don’t,” lamented Jennifer Bryan, MD, board chair of the Mississippi State Medical Association. “I don’t know any good reason why a physician should be advising against vaccination. It’s appropriate for medical boards to look into those situations.”
The Federation of State Medical Boards agrees. In July, it warned that physicians who willfully spread false information about COVID-19 risk suspension or revocation of their medical license. The federation cited a “dramatic increase in the dissemination of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation and disinformation by physicians.” That’s particularly dangerous, it said, because physicians enjoy a high degree of public credibility.
Medical boards will particularly examine cases in which there is a pattern of misinformation or disinformation showing that a physician poses a continuing threat to public health, said Hank Chaudhry, DO, the federation’s CEO. In some cases, he said, boards have contacted physicians and have persuaded them to voluntarily refrain from making false public statements, without taking disciplinary action.
“Words matter,” he said. “Physicians have a really big platform, whether they realize it or not. Misinformation or disinformation in the context of COVID can not only cause harm but also death. We felt it was appropriate to remind physicians to be careful.”
Although medical leaders stress that most physicians are promoting solid science on COVID-19, the London-based Center for Countering Digital Hate, in a May report titled “The Disinformation Dozen,” named four U.S. physicians among 12 people who it said produce 65% of the misleading claims and lies about COVID-19 vaccines that abound on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. The leading spreader of false claims, the group said, is Joseph Mercola, MD, an Illinois-licensed osteopath living in Cape Coral, Fla. He did not respond to requests for comment.
But so far, state licensing boards and federal and state medical associations generally have been reluctant to discipline or publicly call out physicians who have spread misinformation about the causes, treatments, vaccines, and prevention strategies for COVID-19. Some of these physicians, such as Dr. Mercola, have a long history predating the COVID-19 pandemic of disseminating scientifically baseless information, often in connection with their marketing of products and services.
For instance, the Medical Licensing Board of Indiana and the state attorney general’s office, which brings medical disciplinary actions, declined to comment on Dr. Stock’s public statements at the August school board meeting. When asked about Dr. Stock, the Indiana State Medical Association, without mentioning his name, said: “We urge Hoosier physicians to share the proven facts [about public health measures recommended by the CDC and the Indiana Department of Health] with their patients and their communities.” Dr. Stock did not respond to a request for comment.
Experts say state medical boards are ill equipped and are often unwilling to address the challenge of disciplining physicians who disseminate dangerously false medical information. That enforcement gap is particularly troubling in the middle of a deadly pandemic such as this one.
“Unless you can show a harm to an individual patient, it’s pretty tough to get the boards to do much,” said Art Caplan, PhD, a professor of bioethics at New York University. “I wish they would, but they just don’t.”
That’s partly because state laws require the boards to engage in lengthy, confidential investigations and adversarial legal processes before imposing disciplinary actions. The laws generally require patients or members of the public to file a complaint before an investigation can start. Some states, however, do allow their medical boards to take rapid emergency action if a physician poses an immediate threat to patients or the public.
Another hurdle is that medical boards that seek to sanction physicians for making dangerously misleading public statements could face lawsuits alleging that such actions violate the physicians’ constitutional free speech rights or their professional autonomy.
“We have free speech, and you can get away with a lot of stuff,” said Stephen Barrett, MD, who for many years has critically documented examples of medical fraud on his website, Quackwatch. “Some doctors would sue if they were challenged by medical boards, and I’m not sure the boards would win that court fight. People have written books with advice that killed people, and I’m not aware of a single case where the author was disciplined.”
In addition, it’s not clear that U.S. physicians who are not government officials have any legal obligation – as opposed to a moral obligation – to the government or the public to promote public health, said Jonathan Moreno, PhD, a professor of medical ethics at University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “Is transmitting misinformation about COVID-19 public health malpractice?” he asked. “Do we as a society see physicians having a special role as guides in an emergency? I’d like to think we do, but we don’t have a strong tradition like that in the U.S.”
But California State Sen. Richard Pan, MD, a pediatrician who represents the Sacramento area, doesn’t buy the arguments about why medical boards can’t discipline physicians for spreading misinformation. He successfully sponsored a 2019 bill that strengthens the medical board’s ability to discipline physicians who dole out medically unjustified vaccine exemptions to children.
“A medical license is a privilege. It’s an imprimatur from the state that the person is someone who upholds professional standards,” Dr. Pan said. “If someone is intentionally spreading disinformation for personal gain and that’s putting the public at risk, the medical board has a duty to act.”
There have been only a few publicly announced disciplinary actions related to COVID-19 misinformation so far.
Last December, the Oregon Medical Board, on an emergency basis, suspended the license of Steven LaTulippe, MD, of Dallas, Ore. He had publicly announced that he and his staff were not wearing masks in his clinic. In addition, he compared COVID-19 to the common cold and denied the governor’s legal authority to adopt public health protection measures. A recorded message on his office phone said he’s challenging the licensure action in court.
Last January, the Medical Board of California made Thomas Cowan, MD, of San Francisco surrender his license after Dr. Cowan posted a YouTube video, which went viral last year, that claimed that 5G Internet networks cause COVID-19. He did not respond to a request for comment.
In May, the College of Physicians and Surgeons of British Columbia reprimanded Stephen Malthouse, MD, and forbade him from speaking on issues related to COVID-19. He had written a widely circulated open letter to the province’s chief health office claiming that the pandemic was “over” and that measures to control the spread of COVID-19 were worse than the virus. He has challenged the disciplinary action in court, alleging it violates his right to free speech.
Attacking the problem from a different angle, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission has issued enforcement actions in cases in which physicians and other health care professionals engaged in deceptive business practices related to COVID-19. That approach may be applicable to a number of physicians accused of spreading COVID-19 misinformation, who allegedly have done so at least partly to sell unproven products and services to prevent or treat the disease.
In June, the FTC settled a case against Stephen Meis, MD, of Porterville, Calif. The settlement required that he stop making unsupported claims that his company’s dietary supplements effectively treat COVID-19 symptoms and that he pay $103,420 in refunds to defrauded customers.
State medical boards in the United States generally are not allowed to disclose investigations or disciplinary processes until they finalize a disciplinary action, so other investigations that have not been publicly disclosed may be pending.
A spokesperson for the Medical Board of California said the board is aware of questionable statements about COVID-19 made by several physicians and “will be looking into it.” That comment was in response to a question about statements made at a news conference last year by two Bakersfield emergency physicians, Artin Massihi, MD, and Dan Erickson, DO. They claimed that their COVID-19 testing data showed that the virus is not that dangerous. Dr. Erickson is an osteopath and is regulated by the Osteopathic Medical Board of California.
The two physicians’ news conference prompted an unusual joint statement from the American College of Emergency Medicine and the American Academy of Emergency Medicine in April 2020 declaring that they “emphatically condemn” Dr. Massihi’s and Dr. Erickson’s “reckless and untested musings.” The groups added that it appeared that the physicians issued the comments “to advance their personal financial interests without regard for the public’s health.”
Neither Dr. Massihi nor Dr. Erickson responded to a request for comment.
As for the physician dubbed by the Center for Countering Digital Hate as the world’s most influential spreader of COVID-19 misinformation on social media: No recent public complaints have been filed, and no disciplinary action has been taken against Dr. Mercola, according to a spokesman for the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation.
According to court records, Dr. Mercola faced disciplinary complaints from the Illinois board in the early 2000s for allegedly providing false and potentially harmful medical advice on his website. There is no record of any final disciplinary action taken against him.
In widely disseminated online posts, Dr. Mercola has called the COVID-19 pandemic a “scam” and said “forced vaccination” is part of a plan to re-set the global economic system. He called COVID-19 vaccines “a medical fraud,” claiming they “alter your genetic coding.” In February, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ordered Dr. Mercola to stop saying on his website that various vitamins and dietary supplements he sells through his website are effective in preventing or treating COVID-19.
The New York Times reported in July that Dr. Mercola’s English-language Facebook page has more than 1.7 million followers, that his Spanish-language page has one million, and that he has 300,000 followers on Twitter and 400,000 on YouTube.
In August, Dr. Mercola announced that he was deleting the large archive of articles he’s written on his website but would continue to post articles every day that would be available on the site for only 48 hours. He explained his decision by saying he’s facing “blatant censorship” as part of a “McCarthyism-like attack” from “the sitting President of the United States.” He encouraged people to read his book, “The Truth about COVID-19.”
The lack of action against Dr. Mercola for his lengthy list of scientifically unfounded statements and marketing claims about COVID-19 and other medical conditions infuriates Quackwatch’s Dr. Barrett. He’s amazed that the Illinois board did not discipline Dr. Mercola despite a number of enforcement actions against him by the FTC and the FDA.
“If a doctor were to say to a patient, ‘Don’t wear a mask and don’t get vaccinated,’ the doctor would be held responsible for a bad outcome,” he said. “But if you say it to millions and as a direct result a dozen people die, shouldn’t the doctor also be held responsible for that misinformation? I think he should lose his license.”
Another of the four physicians cited in the “Disinformation Dozen” report is Sherri Tenpenny, DO, an osteopath licensed in Ohio, who has published posts on social media advocating against masking, testing, and vaccines to prevent COVID-19 infections. A spokesperson for the State Medical Board of Ohio said Dr. Tenpenny’s license expires on Oct. 1, 2021, and that any investigation would be confidential. She added that grounds for disciplinary action include “making a false, fraudulent, deceptive, or misleading statement in relation to the practice of medicine and surgery.” Dr. Tenpenny could not be reached for comment.
A third physician named in the report is Christiane Northrup, MD, an ob.gyn. formerly licensed in Maine, who has published posts advocating unproven cures for COVID-19 and claiming that vaccines increase chronic illness. Dennis Smith, executive director of the Maine Board of Licensure in Medicine, said the board received complaints about Dr. Northrup’s posts but can’t act because she withdrew her Maine license in 2015. He added that the Maine board can issue sanctions against physicians who engage in fraud, deceit, or misrepresentation or who post scientifically unfounded statements online.
The fourth physician identified in the “Disinformation Dozen” report is Rashid Buttar, DO, an osteopath practicing in Mooresville, N.C., who has claimed in social media posts that COVID-19 vaccines cause infertility and that COVID-19 tests contain living microorganisms. A spokeswoman for the North Carolina Medical Board said she could not confirm or deny the existence of any investigation of Dr. Buttar, who signed a consent order with the medical board in 2010 following charges of exorbitant fees, worthless tests and treatment, and false diagnoses. Undisclosed conditions were placed on his medical license in 2013. The spokesperson added that the board would investigate any information alleging that a physician spread false information about COVID-19.
Another physician who has caused widespread consternation over scientifically unfounded statements about COVID-19 is Simone Gold, MD, formerly an emergency department physician in Los Angeles. She founded a group called America’s Frontline Doctors, which filed a federal lawsuit in Alabama this spring to block the FDA from issuing an emergency use authorization allowing teenagers to receive COVID-19 vaccinations. She called the vaccines “an experimental biological agent whose harms are well-documented.”
Last summer, Dr. Gold and other physicians in her group held a news conference on the steps of the U.S. Supreme Court Building promoting hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment. They declared that masks don’t work and that the virus isn’t deadly, and made other false claims. The news conference was livestreamed by conservative media outlets, was promoted on Twitter by then-President Trump and his family, and was viewed online more than 14 million times.
One of the participating physicians, Stella Immanuel, MD, of Houston, claimed in a video that went viral that she had successfully used hydroxychloroquine for more than 400 patients to cure the disease. In response, the Texas Medical Board, without naming Dr. Immanuel, warned that if it received a complaint about any physician who made a false claim about having a cure for COVID-19, it would investigate and potentially take disciplinary action.
Although no publicly known disciplinary action has been taken against Dr. Gold, she told The Washington Post last January that after participating in that July 2020 news conference, she was fired from her emergency department job at two hospitals and that she hasn’t worked as a physician since. Dr. Gold did not respond to a request for comment.
The outcome in her situation is consistent with the view of NYU’s Dr. Caplan that methods other than medical board discipline – such as action by employers, social media pressure, and reprimands from professional societies –will have to be used to hold physicians accountable for spreading COVID-19 misinformation.
“I’m disappointed to have to say it, but I don’t think medical boards are going to be effective,” he said. “We don’t know how to manage misinformation despite being in a plague. We just don’t.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A tall, distinguished-looking physician in shirtsleeves and suspenders walked to the microphone at the Mt. Vernon, Ind., school board meeting on a Friday evening in early August. He launched into an impassioned, 7-minute attack on the public health establishment’s medical guidelines for COVID-19.
“The Center for Disease Control and the Indiana State [Department] of Health are giving you very bad scientific guidance,” said Daniel Stock, MD, a primary care physician with a concierge practice in Noblesville, Ind., He described himself as a “functional family medicine physician,” though he is not board certified in family medicine.
Dr. Stock told the school board members that COVID-19 vaccines are counterproductive because they make coronavirus infections worse. He claimed his treatment of “over 15” COVID-19 patients with vitamin D, ivermectin, and zinc has kept them out of the hospital, and that those treatments reduce mortality risk from the disease by 75%. (A study released in mid-August found that ivermectin is ineffective in treating COVID-19).
In response to Dr. Stock’s remarks, the state health department quickly issued a statement reaffirming that COVID-19 vaccines “are highly effective at preventing hospitalizations and deaths.” But by then, the YouTube video of Dr. Stock’s comments had garnered nearly 600,000 views as of Aug. 12 and had been shared over 10,000 times on Facebook. Opponents of COVID-19 vaccines and masking policies across the country have been citing his comments.
Across the country, state medical licensing boards and state and national medical associations are struggling with how to respond to scientifically baseless public statements about COVID-19 by some physicians such as Dr. Stock. They fear such statements are increasing public confusion and are heightening political conflict. Physicians accused of spreading false information include public officials such as Scott Atlas, MD, who served as President Donald Trump’s COVID-19 advisor, and Kentucky Sen. Rand Paul, an ophthalmologist, whose YouTube account was temporarily suspended in August after he posted a video disputing the effectiveness of masking in stopping the spread of COVID-19.
“That’s the problem – those types of viral videos of someone somewhere who thinks they know something the rest of us don’t,” lamented Jennifer Bryan, MD, board chair of the Mississippi State Medical Association. “I don’t know any good reason why a physician should be advising against vaccination. It’s appropriate for medical boards to look into those situations.”
The Federation of State Medical Boards agrees. In July, it warned that physicians who willfully spread false information about COVID-19 risk suspension or revocation of their medical license. The federation cited a “dramatic increase in the dissemination of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation and disinformation by physicians.” That’s particularly dangerous, it said, because physicians enjoy a high degree of public credibility.
Medical boards will particularly examine cases in which there is a pattern of misinformation or disinformation showing that a physician poses a continuing threat to public health, said Hank Chaudhry, DO, the federation’s CEO. In some cases, he said, boards have contacted physicians and have persuaded them to voluntarily refrain from making false public statements, without taking disciplinary action.
“Words matter,” he said. “Physicians have a really big platform, whether they realize it or not. Misinformation or disinformation in the context of COVID can not only cause harm but also death. We felt it was appropriate to remind physicians to be careful.”
Although medical leaders stress that most physicians are promoting solid science on COVID-19, the London-based Center for Countering Digital Hate, in a May report titled “The Disinformation Dozen,” named four U.S. physicians among 12 people who it said produce 65% of the misleading claims and lies about COVID-19 vaccines that abound on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. The leading spreader of false claims, the group said, is Joseph Mercola, MD, an Illinois-licensed osteopath living in Cape Coral, Fla. He did not respond to requests for comment.
But so far, state licensing boards and federal and state medical associations generally have been reluctant to discipline or publicly call out physicians who have spread misinformation about the causes, treatments, vaccines, and prevention strategies for COVID-19. Some of these physicians, such as Dr. Mercola, have a long history predating the COVID-19 pandemic of disseminating scientifically baseless information, often in connection with their marketing of products and services.
For instance, the Medical Licensing Board of Indiana and the state attorney general’s office, which brings medical disciplinary actions, declined to comment on Dr. Stock’s public statements at the August school board meeting. When asked about Dr. Stock, the Indiana State Medical Association, without mentioning his name, said: “We urge Hoosier physicians to share the proven facts [about public health measures recommended by the CDC and the Indiana Department of Health] with their patients and their communities.” Dr. Stock did not respond to a request for comment.
Experts say state medical boards are ill equipped and are often unwilling to address the challenge of disciplining physicians who disseminate dangerously false medical information. That enforcement gap is particularly troubling in the middle of a deadly pandemic such as this one.
“Unless you can show a harm to an individual patient, it’s pretty tough to get the boards to do much,” said Art Caplan, PhD, a professor of bioethics at New York University. “I wish they would, but they just don’t.”
That’s partly because state laws require the boards to engage in lengthy, confidential investigations and adversarial legal processes before imposing disciplinary actions. The laws generally require patients or members of the public to file a complaint before an investigation can start. Some states, however, do allow their medical boards to take rapid emergency action if a physician poses an immediate threat to patients or the public.
Another hurdle is that medical boards that seek to sanction physicians for making dangerously misleading public statements could face lawsuits alleging that such actions violate the physicians’ constitutional free speech rights or their professional autonomy.
“We have free speech, and you can get away with a lot of stuff,” said Stephen Barrett, MD, who for many years has critically documented examples of medical fraud on his website, Quackwatch. “Some doctors would sue if they were challenged by medical boards, and I’m not sure the boards would win that court fight. People have written books with advice that killed people, and I’m not aware of a single case where the author was disciplined.”
In addition, it’s not clear that U.S. physicians who are not government officials have any legal obligation – as opposed to a moral obligation – to the government or the public to promote public health, said Jonathan Moreno, PhD, a professor of medical ethics at University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “Is transmitting misinformation about COVID-19 public health malpractice?” he asked. “Do we as a society see physicians having a special role as guides in an emergency? I’d like to think we do, but we don’t have a strong tradition like that in the U.S.”
But California State Sen. Richard Pan, MD, a pediatrician who represents the Sacramento area, doesn’t buy the arguments about why medical boards can’t discipline physicians for spreading misinformation. He successfully sponsored a 2019 bill that strengthens the medical board’s ability to discipline physicians who dole out medically unjustified vaccine exemptions to children.
“A medical license is a privilege. It’s an imprimatur from the state that the person is someone who upholds professional standards,” Dr. Pan said. “If someone is intentionally spreading disinformation for personal gain and that’s putting the public at risk, the medical board has a duty to act.”
There have been only a few publicly announced disciplinary actions related to COVID-19 misinformation so far.
Last December, the Oregon Medical Board, on an emergency basis, suspended the license of Steven LaTulippe, MD, of Dallas, Ore. He had publicly announced that he and his staff were not wearing masks in his clinic. In addition, he compared COVID-19 to the common cold and denied the governor’s legal authority to adopt public health protection measures. A recorded message on his office phone said he’s challenging the licensure action in court.
Last January, the Medical Board of California made Thomas Cowan, MD, of San Francisco surrender his license after Dr. Cowan posted a YouTube video, which went viral last year, that claimed that 5G Internet networks cause COVID-19. He did not respond to a request for comment.
In May, the College of Physicians and Surgeons of British Columbia reprimanded Stephen Malthouse, MD, and forbade him from speaking on issues related to COVID-19. He had written a widely circulated open letter to the province’s chief health office claiming that the pandemic was “over” and that measures to control the spread of COVID-19 were worse than the virus. He has challenged the disciplinary action in court, alleging it violates his right to free speech.
Attacking the problem from a different angle, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission has issued enforcement actions in cases in which physicians and other health care professionals engaged in deceptive business practices related to COVID-19. That approach may be applicable to a number of physicians accused of spreading COVID-19 misinformation, who allegedly have done so at least partly to sell unproven products and services to prevent or treat the disease.
In June, the FTC settled a case against Stephen Meis, MD, of Porterville, Calif. The settlement required that he stop making unsupported claims that his company’s dietary supplements effectively treat COVID-19 symptoms and that he pay $103,420 in refunds to defrauded customers.
State medical boards in the United States generally are not allowed to disclose investigations or disciplinary processes until they finalize a disciplinary action, so other investigations that have not been publicly disclosed may be pending.
A spokesperson for the Medical Board of California said the board is aware of questionable statements about COVID-19 made by several physicians and “will be looking into it.” That comment was in response to a question about statements made at a news conference last year by two Bakersfield emergency physicians, Artin Massihi, MD, and Dan Erickson, DO. They claimed that their COVID-19 testing data showed that the virus is not that dangerous. Dr. Erickson is an osteopath and is regulated by the Osteopathic Medical Board of California.
The two physicians’ news conference prompted an unusual joint statement from the American College of Emergency Medicine and the American Academy of Emergency Medicine in April 2020 declaring that they “emphatically condemn” Dr. Massihi’s and Dr. Erickson’s “reckless and untested musings.” The groups added that it appeared that the physicians issued the comments “to advance their personal financial interests without regard for the public’s health.”
Neither Dr. Massihi nor Dr. Erickson responded to a request for comment.
As for the physician dubbed by the Center for Countering Digital Hate as the world’s most influential spreader of COVID-19 misinformation on social media: No recent public complaints have been filed, and no disciplinary action has been taken against Dr. Mercola, according to a spokesman for the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation.
According to court records, Dr. Mercola faced disciplinary complaints from the Illinois board in the early 2000s for allegedly providing false and potentially harmful medical advice on his website. There is no record of any final disciplinary action taken against him.
In widely disseminated online posts, Dr. Mercola has called the COVID-19 pandemic a “scam” and said “forced vaccination” is part of a plan to re-set the global economic system. He called COVID-19 vaccines “a medical fraud,” claiming they “alter your genetic coding.” In February, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ordered Dr. Mercola to stop saying on his website that various vitamins and dietary supplements he sells through his website are effective in preventing or treating COVID-19.
The New York Times reported in July that Dr. Mercola’s English-language Facebook page has more than 1.7 million followers, that his Spanish-language page has one million, and that he has 300,000 followers on Twitter and 400,000 on YouTube.
In August, Dr. Mercola announced that he was deleting the large archive of articles he’s written on his website but would continue to post articles every day that would be available on the site for only 48 hours. He explained his decision by saying he’s facing “blatant censorship” as part of a “McCarthyism-like attack” from “the sitting President of the United States.” He encouraged people to read his book, “The Truth about COVID-19.”
The lack of action against Dr. Mercola for his lengthy list of scientifically unfounded statements and marketing claims about COVID-19 and other medical conditions infuriates Quackwatch’s Dr. Barrett. He’s amazed that the Illinois board did not discipline Dr. Mercola despite a number of enforcement actions against him by the FTC and the FDA.
“If a doctor were to say to a patient, ‘Don’t wear a mask and don’t get vaccinated,’ the doctor would be held responsible for a bad outcome,” he said. “But if you say it to millions and as a direct result a dozen people die, shouldn’t the doctor also be held responsible for that misinformation? I think he should lose his license.”
Another of the four physicians cited in the “Disinformation Dozen” report is Sherri Tenpenny, DO, an osteopath licensed in Ohio, who has published posts on social media advocating against masking, testing, and vaccines to prevent COVID-19 infections. A spokesperson for the State Medical Board of Ohio said Dr. Tenpenny’s license expires on Oct. 1, 2021, and that any investigation would be confidential. She added that grounds for disciplinary action include “making a false, fraudulent, deceptive, or misleading statement in relation to the practice of medicine and surgery.” Dr. Tenpenny could not be reached for comment.
A third physician named in the report is Christiane Northrup, MD, an ob.gyn. formerly licensed in Maine, who has published posts advocating unproven cures for COVID-19 and claiming that vaccines increase chronic illness. Dennis Smith, executive director of the Maine Board of Licensure in Medicine, said the board received complaints about Dr. Northrup’s posts but can’t act because she withdrew her Maine license in 2015. He added that the Maine board can issue sanctions against physicians who engage in fraud, deceit, or misrepresentation or who post scientifically unfounded statements online.
The fourth physician identified in the “Disinformation Dozen” report is Rashid Buttar, DO, an osteopath practicing in Mooresville, N.C., who has claimed in social media posts that COVID-19 vaccines cause infertility and that COVID-19 tests contain living microorganisms. A spokeswoman for the North Carolina Medical Board said she could not confirm or deny the existence of any investigation of Dr. Buttar, who signed a consent order with the medical board in 2010 following charges of exorbitant fees, worthless tests and treatment, and false diagnoses. Undisclosed conditions were placed on his medical license in 2013. The spokesperson added that the board would investigate any information alleging that a physician spread false information about COVID-19.
Another physician who has caused widespread consternation over scientifically unfounded statements about COVID-19 is Simone Gold, MD, formerly an emergency department physician in Los Angeles. She founded a group called America’s Frontline Doctors, which filed a federal lawsuit in Alabama this spring to block the FDA from issuing an emergency use authorization allowing teenagers to receive COVID-19 vaccinations. She called the vaccines “an experimental biological agent whose harms are well-documented.”
Last summer, Dr. Gold and other physicians in her group held a news conference on the steps of the U.S. Supreme Court Building promoting hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment. They declared that masks don’t work and that the virus isn’t deadly, and made other false claims. The news conference was livestreamed by conservative media outlets, was promoted on Twitter by then-President Trump and his family, and was viewed online more than 14 million times.
One of the participating physicians, Stella Immanuel, MD, of Houston, claimed in a video that went viral that she had successfully used hydroxychloroquine for more than 400 patients to cure the disease. In response, the Texas Medical Board, without naming Dr. Immanuel, warned that if it received a complaint about any physician who made a false claim about having a cure for COVID-19, it would investigate and potentially take disciplinary action.
Although no publicly known disciplinary action has been taken against Dr. Gold, she told The Washington Post last January that after participating in that July 2020 news conference, she was fired from her emergency department job at two hospitals and that she hasn’t worked as a physician since. Dr. Gold did not respond to a request for comment.
The outcome in her situation is consistent with the view of NYU’s Dr. Caplan that methods other than medical board discipline – such as action by employers, social media pressure, and reprimands from professional societies –will have to be used to hold physicians accountable for spreading COVID-19 misinformation.
“I’m disappointed to have to say it, but I don’t think medical boards are going to be effective,” he said. “We don’t know how to manage misinformation despite being in a plague. We just don’t.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A tall, distinguished-looking physician in shirtsleeves and suspenders walked to the microphone at the Mt. Vernon, Ind., school board meeting on a Friday evening in early August. He launched into an impassioned, 7-minute attack on the public health establishment’s medical guidelines for COVID-19.
“The Center for Disease Control and the Indiana State [Department] of Health are giving you very bad scientific guidance,” said Daniel Stock, MD, a primary care physician with a concierge practice in Noblesville, Ind., He described himself as a “functional family medicine physician,” though he is not board certified in family medicine.
Dr. Stock told the school board members that COVID-19 vaccines are counterproductive because they make coronavirus infections worse. He claimed his treatment of “over 15” COVID-19 patients with vitamin D, ivermectin, and zinc has kept them out of the hospital, and that those treatments reduce mortality risk from the disease by 75%. (A study released in mid-August found that ivermectin is ineffective in treating COVID-19).
In response to Dr. Stock’s remarks, the state health department quickly issued a statement reaffirming that COVID-19 vaccines “are highly effective at preventing hospitalizations and deaths.” But by then, the YouTube video of Dr. Stock’s comments had garnered nearly 600,000 views as of Aug. 12 and had been shared over 10,000 times on Facebook. Opponents of COVID-19 vaccines and masking policies across the country have been citing his comments.
Across the country, state medical licensing boards and state and national medical associations are struggling with how to respond to scientifically baseless public statements about COVID-19 by some physicians such as Dr. Stock. They fear such statements are increasing public confusion and are heightening political conflict. Physicians accused of spreading false information include public officials such as Scott Atlas, MD, who served as President Donald Trump’s COVID-19 advisor, and Kentucky Sen. Rand Paul, an ophthalmologist, whose YouTube account was temporarily suspended in August after he posted a video disputing the effectiveness of masking in stopping the spread of COVID-19.
“That’s the problem – those types of viral videos of someone somewhere who thinks they know something the rest of us don’t,” lamented Jennifer Bryan, MD, board chair of the Mississippi State Medical Association. “I don’t know any good reason why a physician should be advising against vaccination. It’s appropriate for medical boards to look into those situations.”
The Federation of State Medical Boards agrees. In July, it warned that physicians who willfully spread false information about COVID-19 risk suspension or revocation of their medical license. The federation cited a “dramatic increase in the dissemination of COVID-19 vaccine misinformation and disinformation by physicians.” That’s particularly dangerous, it said, because physicians enjoy a high degree of public credibility.
Medical boards will particularly examine cases in which there is a pattern of misinformation or disinformation showing that a physician poses a continuing threat to public health, said Hank Chaudhry, DO, the federation’s CEO. In some cases, he said, boards have contacted physicians and have persuaded them to voluntarily refrain from making false public statements, without taking disciplinary action.
“Words matter,” he said. “Physicians have a really big platform, whether they realize it or not. Misinformation or disinformation in the context of COVID can not only cause harm but also death. We felt it was appropriate to remind physicians to be careful.”
Although medical leaders stress that most physicians are promoting solid science on COVID-19, the London-based Center for Countering Digital Hate, in a May report titled “The Disinformation Dozen,” named four U.S. physicians among 12 people who it said produce 65% of the misleading claims and lies about COVID-19 vaccines that abound on Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter. The leading spreader of false claims, the group said, is Joseph Mercola, MD, an Illinois-licensed osteopath living in Cape Coral, Fla. He did not respond to requests for comment.
But so far, state licensing boards and federal and state medical associations generally have been reluctant to discipline or publicly call out physicians who have spread misinformation about the causes, treatments, vaccines, and prevention strategies for COVID-19. Some of these physicians, such as Dr. Mercola, have a long history predating the COVID-19 pandemic of disseminating scientifically baseless information, often in connection with their marketing of products and services.
For instance, the Medical Licensing Board of Indiana and the state attorney general’s office, which brings medical disciplinary actions, declined to comment on Dr. Stock’s public statements at the August school board meeting. When asked about Dr. Stock, the Indiana State Medical Association, without mentioning his name, said: “We urge Hoosier physicians to share the proven facts [about public health measures recommended by the CDC and the Indiana Department of Health] with their patients and their communities.” Dr. Stock did not respond to a request for comment.
Experts say state medical boards are ill equipped and are often unwilling to address the challenge of disciplining physicians who disseminate dangerously false medical information. That enforcement gap is particularly troubling in the middle of a deadly pandemic such as this one.
“Unless you can show a harm to an individual patient, it’s pretty tough to get the boards to do much,” said Art Caplan, PhD, a professor of bioethics at New York University. “I wish they would, but they just don’t.”
That’s partly because state laws require the boards to engage in lengthy, confidential investigations and adversarial legal processes before imposing disciplinary actions. The laws generally require patients or members of the public to file a complaint before an investigation can start. Some states, however, do allow their medical boards to take rapid emergency action if a physician poses an immediate threat to patients or the public.
Another hurdle is that medical boards that seek to sanction physicians for making dangerously misleading public statements could face lawsuits alleging that such actions violate the physicians’ constitutional free speech rights or their professional autonomy.
“We have free speech, and you can get away with a lot of stuff,” said Stephen Barrett, MD, who for many years has critically documented examples of medical fraud on his website, Quackwatch. “Some doctors would sue if they were challenged by medical boards, and I’m not sure the boards would win that court fight. People have written books with advice that killed people, and I’m not aware of a single case where the author was disciplined.”
In addition, it’s not clear that U.S. physicians who are not government officials have any legal obligation – as opposed to a moral obligation – to the government or the public to promote public health, said Jonathan Moreno, PhD, a professor of medical ethics at University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. “Is transmitting misinformation about COVID-19 public health malpractice?” he asked. “Do we as a society see physicians having a special role as guides in an emergency? I’d like to think we do, but we don’t have a strong tradition like that in the U.S.”
But California State Sen. Richard Pan, MD, a pediatrician who represents the Sacramento area, doesn’t buy the arguments about why medical boards can’t discipline physicians for spreading misinformation. He successfully sponsored a 2019 bill that strengthens the medical board’s ability to discipline physicians who dole out medically unjustified vaccine exemptions to children.
“A medical license is a privilege. It’s an imprimatur from the state that the person is someone who upholds professional standards,” Dr. Pan said. “If someone is intentionally spreading disinformation for personal gain and that’s putting the public at risk, the medical board has a duty to act.”
There have been only a few publicly announced disciplinary actions related to COVID-19 misinformation so far.
Last December, the Oregon Medical Board, on an emergency basis, suspended the license of Steven LaTulippe, MD, of Dallas, Ore. He had publicly announced that he and his staff were not wearing masks in his clinic. In addition, he compared COVID-19 to the common cold and denied the governor’s legal authority to adopt public health protection measures. A recorded message on his office phone said he’s challenging the licensure action in court.
Last January, the Medical Board of California made Thomas Cowan, MD, of San Francisco surrender his license after Dr. Cowan posted a YouTube video, which went viral last year, that claimed that 5G Internet networks cause COVID-19. He did not respond to a request for comment.
In May, the College of Physicians and Surgeons of British Columbia reprimanded Stephen Malthouse, MD, and forbade him from speaking on issues related to COVID-19. He had written a widely circulated open letter to the province’s chief health office claiming that the pandemic was “over” and that measures to control the spread of COVID-19 were worse than the virus. He has challenged the disciplinary action in court, alleging it violates his right to free speech.
Attacking the problem from a different angle, the U.S. Federal Trade Commission has issued enforcement actions in cases in which physicians and other health care professionals engaged in deceptive business practices related to COVID-19. That approach may be applicable to a number of physicians accused of spreading COVID-19 misinformation, who allegedly have done so at least partly to sell unproven products and services to prevent or treat the disease.
In June, the FTC settled a case against Stephen Meis, MD, of Porterville, Calif. The settlement required that he stop making unsupported claims that his company’s dietary supplements effectively treat COVID-19 symptoms and that he pay $103,420 in refunds to defrauded customers.
State medical boards in the United States generally are not allowed to disclose investigations or disciplinary processes until they finalize a disciplinary action, so other investigations that have not been publicly disclosed may be pending.
A spokesperson for the Medical Board of California said the board is aware of questionable statements about COVID-19 made by several physicians and “will be looking into it.” That comment was in response to a question about statements made at a news conference last year by two Bakersfield emergency physicians, Artin Massihi, MD, and Dan Erickson, DO. They claimed that their COVID-19 testing data showed that the virus is not that dangerous. Dr. Erickson is an osteopath and is regulated by the Osteopathic Medical Board of California.
The two physicians’ news conference prompted an unusual joint statement from the American College of Emergency Medicine and the American Academy of Emergency Medicine in April 2020 declaring that they “emphatically condemn” Dr. Massihi’s and Dr. Erickson’s “reckless and untested musings.” The groups added that it appeared that the physicians issued the comments “to advance their personal financial interests without regard for the public’s health.”
Neither Dr. Massihi nor Dr. Erickson responded to a request for comment.
As for the physician dubbed by the Center for Countering Digital Hate as the world’s most influential spreader of COVID-19 misinformation on social media: No recent public complaints have been filed, and no disciplinary action has been taken against Dr. Mercola, according to a spokesman for the Illinois Department of Financial and Professional Regulation.
According to court records, Dr. Mercola faced disciplinary complaints from the Illinois board in the early 2000s for allegedly providing false and potentially harmful medical advice on his website. There is no record of any final disciplinary action taken against him.
In widely disseminated online posts, Dr. Mercola has called the COVID-19 pandemic a “scam” and said “forced vaccination” is part of a plan to re-set the global economic system. He called COVID-19 vaccines “a medical fraud,” claiming they “alter your genetic coding.” In February, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration ordered Dr. Mercola to stop saying on his website that various vitamins and dietary supplements he sells through his website are effective in preventing or treating COVID-19.
The New York Times reported in July that Dr. Mercola’s English-language Facebook page has more than 1.7 million followers, that his Spanish-language page has one million, and that he has 300,000 followers on Twitter and 400,000 on YouTube.
In August, Dr. Mercola announced that he was deleting the large archive of articles he’s written on his website but would continue to post articles every day that would be available on the site for only 48 hours. He explained his decision by saying he’s facing “blatant censorship” as part of a “McCarthyism-like attack” from “the sitting President of the United States.” He encouraged people to read his book, “The Truth about COVID-19.”
The lack of action against Dr. Mercola for his lengthy list of scientifically unfounded statements and marketing claims about COVID-19 and other medical conditions infuriates Quackwatch’s Dr. Barrett. He’s amazed that the Illinois board did not discipline Dr. Mercola despite a number of enforcement actions against him by the FTC and the FDA.
“If a doctor were to say to a patient, ‘Don’t wear a mask and don’t get vaccinated,’ the doctor would be held responsible for a bad outcome,” he said. “But if you say it to millions and as a direct result a dozen people die, shouldn’t the doctor also be held responsible for that misinformation? I think he should lose his license.”
Another of the four physicians cited in the “Disinformation Dozen” report is Sherri Tenpenny, DO, an osteopath licensed in Ohio, who has published posts on social media advocating against masking, testing, and vaccines to prevent COVID-19 infections. A spokesperson for the State Medical Board of Ohio said Dr. Tenpenny’s license expires on Oct. 1, 2021, and that any investigation would be confidential. She added that grounds for disciplinary action include “making a false, fraudulent, deceptive, or misleading statement in relation to the practice of medicine and surgery.” Dr. Tenpenny could not be reached for comment.
A third physician named in the report is Christiane Northrup, MD, an ob.gyn. formerly licensed in Maine, who has published posts advocating unproven cures for COVID-19 and claiming that vaccines increase chronic illness. Dennis Smith, executive director of the Maine Board of Licensure in Medicine, said the board received complaints about Dr. Northrup’s posts but can’t act because she withdrew her Maine license in 2015. He added that the Maine board can issue sanctions against physicians who engage in fraud, deceit, or misrepresentation or who post scientifically unfounded statements online.
The fourth physician identified in the “Disinformation Dozen” report is Rashid Buttar, DO, an osteopath practicing in Mooresville, N.C., who has claimed in social media posts that COVID-19 vaccines cause infertility and that COVID-19 tests contain living microorganisms. A spokeswoman for the North Carolina Medical Board said she could not confirm or deny the existence of any investigation of Dr. Buttar, who signed a consent order with the medical board in 2010 following charges of exorbitant fees, worthless tests and treatment, and false diagnoses. Undisclosed conditions were placed on his medical license in 2013. The spokesperson added that the board would investigate any information alleging that a physician spread false information about COVID-19.
Another physician who has caused widespread consternation over scientifically unfounded statements about COVID-19 is Simone Gold, MD, formerly an emergency department physician in Los Angeles. She founded a group called America’s Frontline Doctors, which filed a federal lawsuit in Alabama this spring to block the FDA from issuing an emergency use authorization allowing teenagers to receive COVID-19 vaccinations. She called the vaccines “an experimental biological agent whose harms are well-documented.”
Last summer, Dr. Gold and other physicians in her group held a news conference on the steps of the U.S. Supreme Court Building promoting hydroxychloroquine as a COVID-19 treatment. They declared that masks don’t work and that the virus isn’t deadly, and made other false claims. The news conference was livestreamed by conservative media outlets, was promoted on Twitter by then-President Trump and his family, and was viewed online more than 14 million times.
One of the participating physicians, Stella Immanuel, MD, of Houston, claimed in a video that went viral that she had successfully used hydroxychloroquine for more than 400 patients to cure the disease. In response, the Texas Medical Board, without naming Dr. Immanuel, warned that if it received a complaint about any physician who made a false claim about having a cure for COVID-19, it would investigate and potentially take disciplinary action.
Although no publicly known disciplinary action has been taken against Dr. Gold, she told The Washington Post last January that after participating in that July 2020 news conference, she was fired from her emergency department job at two hospitals and that she hasn’t worked as a physician since. Dr. Gold did not respond to a request for comment.
The outcome in her situation is consistent with the view of NYU’s Dr. Caplan that methods other than medical board discipline – such as action by employers, social media pressure, and reprimands from professional societies –will have to be used to hold physicians accountable for spreading COVID-19 misinformation.
“I’m disappointed to have to say it, but I don’t think medical boards are going to be effective,” he said. “We don’t know how to manage misinformation despite being in a plague. We just don’t.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Delta whiplash: How the new surge is affecting mental health
Thanks to the rollout of the COVID-19 vaccines, more than just flowers were blooming this past spring. People came out of lockdown like bears emerging from hibernation, making plans to reunite with friends and loved ones they hadn’t seen in months. But with the tremendous surge in cases brought by the Delta variant, this summer has been anything but sunny and carefree. Case counts have once more reached prevaccination levels. In a repeat of last summer, people are canceling travel plans, and the lead-up to the new school year has become fraught and stressful.
“This whiplash is causing people to feel a variety of emotions: disappointment, uncertainty, anxiety, possibly anger and frustration,” says Vaile Wright, Ph.D., senior director of health care innovation at the American Psychological Association. “When it seemed like there was a light at the end of the tunnel, and we have the tools to overcome [the virus], and we’re not really using them, it can be hard for people to understand.”
The importance of hope
For decades, researchers have been digging into the crucial role hopefulness plays in mental health. The vaccine rollout, earlier than anticipated, provided a much needed burst of hope after months of bad news.
“It was a feeling of almost euphoria in June: ‘We’re going to see everybody!’” says Rachel Goldenberg, a rabbi in Jackson Heights, NY. “We have a theme for our High Holidays, and this year’s is very hopeful: Sow in tears, reap in joy. It felt like the sowing in tears part was behind us, and we were looking forward to reaping in joy. Slowly but surely, with Delta, everything has turned upside down.”
For Roxanne Hawn, a writer in Golden, Colo., vaccination offered a glimpse of something like normal life.
“I wore cute clothes. I stopped and got takeout for lunch. I bought myself flowers. I even had a little uplifting soundtrack for that time of hope and relief,” she says. “With the Delta variant, it feels like that window of normalcy closed quickly.”
Having that little bit of hope dashed can wear down even the sturdiest spirits, says Marissa King, PhD, author of “Social Chemistry: Decoding the Elements of Human Connection”.
“There was a moment when we were able to reconnect, to experience joy and the hope of being able to revitalize relationships,” she says. “The loss of that hope and the fear of being isolated again is causing so much distress.”
A new kind of loneliness
When the pandemic started, mom of three Julie Schwietert Collazo formed a WhatsApp group with several friends who were taking lockdown seriously. They got each other through months of isolation and celebrated the idea of reopening. Then Ms. Collazo’s oldest got COVID, just 5 weeks before her 12th birthday, and their family went back into quarantine. Her moms’ group is no longer on the same page about precautions.
“Last year we were doing it together, and it made it feel a bit easier,” she says. “As things started to normalize, everybody started thinking and moving in different directions. It feels like we’re not working through the same issues collectively like before.”
Dr. King says the feeling Ms. Collazo describes is quite common these days.
“A profound sense of loneliness comes from feeling like you’re the only one,” she says. “There’s such disagreement about the best path forward, it can feel lonely just because you think differently.”
An epidemic of anxiety
As the Delta variant drives case numbers back up again, worries increase as well.
“Is this ever going to end?” asks Ms. Collazo. “Is this our new reality, constantly having to order our lives around COVID?”
This uneasiness affects our well-being.
The National Center for Health Statistics and the Census Bureau have monitored the nation’s mental health via the ongoing Household Pulse Survey during the pandemic. It asks participants about their symptoms of either anxiety or depression. Throughout, more people have reported feeling anxious than depressed.
Anxiety peaked around Thanksgiving and Christmas, with nearly 38% of people reporting symptoms. The first vaccines began to roll out around that time, and anxiety levels steadily went down through the spring and early summer, dipping below 25% in late June. But those numbers have begun to creep back up – the most recent data, which goes through Aug. 2, found 27% of Americans reporting symptoms of anxiety.
“Nervous is the new normal,” says Vivian Pender, MD, president of the American Psychiatric Association. “Uncertainty makes people feel anxious.”
Empathy vs. anger
The way politics play into basic measures like mask-wearing and vaccination adds its own layer of stress. Physical altercations have resulted: In Los Angeles, a participant was stabbed at an antivaccination protest. At an Austin, Tex., elementary school, angry parents physically and verbally assaulted teachers who wore masks. Things have gotten so heated, the Department of Homeland Security issued a National Terrorism Advisory System bulletin last week. It warns that extremists could use new COVID-driven public health restrictions as an excuse to commit domestic terrorism.
Anger goes in the opposite direction, too, with people who’ve been following recommended procedures becoming increasingly fed up with those who flout them. Those intense emotions may not lead to violence, but they do make it harder for us to feel secure.
“It’s a public health crisis, and it’s turned into something different. When we get into us/them situations, we start to lose empathy. Empathy is important to identify solutions and work together as a community,” says Dr. Wright. “That’s what sparks the anger: the sense of ‘You aren’t doing what you’re supposed to be doing.’”
How to cope
Loneliness, anxiety, and anger may be swirling all around you right now. But that doesn’t make you powerless to boost your mental health. These suggestions may help:
- Trust your gut. If your community is reopening faster than feels comfortable to you, do whatever makes your family feel safe. “Ask yourself how you’re feeling, and use your feelings to guide your decisions,” says Dr. Pender. “Get more information, then follow the science.”
- Stop judging yourself. If you’re feeling lonely or mourning the losses COVID has brought, don’t fight it, says Wright. “Let it be an emotion that comes and goes, and try to find ways to feel connected to other people.”
- Practice self-care. It may sound simplistic, but eating healthy foods, exercising, and getting a good night’s sleep can all contribute to a more positive
- Try to ease anxiety. Meditation, calming self-talk, and soothing music can all lift your spirits. Or try diaphragmatic breathing: Breathe in for 5 seconds, hold for 2, and breathe out for 5. Even squeezing a stress ball can give you a tangible sense of
- Take action. Both Rabbi Goldenberg and Ms. Collazo, who runs a nonprofit that works to reunite immigrant families, say helping their community helps them feel better. “To sing and lead Shabbat services, even on Zoom, to see the faces of my people, it’s very healing,” says Rabbi Goldenberg. One small thing you can do: If you have family or friends who are hesitant about vaccination, Dr. Wright suggests having gentle conversations to convince them. “You can be way more influential than a celebrity,” she says.
- Remember you’re not alone. Whether you’re physically isolated from others or just feel like nobody else is following the same protocols as you, there are ways to feel connected. “Reach out to people you’ve been close with in the past, but you may have lost touch,” says Dr. King. “It gives you an opportunity to rekindle joy. Particularly in this moment, when a lot of people are so afraid, it’s easier to reach out to those you already know than try to meet new people.” Dr. King’s research has found it takes as few as two close connections to make people feel supported.
- Stay in the present. Instead of stressing over what’s already happened or worrying about what might still come, just think about today. “We’ve learned a lot about the coronavirus, and we’re still learning more,” says Dr. Wright. “We don’t know what the future looks like, but it won’t be like this forever.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Thanks to the rollout of the COVID-19 vaccines, more than just flowers were blooming this past spring. People came out of lockdown like bears emerging from hibernation, making plans to reunite with friends and loved ones they hadn’t seen in months. But with the tremendous surge in cases brought by the Delta variant, this summer has been anything but sunny and carefree. Case counts have once more reached prevaccination levels. In a repeat of last summer, people are canceling travel plans, and the lead-up to the new school year has become fraught and stressful.
“This whiplash is causing people to feel a variety of emotions: disappointment, uncertainty, anxiety, possibly anger and frustration,” says Vaile Wright, Ph.D., senior director of health care innovation at the American Psychological Association. “When it seemed like there was a light at the end of the tunnel, and we have the tools to overcome [the virus], and we’re not really using them, it can be hard for people to understand.”
The importance of hope
For decades, researchers have been digging into the crucial role hopefulness plays in mental health. The vaccine rollout, earlier than anticipated, provided a much needed burst of hope after months of bad news.
“It was a feeling of almost euphoria in June: ‘We’re going to see everybody!’” says Rachel Goldenberg, a rabbi in Jackson Heights, NY. “We have a theme for our High Holidays, and this year’s is very hopeful: Sow in tears, reap in joy. It felt like the sowing in tears part was behind us, and we were looking forward to reaping in joy. Slowly but surely, with Delta, everything has turned upside down.”
For Roxanne Hawn, a writer in Golden, Colo., vaccination offered a glimpse of something like normal life.
“I wore cute clothes. I stopped and got takeout for lunch. I bought myself flowers. I even had a little uplifting soundtrack for that time of hope and relief,” she says. “With the Delta variant, it feels like that window of normalcy closed quickly.”
Having that little bit of hope dashed can wear down even the sturdiest spirits, says Marissa King, PhD, author of “Social Chemistry: Decoding the Elements of Human Connection”.
“There was a moment when we were able to reconnect, to experience joy and the hope of being able to revitalize relationships,” she says. “The loss of that hope and the fear of being isolated again is causing so much distress.”
A new kind of loneliness
When the pandemic started, mom of three Julie Schwietert Collazo formed a WhatsApp group with several friends who were taking lockdown seriously. They got each other through months of isolation and celebrated the idea of reopening. Then Ms. Collazo’s oldest got COVID, just 5 weeks before her 12th birthday, and their family went back into quarantine. Her moms’ group is no longer on the same page about precautions.
“Last year we were doing it together, and it made it feel a bit easier,” she says. “As things started to normalize, everybody started thinking and moving in different directions. It feels like we’re not working through the same issues collectively like before.”
Dr. King says the feeling Ms. Collazo describes is quite common these days.
“A profound sense of loneliness comes from feeling like you’re the only one,” she says. “There’s such disagreement about the best path forward, it can feel lonely just because you think differently.”
An epidemic of anxiety
As the Delta variant drives case numbers back up again, worries increase as well.
“Is this ever going to end?” asks Ms. Collazo. “Is this our new reality, constantly having to order our lives around COVID?”
This uneasiness affects our well-being.
The National Center for Health Statistics and the Census Bureau have monitored the nation’s mental health via the ongoing Household Pulse Survey during the pandemic. It asks participants about their symptoms of either anxiety or depression. Throughout, more people have reported feeling anxious than depressed.
Anxiety peaked around Thanksgiving and Christmas, with nearly 38% of people reporting symptoms. The first vaccines began to roll out around that time, and anxiety levels steadily went down through the spring and early summer, dipping below 25% in late June. But those numbers have begun to creep back up – the most recent data, which goes through Aug. 2, found 27% of Americans reporting symptoms of anxiety.
“Nervous is the new normal,” says Vivian Pender, MD, president of the American Psychiatric Association. “Uncertainty makes people feel anxious.”
Empathy vs. anger
The way politics play into basic measures like mask-wearing and vaccination adds its own layer of stress. Physical altercations have resulted: In Los Angeles, a participant was stabbed at an antivaccination protest. At an Austin, Tex., elementary school, angry parents physically and verbally assaulted teachers who wore masks. Things have gotten so heated, the Department of Homeland Security issued a National Terrorism Advisory System bulletin last week. It warns that extremists could use new COVID-driven public health restrictions as an excuse to commit domestic terrorism.
Anger goes in the opposite direction, too, with people who’ve been following recommended procedures becoming increasingly fed up with those who flout them. Those intense emotions may not lead to violence, but they do make it harder for us to feel secure.
“It’s a public health crisis, and it’s turned into something different. When we get into us/them situations, we start to lose empathy. Empathy is important to identify solutions and work together as a community,” says Dr. Wright. “That’s what sparks the anger: the sense of ‘You aren’t doing what you’re supposed to be doing.’”
How to cope
Loneliness, anxiety, and anger may be swirling all around you right now. But that doesn’t make you powerless to boost your mental health. These suggestions may help:
- Trust your gut. If your community is reopening faster than feels comfortable to you, do whatever makes your family feel safe. “Ask yourself how you’re feeling, and use your feelings to guide your decisions,” says Dr. Pender. “Get more information, then follow the science.”
- Stop judging yourself. If you’re feeling lonely or mourning the losses COVID has brought, don’t fight it, says Wright. “Let it be an emotion that comes and goes, and try to find ways to feel connected to other people.”
- Practice self-care. It may sound simplistic, but eating healthy foods, exercising, and getting a good night’s sleep can all contribute to a more positive
- Try to ease anxiety. Meditation, calming self-talk, and soothing music can all lift your spirits. Or try diaphragmatic breathing: Breathe in for 5 seconds, hold for 2, and breathe out for 5. Even squeezing a stress ball can give you a tangible sense of
- Take action. Both Rabbi Goldenberg and Ms. Collazo, who runs a nonprofit that works to reunite immigrant families, say helping their community helps them feel better. “To sing and lead Shabbat services, even on Zoom, to see the faces of my people, it’s very healing,” says Rabbi Goldenberg. One small thing you can do: If you have family or friends who are hesitant about vaccination, Dr. Wright suggests having gentle conversations to convince them. “You can be way more influential than a celebrity,” she says.
- Remember you’re not alone. Whether you’re physically isolated from others or just feel like nobody else is following the same protocols as you, there are ways to feel connected. “Reach out to people you’ve been close with in the past, but you may have lost touch,” says Dr. King. “It gives you an opportunity to rekindle joy. Particularly in this moment, when a lot of people are so afraid, it’s easier to reach out to those you already know than try to meet new people.” Dr. King’s research has found it takes as few as two close connections to make people feel supported.
- Stay in the present. Instead of stressing over what’s already happened or worrying about what might still come, just think about today. “We’ve learned a lot about the coronavirus, and we’re still learning more,” says Dr. Wright. “We don’t know what the future looks like, but it won’t be like this forever.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Thanks to the rollout of the COVID-19 vaccines, more than just flowers were blooming this past spring. People came out of lockdown like bears emerging from hibernation, making plans to reunite with friends and loved ones they hadn’t seen in months. But with the tremendous surge in cases brought by the Delta variant, this summer has been anything but sunny and carefree. Case counts have once more reached prevaccination levels. In a repeat of last summer, people are canceling travel plans, and the lead-up to the new school year has become fraught and stressful.
“This whiplash is causing people to feel a variety of emotions: disappointment, uncertainty, anxiety, possibly anger and frustration,” says Vaile Wright, Ph.D., senior director of health care innovation at the American Psychological Association. “When it seemed like there was a light at the end of the tunnel, and we have the tools to overcome [the virus], and we’re not really using them, it can be hard for people to understand.”
The importance of hope
For decades, researchers have been digging into the crucial role hopefulness plays in mental health. The vaccine rollout, earlier than anticipated, provided a much needed burst of hope after months of bad news.
“It was a feeling of almost euphoria in June: ‘We’re going to see everybody!’” says Rachel Goldenberg, a rabbi in Jackson Heights, NY. “We have a theme for our High Holidays, and this year’s is very hopeful: Sow in tears, reap in joy. It felt like the sowing in tears part was behind us, and we were looking forward to reaping in joy. Slowly but surely, with Delta, everything has turned upside down.”
For Roxanne Hawn, a writer in Golden, Colo., vaccination offered a glimpse of something like normal life.
“I wore cute clothes. I stopped and got takeout for lunch. I bought myself flowers. I even had a little uplifting soundtrack for that time of hope and relief,” she says. “With the Delta variant, it feels like that window of normalcy closed quickly.”
Having that little bit of hope dashed can wear down even the sturdiest spirits, says Marissa King, PhD, author of “Social Chemistry: Decoding the Elements of Human Connection”.
“There was a moment when we were able to reconnect, to experience joy and the hope of being able to revitalize relationships,” she says. “The loss of that hope and the fear of being isolated again is causing so much distress.”
A new kind of loneliness
When the pandemic started, mom of three Julie Schwietert Collazo formed a WhatsApp group with several friends who were taking lockdown seriously. They got each other through months of isolation and celebrated the idea of reopening. Then Ms. Collazo’s oldest got COVID, just 5 weeks before her 12th birthday, and their family went back into quarantine. Her moms’ group is no longer on the same page about precautions.
“Last year we were doing it together, and it made it feel a bit easier,” she says. “As things started to normalize, everybody started thinking and moving in different directions. It feels like we’re not working through the same issues collectively like before.”
Dr. King says the feeling Ms. Collazo describes is quite common these days.
“A profound sense of loneliness comes from feeling like you’re the only one,” she says. “There’s such disagreement about the best path forward, it can feel lonely just because you think differently.”
An epidemic of anxiety
As the Delta variant drives case numbers back up again, worries increase as well.
“Is this ever going to end?” asks Ms. Collazo. “Is this our new reality, constantly having to order our lives around COVID?”
This uneasiness affects our well-being.
The National Center for Health Statistics and the Census Bureau have monitored the nation’s mental health via the ongoing Household Pulse Survey during the pandemic. It asks participants about their symptoms of either anxiety or depression. Throughout, more people have reported feeling anxious than depressed.
Anxiety peaked around Thanksgiving and Christmas, with nearly 38% of people reporting symptoms. The first vaccines began to roll out around that time, and anxiety levels steadily went down through the spring and early summer, dipping below 25% in late June. But those numbers have begun to creep back up – the most recent data, which goes through Aug. 2, found 27% of Americans reporting symptoms of anxiety.
“Nervous is the new normal,” says Vivian Pender, MD, president of the American Psychiatric Association. “Uncertainty makes people feel anxious.”
Empathy vs. anger
The way politics play into basic measures like mask-wearing and vaccination adds its own layer of stress. Physical altercations have resulted: In Los Angeles, a participant was stabbed at an antivaccination protest. At an Austin, Tex., elementary school, angry parents physically and verbally assaulted teachers who wore masks. Things have gotten so heated, the Department of Homeland Security issued a National Terrorism Advisory System bulletin last week. It warns that extremists could use new COVID-driven public health restrictions as an excuse to commit domestic terrorism.
Anger goes in the opposite direction, too, with people who’ve been following recommended procedures becoming increasingly fed up with those who flout them. Those intense emotions may not lead to violence, but they do make it harder for us to feel secure.
“It’s a public health crisis, and it’s turned into something different. When we get into us/them situations, we start to lose empathy. Empathy is important to identify solutions and work together as a community,” says Dr. Wright. “That’s what sparks the anger: the sense of ‘You aren’t doing what you’re supposed to be doing.’”
How to cope
Loneliness, anxiety, and anger may be swirling all around you right now. But that doesn’t make you powerless to boost your mental health. These suggestions may help:
- Trust your gut. If your community is reopening faster than feels comfortable to you, do whatever makes your family feel safe. “Ask yourself how you’re feeling, and use your feelings to guide your decisions,” says Dr. Pender. “Get more information, then follow the science.”
- Stop judging yourself. If you’re feeling lonely or mourning the losses COVID has brought, don’t fight it, says Wright. “Let it be an emotion that comes and goes, and try to find ways to feel connected to other people.”
- Practice self-care. It may sound simplistic, but eating healthy foods, exercising, and getting a good night’s sleep can all contribute to a more positive
- Try to ease anxiety. Meditation, calming self-talk, and soothing music can all lift your spirits. Or try diaphragmatic breathing: Breathe in for 5 seconds, hold for 2, and breathe out for 5. Even squeezing a stress ball can give you a tangible sense of
- Take action. Both Rabbi Goldenberg and Ms. Collazo, who runs a nonprofit that works to reunite immigrant families, say helping their community helps them feel better. “To sing and lead Shabbat services, even on Zoom, to see the faces of my people, it’s very healing,” says Rabbi Goldenberg. One small thing you can do: If you have family or friends who are hesitant about vaccination, Dr. Wright suggests having gentle conversations to convince them. “You can be way more influential than a celebrity,” she says.
- Remember you’re not alone. Whether you’re physically isolated from others or just feel like nobody else is following the same protocols as you, there are ways to feel connected. “Reach out to people you’ve been close with in the past, but you may have lost touch,” says Dr. King. “It gives you an opportunity to rekindle joy. Particularly in this moment, when a lot of people are so afraid, it’s easier to reach out to those you already know than try to meet new people.” Dr. King’s research has found it takes as few as two close connections to make people feel supported.
- Stay in the present. Instead of stressing over what’s already happened or worrying about what might still come, just think about today. “We’ve learned a lot about the coronavirus, and we’re still learning more,” says Dr. Wright. “We don’t know what the future looks like, but it won’t be like this forever.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.









