User login
Development of an Integrative Medicine Rotation for Family Medicine and Preventive Medicine Residency
Development of an Integrative Medicine Rotation for Family Medicine and Preventive Medicine Residency
Integrative medicine or complementary alternative medicine (IM/CAM) is increasingly being recognized as an integral part of optimal health and healing. IM/CAM “reaffirms the importance of the relationship between practitioner and patient, focuses on the whole person, is informed by evidence, and makes use of all appropriate therapeutic approaches, healthcare professionals and disciplines.”1 IM/CAM encompasses a wide range of therapies, conceptual frameworks, and health care-related professions, such as acupuncture, massage, dietary supplements, mindfulness, yoga, meditation and guided imagery.1 Research has found that 30% to 98% of patients with chronic conditions seek IM/CAM therapies.1-3
Despite the high prevalence of patients utilizing IM/CAM therapies and the National Institutes of Health grants for IM/CAM education, implementation of IM/CAM instruction in graduate medical education programs remains inconsistent.1 Barriers cited by programs include a lack of IM/CAM experts in the program, faculty training, competing financial resources, and an already full resident education schedule.4 As a result, many physicians have limited or no training in IM/CAM.1,5
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers IM/CAM health programs to veterans and caregivers as part of its whole health care initiative.6 Several VA health care systems have adopted whole health and IM/CAM through programs for mental health integration into primary care; women’s health; integrative pain care; geriatrics, through adoption of Age-Friendly Health Systems standards; and nutrition and physical activity.7-13 The VA provides training to more medical students than any other health system: > 95% of US medical schools are affiliated with a VA medical center (VAMC).14 As part of the training mission, VA seeks to encourage students of diverse professions to consider careers in the VA.14
Residency is a time for newly licensed physicians to acquire additional experience and training to translate knowledge and skills acquired during medical school directly to patient care.15 However, residency curricula have limited time to incorporate IM/CAM training. Residency training is also physically and psychosocially demanding, often resulting in inadequate self-care, poor work-life balance, and disrupted sleep.16-18 Resident wellness is at a historic low, resulting in high rates of burnout during training.4,15
Residency programs are required to provide wellness education; however, most programs include minimal content.19 Despite high rates of burnout, formal curricula on the topic have not been established. 20 IM/CAM education also can provide a path for residents to learn about and engage in mindfulness-based training or cognitive stress reduction for self-care.
INTEGRATIVE WHOLE HEALTH ROTATION
In 2017, the Baltimore Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) established an IM/whole health residency rotation and created a structured curriculum incorporating self-assessment, active reflection, and self-care to complement training in specific IM/CAM modalities for residents in family medicine. The curriculum evaluated how this training improved residents’ perceptions of IM/CAM and how it personally and professionally impacted the practice of self-care as a strategy to decrease burnout. We hypothesized that this structured experience would increase IM/CAM knowledge among clinicians while promoting the importance and practice of self-care to reduce burnout.
The 2-week IM/CAM curriculum was developed by University of Maryland School of Medicine faculty in partnership with the Baltimore GRECC and staff at the VA Maryland Health Care System. The curriculum was designed to expose residents to the 8 components of the whole health Circle of Health (moving the body; surroundings; personal development; food and drink; recharge; family, friends, and coworkers; spirit and soul; and power of the mind) in addition to IM/ CAM modalities the VA is mandated to offer to veterans (acupuncture, chiropractic, meditation, massage therapy, biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, yoga, and tai chi).21 Twelve residents (1 preventive medicine and 11 third-year family medicine residents) rotated individually throughout the year as part of their behavioral health block rotation. All residents completed the 2-week curriculum as their schedules allowed. The curriculum consisted of didactics sessions and activities at the Baltimore, Loch Raven, and Perry Point VAMCs. Residents completed evaluations before and after the rotation. The experience described in this article by the residents and the survey data were collected from the 2018/2019 training year. A rotation syllabus, competencies adapted from Locke and colleagues and skills residents obtain during this rotation that support these competencies, as well as a resident sample schedule were developed (eAppendix is available at doi:10.12788/fp.0544).1

Rotation Overview
for each resident were built around instructional opportunities, which included 1-on-1 didactics, direct observation of treatment modalities, and personal reflection of the residents’ self-care practices. While each resident’s rotation schedule varied slightly due to their schedules, the foundational instruction elements were the same. Didactic session themes included an overview of IM/CAM, nutrition, narrative medicine, pain psychology, music therapy, chaplain services, motor-cognitive training, and exercise guidelines. Assigned readings, including peer-reviewed literature on IM/CAM therapies, complemented all sessions. Residents created an evidence-supported integrative treatment plan for a patient with a condition of interest to them.
Residents observed clinician-led veteran group sessions on IM/CAM treatment modalities, including guided meditation, mindfulness and relaxation, self-awareness, living well with chronic pain, tai chi, drumming for health and balance, anger management, recovery group, acceptance and commitment therapy, and Gerofit exercise. The group classes allowed residents to actively participate in the activity or discussion. Residents also shadowed VA clinicians in sleep, pain, nutrition, acupuncture, and mental health clinics.
Residents were encouraged to practice self-care during the 2-week rotation. The rotation schedule built in free time, including a 1-hour daily lunch period, for residents to consider their own health habits, complete a personal health inventory, and try self-care activities outlined on the syllabus with links to resources. These resources also served as educational materials that residents could share with patients. All materials, including didactic lectures, journal articles and self-care resources, were provided to each resident through a free online course to ensure residents had access throughout and following completion of the rotation. This content, including the rotation evaluation metrics, is available upon request from the corresponding author.
Evaluations
Residents completed a survey before and after the rotation to measure IM/CAM knowledge and application and self-care/ burnout perceptions. Residents were asked to evaluate rotation sessions and comment on whether this rotation benefited them personally and professionally (Table 1). Descriptive statistics were analyzed using Microsoft Excel. Given the small sample size and lack of statistical power, only mean survey results are reported in this article. Because this opportunity is specific to the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the proposed project was part of ordinary educational practice, the study was deemed not human subject research by the University of Maryland Institutional Review Board (HP-00089256).

Perceptions and attitudes toward IM/CAM were assessed using a survey designed by the University of Minnesota Academic Health Center. It included 18 items scored on a 5-point semantic rating scale (1, strongly disagree; 5, strongly agree).22 Residents rated their level of agreement with statements reflecting both positive (eg, clinical care should integrate the best of conventional and CAM practices) and negative (eg, CAM is a threat to public health) views. Three questions adapted from the NHIS Adult Complementary Health Questionnaire and UC Irvine Survey of Health Care Use and Practice assessed the use of IM/CAM resources.23,24
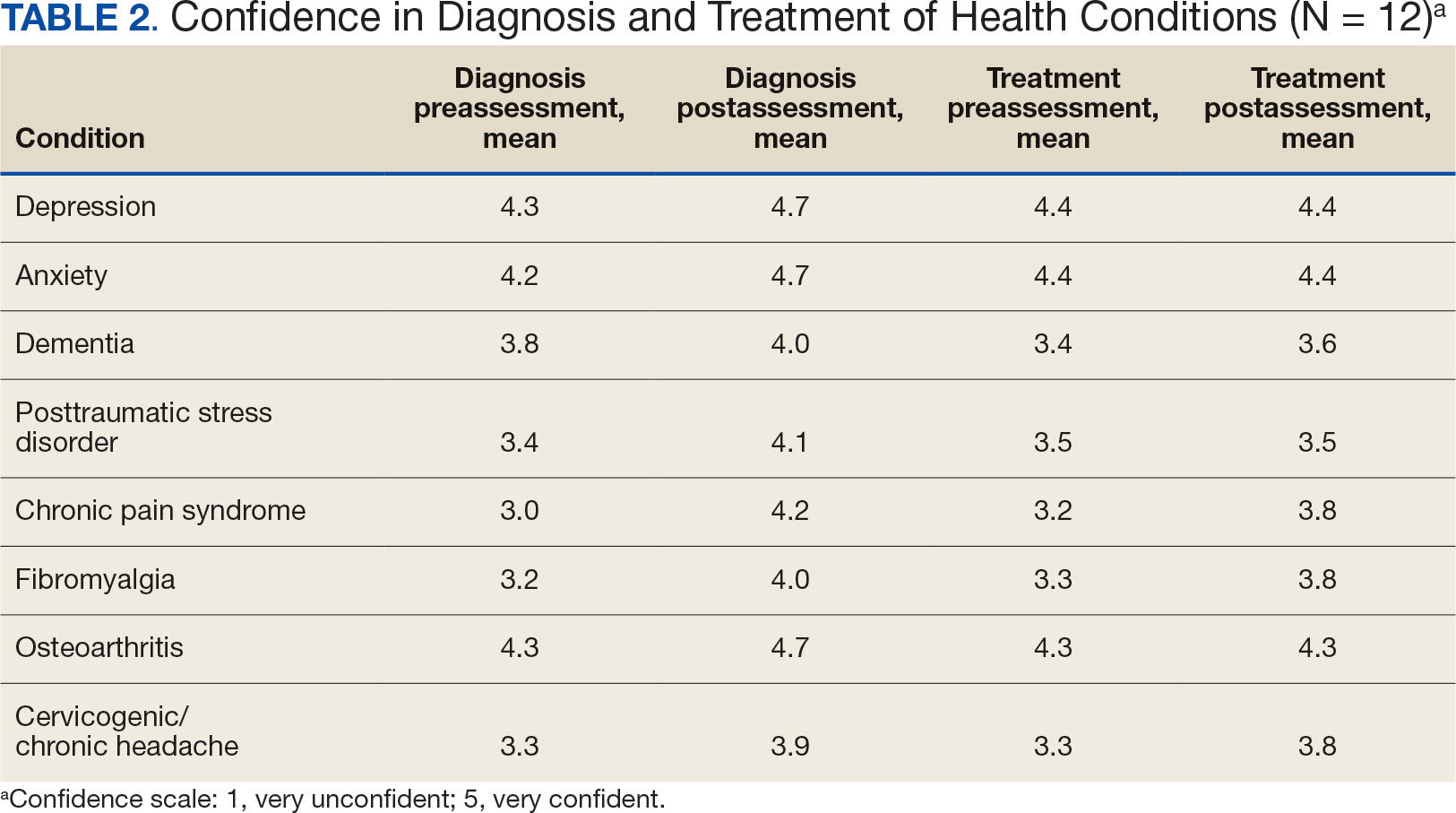
Resident knowledge and application of IM/CAM were measured using a case study designed by the course faculty. The case listed a chief complaint of nerve pain, with a history of chronic pain, neuropathic pain, anxiety, chronic fatigue, depression, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder, history of present illness, past surgical history, medication list, review of symptoms, laboratory values, and physical examination. The residents completed an assessment before and after the rotation. Residents rated their confidence in the diagnosis and treatment of 8 medical conditions using a 5-point semantic rating scale (Table 2). Self-care importance and selfcare frequency were measured by a variety of means, including 3 survey questions, the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire, 2 prompts on a 7-point semantic scale, and a slightly modified version of the validated Perceived Stress Scale.25-28
Survey Results
Residents gave the rotation positive feedback with a mean score of 8.5 out of 10. They reported the beneficial impact of seeing the nontraditional and nonpharmacological practices in treating patients, chronic pain management team approaches, and enjoyed being able to participate in group classes with patients. Many residents expressed a desire for a longer rotation to have more time to experience the behavioral health-focused sessions. Residents also requested additional information on nutritional supplements/natural medicines, battlefield acupuncture training and osteopathic manipulative therapy practices. All residents reported the rotation personally and/or professionally benefited them (Appendix).
Given the sample of 12 residents, values are presented as prerotation to postrotation comparisons without statistical analysis. There was a trend towards an increase in the reported use and recommendation of 26 modalities of nonconventional therapies following the rotation. There was also a slight increase in resource knowledge and use of these resources, and residents reported accessing more types of resources. Mean scores of the case study to gauge knowledge and application of IM increased from 7.5 at baseline to 11.0 after the rotation. Resident confidence in diagnosis increased for all 8 conditions, but confidence in treatment only increased for 4 conditions.
Results of self-care importance, self-care frequency and mindfulness were consistent baseline to postrotation. The mean time residents spent regularly practicing self-care during a work week increased slightly while feelings of burnout decreased. The perceived stress scale average score decreased from 13.4 at baseline to 10.5 after rotation.
DISCUSSION
The implementation of an IM residency rotation that incorporates whole health and interprofessional practices demonstrated improved perception and increased use of IM/CAM resources and knowledge among a small sample of third-year residents. Residents reported they had a positive experience participating in the rotation and gained knowledge, resources, and skills they felt confident discussing with their patients.
Many studies reported favorable attitudes and perceptions of IM/CAM use among physicians, but few have assessed these measures while implementing a training curriculum.3,4,22 Gardiner and colleagues reported on the perception and use of IM resources among family medicine residents.4 The study found that while 58% of all residents reported IM/CAM as an important part of their training, only 60% reported they received it or had specific learning objectives in their curriculum. 4 The program outlined in this study and previous research illustrate that physicians recognize the importance of IM/CAM education in training programs, but most were unaware of the resources available or did not feel comfortable counseling patients about most IM/CAM applications.
Residents in this program slightly increased their use of IM/CAM to diagnose and treat medical conditions after the rotation. A study by Wahner-Roedler and colleagues assessed physician knowledge regarding common IM/CAM therapies.3 On average, physicians only felt knowledgeable and comfortable counseling patients for 3 of 13 listed treatments/techniques and few natural herbal treatments. The study also found that most physicians had difficulty accessing IM/CAM information at their institution despite having free access to electronic databases. However, this study only assessed physician attitudes of IM/CAM and did not include an educational component to increase their knowledge of the modalities.3 This evaluation supports the need for interventions like the program described in this article that provide physicians with access to evidence-based resources combined with the applied experiences to increase their comfort within this growing field.
Though the sample size in this study was small, its results support existing research indicating that clinicians view selfcare as important. Many residents were already using a self-care plan at baseline, but there was slight increase in the practice of self-care during the rotation and a slight decrease in burnout. Previous research reflects high rates of burnout and relatively poor quality of life among primary care physicians.15 Burnout is associated with lower quality of care, lower patient satisfaction and contributes to medical errors. Studies suggest as many as 60% of primary care physicians report symptoms of burnout, which negatively affected the quality of patient care they provide.15
Despite the profound effects burnout has on physicians and patient care, a standardized wellness education or self-care tool kit is not currently available. The University of Massachusetts recently introduced a pilot program to promote resident wellness that demonstrated favorable results.15 A meta-analysis of physicians and medical trainees found decreases in anxiety and symptoms of anxiety as well as a decrease in burnout among participants in cognitive, behavioral and mindfulness interventions.29 However, unlike our program, these programs focused solely on the well-being of medical trainees, residents, and physicians and didn’t focus on the patient-clinician interactions. Given the impact on patient care, there is a need to develop and implement additional programs like our residency rotation that promote health and wellness among physicians while also evaluating how physicians may translate these skills to patient education.
While this program st i l l exists for third-year residents at Baltimore GRECC, it has significantly changed since the COVID-19 pandemic. For about the first 6 months of the pandemic, when physical distancing requirements were in place, family medicine trainees were not able to rotate. Upon return to the facility, many group classes were cancelled and some clinicians no longer offered the sessions. The rotation has evolved to a hybrid format, where many group classes for veteran patients are offered virtually, and residents observe a mix of virtual and in-person shadowing opportunities. Our formal evaluation included administering the survey and occurred from July 2018 to July 2019 but wasn’t implemented upon return to post-COVID activities due to the inconsistent experiences offered to residents over the past few years. Future research should evaluate the impact of this hybrid program on the clinicians and explore dissemination to other VAMCs and their academic affiliates.
Limitations
Project recruitment was limited to 11 family medicine and 1 preventive medicine resident. Perceptions, use of IM/CAM, and knowledge about IM/CAM could be considerably different in different departments with varying schedules, hours worked, and patient volumes. Secondly, the survey was conducted 2 weeks apart. Indications of self-care and burnout may not reflect long-term effects, adoption, or maintenance. Future research should include longer follow up to examine how this type of educational activity may impact burnout rates of physicians following the completion of residency, as well as changes in perspectives of IM/CAM while practicing as a physician. Trainees were exposed to a wide range of health care professions, but additional research is needed regarding medical resident perceptions of the roles of specific professions in a collaborative health care team.30,31
CONCLUSIONS
The residency rotation program illustrates the benefits of establishing a standardized IM/CAM rotation that includes self-care resources in family medicine programs to adequately train clinicians to practice wellness and promote it to their patients. The results of this project suggest this type of training will help residents assess the literature to better counsel patients on IM/CAM options while also providing strategies for maintaining optimal health and well-being for health care professionals. Broadening and shifting the scope of medicine from treatment to prevention, personal wellness, and optimal healing should be a top priority.
- Locke AB, Gordon A, Guerrera MP, Gardiner P, Lebensohn P. Recommended integrative medicine competencies for family medicine residents. Explore (NY). 2013;9(5):308-313. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2013.06.005
- Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569-1575. doi:10.1001/jama.280.18.1569
- Wahner-Roedler DL, Vincent A, Elkin PL, Loehrer LL, Cha SS, Bauer BA. Physicians’ attitudes toward complementary and alternative medicine and their knowledge of specific therapies: a survey at an academic medical center. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3(4):495-501. doi:10.1093/ecam/nel036
- Gardiner P, Filippelli AC, Lebensohn P, Bonakdar R. Family medicine residency program directors attitudes and knowledge of family medicine CAM competencies. Explore (NY). 2013;9(5):299-307. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2013.06.002
- Sierpina V, Levine R, Astin J, Tan A. Use of mind-body therapies in psychiatry and family medicine faculty and residents: attitudes, barriers, and gender differences. Explore (NY). 2007;3(2):129-135. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2006.12.001
- Krist AH, South-Paul J, Meisnere M, eds. Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation. The National Academies Press; 2023.
- Bokhour BG, DeFaccio R, Gaj L, et al. Changes in patientreported outcomes associated with receiving whole health in the Veteran Health Administration (VHA)’s National Demonstration Project. J Gen Intern Med. 2024;39(1):84-94. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08376-0
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ, Bolton R, Smith S, Harden SM. Using a whole health approach to build biopsychosocial- spiritual personal health plans for veterans with chronic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2024;25(1):69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pmn.2023.09.010
- Gabrielian S, Jones AL, Hoge AE, et al. Enhancing primary care experiences for homeless patients with serious mental illness: results from a national survey. J Prim Care Community Health. 2021;12:2150132721993654. doi:10.1177/2150132721993654
- Matthieu MM, Church KA, Taylor LD, et al. Integrating the age-friendly health systems movement in Veterans Health Administration: national advance care planning via group visits and the 4Ms framework. Health Soc Work. 2023;48(4):277-280. doi:10.1093/hsw/hlad022
- Meisler AW, Gianoli MO, Na PJ, Pietrzak RH. Functional disability in US military veterans: the importance of integrated whole health initiatives. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2023;25(4):22m03461. doi:10.4088/PCC.22m03461
- Ortmeyer HK, Giffuni J, Etchberger D, Katzel L. The role of companion dogs in the VA Maryland Health Care System Whole Health(y) GeroFit Program. Animals (Basel). 2023;13(19):3047. doi:10.3390/ani13193047
- Sullivan MB, Hill K, Ballengee LA, et al. Remotely delivered psychologically informed mindful movement physical therapy for pain care: a framework for operationalization. Glob Adv Integr Med Health. 2023;12:27536130231209751. doi:10.1177/27536130231209751
- (OAA) OoAA. 75th Anniversary: Passion to learn. Power to heal. Washington DC.: US Department of Veterans Affairs; 2021. https://content.yudu.com/web/448fx/0A448g9/75thAnniversary2021/html/index.html?page=24&origin=reader
- Runyan C, Savageau JA, Potts S, Weinreb L. Impact of a family medicine resident wellness curriculum: a feasibility study. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:30648. doi:10.3402/meo.v21.30648
- Lafreniere JP, Rios R, Packer H, Ghazarian S, Wright SM, Levine RB. Burned out at the bedside: patient perceptions of physician burnout in an internal medicine resident continuity clinic. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(2):203-208. doi:10.1007/s11606-015-3503-3
- Freedy JR, Staley C, Mims LD, et al. Social, individual, and environmental characteristics of family medicine resident burnout: a CERA study. Fam Med. 2022;54(4):270-276. doi:10.22454/FamMed.2022.526799
- Alrishan MA, Alshammari SA. Prevalence of sleep deprivation and its effect on the performance of family medicine residents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med. 2020;27(2):125-130. doi:10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_9_20
- ACGME. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Family Medicine. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/120_familymedicine_2024.pdf
- Nene Y, Tadi P. Resident Burnout. In: StatPearls; 2023.
- Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the veterans affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58(4):295-300. doi:10.1097/MLF.0000000000001316
- Kreitzer MJ, Mitten D, Harris I, Shandeling J. Attitudes toward CAM among medical, nursing, and pharmacy faculty and students: a comparative analysis. Altern Ther Health Med. 2002;8(6):44-53.
- Clarke TC, Black LI, Stussman BJ, Barnes PM, Nahin RL. Trends in the use of complementary health approaches among adults: United States, 2002-2012. Natl Health Stat Report. 2015(79):1-16.
- Nguyen J, Liu MA, Patel RJ, Tahara K, Nguyen AL. Use and interest in complementary and alternative medicine among college students seeking healthcare at a university campus student health center. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2016;24:103-108. doi:10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.06.001
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Hopkins J, Krietemeyer J, Toney L. Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment. 2006;13(1):27-45. doi:10.1177/1073191105283504
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Lykins E, et al. Construct validity of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment. 2008;15(3):329-342. doi:10.1177/1073191107313003
- West CP, Dyrbye LN, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Single item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are useful for assessing burnout in medical professionals. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(12):1318- 1321. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1129-z
- Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. J Health Soc Behav. 1983;24(4):385-396.
- Regehr C, Glancy D, Pitts A, LeBlanc VR. Interventions to reduce the consequences of stress in physicians: a review and meta-analysis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014;202(5):353-359. doi:10.1097/NMD.0000000000000130
- Visser CLF, Ket JCF, Croiset G, Kusurkar RA. Perceptions of residents, medical and nursing students about interprofessional education: a systematic review of the quantitative and qualitative literature. BMC Med Educ. 2017;17(1):77. doi:10.1186/s12909-017-0909-0
- Lingard L, Espin S, Evans C, Hawryluck L. The rules of the game: interprofessional collaboration on the intensive care unit team. Crit Care. 2004;8(6):R403-408. doi:10.1186/cc2958
Integrative medicine or complementary alternative medicine (IM/CAM) is increasingly being recognized as an integral part of optimal health and healing. IM/CAM “reaffirms the importance of the relationship between practitioner and patient, focuses on the whole person, is informed by evidence, and makes use of all appropriate therapeutic approaches, healthcare professionals and disciplines.”1 IM/CAM encompasses a wide range of therapies, conceptual frameworks, and health care-related professions, such as acupuncture, massage, dietary supplements, mindfulness, yoga, meditation and guided imagery.1 Research has found that 30% to 98% of patients with chronic conditions seek IM/CAM therapies.1-3
Despite the high prevalence of patients utilizing IM/CAM therapies and the National Institutes of Health grants for IM/CAM education, implementation of IM/CAM instruction in graduate medical education programs remains inconsistent.1 Barriers cited by programs include a lack of IM/CAM experts in the program, faculty training, competing financial resources, and an already full resident education schedule.4 As a result, many physicians have limited or no training in IM/CAM.1,5
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers IM/CAM health programs to veterans and caregivers as part of its whole health care initiative.6 Several VA health care systems have adopted whole health and IM/CAM through programs for mental health integration into primary care; women’s health; integrative pain care; geriatrics, through adoption of Age-Friendly Health Systems standards; and nutrition and physical activity.7-13 The VA provides training to more medical students than any other health system: > 95% of US medical schools are affiliated with a VA medical center (VAMC).14 As part of the training mission, VA seeks to encourage students of diverse professions to consider careers in the VA.14
Residency is a time for newly licensed physicians to acquire additional experience and training to translate knowledge and skills acquired during medical school directly to patient care.15 However, residency curricula have limited time to incorporate IM/CAM training. Residency training is also physically and psychosocially demanding, often resulting in inadequate self-care, poor work-life balance, and disrupted sleep.16-18 Resident wellness is at a historic low, resulting in high rates of burnout during training.4,15
Residency programs are required to provide wellness education; however, most programs include minimal content.19 Despite high rates of burnout, formal curricula on the topic have not been established. 20 IM/CAM education also can provide a path for residents to learn about and engage in mindfulness-based training or cognitive stress reduction for self-care.
INTEGRATIVE WHOLE HEALTH ROTATION
In 2017, the Baltimore Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) established an IM/whole health residency rotation and created a structured curriculum incorporating self-assessment, active reflection, and self-care to complement training in specific IM/CAM modalities for residents in family medicine. The curriculum evaluated how this training improved residents’ perceptions of IM/CAM and how it personally and professionally impacted the practice of self-care as a strategy to decrease burnout. We hypothesized that this structured experience would increase IM/CAM knowledge among clinicians while promoting the importance and practice of self-care to reduce burnout.
The 2-week IM/CAM curriculum was developed by University of Maryland School of Medicine faculty in partnership with the Baltimore GRECC and staff at the VA Maryland Health Care System. The curriculum was designed to expose residents to the 8 components of the whole health Circle of Health (moving the body; surroundings; personal development; food and drink; recharge; family, friends, and coworkers; spirit and soul; and power of the mind) in addition to IM/ CAM modalities the VA is mandated to offer to veterans (acupuncture, chiropractic, meditation, massage therapy, biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, yoga, and tai chi).21 Twelve residents (1 preventive medicine and 11 third-year family medicine residents) rotated individually throughout the year as part of their behavioral health block rotation. All residents completed the 2-week curriculum as their schedules allowed. The curriculum consisted of didactics sessions and activities at the Baltimore, Loch Raven, and Perry Point VAMCs. Residents completed evaluations before and after the rotation. The experience described in this article by the residents and the survey data were collected from the 2018/2019 training year. A rotation syllabus, competencies adapted from Locke and colleagues and skills residents obtain during this rotation that support these competencies, as well as a resident sample schedule were developed (eAppendix is available at doi:10.12788/fp.0544).1

Rotation Overview
for each resident were built around instructional opportunities, which included 1-on-1 didactics, direct observation of treatment modalities, and personal reflection of the residents’ self-care practices. While each resident’s rotation schedule varied slightly due to their schedules, the foundational instruction elements were the same. Didactic session themes included an overview of IM/CAM, nutrition, narrative medicine, pain psychology, music therapy, chaplain services, motor-cognitive training, and exercise guidelines. Assigned readings, including peer-reviewed literature on IM/CAM therapies, complemented all sessions. Residents created an evidence-supported integrative treatment plan for a patient with a condition of interest to them.
Residents observed clinician-led veteran group sessions on IM/CAM treatment modalities, including guided meditation, mindfulness and relaxation, self-awareness, living well with chronic pain, tai chi, drumming for health and balance, anger management, recovery group, acceptance and commitment therapy, and Gerofit exercise. The group classes allowed residents to actively participate in the activity or discussion. Residents also shadowed VA clinicians in sleep, pain, nutrition, acupuncture, and mental health clinics.
Residents were encouraged to practice self-care during the 2-week rotation. The rotation schedule built in free time, including a 1-hour daily lunch period, for residents to consider their own health habits, complete a personal health inventory, and try self-care activities outlined on the syllabus with links to resources. These resources also served as educational materials that residents could share with patients. All materials, including didactic lectures, journal articles and self-care resources, were provided to each resident through a free online course to ensure residents had access throughout and following completion of the rotation. This content, including the rotation evaluation metrics, is available upon request from the corresponding author.
Evaluations
Residents completed a survey before and after the rotation to measure IM/CAM knowledge and application and self-care/ burnout perceptions. Residents were asked to evaluate rotation sessions and comment on whether this rotation benefited them personally and professionally (Table 1). Descriptive statistics were analyzed using Microsoft Excel. Given the small sample size and lack of statistical power, only mean survey results are reported in this article. Because this opportunity is specific to the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the proposed project was part of ordinary educational practice, the study was deemed not human subject research by the University of Maryland Institutional Review Board (HP-00089256).

Perceptions and attitudes toward IM/CAM were assessed using a survey designed by the University of Minnesota Academic Health Center. It included 18 items scored on a 5-point semantic rating scale (1, strongly disagree; 5, strongly agree).22 Residents rated their level of agreement with statements reflecting both positive (eg, clinical care should integrate the best of conventional and CAM practices) and negative (eg, CAM is a threat to public health) views. Three questions adapted from the NHIS Adult Complementary Health Questionnaire and UC Irvine Survey of Health Care Use and Practice assessed the use of IM/CAM resources.23,24
Resident knowledge and application of IM/CAM were measured using a case study designed by the course faculty. The case listed a chief complaint of nerve pain, with a history of chronic pain, neuropathic pain, anxiety, chronic fatigue, depression, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder, history of present illness, past surgical history, medication list, review of symptoms, laboratory values, and physical examination. The residents completed an assessment before and after the rotation. Residents rated their confidence in the diagnosis and treatment of 8 medical conditions using a 5-point semantic rating scale (Table 2). Self-care importance and selfcare frequency were measured by a variety of means, including 3 survey questions, the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire, 2 prompts on a 7-point semantic scale, and a slightly modified version of the validated Perceived Stress Scale.25-28

Survey Results
Residents gave the rotation positive feedback with a mean score of 8.5 out of 10. They reported the beneficial impact of seeing the nontraditional and nonpharmacological practices in treating patients, chronic pain management team approaches, and enjoyed being able to participate in group classes with patients. Many residents expressed a desire for a longer rotation to have more time to experience the behavioral health-focused sessions. Residents also requested additional information on nutritional supplements/natural medicines, battlefield acupuncture training and osteopathic manipulative therapy practices. All residents reported the rotation personally and/or professionally benefited them (Appendix).
Given the sample of 12 residents, values are presented as prerotation to postrotation comparisons without statistical analysis. There was a trend towards an increase in the reported use and recommendation of 26 modalities of nonconventional therapies following the rotation. There was also a slight increase in resource knowledge and use of these resources, and residents reported accessing more types of resources. Mean scores of the case study to gauge knowledge and application of IM increased from 7.5 at baseline to 11.0 after the rotation. Resident confidence in diagnosis increased for all 8 conditions, but confidence in treatment only increased for 4 conditions.
Results of self-care importance, self-care frequency and mindfulness were consistent baseline to postrotation. The mean time residents spent regularly practicing self-care during a work week increased slightly while feelings of burnout decreased. The perceived stress scale average score decreased from 13.4 at baseline to 10.5 after rotation.
DISCUSSION
The implementation of an IM residency rotation that incorporates whole health and interprofessional practices demonstrated improved perception and increased use of IM/CAM resources and knowledge among a small sample of third-year residents. Residents reported they had a positive experience participating in the rotation and gained knowledge, resources, and skills they felt confident discussing with their patients.
Many studies reported favorable attitudes and perceptions of IM/CAM use among physicians, but few have assessed these measures while implementing a training curriculum.3,4,22 Gardiner and colleagues reported on the perception and use of IM resources among family medicine residents.4 The study found that while 58% of all residents reported IM/CAM as an important part of their training, only 60% reported they received it or had specific learning objectives in their curriculum. 4 The program outlined in this study and previous research illustrate that physicians recognize the importance of IM/CAM education in training programs, but most were unaware of the resources available or did not feel comfortable counseling patients about most IM/CAM applications.
Residents in this program slightly increased their use of IM/CAM to diagnose and treat medical conditions after the rotation. A study by Wahner-Roedler and colleagues assessed physician knowledge regarding common IM/CAM therapies.3 On average, physicians only felt knowledgeable and comfortable counseling patients for 3 of 13 listed treatments/techniques and few natural herbal treatments. The study also found that most physicians had difficulty accessing IM/CAM information at their institution despite having free access to electronic databases. However, this study only assessed physician attitudes of IM/CAM and did not include an educational component to increase their knowledge of the modalities.3 This evaluation supports the need for interventions like the program described in this article that provide physicians with access to evidence-based resources combined with the applied experiences to increase their comfort within this growing field.
Though the sample size in this study was small, its results support existing research indicating that clinicians view selfcare as important. Many residents were already using a self-care plan at baseline, but there was slight increase in the practice of self-care during the rotation and a slight decrease in burnout. Previous research reflects high rates of burnout and relatively poor quality of life among primary care physicians.15 Burnout is associated with lower quality of care, lower patient satisfaction and contributes to medical errors. Studies suggest as many as 60% of primary care physicians report symptoms of burnout, which negatively affected the quality of patient care they provide.15
Despite the profound effects burnout has on physicians and patient care, a standardized wellness education or self-care tool kit is not currently available. The University of Massachusetts recently introduced a pilot program to promote resident wellness that demonstrated favorable results.15 A meta-analysis of physicians and medical trainees found decreases in anxiety and symptoms of anxiety as well as a decrease in burnout among participants in cognitive, behavioral and mindfulness interventions.29 However, unlike our program, these programs focused solely on the well-being of medical trainees, residents, and physicians and didn’t focus on the patient-clinician interactions. Given the impact on patient care, there is a need to develop and implement additional programs like our residency rotation that promote health and wellness among physicians while also evaluating how physicians may translate these skills to patient education.
While this program st i l l exists for third-year residents at Baltimore GRECC, it has significantly changed since the COVID-19 pandemic. For about the first 6 months of the pandemic, when physical distancing requirements were in place, family medicine trainees were not able to rotate. Upon return to the facility, many group classes were cancelled and some clinicians no longer offered the sessions. The rotation has evolved to a hybrid format, where many group classes for veteran patients are offered virtually, and residents observe a mix of virtual and in-person shadowing opportunities. Our formal evaluation included administering the survey and occurred from July 2018 to July 2019 but wasn’t implemented upon return to post-COVID activities due to the inconsistent experiences offered to residents over the past few years. Future research should evaluate the impact of this hybrid program on the clinicians and explore dissemination to other VAMCs and their academic affiliates.
Limitations
Project recruitment was limited to 11 family medicine and 1 preventive medicine resident. Perceptions, use of IM/CAM, and knowledge about IM/CAM could be considerably different in different departments with varying schedules, hours worked, and patient volumes. Secondly, the survey was conducted 2 weeks apart. Indications of self-care and burnout may not reflect long-term effects, adoption, or maintenance. Future research should include longer follow up to examine how this type of educational activity may impact burnout rates of physicians following the completion of residency, as well as changes in perspectives of IM/CAM while practicing as a physician. Trainees were exposed to a wide range of health care professions, but additional research is needed regarding medical resident perceptions of the roles of specific professions in a collaborative health care team.30,31
CONCLUSIONS
The residency rotation program illustrates the benefits of establishing a standardized IM/CAM rotation that includes self-care resources in family medicine programs to adequately train clinicians to practice wellness and promote it to their patients. The results of this project suggest this type of training will help residents assess the literature to better counsel patients on IM/CAM options while also providing strategies for maintaining optimal health and well-being for health care professionals. Broadening and shifting the scope of medicine from treatment to prevention, personal wellness, and optimal healing should be a top priority.
Integrative medicine or complementary alternative medicine (IM/CAM) is increasingly being recognized as an integral part of optimal health and healing. IM/CAM “reaffirms the importance of the relationship between practitioner and patient, focuses on the whole person, is informed by evidence, and makes use of all appropriate therapeutic approaches, healthcare professionals and disciplines.”1 IM/CAM encompasses a wide range of therapies, conceptual frameworks, and health care-related professions, such as acupuncture, massage, dietary supplements, mindfulness, yoga, meditation and guided imagery.1 Research has found that 30% to 98% of patients with chronic conditions seek IM/CAM therapies.1-3
Despite the high prevalence of patients utilizing IM/CAM therapies and the National Institutes of Health grants for IM/CAM education, implementation of IM/CAM instruction in graduate medical education programs remains inconsistent.1 Barriers cited by programs include a lack of IM/CAM experts in the program, faculty training, competing financial resources, and an already full resident education schedule.4 As a result, many physicians have limited or no training in IM/CAM.1,5
The US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) offers IM/CAM health programs to veterans and caregivers as part of its whole health care initiative.6 Several VA health care systems have adopted whole health and IM/CAM through programs for mental health integration into primary care; women’s health; integrative pain care; geriatrics, through adoption of Age-Friendly Health Systems standards; and nutrition and physical activity.7-13 The VA provides training to more medical students than any other health system: > 95% of US medical schools are affiliated with a VA medical center (VAMC).14 As part of the training mission, VA seeks to encourage students of diverse professions to consider careers in the VA.14
Residency is a time for newly licensed physicians to acquire additional experience and training to translate knowledge and skills acquired during medical school directly to patient care.15 However, residency curricula have limited time to incorporate IM/CAM training. Residency training is also physically and psychosocially demanding, often resulting in inadequate self-care, poor work-life balance, and disrupted sleep.16-18 Resident wellness is at a historic low, resulting in high rates of burnout during training.4,15
Residency programs are required to provide wellness education; however, most programs include minimal content.19 Despite high rates of burnout, formal curricula on the topic have not been established. 20 IM/CAM education also can provide a path for residents to learn about and engage in mindfulness-based training or cognitive stress reduction for self-care.
INTEGRATIVE WHOLE HEALTH ROTATION
In 2017, the Baltimore Geriatric Research Education and Clinical Center (GRECC) established an IM/whole health residency rotation and created a structured curriculum incorporating self-assessment, active reflection, and self-care to complement training in specific IM/CAM modalities for residents in family medicine. The curriculum evaluated how this training improved residents’ perceptions of IM/CAM and how it personally and professionally impacted the practice of self-care as a strategy to decrease burnout. We hypothesized that this structured experience would increase IM/CAM knowledge among clinicians while promoting the importance and practice of self-care to reduce burnout.
The 2-week IM/CAM curriculum was developed by University of Maryland School of Medicine faculty in partnership with the Baltimore GRECC and staff at the VA Maryland Health Care System. The curriculum was designed to expose residents to the 8 components of the whole health Circle of Health (moving the body; surroundings; personal development; food and drink; recharge; family, friends, and coworkers; spirit and soul; and power of the mind) in addition to IM/ CAM modalities the VA is mandated to offer to veterans (acupuncture, chiropractic, meditation, massage therapy, biofeedback, clinical hypnosis, guided imagery, yoga, and tai chi).21 Twelve residents (1 preventive medicine and 11 third-year family medicine residents) rotated individually throughout the year as part of their behavioral health block rotation. All residents completed the 2-week curriculum as their schedules allowed. The curriculum consisted of didactics sessions and activities at the Baltimore, Loch Raven, and Perry Point VAMCs. Residents completed evaluations before and after the rotation. The experience described in this article by the residents and the survey data were collected from the 2018/2019 training year. A rotation syllabus, competencies adapted from Locke and colleagues and skills residents obtain during this rotation that support these competencies, as well as a resident sample schedule were developed (eAppendix is available at doi:10.12788/fp.0544).1

Rotation Overview
for each resident were built around instructional opportunities, which included 1-on-1 didactics, direct observation of treatment modalities, and personal reflection of the residents’ self-care practices. While each resident’s rotation schedule varied slightly due to their schedules, the foundational instruction elements were the same. Didactic session themes included an overview of IM/CAM, nutrition, narrative medicine, pain psychology, music therapy, chaplain services, motor-cognitive training, and exercise guidelines. Assigned readings, including peer-reviewed literature on IM/CAM therapies, complemented all sessions. Residents created an evidence-supported integrative treatment plan for a patient with a condition of interest to them.
Residents observed clinician-led veteran group sessions on IM/CAM treatment modalities, including guided meditation, mindfulness and relaxation, self-awareness, living well with chronic pain, tai chi, drumming for health and balance, anger management, recovery group, acceptance and commitment therapy, and Gerofit exercise. The group classes allowed residents to actively participate in the activity or discussion. Residents also shadowed VA clinicians in sleep, pain, nutrition, acupuncture, and mental health clinics.
Residents were encouraged to practice self-care during the 2-week rotation. The rotation schedule built in free time, including a 1-hour daily lunch period, for residents to consider their own health habits, complete a personal health inventory, and try self-care activities outlined on the syllabus with links to resources. These resources also served as educational materials that residents could share with patients. All materials, including didactic lectures, journal articles and self-care resources, were provided to each resident through a free online course to ensure residents had access throughout and following completion of the rotation. This content, including the rotation evaluation metrics, is available upon request from the corresponding author.
Evaluations
Residents completed a survey before and after the rotation to measure IM/CAM knowledge and application and self-care/ burnout perceptions. Residents were asked to evaluate rotation sessions and comment on whether this rotation benefited them personally and professionally (Table 1). Descriptive statistics were analyzed using Microsoft Excel. Given the small sample size and lack of statistical power, only mean survey results are reported in this article. Because this opportunity is specific to the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the proposed project was part of ordinary educational practice, the study was deemed not human subject research by the University of Maryland Institutional Review Board (HP-00089256).

Perceptions and attitudes toward IM/CAM were assessed using a survey designed by the University of Minnesota Academic Health Center. It included 18 items scored on a 5-point semantic rating scale (1, strongly disagree; 5, strongly agree).22 Residents rated their level of agreement with statements reflecting both positive (eg, clinical care should integrate the best of conventional and CAM practices) and negative (eg, CAM is a threat to public health) views. Three questions adapted from the NHIS Adult Complementary Health Questionnaire and UC Irvine Survey of Health Care Use and Practice assessed the use of IM/CAM resources.23,24
Resident knowledge and application of IM/CAM were measured using a case study designed by the course faculty. The case listed a chief complaint of nerve pain, with a history of chronic pain, neuropathic pain, anxiety, chronic fatigue, depression, insomnia, posttraumatic stress disorder, history of present illness, past surgical history, medication list, review of symptoms, laboratory values, and physical examination. The residents completed an assessment before and after the rotation. Residents rated their confidence in the diagnosis and treatment of 8 medical conditions using a 5-point semantic rating scale (Table 2). Self-care importance and selfcare frequency were measured by a variety of means, including 3 survey questions, the Five Facet Mindfulness Questionnaire, 2 prompts on a 7-point semantic scale, and a slightly modified version of the validated Perceived Stress Scale.25-28

Survey Results
Residents gave the rotation positive feedback with a mean score of 8.5 out of 10. They reported the beneficial impact of seeing the nontraditional and nonpharmacological practices in treating patients, chronic pain management team approaches, and enjoyed being able to participate in group classes with patients. Many residents expressed a desire for a longer rotation to have more time to experience the behavioral health-focused sessions. Residents also requested additional information on nutritional supplements/natural medicines, battlefield acupuncture training and osteopathic manipulative therapy practices. All residents reported the rotation personally and/or professionally benefited them (Appendix).
Given the sample of 12 residents, values are presented as prerotation to postrotation comparisons without statistical analysis. There was a trend towards an increase in the reported use and recommendation of 26 modalities of nonconventional therapies following the rotation. There was also a slight increase in resource knowledge and use of these resources, and residents reported accessing more types of resources. Mean scores of the case study to gauge knowledge and application of IM increased from 7.5 at baseline to 11.0 after the rotation. Resident confidence in diagnosis increased for all 8 conditions, but confidence in treatment only increased for 4 conditions.
Results of self-care importance, self-care frequency and mindfulness were consistent baseline to postrotation. The mean time residents spent regularly practicing self-care during a work week increased slightly while feelings of burnout decreased. The perceived stress scale average score decreased from 13.4 at baseline to 10.5 after rotation.
DISCUSSION
The implementation of an IM residency rotation that incorporates whole health and interprofessional practices demonstrated improved perception and increased use of IM/CAM resources and knowledge among a small sample of third-year residents. Residents reported they had a positive experience participating in the rotation and gained knowledge, resources, and skills they felt confident discussing with their patients.
Many studies reported favorable attitudes and perceptions of IM/CAM use among physicians, but few have assessed these measures while implementing a training curriculum.3,4,22 Gardiner and colleagues reported on the perception and use of IM resources among family medicine residents.4 The study found that while 58% of all residents reported IM/CAM as an important part of their training, only 60% reported they received it or had specific learning objectives in their curriculum. 4 The program outlined in this study and previous research illustrate that physicians recognize the importance of IM/CAM education in training programs, but most were unaware of the resources available or did not feel comfortable counseling patients about most IM/CAM applications.
Residents in this program slightly increased their use of IM/CAM to diagnose and treat medical conditions after the rotation. A study by Wahner-Roedler and colleagues assessed physician knowledge regarding common IM/CAM therapies.3 On average, physicians only felt knowledgeable and comfortable counseling patients for 3 of 13 listed treatments/techniques and few natural herbal treatments. The study also found that most physicians had difficulty accessing IM/CAM information at their institution despite having free access to electronic databases. However, this study only assessed physician attitudes of IM/CAM and did not include an educational component to increase their knowledge of the modalities.3 This evaluation supports the need for interventions like the program described in this article that provide physicians with access to evidence-based resources combined with the applied experiences to increase their comfort within this growing field.
Though the sample size in this study was small, its results support existing research indicating that clinicians view selfcare as important. Many residents were already using a self-care plan at baseline, but there was slight increase in the practice of self-care during the rotation and a slight decrease in burnout. Previous research reflects high rates of burnout and relatively poor quality of life among primary care physicians.15 Burnout is associated with lower quality of care, lower patient satisfaction and contributes to medical errors. Studies suggest as many as 60% of primary care physicians report symptoms of burnout, which negatively affected the quality of patient care they provide.15
Despite the profound effects burnout has on physicians and patient care, a standardized wellness education or self-care tool kit is not currently available. The University of Massachusetts recently introduced a pilot program to promote resident wellness that demonstrated favorable results.15 A meta-analysis of physicians and medical trainees found decreases in anxiety and symptoms of anxiety as well as a decrease in burnout among participants in cognitive, behavioral and mindfulness interventions.29 However, unlike our program, these programs focused solely on the well-being of medical trainees, residents, and physicians and didn’t focus on the patient-clinician interactions. Given the impact on patient care, there is a need to develop and implement additional programs like our residency rotation that promote health and wellness among physicians while also evaluating how physicians may translate these skills to patient education.
While this program st i l l exists for third-year residents at Baltimore GRECC, it has significantly changed since the COVID-19 pandemic. For about the first 6 months of the pandemic, when physical distancing requirements were in place, family medicine trainees were not able to rotate. Upon return to the facility, many group classes were cancelled and some clinicians no longer offered the sessions. The rotation has evolved to a hybrid format, where many group classes for veteran patients are offered virtually, and residents observe a mix of virtual and in-person shadowing opportunities. Our formal evaluation included administering the survey and occurred from July 2018 to July 2019 but wasn’t implemented upon return to post-COVID activities due to the inconsistent experiences offered to residents over the past few years. Future research should evaluate the impact of this hybrid program on the clinicians and explore dissemination to other VAMCs and their academic affiliates.
Limitations
Project recruitment was limited to 11 family medicine and 1 preventive medicine resident. Perceptions, use of IM/CAM, and knowledge about IM/CAM could be considerably different in different departments with varying schedules, hours worked, and patient volumes. Secondly, the survey was conducted 2 weeks apart. Indications of self-care and burnout may not reflect long-term effects, adoption, or maintenance. Future research should include longer follow up to examine how this type of educational activity may impact burnout rates of physicians following the completion of residency, as well as changes in perspectives of IM/CAM while practicing as a physician. Trainees were exposed to a wide range of health care professions, but additional research is needed regarding medical resident perceptions of the roles of specific professions in a collaborative health care team.30,31
CONCLUSIONS
The residency rotation program illustrates the benefits of establishing a standardized IM/CAM rotation that includes self-care resources in family medicine programs to adequately train clinicians to practice wellness and promote it to their patients. The results of this project suggest this type of training will help residents assess the literature to better counsel patients on IM/CAM options while also providing strategies for maintaining optimal health and well-being for health care professionals. Broadening and shifting the scope of medicine from treatment to prevention, personal wellness, and optimal healing should be a top priority.
- Locke AB, Gordon A, Guerrera MP, Gardiner P, Lebensohn P. Recommended integrative medicine competencies for family medicine residents. Explore (NY). 2013;9(5):308-313. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2013.06.005
- Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569-1575. doi:10.1001/jama.280.18.1569
- Wahner-Roedler DL, Vincent A, Elkin PL, Loehrer LL, Cha SS, Bauer BA. Physicians’ attitudes toward complementary and alternative medicine and their knowledge of specific therapies: a survey at an academic medical center. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3(4):495-501. doi:10.1093/ecam/nel036
- Gardiner P, Filippelli AC, Lebensohn P, Bonakdar R. Family medicine residency program directors attitudes and knowledge of family medicine CAM competencies. Explore (NY). 2013;9(5):299-307. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2013.06.002
- Sierpina V, Levine R, Astin J, Tan A. Use of mind-body therapies in psychiatry and family medicine faculty and residents: attitudes, barriers, and gender differences. Explore (NY). 2007;3(2):129-135. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2006.12.001
- Krist AH, South-Paul J, Meisnere M, eds. Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation. The National Academies Press; 2023.
- Bokhour BG, DeFaccio R, Gaj L, et al. Changes in patientreported outcomes associated with receiving whole health in the Veteran Health Administration (VHA)’s National Demonstration Project. J Gen Intern Med. 2024;39(1):84-94. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08376-0
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ, Bolton R, Smith S, Harden SM. Using a whole health approach to build biopsychosocial- spiritual personal health plans for veterans with chronic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2024;25(1):69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pmn.2023.09.010
- Gabrielian S, Jones AL, Hoge AE, et al. Enhancing primary care experiences for homeless patients with serious mental illness: results from a national survey. J Prim Care Community Health. 2021;12:2150132721993654. doi:10.1177/2150132721993654
- Matthieu MM, Church KA, Taylor LD, et al. Integrating the age-friendly health systems movement in Veterans Health Administration: national advance care planning via group visits and the 4Ms framework. Health Soc Work. 2023;48(4):277-280. doi:10.1093/hsw/hlad022
- Meisler AW, Gianoli MO, Na PJ, Pietrzak RH. Functional disability in US military veterans: the importance of integrated whole health initiatives. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2023;25(4):22m03461. doi:10.4088/PCC.22m03461
- Ortmeyer HK, Giffuni J, Etchberger D, Katzel L. The role of companion dogs in the VA Maryland Health Care System Whole Health(y) GeroFit Program. Animals (Basel). 2023;13(19):3047. doi:10.3390/ani13193047
- Sullivan MB, Hill K, Ballengee LA, et al. Remotely delivered psychologically informed mindful movement physical therapy for pain care: a framework for operationalization. Glob Adv Integr Med Health. 2023;12:27536130231209751. doi:10.1177/27536130231209751
- (OAA) OoAA. 75th Anniversary: Passion to learn. Power to heal. Washington DC.: US Department of Veterans Affairs; 2021. https://content.yudu.com/web/448fx/0A448g9/75thAnniversary2021/html/index.html?page=24&origin=reader
- Runyan C, Savageau JA, Potts S, Weinreb L. Impact of a family medicine resident wellness curriculum: a feasibility study. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:30648. doi:10.3402/meo.v21.30648
- Lafreniere JP, Rios R, Packer H, Ghazarian S, Wright SM, Levine RB. Burned out at the bedside: patient perceptions of physician burnout in an internal medicine resident continuity clinic. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(2):203-208. doi:10.1007/s11606-015-3503-3
- Freedy JR, Staley C, Mims LD, et al. Social, individual, and environmental characteristics of family medicine resident burnout: a CERA study. Fam Med. 2022;54(4):270-276. doi:10.22454/FamMed.2022.526799
- Alrishan MA, Alshammari SA. Prevalence of sleep deprivation and its effect on the performance of family medicine residents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med. 2020;27(2):125-130. doi:10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_9_20
- ACGME. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Family Medicine. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/120_familymedicine_2024.pdf
- Nene Y, Tadi P. Resident Burnout. In: StatPearls; 2023.
- Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the veterans affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58(4):295-300. doi:10.1097/MLF.0000000000001316
- Kreitzer MJ, Mitten D, Harris I, Shandeling J. Attitudes toward CAM among medical, nursing, and pharmacy faculty and students: a comparative analysis. Altern Ther Health Med. 2002;8(6):44-53.
- Clarke TC, Black LI, Stussman BJ, Barnes PM, Nahin RL. Trends in the use of complementary health approaches among adults: United States, 2002-2012. Natl Health Stat Report. 2015(79):1-16.
- Nguyen J, Liu MA, Patel RJ, Tahara K, Nguyen AL. Use and interest in complementary and alternative medicine among college students seeking healthcare at a university campus student health center. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2016;24:103-108. doi:10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.06.001
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Hopkins J, Krietemeyer J, Toney L. Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment. 2006;13(1):27-45. doi:10.1177/1073191105283504
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Lykins E, et al. Construct validity of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment. 2008;15(3):329-342. doi:10.1177/1073191107313003
- West CP, Dyrbye LN, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Single item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are useful for assessing burnout in medical professionals. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(12):1318- 1321. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1129-z
- Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. J Health Soc Behav. 1983;24(4):385-396.
- Regehr C, Glancy D, Pitts A, LeBlanc VR. Interventions to reduce the consequences of stress in physicians: a review and meta-analysis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014;202(5):353-359. doi:10.1097/NMD.0000000000000130
- Visser CLF, Ket JCF, Croiset G, Kusurkar RA. Perceptions of residents, medical and nursing students about interprofessional education: a systematic review of the quantitative and qualitative literature. BMC Med Educ. 2017;17(1):77. doi:10.1186/s12909-017-0909-0
- Lingard L, Espin S, Evans C, Hawryluck L. The rules of the game: interprofessional collaboration on the intensive care unit team. Crit Care. 2004;8(6):R403-408. doi:10.1186/cc2958
- Locke AB, Gordon A, Guerrera MP, Gardiner P, Lebensohn P. Recommended integrative medicine competencies for family medicine residents. Explore (NY). 2013;9(5):308-313. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2013.06.005
- Eisenberg DM, Davis RB, Ettner SL, et al. Trends in alternative medicine use in the United States, 1990-1997: results of a follow-up national survey. JAMA. 1998;280(18):1569-1575. doi:10.1001/jama.280.18.1569
- Wahner-Roedler DL, Vincent A, Elkin PL, Loehrer LL, Cha SS, Bauer BA. Physicians’ attitudes toward complementary and alternative medicine and their knowledge of specific therapies: a survey at an academic medical center. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3(4):495-501. doi:10.1093/ecam/nel036
- Gardiner P, Filippelli AC, Lebensohn P, Bonakdar R. Family medicine residency program directors attitudes and knowledge of family medicine CAM competencies. Explore (NY). 2013;9(5):299-307. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2013.06.002
- Sierpina V, Levine R, Astin J, Tan A. Use of mind-body therapies in psychiatry and family medicine faculty and residents: attitudes, barriers, and gender differences. Explore (NY). 2007;3(2):129-135. doi:10.1016/j.explore.2006.12.001
- Krist AH, South-Paul J, Meisnere M, eds. Achieving Whole Health: A New Approach for Veterans and the Nation. The National Academies Press; 2023.
- Bokhour BG, DeFaccio R, Gaj L, et al. Changes in patientreported outcomes associated with receiving whole health in the Veteran Health Administration (VHA)’s National Demonstration Project. J Gen Intern Med. 2024;39(1):84-94. doi:10.1007/s11606-023-08376-0
- Courtney RE, Schadegg MJ, Bolton R, Smith S, Harden SM. Using a whole health approach to build biopsychosocial- spiritual personal health plans for veterans with chronic pain. Pain Manag Nurs. 2024;25(1):69-74. doi:10.1016/j.pmn.2023.09.010
- Gabrielian S, Jones AL, Hoge AE, et al. Enhancing primary care experiences for homeless patients with serious mental illness: results from a national survey. J Prim Care Community Health. 2021;12:2150132721993654. doi:10.1177/2150132721993654
- Matthieu MM, Church KA, Taylor LD, et al. Integrating the age-friendly health systems movement in Veterans Health Administration: national advance care planning via group visits and the 4Ms framework. Health Soc Work. 2023;48(4):277-280. doi:10.1093/hsw/hlad022
- Meisler AW, Gianoli MO, Na PJ, Pietrzak RH. Functional disability in US military veterans: the importance of integrated whole health initiatives. Prim Care Companion CNS Disord. 2023;25(4):22m03461. doi:10.4088/PCC.22m03461
- Ortmeyer HK, Giffuni J, Etchberger D, Katzel L. The role of companion dogs in the VA Maryland Health Care System Whole Health(y) GeroFit Program. Animals (Basel). 2023;13(19):3047. doi:10.3390/ani13193047
- Sullivan MB, Hill K, Ballengee LA, et al. Remotely delivered psychologically informed mindful movement physical therapy for pain care: a framework for operationalization. Glob Adv Integr Med Health. 2023;12:27536130231209751. doi:10.1177/27536130231209751
- (OAA) OoAA. 75th Anniversary: Passion to learn. Power to heal. Washington DC.: US Department of Veterans Affairs; 2021. https://content.yudu.com/web/448fx/0A448g9/75thAnniversary2021/html/index.html?page=24&origin=reader
- Runyan C, Savageau JA, Potts S, Weinreb L. Impact of a family medicine resident wellness curriculum: a feasibility study. Med Educ Online. 2016;21:30648. doi:10.3402/meo.v21.30648
- Lafreniere JP, Rios R, Packer H, Ghazarian S, Wright SM, Levine RB. Burned out at the bedside: patient perceptions of physician burnout in an internal medicine resident continuity clinic. J Gen Intern Med. 2016;31(2):203-208. doi:10.1007/s11606-015-3503-3
- Freedy JR, Staley C, Mims LD, et al. Social, individual, and environmental characteristics of family medicine resident burnout: a CERA study. Fam Med. 2022;54(4):270-276. doi:10.22454/FamMed.2022.526799
- Alrishan MA, Alshammari SA. Prevalence of sleep deprivation and its effect on the performance of family medicine residents in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. J Family Community Med. 2020;27(2):125-130. doi:10.4103/jfcm.JFCM_9_20
- ACGME. ACGME Program Requirements for Graduate Medical Education in Family Medicine. https://www.acgme.org/globalassets/pfassets/programrequirements/120_familymedicine_2024.pdf
- Nene Y, Tadi P. Resident Burnout. In: StatPearls; 2023.
- Bokhour BG, Haun JN, Hyde J, Charns M, Kligler B. Transforming the veterans affairs to a whole health system of care: time for action and research. Med Care. 2020;58(4):295-300. doi:10.1097/MLF.0000000000001316
- Kreitzer MJ, Mitten D, Harris I, Shandeling J. Attitudes toward CAM among medical, nursing, and pharmacy faculty and students: a comparative analysis. Altern Ther Health Med. 2002;8(6):44-53.
- Clarke TC, Black LI, Stussman BJ, Barnes PM, Nahin RL. Trends in the use of complementary health approaches among adults: United States, 2002-2012. Natl Health Stat Report. 2015(79):1-16.
- Nguyen J, Liu MA, Patel RJ, Tahara K, Nguyen AL. Use and interest in complementary and alternative medicine among college students seeking healthcare at a university campus student health center. Complement Ther Clin Pract. 2016;24:103-108. doi:10.1016/j.ctcp.2016.06.001
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Hopkins J, Krietemeyer J, Toney L. Using self-report assessment methods to explore facets of mindfulness. Assessment. 2006;13(1):27-45. doi:10.1177/1073191105283504
- Baer RA, Smith GT, Lykins E, et al. Construct validity of the five facet mindfulness questionnaire in meditating and nonmeditating samples. Assessment. 2008;15(3):329-342. doi:10.1177/1073191107313003
- West CP, Dyrbye LN, Sloan JA, Shanafelt TD. Single item measures of emotional exhaustion and depersonalization are useful for assessing burnout in medical professionals. J Gen Intern Med. 2009;24(12):1318- 1321. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1129-z
- Cohen S, Kamarck T, Mermelstein R. A global measure of perceived stress. J Health Soc Behav. 1983;24(4):385-396.
- Regehr C, Glancy D, Pitts A, LeBlanc VR. Interventions to reduce the consequences of stress in physicians: a review and meta-analysis. J Nerv Ment Dis. 2014;202(5):353-359. doi:10.1097/NMD.0000000000000130
- Visser CLF, Ket JCF, Croiset G, Kusurkar RA. Perceptions of residents, medical and nursing students about interprofessional education: a systematic review of the quantitative and qualitative literature. BMC Med Educ. 2017;17(1):77. doi:10.1186/s12909-017-0909-0
- Lingard L, Espin S, Evans C, Hawryluck L. The rules of the game: interprofessional collaboration on the intensive care unit team. Crit Care. 2004;8(6):R403-408. doi:10.1186/cc2958
Development of an Integrative Medicine Rotation for Family Medicine and Preventive Medicine Residency
Development of an Integrative Medicine Rotation for Family Medicine and Preventive Medicine Residency
Physician Attitudes About Veterans Affairs Video Connect Encounters
Physician Attitudes About Veterans Affairs Video Connect Encounters
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, health care systems had been increasingly focused on expanding care delivery through clinical video telehealth (CVT) services.1-3 These modalities offer clinicians and patients opportunities to interact without needing face-to-face visits. CVT services offer significant advantages to patients who encounter challenges accessing traditional face-to-face services, including those living in rural or underserved areas, individuals with mobility limitations, and those with difficulty attending appointments due to work or caregiving commitments.4 The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the expansion of CVT services to mitigate the spread of the virus.1
Despite its evident advantages, widespread adoption of CVT has encountered resistance.2 Physicians have frequently expressed concerns about the reliability and functionality of CVT platforms for scheduled encounters and frustration with inadequate training.4-6 Additionally, there is a lack trust in the technology, as physicians are unfamiliar with reimbursement or workload capture associated with CVT. Physicians have concerns that telecommunication may diminish the intangible aspects of the “art of medicine.”4 As a result, the implementation of telehealth services has been inconsistent, with successful adoption limited to specific medical and surgical specialties.4 Only recently have entire departments within major health care systems expressed interest in providing comprehensive CVT services in response to the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.4
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provides an appropriate setting for assessing clinician perceptions of telehealth services. Since 2003, the VHA has significantly expanded CVT services to eligible veterans and has used the VA Video Connect (VVC) platform since 2018.7-10 Through VVC, VA staff and clinicians may schedule video visits with patients, meet with patients through virtual face-to-face interaction, and share relevant laboratory results and imaging through screen sharing. Prior research has shown increased accessibility to care through VVC. For example, a single-site study demonstrated that VVC implementation for delivering psychotherapies significantly increased CVT encounters from 15% to 85% among veterans with anxiety and/or depression.11
The VA New Mexico Healthcare System (VANMHCS) serves a high volume of veterans living in remote and rural regions and significantly increased its use of CVT during the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce in-person visits. Expectedly, this was met with a variety of challenges. Herein, we sought to assess physician perspectives, concerns, and attitudes toward VVC via semistructured interviews. Our hypothesis was that VA physicians may feel uncomfortable with video encounters but recognize the growing importance of such practices providing specialty care to veterans in rural areas.
METHODS
A semistructured interview protocol was created following discussions with physicians from the VANMHCS Medicine Service. Questions were constructed to assess the following domains: overarching views of video telehealth, perceptions of various applications for conducting VVC encounters, and barriers to the broad implementation of video telehealth. A qualitative investigation specialist aided with question development. Two pilot interviews were conducted prior to performing the interviews with the recruited participants to evaluate the quality and delivery of questions.
All VANMHCS physicians who provided outpatient care within the Department of Medicine and had completed ≥ 1 VVC encounter were eligible to participate. Invitations were disseminated via email, and follow-up emails to encourage participation were sent periodically for 2 months following the initial request. Union approval was obtained to interview employees for a research study. In total, 64 physicians were invited and 13 (20%) chose to participate. As the study did not involve assessing medical interventions among patients, a waiver of informed consent was granted by the VANMHCS Institutional Review Board. Physicians who participated in this study were informed that their responses would be used for reporting purposes and could be rescinded at any time.
Data Analysis
Semistructured interviews were conducted by a single interviewer and recorded using Microsoft Teams. The interviews took place between February 2021 and December 2021 and lasted 5 to 15 minutes, with a mean duration of 9 minutes. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all participants before the interviews. Interviewees were encouraged to expand on their responses to structured questions by recounting past experiences with VVC. Recorded audio was additionally transcribed via Microsoft Teams, and the research team reviewed the transcriptions to ensure accuracy.
The tracking and coding of responses to interview questions were conducted using Microsoft Excel. Initially, 5 transcripts were reviewed and responses were assessed by 2 study team members through open coding. All team members examined the 5 coded transcripts to identify differences and reach a consensus for any discrepancies. Based on recommendations from all team members regarding nuanced excerpts of transcripts, 1 study team member coded the remaining interviews. Thematic analysis was subsequently conducted according to the method described by Braun and Clarke.12 Themes were developed both deductively and inductively by reviewing the direct responses to interview questions and identifying emerging patterns of data, respectively. Indicative quotes representing each theme were carefully chosen for reporting.
RESULTS
Thirteen interviews were conducted and 9 participants (69%) were female. Participating physicians included 3 internal medicine/primary care physicians (23%), 2 nephrologists (15%), and 1 (8%) from cardiology, endocrinology, hematology, infectious diseases, palliative care, critical care, pulmonology, and sleep medicine. Years of post training experience among physicians ranged from 1 to 9 years (n = 5, 38%), 10 to 19 years (n = 3, 23%), and . 20 years (n = 5, 38%). Seven participants (54%) had conducted ≥ 5 VVC visits, with 1 physician completing > 50 video visits (Table).
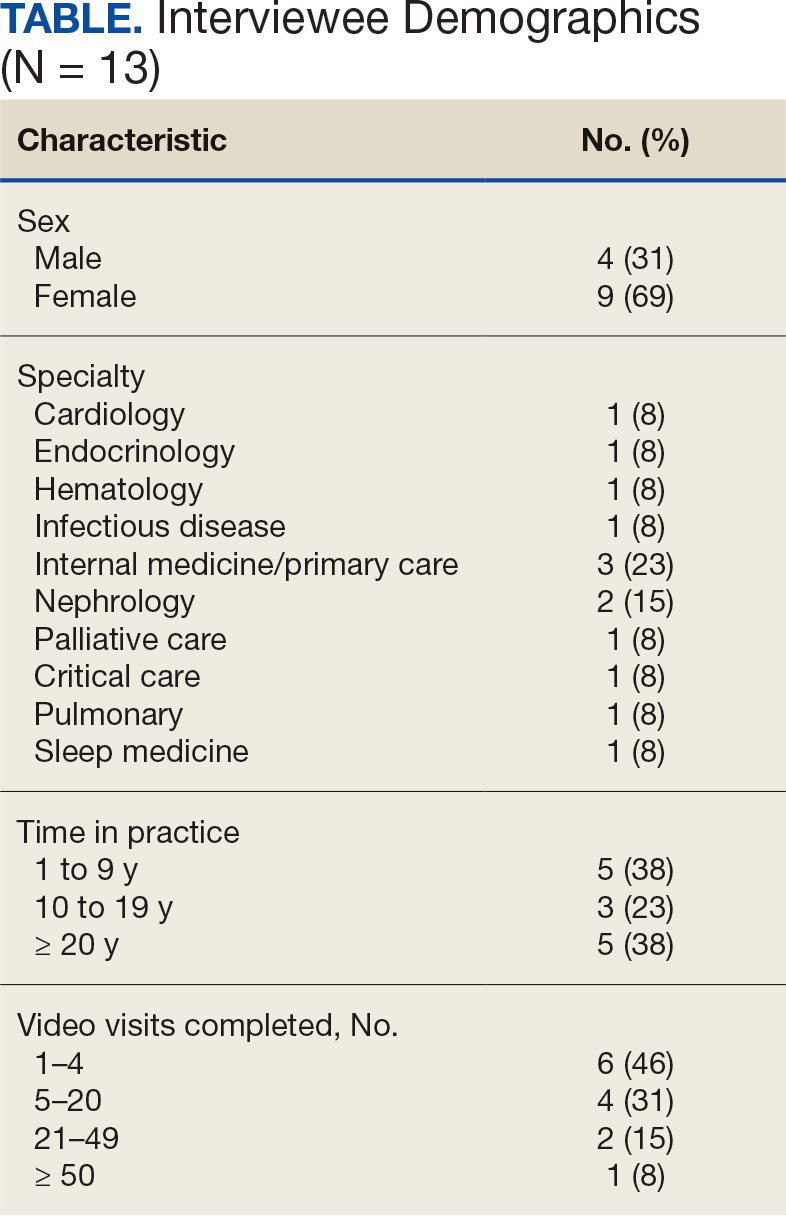
Using open coding and a deductive approach to thematic analysis, 5 themes were identified: (1) VVC software and internet connection issues affected implementation; (2) patient technological literacy affected veteran and physician comfort with VVC; (3) integration of supportive measures was desired; (4) CVT services may increasingly be used to enhance access to care; and (5) in-person encounters afforded unique advantages over CVT. Illustrative quotes from physicians that reflect these themes can be found in the Appendix.
Theme 1: VVC software and internet connection issues affected its implementation. Most participants expressed concern about the technical challenges with VVC. Interviewees cited inconsistencies for both patients and physicians receiving emails with links to join VVC visits, which should be generated when appointments are scheduled. Some physicians were unaware of scheduled VVC visits until the day of the appointment and only received the link via email. Such issues appeared to occur regardless whether the physicians or support staff scheduled the encounter. Poor video and audio quality was also cited as significant barriers to successful VVC visits and were often not resolvable through troubleshooting efforts by physicians, patients, or support personnel. Given the limited time allotted to each patient encounter, such issues could significantly impact the physician’s ability to remain on schedule. Moreover, connectivity problems led to significant lapses, delays in audio and video transmission, and complete disconnections from the VVC encounter. This was a significant concern for participants, given the rural nature of New Mexico and the large geographical gaps in internet service throughout the state.
Theme 2: Patient technological literacy affected veteran and physician comfort with VVC. Successful VVC appointments require high-speed Internet and compatible hardware. Physicians indicated that some patients reported difficulties with critical steps in the process, such as logging into the VVC platform or ensuring their microphones and cameras were active. Physicians also expressed concern about older veterans’ ability to utilize electronic devices, noting they may generally be less technology savvy. Additionally, physicians reported that despite offering the option of a virtual visit, many veterans preferred in-person visits, regardless of the drive time required. This appeared related to a fear of using the technology, which led veterans to believe that virtual visits do not provide the same quality of care as in-person visits.
Theme 3: Integration of supportive measures is desired. Interviewees felt that integrated VVC technical assistance and technology literacy education were imperative. First, training the patient or the patient’s caregiver on how to complete a VVC encounter using the preferred device and the VVC platform would be beneficial. Second, education to inform physicians about common troubleshooting issues could help streamline VVC encounters. Third, managing a VVC encounter similarly to standard in-person visits could allow for better patient and physician experience. For example, physicians suggested that a medical assistant or a nurse triage the patient, take vital signs, and set them up in a room, potentially at a regional VA community based outpatient clinic. Such efforts would also allow patients to receive specialty care in remote areas where only primary care is generally offered. Support staff could assist with technological issues, such as setting up the VVC encounter and addressing potential problems before the physician joins the encounter, thereby preventing delays in patient care. Finally, physicians felt that designating a day solely for CVT visits would help prevent disruption in care with in-person visits.
Theme 4: CVT services may increasingly be used to enhance access to care. Physicians felt that VVC would help patients encountering obstacles in accessing conventional in person services, including patients in rural and underserved areas, with disabilities, or with scheduling challenges.4 Patients with chronic conditions might drive the use of virtual visits, as many of these patients are already accustomed to remote medical monitoring. Data from devices such as scales and continuous glucose monitors can be easily reviewed during VVC visits. Second, video encounters facilitate closer monitoring that some patients might otherwise skip due to significant travel barriers, especially in a rural state like New Mexico. Lastly, VVC may be more efficient than in person visits as they eliminate the need for lengthy parking, checking in, and checking out processes. Thus, if technological issues are resolved, a typical physician’s day in the clinic may be more efficient with virtual visits.
Theme 5: In-person encounters afforded unique advantages over CVT. Some physicians felt in-person visits still offer unique advantages. They opined that the selection of appropriate candidates for CVT is critical. Patients requiring a physical examination should be scheduled for in person visits. For example, patients with advanced chronic kidney disease who require accurate volume status assessment or patients who have recently undergone surgery and need detailed wound inspection should be seen in the clinic. In-person visits may also be preferable for patients with recurrent admissions, or those whose condition is difficult to assess; accurate assessments of such patients may help prevent readmissions. Finally, many patients are more comfortable and satisfied with in-person visits, which are perceived as a more standard or traditional process. Respondents noted that some patients felt physicians may not focus as much attention during a VVC visit as they do during in-person visits. There were also concerns that some patients feel more motivation to come to in-person visits, as they see the VA as a place to interact with other veterans and staff with whom they are familiar and comfortable.
DISCUSSION
VANMHCS physicians, which serves veterans across an expansive territory ranging from Southern Colorado to West Texas. About 4.6 million veterans reside in rural regions, constituting roughly 25% of the total veteran population, a pattern mirrored in New Mexico.13 Medicine Service physicians agreed on a number of themes: VVC user-interface issues may affect its use and effectiveness, technological literacy was important for both patients and health care staff, technical support staff roles before and during VVC visits should be standardized, CVT is likely to increase health care delivery, and in-person encounters are preferred for many patients.
This is the first study to qualitatively evaluate a diverse group of physicians at a VA medical center incorporating CVT services across specialties. A few related qualitative studies have been conducted external to VHA, generally evaluating clinicians within a single specialty. Kalicki and colleagues surveyed 16 physicians working at a large home-based primary care program in New York City between April and June 2020 to identify and explore barriers to telehealth among homebound older adults. Similarly to our study, physicians noted that many patients required assistance (family members or caregivers) with the visit, either due to technological literacy issues or medical conditions like dementia.14
Heyer and colleagues surveyed 29 oncologists at an urban academic center prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. Similar to our observations, the oncologists said telemedicine helped eliminate travel as a barrier to health care. Heyer and colleagues noted difficulty for oncologists in performing virtual physical examinations, despite training. This group did note the benefits when being selective as to which clinical issues they would handle virtually vs in person.15
Budhwani and colleagues reported that mental health professionals in an academic setting cited difficulty establishing therapeutic relationships via telehealth and felt that this affected quality of care.16 While this was not a topic during our interviews, it is reasonable to question how potentially missed nonverbal cues may impact patient assessments.
Notably, technological issues were common among all reviewed studies. These ranged from internet connectivity issues to necessary electronic devices. As mentioned, these barriers are more prevalent in rural states like New Mexico.
Limitations
All participants in this study were Medicine Service physicians of a single VA health care system, which may limit generalizability. Many of our respondents were female (69%), compared with 39.2% of active internal medicine physicians and therefore may not be representative.17 Nearly one-half of our participants only completed 1 to 4 VVC encounters, which may have contributed to the emergence of a common theme regarding technological issues. Physicians with more experience with CVT services may be more skilled at troubleshooting technological issues that arise during visits.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study, conducted with VANMHCS physicians, illuminated 5 key themes influencing the use and implementation of video encounters: technological issues, technological literacy, a desire for integrated support measures, perceived future growth of video telehealth, and the unique advantages of in-person visits. Addressing technological barriers and providing more extensive training may streamline CVT use. However, it is vital to recognize the unique benefits of in-person visits and consider the benefits of each modality along with patient preferences when selecting the best care venue. As health care evolves, better understanding and acting upon these themes will optimize telehealth services, particularly in rural areas. Future research should involve patients and other health care team members to further explore strategies for effective CVT service integration.
Appendix
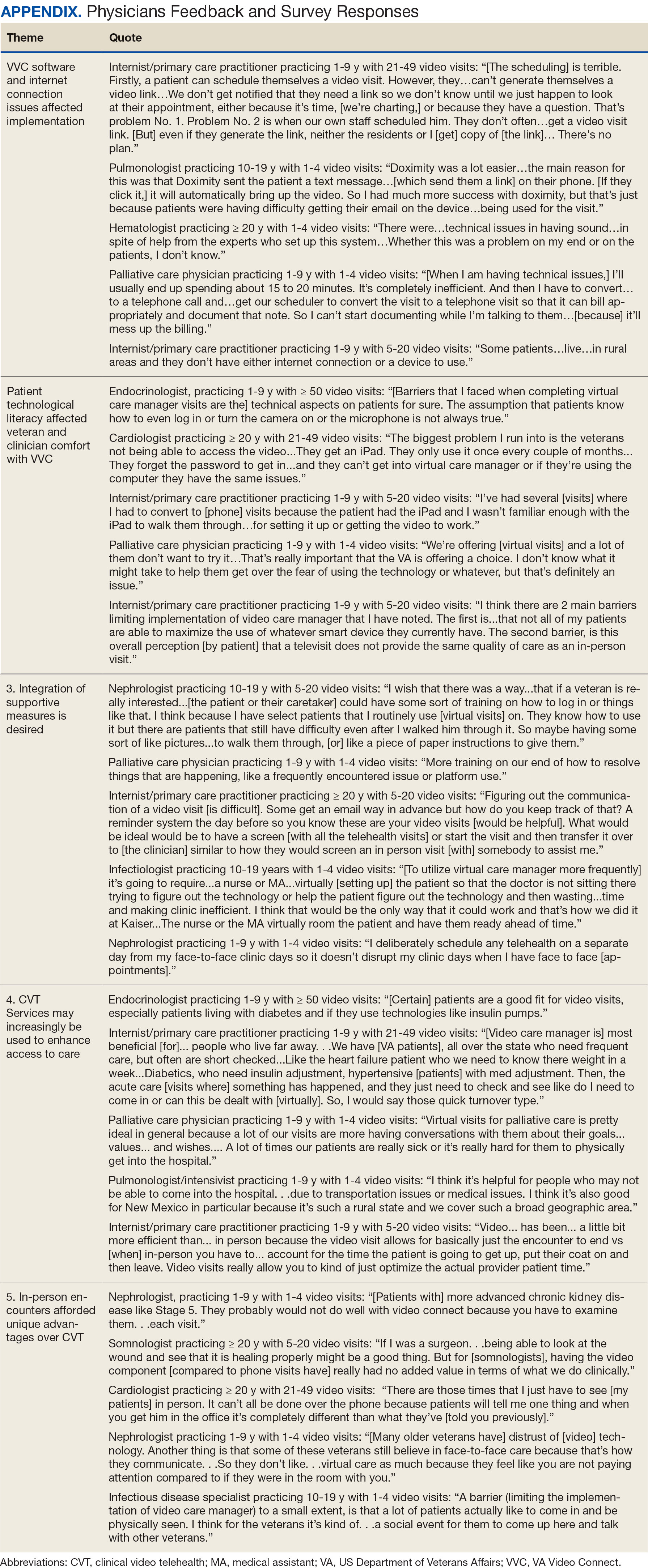
- Monaghesh E, Hajizadeh A. The role of telehealth during covid-19 outbreak: a systematic review based on current evidence. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1193. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4
- Scott Kruse C, Karem P, Shifflett K, Vegi L, Ravi K, Brooks M. Evaluating barriers to adopting telemedicine worldwide: a systematic review. J Telemed Telecare. 2018;24(1):4-12. doi:10.1177/1357633X16674087
- Bashshur RL, Howell JD, Krupinski EA, Harms KM, Bashshur N, Doarn CR. The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(5):342-375. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
- Yellowlees P, Nakagawa K, Pakyurek M, Hanson A, Elder J, Kales HC. Rapid conversion of an outpatient psychiatric clinic to a 100% virtual telepsychiatry clinic in response to covid-19. Pyschiatr Serv. 2020;71(7):749-752. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.202000230
- Hailey D, Ohinmaa A, Roine R. Study quality and evidence of benefit in recent assessments of telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. 2004;10(6):318-324. doi:10.1258/1357633042602053
- Osuji TA, Macias M, McMullen C, et al. Clinician perspectives on implementing video visits in home-based palliative care. Palliat Med Rep. 2020;1(1):221-226. doi:10.1089/pmr.2020.0074
- Darkins A. The growth of telehealth services in the Veterans Health Administration between 1994 and 2014: a study in the diffusion of innovation. Telemed J E Health. 2014;20(9):761-768. doi:10.1089/tmj.2014.0143
- Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-161. doi:10.1056/nejmra1601705
- Alexander NB, Phillips K, Wagner-Felkey J, et al. Team VA video connect (VVC) to optimize mobility and physical activity in post-hospital discharge older veterans: Baseline assessment. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):502. doi:10.1186/s12877-021-02454-w
- Padala KP, Wilson KB, Gauss CH, Stovall JD, Padala PR. VA video connect for clinical care in older adults in a rural state during the covid-19 pandemic: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(9)e21561. doi:10.2196/21561
- Myers US, Coulon S, Knies K, et al. Lessons learned in implementing VA video connect for evidence-based psychotherapies for anxiety and depression in the veterans healthcare administration. J Technol Behav Sci. 2020;6(2):320-326. doi:10.1007/s41347-020-00161-8
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77-101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Feterans Analysis and Statistics. Accessed September 18, 2024. www.va.gov/vetdata/report.asp
- Kalicki AV, Moody KA, Franzosa E, Gliatto PM, Ornstein KA. Barriers to telehealth access among homebound older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(9):2404-2411. doi:10.1111/jgs.17163
- Heyer A, Granberg RE, Rising KL, Binder AF, Gentsch AT, Handley NR. Medical oncology professionals’ perceptions of telehealth video visits. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1) e2033967. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33967
- Budhwani S, Fujioka JK, Chu C, et al. Delivering mental health care virtually during the COVID-19 pandemic: qualitative evaluation of provider experiences in a scaled context. JMIR Form Res. 2021;5(9)e30280. doi:10.2196/30280
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Active physicians by sex and specialty, 2021. AAMC. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/active-physicians-sex-specialty-2021
Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, health care systems had been increasingly focused on expanding care delivery through clinical video telehealth (CVT) services.1-3 These modalities offer clinicians and patients opportunities to interact without needing face-to-face visits. CVT services offer significant advantages to patients who encounter challenges accessing traditional face-to-face services, including those living in rural or underserved areas, individuals with mobility limitations, and those with difficulty attending appointments due to work or caregiving commitments.4 The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the expansion of CVT services to mitigate the spread of the virus.1
Despite its evident advantages, widespread adoption of CVT has encountered resistance.2 Physicians have frequently expressed concerns about the reliability and functionality of CVT platforms for scheduled encounters and frustration with inadequate training.4-6 Additionally, there is a lack trust in the technology, as physicians are unfamiliar with reimbursement or workload capture associated with CVT. Physicians have concerns that telecommunication may diminish the intangible aspects of the “art of medicine.”4 As a result, the implementation of telehealth services has been inconsistent, with successful adoption limited to specific medical and surgical specialties.4 Only recently have entire departments within major health care systems expressed interest in providing comprehensive CVT services in response to the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.4
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provides an appropriate setting for assessing clinician perceptions of telehealth services. Since 2003, the VHA has significantly expanded CVT services to eligible veterans and has used the VA Video Connect (VVC) platform since 2018.7-10 Through VVC, VA staff and clinicians may schedule video visits with patients, meet with patients through virtual face-to-face interaction, and share relevant laboratory results and imaging through screen sharing. Prior research has shown increased accessibility to care through VVC. For example, a single-site study demonstrated that VVC implementation for delivering psychotherapies significantly increased CVT encounters from 15% to 85% among veterans with anxiety and/or depression.11
The VA New Mexico Healthcare System (VANMHCS) serves a high volume of veterans living in remote and rural regions and significantly increased its use of CVT during the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce in-person visits. Expectedly, this was met with a variety of challenges. Herein, we sought to assess physician perspectives, concerns, and attitudes toward VVC via semistructured interviews. Our hypothesis was that VA physicians may feel uncomfortable with video encounters but recognize the growing importance of such practices providing specialty care to veterans in rural areas.
METHODS
A semistructured interview protocol was created following discussions with physicians from the VANMHCS Medicine Service. Questions were constructed to assess the following domains: overarching views of video telehealth, perceptions of various applications for conducting VVC encounters, and barriers to the broad implementation of video telehealth. A qualitative investigation specialist aided with question development. Two pilot interviews were conducted prior to performing the interviews with the recruited participants to evaluate the quality and delivery of questions.
All VANMHCS physicians who provided outpatient care within the Department of Medicine and had completed ≥ 1 VVC encounter were eligible to participate. Invitations were disseminated via email, and follow-up emails to encourage participation were sent periodically for 2 months following the initial request. Union approval was obtained to interview employees for a research study. In total, 64 physicians were invited and 13 (20%) chose to participate. As the study did not involve assessing medical interventions among patients, a waiver of informed consent was granted by the VANMHCS Institutional Review Board. Physicians who participated in this study were informed that their responses would be used for reporting purposes and could be rescinded at any time.
Data Analysis
Semistructured interviews were conducted by a single interviewer and recorded using Microsoft Teams. The interviews took place between February 2021 and December 2021 and lasted 5 to 15 minutes, with a mean duration of 9 minutes. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all participants before the interviews. Interviewees were encouraged to expand on their responses to structured questions by recounting past experiences with VVC. Recorded audio was additionally transcribed via Microsoft Teams, and the research team reviewed the transcriptions to ensure accuracy.
The tracking and coding of responses to interview questions were conducted using Microsoft Excel. Initially, 5 transcripts were reviewed and responses were assessed by 2 study team members through open coding. All team members examined the 5 coded transcripts to identify differences and reach a consensus for any discrepancies. Based on recommendations from all team members regarding nuanced excerpts of transcripts, 1 study team member coded the remaining interviews. Thematic analysis was subsequently conducted according to the method described by Braun and Clarke.12 Themes were developed both deductively and inductively by reviewing the direct responses to interview questions and identifying emerging patterns of data, respectively. Indicative quotes representing each theme were carefully chosen for reporting.
RESULTS
Thirteen interviews were conducted and 9 participants (69%) were female. Participating physicians included 3 internal medicine/primary care physicians (23%), 2 nephrologists (15%), and 1 (8%) from cardiology, endocrinology, hematology, infectious diseases, palliative care, critical care, pulmonology, and sleep medicine. Years of post training experience among physicians ranged from 1 to 9 years (n = 5, 38%), 10 to 19 years (n = 3, 23%), and . 20 years (n = 5, 38%). Seven participants (54%) had conducted ≥ 5 VVC visits, with 1 physician completing > 50 video visits (Table).

Using open coding and a deductive approach to thematic analysis, 5 themes were identified: (1) VVC software and internet connection issues affected implementation; (2) patient technological literacy affected veteran and physician comfort with VVC; (3) integration of supportive measures was desired; (4) CVT services may increasingly be used to enhance access to care; and (5) in-person encounters afforded unique advantages over CVT. Illustrative quotes from physicians that reflect these themes can be found in the Appendix.
Theme 1: VVC software and internet connection issues affected its implementation. Most participants expressed concern about the technical challenges with VVC. Interviewees cited inconsistencies for both patients and physicians receiving emails with links to join VVC visits, which should be generated when appointments are scheduled. Some physicians were unaware of scheduled VVC visits until the day of the appointment and only received the link via email. Such issues appeared to occur regardless whether the physicians or support staff scheduled the encounter. Poor video and audio quality was also cited as significant barriers to successful VVC visits and were often not resolvable through troubleshooting efforts by physicians, patients, or support personnel. Given the limited time allotted to each patient encounter, such issues could significantly impact the physician’s ability to remain on schedule. Moreover, connectivity problems led to significant lapses, delays in audio and video transmission, and complete disconnections from the VVC encounter. This was a significant concern for participants, given the rural nature of New Mexico and the large geographical gaps in internet service throughout the state.
Theme 2: Patient technological literacy affected veteran and physician comfort with VVC. Successful VVC appointments require high-speed Internet and compatible hardware. Physicians indicated that some patients reported difficulties with critical steps in the process, such as logging into the VVC platform or ensuring their microphones and cameras were active. Physicians also expressed concern about older veterans’ ability to utilize electronic devices, noting they may generally be less technology savvy. Additionally, physicians reported that despite offering the option of a virtual visit, many veterans preferred in-person visits, regardless of the drive time required. This appeared related to a fear of using the technology, which led veterans to believe that virtual visits do not provide the same quality of care as in-person visits.
Theme 3: Integration of supportive measures is desired. Interviewees felt that integrated VVC technical assistance and technology literacy education were imperative. First, training the patient or the patient’s caregiver on how to complete a VVC encounter using the preferred device and the VVC platform would be beneficial. Second, education to inform physicians about common troubleshooting issues could help streamline VVC encounters. Third, managing a VVC encounter similarly to standard in-person visits could allow for better patient and physician experience. For example, physicians suggested that a medical assistant or a nurse triage the patient, take vital signs, and set them up in a room, potentially at a regional VA community based outpatient clinic. Such efforts would also allow patients to receive specialty care in remote areas where only primary care is generally offered. Support staff could assist with technological issues, such as setting up the VVC encounter and addressing potential problems before the physician joins the encounter, thereby preventing delays in patient care. Finally, physicians felt that designating a day solely for CVT visits would help prevent disruption in care with in-person visits.
Theme 4: CVT services may increasingly be used to enhance access to care. Physicians felt that VVC would help patients encountering obstacles in accessing conventional in person services, including patients in rural and underserved areas, with disabilities, or with scheduling challenges.4 Patients with chronic conditions might drive the use of virtual visits, as many of these patients are already accustomed to remote medical monitoring. Data from devices such as scales and continuous glucose monitors can be easily reviewed during VVC visits. Second, video encounters facilitate closer monitoring that some patients might otherwise skip due to significant travel barriers, especially in a rural state like New Mexico. Lastly, VVC may be more efficient than in person visits as they eliminate the need for lengthy parking, checking in, and checking out processes. Thus, if technological issues are resolved, a typical physician’s day in the clinic may be more efficient with virtual visits.
Theme 5: In-person encounters afforded unique advantages over CVT. Some physicians felt in-person visits still offer unique advantages. They opined that the selection of appropriate candidates for CVT is critical. Patients requiring a physical examination should be scheduled for in person visits. For example, patients with advanced chronic kidney disease who require accurate volume status assessment or patients who have recently undergone surgery and need detailed wound inspection should be seen in the clinic. In-person visits may also be preferable for patients with recurrent admissions, or those whose condition is difficult to assess; accurate assessments of such patients may help prevent readmissions. Finally, many patients are more comfortable and satisfied with in-person visits, which are perceived as a more standard or traditional process. Respondents noted that some patients felt physicians may not focus as much attention during a VVC visit as they do during in-person visits. There were also concerns that some patients feel more motivation to come to in-person visits, as they see the VA as a place to interact with other veterans and staff with whom they are familiar and comfortable.
DISCUSSION
VANMHCS physicians, which serves veterans across an expansive territory ranging from Southern Colorado to West Texas. About 4.6 million veterans reside in rural regions, constituting roughly 25% of the total veteran population, a pattern mirrored in New Mexico.13 Medicine Service physicians agreed on a number of themes: VVC user-interface issues may affect its use and effectiveness, technological literacy was important for both patients and health care staff, technical support staff roles before and during VVC visits should be standardized, CVT is likely to increase health care delivery, and in-person encounters are preferred for many patients.
This is the first study to qualitatively evaluate a diverse group of physicians at a VA medical center incorporating CVT services across specialties. A few related qualitative studies have been conducted external to VHA, generally evaluating clinicians within a single specialty. Kalicki and colleagues surveyed 16 physicians working at a large home-based primary care program in New York City between April and June 2020 to identify and explore barriers to telehealth among homebound older adults. Similarly to our study, physicians noted that many patients required assistance (family members or caregivers) with the visit, either due to technological literacy issues or medical conditions like dementia.14
Heyer and colleagues surveyed 29 oncologists at an urban academic center prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. Similar to our observations, the oncologists said telemedicine helped eliminate travel as a barrier to health care. Heyer and colleagues noted difficulty for oncologists in performing virtual physical examinations, despite training. This group did note the benefits when being selective as to which clinical issues they would handle virtually vs in person.15
Budhwani and colleagues reported that mental health professionals in an academic setting cited difficulty establishing therapeutic relationships via telehealth and felt that this affected quality of care.16 While this was not a topic during our interviews, it is reasonable to question how potentially missed nonverbal cues may impact patient assessments.
Notably, technological issues were common among all reviewed studies. These ranged from internet connectivity issues to necessary electronic devices. As mentioned, these barriers are more prevalent in rural states like New Mexico.
Limitations
All participants in this study were Medicine Service physicians of a single VA health care system, which may limit generalizability. Many of our respondents were female (69%), compared with 39.2% of active internal medicine physicians and therefore may not be representative.17 Nearly one-half of our participants only completed 1 to 4 VVC encounters, which may have contributed to the emergence of a common theme regarding technological issues. Physicians with more experience with CVT services may be more skilled at troubleshooting technological issues that arise during visits.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study, conducted with VANMHCS physicians, illuminated 5 key themes influencing the use and implementation of video encounters: technological issues, technological literacy, a desire for integrated support measures, perceived future growth of video telehealth, and the unique advantages of in-person visits. Addressing technological barriers and providing more extensive training may streamline CVT use. However, it is vital to recognize the unique benefits of in-person visits and consider the benefits of each modality along with patient preferences when selecting the best care venue. As health care evolves, better understanding and acting upon these themes will optimize telehealth services, particularly in rural areas. Future research should involve patients and other health care team members to further explore strategies for effective CVT service integration.
Appendix

Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, health care systems had been increasingly focused on expanding care delivery through clinical video telehealth (CVT) services.1-3 These modalities offer clinicians and patients opportunities to interact without needing face-to-face visits. CVT services offer significant advantages to patients who encounter challenges accessing traditional face-to-face services, including those living in rural or underserved areas, individuals with mobility limitations, and those with difficulty attending appointments due to work or caregiving commitments.4 The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the expansion of CVT services to mitigate the spread of the virus.1
Despite its evident advantages, widespread adoption of CVT has encountered resistance.2 Physicians have frequently expressed concerns about the reliability and functionality of CVT platforms for scheduled encounters and frustration with inadequate training.4-6 Additionally, there is a lack trust in the technology, as physicians are unfamiliar with reimbursement or workload capture associated with CVT. Physicians have concerns that telecommunication may diminish the intangible aspects of the “art of medicine.”4 As a result, the implementation of telehealth services has been inconsistent, with successful adoption limited to specific medical and surgical specialties.4 Only recently have entire departments within major health care systems expressed interest in providing comprehensive CVT services in response to the challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.4
The Veterans Health Administration (VHA) of the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) provides an appropriate setting for assessing clinician perceptions of telehealth services. Since 2003, the VHA has significantly expanded CVT services to eligible veterans and has used the VA Video Connect (VVC) platform since 2018.7-10 Through VVC, VA staff and clinicians may schedule video visits with patients, meet with patients through virtual face-to-face interaction, and share relevant laboratory results and imaging through screen sharing. Prior research has shown increased accessibility to care through VVC. For example, a single-site study demonstrated that VVC implementation for delivering psychotherapies significantly increased CVT encounters from 15% to 85% among veterans with anxiety and/or depression.11
The VA New Mexico Healthcare System (VANMHCS) serves a high volume of veterans living in remote and rural regions and significantly increased its use of CVT during the COVID-19 pandemic to reduce in-person visits. Expectedly, this was met with a variety of challenges. Herein, we sought to assess physician perspectives, concerns, and attitudes toward VVC via semistructured interviews. Our hypothesis was that VA physicians may feel uncomfortable with video encounters but recognize the growing importance of such practices providing specialty care to veterans in rural areas.
METHODS
A semistructured interview protocol was created following discussions with physicians from the VANMHCS Medicine Service. Questions were constructed to assess the following domains: overarching views of video telehealth, perceptions of various applications for conducting VVC encounters, and barriers to the broad implementation of video telehealth. A qualitative investigation specialist aided with question development. Two pilot interviews were conducted prior to performing the interviews with the recruited participants to evaluate the quality and delivery of questions.
All VANMHCS physicians who provided outpatient care within the Department of Medicine and had completed ≥ 1 VVC encounter were eligible to participate. Invitations were disseminated via email, and follow-up emails to encourage participation were sent periodically for 2 months following the initial request. Union approval was obtained to interview employees for a research study. In total, 64 physicians were invited and 13 (20%) chose to participate. As the study did not involve assessing medical interventions among patients, a waiver of informed consent was granted by the VANMHCS Institutional Review Board. Physicians who participated in this study were informed that their responses would be used for reporting purposes and could be rescinded at any time.
Data Analysis
Semistructured interviews were conducted by a single interviewer and recorded using Microsoft Teams. The interviews took place between February 2021 and December 2021 and lasted 5 to 15 minutes, with a mean duration of 9 minutes. Verbal informed consent was obtained from all participants before the interviews. Interviewees were encouraged to expand on their responses to structured questions by recounting past experiences with VVC. Recorded audio was additionally transcribed via Microsoft Teams, and the research team reviewed the transcriptions to ensure accuracy.
The tracking and coding of responses to interview questions were conducted using Microsoft Excel. Initially, 5 transcripts were reviewed and responses were assessed by 2 study team members through open coding. All team members examined the 5 coded transcripts to identify differences and reach a consensus for any discrepancies. Based on recommendations from all team members regarding nuanced excerpts of transcripts, 1 study team member coded the remaining interviews. Thematic analysis was subsequently conducted according to the method described by Braun and Clarke.12 Themes were developed both deductively and inductively by reviewing the direct responses to interview questions and identifying emerging patterns of data, respectively. Indicative quotes representing each theme were carefully chosen for reporting.
RESULTS
Thirteen interviews were conducted and 9 participants (69%) were female. Participating physicians included 3 internal medicine/primary care physicians (23%), 2 nephrologists (15%), and 1 (8%) from cardiology, endocrinology, hematology, infectious diseases, palliative care, critical care, pulmonology, and sleep medicine. Years of post training experience among physicians ranged from 1 to 9 years (n = 5, 38%), 10 to 19 years (n = 3, 23%), and . 20 years (n = 5, 38%). Seven participants (54%) had conducted ≥ 5 VVC visits, with 1 physician completing > 50 video visits (Table).

Using open coding and a deductive approach to thematic analysis, 5 themes were identified: (1) VVC software and internet connection issues affected implementation; (2) patient technological literacy affected veteran and physician comfort with VVC; (3) integration of supportive measures was desired; (4) CVT services may increasingly be used to enhance access to care; and (5) in-person encounters afforded unique advantages over CVT. Illustrative quotes from physicians that reflect these themes can be found in the Appendix.
Theme 1: VVC software and internet connection issues affected its implementation. Most participants expressed concern about the technical challenges with VVC. Interviewees cited inconsistencies for both patients and physicians receiving emails with links to join VVC visits, which should be generated when appointments are scheduled. Some physicians were unaware of scheduled VVC visits until the day of the appointment and only received the link via email. Such issues appeared to occur regardless whether the physicians or support staff scheduled the encounter. Poor video and audio quality was also cited as significant barriers to successful VVC visits and were often not resolvable through troubleshooting efforts by physicians, patients, or support personnel. Given the limited time allotted to each patient encounter, such issues could significantly impact the physician’s ability to remain on schedule. Moreover, connectivity problems led to significant lapses, delays in audio and video transmission, and complete disconnections from the VVC encounter. This was a significant concern for participants, given the rural nature of New Mexico and the large geographical gaps in internet service throughout the state.
Theme 2: Patient technological literacy affected veteran and physician comfort with VVC. Successful VVC appointments require high-speed Internet and compatible hardware. Physicians indicated that some patients reported difficulties with critical steps in the process, such as logging into the VVC platform or ensuring their microphones and cameras were active. Physicians also expressed concern about older veterans’ ability to utilize electronic devices, noting they may generally be less technology savvy. Additionally, physicians reported that despite offering the option of a virtual visit, many veterans preferred in-person visits, regardless of the drive time required. This appeared related to a fear of using the technology, which led veterans to believe that virtual visits do not provide the same quality of care as in-person visits.
Theme 3: Integration of supportive measures is desired. Interviewees felt that integrated VVC technical assistance and technology literacy education were imperative. First, training the patient or the patient’s caregiver on how to complete a VVC encounter using the preferred device and the VVC platform would be beneficial. Second, education to inform physicians about common troubleshooting issues could help streamline VVC encounters. Third, managing a VVC encounter similarly to standard in-person visits could allow for better patient and physician experience. For example, physicians suggested that a medical assistant or a nurse triage the patient, take vital signs, and set them up in a room, potentially at a regional VA community based outpatient clinic. Such efforts would also allow patients to receive specialty care in remote areas where only primary care is generally offered. Support staff could assist with technological issues, such as setting up the VVC encounter and addressing potential problems before the physician joins the encounter, thereby preventing delays in patient care. Finally, physicians felt that designating a day solely for CVT visits would help prevent disruption in care with in-person visits.
Theme 4: CVT services may increasingly be used to enhance access to care. Physicians felt that VVC would help patients encountering obstacles in accessing conventional in person services, including patients in rural and underserved areas, with disabilities, or with scheduling challenges.4 Patients with chronic conditions might drive the use of virtual visits, as many of these patients are already accustomed to remote medical monitoring. Data from devices such as scales and continuous glucose monitors can be easily reviewed during VVC visits. Second, video encounters facilitate closer monitoring that some patients might otherwise skip due to significant travel barriers, especially in a rural state like New Mexico. Lastly, VVC may be more efficient than in person visits as they eliminate the need for lengthy parking, checking in, and checking out processes. Thus, if technological issues are resolved, a typical physician’s day in the clinic may be more efficient with virtual visits.
Theme 5: In-person encounters afforded unique advantages over CVT. Some physicians felt in-person visits still offer unique advantages. They opined that the selection of appropriate candidates for CVT is critical. Patients requiring a physical examination should be scheduled for in person visits. For example, patients with advanced chronic kidney disease who require accurate volume status assessment or patients who have recently undergone surgery and need detailed wound inspection should be seen in the clinic. In-person visits may also be preferable for patients with recurrent admissions, or those whose condition is difficult to assess; accurate assessments of such patients may help prevent readmissions. Finally, many patients are more comfortable and satisfied with in-person visits, which are perceived as a more standard or traditional process. Respondents noted that some patients felt physicians may not focus as much attention during a VVC visit as they do during in-person visits. There were also concerns that some patients feel more motivation to come to in-person visits, as they see the VA as a place to interact with other veterans and staff with whom they are familiar and comfortable.
DISCUSSION
VANMHCS physicians, which serves veterans across an expansive territory ranging from Southern Colorado to West Texas. About 4.6 million veterans reside in rural regions, constituting roughly 25% of the total veteran population, a pattern mirrored in New Mexico.13 Medicine Service physicians agreed on a number of themes: VVC user-interface issues may affect its use and effectiveness, technological literacy was important for both patients and health care staff, technical support staff roles before and during VVC visits should be standardized, CVT is likely to increase health care delivery, and in-person encounters are preferred for many patients.
This is the first study to qualitatively evaluate a diverse group of physicians at a VA medical center incorporating CVT services across specialties. A few related qualitative studies have been conducted external to VHA, generally evaluating clinicians within a single specialty. Kalicki and colleagues surveyed 16 physicians working at a large home-based primary care program in New York City between April and June 2020 to identify and explore barriers to telehealth among homebound older adults. Similarly to our study, physicians noted that many patients required assistance (family members or caregivers) with the visit, either due to technological literacy issues or medical conditions like dementia.14
Heyer and colleagues surveyed 29 oncologists at an urban academic center prior to the COVID-19 pandemic. Similar to our observations, the oncologists said telemedicine helped eliminate travel as a barrier to health care. Heyer and colleagues noted difficulty for oncologists in performing virtual physical examinations, despite training. This group did note the benefits when being selective as to which clinical issues they would handle virtually vs in person.15
Budhwani and colleagues reported that mental health professionals in an academic setting cited difficulty establishing therapeutic relationships via telehealth and felt that this affected quality of care.16 While this was not a topic during our interviews, it is reasonable to question how potentially missed nonverbal cues may impact patient assessments.
Notably, technological issues were common among all reviewed studies. These ranged from internet connectivity issues to necessary electronic devices. As mentioned, these barriers are more prevalent in rural states like New Mexico.
Limitations
All participants in this study were Medicine Service physicians of a single VA health care system, which may limit generalizability. Many of our respondents were female (69%), compared with 39.2% of active internal medicine physicians and therefore may not be representative.17 Nearly one-half of our participants only completed 1 to 4 VVC encounters, which may have contributed to the emergence of a common theme regarding technological issues. Physicians with more experience with CVT services may be more skilled at troubleshooting technological issues that arise during visits.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study, conducted with VANMHCS physicians, illuminated 5 key themes influencing the use and implementation of video encounters: technological issues, technological literacy, a desire for integrated support measures, perceived future growth of video telehealth, and the unique advantages of in-person visits. Addressing technological barriers and providing more extensive training may streamline CVT use. However, it is vital to recognize the unique benefits of in-person visits and consider the benefits of each modality along with patient preferences when selecting the best care venue. As health care evolves, better understanding and acting upon these themes will optimize telehealth services, particularly in rural areas. Future research should involve patients and other health care team members to further explore strategies for effective CVT service integration.
Appendix

- Monaghesh E, Hajizadeh A. The role of telehealth during covid-19 outbreak: a systematic review based on current evidence. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1193. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4
- Scott Kruse C, Karem P, Shifflett K, Vegi L, Ravi K, Brooks M. Evaluating barriers to adopting telemedicine worldwide: a systematic review. J Telemed Telecare. 2018;24(1):4-12. doi:10.1177/1357633X16674087
- Bashshur RL, Howell JD, Krupinski EA, Harms KM, Bashshur N, Doarn CR. The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(5):342-375. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
- Yellowlees P, Nakagawa K, Pakyurek M, Hanson A, Elder J, Kales HC. Rapid conversion of an outpatient psychiatric clinic to a 100% virtual telepsychiatry clinic in response to covid-19. Pyschiatr Serv. 2020;71(7):749-752. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.202000230
- Hailey D, Ohinmaa A, Roine R. Study quality and evidence of benefit in recent assessments of telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. 2004;10(6):318-324. doi:10.1258/1357633042602053
- Osuji TA, Macias M, McMullen C, et al. Clinician perspectives on implementing video visits in home-based palliative care. Palliat Med Rep. 2020;1(1):221-226. doi:10.1089/pmr.2020.0074
- Darkins A. The growth of telehealth services in the Veterans Health Administration between 1994 and 2014: a study in the diffusion of innovation. Telemed J E Health. 2014;20(9):761-768. doi:10.1089/tmj.2014.0143
- Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-161. doi:10.1056/nejmra1601705
- Alexander NB, Phillips K, Wagner-Felkey J, et al. Team VA video connect (VVC) to optimize mobility and physical activity in post-hospital discharge older veterans: Baseline assessment. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):502. doi:10.1186/s12877-021-02454-w
- Padala KP, Wilson KB, Gauss CH, Stovall JD, Padala PR. VA video connect for clinical care in older adults in a rural state during the covid-19 pandemic: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(9)e21561. doi:10.2196/21561
- Myers US, Coulon S, Knies K, et al. Lessons learned in implementing VA video connect for evidence-based psychotherapies for anxiety and depression in the veterans healthcare administration. J Technol Behav Sci. 2020;6(2):320-326. doi:10.1007/s41347-020-00161-8
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77-101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Feterans Analysis and Statistics. Accessed September 18, 2024. www.va.gov/vetdata/report.asp
- Kalicki AV, Moody KA, Franzosa E, Gliatto PM, Ornstein KA. Barriers to telehealth access among homebound older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(9):2404-2411. doi:10.1111/jgs.17163
- Heyer A, Granberg RE, Rising KL, Binder AF, Gentsch AT, Handley NR. Medical oncology professionals’ perceptions of telehealth video visits. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1) e2033967. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33967
- Budhwani S, Fujioka JK, Chu C, et al. Delivering mental health care virtually during the COVID-19 pandemic: qualitative evaluation of provider experiences in a scaled context. JMIR Form Res. 2021;5(9)e30280. doi:10.2196/30280
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Active physicians by sex and specialty, 2021. AAMC. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/active-physicians-sex-specialty-2021
- Monaghesh E, Hajizadeh A. The role of telehealth during covid-19 outbreak: a systematic review based on current evidence. BMC Public Health. 2020;20(1):1193. doi:10.1186/s12889-020-09301-4
- Scott Kruse C, Karem P, Shifflett K, Vegi L, Ravi K, Brooks M. Evaluating barriers to adopting telemedicine worldwide: a systematic review. J Telemed Telecare. 2018;24(1):4-12. doi:10.1177/1357633X16674087
- Bashshur RL, Howell JD, Krupinski EA, Harms KM, Bashshur N, Doarn CR. The empirical foundations of telemedicine interventions in primary care. Telemed J E Health. 2016;22(5):342-375. doi:10.1089/tmj.2016.0045
- Yellowlees P, Nakagawa K, Pakyurek M, Hanson A, Elder J, Kales HC. Rapid conversion of an outpatient psychiatric clinic to a 100% virtual telepsychiatry clinic in response to covid-19. Pyschiatr Serv. 2020;71(7):749-752. doi:10.1176/appi.ps.202000230
- Hailey D, Ohinmaa A, Roine R. Study quality and evidence of benefit in recent assessments of telemedicine. J Telemed Telecare. 2004;10(6):318-324. doi:10.1258/1357633042602053
- Osuji TA, Macias M, McMullen C, et al. Clinician perspectives on implementing video visits in home-based palliative care. Palliat Med Rep. 2020;1(1):221-226. doi:10.1089/pmr.2020.0074
- Darkins A. The growth of telehealth services in the Veterans Health Administration between 1994 and 2014: a study in the diffusion of innovation. Telemed J E Health. 2014;20(9):761-768. doi:10.1089/tmj.2014.0143
- Dorsey ER, Topol EJ. State of telehealth. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(2):154-161. doi:10.1056/nejmra1601705
- Alexander NB, Phillips K, Wagner-Felkey J, et al. Team VA video connect (VVC) to optimize mobility and physical activity in post-hospital discharge older veterans: Baseline assessment. BMC Geriatr. 2021;21(1):502. doi:10.1186/s12877-021-02454-w
- Padala KP, Wilson KB, Gauss CH, Stovall JD, Padala PR. VA video connect for clinical care in older adults in a rural state during the covid-19 pandemic: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22(9)e21561. doi:10.2196/21561
- Myers US, Coulon S, Knies K, et al. Lessons learned in implementing VA video connect for evidence-based psychotherapies for anxiety and depression in the veterans healthcare administration. J Technol Behav Sci. 2020;6(2):320-326. doi:10.1007/s41347-020-00161-8
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol. 2006;3(2):77-101. doi:10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, National Center for Feterans Analysis and Statistics. Accessed September 18, 2024. www.va.gov/vetdata/report.asp
- Kalicki AV, Moody KA, Franzosa E, Gliatto PM, Ornstein KA. Barriers to telehealth access among homebound older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2021;69(9):2404-2411. doi:10.1111/jgs.17163
- Heyer A, Granberg RE, Rising KL, Binder AF, Gentsch AT, Handley NR. Medical oncology professionals’ perceptions of telehealth video visits. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(1) e2033967. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.33967
- Budhwani S, Fujioka JK, Chu C, et al. Delivering mental health care virtually during the COVID-19 pandemic: qualitative evaluation of provider experiences in a scaled context. JMIR Form Res. 2021;5(9)e30280. doi:10.2196/30280
- Association of American Medical Colleges. Active physicians by sex and specialty, 2021. AAMC. Accessed September 18, 2024. https://www.aamc.org/data-reports/workforce/data/active-physicians-sex-specialty-2021
Physician Attitudes About Veterans Affairs Video Connect Encounters
Physician Attitudes About Veterans Affairs Video Connect Encounters
Pharmacist-Driven Deprescribing to Reduce Anticholinergic Burden in Veterans With Dementia
Pharmacist-Driven Deprescribing to Reduce Anticholinergic Burden in Veterans With Dementia
Anticholinergic medications block the activity of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by binding to either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors in both the peripheral and central nervous system. Anticholinergic medications typically refer to antimuscarinic medications and have been prescribed to treat a variety of conditions common in older adults, including overactive bladder, allergies, muscle spasms, and sleep disorders.1,2 Since muscarinic receptors are present throughout the body, anticholinergic medications are associated with many adverse effects (AEs), including constipation, urinary retention, xerostomia, and delirium. Older adults are more sensitive to these AEs due to physiological changes associated with aging.1
The American Geriatric Society Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medications Use in Older Adults identifies drugs with strong anticholinergic properties. The Beers Criteria strongly recommends avoiding these medications in patients with dementia or cognitive impairment due to the risk of central nervous system AEs. In the updated 2023 Beers Criteria, the rationale was expanded to recognize the risks of the cumulative anticholinergic burden associated with concurrent anticholinergic use.3,4
Given the prevalent use of anticholinergic medications in older adults, there has been significant research demonstrating their AEs, specifically delirium and cognitive impairment in geriatric patients. A systematic review of 14 articles conducted in 7 different countries of patients with median age of 76.4 to 86.1 years reviewed clinical outcomes of anticholinergic use in patients with dementia. Five studies found anticholinergics were associated with increased all-cause mortality in patients with dementia, and 3 studies found anticholinergics were associated with longer hospital stays. Other studies found that anticholinergics were associated with delirium and reduced health-related quality of life.5
About 35% of veterans with dementia have been prescribed a medication regimen with a high anticholinergic burden.6 In 2018, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pharmacy Benfits Management Center for Medical Safety completed a centrally aggregated medication use evaluation (CAMUE) to assess the appropriateness of anticholinergic medication use in patients with dementia. The retrospective chart review included 1094 veterans from 19 sites. Overall, about 15% of the veterans experienced new falls, delirium, or worsening dementia within 30 days of starting an anticholinergic medication. Furthermore, < 40% had documentation of a nonanticholinergic alternative medication trial, and < 20% had documented nonpharmacologic therapy. The documentation of risk-benefit assessment acknowledging the risks of anticholinergic medication use in veterans with dementia occurred only about 13% of the time. The CAMUE concluded that the risks of initiating an anticholinergic medication in veterans with dementia are likely underdocumented and possibly under considered by prescribers.7
Developed within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), VIONE (Vital, Important, Optional, Not Indicated, Every medication has an indication) is a medication management methodology that aims to reduce polypharmacy and improve patient safety consistent with high-reliability organizations. Since it launched in 2016, VIONE has gradually been implemented at many VHA facilities. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard had not been used at the VA Louisville Healthcare System prior to this quality improvement project.
This dashboard uses the Beers Criteria to identify potentially inappropriate anticholinergic medications. It uses the Anticholinergic Cognitive Burden (ACB) scale to calculate the cumulative anticholinergic risk for each patient. Medications with an ACB score of 2 or 3 have clinically relevant cognitive effects such as delirium and dementia (Table 1). For each point increase in total ACB score, a decline in mini-mental state examination score of 0.33 points over 2 years has been shown. Each point increase has also been correlated with a 26% increase in risk of death.8-10
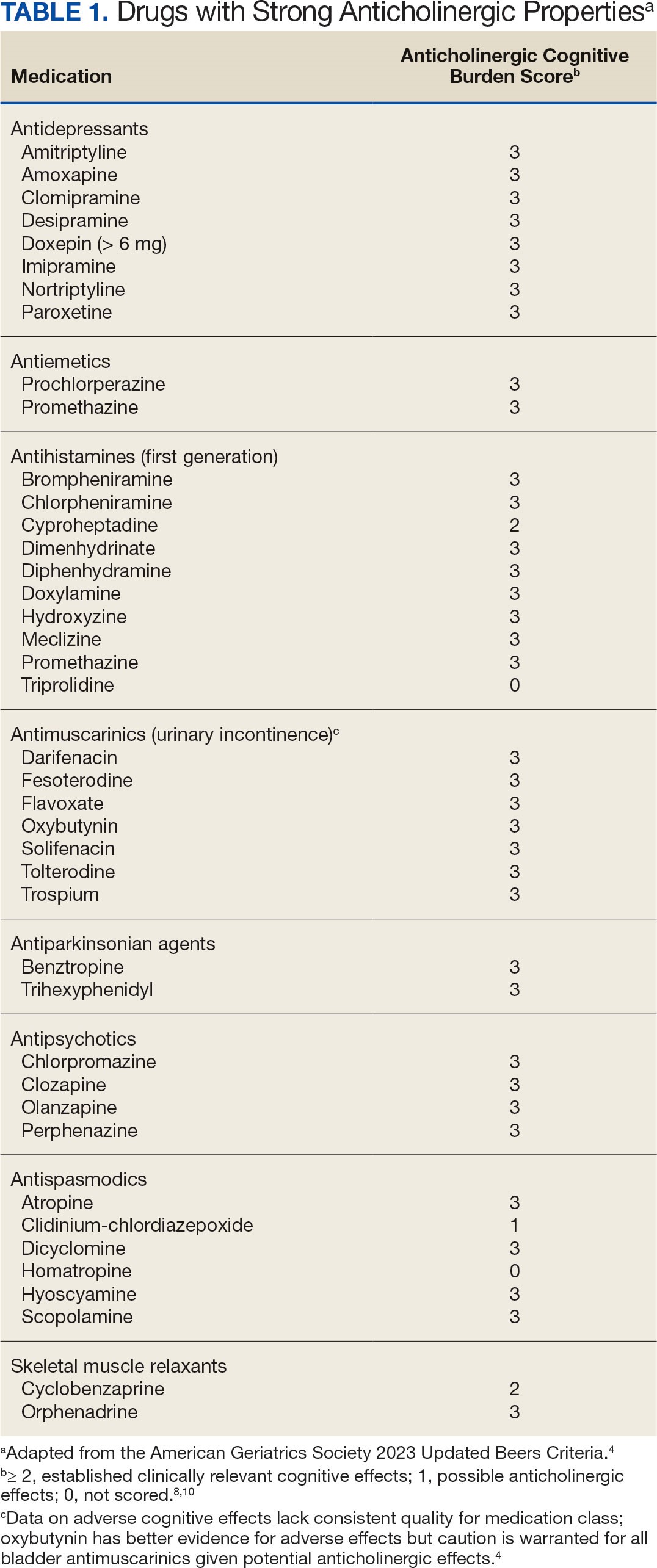
Methods
The purpose of this quality improvement project was to determine the impact of pharmacist-driven deprescribing on the anticholinergic burden in veterans with dementia at VA Louisville Healthcare System. Data were obtained through the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and VIONE deprescribing dashboard and entered in a secure Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Pharmacist deprescribing steps were entered as CPRS progress notes. A deprescribing note template was created, and 11 templates with indication-specific recommendations were created for each anticholinergic indication identified (contact authors for deprescribing note template examples). Usage of anticholinergic medications was reexamined 3 months after the deprescribing note was entered.
Eligible patients identified in the VIONE deprescribing dashboard had an outpatient order for a medication with strong anticholinergic properties as identified using the Beers Criteria and were aged ≥ 65 years. Patients also had to be diagnosed with dementia or cognitive impairment. Patients were excluded if they were receiving hospice care or if the anticholinergic medication was from a non-VA prescriber or filled at a non-VA pharmacy. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard also excluded skeletal muscle relaxants if the patient had a spinal cord-related visit in the previous 2 years, first-generation antihistamines if the patient had a vertigo diagnosis, hydroxyzine if the indication was for anxiety, trospium if the indication was for overactive bladder, and antipsychotics if the patient had been diagnosed with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. The following were included in the deprescribing recommendations if the dashboard identified the patient due to receiving a second strongly anticholinergic medication: first generation antihistamines if the patient was diagnosed with vertigo and hydroxyzine if the indication is for anxiety.
Each eligible patient received a focused medication review by a pharmacist via electronic chart review and a templated CPRS progress note with patient-specific recommendations. The prescriber and the patient’s primary care practitioner were recommended to perform a patient-specific risk-benefit assessment, deprescribe potentially inappropriate anticholinergic medications, and consider nonanticholinergic alternatives (both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic). Data collected included baseline age, sex, prespecified comorbidities (type of dementia, cognitive impairment, delirium, benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms), duration of prescribed anticholinergic medication, indication and deprescribing rate for each anticholinergic agent, and concurrent dementia medications (acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, or both).
The primary outcome was the number of patients that had = 1 medication with strong anticholinergic properties deprescribed. Deprescribing was defined as medication discontinuation or reduction of total daily dose. Secondary outcomes were the mean change in ACB scale, the number of patients with dose tapering, documented patient-specific risk-benefit assessment, and initiated nonanticholinergic alternative per pharmacist recommendation.
Results
The VIONE deprescribing dashboard identified 121 patients; 45 were excluded for non-VA prescriber or pharmacy, and 8 patients were excluded for other reasons. Sixty-eight patients were included in the deprescribing initiative. The mean age was 73.4 years (range, 67-93), 65 (96%) were male, and 34 (50%) had unspecified dementia (Table 2). Thirty-one patients (46%) had concurrent cholinesterase inhibitor prescriptions for dementia. The median duration of use of a strong anticholinergic medication was 11 months.
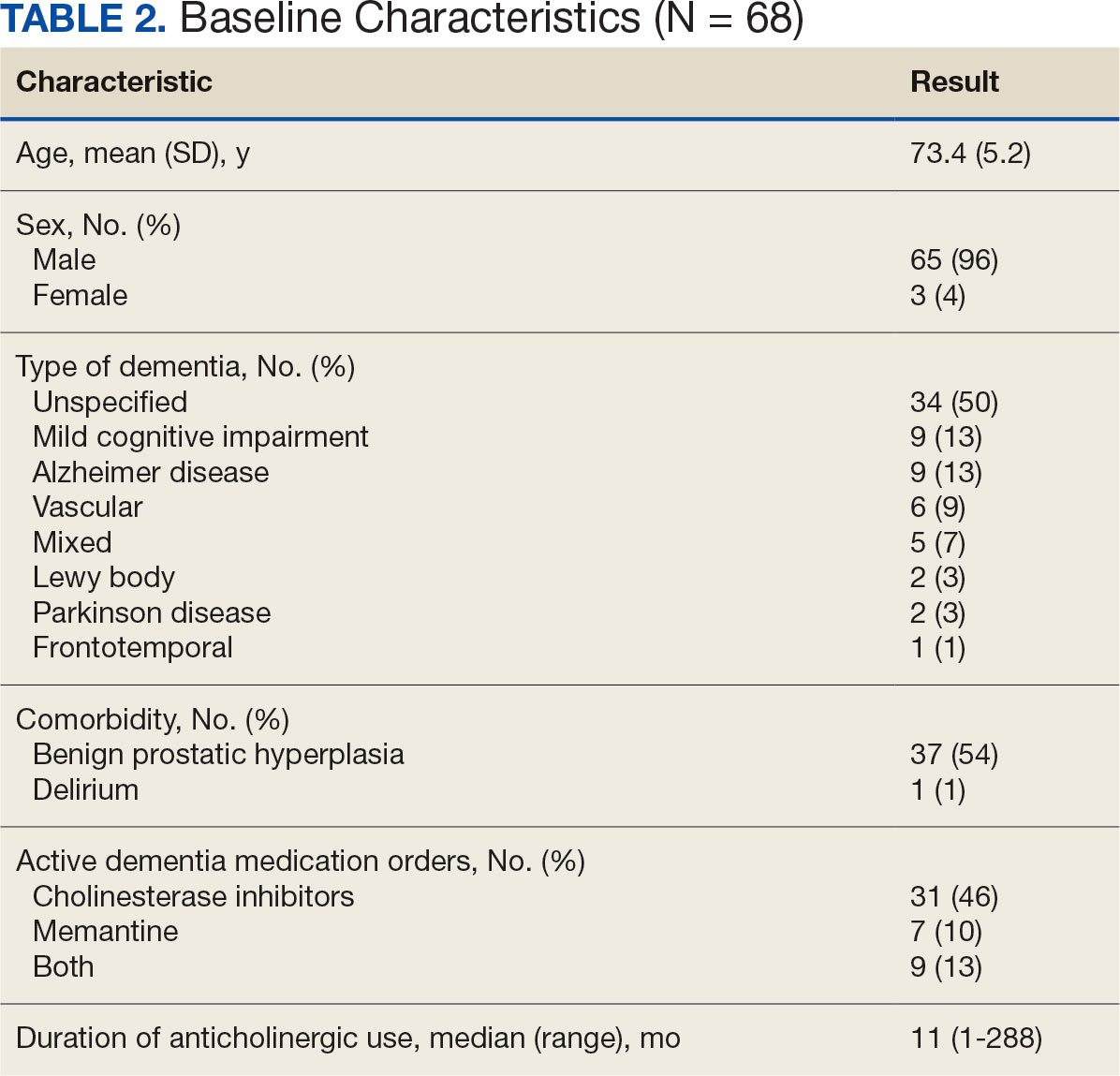
Twenty-nine patients (43%) had ≥ 1 medication with strong anticholinergic properties deprescribed. Anticholinergic medication was discontinued for 26 patients, and the dose was decreased for 3 patients. ACB score fell by a mean of 1.1 per patient. There was an increase in the documented risk-benefit assessment for anticholinergic medications from a baseline of 4 (6%) to 19 (28%) 3 months after the deprescribing note. Cyclobenzaprine, paroxetine, and oxybutynin were deprescribed the most, and amitriptyline had the lowest rate of deprescribing (Table 3). Thirty patients (44%) had a pharmacologic, nonanticholinergic alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendation, and 6 patients (9%) had a nonpharmacologic alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendation.
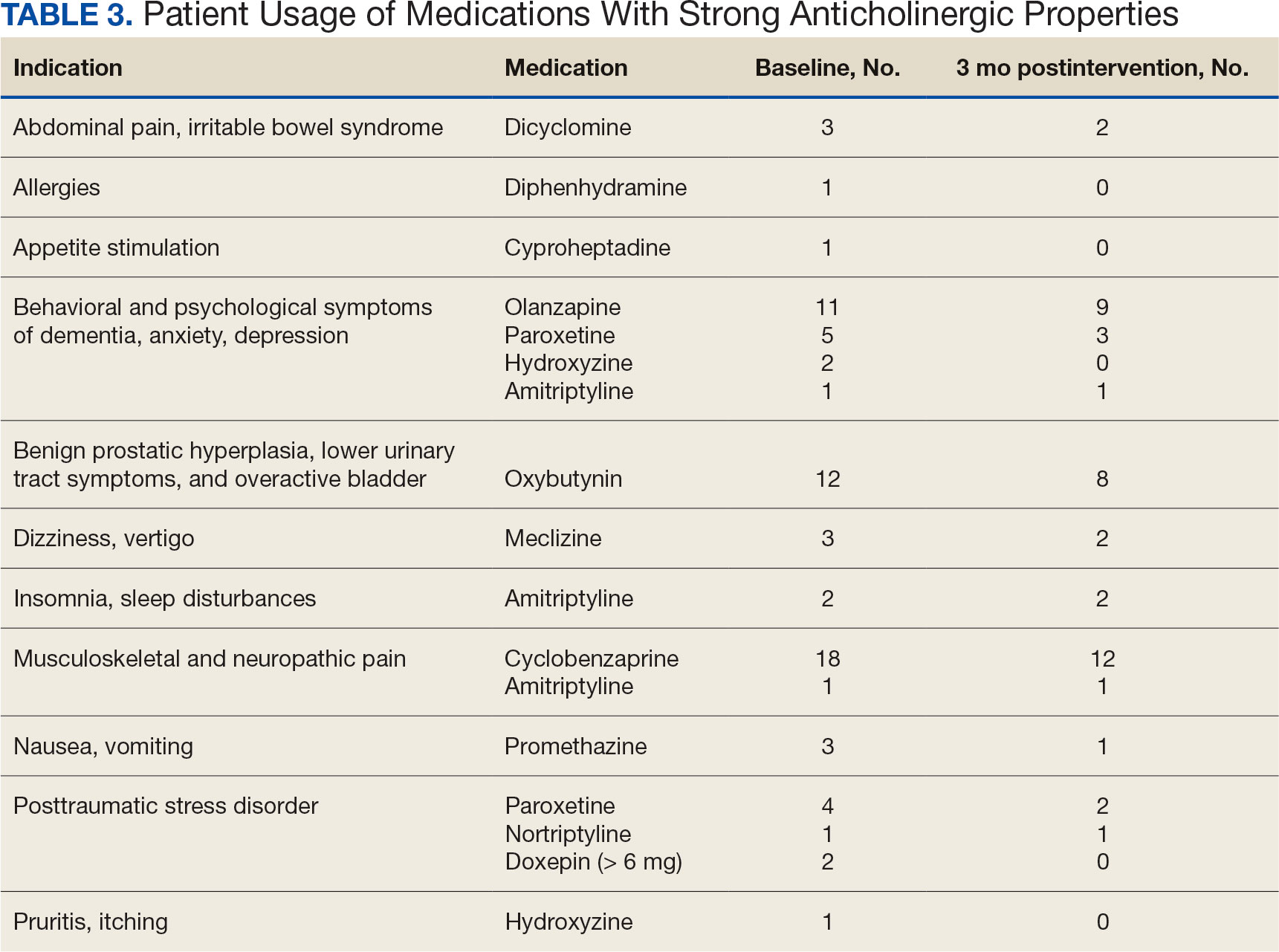
Discussion
This quality improvement project suggests that with the use of population health management tools such as the VIONE deprescribing dashboard, pharmacists can help identify and deprescribe strong anticholinergic medications in patients with cognitive impairment or dementia. Pharmacists can also aid in deprescribing through evidence-based recommendations to guide risk-benefit discussion and consider safer, nonanticholinergic alternatives. The authors were able to help reduce anticholinergic cognitive burden in 43% of patients in this sample. The mean 1.1 ACB score reduction was considered clinically significant based on prior studies that found that each 1-point increase in ACB score correlated with declined cognition and increased mortality.8,10 The VIONE deprescribing dashboard provided real-time patient data and helped target patients at the highest risk of anticholinergic AEs. The creation of the note templates based on the indication helped streamline recommendations. Typically, the prescriber addressed the recommendations at a routine follow-up appointment. The deprescribing method used in this project was time-efficient and could be easily replicated once the CPRS note templates were created. Future deprescribing projects could consider more direct pharmacist intervention and medication management.
Limitations
There was no direct assessment of clinical outcomes such as change in cognition using cognitive function tests. However, multiple studies have demonstrated AEs associated with strong anticholinergic medication use and additive anticholinergic burden in patients with dementia or cognitive impairment.1,5 Also, the 3-month follow-up period was relatively short. The pharmacist’s deprescribing recommendations may have been accepted after 3 months, or patients could have restarted their anticholinergic medications. Longer follow-up time could provide more robust results and conclusions. Thirdly, there was no formal definition of what constituted a risk-benefit assessment of anticholinergic medications. The risk-benefit assessment was determined at the discretion of the authors, which was subjective and allowed for bias. Finally, 6 patients died during the 3-month follow-up. The data for these patients were included in the baseline characteristics but not in the study outcomes. If these patients had been excluded from the results, a higher percentage of patients (47%) would have had ≥ 1 anticholinergic medication deprescribed.
Conclusions
In collaboration with the interdisciplinary team, pharmacist recommendations resulted in deprescribing of anticholinergic medications in veterans with dementia or cognitive impairment. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard, an easily accessible population health management tool, can identify patients prescribed potentially inappropriate medications and help target patients at the highest risk of anticholinergic AEs. To prevent worsening cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, and other AEs, this deprescribing initiative can be replicated at other VHA facilities. Future projects could have a longer follow-up period, incorporate more direct pharmacist intervention, and assess clinical outcomes of deprescribing.
- Gray SL, Hanlon JT. Anticholinergic medication use and dementia: latest evidence and clinical implications. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2016;7(5):217-224. doi:10.1177/2042098616658399
- Kersten H, Wyller TB. Anticholinergic drug burden in older people’s brain - how well is it measured? Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;114(2):151-159. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12140
- By the 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 updated AGS beers criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694. doi:10.1111/jgs.15767
- By the 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052-2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
- Wang K, Alan J, Page AT, Dimopoulos E, Etherton-Beer C. Anticholinergics and clinical outcomes amongst people with pre-existing dementia: a systematic review. Maturitas. 2021;151:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.06.004
- Thorpe JM, Thorpe CT, Gellad WF, et al. Dual health care system use and high-risk prescribing in patients with dementia: a national cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(3):157-163. doi:10.7326/M16-0551
- McCarren M, Burk M, Carico R, Glassman P, Good CB, Cunningham F. Design of a centrally aggregated medication use evaluation (CAMUE): anticholinergics in dementia. Presented at: 2019 HSR&D/QUERI National Conference; October 29-31, 2019; Washington, DC. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/meetings/2019/abstract-display.cfm?AbsNum=4027
- Boustani, M, Campbell, N, Munger S, et al. Impact of anticholinergics on the aging brain: a review and practical application. Aging Health. 2008;4(3):311-320. doi:10.2217/1745509.x
- Constantino-Corpuz JK, Alonso MTD. Assessment of a medication deprescribing tool on polypharmacy and cost avoidance. Fed Pract. 2021;38(7):332-336. doi:10.12788/fp.0146
- Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, et al. Anticholinergic medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(8):1477-1483. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03491.x
Anticholinergic medications block the activity of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by binding to either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors in both the peripheral and central nervous system. Anticholinergic medications typically refer to antimuscarinic medications and have been prescribed to treat a variety of conditions common in older adults, including overactive bladder, allergies, muscle spasms, and sleep disorders.1,2 Since muscarinic receptors are present throughout the body, anticholinergic medications are associated with many adverse effects (AEs), including constipation, urinary retention, xerostomia, and delirium. Older adults are more sensitive to these AEs due to physiological changes associated with aging.1
The American Geriatric Society Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medications Use in Older Adults identifies drugs with strong anticholinergic properties. The Beers Criteria strongly recommends avoiding these medications in patients with dementia or cognitive impairment due to the risk of central nervous system AEs. In the updated 2023 Beers Criteria, the rationale was expanded to recognize the risks of the cumulative anticholinergic burden associated with concurrent anticholinergic use.3,4
Given the prevalent use of anticholinergic medications in older adults, there has been significant research demonstrating their AEs, specifically delirium and cognitive impairment in geriatric patients. A systematic review of 14 articles conducted in 7 different countries of patients with median age of 76.4 to 86.1 years reviewed clinical outcomes of anticholinergic use in patients with dementia. Five studies found anticholinergics were associated with increased all-cause mortality in patients with dementia, and 3 studies found anticholinergics were associated with longer hospital stays. Other studies found that anticholinergics were associated with delirium and reduced health-related quality of life.5
About 35% of veterans with dementia have been prescribed a medication regimen with a high anticholinergic burden.6 In 2018, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pharmacy Benfits Management Center for Medical Safety completed a centrally aggregated medication use evaluation (CAMUE) to assess the appropriateness of anticholinergic medication use in patients with dementia. The retrospective chart review included 1094 veterans from 19 sites. Overall, about 15% of the veterans experienced new falls, delirium, or worsening dementia within 30 days of starting an anticholinergic medication. Furthermore, < 40% had documentation of a nonanticholinergic alternative medication trial, and < 20% had documented nonpharmacologic therapy. The documentation of risk-benefit assessment acknowledging the risks of anticholinergic medication use in veterans with dementia occurred only about 13% of the time. The CAMUE concluded that the risks of initiating an anticholinergic medication in veterans with dementia are likely underdocumented and possibly under considered by prescribers.7
Developed within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), VIONE (Vital, Important, Optional, Not Indicated, Every medication has an indication) is a medication management methodology that aims to reduce polypharmacy and improve patient safety consistent with high-reliability organizations. Since it launched in 2016, VIONE has gradually been implemented at many VHA facilities. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard had not been used at the VA Louisville Healthcare System prior to this quality improvement project.
This dashboard uses the Beers Criteria to identify potentially inappropriate anticholinergic medications. It uses the Anticholinergic Cognitive Burden (ACB) scale to calculate the cumulative anticholinergic risk for each patient. Medications with an ACB score of 2 or 3 have clinically relevant cognitive effects such as delirium and dementia (Table 1). For each point increase in total ACB score, a decline in mini-mental state examination score of 0.33 points over 2 years has been shown. Each point increase has also been correlated with a 26% increase in risk of death.8-10

Methods
The purpose of this quality improvement project was to determine the impact of pharmacist-driven deprescribing on the anticholinergic burden in veterans with dementia at VA Louisville Healthcare System. Data were obtained through the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and VIONE deprescribing dashboard and entered in a secure Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Pharmacist deprescribing steps were entered as CPRS progress notes. A deprescribing note template was created, and 11 templates with indication-specific recommendations were created for each anticholinergic indication identified (contact authors for deprescribing note template examples). Usage of anticholinergic medications was reexamined 3 months after the deprescribing note was entered.
Eligible patients identified in the VIONE deprescribing dashboard had an outpatient order for a medication with strong anticholinergic properties as identified using the Beers Criteria and were aged ≥ 65 years. Patients also had to be diagnosed with dementia or cognitive impairment. Patients were excluded if they were receiving hospice care or if the anticholinergic medication was from a non-VA prescriber or filled at a non-VA pharmacy. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard also excluded skeletal muscle relaxants if the patient had a spinal cord-related visit in the previous 2 years, first-generation antihistamines if the patient had a vertigo diagnosis, hydroxyzine if the indication was for anxiety, trospium if the indication was for overactive bladder, and antipsychotics if the patient had been diagnosed with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. The following were included in the deprescribing recommendations if the dashboard identified the patient due to receiving a second strongly anticholinergic medication: first generation antihistamines if the patient was diagnosed with vertigo and hydroxyzine if the indication is for anxiety.
Each eligible patient received a focused medication review by a pharmacist via electronic chart review and a templated CPRS progress note with patient-specific recommendations. The prescriber and the patient’s primary care practitioner were recommended to perform a patient-specific risk-benefit assessment, deprescribe potentially inappropriate anticholinergic medications, and consider nonanticholinergic alternatives (both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic). Data collected included baseline age, sex, prespecified comorbidities (type of dementia, cognitive impairment, delirium, benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms), duration of prescribed anticholinergic medication, indication and deprescribing rate for each anticholinergic agent, and concurrent dementia medications (acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, or both).
The primary outcome was the number of patients that had = 1 medication with strong anticholinergic properties deprescribed. Deprescribing was defined as medication discontinuation or reduction of total daily dose. Secondary outcomes were the mean change in ACB scale, the number of patients with dose tapering, documented patient-specific risk-benefit assessment, and initiated nonanticholinergic alternative per pharmacist recommendation.
Results
The VIONE deprescribing dashboard identified 121 patients; 45 were excluded for non-VA prescriber or pharmacy, and 8 patients were excluded for other reasons. Sixty-eight patients were included in the deprescribing initiative. The mean age was 73.4 years (range, 67-93), 65 (96%) were male, and 34 (50%) had unspecified dementia (Table 2). Thirty-one patients (46%) had concurrent cholinesterase inhibitor prescriptions for dementia. The median duration of use of a strong anticholinergic medication was 11 months.

Twenty-nine patients (43%) had ≥ 1 medication with strong anticholinergic properties deprescribed. Anticholinergic medication was discontinued for 26 patients, and the dose was decreased for 3 patients. ACB score fell by a mean of 1.1 per patient. There was an increase in the documented risk-benefit assessment for anticholinergic medications from a baseline of 4 (6%) to 19 (28%) 3 months after the deprescribing note. Cyclobenzaprine, paroxetine, and oxybutynin were deprescribed the most, and amitriptyline had the lowest rate of deprescribing (Table 3). Thirty patients (44%) had a pharmacologic, nonanticholinergic alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendation, and 6 patients (9%) had a nonpharmacologic alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendation.

Discussion
This quality improvement project suggests that with the use of population health management tools such as the VIONE deprescribing dashboard, pharmacists can help identify and deprescribe strong anticholinergic medications in patients with cognitive impairment or dementia. Pharmacists can also aid in deprescribing through evidence-based recommendations to guide risk-benefit discussion and consider safer, nonanticholinergic alternatives. The authors were able to help reduce anticholinergic cognitive burden in 43% of patients in this sample. The mean 1.1 ACB score reduction was considered clinically significant based on prior studies that found that each 1-point increase in ACB score correlated with declined cognition and increased mortality.8,10 The VIONE deprescribing dashboard provided real-time patient data and helped target patients at the highest risk of anticholinergic AEs. The creation of the note templates based on the indication helped streamline recommendations. Typically, the prescriber addressed the recommendations at a routine follow-up appointment. The deprescribing method used in this project was time-efficient and could be easily replicated once the CPRS note templates were created. Future deprescribing projects could consider more direct pharmacist intervention and medication management.
Limitations
There was no direct assessment of clinical outcomes such as change in cognition using cognitive function tests. However, multiple studies have demonstrated AEs associated with strong anticholinergic medication use and additive anticholinergic burden in patients with dementia or cognitive impairment.1,5 Also, the 3-month follow-up period was relatively short. The pharmacist’s deprescribing recommendations may have been accepted after 3 months, or patients could have restarted their anticholinergic medications. Longer follow-up time could provide more robust results and conclusions. Thirdly, there was no formal definition of what constituted a risk-benefit assessment of anticholinergic medications. The risk-benefit assessment was determined at the discretion of the authors, which was subjective and allowed for bias. Finally, 6 patients died during the 3-month follow-up. The data for these patients were included in the baseline characteristics but not in the study outcomes. If these patients had been excluded from the results, a higher percentage of patients (47%) would have had ≥ 1 anticholinergic medication deprescribed.
Conclusions
In collaboration with the interdisciplinary team, pharmacist recommendations resulted in deprescribing of anticholinergic medications in veterans with dementia or cognitive impairment. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard, an easily accessible population health management tool, can identify patients prescribed potentially inappropriate medications and help target patients at the highest risk of anticholinergic AEs. To prevent worsening cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, and other AEs, this deprescribing initiative can be replicated at other VHA facilities. Future projects could have a longer follow-up period, incorporate more direct pharmacist intervention, and assess clinical outcomes of deprescribing.
Anticholinergic medications block the activity of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine by binding to either muscarinic or nicotinic receptors in both the peripheral and central nervous system. Anticholinergic medications typically refer to antimuscarinic medications and have been prescribed to treat a variety of conditions common in older adults, including overactive bladder, allergies, muscle spasms, and sleep disorders.1,2 Since muscarinic receptors are present throughout the body, anticholinergic medications are associated with many adverse effects (AEs), including constipation, urinary retention, xerostomia, and delirium. Older adults are more sensitive to these AEs due to physiological changes associated with aging.1
The American Geriatric Society Beers Criteria for Potentially Inappropriate Medications Use in Older Adults identifies drugs with strong anticholinergic properties. The Beers Criteria strongly recommends avoiding these medications in patients with dementia or cognitive impairment due to the risk of central nervous system AEs. In the updated 2023 Beers Criteria, the rationale was expanded to recognize the risks of the cumulative anticholinergic burden associated with concurrent anticholinergic use.3,4
Given the prevalent use of anticholinergic medications in older adults, there has been significant research demonstrating their AEs, specifically delirium and cognitive impairment in geriatric patients. A systematic review of 14 articles conducted in 7 different countries of patients with median age of 76.4 to 86.1 years reviewed clinical outcomes of anticholinergic use in patients with dementia. Five studies found anticholinergics were associated with increased all-cause mortality in patients with dementia, and 3 studies found anticholinergics were associated with longer hospital stays. Other studies found that anticholinergics were associated with delirium and reduced health-related quality of life.5
About 35% of veterans with dementia have been prescribed a medication regimen with a high anticholinergic burden.6 In 2018, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) Pharmacy Benfits Management Center for Medical Safety completed a centrally aggregated medication use evaluation (CAMUE) to assess the appropriateness of anticholinergic medication use in patients with dementia. The retrospective chart review included 1094 veterans from 19 sites. Overall, about 15% of the veterans experienced new falls, delirium, or worsening dementia within 30 days of starting an anticholinergic medication. Furthermore, < 40% had documentation of a nonanticholinergic alternative medication trial, and < 20% had documented nonpharmacologic therapy. The documentation of risk-benefit assessment acknowledging the risks of anticholinergic medication use in veterans with dementia occurred only about 13% of the time. The CAMUE concluded that the risks of initiating an anticholinergic medication in veterans with dementia are likely underdocumented and possibly under considered by prescribers.7
Developed within the Veterans Health Administration (VHA), VIONE (Vital, Important, Optional, Not Indicated, Every medication has an indication) is a medication management methodology that aims to reduce polypharmacy and improve patient safety consistent with high-reliability organizations. Since it launched in 2016, VIONE has gradually been implemented at many VHA facilities. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard had not been used at the VA Louisville Healthcare System prior to this quality improvement project.
This dashboard uses the Beers Criteria to identify potentially inappropriate anticholinergic medications. It uses the Anticholinergic Cognitive Burden (ACB) scale to calculate the cumulative anticholinergic risk for each patient. Medications with an ACB score of 2 or 3 have clinically relevant cognitive effects such as delirium and dementia (Table 1). For each point increase in total ACB score, a decline in mini-mental state examination score of 0.33 points over 2 years has been shown. Each point increase has also been correlated with a 26% increase in risk of death.8-10

Methods
The purpose of this quality improvement project was to determine the impact of pharmacist-driven deprescribing on the anticholinergic burden in veterans with dementia at VA Louisville Healthcare System. Data were obtained through the Computerized Patient Record System (CPRS) and VIONE deprescribing dashboard and entered in a secure Microsoft Excel spreadsheet. Pharmacist deprescribing steps were entered as CPRS progress notes. A deprescribing note template was created, and 11 templates with indication-specific recommendations were created for each anticholinergic indication identified (contact authors for deprescribing note template examples). Usage of anticholinergic medications was reexamined 3 months after the deprescribing note was entered.
Eligible patients identified in the VIONE deprescribing dashboard had an outpatient order for a medication with strong anticholinergic properties as identified using the Beers Criteria and were aged ≥ 65 years. Patients also had to be diagnosed with dementia or cognitive impairment. Patients were excluded if they were receiving hospice care or if the anticholinergic medication was from a non-VA prescriber or filled at a non-VA pharmacy. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard also excluded skeletal muscle relaxants if the patient had a spinal cord-related visit in the previous 2 years, first-generation antihistamines if the patient had a vertigo diagnosis, hydroxyzine if the indication was for anxiety, trospium if the indication was for overactive bladder, and antipsychotics if the patient had been diagnosed with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. The following were included in the deprescribing recommendations if the dashboard identified the patient due to receiving a second strongly anticholinergic medication: first generation antihistamines if the patient was diagnosed with vertigo and hydroxyzine if the indication is for anxiety.
Each eligible patient received a focused medication review by a pharmacist via electronic chart review and a templated CPRS progress note with patient-specific recommendations. The prescriber and the patient’s primary care practitioner were recommended to perform a patient-specific risk-benefit assessment, deprescribe potentially inappropriate anticholinergic medications, and consider nonanticholinergic alternatives (both pharmacologic and nonpharmacologic). Data collected included baseline age, sex, prespecified comorbidities (type of dementia, cognitive impairment, delirium, benign prostatic hyperplasia/lower urinary tract symptoms), duration of prescribed anticholinergic medication, indication and deprescribing rate for each anticholinergic agent, and concurrent dementia medications (acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, memantine, or both).
The primary outcome was the number of patients that had = 1 medication with strong anticholinergic properties deprescribed. Deprescribing was defined as medication discontinuation or reduction of total daily dose. Secondary outcomes were the mean change in ACB scale, the number of patients with dose tapering, documented patient-specific risk-benefit assessment, and initiated nonanticholinergic alternative per pharmacist recommendation.
Results
The VIONE deprescribing dashboard identified 121 patients; 45 were excluded for non-VA prescriber or pharmacy, and 8 patients were excluded for other reasons. Sixty-eight patients were included in the deprescribing initiative. The mean age was 73.4 years (range, 67-93), 65 (96%) were male, and 34 (50%) had unspecified dementia (Table 2). Thirty-one patients (46%) had concurrent cholinesterase inhibitor prescriptions for dementia. The median duration of use of a strong anticholinergic medication was 11 months.

Twenty-nine patients (43%) had ≥ 1 medication with strong anticholinergic properties deprescribed. Anticholinergic medication was discontinued for 26 patients, and the dose was decreased for 3 patients. ACB score fell by a mean of 1.1 per patient. There was an increase in the documented risk-benefit assessment for anticholinergic medications from a baseline of 4 (6%) to 19 (28%) 3 months after the deprescribing note. Cyclobenzaprine, paroxetine, and oxybutynin were deprescribed the most, and amitriptyline had the lowest rate of deprescribing (Table 3). Thirty patients (44%) had a pharmacologic, nonanticholinergic alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendation, and 6 patients (9%) had a nonpharmacologic alternative initiated per pharmacist recommendation.

Discussion
This quality improvement project suggests that with the use of population health management tools such as the VIONE deprescribing dashboard, pharmacists can help identify and deprescribe strong anticholinergic medications in patients with cognitive impairment or dementia. Pharmacists can also aid in deprescribing through evidence-based recommendations to guide risk-benefit discussion and consider safer, nonanticholinergic alternatives. The authors were able to help reduce anticholinergic cognitive burden in 43% of patients in this sample. The mean 1.1 ACB score reduction was considered clinically significant based on prior studies that found that each 1-point increase in ACB score correlated with declined cognition and increased mortality.8,10 The VIONE deprescribing dashboard provided real-time patient data and helped target patients at the highest risk of anticholinergic AEs. The creation of the note templates based on the indication helped streamline recommendations. Typically, the prescriber addressed the recommendations at a routine follow-up appointment. The deprescribing method used in this project was time-efficient and could be easily replicated once the CPRS note templates were created. Future deprescribing projects could consider more direct pharmacist intervention and medication management.
Limitations
There was no direct assessment of clinical outcomes such as change in cognition using cognitive function tests. However, multiple studies have demonstrated AEs associated with strong anticholinergic medication use and additive anticholinergic burden in patients with dementia or cognitive impairment.1,5 Also, the 3-month follow-up period was relatively short. The pharmacist’s deprescribing recommendations may have been accepted after 3 months, or patients could have restarted their anticholinergic medications. Longer follow-up time could provide more robust results and conclusions. Thirdly, there was no formal definition of what constituted a risk-benefit assessment of anticholinergic medications. The risk-benefit assessment was determined at the discretion of the authors, which was subjective and allowed for bias. Finally, 6 patients died during the 3-month follow-up. The data for these patients were included in the baseline characteristics but not in the study outcomes. If these patients had been excluded from the results, a higher percentage of patients (47%) would have had ≥ 1 anticholinergic medication deprescribed.
Conclusions
In collaboration with the interdisciplinary team, pharmacist recommendations resulted in deprescribing of anticholinergic medications in veterans with dementia or cognitive impairment. The VIONE deprescribing dashboard, an easily accessible population health management tool, can identify patients prescribed potentially inappropriate medications and help target patients at the highest risk of anticholinergic AEs. To prevent worsening cognitive impairment, delirium, falls, and other AEs, this deprescribing initiative can be replicated at other VHA facilities. Future projects could have a longer follow-up period, incorporate more direct pharmacist intervention, and assess clinical outcomes of deprescribing.
- Gray SL, Hanlon JT. Anticholinergic medication use and dementia: latest evidence and clinical implications. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2016;7(5):217-224. doi:10.1177/2042098616658399
- Kersten H, Wyller TB. Anticholinergic drug burden in older people’s brain - how well is it measured? Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;114(2):151-159. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12140
- By the 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 updated AGS beers criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694. doi:10.1111/jgs.15767
- By the 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052-2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
- Wang K, Alan J, Page AT, Dimopoulos E, Etherton-Beer C. Anticholinergics and clinical outcomes amongst people with pre-existing dementia: a systematic review. Maturitas. 2021;151:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.06.004
- Thorpe JM, Thorpe CT, Gellad WF, et al. Dual health care system use and high-risk prescribing in patients with dementia: a national cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(3):157-163. doi:10.7326/M16-0551
- McCarren M, Burk M, Carico R, Glassman P, Good CB, Cunningham F. Design of a centrally aggregated medication use evaluation (CAMUE): anticholinergics in dementia. Presented at: 2019 HSR&D/QUERI National Conference; October 29-31, 2019; Washington, DC. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/meetings/2019/abstract-display.cfm?AbsNum=4027
- Boustani, M, Campbell, N, Munger S, et al. Impact of anticholinergics on the aging brain: a review and practical application. Aging Health. 2008;4(3):311-320. doi:10.2217/1745509.x
- Constantino-Corpuz JK, Alonso MTD. Assessment of a medication deprescribing tool on polypharmacy and cost avoidance. Fed Pract. 2021;38(7):332-336. doi:10.12788/fp.0146
- Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, et al. Anticholinergic medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(8):1477-1483. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03491.x
- Gray SL, Hanlon JT. Anticholinergic medication use and dementia: latest evidence and clinical implications. Ther Adv Drug Saf. 2016;7(5):217-224. doi:10.1177/2042098616658399
- Kersten H, Wyller TB. Anticholinergic drug burden in older people’s brain - how well is it measured? Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;114(2):151-159. doi:10.1111/bcpt.12140
- By the 2019 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2019 updated AGS beers criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(4):674-694. doi:10.1111/jgs.15767
- By the 2023 American Geriatrics Society Beers Criteria® Update Expert Panel. American Geriatrics Society 2023 updated AGS Beers Criteria® for potentially inappropriate medication use in older adults J Am Geriatr Soc. 2023;71(7):2052-2081. doi:10.1111/jgs.18372
- Wang K, Alan J, Page AT, Dimopoulos E, Etherton-Beer C. Anticholinergics and clinical outcomes amongst people with pre-existing dementia: a systematic review. Maturitas. 2021;151:1-14. doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2021.06.004
- Thorpe JM, Thorpe CT, Gellad WF, et al. Dual health care system use and high-risk prescribing in patients with dementia: a national cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2017;166(3):157-163. doi:10.7326/M16-0551
- McCarren M, Burk M, Carico R, Glassman P, Good CB, Cunningham F. Design of a centrally aggregated medication use evaluation (CAMUE): anticholinergics in dementia. Presented at: 2019 HSR&D/QUERI National Conference; October 29-31, 2019; Washington, DC. https://www.hsrd.research.va.gov/meetings/2019/abstract-display.cfm?AbsNum=4027
- Boustani, M, Campbell, N, Munger S, et al. Impact of anticholinergics on the aging brain: a review and practical application. Aging Health. 2008;4(3):311-320. doi:10.2217/1745509.x
- Constantino-Corpuz JK, Alonso MTD. Assessment of a medication deprescribing tool on polypharmacy and cost avoidance. Fed Pract. 2021;38(7):332-336. doi:10.12788/fp.0146
- Fox C, Richardson K, Maidment ID, et al. Anticholinergic medication use and cognitive impairment in the older population: the medical research council cognitive function and ageing study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2011;59(8):1477-1483. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2011.03491.x
Pharmacist-Driven Deprescribing to Reduce Anticholinergic Burden in Veterans With Dementia
Pharmacist-Driven Deprescribing to Reduce Anticholinergic Burden in Veterans With Dementia
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.
Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.

Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
Supporting meaningful research that has a positive impact on the health and quality of life of veterans is a priority of the US Department of Veterans Affairs Office of Research and Development.1 For nearly a century, VA researchers have been conducting high quality studies. To continue this trajectory, it is imperative to attract, train, and retain exceptional investigators while nurturing their development throughout their careers.2
Mentorship is defined as guidance provided by an experienced and trusted party to another (usually junior) individual with the intent of helping the person succeed. It benefits the mentee, mentor, and their institutions.3 Mentorship is crucial for personal and professional development as well as productivity, which may help reduce clinician burnout.4-7 Conversely, a lack of mentorship could have negative effects on work satisfaction and stagnate career progression.8
Mentorship is vital for developing and advancing a VA investigator’s research agenda. Funding, grant writing, and research design were among the most discussed topics in a large comprehensive mentorship program for academic faculty.9 However, there are several known barriers to effective research mentorship; among them include a lack of resources, time constraints, and competing clinical priorities.10,11
Finding time for effective one-on-one research mentoring is difficult within the time constraints of clinical duties; a group mentorship model may help overcome this barrier. Group mentorship can aid in personal and professional development because no single mentor can effectively meet every mentoring need of an individual.12 Group mentorship also allows for the exchange of ideas among individuals with different backgrounds and the ability to utilize the strengths of each member of the group. For example, a member may have methodological expertise, while another may be skilled in grantsmanship. A team of mentors may be more beneficial for both the mentors (eg, establish a more manageable workload) and the mentee (eg, gains a broader perspective of expertise) when compared to having a single mentor.3
Peer mentorship within the group setting may also yield additional benefits. For example, having a supportive peer group may help reduce stress levels and burnout, while also improving overall well-being.3,13 Formal mentorship programs do not frequently discuss concerns such as work-life balance, so including peers as mentors may help fill this void.9 Peer mentorship has also been found to be beneficial in providing mentees with pooled resources and shared learning.12,13 This article describes the components, benefits, impacts, and challenges of a group research mentorship program for VA clinicians interested in conducting VA-relevant research.
Program Description
The VA Clinical Research Mentorship Program was initiated at the VA Ann Arbor Healthcare System (VAAAHS) in October 2015 by the Chief of Medicine to assist VA clinician investigators with developing and submitting VA clinical science and health services research grant applications. The program offers group and one-on-one consultation services through the expertise of 2 experienced investigators/faculty mentors who also serve as program directors, each of whom devote about 3 to 5 hours per month to activities associated with the mentorship program (eg, attending the meeting, reviewing materials sent by mentees, and one-on-one discussions with mentees).
The program also fostered peer-led mentorship. This encourages all attendees to provide feedback during group sessions and communication by mentees outside the group sessions. An experienced project manager serves as program coordinator and contributes about 4 hours per month for activities such as attending, scheduling, and sending reminders for each meeting, distributing handouts, reviewing materials, and answering mentee’s questions via email. A statistician and additional research staff (ie, an epidemiologist and research assistant) do not attend the recurring meetings, but are available for offline consultation as needed. The program runs on a 12-month cycle with regular meetings occurring twice monthly during the 9-month academic period. Resources to support the program, primarily program director(s) and project coordinator effort, are provided by the Chief of Medicine and through the VAAAHS affiliated VA Health Systems Research (formerly Health Services Research & Development) Center of Innovation.
Invitations for new mentees are sent annually. Mentees expressing interest in the program outside of its annual recruitment period are evaluated for inclusion on a rolling basis. Recruitment begins with the program coordinator sending email notifications to all VAAAHS Medicine Service faculty, section chiefs, and division chiefs at the VAAAHS academic affiliate. Recipients are encouraged to distribute the announcement to eligible applicants and refer them to the application materials for entry consideration into the program. The application consists of the applicant’s curriculum vitae and a 1-page summary that includes a description of their research area of interest, how it is relevant to the VA, in addition to an idea for a research study, its potential significance, and proposed methodology. Applicant materials are reviewed by the program coordinator and program directors. The applicants are evaluated using a simple scoring approach that focuses on the applicant’s research area and agenda, past research training, past research productivity, potential for obtaining VA funding, and whether they have sufficient research time.
Program eligibility initially required being a physician with ≥ 1/8 VA appointment from the Medicine Service. However, clinicians with clinical appointments from other VA services are also accepted for participation as needed. Applicants must have previous research experience and have a career goal to obtain external funding for conducting and publishing original research. Those who have previously served as a principal investigator on a funded VA grant proposal are not eligible as new applicants but can remain in the program as peer mentors. The number of annual applicants varies and ranges from 1 to 11; on average, about 90% of applicants receive invitations to join the program.
Sessions
The program holds recurring meetings twice monthly for 1 hour during the 9-month academic year. However, program directors are available year-round, and mentees are encouraged to communicate questions or concerns via email during nonacademic months. Prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, all meetings were held in-person. However, the group pivoted to virtual meetings and continues to utilize this format. The dedicated program coordinator is responsible for coordinating meetings and distributing meeting materials.
Each session is informal, flexible, and supportive. Attendance is not enforced, and mentees are allowed to join meetings as their schedules permit; however, program directors and program coordinator attend each meeting. In advance of each session, the program coordinator sends out a call for agenda items to all active members invited to discuss any research related items. Each mentee presents their ideas to lead the discussion for their portion of the meeting with no defined format required.
A variety of topics are covered including, but not limited to: (1) grant-specific concerns (eg, questions related to specific aim pages, grantsmanship, postsubmission comments from reviewers, or postaward logistics); (2) research procedures (eg, questions related to methodological practices or institutional review board concerns); (3) manuscript or presentation preparation; and (4) careerrelated issues. The program coordinator distributes handouts prior to meetings and mentees may record their presentations. These handouts may include, but are not limited to, specific aims pages, analytical plans, grant solicitations, and PowerPoint presentations. If a resource that can benefit the entire group is mentioned during the meeting, the program coordinator is responsible for distribution.
The program follows a group facilitated discussion format. Program directors facilitate each meeting, but input is encouraged from all attendees. This model allows for mentees to learn from the faculty mentors as well as peer mentees in a simultaneous and efficient fashion. Group discussions foster collective problem solving, peer support, and resource sharing that would not be possible through individualized mentorship. Participants have access to varied expertise during each session which reduces the need to seek specialized help elsewhere. Participants are also encouraged to contact the program directors or research staff for consultation as needed. Some one-on-one consultations have transitioned to a more sustained and ongoing mentorship relationship between a program director and mentee, but most are often brief email exchanges or a single meeting.

Participants
Since its inception in 2015, 35 clinicians have enrolled in the program. The mentees are equally distributed by sex and practice in a variety of disciplines including gastroenterology, hematology/oncology, cardiology, and general medicine (Table 1). Mentees have submitted 33 grant proposals addressing a variety of health care issues to a diverse group of federal and nonfederal funding agencies (Table 2). As of May 15, 2024, 19 (58%) of the submitted applications have been funded.

Many factors contribute to a successfully funded grant application, and several mentees report that participating in the mentorship program was helpful. For example, a mentee became the first lead investigator for a VA Cooperative Studies Program funded at VAAAHS. The VA Cooperative Studies Program, a division of the Office of Research and Development, plans and conducts large multicenter clinical trials and epidemiological studies within the VA via a vast network of clinician investigators, statisticians, and other key research experts.14
Several program mentees have also received VA Clinical Science Research and Development Career Development Awards. The VA Career Development program supports investigators during their early research careers with a goal of retaining talented researchers committed to improving the health and care of veterans.15
Survey Responses
Mentee productivity and updates are tracked through direct mentee input, as requested by the program coordinator. Since 2022, participants could complete an end-of-year survey based on an assessment tool used in a VAAAHS nonresearch mentorship program.16 The survey, distributed to mentees and program directors, requests feedback on logistics (eg, if the meeting was a good use of time and barriers to attendance); perceptions of effectiveness (eg, ability to discuss agenda items, helpfulness with setting and reaching research goals, and quality of mentors’ feedback); and the impact of the mentoring program on work satisfaction and clinician burnout. Respondents are also encouraged to leave open-ended qualitative feedback.
To date the survey has elicited 19 responses. Seventeen (89%) indicated that they agree or strongly agree the meetings were an effective use of their time and 11 (58%) indicated that they were able to discuss all or most of the items they wanted to during the meeting. Sixteen respondents (84%) agreed the program helped them set and achieve their research goals and 14 respondents (74%) agreed the feedback they received during the meeting was specific, actionable, and focused on how to improve their research agenda. Seventeen respondents (89%) agreed the program increased their work satisfaction, while 13 respondents (68%) felt the program reduced levels of clinician burnout.
As attendance was not mandatory, the survey asked participants how often they attended meetings during the past year. Responses were mixed: 4 (21%) respondents attended regularly (12 to 16 times per year) and 8 (42%) attended most sessions (8 to 11 times per year). Noted barriers to attendance included conflicts with patient care activities and conflicts with other high priority meetings.
Mentees also provided qualitive feedback regarding the program. They highlighted the supportive environment, valuable expertise of the mentors, and usefulness of obtaining tailored feedback from the group. “This group is an amazing resource to anyone developing a research career,” a mentee noted, adding that the program directors “fostered an incredibly supportive group where research ideas and methodology can be explored in a nonthreatening and creative environment.”
Conclusions
This mentorship program aims to help aspiring VA clinician investigators develop and submit competitive research grant applications. The addition of the program to the existing robust research environments at VAAAHS and its academic affiliate appears to have contributed to this success, with 58% of applications submitted by program mentees receiving funding.
In addition to funding success, we also found that most participants have a favorable impression of the program. Of the participants who responded to the program evaluation survey, nearly all indicated the program was an effective use of their time. The program also appeared to increase work satisfaction and reduce levels of clinician burnout. Barriers to attendance were also noted, with the most frequent being scheduling conflicts.
This program’s format includes facilitated group discussion as well as peer mentorship. This collaborative structure allows for an efficient and rich learning experience. Feedback from multiple perspectives encourages natural networking and relationship building. Incorporating the collective wisdom of the faculty mentors and peer mentees is beneficial; it not only empowers the mentees but also enriches the experience for the mentors. This program can serve as a model for other VA facilities—or non-VA academic medical centers—to enhance their research programs.
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Strategic priorities for VA research. Published March 10, 2021. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/strategic_priorities.cfm
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. About the Office of Research & Development. Published November 11, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/about/default.cfm
- Chopra V, Vaughn V, Saint S. The Mentoring Guide: Helping Mentors and Mentees Succeed. Michigan Publishing Services; 2019.
- Gilster SD, Accorinti KL. Mentoring program yields staff satisfaction. Mentoring through the exchange of information across all organizational levels can help administrators retain valuable staff. Provider. 1999;25(10):99-100.
- Ramanan RA, Phillips RS, Davis RB, Silen W, Reede JY. Mentoring in medicine: keys to satisfaction. Am J Med. 2002;112(4):336-341. doi:10.1016/s0002-9343(02)01032-x
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. Mentoring in academic medicine: a systematic review. JAMA. 2006;296(9):1103-1115. doi:10.1001/jama.296.9.1103
- Sambunjak D, Straus SE, Marusi' A. A systematic review of qualitative research on the meaning and characteristics of mentoring in academic medicine. J Gen Intern Med. 2010;25(1):72-78. doi:10.1007/s11606-009-1165-8
- Jackson VA, Palepu A, Szalacha L, Caswell C, Carr PL, Inui T. “Having the right chemistry”: a qualitative study of mentoring in academic medicine. Acad Med. 2003;78(3):328-334. doi:10.1097/00001888-200303000-00020
- Feldman MD, Arean PA, Marshall SJ, Lovett M, O’Sullivan P. Does mentoring matter: results from a survey of faculty mentees at a large health sciences university. Med Educ Online. 2010;15:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063. doi:10.3402/meo.v15i0.5063
- Leary JC, Schainker EG, Leyenaar JK. The unwritten rules of mentorship: facilitators of and barriers to effective mentorship in pediatric hospital medicine. Hosp Pediatr. 2016;6(4):219-225. doi:10.1542/hpeds.2015-0108
- Rustgi AK, Hecht GA. Mentorship in academic medicine. Gastroenterology. 2011;141(3):789-792. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2011.07.024
- DeCastro R, Sambuco D, Ubel PA, Stewart A, Jagsi R. Mentor networks in academic medicine: moving beyond a dyadic conception of mentoring for junior faculty researchers. Acad Med. 2013;88(4):488-496. doi:10.1097/ACM.0b013e318285d302
- McDaugall M, Beattie RS. Peer mentoring at work: the nature and outcomes of non-hierarchical developmental relationships. Management Learning. 2016;28(4):423-437. doi:10.1177/1350507697284003
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Rsearch and Development. VA Cooperative Studies Program (CSP). Updated July 2019. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.vacsp.research.va.gov
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Office of Research and Development. Career development program for biomedical laboratory and clinical science R&D services. Published April 17, 2023. Accessed September 17, 2024. https://www.research.va.gov/services/shared_docs/career_dev.cfm
- Houchens N, Kuhn L, Ratz D, Su G, Saint S. Committed to success: a structured mentoring program for clinically-oriented physicians. Mayo Clin Pro Innov Qual Outcomes. 2024;8(4):356-363. doi:10.1016/j.mayocpiqo.2024.05.002
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
A Group Approach to Clinical Research Mentorship at a Veterans Affairs Medical Center
Vancomycin AUC-Dosing Initiative at a Regional Antibiotic Stewardship Collaborative
Antimicrobial resistance is a global threat and burden to health care, with > 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occurring annually in the United States.1 To combat this issue and improve patient care, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has implemented antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) across its health care systems. ASPs are multidisciplinary teams that promote evidence-based use of antimicrobials through activities supporting appropriate selection, dosing, route, and duration of antimicrobial therapy. ASP best practices are also included in the Joint Commission and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services accreditation standards.2
The foundational charge for VA facilities to develop and maintain ASPs was outlined in 2014 and updated in 2023 in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1031 on antimicrobial stewardship programs.2 This directive outlines specific requirements for all VA ASPs, including personnel, staffing levels, and the roles and responsibilities of all team members. VHA now requires that Veterans Integrated Services Networks (VISNs) establish robust ASP collaboratives. A VISN ASP collaborative consists of stewardship champions from each VA medical center in the VISN and is designed to support, develop, and enhance ASP programs across all facilities within that VISN.2 Some VISNs may lack an ASP collaborative altogether, and others with existing groups may seek ways to expand their collaboratives in line with the updated directive. Prior to VHA Directive 1031, the VA Sunshine Healthcare Network (VISN 8) established an ASP collaborative. This article describes the structure and activities of the VISN 8 ASP collaborative and highlights a recent VISN 8 quality assurance initiative related to vancomycin area under the curve (AUC) dosing that illustrates how ASP collaboratives can enhance stewardship and clinical care across broad geographic areas.
VISN 8 ASP
The VHA, the largest integrated US health care system, is divided into 18 VISNs that provide regional systems of care to enhance access and meet the local health care needs of veterans.3 VISN 8 serves > 1.5 million veterans across 165,759 km2 in Florida, South Georgia, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands.4 The network is composed of 7 health systems with 8 medical centers and > 60 outpatient clinics. These facilities provide comprehensive acute, primary, and specialty care, as well as mental health and extended care services in inpatient, outpatient, nursing home, and home care settings.4
The 2023 VHA Directive 1031 update recognizes the importance of VISN-level coordination of ASP activities to enhance the standardization of care and build partnerships in stewardship across all levels of care. The VISN 8 ASP collaborative workgroup (ASPWG) was established in 2015. Consistent with Directive 1031, the ASPWG is guided by clinician and pharmacist VISN leads. These leads serve as subject matter experts, facilitate access to resources, establish VISN-level consensus, and enhance communication among local ASP champions at medical centers within the VISN. All 7 health systems include = 1 ASP champion (clinician or pharmacist) in the ASPWG. Ad hoc members, whose routine duties are not solely focused on antimicrobial stewardship, contribute to specific stewardship projects as needed. For example, the ASPWG has included internal medicine, emergency department, community living center pharmacists, representatives from pharmacy administration, and trainees (pharmacy students and residents, and infectious diseases fellows) in antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. The inclusion of non-ASP champions is not discussed in VHA Directive 1031. However, these members have made valuable contributions to the ASPWG.
The ASPWG meets monthly. Agendas and priorities are developed by the VISN pharmacist and health care practitioner (HCP) leads. Monthly discussions may include but are not limited to a review of national formulary decisions, VISN goals and metrics, infectious diseases hot topics, pharmacoeconomic initiatives, strong practice presentations, regulatory and accreditation preparation, preparation of tracking reports, as well as the development of both patient-level and HCPlevel tools, resources, and education materials. This forum facilitates collaborative learning: members process and synthesize information, share and reframe ideas, and listen to other viewpoints to gain a complete understanding as a group.5 For example, ASPWG members have leaned on each other to prepare for Joint Commission accreditation surveys and strengthen the VISN 8 COVID-19 program through the rollout of vaccines and treatments. Other collaborative projects completed over the past few years included a penicillin allergy testing initiative and anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and pseudomonal medication use evaluations. This team-centric problem-solving approach is highly effective while also fostering professional and social relationships. However, collaboratives could be perceived to have drawbacks. There may be opportunity costs if ASP time is allocated for issues that have already been addressed locally or concerns that standardization might hinder rapid adoption of practices at individual sites. Therefore, participation in each distinct group initiative is optional. This allows sites to choose projects related to their high priority areas and maintain bandwidth to implement practices not yet adopted by the larger group.
The ASPWG tracks metrics related to antimicrobial use with quarterly data presented by the VISN pharmacist lead. Both inpatient and outpatient metrics are evaluated, such as days of therapy per 1000 days and outpatient antibiotic prescriptions per 1000 unique patients. Facilities are benchmarked against their own historical data and other VISN sites, as well as other VISNs across the country. When outliers are identified, facilities are encouraged to conduct local projects to identify reasons for different antimicrobial use patterns and subsequent initiatives to optimize antimicrobial use. Benchmarking against VISN facilities can be useful since VISN facilities may be more similar than facilities in different geographic regions. Each year, the ASPWG reviews the current metrics, makes adjustments to address VISN priorities, and votes for approval of the metrics that will be tracked in the coming year.
Participation in an ASP collaborative streamlines the rollout of ASP and quality improvement initiatives across multiple sites, allowing ASPs to impact a greater number of veterans and evaluate initiatives on a larger scale. In 2019, with the anticipation of revised vancomycin dosing and monitoring guidelines, our ASPWG began to strategize the transition to AUC-based vancomycin monitoring.6 This multisite initiative showcases the strengths of implementing and evaluating practice changes as part of an ASP collaborative.
Vancomycin Dosing
The antibiotic vancomycin is used primarily for the treatment of MRSA infections.6 The 2020 consensus guidelines for vancomycin therapeutic monitoring recommend using the AUC to minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ratio as the pharmacodynamic target for serious MRSA infections, with an AUC/MIC goal of 400 to 600 mcg*h/mL.6 Prior guidelines recommended using vancomycin trough concentrations of 15 to 20 mcg/mL as a surrogate for this AUC target. However, subsequent studies have shown that trough-based dosing is associated with higher vancomycin exposures, supratherapeutic AUCs, and increased risk of vancomycin-associated acute kidney injury (AKI).7,8 Therefore, more direct AUC estimation is now recommended.6 The preferred approach for AUC calculations is through Bayesian modeling. Due to limited resources and software availability, many facilities use an alternative method involving 2 postdistributive serum vancomycin concentrations and first-order pharmacokinetic equations. This approach can optimize vancomycin dosing but is more mathematically and logistically challenging. Transitioning from troughto AUC-based vancomycin monitoring requires careful planning and comprehensive staff education.
In 2019, the VISN 8 ASPWG created a comprehensive vancomycin AUC toolkit to facilitate implementation. Components included a pharmacokinetic management policy and procedure, a vancomycin dosing guide, a progress note template, educational materials specific to pharmacy, nursing, laboratory, and medical services, a pharmacist competency examination, and a vancomycin AUC calculator (eAppendix). Each component was developed by a subgroup with the understanding that sites could incorporate variations based on local practices and needs.

The vancomycin AUC calculator was developed to be user-friendly and included safety validation protocols to prevent the entry of erroneous data (eg, unrealistic patient weight or laboratory values). The calculator allowed users to copy data into the electronic health record to avoid manual transcription errors and improve operational efficiency. It offered suggested volume of distribution estimates and 2 methods to estimate elimination constant (Ke ) depending on the patient’s weight.9,10 Creatinine clearance could be estimated using serum creatinine or cystatin C and considered amputation history. The default AUC goal in the calculator was 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL. This range was chosen based on consensus guidelines, data suggesting increased risk of AKI with AUCs > 515 mcg*h/mL, and the preference for conservative empiric dosing in the generally older VA population.11 The calculator suggested loading doses of about 25 mg/kg with a 2500 mg limit. VHA facilities could make limited modifications to the calculator based on local policies and procedures (eg, adjusting default infusion times or a dosing intervals).
The VISN 8 Pharmacy Pharmacokinetic Dosing Manual was developed as a comprehensive document to guide pharmacy staff with dosing vancomycin across diverse patient populations. This document included recommendations for renal function assessment, patient-specific considerations when choosing an empiric vancomycin dose, methods of ordering vancomycin peak, trough, and surveillance levels, dose determination based on 2 levels, and other clinical insights or frequently asked questions.
ASPWG members presented an accredited continuing education webinar for pharmacists, which reviewed the rationale for AUC-targeted dosing, changes to the current pharmacokinetic dosing program, case-based scenarios across various patient populations, and potential challenges associated with vancomycin AUC-based dosing. A recording of the live training was also made available. A vancomycin AUC dosing competency test was developed with 11 basic pharmacokinetic and case-based questions and comprehensive explanations provided for each answer.
VHA facilities implemented AUC dosing in a staggered manner, allowing for lessons learned at earlier adopters to be addressed proactively at later sites. The dosing calculator and education documents were updated iteratively as opportunities for improvement were discovered. ASPWG members held local office hours to address questions or concerns from staff at their facilities. Sharing standardized materials across the VISN reduced individual site workload and complications in rolling out this complex new process.
VISN-WIDE QUALITY ASSURANCE
At the time of project conception, 4 of 7 VISN 8 health systems had transitioned to AUC-based dosing. A quality assurance protocol to compare patient outcomes before and after changing to AUC dosing was developed. Each site followed local protocols for project approval and data were deidentified, collected, and aggregated for analysis.
The primary objectives were to compare the incidence of AKI and persistent bacteremia and assess rates of AUC target attainment (400-600 mcg*h/mL) in the AUC-based and trough-based dosing groups.6 Data for both groups included anthropomorphic measurements, serum creatinine, amputation status, vancomycin dosing, and infection characteristics. The X2 test was used for categorical data and the t test was used for continuous data. A 2-tailed α of 0.05 was used to determine significance. Each site sequentially reviewed all patients receiving ≥ 48 hours of intravenous vancomycin over a 3-month period and contributed up to 50 patients for each group. Due to staggered implementation, the study periods for sites spanned 2018 to 2023. A minimum 6-month washout period was observed between the trough and AUC groups at each site. Patients were excluded if pregnant, receiving renal replacement therapy, or presenting with AKI at the time of vancomycin initiation.
There were 168 patients in the AUC group and 172 patients in the trough group (Table 1). The rate of AUC target attainment with the initial dosing regimen varied across sites from 18% to 69% (mean, 48%). Total daily vancomycin exposure was lower in the AUC group compared with the trough group (2402 mg vs 2605 mg, respectively), with AUC-dosed patients being less likely to experience troughs level ≥ 15 or 20 mcg/mL (Table 2). There was a statistically significant lower rate of AKI in the AUC group: 2.4% in the AUC group (range, 2%-3%) vs 10.4% (range 7%-12%) in the trough group (P = .002). Rates of AKI were comparable to those observed in previous interventions.6 There was no statistical difference in length of stay, time to blood culture clearance, or rate of persistent bacteremia in the 2 groups, but these assessments were limited by sample size.
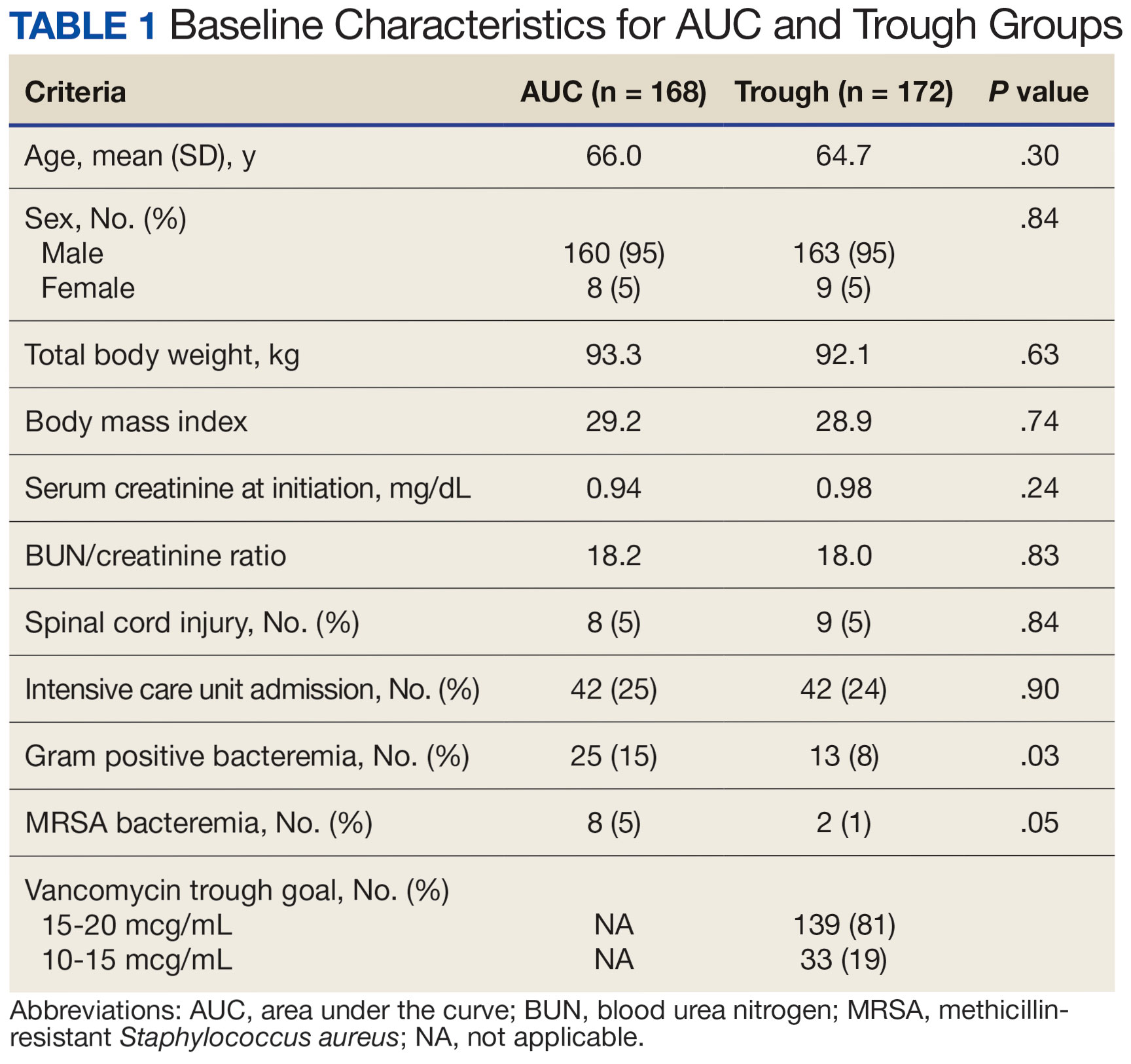

We did not anticipate such variability in initial target attainment across sites. The multisite quality assurance design allowed for qualitative evaluation of variability in dosing practices, which likely arose from sites and individual pharmacists having some flexibility in adjusting dosing tool parameters. Further analysis revealed that the facility with low initial target attainment was not routinely utilizing vancomycin loading doses. Sites routinely use robust loading doses achieved earlier and more consistent target attainment. Some sites used a narrower AUC target range in certain clinical scenarios (eg, > 500 mcg*h/mL for septic patients and < 500 mcg*h/mL for patients with less severe infections) rather than the 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL range for all patients. Sites targeting broader AUC ranges for all patients had higher rates of target attainment. Reviewing differences among sites allowed the ASPWG to identify best practices to optimize future care.
CONCLUSIONS
VHA ASPs must meet the standards outlined in VHA Directive 1031, including the new requirement for each VISN to develop an ASP collaborative. The VISN 8 ASPWG demonstrates how ASP champions can collaborate to solve common issues, complete tasks, explore new infectious diseases concepts, and impact large veteran populations. Furthermore, ASP collaboratives can harness their collective size to complete robust quality assurance evaluations that might otherwise be underpowered if completed at a single center. A limitation of the collaborative model is that a site with a robust ASP may already have specific practices in place. Expanding the ASP collaborative model further highlights the VHA role as a nationwide leader in ASP best practices.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. Updated December 2019. Accessed September 10, 2024. https:// www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/media/pdfs/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Antimicrobial stewardship programs. Updated September 22, 2023. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11458
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration. Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/visns.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Integrated Service Networks, VISN 08. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://department.va.gov/integrated-service-networks/visn-08/
- Andreev I. What is collaborative learning? Theory, examples of activities. Valamis. Updated July 10, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.valamis.com/hub/collaborative-learning
- Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infections: a revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77(11):835-864. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxaa036
- Finch NA, Zasowski EJ, Murray KP, et al. A quasi-experiment to study the impact of vancomycin area under the concentration-time curve-guided dosing on vancomycinassociated nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(12):e01293-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01293-17
- Zasowski EJ, Murray KP, Trinh TD, et al. Identification of vancomycin exposure-toxicity thresholds in hospitalized patients receiving intravenous vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;62(1):e01684-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01684-17
- Matzke GR, Kovarik JM, Rybak MJ, Boike SC. Evaluation of the vancomycin-clearance: creatinine-clearance relationship for predicting vancomycin dosage. Clin Pharm. 1985;4(3):311-315.
- Crass RL, Dunn R, Hong J, Krop LC, Pai MP. Dosing vancomycin in the super obese: less is more. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(11):3081-3086. doi:10.1093/jac/dky310
- Lodise TP, Rosenkranz SL, Finnemeyer M, et al. The emperor’s new clothes: prospective observational evaluation of the association between initial vancomycIn exposure and failure rates among adult hospitalized patients with methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections (PROVIDE). Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(8):1536-1545. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz460
Antimicrobial resistance is a global threat and burden to health care, with > 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occurring annually in the United States.1 To combat this issue and improve patient care, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has implemented antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) across its health care systems. ASPs are multidisciplinary teams that promote evidence-based use of antimicrobials through activities supporting appropriate selection, dosing, route, and duration of antimicrobial therapy. ASP best practices are also included in the Joint Commission and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services accreditation standards.2
The foundational charge for VA facilities to develop and maintain ASPs was outlined in 2014 and updated in 2023 in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1031 on antimicrobial stewardship programs.2 This directive outlines specific requirements for all VA ASPs, including personnel, staffing levels, and the roles and responsibilities of all team members. VHA now requires that Veterans Integrated Services Networks (VISNs) establish robust ASP collaboratives. A VISN ASP collaborative consists of stewardship champions from each VA medical center in the VISN and is designed to support, develop, and enhance ASP programs across all facilities within that VISN.2 Some VISNs may lack an ASP collaborative altogether, and others with existing groups may seek ways to expand their collaboratives in line with the updated directive. Prior to VHA Directive 1031, the VA Sunshine Healthcare Network (VISN 8) established an ASP collaborative. This article describes the structure and activities of the VISN 8 ASP collaborative and highlights a recent VISN 8 quality assurance initiative related to vancomycin area under the curve (AUC) dosing that illustrates how ASP collaboratives can enhance stewardship and clinical care across broad geographic areas.
VISN 8 ASP
The VHA, the largest integrated US health care system, is divided into 18 VISNs that provide regional systems of care to enhance access and meet the local health care needs of veterans.3 VISN 8 serves > 1.5 million veterans across 165,759 km2 in Florida, South Georgia, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands.4 The network is composed of 7 health systems with 8 medical centers and > 60 outpatient clinics. These facilities provide comprehensive acute, primary, and specialty care, as well as mental health and extended care services in inpatient, outpatient, nursing home, and home care settings.4
The 2023 VHA Directive 1031 update recognizes the importance of VISN-level coordination of ASP activities to enhance the standardization of care and build partnerships in stewardship across all levels of care. The VISN 8 ASP collaborative workgroup (ASPWG) was established in 2015. Consistent with Directive 1031, the ASPWG is guided by clinician and pharmacist VISN leads. These leads serve as subject matter experts, facilitate access to resources, establish VISN-level consensus, and enhance communication among local ASP champions at medical centers within the VISN. All 7 health systems include = 1 ASP champion (clinician or pharmacist) in the ASPWG. Ad hoc members, whose routine duties are not solely focused on antimicrobial stewardship, contribute to specific stewardship projects as needed. For example, the ASPWG has included internal medicine, emergency department, community living center pharmacists, representatives from pharmacy administration, and trainees (pharmacy students and residents, and infectious diseases fellows) in antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. The inclusion of non-ASP champions is not discussed in VHA Directive 1031. However, these members have made valuable contributions to the ASPWG.
The ASPWG meets monthly. Agendas and priorities are developed by the VISN pharmacist and health care practitioner (HCP) leads. Monthly discussions may include but are not limited to a review of national formulary decisions, VISN goals and metrics, infectious diseases hot topics, pharmacoeconomic initiatives, strong practice presentations, regulatory and accreditation preparation, preparation of tracking reports, as well as the development of both patient-level and HCPlevel tools, resources, and education materials. This forum facilitates collaborative learning: members process and synthesize information, share and reframe ideas, and listen to other viewpoints to gain a complete understanding as a group.5 For example, ASPWG members have leaned on each other to prepare for Joint Commission accreditation surveys and strengthen the VISN 8 COVID-19 program through the rollout of vaccines and treatments. Other collaborative projects completed over the past few years included a penicillin allergy testing initiative and anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and pseudomonal medication use evaluations. This team-centric problem-solving approach is highly effective while also fostering professional and social relationships. However, collaboratives could be perceived to have drawbacks. There may be opportunity costs if ASP time is allocated for issues that have already been addressed locally or concerns that standardization might hinder rapid adoption of practices at individual sites. Therefore, participation in each distinct group initiative is optional. This allows sites to choose projects related to their high priority areas and maintain bandwidth to implement practices not yet adopted by the larger group.
The ASPWG tracks metrics related to antimicrobial use with quarterly data presented by the VISN pharmacist lead. Both inpatient and outpatient metrics are evaluated, such as days of therapy per 1000 days and outpatient antibiotic prescriptions per 1000 unique patients. Facilities are benchmarked against their own historical data and other VISN sites, as well as other VISNs across the country. When outliers are identified, facilities are encouraged to conduct local projects to identify reasons for different antimicrobial use patterns and subsequent initiatives to optimize antimicrobial use. Benchmarking against VISN facilities can be useful since VISN facilities may be more similar than facilities in different geographic regions. Each year, the ASPWG reviews the current metrics, makes adjustments to address VISN priorities, and votes for approval of the metrics that will be tracked in the coming year.
Participation in an ASP collaborative streamlines the rollout of ASP and quality improvement initiatives across multiple sites, allowing ASPs to impact a greater number of veterans and evaluate initiatives on a larger scale. In 2019, with the anticipation of revised vancomycin dosing and monitoring guidelines, our ASPWG began to strategize the transition to AUC-based vancomycin monitoring.6 This multisite initiative showcases the strengths of implementing and evaluating practice changes as part of an ASP collaborative.
Vancomycin Dosing
The antibiotic vancomycin is used primarily for the treatment of MRSA infections.6 The 2020 consensus guidelines for vancomycin therapeutic monitoring recommend using the AUC to minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ratio as the pharmacodynamic target for serious MRSA infections, with an AUC/MIC goal of 400 to 600 mcg*h/mL.6 Prior guidelines recommended using vancomycin trough concentrations of 15 to 20 mcg/mL as a surrogate for this AUC target. However, subsequent studies have shown that trough-based dosing is associated with higher vancomycin exposures, supratherapeutic AUCs, and increased risk of vancomycin-associated acute kidney injury (AKI).7,8 Therefore, more direct AUC estimation is now recommended.6 The preferred approach for AUC calculations is through Bayesian modeling. Due to limited resources and software availability, many facilities use an alternative method involving 2 postdistributive serum vancomycin concentrations and first-order pharmacokinetic equations. This approach can optimize vancomycin dosing but is more mathematically and logistically challenging. Transitioning from troughto AUC-based vancomycin monitoring requires careful planning and comprehensive staff education.
In 2019, the VISN 8 ASPWG created a comprehensive vancomycin AUC toolkit to facilitate implementation. Components included a pharmacokinetic management policy and procedure, a vancomycin dosing guide, a progress note template, educational materials specific to pharmacy, nursing, laboratory, and medical services, a pharmacist competency examination, and a vancomycin AUC calculator (eAppendix). Each component was developed by a subgroup with the understanding that sites could incorporate variations based on local practices and needs.

The vancomycin AUC calculator was developed to be user-friendly and included safety validation protocols to prevent the entry of erroneous data (eg, unrealistic patient weight or laboratory values). The calculator allowed users to copy data into the electronic health record to avoid manual transcription errors and improve operational efficiency. It offered suggested volume of distribution estimates and 2 methods to estimate elimination constant (Ke ) depending on the patient’s weight.9,10 Creatinine clearance could be estimated using serum creatinine or cystatin C and considered amputation history. The default AUC goal in the calculator was 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL. This range was chosen based on consensus guidelines, data suggesting increased risk of AKI with AUCs > 515 mcg*h/mL, and the preference for conservative empiric dosing in the generally older VA population.11 The calculator suggested loading doses of about 25 mg/kg with a 2500 mg limit. VHA facilities could make limited modifications to the calculator based on local policies and procedures (eg, adjusting default infusion times or a dosing intervals).
The VISN 8 Pharmacy Pharmacokinetic Dosing Manual was developed as a comprehensive document to guide pharmacy staff with dosing vancomycin across diverse patient populations. This document included recommendations for renal function assessment, patient-specific considerations when choosing an empiric vancomycin dose, methods of ordering vancomycin peak, trough, and surveillance levels, dose determination based on 2 levels, and other clinical insights or frequently asked questions.
ASPWG members presented an accredited continuing education webinar for pharmacists, which reviewed the rationale for AUC-targeted dosing, changes to the current pharmacokinetic dosing program, case-based scenarios across various patient populations, and potential challenges associated with vancomycin AUC-based dosing. A recording of the live training was also made available. A vancomycin AUC dosing competency test was developed with 11 basic pharmacokinetic and case-based questions and comprehensive explanations provided for each answer.
VHA facilities implemented AUC dosing in a staggered manner, allowing for lessons learned at earlier adopters to be addressed proactively at later sites. The dosing calculator and education documents were updated iteratively as opportunities for improvement were discovered. ASPWG members held local office hours to address questions or concerns from staff at their facilities. Sharing standardized materials across the VISN reduced individual site workload and complications in rolling out this complex new process.
VISN-WIDE QUALITY ASSURANCE
At the time of project conception, 4 of 7 VISN 8 health systems had transitioned to AUC-based dosing. A quality assurance protocol to compare patient outcomes before and after changing to AUC dosing was developed. Each site followed local protocols for project approval and data were deidentified, collected, and aggregated for analysis.
The primary objectives were to compare the incidence of AKI and persistent bacteremia and assess rates of AUC target attainment (400-600 mcg*h/mL) in the AUC-based and trough-based dosing groups.6 Data for both groups included anthropomorphic measurements, serum creatinine, amputation status, vancomycin dosing, and infection characteristics. The X2 test was used for categorical data and the t test was used for continuous data. A 2-tailed α of 0.05 was used to determine significance. Each site sequentially reviewed all patients receiving ≥ 48 hours of intravenous vancomycin over a 3-month period and contributed up to 50 patients for each group. Due to staggered implementation, the study periods for sites spanned 2018 to 2023. A minimum 6-month washout period was observed between the trough and AUC groups at each site. Patients were excluded if pregnant, receiving renal replacement therapy, or presenting with AKI at the time of vancomycin initiation.
There were 168 patients in the AUC group and 172 patients in the trough group (Table 1). The rate of AUC target attainment with the initial dosing regimen varied across sites from 18% to 69% (mean, 48%). Total daily vancomycin exposure was lower in the AUC group compared with the trough group (2402 mg vs 2605 mg, respectively), with AUC-dosed patients being less likely to experience troughs level ≥ 15 or 20 mcg/mL (Table 2). There was a statistically significant lower rate of AKI in the AUC group: 2.4% in the AUC group (range, 2%-3%) vs 10.4% (range 7%-12%) in the trough group (P = .002). Rates of AKI were comparable to those observed in previous interventions.6 There was no statistical difference in length of stay, time to blood culture clearance, or rate of persistent bacteremia in the 2 groups, but these assessments were limited by sample size.


We did not anticipate such variability in initial target attainment across sites. The multisite quality assurance design allowed for qualitative evaluation of variability in dosing practices, which likely arose from sites and individual pharmacists having some flexibility in adjusting dosing tool parameters. Further analysis revealed that the facility with low initial target attainment was not routinely utilizing vancomycin loading doses. Sites routinely use robust loading doses achieved earlier and more consistent target attainment. Some sites used a narrower AUC target range in certain clinical scenarios (eg, > 500 mcg*h/mL for septic patients and < 500 mcg*h/mL for patients with less severe infections) rather than the 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL range for all patients. Sites targeting broader AUC ranges for all patients had higher rates of target attainment. Reviewing differences among sites allowed the ASPWG to identify best practices to optimize future care.
CONCLUSIONS
VHA ASPs must meet the standards outlined in VHA Directive 1031, including the new requirement for each VISN to develop an ASP collaborative. The VISN 8 ASPWG demonstrates how ASP champions can collaborate to solve common issues, complete tasks, explore new infectious diseases concepts, and impact large veteran populations. Furthermore, ASP collaboratives can harness their collective size to complete robust quality assurance evaluations that might otherwise be underpowered if completed at a single center. A limitation of the collaborative model is that a site with a robust ASP may already have specific practices in place. Expanding the ASP collaborative model further highlights the VHA role as a nationwide leader in ASP best practices.
Antimicrobial resistance is a global threat and burden to health care, with > 2.8 million antibiotic-resistant infections occurring annually in the United States.1 To combat this issue and improve patient care, the US Department of Veterans Affairs (VA) has implemented antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) across its health care systems. ASPs are multidisciplinary teams that promote evidence-based use of antimicrobials through activities supporting appropriate selection, dosing, route, and duration of antimicrobial therapy. ASP best practices are also included in the Joint Commission and Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services accreditation standards.2
The foundational charge for VA facilities to develop and maintain ASPs was outlined in 2014 and updated in 2023 in the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Directive 1031 on antimicrobial stewardship programs.2 This directive outlines specific requirements for all VA ASPs, including personnel, staffing levels, and the roles and responsibilities of all team members. VHA now requires that Veterans Integrated Services Networks (VISNs) establish robust ASP collaboratives. A VISN ASP collaborative consists of stewardship champions from each VA medical center in the VISN and is designed to support, develop, and enhance ASP programs across all facilities within that VISN.2 Some VISNs may lack an ASP collaborative altogether, and others with existing groups may seek ways to expand their collaboratives in line with the updated directive. Prior to VHA Directive 1031, the VA Sunshine Healthcare Network (VISN 8) established an ASP collaborative. This article describes the structure and activities of the VISN 8 ASP collaborative and highlights a recent VISN 8 quality assurance initiative related to vancomycin area under the curve (AUC) dosing that illustrates how ASP collaboratives can enhance stewardship and clinical care across broad geographic areas.
VISN 8 ASP
The VHA, the largest integrated US health care system, is divided into 18 VISNs that provide regional systems of care to enhance access and meet the local health care needs of veterans.3 VISN 8 serves > 1.5 million veterans across 165,759 km2 in Florida, South Georgia, Puerto Rico, and the US Virgin Islands.4 The network is composed of 7 health systems with 8 medical centers and > 60 outpatient clinics. These facilities provide comprehensive acute, primary, and specialty care, as well as mental health and extended care services in inpatient, outpatient, nursing home, and home care settings.4
The 2023 VHA Directive 1031 update recognizes the importance of VISN-level coordination of ASP activities to enhance the standardization of care and build partnerships in stewardship across all levels of care. The VISN 8 ASP collaborative workgroup (ASPWG) was established in 2015. Consistent with Directive 1031, the ASPWG is guided by clinician and pharmacist VISN leads. These leads serve as subject matter experts, facilitate access to resources, establish VISN-level consensus, and enhance communication among local ASP champions at medical centers within the VISN. All 7 health systems include = 1 ASP champion (clinician or pharmacist) in the ASPWG. Ad hoc members, whose routine duties are not solely focused on antimicrobial stewardship, contribute to specific stewardship projects as needed. For example, the ASPWG has included internal medicine, emergency department, community living center pharmacists, representatives from pharmacy administration, and trainees (pharmacy students and residents, and infectious diseases fellows) in antimicrobial stewardship initiatives. The inclusion of non-ASP champions is not discussed in VHA Directive 1031. However, these members have made valuable contributions to the ASPWG.
The ASPWG meets monthly. Agendas and priorities are developed by the VISN pharmacist and health care practitioner (HCP) leads. Monthly discussions may include but are not limited to a review of national formulary decisions, VISN goals and metrics, infectious diseases hot topics, pharmacoeconomic initiatives, strong practice presentations, regulatory and accreditation preparation, preparation of tracking reports, as well as the development of both patient-level and HCPlevel tools, resources, and education materials. This forum facilitates collaborative learning: members process and synthesize information, share and reframe ideas, and listen to other viewpoints to gain a complete understanding as a group.5 For example, ASPWG members have leaned on each other to prepare for Joint Commission accreditation surveys and strengthen the VISN 8 COVID-19 program through the rollout of vaccines and treatments. Other collaborative projects completed over the past few years included a penicillin allergy testing initiative and anti-methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) and pseudomonal medication use evaluations. This team-centric problem-solving approach is highly effective while also fostering professional and social relationships. However, collaboratives could be perceived to have drawbacks. There may be opportunity costs if ASP time is allocated for issues that have already been addressed locally or concerns that standardization might hinder rapid adoption of practices at individual sites. Therefore, participation in each distinct group initiative is optional. This allows sites to choose projects related to their high priority areas and maintain bandwidth to implement practices not yet adopted by the larger group.
The ASPWG tracks metrics related to antimicrobial use with quarterly data presented by the VISN pharmacist lead. Both inpatient and outpatient metrics are evaluated, such as days of therapy per 1000 days and outpatient antibiotic prescriptions per 1000 unique patients. Facilities are benchmarked against their own historical data and other VISN sites, as well as other VISNs across the country. When outliers are identified, facilities are encouraged to conduct local projects to identify reasons for different antimicrobial use patterns and subsequent initiatives to optimize antimicrobial use. Benchmarking against VISN facilities can be useful since VISN facilities may be more similar than facilities in different geographic regions. Each year, the ASPWG reviews the current metrics, makes adjustments to address VISN priorities, and votes for approval of the metrics that will be tracked in the coming year.
Participation in an ASP collaborative streamlines the rollout of ASP and quality improvement initiatives across multiple sites, allowing ASPs to impact a greater number of veterans and evaluate initiatives on a larger scale. In 2019, with the anticipation of revised vancomycin dosing and monitoring guidelines, our ASPWG began to strategize the transition to AUC-based vancomycin monitoring.6 This multisite initiative showcases the strengths of implementing and evaluating practice changes as part of an ASP collaborative.
Vancomycin Dosing
The antibiotic vancomycin is used primarily for the treatment of MRSA infections.6 The 2020 consensus guidelines for vancomycin therapeutic monitoring recommend using the AUC to minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) ratio as the pharmacodynamic target for serious MRSA infections, with an AUC/MIC goal of 400 to 600 mcg*h/mL.6 Prior guidelines recommended using vancomycin trough concentrations of 15 to 20 mcg/mL as a surrogate for this AUC target. However, subsequent studies have shown that trough-based dosing is associated with higher vancomycin exposures, supratherapeutic AUCs, and increased risk of vancomycin-associated acute kidney injury (AKI).7,8 Therefore, more direct AUC estimation is now recommended.6 The preferred approach for AUC calculations is through Bayesian modeling. Due to limited resources and software availability, many facilities use an alternative method involving 2 postdistributive serum vancomycin concentrations and first-order pharmacokinetic equations. This approach can optimize vancomycin dosing but is more mathematically and logistically challenging. Transitioning from troughto AUC-based vancomycin monitoring requires careful planning and comprehensive staff education.
In 2019, the VISN 8 ASPWG created a comprehensive vancomycin AUC toolkit to facilitate implementation. Components included a pharmacokinetic management policy and procedure, a vancomycin dosing guide, a progress note template, educational materials specific to pharmacy, nursing, laboratory, and medical services, a pharmacist competency examination, and a vancomycin AUC calculator (eAppendix). Each component was developed by a subgroup with the understanding that sites could incorporate variations based on local practices and needs.

The vancomycin AUC calculator was developed to be user-friendly and included safety validation protocols to prevent the entry of erroneous data (eg, unrealistic patient weight or laboratory values). The calculator allowed users to copy data into the electronic health record to avoid manual transcription errors and improve operational efficiency. It offered suggested volume of distribution estimates and 2 methods to estimate elimination constant (Ke ) depending on the patient’s weight.9,10 Creatinine clearance could be estimated using serum creatinine or cystatin C and considered amputation history. The default AUC goal in the calculator was 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL. This range was chosen based on consensus guidelines, data suggesting increased risk of AKI with AUCs > 515 mcg*h/mL, and the preference for conservative empiric dosing in the generally older VA population.11 The calculator suggested loading doses of about 25 mg/kg with a 2500 mg limit. VHA facilities could make limited modifications to the calculator based on local policies and procedures (eg, adjusting default infusion times or a dosing intervals).
The VISN 8 Pharmacy Pharmacokinetic Dosing Manual was developed as a comprehensive document to guide pharmacy staff with dosing vancomycin across diverse patient populations. This document included recommendations for renal function assessment, patient-specific considerations when choosing an empiric vancomycin dose, methods of ordering vancomycin peak, trough, and surveillance levels, dose determination based on 2 levels, and other clinical insights or frequently asked questions.
ASPWG members presented an accredited continuing education webinar for pharmacists, which reviewed the rationale for AUC-targeted dosing, changes to the current pharmacokinetic dosing program, case-based scenarios across various patient populations, and potential challenges associated with vancomycin AUC-based dosing. A recording of the live training was also made available. A vancomycin AUC dosing competency test was developed with 11 basic pharmacokinetic and case-based questions and comprehensive explanations provided for each answer.
VHA facilities implemented AUC dosing in a staggered manner, allowing for lessons learned at earlier adopters to be addressed proactively at later sites. The dosing calculator and education documents were updated iteratively as opportunities for improvement were discovered. ASPWG members held local office hours to address questions or concerns from staff at their facilities. Sharing standardized materials across the VISN reduced individual site workload and complications in rolling out this complex new process.
VISN-WIDE QUALITY ASSURANCE
At the time of project conception, 4 of 7 VISN 8 health systems had transitioned to AUC-based dosing. A quality assurance protocol to compare patient outcomes before and after changing to AUC dosing was developed. Each site followed local protocols for project approval and data were deidentified, collected, and aggregated for analysis.
The primary objectives were to compare the incidence of AKI and persistent bacteremia and assess rates of AUC target attainment (400-600 mcg*h/mL) in the AUC-based and trough-based dosing groups.6 Data for both groups included anthropomorphic measurements, serum creatinine, amputation status, vancomycin dosing, and infection characteristics. The X2 test was used for categorical data and the t test was used for continuous data. A 2-tailed α of 0.05 was used to determine significance. Each site sequentially reviewed all patients receiving ≥ 48 hours of intravenous vancomycin over a 3-month period and contributed up to 50 patients for each group. Due to staggered implementation, the study periods for sites spanned 2018 to 2023. A minimum 6-month washout period was observed between the trough and AUC groups at each site. Patients were excluded if pregnant, receiving renal replacement therapy, or presenting with AKI at the time of vancomycin initiation.
There were 168 patients in the AUC group and 172 patients in the trough group (Table 1). The rate of AUC target attainment with the initial dosing regimen varied across sites from 18% to 69% (mean, 48%). Total daily vancomycin exposure was lower in the AUC group compared with the trough group (2402 mg vs 2605 mg, respectively), with AUC-dosed patients being less likely to experience troughs level ≥ 15 or 20 mcg/mL (Table 2). There was a statistically significant lower rate of AKI in the AUC group: 2.4% in the AUC group (range, 2%-3%) vs 10.4% (range 7%-12%) in the trough group (P = .002). Rates of AKI were comparable to those observed in previous interventions.6 There was no statistical difference in length of stay, time to blood culture clearance, or rate of persistent bacteremia in the 2 groups, but these assessments were limited by sample size.


We did not anticipate such variability in initial target attainment across sites. The multisite quality assurance design allowed for qualitative evaluation of variability in dosing practices, which likely arose from sites and individual pharmacists having some flexibility in adjusting dosing tool parameters. Further analysis revealed that the facility with low initial target attainment was not routinely utilizing vancomycin loading doses. Sites routinely use robust loading doses achieved earlier and more consistent target attainment. Some sites used a narrower AUC target range in certain clinical scenarios (eg, > 500 mcg*h/mL for septic patients and < 500 mcg*h/mL for patients with less severe infections) rather than the 400 to 550 mcg*h/mL range for all patients. Sites targeting broader AUC ranges for all patients had higher rates of target attainment. Reviewing differences among sites allowed the ASPWG to identify best practices to optimize future care.
CONCLUSIONS
VHA ASPs must meet the standards outlined in VHA Directive 1031, including the new requirement for each VISN to develop an ASP collaborative. The VISN 8 ASPWG demonstrates how ASP champions can collaborate to solve common issues, complete tasks, explore new infectious diseases concepts, and impact large veteran populations. Furthermore, ASP collaboratives can harness their collective size to complete robust quality assurance evaluations that might otherwise be underpowered if completed at a single center. A limitation of the collaborative model is that a site with a robust ASP may already have specific practices in place. Expanding the ASP collaborative model further highlights the VHA role as a nationwide leader in ASP best practices.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. Updated December 2019. Accessed September 10, 2024. https:// www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/media/pdfs/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Antimicrobial stewardship programs. Updated September 22, 2023. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11458
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration. Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/visns.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Integrated Service Networks, VISN 08. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://department.va.gov/integrated-service-networks/visn-08/
- Andreev I. What is collaborative learning? Theory, examples of activities. Valamis. Updated July 10, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.valamis.com/hub/collaborative-learning
- Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infections: a revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77(11):835-864. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxaa036
- Finch NA, Zasowski EJ, Murray KP, et al. A quasi-experiment to study the impact of vancomycin area under the concentration-time curve-guided dosing on vancomycinassociated nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(12):e01293-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01293-17
- Zasowski EJ, Murray KP, Trinh TD, et al. Identification of vancomycin exposure-toxicity thresholds in hospitalized patients receiving intravenous vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;62(1):e01684-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01684-17
- Matzke GR, Kovarik JM, Rybak MJ, Boike SC. Evaluation of the vancomycin-clearance: creatinine-clearance relationship for predicting vancomycin dosage. Clin Pharm. 1985;4(3):311-315.
- Crass RL, Dunn R, Hong J, Krop LC, Pai MP. Dosing vancomycin in the super obese: less is more. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(11):3081-3086. doi:10.1093/jac/dky310
- Lodise TP, Rosenkranz SL, Finnemeyer M, et al. The emperor’s new clothes: prospective observational evaluation of the association between initial vancomycIn exposure and failure rates among adult hospitalized patients with methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections (PROVIDE). Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(8):1536-1545. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz460
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Antibiotic resistance threats in the United States, 2019. Updated December 2019. Accessed September 10, 2024. https:// www.cdc.gov/antimicrobial-resistance/media/pdfs/2019-ar-threats-report-508.pdf
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Antimicrobial stewardship programs. Updated September 22, 2023. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.va.gov/vhapublications/ViewPublication.asp?pub_ID=11458
- US Department of Veterans Affairs, Veteran Health Administration. Veterans Integrated Service Networks (VISNs). Accessed September 13, 2024. https://www.va.gov/HEALTH/visns.asp
- US Department of Veterans Affairs. Veterans Health Administration, Veterans Integrated Service Networks, VISN 08. Updated September 10, 2024. Accessed September 13, 2024. https://department.va.gov/integrated-service-networks/visn-08/
- Andreev I. What is collaborative learning? Theory, examples of activities. Valamis. Updated July 10, 2024. Accessed September 10, 2024. https://www.valamis.com/hub/collaborative-learning
- Rybak MJ, Le J, Lodise TP, et al. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin for serious methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus infections: a revised consensus guideline and review by the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2020;77(11):835-864. doi:10.1093/ajhp/zxaa036
- Finch NA, Zasowski EJ, Murray KP, et al. A quasi-experiment to study the impact of vancomycin area under the concentration-time curve-guided dosing on vancomycinassociated nephrotoxicity. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;61(12):e01293-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01293-17
- Zasowski EJ, Murray KP, Trinh TD, et al. Identification of vancomycin exposure-toxicity thresholds in hospitalized patients receiving intravenous vancomycin. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017;62(1):e01684-17. doi:10.1128/AAC.01684-17
- Matzke GR, Kovarik JM, Rybak MJ, Boike SC. Evaluation of the vancomycin-clearance: creatinine-clearance relationship for predicting vancomycin dosage. Clin Pharm. 1985;4(3):311-315.
- Crass RL, Dunn R, Hong J, Krop LC, Pai MP. Dosing vancomycin in the super obese: less is more. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2018;73(11):3081-3086. doi:10.1093/jac/dky310
- Lodise TP, Rosenkranz SL, Finnemeyer M, et al. The emperor’s new clothes: prospective observational evaluation of the association between initial vancomycIn exposure and failure rates among adult hospitalized patients with methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections (PROVIDE). Clin Infect Dis. 2020;70(8):1536-1545. doi:10.1093/cid/ciz460
Implementation of a Prior Authorization Drug Review Process for Care in the Community Oncology Prescriptions
Background
Veterans receiving care in the community (CITC) are prescribed oral oncology medications to be filled at VA pharmacies. Many of the outpatient prescriptions written for oncology medications require a prior authorization review by a pharmacist. A standardized workflow to obtain outside records to ensure patient safety, appropriate therapeutic selections, and maximize cost avoidance was established in March 2023. This quality improvement project evaluated the implementation of a clinical peer-to-peer prescription referral process between operational and oncology clinical pharmacists (CPS) to include a prior authorization drug request (PADR) review.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was completed to assess the effectiveness of the CITC Rx review process. Patients who had a CITC PADR consult entered between April 2023 and March 2024 were included. Metrics obtained included medication ordered, diagnosis, line of treatment, date prescription received, time to PADR completion, PADR outcome, FDA approval status, and conformity to VA National Oncology Program (NOP) disease pathway. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the data.
Results
Top reasons for referral for CITC included best medical interest and drive time. Fifty-one PADR requests were submitted for 41 patients. Forty-six PADR consults were completed. Approval rate was 85%. Consults involved 32 different oncolytics, 78% had VA Pharmacy Benefits Manager criteria for use. Thirty-seven percent of the PADR requests adhered to the NOP pathways. Approximately 30% of PADR requests did not have an associated NOP pathway. Seventy-four percent of drugs had an associated FDA approval. On average, two calls were made to CITC provider by the operational pharmacist to obtain necessary information for clinical review, resulting in a 5 day time to PADR entry. The average time to PADR consult completion was 9.5 hours. Four interventions addressed drug interactions or dosing adjustments.
Conclusions
This review demonstrated the feasibility and framework for implementing a standardized peer-to-peer PADR consult review process for CITC prescriptions requiring prior authorization. Having separate intake of CITC prescriptions by the operational pharmacist who is responsible for obtaining outside records, the CPS provided a timely clinical review of PADR consults, assuring appropriate therapeutic selections to maximize cost avoidance while maintaining patient safety.
Background
Veterans receiving care in the community (CITC) are prescribed oral oncology medications to be filled at VA pharmacies. Many of the outpatient prescriptions written for oncology medications require a prior authorization review by a pharmacist. A standardized workflow to obtain outside records to ensure patient safety, appropriate therapeutic selections, and maximize cost avoidance was established in March 2023. This quality improvement project evaluated the implementation of a clinical peer-to-peer prescription referral process between operational and oncology clinical pharmacists (CPS) to include a prior authorization drug request (PADR) review.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was completed to assess the effectiveness of the CITC Rx review process. Patients who had a CITC PADR consult entered between April 2023 and March 2024 were included. Metrics obtained included medication ordered, diagnosis, line of treatment, date prescription received, time to PADR completion, PADR outcome, FDA approval status, and conformity to VA National Oncology Program (NOP) disease pathway. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the data.
Results
Top reasons for referral for CITC included best medical interest and drive time. Fifty-one PADR requests were submitted for 41 patients. Forty-six PADR consults were completed. Approval rate was 85%. Consults involved 32 different oncolytics, 78% had VA Pharmacy Benefits Manager criteria for use. Thirty-seven percent of the PADR requests adhered to the NOP pathways. Approximately 30% of PADR requests did not have an associated NOP pathway. Seventy-four percent of drugs had an associated FDA approval. On average, two calls were made to CITC provider by the operational pharmacist to obtain necessary information for clinical review, resulting in a 5 day time to PADR entry. The average time to PADR consult completion was 9.5 hours. Four interventions addressed drug interactions or dosing adjustments.
Conclusions
This review demonstrated the feasibility and framework for implementing a standardized peer-to-peer PADR consult review process for CITC prescriptions requiring prior authorization. Having separate intake of CITC prescriptions by the operational pharmacist who is responsible for obtaining outside records, the CPS provided a timely clinical review of PADR consults, assuring appropriate therapeutic selections to maximize cost avoidance while maintaining patient safety.
Background
Veterans receiving care in the community (CITC) are prescribed oral oncology medications to be filled at VA pharmacies. Many of the outpatient prescriptions written for oncology medications require a prior authorization review by a pharmacist. A standardized workflow to obtain outside records to ensure patient safety, appropriate therapeutic selections, and maximize cost avoidance was established in March 2023. This quality improvement project evaluated the implementation of a clinical peer-to-peer prescription referral process between operational and oncology clinical pharmacists (CPS) to include a prior authorization drug request (PADR) review.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was completed to assess the effectiveness of the CITC Rx review process. Patients who had a CITC PADR consult entered between April 2023 and March 2024 were included. Metrics obtained included medication ordered, diagnosis, line of treatment, date prescription received, time to PADR completion, PADR outcome, FDA approval status, and conformity to VA National Oncology Program (NOP) disease pathway. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the data.
Results
Top reasons for referral for CITC included best medical interest and drive time. Fifty-one PADR requests were submitted for 41 patients. Forty-six PADR consults were completed. Approval rate was 85%. Consults involved 32 different oncolytics, 78% had VA Pharmacy Benefits Manager criteria for use. Thirty-seven percent of the PADR requests adhered to the NOP pathways. Approximately 30% of PADR requests did not have an associated NOP pathway. Seventy-four percent of drugs had an associated FDA approval. On average, two calls were made to CITC provider by the operational pharmacist to obtain necessary information for clinical review, resulting in a 5 day time to PADR entry. The average time to PADR consult completion was 9.5 hours. Four interventions addressed drug interactions or dosing adjustments.
Conclusions
This review demonstrated the feasibility and framework for implementing a standardized peer-to-peer PADR consult review process for CITC prescriptions requiring prior authorization. Having separate intake of CITC prescriptions by the operational pharmacist who is responsible for obtaining outside records, the CPS provided a timely clinical review of PADR consults, assuring appropriate therapeutic selections to maximize cost avoidance while maintaining patient safety.
The OCTAGON Project: A Novel VA-Based Telehealth Intervention for Oral Chemotherapy Monitoring
Background
Many Veterans with cancer experience substantial side effects related to their chemotherapy treatments resulting in impaired quality of life. Prompt management of such symptoms can improve adherence to therapy and potentially clinical outcomes. Previous studies in cancer patients have shown that mobile apps can improve symptom management and quality of life, though there are limited studies using oncology-focused apps in the VA population. The VA Annie App is an optimal platform for Veterans since it relies primarily on SMS-based texting and not on internet capabilities. This would address several well-known barriers to Veterans’ care access (limited internet connectivity, transportation) and enhance symptom reporting between infrequent provider visits. Providers can securely collect app responses within the VA system and there is already considerable VA developer experience with designing complex protocols. The OCTAGON project (Optimizing Cancer Care with Telehealth Assessment for Goal-Oriented Needs) will have the following goals: 1) To develop Annie App protocols to assist in management of cancer and/or chemotherapy-related symptoms (OCTAGON intervention), 2) To examine initial acceptability, feasibility, and Veteran-reported outcomes, 3) To explore short term effects on the utilization of VA encounters.
Methods
All patients who are primarily being managed at the VA Ann Arbor for their cancer therapy and are receiving one of the following therapies are considered eligible: EGFR inhibitors (lung cancer), antiandrogen therapies (prostate cancer), BTK inhibitors (lymphoma).
Discussion
Drug-specific protocols will be developed in conjunction with clinical pharmacists with experience in outpatient oral chemotherapy toxicity monitoring. Questions will have either a Yes/No, or numerical response. Interventions will be administered weekly for the first 3 months after enrollment, then decrease to monthly for a total of 6 months on protocol. Patients will be directed to contact their providers with any significant changes in tolerability. Planned data collected will include intervention question responses, adverse events, demographics, diagnosis, disease response, hospitalizations, treatment dose reductions or interruptions, provider and staff utilization. Survey responses to assess treatment acceptability (Treatment Acceptability/Adherence Scale), usability (System Usability Scale), general health (PROMIS-GH), and patient satisfaction will also be collected. Funding: VA Telehealth Research and Innovation for Veterans with Cancer (THRIVE).
Background
Many Veterans with cancer experience substantial side effects related to their chemotherapy treatments resulting in impaired quality of life. Prompt management of such symptoms can improve adherence to therapy and potentially clinical outcomes. Previous studies in cancer patients have shown that mobile apps can improve symptom management and quality of life, though there are limited studies using oncology-focused apps in the VA population. The VA Annie App is an optimal platform for Veterans since it relies primarily on SMS-based texting and not on internet capabilities. This would address several well-known barriers to Veterans’ care access (limited internet connectivity, transportation) and enhance symptom reporting between infrequent provider visits. Providers can securely collect app responses within the VA system and there is already considerable VA developer experience with designing complex protocols. The OCTAGON project (Optimizing Cancer Care with Telehealth Assessment for Goal-Oriented Needs) will have the following goals: 1) To develop Annie App protocols to assist in management of cancer and/or chemotherapy-related symptoms (OCTAGON intervention), 2) To examine initial acceptability, feasibility, and Veteran-reported outcomes, 3) To explore short term effects on the utilization of VA encounters.
Methods
All patients who are primarily being managed at the VA Ann Arbor for their cancer therapy and are receiving one of the following therapies are considered eligible: EGFR inhibitors (lung cancer), antiandrogen therapies (prostate cancer), BTK inhibitors (lymphoma).
Discussion
Drug-specific protocols will be developed in conjunction with clinical pharmacists with experience in outpatient oral chemotherapy toxicity monitoring. Questions will have either a Yes/No, or numerical response. Interventions will be administered weekly for the first 3 months after enrollment, then decrease to monthly for a total of 6 months on protocol. Patients will be directed to contact their providers with any significant changes in tolerability. Planned data collected will include intervention question responses, adverse events, demographics, diagnosis, disease response, hospitalizations, treatment dose reductions or interruptions, provider and staff utilization. Survey responses to assess treatment acceptability (Treatment Acceptability/Adherence Scale), usability (System Usability Scale), general health (PROMIS-GH), and patient satisfaction will also be collected. Funding: VA Telehealth Research and Innovation for Veterans with Cancer (THRIVE).
Background
Many Veterans with cancer experience substantial side effects related to their chemotherapy treatments resulting in impaired quality of life. Prompt management of such symptoms can improve adherence to therapy and potentially clinical outcomes. Previous studies in cancer patients have shown that mobile apps can improve symptom management and quality of life, though there are limited studies using oncology-focused apps in the VA population. The VA Annie App is an optimal platform for Veterans since it relies primarily on SMS-based texting and not on internet capabilities. This would address several well-known barriers to Veterans’ care access (limited internet connectivity, transportation) and enhance symptom reporting between infrequent provider visits. Providers can securely collect app responses within the VA system and there is already considerable VA developer experience with designing complex protocols. The OCTAGON project (Optimizing Cancer Care with Telehealth Assessment for Goal-Oriented Needs) will have the following goals: 1) To develop Annie App protocols to assist in management of cancer and/or chemotherapy-related symptoms (OCTAGON intervention), 2) To examine initial acceptability, feasibility, and Veteran-reported outcomes, 3) To explore short term effects on the utilization of VA encounters.
Methods
All patients who are primarily being managed at the VA Ann Arbor for their cancer therapy and are receiving one of the following therapies are considered eligible: EGFR inhibitors (lung cancer), antiandrogen therapies (prostate cancer), BTK inhibitors (lymphoma).
Discussion
Drug-specific protocols will be developed in conjunction with clinical pharmacists with experience in outpatient oral chemotherapy toxicity monitoring. Questions will have either a Yes/No, or numerical response. Interventions will be administered weekly for the first 3 months after enrollment, then decrease to monthly for a total of 6 months on protocol. Patients will be directed to contact their providers with any significant changes in tolerability. Planned data collected will include intervention question responses, adverse events, demographics, diagnosis, disease response, hospitalizations, treatment dose reductions or interruptions, provider and staff utilization. Survey responses to assess treatment acceptability (Treatment Acceptability/Adherence Scale), usability (System Usability Scale), general health (PROMIS-GH), and patient satisfaction will also be collected. Funding: VA Telehealth Research and Innovation for Veterans with Cancer (THRIVE).
How to Make Keeping Up With the Drugs as Easy as Keeping Up With the Kardashians: Implementing a Local Oncology Drug Review Committee
Background
From 2000-2022 there were over 200 new drug and over 500 indication approvals specific to oncology. The rate of approvals has increased exponentially, making it difficult to maintain an up-to-date, standardized practice. Nationally, Veterans Affairs (VA) formulary decisions can take time given a lengthy approval process. Locally, the need was identified to incorporate new drugs and data into practice more rapidly. When bringing requests to the facility Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee, it was recognized that the membership consisting of non-oncology practitioners did not allow for meaningful discussion of utilization. In 2017, a dedicated oncology drug review committee (DRC) comprised of oncology practitioners and a facility formulary representative was created as a P&T workgroup. Purpose: Evaluate and describe the utility of forming a local oncology DRC to incorporate new drugs and data into practice.
Methods
DRC minutes from December 2017 to May 2023 were reviewed. Discussion items were categorized into type of review. Date of local review was compared to national formulary criteria for use publication dates, and date of FDA approval for new drugs or publication date for new data, where applicable. Items were excluded if crucial information was missing from minutes. Descriptive statistics were used.
Results
Over 65 months, 38 meetings were held. Thirty total members include: pharmacists, physicians, fellows, and advanced practice providers. Items reviewed included: 36 new drugs (ND), 36 new indications/data (NI), 14 institutional preferences, 10 new dosage form/biosimilars, 4 drug shortages and 2 others. The median time from ND approval to discussion was 3 months (n= 36, IQR 3-6) and NI from publication was 3 months (n=30, IQR 1-8). Nearly all (34/36, 94%) ND were reviewed prior to national review. Local review was a median of 7 months before national, with 11 drugs currently having no published national criteria for use (n=25, IQR 2-12).
Conclusions
DRC formation has enabled faster incorporation of new drugs/indications into practice. It has also created an appropriate forum for in-depth utilization discussions, pharmacoeconomic stewardship, and sharing of formulary and medication related information. VA Health Systems could consider implementing similar committees to review and implement up-to-date oncology practices.
Background
From 2000-2022 there were over 200 new drug and over 500 indication approvals specific to oncology. The rate of approvals has increased exponentially, making it difficult to maintain an up-to-date, standardized practice. Nationally, Veterans Affairs (VA) formulary decisions can take time given a lengthy approval process. Locally, the need was identified to incorporate new drugs and data into practice more rapidly. When bringing requests to the facility Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee, it was recognized that the membership consisting of non-oncology practitioners did not allow for meaningful discussion of utilization. In 2017, a dedicated oncology drug review committee (DRC) comprised of oncology practitioners and a facility formulary representative was created as a P&T workgroup. Purpose: Evaluate and describe the utility of forming a local oncology DRC to incorporate new drugs and data into practice.
Methods
DRC minutes from December 2017 to May 2023 were reviewed. Discussion items were categorized into type of review. Date of local review was compared to national formulary criteria for use publication dates, and date of FDA approval for new drugs or publication date for new data, where applicable. Items were excluded if crucial information was missing from minutes. Descriptive statistics were used.
Results
Over 65 months, 38 meetings were held. Thirty total members include: pharmacists, physicians, fellows, and advanced practice providers. Items reviewed included: 36 new drugs (ND), 36 new indications/data (NI), 14 institutional preferences, 10 new dosage form/biosimilars, 4 drug shortages and 2 others. The median time from ND approval to discussion was 3 months (n= 36, IQR 3-6) and NI from publication was 3 months (n=30, IQR 1-8). Nearly all (34/36, 94%) ND were reviewed prior to national review. Local review was a median of 7 months before national, with 11 drugs currently having no published national criteria for use (n=25, IQR 2-12).
Conclusions
DRC formation has enabled faster incorporation of new drugs/indications into practice. It has also created an appropriate forum for in-depth utilization discussions, pharmacoeconomic stewardship, and sharing of formulary and medication related information. VA Health Systems could consider implementing similar committees to review and implement up-to-date oncology practices.
Background
From 2000-2022 there were over 200 new drug and over 500 indication approvals specific to oncology. The rate of approvals has increased exponentially, making it difficult to maintain an up-to-date, standardized practice. Nationally, Veterans Affairs (VA) formulary decisions can take time given a lengthy approval process. Locally, the need was identified to incorporate new drugs and data into practice more rapidly. When bringing requests to the facility Pharmacy and Therapeutics (P&T) Committee, it was recognized that the membership consisting of non-oncology practitioners did not allow for meaningful discussion of utilization. In 2017, a dedicated oncology drug review committee (DRC) comprised of oncology practitioners and a facility formulary representative was created as a P&T workgroup. Purpose: Evaluate and describe the utility of forming a local oncology DRC to incorporate new drugs and data into practice.
Methods
DRC minutes from December 2017 to May 2023 were reviewed. Discussion items were categorized into type of review. Date of local review was compared to national formulary criteria for use publication dates, and date of FDA approval for new drugs or publication date for new data, where applicable. Items were excluded if crucial information was missing from minutes. Descriptive statistics were used.
Results
Over 65 months, 38 meetings were held. Thirty total members include: pharmacists, physicians, fellows, and advanced practice providers. Items reviewed included: 36 new drugs (ND), 36 new indications/data (NI), 14 institutional preferences, 10 new dosage form/biosimilars, 4 drug shortages and 2 others. The median time from ND approval to discussion was 3 months (n= 36, IQR 3-6) and NI from publication was 3 months (n=30, IQR 1-8). Nearly all (34/36, 94%) ND were reviewed prior to national review. Local review was a median of 7 months before national, with 11 drugs currently having no published national criteria for use (n=25, IQR 2-12).
Conclusions
DRC formation has enabled faster incorporation of new drugs/indications into practice. It has also created an appropriate forum for in-depth utilization discussions, pharmacoeconomic stewardship, and sharing of formulary and medication related information. VA Health Systems could consider implementing similar committees to review and implement up-to-date oncology practices.
PHASER Testing Initiative for Patients Newly Diagnosed With a GI Malignancy
Background
In December of 2023, the Survivorship Coordinator at VA Connecticut spearheaded a multidisciplinary collaboration to offer PHASER testing to all patients newly diagnosed with a GI malignancy and/ or patients with a known GI malignancy and a new recurrence that might necessitate chemotherapy. The PHASER panel includes two genes that are involved in the metabolism of two commonly used chemotherapy drugs in this patient population.
Methods
By identifying patients who may have impaired metabolism prior to starting treatment, the doses of the appropriate drugs, 5FU and irinotecan, can be adjusted if appropriate, leading to less toxicity for patients while on treatment and fewer lingering side-effects from treatment. We are tracking all of the patients who are being tested and will report quarterly to the Cancer Committee on any findings with a specific focus on whether any dose-adjustments were made to Veteran’s chemotherapy regimens as the result of this testing.
Discussion
We have developed a systematic process centered around GI tumor boards to ensure that testing is done at least two weeks prior to planned chemotherapy start-date to ensure adequate time for testing results to be received. We have developed a systematic process whereby primary care providers and pharmacists are alerted to the PHASER results and patients’ non-oncology medications are reviewed for any recommended adjustments. We will have 9 months of data to report on at AVAHO as well as lessons learned from this new quality improvement process. Despite access to pharmacogenomic testing at VA, there can be variations between VA sites in terms of uptake of this new testing. VA Connecticut’s PHASER testing initiative for patients with GI malignancies is a model that can be replicated throughout the VA. This initiative is part of a broader focus at VA Connecticut on “pre-habilitation” and pre-treatment testing that is designed to reduce toxicity of treatment and improve quality of life for cancer survivors.
Background
In December of 2023, the Survivorship Coordinator at VA Connecticut spearheaded a multidisciplinary collaboration to offer PHASER testing to all patients newly diagnosed with a GI malignancy and/ or patients with a known GI malignancy and a new recurrence that might necessitate chemotherapy. The PHASER panel includes two genes that are involved in the metabolism of two commonly used chemotherapy drugs in this patient population.
Methods
By identifying patients who may have impaired metabolism prior to starting treatment, the doses of the appropriate drugs, 5FU and irinotecan, can be adjusted if appropriate, leading to less toxicity for patients while on treatment and fewer lingering side-effects from treatment. We are tracking all of the patients who are being tested and will report quarterly to the Cancer Committee on any findings with a specific focus on whether any dose-adjustments were made to Veteran’s chemotherapy regimens as the result of this testing.
Discussion
We have developed a systematic process centered around GI tumor boards to ensure that testing is done at least two weeks prior to planned chemotherapy start-date to ensure adequate time for testing results to be received. We have developed a systematic process whereby primary care providers and pharmacists are alerted to the PHASER results and patients’ non-oncology medications are reviewed for any recommended adjustments. We will have 9 months of data to report on at AVAHO as well as lessons learned from this new quality improvement process. Despite access to pharmacogenomic testing at VA, there can be variations between VA sites in terms of uptake of this new testing. VA Connecticut’s PHASER testing initiative for patients with GI malignancies is a model that can be replicated throughout the VA. This initiative is part of a broader focus at VA Connecticut on “pre-habilitation” and pre-treatment testing that is designed to reduce toxicity of treatment and improve quality of life for cancer survivors.
Background
In December of 2023, the Survivorship Coordinator at VA Connecticut spearheaded a multidisciplinary collaboration to offer PHASER testing to all patients newly diagnosed with a GI malignancy and/ or patients with a known GI malignancy and a new recurrence that might necessitate chemotherapy. The PHASER panel includes two genes that are involved in the metabolism of two commonly used chemotherapy drugs in this patient population.
Methods
By identifying patients who may have impaired metabolism prior to starting treatment, the doses of the appropriate drugs, 5FU and irinotecan, can be adjusted if appropriate, leading to less toxicity for patients while on treatment and fewer lingering side-effects from treatment. We are tracking all of the patients who are being tested and will report quarterly to the Cancer Committee on any findings with a specific focus on whether any dose-adjustments were made to Veteran’s chemotherapy regimens as the result of this testing.
Discussion
We have developed a systematic process centered around GI tumor boards to ensure that testing is done at least two weeks prior to planned chemotherapy start-date to ensure adequate time for testing results to be received. We have developed a systematic process whereby primary care providers and pharmacists are alerted to the PHASER results and patients’ non-oncology medications are reviewed for any recommended adjustments. We will have 9 months of data to report on at AVAHO as well as lessons learned from this new quality improvement process. Despite access to pharmacogenomic testing at VA, there can be variations between VA sites in terms of uptake of this new testing. VA Connecticut’s PHASER testing initiative for patients with GI malignancies is a model that can be replicated throughout the VA. This initiative is part of a broader focus at VA Connecticut on “pre-habilitation” and pre-treatment testing that is designed to reduce toxicity of treatment and improve quality of life for cancer survivors.
Barriers from Detection to Treatment in Lung Cancer: A Single Veteran Affair Institution Review
Background
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related deaths in the United States. The impact of treatment delay proves difficult to quantify, but increased time to treatment and subsequent progression can limit a patient’s chance for curative intent therapy. Reducing time to treatment aims to improve patient outcome and experience. This study aims to identify the median timeframes that occur in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer patients within a single Veteran Affair (VA) Medical Center.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was conducted on 123 new primary lung cancer cases detected by imaging between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2022 within a single VA medical center. Exclusions were preexisting lung cancer or other malignancy. The following data was collected: time to PET scan, referrals, and treatment initiation. KruskalWallis test and Mann-Whitney U test was employed to assess differences in treatment times based on treatment modality and disease stage, respectively
Results
The median time from first abnormal image to PET scan was 26 days. The median time from initial abnormal scan to treatment was 91 days. Treatment initiation was significantly shorter in late-state disease (IV, extensive stage) at 57 days compared to early-stage disease (I-III, limited stage) at 98.5 days (p= 0.00008). There was a difference in the median time from abnormal scan to treatment initiation based on treatment modality: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgical intervention occurred at 60 days, 86 days, and 98 days, respectively (p= 0.005).
Conclusions
At our institution, patients with latestage lung cancer initiate therapy significantly faster than those diagnosed with early-stage cancer. We feel this is largely due to complex, multidisciplinary coordination of early-stage disease, in contrast to those diagnosed at later stage disease who are treated in a palliative, systemic fashion. This study was instrumental at identifying key areas along the process that can be improved upon. Based on this data, changes will be implemented and studied in effort to shorten time to treatment.
Background
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related deaths in the United States. The impact of treatment delay proves difficult to quantify, but increased time to treatment and subsequent progression can limit a patient’s chance for curative intent therapy. Reducing time to treatment aims to improve patient outcome and experience. This study aims to identify the median timeframes that occur in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer patients within a single Veteran Affair (VA) Medical Center.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was conducted on 123 new primary lung cancer cases detected by imaging between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2022 within a single VA medical center. Exclusions were preexisting lung cancer or other malignancy. The following data was collected: time to PET scan, referrals, and treatment initiation. KruskalWallis test and Mann-Whitney U test was employed to assess differences in treatment times based on treatment modality and disease stage, respectively
Results
The median time from first abnormal image to PET scan was 26 days. The median time from initial abnormal scan to treatment was 91 days. Treatment initiation was significantly shorter in late-state disease (IV, extensive stage) at 57 days compared to early-stage disease (I-III, limited stage) at 98.5 days (p= 0.00008). There was a difference in the median time from abnormal scan to treatment initiation based on treatment modality: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgical intervention occurred at 60 days, 86 days, and 98 days, respectively (p= 0.005).
Conclusions
At our institution, patients with latestage lung cancer initiate therapy significantly faster than those diagnosed with early-stage cancer. We feel this is largely due to complex, multidisciplinary coordination of early-stage disease, in contrast to those diagnosed at later stage disease who are treated in a palliative, systemic fashion. This study was instrumental at identifying key areas along the process that can be improved upon. Based on this data, changes will be implemented and studied in effort to shorten time to treatment.
Background
Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer related deaths in the United States. The impact of treatment delay proves difficult to quantify, but increased time to treatment and subsequent progression can limit a patient’s chance for curative intent therapy. Reducing time to treatment aims to improve patient outcome and experience. This study aims to identify the median timeframes that occur in the diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer patients within a single Veteran Affair (VA) Medical Center.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was conducted on 123 new primary lung cancer cases detected by imaging between January 1, 2019 and December 31, 2022 within a single VA medical center. Exclusions were preexisting lung cancer or other malignancy. The following data was collected: time to PET scan, referrals, and treatment initiation. KruskalWallis test and Mann-Whitney U test was employed to assess differences in treatment times based on treatment modality and disease stage, respectively
Results
The median time from first abnormal image to PET scan was 26 days. The median time from initial abnormal scan to treatment was 91 days. Treatment initiation was significantly shorter in late-state disease (IV, extensive stage) at 57 days compared to early-stage disease (I-III, limited stage) at 98.5 days (p= 0.00008). There was a difference in the median time from abnormal scan to treatment initiation based on treatment modality: chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and surgical intervention occurred at 60 days, 86 days, and 98 days, respectively (p= 0.005).
Conclusions
At our institution, patients with latestage lung cancer initiate therapy significantly faster than those diagnosed with early-stage cancer. We feel this is largely due to complex, multidisciplinary coordination of early-stage disease, in contrast to those diagnosed at later stage disease who are treated in a palliative, systemic fashion. This study was instrumental at identifying key areas along the process that can be improved upon. Based on this data, changes will be implemented and studied in effort to shorten time to treatment.

