User login
Survival data reported from largest CAR T trial in B-cell lymphoma
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
ORLANDO – Updated results from the TRANSCEND NHL trial include survival data with lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel), an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphomas.
The median progression-free survival (PFS) was 6.8 months, and the median overall survival was 21.1 months. PFS results were best among complete responders and among patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma.
Jeremy S. Abramson, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital in Boston, presented these results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“TRANSCEND NHL is the largest clinical study to date of CD19-directed CAR T cells in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma,” Dr. Abramson said.
The phase 1 trial (NCT02631044) includes 269 patients who received liso-cel. They were diagnosed with transformed follicular lymphoma (22%) or other indolent lymphoma (7%), high-grade B-cell lymphoma (13%), primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma (6%), grade 3B follicular lymphoma (1%), or diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified (51%).
At baseline, patients had received a median of three prior systemic therapies (range, one to eight). Some patients had received autologous (33%) or allogeneic (3%) transplant. Many patients were chemotherapy refractory (67%) or had never achieved a complete response to prior therapy (44%).
More than half of patients (59%) received bridging therapy during liso-cel manufacturing. All patients received lymphodepletion with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by liso-cel at 50 x 106 CAR T cells, 100 x 106 CAR T cells, or 150 x 106 CAR T cells.
Response and survival
The median follow-up was 12.0 months. The overall response rate was 73%, and the complete response rate was 53%.
“Remissions were rapid, with a median of 1 month from CAR T-cell infusion, and durable, with a median duration of response that has not been reached and 55% of patients remaining in response at 1 year,” Dr. Abramson said.
The median PFS was 6.8 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 2.8 months for patients with a partial response, and 1.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
The median PFS was not reached for patients with primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma or transformed follicular lymphoma, 5.0 months for high-grade B-cell lymphoma, 3.0 months for diffuse large B-cell lymphoma not otherwise specified, and 2.9 months in transformed indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
The median overall survival was 21.1 months overall, not reached for patients who achieved a complete response, 9.0 months for patients who had a partial response, and 5.1 months for patients with stable disease or progressive disease.
Safety
Common treatment-emergent adverse events were neutropenia (63%), anemia (48%), fatigue (44%), nausea (33%), thrombocytopenia (31%), headache (30%), decreased appetite (28%), and diarrhea (26%).
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 42% of patients, and neurologic events occurred in 30%. Grade 3-4 CRS occurred in 2% of patients, and grade 3-4 neurologic events occurred in 10%. There were no cases of grade 5 CRS or neurologic events.
The median time to CRS onset was 5 days, and the median time to onset of neurologic events was 9 days. The median time to resolution of CRS and neurologic events was 5 days and 11 days, respectively.
“The low incidence of severe CRS and neurologic events and their late time of onset support using this product in a large range of patients and in the outpatient setting,” Dr. Abramson said.
There were seven grade 5 treatment-related adverse events, including diffuse alveolar damage, pulmonary hemorrhage, multiple organ dysfunction syndrome, cardiomyopathy, fludarabine leukoencephalopathy, septic shock, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
This trial is sponsored by Bristol-Myers Squibb. Dr. Abramson reported relationships with Juno Therapeutics and Celgene, now owned by Bristol-Myers Squibb, and a range of other companies.
SOURCE: Abramson JS et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 241.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Age, sex, and other factors linked to risk of intracranial hemorrhage in ITP
ORLANDO – A large, retrospective study suggests several factors are associated with an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with immune thrombocytopenia.
Data on more than 300,000 immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) hospitalizations indicated that older age, male sex, not having private insurance, having a gastrointestinal or “other” bleed, and receiving treatment at a hospital in the western United States, a medium- or large-sized hospital, or an urban teaching hospital were all associated with an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
Mayank Sharma, of the University of Miami, detailed these findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Mr. Sharma and colleagues analyzed data from the National Inpatient Sample database from 2007 to 2016. Of the 348,906 ITP hospitalizations included, there were 3,408 (0.98%) cases of ICH.
The overall incidence of ICH was low and remained stable over time, “which is reassuring,” Mr. Sharma said. However, the mortality rate was higher among patients with ICH than among those without it – 26.7% and 3.2%, respectively.
A multivariate analysis showed that female patients had a decreased likelihood of ICH, with an odds ratio of 0.81 (95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.97). Patients with private insurance had a decreased likelihood of ICH as well, with an OR of 0.81 (95% CI, 0.61-1.08).
Conversely, older patients had an increased likelihood of ICH. The OR was 2.23 (95% CI, 1.51-3.31) for patients aged 25-64 years, and the OR was 3.69 (95% CI, 2.34-5.84) for patients aged 65 years and older.
Patients with a gastrointestinal bleed or an other bleed (not including hematuria or epistaxis) had an increased likelihood of ICH. The ORs were 1.60 (95% CI, 1.18-2.16) and 1.69 (95% CI, 1.19-2.42), respectively.
Patients hospitalized in the western United States (OR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.26-2.08), at a medium-sized hospital (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.08-2.47), at a large hospital (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.65-3.55), or at an urban teaching hospital (OR, 2.73; 95% CI, 1.80-4.13) all had an increased likelihood of ICH.
“Our second objective was to study the factors associated with mortality in ITP patients with ICH,” Mr. Sharma said. “We found female gender and Medicaid, private, or self-pay as primary payers to be associated with a lower mortality in ITP with ICH.
“[A]ge of 25-64 and 65 years and above, coexistence of a GI bleed or other bleed, and admission to a large or urban teaching hospital were associated with a higher mortality,” he added.
Mr. Sharma said the study’s strengths are that it is the most recent study on trends in ITP/ICH hospitalizations, and that it’s a longitudinal assessment of data from a nationally representative database.
The study’s limitations include its retrospective nature and the use of ICD codes, which could lead to inaccuracies. Data on prior therapies and long-term outcomes were not available, and the researchers were unable to differentiate between acute and chronic ITP.
Mr. Sharma said he had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 55.
ORLANDO – A large, retrospective study suggests several factors are associated with an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with immune thrombocytopenia.
Data on more than 300,000 immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) hospitalizations indicated that older age, male sex, not having private insurance, having a gastrointestinal or “other” bleed, and receiving treatment at a hospital in the western United States, a medium- or large-sized hospital, or an urban teaching hospital were all associated with an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
Mayank Sharma, of the University of Miami, detailed these findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Mr. Sharma and colleagues analyzed data from the National Inpatient Sample database from 2007 to 2016. Of the 348,906 ITP hospitalizations included, there were 3,408 (0.98%) cases of ICH.
The overall incidence of ICH was low and remained stable over time, “which is reassuring,” Mr. Sharma said. However, the mortality rate was higher among patients with ICH than among those without it – 26.7% and 3.2%, respectively.
A multivariate analysis showed that female patients had a decreased likelihood of ICH, with an odds ratio of 0.81 (95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.97). Patients with private insurance had a decreased likelihood of ICH as well, with an OR of 0.81 (95% CI, 0.61-1.08).
Conversely, older patients had an increased likelihood of ICH. The OR was 2.23 (95% CI, 1.51-3.31) for patients aged 25-64 years, and the OR was 3.69 (95% CI, 2.34-5.84) for patients aged 65 years and older.
Patients with a gastrointestinal bleed or an other bleed (not including hematuria or epistaxis) had an increased likelihood of ICH. The ORs were 1.60 (95% CI, 1.18-2.16) and 1.69 (95% CI, 1.19-2.42), respectively.
Patients hospitalized in the western United States (OR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.26-2.08), at a medium-sized hospital (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.08-2.47), at a large hospital (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.65-3.55), or at an urban teaching hospital (OR, 2.73; 95% CI, 1.80-4.13) all had an increased likelihood of ICH.
“Our second objective was to study the factors associated with mortality in ITP patients with ICH,” Mr. Sharma said. “We found female gender and Medicaid, private, or self-pay as primary payers to be associated with a lower mortality in ITP with ICH.
“[A]ge of 25-64 and 65 years and above, coexistence of a GI bleed or other bleed, and admission to a large or urban teaching hospital were associated with a higher mortality,” he added.
Mr. Sharma said the study’s strengths are that it is the most recent study on trends in ITP/ICH hospitalizations, and that it’s a longitudinal assessment of data from a nationally representative database.
The study’s limitations include its retrospective nature and the use of ICD codes, which could lead to inaccuracies. Data on prior therapies and long-term outcomes were not available, and the researchers were unable to differentiate between acute and chronic ITP.
Mr. Sharma said he had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 55.
ORLANDO – A large, retrospective study suggests several factors are associated with an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage in patients with immune thrombocytopenia.
Data on more than 300,000 immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) hospitalizations indicated that older age, male sex, not having private insurance, having a gastrointestinal or “other” bleed, and receiving treatment at a hospital in the western United States, a medium- or large-sized hospital, or an urban teaching hospital were all associated with an increased risk of intracranial hemorrhage (ICH).
Mayank Sharma, of the University of Miami, detailed these findings at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Mr. Sharma and colleagues analyzed data from the National Inpatient Sample database from 2007 to 2016. Of the 348,906 ITP hospitalizations included, there were 3,408 (0.98%) cases of ICH.
The overall incidence of ICH was low and remained stable over time, “which is reassuring,” Mr. Sharma said. However, the mortality rate was higher among patients with ICH than among those without it – 26.7% and 3.2%, respectively.
A multivariate analysis showed that female patients had a decreased likelihood of ICH, with an odds ratio of 0.81 (95% confidence interval, 0.68-0.97). Patients with private insurance had a decreased likelihood of ICH as well, with an OR of 0.81 (95% CI, 0.61-1.08).
Conversely, older patients had an increased likelihood of ICH. The OR was 2.23 (95% CI, 1.51-3.31) for patients aged 25-64 years, and the OR was 3.69 (95% CI, 2.34-5.84) for patients aged 65 years and older.
Patients with a gastrointestinal bleed or an other bleed (not including hematuria or epistaxis) had an increased likelihood of ICH. The ORs were 1.60 (95% CI, 1.18-2.16) and 1.69 (95% CI, 1.19-2.42), respectively.
Patients hospitalized in the western United States (OR, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.26-2.08), at a medium-sized hospital (OR, 1.64; 95% CI, 1.08-2.47), at a large hospital (OR, 2.42; 95% CI, 1.65-3.55), or at an urban teaching hospital (OR, 2.73; 95% CI, 1.80-4.13) all had an increased likelihood of ICH.
“Our second objective was to study the factors associated with mortality in ITP patients with ICH,” Mr. Sharma said. “We found female gender and Medicaid, private, or self-pay as primary payers to be associated with a lower mortality in ITP with ICH.
“[A]ge of 25-64 and 65 years and above, coexistence of a GI bleed or other bleed, and admission to a large or urban teaching hospital were associated with a higher mortality,” he added.
Mr. Sharma said the study’s strengths are that it is the most recent study on trends in ITP/ICH hospitalizations, and that it’s a longitudinal assessment of data from a nationally representative database.
The study’s limitations include its retrospective nature and the use of ICD codes, which could lead to inaccuracies. Data on prior therapies and long-term outcomes were not available, and the researchers were unable to differentiate between acute and chronic ITP.
Mr. Sharma said he had no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Sharma M et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 55.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
D-RVd for frontline myeloma looks robust in GRIFFIN trial update
ORLANDO – While the benefit of daratumumab added to lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (D-RVd) continues to improve with longer follow-up of the GRIFFIN trial, even early adopters may want to wait for additional data before declaring the combination a first-line standard for transplant-eligible multiple myeloma, according to an investigator on the trial.
D-RVd has significantly improved both response rates and depth of response, compared with RVd alone, Peter M. Voorhees, MD, of Levine Cancer Institute, Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C., reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Additionally, rates of response and minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity with D-RVd have increased with longer follow-up beyond posttransplant consolidation, in the ongoing randomized phase 2 trial, Dr. Voorhees said.
“Those of you that are early adopters have good ammunition based on this result, but I would argue that we do need to confirm that the increased MRD-negative rate that we’re seeing translates into a sustained improvement in MRD negativity,” said Dr. Voorhees while presenting the updated results.
Most importantly, it needs to be confirmed that improved depth of response with D-RVd translates into an improvement in progression-free survival, not only in GRIFFIN, he said, but in PERSEUS, a large, randomized European phase 3 trial of subcutaneous daratumumab plus RVd versus RVd alone.
In the GRIFFIN trial, a total of 207 patients with transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma were randomized to intravenous daratumumab plus RVd versus RVd alone, with a primary endpoint of stringent complete response (sCR) by the end of consolidation.
Primary findings, presented in September at the 17th International Myeloma Workshop (IMW) meeting in Boston, indicated an sCR of 42.4% for D-RVd versus 32.0% for RVd at a median follow-up of 13.5 months, a difference that Dr. Voorhees said was statistically significant as defined by the protocol (1-sided P = .068), with an odds ratio of 1.57 (95% confidence interval, 0.87-2.82) in favor of the D-RVd arm.
With longer follow-up data, which Dr. Voorhees reported at ASH, the responses have “deepened over time” in both arms of the study, though he said the daratumumab arm continues to perform better. The sCR with 22.1 months of follow-up was 62.6% for D-RVd versus 45.4% for RVd.
The rates of MRD negativity at this clinical cutoff were 51.0% versus 20.4% for the D-RVd and RVd arms, respectively (P less than .0001), while the 24-month PFS rates were 95.8% for D-RVd and 89.8% for RVd. “Suffice it to say that both groups of patients are doing incredibly well at 2 years,” Dr. Voorhees said.
Rates of grade 3 and 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were higher in the D-RVd arm, and there were more infections, though this was largely driven by an increased incidence of grade 1 or 2 upper respiratory tract infections, according to Dr. Voorhees.
Daratumumab did not impact time to engraftment, with a median CD34+ cell yield of 8.2 x 106 cells/kg for D-RVd and 9.4 x 106 cells/kg for RVd, a difference that Dr. Voorhees said was “not of clinical significance.”
Dr. Voorhees reported disclosures related to Takeda, Oncopeptides, Novartis, GSK, Janssen, Celgene, BMS, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, and TeneBio.
SOURCE: Voorhees PM et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 691.
ORLANDO – While the benefit of daratumumab added to lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (D-RVd) continues to improve with longer follow-up of the GRIFFIN trial, even early adopters may want to wait for additional data before declaring the combination a first-line standard for transplant-eligible multiple myeloma, according to an investigator on the trial.
D-RVd has significantly improved both response rates and depth of response, compared with RVd alone, Peter M. Voorhees, MD, of Levine Cancer Institute, Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C., reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Additionally, rates of response and minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity with D-RVd have increased with longer follow-up beyond posttransplant consolidation, in the ongoing randomized phase 2 trial, Dr. Voorhees said.
“Those of you that are early adopters have good ammunition based on this result, but I would argue that we do need to confirm that the increased MRD-negative rate that we’re seeing translates into a sustained improvement in MRD negativity,” said Dr. Voorhees while presenting the updated results.
Most importantly, it needs to be confirmed that improved depth of response with D-RVd translates into an improvement in progression-free survival, not only in GRIFFIN, he said, but in PERSEUS, a large, randomized European phase 3 trial of subcutaneous daratumumab plus RVd versus RVd alone.
In the GRIFFIN trial, a total of 207 patients with transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma were randomized to intravenous daratumumab plus RVd versus RVd alone, with a primary endpoint of stringent complete response (sCR) by the end of consolidation.
Primary findings, presented in September at the 17th International Myeloma Workshop (IMW) meeting in Boston, indicated an sCR of 42.4% for D-RVd versus 32.0% for RVd at a median follow-up of 13.5 months, a difference that Dr. Voorhees said was statistically significant as defined by the protocol (1-sided P = .068), with an odds ratio of 1.57 (95% confidence interval, 0.87-2.82) in favor of the D-RVd arm.
With longer follow-up data, which Dr. Voorhees reported at ASH, the responses have “deepened over time” in both arms of the study, though he said the daratumumab arm continues to perform better. The sCR with 22.1 months of follow-up was 62.6% for D-RVd versus 45.4% for RVd.
The rates of MRD negativity at this clinical cutoff were 51.0% versus 20.4% for the D-RVd and RVd arms, respectively (P less than .0001), while the 24-month PFS rates were 95.8% for D-RVd and 89.8% for RVd. “Suffice it to say that both groups of patients are doing incredibly well at 2 years,” Dr. Voorhees said.
Rates of grade 3 and 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were higher in the D-RVd arm, and there were more infections, though this was largely driven by an increased incidence of grade 1 or 2 upper respiratory tract infections, according to Dr. Voorhees.
Daratumumab did not impact time to engraftment, with a median CD34+ cell yield of 8.2 x 106 cells/kg for D-RVd and 9.4 x 106 cells/kg for RVd, a difference that Dr. Voorhees said was “not of clinical significance.”
Dr. Voorhees reported disclosures related to Takeda, Oncopeptides, Novartis, GSK, Janssen, Celgene, BMS, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, and TeneBio.
SOURCE: Voorhees PM et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 691.
ORLANDO – While the benefit of daratumumab added to lenalidomide, bortezomib, and dexamethasone (D-RVd) continues to improve with longer follow-up of the GRIFFIN trial, even early adopters may want to wait for additional data before declaring the combination a first-line standard for transplant-eligible multiple myeloma, according to an investigator on the trial.
D-RVd has significantly improved both response rates and depth of response, compared with RVd alone, Peter M. Voorhees, MD, of Levine Cancer Institute, Atrium Health, Charlotte, N.C., reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Additionally, rates of response and minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity with D-RVd have increased with longer follow-up beyond posttransplant consolidation, in the ongoing randomized phase 2 trial, Dr. Voorhees said.
“Those of you that are early adopters have good ammunition based on this result, but I would argue that we do need to confirm that the increased MRD-negative rate that we’re seeing translates into a sustained improvement in MRD negativity,” said Dr. Voorhees while presenting the updated results.
Most importantly, it needs to be confirmed that improved depth of response with D-RVd translates into an improvement in progression-free survival, not only in GRIFFIN, he said, but in PERSEUS, a large, randomized European phase 3 trial of subcutaneous daratumumab plus RVd versus RVd alone.
In the GRIFFIN trial, a total of 207 patients with transplant-eligible newly diagnosed multiple myeloma were randomized to intravenous daratumumab plus RVd versus RVd alone, with a primary endpoint of stringent complete response (sCR) by the end of consolidation.
Primary findings, presented in September at the 17th International Myeloma Workshop (IMW) meeting in Boston, indicated an sCR of 42.4% for D-RVd versus 32.0% for RVd at a median follow-up of 13.5 months, a difference that Dr. Voorhees said was statistically significant as defined by the protocol (1-sided P = .068), with an odds ratio of 1.57 (95% confidence interval, 0.87-2.82) in favor of the D-RVd arm.
With longer follow-up data, which Dr. Voorhees reported at ASH, the responses have “deepened over time” in both arms of the study, though he said the daratumumab arm continues to perform better. The sCR with 22.1 months of follow-up was 62.6% for D-RVd versus 45.4% for RVd.
The rates of MRD negativity at this clinical cutoff were 51.0% versus 20.4% for the D-RVd and RVd arms, respectively (P less than .0001), while the 24-month PFS rates were 95.8% for D-RVd and 89.8% for RVd. “Suffice it to say that both groups of patients are doing incredibly well at 2 years,” Dr. Voorhees said.
Rates of grade 3 and 4 neutropenia and thrombocytopenia were higher in the D-RVd arm, and there were more infections, though this was largely driven by an increased incidence of grade 1 or 2 upper respiratory tract infections, according to Dr. Voorhees.
Daratumumab did not impact time to engraftment, with a median CD34+ cell yield of 8.2 x 106 cells/kg for D-RVd and 9.4 x 106 cells/kg for RVd, a difference that Dr. Voorhees said was “not of clinical significance.”
Dr. Voorhees reported disclosures related to Takeda, Oncopeptides, Novartis, GSK, Janssen, Celgene, BMS, Adaptive Biotechnologies, Amgen, and TeneBio.
SOURCE: Voorhees PM et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 691.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Zanubrutinib achieved high response rate in del(17p) CLL cohort
ORLANDO – Zanubrutinib has produced a high overall response rate in one the largest cohorts of patients with treatment-naive 17p-deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studied to date.
An overall response rate of nearly 93% was seen in this 109-patient, high-risk cohort, enrolled as part of the phase 3 SEQUOIA study (BGB-3111-304), said Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne.
Tolerability of zanubrutinib was essentially consistent with previous reports of the agent as used in other B-cell malignancies, Dr. Tam said in an oral presentation of the results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Deletion of chromosome 17p13.1, or del(17p), is a marker of poor prognosis and poor response to chemotherapy in patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For patients with del(17p) CLL, the first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has become a standard of care, Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib, a next-generation BTK inhibitor, was developed to improve BTK occupancy and minimize off-target inhibition of TEC and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. “What this effectively means is that we are able to dose this drug at levels much higher than that achievable with ibrutinib, and not get intolerable side effects,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib has been approved in the United States for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, and generated durable responses among CLL/SLL patients with or without del(17p) in a phase 1/2 study, according to Dr. Tam.
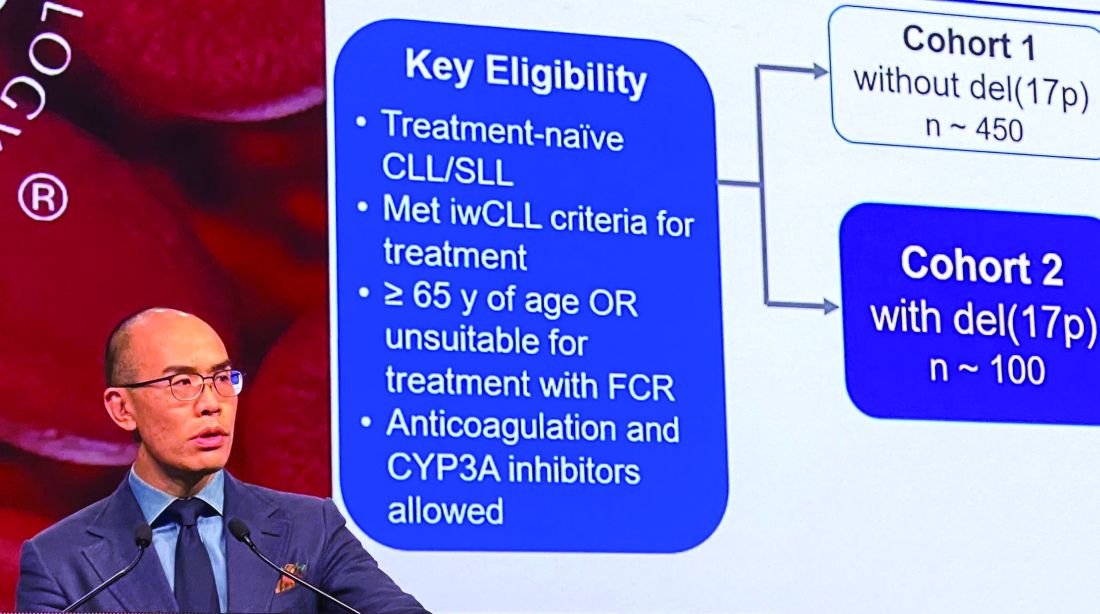
In the present study, which exclusively enrolled patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL, patients received 160 mg twice daily of zanubrutinib, Dr. Tam said. Out of 109 patients enrolled, 10 (9.2%) had SLL. All patients were aged at least 65 years or were deemed unsuitable for treatment with the combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab.
Of 109 patients enrolled, 104 received on-study treatment. The median age was 70 years, Dr. Tam reported, and a number of patients had other high-risk markers beyond del(17p), including unmutated IgVH status in 61.5% of patients.
With a median follow-up of 10 months, the overall response rate was 92.7%, including 1.9% complete responses and 78.9% partial responses. “Only one patient had primary progressive disease after starting this drug,” Dr. Tam said.
Time to response was rapid, according to the investigator, at about 2.8 months; after 6 months, 95% of responders remained in response.
Further analysis showed that the response rate was consistent across subgroups. “There was not a single group that did not respond with a high response rate, including poor prognostic groups,” Dr. Tam said.
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity, and the most common events included confusion and upper respiratory tract infection. The only common grade 3 event, according to Dr. Tam, was neutropenia. Rates of grade 3 major bleeding were low, he said, and the rate of grade 3 atrial fibrillation was 0.9%. One patient died due to pneumonia.
The ongoing SEQUOIA study, designed to compare zanubrutinib to the combination of bendamustine and rituximab in patients with previously untreated CLL or SLL, is sponsored by BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Novartis, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, Janssen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 499.
ORLANDO – Zanubrutinib has produced a high overall response rate in one the largest cohorts of patients with treatment-naive 17p-deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studied to date.
An overall response rate of nearly 93% was seen in this 109-patient, high-risk cohort, enrolled as part of the phase 3 SEQUOIA study (BGB-3111-304), said Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne.
Tolerability of zanubrutinib was essentially consistent with previous reports of the agent as used in other B-cell malignancies, Dr. Tam said in an oral presentation of the results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Deletion of chromosome 17p13.1, or del(17p), is a marker of poor prognosis and poor response to chemotherapy in patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For patients with del(17p) CLL, the first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has become a standard of care, Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib, a next-generation BTK inhibitor, was developed to improve BTK occupancy and minimize off-target inhibition of TEC and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. “What this effectively means is that we are able to dose this drug at levels much higher than that achievable with ibrutinib, and not get intolerable side effects,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib has been approved in the United States for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, and generated durable responses among CLL/SLL patients with or without del(17p) in a phase 1/2 study, according to Dr. Tam.
In the present study, which exclusively enrolled patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL, patients received 160 mg twice daily of zanubrutinib, Dr. Tam said. Out of 109 patients enrolled, 10 (9.2%) had SLL. All patients were aged at least 65 years or were deemed unsuitable for treatment with the combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab.
Of 109 patients enrolled, 104 received on-study treatment. The median age was 70 years, Dr. Tam reported, and a number of patients had other high-risk markers beyond del(17p), including unmutated IgVH status in 61.5% of patients.
With a median follow-up of 10 months, the overall response rate was 92.7%, including 1.9% complete responses and 78.9% partial responses. “Only one patient had primary progressive disease after starting this drug,” Dr. Tam said.
Time to response was rapid, according to the investigator, at about 2.8 months; after 6 months, 95% of responders remained in response.
Further analysis showed that the response rate was consistent across subgroups. “There was not a single group that did not respond with a high response rate, including poor prognostic groups,” Dr. Tam said.
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity, and the most common events included confusion and upper respiratory tract infection. The only common grade 3 event, according to Dr. Tam, was neutropenia. Rates of grade 3 major bleeding were low, he said, and the rate of grade 3 atrial fibrillation was 0.9%. One patient died due to pneumonia.
The ongoing SEQUOIA study, designed to compare zanubrutinib to the combination of bendamustine and rituximab in patients with previously untreated CLL or SLL, is sponsored by BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Novartis, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, Janssen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 499.
ORLANDO – Zanubrutinib has produced a high overall response rate in one the largest cohorts of patients with treatment-naive 17p-deletion chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) studied to date.
An overall response rate of nearly 93% was seen in this 109-patient, high-risk cohort, enrolled as part of the phase 3 SEQUOIA study (BGB-3111-304), said Constantine S. Tam, MBBS, MD, of St. Vincent’s Hospital and Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne.
Tolerability of zanubrutinib was essentially consistent with previous reports of the agent as used in other B-cell malignancies, Dr. Tam said in an oral presentation of the results at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Deletion of chromosome 17p13.1, or del(17p), is a marker of poor prognosis and poor response to chemotherapy in patients with CLL or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). For patients with del(17p) CLL, the first-generation Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib has become a standard of care, Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib, a next-generation BTK inhibitor, was developed to improve BTK occupancy and minimize off-target inhibition of TEC and epidermal growth factor receptor kinases. “What this effectively means is that we are able to dose this drug at levels much higher than that achievable with ibrutinib, and not get intolerable side effects,” Dr. Tam said.
Zanubrutinib has been approved in the United States for previously treated mantle cell lymphoma, and generated durable responses among CLL/SLL patients with or without del(17p) in a phase 1/2 study, according to Dr. Tam.
In the present study, which exclusively enrolled patients with del(17p) CLL/SLL, patients received 160 mg twice daily of zanubrutinib, Dr. Tam said. Out of 109 patients enrolled, 10 (9.2%) had SLL. All patients were aged at least 65 years or were deemed unsuitable for treatment with the combination of fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab.
Of 109 patients enrolled, 104 received on-study treatment. The median age was 70 years, Dr. Tam reported, and a number of patients had other high-risk markers beyond del(17p), including unmutated IgVH status in 61.5% of patients.
With a median follow-up of 10 months, the overall response rate was 92.7%, including 1.9% complete responses and 78.9% partial responses. “Only one patient had primary progressive disease after starting this drug,” Dr. Tam said.
Time to response was rapid, according to the investigator, at about 2.8 months; after 6 months, 95% of responders remained in response.
Further analysis showed that the response rate was consistent across subgroups. “There was not a single group that did not respond with a high response rate, including poor prognostic groups,” Dr. Tam said.
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in severity, and the most common events included confusion and upper respiratory tract infection. The only common grade 3 event, according to Dr. Tam, was neutropenia. Rates of grade 3 major bleeding were low, he said, and the rate of grade 3 atrial fibrillation was 0.9%. One patient died due to pneumonia.
The ongoing SEQUOIA study, designed to compare zanubrutinib to the combination of bendamustine and rituximab in patients with previously untreated CLL or SLL, is sponsored by BeiGene. Dr. Tam reported disclosures related to Novartis, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, BeiGene, Janssen, and Roche.
SOURCE: Tam C et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 499.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Some MCL patients can safely stop venetoclax-ibrutinib, study suggests
ORLANDO – Updated trial results have revealed durable responses with venetoclax and ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing some patients to stop treatment.
Five of 24 patients were able to stop treatment after achieving minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative complete responses (CRs). Four of these patients remain in CR at up to 18 months off treatment, although one patient ultimately progressed and died.
“Treatment cessation was feasible for patients in MRD-negative complete responses, raising the prospect of limited-duration, targeted-agent therapy in the management of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” said Sasanka M. Handunnetti, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne. Dr. Handunnetti presented these results, from the AIM trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 24 patients. At baseline, patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 47-81 years), and 88% were men. One patient was treatment-naive, but the rest had relapsed/refractory MCL. These patients had received a median of two prior therapies (range, 1-6).
The patients received venetoclax at 400 mg daily and ibrutinib at 560 mg daily.
In the primary analysis, the CR rate was 62% at week 16 and 71% overall, according to positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. MRD negativity was achieved by 67% of patients according to flow cytometry and 38% according to allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378[13]:1211-23).
Response and survival
For the current analysis, the median follow up was 37.5 months (range, 1.4-45.3 months). The median duration of response has not been reached, the median progression-free survival is 29 months, and the median overall survival is 32 months.
Thirteen patients have died, 8 of them due to progressive disease. The remaining 11 patients are still alive, and 9 of them are still in CR. One patient is still in partial response, and one has not responded but remains on ibrutinib and venetoclax.
Dr. Handunnetti pointed out that 12 patients had TP53 aberrations, and 8 of them died, but 4 remain alive and in CR. All four patients with SMARCA4 aberrations died.
Treatment status
Five patients are still receiving treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax, and one patient is receiving only venetoclax. One patient went off study treatment due to a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome, but that patient’s MCL is still in CR.
Five patients were able to stop treatment after achieving MRD-negative CR and were placed under “stringent surveillance,” Dr. Handunnetti said.
One of the five patients who stopped treatment progressed at 7 months and died. The remaining four patients are still alive and in CR at 6 months, 13 months, 17 months, and 18 months off treatment.
Safety update
Within the first 56 weeks of treatment, 15 patients required dose adjustments. Twelve patients required an adjustment to ibrutinib, seven to venetoclax, and four to both drugs. After 56 weeks, there were no dose adjustments.
Two patients developed therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome. One patient had previously received FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and BR (bendamustine and rituximab). The other patient had received R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
This investigator-initiated trial was funded by Janssen and Abbvie. Dr. Handunnetti reported relationships with Abbvie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Handunnetti S et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 756.
ORLANDO – Updated trial results have revealed durable responses with venetoclax and ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing some patients to stop treatment.
Five of 24 patients were able to stop treatment after achieving minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative complete responses (CRs). Four of these patients remain in CR at up to 18 months off treatment, although one patient ultimately progressed and died.
“Treatment cessation was feasible for patients in MRD-negative complete responses, raising the prospect of limited-duration, targeted-agent therapy in the management of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” said Sasanka M. Handunnetti, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne. Dr. Handunnetti presented these results, from the AIM trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 24 patients. At baseline, patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 47-81 years), and 88% were men. One patient was treatment-naive, but the rest had relapsed/refractory MCL. These patients had received a median of two prior therapies (range, 1-6).
The patients received venetoclax at 400 mg daily and ibrutinib at 560 mg daily.
In the primary analysis, the CR rate was 62% at week 16 and 71% overall, according to positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. MRD negativity was achieved by 67% of patients according to flow cytometry and 38% according to allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378[13]:1211-23).
Response and survival
For the current analysis, the median follow up was 37.5 months (range, 1.4-45.3 months). The median duration of response has not been reached, the median progression-free survival is 29 months, and the median overall survival is 32 months.
Thirteen patients have died, 8 of them due to progressive disease. The remaining 11 patients are still alive, and 9 of them are still in CR. One patient is still in partial response, and one has not responded but remains on ibrutinib and venetoclax.
Dr. Handunnetti pointed out that 12 patients had TP53 aberrations, and 8 of them died, but 4 remain alive and in CR. All four patients with SMARCA4 aberrations died.
Treatment status
Five patients are still receiving treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax, and one patient is receiving only venetoclax. One patient went off study treatment due to a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome, but that patient’s MCL is still in CR.
Five patients were able to stop treatment after achieving MRD-negative CR and were placed under “stringent surveillance,” Dr. Handunnetti said.
One of the five patients who stopped treatment progressed at 7 months and died. The remaining four patients are still alive and in CR at 6 months, 13 months, 17 months, and 18 months off treatment.
Safety update
Within the first 56 weeks of treatment, 15 patients required dose adjustments. Twelve patients required an adjustment to ibrutinib, seven to venetoclax, and four to both drugs. After 56 weeks, there were no dose adjustments.
Two patients developed therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome. One patient had previously received FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and BR (bendamustine and rituximab). The other patient had received R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
This investigator-initiated trial was funded by Janssen and Abbvie. Dr. Handunnetti reported relationships with Abbvie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Handunnetti S et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 756.
ORLANDO – Updated trial results have revealed durable responses with venetoclax and ibrutinib in patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL), allowing some patients to stop treatment.
Five of 24 patients were able to stop treatment after achieving minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative complete responses (CRs). Four of these patients remain in CR at up to 18 months off treatment, although one patient ultimately progressed and died.
“Treatment cessation was feasible for patients in MRD-negative complete responses, raising the prospect of limited-duration, targeted-agent therapy in the management of relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” said Sasanka M. Handunnetti, MBBS, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne. Dr. Handunnetti presented these results, from the AIM trial, at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
The phase 2 trial enrolled 24 patients. At baseline, patients had a median age of 68 years (range, 47-81 years), and 88% were men. One patient was treatment-naive, but the rest had relapsed/refractory MCL. These patients had received a median of two prior therapies (range, 1-6).
The patients received venetoclax at 400 mg daily and ibrutinib at 560 mg daily.
In the primary analysis, the CR rate was 62% at week 16 and 71% overall, according to positron-emission tomography/computed tomography. MRD negativity was achieved by 67% of patients according to flow cytometry and 38% according to allele-specific oligonucleotide polymerase chain reaction (N Engl J Med. 2018 Mar 29;378[13]:1211-23).
Response and survival
For the current analysis, the median follow up was 37.5 months (range, 1.4-45.3 months). The median duration of response has not been reached, the median progression-free survival is 29 months, and the median overall survival is 32 months.
Thirteen patients have died, 8 of them due to progressive disease. The remaining 11 patients are still alive, and 9 of them are still in CR. One patient is still in partial response, and one has not responded but remains on ibrutinib and venetoclax.
Dr. Handunnetti pointed out that 12 patients had TP53 aberrations, and 8 of them died, but 4 remain alive and in CR. All four patients with SMARCA4 aberrations died.
Treatment status
Five patients are still receiving treatment with ibrutinib and venetoclax, and one patient is receiving only venetoclax. One patient went off study treatment due to a diagnosis of myelodysplastic syndrome, but that patient’s MCL is still in CR.
Five patients were able to stop treatment after achieving MRD-negative CR and were placed under “stringent surveillance,” Dr. Handunnetti said.
One of the five patients who stopped treatment progressed at 7 months and died. The remaining four patients are still alive and in CR at 6 months, 13 months, 17 months, and 18 months off treatment.
Safety update
Within the first 56 weeks of treatment, 15 patients required dose adjustments. Twelve patients required an adjustment to ibrutinib, seven to venetoclax, and four to both drugs. After 56 weeks, there were no dose adjustments.
Two patients developed therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome. One patient had previously received FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab) and BR (bendamustine and rituximab). The other patient had received R-CHOP (rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone).
This investigator-initiated trial was funded by Janssen and Abbvie. Dr. Handunnetti reported relationships with Abbvie and Gilead.
SOURCE: Handunnetti S et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 756.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
BCL11A-directed gene therapy advances in sickle cell disease
ORLANDO – A gene therapy approach that targets a major repressor of fetal hemoglobin appears to be acceptably safe and to mitigate the pathology of sickle cell disease among the five patients infused so far, an investigator reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Knocking down BCL11A using a lentiviral vector-based approach resulted in effective induction of fetal hemoglobin and significant attenuation of the sickling phenotype, with no vector-related adverse events, investigator Erica B. Esrick, MD, of Children’s Hospital Boston, said during the meeting’s late-breaking abstracts session.
The single-center pilot and feasibility study, originally designed to include a total of seven patients, now has an expanded enrollment goal of 15 patients, and a multicenter phase 2/3 study is planned that will enroll a larger group of patients with sickle cell disease, according to Dr. Esrick.
BCL11A represents a promising target in sickle cell disease because of its regulation of the fetal-adult hemoglobin switch at the gamma-globin locus, investigators said in their late-breaking study abstract.
Dr. Esrick described BCH-BB694, a lentiviral vector encoding a BCL11A-targeting small hairpin RNA embedded in a microRNA scaffold (shmiR). “The advantage of this approach is that it harnesses the physiologic switch machinery, simultaneously increasing fetal hemoglobin and decreasing sickle hemoglobin, thus maintaining the alpha to beta globin ratio in the cell,” she said.
The results of the pilot study of the shmiR vector approach, although preliminary and in need of longer follow-up, contribute to a larger body of research showing that multiple gene therapy approaches hold promise in this disease, said Robert Brodsky, MD, professor of medicine and director of the division of hematology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore.
“The exciting thing is that there are now multiple ways of going at this previously incurable disease,” Dr. Brodsky, who was not involved in the research, said during a press conference.
Development of the gene therapy described by Dr. Esrick involves mobilization of the patient’s peripheral stem cells using plerixafor, followed by selection of CD34+ cells that were transduced with the shmiR lentiviral vector, followed by infusion of gene modified cells into the patient after a busulfan conditioning regimen.
“In our treated patients, we’ve seen a consistent and substantial induction in fetal hemoglobin,” Dr. Esrick said, noting that the longest follow-up to date for the five treated patients is now 18 months.
The patients, who range in age from 12 to 26 years, are producing and maintaining very high numbers of F cells, or erythrocytes with measurable fetal hemoglobin, she said.
Total fetal hemoglobin has increased and remained stable at between 23% and 43% for the five patients, who are producing “stably high” average amounts of fetal hemoglobin per F cell, at 10 to 16 picograms of fetal hemoglobin per cell, while 37% to 62% of the F cells’ total hemoglobin is fetal hemoglobin, she added.
Following gene therapy, treated patients have had no instances of vaso-occlusive pain crises, respiratory events, or neurologic events. No patients have required transfusion, except one with severe underlying vascular disease for whom post–gene therapy transfusions were planned, she said.
Validated assays at the single-cell level are needed to better understand the effect of this gene therapy and eventually compare it to other therapeutic approaches in sickle cell disease, according to Dr. Esrick.
“We’re collaborating with several colleagues on exploratory assays to accomplish this,” she said, adding that the work is ongoing.
Dr. Esrick reported having no disclosures. Her coauthors reported disclosures related to Alerion Biosciences, Novartis, Orchard Therapeutics, Roche, AstraZeneca, and bluebird bio, among others.
SOURCE: Esrick EB et al. ASH 2019. Abstract LBA-5.
ORLANDO – A gene therapy approach that targets a major repressor of fetal hemoglobin appears to be acceptably safe and to mitigate the pathology of sickle cell disease among the five patients infused so far, an investigator reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Knocking down BCL11A using a lentiviral vector-based approach resulted in effective induction of fetal hemoglobin and significant attenuation of the sickling phenotype, with no vector-related adverse events, investigator Erica B. Esrick, MD, of Children’s Hospital Boston, said during the meeting’s late-breaking abstracts session.
The single-center pilot and feasibility study, originally designed to include a total of seven patients, now has an expanded enrollment goal of 15 patients, and a multicenter phase 2/3 study is planned that will enroll a larger group of patients with sickle cell disease, according to Dr. Esrick.
BCL11A represents a promising target in sickle cell disease because of its regulation of the fetal-adult hemoglobin switch at the gamma-globin locus, investigators said in their late-breaking study abstract.
Dr. Esrick described BCH-BB694, a lentiviral vector encoding a BCL11A-targeting small hairpin RNA embedded in a microRNA scaffold (shmiR). “The advantage of this approach is that it harnesses the physiologic switch machinery, simultaneously increasing fetal hemoglobin and decreasing sickle hemoglobin, thus maintaining the alpha to beta globin ratio in the cell,” she said.
The results of the pilot study of the shmiR vector approach, although preliminary and in need of longer follow-up, contribute to a larger body of research showing that multiple gene therapy approaches hold promise in this disease, said Robert Brodsky, MD, professor of medicine and director of the division of hematology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore.
“The exciting thing is that there are now multiple ways of going at this previously incurable disease,” Dr. Brodsky, who was not involved in the research, said during a press conference.
Development of the gene therapy described by Dr. Esrick involves mobilization of the patient’s peripheral stem cells using plerixafor, followed by selection of CD34+ cells that were transduced with the shmiR lentiviral vector, followed by infusion of gene modified cells into the patient after a busulfan conditioning regimen.
“In our treated patients, we’ve seen a consistent and substantial induction in fetal hemoglobin,” Dr. Esrick said, noting that the longest follow-up to date for the five treated patients is now 18 months.
The patients, who range in age from 12 to 26 years, are producing and maintaining very high numbers of F cells, or erythrocytes with measurable fetal hemoglobin, she said.
Total fetal hemoglobin has increased and remained stable at between 23% and 43% for the five patients, who are producing “stably high” average amounts of fetal hemoglobin per F cell, at 10 to 16 picograms of fetal hemoglobin per cell, while 37% to 62% of the F cells’ total hemoglobin is fetal hemoglobin, she added.
Following gene therapy, treated patients have had no instances of vaso-occlusive pain crises, respiratory events, or neurologic events. No patients have required transfusion, except one with severe underlying vascular disease for whom post–gene therapy transfusions were planned, she said.
Validated assays at the single-cell level are needed to better understand the effect of this gene therapy and eventually compare it to other therapeutic approaches in sickle cell disease, according to Dr. Esrick.
“We’re collaborating with several colleagues on exploratory assays to accomplish this,” she said, adding that the work is ongoing.
Dr. Esrick reported having no disclosures. Her coauthors reported disclosures related to Alerion Biosciences, Novartis, Orchard Therapeutics, Roche, AstraZeneca, and bluebird bio, among others.
SOURCE: Esrick EB et al. ASH 2019. Abstract LBA-5.
ORLANDO – A gene therapy approach that targets a major repressor of fetal hemoglobin appears to be acceptably safe and to mitigate the pathology of sickle cell disease among the five patients infused so far, an investigator reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Knocking down BCL11A using a lentiviral vector-based approach resulted in effective induction of fetal hemoglobin and significant attenuation of the sickling phenotype, with no vector-related adverse events, investigator Erica B. Esrick, MD, of Children’s Hospital Boston, said during the meeting’s late-breaking abstracts session.
The single-center pilot and feasibility study, originally designed to include a total of seven patients, now has an expanded enrollment goal of 15 patients, and a multicenter phase 2/3 study is planned that will enroll a larger group of patients with sickle cell disease, according to Dr. Esrick.
BCL11A represents a promising target in sickle cell disease because of its regulation of the fetal-adult hemoglobin switch at the gamma-globin locus, investigators said in their late-breaking study abstract.
Dr. Esrick described BCH-BB694, a lentiviral vector encoding a BCL11A-targeting small hairpin RNA embedded in a microRNA scaffold (shmiR). “The advantage of this approach is that it harnesses the physiologic switch machinery, simultaneously increasing fetal hemoglobin and decreasing sickle hemoglobin, thus maintaining the alpha to beta globin ratio in the cell,” she said.
The results of the pilot study of the shmiR vector approach, although preliminary and in need of longer follow-up, contribute to a larger body of research showing that multiple gene therapy approaches hold promise in this disease, said Robert Brodsky, MD, professor of medicine and director of the division of hematology at Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore.
“The exciting thing is that there are now multiple ways of going at this previously incurable disease,” Dr. Brodsky, who was not involved in the research, said during a press conference.
Development of the gene therapy described by Dr. Esrick involves mobilization of the patient’s peripheral stem cells using plerixafor, followed by selection of CD34+ cells that were transduced with the shmiR lentiviral vector, followed by infusion of gene modified cells into the patient after a busulfan conditioning regimen.
“In our treated patients, we’ve seen a consistent and substantial induction in fetal hemoglobin,” Dr. Esrick said, noting that the longest follow-up to date for the five treated patients is now 18 months.
The patients, who range in age from 12 to 26 years, are producing and maintaining very high numbers of F cells, or erythrocytes with measurable fetal hemoglobin, she said.
Total fetal hemoglobin has increased and remained stable at between 23% and 43% for the five patients, who are producing “stably high” average amounts of fetal hemoglobin per F cell, at 10 to 16 picograms of fetal hemoglobin per cell, while 37% to 62% of the F cells’ total hemoglobin is fetal hemoglobin, she added.
Following gene therapy, treated patients have had no instances of vaso-occlusive pain crises, respiratory events, or neurologic events. No patients have required transfusion, except one with severe underlying vascular disease for whom post–gene therapy transfusions were planned, she said.
Validated assays at the single-cell level are needed to better understand the effect of this gene therapy and eventually compare it to other therapeutic approaches in sickle cell disease, according to Dr. Esrick.
“We’re collaborating with several colleagues on exploratory assays to accomplish this,” she said, adding that the work is ongoing.
Dr. Esrick reported having no disclosures. Her coauthors reported disclosures related to Alerion Biosciences, Novartis, Orchard Therapeutics, Roche, AstraZeneca, and bluebird bio, among others.
SOURCE: Esrick EB et al. ASH 2019. Abstract LBA-5.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
KTE-X19 produces highest response rate in MCL subgroup
ORLANDO – KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in the ZUMA-2 trial, according to an investigator involved in the study.
KTE-X19 produced a 93% overall response rate in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). This is the highest reported response rate in patients who have failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, said Michael L. Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr. Wang presented results from ZUMA-2 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Patients with relapsed/refractory MCL have very poor outcomes,” Dr. Wang noted. “In patients who progress after BTK inhibition therapy, the overall response rate is only between 25% and 42%, and the overall survival is only between 6 and 10 months. Few patients proceed to allogeneic transplantation.”
The phase 2 ZUMA-2 trial was designed to test KTE-X19 in these patients. KTE-X19 is an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy containing a CD3-zeta T-cell activation domain and a CD28 signaling domain. KTE-X19 is distinct from axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19) because the manufacturing process for KTE-X19 removes circulating tumor cells.
The trial enrolled 74 patients, and 68 of them received KTE-X19. Manufacturing failed for three patients, two patients died of progressive disease before they could receive KTE-X19, and one patient was found to be ineligible for treatment.
The 68 patients had a median age of 65 years (range, 38-79 years), and 84% were men. A majority of patients (85%) had stage IV disease and classical (59%) or blastoid (25%) morphology. Most patients (69%) had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater, and most (56%) were intermediate- or high-risk according to the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
Patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, one to five). All had been treated with a BTK inhibitor, with 85% receiving ibrutinib, 24% receiving acalabrutinib, and 9% receiving both. Most patients (68%) were refractory to BTK inhibition, and 32% relapsed on or after BTK inhibitor therapy.
In this study, patients could receive bridging therapy to keep their disease stable while KTE-X19 was being manufactured. There were 25 patients who received bridging therapy, which consisted of ibrutinib (n = 14), acalabrutinib (n = 5), dexamethasone (n = 12), and/or methylprednisolone (n = 2). Six patients received both BTK inhibitors and steroids.
All patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of KTE-X19 at 2x106.
Efficacy
Sixty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up was 12.3 months (range, 7.0-32.3 months).
The overall response rate was 93%, with 67% of patients achieving a complete response and 27% achieving a partial response. Three percent of patients had stable disease, and 3% had progressive disease.
“The overall response rate was consistent across key subgroups, without any statistical difference,” Dr. Wang said. “This includes Ki-67, MIPI, and prior use of either steroids or bridging therapy.”
The median time to response was 1.0 month, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. Responses deepened over time, with 35% of patients converting from a partial response to a complete response, and 5% converting from stable disease to complete response.
The median duration of response has not been reached. At last follow-up, 57% of all patients and 78% of complete responders were still in response.
The median progression-free and overall survival have not been reached. At 12 months, the progression-free survival rate was 61%, and the overall survival rate was 83%.
Safety
All 68 patients were evaluable for safety. The most common adverse events were pyrexia (94%), neutropenia (87%), thrombocytopenia (74%), anemia (68%), and hypotension (51%).
Grade 3/4 adverse events included pyrexia (13%), neutropenia (85%), thrombocytopenia (51%), anemia (50%), hypotension (22%), hypoxia (21%), hypophosphatemia (22%), fatigue (1%), and headache (1%).
There were two grade 5 treatment-related adverse events – organizing pneumonia on day 37 and staphylococcal bacteremia on day 134.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 91% of patients, with 15% experiencing grade 3 or higher CRS. Patients were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and all CRS events resolved.
Neurologic adverse events occurred in 63% of patients, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 31%. Neurologic events were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and 86% of neurologic events resolved.
This trial was sponsored by Kite, a Gilead company. Dr. Wang reported financial relationships with Kite and other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 754.
ORLANDO – KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in the ZUMA-2 trial, according to an investigator involved in the study.
KTE-X19 produced a 93% overall response rate in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). This is the highest reported response rate in patients who have failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, said Michael L. Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr. Wang presented results from ZUMA-2 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Patients with relapsed/refractory MCL have very poor outcomes,” Dr. Wang noted. “In patients who progress after BTK inhibition therapy, the overall response rate is only between 25% and 42%, and the overall survival is only between 6 and 10 months. Few patients proceed to allogeneic transplantation.”
The phase 2 ZUMA-2 trial was designed to test KTE-X19 in these patients. KTE-X19 is an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy containing a CD3-zeta T-cell activation domain and a CD28 signaling domain. KTE-X19 is distinct from axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19) because the manufacturing process for KTE-X19 removes circulating tumor cells.
The trial enrolled 74 patients, and 68 of them received KTE-X19. Manufacturing failed for three patients, two patients died of progressive disease before they could receive KTE-X19, and one patient was found to be ineligible for treatment.
The 68 patients had a median age of 65 years (range, 38-79 years), and 84% were men. A majority of patients (85%) had stage IV disease and classical (59%) or blastoid (25%) morphology. Most patients (69%) had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater, and most (56%) were intermediate- or high-risk according to the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
Patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, one to five). All had been treated with a BTK inhibitor, with 85% receiving ibrutinib, 24% receiving acalabrutinib, and 9% receiving both. Most patients (68%) were refractory to BTK inhibition, and 32% relapsed on or after BTK inhibitor therapy.
In this study, patients could receive bridging therapy to keep their disease stable while KTE-X19 was being manufactured. There were 25 patients who received bridging therapy, which consisted of ibrutinib (n = 14), acalabrutinib (n = 5), dexamethasone (n = 12), and/or methylprednisolone (n = 2). Six patients received both BTK inhibitors and steroids.
All patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of KTE-X19 at 2x106.
Efficacy
Sixty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up was 12.3 months (range, 7.0-32.3 months).
The overall response rate was 93%, with 67% of patients achieving a complete response and 27% achieving a partial response. Three percent of patients had stable disease, and 3% had progressive disease.
“The overall response rate was consistent across key subgroups, without any statistical difference,” Dr. Wang said. “This includes Ki-67, MIPI, and prior use of either steroids or bridging therapy.”
The median time to response was 1.0 month, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. Responses deepened over time, with 35% of patients converting from a partial response to a complete response, and 5% converting from stable disease to complete response.
The median duration of response has not been reached. At last follow-up, 57% of all patients and 78% of complete responders were still in response.
The median progression-free and overall survival have not been reached. At 12 months, the progression-free survival rate was 61%, and the overall survival rate was 83%.
Safety
All 68 patients were evaluable for safety. The most common adverse events were pyrexia (94%), neutropenia (87%), thrombocytopenia (74%), anemia (68%), and hypotension (51%).
Grade 3/4 adverse events included pyrexia (13%), neutropenia (85%), thrombocytopenia (51%), anemia (50%), hypotension (22%), hypoxia (21%), hypophosphatemia (22%), fatigue (1%), and headache (1%).
There were two grade 5 treatment-related adverse events – organizing pneumonia on day 37 and staphylococcal bacteremia on day 134.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 91% of patients, with 15% experiencing grade 3 or higher CRS. Patients were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and all CRS events resolved.
Neurologic adverse events occurred in 63% of patients, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 31%. Neurologic events were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and 86% of neurologic events resolved.
This trial was sponsored by Kite, a Gilead company. Dr. Wang reported financial relationships with Kite and other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 754.
ORLANDO – KTE-X19, an anti-CD19 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, demonstrated unprecedented efficacy in the ZUMA-2 trial, according to an investigator involved in the study.
KTE-X19 produced a 93% overall response rate in patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma (MCL). This is the highest reported response rate in patients who have failed treatment with a Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor, said Michael L. Wang, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston.
Dr. Wang presented results from ZUMA-2 at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
“Patients with relapsed/refractory MCL have very poor outcomes,” Dr. Wang noted. “In patients who progress after BTK inhibition therapy, the overall response rate is only between 25% and 42%, and the overall survival is only between 6 and 10 months. Few patients proceed to allogeneic transplantation.”
The phase 2 ZUMA-2 trial was designed to test KTE-X19 in these patients. KTE-X19 is an anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy containing a CD3-zeta T-cell activation domain and a CD28 signaling domain. KTE-X19 is distinct from axicabtagene ciloleucel (KTE-C19) because the manufacturing process for KTE-X19 removes circulating tumor cells.
The trial enrolled 74 patients, and 68 of them received KTE-X19. Manufacturing failed for three patients, two patients died of progressive disease before they could receive KTE-X19, and one patient was found to be ineligible for treatment.
The 68 patients had a median age of 65 years (range, 38-79 years), and 84% were men. A majority of patients (85%) had stage IV disease and classical (59%) or blastoid (25%) morphology. Most patients (69%) had a Ki-67 proliferation index of 50% or greater, and most (56%) were intermediate- or high-risk according to the Mantle Cell Lymphoma International Prognostic Index (MIPI).
Patients had received a median of three prior therapies (range, one to five). All had been treated with a BTK inhibitor, with 85% receiving ibrutinib, 24% receiving acalabrutinib, and 9% receiving both. Most patients (68%) were refractory to BTK inhibition, and 32% relapsed on or after BTK inhibitor therapy.
In this study, patients could receive bridging therapy to keep their disease stable while KTE-X19 was being manufactured. There were 25 patients who received bridging therapy, which consisted of ibrutinib (n = 14), acalabrutinib (n = 5), dexamethasone (n = 12), and/or methylprednisolone (n = 2). Six patients received both BTK inhibitors and steroids.
All patients received conditioning with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide, followed by a single infusion of KTE-X19 at 2x106.
Efficacy
Sixty patients were evaluable for efficacy, and the median follow-up was 12.3 months (range, 7.0-32.3 months).
The overall response rate was 93%, with 67% of patients achieving a complete response and 27% achieving a partial response. Three percent of patients had stable disease, and 3% had progressive disease.
“The overall response rate was consistent across key subgroups, without any statistical difference,” Dr. Wang said. “This includes Ki-67, MIPI, and prior use of either steroids or bridging therapy.”
The median time to response was 1.0 month, and the median time to complete response was 3.0 months. Responses deepened over time, with 35% of patients converting from a partial response to a complete response, and 5% converting from stable disease to complete response.
The median duration of response has not been reached. At last follow-up, 57% of all patients and 78% of complete responders were still in response.
The median progression-free and overall survival have not been reached. At 12 months, the progression-free survival rate was 61%, and the overall survival rate was 83%.
Safety
All 68 patients were evaluable for safety. The most common adverse events were pyrexia (94%), neutropenia (87%), thrombocytopenia (74%), anemia (68%), and hypotension (51%).
Grade 3/4 adverse events included pyrexia (13%), neutropenia (85%), thrombocytopenia (51%), anemia (50%), hypotension (22%), hypoxia (21%), hypophosphatemia (22%), fatigue (1%), and headache (1%).
There were two grade 5 treatment-related adverse events – organizing pneumonia on day 37 and staphylococcal bacteremia on day 134.
Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) occurred in 91% of patients, with 15% experiencing grade 3 or higher CRS. Patients were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and all CRS events resolved.
Neurologic adverse events occurred in 63% of patients, with grade 3 or higher events occurring in 31%. Neurologic events were treated with tocilizumab or corticosteroids, and 86% of neurologic events resolved.
This trial was sponsored by Kite, a Gilead company. Dr. Wang reported financial relationships with Kite and other companies.
SOURCE: Wang M et al. ASH 2019. Abstract 754.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Sutimlimab boosts hemoglobin, quality of life in cold agglutinin disease
ORLANDO – An investigational selective inhibitor of the complement pathway, sutimlimab, induced rapid and sustained benefits in patients with cold agglutinin disease, a rare autoimmune hemolytic anemia with no currently approved effective therapies.
Among 24 patients with cold agglutinin disease who received at least one dose of sutimlimab in a phase 3 trial, 20 had a mean increase in hemoglobin of at least 1 g/dL, and 17 remained transfusion free from weeks 5 to 26 following sutimlimab infusion.
“Sutimlimab has the potential to change treatment practices for patients with this disease,” said lead author Alexander Röth, MD, from the University of Duisburg-Essen (Germany), at a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Mean total bilirubin rapidly normalized within 1-3 weeks of infusion of sutimlimab, and patients had a mean improvement of 11 points on the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Fatigue scale (FACIT-F), indicating a substantial improvement in their quality of life, Dr. Röth said.
Cold agglutinin disease is an acquired hemolytic anemia with an underlying lymphoproliferative disorder. The estimated prevalence of the disease is 16 per 1 million persons. The disease is characterized by hemolysis driven by activation of the complement pathway, leading to opsonization of erythrocytes (coating of erythrocytes with particles that facilitate phagocytosis and other immune reactions), extravascular hemolysis (primarily in the liver), intravascular hemolysis, and anemia.
Patients experience severe fatigue and poor quality of life, as well as increased risk for thrombosis and mortality, compared with matched cohorts.
Sutimlimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the C1s component of the classical complement pathway, thereby stopping pathway activation while leaving alternative lectin pathways intact.
Dr. Röth presented results of the phase 3, open-label Cardinal study. Patients with cold agglutinin disease with baseline hemoglobin of 10 g/dL or less, active hemolysis signaled by total bilirubin levels above normal, and at least one blood transfusion within the past 6 months were eligible for the study. Patients with secondary cold agglutinin syndrome or rituximab therapy within the last 3 months or combination therapies within the last 6 months were excluded.
Sutimlimab was delivered intravenously at a dose of 6.5 g for patients under 75 kg in weight and 7.5 g for those 75 kg and over at day 0 and 7, then every 2 weeks thereafter.
A total of 24 patients with a mean age of 71 years were enrolled. Of the 24 patients, 15 (62.5%) were women.
The patients had received a mean of 3.2 transfusions (range 1-19) in the previous 6 months, and 15 had received one or more prior targeted therapies for the disease within the last 5 years. The mean baseline hemoglobin level was 8.6 (range 4.9-11.1) g/dL.
Hemoglobin levels increased rapidly after the first infusion, with a mean increase of 1.2 g/dL at the end of week 1, and 2.3 g/dL after week 3.
The estimated mean increase at treatment assessment (an average of weeks 23, 25, and 26) – the primary endpoint – was 2.6 g/dL, exceeding the prespecified increase of at least 2 g/dL. Normalization of hemoglobin to 12 g/dL or greater was an alternative primary endpoint. The trial met the primary endpoint, with 13 of 24 patients (54.2%) achieving either of the two prespecified events.
The mean overall hemoglobin level was maintained above 11 g/dL after week 3. Of the 24 patients, 20 had hemoglobin increases of 1 g/dL or greater.
Mean total bilirubin, a marker of hemolysis, dropped markedly within hours of infusion and was normalized by week 3.
As noted before, patient quality of life, as measured by the FACIT-F scale, improved by a mean of 11 points from a mean baseline of 32 out of 52 points.
All but two patients had one or more treatment-emergent adverse events, and seven of these patients had a serious treatment-related event, although none of the serious events were thought to be related to sutimlimab. One patient with liver cancer died from causes deemed unrelated to the drug. There were no meningococcal infections.
All 22 patients who completed the 26 weeks of therapy continued on an extended safety phase of the study.
The study results demonstrate that targeting the complement pathways is an novel and effective approach to managing cold agglutinin disease, Dr. Röth concluded.
In a press briefing the day before the presentation, moderator Robert Brodsky, MD, professor of medicine and director of the division of hematology at Johns Hopkins School, Baltimore, who treats patients with cold agglutinin disease, said that the results “are very exciting.”
“These patients are very difficult to treat and there really is no approved drug,” he said. “Right now, we usually use [rituximab] first line, but only half of those patients respond, and usually it only lasts for 6 months or so, so this is a welcome addition.”
Sutimlimab was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and Orphan Drug status by the FDA, European Medicines Agency, and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency in Japan.
The study was supported by Sanofi. Dr. Röth reported financial relationships with Sanofi and other companies.
SOURCE: Röth A et al. ASH 2019, Abstract LBA-2.
ORLANDO – An investigational selective inhibitor of the complement pathway, sutimlimab, induced rapid and sustained benefits in patients with cold agglutinin disease, a rare autoimmune hemolytic anemia with no currently approved effective therapies.
Among 24 patients with cold agglutinin disease who received at least one dose of sutimlimab in a phase 3 trial, 20 had a mean increase in hemoglobin of at least 1 g/dL, and 17 remained transfusion free from weeks 5 to 26 following sutimlimab infusion.
“Sutimlimab has the potential to change treatment practices for patients with this disease,” said lead author Alexander Röth, MD, from the University of Duisburg-Essen (Germany), at a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Mean total bilirubin rapidly normalized within 1-3 weeks of infusion of sutimlimab, and patients had a mean improvement of 11 points on the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Fatigue scale (FACIT-F), indicating a substantial improvement in their quality of life, Dr. Röth said.
Cold agglutinin disease is an acquired hemolytic anemia with an underlying lymphoproliferative disorder. The estimated prevalence of the disease is 16 per 1 million persons. The disease is characterized by hemolysis driven by activation of the complement pathway, leading to opsonization of erythrocytes (coating of erythrocytes with particles that facilitate phagocytosis and other immune reactions), extravascular hemolysis (primarily in the liver), intravascular hemolysis, and anemia.
Patients experience severe fatigue and poor quality of life, as well as increased risk for thrombosis and mortality, compared with matched cohorts.
Sutimlimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the C1s component of the classical complement pathway, thereby stopping pathway activation while leaving alternative lectin pathways intact.
Dr. Röth presented results of the phase 3, open-label Cardinal study. Patients with cold agglutinin disease with baseline hemoglobin of 10 g/dL or less, active hemolysis signaled by total bilirubin levels above normal, and at least one blood transfusion within the past 6 months were eligible for the study. Patients with secondary cold agglutinin syndrome or rituximab therapy within the last 3 months or combination therapies within the last 6 months were excluded.
Sutimlimab was delivered intravenously at a dose of 6.5 g for patients under 75 kg in weight and 7.5 g for those 75 kg and over at day 0 and 7, then every 2 weeks thereafter.
A total of 24 patients with a mean age of 71 years were enrolled. Of the 24 patients, 15 (62.5%) were women.
The patients had received a mean of 3.2 transfusions (range 1-19) in the previous 6 months, and 15 had received one or more prior targeted therapies for the disease within the last 5 years. The mean baseline hemoglobin level was 8.6 (range 4.9-11.1) g/dL.
Hemoglobin levels increased rapidly after the first infusion, with a mean increase of 1.2 g/dL at the end of week 1, and 2.3 g/dL after week 3.
The estimated mean increase at treatment assessment (an average of weeks 23, 25, and 26) – the primary endpoint – was 2.6 g/dL, exceeding the prespecified increase of at least 2 g/dL. Normalization of hemoglobin to 12 g/dL or greater was an alternative primary endpoint. The trial met the primary endpoint, with 13 of 24 patients (54.2%) achieving either of the two prespecified events.
The mean overall hemoglobin level was maintained above 11 g/dL after week 3. Of the 24 patients, 20 had hemoglobin increases of 1 g/dL or greater.
Mean total bilirubin, a marker of hemolysis, dropped markedly within hours of infusion and was normalized by week 3.
As noted before, patient quality of life, as measured by the FACIT-F scale, improved by a mean of 11 points from a mean baseline of 32 out of 52 points.
All but two patients had one or more treatment-emergent adverse events, and seven of these patients had a serious treatment-related event, although none of the serious events were thought to be related to sutimlimab. One patient with liver cancer died from causes deemed unrelated to the drug. There were no meningococcal infections.
All 22 patients who completed the 26 weeks of therapy continued on an extended safety phase of the study.
The study results demonstrate that targeting the complement pathways is an novel and effective approach to managing cold agglutinin disease, Dr. Röth concluded.
In a press briefing the day before the presentation, moderator Robert Brodsky, MD, professor of medicine and director of the division of hematology at Johns Hopkins School, Baltimore, who treats patients with cold agglutinin disease, said that the results “are very exciting.”
“These patients are very difficult to treat and there really is no approved drug,” he said. “Right now, we usually use [rituximab] first line, but only half of those patients respond, and usually it only lasts for 6 months or so, so this is a welcome addition.”
Sutimlimab was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and Orphan Drug status by the FDA, European Medicines Agency, and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency in Japan.
The study was supported by Sanofi. Dr. Röth reported financial relationships with Sanofi and other companies.
SOURCE: Röth A et al. ASH 2019, Abstract LBA-2.
ORLANDO – An investigational selective inhibitor of the complement pathway, sutimlimab, induced rapid and sustained benefits in patients with cold agglutinin disease, a rare autoimmune hemolytic anemia with no currently approved effective therapies.
Among 24 patients with cold agglutinin disease who received at least one dose of sutimlimab in a phase 3 trial, 20 had a mean increase in hemoglobin of at least 1 g/dL, and 17 remained transfusion free from weeks 5 to 26 following sutimlimab infusion.
“Sutimlimab has the potential to change treatment practices for patients with this disease,” said lead author Alexander Röth, MD, from the University of Duisburg-Essen (Germany), at a late-breaking abstract session at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
Mean total bilirubin rapidly normalized within 1-3 weeks of infusion of sutimlimab, and patients had a mean improvement of 11 points on the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy–Fatigue scale (FACIT-F), indicating a substantial improvement in their quality of life, Dr. Röth said.
Cold agglutinin disease is an acquired hemolytic anemia with an underlying lymphoproliferative disorder. The estimated prevalence of the disease is 16 per 1 million persons. The disease is characterized by hemolysis driven by activation of the complement pathway, leading to opsonization of erythrocytes (coating of erythrocytes with particles that facilitate phagocytosis and other immune reactions), extravascular hemolysis (primarily in the liver), intravascular hemolysis, and anemia.
Patients experience severe fatigue and poor quality of life, as well as increased risk for thrombosis and mortality, compared with matched cohorts.
Sutimlimab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that blocks the C1s component of the classical complement pathway, thereby stopping pathway activation while leaving alternative lectin pathways intact.
Dr. Röth presented results of the phase 3, open-label Cardinal study. Patients with cold agglutinin disease with baseline hemoglobin of 10 g/dL or less, active hemolysis signaled by total bilirubin levels above normal, and at least one blood transfusion within the past 6 months were eligible for the study. Patients with secondary cold agglutinin syndrome or rituximab therapy within the last 3 months or combination therapies within the last 6 months were excluded.
Sutimlimab was delivered intravenously at a dose of 6.5 g for patients under 75 kg in weight and 7.5 g for those 75 kg and over at day 0 and 7, then every 2 weeks thereafter.
A total of 24 patients with a mean age of 71 years were enrolled. Of the 24 patients, 15 (62.5%) were women.
The patients had received a mean of 3.2 transfusions (range 1-19) in the previous 6 months, and 15 had received one or more prior targeted therapies for the disease within the last 5 years. The mean baseline hemoglobin level was 8.6 (range 4.9-11.1) g/dL.
Hemoglobin levels increased rapidly after the first infusion, with a mean increase of 1.2 g/dL at the end of week 1, and 2.3 g/dL after week 3.
The estimated mean increase at treatment assessment (an average of weeks 23, 25, and 26) – the primary endpoint – was 2.6 g/dL, exceeding the prespecified increase of at least 2 g/dL. Normalization of hemoglobin to 12 g/dL or greater was an alternative primary endpoint. The trial met the primary endpoint, with 13 of 24 patients (54.2%) achieving either of the two prespecified events.
The mean overall hemoglobin level was maintained above 11 g/dL after week 3. Of the 24 patients, 20 had hemoglobin increases of 1 g/dL or greater.
Mean total bilirubin, a marker of hemolysis, dropped markedly within hours of infusion and was normalized by week 3.
As noted before, patient quality of life, as measured by the FACIT-F scale, improved by a mean of 11 points from a mean baseline of 32 out of 52 points.
All but two patients had one or more treatment-emergent adverse events, and seven of these patients had a serious treatment-related event, although none of the serious events were thought to be related to sutimlimab. One patient with liver cancer died from causes deemed unrelated to the drug. There were no meningococcal infections.
All 22 patients who completed the 26 weeks of therapy continued on an extended safety phase of the study.
The study results demonstrate that targeting the complement pathways is an novel and effective approach to managing cold agglutinin disease, Dr. Röth concluded.
In a press briefing the day before the presentation, moderator Robert Brodsky, MD, professor of medicine and director of the division of hematology at Johns Hopkins School, Baltimore, who treats patients with cold agglutinin disease, said that the results “are very exciting.”
“These patients are very difficult to treat and there really is no approved drug,” he said. “Right now, we usually use [rituximab] first line, but only half of those patients respond, and usually it only lasts for 6 months or so, so this is a welcome addition.”
Sutimlimab was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the Food and Drug Administration, and Orphan Drug status by the FDA, European Medicines Agency, and the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency in Japan.
The study was supported by Sanofi. Dr. Röth reported financial relationships with Sanofi and other companies.
SOURCE: Röth A et al. ASH 2019, Abstract LBA-2.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
Orelabrutinib could be ‘preferred’ BTK inhibitor for MCL
ORLANDO – A novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has produced favorable results in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In a phase 2 trial, orelabrutinib produced an overall response rate of 86% and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 64%. Safety results with orelabrutinib were superior to historical results with ibrutinib.
The efficacy and safety profile of orelabrutinib, as well as its “convenient” dosing, may make it the “preferred therapeutic choice for B-cell malignancy,” said Lijuan Deng, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, who presented the phase 2 trial of orelabrutinib at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 106 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who were treated at 22 centers in China. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 62 years (range, 37-73 years), and 79.2% were men. Most patients (94.4%) had stage III-IV disease.
Prior therapies included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone)-based (69.8%), EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin)-based (22.6%), DHAP (dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (22.6%), CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone)-based (12.3%), and ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (4.7%) regimens, and 88.7% of patients had received prior anti-CD20 therapy.
Patients received orelabrutinib at 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) or 150 mg once a day (n = 86). All 106 patients were evaluable for safety, and 99 were evaluable for efficacy.
Efficacy
“Orelabrutinib achieved high response and durable remissions,” Dr. Deng said.
The overall response rate was 85.9% in the evaluable efficacy population and 83.5% in the 150-mg dosing arm. The complete response rates were 27.3% and 29.1%, respectively. The median time to response, overall, was 1.9 months.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival were not reached at a median follow-up of 10.5 months. At 12 months, 74.3% of patients were still in response, and the progression-free survival rate was 64%.
Safety
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in nature. The most common grade 3 or higher events were platelet count decrease (11.3%), neutrophil count decrease (8.5%), anemia (7.5%), hypertension (3.8%), pneumonia (2.8%), white blood count decrease (1.9%), and hypokalemia (1.9%).
Adverse events of interest included grade 3 or higher hypertension (3.8%), diarrhea (6.6%), and infection (10.4%), as well as secondary malignancy (0.9%, n = 1). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, grade 3 or higher atrial fibrillation/flutter, or grade 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Dr. Deng noted that rates of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, and infection, as well as rates of secondary malignancies, have historically been higher with ibrutinib (Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126[6]:739-45; Lancet. 2016 Feb 20;387[10020]:770-8).
“Orelabrutinib has an improved safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Dr. Deng said. “The most common adverse events were cytopenia and infections, which are considered mechanism based.”
The study was sponsored by InnoCare Pharma. Dr. Deng reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Deng L et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 755.
ORLANDO – A novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has produced favorable results in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In a phase 2 trial, orelabrutinib produced an overall response rate of 86% and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 64%. Safety results with orelabrutinib were superior to historical results with ibrutinib.
The efficacy and safety profile of orelabrutinib, as well as its “convenient” dosing, may make it the “preferred therapeutic choice for B-cell malignancy,” said Lijuan Deng, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, who presented the phase 2 trial of orelabrutinib at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 106 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who were treated at 22 centers in China. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 62 years (range, 37-73 years), and 79.2% were men. Most patients (94.4%) had stage III-IV disease.
Prior therapies included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone)-based (69.8%), EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin)-based (22.6%), DHAP (dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (22.6%), CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone)-based (12.3%), and ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (4.7%) regimens, and 88.7% of patients had received prior anti-CD20 therapy.
Patients received orelabrutinib at 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) or 150 mg once a day (n = 86). All 106 patients were evaluable for safety, and 99 were evaluable for efficacy.
Efficacy
“Orelabrutinib achieved high response and durable remissions,” Dr. Deng said.
The overall response rate was 85.9% in the evaluable efficacy population and 83.5% in the 150-mg dosing arm. The complete response rates were 27.3% and 29.1%, respectively. The median time to response, overall, was 1.9 months.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival were not reached at a median follow-up of 10.5 months. At 12 months, 74.3% of patients were still in response, and the progression-free survival rate was 64%.
Safety
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in nature. The most common grade 3 or higher events were platelet count decrease (11.3%), neutrophil count decrease (8.5%), anemia (7.5%), hypertension (3.8%), pneumonia (2.8%), white blood count decrease (1.9%), and hypokalemia (1.9%).
Adverse events of interest included grade 3 or higher hypertension (3.8%), diarrhea (6.6%), and infection (10.4%), as well as secondary malignancy (0.9%, n = 1). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, grade 3 or higher atrial fibrillation/flutter, or grade 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Dr. Deng noted that rates of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, and infection, as well as rates of secondary malignancies, have historically been higher with ibrutinib (Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126[6]:739-45; Lancet. 2016 Feb 20;387[10020]:770-8).
“Orelabrutinib has an improved safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Dr. Deng said. “The most common adverse events were cytopenia and infections, which are considered mechanism based.”
The study was sponsored by InnoCare Pharma. Dr. Deng reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Deng L et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 755.
ORLANDO – A novel Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor has produced favorable results in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma, according to findings presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology.
In a phase 2 trial, orelabrutinib produced an overall response rate of 86% and a 12-month progression-free survival rate of 64%. Safety results with orelabrutinib were superior to historical results with ibrutinib.
The efficacy and safety profile of orelabrutinib, as well as its “convenient” dosing, may make it the “preferred therapeutic choice for B-cell malignancy,” said Lijuan Deng, MD, PhD, of Peking University Cancer Hospital & Institute, Beijing, who presented the phase 2 trial of orelabrutinib at ASH 2019.
The trial enrolled 106 patients with relapsed/refractory mantle cell lymphoma who were treated at 22 centers in China. At baseline, the patients had a median age of 62 years (range, 37-73 years), and 79.2% were men. Most patients (94.4%) had stage III-IV disease.
Prior therapies included CHOP (cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisolone)-based (69.8%), EPOCH (etoposide, prednisone, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, and doxorubicin)-based (22.6%), DHAP (dexamethasone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (22.6%), CVAD (cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, dexamethasone)-based (12.3%), and ESHAP (etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine, and cisplatin)-based (4.7%) regimens, and 88.7% of patients had received prior anti-CD20 therapy.
Patients received orelabrutinib at 100 mg twice daily (n = 20) or 150 mg once a day (n = 86). All 106 patients were evaluable for safety, and 99 were evaluable for efficacy.
Efficacy
“Orelabrutinib achieved high response and durable remissions,” Dr. Deng said.
The overall response rate was 85.9% in the evaluable efficacy population and 83.5% in the 150-mg dosing arm. The complete response rates were 27.3% and 29.1%, respectively. The median time to response, overall, was 1.9 months.
The median duration of response and median progression-free survival were not reached at a median follow-up of 10.5 months. At 12 months, 74.3% of patients were still in response, and the progression-free survival rate was 64%.
Safety
Most adverse events were grade 1-2 in nature. The most common grade 3 or higher events were platelet count decrease (11.3%), neutrophil count decrease (8.5%), anemia (7.5%), hypertension (3.8%), pneumonia (2.8%), white blood count decrease (1.9%), and hypokalemia (1.9%).
Adverse events of interest included grade 3 or higher hypertension (3.8%), diarrhea (6.6%), and infection (10.4%), as well as secondary malignancy (0.9%, n = 1). There were no cases of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, grade 3 or higher atrial fibrillation/flutter, or grade 5 treatment-related adverse events.
Dr. Deng noted that rates of grade 3 or higher hemorrhage, atrial fibrillation, diarrhea, and infection, as well as rates of secondary malignancies, have historically been higher with ibrutinib (Blood. 2015 Aug 6;126[6]:739-45; Lancet. 2016 Feb 20;387[10020]:770-8).
“Orelabrutinib has an improved safety profile in patients with relapsed or refractory mantle cell lymphoma,” Dr. Deng said. “The most common adverse events were cytopenia and infections, which are considered mechanism based.”
The study was sponsored by InnoCare Pharma. Dr. Deng reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Deng L et al. ASH 2019, Abstract 755.
REPORTING FROM ASH 2019
New ASH guideline: VTE prophylaxis after major surgery
ORLANDO – The latest American Society of Hematology guideline on venous thromboembolism (VTE) tackles 30 key questions regarding prophylaxis in hospitalized patients undergoing surgery, according to the chair of the guideline panel, who highlighted 9 of those questions during a special session at the society’s annual meeting.
The clinical practice guideline, published just about a week before the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, focuses mainly on pharmacologic prophylaxis in specific surgical settings, said David R. Anderson, MD, dean of the faculty of medicine of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S.
“Our guidelines focused upon clinically important symptomatic outcomes, with less emphasis being placed on asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis detected by screening tests,” Dr. Anderson said.
At the special education session, Dr. Anderson highlighted several specific recommendations on prophylaxis in surgical patients.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients experiencing major trauma deemed to be at high risk of bleeding. Its use does reduce risk of symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by about 10 events per 1,000 patients treated; however, Dr. Anderson said, the panel’s opinion was that this benefit was outweighed by increased risk of major bleeding, at 24 events per 1,000 patients treated.
“We do recommend, however that this risk of bleeding must be reevaluated over the course of recovery of patients, and this may change the decision around this intervention over time,” Dr. Anderson told attendees at the special session.
That’s because pharmacologic prophylaxis is recommended in surgical patients at low to moderate risk of bleeding. In this scenario, the incremental risk of major bleeding (14 events per 1,000 patients treated) is outweighed by the benefit of the reduction of symptomatic VTE events, according to Dr. Anderson.
When pharmacologic prophylaxis is used, the panel recommends combined prophylaxis – mechanical prophylaxis in addition to pharmacologic prophylaxis – especially in those patients at high or very high risk of VTE. Evidence shows that the combination approach significantly reduces risk of PE, and strongly suggests it may also reduce risk of symptomatic proximal DVT, Dr. Anderson said.
In surgical patients not receiving pharmacologic prophylaxis, mechanical prophylaxis is recommended over no mechanical prophylaxis, he added. Moreover, in those patients receiving mechanical prophylaxis, the ASH panel recommends use of intermittent compression devices over graduated compression stockings.
The panel comes out against prophylactic inferior vena cava (IVC) filter insertion in the guidelines. Dr. Anderson said that the “small reduction” in PE risk seen in observational studies is outweighed by increased risk of DVT, and a resulting trend for increased mortality, associated with insertion of the devices.
“We did not consider other risks of IVC filters such as filter embolization or perforation, which again would be complications that would support our recommendation against routine use of these devices in patients undergoing major surgery,” he said.
In terms of the type of pharmacologic prophylaxis to use, the panel said low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin would be reasonable choices in this setting. Available data do not demonstrate any significant differences between these choices for major clinical outcomes, Dr. Anderson added.
The guideline also addresses duration of pharmacologic prophylaxis, stating that extended prophylaxis – of at least 3 weeks – is favored over short-term prophylaxis, or up to 2 weeks of treatment. The extended approach significantly reduces risk of symptomatic PE and proximal DVT, though most of the supporting data come from studies of major joint arthroplasty and major general surgical procedures for patients with cancer. “We need more studies in other clinical areas to examine this particular question,” Dr. Anderson said.
The guideline on prophylaxis in surgical patients was published in Blood Advances (2019 Dec 3;3[23]:3898-944). Six other ASH VTE guidelines, all published in 2018, covered prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, VTE in pregnancy, optimal anticoagulation, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pediatric considerations. The guidelines are available on the ASH website.
Dr. Anderson reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – The latest American Society of Hematology guideline on venous thromboembolism (VTE) tackles 30 key questions regarding prophylaxis in hospitalized patients undergoing surgery, according to the chair of the guideline panel, who highlighted 9 of those questions during a special session at the society’s annual meeting.
The clinical practice guideline, published just about a week before the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, focuses mainly on pharmacologic prophylaxis in specific surgical settings, said David R. Anderson, MD, dean of the faculty of medicine of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S.
“Our guidelines focused upon clinically important symptomatic outcomes, with less emphasis being placed on asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis detected by screening tests,” Dr. Anderson said.
At the special education session, Dr. Anderson highlighted several specific recommendations on prophylaxis in surgical patients.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients experiencing major trauma deemed to be at high risk of bleeding. Its use does reduce risk of symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by about 10 events per 1,000 patients treated; however, Dr. Anderson said, the panel’s opinion was that this benefit was outweighed by increased risk of major bleeding, at 24 events per 1,000 patients treated.
“We do recommend, however that this risk of bleeding must be reevaluated over the course of recovery of patients, and this may change the decision around this intervention over time,” Dr. Anderson told attendees at the special session.
That’s because pharmacologic prophylaxis is recommended in surgical patients at low to moderate risk of bleeding. In this scenario, the incremental risk of major bleeding (14 events per 1,000 patients treated) is outweighed by the benefit of the reduction of symptomatic VTE events, according to Dr. Anderson.
When pharmacologic prophylaxis is used, the panel recommends combined prophylaxis – mechanical prophylaxis in addition to pharmacologic prophylaxis – especially in those patients at high or very high risk of VTE. Evidence shows that the combination approach significantly reduces risk of PE, and strongly suggests it may also reduce risk of symptomatic proximal DVT, Dr. Anderson said.
In surgical patients not receiving pharmacologic prophylaxis, mechanical prophylaxis is recommended over no mechanical prophylaxis, he added. Moreover, in those patients receiving mechanical prophylaxis, the ASH panel recommends use of intermittent compression devices over graduated compression stockings.
The panel comes out against prophylactic inferior vena cava (IVC) filter insertion in the guidelines. Dr. Anderson said that the “small reduction” in PE risk seen in observational studies is outweighed by increased risk of DVT, and a resulting trend for increased mortality, associated with insertion of the devices.
“We did not consider other risks of IVC filters such as filter embolization or perforation, which again would be complications that would support our recommendation against routine use of these devices in patients undergoing major surgery,” he said.
In terms of the type of pharmacologic prophylaxis to use, the panel said low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin would be reasonable choices in this setting. Available data do not demonstrate any significant differences between these choices for major clinical outcomes, Dr. Anderson added.
The guideline also addresses duration of pharmacologic prophylaxis, stating that extended prophylaxis – of at least 3 weeks – is favored over short-term prophylaxis, or up to 2 weeks of treatment. The extended approach significantly reduces risk of symptomatic PE and proximal DVT, though most of the supporting data come from studies of major joint arthroplasty and major general surgical procedures for patients with cancer. “We need more studies in other clinical areas to examine this particular question,” Dr. Anderson said.
The guideline on prophylaxis in surgical patients was published in Blood Advances (2019 Dec 3;3[23]:3898-944). Six other ASH VTE guidelines, all published in 2018, covered prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, VTE in pregnancy, optimal anticoagulation, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pediatric considerations. The guidelines are available on the ASH website.
Dr. Anderson reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
ORLANDO – The latest American Society of Hematology guideline on venous thromboembolism (VTE) tackles 30 key questions regarding prophylaxis in hospitalized patients undergoing surgery, according to the chair of the guideline panel, who highlighted 9 of those questions during a special session at the society’s annual meeting.
The clinical practice guideline, published just about a week before the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology, focuses mainly on pharmacologic prophylaxis in specific surgical settings, said David R. Anderson, MD, dean of the faculty of medicine of Dalhousie University, Halifax, N.S.
“Our guidelines focused upon clinically important symptomatic outcomes, with less emphasis being placed on asymptomatic deep vein thrombosis detected by screening tests,” Dr. Anderson said.
At the special education session, Dr. Anderson highlighted several specific recommendations on prophylaxis in surgical patients.
Pharmacologic prophylaxis is not recommended for patients experiencing major trauma deemed to be at high risk of bleeding. Its use does reduce risk of symptomatic pulmonary embolism (PE) and deep vein thrombosis (DVT) by about 10 events per 1,000 patients treated; however, Dr. Anderson said, the panel’s opinion was that this benefit was outweighed by increased risk of major bleeding, at 24 events per 1,000 patients treated.
“We do recommend, however that this risk of bleeding must be reevaluated over the course of recovery of patients, and this may change the decision around this intervention over time,” Dr. Anderson told attendees at the special session.
That’s because pharmacologic prophylaxis is recommended in surgical patients at low to moderate risk of bleeding. In this scenario, the incremental risk of major bleeding (14 events per 1,000 patients treated) is outweighed by the benefit of the reduction of symptomatic VTE events, according to Dr. Anderson.
When pharmacologic prophylaxis is used, the panel recommends combined prophylaxis – mechanical prophylaxis in addition to pharmacologic prophylaxis – especially in those patients at high or very high risk of VTE. Evidence shows that the combination approach significantly reduces risk of PE, and strongly suggests it may also reduce risk of symptomatic proximal DVT, Dr. Anderson said.
In surgical patients not receiving pharmacologic prophylaxis, mechanical prophylaxis is recommended over no mechanical prophylaxis, he added. Moreover, in those patients receiving mechanical prophylaxis, the ASH panel recommends use of intermittent compression devices over graduated compression stockings.
The panel comes out against prophylactic inferior vena cava (IVC) filter insertion in the guidelines. Dr. Anderson said that the “small reduction” in PE risk seen in observational studies is outweighed by increased risk of DVT, and a resulting trend for increased mortality, associated with insertion of the devices.
“We did not consider other risks of IVC filters such as filter embolization or perforation, which again would be complications that would support our recommendation against routine use of these devices in patients undergoing major surgery,” he said.
In terms of the type of pharmacologic prophylaxis to use, the panel said low-molecular-weight heparin or unfractionated heparin would be reasonable choices in this setting. Available data do not demonstrate any significant differences between these choices for major clinical outcomes, Dr. Anderson added.
The guideline also addresses duration of pharmacologic prophylaxis, stating that extended prophylaxis – of at least 3 weeks – is favored over short-term prophylaxis, or up to 2 weeks of treatment. The extended approach significantly reduces risk of symptomatic PE and proximal DVT, though most of the supporting data come from studies of major joint arthroplasty and major general surgical procedures for patients with cancer. “We need more studies in other clinical areas to examine this particular question,” Dr. Anderson said.
The guideline on prophylaxis in surgical patients was published in Blood Advances (2019 Dec 3;3[23]:3898-944). Six other ASH VTE guidelines, all published in 2018, covered prophylaxis in medical patients, diagnosis, VTE in pregnancy, optimal anticoagulation, heparin-induced thrombocytopenia, and pediatric considerations. The guidelines are available on the ASH website.
Dr. Anderson reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASH 2019