User login
‘No justification’ for suicide warning on all antiseizure meds
, new research shows. “There appears to be no justification for the FDA to label every new antiseizure medication with a warning that it may increase risk of suicidality,” said study investigator Michael R. Sperling, MD, professor of neurology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
“How many patients are afraid of their medication and do not take it because of the warning – and are consequently at risk because of that? We do not know, but have anecdotal experience that this is certainly an issue,” Dr. Sperling, who is director of the Jefferson Comprehensive Epilepsy Center, added.
The study was published online August 2 in JAMA Neurology.
Blanket warning
In 2008, the FDA issued an alert stating that antiseizure medications increase suicidality. The alert was based on pooled data from placebo-controlled clinical trials that included 11 antiseizure medications – carbamazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine, topiramate, valproate, and zonisamide.
The meta-analytic review showed that, compared with placebo, antiseizure medications nearly doubled suicide risk among patients treated for epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and other diseases. As a result of the FDA study, all antiseizure medications that have been approved since 2008 carry a warning for suicidality.
However, subsequent analyses did not show the same results, Dr. Sperling and colleagues noted.
“Pivotal” antiseizure medication epilepsy trials since 2008 have evaluated suicidality prospectively. Since 2011, trials have included the validated Columbia Suicidality Severity Rating Scale, they noted.
Meta analysis showed no increased risk
Dr. Sperling and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled epilepsy trials of five antiseizure medications approved since 2008. These antiseizure medications were eslicarbazepine, perampanel, brivaracetam, cannabidiol, and cenobamate. The trials involved 5,996 patients, including 4,000 who were treated with antiseizure medications and 1,996 who were treated with placebo.
Confining the analysis to epilepsy trials avoids potential confounders, such as possible differences in suicidality risks between different diseases, the researchers noted.
They found no evidence of increased risk for suicidal ideation (overall risk ratio, antiseizure medications vs. placebo: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.35-1.60) or suicide attempt (risk ratio, 0.75; 95% CI: 0.30-1.87) overall or for any individual antiseizure medication.
Suicidal ideation occurred in 12 of 4,000 patients treated with antiseizure medications (0.30%), versus 7 of 1,996 patients treated with placebo (0.35%) (P = .74). Three patients who were treated with antiseizure medications attempted suicide; no patients who were treated with placebo attempted suicide (P = .22). There were no completed suicides.
“There is no current evidence that the five antiseizure medications evaluated in this study increase suicidality in epilepsy and merit a suicidality class warning,” the investigators wrote. When prescribed for epilepsy, “evidence does not support the FDA’s labeling practice of a blanket assumption of increased suicidality,” said Dr. Sperling.
“Our findings indicate the nonspecific suicide warning for all epilepsy drugs is simply not justifiable,” he said. “The results are not surprising. Different drugs affect cells in different ways. So there’s no reason to expect that every drug would increase suicide risk for every patient,” Dr. Sperling said in a statement.
“It’s important to recognize that epilepsy has many causes – perinatal injury, stroke, tumor, head trauma, developmental malformations, genetic causes, and others – and these underlying etiologies may well contribute to the presence of depression and suicidality in this population,” he said in an interview. “Psychodynamic influences also may occur as a consequence of having seizures. This is a complicated area, and drugs are simply one piece of the puzzle,” he added.
Dr. Sperling said the FDA has accomplished “one useful thing with its warning – it highlighted that physicians and other health care providers must pay attention to their patients’ psychological state, ask questions, and treat accordingly.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sperling has received grants from Eisai, Medtronic, Neurelis, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, Xenon, Cerevel Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, and Engage Pharma; personal fees from Neurelis, Medscape, Neurology Live, International Medical Press, UCB Pharma, Eisai, Oxford University Press, and Projects in Knowledge. He has also consulted for Medtronic outside the submitted work; payments went to Thomas Jefferson University. A complete list of authors’ disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows. “There appears to be no justification for the FDA to label every new antiseizure medication with a warning that it may increase risk of suicidality,” said study investigator Michael R. Sperling, MD, professor of neurology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
“How many patients are afraid of their medication and do not take it because of the warning – and are consequently at risk because of that? We do not know, but have anecdotal experience that this is certainly an issue,” Dr. Sperling, who is director of the Jefferson Comprehensive Epilepsy Center, added.
The study was published online August 2 in JAMA Neurology.
Blanket warning
In 2008, the FDA issued an alert stating that antiseizure medications increase suicidality. The alert was based on pooled data from placebo-controlled clinical trials that included 11 antiseizure medications – carbamazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine, topiramate, valproate, and zonisamide.
The meta-analytic review showed that, compared with placebo, antiseizure medications nearly doubled suicide risk among patients treated for epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and other diseases. As a result of the FDA study, all antiseizure medications that have been approved since 2008 carry a warning for suicidality.
However, subsequent analyses did not show the same results, Dr. Sperling and colleagues noted.
“Pivotal” antiseizure medication epilepsy trials since 2008 have evaluated suicidality prospectively. Since 2011, trials have included the validated Columbia Suicidality Severity Rating Scale, they noted.
Meta analysis showed no increased risk
Dr. Sperling and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled epilepsy trials of five antiseizure medications approved since 2008. These antiseizure medications were eslicarbazepine, perampanel, brivaracetam, cannabidiol, and cenobamate. The trials involved 5,996 patients, including 4,000 who were treated with antiseizure medications and 1,996 who were treated with placebo.
Confining the analysis to epilepsy trials avoids potential confounders, such as possible differences in suicidality risks between different diseases, the researchers noted.
They found no evidence of increased risk for suicidal ideation (overall risk ratio, antiseizure medications vs. placebo: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.35-1.60) or suicide attempt (risk ratio, 0.75; 95% CI: 0.30-1.87) overall or for any individual antiseizure medication.
Suicidal ideation occurred in 12 of 4,000 patients treated with antiseizure medications (0.30%), versus 7 of 1,996 patients treated with placebo (0.35%) (P = .74). Three patients who were treated with antiseizure medications attempted suicide; no patients who were treated with placebo attempted suicide (P = .22). There were no completed suicides.
“There is no current evidence that the five antiseizure medications evaluated in this study increase suicidality in epilepsy and merit a suicidality class warning,” the investigators wrote. When prescribed for epilepsy, “evidence does not support the FDA’s labeling practice of a blanket assumption of increased suicidality,” said Dr. Sperling.
“Our findings indicate the nonspecific suicide warning for all epilepsy drugs is simply not justifiable,” he said. “The results are not surprising. Different drugs affect cells in different ways. So there’s no reason to expect that every drug would increase suicide risk for every patient,” Dr. Sperling said in a statement.
“It’s important to recognize that epilepsy has many causes – perinatal injury, stroke, tumor, head trauma, developmental malformations, genetic causes, and others – and these underlying etiologies may well contribute to the presence of depression and suicidality in this population,” he said in an interview. “Psychodynamic influences also may occur as a consequence of having seizures. This is a complicated area, and drugs are simply one piece of the puzzle,” he added.
Dr. Sperling said the FDA has accomplished “one useful thing with its warning – it highlighted that physicians and other health care providers must pay attention to their patients’ psychological state, ask questions, and treat accordingly.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sperling has received grants from Eisai, Medtronic, Neurelis, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, Xenon, Cerevel Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, and Engage Pharma; personal fees from Neurelis, Medscape, Neurology Live, International Medical Press, UCB Pharma, Eisai, Oxford University Press, and Projects in Knowledge. He has also consulted for Medtronic outside the submitted work; payments went to Thomas Jefferson University. A complete list of authors’ disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows. “There appears to be no justification for the FDA to label every new antiseizure medication with a warning that it may increase risk of suicidality,” said study investigator Michael R. Sperling, MD, professor of neurology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia.
“How many patients are afraid of their medication and do not take it because of the warning – and are consequently at risk because of that? We do not know, but have anecdotal experience that this is certainly an issue,” Dr. Sperling, who is director of the Jefferson Comprehensive Epilepsy Center, added.
The study was published online August 2 in JAMA Neurology.
Blanket warning
In 2008, the FDA issued an alert stating that antiseizure medications increase suicidality. The alert was based on pooled data from placebo-controlled clinical trials that included 11 antiseizure medications – carbamazepine, felbamate, gabapentin, lamotrigine, levetiracetam, oxcarbazepine, pregabalin, tiagabine, topiramate, valproate, and zonisamide.
The meta-analytic review showed that, compared with placebo, antiseizure medications nearly doubled suicide risk among patients treated for epilepsy, psychiatric disorders, and other diseases. As a result of the FDA study, all antiseizure medications that have been approved since 2008 carry a warning for suicidality.
However, subsequent analyses did not show the same results, Dr. Sperling and colleagues noted.
“Pivotal” antiseizure medication epilepsy trials since 2008 have evaluated suicidality prospectively. Since 2011, trials have included the validated Columbia Suicidality Severity Rating Scale, they noted.
Meta analysis showed no increased risk
Dr. Sperling and colleagues conducted a meta-analysis of 17 randomized placebo-controlled epilepsy trials of five antiseizure medications approved since 2008. These antiseizure medications were eslicarbazepine, perampanel, brivaracetam, cannabidiol, and cenobamate. The trials involved 5,996 patients, including 4,000 who were treated with antiseizure medications and 1,996 who were treated with placebo.
Confining the analysis to epilepsy trials avoids potential confounders, such as possible differences in suicidality risks between different diseases, the researchers noted.
They found no evidence of increased risk for suicidal ideation (overall risk ratio, antiseizure medications vs. placebo: 0.75; 95% confidence interval: 0.35-1.60) or suicide attempt (risk ratio, 0.75; 95% CI: 0.30-1.87) overall or for any individual antiseizure medication.
Suicidal ideation occurred in 12 of 4,000 patients treated with antiseizure medications (0.30%), versus 7 of 1,996 patients treated with placebo (0.35%) (P = .74). Three patients who were treated with antiseizure medications attempted suicide; no patients who were treated with placebo attempted suicide (P = .22). There were no completed suicides.
“There is no current evidence that the five antiseizure medications evaluated in this study increase suicidality in epilepsy and merit a suicidality class warning,” the investigators wrote. When prescribed for epilepsy, “evidence does not support the FDA’s labeling practice of a blanket assumption of increased suicidality,” said Dr. Sperling.
“Our findings indicate the nonspecific suicide warning for all epilepsy drugs is simply not justifiable,” he said. “The results are not surprising. Different drugs affect cells in different ways. So there’s no reason to expect that every drug would increase suicide risk for every patient,” Dr. Sperling said in a statement.
“It’s important to recognize that epilepsy has many causes – perinatal injury, stroke, tumor, head trauma, developmental malformations, genetic causes, and others – and these underlying etiologies may well contribute to the presence of depression and suicidality in this population,” he said in an interview. “Psychodynamic influences also may occur as a consequence of having seizures. This is a complicated area, and drugs are simply one piece of the puzzle,” he added.
Dr. Sperling said the FDA has accomplished “one useful thing with its warning – it highlighted that physicians and other health care providers must pay attention to their patients’ psychological state, ask questions, and treat accordingly.”
The study had no specific funding. Dr. Sperling has received grants from Eisai, Medtronic, Neurelis, SK Life Science, Sunovion, Takeda, Xenon, Cerevel Therapeutics, UCB Pharma, and Engage Pharma; personal fees from Neurelis, Medscape, Neurology Live, International Medical Press, UCB Pharma, Eisai, Oxford University Press, and Projects in Knowledge. He has also consulted for Medtronic outside the submitted work; payments went to Thomas Jefferson University. A complete list of authors’ disclosures is available with the original article.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Exercise tied to 50% reduction in mortality after stroke
, with a greater than 50% reduction in risk.
Lead study author Raed A. Joundi, MD, DPhil, of the University of Calgary (Alta.), said he expected results to show exercise was beneficial, but was surprised by the magnitude of the association between physical activity and lower mortality risk.
The impact of physical activity also differed significantly by age; those younger than 75 had a 79% reduction in mortality risk, compared with 32% in those age 75 and older.
“This is even after adjusting for factors such heart disease, respiratory conditions, smoking, and other functional limitations,” said Dr. Joundi.
The study was published online Aug. 11 in the journal Neurology.
For this analysis, the researchers used data on a cohort of people across Canada (excluding the province of Quebec) over 3-9 years. The 895 patients with prior stroke averaged 72 years of age, while the 97,805 in the control group had an average age of 63.
Weekly physical activity averages were evaluated using the self-reporting Canadian Community Health Survey, which was linked with administrative databases to evaluate the association of physical activity with long-term risk for mortality among stroke survivors, compared with controls.
Physical activity was measured in metabolic equivalents (METs); meeting minimum physical activity guidelines was defined as 10 MET-hours/week.
During the study period, more stroke patients than controls died (24.7% vs. 5.7%). However, those who met the physical activity guideline recommendations of 10 MET-hours/week had a lower mortality, both in the stroke survivor group (14.6% vs. 33.2%; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% confidence interval, 0.29-0.73) and among control participants (3.6% vs. 7.9%; aHR 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.76).
The largest absolute and relative reduction in mortality was among stroke respondents younger than 75 (10.5% vs. 29%; aHR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.10-0.43), the researchers note.
There was a significant interaction with age for the stroke patients but not the control group.
“The greatest reduction in mortality was seen between 0 and 10 METs per week … so the main point is that something is better than nothing,” said Dr. Joundi.
Exercise guidelines for the future
Although current guidelines recommend physical activity in stroke survivors, investigators noted that these are largely based on studies in the general population. Therefore, the aim of this research was to get a better understanding of the role of physical activity in the health of stroke survivors in the community, which could ultimately be used to design improved public health campaigns and physical activity interventions.
Given that this is a large study of stroke survivors in the community, Dr. Joundi hopes the results will influence future activity guidelines for those who have suffered a stroke.
“We found a log-linear relationship between physical activity and mortality such that 10 MET-hours/week was associated with large reductions in mortality with most benefit achieved by 20 MET-hours/week,” the authors concluded. “These thresholds could be considered for use in future guidelines for stroke.”
Clinical trials are underway to provide evidence for the implementation of exercise programs after stroke, they add, and offering physical activity programs to stroke survivors in the community “is an increasing priority in the U.S., Canada, and Europe.”
“People are at higher risk of death early on after a stroke but also months and years later, so if we can identify a relatively low-cost and easy intervention like physical activity to improve health and reduce the risk of death for stroke survivors it would be important,” Dr. Joundi said.
Key barriers
Paul George, MD, PhD, a stroke and vascular neurologist at Stanford (Calif.) University, said findings such as these further strengthen the argument that physical exercise is important after stroke.
“Because the study looked specifically at stroke patients, it can provide further guidance on physical activity recommendations that we provide to our patients following stroke,” said Dr. George, who was not associated with the study.
Going forward, he said, more research is needed to identify specifically what is preventing stroke patients from exercising more. What is required, he said, is “future research to determine the key barriers to physical activity following stroke and methods to reduce these will also be important to increasing physical activity in stroke survivors.”
Dr. Joundi said determining how to tailor exercise recommendations to meet the wide range of capabilities of stroke survivors will be another key factor.
“Stroke survivors may have some disabilities, so we need to be able to engage them at an [exercise] level that’s possible for them,” he said.
The study did not include stroke survivors living in long-term care homes.
The study had no targeted funding. Coauthor Eric E. Smith, MD, MPH, reports royalties from UpToDate, and consulting fees from Alnylam, Biogen, and Javelin. Dr. Joundi and the other coauthors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, with a greater than 50% reduction in risk.
Lead study author Raed A. Joundi, MD, DPhil, of the University of Calgary (Alta.), said he expected results to show exercise was beneficial, but was surprised by the magnitude of the association between physical activity and lower mortality risk.
The impact of physical activity also differed significantly by age; those younger than 75 had a 79% reduction in mortality risk, compared with 32% in those age 75 and older.
“This is even after adjusting for factors such heart disease, respiratory conditions, smoking, and other functional limitations,” said Dr. Joundi.
The study was published online Aug. 11 in the journal Neurology.
For this analysis, the researchers used data on a cohort of people across Canada (excluding the province of Quebec) over 3-9 years. The 895 patients with prior stroke averaged 72 years of age, while the 97,805 in the control group had an average age of 63.
Weekly physical activity averages were evaluated using the self-reporting Canadian Community Health Survey, which was linked with administrative databases to evaluate the association of physical activity with long-term risk for mortality among stroke survivors, compared with controls.
Physical activity was measured in metabolic equivalents (METs); meeting minimum physical activity guidelines was defined as 10 MET-hours/week.
During the study period, more stroke patients than controls died (24.7% vs. 5.7%). However, those who met the physical activity guideline recommendations of 10 MET-hours/week had a lower mortality, both in the stroke survivor group (14.6% vs. 33.2%; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% confidence interval, 0.29-0.73) and among control participants (3.6% vs. 7.9%; aHR 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.76).
The largest absolute and relative reduction in mortality was among stroke respondents younger than 75 (10.5% vs. 29%; aHR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.10-0.43), the researchers note.
There was a significant interaction with age for the stroke patients but not the control group.
“The greatest reduction in mortality was seen between 0 and 10 METs per week … so the main point is that something is better than nothing,” said Dr. Joundi.
Exercise guidelines for the future
Although current guidelines recommend physical activity in stroke survivors, investigators noted that these are largely based on studies in the general population. Therefore, the aim of this research was to get a better understanding of the role of physical activity in the health of stroke survivors in the community, which could ultimately be used to design improved public health campaigns and physical activity interventions.
Given that this is a large study of stroke survivors in the community, Dr. Joundi hopes the results will influence future activity guidelines for those who have suffered a stroke.
“We found a log-linear relationship between physical activity and mortality such that 10 MET-hours/week was associated with large reductions in mortality with most benefit achieved by 20 MET-hours/week,” the authors concluded. “These thresholds could be considered for use in future guidelines for stroke.”
Clinical trials are underway to provide evidence for the implementation of exercise programs after stroke, they add, and offering physical activity programs to stroke survivors in the community “is an increasing priority in the U.S., Canada, and Europe.”
“People are at higher risk of death early on after a stroke but also months and years later, so if we can identify a relatively low-cost and easy intervention like physical activity to improve health and reduce the risk of death for stroke survivors it would be important,” Dr. Joundi said.
Key barriers
Paul George, MD, PhD, a stroke and vascular neurologist at Stanford (Calif.) University, said findings such as these further strengthen the argument that physical exercise is important after stroke.
“Because the study looked specifically at stroke patients, it can provide further guidance on physical activity recommendations that we provide to our patients following stroke,” said Dr. George, who was not associated with the study.
Going forward, he said, more research is needed to identify specifically what is preventing stroke patients from exercising more. What is required, he said, is “future research to determine the key barriers to physical activity following stroke and methods to reduce these will also be important to increasing physical activity in stroke survivors.”
Dr. Joundi said determining how to tailor exercise recommendations to meet the wide range of capabilities of stroke survivors will be another key factor.
“Stroke survivors may have some disabilities, so we need to be able to engage them at an [exercise] level that’s possible for them,” he said.
The study did not include stroke survivors living in long-term care homes.
The study had no targeted funding. Coauthor Eric E. Smith, MD, MPH, reports royalties from UpToDate, and consulting fees from Alnylam, Biogen, and Javelin. Dr. Joundi and the other coauthors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, with a greater than 50% reduction in risk.
Lead study author Raed A. Joundi, MD, DPhil, of the University of Calgary (Alta.), said he expected results to show exercise was beneficial, but was surprised by the magnitude of the association between physical activity and lower mortality risk.
The impact of physical activity also differed significantly by age; those younger than 75 had a 79% reduction in mortality risk, compared with 32% in those age 75 and older.
“This is even after adjusting for factors such heart disease, respiratory conditions, smoking, and other functional limitations,” said Dr. Joundi.
The study was published online Aug. 11 in the journal Neurology.
For this analysis, the researchers used data on a cohort of people across Canada (excluding the province of Quebec) over 3-9 years. The 895 patients with prior stroke averaged 72 years of age, while the 97,805 in the control group had an average age of 63.
Weekly physical activity averages were evaluated using the self-reporting Canadian Community Health Survey, which was linked with administrative databases to evaluate the association of physical activity with long-term risk for mortality among stroke survivors, compared with controls.
Physical activity was measured in metabolic equivalents (METs); meeting minimum physical activity guidelines was defined as 10 MET-hours/week.
During the study period, more stroke patients than controls died (24.7% vs. 5.7%). However, those who met the physical activity guideline recommendations of 10 MET-hours/week had a lower mortality, both in the stroke survivor group (14.6% vs. 33.2%; adjusted hazard ratio, 0.46; 95% confidence interval, 0.29-0.73) and among control participants (3.6% vs. 7.9%; aHR 0.69; 95% CI, 0.62-0.76).
The largest absolute and relative reduction in mortality was among stroke respondents younger than 75 (10.5% vs. 29%; aHR, 0.21; 95% CI, 0.10-0.43), the researchers note.
There was a significant interaction with age for the stroke patients but not the control group.
“The greatest reduction in mortality was seen between 0 and 10 METs per week … so the main point is that something is better than nothing,” said Dr. Joundi.
Exercise guidelines for the future
Although current guidelines recommend physical activity in stroke survivors, investigators noted that these are largely based on studies in the general population. Therefore, the aim of this research was to get a better understanding of the role of physical activity in the health of stroke survivors in the community, which could ultimately be used to design improved public health campaigns and physical activity interventions.
Given that this is a large study of stroke survivors in the community, Dr. Joundi hopes the results will influence future activity guidelines for those who have suffered a stroke.
“We found a log-linear relationship between physical activity and mortality such that 10 MET-hours/week was associated with large reductions in mortality with most benefit achieved by 20 MET-hours/week,” the authors concluded. “These thresholds could be considered for use in future guidelines for stroke.”
Clinical trials are underway to provide evidence for the implementation of exercise programs after stroke, they add, and offering physical activity programs to stroke survivors in the community “is an increasing priority in the U.S., Canada, and Europe.”
“People are at higher risk of death early on after a stroke but also months and years later, so if we can identify a relatively low-cost and easy intervention like physical activity to improve health and reduce the risk of death for stroke survivors it would be important,” Dr. Joundi said.
Key barriers
Paul George, MD, PhD, a stroke and vascular neurologist at Stanford (Calif.) University, said findings such as these further strengthen the argument that physical exercise is important after stroke.
“Because the study looked specifically at stroke patients, it can provide further guidance on physical activity recommendations that we provide to our patients following stroke,” said Dr. George, who was not associated with the study.
Going forward, he said, more research is needed to identify specifically what is preventing stroke patients from exercising more. What is required, he said, is “future research to determine the key barriers to physical activity following stroke and methods to reduce these will also be important to increasing physical activity in stroke survivors.”
Dr. Joundi said determining how to tailor exercise recommendations to meet the wide range of capabilities of stroke survivors will be another key factor.
“Stroke survivors may have some disabilities, so we need to be able to engage them at an [exercise] level that’s possible for them,” he said.
The study did not include stroke survivors living in long-term care homes.
The study had no targeted funding. Coauthor Eric E. Smith, MD, MPH, reports royalties from UpToDate, and consulting fees from Alnylam, Biogen, and Javelin. Dr. Joundi and the other coauthors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Flavonoids dietary ‘powerhouses’ for cognitive decline prevention
, new research shows.
Among the different types of flavonoids, flavones (found in some spices and yellow or orange fruits and vegetables) and anthocyanins (found in blueberries, blackberries, and cherries) seem to have most protective effect, the researchers report.
“There is mounting evidence suggesting flavonoids are powerhouses when it comes to preventing your thinking skills from declining as you get older,” study investigator Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, Harvard University, Boston, said in a statement.
“Our results are exciting because they show that making simple changes to your diet could help prevent cognitive decline,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was published online July 28 in the journal Neurology.
Antioxidant punch
Flavonoids, naturally occurring phytochemicals found in plants, are strong antioxidants. Considering the likely role of oxidative stress in age-related cognitive decline, flavonoids have been proposed as a potentially important preventive.
For the study, Dr. Willett and colleagues prospectively examined associations between long-term dietary flavonoids (flavonols, flavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanins, polymeric flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins) and subjective cognitive decline in 49,493 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984-2006) and 27,842 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2002).
Those in the highest quintile of flavonoid consumption consumed about 600 mg daily on average while those in the lowest quintile got only about 150 mg daily.
After adjusting for age, total energy intake, major nondietary factors, and specific dietary factors, a higher intake of total flavonoids was associated with lower likelihood of self-reported subjective cognitive decline during follow up.
Individuals in the highest quintile of daily consumption had about a 20% lower risk of subjective cognitive decline relative to peers in the lowest quintile (pooled multivariable-adjusted odds ratio: 0.81; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.89).
The strongest protective associations were found for flavones (OR, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.68), flavanones (OR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.58-0.68), and anthocyanins (OR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.72-0.84) (P trend < .0001 for all groups).
“The people in our study who did the best over time ate an average of at least half a serving per day of foods like orange juice, oranges, peppers, celery, grapefruits, grapefruit juice, apples, and pears,” Dr. Willett said.
“While it is possible other phytochemicals are at work here, a colorful diet rich in flavonoids – and specifically flavones and anthocyanins – seems to be a good bet for promoting long-term brain health,” he added.
A limitation of the study is that participants reported on their diets and may not recall perfectly what they ate or how much.
Healthy diet best bet for brain health
Reached for comment, Christopher Weber, PhD, director of global science initiatives for the Alzheimer’s Association, said this study “adds to our understanding of which elements of a healthy diet may be important in reducing dementia risk; flavonols may be one of those elements.”
“However, at this point, people should not put too much stock in specific nutrients – including subsets of flavonols – for reducing dementia risk until more research is done. Rather, they should focus on eating an overall healthy diet,” he said.
“It would be wonderful if a particular food or supplement could delay or prevent Alzheimer’s disease, but we do not have scientific evidence to support such claims. Randomized controlled clinical trials are necessary to evaluate whether any food or supplement has a scientifically proven beneficial effect,” Dr. Weber added.
For now, the Alzheimer’s Association “encourages everyone to eat a healthy and balanced diet as a way to help reduce the risk of cognitive decline,” Dr. Weber said.
“With more than 6 million Americans living with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementia today, there is a pressing need to test the effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle regimen to reduce risk of cognitive decline in a large and diverse population,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association has launched a 2-year clinical trial, called the U.S. Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER), to do just that.
“While we research that definitive lifestyle ‘recipe,’ there are things we can do today that may decrease our risk of cognitive decline as we age. Eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and staying cognitively engaged are just a few,” Dr. Weber added.
Also weighing in, Taylor Wallace, PhD, adjunct professor, department of nutrition and food studies, George Mason University, Fairfax, Va., said the study results are not surprising.
“Scientific data on the ability of flavonoids to prevent age-related chronic diseases, including cognitive decline, has accumulated immensely over the last decade. This epidemiological study reinforces findings from smaller shorter-duration clinical trials and mechanistic studies,” said Dr. Wallace, who was not involved in the study.
“Flavonoids show great potential in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. They are also vasodilators that help improve blood flow, which is important for the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems,” he noted.
“Typically, foods rich in flavonoids are also nutrient-dense in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber (eg, fruits and vegetables). Anthocyanins in blueberries have long been known to prevent cognitive decline with age,” Dr. Wallace said.
Dr. Wallace was part of a 14-member panel of nutrition scientists who recently reviewed available evidence around fruit and vegetable intake and health.
“Our findings are consistent with this study in regard to cognitive decline and other disease states. Cruciferous vegetables, dark-green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, and dark-colored berries seem to have superior effects on health promotion and disease prevention in general,” said Dr. Wallace.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Weber has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wallace is principal and chief executive officer of the Think Healthy Group; editor of the Journal of Dietary Supplements; and deputy editor-in-chief of the Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Among the different types of flavonoids, flavones (found in some spices and yellow or orange fruits and vegetables) and anthocyanins (found in blueberries, blackberries, and cherries) seem to have most protective effect, the researchers report.
“There is mounting evidence suggesting flavonoids are powerhouses when it comes to preventing your thinking skills from declining as you get older,” study investigator Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, Harvard University, Boston, said in a statement.
“Our results are exciting because they show that making simple changes to your diet could help prevent cognitive decline,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was published online July 28 in the journal Neurology.
Antioxidant punch
Flavonoids, naturally occurring phytochemicals found in plants, are strong antioxidants. Considering the likely role of oxidative stress in age-related cognitive decline, flavonoids have been proposed as a potentially important preventive.
For the study, Dr. Willett and colleagues prospectively examined associations between long-term dietary flavonoids (flavonols, flavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanins, polymeric flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins) and subjective cognitive decline in 49,493 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984-2006) and 27,842 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2002).
Those in the highest quintile of flavonoid consumption consumed about 600 mg daily on average while those in the lowest quintile got only about 150 mg daily.
After adjusting for age, total energy intake, major nondietary factors, and specific dietary factors, a higher intake of total flavonoids was associated with lower likelihood of self-reported subjective cognitive decline during follow up.
Individuals in the highest quintile of daily consumption had about a 20% lower risk of subjective cognitive decline relative to peers in the lowest quintile (pooled multivariable-adjusted odds ratio: 0.81; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.89).
The strongest protective associations were found for flavones (OR, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.68), flavanones (OR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.58-0.68), and anthocyanins (OR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.72-0.84) (P trend < .0001 for all groups).
“The people in our study who did the best over time ate an average of at least half a serving per day of foods like orange juice, oranges, peppers, celery, grapefruits, grapefruit juice, apples, and pears,” Dr. Willett said.
“While it is possible other phytochemicals are at work here, a colorful diet rich in flavonoids – and specifically flavones and anthocyanins – seems to be a good bet for promoting long-term brain health,” he added.
A limitation of the study is that participants reported on their diets and may not recall perfectly what they ate or how much.
Healthy diet best bet for brain health
Reached for comment, Christopher Weber, PhD, director of global science initiatives for the Alzheimer’s Association, said this study “adds to our understanding of which elements of a healthy diet may be important in reducing dementia risk; flavonols may be one of those elements.”
“However, at this point, people should not put too much stock in specific nutrients – including subsets of flavonols – for reducing dementia risk until more research is done. Rather, they should focus on eating an overall healthy diet,” he said.
“It would be wonderful if a particular food or supplement could delay or prevent Alzheimer’s disease, but we do not have scientific evidence to support such claims. Randomized controlled clinical trials are necessary to evaluate whether any food or supplement has a scientifically proven beneficial effect,” Dr. Weber added.
For now, the Alzheimer’s Association “encourages everyone to eat a healthy and balanced diet as a way to help reduce the risk of cognitive decline,” Dr. Weber said.
“With more than 6 million Americans living with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementia today, there is a pressing need to test the effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle regimen to reduce risk of cognitive decline in a large and diverse population,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association has launched a 2-year clinical trial, called the U.S. Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER), to do just that.
“While we research that definitive lifestyle ‘recipe,’ there are things we can do today that may decrease our risk of cognitive decline as we age. Eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and staying cognitively engaged are just a few,” Dr. Weber added.
Also weighing in, Taylor Wallace, PhD, adjunct professor, department of nutrition and food studies, George Mason University, Fairfax, Va., said the study results are not surprising.
“Scientific data on the ability of flavonoids to prevent age-related chronic diseases, including cognitive decline, has accumulated immensely over the last decade. This epidemiological study reinforces findings from smaller shorter-duration clinical trials and mechanistic studies,” said Dr. Wallace, who was not involved in the study.
“Flavonoids show great potential in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. They are also vasodilators that help improve blood flow, which is important for the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems,” he noted.
“Typically, foods rich in flavonoids are also nutrient-dense in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber (eg, fruits and vegetables). Anthocyanins in blueberries have long been known to prevent cognitive decline with age,” Dr. Wallace said.
Dr. Wallace was part of a 14-member panel of nutrition scientists who recently reviewed available evidence around fruit and vegetable intake and health.
“Our findings are consistent with this study in regard to cognitive decline and other disease states. Cruciferous vegetables, dark-green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, and dark-colored berries seem to have superior effects on health promotion and disease prevention in general,” said Dr. Wallace.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Weber has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wallace is principal and chief executive officer of the Think Healthy Group; editor of the Journal of Dietary Supplements; and deputy editor-in-chief of the Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research shows.
Among the different types of flavonoids, flavones (found in some spices and yellow or orange fruits and vegetables) and anthocyanins (found in blueberries, blackberries, and cherries) seem to have most protective effect, the researchers report.
“There is mounting evidence suggesting flavonoids are powerhouses when it comes to preventing your thinking skills from declining as you get older,” study investigator Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, Harvard University, Boston, said in a statement.
“Our results are exciting because they show that making simple changes to your diet could help prevent cognitive decline,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was published online July 28 in the journal Neurology.
Antioxidant punch
Flavonoids, naturally occurring phytochemicals found in plants, are strong antioxidants. Considering the likely role of oxidative stress in age-related cognitive decline, flavonoids have been proposed as a potentially important preventive.
For the study, Dr. Willett and colleagues prospectively examined associations between long-term dietary flavonoids (flavonols, flavones, flavanones, flavan-3-ols, anthocyanins, polymeric flavonoids, and proanthocyanidins) and subjective cognitive decline in 49,493 women from the Nurses’ Health Study (1984-2006) and 27,842 men from the Health Professionals Follow-up Study (1986-2002).
Those in the highest quintile of flavonoid consumption consumed about 600 mg daily on average while those in the lowest quintile got only about 150 mg daily.
After adjusting for age, total energy intake, major nondietary factors, and specific dietary factors, a higher intake of total flavonoids was associated with lower likelihood of self-reported subjective cognitive decline during follow up.
Individuals in the highest quintile of daily consumption had about a 20% lower risk of subjective cognitive decline relative to peers in the lowest quintile (pooled multivariable-adjusted odds ratio: 0.81; 95% confidence interval, 0.76-0.89).
The strongest protective associations were found for flavones (OR, 0.62; 95% confidence interval, 0.57-0.68), flavanones (OR, 0.64; 95% CI, 0.58-0.68), and anthocyanins (OR, 0.76; 95% CI, 0.72-0.84) (P trend < .0001 for all groups).
“The people in our study who did the best over time ate an average of at least half a serving per day of foods like orange juice, oranges, peppers, celery, grapefruits, grapefruit juice, apples, and pears,” Dr. Willett said.
“While it is possible other phytochemicals are at work here, a colorful diet rich in flavonoids – and specifically flavones and anthocyanins – seems to be a good bet for promoting long-term brain health,” he added.
A limitation of the study is that participants reported on their diets and may not recall perfectly what they ate or how much.
Healthy diet best bet for brain health
Reached for comment, Christopher Weber, PhD, director of global science initiatives for the Alzheimer’s Association, said this study “adds to our understanding of which elements of a healthy diet may be important in reducing dementia risk; flavonols may be one of those elements.”
“However, at this point, people should not put too much stock in specific nutrients – including subsets of flavonols – for reducing dementia risk until more research is done. Rather, they should focus on eating an overall healthy diet,” he said.
“It would be wonderful if a particular food or supplement could delay or prevent Alzheimer’s disease, but we do not have scientific evidence to support such claims. Randomized controlled clinical trials are necessary to evaluate whether any food or supplement has a scientifically proven beneficial effect,” Dr. Weber added.
For now, the Alzheimer’s Association “encourages everyone to eat a healthy and balanced diet as a way to help reduce the risk of cognitive decline,” Dr. Weber said.
“With more than 6 million Americans living with Alzheimer’s disease and other dementia today, there is a pressing need to test the effectiveness of a healthy lifestyle regimen to reduce risk of cognitive decline in a large and diverse population,” he added.
The Alzheimer’s Association has launched a 2-year clinical trial, called the U.S. Study to Protect Brain Health Through Lifestyle Intervention to Reduce Risk (U.S. POINTER), to do just that.
“While we research that definitive lifestyle ‘recipe,’ there are things we can do today that may decrease our risk of cognitive decline as we age. Eating a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and staying cognitively engaged are just a few,” Dr. Weber added.
Also weighing in, Taylor Wallace, PhD, adjunct professor, department of nutrition and food studies, George Mason University, Fairfax, Va., said the study results are not surprising.
“Scientific data on the ability of flavonoids to prevent age-related chronic diseases, including cognitive decline, has accumulated immensely over the last decade. This epidemiological study reinforces findings from smaller shorter-duration clinical trials and mechanistic studies,” said Dr. Wallace, who was not involved in the study.
“Flavonoids show great potential in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in the body. They are also vasodilators that help improve blood flow, which is important for the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular systems,” he noted.
“Typically, foods rich in flavonoids are also nutrient-dense in vitamins, minerals, and dietary fiber (eg, fruits and vegetables). Anthocyanins in blueberries have long been known to prevent cognitive decline with age,” Dr. Wallace said.
Dr. Wallace was part of a 14-member panel of nutrition scientists who recently reviewed available evidence around fruit and vegetable intake and health.
“Our findings are consistent with this study in regard to cognitive decline and other disease states. Cruciferous vegetables, dark-green leafy vegetables, citrus fruits, and dark-colored berries seem to have superior effects on health promotion and disease prevention in general,” said Dr. Wallace.
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Weber has no relevant disclosures. Dr. Wallace is principal and chief executive officer of the Think Healthy Group; editor of the Journal of Dietary Supplements; and deputy editor-in-chief of the Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Short-term approach is best for seizure prevention after intracerebral hemorrhage
(sICH), new research shows.
Investigators created a model that simulated common clinical scenarios to compare four antiseizure drug strategies – conservative, moderate, aggressive, and risk-guided. They used the 2HELPS2B score as a risk stratification tool to guide clinical decisions.
The investigators found that the short-term, early-seizure prophylaxis strategies “dominated” long-term therapy under most clinical scenarios, underscoring the importance of early discontinuation of antiseizure drug therapy.
“The main message here was that strategies that involved long-term antiseizure drug prescription (moderate and aggressive) fail to provide better outcomes in most clinical scenarios, when compared with strategies using short-term prophylaxis (conservative and risk-guided),” senior investigator Lidia M.V.R. Moura, MD, MPH, assistant professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 26 in JAMA Neurology.
Common complication
“Acute asymptomatic seizures [early seizures ≤7 days after stroke] are a common complication of sICH,” the authors noted.
Potential safety concerns have prompted recommendations against the use of antiseizure medications for primary prophylaxis. However, approximately 40% of U.S. patients with sICH do receive prophylactic levetiracetam before seizure development. For these patients, the duration of prophylaxis varies widely.
“Because seizure risk is a key determinant of which patient groups might benefit most from different prophylaxis strategies, validated tools for predicting early ... and late ... seizure risks could aid physicians in treatment decisions. However, no clinical trials or prospective studies have evaluated the net benefit of various strategies after sICH,” the investigators noted.
“Our patients who were survivors of an intracerebral hemorrhage motivated us to conduct the study,” said Dr. Moura, who is also director of the MGH NeuroValue Laboratory. “Some would come to the clinic with a long list of medications; some of them were taking antiseizure drugs for many years, but they never had a documented seizure.” These patients did not know why they had been taking an antiseizure drug for so long.
“In these conversations, we noted so much variability in indications and variability in patient access to specialty care to make treatment decisions. We noted that the evidence behind our current guidelines on seizure management was limited,” she added.
Dr. Moura and colleagues were “committed to improve outcome for people with neurological conditions by leveraging research methods that can help guide providers and systems, especially when data from clinical trials is lacking,” so they “decided to compare different strategies head to head using available data and generate evidence that could be used in situations with many trade-offs in risks and benefits.”
To investigate, the researchers used a simulation model and decision analysis to compare four treatment strategies on the basis of type of therapy (primary vs. secondary prophylaxis), timing of event (early vs. late seizures), and duration of therapy (1-week [short-term] versus indefinite [long-term] therapy).
These four strategies were as follows:
- Conservative: short-term (7-day) secondary early-seizure prophylaxis with long-term therapy after late seizure
- Moderate: long-term secondary early-seizure prophylaxis or late-seizure therapy
- Aggressive: long-term primary prophylaxis
- Risk-guided: short-term secondary early-seizure prophylaxis among low-risk patients (2HELPS2b score, 0), short-term primary prophylaxis among patients at higher risk (2HELPS2B score ≥1), and long-term secondary therapy for late seizure
The decision tree’s outcome measure was the number of expected quality-adjusted life-years.
Primary prophylaxis was defined as “treatment initiated immediately on hospital admission.” Secondary prophylaxis was defined as “treatment started after a seizure” and was subdivided into secondary early-seizure prophylaxis, defined as treatment started after a seizure occurring in the first 7 days after the stroke, or secondary late-seizure therapy, defined as treatment started or restarted after a seizure occurring after the first poststroke week.
Incorporate early-risk stratification tool
The researchers created four common clinical scenarios and then applied the decision-making model to each. They found that the preferred strategies differed, depending on the particular scenario.
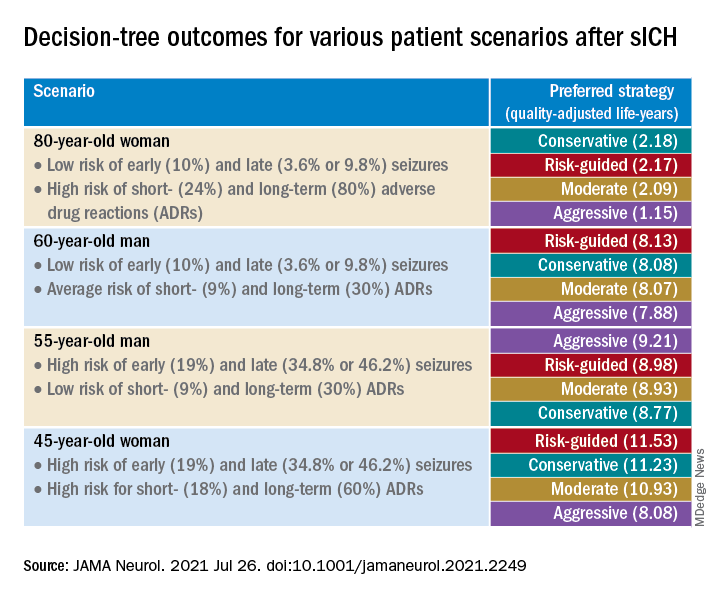
Sensitivity analyses revealed that short-term strategies, including the conservative and risk-guided approaches, were preferable in most cases, with the risk-guided strategy performing comparably or even better than alternative strategies in most cases.
“Our findings suggest that a strategy that incorporates an early-seizure risk stratification tool [2HELPS2B] is favored over alternative strategies in most settings,” Dr. Moura commented.
“Current services with rapidly available EEG may consider using a 1-hour screening with EEG upon admission for all patients presenting with sICH to risk-stratify those patients, using the 2HELPS2B tool,” she continued. “If EEG is unavailable for early-seizure risk stratification, the conservative strategy seems most reasonable.”
‘Potential fallacies’
Commenting on the study, José Biller, MD, professor and chairman, department of neurology, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Ill., called it a “well-written and intriguing contribution [to the field], with potential fallacies.”
The bottom line, he said, is that only a randomized, long-term, prospective, multicenter, high-quality study with larger cohorts can prove or disprove the investigators’ assumption.
The authors acknowledged that a limitation of the study was the use of published literature to obtain data to estimate model parameters and that they did not account for other possible factors that might modify some parameter estimates.
Nevertheless, Dr. Moura said the findings have important practical implications because they “highlight the importance of discontinuing antiseizure medications that were started during a hospitalization for sICH in patients that only had an early seizure.”
It is “of great importance for all providers to reassess the indication of antiseizure medications. Those drugs are not free of risks and can impact the patient’s health and quality of life,” she added.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Moura reported receiving funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the NIH, and the Epilepsy Foundation of America (Epilepsy Learning Healthcare System) as the director of the data coordinating center. Dr. Biller is the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases and a section editor of UpToDate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(sICH), new research shows.
Investigators created a model that simulated common clinical scenarios to compare four antiseizure drug strategies – conservative, moderate, aggressive, and risk-guided. They used the 2HELPS2B score as a risk stratification tool to guide clinical decisions.
The investigators found that the short-term, early-seizure prophylaxis strategies “dominated” long-term therapy under most clinical scenarios, underscoring the importance of early discontinuation of antiseizure drug therapy.
“The main message here was that strategies that involved long-term antiseizure drug prescription (moderate and aggressive) fail to provide better outcomes in most clinical scenarios, when compared with strategies using short-term prophylaxis (conservative and risk-guided),” senior investigator Lidia M.V.R. Moura, MD, MPH, assistant professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 26 in JAMA Neurology.
Common complication
“Acute asymptomatic seizures [early seizures ≤7 days after stroke] are a common complication of sICH,” the authors noted.
Potential safety concerns have prompted recommendations against the use of antiseizure medications for primary prophylaxis. However, approximately 40% of U.S. patients with sICH do receive prophylactic levetiracetam before seizure development. For these patients, the duration of prophylaxis varies widely.
“Because seizure risk is a key determinant of which patient groups might benefit most from different prophylaxis strategies, validated tools for predicting early ... and late ... seizure risks could aid physicians in treatment decisions. However, no clinical trials or prospective studies have evaluated the net benefit of various strategies after sICH,” the investigators noted.
“Our patients who were survivors of an intracerebral hemorrhage motivated us to conduct the study,” said Dr. Moura, who is also director of the MGH NeuroValue Laboratory. “Some would come to the clinic with a long list of medications; some of them were taking antiseizure drugs for many years, but they never had a documented seizure.” These patients did not know why they had been taking an antiseizure drug for so long.
“In these conversations, we noted so much variability in indications and variability in patient access to specialty care to make treatment decisions. We noted that the evidence behind our current guidelines on seizure management was limited,” she added.
Dr. Moura and colleagues were “committed to improve outcome for people with neurological conditions by leveraging research methods that can help guide providers and systems, especially when data from clinical trials is lacking,” so they “decided to compare different strategies head to head using available data and generate evidence that could be used in situations with many trade-offs in risks and benefits.”
To investigate, the researchers used a simulation model and decision analysis to compare four treatment strategies on the basis of type of therapy (primary vs. secondary prophylaxis), timing of event (early vs. late seizures), and duration of therapy (1-week [short-term] versus indefinite [long-term] therapy).
These four strategies were as follows:
- Conservative: short-term (7-day) secondary early-seizure prophylaxis with long-term therapy after late seizure
- Moderate: long-term secondary early-seizure prophylaxis or late-seizure therapy
- Aggressive: long-term primary prophylaxis
- Risk-guided: short-term secondary early-seizure prophylaxis among low-risk patients (2HELPS2b score, 0), short-term primary prophylaxis among patients at higher risk (2HELPS2B score ≥1), and long-term secondary therapy for late seizure
The decision tree’s outcome measure was the number of expected quality-adjusted life-years.
Primary prophylaxis was defined as “treatment initiated immediately on hospital admission.” Secondary prophylaxis was defined as “treatment started after a seizure” and was subdivided into secondary early-seizure prophylaxis, defined as treatment started after a seizure occurring in the first 7 days after the stroke, or secondary late-seizure therapy, defined as treatment started or restarted after a seizure occurring after the first poststroke week.
Incorporate early-risk stratification tool
The researchers created four common clinical scenarios and then applied the decision-making model to each. They found that the preferred strategies differed, depending on the particular scenario.

Sensitivity analyses revealed that short-term strategies, including the conservative and risk-guided approaches, were preferable in most cases, with the risk-guided strategy performing comparably or even better than alternative strategies in most cases.
“Our findings suggest that a strategy that incorporates an early-seizure risk stratification tool [2HELPS2B] is favored over alternative strategies in most settings,” Dr. Moura commented.
“Current services with rapidly available EEG may consider using a 1-hour screening with EEG upon admission for all patients presenting with sICH to risk-stratify those patients, using the 2HELPS2B tool,” she continued. “If EEG is unavailable for early-seizure risk stratification, the conservative strategy seems most reasonable.”
‘Potential fallacies’
Commenting on the study, José Biller, MD, professor and chairman, department of neurology, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Ill., called it a “well-written and intriguing contribution [to the field], with potential fallacies.”
The bottom line, he said, is that only a randomized, long-term, prospective, multicenter, high-quality study with larger cohorts can prove or disprove the investigators’ assumption.
The authors acknowledged that a limitation of the study was the use of published literature to obtain data to estimate model parameters and that they did not account for other possible factors that might modify some parameter estimates.
Nevertheless, Dr. Moura said the findings have important practical implications because they “highlight the importance of discontinuing antiseizure medications that were started during a hospitalization for sICH in patients that only had an early seizure.”
It is “of great importance for all providers to reassess the indication of antiseizure medications. Those drugs are not free of risks and can impact the patient’s health and quality of life,” she added.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Moura reported receiving funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the NIH, and the Epilepsy Foundation of America (Epilepsy Learning Healthcare System) as the director of the data coordinating center. Dr. Biller is the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases and a section editor of UpToDate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
(sICH), new research shows.
Investigators created a model that simulated common clinical scenarios to compare four antiseizure drug strategies – conservative, moderate, aggressive, and risk-guided. They used the 2HELPS2B score as a risk stratification tool to guide clinical decisions.
The investigators found that the short-term, early-seizure prophylaxis strategies “dominated” long-term therapy under most clinical scenarios, underscoring the importance of early discontinuation of antiseizure drug therapy.
“The main message here was that strategies that involved long-term antiseizure drug prescription (moderate and aggressive) fail to provide better outcomes in most clinical scenarios, when compared with strategies using short-term prophylaxis (conservative and risk-guided),” senior investigator Lidia M.V.R. Moura, MD, MPH, assistant professor of neurology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, said in an interview.
The study was published online July 26 in JAMA Neurology.
Common complication
“Acute asymptomatic seizures [early seizures ≤7 days after stroke] are a common complication of sICH,” the authors noted.
Potential safety concerns have prompted recommendations against the use of antiseizure medications for primary prophylaxis. However, approximately 40% of U.S. patients with sICH do receive prophylactic levetiracetam before seizure development. For these patients, the duration of prophylaxis varies widely.
“Because seizure risk is a key determinant of which patient groups might benefit most from different prophylaxis strategies, validated tools for predicting early ... and late ... seizure risks could aid physicians in treatment decisions. However, no clinical trials or prospective studies have evaluated the net benefit of various strategies after sICH,” the investigators noted.
“Our patients who were survivors of an intracerebral hemorrhage motivated us to conduct the study,” said Dr. Moura, who is also director of the MGH NeuroValue Laboratory. “Some would come to the clinic with a long list of medications; some of them were taking antiseizure drugs for many years, but they never had a documented seizure.” These patients did not know why they had been taking an antiseizure drug for so long.
“In these conversations, we noted so much variability in indications and variability in patient access to specialty care to make treatment decisions. We noted that the evidence behind our current guidelines on seizure management was limited,” she added.
Dr. Moura and colleagues were “committed to improve outcome for people with neurological conditions by leveraging research methods that can help guide providers and systems, especially when data from clinical trials is lacking,” so they “decided to compare different strategies head to head using available data and generate evidence that could be used in situations with many trade-offs in risks and benefits.”
To investigate, the researchers used a simulation model and decision analysis to compare four treatment strategies on the basis of type of therapy (primary vs. secondary prophylaxis), timing of event (early vs. late seizures), and duration of therapy (1-week [short-term] versus indefinite [long-term] therapy).
These four strategies were as follows:
- Conservative: short-term (7-day) secondary early-seizure prophylaxis with long-term therapy after late seizure
- Moderate: long-term secondary early-seizure prophylaxis or late-seizure therapy
- Aggressive: long-term primary prophylaxis
- Risk-guided: short-term secondary early-seizure prophylaxis among low-risk patients (2HELPS2b score, 0), short-term primary prophylaxis among patients at higher risk (2HELPS2B score ≥1), and long-term secondary therapy for late seizure
The decision tree’s outcome measure was the number of expected quality-adjusted life-years.
Primary prophylaxis was defined as “treatment initiated immediately on hospital admission.” Secondary prophylaxis was defined as “treatment started after a seizure” and was subdivided into secondary early-seizure prophylaxis, defined as treatment started after a seizure occurring in the first 7 days after the stroke, or secondary late-seizure therapy, defined as treatment started or restarted after a seizure occurring after the first poststroke week.
Incorporate early-risk stratification tool
The researchers created four common clinical scenarios and then applied the decision-making model to each. They found that the preferred strategies differed, depending on the particular scenario.

Sensitivity analyses revealed that short-term strategies, including the conservative and risk-guided approaches, were preferable in most cases, with the risk-guided strategy performing comparably or even better than alternative strategies in most cases.
“Our findings suggest that a strategy that incorporates an early-seizure risk stratification tool [2HELPS2B] is favored over alternative strategies in most settings,” Dr. Moura commented.
“Current services with rapidly available EEG may consider using a 1-hour screening with EEG upon admission for all patients presenting with sICH to risk-stratify those patients, using the 2HELPS2B tool,” she continued. “If EEG is unavailable for early-seizure risk stratification, the conservative strategy seems most reasonable.”
‘Potential fallacies’
Commenting on the study, José Biller, MD, professor and chairman, department of neurology, Loyola University Chicago, Maywood, Ill., called it a “well-written and intriguing contribution [to the field], with potential fallacies.”
The bottom line, he said, is that only a randomized, long-term, prospective, multicenter, high-quality study with larger cohorts can prove or disprove the investigators’ assumption.
The authors acknowledged that a limitation of the study was the use of published literature to obtain data to estimate model parameters and that they did not account for other possible factors that might modify some parameter estimates.
Nevertheless, Dr. Moura said the findings have important practical implications because they “highlight the importance of discontinuing antiseizure medications that were started during a hospitalization for sICH in patients that only had an early seizure.”
It is “of great importance for all providers to reassess the indication of antiseizure medications. Those drugs are not free of risks and can impact the patient’s health and quality of life,” she added.
The study was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Moura reported receiving funding from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the NIH, and the Epilepsy Foundation of America (Epilepsy Learning Healthcare System) as the director of the data coordinating center. Dr. Biller is the editor-in-chief of the Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases and a section editor of UpToDate.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Virtual roller-coaster may explain the ups and downs of migraine
and may explain the mechanisms underlying common symptoms and increased activity in certain brain regions in migraine patients.
In a new study, the prevalence of dizziness was 65% among patients with migraine who underwent a virtual roller-coaster ride versus 30% among those without migraine. In addition, imaging showed greater neuronal activity after the simulation in those with migraine.
“Migraine patients reported more dizziness and motion sickness, as well as longer symptom duration and intensity, in a virtual roller-coaster ride,” even though the videos and timing were identical for both groups, said study investigator Arne May, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Hamburg (Germany).
“We found differences not just in behavioral results but also in specific activations of areas within the cerebellum and the frontal gyrus. Migraine patients process such visual input differently from controls and activate a specific brain network to do so,” he added.
The findings were published online July 21, 2021, in Neurology.
The brain’s response
Nausea, which is among the diagnostic criteria for migraine, is the main symptom of motion sickness. Vestibular symptoms such as dizziness are also components of migraine.
Previous research has examined how the brain processes visual and motion stimuli in migraine, but the reasons patients with migraine are susceptible to motion sickness and dizziness remain unclear.
The researchers used a simulated roller-coaster ride to study the clinical and brain responses to motion among participants with and participants without migraine. They enrolled 20 consecutive patients with migraine who presented to a tertiary headache clinic between January and March 2020 and enrolled 20 healthy participants from a university hospital and the community. The average age of the study population was 30 years, and more than 80% were women.
In response to a questionnaire, participants provided information about demographics and headache features, including onset, frequency, and intensity. They also provided information about their status within the migraine phase and about vestibular symptoms experienced in daily life.
While undergoing functional MRI (fMRI), all participants watched two short videos that provided a first-person perspective of a roller-coaster ride. During the videos, they wore ear buds that conveyed the sound of a car riding over the rails.
The first video included more horizontal perspectives, and the second had more vertical perspectives. Each video was shown three times in random order.
During fMRI, participants reported intensity of nausea and vestibular symptoms using an 11-point Likert scale. After the experiment, they responded to a questionnaire that evaluated intensity and duration of nausea, dizziness, and vertigo experienced during the videos.
Participants also were given the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ), which assessed motion sickness. A 100-point visual analog scale (VAS) was used to rate how realistic the roller-coaster experience had been.
There were no differences in sex or age between the migraine group and the healthy control group. Half of the patients with migraine reported aura. The mean number of migraine attacks within the previous month was 3.7. The mean Migraine Disability Assessment score was 21.5, which indicates severe disability.
Nausea, dizziness often neglected
Baseline prevalence of vestibular symptoms was 75% in the migraine group and 5% in the control group (P < .0001). These symptoms included dizziness (60% and 5%, respectively; P < .0001) and postural symptoms (40% and 0%, respectively; P = .003).
At baseline, vestibular symptoms were more frequent (P = .001), more intense (P < .0001), and were associated with greater disability (P = .001) in patients with migraine, compared with participants without migraine. The patients with migraine were also more susceptible to motion sickness (P = .02) and had higher depression scores (P = .001).
During the roller-coaster simulation, dizziness was more prevalent among patients with migraine than among those without migraine (65% vs. 30%; P = .03). Patients with migraine also reported more motion sickness (SSQ score, 47.3 vs. 24.3; P = .004), longer symptom duration (1:19 minutes vs. 00:27 minutes; P = .03), and symptoms of greater intensity (VAS, 22.0 vs. 9.9; P = .03).
Brain activity also differed between groups. Among patients with migraine, neuronal activity was greater in clusters within the right superior and left inferior occipital gyrus, the left pontine nuclei, and the left cerebellar lobules V and VI.
There was a moderately negative correlation of activation of the inferior occipital gyrus with migraine disability (r = –0.46; P = .04). Activation within the pontine nuclei correlated positively with motion sickness scores (r = 0.32; P = .04).
In addition, among patients with migraine, activity in the cerebellar lobule VIIb and in the left middle frontal gyrus was decreased in comparison with persons without migraine. Also among patients with migraine, there was enhanced connectivity between the pontine nuclei, cerebellar areas V and VI, and the interior and superior occipital gyrus and numerous cortical areas.
Clinicians often neglect to treat dizziness and nausea in patients with migraine, said Dr. May. However, these symptoms are part of migraine, even when attacks are not occurring.
“I have learned that if we can explain such symptoms, they are better accepted,” said Dr. May. “We need more and better basic research because we need to understand before we treat.”
Toward faster, more effective treatment
Commenting on the study, Erik Viirre, MD, PhD, professor in the department of neurosciences, University of California, San Diego, said, “we can be excited and celebrate that these researchers are using these news tools to investigate the operation of the migraine brain.
“That will combine with the new therapies and the genomics to give us a powerful approach to this particular condition,” said Dr. Viirre, who was not involved with the research.
The findings provide significant detail about the interconnections between the various brain regions affected by migraine, he noted. These regions include not just the sensory centers but also areas involved in higher executive function and emotional responses.
By identifying these regions, the findings show “some of the underlying mechanisms of these clinically relevant features,” said Dr. Viirre, who is also director of UCSD’s Arthur C. Clarke Center for Human Imagination.
The investigators set up the motion simulation well and used sound fMRI methodology, he added. However, imaging studies of the brain’s response to motion pose several challenges.
“The biggest challenge in any of these circumstances is that you can’t put an actual fMRI scanner on a roller-coaster,” said Dr. Viirre. “The actual acceleration and gravitational sensations delivered by a roller-coaster and gravity, of course, do not occur when you’re lying still in an MRI scanner.” Nevertheless, the pseudoacceleration produced by a visual stimulus is a reasonable proxy.
The findings also suggest that researchers in the future could examine whether any new therapeutic interventions for migraine modulate the brain functions differently for individuals with migraine than for those without migraine, he noted.
“That’s going to lead us to a faster, more effective, more reliable suite of migraine therapies,” said Dr. Viirre.
The study also reminds clinicians to take a broader approach to patients with migraine, and it underscores the value of strategies such as self-calming techniques, which can reduce the number and intensity of headaches, he said.
“Literally demonstrating these functional differences in the migraine brain is a hugely important message of advocacy for people with migraine,” Dr. Viirre concluded.
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation. Drs. May and Viirre have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and may explain the mechanisms underlying common symptoms and increased activity in certain brain regions in migraine patients.
In a new study, the prevalence of dizziness was 65% among patients with migraine who underwent a virtual roller-coaster ride versus 30% among those without migraine. In addition, imaging showed greater neuronal activity after the simulation in those with migraine.
“Migraine patients reported more dizziness and motion sickness, as well as longer symptom duration and intensity, in a virtual roller-coaster ride,” even though the videos and timing were identical for both groups, said study investigator Arne May, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Hamburg (Germany).
“We found differences not just in behavioral results but also in specific activations of areas within the cerebellum and the frontal gyrus. Migraine patients process such visual input differently from controls and activate a specific brain network to do so,” he added.
The findings were published online July 21, 2021, in Neurology.
The brain’s response
Nausea, which is among the diagnostic criteria for migraine, is the main symptom of motion sickness. Vestibular symptoms such as dizziness are also components of migraine.
Previous research has examined how the brain processes visual and motion stimuli in migraine, but the reasons patients with migraine are susceptible to motion sickness and dizziness remain unclear.
The researchers used a simulated roller-coaster ride to study the clinical and brain responses to motion among participants with and participants without migraine. They enrolled 20 consecutive patients with migraine who presented to a tertiary headache clinic between January and March 2020 and enrolled 20 healthy participants from a university hospital and the community. The average age of the study population was 30 years, and more than 80% were women.
In response to a questionnaire, participants provided information about demographics and headache features, including onset, frequency, and intensity. They also provided information about their status within the migraine phase and about vestibular symptoms experienced in daily life.
While undergoing functional MRI (fMRI), all participants watched two short videos that provided a first-person perspective of a roller-coaster ride. During the videos, they wore ear buds that conveyed the sound of a car riding over the rails.
The first video included more horizontal perspectives, and the second had more vertical perspectives. Each video was shown three times in random order.
During fMRI, participants reported intensity of nausea and vestibular symptoms using an 11-point Likert scale. After the experiment, they responded to a questionnaire that evaluated intensity and duration of nausea, dizziness, and vertigo experienced during the videos.
Participants also were given the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ), which assessed motion sickness. A 100-point visual analog scale (VAS) was used to rate how realistic the roller-coaster experience had been.
There were no differences in sex or age between the migraine group and the healthy control group. Half of the patients with migraine reported aura. The mean number of migraine attacks within the previous month was 3.7. The mean Migraine Disability Assessment score was 21.5, which indicates severe disability.
Nausea, dizziness often neglected
Baseline prevalence of vestibular symptoms was 75% in the migraine group and 5% in the control group (P < .0001). These symptoms included dizziness (60% and 5%, respectively; P < .0001) and postural symptoms (40% and 0%, respectively; P = .003).
At baseline, vestibular symptoms were more frequent (P = .001), more intense (P < .0001), and were associated with greater disability (P = .001) in patients with migraine, compared with participants without migraine. The patients with migraine were also more susceptible to motion sickness (P = .02) and had higher depression scores (P = .001).
During the roller-coaster simulation, dizziness was more prevalent among patients with migraine than among those without migraine (65% vs. 30%; P = .03). Patients with migraine also reported more motion sickness (SSQ score, 47.3 vs. 24.3; P = .004), longer symptom duration (1:19 minutes vs. 00:27 minutes; P = .03), and symptoms of greater intensity (VAS, 22.0 vs. 9.9; P = .03).
Brain activity also differed between groups. Among patients with migraine, neuronal activity was greater in clusters within the right superior and left inferior occipital gyrus, the left pontine nuclei, and the left cerebellar lobules V and VI.
There was a moderately negative correlation of activation of the inferior occipital gyrus with migraine disability (r = –0.46; P = .04). Activation within the pontine nuclei correlated positively with motion sickness scores (r = 0.32; P = .04).
In addition, among patients with migraine, activity in the cerebellar lobule VIIb and in the left middle frontal gyrus was decreased in comparison with persons without migraine. Also among patients with migraine, there was enhanced connectivity between the pontine nuclei, cerebellar areas V and VI, and the interior and superior occipital gyrus and numerous cortical areas.
Clinicians often neglect to treat dizziness and nausea in patients with migraine, said Dr. May. However, these symptoms are part of migraine, even when attacks are not occurring.
“I have learned that if we can explain such symptoms, they are better accepted,” said Dr. May. “We need more and better basic research because we need to understand before we treat.”
Toward faster, more effective treatment
Commenting on the study, Erik Viirre, MD, PhD, professor in the department of neurosciences, University of California, San Diego, said, “we can be excited and celebrate that these researchers are using these news tools to investigate the operation of the migraine brain.
“That will combine with the new therapies and the genomics to give us a powerful approach to this particular condition,” said Dr. Viirre, who was not involved with the research.
The findings provide significant detail about the interconnections between the various brain regions affected by migraine, he noted. These regions include not just the sensory centers but also areas involved in higher executive function and emotional responses.
By identifying these regions, the findings show “some of the underlying mechanisms of these clinically relevant features,” said Dr. Viirre, who is also director of UCSD’s Arthur C. Clarke Center for Human Imagination.
The investigators set up the motion simulation well and used sound fMRI methodology, he added. However, imaging studies of the brain’s response to motion pose several challenges.
“The biggest challenge in any of these circumstances is that you can’t put an actual fMRI scanner on a roller-coaster,” said Dr. Viirre. “The actual acceleration and gravitational sensations delivered by a roller-coaster and gravity, of course, do not occur when you’re lying still in an MRI scanner.” Nevertheless, the pseudoacceleration produced by a visual stimulus is a reasonable proxy.
The findings also suggest that researchers in the future could examine whether any new therapeutic interventions for migraine modulate the brain functions differently for individuals with migraine than for those without migraine, he noted.
“That’s going to lead us to a faster, more effective, more reliable suite of migraine therapies,” said Dr. Viirre.
The study also reminds clinicians to take a broader approach to patients with migraine, and it underscores the value of strategies such as self-calming techniques, which can reduce the number and intensity of headaches, he said.
“Literally demonstrating these functional differences in the migraine brain is a hugely important message of advocacy for people with migraine,” Dr. Viirre concluded.
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation. Drs. May and Viirre have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
and may explain the mechanisms underlying common symptoms and increased activity in certain brain regions in migraine patients.
In a new study, the prevalence of dizziness was 65% among patients with migraine who underwent a virtual roller-coaster ride versus 30% among those without migraine. In addition, imaging showed greater neuronal activity after the simulation in those with migraine.
“Migraine patients reported more dizziness and motion sickness, as well as longer symptom duration and intensity, in a virtual roller-coaster ride,” even though the videos and timing were identical for both groups, said study investigator Arne May, MD, PhD, professor of neurology at the University of Hamburg (Germany).
“We found differences not just in behavioral results but also in specific activations of areas within the cerebellum and the frontal gyrus. Migraine patients process such visual input differently from controls and activate a specific brain network to do so,” he added.
The findings were published online July 21, 2021, in Neurology.
The brain’s response
Nausea, which is among the diagnostic criteria for migraine, is the main symptom of motion sickness. Vestibular symptoms such as dizziness are also components of migraine.
Previous research has examined how the brain processes visual and motion stimuli in migraine, but the reasons patients with migraine are susceptible to motion sickness and dizziness remain unclear.
The researchers used a simulated roller-coaster ride to study the clinical and brain responses to motion among participants with and participants without migraine. They enrolled 20 consecutive patients with migraine who presented to a tertiary headache clinic between January and March 2020 and enrolled 20 healthy participants from a university hospital and the community. The average age of the study population was 30 years, and more than 80% were women.
In response to a questionnaire, participants provided information about demographics and headache features, including onset, frequency, and intensity. They also provided information about their status within the migraine phase and about vestibular symptoms experienced in daily life.
While undergoing functional MRI (fMRI), all participants watched two short videos that provided a first-person perspective of a roller-coaster ride. During the videos, they wore ear buds that conveyed the sound of a car riding over the rails.
The first video included more horizontal perspectives, and the second had more vertical perspectives. Each video was shown three times in random order.
During fMRI, participants reported intensity of nausea and vestibular symptoms using an 11-point Likert scale. After the experiment, they responded to a questionnaire that evaluated intensity and duration of nausea, dizziness, and vertigo experienced during the videos.
Participants also were given the Simulator Sickness Questionnaire (SSQ), which assessed motion sickness. A 100-point visual analog scale (VAS) was used to rate how realistic the roller-coaster experience had been.
There were no differences in sex or age between the migraine group and the healthy control group. Half of the patients with migraine reported aura. The mean number of migraine attacks within the previous month was 3.7. The mean Migraine Disability Assessment score was 21.5, which indicates severe disability.
Nausea, dizziness often neglected
Baseline prevalence of vestibular symptoms was 75% in the migraine group and 5% in the control group (P < .0001). These symptoms included dizziness (60% and 5%, respectively; P < .0001) and postural symptoms (40% and 0%, respectively; P = .003).
At baseline, vestibular symptoms were more frequent (P = .001), more intense (P < .0001), and were associated with greater disability (P = .001) in patients with migraine, compared with participants without migraine. The patients with migraine were also more susceptible to motion sickness (P = .02) and had higher depression scores (P = .001).
During the roller-coaster simulation, dizziness was more prevalent among patients with migraine than among those without migraine (65% vs. 30%; P = .03). Patients with migraine also reported more motion sickness (SSQ score, 47.3 vs. 24.3; P = .004), longer symptom duration (1:19 minutes vs. 00:27 minutes; P = .03), and symptoms of greater intensity (VAS, 22.0 vs. 9.9; P = .03).
Brain activity also differed between groups. Among patients with migraine, neuronal activity was greater in clusters within the right superior and left inferior occipital gyrus, the left pontine nuclei, and the left cerebellar lobules V and VI.
There was a moderately negative correlation of activation of the inferior occipital gyrus with migraine disability (r = –0.46; P = .04). Activation within the pontine nuclei correlated positively with motion sickness scores (r = 0.32; P = .04).
In addition, among patients with migraine, activity in the cerebellar lobule VIIb and in the left middle frontal gyrus was decreased in comparison with persons without migraine. Also among patients with migraine, there was enhanced connectivity between the pontine nuclei, cerebellar areas V and VI, and the interior and superior occipital gyrus and numerous cortical areas.
Clinicians often neglect to treat dizziness and nausea in patients with migraine, said Dr. May. However, these symptoms are part of migraine, even when attacks are not occurring.
“I have learned that if we can explain such symptoms, they are better accepted,” said Dr. May. “We need more and better basic research because we need to understand before we treat.”
Toward faster, more effective treatment
Commenting on the study, Erik Viirre, MD, PhD, professor in the department of neurosciences, University of California, San Diego, said, “we can be excited and celebrate that these researchers are using these news tools to investigate the operation of the migraine brain.
“That will combine with the new therapies and the genomics to give us a powerful approach to this particular condition,” said Dr. Viirre, who was not involved with the research.
The findings provide significant detail about the interconnections between the various brain regions affected by migraine, he noted. These regions include not just the sensory centers but also areas involved in higher executive function and emotional responses.
By identifying these regions, the findings show “some of the underlying mechanisms of these clinically relevant features,” said Dr. Viirre, who is also director of UCSD’s Arthur C. Clarke Center for Human Imagination.
The investigators set up the motion simulation well and used sound fMRI methodology, he added. However, imaging studies of the brain’s response to motion pose several challenges.
“The biggest challenge in any of these circumstances is that you can’t put an actual fMRI scanner on a roller-coaster,” said Dr. Viirre. “The actual acceleration and gravitational sensations delivered by a roller-coaster and gravity, of course, do not occur when you’re lying still in an MRI scanner.” Nevertheless, the pseudoacceleration produced by a visual stimulus is a reasonable proxy.
The findings also suggest that researchers in the future could examine whether any new therapeutic interventions for migraine modulate the brain functions differently for individuals with migraine than for those without migraine, he noted.
“That’s going to lead us to a faster, more effective, more reliable suite of migraine therapies,” said Dr. Viirre.
The study also reminds clinicians to take a broader approach to patients with migraine, and it underscores the value of strategies such as self-calming techniques, which can reduce the number and intensity of headaches, he said.
“Literally demonstrating these functional differences in the migraine brain is a hugely important message of advocacy for people with migraine,” Dr. Viirre concluded.
The study was funded by the German Research Foundation. Drs. May and Viirre have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mobile stroke teams treat patients faster and reduce disability
Having a mobile interventional stroke team (MIST) travel to treat stroke patients soon after stroke onset may improve patient outcomes, according to a new study. A retrospective analysis of a pilot program in New York found that
“The use of a Mobile Interventional Stroke Team (MIST) traveling to Thrombectomy Capable Stroke Centers to perform endovascular thrombectomy has been shown to be significantly faster with improved discharge outcomes,” wrote lead author Jacob Morey, a doctoral Candidate at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York and coauthors in the paper. Prior to this study, “the effect of the MIST model stratified by time of presentation” had yet to be studied.
The findings were published online on Aug. 5 in Stroke.
MIST model versus drip-and-ship
The researchers analyzed 226 patients who underwent endovascular thrombectomy between January 2017 and February 2020 at four hospitals in the Mount Sinai health system using the NYC MIST Trial and a stroke database. At baseline, all patients were functionally independent as assessed by the modified Rankin Scale (mRS, score of 0-2). 106 patients were treated by a MIST team – staffed by a neurointerventionalist, a fellow or physician assistant, and radiologic technologist – that traveled to the patient’s location. A total of 120 patients were transferred to a comprehensive stroke center (CSC) or a hospital with endovascular thrombectomy expertise. The analysis was stratified based on whether the patient presented in the early time window (≤ 6 hours) or late time window (> 6 hours).
Patients treated in the early time window were significantly more likely to be mobile and able to perform daily tasks (mRS ≤ 2) 90 days after the procedure in the MIST group (54%), compared with the transferred group (28%, P < 0.01). Outcomes did not differ significantly between groups in the late time window (35% vs. 41%, P = 0.77).
Similarly, early-time-window patients in the MIST group were more likely to have higher functionality at discharge, compared with transferred patients, based on the on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (median score of 5.0 vs. 12.0, P < 0.01). There was no significant difference between groups treated in the late time window (median score of 5.0 vs. 11.0, P = 0.11).
“Ischemic strokes often progress rapidly and can cause severe damage because brain tissue dies quickly without oxygen, resulting in serious long-term disabilities or death,“ said Johanna Fifi, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine, said in a statement to the American Heart Association. “Assessing and treating stroke patients in the early window means that a greater number of fast-progressing strokes are identified and treated.”
Time is brain
Endovascular thrombectomy is a time-sensitive surgical procedure to remove large blood clots in acute ischemic stroke that has “historically been limited to comprehensive stroke centers,” the authors wrote in their paper. It is considered the standard of care in ischemic strokes, which make up 90% of all strokes. “Less than 50% of Americans have direct access to endovascular thrombectomy, the others must be transferred to a thrombectomy-capable hospital for treatment, often losing over 2 hours of time to treatment,” said Dr. Fifi. “Every minute is precious in treating stroke, and getting to a center that offers thrombectomy is very important. The MIST model would address this by providing faster access to this potentially life-saving, disability-reducing procedure.”
Access to timely endovascular thrombectomy is gradually improving as “more institutions and cities have implemented the [MIST] model.” Dr. Fifi said.
“This study stresses the importance of ‘time is brain,’ especially for patients in the early time window. Although the study is limited by the observational, retrospective design and was performed at a single integrated center, the findings are provocative,” said Louise McCullough, MD, of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston said in a statement to the American Heart Association. “The use of a MIST model highlights the potential benefit of early and urgent treatment for patients with large-vessel stroke. Stroke systems of care need to take advantage of any opportunity to treat patients early, wherever they are.”
The study was partly funded by a Stryker Foundation grant.
Having a mobile interventional stroke team (MIST) travel to treat stroke patients soon after stroke onset may improve patient outcomes, according to a new study. A retrospective analysis of a pilot program in New York found that
“The use of a Mobile Interventional Stroke Team (MIST) traveling to Thrombectomy Capable Stroke Centers to perform endovascular thrombectomy has been shown to be significantly faster with improved discharge outcomes,” wrote lead author Jacob Morey, a doctoral Candidate at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York and coauthors in the paper. Prior to this study, “the effect of the MIST model stratified by time of presentation” had yet to be studied.
The findings were published online on Aug. 5 in Stroke.
MIST model versus drip-and-ship
The researchers analyzed 226 patients who underwent endovascular thrombectomy between January 2017 and February 2020 at four hospitals in the Mount Sinai health system using the NYC MIST Trial and a stroke database. At baseline, all patients were functionally independent as assessed by the modified Rankin Scale (mRS, score of 0-2). 106 patients were treated by a MIST team – staffed by a neurointerventionalist, a fellow or physician assistant, and radiologic technologist – that traveled to the patient’s location. A total of 120 patients were transferred to a comprehensive stroke center (CSC) or a hospital with endovascular thrombectomy expertise. The analysis was stratified based on whether the patient presented in the early time window (≤ 6 hours) or late time window (> 6 hours).
Patients treated in the early time window were significantly more likely to be mobile and able to perform daily tasks (mRS ≤ 2) 90 days after the procedure in the MIST group (54%), compared with the transferred group (28%, P < 0.01). Outcomes did not differ significantly between groups in the late time window (35% vs. 41%, P = 0.77).
Similarly, early-time-window patients in the MIST group were more likely to have higher functionality at discharge, compared with transferred patients, based on the on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (median score of 5.0 vs. 12.0, P < 0.01). There was no significant difference between groups treated in the late time window (median score of 5.0 vs. 11.0, P = 0.11).
“Ischemic strokes often progress rapidly and can cause severe damage because brain tissue dies quickly without oxygen, resulting in serious long-term disabilities or death,“ said Johanna Fifi, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine, said in a statement to the American Heart Association. “Assessing and treating stroke patients in the early window means that a greater number of fast-progressing strokes are identified and treated.”
Time is brain
Endovascular thrombectomy is a time-sensitive surgical procedure to remove large blood clots in acute ischemic stroke that has “historically been limited to comprehensive stroke centers,” the authors wrote in their paper. It is considered the standard of care in ischemic strokes, which make up 90% of all strokes. “Less than 50% of Americans have direct access to endovascular thrombectomy, the others must be transferred to a thrombectomy-capable hospital for treatment, often losing over 2 hours of time to treatment,” said Dr. Fifi. “Every minute is precious in treating stroke, and getting to a center that offers thrombectomy is very important. The MIST model would address this by providing faster access to this potentially life-saving, disability-reducing procedure.”
Access to timely endovascular thrombectomy is gradually improving as “more institutions and cities have implemented the [MIST] model.” Dr. Fifi said.
“This study stresses the importance of ‘time is brain,’ especially for patients in the early time window. Although the study is limited by the observational, retrospective design and was performed at a single integrated center, the findings are provocative,” said Louise McCullough, MD, of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston said in a statement to the American Heart Association. “The use of a MIST model highlights the potential benefit of early and urgent treatment for patients with large-vessel stroke. Stroke systems of care need to take advantage of any opportunity to treat patients early, wherever they are.”
The study was partly funded by a Stryker Foundation grant.
Having a mobile interventional stroke team (MIST) travel to treat stroke patients soon after stroke onset may improve patient outcomes, according to a new study. A retrospective analysis of a pilot program in New York found that
“The use of a Mobile Interventional Stroke Team (MIST) traveling to Thrombectomy Capable Stroke Centers to perform endovascular thrombectomy has been shown to be significantly faster with improved discharge outcomes,” wrote lead author Jacob Morey, a doctoral Candidate at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York and coauthors in the paper. Prior to this study, “the effect of the MIST model stratified by time of presentation” had yet to be studied.
The findings were published online on Aug. 5 in Stroke.
MIST model versus drip-and-ship
The researchers analyzed 226 patients who underwent endovascular thrombectomy between January 2017 and February 2020 at four hospitals in the Mount Sinai health system using the NYC MIST Trial and a stroke database. At baseline, all patients were functionally independent as assessed by the modified Rankin Scale (mRS, score of 0-2). 106 patients were treated by a MIST team – staffed by a neurointerventionalist, a fellow or physician assistant, and radiologic technologist – that traveled to the patient’s location. A total of 120 patients were transferred to a comprehensive stroke center (CSC) or a hospital with endovascular thrombectomy expertise. The analysis was stratified based on whether the patient presented in the early time window (≤ 6 hours) or late time window (> 6 hours).
Patients treated in the early time window were significantly more likely to be mobile and able to perform daily tasks (mRS ≤ 2) 90 days after the procedure in the MIST group (54%), compared with the transferred group (28%, P < 0.01). Outcomes did not differ significantly between groups in the late time window (35% vs. 41%, P = 0.77).
Similarly, early-time-window patients in the MIST group were more likely to have higher functionality at discharge, compared with transferred patients, based on the on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (median score of 5.0 vs. 12.0, P < 0.01). There was no significant difference between groups treated in the late time window (median score of 5.0 vs. 11.0, P = 0.11).
“Ischemic strokes often progress rapidly and can cause severe damage because brain tissue dies quickly without oxygen, resulting in serious long-term disabilities or death,“ said Johanna Fifi, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine, said in a statement to the American Heart Association. “Assessing and treating stroke patients in the early window means that a greater number of fast-progressing strokes are identified and treated.”
Time is brain
Endovascular thrombectomy is a time-sensitive surgical procedure to remove large blood clots in acute ischemic stroke that has “historically been limited to comprehensive stroke centers,” the authors wrote in their paper. It is considered the standard of care in ischemic strokes, which make up 90% of all strokes. “Less than 50% of Americans have direct access to endovascular thrombectomy, the others must be transferred to a thrombectomy-capable hospital for treatment, often losing over 2 hours of time to treatment,” said Dr. Fifi. “Every minute is precious in treating stroke, and getting to a center that offers thrombectomy is very important. The MIST model would address this by providing faster access to this potentially life-saving, disability-reducing procedure.”
Access to timely endovascular thrombectomy is gradually improving as “more institutions and cities have implemented the [MIST] model.” Dr. Fifi said.
“This study stresses the importance of ‘time is brain,’ especially for patients in the early time window. Although the study is limited by the observational, retrospective design and was performed at a single integrated center, the findings are provocative,” said Louise McCullough, MD, of the University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston said in a statement to the American Heart Association. “The use of a MIST model highlights the potential benefit of early and urgent treatment for patients with large-vessel stroke. Stroke systems of care need to take advantage of any opportunity to treat patients early, wherever they are.”
The study was partly funded by a Stryker Foundation grant.
FROM STROKE
Prevalence of dementia before age 65 much higher than expected
Results of a large meta-analysis show that currently 3.9 million individuals are living with young-onset dementia. Among these patients, symptoms of the disease start before age 65.
Recent global young-onset dementia estimates have ranged from 42.3 to 54.0 per 100,000 population, the researchers noted. However, the new study, which included 74 global studies with 2.7 million participants, shows that the global age-standardized prevalence of young-onset dementia is 119.00 per 100,000 among individuals aged 30-64 years; there was little difference in prevalence between men and women. On the basis of the latest population estimates, these new prevalence data imply that there are approximately 175,000 persons with young-onset dementia in the United States.
Although the new global estimate of young-onset dementia is higher than previously thought, “it is still probably an underestimation owing to lack of high-quality data. This should raise awareness for policy makers and health care professionals to organize more and better care for this subgroup of individuals with dementia,” wrote the investigators, with first author Stevie Hendriks, MSc, Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, and the Young-Onset Dementia Epidemiology Study Group.
The study was published online July 19, 2021, in JAMA Neurology.
‘Essential’ data
Young-onset dementia is exceedingly rare in those aged 30-63 years (1.1 per 100,000) but is more prevalent at age 60-64 years (77.4 per 100,000). “Our findings fit the general observation that prevalence of dementia increases exponentially from 60 years of age onward,” they wrote.
The prevalence of young-onset dementia was similar in men and women, lower in the United States than in Europe, highest in upper- to middle-income countries, and highest for Alzheimer’s disease, followed by vascular dementia and frontotemporal dementia.
Monitoring the prevalence of young-onset dementia is “essential” to adequately plan and organize health services, the investigators noted.
To ensure more accurate prevalence estimates in the future, “efforts should be made to conduct more cohort studies and to standardize procedures and reporting of prevalence studies. In addition, more data are needed from low-income countries as well as studies that include younger age ranges,” they said.
New insights
In an accompanying editorial, David S. Knopman, MD, department of neurology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the study provides new insights into an “underappreciated problem.”.
Young-onset dementia is a “particularly disheartening diagnosis because it affects individuals in their prime years, in the midst of their careers, and while raising families,” Dr. Knopman wrote.
“Most dementia care is geared for older patients, and as a consequence, services are rarely available to address the needs of someone diagnosed with dementia in their 50s who has dependent children at home and a spouse who must continue working. Understanding the prevalence and incidence of young-onset dementia is a first step in addressing this challenge,” Dr. Knopman wrote.
He noted that the authors of this analysis have “done a service to the dementia community by collecting and analyzing the dozens of individual studies of young-onset dementia.
“The product, a rationally derived estimate of dementia prevalence across the population aged 30-64 years, provides a basis for initiating more efforts to improve methods for timely diagnosis and to address the unique needs of patients with young-onset dementia,” Dr. Knopman concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a large meta-analysis show that currently 3.9 million individuals are living with young-onset dementia. Among these patients, symptoms of the disease start before age 65.
Recent global young-onset dementia estimates have ranged from 42.3 to 54.0 per 100,000 population, the researchers noted. However, the new study, which included 74 global studies with 2.7 million participants, shows that the global age-standardized prevalence of young-onset dementia is 119.00 per 100,000 among individuals aged 30-64 years; there was little difference in prevalence between men and women. On the basis of the latest population estimates, these new prevalence data imply that there are approximately 175,000 persons with young-onset dementia in the United States.
Although the new global estimate of young-onset dementia is higher than previously thought, “it is still probably an underestimation owing to lack of high-quality data. This should raise awareness for policy makers and health care professionals to organize more and better care for this subgroup of individuals with dementia,” wrote the investigators, with first author Stevie Hendriks, MSc, Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, and the Young-Onset Dementia Epidemiology Study Group.
The study was published online July 19, 2021, in JAMA Neurology.
‘Essential’ data
Young-onset dementia is exceedingly rare in those aged 30-63 years (1.1 per 100,000) but is more prevalent at age 60-64 years (77.4 per 100,000). “Our findings fit the general observation that prevalence of dementia increases exponentially from 60 years of age onward,” they wrote.
The prevalence of young-onset dementia was similar in men and women, lower in the United States than in Europe, highest in upper- to middle-income countries, and highest for Alzheimer’s disease, followed by vascular dementia and frontotemporal dementia.
Monitoring the prevalence of young-onset dementia is “essential” to adequately plan and organize health services, the investigators noted.
To ensure more accurate prevalence estimates in the future, “efforts should be made to conduct more cohort studies and to standardize procedures and reporting of prevalence studies. In addition, more data are needed from low-income countries as well as studies that include younger age ranges,” they said.
New insights
In an accompanying editorial, David S. Knopman, MD, department of neurology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the study provides new insights into an “underappreciated problem.”.
Young-onset dementia is a “particularly disheartening diagnosis because it affects individuals in their prime years, in the midst of their careers, and while raising families,” Dr. Knopman wrote.
“Most dementia care is geared for older patients, and as a consequence, services are rarely available to address the needs of someone diagnosed with dementia in their 50s who has dependent children at home and a spouse who must continue working. Understanding the prevalence and incidence of young-onset dementia is a first step in addressing this challenge,” Dr. Knopman wrote.
He noted that the authors of this analysis have “done a service to the dementia community by collecting and analyzing the dozens of individual studies of young-onset dementia.
“The product, a rationally derived estimate of dementia prevalence across the population aged 30-64 years, provides a basis for initiating more efforts to improve methods for timely diagnosis and to address the unique needs of patients with young-onset dementia,” Dr. Knopman concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a large meta-analysis show that currently 3.9 million individuals are living with young-onset dementia. Among these patients, symptoms of the disease start before age 65.
Recent global young-onset dementia estimates have ranged from 42.3 to 54.0 per 100,000 population, the researchers noted. However, the new study, which included 74 global studies with 2.7 million participants, shows that the global age-standardized prevalence of young-onset dementia is 119.00 per 100,000 among individuals aged 30-64 years; there was little difference in prevalence between men and women. On the basis of the latest population estimates, these new prevalence data imply that there are approximately 175,000 persons with young-onset dementia in the United States.
Although the new global estimate of young-onset dementia is higher than previously thought, “it is still probably an underestimation owing to lack of high-quality data. This should raise awareness for policy makers and health care professionals to organize more and better care for this subgroup of individuals with dementia,” wrote the investigators, with first author Stevie Hendriks, MSc, Maastricht (the Netherlands) University, and the Young-Onset Dementia Epidemiology Study Group.
The study was published online July 19, 2021, in JAMA Neurology.
‘Essential’ data
Young-onset dementia is exceedingly rare in those aged 30-63 years (1.1 per 100,000) but is more prevalent at age 60-64 years (77.4 per 100,000). “Our findings fit the general observation that prevalence of dementia increases exponentially from 60 years of age onward,” they wrote.
The prevalence of young-onset dementia was similar in men and women, lower in the United States than in Europe, highest in upper- to middle-income countries, and highest for Alzheimer’s disease, followed by vascular dementia and frontotemporal dementia.
Monitoring the prevalence of young-onset dementia is “essential” to adequately plan and organize health services, the investigators noted.
To ensure more accurate prevalence estimates in the future, “efforts should be made to conduct more cohort studies and to standardize procedures and reporting of prevalence studies. In addition, more data are needed from low-income countries as well as studies that include younger age ranges,” they said.
New insights
In an accompanying editorial, David S. Knopman, MD, department of neurology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., noted that the study provides new insights into an “underappreciated problem.”.
Young-onset dementia is a “particularly disheartening diagnosis because it affects individuals in their prime years, in the midst of their careers, and while raising families,” Dr. Knopman wrote.
“Most dementia care is geared for older patients, and as a consequence, services are rarely available to address the needs of someone diagnosed with dementia in their 50s who has dependent children at home and a spouse who must continue working. Understanding the prevalence and incidence of young-onset dementia is a first step in addressing this challenge,” Dr. Knopman wrote.
He noted that the authors of this analysis have “done a service to the dementia community by collecting and analyzing the dozens of individual studies of young-onset dementia.
“The product, a rationally derived estimate of dementia prevalence across the population aged 30-64 years, provides a basis for initiating more efforts to improve methods for timely diagnosis and to address the unique needs of patients with young-onset dementia,” Dr. Knopman concluded.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Can a supplement that mimics the keto diet reduce seizures?
early research suggests. However, at least one expert has concerns.
In an open-label feasibility study, researchers assessed a liquid supplement known as K.Vita (Vitaflo International), which contains both decanoic acid and octanoic acid.
Although the study was small, the findings are promising, said coinvestigator Matthew Walker, MD, PhD, University College London Institute of Neurology, department of clinical and experimental epilepsy.
“The dietary supplement was reasonably well tolerated and while we weren’t specifically looking for efficacy here, we did see some patients had quite dramatic results in terms of reduced seizures,” Dr. Walker said.
Unlike the ketogenic diet, this dietary supplement is “very easy” to follow, involves only minor dietary modifications, and doesn’t require the intervention of a dietitian, he added.
The findings were published online July 23, 2021, in Brain Communications.
Key ingredients
In the ketogenic diet, the body uses body fat as its primary fuel source. The switch from carbohydrates to fat for body fuel results in built-up ketones.
Previous research shows the ketogenic diet is effective in reducing seizures in some patients with epilepsy. However, many patients find it difficult to tolerate, especially for extended periods. Dr. Walker also noted that ketones may have other long-term side effects, including osteoporosis.
He added that his team was keen to learn what elements of the ketogenic diet affect seizures. “Interestingly, we found that one of the fats used in the ketogenic diet, decanoic acid, has quite marked antiseizure effects,” Dr. Walker said.
Previous research has shown that decanoic acid, a medium-chain triglyceride–derived fatty acid, can cross the blood-brain barrier and decrease excitatory neurotransmission and network excitability in vitro.
Dr. Walker noted that ketones are necessary in order to reduce seizures.
“Rather than have a very high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that causes ketones, we thought ‘why don’t we use a diet in which we just use mainly this fat, this decanoic acid, and avoid ketosis,’ ” he said.
The researchers then went to work developing the K.Vita dietary supplement, which mainly contains decanoic acid but also another fat, octanoic acid.
Assessing feasibility
The feasibility study included 61 patients (59% female) who began taking the supplement. Of these, 35 were children (aged 3-18 years) and 26 were adults. The children had Dravet syndrome or another genetically driven form of epilepsy, while most of the adults had a focal epilepsy.
All participants had failed multiple antiseizure medications – a median of 3 for children and 10 for adults who completed the trial. Of the 61 original participants, 20 (19 children and 1 adult) had tried the ketogenic diet but had stopped it for various reasons, including noncompliance and lack of efficacy.
The liquid supplement was introduced gradually. The amount administered was based on weight in the children and was a standard amount in adults, with the target being 240 mL.
Participants consumed the supplement in equal servings taken at regular intervals as part of a meal or snack. They could take it alone or mix it with yogurt or another food.
Patients with feeding tubes took the supplement immediately before or after or mixed into an enteral feed, with a water flush afterward.
Researchers provided patients and caregivers with guidance on excluding highly refined sugary foods and beverages. Starchy foods such as bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes were not restricted.
The study consisted of three visits: baseline, 5 weeks, and 12 weeks, in addition to regular phone and email contact. Participants were also asked to keep a seizure diary.
Highly acceptable to patients
Overall, the study withdrawal rate was 33%. After a protocol change involving a slower introduction of the supplement, there were fewer withdrawals, Dr. Walker reported. He noted that the proportion of participants who completed the study (41 of 61) is “much better than with most studies of adults following the ketogenic diet.”
The most frequently reported gastrointestinal symptoms with the supplement were bloating and constipation, but these were predominantly mild and tended to decrease over time. This, said Dr. Walker, contrasts to the ketogenic diet where side effects tend to persist.
There was no significant change in body weight or body mass index. “We did not see weight gain as a problem at all,” Dr. Walker said.
Of 15 caregivers and 19 adults who returned an acceptability questionnaire, 84% agreed or strongly agreed the supplement had a good flavor (strawberry); 88% liked the appearance and color; 77% liked the texture and consistency; and 88% agreed or strongly agreed it was easy to take.
About one-third of adults and two-thirds of caregivers said they believed the supplement reduced seizures.
50% seizure reduction
Only three children and one adult became ketotic. This is typically classified as a beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) greater than 1 mmol/L (10.4 mg/dL). The BHB levels detected were markedly lower than those observed in individuals following a ketogenic diet, the investigators note.
Of the 41 participants, 19 completed the diaries. There were also data from physician recordings, so researchers were able to retrieve seizure frequencies for 32 of the 41 (78%). Of these 32 patients, 14 (44%) had a 50% or greater reduction in seizures. Overall, children and adults “responded similarly,” Dr. Walker said.
He acknowledged the study numbers are small and emphasized that larger studies are needed to determine efficacy. He also hopes for a future randomized controlled trial comparing K.Vita with another supplement that contains different types of fats.
Interestingly, the product has already “passed” the regulatory approval process in the United Kingdom, so it can be labeled as a medicinal food and should be available for use at the beginning of 2022, Dr. Walker said.
Study concerns
Asked to comment on the findings, Daniel Goldenholz, MD, PhD, instructor in the department of neurology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said the supplement may be helpful, but he has concerns about the study.
Many patients with epilepsy are “desperate” for therapies that will help treat their seizures, said Dr. Goldenholz, who was not involved with the research. “If there’s a dietary therapy that has the potential for being helpful, I’m loving that. I need that. My patients are begging for something that works.” It is “really exciting” that researchers are working on that goal, Dr. Goldenholz added.
However, he noted that it is too soon to start talking to patients about this new product. He also pointed out that a significant fraction of the study participants dropped out, many because they couldn’t tolerate the supplement. In addition, others didn’t produce a seizure diary.
Dr. Goldenholz and colleagues have published several studies showing that patients with no intervention at all can sometimes show a reduction in seizures compared with their baseline results.
“We found sizable 50% reductions attributable entirely to the natural fluctuations in seizure rates, rather than any therapy at all, he said.
Dr. Goldenholz added that he hopes to see future studies on this topic, and on similar therapies “with sufficient data and more reliable metrics for efficacy.”
The study was funded by Vitaflo International. Dr. Walker reports having received grants from Vitaflo International and personal fees from UCB Pharma, Eisai, and Sage. In addition, along with colleagues, he has a patent (Nutritional product) pending.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
early research suggests. However, at least one expert has concerns.
In an open-label feasibility study, researchers assessed a liquid supplement known as K.Vita (Vitaflo International), which contains both decanoic acid and octanoic acid.
Although the study was small, the findings are promising, said coinvestigator Matthew Walker, MD, PhD, University College London Institute of Neurology, department of clinical and experimental epilepsy.
“The dietary supplement was reasonably well tolerated and while we weren’t specifically looking for efficacy here, we did see some patients had quite dramatic results in terms of reduced seizures,” Dr. Walker said.
Unlike the ketogenic diet, this dietary supplement is “very easy” to follow, involves only minor dietary modifications, and doesn’t require the intervention of a dietitian, he added.
The findings were published online July 23, 2021, in Brain Communications.
Key ingredients
In the ketogenic diet, the body uses body fat as its primary fuel source. The switch from carbohydrates to fat for body fuel results in built-up ketones.
Previous research shows the ketogenic diet is effective in reducing seizures in some patients with epilepsy. However, many patients find it difficult to tolerate, especially for extended periods. Dr. Walker also noted that ketones may have other long-term side effects, including osteoporosis.
He added that his team was keen to learn what elements of the ketogenic diet affect seizures. “Interestingly, we found that one of the fats used in the ketogenic diet, decanoic acid, has quite marked antiseizure effects,” Dr. Walker said.
Previous research has shown that decanoic acid, a medium-chain triglyceride–derived fatty acid, can cross the blood-brain barrier and decrease excitatory neurotransmission and network excitability in vitro.
Dr. Walker noted that ketones are necessary in order to reduce seizures.
“Rather than have a very high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that causes ketones, we thought ‘why don’t we use a diet in which we just use mainly this fat, this decanoic acid, and avoid ketosis,’ ” he said.
The researchers then went to work developing the K.Vita dietary supplement, which mainly contains decanoic acid but also another fat, octanoic acid.
Assessing feasibility
The feasibility study included 61 patients (59% female) who began taking the supplement. Of these, 35 were children (aged 3-18 years) and 26 were adults. The children had Dravet syndrome or another genetically driven form of epilepsy, while most of the adults had a focal epilepsy.
All participants had failed multiple antiseizure medications – a median of 3 for children and 10 for adults who completed the trial. Of the 61 original participants, 20 (19 children and 1 adult) had tried the ketogenic diet but had stopped it for various reasons, including noncompliance and lack of efficacy.
The liquid supplement was introduced gradually. The amount administered was based on weight in the children and was a standard amount in adults, with the target being 240 mL.
Participants consumed the supplement in equal servings taken at regular intervals as part of a meal or snack. They could take it alone or mix it with yogurt or another food.
Patients with feeding tubes took the supplement immediately before or after or mixed into an enteral feed, with a water flush afterward.
Researchers provided patients and caregivers with guidance on excluding highly refined sugary foods and beverages. Starchy foods such as bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes were not restricted.
The study consisted of three visits: baseline, 5 weeks, and 12 weeks, in addition to regular phone and email contact. Participants were also asked to keep a seizure diary.
Highly acceptable to patients
Overall, the study withdrawal rate was 33%. After a protocol change involving a slower introduction of the supplement, there were fewer withdrawals, Dr. Walker reported. He noted that the proportion of participants who completed the study (41 of 61) is “much better than with most studies of adults following the ketogenic diet.”
The most frequently reported gastrointestinal symptoms with the supplement were bloating and constipation, but these were predominantly mild and tended to decrease over time. This, said Dr. Walker, contrasts to the ketogenic diet where side effects tend to persist.
There was no significant change in body weight or body mass index. “We did not see weight gain as a problem at all,” Dr. Walker said.
Of 15 caregivers and 19 adults who returned an acceptability questionnaire, 84% agreed or strongly agreed the supplement had a good flavor (strawberry); 88% liked the appearance and color; 77% liked the texture and consistency; and 88% agreed or strongly agreed it was easy to take.
About one-third of adults and two-thirds of caregivers said they believed the supplement reduced seizures.
50% seizure reduction
Only three children and one adult became ketotic. This is typically classified as a beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) greater than 1 mmol/L (10.4 mg/dL). The BHB levels detected were markedly lower than those observed in individuals following a ketogenic diet, the investigators note.
Of the 41 participants, 19 completed the diaries. There were also data from physician recordings, so researchers were able to retrieve seizure frequencies for 32 of the 41 (78%). Of these 32 patients, 14 (44%) had a 50% or greater reduction in seizures. Overall, children and adults “responded similarly,” Dr. Walker said.
He acknowledged the study numbers are small and emphasized that larger studies are needed to determine efficacy. He also hopes for a future randomized controlled trial comparing K.Vita with another supplement that contains different types of fats.
Interestingly, the product has already “passed” the regulatory approval process in the United Kingdom, so it can be labeled as a medicinal food and should be available for use at the beginning of 2022, Dr. Walker said.
Study concerns
Asked to comment on the findings, Daniel Goldenholz, MD, PhD, instructor in the department of neurology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said the supplement may be helpful, but he has concerns about the study.
Many patients with epilepsy are “desperate” for therapies that will help treat their seizures, said Dr. Goldenholz, who was not involved with the research. “If there’s a dietary therapy that has the potential for being helpful, I’m loving that. I need that. My patients are begging for something that works.” It is “really exciting” that researchers are working on that goal, Dr. Goldenholz added.
However, he noted that it is too soon to start talking to patients about this new product. He also pointed out that a significant fraction of the study participants dropped out, many because they couldn’t tolerate the supplement. In addition, others didn’t produce a seizure diary.
Dr. Goldenholz and colleagues have published several studies showing that patients with no intervention at all can sometimes show a reduction in seizures compared with their baseline results.
“We found sizable 50% reductions attributable entirely to the natural fluctuations in seizure rates, rather than any therapy at all, he said.
Dr. Goldenholz added that he hopes to see future studies on this topic, and on similar therapies “with sufficient data and more reliable metrics for efficacy.”
The study was funded by Vitaflo International. Dr. Walker reports having received grants from Vitaflo International and personal fees from UCB Pharma, Eisai, and Sage. In addition, along with colleagues, he has a patent (Nutritional product) pending.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
early research suggests. However, at least one expert has concerns.
In an open-label feasibility study, researchers assessed a liquid supplement known as K.Vita (Vitaflo International), which contains both decanoic acid and octanoic acid.
Although the study was small, the findings are promising, said coinvestigator Matthew Walker, MD, PhD, University College London Institute of Neurology, department of clinical and experimental epilepsy.
“The dietary supplement was reasonably well tolerated and while we weren’t specifically looking for efficacy here, we did see some patients had quite dramatic results in terms of reduced seizures,” Dr. Walker said.
Unlike the ketogenic diet, this dietary supplement is “very easy” to follow, involves only minor dietary modifications, and doesn’t require the intervention of a dietitian, he added.
The findings were published online July 23, 2021, in Brain Communications.
Key ingredients
In the ketogenic diet, the body uses body fat as its primary fuel source. The switch from carbohydrates to fat for body fuel results in built-up ketones.
Previous research shows the ketogenic diet is effective in reducing seizures in some patients with epilepsy. However, many patients find it difficult to tolerate, especially for extended periods. Dr. Walker also noted that ketones may have other long-term side effects, including osteoporosis.
He added that his team was keen to learn what elements of the ketogenic diet affect seizures. “Interestingly, we found that one of the fats used in the ketogenic diet, decanoic acid, has quite marked antiseizure effects,” Dr. Walker said.
Previous research has shown that decanoic acid, a medium-chain triglyceride–derived fatty acid, can cross the blood-brain barrier and decrease excitatory neurotransmission and network excitability in vitro.
Dr. Walker noted that ketones are necessary in order to reduce seizures.
“Rather than have a very high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that causes ketones, we thought ‘why don’t we use a diet in which we just use mainly this fat, this decanoic acid, and avoid ketosis,’ ” he said.
The researchers then went to work developing the K.Vita dietary supplement, which mainly contains decanoic acid but also another fat, octanoic acid.
Assessing feasibility
The feasibility study included 61 patients (59% female) who began taking the supplement. Of these, 35 were children (aged 3-18 years) and 26 were adults. The children had Dravet syndrome or another genetically driven form of epilepsy, while most of the adults had a focal epilepsy.
All participants had failed multiple antiseizure medications – a median of 3 for children and 10 for adults who completed the trial. Of the 61 original participants, 20 (19 children and 1 adult) had tried the ketogenic diet but had stopped it for various reasons, including noncompliance and lack of efficacy.
The liquid supplement was introduced gradually. The amount administered was based on weight in the children and was a standard amount in adults, with the target being 240 mL.
Participants consumed the supplement in equal servings taken at regular intervals as part of a meal or snack. They could take it alone or mix it with yogurt or another food.
Patients with feeding tubes took the supplement immediately before or after or mixed into an enteral feed, with a water flush afterward.
Researchers provided patients and caregivers with guidance on excluding highly refined sugary foods and beverages. Starchy foods such as bread, pasta, rice, and potatoes were not restricted.
The study consisted of three visits: baseline, 5 weeks, and 12 weeks, in addition to regular phone and email contact. Participants were also asked to keep a seizure diary.
Highly acceptable to patients
Overall, the study withdrawal rate was 33%. After a protocol change involving a slower introduction of the supplement, there were fewer withdrawals, Dr. Walker reported. He noted that the proportion of participants who completed the study (41 of 61) is “much better than with most studies of adults following the ketogenic diet.”
The most frequently reported gastrointestinal symptoms with the supplement were bloating and constipation, but these were predominantly mild and tended to decrease over time. This, said Dr. Walker, contrasts to the ketogenic diet where side effects tend to persist.
There was no significant change in body weight or body mass index. “We did not see weight gain as a problem at all,” Dr. Walker said.
Of 15 caregivers and 19 adults who returned an acceptability questionnaire, 84% agreed or strongly agreed the supplement had a good flavor (strawberry); 88% liked the appearance and color; 77% liked the texture and consistency; and 88% agreed or strongly agreed it was easy to take.
About one-third of adults and two-thirds of caregivers said they believed the supplement reduced seizures.
50% seizure reduction
Only three children and one adult became ketotic. This is typically classified as a beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) greater than 1 mmol/L (10.4 mg/dL). The BHB levels detected were markedly lower than those observed in individuals following a ketogenic diet, the investigators note.
Of the 41 participants, 19 completed the diaries. There were also data from physician recordings, so researchers were able to retrieve seizure frequencies for 32 of the 41 (78%). Of these 32 patients, 14 (44%) had a 50% or greater reduction in seizures. Overall, children and adults “responded similarly,” Dr. Walker said.
He acknowledged the study numbers are small and emphasized that larger studies are needed to determine efficacy. He also hopes for a future randomized controlled trial comparing K.Vita with another supplement that contains different types of fats.
Interestingly, the product has already “passed” the regulatory approval process in the United Kingdom, so it can be labeled as a medicinal food and should be available for use at the beginning of 2022, Dr. Walker said.
Study concerns
Asked to comment on the findings, Daniel Goldenholz, MD, PhD, instructor in the department of neurology, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston, said the supplement may be helpful, but he has concerns about the study.
Many patients with epilepsy are “desperate” for therapies that will help treat their seizures, said Dr. Goldenholz, who was not involved with the research. “If there’s a dietary therapy that has the potential for being helpful, I’m loving that. I need that. My patients are begging for something that works.” It is “really exciting” that researchers are working on that goal, Dr. Goldenholz added.
However, he noted that it is too soon to start talking to patients about this new product. He also pointed out that a significant fraction of the study participants dropped out, many because they couldn’t tolerate the supplement. In addition, others didn’t produce a seizure diary.
Dr. Goldenholz and colleagues have published several studies showing that patients with no intervention at all can sometimes show a reduction in seizures compared with their baseline results.
“We found sizable 50% reductions attributable entirely to the natural fluctuations in seizure rates, rather than any therapy at all, he said.
Dr. Goldenholz added that he hopes to see future studies on this topic, and on similar therapies “with sufficient data and more reliable metrics for efficacy.”
The study was funded by Vitaflo International. Dr. Walker reports having received grants from Vitaflo International and personal fees from UCB Pharma, Eisai, and Sage. In addition, along with colleagues, he has a patent (Nutritional product) pending.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM BRAIN COMMUNICATION
Coffee and the brain: ‘Concerning’ new data
according to the results of a large study.
“With coffee intake, moderation is the key, and especially high levels of consumption may have adverse long-term effects on the brain,” said study investigator Elina Hypponen, PhD, professor of nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Center for Precision Health at the University of South Australia.
“These new data are concerning, and there is a need to conduct further carefully controlled studies to clarify the effects of coffee on the brain.”
The study was published online June 24 in Nutritional Neuroscience.
Potent stimulant
Coffee is a potent nervous system stimulant and is among the most popular nonalcoholic beverages. Some previous research suggests it benefits the brain, but the investigators noted that other research shows a negative or U-shaped relationship.
To investigate, the researchers examined data from the U.K. Biobank, a long-term prospective epidemiologic study of more than 500,000 participants aged 37-73 years who were recruited in 22 assessment centers in the United Kingdom between March 2006 and October 2010.
During the baseline assessment, information was gathered using touchscreen questionnaires, verbal interviews, and physical examinations that involved collection of blood, urine, and saliva samples. An imaging substudy was incorporated in 2014, the goal of which was to conduct brain, heart, and body MRI imaging for 100,000 participants.
The investigators conducted analyses on disease outcomes for 398,646 participants for whom information on habitual coffee consumption was available. Brain volume analyses were conducted in 17,702 participants for whom valid brain imaging data were available.
Participants reported coffee intake in cups per day. Researchers grouped coffee consumption into seven categories: nondrinkers, decaffeinated coffee drinkers, and caffeinated coffee drinkers who consumed less than 1 cup/d, 1-2 cups/d, 3-4 cups/d, 5-6 cups/d, and more than 6 cups/d.
The reference category was those who consumed 1-2 cups/d, rather than those who abstained from coffee, because persons who abstain are more likely to be at suboptimal health.
“Comparing the health of coffee drinkers to the health of those choosing to abstain from coffee will typically lead to an impression of a health benefit, even if there would not be one,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The researchers obtained total and regional brain volumes from the MRI imaging substudy starting 4-6 years after baseline assessment. They accessed information on incident dementia and stroke using primary care data, hospital admission electronic health records, national death registers, and self-reported medical conditions.
Covariates included socioeconomic, health, and other factors, such as smoking, alcohol and tea consumption, physical activity, stressful life events, and body mass index.
The investigators found that there was a linear inverse association between coffee consumption and total brain volume (fully adjusted beta per cup, –1.42; 95% confidence interval, –1.89 to –0.94), with consistent patterns for gray matter, white matter, and hippocampal volumes.
There was no evidence to support an association with white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume (beta –0.01; 95% CI, –0.07 to 0.05).
Higher consumption, higher risk
The analysis also revealed a nonlinear association between coffee consumption and the odds of dementia (P nonlinearity = .0001), with slightly higher odds seen with non–coffee drinkers and decaffeinated-coffee drinkers and more notable increases for participants in the highest categories of coffee consumption compared with light coffee drinkers.
After adjustment for all covariates, the odds ratio of dementia among persons in the category of coffee intake was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.28-1.83). After full adjustments, the association with heavy coffee consumption and stroke was not significant, although “we can’t exclude a weak effect,” said Dr. Hypponen.
“For the highest coffee consumption group, the data support an association which may be anywhere from 0% to 37% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment,” she added.
People at risk for hypertension may develop “unpleasant sensations” and stop drinking coffee before a serious adverse event occurs, said Dr. Hypponen. In a previous study, she and her colleagues showed that those who have genetically higher blood pressure tend to drink less coffee than their counterparts without the condition.
“This type of effect might be expected to naturally limit the adverse effects of coffee on the risk of stroke,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The odds remained elevated for participants drinking more than 6 cups/d after the researchers accounted for sleep quality. There were no differences in risk between men and women or by age.
An examination of the consumption of tea, which often contains caffeine, did not show an association with brain volume or the odds of dementia or stroke.
“We don’t know whether the difference between associations seen for coffee and tea intake reflects the difference in related caffeine intake or some other explanation, such as dehydration or effects operating through blood cholesterol,” said Dr. Hypponen.
Although reverse causation is possible, there’s no reason to believe that it is relevant to the study results. Genetic evidence suggests a causal role of higher coffee intake on risk for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, results of a clinical trial support the association between higher caffeine intake and smaller gray matter volume, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanisms linking coffee consumption to brain volumes and dementia are not well established. However, Dr. Hypponen noted that caffeine has been used to induce apoptosis in cancer studies using glial cells.
“Furthermore, adenosine receptors, which mediate many of the effects of caffeine in the brain, have been suggested to influence the release of growth factors, which in turn can have an influence on astrocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the brain,” she said.
Some types of coffee contain cafestol, which increases blood cholesterol and can have adverse effects though related mechanisms, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanism may also involve dehydration, which may have a harmful effect on the brain. The study suggested a correlation between dehydration and high coffee intake. “Of course, if this is the case, it is good news, as then we can do something about it simply by drinking some water every time we have a cup of coffee,” she said.
Misleading conclusions
Coffee contains antioxidants, and although previous studies have suggested it might be beneficial, this hypothesis is “too simplistic,” said Dr. Hypponen. “While coffee is not going to be all ‘bad’ either, there are a lot of controversies and suggestions about beneficial effects of coffee which may not be true, or at least do not reflect the full story.”
If the drinking of coffee is at least partly determined by an individual’s health status, then that would often lead to misleading conclusions in observational studies, said Dr. Hypponen.
“When one uses as a comparison people who already have poor health and who do not drink coffee because of that, coffee intake will by default appear beneficial simply because there are more people with disease among those choosing abstinence,” she said.
Before now, there was “very little evidence about the association between coffee intake and brain morphology,” and the studies that were conducted were relatively small, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of these smaller studies included a group of women aged 13-30 years. It found that coffee consumption was not associated with total brain volumes, but the findings suggested a U-shaped association with hippocampal volume; higher values were seen both for nondrinkers and the groups with higher consumption.
A small study of elderly patients with diabetes showed no evidence of an association with white matter volume, but there was a possible age-dependent association with gray matter volume.
The largest of the earlier studies had results that were very similar to those of the current study, suggesting that increasing coffee intake is associated with smaller hippocampal volumes, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of the study’s limitations included the fact that full dietary information was available only for a subsample and that factors such as dehydration were measured at baseline rather than at the time of brain MRI.
Another possible study limitation was the use of self-reported data and the fact that lifestyle changes may have occurred between baseline and MRI or covariate measurement.
In addition, the study is subject to a healthy-volunteer bias, and its implications are restricted to White British persons. The association needs to be studied in other ethnic populations, the authors noted.
A reason to cut back?
Commenting on the findings, Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said the study is large and quite well done.
“It does raise questions about an increase in risk of dementia with six or more cups of coffee per day,” said Dr. Willett. “At the same time, it provides reassurance about lack of adverse effects of coffee for those consuming three or four cups per day, and little increase in risk, if any, with five cups per day.”
It’s not entirely clear whether the increase in risk with six or more cups of coffee per day represents a “true effect” of coffee, inasmuch as the study did not seem to adjust fully for dietary factors, high consumption of alcohol, or past smoking, said Dr. Willett.
The findings don’t suggest that coffee lovers should give up their Java. “But six or more cups per day is a lot, and those who drink that much might consider cutting back a bit while research continues,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the results of a large study.
“With coffee intake, moderation is the key, and especially high levels of consumption may have adverse long-term effects on the brain,” said study investigator Elina Hypponen, PhD, professor of nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Center for Precision Health at the University of South Australia.
“These new data are concerning, and there is a need to conduct further carefully controlled studies to clarify the effects of coffee on the brain.”
The study was published online June 24 in Nutritional Neuroscience.
Potent stimulant
Coffee is a potent nervous system stimulant and is among the most popular nonalcoholic beverages. Some previous research suggests it benefits the brain, but the investigators noted that other research shows a negative or U-shaped relationship.
To investigate, the researchers examined data from the U.K. Biobank, a long-term prospective epidemiologic study of more than 500,000 participants aged 37-73 years who were recruited in 22 assessment centers in the United Kingdom between March 2006 and October 2010.
During the baseline assessment, information was gathered using touchscreen questionnaires, verbal interviews, and physical examinations that involved collection of blood, urine, and saliva samples. An imaging substudy was incorporated in 2014, the goal of which was to conduct brain, heart, and body MRI imaging for 100,000 participants.
The investigators conducted analyses on disease outcomes for 398,646 participants for whom information on habitual coffee consumption was available. Brain volume analyses were conducted in 17,702 participants for whom valid brain imaging data were available.
Participants reported coffee intake in cups per day. Researchers grouped coffee consumption into seven categories: nondrinkers, decaffeinated coffee drinkers, and caffeinated coffee drinkers who consumed less than 1 cup/d, 1-2 cups/d, 3-4 cups/d, 5-6 cups/d, and more than 6 cups/d.
The reference category was those who consumed 1-2 cups/d, rather than those who abstained from coffee, because persons who abstain are more likely to be at suboptimal health.
“Comparing the health of coffee drinkers to the health of those choosing to abstain from coffee will typically lead to an impression of a health benefit, even if there would not be one,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The researchers obtained total and regional brain volumes from the MRI imaging substudy starting 4-6 years after baseline assessment. They accessed information on incident dementia and stroke using primary care data, hospital admission electronic health records, national death registers, and self-reported medical conditions.
Covariates included socioeconomic, health, and other factors, such as smoking, alcohol and tea consumption, physical activity, stressful life events, and body mass index.
The investigators found that there was a linear inverse association between coffee consumption and total brain volume (fully adjusted beta per cup, –1.42; 95% confidence interval, –1.89 to –0.94), with consistent patterns for gray matter, white matter, and hippocampal volumes.
There was no evidence to support an association with white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume (beta –0.01; 95% CI, –0.07 to 0.05).
Higher consumption, higher risk
The analysis also revealed a nonlinear association between coffee consumption and the odds of dementia (P nonlinearity = .0001), with slightly higher odds seen with non–coffee drinkers and decaffeinated-coffee drinkers and more notable increases for participants in the highest categories of coffee consumption compared with light coffee drinkers.
After adjustment for all covariates, the odds ratio of dementia among persons in the category of coffee intake was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.28-1.83). After full adjustments, the association with heavy coffee consumption and stroke was not significant, although “we can’t exclude a weak effect,” said Dr. Hypponen.
“For the highest coffee consumption group, the data support an association which may be anywhere from 0% to 37% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment,” she added.
People at risk for hypertension may develop “unpleasant sensations” and stop drinking coffee before a serious adverse event occurs, said Dr. Hypponen. In a previous study, she and her colleagues showed that those who have genetically higher blood pressure tend to drink less coffee than their counterparts without the condition.
“This type of effect might be expected to naturally limit the adverse effects of coffee on the risk of stroke,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The odds remained elevated for participants drinking more than 6 cups/d after the researchers accounted for sleep quality. There were no differences in risk between men and women or by age.
An examination of the consumption of tea, which often contains caffeine, did not show an association with brain volume or the odds of dementia or stroke.
“We don’t know whether the difference between associations seen for coffee and tea intake reflects the difference in related caffeine intake or some other explanation, such as dehydration or effects operating through blood cholesterol,” said Dr. Hypponen.
Although reverse causation is possible, there’s no reason to believe that it is relevant to the study results. Genetic evidence suggests a causal role of higher coffee intake on risk for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, results of a clinical trial support the association between higher caffeine intake and smaller gray matter volume, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanisms linking coffee consumption to brain volumes and dementia are not well established. However, Dr. Hypponen noted that caffeine has been used to induce apoptosis in cancer studies using glial cells.
“Furthermore, adenosine receptors, which mediate many of the effects of caffeine in the brain, have been suggested to influence the release of growth factors, which in turn can have an influence on astrocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the brain,” she said.
Some types of coffee contain cafestol, which increases blood cholesterol and can have adverse effects though related mechanisms, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanism may also involve dehydration, which may have a harmful effect on the brain. The study suggested a correlation between dehydration and high coffee intake. “Of course, if this is the case, it is good news, as then we can do something about it simply by drinking some water every time we have a cup of coffee,” she said.
Misleading conclusions
Coffee contains antioxidants, and although previous studies have suggested it might be beneficial, this hypothesis is “too simplistic,” said Dr. Hypponen. “While coffee is not going to be all ‘bad’ either, there are a lot of controversies and suggestions about beneficial effects of coffee which may not be true, or at least do not reflect the full story.”
If the drinking of coffee is at least partly determined by an individual’s health status, then that would often lead to misleading conclusions in observational studies, said Dr. Hypponen.
“When one uses as a comparison people who already have poor health and who do not drink coffee because of that, coffee intake will by default appear beneficial simply because there are more people with disease among those choosing abstinence,” she said.
Before now, there was “very little evidence about the association between coffee intake and brain morphology,” and the studies that were conducted were relatively small, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of these smaller studies included a group of women aged 13-30 years. It found that coffee consumption was not associated with total brain volumes, but the findings suggested a U-shaped association with hippocampal volume; higher values were seen both for nondrinkers and the groups with higher consumption.
A small study of elderly patients with diabetes showed no evidence of an association with white matter volume, but there was a possible age-dependent association with gray matter volume.
The largest of the earlier studies had results that were very similar to those of the current study, suggesting that increasing coffee intake is associated with smaller hippocampal volumes, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of the study’s limitations included the fact that full dietary information was available only for a subsample and that factors such as dehydration were measured at baseline rather than at the time of brain MRI.
Another possible study limitation was the use of self-reported data and the fact that lifestyle changes may have occurred between baseline and MRI or covariate measurement.
In addition, the study is subject to a healthy-volunteer bias, and its implications are restricted to White British persons. The association needs to be studied in other ethnic populations, the authors noted.
A reason to cut back?
Commenting on the findings, Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said the study is large and quite well done.
“It does raise questions about an increase in risk of dementia with six or more cups of coffee per day,” said Dr. Willett. “At the same time, it provides reassurance about lack of adverse effects of coffee for those consuming three or four cups per day, and little increase in risk, if any, with five cups per day.”
It’s not entirely clear whether the increase in risk with six or more cups of coffee per day represents a “true effect” of coffee, inasmuch as the study did not seem to adjust fully for dietary factors, high consumption of alcohol, or past smoking, said Dr. Willett.
The findings don’t suggest that coffee lovers should give up their Java. “But six or more cups per day is a lot, and those who drink that much might consider cutting back a bit while research continues,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to the results of a large study.
“With coffee intake, moderation is the key, and especially high levels of consumption may have adverse long-term effects on the brain,” said study investigator Elina Hypponen, PhD, professor of nutritional and genetic epidemiology and director of the Australian Center for Precision Health at the University of South Australia.
“These new data are concerning, and there is a need to conduct further carefully controlled studies to clarify the effects of coffee on the brain.”
The study was published online June 24 in Nutritional Neuroscience.
Potent stimulant
Coffee is a potent nervous system stimulant and is among the most popular nonalcoholic beverages. Some previous research suggests it benefits the brain, but the investigators noted that other research shows a negative or U-shaped relationship.
To investigate, the researchers examined data from the U.K. Biobank, a long-term prospective epidemiologic study of more than 500,000 participants aged 37-73 years who were recruited in 22 assessment centers in the United Kingdom between March 2006 and October 2010.
During the baseline assessment, information was gathered using touchscreen questionnaires, verbal interviews, and physical examinations that involved collection of blood, urine, and saliva samples. An imaging substudy was incorporated in 2014, the goal of which was to conduct brain, heart, and body MRI imaging for 100,000 participants.
The investigators conducted analyses on disease outcomes for 398,646 participants for whom information on habitual coffee consumption was available. Brain volume analyses were conducted in 17,702 participants for whom valid brain imaging data were available.
Participants reported coffee intake in cups per day. Researchers grouped coffee consumption into seven categories: nondrinkers, decaffeinated coffee drinkers, and caffeinated coffee drinkers who consumed less than 1 cup/d, 1-2 cups/d, 3-4 cups/d, 5-6 cups/d, and more than 6 cups/d.
The reference category was those who consumed 1-2 cups/d, rather than those who abstained from coffee, because persons who abstain are more likely to be at suboptimal health.
“Comparing the health of coffee drinkers to the health of those choosing to abstain from coffee will typically lead to an impression of a health benefit, even if there would not be one,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The researchers obtained total and regional brain volumes from the MRI imaging substudy starting 4-6 years after baseline assessment. They accessed information on incident dementia and stroke using primary care data, hospital admission electronic health records, national death registers, and self-reported medical conditions.
Covariates included socioeconomic, health, and other factors, such as smoking, alcohol and tea consumption, physical activity, stressful life events, and body mass index.
The investigators found that there was a linear inverse association between coffee consumption and total brain volume (fully adjusted beta per cup, –1.42; 95% confidence interval, –1.89 to –0.94), with consistent patterns for gray matter, white matter, and hippocampal volumes.
There was no evidence to support an association with white matter hyperintensity (WMH) volume (beta –0.01; 95% CI, –0.07 to 0.05).
Higher consumption, higher risk
The analysis also revealed a nonlinear association between coffee consumption and the odds of dementia (P nonlinearity = .0001), with slightly higher odds seen with non–coffee drinkers and decaffeinated-coffee drinkers and more notable increases for participants in the highest categories of coffee consumption compared with light coffee drinkers.
After adjustment for all covariates, the odds ratio of dementia among persons in the category of coffee intake was 1.53 (95% CI, 1.28-1.83). After full adjustments, the association with heavy coffee consumption and stroke was not significant, although “we can’t exclude a weak effect,” said Dr. Hypponen.
“For the highest coffee consumption group, the data support an association which may be anywhere from 0% to 37% higher odds of stroke after full adjustment,” she added.
People at risk for hypertension may develop “unpleasant sensations” and stop drinking coffee before a serious adverse event occurs, said Dr. Hypponen. In a previous study, she and her colleagues showed that those who have genetically higher blood pressure tend to drink less coffee than their counterparts without the condition.
“This type of effect might be expected to naturally limit the adverse effects of coffee on the risk of stroke,” said Dr. Hypponen.
The odds remained elevated for participants drinking more than 6 cups/d after the researchers accounted for sleep quality. There were no differences in risk between men and women or by age.
An examination of the consumption of tea, which often contains caffeine, did not show an association with brain volume or the odds of dementia or stroke.
“We don’t know whether the difference between associations seen for coffee and tea intake reflects the difference in related caffeine intake or some other explanation, such as dehydration or effects operating through blood cholesterol,” said Dr. Hypponen.
Although reverse causation is possible, there’s no reason to believe that it is relevant to the study results. Genetic evidence suggests a causal role of higher coffee intake on risk for Alzheimer’s disease. In addition, results of a clinical trial support the association between higher caffeine intake and smaller gray matter volume, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanisms linking coffee consumption to brain volumes and dementia are not well established. However, Dr. Hypponen noted that caffeine has been used to induce apoptosis in cancer studies using glial cells.
“Furthermore, adenosine receptors, which mediate many of the effects of caffeine in the brain, have been suggested to influence the release of growth factors, which in turn can have an influence on astrocyte proliferation and angiogenesis in the brain,” she said.
Some types of coffee contain cafestol, which increases blood cholesterol and can have adverse effects though related mechanisms, said Dr. Hypponen.
The mechanism may also involve dehydration, which may have a harmful effect on the brain. The study suggested a correlation between dehydration and high coffee intake. “Of course, if this is the case, it is good news, as then we can do something about it simply by drinking some water every time we have a cup of coffee,” she said.
Misleading conclusions
Coffee contains antioxidants, and although previous studies have suggested it might be beneficial, this hypothesis is “too simplistic,” said Dr. Hypponen. “While coffee is not going to be all ‘bad’ either, there are a lot of controversies and suggestions about beneficial effects of coffee which may not be true, or at least do not reflect the full story.”
If the drinking of coffee is at least partly determined by an individual’s health status, then that would often lead to misleading conclusions in observational studies, said Dr. Hypponen.
“When one uses as a comparison people who already have poor health and who do not drink coffee because of that, coffee intake will by default appear beneficial simply because there are more people with disease among those choosing abstinence,” she said.
Before now, there was “very little evidence about the association between coffee intake and brain morphology,” and the studies that were conducted were relatively small, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of these smaller studies included a group of women aged 13-30 years. It found that coffee consumption was not associated with total brain volumes, but the findings suggested a U-shaped association with hippocampal volume; higher values were seen both for nondrinkers and the groups with higher consumption.
A small study of elderly patients with diabetes showed no evidence of an association with white matter volume, but there was a possible age-dependent association with gray matter volume.
The largest of the earlier studies had results that were very similar to those of the current study, suggesting that increasing coffee intake is associated with smaller hippocampal volumes, said Dr. Hypponen.
One of the study’s limitations included the fact that full dietary information was available only for a subsample and that factors such as dehydration were measured at baseline rather than at the time of brain MRI.
Another possible study limitation was the use of self-reported data and the fact that lifestyle changes may have occurred between baseline and MRI or covariate measurement.
In addition, the study is subject to a healthy-volunteer bias, and its implications are restricted to White British persons. The association needs to be studied in other ethnic populations, the authors noted.
A reason to cut back?
Commenting on the findings, Walter Willett, MD, DrPH, professor of epidemiology and nutrition, Harvard T. H. Chan School of Public Health, Boston, said the study is large and quite well done.
“It does raise questions about an increase in risk of dementia with six or more cups of coffee per day,” said Dr. Willett. “At the same time, it provides reassurance about lack of adverse effects of coffee for those consuming three or four cups per day, and little increase in risk, if any, with five cups per day.”
It’s not entirely clear whether the increase in risk with six or more cups of coffee per day represents a “true effect” of coffee, inasmuch as the study did not seem to adjust fully for dietary factors, high consumption of alcohol, or past smoking, said Dr. Willett.
The findings don’t suggest that coffee lovers should give up their Java. “But six or more cups per day is a lot, and those who drink that much might consider cutting back a bit while research continues,” said Dr. Willett.
The study was supported by the National Health and Medical Research Council.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NUTRITIONAL NEUROSCIENCE
Occipital nerve stimulation offers relief for patients with intractable chronic cluster headache
Occipital nerve stimulation may help safely prevent attacks of medically intractable chronic cluster headache, according to a new study.
Medically intractable chronic cluster headaches are unilateral headaches that cause excruciating pain during attacks, which may happen as frequently as eight times per day. They are refractory to, or intolerant of, preventive medications typically used in chronic cluster headaches.
“ONS was associated with a major, rapid, and sustained improvement of severe and long-lasting medically intractable chronic cluster headache, both at high and low intensity,” Leopoldine A. Wilbrink, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Centre, and coauthors wrote in their paper.
The findings were published online.
The multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial was carried out at seven hospitals in the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, and Hungary. A total of 150 patients with suspected medically intractable chronic cluster headache were enrolled between October 2010 and December 2017, and observed for 12 weeks at baseline. Of those initially enrolled, 131 patients with at least four medically intractable chronic cluster headache attacks per week and a history of nonresponsiveness to at least three standard preventive medications were randomly allocated to one of two groups: Sixty-five patients received 24 weeks of ONS at high intensity (100% intensity, or the intensity 10% below the threshold of discomfort as reported by the patient) while 66 received low-intensity (30%) ONS. At 25-48 weeks, the patients received open-label ONS.
Safe and well tolerated
“Because ONS causes paraesthesia, preventing masked comparison versus placebo, we compared high-intensity versus low-intensity ONS, which are hypothesised to cause similar paraesthesia, but with different efficacy,” wrote Dr. Wilbrink and colleagues.
From baseline to weeks 21-24, the median weekly mean attack frequencies decreased to 7.38 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.5-18.5, P < .0001). A median decrease in 5.21 attacks per week (–11.18 to –0.19, P < .0001) was observed.
The 100% ONS group saw a decrease in mean attack frequency from 17.58 at baseline (range, 9.83-29.33) to 9.5 (3-21.25) at 21-24 weeks with a median change of –4.08 (–11.92 to –0.25). In the 30% ONS group, the mean attack frequency decreased from 15 (9.25 to 22.33) to 6.75 (1.5-16.5) with a median change of –6.5 (–10.83 to –0.08).
At weeks 21-24, the difference in median weekly mean attack frequency between the groups was –2.42 (–5.17 to 3.33).
The authors stated that, in both groups, ONS was “safe and well tolerated.” A total of 129 adverse events were reported in the 100% ONS group and 95 in the 30% ONS group, of which 17 and 9 were considered serious, respectively. The serious adverse events required a short hospital stay to resolve minor hardware issues. The adverse events most frequently observed were local pain, impaired wound healing, neck stiffness, and hardware damage.
Low intensity stimulation may be best
“The main limitation of the study comes from the difficulty in defining the electrical dose, which was not constant across patients within each group, but individually adjusted depending on the perception of the ONS-induced paraesthesia,” Denys Fontaine, MD, and Michel Lanteri-Minet, MD, both from Université Cote D’Azur in France, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Given that the primary outcome did not differ significantly between the treatment groups, the editorialists stated that “the lowest stimulation intensity that induces paraesthesia is sufficient to obtain an effect in the patients who respond. Increasing the electrical dose or intensity does not seem to bring better efficacy and might even induce discomfort (painful paraesthesia or shock-like sensations) that might substantially reduce the tolerance of this approach.”
While the trial did not provide convincing evidence of high intensity ONS in medically intractable chronic cluster headache, the editorialists are otherwise optimistic about the findings: “… considering the significant difference between baseline and the end of the randomised stimulation phase in both groups (about half of the patients showed a 50% decrease in attack frequency), the findings of this study support the favourable results of previous real-world studies, and indicate that a substantial proportion of patients with intractable chronic cluster headache, although not all, could have their condition substantially improved by ONS.” Dr. Fontaine and Dr. Lanteri-Minet added that they hope that “these data will help health authorities to recognise the efficacy of ONS and consider its approval for use in patients with intractable chronic cluster headache.”
Priorities for future research in this area should “focus on optimising stimulation protocols and disentangling the underlying mechanism of action,” Dr. Wilbrink and colleagues wrote.
The study was funded by the Spinoza 2009 Lifetime Scientific Research Achievement Premium, the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research, the Dutch Ministry of Health (as part of a national provisional reimbursement program for promising new treatments), the NutsOhra Foundation from the Dutch Health Insurance Companies, and an unrestricted grant from Medtronic, all to Dr. Ferrari.
Occipital nerve stimulation may help safely prevent attacks of medically intractable chronic cluster headache, according to a new study.
Medically intractable chronic cluster headaches are unilateral headaches that cause excruciating pain during attacks, which may happen as frequently as eight times per day. They are refractory to, or intolerant of, preventive medications typically used in chronic cluster headaches.
“ONS was associated with a major, rapid, and sustained improvement of severe and long-lasting medically intractable chronic cluster headache, both at high and low intensity,” Leopoldine A. Wilbrink, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Centre, and coauthors wrote in their paper.
The findings were published online.
The multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial was carried out at seven hospitals in the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, and Hungary. A total of 150 patients with suspected medically intractable chronic cluster headache were enrolled between October 2010 and December 2017, and observed for 12 weeks at baseline. Of those initially enrolled, 131 patients with at least four medically intractable chronic cluster headache attacks per week and a history of nonresponsiveness to at least three standard preventive medications were randomly allocated to one of two groups: Sixty-five patients received 24 weeks of ONS at high intensity (100% intensity, or the intensity 10% below the threshold of discomfort as reported by the patient) while 66 received low-intensity (30%) ONS. At 25-48 weeks, the patients received open-label ONS.
Safe and well tolerated
“Because ONS causes paraesthesia, preventing masked comparison versus placebo, we compared high-intensity versus low-intensity ONS, which are hypothesised to cause similar paraesthesia, but with different efficacy,” wrote Dr. Wilbrink and colleagues.
From baseline to weeks 21-24, the median weekly mean attack frequencies decreased to 7.38 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.5-18.5, P < .0001). A median decrease in 5.21 attacks per week (–11.18 to –0.19, P < .0001) was observed.
The 100% ONS group saw a decrease in mean attack frequency from 17.58 at baseline (range, 9.83-29.33) to 9.5 (3-21.25) at 21-24 weeks with a median change of –4.08 (–11.92 to –0.25). In the 30% ONS group, the mean attack frequency decreased from 15 (9.25 to 22.33) to 6.75 (1.5-16.5) with a median change of –6.5 (–10.83 to –0.08).
At weeks 21-24, the difference in median weekly mean attack frequency between the groups was –2.42 (–5.17 to 3.33).
The authors stated that, in both groups, ONS was “safe and well tolerated.” A total of 129 adverse events were reported in the 100% ONS group and 95 in the 30% ONS group, of which 17 and 9 were considered serious, respectively. The serious adverse events required a short hospital stay to resolve minor hardware issues. The adverse events most frequently observed were local pain, impaired wound healing, neck stiffness, and hardware damage.
Low intensity stimulation may be best
“The main limitation of the study comes from the difficulty in defining the electrical dose, which was not constant across patients within each group, but individually adjusted depending on the perception of the ONS-induced paraesthesia,” Denys Fontaine, MD, and Michel Lanteri-Minet, MD, both from Université Cote D’Azur in France, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Given that the primary outcome did not differ significantly between the treatment groups, the editorialists stated that “the lowest stimulation intensity that induces paraesthesia is sufficient to obtain an effect in the patients who respond. Increasing the electrical dose or intensity does not seem to bring better efficacy and might even induce discomfort (painful paraesthesia or shock-like sensations) that might substantially reduce the tolerance of this approach.”
While the trial did not provide convincing evidence of high intensity ONS in medically intractable chronic cluster headache, the editorialists are otherwise optimistic about the findings: “… considering the significant difference between baseline and the end of the randomised stimulation phase in both groups (about half of the patients showed a 50% decrease in attack frequency), the findings of this study support the favourable results of previous real-world studies, and indicate that a substantial proportion of patients with intractable chronic cluster headache, although not all, could have their condition substantially improved by ONS.” Dr. Fontaine and Dr. Lanteri-Minet added that they hope that “these data will help health authorities to recognise the efficacy of ONS and consider its approval for use in patients with intractable chronic cluster headache.”
Priorities for future research in this area should “focus on optimising stimulation protocols and disentangling the underlying mechanism of action,” Dr. Wilbrink and colleagues wrote.
The study was funded by the Spinoza 2009 Lifetime Scientific Research Achievement Premium, the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research, the Dutch Ministry of Health (as part of a national provisional reimbursement program for promising new treatments), the NutsOhra Foundation from the Dutch Health Insurance Companies, and an unrestricted grant from Medtronic, all to Dr. Ferrari.
Occipital nerve stimulation may help safely prevent attacks of medically intractable chronic cluster headache, according to a new study.
Medically intractable chronic cluster headaches are unilateral headaches that cause excruciating pain during attacks, which may happen as frequently as eight times per day. They are refractory to, or intolerant of, preventive medications typically used in chronic cluster headaches.
“ONS was associated with a major, rapid, and sustained improvement of severe and long-lasting medically intractable chronic cluster headache, both at high and low intensity,” Leopoldine A. Wilbrink, MD, of Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Centre, and coauthors wrote in their paper.
The findings were published online.
The multicenter, randomized, double-blind, phase 3 clinical trial was carried out at seven hospitals in the Netherlands, Belgium, Germany, and Hungary. A total of 150 patients with suspected medically intractable chronic cluster headache were enrolled between October 2010 and December 2017, and observed for 12 weeks at baseline. Of those initially enrolled, 131 patients with at least four medically intractable chronic cluster headache attacks per week and a history of nonresponsiveness to at least three standard preventive medications were randomly allocated to one of two groups: Sixty-five patients received 24 weeks of ONS at high intensity (100% intensity, or the intensity 10% below the threshold of discomfort as reported by the patient) while 66 received low-intensity (30%) ONS. At 25-48 weeks, the patients received open-label ONS.
Safe and well tolerated
“Because ONS causes paraesthesia, preventing masked comparison versus placebo, we compared high-intensity versus low-intensity ONS, which are hypothesised to cause similar paraesthesia, but with different efficacy,” wrote Dr. Wilbrink and colleagues.
From baseline to weeks 21-24, the median weekly mean attack frequencies decreased to 7.38 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.5-18.5, P < .0001). A median decrease in 5.21 attacks per week (–11.18 to –0.19, P < .0001) was observed.
The 100% ONS group saw a decrease in mean attack frequency from 17.58 at baseline (range, 9.83-29.33) to 9.5 (3-21.25) at 21-24 weeks with a median change of –4.08 (–11.92 to –0.25). In the 30% ONS group, the mean attack frequency decreased from 15 (9.25 to 22.33) to 6.75 (1.5-16.5) with a median change of –6.5 (–10.83 to –0.08).
At weeks 21-24, the difference in median weekly mean attack frequency between the groups was –2.42 (–5.17 to 3.33).
The authors stated that, in both groups, ONS was “safe and well tolerated.” A total of 129 adverse events were reported in the 100% ONS group and 95 in the 30% ONS group, of which 17 and 9 were considered serious, respectively. The serious adverse events required a short hospital stay to resolve minor hardware issues. The adverse events most frequently observed were local pain, impaired wound healing, neck stiffness, and hardware damage.
Low intensity stimulation may be best
“The main limitation of the study comes from the difficulty in defining the electrical dose, which was not constant across patients within each group, but individually adjusted depending on the perception of the ONS-induced paraesthesia,” Denys Fontaine, MD, and Michel Lanteri-Minet, MD, both from Université Cote D’Azur in France, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
Given that the primary outcome did not differ significantly between the treatment groups, the editorialists stated that “the lowest stimulation intensity that induces paraesthesia is sufficient to obtain an effect in the patients who respond. Increasing the electrical dose or intensity does not seem to bring better efficacy and might even induce discomfort (painful paraesthesia or shock-like sensations) that might substantially reduce the tolerance of this approach.”
While the trial did not provide convincing evidence of high intensity ONS in medically intractable chronic cluster headache, the editorialists are otherwise optimistic about the findings: “… considering the significant difference between baseline and the end of the randomised stimulation phase in both groups (about half of the patients showed a 50% decrease in attack frequency), the findings of this study support the favourable results of previous real-world studies, and indicate that a substantial proportion of patients with intractable chronic cluster headache, although not all, could have their condition substantially improved by ONS.” Dr. Fontaine and Dr. Lanteri-Minet added that they hope that “these data will help health authorities to recognise the efficacy of ONS and consider its approval for use in patients with intractable chronic cluster headache.”
Priorities for future research in this area should “focus on optimising stimulation protocols and disentangling the underlying mechanism of action,” Dr. Wilbrink and colleagues wrote.
The study was funded by the Spinoza 2009 Lifetime Scientific Research Achievement Premium, the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research, the Dutch Ministry of Health (as part of a national provisional reimbursement program for promising new treatments), the NutsOhra Foundation from the Dutch Health Insurance Companies, and an unrestricted grant from Medtronic, all to Dr. Ferrari.
FROM LANCET NEUROLOGY

