User login
What is your diagnosis?
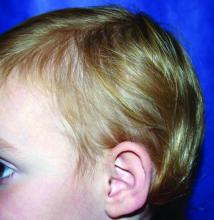
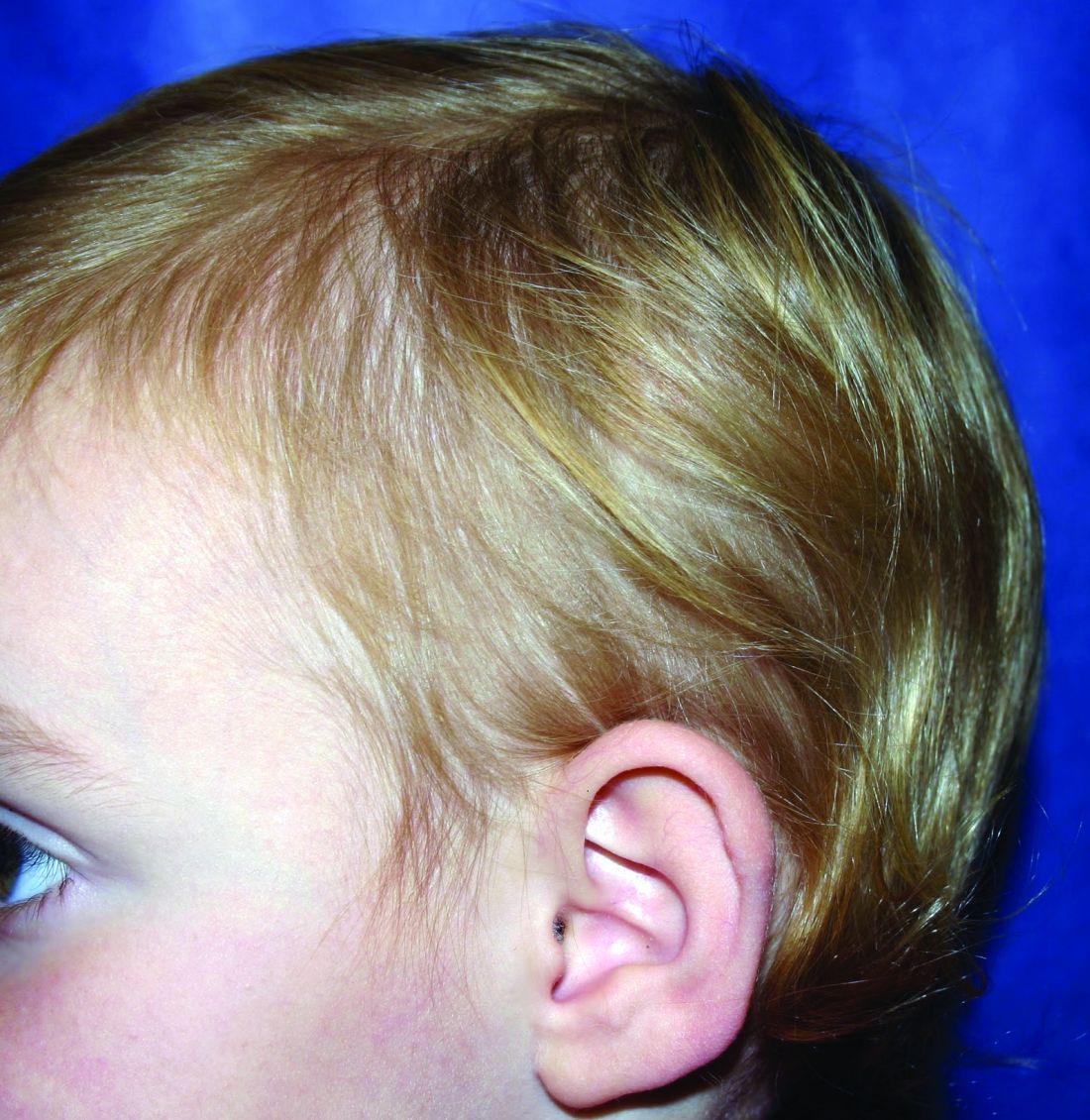
It most commonly affects young girls. The pathogenesis of LAHS is thought to involve a sporadic, autosomal dominant mutation that leads to a defect between the hair cuticle and the inner root sheath.1 This defect results in the hair being poorly anchored to the scalp, and therefore easily and painlessly plucked or lost during normal hair care.
The classic presentation of LAHS is that of hair thinning and hair that may be unruly and/or lackluster; the hair rarely, if ever, requires cutting.2 The key feature is the ability to easily and painlessly pluck hairs from the patient’s scalp. The affected area is limited to the scalp, and loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair should not be seen.
Diagnosis and consideration of the differential
The diagnosis of LAHS can in some cases be made on history and physical exam alone. Patients with LAHS typically will show hair thinning with or without dullness or unruliness. They lack evidence of scalp inflammation, such as erythema, scale, pruritus, and pain. Areas of hair thinning or aberration are typically not well demarcated, and there are typically not areas of complete hair loss. There is no scarring or atrophy of the scalp itself.
Diagnostic tests include the “hair pull test,” as well as trichogram testing. In the “hair pull test” a provider grasps a set of hair at the proximal shaft near the scalp. The traction applied should result in the painless and easy extraction of more than 10% of grasped hairs in a patient with LAHS. Removal of less than 10% of hair is a normal finding, as patients without LAHS typically have about 10% of their scalp hair in the telogen phase at any given time, which would result in removal during the hair pull test.3 In trichography, plucked hairs are examined under magnification, with or without the use of selective dyes. Cinnamaldehyde is a dye that stains citrulline, which is abundant in the inner root sheath, and can be a tool in identifying its presence and/or aberrations.4 A trichogram of the pulled hairs in a patient with LAHS may classically show ruffled appearance of the cuticle, misshapen anagen hair bulbs, and absence of the inner root sheath.5 Examination under magnification also allows providers to better identify telogen versus anagen hairs, which aids in the diagnosis. By carefully considering the patient history, physical exam, and results of additional hair tests, providers can make the diagnosis of LAHS and avoid unnecessary blood work and invasive procedures like scalp biopsies.
The differential diagnosis of hair loss frequently includes alopecia areata. However, in alopecia areata, patients typically have sharply demarcated areas of hair loss, which may involve the eyebrows, eyelids, and body hairs. In alopecia areata, providers may be able to identify the “exclamation point sign” in which the hair shaft thins proximally, leading to the appearance of more pigmented, thicker hairs floating above the scalp.
Telogen effluvium is a condition in which a medical illness or stress, such as systemic illness, surgery, severe emotional distress, childbirth, dietary changes, or another traumatic event, causes a disruption in the natural cycle of hair growth such that the percentage of hairs in the telogen phase increases from about 10% to up to 70%.6 Unlike in LAHS, in which shed hairs are in the anagen phase, the hair that is shed in telogen effluvium is in the telogen phase and will have a different appearance when magnified.
Anagen effluvium, loss of hairs in their growing phase, is typically associated with chemotherapy. The hairs become broken and fractured at the shaft leading to breakage at different points throughout the scalp. Affected areas can include the eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair. In the absence of a history of administration of a chemotherapy agent (or other drug known to trigger hair loss), the diagnosis of anagen effluvium should not be made.
Patients with trichotillosis (also known as trichotillomania) present with areas of hair loss caused by intentional or subconscious hair pulling. It is considered a psychological condition that can be associated with obsessive compulsive disorder, although the presence of a secondary psychological diagnosis is not required. Providers may see irregular geometric shapes of hair loss, and on close inspection see broken hair shafts of different lengths. Patients most often pull hair from their scalps (over 70% of patients), but also can pull eyelashes, eyebrow hairs, and pubic hairs.7
Treatment
LAHS is self-limited and does not necessitate treatment. However, if patients or parents feel there is significant disease burden, perhaps with poor effects on quality of life or with psychosocial impairment, treatment with minoxidil 5% solution has been studied with some success reported in the literature.1,8,9
Ms. Natsis is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Ms. Natsis and Dr. Eichenfield had no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(4):501-6.
2. Int J Trichology. 2010;2(2):96-100.
3. Pediatric Dermatol. 2016:33(50):507-10.
4. Dermatol Clin. 1986;14:745-51.
5. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145(10):1123-8.
6. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(9):WE01-3.
7. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(9):868-74.
8. Australas J Dermatol. 2018;59:e286-e287.
9. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:389-90.
It most commonly affects young girls. The pathogenesis of LAHS is thought to involve a sporadic, autosomal dominant mutation that leads to a defect between the hair cuticle and the inner root sheath.1 This defect results in the hair being poorly anchored to the scalp, and therefore easily and painlessly plucked or lost during normal hair care.
The classic presentation of LAHS is that of hair thinning and hair that may be unruly and/or lackluster; the hair rarely, if ever, requires cutting.2 The key feature is the ability to easily and painlessly pluck hairs from the patient’s scalp. The affected area is limited to the scalp, and loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair should not be seen.
Diagnosis and consideration of the differential
The diagnosis of LAHS can in some cases be made on history and physical exam alone. Patients with LAHS typically will show hair thinning with or without dullness or unruliness. They lack evidence of scalp inflammation, such as erythema, scale, pruritus, and pain. Areas of hair thinning or aberration are typically not well demarcated, and there are typically not areas of complete hair loss. There is no scarring or atrophy of the scalp itself.
Diagnostic tests include the “hair pull test,” as well as trichogram testing. In the “hair pull test” a provider grasps a set of hair at the proximal shaft near the scalp. The traction applied should result in the painless and easy extraction of more than 10% of grasped hairs in a patient with LAHS. Removal of less than 10% of hair is a normal finding, as patients without LAHS typically have about 10% of their scalp hair in the telogen phase at any given time, which would result in removal during the hair pull test.3 In trichography, plucked hairs are examined under magnification, with or without the use of selective dyes. Cinnamaldehyde is a dye that stains citrulline, which is abundant in the inner root sheath, and can be a tool in identifying its presence and/or aberrations.4 A trichogram of the pulled hairs in a patient with LAHS may classically show ruffled appearance of the cuticle, misshapen anagen hair bulbs, and absence of the inner root sheath.5 Examination under magnification also allows providers to better identify telogen versus anagen hairs, which aids in the diagnosis. By carefully considering the patient history, physical exam, and results of additional hair tests, providers can make the diagnosis of LAHS and avoid unnecessary blood work and invasive procedures like scalp biopsies.
The differential diagnosis of hair loss frequently includes alopecia areata. However, in alopecia areata, patients typically have sharply demarcated areas of hair loss, which may involve the eyebrows, eyelids, and body hairs. In alopecia areata, providers may be able to identify the “exclamation point sign” in which the hair shaft thins proximally, leading to the appearance of more pigmented, thicker hairs floating above the scalp.
Telogen effluvium is a condition in which a medical illness or stress, such as systemic illness, surgery, severe emotional distress, childbirth, dietary changes, or another traumatic event, causes a disruption in the natural cycle of hair growth such that the percentage of hairs in the telogen phase increases from about 10% to up to 70%.6 Unlike in LAHS, in which shed hairs are in the anagen phase, the hair that is shed in telogen effluvium is in the telogen phase and will have a different appearance when magnified.
Anagen effluvium, loss of hairs in their growing phase, is typically associated with chemotherapy. The hairs become broken and fractured at the shaft leading to breakage at different points throughout the scalp. Affected areas can include the eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair. In the absence of a history of administration of a chemotherapy agent (or other drug known to trigger hair loss), the diagnosis of anagen effluvium should not be made.
Patients with trichotillosis (also known as trichotillomania) present with areas of hair loss caused by intentional or subconscious hair pulling. It is considered a psychological condition that can be associated with obsessive compulsive disorder, although the presence of a secondary psychological diagnosis is not required. Providers may see irregular geometric shapes of hair loss, and on close inspection see broken hair shafts of different lengths. Patients most often pull hair from their scalps (over 70% of patients), but also can pull eyelashes, eyebrow hairs, and pubic hairs.7
Treatment
LAHS is self-limited and does not necessitate treatment. However, if patients or parents feel there is significant disease burden, perhaps with poor effects on quality of life or with psychosocial impairment, treatment with minoxidil 5% solution has been studied with some success reported in the literature.1,8,9
Ms. Natsis is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Ms. Natsis and Dr. Eichenfield had no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(4):501-6.
2. Int J Trichology. 2010;2(2):96-100.
3. Pediatric Dermatol. 2016:33(50):507-10.
4. Dermatol Clin. 1986;14:745-51.
5. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145(10):1123-8.
6. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(9):WE01-3.
7. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(9):868-74.
8. Australas J Dermatol. 2018;59:e286-e287.
9. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:389-90.
It most commonly affects young girls. The pathogenesis of LAHS is thought to involve a sporadic, autosomal dominant mutation that leads to a defect between the hair cuticle and the inner root sheath.1 This defect results in the hair being poorly anchored to the scalp, and therefore easily and painlessly plucked or lost during normal hair care.
The classic presentation of LAHS is that of hair thinning and hair that may be unruly and/or lackluster; the hair rarely, if ever, requires cutting.2 The key feature is the ability to easily and painlessly pluck hairs from the patient’s scalp. The affected area is limited to the scalp, and loss of eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair should not be seen.
Diagnosis and consideration of the differential
The diagnosis of LAHS can in some cases be made on history and physical exam alone. Patients with LAHS typically will show hair thinning with or without dullness or unruliness. They lack evidence of scalp inflammation, such as erythema, scale, pruritus, and pain. Areas of hair thinning or aberration are typically not well demarcated, and there are typically not areas of complete hair loss. There is no scarring or atrophy of the scalp itself.
Diagnostic tests include the “hair pull test,” as well as trichogram testing. In the “hair pull test” a provider grasps a set of hair at the proximal shaft near the scalp. The traction applied should result in the painless and easy extraction of more than 10% of grasped hairs in a patient with LAHS. Removal of less than 10% of hair is a normal finding, as patients without LAHS typically have about 10% of their scalp hair in the telogen phase at any given time, which would result in removal during the hair pull test.3 In trichography, plucked hairs are examined under magnification, with or without the use of selective dyes. Cinnamaldehyde is a dye that stains citrulline, which is abundant in the inner root sheath, and can be a tool in identifying its presence and/or aberrations.4 A trichogram of the pulled hairs in a patient with LAHS may classically show ruffled appearance of the cuticle, misshapen anagen hair bulbs, and absence of the inner root sheath.5 Examination under magnification also allows providers to better identify telogen versus anagen hairs, which aids in the diagnosis. By carefully considering the patient history, physical exam, and results of additional hair tests, providers can make the diagnosis of LAHS and avoid unnecessary blood work and invasive procedures like scalp biopsies.
The differential diagnosis of hair loss frequently includes alopecia areata. However, in alopecia areata, patients typically have sharply demarcated areas of hair loss, which may involve the eyebrows, eyelids, and body hairs. In alopecia areata, providers may be able to identify the “exclamation point sign” in which the hair shaft thins proximally, leading to the appearance of more pigmented, thicker hairs floating above the scalp.
Telogen effluvium is a condition in which a medical illness or stress, such as systemic illness, surgery, severe emotional distress, childbirth, dietary changes, or another traumatic event, causes a disruption in the natural cycle of hair growth such that the percentage of hairs in the telogen phase increases from about 10% to up to 70%.6 Unlike in LAHS, in which shed hairs are in the anagen phase, the hair that is shed in telogen effluvium is in the telogen phase and will have a different appearance when magnified.
Anagen effluvium, loss of hairs in their growing phase, is typically associated with chemotherapy. The hairs become broken and fractured at the shaft leading to breakage at different points throughout the scalp. Affected areas can include the eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair. In the absence of a history of administration of a chemotherapy agent (or other drug known to trigger hair loss), the diagnosis of anagen effluvium should not be made.
Patients with trichotillosis (also known as trichotillomania) present with areas of hair loss caused by intentional or subconscious hair pulling. It is considered a psychological condition that can be associated with obsessive compulsive disorder, although the presence of a secondary psychological diagnosis is not required. Providers may see irregular geometric shapes of hair loss, and on close inspection see broken hair shafts of different lengths. Patients most often pull hair from their scalps (over 70% of patients), but also can pull eyelashes, eyebrow hairs, and pubic hairs.7
Treatment
LAHS is self-limited and does not necessitate treatment. However, if patients or parents feel there is significant disease burden, perhaps with poor effects on quality of life or with psychosocial impairment, treatment with minoxidil 5% solution has been studied with some success reported in the literature.1,8,9
Ms. Natsis is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital-San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. Ms. Natsis and Dr. Eichenfield had no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Arch Dermatol. 2002;138(4):501-6.
2. Int J Trichology. 2010;2(2):96-100.
3. Pediatric Dermatol. 2016:33(50):507-10.
4. Dermatol Clin. 1986;14:745-51.
5. Arch Dermatol. 2009;145(10):1123-8.
6. J Clin Diagn Res. 2015;9(9):WE01-3.
7. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173(9):868-74.
8. Australas J Dermatol. 2018;59:e286-e287.
9. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014;31:389-90.
A 5-year-old female is brought to clinic for hair loss. The mother reports that when styling her daughter's hair, she has noticed areas of hair thinning, especially at the temples and at the occiput. The mother denies scale, pruritus, and erythema. The patient reports that her scalp does not hurt. She has never had a haircut because her hair hasn't grown long enough to cut. There is no history of specific bald spots. The patient has no personal history of psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, or autoimmune disease. No picking has been noted, and there is no history of compulsive behaviors or anxiety. The patient's mother has a history of Graves disease. The mother reports that the patient's older sister may have had hair thinning when she was younger as well, but no longer has thin hair.
The patient was previously seen by another provider who prescribed hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment, which the mother has been applying nightly without improvement.
The child is otherwise medically well and thriving, with no recent change in activity level and with growth parameters consistently around the 75th percentile for height and weight. On physical exam, the patient has blondish, fine hair with areas of poorly demarcated hair thinning at the left temple and at the occiput. The hair remaining at the occiput is normal in texture. There are no areas of complete hair loss. There is no scale, erythema, or abnormal pigmentation, and no cervical or occipital adenopathy. The patient has intact eyebrows and eyelashes.
What's your diagnosis?
The patient was diagnosed with lichen spinulosus (LS) based on the physical appearance of the lesions (hyperkeratotic spiny papules forming plaques), the lack of pruritus, and negative personal history of atopic dermatitis.
Lichen spinulosus is an underreported entity, first described in 1908 by Adamson as superficial circumscribed chronic dermatitis in children and adolescents. The median age of presentation is age 16 years. There are several reports of possible associations with systemic infections such as HIV, fungi, and syphilis, as well as chronic diseases such as Crohn’s disease, Hodgkin disease, seborrhea, and secondary to certain medications such as omeprazole. There are no prior reports of infliximab being associated with LS, but it has been reported to cause other lichenoid reactions such as lichen planus and lichen planopilaris.
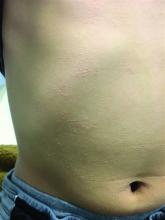
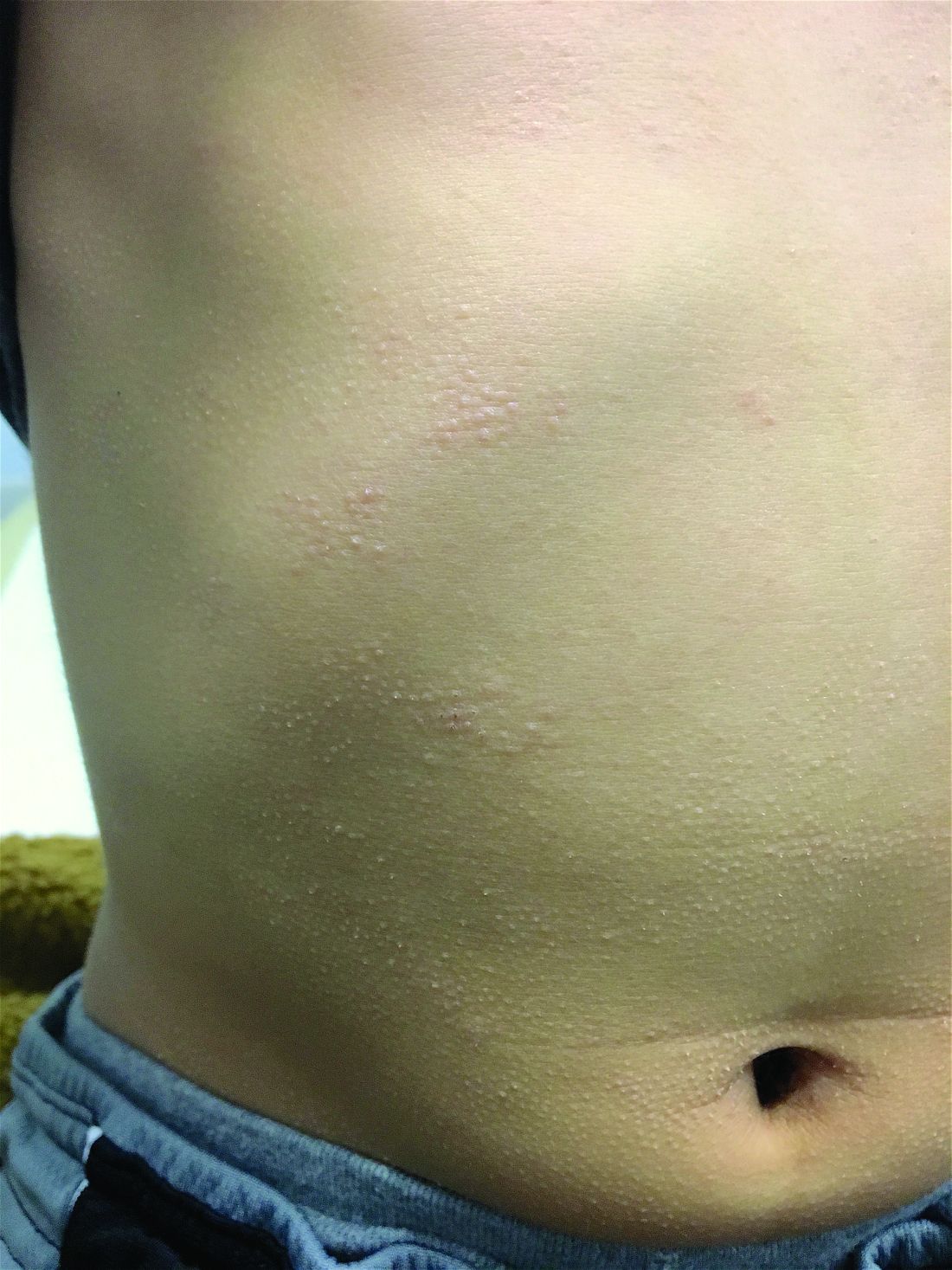
Clinically the lesions are characterized by asymptomatic, small (1 cm), skin color, hyperkeratotic, follicular papules that coalesce into plaques. The lesions usually occur on the extensor surfaces of the arms, neck, torso, and buttocks. Mild pruritus can occur in some patients.
The lesions in keratosis pilaris can be very similar to lichen spinulosus, but usually they don’t coalesce into plaques and are commonly present on the extensor surfaces of the arms, thighs, and cheeks. Histopathology of both conditions is very similar.
Another condition to consider includes papular eczema. The lesions in papular eczema tend to be pruritic and are not as circumscribed as LS lesions. Papular eczema responds well to the use of topical corticosteroids, while LS lesions usually do not. Lichen nitidus (LN) is characterized by monomorphic, skin color, 1-mm, flat-topped papules. Lesions tend to occur in crops rather than circumscribed papules forming plaques. LN most commonly presents on the extensor surface of the arms, trunk, dorsal hands, and genitalia. Koebner phenomenon is usually seen. Although uncommon in children, a more generalized type of follicular mucinosis can present very similar to lichen spinulosus. A recent study found LS-like lesions with associated hypopigmentation and hair loss should be suspicious for folliculotropic mycosis fungoides.
Keratolytics such as lactic acid, urea, and salicylic acid can help improve LS, although they do not cure it. Other reported treatments include the use of topical adapalene, tacalcitol cream, and tretinoin gel with hydroactive adhesive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
The patient was diagnosed with lichen spinulosus (LS) based on the physical appearance of the lesions (hyperkeratotic spiny papules forming plaques), the lack of pruritus, and negative personal history of atopic dermatitis.
Lichen spinulosus is an underreported entity, first described in 1908 by Adamson as superficial circumscribed chronic dermatitis in children and adolescents. The median age of presentation is age 16 years. There are several reports of possible associations with systemic infections such as HIV, fungi, and syphilis, as well as chronic diseases such as Crohn’s disease, Hodgkin disease, seborrhea, and secondary to certain medications such as omeprazole. There are no prior reports of infliximab being associated with LS, but it has been reported to cause other lichenoid reactions such as lichen planus and lichen planopilaris.
Clinically the lesions are characterized by asymptomatic, small (1 cm), skin color, hyperkeratotic, follicular papules that coalesce into plaques. The lesions usually occur on the extensor surfaces of the arms, neck, torso, and buttocks. Mild pruritus can occur in some patients.
The lesions in keratosis pilaris can be very similar to lichen spinulosus, but usually they don’t coalesce into plaques and are commonly present on the extensor surfaces of the arms, thighs, and cheeks. Histopathology of both conditions is very similar.
Another condition to consider includes papular eczema. The lesions in papular eczema tend to be pruritic and are not as circumscribed as LS lesions. Papular eczema responds well to the use of topical corticosteroids, while LS lesions usually do not. Lichen nitidus (LN) is characterized by monomorphic, skin color, 1-mm, flat-topped papules. Lesions tend to occur in crops rather than circumscribed papules forming plaques. LN most commonly presents on the extensor surface of the arms, trunk, dorsal hands, and genitalia. Koebner phenomenon is usually seen. Although uncommon in children, a more generalized type of follicular mucinosis can present very similar to lichen spinulosus. A recent study found LS-like lesions with associated hypopigmentation and hair loss should be suspicious for folliculotropic mycosis fungoides.
Keratolytics such as lactic acid, urea, and salicylic acid can help improve LS, although they do not cure it. Other reported treatments include the use of topical adapalene, tacalcitol cream, and tretinoin gel with hydroactive adhesive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
The patient was diagnosed with lichen spinulosus (LS) based on the physical appearance of the lesions (hyperkeratotic spiny papules forming plaques), the lack of pruritus, and negative personal history of atopic dermatitis.
Lichen spinulosus is an underreported entity, first described in 1908 by Adamson as superficial circumscribed chronic dermatitis in children and adolescents. The median age of presentation is age 16 years. There are several reports of possible associations with systemic infections such as HIV, fungi, and syphilis, as well as chronic diseases such as Crohn’s disease, Hodgkin disease, seborrhea, and secondary to certain medications such as omeprazole. There are no prior reports of infliximab being associated with LS, but it has been reported to cause other lichenoid reactions such as lichen planus and lichen planopilaris.
Clinically the lesions are characterized by asymptomatic, small (1 cm), skin color, hyperkeratotic, follicular papules that coalesce into plaques. The lesions usually occur on the extensor surfaces of the arms, neck, torso, and buttocks. Mild pruritus can occur in some patients.
The lesions in keratosis pilaris can be very similar to lichen spinulosus, but usually they don’t coalesce into plaques and are commonly present on the extensor surfaces of the arms, thighs, and cheeks. Histopathology of both conditions is very similar.
Another condition to consider includes papular eczema. The lesions in papular eczema tend to be pruritic and are not as circumscribed as LS lesions. Papular eczema responds well to the use of topical corticosteroids, while LS lesions usually do not. Lichen nitidus (LN) is characterized by monomorphic, skin color, 1-mm, flat-topped papules. Lesions tend to occur in crops rather than circumscribed papules forming plaques. LN most commonly presents on the extensor surface of the arms, trunk, dorsal hands, and genitalia. Koebner phenomenon is usually seen. Although uncommon in children, a more generalized type of follicular mucinosis can present very similar to lichen spinulosus. A recent study found LS-like lesions with associated hypopigmentation and hair loss should be suspicious for folliculotropic mycosis fungoides.
Keratolytics such as lactic acid, urea, and salicylic acid can help improve LS, although they do not cure it. Other reported treatments include the use of topical adapalene, tacalcitol cream, and tretinoin gel with hydroactive adhesive.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
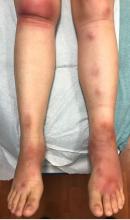
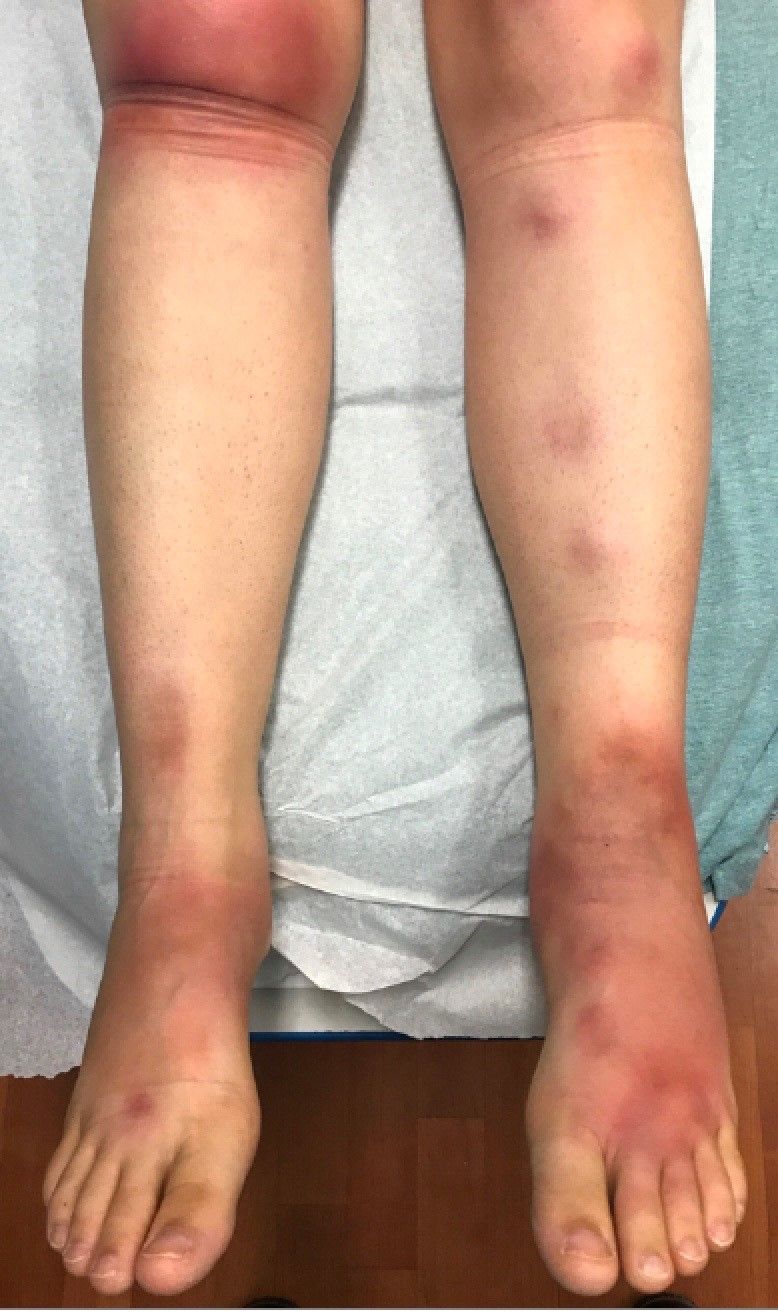
A 7-year-old male with a history of Crohn's disease presents with 6 months of asymptomatic, bumpy lesions on the torso and extremities. He has been using over-the-counter hydrocortisone and moisturizers without it helping. His Crohn's disease has been controlled with infliximab infusions for 2 years. The mother is concerned the rash could be a side effect of the medication.
He denies any prior history of atopic dermatitis or psoriasis. The mother had eczema as a child. He has two brothers who have been diagnosed and treated for allergic rhinitis.
On physical examination, he is a thin, pleasant young boy in no distress.
His skin is somewhat dry, and there are several hyperkeratotic follicular papules forming plaques on the torso and extremities. There is no associated hair loss on the affected areas or inflammation noted.
What is your diagnosis?
Epidermal nevi are a subset of cutaneous hamartomas resulting from somatic mutations of epidermal cells, presenting as keratinocyte or epidermal appendage overgrowths. The most common type appear in a linear distribution and are termed linear epidermal nevi or linear verrucous epidermal nevi.
There are variations of epidermal nevi (EN) that can be composed of superficial epidermal keratinocytes, sebaceous glands, apocrine or eccrine glands, hair follicles, or smooth muscle. For example, many consider a nevus sebaceous to be a type of epidermal nevus as well. The incidence of EN is approximately 1 in 1,000 newborns. Postzygotic cell mutations result in a mosaic distribution that follows embryonic migration patterns, appearing in a Blaschkoid distribution.
EN present most frequently as unilateral linear or whorled hyperpigmented coalescing papules. The lesions can be present at birth or during childhood, and after appearing, grow with the patient. Typically the lesions become more raised and verrucous around puberty. The differential diagnosis of linear EN include lichen striatus, warts, and incontinentia pigmenti. Lichen striatus can be differentiated because it presents later in life and self-resolves. Verrucae are the most commonly mistaken diagnosis for EN; warts do not usually persist in the same pattern over time with proportionate growth and typically respond to locally destructive treatments such as liquid nitrogen, unlike EN. Incontinentia pigmenti presents as vesicles initially and shows a quick evolution, differentiating it from EN. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a variant of linear EN that has associated chronic and intermittent erythema, scale, and pruritus. Lichen nitidus often has a pruritic presentation; however, it is flat topped and skin colored, helping differentiate it from linear EN.
There has been recent research advancing gene associations for linear EN displaying many lesions associated with mosaic mutations in oncogenes. Multiple genes have been identified with EN including RAS, FGFR3, and PIK3CA1. FGFR3 and PIK3CA mutations are associated with 50% of keratinocytic nevi. Of the RAS family, the HRAS pathway has been most closely associated with nevus sebaceous. While KRAS and NRAS genes have been associated with EN, it is to a lesser degree. However, there are multiple recent case reports demonstrating a potential association of G12D mosaicism of the KRAS gene in EN with rhabdomyosarcoma and bladder cancers2.
The diagnosis of epidermal nevus syndrome should be considered when there is a nevus with associated developmental abnormality of the central nervous system, eyes, or musculoskeletal systems. The most common systemic symptoms include delays in developmental milestones, seizure disorders, coloboma, strabismus, muscle weakness, and hemihypertrophy. To date, there are six specific epidermal nevus syndromes identified: sebaceous nevus syndrome, nevus comedonicus syndrome, Becker nevus syndrome, phakomatosis pigmentokeratotica, Proteus syndrome, congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform nevus and limb defects, and cutaneous-skeletal hypophosphatemia syndrome3. In addition to the syndromes described, there are reports of associations between keratinocytic nevi and ILVEN with hypophosphatemic rickets and precocious puberty.
Linear EN are rarely associated with malignant transformation to basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, depending on the cell type involved. Given the low risk of malignancy, the lesions do not need to be removed routinely. For small lesions, monitoring often is the preferred management. However, lesions with functional significance, or causing strangulation or deformity, can be treated with surgical excision, curettage, or laser destruction
Dr. Kaushik is with the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego, and Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Dr. Kaushik or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jul-Aug;21(4):432-9.
2. J Med Genet. 2010 Dec;47(12):859-62.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jan;35(1):21-9.
Epidermal nevi are a subset of cutaneous hamartomas resulting from somatic mutations of epidermal cells, presenting as keratinocyte or epidermal appendage overgrowths. The most common type appear in a linear distribution and are termed linear epidermal nevi or linear verrucous epidermal nevi.
There are variations of epidermal nevi (EN) that can be composed of superficial epidermal keratinocytes, sebaceous glands, apocrine or eccrine glands, hair follicles, or smooth muscle. For example, many consider a nevus sebaceous to be a type of epidermal nevus as well. The incidence of EN is approximately 1 in 1,000 newborns. Postzygotic cell mutations result in a mosaic distribution that follows embryonic migration patterns, appearing in a Blaschkoid distribution.
EN present most frequently as unilateral linear or whorled hyperpigmented coalescing papules. The lesions can be present at birth or during childhood, and after appearing, grow with the patient. Typically the lesions become more raised and verrucous around puberty. The differential diagnosis of linear EN include lichen striatus, warts, and incontinentia pigmenti. Lichen striatus can be differentiated because it presents later in life and self-resolves. Verrucae are the most commonly mistaken diagnosis for EN; warts do not usually persist in the same pattern over time with proportionate growth and typically respond to locally destructive treatments such as liquid nitrogen, unlike EN. Incontinentia pigmenti presents as vesicles initially and shows a quick evolution, differentiating it from EN. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a variant of linear EN that has associated chronic and intermittent erythema, scale, and pruritus. Lichen nitidus often has a pruritic presentation; however, it is flat topped and skin colored, helping differentiate it from linear EN.
There has been recent research advancing gene associations for linear EN displaying many lesions associated with mosaic mutations in oncogenes. Multiple genes have been identified with EN including RAS, FGFR3, and PIK3CA1. FGFR3 and PIK3CA mutations are associated with 50% of keratinocytic nevi. Of the RAS family, the HRAS pathway has been most closely associated with nevus sebaceous. While KRAS and NRAS genes have been associated with EN, it is to a lesser degree. However, there are multiple recent case reports demonstrating a potential association of G12D mosaicism of the KRAS gene in EN with rhabdomyosarcoma and bladder cancers2.
The diagnosis of epidermal nevus syndrome should be considered when there is a nevus with associated developmental abnormality of the central nervous system, eyes, or musculoskeletal systems. The most common systemic symptoms include delays in developmental milestones, seizure disorders, coloboma, strabismus, muscle weakness, and hemihypertrophy. To date, there are six specific epidermal nevus syndromes identified: sebaceous nevus syndrome, nevus comedonicus syndrome, Becker nevus syndrome, phakomatosis pigmentokeratotica, Proteus syndrome, congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform nevus and limb defects, and cutaneous-skeletal hypophosphatemia syndrome3. In addition to the syndromes described, there are reports of associations between keratinocytic nevi and ILVEN with hypophosphatemic rickets and precocious puberty.
Linear EN are rarely associated with malignant transformation to basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, depending on the cell type involved. Given the low risk of malignancy, the lesions do not need to be removed routinely. For small lesions, monitoring often is the preferred management. However, lesions with functional significance, or causing strangulation or deformity, can be treated with surgical excision, curettage, or laser destruction
Dr. Kaushik is with the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego, and Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Dr. Kaushik or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jul-Aug;21(4):432-9.
2. J Med Genet. 2010 Dec;47(12):859-62.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jan;35(1):21-9.
Epidermal nevi are a subset of cutaneous hamartomas resulting from somatic mutations of epidermal cells, presenting as keratinocyte or epidermal appendage overgrowths. The most common type appear in a linear distribution and are termed linear epidermal nevi or linear verrucous epidermal nevi.
There are variations of epidermal nevi (EN) that can be composed of superficial epidermal keratinocytes, sebaceous glands, apocrine or eccrine glands, hair follicles, or smooth muscle. For example, many consider a nevus sebaceous to be a type of epidermal nevus as well. The incidence of EN is approximately 1 in 1,000 newborns. Postzygotic cell mutations result in a mosaic distribution that follows embryonic migration patterns, appearing in a Blaschkoid distribution.
EN present most frequently as unilateral linear or whorled hyperpigmented coalescing papules. The lesions can be present at birth or during childhood, and after appearing, grow with the patient. Typically the lesions become more raised and verrucous around puberty. The differential diagnosis of linear EN include lichen striatus, warts, and incontinentia pigmenti. Lichen striatus can be differentiated because it presents later in life and self-resolves. Verrucae are the most commonly mistaken diagnosis for EN; warts do not usually persist in the same pattern over time with proportionate growth and typically respond to locally destructive treatments such as liquid nitrogen, unlike EN. Incontinentia pigmenti presents as vesicles initially and shows a quick evolution, differentiating it from EN. Inflammatory linear verrucous epidermal nevus (ILVEN) is a variant of linear EN that has associated chronic and intermittent erythema, scale, and pruritus. Lichen nitidus often has a pruritic presentation; however, it is flat topped and skin colored, helping differentiate it from linear EN.
There has been recent research advancing gene associations for linear EN displaying many lesions associated with mosaic mutations in oncogenes. Multiple genes have been identified with EN including RAS, FGFR3, and PIK3CA1. FGFR3 and PIK3CA mutations are associated with 50% of keratinocytic nevi. Of the RAS family, the HRAS pathway has been most closely associated with nevus sebaceous. While KRAS and NRAS genes have been associated with EN, it is to a lesser degree. However, there are multiple recent case reports demonstrating a potential association of G12D mosaicism of the KRAS gene in EN with rhabdomyosarcoma and bladder cancers2.
The diagnosis of epidermal nevus syndrome should be considered when there is a nevus with associated developmental abnormality of the central nervous system, eyes, or musculoskeletal systems. The most common systemic symptoms include delays in developmental milestones, seizure disorders, coloboma, strabismus, muscle weakness, and hemihypertrophy. To date, there are six specific epidermal nevus syndromes identified: sebaceous nevus syndrome, nevus comedonicus syndrome, Becker nevus syndrome, phakomatosis pigmentokeratotica, Proteus syndrome, congenital hemidysplasia with ichthyosiform nevus and limb defects, and cutaneous-skeletal hypophosphatemia syndrome3. In addition to the syndromes described, there are reports of associations between keratinocytic nevi and ILVEN with hypophosphatemic rickets and precocious puberty.
Linear EN are rarely associated with malignant transformation to basal cell carcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma, depending on the cell type involved. Given the low risk of malignancy, the lesions do not need to be removed routinely. For small lesions, monitoring often is the preferred management. However, lesions with functional significance, or causing strangulation or deformity, can be treated with surgical excision, curettage, or laser destruction
Dr. Kaushik is with the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego, and Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Dr. Kaushik or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jul-Aug;21(4):432-9.
2. J Med Genet. 2010 Dec;47(12):859-62.
3. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 Jan;35(1):21-9.
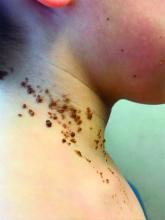
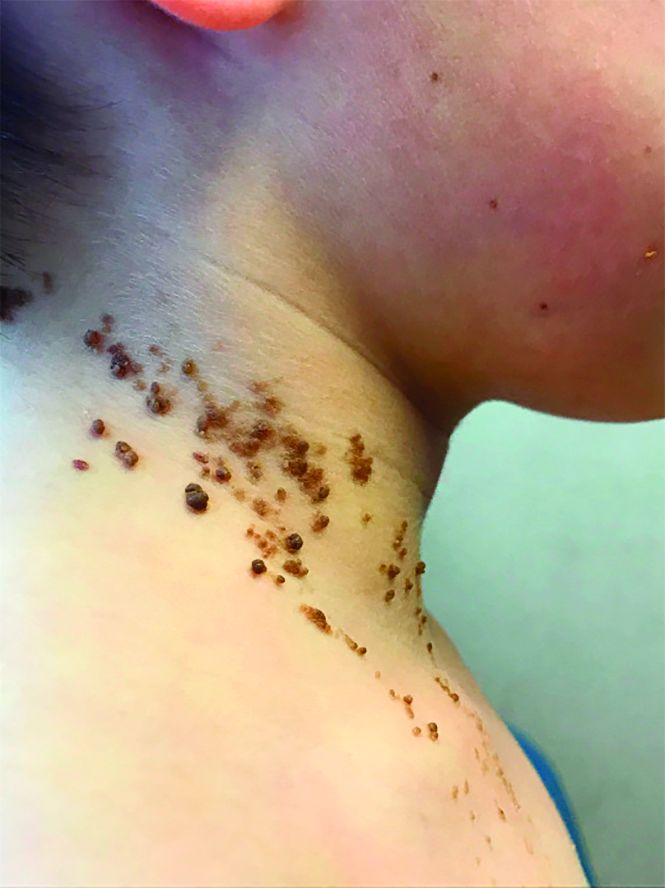
A 6-year-old, otherwise-healthy male is brought into clinic for evaluation of papules on his neck. The rash has been present since 1 year of age and has been growing in size proportionately. He claims there is occasional itching but no pain or redness. He does not seem to be disturbed by his rash. He has two siblings, aged 2 and 4 years, without lesions.
On physical exam, he is noted to have a linear plaque of hyperpigmented verrucous papules on his neck.
What is your diagnosis? - December 2018
A KOH (potassium hydroxide) test done at the visit was negative as well as a fungal culture of each toenail.
The patient was diagnosed with congenital malalignment of the great toenails (CMGTN) based on history and morphologic appearance.
Congenital malalignment of the great toenails is an underrecognized and underreported nail disorder characterized by lateral deviation of the nail plate, which is not parallel to the longitudinal axis of the distal phalanx.1 The cause is unknown. Some reports suggest a genetic cause being transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion with variable expression.2 There have been reports of CMGTN in monozygotic and dizygotic twins making this theory likely.3 Other authors consider an external cause such as amniotic bands, neonatal asphyxia, vascular malformations, and uterine pressure. This condition also has been reported in patients with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.4
The nail changes can occur at birth but in some cases, such as our patient, the nails become dystrophic months to years after birth. Characteristic nail changes include shorter, discolored, hyperkeratotic nails with transverse groove or ridges. In some cases, the dystrophic nails may cause inflammation and tenderness and is the most common cause of ingrown toenails in children.
The differential diagnosis includes onychomycosis, traumatic nails, nail psoriasis, pachyonychia congenital (PC), and onychomadesis. Onychomycosis can present with white or yellow discoloration of the nail that in some cases can be associated with nail breakage, hyperkeratosis, onycholysis, and subungual debris. Either fungal culture or periodic acid shift stain of nail clippings can help confirm or exclude this diagnosis. Psoriatic nails present with nail pits, oils spots, and onycholysis. Traumatic nail changes may occur from using small shoes and trauma from running or playing soccer, and presents with subungual hemorrhage and nail dystrophy of the first or second toenail. PC is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in certain keratin proteins of the skin (k6a, k6b, K16 and K17). These patients usually have other skin findings including palmoplantar keratoderma, white plaques on the mouth, and skin cysts (steatocystoma multiplex and vellus hair cysts). Nail changes characteristic of PC includes subungual hyperkeratosis that causes a wedge shape thickening of the nail bed (pincer nails).5 Onychomadesis can be seen after viral infections such as hand-foot-mouth disease or in patients taking chemotherapy drugs that affect nail growth.
CMGTN usually resolves with time, but some patients with severe deviation and paronychia may need surgical correction.6
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2014 Jan 15;20(1):21251.
2. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012 May;10(5):326-30.
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007 Oct;57(4):711-5.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jan-Feb;21(1):44-7.
5. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014 Aug;26(4):440-5.
6. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Oct;4(4):230-5.
A KOH (potassium hydroxide) test done at the visit was negative as well as a fungal culture of each toenail.
The patient was diagnosed with congenital malalignment of the great toenails (CMGTN) based on history and morphologic appearance.
Congenital malalignment of the great toenails is an underrecognized and underreported nail disorder characterized by lateral deviation of the nail plate, which is not parallel to the longitudinal axis of the distal phalanx.1 The cause is unknown. Some reports suggest a genetic cause being transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion with variable expression.2 There have been reports of CMGTN in monozygotic and dizygotic twins making this theory likely.3 Other authors consider an external cause such as amniotic bands, neonatal asphyxia, vascular malformations, and uterine pressure. This condition also has been reported in patients with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.4
The nail changes can occur at birth but in some cases, such as our patient, the nails become dystrophic months to years after birth. Characteristic nail changes include shorter, discolored, hyperkeratotic nails with transverse groove or ridges. In some cases, the dystrophic nails may cause inflammation and tenderness and is the most common cause of ingrown toenails in children.
The differential diagnosis includes onychomycosis, traumatic nails, nail psoriasis, pachyonychia congenital (PC), and onychomadesis. Onychomycosis can present with white or yellow discoloration of the nail that in some cases can be associated with nail breakage, hyperkeratosis, onycholysis, and subungual debris. Either fungal culture or periodic acid shift stain of nail clippings can help confirm or exclude this diagnosis. Psoriatic nails present with nail pits, oils spots, and onycholysis. Traumatic nail changes may occur from using small shoes and trauma from running or playing soccer, and presents with subungual hemorrhage and nail dystrophy of the first or second toenail. PC is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in certain keratin proteins of the skin (k6a, k6b, K16 and K17). These patients usually have other skin findings including palmoplantar keratoderma, white plaques on the mouth, and skin cysts (steatocystoma multiplex and vellus hair cysts). Nail changes characteristic of PC includes subungual hyperkeratosis that causes a wedge shape thickening of the nail bed (pincer nails).5 Onychomadesis can be seen after viral infections such as hand-foot-mouth disease or in patients taking chemotherapy drugs that affect nail growth.
CMGTN usually resolves with time, but some patients with severe deviation and paronychia may need surgical correction.6
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2014 Jan 15;20(1):21251.
2. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012 May;10(5):326-30.
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007 Oct;57(4):711-5.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jan-Feb;21(1):44-7.
5. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014 Aug;26(4):440-5.
6. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Oct;4(4):230-5.
A KOH (potassium hydroxide) test done at the visit was negative as well as a fungal culture of each toenail.
The patient was diagnosed with congenital malalignment of the great toenails (CMGTN) based on history and morphologic appearance.
Congenital malalignment of the great toenails is an underrecognized and underreported nail disorder characterized by lateral deviation of the nail plate, which is not parallel to the longitudinal axis of the distal phalanx.1 The cause is unknown. Some reports suggest a genetic cause being transmitted in an autosomal dominant fashion with variable expression.2 There have been reports of CMGTN in monozygotic and dizygotic twins making this theory likely.3 Other authors consider an external cause such as amniotic bands, neonatal asphyxia, vascular malformations, and uterine pressure. This condition also has been reported in patients with Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome.4
The nail changes can occur at birth but in some cases, such as our patient, the nails become dystrophic months to years after birth. Characteristic nail changes include shorter, discolored, hyperkeratotic nails with transverse groove or ridges. In some cases, the dystrophic nails may cause inflammation and tenderness and is the most common cause of ingrown toenails in children.
The differential diagnosis includes onychomycosis, traumatic nails, nail psoriasis, pachyonychia congenital (PC), and onychomadesis. Onychomycosis can present with white or yellow discoloration of the nail that in some cases can be associated with nail breakage, hyperkeratosis, onycholysis, and subungual debris. Either fungal culture or periodic acid shift stain of nail clippings can help confirm or exclude this diagnosis. Psoriatic nails present with nail pits, oils spots, and onycholysis. Traumatic nail changes may occur from using small shoes and trauma from running or playing soccer, and presents with subungual hemorrhage and nail dystrophy of the first or second toenail. PC is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in certain keratin proteins of the skin (k6a, k6b, K16 and K17). These patients usually have other skin findings including palmoplantar keratoderma, white plaques on the mouth, and skin cysts (steatocystoma multiplex and vellus hair cysts). Nail changes characteristic of PC includes subungual hyperkeratosis that causes a wedge shape thickening of the nail bed (pincer nails).5 Onychomadesis can be seen after viral infections such as hand-foot-mouth disease or in patients taking chemotherapy drugs that affect nail growth.
CMGTN usually resolves with time, but some patients with severe deviation and paronychia may need surgical correction.6
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected].
References
1. Dermatol Online J. 2014 Jan 15;20(1):21251.
2. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012 May;10(5):326-30.
3. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007 Oct;57(4):711-5.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004 Jan-Feb;21(1):44-7.
5. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2014 Aug;26(4):440-5.
6. Skin Appendage Disord. 2018 Oct;4(4):230-5.
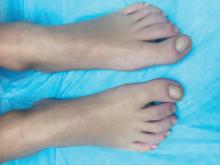
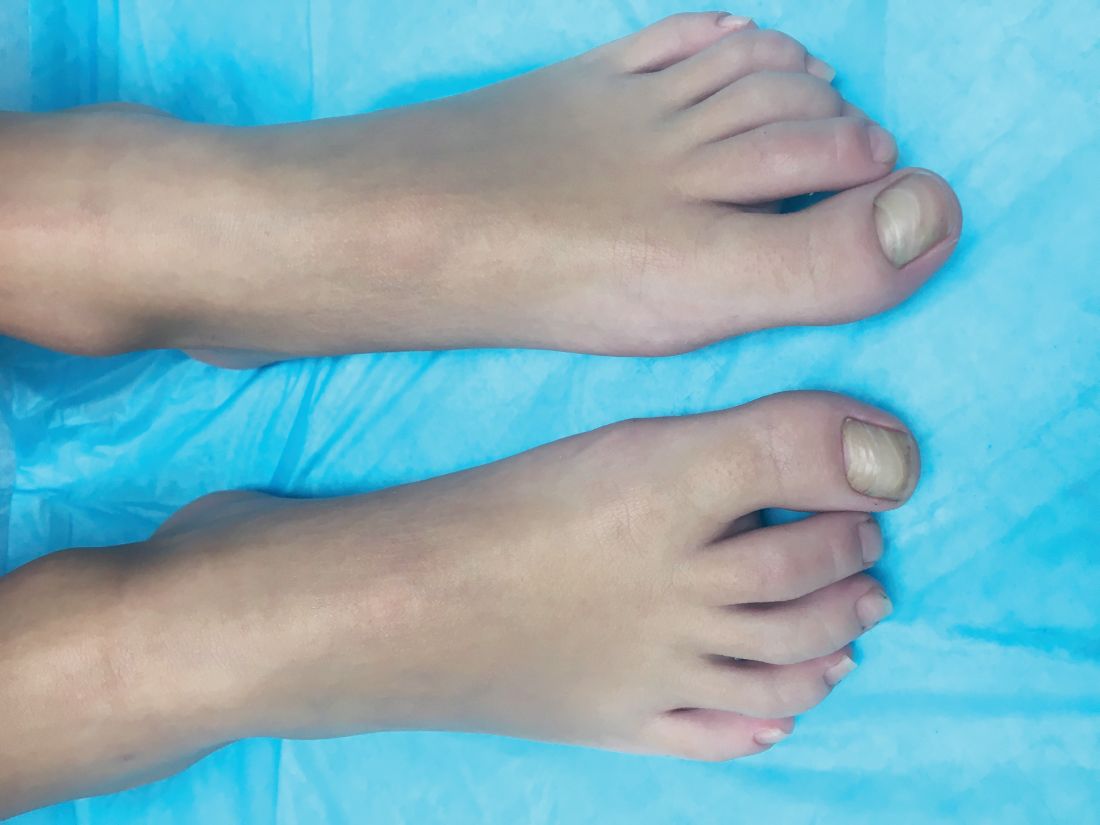
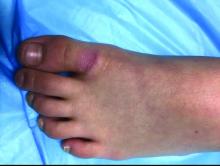
A 4-year-old boy is brought to our pediatric dermatology clinic by his mother with the concern of difficult to treat toenail fungus.
The mother reported that she started noticing the toenail changes at around 8 months of age, and it has been progressively getting worse.
He has been treated with several courses of topical antifungals and 3 months of oral terbinafine without success.
A fungal culture done 1 year prior showed slight growth of Cladosporium Sp., but the nails failed to improve after systemic therapy. He denied any associated pain or inflammation. He likes playing softball and plays soccer sometimes. The mother is very worried because the father also has a history of onychomycosis that he has not been able to clear for years.
On physical exam, he is a very pleasant young boy. His cutaneous exam is normal including hair and teeth except for thickening of the bilateral first toenails associated with transverse ridging and yellow discoloration.
What is your diagnosis?
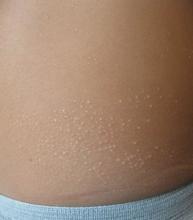
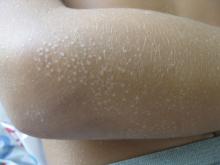
Lichen nitidus, which literally means “shiny moss,” is a relatively rare, chronic skin eruption that is characterized clinically by asymptomatic, flat-topped, sharply-demarcated, skin-colored papules, which are sometimes described as being “pinpoint.”
Lichen nitidus mainly affects children and young adults. The most common sites of involvement are the trunk, flexor aspects of upper extremities, dorsal aspects of hands, and genitalia, but lesions can occur anywhere on the skin. The lesions also can develop in sites of trauma (Koebner phenomenon), and this can be a significant clinical clue to aid in the diagnosis of lichen nitidus in favor of other conditions which may present as many small papules.1 Nail changes can occur but are rare, presenting as dystrophy, pitting, riding, or loss of nail(s).2
Lichen nitidus can be a challenging diagnosis to make, especially if a practitioner is not used to seeing it. Many dermatologic conditions present with many fine papules, including the other answer choices in the given quiz question (molluscum contagiosum, keratosis pilaris, verruca vulgaris, papular eczema). What allows for a clearer diagnosis of lichen nitidus is the history provided by the patient as well as the exam. Lichen nitidus lesions typically arise without a known trigger and often persist for months while remaining asymptomatic.
Molluscum contagiosum tends to include papules that are larger and more substantial than lichen nitidus papules and may be accompanied by background hyperpigmentation or erythema, known as the “beginning of the end” sign. Keratosis pilaris is commonly thought of as a skin type more so than a skin condition, and is more commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals along the lateral arms and cheeks. It is commonly paired with a background of erythema and skin than tends to be more xerotic. Verruca are typically larger lesions, sometimes with a rough surface, and are not typically shiny. Verruca are more likely to present as a single lesion or a few lesions at a given location, as opposed to lichen nitidus which has many individual papules at a single location. Papular eczema typically is intensely pruritic and is associated with xerosis and atopy.
The cause of lichen nitidus is unknown, and there are no reported genetic factors that contribute to its presentation.3 It is thought to be a subtype of lichen planus, although this is still debated. There is more work that needs to be done to find answers to these questions and to assess what triggers these fine papules to present and in whom.
The dermatoscopic features of lichen nitidus were reported in a series of eight cases and include absent dermatoglyphics, radial ridges, ill-defined hypopigmentation, diffuse erythema, linear vessels within the lesion, and peripheral scaling.4 These features are distinctive in combination and can in some cases be used to clinically diagnose lichen nitidus without the need for a skin biopsy, which is an invasive procedure that should be avoided when possible, especially given the benign nature of lichen nitidus.
If a biopsy is performed, the histologic features that commonly are seen include well-circumscribed granuloma-like lymphohistiocytic infiltrates in the papillary dermis adjacent to ridges, mimicking a “ball-and-claw” formation.1,5
Lichen nitidus generally is self-limiting, with minimal cosmetic disruption; therefore, treatment usually is not necessary. The lesions typically resolve within 1 year of presentation – and often sooner. Topical steroids can be used for symptomatic relief of pruritus, but generally do not hasten resolution of the papules themselves. Additionally, there have been reports in the literature of the successful resolution of lesions using topical calcineurin inhibitors and UVB therapy.
In a case report of an 8-year-old child with histologically confirmed lichen nitidus that had been present for 2 years, pimecrolimus 1% cream was used twice daily for 2 months with improvement and flattening of the papules.6 This report is compelling because the lesions persisted for twice the expected time of resolution without improvement and then showed relatively quick response to pimecrolimus. In a case of a 32-year-old male with lichen nitidus on his penis, tacrolimus 0.1% was used for 4 weeks with resolution of the papules.7 Although given that lichen nitidus can self-resolve in this same time period, it is unclear in this case whether the tacrolimus was the independent cause of the resolution.
With regard to UVB therapy, there have been reports of lichen nitidus resolution after 17-30 irradiation sessions in patients with lesions present for 3-6 months, although again, it is possible that the resolution observed was simply the natural course of the lichen nitidus for these patients rather than a therapeutic benefit of UVB therapy.8,9
Given that lichen nitidus is benign and typically asymptomatic or with mild pruritus, it is reasonable to monitor the lesions without treating them. If the lesions persist beyond 1 year, it also is reasonable to trial therapies, such as topical calcineurin inhibitors and UVB therapy, although using these treatments earlier in the disease course has only limited supporting data and any improvement seen within 1 year of onset may be attributed to the natural disease course as opposed to an effect of the intervention. Considerations of the cost of therapy, as well as the degree to which the patient is bothered by the lesions and how long the lesions have persisted, should be undertaken when considering whether an intervention should be made.
Ms. Natsis is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Ms. Natsis or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Cutis. 1999 Aug 1;64(2):135-6.
2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
3. Papulosquamous diseases, in “Pediatric Dermatology,” 4th ed. (St Louis: Mosby; 2011, Vol. 2.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018. doi: 10.1111/pde.13576.
5. Cutis. 2013 Dec;92(6):288, 297-8.
6. Dermatol Online J. 2011 Jul 15;17(7):11.
7. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004 Nov-Dec;3(6):683-4.
8. Int J Dermatol. 2004 Dec 23;45:615-7.
9. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2013 Aug;29(4):215-7.
Lichen nitidus, which literally means “shiny moss,” is a relatively rare, chronic skin eruption that is characterized clinically by asymptomatic, flat-topped, sharply-demarcated, skin-colored papules, which are sometimes described as being “pinpoint.”
Lichen nitidus mainly affects children and young adults. The most common sites of involvement are the trunk, flexor aspects of upper extremities, dorsal aspects of hands, and genitalia, but lesions can occur anywhere on the skin. The lesions also can develop in sites of trauma (Koebner phenomenon), and this can be a significant clinical clue to aid in the diagnosis of lichen nitidus in favor of other conditions which may present as many small papules.1 Nail changes can occur but are rare, presenting as dystrophy, pitting, riding, or loss of nail(s).2
Lichen nitidus can be a challenging diagnosis to make, especially if a practitioner is not used to seeing it. Many dermatologic conditions present with many fine papules, including the other answer choices in the given quiz question (molluscum contagiosum, keratosis pilaris, verruca vulgaris, papular eczema). What allows for a clearer diagnosis of lichen nitidus is the history provided by the patient as well as the exam. Lichen nitidus lesions typically arise without a known trigger and often persist for months while remaining asymptomatic.
Molluscum contagiosum tends to include papules that are larger and more substantial than lichen nitidus papules and may be accompanied by background hyperpigmentation or erythema, known as the “beginning of the end” sign. Keratosis pilaris is commonly thought of as a skin type more so than a skin condition, and is more commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals along the lateral arms and cheeks. It is commonly paired with a background of erythema and skin than tends to be more xerotic. Verruca are typically larger lesions, sometimes with a rough surface, and are not typically shiny. Verruca are more likely to present as a single lesion or a few lesions at a given location, as opposed to lichen nitidus which has many individual papules at a single location. Papular eczema typically is intensely pruritic and is associated with xerosis and atopy.
The cause of lichen nitidus is unknown, and there are no reported genetic factors that contribute to its presentation.3 It is thought to be a subtype of lichen planus, although this is still debated. There is more work that needs to be done to find answers to these questions and to assess what triggers these fine papules to present and in whom.
The dermatoscopic features of lichen nitidus were reported in a series of eight cases and include absent dermatoglyphics, radial ridges, ill-defined hypopigmentation, diffuse erythema, linear vessels within the lesion, and peripheral scaling.4 These features are distinctive in combination and can in some cases be used to clinically diagnose lichen nitidus without the need for a skin biopsy, which is an invasive procedure that should be avoided when possible, especially given the benign nature of lichen nitidus.
If a biopsy is performed, the histologic features that commonly are seen include well-circumscribed granuloma-like lymphohistiocytic infiltrates in the papillary dermis adjacent to ridges, mimicking a “ball-and-claw” formation.1,5
Lichen nitidus generally is self-limiting, with minimal cosmetic disruption; therefore, treatment usually is not necessary. The lesions typically resolve within 1 year of presentation – and often sooner. Topical steroids can be used for symptomatic relief of pruritus, but generally do not hasten resolution of the papules themselves. Additionally, there have been reports in the literature of the successful resolution of lesions using topical calcineurin inhibitors and UVB therapy.
In a case report of an 8-year-old child with histologically confirmed lichen nitidus that had been present for 2 years, pimecrolimus 1% cream was used twice daily for 2 months with improvement and flattening of the papules.6 This report is compelling because the lesions persisted for twice the expected time of resolution without improvement and then showed relatively quick response to pimecrolimus. In a case of a 32-year-old male with lichen nitidus on his penis, tacrolimus 0.1% was used for 4 weeks with resolution of the papules.7 Although given that lichen nitidus can self-resolve in this same time period, it is unclear in this case whether the tacrolimus was the independent cause of the resolution.
With regard to UVB therapy, there have been reports of lichen nitidus resolution after 17-30 irradiation sessions in patients with lesions present for 3-6 months, although again, it is possible that the resolution observed was simply the natural course of the lichen nitidus for these patients rather than a therapeutic benefit of UVB therapy.8,9
Given that lichen nitidus is benign and typically asymptomatic or with mild pruritus, it is reasonable to monitor the lesions without treating them. If the lesions persist beyond 1 year, it also is reasonable to trial therapies, such as topical calcineurin inhibitors and UVB therapy, although using these treatments earlier in the disease course has only limited supporting data and any improvement seen within 1 year of onset may be attributed to the natural disease course as opposed to an effect of the intervention. Considerations of the cost of therapy, as well as the degree to which the patient is bothered by the lesions and how long the lesions have persisted, should be undertaken when considering whether an intervention should be made.
Ms. Natsis is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Ms. Natsis or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Cutis. 1999 Aug 1;64(2):135-6.
2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
3. Papulosquamous diseases, in “Pediatric Dermatology,” 4th ed. (St Louis: Mosby; 2011, Vol. 2.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018. doi: 10.1111/pde.13576.
5. Cutis. 2013 Dec;92(6):288, 297-8.
6. Dermatol Online J. 2011 Jul 15;17(7):11.
7. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004 Nov-Dec;3(6):683-4.
8. Int J Dermatol. 2004 Dec 23;45:615-7.
9. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2013 Aug;29(4):215-7.
Lichen nitidus, which literally means “shiny moss,” is a relatively rare, chronic skin eruption that is characterized clinically by asymptomatic, flat-topped, sharply-demarcated, skin-colored papules, which are sometimes described as being “pinpoint.”
Lichen nitidus mainly affects children and young adults. The most common sites of involvement are the trunk, flexor aspects of upper extremities, dorsal aspects of hands, and genitalia, but lesions can occur anywhere on the skin. The lesions also can develop in sites of trauma (Koebner phenomenon), and this can be a significant clinical clue to aid in the diagnosis of lichen nitidus in favor of other conditions which may present as many small papules.1 Nail changes can occur but are rare, presenting as dystrophy, pitting, riding, or loss of nail(s).2
Lichen nitidus can be a challenging diagnosis to make, especially if a practitioner is not used to seeing it. Many dermatologic conditions present with many fine papules, including the other answer choices in the given quiz question (molluscum contagiosum, keratosis pilaris, verruca vulgaris, papular eczema). What allows for a clearer diagnosis of lichen nitidus is the history provided by the patient as well as the exam. Lichen nitidus lesions typically arise without a known trigger and often persist for months while remaining asymptomatic.
Molluscum contagiosum tends to include papules that are larger and more substantial than lichen nitidus papules and may be accompanied by background hyperpigmentation or erythema, known as the “beginning of the end” sign. Keratosis pilaris is commonly thought of as a skin type more so than a skin condition, and is more commonly seen in fair-skinned individuals along the lateral arms and cheeks. It is commonly paired with a background of erythema and skin than tends to be more xerotic. Verruca are typically larger lesions, sometimes with a rough surface, and are not typically shiny. Verruca are more likely to present as a single lesion or a few lesions at a given location, as opposed to lichen nitidus which has many individual papules at a single location. Papular eczema typically is intensely pruritic and is associated with xerosis and atopy.
The cause of lichen nitidus is unknown, and there are no reported genetic factors that contribute to its presentation.3 It is thought to be a subtype of lichen planus, although this is still debated. There is more work that needs to be done to find answers to these questions and to assess what triggers these fine papules to present and in whom.
The dermatoscopic features of lichen nitidus were reported in a series of eight cases and include absent dermatoglyphics, radial ridges, ill-defined hypopigmentation, diffuse erythema, linear vessels within the lesion, and peripheral scaling.4 These features are distinctive in combination and can in some cases be used to clinically diagnose lichen nitidus without the need for a skin biopsy, which is an invasive procedure that should be avoided when possible, especially given the benign nature of lichen nitidus.
If a biopsy is performed, the histologic features that commonly are seen include well-circumscribed granuloma-like lymphohistiocytic infiltrates in the papillary dermis adjacent to ridges, mimicking a “ball-and-claw” formation.1,5
Lichen nitidus generally is self-limiting, with minimal cosmetic disruption; therefore, treatment usually is not necessary. The lesions typically resolve within 1 year of presentation – and often sooner. Topical steroids can be used for symptomatic relief of pruritus, but generally do not hasten resolution of the papules themselves. Additionally, there have been reports in the literature of the successful resolution of lesions using topical calcineurin inhibitors and UVB therapy.
In a case report of an 8-year-old child with histologically confirmed lichen nitidus that had been present for 2 years, pimecrolimus 1% cream was used twice daily for 2 months with improvement and flattening of the papules.6 This report is compelling because the lesions persisted for twice the expected time of resolution without improvement and then showed relatively quick response to pimecrolimus. In a case of a 32-year-old male with lichen nitidus on his penis, tacrolimus 0.1% was used for 4 weeks with resolution of the papules.7 Although given that lichen nitidus can self-resolve in this same time period, it is unclear in this case whether the tacrolimus was the independent cause of the resolution.
With regard to UVB therapy, there have been reports of lichen nitidus resolution after 17-30 irradiation sessions in patients with lesions present for 3-6 months, although again, it is possible that the resolution observed was simply the natural course of the lichen nitidus for these patients rather than a therapeutic benefit of UVB therapy.8,9
Given that lichen nitidus is benign and typically asymptomatic or with mild pruritus, it is reasonable to monitor the lesions without treating them. If the lesions persist beyond 1 year, it also is reasonable to trial therapies, such as topical calcineurin inhibitors and UVB therapy, although using these treatments earlier in the disease course has only limited supporting data and any improvement seen within 1 year of onset may be attributed to the natural disease course as opposed to an effect of the intervention. Considerations of the cost of therapy, as well as the degree to which the patient is bothered by the lesions and how long the lesions have persisted, should be undertaken when considering whether an intervention should be made.
Ms. Natsis is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego. There are no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures for Ms. Natsis or Dr. Eichenfield. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Cutis. 1999 Aug 1;64(2):135-6.
2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2004 Oct;51(4):606-24.
3. Papulosquamous diseases, in “Pediatric Dermatology,” 4th ed. (St Louis: Mosby; 2011, Vol. 2.
4. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018. doi: 10.1111/pde.13576.
5. Cutis. 2013 Dec;92(6):288, 297-8.
6. Dermatol Online J. 2011 Jul 15;17(7):11.
7. J Drugs Dermatol. 2004 Nov-Dec;3(6):683-4.
8. Int J Dermatol. 2004 Dec 23;45:615-7.
9. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2013 Aug;29(4):215-7.
What is the Diagnosis - September 2018
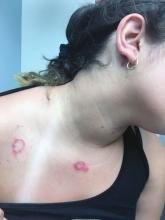
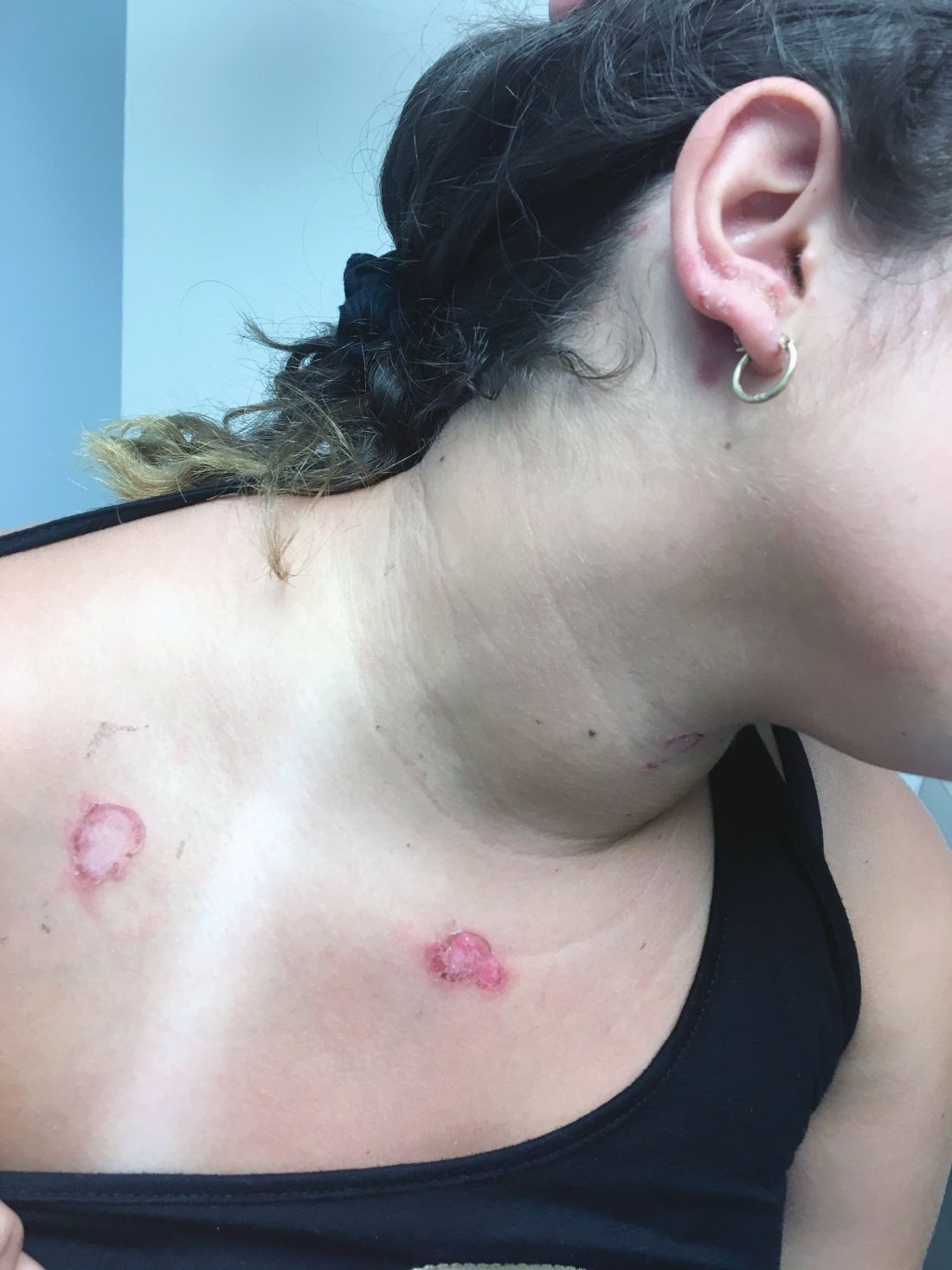
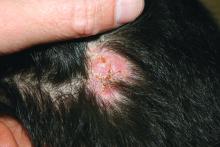
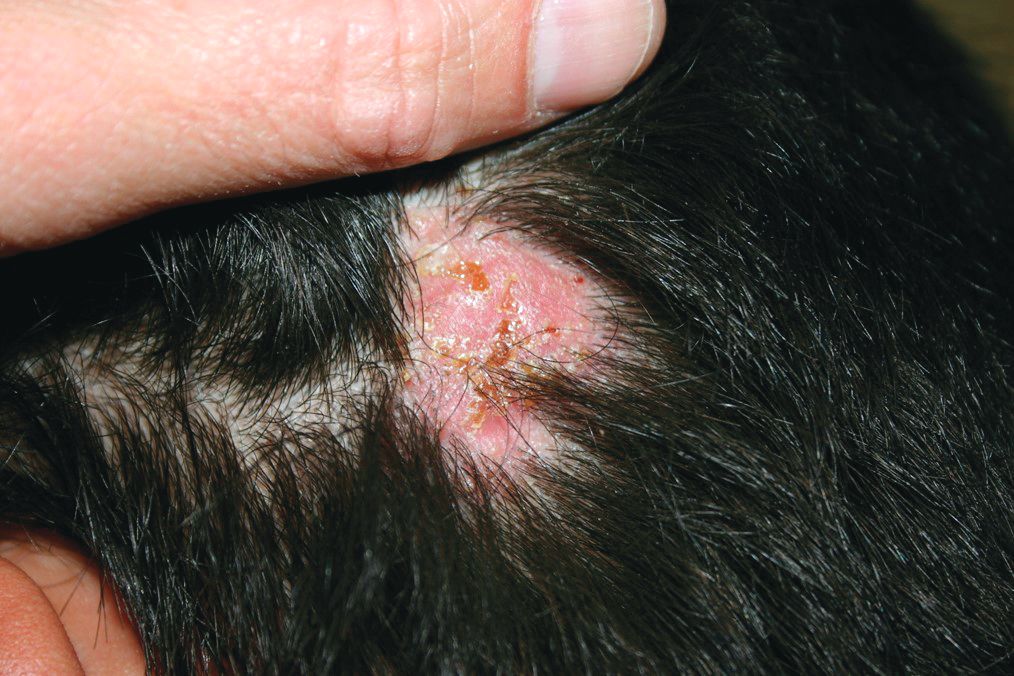
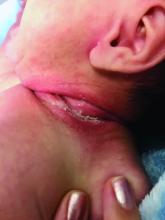
At the visit, the girl’s skin scrapings were analyzed under the microscope with potassium hydroxide (KOH) and no fungal elements were seen. A culture from one of the lesions was positive for methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus.
She was diagnosed with bullous impetigo (BI).
Impetigo is the most common superficial skin infection and can present as a nonbullous (most common) and bullous (least common) form.1 Nonbullous impetigo is usually caused the Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes and tends to occur at sites of prior trauma like insect bites, scratches, atopic dermatitis, or varicella. On the other hand, bullous impetigo is caused by the local production of exfoliative toxins (ETA or ETB) by phage group II of Staphylococcus aureus. The exfoliative toxin binds to desmoglin-1, one of the desmosomal proteins of the skin, causing acantholysis at the level of the granular layer and blister formation. Different from nonbullous impetigo, bullous impetigo tends to occur in normal, undamaged skin. Lesions are more common in neonates and young infants but children also can be affected.
The characteristic lesions in bullous impetigo are small blisters that enlarge to 1-cm to 5-cm bullae that easily rupture, leaving an erythematous plaque with a collarette of scale or “double ring scale,” with minimal crust and mild erythema. They commonly occur on the face, trunk, buttocks, and intertriginous areas. The lesions heal within 4-6 weeks, leaving no scarring. Associated systemic symptoms are rare but some patients can present with weakness, fever, and diarrhea. The toxin can disseminate and cause staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in neonates or older patients with renal failure or immunodeficiency.
The transmission of Staphylococcus aureus can occur from colonized or infected family members, children in contact sports, as well as contact with animals such as dogs, cattle, and poultry.2 Transmission from a pet rabbit also has been reported. In our patient, transmission from her pet hamster could have occurred as the areas on the body where there were lesions were areas where she was holding and cuddling her new pet.
The differential diagnosis of the type of lesions our patient presented with includes tinea corporis, and bullous tinea, which also can be transmitted by animals such as kittens. A KOH analysis ruled out this diagnosis. Tinea skin lesions tend to be more scaly than bullous impetigo lesions, which are more inflamed and crusted. Bullous arthropod reactions should be considered in the differential diagnosis as well. Bullous bite reaction lesions present with tense bullae, as they are subepidermal in nature and are pruritic. Subacute cutaneous lupus lesions present as annular scaly plaques with an erythematous border and central clearing usually in sun exposed areas similar to the distribution of our patient. Severe contact dermatitis reactions also can blister and form similar lesions as seen in our patient but with the difference that our patient didn’t complain of pruritus, which is a characteristic feature of allergic contact dermatitis. In neonates or young infants with bullous lesions other conditions such as herpes simplex infection, epidermolysis bullosa, bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, bullous mastocytosis, and bullous erythema multiforme should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
First line treatment for impetigo consists of the use of topical application of mupirocin (Bactroban) 2% ointment, retapamulin (Altabax) 1% ointment, or fusidic acid 2% cream. A Cochrane review compared systemic versus topical treatment for impetigo concluding that topical treatment with either mupirocin or retapamulin is equally if not more effective than oral antibiotics.3 Ozenoxacin (Xepi), a new nonfluorinated topical quinolone has recently been Food and Drug Administration approved for the treatment of localized impetigo in patients 2 months of age and older.4 When there is treatment failure with topical antibiotics, widespread disease, or systemic symptoms, oral antimicrobials should be consider, such as beta-lactamase–resistant penicillin, first-generation cephalosporins, or clindamycin. The use of bleach baths and general hygiene measures for 4 months can reduce the risks of recurrence in 20% of the patients as noted by a study by Kaplan et al.5
Our patient was treated with oral cephalexin for 7 days as well as topical mupirocin with fast resolution of the lesions. Sadly, the parents gave her hamster pet away.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected]
References
1. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Aug 15;90(4):229-35.
2. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Jun;265(1-2):218-26.
3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD003261.
4. Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Jun 1:1060028018786510.
5. Clin Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;58(5):679-82.
At the visit, the girl’s skin scrapings were analyzed under the microscope with potassium hydroxide (KOH) and no fungal elements were seen. A culture from one of the lesions was positive for methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus.
She was diagnosed with bullous impetigo (BI).
Impetigo is the most common superficial skin infection and can present as a nonbullous (most common) and bullous (least common) form.1 Nonbullous impetigo is usually caused the Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes and tends to occur at sites of prior trauma like insect bites, scratches, atopic dermatitis, or varicella. On the other hand, bullous impetigo is caused by the local production of exfoliative toxins (ETA or ETB) by phage group II of Staphylococcus aureus. The exfoliative toxin binds to desmoglin-1, one of the desmosomal proteins of the skin, causing acantholysis at the level of the granular layer and blister formation. Different from nonbullous impetigo, bullous impetigo tends to occur in normal, undamaged skin. Lesions are more common in neonates and young infants but children also can be affected.
The characteristic lesions in bullous impetigo are small blisters that enlarge to 1-cm to 5-cm bullae that easily rupture, leaving an erythematous plaque with a collarette of scale or “double ring scale,” with minimal crust and mild erythema. They commonly occur on the face, trunk, buttocks, and intertriginous areas. The lesions heal within 4-6 weeks, leaving no scarring. Associated systemic symptoms are rare but some patients can present with weakness, fever, and diarrhea. The toxin can disseminate and cause staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in neonates or older patients with renal failure or immunodeficiency.
The transmission of Staphylococcus aureus can occur from colonized or infected family members, children in contact sports, as well as contact with animals such as dogs, cattle, and poultry.2 Transmission from a pet rabbit also has been reported. In our patient, transmission from her pet hamster could have occurred as the areas on the body where there were lesions were areas where she was holding and cuddling her new pet.
The differential diagnosis of the type of lesions our patient presented with includes tinea corporis, and bullous tinea, which also can be transmitted by animals such as kittens. A KOH analysis ruled out this diagnosis. Tinea skin lesions tend to be more scaly than bullous impetigo lesions, which are more inflamed and crusted. Bullous arthropod reactions should be considered in the differential diagnosis as well. Bullous bite reaction lesions present with tense bullae, as they are subepidermal in nature and are pruritic. Subacute cutaneous lupus lesions present as annular scaly plaques with an erythematous border and central clearing usually in sun exposed areas similar to the distribution of our patient. Severe contact dermatitis reactions also can blister and form similar lesions as seen in our patient but with the difference that our patient didn’t complain of pruritus, which is a characteristic feature of allergic contact dermatitis. In neonates or young infants with bullous lesions other conditions such as herpes simplex infection, epidermolysis bullosa, bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, bullous mastocytosis, and bullous erythema multiforme should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
First line treatment for impetigo consists of the use of topical application of mupirocin (Bactroban) 2% ointment, retapamulin (Altabax) 1% ointment, or fusidic acid 2% cream. A Cochrane review compared systemic versus topical treatment for impetigo concluding that topical treatment with either mupirocin or retapamulin is equally if not more effective than oral antibiotics.3 Ozenoxacin (Xepi), a new nonfluorinated topical quinolone has recently been Food and Drug Administration approved for the treatment of localized impetigo in patients 2 months of age and older.4 When there is treatment failure with topical antibiotics, widespread disease, or systemic symptoms, oral antimicrobials should be consider, such as beta-lactamase–resistant penicillin, first-generation cephalosporins, or clindamycin. The use of bleach baths and general hygiene measures for 4 months can reduce the risks of recurrence in 20% of the patients as noted by a study by Kaplan et al.5
Our patient was treated with oral cephalexin for 7 days as well as topical mupirocin with fast resolution of the lesions. Sadly, the parents gave her hamster pet away.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected]
References
1. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Aug 15;90(4):229-35.
2. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Jun;265(1-2):218-26.
3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD003261.
4. Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Jun 1:1060028018786510.
5. Clin Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;58(5):679-82.
At the visit, the girl’s skin scrapings were analyzed under the microscope with potassium hydroxide (KOH) and no fungal elements were seen. A culture from one of the lesions was positive for methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus.
She was diagnosed with bullous impetigo (BI).
Impetigo is the most common superficial skin infection and can present as a nonbullous (most common) and bullous (least common) form.1 Nonbullous impetigo is usually caused the Staphylococcus aureus or Streptococcus pyogenes and tends to occur at sites of prior trauma like insect bites, scratches, atopic dermatitis, or varicella. On the other hand, bullous impetigo is caused by the local production of exfoliative toxins (ETA or ETB) by phage group II of Staphylococcus aureus. The exfoliative toxin binds to desmoglin-1, one of the desmosomal proteins of the skin, causing acantholysis at the level of the granular layer and blister formation. Different from nonbullous impetigo, bullous impetigo tends to occur in normal, undamaged skin. Lesions are more common in neonates and young infants but children also can be affected.
The characteristic lesions in bullous impetigo are small blisters that enlarge to 1-cm to 5-cm bullae that easily rupture, leaving an erythematous plaque with a collarette of scale or “double ring scale,” with minimal crust and mild erythema. They commonly occur on the face, trunk, buttocks, and intertriginous areas. The lesions heal within 4-6 weeks, leaving no scarring. Associated systemic symptoms are rare but some patients can present with weakness, fever, and diarrhea. The toxin can disseminate and cause staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome in neonates or older patients with renal failure or immunodeficiency.
The transmission of Staphylococcus aureus can occur from colonized or infected family members, children in contact sports, as well as contact with animals such as dogs, cattle, and poultry.2 Transmission from a pet rabbit also has been reported. In our patient, transmission from her pet hamster could have occurred as the areas on the body where there were lesions were areas where she was holding and cuddling her new pet.
The differential diagnosis of the type of lesions our patient presented with includes tinea corporis, and bullous tinea, which also can be transmitted by animals such as kittens. A KOH analysis ruled out this diagnosis. Tinea skin lesions tend to be more scaly than bullous impetigo lesions, which are more inflamed and crusted. Bullous arthropod reactions should be considered in the differential diagnosis as well. Bullous bite reaction lesions present with tense bullae, as they are subepidermal in nature and are pruritic. Subacute cutaneous lupus lesions present as annular scaly plaques with an erythematous border and central clearing usually in sun exposed areas similar to the distribution of our patient. Severe contact dermatitis reactions also can blister and form similar lesions as seen in our patient but with the difference that our patient didn’t complain of pruritus, which is a characteristic feature of allergic contact dermatitis. In neonates or young infants with bullous lesions other conditions such as herpes simplex infection, epidermolysis bullosa, bullous pemphigoid, linear IgA bullous dermatosis, bullous mastocytosis, and bullous erythema multiforme should be considered in the differential diagnosis.
First line treatment for impetigo consists of the use of topical application of mupirocin (Bactroban) 2% ointment, retapamulin (Altabax) 1% ointment, or fusidic acid 2% cream. A Cochrane review compared systemic versus topical treatment for impetigo concluding that topical treatment with either mupirocin or retapamulin is equally if not more effective than oral antibiotics.3 Ozenoxacin (Xepi), a new nonfluorinated topical quinolone has recently been Food and Drug Administration approved for the treatment of localized impetigo in patients 2 months of age and older.4 When there is treatment failure with topical antibiotics, widespread disease, or systemic symptoms, oral antimicrobials should be consider, such as beta-lactamase–resistant penicillin, first-generation cephalosporins, or clindamycin. The use of bleach baths and general hygiene measures for 4 months can reduce the risks of recurrence in 20% of the patients as noted by a study by Kaplan et al.5
Our patient was treated with oral cephalexin for 7 days as well as topical mupirocin with fast resolution of the lesions. Sadly, the parents gave her hamster pet away.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego. Email her at [email protected]
References
1. Am Fam Physician. 2014 Aug 15;90(4):229-35.
2. Zentralbl Bakteriol Mikrobiol Hyg A. 1987 Jun;265(1-2):218-26.
3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Jan 18;1:CD003261.
4. Ann Pharmacother. 2018 Jun 1:1060028018786510.
5. Clin Infect Dis. 2014 Mar;58(5):679-82.
On physical exam, the girl is in no acute distress. Her vital signs are stable, and she has no fever.
On skin examination, she has several erythematous, crusted scaly plaques with double ring of scale on the nose, ears, neck, upper chest, and few on the abdomen. On her left abdomen, there is a small blister. Her seborrheic dermatitis is well controlled with mild erythema behind her ears and minimal scale on her scalp.
What is your treatment plan?
The treatment choice is oral terbinafine for tinea capitis with kerion, a scalp dermatophyte infection with a concurrent inflammatory process. Tinea capitis is a very common infection with the peak occurrence at age 3-7 years. Tinea capitis is caused by a variety of dermatophyte species, most commonly by Trichophyton tonsurans or Microsporum canis. T. tonsurans is an endothrix infection, invading the hair shaft and superficial hair while M. canis is an ectothrix infection. T. tonsurans has a person to person transmission; in contrast, M. canis is a zoonotic infection most commonly acquired from infected pets.1 The epidemiology of tinea capitis is affected by multiple factors, including immigration patterns. For example, in Montreal, a study showed a sixfold increase of African dermatophyte species, M. audouinii and T. soudanense.2 Similarly, global variation has increased prevalence of T. violaceum, more commonly found in Europe and Africa, which has been seen in immigrant populations in the United States.1 Kerion is thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction to dermatophytes. Often, misdiagnosis of kerion can result in unnecessary antibiotic prescription and delays in initiation of antifungal therapy.3,4
Tinea capitis can present with focal, “patchy,” well-demarcated hair loss and overlying scale, broken-off hairs at the scalp, and often with pustules. It may be associated with occipital or posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. which presents as a painful boggy scalp mass with or without purulent drainage. Kerions can have associated fever. It is important to differentiate tinea capitis with kerion from processes requiring a different treatment course.3,5 Bacterial folliculitis may have erythema and pustules but only rarely causes hair loss. Similarly, alopecia areata can present with focal alopecia but lacks the scalp inflammation and pustules. Scalp psoriasis is quite scaly, but is more thickened, and usually does not have pustules, nor would purulent drainage be evident. There is a broader differential for other inflammatory focal alopecias including discoid lupus, lichen planopilaris, and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp, which can have similar pus-filled lumps, and cause permanent hair loss, but may be differentiated by associated conditions such as acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pilonidal sinus.
While some clinicians advocate clinical diagnosis of tinea capitis, we advocate confirmation of infection by fungal culture, which can identify the causative organism and influence therapy selection.1 The presence of a fungal infection can be confirmed on potassium hydroxide wet mount prep if hyphae and small spores are seen.6,7 Wood lamp examination will fluoresce if there are ectothrix species, however a negative fluorescence does not differentiate between an endothrix species or lack of infection.
It is important that tinea capitis with kerion is treated with systemic antifungal treatments to allow resolution of the infection, recovery of hair growth, and to prevent or minimize scarring. Systemic antifungal options include terbinafine, griseofulvin, and azoles. Terbinafine is becoming the treatment of choice given shorter duration of treatment with similar efficacy.1T. tonsurans also is thought to respond better to terbinafine than to griseofulvin.8 Griseofulvin is the historical treatment of choice because of its history of clinical safety and no need for laboratory testing. It is important to note that higher doses of griseofulvin (20-25 mg/kg) are recommended, as older lower dose regimens have high rates of failure. Griseofulvin may be more effective for treatment of Microsporum spp than is terbinafine.8 Fluconazole is the only oral antifungal agent that is approved for patients younger than 2 years of age, however it has lower cure rates, compared with terbinafine and griseofulvin.1 Tinea capitis with kerion does not generally require antibiotics unless there is superimposed bacterial infection. Kerion also do not require incision or drainage, which may increase scarring and complicate the clinical course.
Management of tinea capitis should include evaluation of any other household members for coinfection. Depending on the dermatophyte involved there can be risk of person-to-person transmission.5 Families should be educated about fomite transmission via shared combs or hats. Additionally, if a zoophilic dermatophyte is suspected, pets also should be appropriately examined and treated. Topical antifungals are insufficient to eradicate tinea capitis but can be used as adjunctive therapy. Kerion can be treated with oral prednisone in addition to oral antifungals if the lesions are very painful, however there is limited data on this treatment option.9
Ms. Kaushik is a research fellow and Dr. Eichenfield is professor of dermatology and pediatrics in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, both in San Diego. They have no conflicts of interest or relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. “Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases,” 31st Edition, (Elk Grove Village, Ill.: American Academy of Pediatrics, 2018, p. 1264).
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 May;35(3):323-8
3. Arch Dis Child. 2016 May;101(5):503.
4. IDCases. 2018 Jun 28;14:e00418.
5. Int J Dermatol. 2018 Jan;57(1):3-9.
6. Pediatr Rev. 2007 May;28(5):164-74.
7. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2010;3:89-98.
8. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 12;(5):CD004685.
9. Med Mycol. 1999 Apr;37(2):97-9.
The treatment choice is oral terbinafine for tinea capitis with kerion, a scalp dermatophyte infection with a concurrent inflammatory process. Tinea capitis is a very common infection with the peak occurrence at age 3-7 years. Tinea capitis is caused by a variety of dermatophyte species, most commonly by Trichophyton tonsurans or Microsporum canis. T. tonsurans is an endothrix infection, invading the hair shaft and superficial hair while M. canis is an ectothrix infection. T. tonsurans has a person to person transmission; in contrast, M. canis is a zoonotic infection most commonly acquired from infected pets.1 The epidemiology of tinea capitis is affected by multiple factors, including immigration patterns. For example, in Montreal, a study showed a sixfold increase of African dermatophyte species, M. audouinii and T. soudanense.2 Similarly, global variation has increased prevalence of T. violaceum, more commonly found in Europe and Africa, which has been seen in immigrant populations in the United States.1 Kerion is thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction to dermatophytes. Often, misdiagnosis of kerion can result in unnecessary antibiotic prescription and delays in initiation of antifungal therapy.3,4
Tinea capitis can present with focal, “patchy,” well-demarcated hair loss and overlying scale, broken-off hairs at the scalp, and often with pustules. It may be associated with occipital or posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. which presents as a painful boggy scalp mass with or without purulent drainage. Kerions can have associated fever. It is important to differentiate tinea capitis with kerion from processes requiring a different treatment course.3,5 Bacterial folliculitis may have erythema and pustules but only rarely causes hair loss. Similarly, alopecia areata can present with focal alopecia but lacks the scalp inflammation and pustules. Scalp psoriasis is quite scaly, but is more thickened, and usually does not have pustules, nor would purulent drainage be evident. There is a broader differential for other inflammatory focal alopecias including discoid lupus, lichen planopilaris, and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp, which can have similar pus-filled lumps, and cause permanent hair loss, but may be differentiated by associated conditions such as acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pilonidal sinus.
While some clinicians advocate clinical diagnosis of tinea capitis, we advocate confirmation of infection by fungal culture, which can identify the causative organism and influence therapy selection.1 The presence of a fungal infection can be confirmed on potassium hydroxide wet mount prep if hyphae and small spores are seen.6,7 Wood lamp examination will fluoresce if there are ectothrix species, however a negative fluorescence does not differentiate between an endothrix species or lack of infection.
It is important that tinea capitis with kerion is treated with systemic antifungal treatments to allow resolution of the infection, recovery of hair growth, and to prevent or minimize scarring. Systemic antifungal options include terbinafine, griseofulvin, and azoles. Terbinafine is becoming the treatment of choice given shorter duration of treatment with similar efficacy.1T. tonsurans also is thought to respond better to terbinafine than to griseofulvin.8 Griseofulvin is the historical treatment of choice because of its history of clinical safety and no need for laboratory testing. It is important to note that higher doses of griseofulvin (20-25 mg/kg) are recommended, as older lower dose regimens have high rates of failure. Griseofulvin may be more effective for treatment of Microsporum spp than is terbinafine.8 Fluconazole is the only oral antifungal agent that is approved for patients younger than 2 years of age, however it has lower cure rates, compared with terbinafine and griseofulvin.1 Tinea capitis with kerion does not generally require antibiotics unless there is superimposed bacterial infection. Kerion also do not require incision or drainage, which may increase scarring and complicate the clinical course.
Management of tinea capitis should include evaluation of any other household members for coinfection. Depending on the dermatophyte involved there can be risk of person-to-person transmission.5 Families should be educated about fomite transmission via shared combs or hats. Additionally, if a zoophilic dermatophyte is suspected, pets also should be appropriately examined and treated. Topical antifungals are insufficient to eradicate tinea capitis but can be used as adjunctive therapy. Kerion can be treated with oral prednisone in addition to oral antifungals if the lesions are very painful, however there is limited data on this treatment option.9
Ms. Kaushik is a research fellow and Dr. Eichenfield is professor of dermatology and pediatrics in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, both in San Diego. They have no conflicts of interest or relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. “Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases,” 31st Edition, (Elk Grove Village, Ill.: American Academy of Pediatrics, 2018, p. 1264).
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 May;35(3):323-8
3. Arch Dis Child. 2016 May;101(5):503.
4. IDCases. 2018 Jun 28;14:e00418.
5. Int J Dermatol. 2018 Jan;57(1):3-9.
6. Pediatr Rev. 2007 May;28(5):164-74.
7. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2010;3:89-98.
8. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 12;(5):CD004685.
9. Med Mycol. 1999 Apr;37(2):97-9.
The treatment choice is oral terbinafine for tinea capitis with kerion, a scalp dermatophyte infection with a concurrent inflammatory process. Tinea capitis is a very common infection with the peak occurrence at age 3-7 years. Tinea capitis is caused by a variety of dermatophyte species, most commonly by Trichophyton tonsurans or Microsporum canis. T. tonsurans is an endothrix infection, invading the hair shaft and superficial hair while M. canis is an ectothrix infection. T. tonsurans has a person to person transmission; in contrast, M. canis is a zoonotic infection most commonly acquired from infected pets.1 The epidemiology of tinea capitis is affected by multiple factors, including immigration patterns. For example, in Montreal, a study showed a sixfold increase of African dermatophyte species, M. audouinii and T. soudanense.2 Similarly, global variation has increased prevalence of T. violaceum, more commonly found in Europe and Africa, which has been seen in immigrant populations in the United States.1 Kerion is thought to be a hypersensitivity reaction to dermatophytes. Often, misdiagnosis of kerion can result in unnecessary antibiotic prescription and delays in initiation of antifungal therapy.3,4
Tinea capitis can present with focal, “patchy,” well-demarcated hair loss and overlying scale, broken-off hairs at the scalp, and often with pustules. It may be associated with occipital or posterior cervical lymphadenopathy. which presents as a painful boggy scalp mass with or without purulent drainage. Kerions can have associated fever. It is important to differentiate tinea capitis with kerion from processes requiring a different treatment course.3,5 Bacterial folliculitis may have erythema and pustules but only rarely causes hair loss. Similarly, alopecia areata can present with focal alopecia but lacks the scalp inflammation and pustules. Scalp psoriasis is quite scaly, but is more thickened, and usually does not have pustules, nor would purulent drainage be evident. There is a broader differential for other inflammatory focal alopecias including discoid lupus, lichen planopilaris, and dissecting cellulitis of the scalp, which can have similar pus-filled lumps, and cause permanent hair loss, but may be differentiated by associated conditions such as acne conglobata, hidradenitis suppurativa, and pilonidal sinus.
While some clinicians advocate clinical diagnosis of tinea capitis, we advocate confirmation of infection by fungal culture, which can identify the causative organism and influence therapy selection.1 The presence of a fungal infection can be confirmed on potassium hydroxide wet mount prep if hyphae and small spores are seen.6,7 Wood lamp examination will fluoresce if there are ectothrix species, however a negative fluorescence does not differentiate between an endothrix species or lack of infection.
It is important that tinea capitis with kerion is treated with systemic antifungal treatments to allow resolution of the infection, recovery of hair growth, and to prevent or minimize scarring. Systemic antifungal options include terbinafine, griseofulvin, and azoles. Terbinafine is becoming the treatment of choice given shorter duration of treatment with similar efficacy.1T. tonsurans also is thought to respond better to terbinafine than to griseofulvin.8 Griseofulvin is the historical treatment of choice because of its history of clinical safety and no need for laboratory testing. It is important to note that higher doses of griseofulvin (20-25 mg/kg) are recommended, as older lower dose regimens have high rates of failure. Griseofulvin may be more effective for treatment of Microsporum spp than is terbinafine.8 Fluconazole is the only oral antifungal agent that is approved for patients younger than 2 years of age, however it has lower cure rates, compared with terbinafine and griseofulvin.1 Tinea capitis with kerion does not generally require antibiotics unless there is superimposed bacterial infection. Kerion also do not require incision or drainage, which may increase scarring and complicate the clinical course.
Management of tinea capitis should include evaluation of any other household members for coinfection. Depending on the dermatophyte involved there can be risk of person-to-person transmission.5 Families should be educated about fomite transmission via shared combs or hats. Additionally, if a zoophilic dermatophyte is suspected, pets also should be appropriately examined and treated. Topical antifungals are insufficient to eradicate tinea capitis but can be used as adjunctive therapy. Kerion can be treated with oral prednisone in addition to oral antifungals if the lesions are very painful, however there is limited data on this treatment option.9
Ms. Kaushik is a research fellow and Dr. Eichenfield is professor of dermatology and pediatrics in the division of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital and the University of California, both in San Diego. They have no conflicts of interest or relevant financial disclosures.
References
1. “Red Book: Report of the Committee on Infectious Diseases,” 31st Edition, (Elk Grove Village, Ill.: American Academy of Pediatrics, 2018, p. 1264).
2. Pediatr Dermatol. 2018 May;35(3):323-8
3. Arch Dis Child. 2016 May;101(5):503.
4. IDCases. 2018 Jun 28;14:e00418.
5. Int J Dermatol. 2018 Jan;57(1):3-9.
6. Pediatr Rev. 2007 May;28(5):164-74.
7. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2010;3:89-98.
8. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2016 May 12;(5):CD004685.
9. Med Mycol. 1999 Apr;37(2):97-9.
A 10-year-old otherwise-healthy male presents for a progressing lesion on his scalp. One month prior to coming in, he developed some peeling and itch followed by loss of hair. This had worsened, becoming a painful and boggy mass on the back of his head with focal alopecia. He went to the local ED, where he had plain films of his skull, which were normal and was prescribed cephalexin. He has not shown any improvement after starting the antibiotics. He has had no fevers in this time, but the pain persists.
On physical exam, he is noted to have a hairless patch on a boggy left occipital mass, which is tender to palpation. There is a small amount of overlying honey-colored crusting. He has associated posterior occipital nontender lymphadenopathy.
The patient's older sister has a small area of scalp hair loss.
What is your diagnosis?
Laboratory work revealed a normal CBC and differential, an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and sedimentation rate (ESR), negative antistreptolysin O (ASO) titers, negative pregnancy test, a normal urinalysis, and negative blood, throat, and urine cultures. A chest x-ray also was negative as well as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels. Tuberculosis interferon-gamma release essay was negative.
The patient was diagnosed with erythema nodosum (EN), based on physical exam and history of the lesions. In her particular case, infectious causes including streptococcus infection, tuberculosis, and coccidioidomycosis were ruled out. There were no x-ray findings that suggested sarcoidosis and her ACE level was within normal limits. The pregnancy test also was negative. Given her recent start on OCs, this was thought to be the cause of the lesions.
She was treated with elevation, compression stockings, and NSAIDs and discontinuation of OCs. The lesions resolved after 6 weeks leaving bruiselike patches (erythema contusiformis).
EN is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction, causing inflammation on the fat (panniculitis) most commonly on the shins, but it can also occur on the arms, face, neck, and thighs. It is the most common type of panniculitis and is usually seen more often in women from the second to fourth decade of life. Erythematous tender nodules in crops commonly located on the shins are the characteristic physical finding. Systemic symptoms can occur including fever, malaise, and joint pain. The lesions usually last up to 6-8 weeks and may leave bruiselike patches or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation that can take months to improve.1
The diagnosis of EN usually is made by physical examination and natural history. In unusual severe cases or lesions in atypical locations, a skin biopsy is indicated. Histologic examination of one of the lesions reveals a septal panniculitis without vasculitis. Miescher’s radial granulomas (grouped macrophages around neutrophils or septa-like spaces) often are present and are a characteristic feature of EN.
EN can be triggered by different types of infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, or bacterial gastroenteritis; medications such as OCs, sulfonamides, iodides, penicillin, or bromides; medical conditions that include inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, or sarcoidosis; or neutrophilic dermatosis and malignancy such as leukemia and Hodgkin disease.2,3 A third of the cases are idiopathic. In children, streptococcal infections are responsible for most cases of EN.4
Recommended work-up to investigate possible triggers includes a CBC with differential, sedimentation rate, CRP, ASO titers or anti-DNase B titers, tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma TB test and a chest X ray. If there are any other symptoms, physical signs, or risk factors are present for the other not so common causes, further ancillary testing may be warranted.
Erythematous nodules and papules on the shin in children are commonly caused by arthropod bites also known as papular urticaria. These lesions are pruritic rather than tender and usually respond to topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. Subcutaneous bacterial, fungal, or atypical mycobacterial infections can present with tender nodules that can ulcerate and drain on the shins, feet, or any other body part. These patients may have a history of immunodeficiency and usually systemic symptoms of infection are present. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) also can present with tender nodules on the legs but these lesions usually necrose and ulcerate and may be associated with livedo racemosa, a transient or persistent, blotchy, reddish-blue to purple, netlike cyanotic pattern. On pathology, PAN presents with necrotizing medium vessel vasculitis. Malignant nodules also can occur on the shin. Pathology will show atypical cells. Other forms of panniculitis, such as erythema induratum and pancreatic panniculitis, can present with tender nodules but these lesions usually occur on the calves and ulcerate.
Management of EN starts with treating the underlying infection or stopping the causative medication. Initial measures include bed rest, leg elevation, compression bandages, and NSAIDs. Potassium iodide is a very effective therapy as it may control the symptoms within 24 hours. When there is no response to the above, or the patient has severe symptoms, a short course of systemic glucocorticoids can be started. Other medications for recalcitrant or recurrent lesions include colchicine, dapsone, or hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Panniculitis, in “Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2012, p. 1641).
2. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):584-92.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Sep 1;25(25):4011-2.
4. Turk J Pediatr. 2014 Mar-Apr;56(2):144-9.
Laboratory work revealed a normal CBC and differential, an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and sedimentation rate (ESR), negative antistreptolysin O (ASO) titers, negative pregnancy test, a normal urinalysis, and negative blood, throat, and urine cultures. A chest x-ray also was negative as well as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels. Tuberculosis interferon-gamma release essay was negative.
The patient was diagnosed with erythema nodosum (EN), based on physical exam and history of the lesions. In her particular case, infectious causes including streptococcus infection, tuberculosis, and coccidioidomycosis were ruled out. There were no x-ray findings that suggested sarcoidosis and her ACE level was within normal limits. The pregnancy test also was negative. Given her recent start on OCs, this was thought to be the cause of the lesions.
She was treated with elevation, compression stockings, and NSAIDs and discontinuation of OCs. The lesions resolved after 6 weeks leaving bruiselike patches (erythema contusiformis).
EN is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction, causing inflammation on the fat (panniculitis) most commonly on the shins, but it can also occur on the arms, face, neck, and thighs. It is the most common type of panniculitis and is usually seen more often in women from the second to fourth decade of life. Erythematous tender nodules in crops commonly located on the shins are the characteristic physical finding. Systemic symptoms can occur including fever, malaise, and joint pain. The lesions usually last up to 6-8 weeks and may leave bruiselike patches or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation that can take months to improve.1
The diagnosis of EN usually is made by physical examination and natural history. In unusual severe cases or lesions in atypical locations, a skin biopsy is indicated. Histologic examination of one of the lesions reveals a septal panniculitis without vasculitis. Miescher’s radial granulomas (grouped macrophages around neutrophils or septa-like spaces) often are present and are a characteristic feature of EN.
EN can be triggered by different types of infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, or bacterial gastroenteritis; medications such as OCs, sulfonamides, iodides, penicillin, or bromides; medical conditions that include inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, or sarcoidosis; or neutrophilic dermatosis and malignancy such as leukemia and Hodgkin disease.2,3 A third of the cases are idiopathic. In children, streptococcal infections are responsible for most cases of EN.4
Recommended work-up to investigate possible triggers includes a CBC with differential, sedimentation rate, CRP, ASO titers or anti-DNase B titers, tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma TB test and a chest X ray. If there are any other symptoms, physical signs, or risk factors are present for the other not so common causes, further ancillary testing may be warranted.
Erythematous nodules and papules on the shin in children are commonly caused by arthropod bites also known as papular urticaria. These lesions are pruritic rather than tender and usually respond to topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. Subcutaneous bacterial, fungal, or atypical mycobacterial infections can present with tender nodules that can ulcerate and drain on the shins, feet, or any other body part. These patients may have a history of immunodeficiency and usually systemic symptoms of infection are present. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) also can present with tender nodules on the legs but these lesions usually necrose and ulcerate and may be associated with livedo racemosa, a transient or persistent, blotchy, reddish-blue to purple, netlike cyanotic pattern. On pathology, PAN presents with necrotizing medium vessel vasculitis. Malignant nodules also can occur on the shin. Pathology will show atypical cells. Other forms of panniculitis, such as erythema induratum and pancreatic panniculitis, can present with tender nodules but these lesions usually occur on the calves and ulcerate.
Management of EN starts with treating the underlying infection or stopping the causative medication. Initial measures include bed rest, leg elevation, compression bandages, and NSAIDs. Potassium iodide is a very effective therapy as it may control the symptoms within 24 hours. When there is no response to the above, or the patient has severe symptoms, a short course of systemic glucocorticoids can be started. Other medications for recalcitrant or recurrent lesions include colchicine, dapsone, or hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Panniculitis, in “Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2012, p. 1641).
2. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):584-92.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Sep 1;25(25):4011-2.
4. Turk J Pediatr. 2014 Mar-Apr;56(2):144-9.
Laboratory work revealed a normal CBC and differential, an elevated C-reactive protein (CRP) and sedimentation rate (ESR), negative antistreptolysin O (ASO) titers, negative pregnancy test, a normal urinalysis, and negative blood, throat, and urine cultures. A chest x-ray also was negative as well as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) levels. Tuberculosis interferon-gamma release essay was negative.
The patient was diagnosed with erythema nodosum (EN), based on physical exam and history of the lesions. In her particular case, infectious causes including streptococcus infection, tuberculosis, and coccidioidomycosis were ruled out. There were no x-ray findings that suggested sarcoidosis and her ACE level was within normal limits. The pregnancy test also was negative. Given her recent start on OCs, this was thought to be the cause of the lesions.
She was treated with elevation, compression stockings, and NSAIDs and discontinuation of OCs. The lesions resolved after 6 weeks leaving bruiselike patches (erythema contusiformis).
EN is a delayed-type hypersensitivity reaction, causing inflammation on the fat (panniculitis) most commonly on the shins, but it can also occur on the arms, face, neck, and thighs. It is the most common type of panniculitis and is usually seen more often in women from the second to fourth decade of life. Erythematous tender nodules in crops commonly located on the shins are the characteristic physical finding. Systemic symptoms can occur including fever, malaise, and joint pain. The lesions usually last up to 6-8 weeks and may leave bruiselike patches or postinflammatory hyperpigmentation that can take months to improve.1
The diagnosis of EN usually is made by physical examination and natural history. In unusual severe cases or lesions in atypical locations, a skin biopsy is indicated. Histologic examination of one of the lesions reveals a septal panniculitis without vasculitis. Miescher’s radial granulomas (grouped macrophages around neutrophils or septa-like spaces) often are present and are a characteristic feature of EN.
EN can be triggered by different types of infections such as streptococcus, mycoplasma, tuberculosis, or bacterial gastroenteritis; medications such as OCs, sulfonamides, iodides, penicillin, or bromides; medical conditions that include inflammatory bowel disease, pregnancy, or sarcoidosis; or neutrophilic dermatosis and malignancy such as leukemia and Hodgkin disease.2,3 A third of the cases are idiopathic. In children, streptococcal infections are responsible for most cases of EN.4
Recommended work-up to investigate possible triggers includes a CBC with differential, sedimentation rate, CRP, ASO titers or anti-DNase B titers, tuberculin skin test or interferon-gamma TB test and a chest X ray. If there are any other symptoms, physical signs, or risk factors are present for the other not so common causes, further ancillary testing may be warranted.
Erythematous nodules and papules on the shin in children are commonly caused by arthropod bites also known as papular urticaria. These lesions are pruritic rather than tender and usually respond to topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines. Subcutaneous bacterial, fungal, or atypical mycobacterial infections can present with tender nodules that can ulcerate and drain on the shins, feet, or any other body part. These patients may have a history of immunodeficiency and usually systemic symptoms of infection are present. Cutaneous polyarteritis nodosa (PAN) also can present with tender nodules on the legs but these lesions usually necrose and ulcerate and may be associated with livedo racemosa, a transient or persistent, blotchy, reddish-blue to purple, netlike cyanotic pattern. On pathology, PAN presents with necrotizing medium vessel vasculitis. Malignant nodules also can occur on the shin. Pathology will show atypical cells. Other forms of panniculitis, such as erythema induratum and pancreatic panniculitis, can present with tender nodules but these lesions usually occur on the calves and ulcerate.
Management of EN starts with treating the underlying infection or stopping the causative medication. Initial measures include bed rest, leg elevation, compression bandages, and NSAIDs. Potassium iodide is a very effective therapy as it may control the symptoms within 24 hours. When there is no response to the above, or the patient has severe symptoms, a short course of systemic glucocorticoids can be started. Other medications for recalcitrant or recurrent lesions include colchicine, dapsone, or hydroxychloroquine.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego.
References
1. Panniculitis, in “Dermatology,” 3rd ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders, 2012, p. 1641).
2. Arthritis Rheum. 2000 Mar;43(3):584-92.
3. J Clin Oncol. 2007 Sep 1;25(25):4011-2.
4. Turk J Pediatr. 2014 Mar-Apr;56(2):144-9.
A 16-year-old female came to the dermatology clinic for acne follow-up. She reported some improvement on her acne since she started taking OCs. She also had been using benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin on her face. In addition to the acne, she also wanted us to check some tender bumps she had been getting on her shins after she came back from a camping trip. Initially she thought they were bug bites, but the lesions were getting larger, more tender, and not improving with diphenhydramine.
The physical exam did not reveal acute distress. She was afebrile. On skin examination, she had comedones, papules and scars on her face, chest, and back. On her shins there were several erythematous tender nodules and plaques. There was no edema on her legs and pulses were present.
Pediatric Dermatology Consult - July 2018
Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.
8. Pediatrics in Review. 1991;12(8):248-55.
9. J Pediatr. 2017 May;184:230-1.e1.
Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.
8. Pediatrics in Review. 1991;12(8):248-55.
9. J Pediatr. 2017 May;184:230-1.e1.
Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.
8. Pediatrics in Review. 1991;12(8):248-55.
9. J Pediatr. 2017 May;184:230-1.e1.
An 8-week-old male with a history of cradle cap presented for a second evaluation of an erythematous rash on the neck that started 1.5 weeks before, and it had since worsened. The parents note that their infant has been more irritable, but they otherwise deny any fever, diarrhea, constipation, or decrease in oral intake.
The patient’s first evaluation had been 3 days prior; nystatin cream was prescribed, and the parents applied it twice a day but without improvement to the rash. The patient also had a rash behind the ears bilaterally, which was treated with hydrocortisone 2.5% ointment with some improvement
On physical exam, the central neck is covered by a bright, beefy red, erythematous plaque with distinct borders and strong odor. There is faint scale and superficial desquamation between the skin folds. There are no surrounding papules or pustules. The patient’s chin is moist with drool. In the postauricular skin folds bilaterally, there are fainter but still erythematous plaques with mild scale.
Pediatric Dermatology Consult - June 2018
The patient was diagnosed with granuloma annulare on the basis of history and clinical exam. A potassium hydroxide prep of skin scrapings was performed to rule out tinea corporis, and did not show evidence of fungal elements. The patient was treated with topical betamethasone with partial improvement.
First described as a “ringed eruption of the fingers” by Thomas Colcott Fox in 1895, granuloma annulare (GA) is a relatively common, benign, and self-limited condition whose precise etiology remains unclear. It is characterized commonly by pink to violaceous aciform or annular plaques on clinical examination. In some cases of GA, annular lesions are not present, or may be formed of grouped papules.
GA is characterized histologically by patchy interstitial lymphocytes and histiocytes palisading around mucin. Deep GA, an unusual subtype observed only in children, features a fibrin rather than a mucin core. This granulomatous picture is consistent with a Th1-mediated inflammatory process, and indeed, macrophage tumor necrosis factor production, as well as interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production have been observed in GA. The reason for this exaggerated Th1 response is unknown, although in susceptible individuals trauma3 (an example of the Koebner phenomenon), arthropod assault,4 and herpes simplex infection5 (an example of Wolf isotopic response) all have been observed to trigger localized and/or generalized GA. Generalized GA has been associated with hyperlipidemia and the human leukocyte antigen–BW35 allele. GA has been described as a paraneoplastic eruption; atypical features such as associated pain or appearance in an uncharacteristic location often are present in such cases.6,7
Diagnosis of typical GA is clinical. If unusual features make you suspect tinea, leprosy, mycosis fungoides, or other annular lesions, then biopsy showing features typical of GA can reveal the correct diagnosis. Biopsy also can help to distinguish papular GA from warts or molluscum contagiosum. If extensive GA are present, then serum lipid testing for hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia should be considered.
Other annular and raised lesions are on the differential for GA, but careful attention to the patient’s history and examination can clarify the diagnosis. Urticaria multiforme, a variant of annular urticaria, presents with numerous annular and polycyclic wheals, sometimes with central darkening that may be mistaken for necrosis. This patient did not present with polycyclic wheals. Furthermore, the lesions in urticaria multiforme are typically transient, with individual lesions lasting less than 24 hours, which was not the case with this patient. Wells syndrome, also known as eosinophilic cellulitis, is a condition marked by recurrent episodes of pruritus followed by appearance of edematous, painful, indurated, or edematous papules or plaques, although bullae and vesicles also may be present. The face and extremities are frequently involved and spontaneous resolution typically occurs in 2 months. Annular lesions are possible but papules, plaques, and nodules are more common in Wells syndrome. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG), also known as actinic granuloma and Miescher granuloma of the face, is an entity characterized clinically by chronic, persistent, sun-distributed, annular plaques typically seen in older women with significant sun damage. AEGCG is considered by some to be a variant of GA, but if this is the case, it is a distinct subtype with different epidemiologic, clinical, and histopathologic characteristics from GA. Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is histologically and clinically distinct from GA, presenting as subtly erythematous cords or extensive annular or serpiginous plaques in the axilla, groin, buttocks, or chest, typically in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis. Tinea corporis, the clinical manifestation of cutaneous dermatophyte infection, may be mistaken for granuloma annulare. However, tinea corporis lesions are scaly, whereas GA does not scale. Histologic examination of tinea corporis reveals hyphae, which are not present in GA.
GA is a relatively common, idiopathic, benign skin disease with numerous annular and papular mimics. Absence of scale, pain, and significant pruritus are important clues to the diagnosis, and biopsy can be helpful when the diagnosis is unclear. Treatment, although not necessary, may be offered using any of a number of modalities. The most consistent and effective healer of GA, however, is time.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980 Sep;3(3):217-30.
2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75(3):457-65.
3. Dermatol Online J. 2013 Dec 16;19(12):20719.
4. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88(5):519-20.
5. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014 Nov;18(6):413-9.
6. South Med J. 1997 Oct;90(10):1056-9.
7. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003 Apr;25(2):113-6.
8. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013 Aug;14(4):279-90.
9. Br J Dermatol. 1994 Apr;130(4):494-7.
The patient was diagnosed with granuloma annulare on the basis of history and clinical exam. A potassium hydroxide prep of skin scrapings was performed to rule out tinea corporis, and did not show evidence of fungal elements. The patient was treated with topical betamethasone with partial improvement.
First described as a “ringed eruption of the fingers” by Thomas Colcott Fox in 1895, granuloma annulare (GA) is a relatively common, benign, and self-limited condition whose precise etiology remains unclear. It is characterized commonly by pink to violaceous aciform or annular plaques on clinical examination. In some cases of GA, annular lesions are not present, or may be formed of grouped papules.
GA is characterized histologically by patchy interstitial lymphocytes and histiocytes palisading around mucin. Deep GA, an unusual subtype observed only in children, features a fibrin rather than a mucin core. This granulomatous picture is consistent with a Th1-mediated inflammatory process, and indeed, macrophage tumor necrosis factor production, as well as interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production have been observed in GA. The reason for this exaggerated Th1 response is unknown, although in susceptible individuals trauma3 (an example of the Koebner phenomenon), arthropod assault,4 and herpes simplex infection5 (an example of Wolf isotopic response) all have been observed to trigger localized and/or generalized GA. Generalized GA has been associated with hyperlipidemia and the human leukocyte antigen–BW35 allele. GA has been described as a paraneoplastic eruption; atypical features such as associated pain or appearance in an uncharacteristic location often are present in such cases.6,7
Diagnosis of typical GA is clinical. If unusual features make you suspect tinea, leprosy, mycosis fungoides, or other annular lesions, then biopsy showing features typical of GA can reveal the correct diagnosis. Biopsy also can help to distinguish papular GA from warts or molluscum contagiosum. If extensive GA are present, then serum lipid testing for hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia should be considered.
Other annular and raised lesions are on the differential for GA, but careful attention to the patient’s history and examination can clarify the diagnosis. Urticaria multiforme, a variant of annular urticaria, presents with numerous annular and polycyclic wheals, sometimes with central darkening that may be mistaken for necrosis. This patient did not present with polycyclic wheals. Furthermore, the lesions in urticaria multiforme are typically transient, with individual lesions lasting less than 24 hours, which was not the case with this patient. Wells syndrome, also known as eosinophilic cellulitis, is a condition marked by recurrent episodes of pruritus followed by appearance of edematous, painful, indurated, or edematous papules or plaques, although bullae and vesicles also may be present. The face and extremities are frequently involved and spontaneous resolution typically occurs in 2 months. Annular lesions are possible but papules, plaques, and nodules are more common in Wells syndrome. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG), also known as actinic granuloma and Miescher granuloma of the face, is an entity characterized clinically by chronic, persistent, sun-distributed, annular plaques typically seen in older women with significant sun damage. AEGCG is considered by some to be a variant of GA, but if this is the case, it is a distinct subtype with different epidemiologic, clinical, and histopathologic characteristics from GA. Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is histologically and clinically distinct from GA, presenting as subtly erythematous cords or extensive annular or serpiginous plaques in the axilla, groin, buttocks, or chest, typically in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis. Tinea corporis, the clinical manifestation of cutaneous dermatophyte infection, may be mistaken for granuloma annulare. However, tinea corporis lesions are scaly, whereas GA does not scale. Histologic examination of tinea corporis reveals hyphae, which are not present in GA.
GA is a relatively common, idiopathic, benign skin disease with numerous annular and papular mimics. Absence of scale, pain, and significant pruritus are important clues to the diagnosis, and biopsy can be helpful when the diagnosis is unclear. Treatment, although not necessary, may be offered using any of a number of modalities. The most consistent and effective healer of GA, however, is time.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980 Sep;3(3):217-30.
2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75(3):457-65.
3. Dermatol Online J. 2013 Dec 16;19(12):20719.
4. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88(5):519-20.
5. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014 Nov;18(6):413-9.
6. South Med J. 1997 Oct;90(10):1056-9.
7. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003 Apr;25(2):113-6.
8. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013 Aug;14(4):279-90.
9. Br J Dermatol. 1994 Apr;130(4):494-7.
The patient was diagnosed with granuloma annulare on the basis of history and clinical exam. A potassium hydroxide prep of skin scrapings was performed to rule out tinea corporis, and did not show evidence of fungal elements. The patient was treated with topical betamethasone with partial improvement.
First described as a “ringed eruption of the fingers” by Thomas Colcott Fox in 1895, granuloma annulare (GA) is a relatively common, benign, and self-limited condition whose precise etiology remains unclear. It is characterized commonly by pink to violaceous aciform or annular plaques on clinical examination. In some cases of GA, annular lesions are not present, or may be formed of grouped papules.
GA is characterized histologically by patchy interstitial lymphocytes and histiocytes palisading around mucin. Deep GA, an unusual subtype observed only in children, features a fibrin rather than a mucin core. This granulomatous picture is consistent with a Th1-mediated inflammatory process, and indeed, macrophage tumor necrosis factor production, as well as interleukin-2 and interferon-gamma production have been observed in GA. The reason for this exaggerated Th1 response is unknown, although in susceptible individuals trauma3 (an example of the Koebner phenomenon), arthropod assault,4 and herpes simplex infection5 (an example of Wolf isotopic response) all have been observed to trigger localized and/or generalized GA. Generalized GA has been associated with hyperlipidemia and the human leukocyte antigen–BW35 allele. GA has been described as a paraneoplastic eruption; atypical features such as associated pain or appearance in an uncharacteristic location often are present in such cases.6,7
Diagnosis of typical GA is clinical. If unusual features make you suspect tinea, leprosy, mycosis fungoides, or other annular lesions, then biopsy showing features typical of GA can reveal the correct diagnosis. Biopsy also can help to distinguish papular GA from warts or molluscum contagiosum. If extensive GA are present, then serum lipid testing for hypercholesterolemia or hypertriglyceridemia should be considered.
Other annular and raised lesions are on the differential for GA, but careful attention to the patient’s history and examination can clarify the diagnosis. Urticaria multiforme, a variant of annular urticaria, presents with numerous annular and polycyclic wheals, sometimes with central darkening that may be mistaken for necrosis. This patient did not present with polycyclic wheals. Furthermore, the lesions in urticaria multiforme are typically transient, with individual lesions lasting less than 24 hours, which was not the case with this patient. Wells syndrome, also known as eosinophilic cellulitis, is a condition marked by recurrent episodes of pruritus followed by appearance of edematous, painful, indurated, or edematous papules or plaques, although bullae and vesicles also may be present. The face and extremities are frequently involved and spontaneous resolution typically occurs in 2 months. Annular lesions are possible but papules, plaques, and nodules are more common in Wells syndrome. Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma (AEGCG), also known as actinic granuloma and Miescher granuloma of the face, is an entity characterized clinically by chronic, persistent, sun-distributed, annular plaques typically seen in older women with significant sun damage. AEGCG is considered by some to be a variant of GA, but if this is the case, it is a distinct subtype with different epidemiologic, clinical, and histopathologic characteristics from GA. Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis is histologically and clinically distinct from GA, presenting as subtly erythematous cords or extensive annular or serpiginous plaques in the axilla, groin, buttocks, or chest, typically in adult patients with rheumatoid arthritis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, or ankylosing spondylitis. Tinea corporis, the clinical manifestation of cutaneous dermatophyte infection, may be mistaken for granuloma annulare. However, tinea corporis lesions are scaly, whereas GA does not scale. Histologic examination of tinea corporis reveals hyphae, which are not present in GA.
GA is a relatively common, idiopathic, benign skin disease with numerous annular and papular mimics. Absence of scale, pain, and significant pruritus are important clues to the diagnosis, and biopsy can be helpful when the diagnosis is unclear. Treatment, although not necessary, may be offered using any of a number of modalities. The most consistent and effective healer of GA, however, is time.
References
1. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1980 Sep;3(3):217-30.
2. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2016 Sep;75(3):457-65.
3. Dermatol Online J. 2013 Dec 16;19(12):20719.
4. Acta Derm Venereol. 2008;88(5):519-20.
5. J Cutan Med Surg. 2014 Nov;18(6):413-9.
6. South Med J. 1997 Oct;90(10):1056-9.
7. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003 Apr;25(2):113-6.
8. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2013 Aug;14(4):279-90.
9. Br J Dermatol. 1994 Apr;130(4):494-7.
A 9-year-old girl presented to the dermatology clinic, referred by her pediatrician, for evaluation of asymptomatic lesions on her shins and feet for 2 months. She started developing one lesion over her right shin with other lesions appearing on the opposite leg a few weeks after, and treated the areas initially with an over-the-counter antifungal cream without improvement. She has been healthy and denied any recent fevers or upper respiratory infections, and said she had not taken any medications or vitamin supplements. She reported camping with her father occasionally but denied any bug or tick bites. No other family members were affected. There was no personal or family history of diabetes mellitus or high cholesterol, and there are no pets at home.