User login
20 years of clinical research in cardiology
In February 2003, when Cardiology News published its first edition, there were a handful of articles reporting results from randomized clinical trials. These included a trial of bivalirudin for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) anticoagulation (REPLACE-2) and a small controlled pilot study of soy nuts for blood pressure reduction in postmenopausal women. Also included was a considered discussion of the ALLHAT findings.
These trials and the incremental gain they offered belie the enormous global impact the cardiology community has had in clinical research over the last several decades. In fact, more than any other medical specialty, cardiology has led the way in evidence-based practice.
“When you step back and take a look at the compendium of cardiology advances, it’s unbelievable how much we’ve accomplished in the last 20 years,” said Steven E. Nissen, MD.
Dr. Nissen, a prodigious researcher, is the chief academic officer at the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, and holds the Lewis and Patricia Dickey Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
The needle mover: LDL lowering
“From a population health perspective, LDL cholesterol lowering is clearly the big winner,” said Christopher Cannon, MD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“We’ve been at it with LDL cholesterol for about 50 years now, but I think things really accelerated over the last 20 years when the conversation shifted from just lowering LDL-C to recognizing that lower is better. This pushed us toward high-intensity statin treatment and add-on drugs to push LDL down further,” he said.
“Concurrent with this increase in the use of statins and other LDL-lowering drugs, cardiovascular death has fallen significantly, which in my mind is likely a result of better LDL lowering and getting people to stop smoking, which we’ve also done a better job of in the last 20 years,” said Dr. Cannon.
Indeed, until cardiovascular mortality started rising in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality rates had been dropping steadily for several decades. The progress in the past 2 decades has been so fast, noted Dr. Cannon, that the American Heart Association’s stated goal in 1998 of reducing coronary heart disease, stroke, and risk by 25% by the year 2008 was accomplished about 4 years ahead of schedule.
Coincidentally, Dr. Cannon and Dr. Nissen were both important players in this advance. Dr. Cannon led the PROVE-IT trial, which showed in 2004 that an intensive lipid-lowering statin regimen offers greater protection against death or major cardiovascular events than does a standard regimen in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
That trial was published just months after REVERSAL, Dr. Nissen’s trial that showed for the first time that intensive lipid-lowering treatment reduced progression of coronary atherosclerosis, compared with a moderate lipid-lowering approach.
“Added to this, we have drugs like ezetimibe and the PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and now they’re even using CRISPR gene editing to permanently switch off the gene that codes for PCSK9, testing this in people with familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Cannon. “In the preclinical study, they showed that with one treatment they lowered blood PCSK9 protein levels by 83% and LDL-C by 69%..”
At the same time as we’ve seen what works, we’ve also seen what doesn’t work, added Dr. Nissen. “Shortly after we saw the power of LDL lowering, everyone wanted to target HDL and we had epidemiological evidence suggesting this was a good idea, but several landmark trials testing the HDL hypothesis were complete failures.” Debate continues as to whether HDL cholesterol is a suitable target for prevention.
Not only has the recent past in lipidology been needle-moving, but the hits keep coming. Inclisiran, a first-in-class LDL cholesterol–lowering drug that shows potent lipid-lowering efficacy and excellent safety and tolerability in phase 3 study, received Food and Drug Administration approval in December 2021. The drugs twice-a-year dosing has been called a game changer for adherence.
And at the 2023 annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology in March, Dr. Nissen presented results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial on bempedoic acid (Nexletol), a 14,000-patient, placebo-controlled trial of bempedoic acid in statin intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk. Bempedoic acid is a novel compound that inhibits ATP citrate lyase, which catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol upstream of HMG-CoA reductase, the target of statins.
Findings revealed a significant reduction in risk for a composite 4-point major adverse cardiovascular events endpoint of time to first cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial marks the first time an oral nonstatin drug has met the MACE-4 primary endpoint, Dr. Nissen reported.
“We also have new therapies for lowering lipoprotein(a) and outcome trials underway for antisense and short interfering RNA targeting of Lp(a), which I frankly think herald a new era in which we can have these longer-acting directly targeted drugs that work at the translation level to prevent a protein that is not desirable,” added Dr. Nissen. “These drugs will undoubtedly change the face of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the next 2 decades.”
Other important successes and equally important failures
Perhaps consideration of some of the treatments we didn’t have 20 years ago is more revealing than a list of advances. Two decades ago, there were no direct direct-acting anticoagulants on the market, “so no alternative to warfarin, which is difficult to use and associated with excess bleeding,” said Dr. Cannon. These days, warfarin is little used, mostly after valve replacement, Dr. Nissen added.
There were also no percutaneous options for the treatment of valvular heart disease and no catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation, “huge developments that are now being done everywhere,” Dr. Nissen said.
Also in the catheterization laboratory, there was also a far less sophisticated understanding of the optimal role of PCI in treating coronary artery disease.
“We’ve moved from what we called the ‘oculostenotic reflex’– if you see an obstruction, you treat it – to a far more nuanced understanding of who should and shouldn’t have PCI, such that now PCI has contracted to the point where most of the time it’s being done for urgent indications like ST-segment elevation MI or an unstable non-STEMI. And this is based on a solid evidence base, which is terribly important,” said Dr. Nissen.
The rise and fall of CVOTs
Certainly, the heart failure world has seen important advances in recent years, including the first mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, spironolactone, shown in the 1999 RALES trial to be life prolonging in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and a first in class angiotensin neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan. But it’s a fair guess that heart failure has never seen anything like the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Likely very few in the cardiology world had ever heard of SGLT2 inhibition 20 years ago, even though the idea of SGLT2 inhibition dates back more than 150 years, to when a French chemist isolated a substance known as phlorizin from the bark of the apple tree and subsequent investigations found that ingestion of it caused glucosuria. The SGLT2 story is one of great serendipity and one in which Dr. Nissen played a prominent role. It also hints to something that has both come and gone in the last 20 years: the FDA-mandated cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT).
It was Dr. Nissen’s meta-analysis published in 2007 that started the ball rolling for what has been dubbed the CVOT or cardiovascular outcomes trials.
His analysis suggested increased cardiovascular risk associated with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (Avandia), then a best-selling diabetes drug.
“At the time, Avandia was the top selling diabetes drug in the world, and our meta-analysis was terribly controversial,” said Dr. Nissen. In 2008, he gave a presentation to the FDA where he suggested they should require properly powered trials to rule out excess cardiovascular risk for any new diabetes drugs.
Others also recognized that the findings of his meta-analysis hinted to a failure of the approval process and the postapproval monitoring process, something which had been seen previously, with cardiac safety concerns emerging over other antihyperglycemic medications. The FDA was also responding to concerns that, given the high prevalence of cardiovascular disease in diabetes, approving a drug with cardiovascular risk could be disastrous.
In 2008 they mandated the CVOT, one of which, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial, showed that the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 14% (P = .04), driven by a 38% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death (P < .001).Treatment with empagliflozin was also associated with a 35% reduction in heart failure hospitalization and a 32% reduction in all-cause death in that trial.
Additional groundbreaking CVOTs of empagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors went on to show significant cardiorenal benefits and risk reduction in patients across the spectrum of heart failure, including those with preserved ejection fraction and in those with kidney disease.
“I think it’s fair to say that, had the FDA not mandated CVOTs for all new diabetes drugs, then the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists would have been approved on the basis of trials involving a few thousand patients showing that they lowered blood sugar, and we might never have found out what we know now about their benefits in individuals with established cardiovascular disease, in heart failure, and their ability to help people lose weight,” said Dr. Nissen. “And, of course, Avandia is long gone, which is a good thing.”
Interestingly, the FDA no longer requires extensive cardiovascular testing for new glucose-lowering agents in the absence of specific safety signals, replacing the CVOT mandate with one requiring broader inclusion of patients with underlying CV disease, chronic kidney disease, and older patients in stage 3 clinical trials of new agents.
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are already hugely important and with the growing prevalence of diabetes, their role is just going to get bigger. And it looks like the same thing will happen with the GLP-1 receptor agonists and obesity. We don’t have the outcomes trials for semaglutide and tirzepatide yet in patients with obesity, but given every other trial of this class in patients with diabetes has shown cardiovascular benefit, assuming those trials do too, those drugs are going to be very important,” added Dr. Cannon.
“The truth is, everywhere you look in cardiology, there have been major advances,” Dr. Cannon said. “It’s a wonderful time to work in this field because we’re making important progress across the board and it doesn’t appear to be slowing down at all.”
Clinical research for the next 20 years
Twenty years ago, clinical research was relatively simple, or at least it seemed so. All that was needed was a basic understanding of the scientific method and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a solid research question, a target sample of sufficient size to ensure statistical power, and some basic statistical analysis, et violà, evidence generation.
Turns out, that might have been in large part true because medicine was in a more simplistic age. While RCTs remain the cornerstone of determining the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic strategies, they traditionally have severely lacked in age, gender, ethnic, and racial diversity. These issues limit their clinical relevance, to the chagrin of the large proportion of the population (women, minorities, children, and anyone with comorbidities) not included in most studies.
RCTs have also grown exceedingly time consuming and expensive. “We really saw the limitations of our clinical trial system during the pandemic when so many of the randomized COVID-19 trials done in the United States had complex protocols with a focus on surrogate outcomes such that, with only the 500 patients they enrolled, they ended up showing nothing,” Dr. Cannon said in an interview.
“And then we looked at the RECOVERY trial program that Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, and the folks at Oxford [England] University pioneered. They ran multiple trials for relatively little costs, used a pragmatic design, and asked simple straightforward questions, and included 10,000-15,000 patients in each trial and gave us answers quickly,” he said.
RECOVERY is an ongoing adaptive multicenter randomized controlled trial evaluating several potential treatments for COVID-19. The RECOVERY Collaborative are credited with running multiple streamlined and easy to administer trials that included more than 47,000 participants spread across almost 200 hospital sites in six countries. The trials resulted in finding four effective COVID-19 treatments and proving that five others clearly were not effective.
Importantly, only essential data were collected and, wherever possible, much of the follow-up information was derived from national electronic health records.
“Now the question is, Can the U.S. move to doing more of these pragmatic trials?” asked Dr. Cannon.
Time to be inclusive
Where the rules of generating evidence have changed and will continue to change over the next many years is inclusivity. Gone are the days when researchers can get away with running a randomized trial with, say, few minority patients, 20% representation of women, and no elderly patients with comorbidities.
“I’m proud of the fact that 48% of more than 14,000 participants in the CLEAR outcomes trial that I presented at the ACC meeting are women,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“Should it have been like that 20 years ago? Yes, probably. But we weren’t as conscious of these things. Now we’re working very hard to enroll more women and more underrepresented groups into trials, and this is a good thing.”
In a joint statement entitled “Randomized trials fit for the 21st century,” the leadership of the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and the World Heart Federation urge investigators and professional societies to “promote trials that are relevant to a broad and varied population; assuring diversity of participants and funded researchers (e.g., with appropriate sex, age, racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic diversity).”
The statement also recognizes that the present clinical research model is “unsustainable” and encourages wider adoption of “highly streamlined” conduct like that taken by the RECOVERY investigators during the pandemic.
Stick with randomization
Some have suggested that loosening the standards for evidence generation in medicine to include observational data, big data, artificial intelligence, and alternative trial strategies, such as Mendelian randomization and causal inference of nonrandomized data, might help drive new treatments to the clinic faster. To this, Dr. Nissen and Dr. Cannon offer an emphatic no.
“The idea that you can use big data or any kind of nonrandomized data to replace randomized control trials is a bad idea, and the reason is that nonrandomized data is often bad data,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“I can’t count how many bad studies we’ve seen that were enormous in size, and where they tried to control the variables to balance it out, and they still get the wrong answer,” he added. “The bottom line is that observational data has failed us over and over again.”
Not to say that observational studies have no value, it’s just not for determining which treatments are most efficacious or safe, said Dr. Cannon. “If you want to identify markers of disease or risk factors, you can use observational data like data collected from wearables and screen for patients who, say, might be at high risk of dying of COVID-19. Or even more directly, you can use a heart rate and temperature monitor to identify people who are about to test positive for COVID-19.
“But the findings of observational analyses, no matter how much you try to control for confounding, are only ever going to be hypothesis generating. They can’t be used to say this biomarker causes death from COVID or this blood thinner is better than that blood thinner.”
Concurring with this, the ESC, AHA, ACC, and WHF statement authors acknowledged the value of nonrandomized evidence in today’s big data, electronic world, but advocated for the “appropriate use of routine EHRs (i.e. ‘real-world’ data) within randomized trials, recognizing the huge potential of centrally or regionally held electronic health data for trial recruitment and follow-up, as well as to highlight the severe limitations of using observational analyses when the purpose is to draw causal inference about the risks and benefits of an intervention.”
In February 2003, when Cardiology News published its first edition, there were a handful of articles reporting results from randomized clinical trials. These included a trial of bivalirudin for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) anticoagulation (REPLACE-2) and a small controlled pilot study of soy nuts for blood pressure reduction in postmenopausal women. Also included was a considered discussion of the ALLHAT findings.
These trials and the incremental gain they offered belie the enormous global impact the cardiology community has had in clinical research over the last several decades. In fact, more than any other medical specialty, cardiology has led the way in evidence-based practice.
“When you step back and take a look at the compendium of cardiology advances, it’s unbelievable how much we’ve accomplished in the last 20 years,” said Steven E. Nissen, MD.
Dr. Nissen, a prodigious researcher, is the chief academic officer at the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, and holds the Lewis and Patricia Dickey Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
The needle mover: LDL lowering
“From a population health perspective, LDL cholesterol lowering is clearly the big winner,” said Christopher Cannon, MD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“We’ve been at it with LDL cholesterol for about 50 years now, but I think things really accelerated over the last 20 years when the conversation shifted from just lowering LDL-C to recognizing that lower is better. This pushed us toward high-intensity statin treatment and add-on drugs to push LDL down further,” he said.
“Concurrent with this increase in the use of statins and other LDL-lowering drugs, cardiovascular death has fallen significantly, which in my mind is likely a result of better LDL lowering and getting people to stop smoking, which we’ve also done a better job of in the last 20 years,” said Dr. Cannon.
Indeed, until cardiovascular mortality started rising in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality rates had been dropping steadily for several decades. The progress in the past 2 decades has been so fast, noted Dr. Cannon, that the American Heart Association’s stated goal in 1998 of reducing coronary heart disease, stroke, and risk by 25% by the year 2008 was accomplished about 4 years ahead of schedule.
Coincidentally, Dr. Cannon and Dr. Nissen were both important players in this advance. Dr. Cannon led the PROVE-IT trial, which showed in 2004 that an intensive lipid-lowering statin regimen offers greater protection against death or major cardiovascular events than does a standard regimen in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
That trial was published just months after REVERSAL, Dr. Nissen’s trial that showed for the first time that intensive lipid-lowering treatment reduced progression of coronary atherosclerosis, compared with a moderate lipid-lowering approach.
“Added to this, we have drugs like ezetimibe and the PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and now they’re even using CRISPR gene editing to permanently switch off the gene that codes for PCSK9, testing this in people with familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Cannon. “In the preclinical study, they showed that with one treatment they lowered blood PCSK9 protein levels by 83% and LDL-C by 69%..”
At the same time as we’ve seen what works, we’ve also seen what doesn’t work, added Dr. Nissen. “Shortly after we saw the power of LDL lowering, everyone wanted to target HDL and we had epidemiological evidence suggesting this was a good idea, but several landmark trials testing the HDL hypothesis were complete failures.” Debate continues as to whether HDL cholesterol is a suitable target for prevention.
Not only has the recent past in lipidology been needle-moving, but the hits keep coming. Inclisiran, a first-in-class LDL cholesterol–lowering drug that shows potent lipid-lowering efficacy and excellent safety and tolerability in phase 3 study, received Food and Drug Administration approval in December 2021. The drugs twice-a-year dosing has been called a game changer for adherence.
And at the 2023 annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology in March, Dr. Nissen presented results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial on bempedoic acid (Nexletol), a 14,000-patient, placebo-controlled trial of bempedoic acid in statin intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk. Bempedoic acid is a novel compound that inhibits ATP citrate lyase, which catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol upstream of HMG-CoA reductase, the target of statins.
Findings revealed a significant reduction in risk for a composite 4-point major adverse cardiovascular events endpoint of time to first cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial marks the first time an oral nonstatin drug has met the MACE-4 primary endpoint, Dr. Nissen reported.
“We also have new therapies for lowering lipoprotein(a) and outcome trials underway for antisense and short interfering RNA targeting of Lp(a), which I frankly think herald a new era in which we can have these longer-acting directly targeted drugs that work at the translation level to prevent a protein that is not desirable,” added Dr. Nissen. “These drugs will undoubtedly change the face of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the next 2 decades.”
Other important successes and equally important failures
Perhaps consideration of some of the treatments we didn’t have 20 years ago is more revealing than a list of advances. Two decades ago, there were no direct direct-acting anticoagulants on the market, “so no alternative to warfarin, which is difficult to use and associated with excess bleeding,” said Dr. Cannon. These days, warfarin is little used, mostly after valve replacement, Dr. Nissen added.
There were also no percutaneous options for the treatment of valvular heart disease and no catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation, “huge developments that are now being done everywhere,” Dr. Nissen said.
Also in the catheterization laboratory, there was also a far less sophisticated understanding of the optimal role of PCI in treating coronary artery disease.
“We’ve moved from what we called the ‘oculostenotic reflex’– if you see an obstruction, you treat it – to a far more nuanced understanding of who should and shouldn’t have PCI, such that now PCI has contracted to the point where most of the time it’s being done for urgent indications like ST-segment elevation MI or an unstable non-STEMI. And this is based on a solid evidence base, which is terribly important,” said Dr. Nissen.
The rise and fall of CVOTs
Certainly, the heart failure world has seen important advances in recent years, including the first mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, spironolactone, shown in the 1999 RALES trial to be life prolonging in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and a first in class angiotensin neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan. But it’s a fair guess that heart failure has never seen anything like the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Likely very few in the cardiology world had ever heard of SGLT2 inhibition 20 years ago, even though the idea of SGLT2 inhibition dates back more than 150 years, to when a French chemist isolated a substance known as phlorizin from the bark of the apple tree and subsequent investigations found that ingestion of it caused glucosuria. The SGLT2 story is one of great serendipity and one in which Dr. Nissen played a prominent role. It also hints to something that has both come and gone in the last 20 years: the FDA-mandated cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT).
It was Dr. Nissen’s meta-analysis published in 2007 that started the ball rolling for what has been dubbed the CVOT or cardiovascular outcomes trials.
His analysis suggested increased cardiovascular risk associated with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (Avandia), then a best-selling diabetes drug.
“At the time, Avandia was the top selling diabetes drug in the world, and our meta-analysis was terribly controversial,” said Dr. Nissen. In 2008, he gave a presentation to the FDA where he suggested they should require properly powered trials to rule out excess cardiovascular risk for any new diabetes drugs.
Others also recognized that the findings of his meta-analysis hinted to a failure of the approval process and the postapproval monitoring process, something which had been seen previously, with cardiac safety concerns emerging over other antihyperglycemic medications. The FDA was also responding to concerns that, given the high prevalence of cardiovascular disease in diabetes, approving a drug with cardiovascular risk could be disastrous.
In 2008 they mandated the CVOT, one of which, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial, showed that the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 14% (P = .04), driven by a 38% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death (P < .001).Treatment with empagliflozin was also associated with a 35% reduction in heart failure hospitalization and a 32% reduction in all-cause death in that trial.
Additional groundbreaking CVOTs of empagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors went on to show significant cardiorenal benefits and risk reduction in patients across the spectrum of heart failure, including those with preserved ejection fraction and in those with kidney disease.
“I think it’s fair to say that, had the FDA not mandated CVOTs for all new diabetes drugs, then the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists would have been approved on the basis of trials involving a few thousand patients showing that they lowered blood sugar, and we might never have found out what we know now about their benefits in individuals with established cardiovascular disease, in heart failure, and their ability to help people lose weight,” said Dr. Nissen. “And, of course, Avandia is long gone, which is a good thing.”
Interestingly, the FDA no longer requires extensive cardiovascular testing for new glucose-lowering agents in the absence of specific safety signals, replacing the CVOT mandate with one requiring broader inclusion of patients with underlying CV disease, chronic kidney disease, and older patients in stage 3 clinical trials of new agents.
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are already hugely important and with the growing prevalence of diabetes, their role is just going to get bigger. And it looks like the same thing will happen with the GLP-1 receptor agonists and obesity. We don’t have the outcomes trials for semaglutide and tirzepatide yet in patients with obesity, but given every other trial of this class in patients with diabetes has shown cardiovascular benefit, assuming those trials do too, those drugs are going to be very important,” added Dr. Cannon.
“The truth is, everywhere you look in cardiology, there have been major advances,” Dr. Cannon said. “It’s a wonderful time to work in this field because we’re making important progress across the board and it doesn’t appear to be slowing down at all.”
Clinical research for the next 20 years
Twenty years ago, clinical research was relatively simple, or at least it seemed so. All that was needed was a basic understanding of the scientific method and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a solid research question, a target sample of sufficient size to ensure statistical power, and some basic statistical analysis, et violà, evidence generation.
Turns out, that might have been in large part true because medicine was in a more simplistic age. While RCTs remain the cornerstone of determining the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic strategies, they traditionally have severely lacked in age, gender, ethnic, and racial diversity. These issues limit their clinical relevance, to the chagrin of the large proportion of the population (women, minorities, children, and anyone with comorbidities) not included in most studies.
RCTs have also grown exceedingly time consuming and expensive. “We really saw the limitations of our clinical trial system during the pandemic when so many of the randomized COVID-19 trials done in the United States had complex protocols with a focus on surrogate outcomes such that, with only the 500 patients they enrolled, they ended up showing nothing,” Dr. Cannon said in an interview.
“And then we looked at the RECOVERY trial program that Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, and the folks at Oxford [England] University pioneered. They ran multiple trials for relatively little costs, used a pragmatic design, and asked simple straightforward questions, and included 10,000-15,000 patients in each trial and gave us answers quickly,” he said.
RECOVERY is an ongoing adaptive multicenter randomized controlled trial evaluating several potential treatments for COVID-19. The RECOVERY Collaborative are credited with running multiple streamlined and easy to administer trials that included more than 47,000 participants spread across almost 200 hospital sites in six countries. The trials resulted in finding four effective COVID-19 treatments and proving that five others clearly were not effective.
Importantly, only essential data were collected and, wherever possible, much of the follow-up information was derived from national electronic health records.
“Now the question is, Can the U.S. move to doing more of these pragmatic trials?” asked Dr. Cannon.
Time to be inclusive
Where the rules of generating evidence have changed and will continue to change over the next many years is inclusivity. Gone are the days when researchers can get away with running a randomized trial with, say, few minority patients, 20% representation of women, and no elderly patients with comorbidities.
“I’m proud of the fact that 48% of more than 14,000 participants in the CLEAR outcomes trial that I presented at the ACC meeting are women,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“Should it have been like that 20 years ago? Yes, probably. But we weren’t as conscious of these things. Now we’re working very hard to enroll more women and more underrepresented groups into trials, and this is a good thing.”
In a joint statement entitled “Randomized trials fit for the 21st century,” the leadership of the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and the World Heart Federation urge investigators and professional societies to “promote trials that are relevant to a broad and varied population; assuring diversity of participants and funded researchers (e.g., with appropriate sex, age, racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic diversity).”
The statement also recognizes that the present clinical research model is “unsustainable” and encourages wider adoption of “highly streamlined” conduct like that taken by the RECOVERY investigators during the pandemic.
Stick with randomization
Some have suggested that loosening the standards for evidence generation in medicine to include observational data, big data, artificial intelligence, and alternative trial strategies, such as Mendelian randomization and causal inference of nonrandomized data, might help drive new treatments to the clinic faster. To this, Dr. Nissen and Dr. Cannon offer an emphatic no.
“The idea that you can use big data or any kind of nonrandomized data to replace randomized control trials is a bad idea, and the reason is that nonrandomized data is often bad data,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“I can’t count how many bad studies we’ve seen that were enormous in size, and where they tried to control the variables to balance it out, and they still get the wrong answer,” he added. “The bottom line is that observational data has failed us over and over again.”
Not to say that observational studies have no value, it’s just not for determining which treatments are most efficacious or safe, said Dr. Cannon. “If you want to identify markers of disease or risk factors, you can use observational data like data collected from wearables and screen for patients who, say, might be at high risk of dying of COVID-19. Or even more directly, you can use a heart rate and temperature monitor to identify people who are about to test positive for COVID-19.
“But the findings of observational analyses, no matter how much you try to control for confounding, are only ever going to be hypothesis generating. They can’t be used to say this biomarker causes death from COVID or this blood thinner is better than that blood thinner.”
Concurring with this, the ESC, AHA, ACC, and WHF statement authors acknowledged the value of nonrandomized evidence in today’s big data, electronic world, but advocated for the “appropriate use of routine EHRs (i.e. ‘real-world’ data) within randomized trials, recognizing the huge potential of centrally or regionally held electronic health data for trial recruitment and follow-up, as well as to highlight the severe limitations of using observational analyses when the purpose is to draw causal inference about the risks and benefits of an intervention.”
In February 2003, when Cardiology News published its first edition, there were a handful of articles reporting results from randomized clinical trials. These included a trial of bivalirudin for percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) anticoagulation (REPLACE-2) and a small controlled pilot study of soy nuts for blood pressure reduction in postmenopausal women. Also included was a considered discussion of the ALLHAT findings.
These trials and the incremental gain they offered belie the enormous global impact the cardiology community has had in clinical research over the last several decades. In fact, more than any other medical specialty, cardiology has led the way in evidence-based practice.
“When you step back and take a look at the compendium of cardiology advances, it’s unbelievable how much we’ve accomplished in the last 20 years,” said Steven E. Nissen, MD.
Dr. Nissen, a prodigious researcher, is the chief academic officer at the Sydell and Arnold Miller Family Heart, Vascular and Thoracic Institute, and holds the Lewis and Patricia Dickey Chair in Cardiovascular Medicine at the Cleveland Clinic.
The needle mover: LDL lowering
“From a population health perspective, LDL cholesterol lowering is clearly the big winner,” said Christopher Cannon, MD, from Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston, said in an interview.
“We’ve been at it with LDL cholesterol for about 50 years now, but I think things really accelerated over the last 20 years when the conversation shifted from just lowering LDL-C to recognizing that lower is better. This pushed us toward high-intensity statin treatment and add-on drugs to push LDL down further,” he said.
“Concurrent with this increase in the use of statins and other LDL-lowering drugs, cardiovascular death has fallen significantly, which in my mind is likely a result of better LDL lowering and getting people to stop smoking, which we’ve also done a better job of in the last 20 years,” said Dr. Cannon.
Indeed, until cardiovascular mortality started rising in 2020, the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic, mortality rates had been dropping steadily for several decades. The progress in the past 2 decades has been so fast, noted Dr. Cannon, that the American Heart Association’s stated goal in 1998 of reducing coronary heart disease, stroke, and risk by 25% by the year 2008 was accomplished about 4 years ahead of schedule.
Coincidentally, Dr. Cannon and Dr. Nissen were both important players in this advance. Dr. Cannon led the PROVE-IT trial, which showed in 2004 that an intensive lipid-lowering statin regimen offers greater protection against death or major cardiovascular events than does a standard regimen in patients with recent acute coronary syndrome.
That trial was published just months after REVERSAL, Dr. Nissen’s trial that showed for the first time that intensive lipid-lowering treatment reduced progression of coronary atherosclerosis, compared with a moderate lipid-lowering approach.
“Added to this, we have drugs like ezetimibe and the PCSK9 [proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9] inhibitor, and now they’re even using CRISPR gene editing to permanently switch off the gene that codes for PCSK9, testing this in people with familial hypercholesterolemia,” said Dr. Cannon. “In the preclinical study, they showed that with one treatment they lowered blood PCSK9 protein levels by 83% and LDL-C by 69%..”
At the same time as we’ve seen what works, we’ve also seen what doesn’t work, added Dr. Nissen. “Shortly after we saw the power of LDL lowering, everyone wanted to target HDL and we had epidemiological evidence suggesting this was a good idea, but several landmark trials testing the HDL hypothesis were complete failures.” Debate continues as to whether HDL cholesterol is a suitable target for prevention.
Not only has the recent past in lipidology been needle-moving, but the hits keep coming. Inclisiran, a first-in-class LDL cholesterol–lowering drug that shows potent lipid-lowering efficacy and excellent safety and tolerability in phase 3 study, received Food and Drug Administration approval in December 2021. The drugs twice-a-year dosing has been called a game changer for adherence.
And at the 2023 annual scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology in March, Dr. Nissen presented results of the CLEAR Outcomes trial on bempedoic acid (Nexletol), a 14,000-patient, placebo-controlled trial of bempedoic acid in statin intolerant patients at high cardiovascular risk. Bempedoic acid is a novel compound that inhibits ATP citrate lyase, which catalyzes a step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol upstream of HMG-CoA reductase, the target of statins.
Findings revealed a significant reduction in risk for a composite 4-point major adverse cardiovascular events endpoint of time to first cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, nonfatal stroke, or coronary revascularization. The trial marks the first time an oral nonstatin drug has met the MACE-4 primary endpoint, Dr. Nissen reported.
“We also have new therapies for lowering lipoprotein(a) and outcome trials underway for antisense and short interfering RNA targeting of Lp(a), which I frankly think herald a new era in which we can have these longer-acting directly targeted drugs that work at the translation level to prevent a protein that is not desirable,” added Dr. Nissen. “These drugs will undoubtedly change the face of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the next 2 decades.”
Other important successes and equally important failures
Perhaps consideration of some of the treatments we didn’t have 20 years ago is more revealing than a list of advances. Two decades ago, there were no direct direct-acting anticoagulants on the market, “so no alternative to warfarin, which is difficult to use and associated with excess bleeding,” said Dr. Cannon. These days, warfarin is little used, mostly after valve replacement, Dr. Nissen added.
There were also no percutaneous options for the treatment of valvular heart disease and no catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation, “huge developments that are now being done everywhere,” Dr. Nissen said.
Also in the catheterization laboratory, there was also a far less sophisticated understanding of the optimal role of PCI in treating coronary artery disease.
“We’ve moved from what we called the ‘oculostenotic reflex’– if you see an obstruction, you treat it – to a far more nuanced understanding of who should and shouldn’t have PCI, such that now PCI has contracted to the point where most of the time it’s being done for urgent indications like ST-segment elevation MI or an unstable non-STEMI. And this is based on a solid evidence base, which is terribly important,” said Dr. Nissen.
The rise and fall of CVOTs
Certainly, the heart failure world has seen important advances in recent years, including the first mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, spironolactone, shown in the 1999 RALES trial to be life prolonging in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction and a first in class angiotensin neprilysin inhibitor, sacubitril/valsartan. But it’s a fair guess that heart failure has never seen anything like the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Likely very few in the cardiology world had ever heard of SGLT2 inhibition 20 years ago, even though the idea of SGLT2 inhibition dates back more than 150 years, to when a French chemist isolated a substance known as phlorizin from the bark of the apple tree and subsequent investigations found that ingestion of it caused glucosuria. The SGLT2 story is one of great serendipity and one in which Dr. Nissen played a prominent role. It also hints to something that has both come and gone in the last 20 years: the FDA-mandated cardiovascular outcome trial (CVOT).
It was Dr. Nissen’s meta-analysis published in 2007 that started the ball rolling for what has been dubbed the CVOT or cardiovascular outcomes trials.
His analysis suggested increased cardiovascular risk associated with the thiazolidinedione rosiglitazone (Avandia), then a best-selling diabetes drug.
“At the time, Avandia was the top selling diabetes drug in the world, and our meta-analysis was terribly controversial,” said Dr. Nissen. In 2008, he gave a presentation to the FDA where he suggested they should require properly powered trials to rule out excess cardiovascular risk for any new diabetes drugs.
Others also recognized that the findings of his meta-analysis hinted to a failure of the approval process and the postapproval monitoring process, something which had been seen previously, with cardiac safety concerns emerging over other antihyperglycemic medications. The FDA was also responding to concerns that, given the high prevalence of cardiovascular disease in diabetes, approving a drug with cardiovascular risk could be disastrous.
In 2008 they mandated the CVOT, one of which, the EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial, showed that the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin significantly reduced the risk of a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal myocardial infarction, or nonfatal stroke by 14% (P = .04), driven by a 38% relative risk reduction in cardiovascular death (P < .001).Treatment with empagliflozin was also associated with a 35% reduction in heart failure hospitalization and a 32% reduction in all-cause death in that trial.
Additional groundbreaking CVOTs of empagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors went on to show significant cardiorenal benefits and risk reduction in patients across the spectrum of heart failure, including those with preserved ejection fraction and in those with kidney disease.
“I think it’s fair to say that, had the FDA not mandated CVOTs for all new diabetes drugs, then the SGLT2 inhibitors and the GLP-1 [glucagonlike peptide–1] receptor agonists would have been approved on the basis of trials involving a few thousand patients showing that they lowered blood sugar, and we might never have found out what we know now about their benefits in individuals with established cardiovascular disease, in heart failure, and their ability to help people lose weight,” said Dr. Nissen. “And, of course, Avandia is long gone, which is a good thing.”
Interestingly, the FDA no longer requires extensive cardiovascular testing for new glucose-lowering agents in the absence of specific safety signals, replacing the CVOT mandate with one requiring broader inclusion of patients with underlying CV disease, chronic kidney disease, and older patients in stage 3 clinical trials of new agents.
“The SGLT2 inhibitors are already hugely important and with the growing prevalence of diabetes, their role is just going to get bigger. And it looks like the same thing will happen with the GLP-1 receptor agonists and obesity. We don’t have the outcomes trials for semaglutide and tirzepatide yet in patients with obesity, but given every other trial of this class in patients with diabetes has shown cardiovascular benefit, assuming those trials do too, those drugs are going to be very important,” added Dr. Cannon.
“The truth is, everywhere you look in cardiology, there have been major advances,” Dr. Cannon said. “It’s a wonderful time to work in this field because we’re making important progress across the board and it doesn’t appear to be slowing down at all.”
Clinical research for the next 20 years
Twenty years ago, clinical research was relatively simple, or at least it seemed so. All that was needed was a basic understanding of the scientific method and randomized controlled trials (RCTs), a solid research question, a target sample of sufficient size to ensure statistical power, and some basic statistical analysis, et violà, evidence generation.
Turns out, that might have been in large part true because medicine was in a more simplistic age. While RCTs remain the cornerstone of determining the safety and efficacy of new therapeutic strategies, they traditionally have severely lacked in age, gender, ethnic, and racial diversity. These issues limit their clinical relevance, to the chagrin of the large proportion of the population (women, minorities, children, and anyone with comorbidities) not included in most studies.
RCTs have also grown exceedingly time consuming and expensive. “We really saw the limitations of our clinical trial system during the pandemic when so many of the randomized COVID-19 trials done in the United States had complex protocols with a focus on surrogate outcomes such that, with only the 500 patients they enrolled, they ended up showing nothing,” Dr. Cannon said in an interview.
“And then we looked at the RECOVERY trial program that Martin Landray, MBChB, PhD, and the folks at Oxford [England] University pioneered. They ran multiple trials for relatively little costs, used a pragmatic design, and asked simple straightforward questions, and included 10,000-15,000 patients in each trial and gave us answers quickly,” he said.
RECOVERY is an ongoing adaptive multicenter randomized controlled trial evaluating several potential treatments for COVID-19. The RECOVERY Collaborative are credited with running multiple streamlined and easy to administer trials that included more than 47,000 participants spread across almost 200 hospital sites in six countries. The trials resulted in finding four effective COVID-19 treatments and proving that five others clearly were not effective.
Importantly, only essential data were collected and, wherever possible, much of the follow-up information was derived from national electronic health records.
“Now the question is, Can the U.S. move to doing more of these pragmatic trials?” asked Dr. Cannon.
Time to be inclusive
Where the rules of generating evidence have changed and will continue to change over the next many years is inclusivity. Gone are the days when researchers can get away with running a randomized trial with, say, few minority patients, 20% representation of women, and no elderly patients with comorbidities.
“I’m proud of the fact that 48% of more than 14,000 participants in the CLEAR outcomes trial that I presented at the ACC meeting are women,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“Should it have been like that 20 years ago? Yes, probably. But we weren’t as conscious of these things. Now we’re working very hard to enroll more women and more underrepresented groups into trials, and this is a good thing.”
In a joint statement entitled “Randomized trials fit for the 21st century,” the leadership of the European Society of Cardiology, American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology, and the World Heart Federation urge investigators and professional societies to “promote trials that are relevant to a broad and varied population; assuring diversity of participants and funded researchers (e.g., with appropriate sex, age, racial, ethnic, and socioeconomic diversity).”
The statement also recognizes that the present clinical research model is “unsustainable” and encourages wider adoption of “highly streamlined” conduct like that taken by the RECOVERY investigators during the pandemic.
Stick with randomization
Some have suggested that loosening the standards for evidence generation in medicine to include observational data, big data, artificial intelligence, and alternative trial strategies, such as Mendelian randomization and causal inference of nonrandomized data, might help drive new treatments to the clinic faster. To this, Dr. Nissen and Dr. Cannon offer an emphatic no.
“The idea that you can use big data or any kind of nonrandomized data to replace randomized control trials is a bad idea, and the reason is that nonrandomized data is often bad data,” Dr. Nissen said in an interview.
“I can’t count how many bad studies we’ve seen that were enormous in size, and where they tried to control the variables to balance it out, and they still get the wrong answer,” he added. “The bottom line is that observational data has failed us over and over again.”
Not to say that observational studies have no value, it’s just not for determining which treatments are most efficacious or safe, said Dr. Cannon. “If you want to identify markers of disease or risk factors, you can use observational data like data collected from wearables and screen for patients who, say, might be at high risk of dying of COVID-19. Or even more directly, you can use a heart rate and temperature monitor to identify people who are about to test positive for COVID-19.
“But the findings of observational analyses, no matter how much you try to control for confounding, are only ever going to be hypothesis generating. They can’t be used to say this biomarker causes death from COVID or this blood thinner is better than that blood thinner.”
Concurring with this, the ESC, AHA, ACC, and WHF statement authors acknowledged the value of nonrandomized evidence in today’s big data, electronic world, but advocated for the “appropriate use of routine EHRs (i.e. ‘real-world’ data) within randomized trials, recognizing the huge potential of centrally or regionally held electronic health data for trial recruitment and follow-up, as well as to highlight the severe limitations of using observational analyses when the purpose is to draw causal inference about the risks and benefits of an intervention.”
By the numbers: Cardiology slow to add women, IMGs join more quickly
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.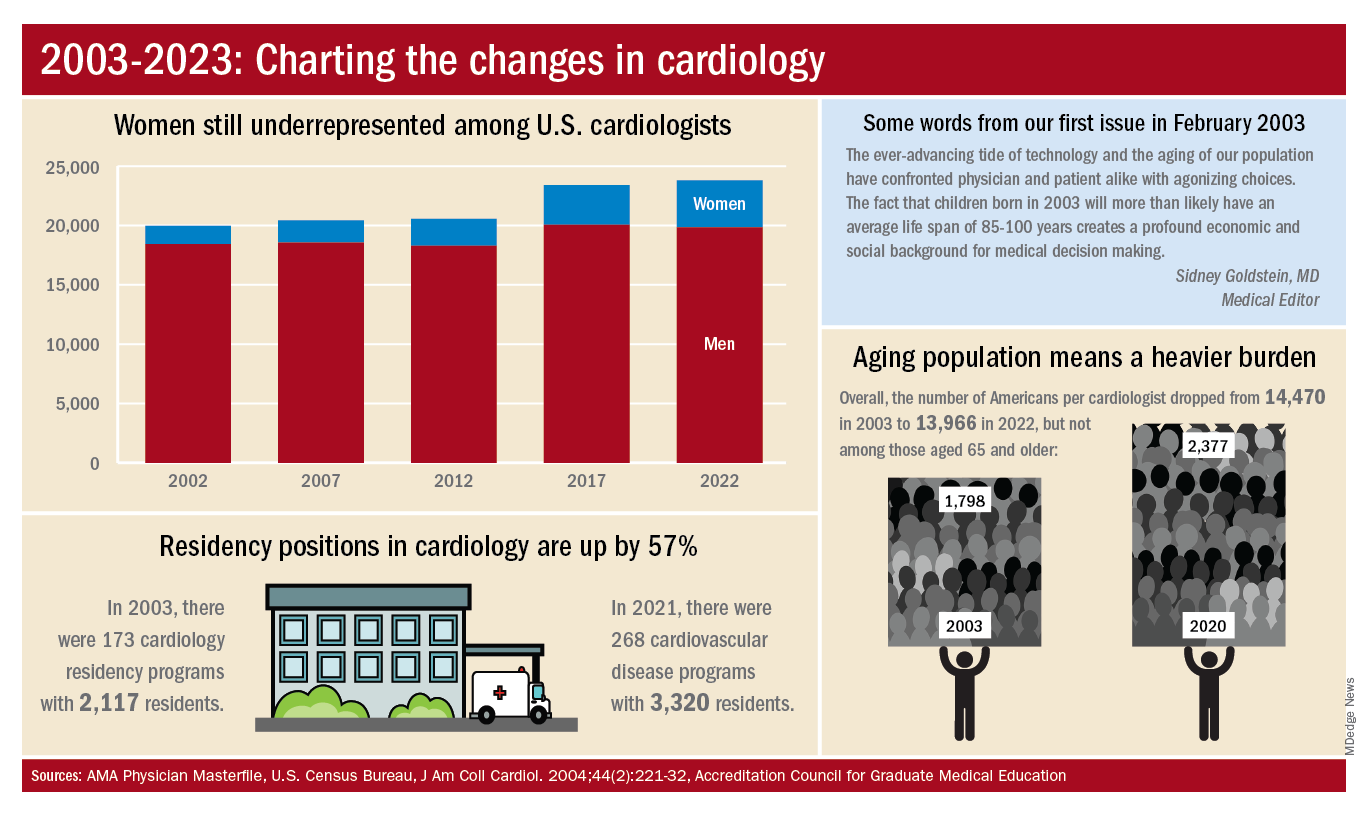
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
Despite Mark Twain’s assertion that “there are three kinds of lies: lies, damned lies, and statistics,” we’re going to dive into 20 years’ worth of data and, hopefully, come up with a few statistics that shed some light on the specialty’s workforce since Cardiology News published its first issue in February 2003.
We start with a major issue over these last 20 years: The participation of women in the specialty.
Back in July of 2002, just a few months before the first issue of Cardiology News was published, W. Bruce Fye, MD, then-president of the American College of Cardiology, wrote, “We need to do more to attract female medical graduates to our specialty because they represent almost one-half of the new doctors trained in this country. Cardiology needs to take full advantage of this large talent pool”
Data from the American Medical Association confirm that assertion: Of the nearly 20,000 postgraduate cardiologists in practice that year, only 7.8% were women. And that was at a time when more than 42% of medical school graduates were women, Dr. Fye noted, while also pointing out that “only 10% of cardiology trainees are female, and just 6% of ACC fellows are women.”
The gap between men and women has closed somewhat in the last 20 years, but the specialty continues to lag behind the profession as a whole. Women represented 16.7% of cardiologists in 2022, versus 37% of physicians overall, AMA data show. In 2019, for the first time, the majority of U.S. medical school students (50.5%) were women, according to the Association of American Medical Colleges.
A look at residency numbers from the Accreditation Council for Graduate Medical Education shows that continued slow improvement in the number of women can be expected, as 25.5% of cardiovascular disease residents were women during the 2021-2022 academic year. Only 2 of the 19 other internal medicine subspecialties were lower, and they happened to be interventional cardiology (20.1%) and clinical cardiac electrophysiology (14.5%).
When men are added to the mix, cardiovascular disease had a total of 3,320 active residents training in 268 programs in 2021-2022, making it the largest of the IM subspecialties in both respects. The resident total is up 57% since 2003, when it came in at 2,117, while programs have increased 55% from the 173 that were operating 2 decades ago. During the year in the middle (2011-2012), there were 2,521 residents in 187 programs, so a larger share of the growth has occurred in the last 10 years, the ACGME data indicate.
The shortage of cardiologists that Dr. Fye and others wrote about 20 years ago has not gone away. A 2018 report from health consulting firm PYA noted the increase in obesity and the low number of medical school graduates choosing the specialty. “Older and fewer physicians specializing in cardiology, coupled with the aging of baby boomers and gravitation toward practice in urban areas, will continue to exacerbate shortages in physician services in the specialty of cardiology, especially in rural areas, over the next decade,” PYA principal Lyle Oelrich wrote.
A little math appears to back up the claims of a cardiologist shortage. Based on census figures for the U.S. population in 2003, there were 14,470 Americans for each of the cardiologists reported by the AMA. That figure dropped to 13,966 by 2022, which seems like an improvement, but it comes with a caveat. The number of Americans aged 65 years and older increased from 1,798 to 2,377 per cardiologist as of 2020, the latest year for which population data were available by age.
One source of growth in the cardiology workforce has been perhaps its most significant minority: international medical graduates. Even by 2004, IMGs represented a much larger segment of all cardiologists (30.0%) than did women (9.3%), based on AMA data. To put it another way, there were more IMGs specializing in cardiovascular disease (6,615) in 2004 than there were women (3,963) in 2022.
The latest data on cardiology training programs – overall numbers were not available – put IMGs at 39.2% for the 2019-2020 academic year. The 2022 fellowship match provides a slightly smaller proportion of IMGs (37.4%) filling cardiovascular disease positions, according to the National Resident Matching Program.
OMERACT continues to set standards on research outcomes, enhancing the patient voice
Clinical research in rheumatology was suffering from an identity crisis of sorts 40 years ago. A lack of consensus across continents resulted in differing views about clinical outcome measures and judgments about treatments.
Patients were not allowed to be the generating source of a clinical outcome, according to Peter Tugwell, MSc, MD. “The only outcomes that were acceptable were clinician assessments, blood tests, and imaging,” said Dr. Tugwell, professor of medicine, epidemiology, and public health at the University of Ottawa (Ont.) and a practicing rheumatologist at Ottawa Hospital.
Clinicians were coming to different conclusions about patient responses to treatment when managing rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice.
OMERACT sought to address this lack of uniformity. This international group, formed in 1992, leverages stakeholder groups to improve outcome measurement in rheumatology endpoints through a consensus-building, data-driven format.
It was originally known as “Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials,” but its leaders have since broadened its scope to “Outcome Measures in Rheumatology.” Over the years, it has evolved into an international network that assesses measurement across a wide variety of intervention studies. Now 30 years old, the network spans 40 active working groups and has influenced work in patient outcomes across 500 peer-reviewed publications.
The network meets every 2 years to address what is always a challenging agenda, said Dr. Tugwell, one of its founding members and chair. “There’s lots of strong opinions.” Participating in the discussions are individuals from all stages of seniority in rheumatology and clinical epidemiology, patient research partners, industry, approval agencies, and many countries who are committed to the spirit of OMERACT.
“The secret to our success has been getting world leaders to come together and have those discussions, work them through, and identify common ground in such a way that the approval agencies accept these outcome measures in clinical trials,” he added.
“My impression was the founders perceived a problem in the early 1990s and devised a consensus method in an attempt to quantify clinical parameters to define disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis – an important first step to do clinical trials and allow comparisons between them,” said Patricia Woo, CBE, FMedSci, FRCP, emeritus professor of pediatric rheumatology and previous head of the Centre for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology at UCL, London. At that time, even disease definitions varied between the United States and Europe and other parts of the world, said Dr. Woo, who is not a part of OMERACT. “This was especially true for pediatric rheumatology.”
Fusing the continental divide
OMERACT arose from a need to streamline clinical outcome measures in rheumatology. Research papers during the 1980s demonstrated a lack of coherence in managing patients with rheumatoid arthritis in routine practice. In addition, the measures used to define clinical endpoints in clinical trials operated in silos – they were either too specific to a certain trial, overlapped with other concepts, or didn’t reflect changes in treatment.
Approval agencies in Europe and North America were approving only outcomes measures developed by their respective researchers. This was also true of patients they tested on. “This seemed crazy,” Dr. Tugwell said.
Dr. Tugwell was involved in the Cochrane collaboration, which conducts systematic reviews of best evidence across the world that assesses the magnitude of benefits versus harms.
To achieve this goal, “you need to pull studies from around the world,” he said. Maarten Boers, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist (and later professor of clinical epidemiology at Amsterdam University Medical Center) from the Netherlands, spent a year in Ontario, Canada, to train as a clinical epidemiologist. Together, Dr. Tugwell and Dr. Boers began discussing options to develop more streamlined outcome measures.
They initiated the first OMERACT conference in Maastricht, the Netherlands, in 1992. The Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency participated, along with leaders of outcomes measurement in Europe and in North America.
Discussions centered on methods to develop outcomes in a meaningful fashion. During the first meeting, North American and European approval agencies agreed to accept each other’s studies and endpoints and patient reported outcomes.
Agreement was achieved on a preliminary set of outcome domains and measures that later became known as the WHO-ILAR (World Health Organization–International League of Associations for Rheumatology) core set. The set included seven outcome domains: tender joints, swollen joints, pain, physician global assessment, patient global assessment, physical disability, and acute phase reactants, and one additional outcome domain for studies lasting 1 year or more: radiographs of the joints.
“A proactive program was planned to test not only the validity of these endpoints, but also the methods for their measurement. This was the start of a continuing process,” OMERACT members said in a joint statement for this article. Meetings have since taken place every 2 years.

OMERACT accomplishments
OMERACT now requires buy-in from four continents: Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.
Its leaders have developed an explicit process for gaining endorsement of core outcome domains and instrument measurement sets. To fully capture the possibilities of “what to measure,” i.e., “measurable aspects of health conditions,” OMERACT has developed a framework of concepts, core areas, and outcome domains. The key concepts are pathophysiology (with a core area termed “manifestations/abnormalities”) and impact (with core areas of “death/lifespan,” and “life impact,” and the optional area of “societal/resource use”). An outcome domain defines an element of a core area to measure the effects of a treatment, such as blood markers, pain intensity, physical function, or emotional well-being.
A core outcome domain set is developed by agreeing to at least one outcome domain within one of the three core areas. Subsequently, a core outcome measurement set is developed by agreeing to at least one applicable measurement instrument for each core outcome domain. This requires documentation of validity, summarized under three metrics: truth, discrimination, and feasibility.
OMERACT’s handbook provides tutelage on establishing and implementing core outcomes, and several workbooks offer guidance on developing core outcome domain sets, selecting instruments for core outcome measurement sets, and OMERACT methodology.
All this work has led to widespread adoption.
Approval agencies have accepted OMERACT’s filter and methods advances, which have been adopted by many research groups in rheumatology and among nonrheumatology research groups. Organizations such as the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke have sought its advice.
Its core outcomes have been adopted and used for approval in the great majority of studies on rheumatoid arthritis, Dr. Tugwell said.
Several BMJ articles underscore the influence and uptake of OMERACT’s core outcome set. One 2017 paper, which analyzed 273 randomized trials of rheumatoid arthritis drug treatments on ClinicalTrials.gov, found that the WHO-ILAR arthritis core outcome set was reported in 81% of the studies. “The adoption of a core outcome set has the potential to increase consistency in outcomes measured across trials and ensure that trials are more likely to measure appropriate outcomes,” the authors concluded.
Since the initial 1992 meeting, OMERACT has broadened its focus from rheumatoid arthritis to 25 other musculoskeletal conditions.
For example, other OMERACT conferences have led to consensus on core sets of measures for osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, psychosocial measures, and a core set of data for cost-effectiveness evaluations.
‘Speed is a limitation’
OMERACT is a bottom-up volunteer organization. It doesn’t represent any official organization of any clinical society. “We’ve not asked to be adopted by the American College of Rheumatology, EULAR [European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology], or other international organizations,” Dr. Tugwell said. It offers a chance for patients, users, and doers of research to work together to agree on rigorous criteria accepted by the approval agencies and take the necessary time to work things through.
This is not a fast process, usually taking 4-6 years to initiate and establish an outcome domain set, he emphasized. “It would be beneficial to do it faster if we had the resources to meet every year. The fact is we’re a volunteer organization that meets every 2 years.”
Speed is a limitation, he acknowledged, but it’s an acceptable trade-off for doing things correctly.
The group has faced other challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, pivoting to a virtual format that had benefits and limitations.
In one respect, moving to a virtual meeting increased uptake in participation and voting, Dr. Tugwell said. Patient participants with severe rheumatoid arthritis no longer faced the challenges of travel. “On the other hand, we didn’t have the same opportunity to achieve common ground virtually,” he said. “Where there are strong disagreements, I’m a great believer that people need to know one another. There needs to be relationship building.”
OMERACT’s emerging leader program has been a cornerstone of its in-person meetings, engaging young rheumatologists to interact with some of the leaders of outcome measurement. The virtual format dampened this process somewhat, eliminating those important “café chats” between the stakeholders.
The hope is to bring people face-to-face once more at the next meeting in May 2023. The agenda will focus on relationship building, identifying controversial areas, and bringing younger people to develop relationships, Dr. Tugwell said. OMERACT will retain a virtual option for the worldwide voting, “which will allow for more buy-in from so many more people,” he added.
A consensus on pain
The onus of developing outcome measures that move with the times is sometimes too great for one group to manage. In 2018, OMERACT became a part of the Red Hat Group (RHG), an organization conceived at the COMET (Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials) VII meeting in Amsterdam.
RHG aims to improve the choice of outcomes in health research. It includes eight groups: COMET; OMERACT; the Cochrane Skin Core Outcome Set Initiative; Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations; Center for Medical Technology Policy; COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments; Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium; and Standardized Outcomes in Nephrology.
The collaboration between groups offers a “very interesting interface between consensus building as well as hard evidence,” Dr. Tugwell said. The focus goes beyond rheumatology to other clinical areas of common interest, exploring how one classifies outcome domains in terms of symptoms, life impact, or death.
Pain is an important common denominator that the RHG has evaluated.
“We believe it’s too general. We’re trying to define pain across all Red Hat Groups because it’s clear that the research community has all these different scales for defining pain severity,” Dr. Tugwell said. “We have to find a way to make ruthless decisions and rules for doing it. And of course, it has to be transparent.”
Looking ahead
As part of its ongoing work, OMERACT is evaluating the robustness of instruments that rheumatologists use as outcome measures in clinical trials, which can be a laborious process. The OMERACT Filter 2.0, part of the latest iteration of the handbook, offers strong guidance for researchers but needs a long-term strategy and key methodological support. “To that end, we set up a technical advisory group to help people in the instrument selection work and that remains an ongoing process,” OMERACT leaders said in their joint statement.
OMERACT is looking at opportunities to create benchmark processes for developing core sets outside of rheumatology and a methodology around outcome measures such as contextual factors, composites, and surrogates.
It will also be taking a step back to solicit opinions from the approval agencies represented by the OMERACT membership on the OMERACT handbook.
The goal is to make sure the handbook aligns with everyone else’s approval and labeling requirements.
OMERACT’s patient participants bring important perspectives
OMERACT over the years has sought to become a more patient-centered group. Patients have been involved in OMERACT activities since its sixth meeting, forming an independent, yet integrated, group within the network. They have their own steering committee and produced and helped to update a glossary for OMERACT patients and professionals.
Catherine (McGowan) Hofstetter, who was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis 30 years ago, chairs OMERACT’s Patient Research Partners Support Team. In a Q&A, she discussed the importance of patient voices and OMERACT’s plans to further educate and include patients in the dialogue on outcomes.
Question: Have patients always been a part of OMERACT meetings?
Answer: Patients have been involved with OMERACT since 2002. The patient voice adds relevance to all the work that OMERACT does. You can’t begin to talk about outcomes unless there is a patient at the table with lived experience.
Q: Can you cite a few examples of how the patient voice enriches the conversation on outcomes research?
A: Outcomes and priorities that are important to patients are often completely different than those of the clinician. For instance, a work outcome is important to someone who doesn’t have any medical insurance or disability insurance, so that you can ensure that there is food on the table and a roof over your head. Or it may be important to someone because the employment provides medical and disability insurance to provide security for them and their family. These are two different perspectives on work and therefore work priorities and outcomes.
Q: What have been some of the challenges of getting patients to participate?
A: Training patients is one challenge. OMERACT’s work has a very steep learning curve, and while the basics are the same between the groups in terms of looking at what we measure and how we measure it, the nuances of different working groups require a lot of time and energy to be comfortable enough with the work, and then be confident enough to bring your perspective and lived experience to the table. It’s also a very accomplished group, which can be quite intimidating. Self-disclosure is a very personal and intimate undertaking that requires patience, compassion, and respect.
Q: Are there any plans to enhance patient engagement?
A: When we had OMERACT 2020 it was a virtual conference that took place over about 6 months. We had far more patient research partners [PRPs] participate than we have ever had at any OMERACT face-to-face meeting. There is a desire and passion on the part of patients to lend their voices to the work. The working groups meet virtually throughout the year to advance their agendas, and PRPs are a part of each of the working groups.
Hopefully, we can start working toward including more voices at the conferences by enabling a hybrid model. The PRP Support Team will begin engaging patients this fall with education, mentoring, and team-building exercises so by the time we meet in person in May 2023, they will have enough background knowledge and information to give them the confidence that will enhance their experience at the face-to-face meeting.
We also need to ensure that those patients who want to stay engaged can. This means that the education and training should continue long after the face-to-face meeting is over. We need to build capacity in the PRP group and look to succession planning and be a resource to working groups struggling to find PRPs to work with them on a longer-term basis.
Clinical research in rheumatology was suffering from an identity crisis of sorts 40 years ago. A lack of consensus across continents resulted in differing views about clinical outcome measures and judgments about treatments.
Patients were not allowed to be the generating source of a clinical outcome, according to Peter Tugwell, MSc, MD. “The only outcomes that were acceptable were clinician assessments, blood tests, and imaging,” said Dr. Tugwell, professor of medicine, epidemiology, and public health at the University of Ottawa (Ont.) and a practicing rheumatologist at Ottawa Hospital.
Clinicians were coming to different conclusions about patient responses to treatment when managing rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice.
OMERACT sought to address this lack of uniformity. This international group, formed in 1992, leverages stakeholder groups to improve outcome measurement in rheumatology endpoints through a consensus-building, data-driven format.
It was originally known as “Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials,” but its leaders have since broadened its scope to “Outcome Measures in Rheumatology.” Over the years, it has evolved into an international network that assesses measurement across a wide variety of intervention studies. Now 30 years old, the network spans 40 active working groups and has influenced work in patient outcomes across 500 peer-reviewed publications.
The network meets every 2 years to address what is always a challenging agenda, said Dr. Tugwell, one of its founding members and chair. “There’s lots of strong opinions.” Participating in the discussions are individuals from all stages of seniority in rheumatology and clinical epidemiology, patient research partners, industry, approval agencies, and many countries who are committed to the spirit of OMERACT.
“The secret to our success has been getting world leaders to come together and have those discussions, work them through, and identify common ground in such a way that the approval agencies accept these outcome measures in clinical trials,” he added.
“My impression was the founders perceived a problem in the early 1990s and devised a consensus method in an attempt to quantify clinical parameters to define disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis – an important first step to do clinical trials and allow comparisons between them,” said Patricia Woo, CBE, FMedSci, FRCP, emeritus professor of pediatric rheumatology and previous head of the Centre for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology at UCL, London. At that time, even disease definitions varied between the United States and Europe and other parts of the world, said Dr. Woo, who is not a part of OMERACT. “This was especially true for pediatric rheumatology.”
Fusing the continental divide
OMERACT arose from a need to streamline clinical outcome measures in rheumatology. Research papers during the 1980s demonstrated a lack of coherence in managing patients with rheumatoid arthritis in routine practice. In addition, the measures used to define clinical endpoints in clinical trials operated in silos – they were either too specific to a certain trial, overlapped with other concepts, or didn’t reflect changes in treatment.
Approval agencies in Europe and North America were approving only outcomes measures developed by their respective researchers. This was also true of patients they tested on. “This seemed crazy,” Dr. Tugwell said.
Dr. Tugwell was involved in the Cochrane collaboration, which conducts systematic reviews of best evidence across the world that assesses the magnitude of benefits versus harms.
To achieve this goal, “you need to pull studies from around the world,” he said. Maarten Boers, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist (and later professor of clinical epidemiology at Amsterdam University Medical Center) from the Netherlands, spent a year in Ontario, Canada, to train as a clinical epidemiologist. Together, Dr. Tugwell and Dr. Boers began discussing options to develop more streamlined outcome measures.
They initiated the first OMERACT conference in Maastricht, the Netherlands, in 1992. The Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency participated, along with leaders of outcomes measurement in Europe and in North America.
Discussions centered on methods to develop outcomes in a meaningful fashion. During the first meeting, North American and European approval agencies agreed to accept each other’s studies and endpoints and patient reported outcomes.
Agreement was achieved on a preliminary set of outcome domains and measures that later became known as the WHO-ILAR (World Health Organization–International League of Associations for Rheumatology) core set. The set included seven outcome domains: tender joints, swollen joints, pain, physician global assessment, patient global assessment, physical disability, and acute phase reactants, and one additional outcome domain for studies lasting 1 year or more: radiographs of the joints.
“A proactive program was planned to test not only the validity of these endpoints, but also the methods for their measurement. This was the start of a continuing process,” OMERACT members said in a joint statement for this article. Meetings have since taken place every 2 years.

OMERACT accomplishments
OMERACT now requires buy-in from four continents: Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.
Its leaders have developed an explicit process for gaining endorsement of core outcome domains and instrument measurement sets. To fully capture the possibilities of “what to measure,” i.e., “measurable aspects of health conditions,” OMERACT has developed a framework of concepts, core areas, and outcome domains. The key concepts are pathophysiology (with a core area termed “manifestations/abnormalities”) and impact (with core areas of “death/lifespan,” and “life impact,” and the optional area of “societal/resource use”). An outcome domain defines an element of a core area to measure the effects of a treatment, such as blood markers, pain intensity, physical function, or emotional well-being.
A core outcome domain set is developed by agreeing to at least one outcome domain within one of the three core areas. Subsequently, a core outcome measurement set is developed by agreeing to at least one applicable measurement instrument for each core outcome domain. This requires documentation of validity, summarized under three metrics: truth, discrimination, and feasibility.
OMERACT’s handbook provides tutelage on establishing and implementing core outcomes, and several workbooks offer guidance on developing core outcome domain sets, selecting instruments for core outcome measurement sets, and OMERACT methodology.
All this work has led to widespread adoption.
Approval agencies have accepted OMERACT’s filter and methods advances, which have been adopted by many research groups in rheumatology and among nonrheumatology research groups. Organizations such as the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke have sought its advice.
Its core outcomes have been adopted and used for approval in the great majority of studies on rheumatoid arthritis, Dr. Tugwell said.
Several BMJ articles underscore the influence and uptake of OMERACT’s core outcome set. One 2017 paper, which analyzed 273 randomized trials of rheumatoid arthritis drug treatments on ClinicalTrials.gov, found that the WHO-ILAR arthritis core outcome set was reported in 81% of the studies. “The adoption of a core outcome set has the potential to increase consistency in outcomes measured across trials and ensure that trials are more likely to measure appropriate outcomes,” the authors concluded.
Since the initial 1992 meeting, OMERACT has broadened its focus from rheumatoid arthritis to 25 other musculoskeletal conditions.
For example, other OMERACT conferences have led to consensus on core sets of measures for osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, psychosocial measures, and a core set of data for cost-effectiveness evaluations.
‘Speed is a limitation’
OMERACT is a bottom-up volunteer organization. It doesn’t represent any official organization of any clinical society. “We’ve not asked to be adopted by the American College of Rheumatology, EULAR [European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology], or other international organizations,” Dr. Tugwell said. It offers a chance for patients, users, and doers of research to work together to agree on rigorous criteria accepted by the approval agencies and take the necessary time to work things through.
This is not a fast process, usually taking 4-6 years to initiate and establish an outcome domain set, he emphasized. “It would be beneficial to do it faster if we had the resources to meet every year. The fact is we’re a volunteer organization that meets every 2 years.”
Speed is a limitation, he acknowledged, but it’s an acceptable trade-off for doing things correctly.
The group has faced other challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, pivoting to a virtual format that had benefits and limitations.
In one respect, moving to a virtual meeting increased uptake in participation and voting, Dr. Tugwell said. Patient participants with severe rheumatoid arthritis no longer faced the challenges of travel. “On the other hand, we didn’t have the same opportunity to achieve common ground virtually,” he said. “Where there are strong disagreements, I’m a great believer that people need to know one another. There needs to be relationship building.”
OMERACT’s emerging leader program has been a cornerstone of its in-person meetings, engaging young rheumatologists to interact with some of the leaders of outcome measurement. The virtual format dampened this process somewhat, eliminating those important “café chats” between the stakeholders.
The hope is to bring people face-to-face once more at the next meeting in May 2023. The agenda will focus on relationship building, identifying controversial areas, and bringing younger people to develop relationships, Dr. Tugwell said. OMERACT will retain a virtual option for the worldwide voting, “which will allow for more buy-in from so many more people,” he added.
A consensus on pain
The onus of developing outcome measures that move with the times is sometimes too great for one group to manage. In 2018, OMERACT became a part of the Red Hat Group (RHG), an organization conceived at the COMET (Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials) VII meeting in Amsterdam.
RHG aims to improve the choice of outcomes in health research. It includes eight groups: COMET; OMERACT; the Cochrane Skin Core Outcome Set Initiative; Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations; Center for Medical Technology Policy; COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments; Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium; and Standardized Outcomes in Nephrology.
The collaboration between groups offers a “very interesting interface between consensus building as well as hard evidence,” Dr. Tugwell said. The focus goes beyond rheumatology to other clinical areas of common interest, exploring how one classifies outcome domains in terms of symptoms, life impact, or death.
Pain is an important common denominator that the RHG has evaluated.
“We believe it’s too general. We’re trying to define pain across all Red Hat Groups because it’s clear that the research community has all these different scales for defining pain severity,” Dr. Tugwell said. “We have to find a way to make ruthless decisions and rules for doing it. And of course, it has to be transparent.”
Looking ahead
As part of its ongoing work, OMERACT is evaluating the robustness of instruments that rheumatologists use as outcome measures in clinical trials, which can be a laborious process. The OMERACT Filter 2.0, part of the latest iteration of the handbook, offers strong guidance for researchers but needs a long-term strategy and key methodological support. “To that end, we set up a technical advisory group to help people in the instrument selection work and that remains an ongoing process,” OMERACT leaders said in their joint statement.
OMERACT is looking at opportunities to create benchmark processes for developing core sets outside of rheumatology and a methodology around outcome measures such as contextual factors, composites, and surrogates.
It will also be taking a step back to solicit opinions from the approval agencies represented by the OMERACT membership on the OMERACT handbook.
The goal is to make sure the handbook aligns with everyone else’s approval and labeling requirements.
OMERACT’s patient participants bring important perspectives
OMERACT over the years has sought to become a more patient-centered group. Patients have been involved in OMERACT activities since its sixth meeting, forming an independent, yet integrated, group within the network. They have their own steering committee and produced and helped to update a glossary for OMERACT patients and professionals.
Catherine (McGowan) Hofstetter, who was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis 30 years ago, chairs OMERACT’s Patient Research Partners Support Team. In a Q&A, she discussed the importance of patient voices and OMERACT’s plans to further educate and include patients in the dialogue on outcomes.
Question: Have patients always been a part of OMERACT meetings?
Answer: Patients have been involved with OMERACT since 2002. The patient voice adds relevance to all the work that OMERACT does. You can’t begin to talk about outcomes unless there is a patient at the table with lived experience.
Q: Can you cite a few examples of how the patient voice enriches the conversation on outcomes research?
A: Outcomes and priorities that are important to patients are often completely different than those of the clinician. For instance, a work outcome is important to someone who doesn’t have any medical insurance or disability insurance, so that you can ensure that there is food on the table and a roof over your head. Or it may be important to someone because the employment provides medical and disability insurance to provide security for them and their family. These are two different perspectives on work and therefore work priorities and outcomes.
Q: What have been some of the challenges of getting patients to participate?
A: Training patients is one challenge. OMERACT’s work has a very steep learning curve, and while the basics are the same between the groups in terms of looking at what we measure and how we measure it, the nuances of different working groups require a lot of time and energy to be comfortable enough with the work, and then be confident enough to bring your perspective and lived experience to the table. It’s also a very accomplished group, which can be quite intimidating. Self-disclosure is a very personal and intimate undertaking that requires patience, compassion, and respect.
Q: Are there any plans to enhance patient engagement?
A: When we had OMERACT 2020 it was a virtual conference that took place over about 6 months. We had far more patient research partners [PRPs] participate than we have ever had at any OMERACT face-to-face meeting. There is a desire and passion on the part of patients to lend their voices to the work. The working groups meet virtually throughout the year to advance their agendas, and PRPs are a part of each of the working groups.
Hopefully, we can start working toward including more voices at the conferences by enabling a hybrid model. The PRP Support Team will begin engaging patients this fall with education, mentoring, and team-building exercises so by the time we meet in person in May 2023, they will have enough background knowledge and information to give them the confidence that will enhance their experience at the face-to-face meeting.
We also need to ensure that those patients who want to stay engaged can. This means that the education and training should continue long after the face-to-face meeting is over. We need to build capacity in the PRP group and look to succession planning and be a resource to working groups struggling to find PRPs to work with them on a longer-term basis.
Clinical research in rheumatology was suffering from an identity crisis of sorts 40 years ago. A lack of consensus across continents resulted in differing views about clinical outcome measures and judgments about treatments.
Patients were not allowed to be the generating source of a clinical outcome, according to Peter Tugwell, MSc, MD. “The only outcomes that were acceptable were clinician assessments, blood tests, and imaging,” said Dr. Tugwell, professor of medicine, epidemiology, and public health at the University of Ottawa (Ont.) and a practicing rheumatologist at Ottawa Hospital.
Clinicians were coming to different conclusions about patient responses to treatment when managing rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice.
OMERACT sought to address this lack of uniformity. This international group, formed in 1992, leverages stakeholder groups to improve outcome measurement in rheumatology endpoints through a consensus-building, data-driven format.
It was originally known as “Outcome Measures in Rheumatoid Arthritis Clinical Trials,” but its leaders have since broadened its scope to “Outcome Measures in Rheumatology.” Over the years, it has evolved into an international network that assesses measurement across a wide variety of intervention studies. Now 30 years old, the network spans 40 active working groups and has influenced work in patient outcomes across 500 peer-reviewed publications.
The network meets every 2 years to address what is always a challenging agenda, said Dr. Tugwell, one of its founding members and chair. “There’s lots of strong opinions.” Participating in the discussions are individuals from all stages of seniority in rheumatology and clinical epidemiology, patient research partners, industry, approval agencies, and many countries who are committed to the spirit of OMERACT.
“The secret to our success has been getting world leaders to come together and have those discussions, work them through, and identify common ground in such a way that the approval agencies accept these outcome measures in clinical trials,” he added.
“My impression was the founders perceived a problem in the early 1990s and devised a consensus method in an attempt to quantify clinical parameters to define disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis – an important first step to do clinical trials and allow comparisons between them,” said Patricia Woo, CBE, FMedSci, FRCP, emeritus professor of pediatric rheumatology and previous head of the Centre for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology at UCL, London. At that time, even disease definitions varied between the United States and Europe and other parts of the world, said Dr. Woo, who is not a part of OMERACT. “This was especially true for pediatric rheumatology.”
Fusing the continental divide
OMERACT arose from a need to streamline clinical outcome measures in rheumatology. Research papers during the 1980s demonstrated a lack of coherence in managing patients with rheumatoid arthritis in routine practice. In addition, the measures used to define clinical endpoints in clinical trials operated in silos – they were either too specific to a certain trial, overlapped with other concepts, or didn’t reflect changes in treatment.
Approval agencies in Europe and North America were approving only outcomes measures developed by their respective researchers. This was also true of patients they tested on. “This seemed crazy,” Dr. Tugwell said.
Dr. Tugwell was involved in the Cochrane collaboration, which conducts systematic reviews of best evidence across the world that assesses the magnitude of benefits versus harms.
To achieve this goal, “you need to pull studies from around the world,” he said. Maarten Boers, MD, PhD, a rheumatologist (and later professor of clinical epidemiology at Amsterdam University Medical Center) from the Netherlands, spent a year in Ontario, Canada, to train as a clinical epidemiologist. Together, Dr. Tugwell and Dr. Boers began discussing options to develop more streamlined outcome measures.
They initiated the first OMERACT conference in Maastricht, the Netherlands, in 1992. The Food and Drug Administration and European Medicines Agency participated, along with leaders of outcomes measurement in Europe and in North America.
Discussions centered on methods to develop outcomes in a meaningful fashion. During the first meeting, North American and European approval agencies agreed to accept each other’s studies and endpoints and patient reported outcomes.
Agreement was achieved on a preliminary set of outcome domains and measures that later became known as the WHO-ILAR (World Health Organization–International League of Associations for Rheumatology) core set. The set included seven outcome domains: tender joints, swollen joints, pain, physician global assessment, patient global assessment, physical disability, and acute phase reactants, and one additional outcome domain for studies lasting 1 year or more: radiographs of the joints.
“A proactive program was planned to test not only the validity of these endpoints, but also the methods for their measurement. This was the start of a continuing process,” OMERACT members said in a joint statement for this article. Meetings have since taken place every 2 years.

OMERACT accomplishments
OMERACT now requires buy-in from four continents: Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.
Its leaders have developed an explicit process for gaining endorsement of core outcome domains and instrument measurement sets. To fully capture the possibilities of “what to measure,” i.e., “measurable aspects of health conditions,” OMERACT has developed a framework of concepts, core areas, and outcome domains. The key concepts are pathophysiology (with a core area termed “manifestations/abnormalities”) and impact (with core areas of “death/lifespan,” and “life impact,” and the optional area of “societal/resource use”). An outcome domain defines an element of a core area to measure the effects of a treatment, such as blood markers, pain intensity, physical function, or emotional well-being.
A core outcome domain set is developed by agreeing to at least one outcome domain within one of the three core areas. Subsequently, a core outcome measurement set is developed by agreeing to at least one applicable measurement instrument for each core outcome domain. This requires documentation of validity, summarized under three metrics: truth, discrimination, and feasibility.
OMERACT’s handbook provides tutelage on establishing and implementing core outcomes, and several workbooks offer guidance on developing core outcome domain sets, selecting instruments for core outcome measurement sets, and OMERACT methodology.
All this work has led to widespread adoption.
Approval agencies have accepted OMERACT’s filter and methods advances, which have been adopted by many research groups in rheumatology and among nonrheumatology research groups. Organizations such as the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke have sought its advice.
Its core outcomes have been adopted and used for approval in the great majority of studies on rheumatoid arthritis, Dr. Tugwell said.
Several BMJ articles underscore the influence and uptake of OMERACT’s core outcome set. One 2017 paper, which analyzed 273 randomized trials of rheumatoid arthritis drug treatments on ClinicalTrials.gov, found that the WHO-ILAR arthritis core outcome set was reported in 81% of the studies. “The adoption of a core outcome set has the potential to increase consistency in outcomes measured across trials and ensure that trials are more likely to measure appropriate outcomes,” the authors concluded.
Since the initial 1992 meeting, OMERACT has broadened its focus from rheumatoid arthritis to 25 other musculoskeletal conditions.
For example, other OMERACT conferences have led to consensus on core sets of measures for osteoarthritis and osteoporosis, psoriasis/psoriatic arthritis, psychosocial measures, and a core set of data for cost-effectiveness evaluations.
‘Speed is a limitation’
OMERACT is a bottom-up volunteer organization. It doesn’t represent any official organization of any clinical society. “We’ve not asked to be adopted by the American College of Rheumatology, EULAR [European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology], or other international organizations,” Dr. Tugwell said. It offers a chance for patients, users, and doers of research to work together to agree on rigorous criteria accepted by the approval agencies and take the necessary time to work things through.
This is not a fast process, usually taking 4-6 years to initiate and establish an outcome domain set, he emphasized. “It would be beneficial to do it faster if we had the resources to meet every year. The fact is we’re a volunteer organization that meets every 2 years.”
Speed is a limitation, he acknowledged, but it’s an acceptable trade-off for doing things correctly.
The group has faced other challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, pivoting to a virtual format that had benefits and limitations.
In one respect, moving to a virtual meeting increased uptake in participation and voting, Dr. Tugwell said. Patient participants with severe rheumatoid arthritis no longer faced the challenges of travel. “On the other hand, we didn’t have the same opportunity to achieve common ground virtually,” he said. “Where there are strong disagreements, I’m a great believer that people need to know one another. There needs to be relationship building.”
OMERACT’s emerging leader program has been a cornerstone of its in-person meetings, engaging young rheumatologists to interact with some of the leaders of outcome measurement. The virtual format dampened this process somewhat, eliminating those important “café chats” between the stakeholders.
The hope is to bring people face-to-face once more at the next meeting in May 2023. The agenda will focus on relationship building, identifying controversial areas, and bringing younger people to develop relationships, Dr. Tugwell said. OMERACT will retain a virtual option for the worldwide voting, “which will allow for more buy-in from so many more people,” he added.
A consensus on pain
The onus of developing outcome measures that move with the times is sometimes too great for one group to manage. In 2018, OMERACT became a part of the Red Hat Group (RHG), an organization conceived at the COMET (Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials) VII meeting in Amsterdam.
RHG aims to improve the choice of outcomes in health research. It includes eight groups: COMET; OMERACT; the Cochrane Skin Core Outcome Set Initiative; Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations; Center for Medical Technology Policy; COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement Instruments; Clinical Data Interchange Standards Consortium; and Standardized Outcomes in Nephrology.
The collaboration between groups offers a “very interesting interface between consensus building as well as hard evidence,” Dr. Tugwell said. The focus goes beyond rheumatology to other clinical areas of common interest, exploring how one classifies outcome domains in terms of symptoms, life impact, or death.
Pain is an important common denominator that the RHG has evaluated.
“We believe it’s too general. We’re trying to define pain across all Red Hat Groups because it’s clear that the research community has all these different scales for defining pain severity,” Dr. Tugwell said. “We have to find a way to make ruthless decisions and rules for doing it. And of course, it has to be transparent.”
Looking ahead
As part of its ongoing work, OMERACT is evaluating the robustness of instruments that rheumatologists use as outcome measures in clinical trials, which can be a laborious process. The OMERACT Filter 2.0, part of the latest iteration of the handbook, offers strong guidance for researchers but needs a long-term strategy and key methodological support. “To that end, we set up a technical advisory group to help people in the instrument selection work and that remains an ongoing process,” OMERACT leaders said in their joint statement.
OMERACT is looking at opportunities to create benchmark processes for developing core sets outside of rheumatology and a methodology around outcome measures such as contextual factors, composites, and surrogates.
It will also be taking a step back to solicit opinions from the approval agencies represented by the OMERACT membership on the OMERACT handbook.
The goal is to make sure the handbook aligns with everyone else’s approval and labeling requirements.
OMERACT’s patient participants bring important perspectives
OMERACT over the years has sought to become a more patient-centered group. Patients have been involved in OMERACT activities since its sixth meeting, forming an independent, yet integrated, group within the network. They have their own steering committee and produced and helped to update a glossary for OMERACT patients and professionals.
Catherine (McGowan) Hofstetter, who was diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis 30 years ago, chairs OMERACT’s Patient Research Partners Support Team. In a Q&A, she discussed the importance of patient voices and OMERACT’s plans to further educate and include patients in the dialogue on outcomes.
Question: Have patients always been a part of OMERACT meetings?
Answer: Patients have been involved with OMERACT since 2002. The patient voice adds relevance to all the work that OMERACT does. You can’t begin to talk about outcomes unless there is a patient at the table with lived experience.
Q: Can you cite a few examples of how the patient voice enriches the conversation on outcomes research?
A: Outcomes and priorities that are important to patients are often completely different than those of the clinician. For instance, a work outcome is important to someone who doesn’t have any medical insurance or disability insurance, so that you can ensure that there is food on the table and a roof over your head. Or it may be important to someone because the employment provides medical and disability insurance to provide security for them and their family. These are two different perspectives on work and therefore work priorities and outcomes.
Q: What have been some of the challenges of getting patients to participate?
A: Training patients is one challenge. OMERACT’s work has a very steep learning curve, and while the basics are the same between the groups in terms of looking at what we measure and how we measure it, the nuances of different working groups require a lot of time and energy to be comfortable enough with the work, and then be confident enough to bring your perspective and lived experience to the table. It’s also a very accomplished group, which can be quite intimidating. Self-disclosure is a very personal and intimate undertaking that requires patience, compassion, and respect.
Q: Are there any plans to enhance patient engagement?
A: When we had OMERACT 2020 it was a virtual conference that took place over about 6 months. We had far more patient research partners [PRPs] participate than we have ever had at any OMERACT face-to-face meeting. There is a desire and passion on the part of patients to lend their voices to the work. The working groups meet virtually throughout the year to advance their agendas, and PRPs are a part of each of the working groups.
Hopefully, we can start working toward including more voices at the conferences by enabling a hybrid model. The PRP Support Team will begin engaging patients this fall with education, mentoring, and team-building exercises so by the time we meet in person in May 2023, they will have enough background knowledge and information to give them the confidence that will enhance their experience at the face-to-face meeting.
We also need to ensure that those patients who want to stay engaged can. This means that the education and training should continue long after the face-to-face meeting is over. We need to build capacity in the PRP group and look to succession planning and be a resource to working groups struggling to find PRPs to work with them on a longer-term basis.
Women in rheumatology: A look back, a look forward
Jean Liew, MD, recalls the long list of women mentors who have guided her career in rheumatology.
It started during her residency, when Jennifer Barton, MD, at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, exposed her to new ways of conducting clinical research on patient outcomes.
In fellowship, she met Lianne Gensler, MD, a leader in axial spondyloarthritis, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Through Dr. Gensler’s mentorship and sponsorship, she was introduced to Maureen Dubreuil, MD, at Boston University, whose research focuses on pharmacoepidemiologic approaches using large databases.
Dr. Liew currently practices rheumatology under the leadership of Tuhina Neogi, MD, a world-renowned expert in osteoarthritis and gout. “She’s my research mentor,” Dr. Liew, an assistant professor of medicine at Boston University, said in an interview.
Her academic timeline reflects the powerful network and influence of women rheumatologists, who represent half of the adult rheumatology workforce in the United States. “In the research arena, many experts are women and they serve as role models and mentors to many,” Dr. Liew said.
But there’s more work to do, she and others acknowledged.
Rheumatology faces ongoing workforce shortages while struggling with a gender gap that’s closing but not as quickly as many women rheumatologists would like to see.
The gap persists, despite overall gains in the field of medicine, Vaneet Sandhu, MD, a rheumatologist with Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said in an interview. Women have exceeded men as enrollees in medical colleges, reported the Association of American Medical Colleges. And yet, “our colleagues reported last year that, in academic rheumatology, women are less likely to be full or associate professors than men,” she said.
The odds of being a fellowship program director or division director is similar in both males and females. “So, we’ve had some gains, but there’s always room for more,” Dr. Sandhu said.
Too few physicians
The next 10 years forecasts a dearth in American physicians.
AAMC projects a shortage of 124,000 doctors in the United States by 2034. Following on a similar trajectory, the ACR in 2015 anticipated a 25% drop in the supply of rheumatology clinical providers by 2030, with demand exceeding supply by more than 4,100 clinical employees.
The ACR’s workforce study projected that more women would come into rheumatology, noted Marcy Bolster, MD, director of the rheumatology fellowship training program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. Women make up at least 50% of the workforce and 66% of fellows If these numbers hold, “we’ll definitely see an increase in the percent of women in the workforce” moving forward, Dr. Bolster said in an interview.
Women have helped the shortage to a great extent, said Nilanjana Bose, MD, a rheumatologist at Lonestar Rheumatology, Houston.
The work-life balance that rheumatology offers, combined with its focus on the cognitive part of internal medicine, explains why the field has attracted so many women. Rheumatology provides flexible work options. Women “get to teach or do rounds in the hospital or have a private practice where you’re mostly outpatient with some hospital work,” Dr. Bose said in an interview.
With anticipated shortages looming over the next decade, the profession needs to be cognizant of the different demands women face in their careers and how it can accommodate the workforce to meet the needs of its providers and maintain access for patients, Dr. Bolster said.
There are many innovative ways to match the demand for access. One thought is to create shared positions. Instead of employing four full-time physicians and one person part time, have two people who are working part time, Dr. Bolster suggested. “It is also important to not only expand our workforce with advanced practice providers, but to ensure their retention in the rheumatology workforce, to improve access to care for those with rheumatic diseases.”
Increasing the number of residency positions is another step toward addressing the shortage, Dr. Sandhu offered.
Women rheumatologists should make their voices heard by contacting members of Congress to support legislation that advocates for workforce shortage solutions, “in addition to generally supporting women’s rights and growth in the workplace,” she said.
The gender divide continues
Rosalind Ramsey-Goldman, MD, DrPH, remembers being the only woman in a group of five during her fellowship in the mid-1980s. Few women role models existed within the ACR, especially those in academic careers. “Now, most fellowships have more than 50% women, reflecting the number of women going to medical school,” said Dr. Ramsey-Goldman, Gallagher Research Professor in Rheumatology at Northwestern University and Northwestern Medicine, Chicago.
As more women enter the profession, women rheumatologists in academic rheumatology have started to outpace men in recent years. Some research suggests they’ve made headway in gaining leadership spots at institutions.
One recent paper, a cross-sectional national study of more than 6,100 rheumatologists, found that women had similar odds of attaining fellowship program or division director positions as men. As directors of training programs, women in rheumatology “instill this collaborative and growth mindset that encourages learners to self-reflect and work as a team,” Dr. Sandhu said.
Women bring a different perspective to training, and how curriculum works, Dr. Bose said. Studies have shown that women tend to be more empathic. They ask more questions. “That’s not to say men aren’t good. Women just have an inborn ability for connecting,” and this perspective helps to enrich the educational experience for trainees.
Women who lead training programs are also attuned to realities that female trainees confront, such as dealing with the challenges of achieving the best possible education while also raising a family, noted Graciela S. Alarcón, MD, MPH, who holds emeritus positions at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia in Lima, Peru.
“These program directors cultivate the ability to relate to women trainees in a very personal manner, supporting them in their efforts to achieve a balance between their training demands and their family/personal responsibilities,” she said.
Other research suggests the gender gap hasn’t gone away. Women continue to have lower odds of holding a higher-level professorship, receiving a federal grant, or speaking at academic conferences. They are also less likely to serve as first authors on rheumatology guidelines or recommendations.
Some studies suggest that women see fewer patients and earn less than their male counterparts. At peak difference, men can earn up to $100,000+ more than women. “My own impression is that it takes more efforts for women to reach the same level of recognition than men, and although overt discrimination is rare nowadays, subtle discrimination still occurs,” according to Dr. Alarcón.
Over a lifetime, female physicians can expect to earn less than their male counterparts, with clear implications for different retirement income levels, she said.
Fixing a leaky academic pipeline
The reality is the academic pipeline, and especially the physician-scientist pipeline, “continues to be leaky,” Dr. Liew said. “We know that caregivers to young children have larger barriers to surmount in academics and in research, and that there is a gender disparity present.” The toll of academic medicine on early career women who are parents is especially pronounced. While the pandemic has intensified this problem, it was around pre-COVID, she added.
Women who start in academia as academic clinicians or clinician researchers aren’t always able to meet their goals for promotion within the appropriate time frame. This is because of inequities in the system and lack of support related to maternity leave, childcare, and other issues. As a result, they leave academia and go into private practice or industry, Dr. Liew said.
The ACR in its 2015 survey projected that more women would be seeking part-time positions.
The good news is many academic institutions are taking a more equitable view about different career paths, offering equal parental leave to both men and women, Dr. Bolster noted. “It is essential that workforce planning encompasses the changing responsibilities within families and account for more parental leave by both men and women.” If certain projections come true, with 50% of the profession retiring between 2015 and 2030, combined with more men and women working part time, “it is requisite that workforce strategies plan for this.”
When Dr. Ramsey-Goldman was a trainee and junior faculty, there were no formal maternity leave policies.
Now, this benefit is available, she said. In another critical change, the ACR has made childcare services and a lactation room available for young mothers during its annual meeting. “Virtual meetings afford further ways to interact with colleagues,” she added.
Whether women choose to stay in academia or go into clinical practice is a very personal decision. “But it is also fair that, in some programs, training directors and faculty members can encourage trainees toward academia and its fascinating research possibilities,” Dr. Alarcón offered.
Making gains in research
Women are increasingly driving groundbreaking rheumatology research at all levels, Dr. Sandhu said. “And women empower women. Not infrequently, our female leaders, veterans in rheumatology research, seek younger female rheumatologists to help them grow in their niches. This has been one of the most beautiful things of the sisterhood in rheumatology that I have been blessed to be part of.”
In pediatric rheumatology, young female researchers are leading global research efforts. Some standouts include Kate Webb, MD, a pediatric rheumatologist in Cape Town, South Africa, and scientist who has worked on multisystem inflammatory syndrome during the pandemic. Sheila Angeles-Han, MD, who works on uveitis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, had a role in recent ACR guidelines. Laura Lewandowski, MD, has also contributed to global rheumatology efforts, especially in low- and middle-income countries, Dr. Liew said.
The 2021 ACR annual meeting highlighted the research efforts of women rheumatologists from around the world. A global rheumatology summit at the meeting featured many women voices, including Dzifa Dey, MD, from Ghana, who received the ACR Distinguished International Rheumatology Professional Award. Ashira Blazer, MD, and Irene Blanco, MD, have spearheaded the ACR’s diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives.
Women researchers have many opportunities to study rheumatologic diseases that disproportionately affect women, Dr. Alarcón said.
Lupus, for example, affects women in a much higher proportion than men (90% vs. 10%). This may be an attractive target for the best and brightest among future women researchers, Dr. Alarcón suggested. “It is a fact that publications related to lupus in leading internal medicine and rheumatology journals often include women either as first or senior authors. In that context, it can be said that several advances in the study of lupus worldwide can be attributed to women.”
This applies to disparities in social determinants of health that account for extremely complex outcomes in lupus among women of color, compared with White women, in addition to the costs associated with the disease and its impact on morbidity, mortality, and quality of life.
Women rheumatologists have advanced the work in reproductive management of rheumatic diseases, including a recent ACR-endorsed publication that provides formal guidance on managing reproductive health in women with rheumatic disease, Dr. Sandhu said. “One thing is clear: Without women, the work on reproductive diseases in rheumatology to date would not likely be where it is.”
Dr. Ramsey-Goldman added that “this critical work will not only set the stage for clinical care of both women and men regarding their reproductive health but will also inform education strategies for trainees and future research activities, and help direct policy regarding access to care, medication development, and costs of treatment.”
Obtaining grant funding to support salaries and researcher endeavors remains a challenge, Dr. Liew said. “It takes working evenings, weekends, and holidays to meet those goals within a set time frame. So you can see why a female faculty member with children might be disadvantaged, compared to a male counterpart without children.”
Competition for grant funding remains fierce as budgets become tighter, she added.
“We will lose a lot more brilliant and compassionate rheumatologists (clinicians, physician-scientists, and scientists alike) if we do not think of ways to make things more equitable or do not acknowledge the privileges that support some to continued career successes and leave others behind,” Dr. Liew said.
Women who choose a research field should seek out mentor and financial support that will allow them enough protected time to balance out research with other clinical activities, such as teaching and patient care, Dr. Alarcón said.
Training directors, mentors, and faculty should prioritize the needs of current and future women researchers, she said. “The guidance provided to young female trainees toward a successful research career is a formidable challenge that may provide, in turn, enormous satisfaction. There are established avenues to seek funding as new investigators.”
Progress in diversity
Rheumatology as a field is attracting more candidates and all races and genders, Dr. Bose said. “I think in the coming years we will see more and more women from minorities being incorporated into the rheumatology workforce.”
Others would like to see further improvements in diversity and attracting women from historically excluded backgrounds. Patients will benefit from rheumatologists who are able to connect with them through shared languages, cultures, and other life experiences, Dr. Liew said. “It is imperative that we work on recruitment, mentorship, and retention in this regard.”
While the representation of women of color is still inadequate, there has been some progress, Dr. Sandhu said. The number of female Hispanic, Latinx, and Black or African American graduates from medical school has seen a steady rise since 2017. And, AAMC has established task forces such as the Women of Color Initiative to identify strategies for furthering the careers of women of color in academic medicine.
“There’s still a lot of room to grow. I am, however, proud to say we will finally have a woman of color as the president of ACR in 2023,” said Dr. Sandhu, referring to Deborah Dyett Desir, MD.
Dr. Desir discussed the importance of diversifying the ACR in a recent interview.
All rheumatologists know that there is a place for them in the ACR, she stressed. “The demographics of our membership should reflect that of our population.”
As growth in diverse representation occurs, so will recruitment, retention, and a greater awareness and distribution of knowledge and means to address implicit biases and microaggressions, Dr. Sandhu said. “We will see a greater quality of health care, where patients may feel more connected to someone they can identify with.”
Looking ahead
Dr. Alarcón expects women to continue to play a major role in rheumatology, not just in research, education, and patient care but in leadership of academic societies and professional organizations.
“Women in rheumatology have come a long way – a piece of history that I have been fortunate to witness from my beginnings in the early 1970s. We have, I think, paved the way for the next generations of leaders in our beloved specialty field.”
Dr. Bolster is a member of the ACR board of directors and board liaison of the ACR Workforce Solutions Committee. Dr. Ramsey-Goldman has been a GlaxoSmithKline consultant for lupus studies, a consultant and site investigator with Exagen Diagnostics for lupus biomarker studies, and a site investigator for Xencor and Horizon Pharma lupus trials. Dr. Sandhu serves on the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues.
Related article
Pioneer days of rheumatology: One veteran looks back
Patricia Woo, CBE, FMedSci, FRCP, has seen it all.
As a member of the British Rheumatology Society and fellow of the Royal College of Physicians, she presented the case for and obtained official training approval for pediatric rheumatology in the 1990s. She also set the wheels in motion to form the Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation and the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Now 74, Dr. Woo remembers the discrimination she faced in the 1970s. “I was told I couldn’t become an investigator or consultant if I were to marry or have children.” Around the same time, she found out a male clinician researcher didn’t want to work with her, not because of her qualifications, but because she was a woman.
That wouldn’t happen now with all the antidiscrimination laws in place, noted Dr. Woo, an emeritus professor of pediatric rheumatology and previous head of the Centre for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology at UCL, London. Looking at the advances made by women in rheumatology, “there’s a major difference between 3 decades ago and today. If anyone discriminates today, they are called out.”
As the founding president of the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society, Dr. Woo is one of many early trailblazers who weathered many changes and made gains in the profession.
It’s important to recognize the work of Barbara Ansell, MD, the founder of pediatric rheumatology in the Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, said Dr. Woo. Back in the 1960s, this wasn’t even a subspecialty. “Sick kids in general were taken either to pediatricians who didn’t know much about undescribed rheumatological conditions, and rheumatologists who didn’t know or have facilities for pediatric care.”
Dr. Ansell started this work, and Dr. Woo took over when she retired. With her colleagues, she set up a syllabus for pediatric rheumatology to formalize training for all junior doctors. This established a model of multidisciplinary clinical care and research. “Over the years, more women doctors have been attracted to pediatric rheumatology and have done well,” she said.
The rise of female leaders in rheumatology over the past few decades has been exponential, she continued. Women have become presidents of rheumatologic societies. Some established themselves as leaders in specific disciplines.
Carol Black, MD, from the United Kingdom is renowned for her international collaborative work in scleroderma research and clinical care. Patience White, MD in Washington, D.C., started research on the process of transitioning from childhood to adolescent to adult clinical care, a discipline that now has a strong international presence, Dr. Woo said.
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, which created a task force on gender equity in academic rheumatology, is evolving, she continued. The Academy of Medical Sciences in the United Kingdom also has active gender equality and mentoring programs, including a program to boost the careers of all researchers.
It’s also much easier now for women to become lead authors on papers since many are heads of lab or clinical services, Dr. Woo continued. “I don’t think there’s much discrimination if you’re a good clinician, and/or a good scientist. If women do their work well, they get the appropriate acknowledgment.”
Jean Liew, MD, recalls the long list of women mentors who have guided her career in rheumatology.
It started during her residency, when Jennifer Barton, MD, at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, exposed her to new ways of conducting clinical research on patient outcomes.
In fellowship, she met Lianne Gensler, MD, a leader in axial spondyloarthritis, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Through Dr. Gensler’s mentorship and sponsorship, she was introduced to Maureen Dubreuil, MD, at Boston University, whose research focuses on pharmacoepidemiologic approaches using large databases.
Dr. Liew currently practices rheumatology under the leadership of Tuhina Neogi, MD, a world-renowned expert in osteoarthritis and gout. “She’s my research mentor,” Dr. Liew, an assistant professor of medicine at Boston University, said in an interview.
Her academic timeline reflects the powerful network and influence of women rheumatologists, who represent half of the adult rheumatology workforce in the United States. “In the research arena, many experts are women and they serve as role models and mentors to many,” Dr. Liew said.
But there’s more work to do, she and others acknowledged.
Rheumatology faces ongoing workforce shortages while struggling with a gender gap that’s closing but not as quickly as many women rheumatologists would like to see.
The gap persists, despite overall gains in the field of medicine, Vaneet Sandhu, MD, a rheumatologist with Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said in an interview. Women have exceeded men as enrollees in medical colleges, reported the Association of American Medical Colleges. And yet, “our colleagues reported last year that, in academic rheumatology, women are less likely to be full or associate professors than men,” she said.
The odds of being a fellowship program director or division director is similar in both males and females. “So, we’ve had some gains, but there’s always room for more,” Dr. Sandhu said.
Too few physicians
The next 10 years forecasts a dearth in American physicians.
AAMC projects a shortage of 124,000 doctors in the United States by 2034. Following on a similar trajectory, the ACR in 2015 anticipated a 25% drop in the supply of rheumatology clinical providers by 2030, with demand exceeding supply by more than 4,100 clinical employees.
The ACR’s workforce study projected that more women would come into rheumatology, noted Marcy Bolster, MD, director of the rheumatology fellowship training program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. Women make up at least 50% of the workforce and 66% of fellows If these numbers hold, “we’ll definitely see an increase in the percent of women in the workforce” moving forward, Dr. Bolster said in an interview.
Women have helped the shortage to a great extent, said Nilanjana Bose, MD, a rheumatologist at Lonestar Rheumatology, Houston.
The work-life balance that rheumatology offers, combined with its focus on the cognitive part of internal medicine, explains why the field has attracted so many women. Rheumatology provides flexible work options. Women “get to teach or do rounds in the hospital or have a private practice where you’re mostly outpatient with some hospital work,” Dr. Bose said in an interview.
With anticipated shortages looming over the next decade, the profession needs to be cognizant of the different demands women face in their careers and how it can accommodate the workforce to meet the needs of its providers and maintain access for patients, Dr. Bolster said.
There are many innovative ways to match the demand for access. One thought is to create shared positions. Instead of employing four full-time physicians and one person part time, have two people who are working part time, Dr. Bolster suggested. “It is also important to not only expand our workforce with advanced practice providers, but to ensure their retention in the rheumatology workforce, to improve access to care for those with rheumatic diseases.”
Increasing the number of residency positions is another step toward addressing the shortage, Dr. Sandhu offered.
Women rheumatologists should make their voices heard by contacting members of Congress to support legislation that advocates for workforce shortage solutions, “in addition to generally supporting women’s rights and growth in the workplace,” she said.
The gender divide continues
Rosalind Ramsey-Goldman, MD, DrPH, remembers being the only woman in a group of five during her fellowship in the mid-1980s. Few women role models existed within the ACR, especially those in academic careers. “Now, most fellowships have more than 50% women, reflecting the number of women going to medical school,” said Dr. Ramsey-Goldman, Gallagher Research Professor in Rheumatology at Northwestern University and Northwestern Medicine, Chicago.
As more women enter the profession, women rheumatologists in academic rheumatology have started to outpace men in recent years. Some research suggests they’ve made headway in gaining leadership spots at institutions.
One recent paper, a cross-sectional national study of more than 6,100 rheumatologists, found that women had similar odds of attaining fellowship program or division director positions as men. As directors of training programs, women in rheumatology “instill this collaborative and growth mindset that encourages learners to self-reflect and work as a team,” Dr. Sandhu said.
Women bring a different perspective to training, and how curriculum works, Dr. Bose said. Studies have shown that women tend to be more empathic. They ask more questions. “That’s not to say men aren’t good. Women just have an inborn ability for connecting,” and this perspective helps to enrich the educational experience for trainees.
Women who lead training programs are also attuned to realities that female trainees confront, such as dealing with the challenges of achieving the best possible education while also raising a family, noted Graciela S. Alarcón, MD, MPH, who holds emeritus positions at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia in Lima, Peru.
“These program directors cultivate the ability to relate to women trainees in a very personal manner, supporting them in their efforts to achieve a balance between their training demands and their family/personal responsibilities,” she said.
Other research suggests the gender gap hasn’t gone away. Women continue to have lower odds of holding a higher-level professorship, receiving a federal grant, or speaking at academic conferences. They are also less likely to serve as first authors on rheumatology guidelines or recommendations.
Some studies suggest that women see fewer patients and earn less than their male counterparts. At peak difference, men can earn up to $100,000+ more than women. “My own impression is that it takes more efforts for women to reach the same level of recognition than men, and although overt discrimination is rare nowadays, subtle discrimination still occurs,” according to Dr. Alarcón.
Over a lifetime, female physicians can expect to earn less than their male counterparts, with clear implications for different retirement income levels, she said.
Fixing a leaky academic pipeline
The reality is the academic pipeline, and especially the physician-scientist pipeline, “continues to be leaky,” Dr. Liew said. “We know that caregivers to young children have larger barriers to surmount in academics and in research, and that there is a gender disparity present.” The toll of academic medicine on early career women who are parents is especially pronounced. While the pandemic has intensified this problem, it was around pre-COVID, she added.
Women who start in academia as academic clinicians or clinician researchers aren’t always able to meet their goals for promotion within the appropriate time frame. This is because of inequities in the system and lack of support related to maternity leave, childcare, and other issues. As a result, they leave academia and go into private practice or industry, Dr. Liew said.
The ACR in its 2015 survey projected that more women would be seeking part-time positions.
The good news is many academic institutions are taking a more equitable view about different career paths, offering equal parental leave to both men and women, Dr. Bolster noted. “It is essential that workforce planning encompasses the changing responsibilities within families and account for more parental leave by both men and women.” If certain projections come true, with 50% of the profession retiring between 2015 and 2030, combined with more men and women working part time, “it is requisite that workforce strategies plan for this.”
When Dr. Ramsey-Goldman was a trainee and junior faculty, there were no formal maternity leave policies.
Now, this benefit is available, she said. In another critical change, the ACR has made childcare services and a lactation room available for young mothers during its annual meeting. “Virtual meetings afford further ways to interact with colleagues,” she added.
Whether women choose to stay in academia or go into clinical practice is a very personal decision. “But it is also fair that, in some programs, training directors and faculty members can encourage trainees toward academia and its fascinating research possibilities,” Dr. Alarcón offered.
Making gains in research
Women are increasingly driving groundbreaking rheumatology research at all levels, Dr. Sandhu said. “And women empower women. Not infrequently, our female leaders, veterans in rheumatology research, seek younger female rheumatologists to help them grow in their niches. This has been one of the most beautiful things of the sisterhood in rheumatology that I have been blessed to be part of.”
In pediatric rheumatology, young female researchers are leading global research efforts. Some standouts include Kate Webb, MD, a pediatric rheumatologist in Cape Town, South Africa, and scientist who has worked on multisystem inflammatory syndrome during the pandemic. Sheila Angeles-Han, MD, who works on uveitis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, had a role in recent ACR guidelines. Laura Lewandowski, MD, has also contributed to global rheumatology efforts, especially in low- and middle-income countries, Dr. Liew said.
The 2021 ACR annual meeting highlighted the research efforts of women rheumatologists from around the world. A global rheumatology summit at the meeting featured many women voices, including Dzifa Dey, MD, from Ghana, who received the ACR Distinguished International Rheumatology Professional Award. Ashira Blazer, MD, and Irene Blanco, MD, have spearheaded the ACR’s diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives.
Women researchers have many opportunities to study rheumatologic diseases that disproportionately affect women, Dr. Alarcón said.
Lupus, for example, affects women in a much higher proportion than men (90% vs. 10%). This may be an attractive target for the best and brightest among future women researchers, Dr. Alarcón suggested. “It is a fact that publications related to lupus in leading internal medicine and rheumatology journals often include women either as first or senior authors. In that context, it can be said that several advances in the study of lupus worldwide can be attributed to women.”
This applies to disparities in social determinants of health that account for extremely complex outcomes in lupus among women of color, compared with White women, in addition to the costs associated with the disease and its impact on morbidity, mortality, and quality of life.
Women rheumatologists have advanced the work in reproductive management of rheumatic diseases, including a recent ACR-endorsed publication that provides formal guidance on managing reproductive health in women with rheumatic disease, Dr. Sandhu said. “One thing is clear: Without women, the work on reproductive diseases in rheumatology to date would not likely be where it is.”
Dr. Ramsey-Goldman added that “this critical work will not only set the stage for clinical care of both women and men regarding their reproductive health but will also inform education strategies for trainees and future research activities, and help direct policy regarding access to care, medication development, and costs of treatment.”
Obtaining grant funding to support salaries and researcher endeavors remains a challenge, Dr. Liew said. “It takes working evenings, weekends, and holidays to meet those goals within a set time frame. So you can see why a female faculty member with children might be disadvantaged, compared to a male counterpart without children.”
Competition for grant funding remains fierce as budgets become tighter, she added.
“We will lose a lot more brilliant and compassionate rheumatologists (clinicians, physician-scientists, and scientists alike) if we do not think of ways to make things more equitable or do not acknowledge the privileges that support some to continued career successes and leave others behind,” Dr. Liew said.
Women who choose a research field should seek out mentor and financial support that will allow them enough protected time to balance out research with other clinical activities, such as teaching and patient care, Dr. Alarcón said.
Training directors, mentors, and faculty should prioritize the needs of current and future women researchers, she said. “The guidance provided to young female trainees toward a successful research career is a formidable challenge that may provide, in turn, enormous satisfaction. There are established avenues to seek funding as new investigators.”
Progress in diversity
Rheumatology as a field is attracting more candidates and all races and genders, Dr. Bose said. “I think in the coming years we will see more and more women from minorities being incorporated into the rheumatology workforce.”
Others would like to see further improvements in diversity and attracting women from historically excluded backgrounds. Patients will benefit from rheumatologists who are able to connect with them through shared languages, cultures, and other life experiences, Dr. Liew said. “It is imperative that we work on recruitment, mentorship, and retention in this regard.”
While the representation of women of color is still inadequate, there has been some progress, Dr. Sandhu said. The number of female Hispanic, Latinx, and Black or African American graduates from medical school has seen a steady rise since 2017. And, AAMC has established task forces such as the Women of Color Initiative to identify strategies for furthering the careers of women of color in academic medicine.
“There’s still a lot of room to grow. I am, however, proud to say we will finally have a woman of color as the president of ACR in 2023,” said Dr. Sandhu, referring to Deborah Dyett Desir, MD.
Dr. Desir discussed the importance of diversifying the ACR in a recent interview.
All rheumatologists know that there is a place for them in the ACR, she stressed. “The demographics of our membership should reflect that of our population.”
As growth in diverse representation occurs, so will recruitment, retention, and a greater awareness and distribution of knowledge and means to address implicit biases and microaggressions, Dr. Sandhu said. “We will see a greater quality of health care, where patients may feel more connected to someone they can identify with.”
Looking ahead
Dr. Alarcón expects women to continue to play a major role in rheumatology, not just in research, education, and patient care but in leadership of academic societies and professional organizations.
“Women in rheumatology have come a long way – a piece of history that I have been fortunate to witness from my beginnings in the early 1970s. We have, I think, paved the way for the next generations of leaders in our beloved specialty field.”
Dr. Bolster is a member of the ACR board of directors and board liaison of the ACR Workforce Solutions Committee. Dr. Ramsey-Goldman has been a GlaxoSmithKline consultant for lupus studies, a consultant and site investigator with Exagen Diagnostics for lupus biomarker studies, and a site investigator for Xencor and Horizon Pharma lupus trials. Dr. Sandhu serves on the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues.
Related article
Pioneer days of rheumatology: One veteran looks back
Patricia Woo, CBE, FMedSci, FRCP, has seen it all.
As a member of the British Rheumatology Society and fellow of the Royal College of Physicians, she presented the case for and obtained official training approval for pediatric rheumatology in the 1990s. She also set the wheels in motion to form the Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation and the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Now 74, Dr. Woo remembers the discrimination she faced in the 1970s. “I was told I couldn’t become an investigator or consultant if I were to marry or have children.” Around the same time, she found out a male clinician researcher didn’t want to work with her, not because of her qualifications, but because she was a woman.
That wouldn’t happen now with all the antidiscrimination laws in place, noted Dr. Woo, an emeritus professor of pediatric rheumatology and previous head of the Centre for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology at UCL, London. Looking at the advances made by women in rheumatology, “there’s a major difference between 3 decades ago and today. If anyone discriminates today, they are called out.”
As the founding president of the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society, Dr. Woo is one of many early trailblazers who weathered many changes and made gains in the profession.
It’s important to recognize the work of Barbara Ansell, MD, the founder of pediatric rheumatology in the Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, said Dr. Woo. Back in the 1960s, this wasn’t even a subspecialty. “Sick kids in general were taken either to pediatricians who didn’t know much about undescribed rheumatological conditions, and rheumatologists who didn’t know or have facilities for pediatric care.”
Dr. Ansell started this work, and Dr. Woo took over when she retired. With her colleagues, she set up a syllabus for pediatric rheumatology to formalize training for all junior doctors. This established a model of multidisciplinary clinical care and research. “Over the years, more women doctors have been attracted to pediatric rheumatology and have done well,” she said.
The rise of female leaders in rheumatology over the past few decades has been exponential, she continued. Women have become presidents of rheumatologic societies. Some established themselves as leaders in specific disciplines.
Carol Black, MD, from the United Kingdom is renowned for her international collaborative work in scleroderma research and clinical care. Patience White, MD in Washington, D.C., started research on the process of transitioning from childhood to adolescent to adult clinical care, a discipline that now has a strong international presence, Dr. Woo said.
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, which created a task force on gender equity in academic rheumatology, is evolving, she continued. The Academy of Medical Sciences in the United Kingdom also has active gender equality and mentoring programs, including a program to boost the careers of all researchers.
It’s also much easier now for women to become lead authors on papers since many are heads of lab or clinical services, Dr. Woo continued. “I don’t think there’s much discrimination if you’re a good clinician, and/or a good scientist. If women do their work well, they get the appropriate acknowledgment.”
Jean Liew, MD, recalls the long list of women mentors who have guided her career in rheumatology.
It started during her residency, when Jennifer Barton, MD, at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, exposed her to new ways of conducting clinical research on patient outcomes.
In fellowship, she met Lianne Gensler, MD, a leader in axial spondyloarthritis, at the annual meeting of the American College of Rheumatology. Through Dr. Gensler’s mentorship and sponsorship, she was introduced to Maureen Dubreuil, MD, at Boston University, whose research focuses on pharmacoepidemiologic approaches using large databases.
Dr. Liew currently practices rheumatology under the leadership of Tuhina Neogi, MD, a world-renowned expert in osteoarthritis and gout. “She’s my research mentor,” Dr. Liew, an assistant professor of medicine at Boston University, said in an interview.
Her academic timeline reflects the powerful network and influence of women rheumatologists, who represent half of the adult rheumatology workforce in the United States. “In the research arena, many experts are women and they serve as role models and mentors to many,” Dr. Liew said.
But there’s more work to do, she and others acknowledged.
Rheumatology faces ongoing workforce shortages while struggling with a gender gap that’s closing but not as quickly as many women rheumatologists would like to see.
The gap persists, despite overall gains in the field of medicine, Vaneet Sandhu, MD, a rheumatologist with Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said in an interview. Women have exceeded men as enrollees in medical colleges, reported the Association of American Medical Colleges. And yet, “our colleagues reported last year that, in academic rheumatology, women are less likely to be full or associate professors than men,” she said.
The odds of being a fellowship program director or division director is similar in both males and females. “So, we’ve had some gains, but there’s always room for more,” Dr. Sandhu said.
Too few physicians
The next 10 years forecasts a dearth in American physicians.
AAMC projects a shortage of 124,000 doctors in the United States by 2034. Following on a similar trajectory, the ACR in 2015 anticipated a 25% drop in the supply of rheumatology clinical providers by 2030, with demand exceeding supply by more than 4,100 clinical employees.
The ACR’s workforce study projected that more women would come into rheumatology, noted Marcy Bolster, MD, director of the rheumatology fellowship training program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. Women make up at least 50% of the workforce and 66% of fellows If these numbers hold, “we’ll definitely see an increase in the percent of women in the workforce” moving forward, Dr. Bolster said in an interview.
Women have helped the shortage to a great extent, said Nilanjana Bose, MD, a rheumatologist at Lonestar Rheumatology, Houston.
The work-life balance that rheumatology offers, combined with its focus on the cognitive part of internal medicine, explains why the field has attracted so many women. Rheumatology provides flexible work options. Women “get to teach or do rounds in the hospital or have a private practice where you’re mostly outpatient with some hospital work,” Dr. Bose said in an interview.
With anticipated shortages looming over the next decade, the profession needs to be cognizant of the different demands women face in their careers and how it can accommodate the workforce to meet the needs of its providers and maintain access for patients, Dr. Bolster said.
There are many innovative ways to match the demand for access. One thought is to create shared positions. Instead of employing four full-time physicians and one person part time, have two people who are working part time, Dr. Bolster suggested. “It is also important to not only expand our workforce with advanced practice providers, but to ensure their retention in the rheumatology workforce, to improve access to care for those with rheumatic diseases.”
Increasing the number of residency positions is another step toward addressing the shortage, Dr. Sandhu offered.
Women rheumatologists should make their voices heard by contacting members of Congress to support legislation that advocates for workforce shortage solutions, “in addition to generally supporting women’s rights and growth in the workplace,” she said.
The gender divide continues
Rosalind Ramsey-Goldman, MD, DrPH, remembers being the only woman in a group of five during her fellowship in the mid-1980s. Few women role models existed within the ACR, especially those in academic careers. “Now, most fellowships have more than 50% women, reflecting the number of women going to medical school,” said Dr. Ramsey-Goldman, Gallagher Research Professor in Rheumatology at Northwestern University and Northwestern Medicine, Chicago.
As more women enter the profession, women rheumatologists in academic rheumatology have started to outpace men in recent years. Some research suggests they’ve made headway in gaining leadership spots at institutions.
One recent paper, a cross-sectional national study of more than 6,100 rheumatologists, found that women had similar odds of attaining fellowship program or division director positions as men. As directors of training programs, women in rheumatology “instill this collaborative and growth mindset that encourages learners to self-reflect and work as a team,” Dr. Sandhu said.
Women bring a different perspective to training, and how curriculum works, Dr. Bose said. Studies have shown that women tend to be more empathic. They ask more questions. “That’s not to say men aren’t good. Women just have an inborn ability for connecting,” and this perspective helps to enrich the educational experience for trainees.
Women who lead training programs are also attuned to realities that female trainees confront, such as dealing with the challenges of achieving the best possible education while also raising a family, noted Graciela S. Alarcón, MD, MPH, who holds emeritus positions at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and the Universidad Peruana Cayetano Heredia in Lima, Peru.
“These program directors cultivate the ability to relate to women trainees in a very personal manner, supporting them in their efforts to achieve a balance between their training demands and their family/personal responsibilities,” she said.
Other research suggests the gender gap hasn’t gone away. Women continue to have lower odds of holding a higher-level professorship, receiving a federal grant, or speaking at academic conferences. They are also less likely to serve as first authors on rheumatology guidelines or recommendations.
Some studies suggest that women see fewer patients and earn less than their male counterparts. At peak difference, men can earn up to $100,000+ more than women. “My own impression is that it takes more efforts for women to reach the same level of recognition than men, and although overt discrimination is rare nowadays, subtle discrimination still occurs,” according to Dr. Alarcón.
Over a lifetime, female physicians can expect to earn less than their male counterparts, with clear implications for different retirement income levels, she said.
Fixing a leaky academic pipeline
The reality is the academic pipeline, and especially the physician-scientist pipeline, “continues to be leaky,” Dr. Liew said. “We know that caregivers to young children have larger barriers to surmount in academics and in research, and that there is a gender disparity present.” The toll of academic medicine on early career women who are parents is especially pronounced. While the pandemic has intensified this problem, it was around pre-COVID, she added.
Women who start in academia as academic clinicians or clinician researchers aren’t always able to meet their goals for promotion within the appropriate time frame. This is because of inequities in the system and lack of support related to maternity leave, childcare, and other issues. As a result, they leave academia and go into private practice or industry, Dr. Liew said.
The ACR in its 2015 survey projected that more women would be seeking part-time positions.
The good news is many academic institutions are taking a more equitable view about different career paths, offering equal parental leave to both men and women, Dr. Bolster noted. “It is essential that workforce planning encompasses the changing responsibilities within families and account for more parental leave by both men and women.” If certain projections come true, with 50% of the profession retiring between 2015 and 2030, combined with more men and women working part time, “it is requisite that workforce strategies plan for this.”
When Dr. Ramsey-Goldman was a trainee and junior faculty, there were no formal maternity leave policies.
Now, this benefit is available, she said. In another critical change, the ACR has made childcare services and a lactation room available for young mothers during its annual meeting. “Virtual meetings afford further ways to interact with colleagues,” she added.
Whether women choose to stay in academia or go into clinical practice is a very personal decision. “But it is also fair that, in some programs, training directors and faculty members can encourage trainees toward academia and its fascinating research possibilities,” Dr. Alarcón offered.
Making gains in research
Women are increasingly driving groundbreaking rheumatology research at all levels, Dr. Sandhu said. “And women empower women. Not infrequently, our female leaders, veterans in rheumatology research, seek younger female rheumatologists to help them grow in their niches. This has been one of the most beautiful things of the sisterhood in rheumatology that I have been blessed to be part of.”
In pediatric rheumatology, young female researchers are leading global research efforts. Some standouts include Kate Webb, MD, a pediatric rheumatologist in Cape Town, South Africa, and scientist who has worked on multisystem inflammatory syndrome during the pandemic. Sheila Angeles-Han, MD, who works on uveitis in juvenile idiopathic arthritis, had a role in recent ACR guidelines. Laura Lewandowski, MD, has also contributed to global rheumatology efforts, especially in low- and middle-income countries, Dr. Liew said.
The 2021 ACR annual meeting highlighted the research efforts of women rheumatologists from around the world. A global rheumatology summit at the meeting featured many women voices, including Dzifa Dey, MD, from Ghana, who received the ACR Distinguished International Rheumatology Professional Award. Ashira Blazer, MD, and Irene Blanco, MD, have spearheaded the ACR’s diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives.
Women researchers have many opportunities to study rheumatologic diseases that disproportionately affect women, Dr. Alarcón said.
Lupus, for example, affects women in a much higher proportion than men (90% vs. 10%). This may be an attractive target for the best and brightest among future women researchers, Dr. Alarcón suggested. “It is a fact that publications related to lupus in leading internal medicine and rheumatology journals often include women either as first or senior authors. In that context, it can be said that several advances in the study of lupus worldwide can be attributed to women.”
This applies to disparities in social determinants of health that account for extremely complex outcomes in lupus among women of color, compared with White women, in addition to the costs associated with the disease and its impact on morbidity, mortality, and quality of life.
Women rheumatologists have advanced the work in reproductive management of rheumatic diseases, including a recent ACR-endorsed publication that provides formal guidance on managing reproductive health in women with rheumatic disease, Dr. Sandhu said. “One thing is clear: Without women, the work on reproductive diseases in rheumatology to date would not likely be where it is.”
Dr. Ramsey-Goldman added that “this critical work will not only set the stage for clinical care of both women and men regarding their reproductive health but will also inform education strategies for trainees and future research activities, and help direct policy regarding access to care, medication development, and costs of treatment.”
Obtaining grant funding to support salaries and researcher endeavors remains a challenge, Dr. Liew said. “It takes working evenings, weekends, and holidays to meet those goals within a set time frame. So you can see why a female faculty member with children might be disadvantaged, compared to a male counterpart without children.”
Competition for grant funding remains fierce as budgets become tighter, she added.
“We will lose a lot more brilliant and compassionate rheumatologists (clinicians, physician-scientists, and scientists alike) if we do not think of ways to make things more equitable or do not acknowledge the privileges that support some to continued career successes and leave others behind,” Dr. Liew said.
Women who choose a research field should seek out mentor and financial support that will allow them enough protected time to balance out research with other clinical activities, such as teaching and patient care, Dr. Alarcón said.
Training directors, mentors, and faculty should prioritize the needs of current and future women researchers, she said. “The guidance provided to young female trainees toward a successful research career is a formidable challenge that may provide, in turn, enormous satisfaction. There are established avenues to seek funding as new investigators.”
Progress in diversity
Rheumatology as a field is attracting more candidates and all races and genders, Dr. Bose said. “I think in the coming years we will see more and more women from minorities being incorporated into the rheumatology workforce.”
Others would like to see further improvements in diversity and attracting women from historically excluded backgrounds. Patients will benefit from rheumatologists who are able to connect with them through shared languages, cultures, and other life experiences, Dr. Liew said. “It is imperative that we work on recruitment, mentorship, and retention in this regard.”
While the representation of women of color is still inadequate, there has been some progress, Dr. Sandhu said. The number of female Hispanic, Latinx, and Black or African American graduates from medical school has seen a steady rise since 2017. And, AAMC has established task forces such as the Women of Color Initiative to identify strategies for furthering the careers of women of color in academic medicine.
“There’s still a lot of room to grow. I am, however, proud to say we will finally have a woman of color as the president of ACR in 2023,” said Dr. Sandhu, referring to Deborah Dyett Desir, MD.
Dr. Desir discussed the importance of diversifying the ACR in a recent interview.
All rheumatologists know that there is a place for them in the ACR, she stressed. “The demographics of our membership should reflect that of our population.”
As growth in diverse representation occurs, so will recruitment, retention, and a greater awareness and distribution of knowledge and means to address implicit biases and microaggressions, Dr. Sandhu said. “We will see a greater quality of health care, where patients may feel more connected to someone they can identify with.”
Looking ahead
Dr. Alarcón expects women to continue to play a major role in rheumatology, not just in research, education, and patient care but in leadership of academic societies and professional organizations.
“Women in rheumatology have come a long way – a piece of history that I have been fortunate to witness from my beginnings in the early 1970s. We have, I think, paved the way for the next generations of leaders in our beloved specialty field.”
Dr. Bolster is a member of the ACR board of directors and board liaison of the ACR Workforce Solutions Committee. Dr. Ramsey-Goldman has been a GlaxoSmithKline consultant for lupus studies, a consultant and site investigator with Exagen Diagnostics for lupus biomarker studies, and a site investigator for Xencor and Horizon Pharma lupus trials. Dr. Sandhu serves on the ACR’s Committee on Rheumatology Training and Workforce Issues.
Related article
Pioneer days of rheumatology: One veteran looks back
Patricia Woo, CBE, FMedSci, FRCP, has seen it all.
As a member of the British Rheumatology Society and fellow of the Royal College of Physicians, she presented the case for and obtained official training approval for pediatric rheumatology in the 1990s. She also set the wheels in motion to form the Paediatric Rheumatology International Trials Organisation and the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society.
Now 74, Dr. Woo remembers the discrimination she faced in the 1970s. “I was told I couldn’t become an investigator or consultant if I were to marry or have children.” Around the same time, she found out a male clinician researcher didn’t want to work with her, not because of her qualifications, but because she was a woman.
That wouldn’t happen now with all the antidiscrimination laws in place, noted Dr. Woo, an emeritus professor of pediatric rheumatology and previous head of the Centre for Paediatric and Adolescent Rheumatology at UCL, London. Looking at the advances made by women in rheumatology, “there’s a major difference between 3 decades ago and today. If anyone discriminates today, they are called out.”
As the founding president of the Paediatric Rheumatology European Society, Dr. Woo is one of many early trailblazers who weathered many changes and made gains in the profession.
It’s important to recognize the work of Barbara Ansell, MD, the founder of pediatric rheumatology in the Canadian Red Cross Memorial Hospital, said Dr. Woo. Back in the 1960s, this wasn’t even a subspecialty. “Sick kids in general were taken either to pediatricians who didn’t know much about undescribed rheumatological conditions, and rheumatologists who didn’t know or have facilities for pediatric care.”
Dr. Ansell started this work, and Dr. Woo took over when she retired. With her colleagues, she set up a syllabus for pediatric rheumatology to formalize training for all junior doctors. This established a model of multidisciplinary clinical care and research. “Over the years, more women doctors have been attracted to pediatric rheumatology and have done well,” she said.
The rise of female leaders in rheumatology over the past few decades has been exponential, she continued. Women have become presidents of rheumatologic societies. Some established themselves as leaders in specific disciplines.
Carol Black, MD, from the United Kingdom is renowned for her international collaborative work in scleroderma research and clinical care. Patience White, MD in Washington, D.C., started research on the process of transitioning from childhood to adolescent to adult clinical care, a discipline that now has a strong international presence, Dr. Woo said.
The European Alliance of Associations for Rheumatology, which created a task force on gender equity in academic rheumatology, is evolving, she continued. The Academy of Medical Sciences in the United Kingdom also has active gender equality and mentoring programs, including a program to boost the careers of all researchers.
It’s also much easier now for women to become lead authors on papers since many are heads of lab or clinical services, Dr. Woo continued. “I don’t think there’s much discrimination if you’re a good clinician, and/or a good scientist. If women do their work well, they get the appropriate acknowledgment.”
Rheumatology News celebrates 20 years
This time around, we’ll examine the first issue of Rheumatology News, which was published in February 2002. You can read the first-ever issue at the "PDF Download" link above.
In that premiere issue, information about early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) featured prominently. A front-page story described new findings showing that early treatment of RA with DMARDs could reduce disease-related disability by one-third or more. A second article described quantitative improvement in MRI-detected synovitis in patients with early RA who were treated with infliximab for 14 weeks, while another reported on clinically relevant responses seen in 66% of patients treated with adalimumab plus methotrexate in a trial of patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate alone.
In other RA news, a report focused on low rates of preventive health care services and screening for other disorders in women, including Pap smears, mammograms, and influenza vaccinations. Another story suggested the possibility that methotrexate may elevate cancer risk in patients with RA. An analysis of two separate prospective studies indicated that women who regularly drink decaffeinated coffee may be at higher risk for developing RA.
Another page 1 story examined the potential of new drugs bosentan and epoprostenol for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with various forms of connective tissue disease.
Etanercept was the focus of two articles, one announcing its approval for psoriatic arthritis, and another describing a small trial of the biologic in treating moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis.
In osteoarthritis news, a front-page report described two placebo-controlled studies of oral glucosamine sulfate supplementation that suggested the formulation might slow the progression of joint space narrowing in postmenopausal women, and another article noted how a combined formulation of tramadol and acetaminophen reduced OA pain flares.
Readers were also treated to a pro and con editorial debate between Frederick Wolfe, MD, and Thomas J. Romano, MD, on whether trauma causes fibromyalgia.
Looking ahead
Throughout 2022, look for articles examining the past and future of rheumatology, including:
- The rise of women in the field;
- the rise of biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs;
- the history and ongoing influence of OMERACT (Outcome Measures in Rheumatology);
- the growth and future of ACR-EULAR collaborations;
- progress and future directions of pediatric rheumatology; and
- the growth in understanding how sociodemographics and racial/ethnic identity affect access to and acceptance and receipt of rheumatologic care.
Are there any topics you think would be valuable to cover in light of Rheumatology News’ 20th anniversary? The editorial staff welcomes your suggestions. Please share them by emailing us at [email protected].
This time around, we’ll examine the first issue of Rheumatology News, which was published in February 2002. You can read the first-ever issue at the "PDF Download" link above.
In that premiere issue, information about early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) featured prominently. A front-page story described new findings showing that early treatment of RA with DMARDs could reduce disease-related disability by one-third or more. A second article described quantitative improvement in MRI-detected synovitis in patients with early RA who were treated with infliximab for 14 weeks, while another reported on clinically relevant responses seen in 66% of patients treated with adalimumab plus methotrexate in a trial of patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate alone.
In other RA news, a report focused on low rates of preventive health care services and screening for other disorders in women, including Pap smears, mammograms, and influenza vaccinations. Another story suggested the possibility that methotrexate may elevate cancer risk in patients with RA. An analysis of two separate prospective studies indicated that women who regularly drink decaffeinated coffee may be at higher risk for developing RA.
Another page 1 story examined the potential of new drugs bosentan and epoprostenol for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with various forms of connective tissue disease.
Etanercept was the focus of two articles, one announcing its approval for psoriatic arthritis, and another describing a small trial of the biologic in treating moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis.
In osteoarthritis news, a front-page report described two placebo-controlled studies of oral glucosamine sulfate supplementation that suggested the formulation might slow the progression of joint space narrowing in postmenopausal women, and another article noted how a combined formulation of tramadol and acetaminophen reduced OA pain flares.
Readers were also treated to a pro and con editorial debate between Frederick Wolfe, MD, and Thomas J. Romano, MD, on whether trauma causes fibromyalgia.
Looking ahead
Throughout 2022, look for articles examining the past and future of rheumatology, including:
- The rise of women in the field;
- the rise of biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs;
- the history and ongoing influence of OMERACT (Outcome Measures in Rheumatology);
- the growth and future of ACR-EULAR collaborations;
- progress and future directions of pediatric rheumatology; and
- the growth in understanding how sociodemographics and racial/ethnic identity affect access to and acceptance and receipt of rheumatologic care.
Are there any topics you think would be valuable to cover in light of Rheumatology News’ 20th anniversary? The editorial staff welcomes your suggestions. Please share them by emailing us at [email protected].
This time around, we’ll examine the first issue of Rheumatology News, which was published in February 2002. You can read the first-ever issue at the "PDF Download" link above.
In that premiere issue, information about early treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and other disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) featured prominently. A front-page story described new findings showing that early treatment of RA with DMARDs could reduce disease-related disability by one-third or more. A second article described quantitative improvement in MRI-detected synovitis in patients with early RA who were treated with infliximab for 14 weeks, while another reported on clinically relevant responses seen in 66% of patients treated with adalimumab plus methotrexate in a trial of patients with an inadequate response to methotrexate alone.
In other RA news, a report focused on low rates of preventive health care services and screening for other disorders in women, including Pap smears, mammograms, and influenza vaccinations. Another story suggested the possibility that methotrexate may elevate cancer risk in patients with RA. An analysis of two separate prospective studies indicated that women who regularly drink decaffeinated coffee may be at higher risk for developing RA.
Another page 1 story examined the potential of new drugs bosentan and epoprostenol for treating pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with various forms of connective tissue disease.
Etanercept was the focus of two articles, one announcing its approval for psoriatic arthritis, and another describing a small trial of the biologic in treating moderate to severe ankylosing spondylitis.
In osteoarthritis news, a front-page report described two placebo-controlled studies of oral glucosamine sulfate supplementation that suggested the formulation might slow the progression of joint space narrowing in postmenopausal women, and another article noted how a combined formulation of tramadol and acetaminophen reduced OA pain flares.
Readers were also treated to a pro and con editorial debate between Frederick Wolfe, MD, and Thomas J. Romano, MD, on whether trauma causes fibromyalgia.
Looking ahead
Throughout 2022, look for articles examining the past and future of rheumatology, including:
- The rise of women in the field;
- the rise of biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs;
- the history and ongoing influence of OMERACT (Outcome Measures in Rheumatology);
- the growth and future of ACR-EULAR collaborations;
- progress and future directions of pediatric rheumatology; and
- the growth in understanding how sociodemographics and racial/ethnic identity affect access to and acceptance and receipt of rheumatologic care.
Are there any topics you think would be valuable to cover in light of Rheumatology News’ 20th anniversary? The editorial staff welcomes your suggestions. Please share them by emailing us at [email protected].















