User login
44-year-old man • elevated total cholesterol • chest pains • ketogenic diet • Dx?
THE CASE
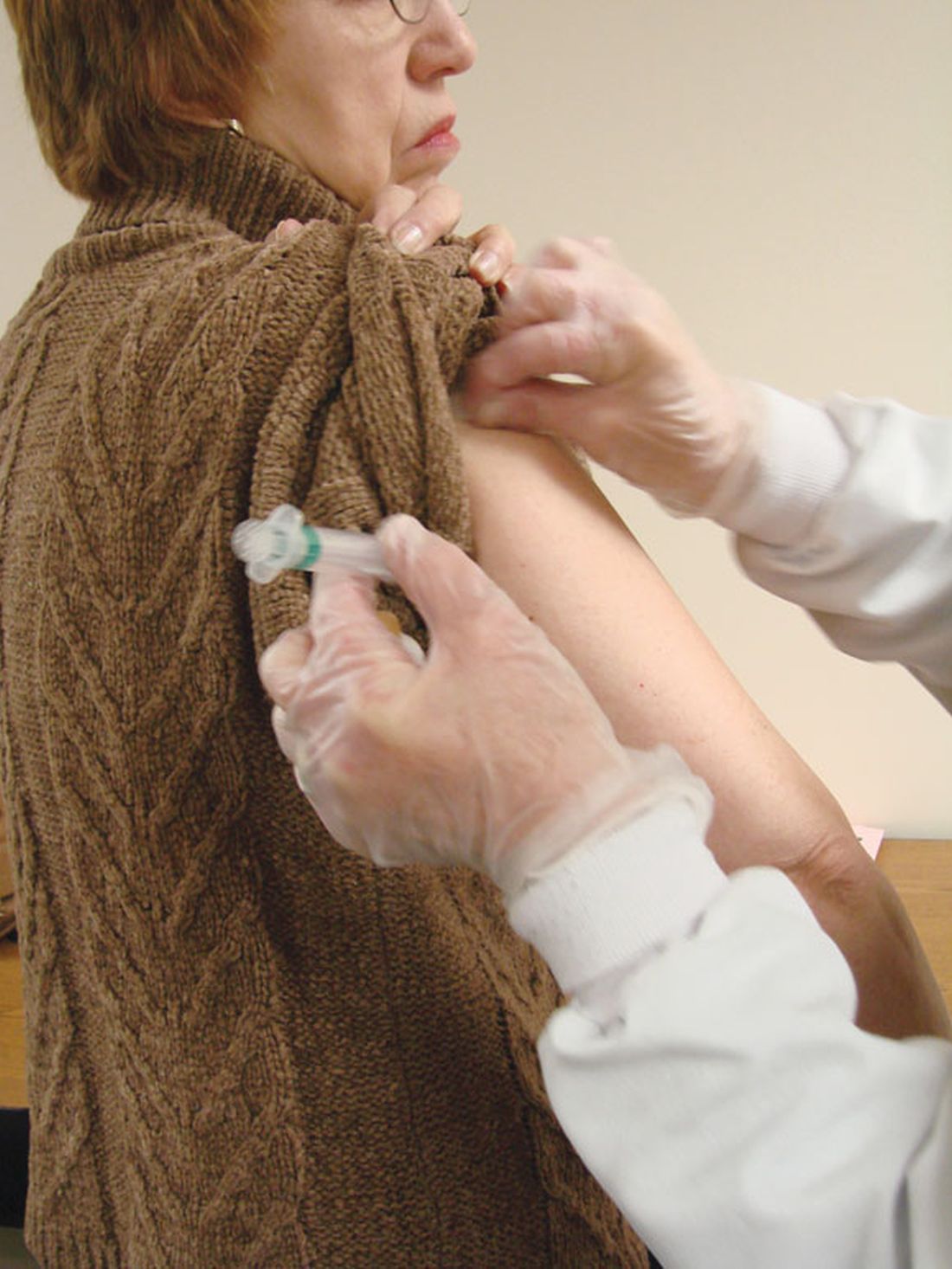
A 44-year-old man with a history of morbid obesity reestablished care in our clinic. He had been treated in our health care system about 5 years previously, and prior lab testing showed a total cholesterol of 203 mg/dL; triglycerides, 191 mg/dL; high-density lipoprotein (HDL), 56 mg/dL; and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), 109 mg/dL. At that time, he weighed 299 lbs (BMI, 39.4). He then started a strict ketogenic diet and a regular exercise program (running ~ 16 miles per week and lifting weights), which he maintained for several years. He had experienced remarkable weight loss; upon reestablishing care, he weighed 199 lbs (BMI, 26.33).
However, lipid testing revealed a severely elevated total cholesterol of 334 mg/dL; LDL, 248 mg/dL; HDL, 67 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 95 mg/dL. He was advised to start statin therapy and to stop his ketogenic diet, but he was hesitant to take either step. He elected to have his lab work reevaluated in 6 months.
About 4 months later, he presented with new and increasing burning pain in his mid chest and upper abdomen. He rated the pain 6/10 in severity and said it occurred during exertion or at night when lying down. Resting would relieve the pain. Reduced intake of spicy foods and caffeine had also helped. He denied dyspnea, diaphoresis, palpitations, or nausea.
The patient was a nonsmoker but did have a strong family history of cardiovascular disease. His vital signs and physical examination were unremarkable, apart from mild epigastric and periumbilical tenderness on palpation.
THE DIAGNOSIS
The patient’s chest pain had features of both gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and coronary artery disease (CAD) with exertional angina. His high-fat diet, nightly symptoms, and the partial relief he achieved by cutting back on spicy foods and caffeine suggested GERD, but the exertional nature of the chest pain and gradual relief with rest was highly suggestive of angina, so an outpatient electrocardiogram treadmill stress test was ordered.
The stress test was markedly abnormal, showing worsening ST depressions and T-wave inversions with exertion, and he experienced chest pain during testing. An urgent left heart catheterization was performed, showing severe multivessel CAD. He subsequently underwent 3-vessel coronary artery bypass grafting. A familial hypercholesterolemia panel failed to reveal any significant variants.
As a result of these findings, the patient received a diagnosis of severe ketogenic diet–associated hypercholesterolemia and early-onset CAD.
Continue to: DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
Low-carbohydrate (low-carb) and ketogenic diets have grown in popularity throughout the United States over the past decade, particularly for weight loss, and the diet has entered the popular consciousness with several celebrities publicly supporting it.1 Simultaneously, there also has been a growing interest in these diets for the treatment of chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes.2 However, the long-term cardiovascular effects of low-carb diets are not well studied, and there is significant heterogeneity among these diets.
Low-carb vs low-fat. Multiple meta-analyses comparing low-carb diets to low-fat diets have found that those following low-carb diets have significantly higher total cholesterol and LDL levels.3,4,5 The National Lipid Association’s review of evidence determined that LDL and total cholesterol responses vary in individuals following a low-carb diet, but that increasing LDL levels in particular were concerning enough to warrant lipid monitoring of patients on low-carb diets.6 Another meta-analysis evaluated the difference in estimated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk between low-carb and low-fat diets, finding those following a low-carb diet to have a lower estimated ASCVD risk but higher LDL levels.7
Weighing the benefits and harms. Since our patient’s dramatic weight loss and greatly increased exercise level would be expected to lower his LDL levels, the severe worsening of his LDL levels was likely related to his ketogenic diet and was a factor in the early onset of CAD. The benefits of low-carb diets for weight loss, contrasted with the consistent worsening of LDL levels, has prompted a debate about which parameters should be considered in estimating the long-term risk of these diets for patients. Diamond et al8 posit that these diets have beneficial effects on “the most reliable [cardiovascular disease] risk factors,” but long-term, patient-oriented outcome data are lacking, and these diets may not be appropriate for certain patients, as our case demonstrates.
A reasonable strategy for patients contemplating a low-carb diet specifically for weight loss would be to use such a diet for 3 to 6 months to achieve initial and rapid results, then continue with a heart-healthy diet and increased exercise levels to maintain weight loss and reduce long-term cardiovascular risk.
Our patient was started on a postoperative medication regimen of aspirin 81 mg/d, evolocumab 140 mg every 14 days, metoprolol tartrate 25 mg bid, and rosuvastatin 10 mg/d. A year later, he was able to resume a high level of physical activity (6-mile runs) without chest pain. His follow-up lipid panel showed a total cholesterol of 153 mg/dL; LDL, 53 mg/dL; HDL, 89 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 55 mg/dL. He had also switched to a regular diet and had been able to maintain his weight loss.
THE TAKEAWAY
Growing evidence suggests that low-carb diets may have a significant and detrimental effect on LDL levels. The long-term safety of these diets hasn’t been well studied, particularly regarding cardiovascular outcomes. At a minimum, patients who initiate low-carb diets should be counseled on general dietary recommendations regarding saturated fat and cholesterol intake, and they should have a follow-up lipid screening to evaluate for any significant worsening in total cholesterol and LDL levels.
CORRESPONDENCE
Samuel Dickmann, MD, 13611 NW 1st Lane, Suite 200, Newberry, FL 32669; [email protected]
1. Gorin A. What is the keto diet – and is it right for you? NBC News BETTER. February 22, 2018. Accessed February 3, 2023. www.nbcnews.com/better/health/what-keto-diet-it-right-you-ncna847256
2. Tinguely D, Gross J, Kosinski, C. Efficacy of ketogenic diets on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Current Diabetes Reports. 2021;21:32. doi: 10.1007/s11892-021-01399-z
3. Mansoor N, Vinknes KJ, Veierod MB, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diets v. low-fat diets on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2016;115:466-479. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515004699
4. Bueno NB, de Melo ISV, de Oliveira SL, et al. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1178-1187. doi: 10.1017/S0007114513000548
5. Chawla S, Tessarolo Silva F, Amaral Medeiros S, et al. The effect of low-fat and low-carbohydrate diets on weight loss and lipid levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12:3774. doi: 10.3390/nu12123774
6. Kirkpatrick CF, Bolick JP, Kris-Etherton PM, et al. Review of current evidence and clinical recommendations on the effects of low-carbohydrate and very-low-carbohydrate (including ketogenic) diets for the management of body weight and other cardiometabolic risk factors: a scientific statement from the National Lipid Association Nutrition and Lifestyle Task Force. J Clin Lipidol. 2019;13:689-711.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.08.003
7. Sackner-Bernstein J, Kanter D, Kaul S. Dietary intervention for overweight and obese adults: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets. a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139817
8. Diamond DM, O’Neill BJ, Volek JS. Low carbohydrate diet: are concerns with saturated fat, lipids, and cardiovascular disease risk justified? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020;27:291-300. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000568
THE CASE
A 44-year-old man with a history of morbid obesity reestablished care in our clinic. He had been treated in our health care system about 5 years previously, and prior lab testing showed a total cholesterol of 203 mg/dL; triglycerides, 191 mg/dL; high-density lipoprotein (HDL), 56 mg/dL; and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), 109 mg/dL. At that time, he weighed 299 lbs (BMI, 39.4). He then started a strict ketogenic diet and a regular exercise program (running ~ 16 miles per week and lifting weights), which he maintained for several years. He had experienced remarkable weight loss; upon reestablishing care, he weighed 199 lbs (BMI, 26.33).
However, lipid testing revealed a severely elevated total cholesterol of 334 mg/dL; LDL, 248 mg/dL; HDL, 67 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 95 mg/dL. He was advised to start statin therapy and to stop his ketogenic diet, but he was hesitant to take either step. He elected to have his lab work reevaluated in 6 months.
About 4 months later, he presented with new and increasing burning pain in his mid chest and upper abdomen. He rated the pain 6/10 in severity and said it occurred during exertion or at night when lying down. Resting would relieve the pain. Reduced intake of spicy foods and caffeine had also helped. He denied dyspnea, diaphoresis, palpitations, or nausea.
The patient was a nonsmoker but did have a strong family history of cardiovascular disease. His vital signs and physical examination were unremarkable, apart from mild epigastric and periumbilical tenderness on palpation.
THE DIAGNOSIS
The patient’s chest pain had features of both gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and coronary artery disease (CAD) with exertional angina. His high-fat diet, nightly symptoms, and the partial relief he achieved by cutting back on spicy foods and caffeine suggested GERD, but the exertional nature of the chest pain and gradual relief with rest was highly suggestive of angina, so an outpatient electrocardiogram treadmill stress test was ordered.
The stress test was markedly abnormal, showing worsening ST depressions and T-wave inversions with exertion, and he experienced chest pain during testing. An urgent left heart catheterization was performed, showing severe multivessel CAD. He subsequently underwent 3-vessel coronary artery bypass grafting. A familial hypercholesterolemia panel failed to reveal any significant variants.
As a result of these findings, the patient received a diagnosis of severe ketogenic diet–associated hypercholesterolemia and early-onset CAD.
Continue to: DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
Low-carbohydrate (low-carb) and ketogenic diets have grown in popularity throughout the United States over the past decade, particularly for weight loss, and the diet has entered the popular consciousness with several celebrities publicly supporting it.1 Simultaneously, there also has been a growing interest in these diets for the treatment of chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes.2 However, the long-term cardiovascular effects of low-carb diets are not well studied, and there is significant heterogeneity among these diets.
Low-carb vs low-fat. Multiple meta-analyses comparing low-carb diets to low-fat diets have found that those following low-carb diets have significantly higher total cholesterol and LDL levels.3,4,5 The National Lipid Association’s review of evidence determined that LDL and total cholesterol responses vary in individuals following a low-carb diet, but that increasing LDL levels in particular were concerning enough to warrant lipid monitoring of patients on low-carb diets.6 Another meta-analysis evaluated the difference in estimated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk between low-carb and low-fat diets, finding those following a low-carb diet to have a lower estimated ASCVD risk but higher LDL levels.7
Weighing the benefits and harms. Since our patient’s dramatic weight loss and greatly increased exercise level would be expected to lower his LDL levels, the severe worsening of his LDL levels was likely related to his ketogenic diet and was a factor in the early onset of CAD. The benefits of low-carb diets for weight loss, contrasted with the consistent worsening of LDL levels, has prompted a debate about which parameters should be considered in estimating the long-term risk of these diets for patients. Diamond et al8 posit that these diets have beneficial effects on “the most reliable [cardiovascular disease] risk factors,” but long-term, patient-oriented outcome data are lacking, and these diets may not be appropriate for certain patients, as our case demonstrates.
A reasonable strategy for patients contemplating a low-carb diet specifically for weight loss would be to use such a diet for 3 to 6 months to achieve initial and rapid results, then continue with a heart-healthy diet and increased exercise levels to maintain weight loss and reduce long-term cardiovascular risk.
Our patient was started on a postoperative medication regimen of aspirin 81 mg/d, evolocumab 140 mg every 14 days, metoprolol tartrate 25 mg bid, and rosuvastatin 10 mg/d. A year later, he was able to resume a high level of physical activity (6-mile runs) without chest pain. His follow-up lipid panel showed a total cholesterol of 153 mg/dL; LDL, 53 mg/dL; HDL, 89 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 55 mg/dL. He had also switched to a regular diet and had been able to maintain his weight loss.
THE TAKEAWAY
Growing evidence suggests that low-carb diets may have a significant and detrimental effect on LDL levels. The long-term safety of these diets hasn’t been well studied, particularly regarding cardiovascular outcomes. At a minimum, patients who initiate low-carb diets should be counseled on general dietary recommendations regarding saturated fat and cholesterol intake, and they should have a follow-up lipid screening to evaluate for any significant worsening in total cholesterol and LDL levels.
CORRESPONDENCE
Samuel Dickmann, MD, 13611 NW 1st Lane, Suite 200, Newberry, FL 32669; [email protected]
THE CASE
A 44-year-old man with a history of morbid obesity reestablished care in our clinic. He had been treated in our health care system about 5 years previously, and prior lab testing showed a total cholesterol of 203 mg/dL; triglycerides, 191 mg/dL; high-density lipoprotein (HDL), 56 mg/dL; and low-density lipoprotein (LDL), 109 mg/dL. At that time, he weighed 299 lbs (BMI, 39.4). He then started a strict ketogenic diet and a regular exercise program (running ~ 16 miles per week and lifting weights), which he maintained for several years. He had experienced remarkable weight loss; upon reestablishing care, he weighed 199 lbs (BMI, 26.33).
However, lipid testing revealed a severely elevated total cholesterol of 334 mg/dL; LDL, 248 mg/dL; HDL, 67 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 95 mg/dL. He was advised to start statin therapy and to stop his ketogenic diet, but he was hesitant to take either step. He elected to have his lab work reevaluated in 6 months.
About 4 months later, he presented with new and increasing burning pain in his mid chest and upper abdomen. He rated the pain 6/10 in severity and said it occurred during exertion or at night when lying down. Resting would relieve the pain. Reduced intake of spicy foods and caffeine had also helped. He denied dyspnea, diaphoresis, palpitations, or nausea.
The patient was a nonsmoker but did have a strong family history of cardiovascular disease. His vital signs and physical examination were unremarkable, apart from mild epigastric and periumbilical tenderness on palpation.
THE DIAGNOSIS
The patient’s chest pain had features of both gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and coronary artery disease (CAD) with exertional angina. His high-fat diet, nightly symptoms, and the partial relief he achieved by cutting back on spicy foods and caffeine suggested GERD, but the exertional nature of the chest pain and gradual relief with rest was highly suggestive of angina, so an outpatient electrocardiogram treadmill stress test was ordered.
The stress test was markedly abnormal, showing worsening ST depressions and T-wave inversions with exertion, and he experienced chest pain during testing. An urgent left heart catheterization was performed, showing severe multivessel CAD. He subsequently underwent 3-vessel coronary artery bypass grafting. A familial hypercholesterolemia panel failed to reveal any significant variants.
As a result of these findings, the patient received a diagnosis of severe ketogenic diet–associated hypercholesterolemia and early-onset CAD.
Continue to: DISCUSSION
DISCUSSION
Low-carbohydrate (low-carb) and ketogenic diets have grown in popularity throughout the United States over the past decade, particularly for weight loss, and the diet has entered the popular consciousness with several celebrities publicly supporting it.1 Simultaneously, there also has been a growing interest in these diets for the treatment of chronic diseases, such as type 2 diabetes.2 However, the long-term cardiovascular effects of low-carb diets are not well studied, and there is significant heterogeneity among these diets.
Low-carb vs low-fat. Multiple meta-analyses comparing low-carb diets to low-fat diets have found that those following low-carb diets have significantly higher total cholesterol and LDL levels.3,4,5 The National Lipid Association’s review of evidence determined that LDL and total cholesterol responses vary in individuals following a low-carb diet, but that increasing LDL levels in particular were concerning enough to warrant lipid monitoring of patients on low-carb diets.6 Another meta-analysis evaluated the difference in estimated atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) risk between low-carb and low-fat diets, finding those following a low-carb diet to have a lower estimated ASCVD risk but higher LDL levels.7
Weighing the benefits and harms. Since our patient’s dramatic weight loss and greatly increased exercise level would be expected to lower his LDL levels, the severe worsening of his LDL levels was likely related to his ketogenic diet and was a factor in the early onset of CAD. The benefits of low-carb diets for weight loss, contrasted with the consistent worsening of LDL levels, has prompted a debate about which parameters should be considered in estimating the long-term risk of these diets for patients. Diamond et al8 posit that these diets have beneficial effects on “the most reliable [cardiovascular disease] risk factors,” but long-term, patient-oriented outcome data are lacking, and these diets may not be appropriate for certain patients, as our case demonstrates.
A reasonable strategy for patients contemplating a low-carb diet specifically for weight loss would be to use such a diet for 3 to 6 months to achieve initial and rapid results, then continue with a heart-healthy diet and increased exercise levels to maintain weight loss and reduce long-term cardiovascular risk.
Our patient was started on a postoperative medication regimen of aspirin 81 mg/d, evolocumab 140 mg every 14 days, metoprolol tartrate 25 mg bid, and rosuvastatin 10 mg/d. A year later, he was able to resume a high level of physical activity (6-mile runs) without chest pain. His follow-up lipid panel showed a total cholesterol of 153 mg/dL; LDL, 53 mg/dL; HDL, 89 mg/dL; and triglycerides, 55 mg/dL. He had also switched to a regular diet and had been able to maintain his weight loss.
THE TAKEAWAY
Growing evidence suggests that low-carb diets may have a significant and detrimental effect on LDL levels. The long-term safety of these diets hasn’t been well studied, particularly regarding cardiovascular outcomes. At a minimum, patients who initiate low-carb diets should be counseled on general dietary recommendations regarding saturated fat and cholesterol intake, and they should have a follow-up lipid screening to evaluate for any significant worsening in total cholesterol and LDL levels.
CORRESPONDENCE
Samuel Dickmann, MD, 13611 NW 1st Lane, Suite 200, Newberry, FL 32669; [email protected]
1. Gorin A. What is the keto diet – and is it right for you? NBC News BETTER. February 22, 2018. Accessed February 3, 2023. www.nbcnews.com/better/health/what-keto-diet-it-right-you-ncna847256
2. Tinguely D, Gross J, Kosinski, C. Efficacy of ketogenic diets on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Current Diabetes Reports. 2021;21:32. doi: 10.1007/s11892-021-01399-z
3. Mansoor N, Vinknes KJ, Veierod MB, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diets v. low-fat diets on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2016;115:466-479. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515004699
4. Bueno NB, de Melo ISV, de Oliveira SL, et al. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1178-1187. doi: 10.1017/S0007114513000548
5. Chawla S, Tessarolo Silva F, Amaral Medeiros S, et al. The effect of low-fat and low-carbohydrate diets on weight loss and lipid levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12:3774. doi: 10.3390/nu12123774
6. Kirkpatrick CF, Bolick JP, Kris-Etherton PM, et al. Review of current evidence and clinical recommendations on the effects of low-carbohydrate and very-low-carbohydrate (including ketogenic) diets for the management of body weight and other cardiometabolic risk factors: a scientific statement from the National Lipid Association Nutrition and Lifestyle Task Force. J Clin Lipidol. 2019;13:689-711.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.08.003
7. Sackner-Bernstein J, Kanter D, Kaul S. Dietary intervention for overweight and obese adults: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets. a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139817
8. Diamond DM, O’Neill BJ, Volek JS. Low carbohydrate diet: are concerns with saturated fat, lipids, and cardiovascular disease risk justified? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020;27:291-300. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000568
1. Gorin A. What is the keto diet – and is it right for you? NBC News BETTER. February 22, 2018. Accessed February 3, 2023. www.nbcnews.com/better/health/what-keto-diet-it-right-you-ncna847256
2. Tinguely D, Gross J, Kosinski, C. Efficacy of ketogenic diets on type 2 diabetes: a systematic review. Current Diabetes Reports. 2021;21:32. doi: 10.1007/s11892-021-01399-z
3. Mansoor N, Vinknes KJ, Veierod MB, et al. Effects of low-carbohydrate diets v. low-fat diets on body weight and cardiovascular risk factors a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2016;115:466-479. doi: 10.1017/S0007114515004699
4. Bueno NB, de Melo ISV, de Oliveira SL, et al. Very-low-carbohydrate ketogenic diet v. low-fat diet for long-term weight loss: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Nutr. 2013;110:1178-1187. doi: 10.1017/S0007114513000548
5. Chawla S, Tessarolo Silva F, Amaral Medeiros S, et al. The effect of low-fat and low-carbohydrate diets on weight loss and lipid levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutrients. 2020;12:3774. doi: 10.3390/nu12123774
6. Kirkpatrick CF, Bolick JP, Kris-Etherton PM, et al. Review of current evidence and clinical recommendations on the effects of low-carbohydrate and very-low-carbohydrate (including ketogenic) diets for the management of body weight and other cardiometabolic risk factors: a scientific statement from the National Lipid Association Nutrition and Lifestyle Task Force. J Clin Lipidol. 2019;13:689-711.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2019.08.003
7. Sackner-Bernstein J, Kanter D, Kaul S. Dietary intervention for overweight and obese adults: comparison of low-carbohydrate and low-fat diets. a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0139817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0139817
8. Diamond DM, O’Neill BJ, Volek JS. Low carbohydrate diet: are concerns with saturated fat, lipids, and cardiovascular disease risk justified? Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2020;27:291-300. doi: 10.1097/MED.0000000000000568
Long-term BP reductions with renal denervation not race specific
WASHINGTON – On the heels the recently published final report from the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 renal denervation trial, a new analysis showed that Black patients, like non-Blacks, had sustained blood pressure control.
Contrary to a signal from earlier results, “there is nothing race specific about renal denervation,” said presenter Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
Black patients are well represented among patients with treatment-resistant hypertension and considered an important subgroup to target, according to Dr. Bhatt, director of Mount Sinai Heart, New York. This is the reason that they were not only a prespecified subgroup in SYMPLICITY HTN-3, but race was one of two stratification factors at enrollment. At the time of the study design, there was an expectation that Black patients would benefit more than non-Blacks.
This did not prove to be the case during the 6-month controlled phase of the trial. When patients randomized to renal denervation or the sham procedure were stratified by race, the primary endpoint of reduction in office systolic blood pressure (SBP) reached significance in the experimental arm among non-Black patients (–6.63 mm Hg; P = .01), but not among Black patients (–2.25 mm Hg; P = .09).
Blacks comprised 26% of SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial
In the initial controlled analysis, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the lack of benefit in the substantial Black enrollment – representing 26% of the study total – weighed against the ability of the trial to demonstrate a benefit, but Dr. Bhatt pointed out that BP reductions were unexpectedly high in the sham group regardless of race. Patients randomized to the sham group were encouraged to adhere to antihypertensive therapy, and based on response, this was particularly effective in the Black sham subgroup.
In SYMPLICITY HTN-3, patients with treatment-resistant hypertension were randomized to renal denervation or a sham procedure in a 2:1 ratio. While the controlled phase lasted just 6 months, the follow-up after the study was unblinded has continued out to 3 years. Safety and efficacy were assessed at 12, 24, and 36 months.
Unlike the disappointing results at 6 months, renal denervation has been consistently associated with significantly lower BP over long-term follow-up, even though those randomized to the sham procedure were permitted to cross over. About two-thirds of the sham group did so.
In the recently published final report of SYMPLICITY, the overall median change in office SBP at 3 years regardless of race was –26.4 mm Hg in the group initially randomized to renal denervation versus –5.7 mm Hg (P < .0001) among those randomized to the sham procedure.
In the subgroup analysis presented by Dr. Bhatt, the relative control of office SBP, as well as other measures of blood pressure, were similarly and significantly reduced in both Black and non-Black patients. In general, the relative control offered by being randomized initially to renal denervation increased over time in both groups.
For example, the relative reduction in office SBP favoring renal denervation climbed from –12.0 mm Hg at 12 months (P = .0066) to –21.0 at 18 months (P = .0002) and then to –24.9 mm Hg (P < .0001) at 36 months in the Black subgroup. In non-Blacks, the same type of relative reductions were seen at each time point, climbing from –13.5 (P < .0001) to –20.5 (P < .0001) and then to –21.0 (P < .0001).
The comparisons for other measures of BP control, including office diastolic BP, 24-hour SBP, and BP control during morning, day, and night periods were also statistically and similarly improved for those initially randomized to renal denervation rather than a sham procedure among both Blacks and non-Blacks.
Renal denervation safe in Black and non-Black patients
Renal denervation was well tolerated in both Black and non-Black participants with no signal of long-term risks over 36 months in either group. Among Blacks, rates of death at 36 months (3% vs. 11%) and stroke (7% vs. 11%) were lower among those randomized to renal denervation relative to sham patients who never crossed over, but Dr. Bhatt said the numbers are too small to draw any conclusions about outcomes.
While this subgroup analysis, along with the final SYMPLICITY report, supports the efficacy of renal denervation over the long term, these data are also consistent with the recently published analysis of SPYRAL ON-MED . Together, these data have led many experts, including Dr. Bhatt, to conclude that renal denervation is effective and deserves regulatory approval.
“In out-of-control blood pressure, when patients have maxed out on medications and lifestyle, I think renal denervation is efficacious, and it is equally efficacious in Blacks and non-Blacks,” Dr. Bhatt said.
This subgroup analysis is important because of the need for options in treatment-resistant hypertension among Black as well as non-Black patients, pointed out Sripal Bangalore, MBBS, director of complex coronary intervention at New York University.
“I am glad that we did not conclude too soon that it does not work in Blacks,” Dr. Bangalore said. If renal denervation is approved, he expects this procedure to be a valuable tool in this racial group.
Dr. Bhatt reported financial relationship with more than 20 pharmaceutical and device companies, including Medtronic, which provided funding for the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Dr. Bangalore has financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Amgen, Biotronik, Inari, Pfizer, Reata, and Truvic.
WASHINGTON – On the heels the recently published final report from the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 renal denervation trial, a new analysis showed that Black patients, like non-Blacks, had sustained blood pressure control.
Contrary to a signal from earlier results, “there is nothing race specific about renal denervation,” said presenter Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
Black patients are well represented among patients with treatment-resistant hypertension and considered an important subgroup to target, according to Dr. Bhatt, director of Mount Sinai Heart, New York. This is the reason that they were not only a prespecified subgroup in SYMPLICITY HTN-3, but race was one of two stratification factors at enrollment. At the time of the study design, there was an expectation that Black patients would benefit more than non-Blacks.
This did not prove to be the case during the 6-month controlled phase of the trial. When patients randomized to renal denervation or the sham procedure were stratified by race, the primary endpoint of reduction in office systolic blood pressure (SBP) reached significance in the experimental arm among non-Black patients (–6.63 mm Hg; P = .01), but not among Black patients (–2.25 mm Hg; P = .09).
Blacks comprised 26% of SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial
In the initial controlled analysis, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the lack of benefit in the substantial Black enrollment – representing 26% of the study total – weighed against the ability of the trial to demonstrate a benefit, but Dr. Bhatt pointed out that BP reductions were unexpectedly high in the sham group regardless of race. Patients randomized to the sham group were encouraged to adhere to antihypertensive therapy, and based on response, this was particularly effective in the Black sham subgroup.
In SYMPLICITY HTN-3, patients with treatment-resistant hypertension were randomized to renal denervation or a sham procedure in a 2:1 ratio. While the controlled phase lasted just 6 months, the follow-up after the study was unblinded has continued out to 3 years. Safety and efficacy were assessed at 12, 24, and 36 months.
Unlike the disappointing results at 6 months, renal denervation has been consistently associated with significantly lower BP over long-term follow-up, even though those randomized to the sham procedure were permitted to cross over. About two-thirds of the sham group did so.
In the recently published final report of SYMPLICITY, the overall median change in office SBP at 3 years regardless of race was –26.4 mm Hg in the group initially randomized to renal denervation versus –5.7 mm Hg (P < .0001) among those randomized to the sham procedure.
In the subgroup analysis presented by Dr. Bhatt, the relative control of office SBP, as well as other measures of blood pressure, were similarly and significantly reduced in both Black and non-Black patients. In general, the relative control offered by being randomized initially to renal denervation increased over time in both groups.
For example, the relative reduction in office SBP favoring renal denervation climbed from –12.0 mm Hg at 12 months (P = .0066) to –21.0 at 18 months (P = .0002) and then to –24.9 mm Hg (P < .0001) at 36 months in the Black subgroup. In non-Blacks, the same type of relative reductions were seen at each time point, climbing from –13.5 (P < .0001) to –20.5 (P < .0001) and then to –21.0 (P < .0001).
The comparisons for other measures of BP control, including office diastolic BP, 24-hour SBP, and BP control during morning, day, and night periods were also statistically and similarly improved for those initially randomized to renal denervation rather than a sham procedure among both Blacks and non-Blacks.
Renal denervation safe in Black and non-Black patients
Renal denervation was well tolerated in both Black and non-Black participants with no signal of long-term risks over 36 months in either group. Among Blacks, rates of death at 36 months (3% vs. 11%) and stroke (7% vs. 11%) were lower among those randomized to renal denervation relative to sham patients who never crossed over, but Dr. Bhatt said the numbers are too small to draw any conclusions about outcomes.
While this subgroup analysis, along with the final SYMPLICITY report, supports the efficacy of renal denervation over the long term, these data are also consistent with the recently published analysis of SPYRAL ON-MED . Together, these data have led many experts, including Dr. Bhatt, to conclude that renal denervation is effective and deserves regulatory approval.
“In out-of-control blood pressure, when patients have maxed out on medications and lifestyle, I think renal denervation is efficacious, and it is equally efficacious in Blacks and non-Blacks,” Dr. Bhatt said.
This subgroup analysis is important because of the need for options in treatment-resistant hypertension among Black as well as non-Black patients, pointed out Sripal Bangalore, MBBS, director of complex coronary intervention at New York University.
“I am glad that we did not conclude too soon that it does not work in Blacks,” Dr. Bangalore said. If renal denervation is approved, he expects this procedure to be a valuable tool in this racial group.
Dr. Bhatt reported financial relationship with more than 20 pharmaceutical and device companies, including Medtronic, which provided funding for the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Dr. Bangalore has financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Amgen, Biotronik, Inari, Pfizer, Reata, and Truvic.
WASHINGTON – On the heels the recently published final report from the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 renal denervation trial, a new analysis showed that Black patients, like non-Blacks, had sustained blood pressure control.
Contrary to a signal from earlier results, “there is nothing race specific about renal denervation,” said presenter Deepak L. Bhatt, MD, at the Cardiovascular Research Technologies conference, sponsored by MedStar Heart & Vascular Institute.
Black patients are well represented among patients with treatment-resistant hypertension and considered an important subgroup to target, according to Dr. Bhatt, director of Mount Sinai Heart, New York. This is the reason that they were not only a prespecified subgroup in SYMPLICITY HTN-3, but race was one of two stratification factors at enrollment. At the time of the study design, there was an expectation that Black patients would benefit more than non-Blacks.
This did not prove to be the case during the 6-month controlled phase of the trial. When patients randomized to renal denervation or the sham procedure were stratified by race, the primary endpoint of reduction in office systolic blood pressure (SBP) reached significance in the experimental arm among non-Black patients (–6.63 mm Hg; P = .01), but not among Black patients (–2.25 mm Hg; P = .09).
Blacks comprised 26% of SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial
In the initial controlled analysis, published in the New England Journal of Medicine, the lack of benefit in the substantial Black enrollment – representing 26% of the study total – weighed against the ability of the trial to demonstrate a benefit, but Dr. Bhatt pointed out that BP reductions were unexpectedly high in the sham group regardless of race. Patients randomized to the sham group were encouraged to adhere to antihypertensive therapy, and based on response, this was particularly effective in the Black sham subgroup.
In SYMPLICITY HTN-3, patients with treatment-resistant hypertension were randomized to renal denervation or a sham procedure in a 2:1 ratio. While the controlled phase lasted just 6 months, the follow-up after the study was unblinded has continued out to 3 years. Safety and efficacy were assessed at 12, 24, and 36 months.
Unlike the disappointing results at 6 months, renal denervation has been consistently associated with significantly lower BP over long-term follow-up, even though those randomized to the sham procedure were permitted to cross over. About two-thirds of the sham group did so.
In the recently published final report of SYMPLICITY, the overall median change in office SBP at 3 years regardless of race was –26.4 mm Hg in the group initially randomized to renal denervation versus –5.7 mm Hg (P < .0001) among those randomized to the sham procedure.
In the subgroup analysis presented by Dr. Bhatt, the relative control of office SBP, as well as other measures of blood pressure, were similarly and significantly reduced in both Black and non-Black patients. In general, the relative control offered by being randomized initially to renal denervation increased over time in both groups.
For example, the relative reduction in office SBP favoring renal denervation climbed from –12.0 mm Hg at 12 months (P = .0066) to –21.0 at 18 months (P = .0002) and then to –24.9 mm Hg (P < .0001) at 36 months in the Black subgroup. In non-Blacks, the same type of relative reductions were seen at each time point, climbing from –13.5 (P < .0001) to –20.5 (P < .0001) and then to –21.0 (P < .0001).
The comparisons for other measures of BP control, including office diastolic BP, 24-hour SBP, and BP control during morning, day, and night periods were also statistically and similarly improved for those initially randomized to renal denervation rather than a sham procedure among both Blacks and non-Blacks.
Renal denervation safe in Black and non-Black patients
Renal denervation was well tolerated in both Black and non-Black participants with no signal of long-term risks over 36 months in either group. Among Blacks, rates of death at 36 months (3% vs. 11%) and stroke (7% vs. 11%) were lower among those randomized to renal denervation relative to sham patients who never crossed over, but Dr. Bhatt said the numbers are too small to draw any conclusions about outcomes.
While this subgroup analysis, along with the final SYMPLICITY report, supports the efficacy of renal denervation over the long term, these data are also consistent with the recently published analysis of SPYRAL ON-MED . Together, these data have led many experts, including Dr. Bhatt, to conclude that renal denervation is effective and deserves regulatory approval.
“In out-of-control blood pressure, when patients have maxed out on medications and lifestyle, I think renal denervation is efficacious, and it is equally efficacious in Blacks and non-Blacks,” Dr. Bhatt said.
This subgroup analysis is important because of the need for options in treatment-resistant hypertension among Black as well as non-Black patients, pointed out Sripal Bangalore, MBBS, director of complex coronary intervention at New York University.
“I am glad that we did not conclude too soon that it does not work in Blacks,” Dr. Bangalore said. If renal denervation is approved, he expects this procedure to be a valuable tool in this racial group.
Dr. Bhatt reported financial relationship with more than 20 pharmaceutical and device companies, including Medtronic, which provided funding for the SYMPLICITY HTN-3 trial. Dr. Bangalore has financial relationships with Abbott Vascular, Amgen, Biotronik, Inari, Pfizer, Reata, and Truvic.
AT CRT 2023
COORDINATEd effort boosts optimal therapy in patients with T2D and ASCVD
NEW ORLEANS – Twenty cardiology clinics successfully intensified the medical care they gave patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) after receiving a simple and scalable investigational intervention that gave the clinics’ staffs guidance on best prescribing practices and implementation and also provided quality-improvement feedback.
Within a year, these clinics quadrupled optimal medical management of these patients, compared with control clinics, in a randomized trial involving a total of 43 clinics and 1,049 patients.
“This multifaceted intervention is effective in increasing the prescription of evidence-based therapies in adults with T2D and ASCVD,” Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“The next step is to scale this intervention across cardiology practices” interested in improving the quality of care they deliver to these patients, added Dr. Pagidipati, a cardiologist specializing in cardiometabolic disease prevention at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
The goal is getting patients on triple therapy
The primary outcome of the COORDINATE-Diabetes trial was the change in the number of patients with T2D and ASCVD who received prescriptions for agents from three recommended medication classes and at recommended dosages: a high-intensity statin, a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi), and at least one agent from either of two classes that have both cardiovascular-protective and antihyperglycemic effects: the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or the glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1)–receptor agonists.
Among the 457 patients treated at the 20 cardiology clinics who received the quality-improvement intervention, 37.9% were on the promoted triple therapy after 12 months, compared with 14.5% of the 588 patients treated at the 23 clinics that continued with their usual care approach. This 23.4–percentage point increase in triple-class prescribing at recommended dosages represented a significant 4.4-fold increase in the goal prescribing endpoint after adjustment for possible confounders, Dr. Pagidipati reported.
Simultaneously with her report, the findings also appeared online in JAMA.
At baseline, 41%-50% of the patients were on both a high-intensity statin and a RASi, with a total of about 58%-67% on a high-intensity statin and about 70%-75% on a RASi. Fewer than 1% of patients were on SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1–receptor agonists at baseline. By design, no patient could be on all three categories of medication at baseline.
At their last follow-up visit (after 12 months for 97% of patients, or after 6 months for the remainder) 71% of the patients at practices that received the intervention were on a high-intensity statin, 81% were taking a RASi, and 60% were on an SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1–receptor agonist. Among the control patients, 58% were on a high-intensity statin, 68% on a RASi, and 36% were on one of the antihyperglycemic agents.
Effective interventions and the need for a champion
The clinics randomized to the active arm received instruction from a three-member team, either from an in-person or virtual one-time visit, on an intervention comprising several initiatives:
- Analysis of the barriers to evidence-based care at each clinic.
- Development of local interdisciplinary care pathways to address the identified barriers.
- Facilitation of care coordination among clinicians – particularly among cardiology, endocrinology, and primary care clinicians.
- Education of the clinic staff, including provision of educational materials.
- Auditing of clinic performance using specified metrics and feedback on the findings.
Clinics in the usual care group were given current clinical practice guidelines.
The investigational intervention was, by design, “low-tech and designed to be scalable,” explained Dr. Pagidipati, and once the COVID pandemic started the intervention team shifted to a virtual consultation with participating practices that was mostly front-loaded, followed by monthly phone calls to give clinics feedback on their progress.
Among the most helpful aspects of the intervention was involving the entire clinic staff, including pharmacists, nurses, and advanced care practitioners; boosting familiarity with the relevant medications and their appropriate use; and advice on navigating insurance-coverage barriers such as prior authorizations.
“What was most critical was having a local champion who took on making this effort an important part” of what the clinic was trying to do, she explained. “All it takes is passion, and the tenacity of a bulldog,” Dr. Pagidipati said.
Research advances often don’t translate into management changes
“We don’t do a great job of translating findings from trials to patient care, so any method we can use to improve that will improve practice,” commented Kristen B. Campbell, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist at Duke who was not involved in the study.
“Although the trial was not powered to look at patient outcomes, we think that patients will benefit” because all the recommended medication uses have been proven to help patients in prior trials, Dr. Campbell noted.
“A particular strength of this study was its simple design. All the interventions are low-tech and scalable.”
The low level of use of guideline-directed medical therapy in American adults with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is “incredible,” said Christopher B. Granger, MD, a senior investigator on the study and a cardiologist and professor at Duke.
The researchers who ran the study are now focused on evaluating which cardiology clinics and patients had the most success from the intervention and are using that information to further refine implementation. They are also planning to encourage cardiology practices as well as other relevant medical groups to incorporate the intervention and implementation model used in the trial. The intervention program is detailed and available at no charge on the COORDINATE-Diabetes website.
COORDINATE-Diabetes received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly. Dr. Pagidipati has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, and CRISPR Therapeutics, and she has received research grants from Amgen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Eggland’s Best. Dr. Campbell had no disclosures. Dr. Granger has received personal fees and research funding from numerous companies.
NEW ORLEANS – Twenty cardiology clinics successfully intensified the medical care they gave patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) after receiving a simple and scalable investigational intervention that gave the clinics’ staffs guidance on best prescribing practices and implementation and also provided quality-improvement feedback.
Within a year, these clinics quadrupled optimal medical management of these patients, compared with control clinics, in a randomized trial involving a total of 43 clinics and 1,049 patients.
“This multifaceted intervention is effective in increasing the prescription of evidence-based therapies in adults with T2D and ASCVD,” Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“The next step is to scale this intervention across cardiology practices” interested in improving the quality of care they deliver to these patients, added Dr. Pagidipati, a cardiologist specializing in cardiometabolic disease prevention at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
The goal is getting patients on triple therapy
The primary outcome of the COORDINATE-Diabetes trial was the change in the number of patients with T2D and ASCVD who received prescriptions for agents from three recommended medication classes and at recommended dosages: a high-intensity statin, a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi), and at least one agent from either of two classes that have both cardiovascular-protective and antihyperglycemic effects: the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or the glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1)–receptor agonists.
Among the 457 patients treated at the 20 cardiology clinics who received the quality-improvement intervention, 37.9% were on the promoted triple therapy after 12 months, compared with 14.5% of the 588 patients treated at the 23 clinics that continued with their usual care approach. This 23.4–percentage point increase in triple-class prescribing at recommended dosages represented a significant 4.4-fold increase in the goal prescribing endpoint after adjustment for possible confounders, Dr. Pagidipati reported.
Simultaneously with her report, the findings also appeared online in JAMA.
At baseline, 41%-50% of the patients were on both a high-intensity statin and a RASi, with a total of about 58%-67% on a high-intensity statin and about 70%-75% on a RASi. Fewer than 1% of patients were on SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1–receptor agonists at baseline. By design, no patient could be on all three categories of medication at baseline.
At their last follow-up visit (after 12 months for 97% of patients, or after 6 months for the remainder) 71% of the patients at practices that received the intervention were on a high-intensity statin, 81% were taking a RASi, and 60% were on an SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1–receptor agonist. Among the control patients, 58% were on a high-intensity statin, 68% on a RASi, and 36% were on one of the antihyperglycemic agents.
Effective interventions and the need for a champion
The clinics randomized to the active arm received instruction from a three-member team, either from an in-person or virtual one-time visit, on an intervention comprising several initiatives:
- Analysis of the barriers to evidence-based care at each clinic.
- Development of local interdisciplinary care pathways to address the identified barriers.
- Facilitation of care coordination among clinicians – particularly among cardiology, endocrinology, and primary care clinicians.
- Education of the clinic staff, including provision of educational materials.
- Auditing of clinic performance using specified metrics and feedback on the findings.
Clinics in the usual care group were given current clinical practice guidelines.
The investigational intervention was, by design, “low-tech and designed to be scalable,” explained Dr. Pagidipati, and once the COVID pandemic started the intervention team shifted to a virtual consultation with participating practices that was mostly front-loaded, followed by monthly phone calls to give clinics feedback on their progress.
Among the most helpful aspects of the intervention was involving the entire clinic staff, including pharmacists, nurses, and advanced care practitioners; boosting familiarity with the relevant medications and their appropriate use; and advice on navigating insurance-coverage barriers such as prior authorizations.
“What was most critical was having a local champion who took on making this effort an important part” of what the clinic was trying to do, she explained. “All it takes is passion, and the tenacity of a bulldog,” Dr. Pagidipati said.
Research advances often don’t translate into management changes
“We don’t do a great job of translating findings from trials to patient care, so any method we can use to improve that will improve practice,” commented Kristen B. Campbell, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist at Duke who was not involved in the study.
“Although the trial was not powered to look at patient outcomes, we think that patients will benefit” because all the recommended medication uses have been proven to help patients in prior trials, Dr. Campbell noted.
“A particular strength of this study was its simple design. All the interventions are low-tech and scalable.”
The low level of use of guideline-directed medical therapy in American adults with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is “incredible,” said Christopher B. Granger, MD, a senior investigator on the study and a cardiologist and professor at Duke.
The researchers who ran the study are now focused on evaluating which cardiology clinics and patients had the most success from the intervention and are using that information to further refine implementation. They are also planning to encourage cardiology practices as well as other relevant medical groups to incorporate the intervention and implementation model used in the trial. The intervention program is detailed and available at no charge on the COORDINATE-Diabetes website.
COORDINATE-Diabetes received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly. Dr. Pagidipati has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, and CRISPR Therapeutics, and she has received research grants from Amgen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Eggland’s Best. Dr. Campbell had no disclosures. Dr. Granger has received personal fees and research funding from numerous companies.
NEW ORLEANS – Twenty cardiology clinics successfully intensified the medical care they gave patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) after receiving a simple and scalable investigational intervention that gave the clinics’ staffs guidance on best prescribing practices and implementation and also provided quality-improvement feedback.
Within a year, these clinics quadrupled optimal medical management of these patients, compared with control clinics, in a randomized trial involving a total of 43 clinics and 1,049 patients.
“This multifaceted intervention is effective in increasing the prescription of evidence-based therapies in adults with T2D and ASCVD,” Neha J. Pagidipati, MD, said at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
“The next step is to scale this intervention across cardiology practices” interested in improving the quality of care they deliver to these patients, added Dr. Pagidipati, a cardiologist specializing in cardiometabolic disease prevention at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
The goal is getting patients on triple therapy
The primary outcome of the COORDINATE-Diabetes trial was the change in the number of patients with T2D and ASCVD who received prescriptions for agents from three recommended medication classes and at recommended dosages: a high-intensity statin, a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor (RASi), and at least one agent from either of two classes that have both cardiovascular-protective and antihyperglycemic effects: the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors, or the glucagonlike peptide 1 (GLP-1)–receptor agonists.
Among the 457 patients treated at the 20 cardiology clinics who received the quality-improvement intervention, 37.9% were on the promoted triple therapy after 12 months, compared with 14.5% of the 588 patients treated at the 23 clinics that continued with their usual care approach. This 23.4–percentage point increase in triple-class prescribing at recommended dosages represented a significant 4.4-fold increase in the goal prescribing endpoint after adjustment for possible confounders, Dr. Pagidipati reported.
Simultaneously with her report, the findings also appeared online in JAMA.
At baseline, 41%-50% of the patients were on both a high-intensity statin and a RASi, with a total of about 58%-67% on a high-intensity statin and about 70%-75% on a RASi. Fewer than 1% of patients were on SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1–receptor agonists at baseline. By design, no patient could be on all three categories of medication at baseline.
At their last follow-up visit (after 12 months for 97% of patients, or after 6 months for the remainder) 71% of the patients at practices that received the intervention were on a high-intensity statin, 81% were taking a RASi, and 60% were on an SGLT2 inhibitor or GLP-1–receptor agonist. Among the control patients, 58% were on a high-intensity statin, 68% on a RASi, and 36% were on one of the antihyperglycemic agents.
Effective interventions and the need for a champion
The clinics randomized to the active arm received instruction from a three-member team, either from an in-person or virtual one-time visit, on an intervention comprising several initiatives:
- Analysis of the barriers to evidence-based care at each clinic.
- Development of local interdisciplinary care pathways to address the identified barriers.
- Facilitation of care coordination among clinicians – particularly among cardiology, endocrinology, and primary care clinicians.
- Education of the clinic staff, including provision of educational materials.
- Auditing of clinic performance using specified metrics and feedback on the findings.
Clinics in the usual care group were given current clinical practice guidelines.
The investigational intervention was, by design, “low-tech and designed to be scalable,” explained Dr. Pagidipati, and once the COVID pandemic started the intervention team shifted to a virtual consultation with participating practices that was mostly front-loaded, followed by monthly phone calls to give clinics feedback on their progress.
Among the most helpful aspects of the intervention was involving the entire clinic staff, including pharmacists, nurses, and advanced care practitioners; boosting familiarity with the relevant medications and their appropriate use; and advice on navigating insurance-coverage barriers such as prior authorizations.
“What was most critical was having a local champion who took on making this effort an important part” of what the clinic was trying to do, she explained. “All it takes is passion, and the tenacity of a bulldog,” Dr. Pagidipati said.
Research advances often don’t translate into management changes
“We don’t do a great job of translating findings from trials to patient care, so any method we can use to improve that will improve practice,” commented Kristen B. Campbell, PharmD, a clinical pharmacist at Duke who was not involved in the study.
“Although the trial was not powered to look at patient outcomes, we think that patients will benefit” because all the recommended medication uses have been proven to help patients in prior trials, Dr. Campbell noted.
“A particular strength of this study was its simple design. All the interventions are low-tech and scalable.”
The low level of use of guideline-directed medical therapy in American adults with type 2 diabetes and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is “incredible,” said Christopher B. Granger, MD, a senior investigator on the study and a cardiologist and professor at Duke.
The researchers who ran the study are now focused on evaluating which cardiology clinics and patients had the most success from the intervention and are using that information to further refine implementation. They are also planning to encourage cardiology practices as well as other relevant medical groups to incorporate the intervention and implementation model used in the trial. The intervention program is detailed and available at no charge on the COORDINATE-Diabetes website.
COORDINATE-Diabetes received funding from Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly. Dr. Pagidipati has received personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, Lilly, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Merck, and CRISPR Therapeutics, and she has received research grants from Amgen, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, and Eggland’s Best. Dr. Campbell had no disclosures. Dr. Granger has received personal fees and research funding from numerous companies.
AT ACC 2023
Med center and top cardio surgeon must pay $8.5 million for fraud, concurrent surgeries
the Department of Justice (DOJ) announced.
The lawsuit alleges that James L. Luketich, MD, the longtime chair of the school’s cardiothoracic surgery department, regularly performed up to three complex surgical procedures simultaneously, moving among multiple operating rooms and attending to matters other than patient care. The investigation began after Jonathan D’Cunha, MD, a former UPMC surgeon, raised concerns about his colleague’s surgical scheduling and billing practices.
Dr. Luketich’s overbooking of procedures led to patients enduring hours of medically unnecessary anesthesia time and risking surgical complications, according to court documents.
In addition, the complaint states that these practices violated the False Claims Act, which prohibits “teaching physicians” like Dr. Luketich from billing Medicare and other government health plans for “concurrent surgeries” – regulations federal authorities say UPMC leadership were aware of and the University of Pittsburgh Physicians (UPP), also named in the suit, permitted Dr. Luketich to skirt.
The whistleblower provision of the False Claims Act allows private parties to file an action on behalf of the United States and receive a portion of the recovery to help deter health care fraud, says the DOJ.
The defendants previously asked the court to dismiss the case, but a judge denied the request in June 2022.
Paul Wood, vice president and chief communications officer for UPMC, told this news organization that the lawsuit pertained to Dr. Luketich’s “most complicated, team-based surgical procedures.”
“At issue was compliance with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS’s) Teaching Physician Regulation and related billing guidance as well as with UPMC’s internal surgical policies,” he said.
“While UPMC continues to believe Dr. Luketich’s surgical practice complies with CMS requirements, it has agreed to [the settlement] to avoid the distraction and expense of further litigation,” said Mr. Wood, adding that all parties agree that UPMC can seek clarity from CMS regarding future billing of these surgeries.
Efrem Grail, JD, Dr. Luketich’s attorney, said in an interview that he and Dr. Luketich are pleased that the settlement puts an end to the case and that he hopes the United States will issue “authoritative guidance” on billing regulations for teaching physicians, something medical schools and hospitals have sought for years.
Dr. Luketich, UPMC, and UPP face more legal challenges from a separate medical malpractice lawsuit. In March 2018, Bernadette Fedorka underwent a lung transplant at UPMC. Although Dr. Luketich did not perform the surgery, Ms. Fedorka alleges that his poor leadership caused understaffing of the lung transplant program and contributed to surgical complications, including a 4-inch piece of wire left in her neck.
Ms. Fedorka claims that suboxone impaired Dr. Luketich’s decision-making. He began taking the drug in 2008 to manage the pain from a slipped disc injury after a history of prescription drug abuse. Both UPMC and Dr. Luketich have denied the validity of Ms. Fedorka’s claims.
The malpractice suit centers on a recording of a conversation between Dr. Luketich and David Wilson, MD, who prescribed the suboxone and treated the surgeon’s opioid use disorder for several years. Dr. Luketich has accused former colleagues, Dr. D’Cunha and Lara Schaheen, MD, of illegally recording the private conversation that discussed Dr. Luketich’s suboxone prescription – something both physicians deny.
For the billing fraud case, Dr. Luketich has agreed to complete a corrective action plan and submit to a third-party audit of his Medicare billings for 1 year.
“This is an important settlement and a just conclusion to the United States’ investigation into Dr. Luketich’s surgical and billing practices and UPMC and UPP’s acceptance of those practices,” Acting U.S. Attorney Troy Rivetti said in a statement that, “no medical provider – however renowned – is excepted from scrutiny or above the law.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the Department of Justice (DOJ) announced.
The lawsuit alleges that James L. Luketich, MD, the longtime chair of the school’s cardiothoracic surgery department, regularly performed up to three complex surgical procedures simultaneously, moving among multiple operating rooms and attending to matters other than patient care. The investigation began after Jonathan D’Cunha, MD, a former UPMC surgeon, raised concerns about his colleague’s surgical scheduling and billing practices.
Dr. Luketich’s overbooking of procedures led to patients enduring hours of medically unnecessary anesthesia time and risking surgical complications, according to court documents.
In addition, the complaint states that these practices violated the False Claims Act, which prohibits “teaching physicians” like Dr. Luketich from billing Medicare and other government health plans for “concurrent surgeries” – regulations federal authorities say UPMC leadership were aware of and the University of Pittsburgh Physicians (UPP), also named in the suit, permitted Dr. Luketich to skirt.
The whistleblower provision of the False Claims Act allows private parties to file an action on behalf of the United States and receive a portion of the recovery to help deter health care fraud, says the DOJ.
The defendants previously asked the court to dismiss the case, but a judge denied the request in June 2022.
Paul Wood, vice president and chief communications officer for UPMC, told this news organization that the lawsuit pertained to Dr. Luketich’s “most complicated, team-based surgical procedures.”
“At issue was compliance with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS’s) Teaching Physician Regulation and related billing guidance as well as with UPMC’s internal surgical policies,” he said.
“While UPMC continues to believe Dr. Luketich’s surgical practice complies with CMS requirements, it has agreed to [the settlement] to avoid the distraction and expense of further litigation,” said Mr. Wood, adding that all parties agree that UPMC can seek clarity from CMS regarding future billing of these surgeries.
Efrem Grail, JD, Dr. Luketich’s attorney, said in an interview that he and Dr. Luketich are pleased that the settlement puts an end to the case and that he hopes the United States will issue “authoritative guidance” on billing regulations for teaching physicians, something medical schools and hospitals have sought for years.
Dr. Luketich, UPMC, and UPP face more legal challenges from a separate medical malpractice lawsuit. In March 2018, Bernadette Fedorka underwent a lung transplant at UPMC. Although Dr. Luketich did not perform the surgery, Ms. Fedorka alleges that his poor leadership caused understaffing of the lung transplant program and contributed to surgical complications, including a 4-inch piece of wire left in her neck.
Ms. Fedorka claims that suboxone impaired Dr. Luketich’s decision-making. He began taking the drug in 2008 to manage the pain from a slipped disc injury after a history of prescription drug abuse. Both UPMC and Dr. Luketich have denied the validity of Ms. Fedorka’s claims.
The malpractice suit centers on a recording of a conversation between Dr. Luketich and David Wilson, MD, who prescribed the suboxone and treated the surgeon’s opioid use disorder for several years. Dr. Luketich has accused former colleagues, Dr. D’Cunha and Lara Schaheen, MD, of illegally recording the private conversation that discussed Dr. Luketich’s suboxone prescription – something both physicians deny.
For the billing fraud case, Dr. Luketich has agreed to complete a corrective action plan and submit to a third-party audit of his Medicare billings for 1 year.
“This is an important settlement and a just conclusion to the United States’ investigation into Dr. Luketich’s surgical and billing practices and UPMC and UPP’s acceptance of those practices,” Acting U.S. Attorney Troy Rivetti said in a statement that, “no medical provider – however renowned – is excepted from scrutiny or above the law.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the Department of Justice (DOJ) announced.
The lawsuit alleges that James L. Luketich, MD, the longtime chair of the school’s cardiothoracic surgery department, regularly performed up to three complex surgical procedures simultaneously, moving among multiple operating rooms and attending to matters other than patient care. The investigation began after Jonathan D’Cunha, MD, a former UPMC surgeon, raised concerns about his colleague’s surgical scheduling and billing practices.
Dr. Luketich’s overbooking of procedures led to patients enduring hours of medically unnecessary anesthesia time and risking surgical complications, according to court documents.
In addition, the complaint states that these practices violated the False Claims Act, which prohibits “teaching physicians” like Dr. Luketich from billing Medicare and other government health plans for “concurrent surgeries” – regulations federal authorities say UPMC leadership were aware of and the University of Pittsburgh Physicians (UPP), also named in the suit, permitted Dr. Luketich to skirt.
The whistleblower provision of the False Claims Act allows private parties to file an action on behalf of the United States and receive a portion of the recovery to help deter health care fraud, says the DOJ.
The defendants previously asked the court to dismiss the case, but a judge denied the request in June 2022.
Paul Wood, vice president and chief communications officer for UPMC, told this news organization that the lawsuit pertained to Dr. Luketich’s “most complicated, team-based surgical procedures.”
“At issue was compliance with the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services’ (CMS’s) Teaching Physician Regulation and related billing guidance as well as with UPMC’s internal surgical policies,” he said.
“While UPMC continues to believe Dr. Luketich’s surgical practice complies with CMS requirements, it has agreed to [the settlement] to avoid the distraction and expense of further litigation,” said Mr. Wood, adding that all parties agree that UPMC can seek clarity from CMS regarding future billing of these surgeries.
Efrem Grail, JD, Dr. Luketich’s attorney, said in an interview that he and Dr. Luketich are pleased that the settlement puts an end to the case and that he hopes the United States will issue “authoritative guidance” on billing regulations for teaching physicians, something medical schools and hospitals have sought for years.
Dr. Luketich, UPMC, and UPP face more legal challenges from a separate medical malpractice lawsuit. In March 2018, Bernadette Fedorka underwent a lung transplant at UPMC. Although Dr. Luketich did not perform the surgery, Ms. Fedorka alleges that his poor leadership caused understaffing of the lung transplant program and contributed to surgical complications, including a 4-inch piece of wire left in her neck.
Ms. Fedorka claims that suboxone impaired Dr. Luketich’s decision-making. He began taking the drug in 2008 to manage the pain from a slipped disc injury after a history of prescription drug abuse. Both UPMC and Dr. Luketich have denied the validity of Ms. Fedorka’s claims.
The malpractice suit centers on a recording of a conversation between Dr. Luketich and David Wilson, MD, who prescribed the suboxone and treated the surgeon’s opioid use disorder for several years. Dr. Luketich has accused former colleagues, Dr. D’Cunha and Lara Schaheen, MD, of illegally recording the private conversation that discussed Dr. Luketich’s suboxone prescription – something both physicians deny.
For the billing fraud case, Dr. Luketich has agreed to complete a corrective action plan and submit to a third-party audit of his Medicare billings for 1 year.
“This is an important settlement and a just conclusion to the United States’ investigation into Dr. Luketich’s surgical and billing practices and UPMC and UPP’s acceptance of those practices,” Acting U.S. Attorney Troy Rivetti said in a statement that, “no medical provider – however renowned – is excepted from scrutiny or above the law.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Causal AI quantifies CV risk, providing patient-specific goals
NEW ORLEANS – Causal artificial intelligence (AI) can translate polygenic scores (PGS) and other genetic information into risk reduction strategies for coronary artery disease (CAD) that is tailored for each individual patient, according to an analysis presented at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
Tested for LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) and systolic blood pressure (SBP), causal AI explained how much each of these risk factors must improve at the level of each individual patient “to overcome overall inherited risk,” reported Brian Ference, MD, MPhil, director of translational therapeutics, University of Cambridge (England).
Unlike the “black box” risk assessments common to machine learning, which relies on disparate forms of information of often unknown relative significance, causal AI explains cause and effect. In the case of CAD, its ability to encode the biological causes means that it can “both predict outcomes and prescribe specific actions to change those outcomes,” Dr. Ference explained.
The concept is testable against observed biology using randomized evidence, which was the objective of the study Dr. Ference presented in the late-breaker session.
Causal AI trained on nearly 2 million patients
This study employed a causal AI platform trained on roughly 1.3 million participants in Mendelian randomization studies, as well as more than 500,000 participants in randomized clinical trials. The PGS estimate of inherited risk was constructed from almost 4.1 million variants from genomewide association studies.
To test the ability of causal AI to reveal how much LDL-C or SBP had to be reduced to overcome the inherited risk of CAD based on PGS, it was applied to 445,765 participants of European ancestry in the UK Biobank. The goal was to determine how much those with greater than average risk would need to lower their LDL-C or SBP to achieve average CAD risk.
When validated against observed rates of events, causal AI accurately characterized risk before estimating what reductions in LDL-C, SBP, or both would attenuate that risk.
Providing examples, Dr. Ference explained that a PGS in the 80th percentile can be overcome by lowering LDL-C by 14 mg/dL. Alternatively, the 80th percentile risk could also be overcome by simultaneously lowering LDL-C and SBP by 7 mg/dL and 2.5 mm Hg, respectively.
Required risk factor reductions increase with age because of the increased risk of the events. For example, while a 14.8 mg/dL reduction in LDL-C would be adequate to overcome risk defined by a PGS in the 80th percentile at age 35, reductions of 18.2 mg/dL, 28.9 mg/dL, and 42.6 mg/dL would be required, respectively, at ages 45, 55, and 65 years. The values climb similarly for SBP.
Family history of CAD adds an independent variable that further contributes to the ability of causal AI to estimate risk and the degree of risk factor attenuation to overcome the risk.
Even though family history is equivalent to having PGS above the 95th percentile, it is an independent and additive variable, according to Dr. Ference. As a result, inherited risk of CAD depends on both.
Still when family history is factored into the analysis, “causal AI accurately estimated the magnitude of lower LDL-C, SBP, or both needed to overcome overall inherited risk at all levels of higher or lower PGS,” he reported.
According to Dr. Ference, the value of causal AI is that it can generate very specific goals for each patient regarding modifiable risk factors. Causal effects of risk factors encoded in time units of exposure allow the patient and the clinician to understand the biology and the basis of the disease burden.
Treatments become understandable to patients
“Encoding biology creates algorithms that are deeply explainable because they reveal why a person is at risk, how to reduce that risk, and how much each person will benefit from specific actions to reduce risk,” Dr. Ference said.
A real-world, randomized trial to confirm that the information from causal AI can reduce the risk of CAD is expected to start in 2023, but Dr. Ference thinks that causal AI for managing CAD risk, independent of this planned trial, is essentially inevitable. PGS, which he thinks will be performed routinely in all individuals within 10 years, is only likely to improve. He foresees large advantages of this form of personalized medicine.
Ami Bhatt, MD, chief innovation officer for the American College of Cardiology, Washington, agreed, seeing a direct relationship between precision health as the pathway to improvements in population health.
By explaining risk factors in terms of mechanisms and specific goals to ameliorate these risks, it “engages our patients with agency,” said Dr. Bhatt. She suggested that the information provided by causal AI has the potential to empower patients while creating a collaborative approach with clinicians to CAD prevention.
With patient-specific information provided in the context of the disease biology, “you increase the sense of transparency,” Dr. Bhatt said.
She suggested this direction of research is wholly consistent with initiatives such as those from the World Health Organization to improve precision medicine as a step toward equipping patients to manage their own health.
Dr. Ference reported financial relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, CiVi Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, DalCOR, Esperion, Eli Lilly, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, KrKA, Medicines Company, Merck, Mylan, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Sanofi, and Viatris. Dr. Bhatt reported no potential conflicts of interest.
NEW ORLEANS – Causal artificial intelligence (AI) can translate polygenic scores (PGS) and other genetic information into risk reduction strategies for coronary artery disease (CAD) that is tailored for each individual patient, according to an analysis presented at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
Tested for LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) and systolic blood pressure (SBP), causal AI explained how much each of these risk factors must improve at the level of each individual patient “to overcome overall inherited risk,” reported Brian Ference, MD, MPhil, director of translational therapeutics, University of Cambridge (England).
Unlike the “black box” risk assessments common to machine learning, which relies on disparate forms of information of often unknown relative significance, causal AI explains cause and effect. In the case of CAD, its ability to encode the biological causes means that it can “both predict outcomes and prescribe specific actions to change those outcomes,” Dr. Ference explained.
The concept is testable against observed biology using randomized evidence, which was the objective of the study Dr. Ference presented in the late-breaker session.
Causal AI trained on nearly 2 million patients
This study employed a causal AI platform trained on roughly 1.3 million participants in Mendelian randomization studies, as well as more than 500,000 participants in randomized clinical trials. The PGS estimate of inherited risk was constructed from almost 4.1 million variants from genomewide association studies.
To test the ability of causal AI to reveal how much LDL-C or SBP had to be reduced to overcome the inherited risk of CAD based on PGS, it was applied to 445,765 participants of European ancestry in the UK Biobank. The goal was to determine how much those with greater than average risk would need to lower their LDL-C or SBP to achieve average CAD risk.
When validated against observed rates of events, causal AI accurately characterized risk before estimating what reductions in LDL-C, SBP, or both would attenuate that risk.
Providing examples, Dr. Ference explained that a PGS in the 80th percentile can be overcome by lowering LDL-C by 14 mg/dL. Alternatively, the 80th percentile risk could also be overcome by simultaneously lowering LDL-C and SBP by 7 mg/dL and 2.5 mm Hg, respectively.
Required risk factor reductions increase with age because of the increased risk of the events. For example, while a 14.8 mg/dL reduction in LDL-C would be adequate to overcome risk defined by a PGS in the 80th percentile at age 35, reductions of 18.2 mg/dL, 28.9 mg/dL, and 42.6 mg/dL would be required, respectively, at ages 45, 55, and 65 years. The values climb similarly for SBP.
Family history of CAD adds an independent variable that further contributes to the ability of causal AI to estimate risk and the degree of risk factor attenuation to overcome the risk.
Even though family history is equivalent to having PGS above the 95th percentile, it is an independent and additive variable, according to Dr. Ference. As a result, inherited risk of CAD depends on both.
Still when family history is factored into the analysis, “causal AI accurately estimated the magnitude of lower LDL-C, SBP, or both needed to overcome overall inherited risk at all levels of higher or lower PGS,” he reported.
According to Dr. Ference, the value of causal AI is that it can generate very specific goals for each patient regarding modifiable risk factors. Causal effects of risk factors encoded in time units of exposure allow the patient and the clinician to understand the biology and the basis of the disease burden.
Treatments become understandable to patients
“Encoding biology creates algorithms that are deeply explainable because they reveal why a person is at risk, how to reduce that risk, and how much each person will benefit from specific actions to reduce risk,” Dr. Ference said.
A real-world, randomized trial to confirm that the information from causal AI can reduce the risk of CAD is expected to start in 2023, but Dr. Ference thinks that causal AI for managing CAD risk, independent of this planned trial, is essentially inevitable. PGS, which he thinks will be performed routinely in all individuals within 10 years, is only likely to improve. He foresees large advantages of this form of personalized medicine.
Ami Bhatt, MD, chief innovation officer for the American College of Cardiology, Washington, agreed, seeing a direct relationship between precision health as the pathway to improvements in population health.
By explaining risk factors in terms of mechanisms and specific goals to ameliorate these risks, it “engages our patients with agency,” said Dr. Bhatt. She suggested that the information provided by causal AI has the potential to empower patients while creating a collaborative approach with clinicians to CAD prevention.
With patient-specific information provided in the context of the disease biology, “you increase the sense of transparency,” Dr. Bhatt said.
She suggested this direction of research is wholly consistent with initiatives such as those from the World Health Organization to improve precision medicine as a step toward equipping patients to manage their own health.
Dr. Ference reported financial relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, CiVi Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, DalCOR, Esperion, Eli Lilly, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, KrKA, Medicines Company, Merck, Mylan, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Sanofi, and Viatris. Dr. Bhatt reported no potential conflicts of interest.
NEW ORLEANS – Causal artificial intelligence (AI) can translate polygenic scores (PGS) and other genetic information into risk reduction strategies for coronary artery disease (CAD) that is tailored for each individual patient, according to an analysis presented at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
Tested for LDL cholesterol (LDL-C) and systolic blood pressure (SBP), causal AI explained how much each of these risk factors must improve at the level of each individual patient “to overcome overall inherited risk,” reported Brian Ference, MD, MPhil, director of translational therapeutics, University of Cambridge (England).
Unlike the “black box” risk assessments common to machine learning, which relies on disparate forms of information of often unknown relative significance, causal AI explains cause and effect. In the case of CAD, its ability to encode the biological causes means that it can “both predict outcomes and prescribe specific actions to change those outcomes,” Dr. Ference explained.
The concept is testable against observed biology using randomized evidence, which was the objective of the study Dr. Ference presented in the late-breaker session.
Causal AI trained on nearly 2 million patients
This study employed a causal AI platform trained on roughly 1.3 million participants in Mendelian randomization studies, as well as more than 500,000 participants in randomized clinical trials. The PGS estimate of inherited risk was constructed from almost 4.1 million variants from genomewide association studies.
To test the ability of causal AI to reveal how much LDL-C or SBP had to be reduced to overcome the inherited risk of CAD based on PGS, it was applied to 445,765 participants of European ancestry in the UK Biobank. The goal was to determine how much those with greater than average risk would need to lower their LDL-C or SBP to achieve average CAD risk.
When validated against observed rates of events, causal AI accurately characterized risk before estimating what reductions in LDL-C, SBP, or both would attenuate that risk.
Providing examples, Dr. Ference explained that a PGS in the 80th percentile can be overcome by lowering LDL-C by 14 mg/dL. Alternatively, the 80th percentile risk could also be overcome by simultaneously lowering LDL-C and SBP by 7 mg/dL and 2.5 mm Hg, respectively.
Required risk factor reductions increase with age because of the increased risk of the events. For example, while a 14.8 mg/dL reduction in LDL-C would be adequate to overcome risk defined by a PGS in the 80th percentile at age 35, reductions of 18.2 mg/dL, 28.9 mg/dL, and 42.6 mg/dL would be required, respectively, at ages 45, 55, and 65 years. The values climb similarly for SBP.
Family history of CAD adds an independent variable that further contributes to the ability of causal AI to estimate risk and the degree of risk factor attenuation to overcome the risk.
Even though family history is equivalent to having PGS above the 95th percentile, it is an independent and additive variable, according to Dr. Ference. As a result, inherited risk of CAD depends on both.
Still when family history is factored into the analysis, “causal AI accurately estimated the magnitude of lower LDL-C, SBP, or both needed to overcome overall inherited risk at all levels of higher or lower PGS,” he reported.
According to Dr. Ference, the value of causal AI is that it can generate very specific goals for each patient regarding modifiable risk factors. Causal effects of risk factors encoded in time units of exposure allow the patient and the clinician to understand the biology and the basis of the disease burden.
Treatments become understandable to patients
“Encoding biology creates algorithms that are deeply explainable because they reveal why a person is at risk, how to reduce that risk, and how much each person will benefit from specific actions to reduce risk,” Dr. Ference said.
A real-world, randomized trial to confirm that the information from causal AI can reduce the risk of CAD is expected to start in 2023, but Dr. Ference thinks that causal AI for managing CAD risk, independent of this planned trial, is essentially inevitable. PGS, which he thinks will be performed routinely in all individuals within 10 years, is only likely to improve. He foresees large advantages of this form of personalized medicine.
Ami Bhatt, MD, chief innovation officer for the American College of Cardiology, Washington, agreed, seeing a direct relationship between precision health as the pathway to improvements in population health.
By explaining risk factors in terms of mechanisms and specific goals to ameliorate these risks, it “engages our patients with agency,” said Dr. Bhatt. She suggested that the information provided by causal AI has the potential to empower patients while creating a collaborative approach with clinicians to CAD prevention.
With patient-specific information provided in the context of the disease biology, “you increase the sense of transparency,” Dr. Bhatt said.
She suggested this direction of research is wholly consistent with initiatives such as those from the World Health Organization to improve precision medicine as a step toward equipping patients to manage their own health.
Dr. Ference reported financial relationships with Amgen, AstraZeneca, CiVi Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, DalCOR, Esperion, Eli Lilly, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, KrKA, Medicines Company, Merck, Mylan, Novo Nordisk, Novartis, and Sanofi, and Viatris. Dr. Bhatt reported no potential conflicts of interest.
AT ACC 2023
Biomarkers linked to elevated T2D MACE risk in DECLARE-TIMI 58
The researchers found that N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hsTnT) levels helped identify a subset of T2D patients at higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events who would benefit most from dapagliflozin.
“We’ve shown previously that these two biomarkers are very robust risk indicators for cardiovascular death and heart failure events,” senior study author David A. Morrow, MD, of Harvard University, Boston, said in an interview. “In this study, we now show that the two biomarkers also yield important prognostic information for MACE [major adverse cardiovascular events].”
Although NT-proBNP is typically measured to diagnose heart failure, and hsTnT to diagnose acute MI, Dr. Morrow pointed out that this analysis demonstrated the potential for using the two tests to evaluate risks in T2D patients.
Study results
The secondary analysis included 14,565 patients in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial. The patients had T2D and multiple risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (about 60%) or established ASCVD (about 40%). All patients had available blood samples and the data were collected from May 2013 to September 2018. The primary outcome was MACE, a composite of MI, ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death. The results were reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
The analysis found that higher baseline concentrations of NT-proBNP increased MACE risks by 62% (95% confidence interval, 1.49-1.76) and hsTnT elevated those risks by 59% (95% CI, 1.46-1.74).
Among placebo patients, when divided into risk quartiles, those in the highest quartile had significantly higher risk with both elevated NT-proBNP and hsTnT, compared with those with low concentrations. For example, patients with established ASCVD had a 22.9% risk vs. 9.5% with elevated NT-proBNP (P < .001) and a 24.2% vs. 7.2% risk with elevated hsTnT (P < .001). The gap was similar for patients with multiple risk factors.
Dr. Morrow noted that the main DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial showed that dapagliflozin reduced the rates of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure in patients with T2D, when compared to placebo, but didn’t reach statistical significance for MACE (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347-57).
“We have previously shown that among patients with T2D who have high risk indicators, such as prior MI or long-standing diabetes, dapagliflozin also appeared to reduce MACE,” Dr. Morrow said. “In this study, we find that these two widely available biomarkers also identify a high-risk group who may have even more potential benefits from treatment with an SGLT2i.”
Dr. Morrow noted that the study design – a nested prospective biomarker study within a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial – “is a particular strength.”
Results clarify which patients will benefit
This secondary analysis of DECLARE-TIMI 58 brings more clarity to the types of T2D patients who will get the most cardiovascular benefits from dapagliflozin, said Matthew J. Budoff, MD, professor of medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, and Endowed Chair of Preventive Cardiology at the Lundquist Institute in Torrance, Calif.
“The big picture is, we’ve known for some time from epidemiologic studies that these biomarkers, when they’re elevated, mean that the patient is at higher risk of having a cardiovascular event,” he said, “but I think what it helps us with is in knowing in whom to use dapagliflozin for prevention of ASCVD. The effect in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial was quite modest, but if you can subgroup it, in these high-risk people there’s a more profound effect. It helps in risk stratification because the absolute benefit is larger.”
The specific biomarkers, NT-proBNP and hsTnT, “haven’t been explored very much in clinical trials,” Dr. Budoff said, “so I do think that it’s nice that in a randomized trial it plays out the way we might expect.”
He added that “for many clinicians this is novel, because I don’t think they were aware of the biomarker data, so I think that this does add some clinical benefit in that context.” The findings also strengthen the case to get T2D patients with higher ASCVD risk onto SGLT2 inhibitors if they’re not already, he said.
Dr. Morrow disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, Anthos Therapeutics, ARCA Biopharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Siemens, and InCarda outside the reported work.
Dr. Budoff has no relevant disclosures.
The researchers found that N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hsTnT) levels helped identify a subset of T2D patients at higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events who would benefit most from dapagliflozin.
“We’ve shown previously that these two biomarkers are very robust risk indicators for cardiovascular death and heart failure events,” senior study author David A. Morrow, MD, of Harvard University, Boston, said in an interview. “In this study, we now show that the two biomarkers also yield important prognostic information for MACE [major adverse cardiovascular events].”
Although NT-proBNP is typically measured to diagnose heart failure, and hsTnT to diagnose acute MI, Dr. Morrow pointed out that this analysis demonstrated the potential for using the two tests to evaluate risks in T2D patients.
Study results
The secondary analysis included 14,565 patients in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial. The patients had T2D and multiple risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (about 60%) or established ASCVD (about 40%). All patients had available blood samples and the data were collected from May 2013 to September 2018. The primary outcome was MACE, a composite of MI, ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death. The results were reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
The analysis found that higher baseline concentrations of NT-proBNP increased MACE risks by 62% (95% confidence interval, 1.49-1.76) and hsTnT elevated those risks by 59% (95% CI, 1.46-1.74).
Among placebo patients, when divided into risk quartiles, those in the highest quartile had significantly higher risk with both elevated NT-proBNP and hsTnT, compared with those with low concentrations. For example, patients with established ASCVD had a 22.9% risk vs. 9.5% with elevated NT-proBNP (P < .001) and a 24.2% vs. 7.2% risk with elevated hsTnT (P < .001). The gap was similar for patients with multiple risk factors.
Dr. Morrow noted that the main DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial showed that dapagliflozin reduced the rates of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure in patients with T2D, when compared to placebo, but didn’t reach statistical significance for MACE (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347-57).
“We have previously shown that among patients with T2D who have high risk indicators, such as prior MI or long-standing diabetes, dapagliflozin also appeared to reduce MACE,” Dr. Morrow said. “In this study, we find that these two widely available biomarkers also identify a high-risk group who may have even more potential benefits from treatment with an SGLT2i.”
Dr. Morrow noted that the study design – a nested prospective biomarker study within a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial – “is a particular strength.”
Results clarify which patients will benefit
This secondary analysis of DECLARE-TIMI 58 brings more clarity to the types of T2D patients who will get the most cardiovascular benefits from dapagliflozin, said Matthew J. Budoff, MD, professor of medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, and Endowed Chair of Preventive Cardiology at the Lundquist Institute in Torrance, Calif.
“The big picture is, we’ve known for some time from epidemiologic studies that these biomarkers, when they’re elevated, mean that the patient is at higher risk of having a cardiovascular event,” he said, “but I think what it helps us with is in knowing in whom to use dapagliflozin for prevention of ASCVD. The effect in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial was quite modest, but if you can subgroup it, in these high-risk people there’s a more profound effect. It helps in risk stratification because the absolute benefit is larger.”
The specific biomarkers, NT-proBNP and hsTnT, “haven’t been explored very much in clinical trials,” Dr. Budoff said, “so I do think that it’s nice that in a randomized trial it plays out the way we might expect.”
He added that “for many clinicians this is novel, because I don’t think they were aware of the biomarker data, so I think that this does add some clinical benefit in that context.” The findings also strengthen the case to get T2D patients with higher ASCVD risk onto SGLT2 inhibitors if they’re not already, he said.
Dr. Morrow disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, Anthos Therapeutics, ARCA Biopharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Siemens, and InCarda outside the reported work.
Dr. Budoff has no relevant disclosures.
The researchers found that N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T (hsTnT) levels helped identify a subset of T2D patients at higher risk of major adverse cardiovascular events who would benefit most from dapagliflozin.
“We’ve shown previously that these two biomarkers are very robust risk indicators for cardiovascular death and heart failure events,” senior study author David A. Morrow, MD, of Harvard University, Boston, said in an interview. “In this study, we now show that the two biomarkers also yield important prognostic information for MACE [major adverse cardiovascular events].”
Although NT-proBNP is typically measured to diagnose heart failure, and hsTnT to diagnose acute MI, Dr. Morrow pointed out that this analysis demonstrated the potential for using the two tests to evaluate risks in T2D patients.
Study results
The secondary analysis included 14,565 patients in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial. The patients had T2D and multiple risk factors for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (about 60%) or established ASCVD (about 40%). All patients had available blood samples and the data were collected from May 2013 to September 2018. The primary outcome was MACE, a composite of MI, ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death. The results were reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
The analysis found that higher baseline concentrations of NT-proBNP increased MACE risks by 62% (95% confidence interval, 1.49-1.76) and hsTnT elevated those risks by 59% (95% CI, 1.46-1.74).
Among placebo patients, when divided into risk quartiles, those in the highest quartile had significantly higher risk with both elevated NT-proBNP and hsTnT, compared with those with low concentrations. For example, patients with established ASCVD had a 22.9% risk vs. 9.5% with elevated NT-proBNP (P < .001) and a 24.2% vs. 7.2% risk with elevated hsTnT (P < .001). The gap was similar for patients with multiple risk factors.
Dr. Morrow noted that the main DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial showed that dapagliflozin reduced the rates of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure in patients with T2D, when compared to placebo, but didn’t reach statistical significance for MACE (N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347-57).
“We have previously shown that among patients with T2D who have high risk indicators, such as prior MI or long-standing diabetes, dapagliflozin also appeared to reduce MACE,” Dr. Morrow said. “In this study, we find that these two widely available biomarkers also identify a high-risk group who may have even more potential benefits from treatment with an SGLT2i.”
Dr. Morrow noted that the study design – a nested prospective biomarker study within a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial – “is a particular strength.”
Results clarify which patients will benefit
This secondary analysis of DECLARE-TIMI 58 brings more clarity to the types of T2D patients who will get the most cardiovascular benefits from dapagliflozin, said Matthew J. Budoff, MD, professor of medicine at University of California, Los Angeles, and Endowed Chair of Preventive Cardiology at the Lundquist Institute in Torrance, Calif.
“The big picture is, we’ve known for some time from epidemiologic studies that these biomarkers, when they’re elevated, mean that the patient is at higher risk of having a cardiovascular event,” he said, “but I think what it helps us with is in knowing in whom to use dapagliflozin for prevention of ASCVD. The effect in the DECLARE-TIMI 58 trial was quite modest, but if you can subgroup it, in these high-risk people there’s a more profound effect. It helps in risk stratification because the absolute benefit is larger.”
The specific biomarkers, NT-proBNP and hsTnT, “haven’t been explored very much in clinical trials,” Dr. Budoff said, “so I do think that it’s nice that in a randomized trial it plays out the way we might expect.”
He added that “for many clinicians this is novel, because I don’t think they were aware of the biomarker data, so I think that this does add some clinical benefit in that context.” The findings also strengthen the case to get T2D patients with higher ASCVD risk onto SGLT2 inhibitors if they’re not already, he said.
Dr. Morrow disclosed relationships with AstraZeneca, Roche Diagnostics, Abbott Laboratories, Anthos Therapeutics, ARCA Biopharma, Merck, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Siemens, and InCarda outside the reported work.
Dr. Budoff has no relevant disclosures.
FROM JAMA CARDIOLOGY
NUDGE-FLU: Electronic ‘nudges’ boost flu shot uptake in seniors
Two types of electronically delivered letter strategies – a letter highlighting potential cardiovascular benefits of influenza vaccination and a repeat reminder letter – increased flu shot uptake, compared with usual care alone, in a national study of seniors in Denmark.
And in a prespecified subanalysis focusing on older adults with cardiovascular disease, these two strategies were also effective in boosting vaccine uptake in those with or without CVD.
The findings are from the Nationwide Utilization of Danish Government Electronic Letter System for Increasing Influenza Vaccine Uptake (NUDGE-FLU) trial, which compared usual care alone with one of nine different electronic letter “behavioral nudge” strategies during the 2022-2023 flu season in people aged 65 years and older.
Niklas Dyrby Johansen, MD, Hospital–Herlev and Gentofte and Copenhagen University, presented the main study findings in a late-breaking clinical trial session at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation, and the article was simultaneously published in The Lancet
The subanalysis in patients with CVD was published online March 5 in Circulation.
“Despite modest effect sizes, the results may have important implications when translated to a population level,” Dr. Dyrby Johansen concluded during his presentation. Still, the authors write, “the low-touch (no person-to-person interaction), inexpensive, and highly scalable nature of these electronic letters might have important population-level public health implications.”
They note that, among approximately 63 million Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, a 0.89–percentage point absolute increase in vaccination rate achieved through the most successful electronic letter in NUDGE-FLU, the one highlighting cardiovascular gain, would be expected to lead to 500,000 additional vaccinations and potentially prevent 7,849 illnesses, 4,395 medical visits, 714 hospitalizations, and 66 deaths each year.
Electronic letter systems similar to the one used in this trial are already in place in several European countries, including Sweden, Norway, and Ireland, the researchers note.
In countries such as the United States, where implementing a nationwide government electronic letter system might not be feasible, nudges could be done via email, text message, or other systems, but whether this would be as effective remains to be seen.
Commenting on the findings, David Cho, MD, UCLA Health and chair of the ACC Health Care Innovation Council, commended the researchers on engaging patients with more than a million separate nudges sent out during one flu season, and randomly assigning participants to 10 different types of nudges, calling it “impressive.”
“I think the concept that the nudge is to plant an idea that leads to an action is pretty much the basis of a lot of these health care interventions, which seems like a small way to have a big impact at outcome,” Dr. Cho noted. “The behavioral science aspects of the nudges are also fascinating to me personally, and I think to a lot of the cardiologists in the audience – about how you actually get people to act. I think it’s been a lifelong question for people in general, how do you get people to follow through on an action?”
“So I found the fact that secondary gain from a cardiovascular health standpoint, but also the repeated nudges were sort of simple ways that you could have people take ownership and get their flu vaccination,” he said.
“This is ACC, this is a cardiovascular conference, but the influence of vaccine is not just a primary care problem, it is also directly affecting cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Cho concluded.
‘Small but important effect’
In an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2023 Mar 5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00453-1), Melissa Stockwell, MD, Columbia University, New York, writes, “The study by Johansen and colleagues highlights the small but still important effect of scalable, digital interventions across an entire at-risk population.”
A difference of 0.89% in the entire study population of over 960,000 adults age 65 years or older would be more than 8,500 additional adults protected, she notes. “That increase is important for a scalable intervention that has a low cost per letter.”
Moreover, “that the cardiovascular gain–framed messages worked best in those who had not been vaccinated in the previous season further highlights the potential impact on a more vaccine-hesitant population,” Dr. Stockwell notes.
However, with the mandatory government electronic notification system in Denmark, “notifications are sent via regular email and SMS message, and recipients log in through a portal or smartphone app to view the letter.” Similar studies in the United States that included this extra step of needing to sign in online have not been effective in older populations.
Another limitation is that the intervention may have a different effect in populations for which there is a digital divide between people with or without Internet access of sufficient data on their mobile phones.
First-of-its kind, nationwide pragmatic trial
The NUDGE-FLU protocol was previously published in the American Heart Journal. NUDGE-FLU is a first-of-its kind nationwide, pragmatic, registry-based, cluster-randomized implementation trial of electronically delivered nudges to increase influenza vaccination uptake, the researchers note.
They identified 964,870 individuals who were 65 years or older (or would turn 65 by Jan. 15, 2023) who lived in one of 691,820 households in Denmark.
This excluded individuals who lived in a nursing home or were exempt from the government’s mandatory electronic letter system that is used for official communications.
Households were randomly assigned 9:1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1 to receive usual care alone or to one of nine electronic letter strategies based on different behavioral science approaches to encourage influenza vaccination uptake:
- Standard electronic letter
- Standard electronic letter sent at randomization and again 14 days later (repeated letter)
- Depersonalized letter without the recipient’s name
- Gain-framing nudge (“Vaccinations help end pandemics, like COVID-19 and the flu. Protect yourself and your loved ones.”)
- Loss-framing nudge (“When too few people get vaccinated, pandemics from diseases like COVID-19 and the flu can spread and place you and your loved ones at risk.”)
- Collective-goal nudge (“78% of Danes 65 and above were vaccinated against influenza last year. Help us achieve an even higher goal this year.”)
- Active choice or implementation-intention prompt (“We encourage you to record your appointment time here.”)
- Cardiovascular gain–framing nudge (“In addition to its protection against influenza infection, influenza vaccination also seems to protect against cardiovascular disease such as heart attacks and heart failure.”)
- Expert-authority statement (“I recommend everyone over the age of 65 years to get vaccinated against influenza – Tyra Grove Krause, Executive Vice President, Statens Serum Institut.”)
The electronic letters were sent out Sept. 16, 2022, and the primary endpoint was vaccine receipt on or before Jan. 1, 2023.
All individuals received an informative vaccination encouragement letter from the Danish Health Authority (usual care) delivered via the same electronic letter system during Sept. 17 through Sept. 21, 2022.
The individuals had a mean age of 73.8 years, 51.5% were women, and 27.4% had chronic cardiovascular disease.
The analyses were done in one randomly selected individual per household.
Influenza vaccination rates were significantly higher in the cardiovascular gain–framing nudge group vs. usual care (81.00% vs. 80.12%; difference, 0.89 percentage points; P < .0001) and in the repeat-letter group vs. usual care (80.85% vs 80.12%; difference, 0.73 percentage points; P = .0006).
These two strategies also improved vaccination rates across major subgroups.
The cardiovascular gain–framed letter was particularly effective among participants who had not been vaccinated for influenza in the previous season.
The seven other letter strategies did not increase flu shot uptake.
Subanalysis in CVD
In the prespecified subanalysis of the NUDGE-FLU trial of patients aged 65 and older that focused on patients with CVD, Daniel Modin, MB, and colleagues report that 83.1% of patients with CVD vs. 79.2% of patients without CVD received influenza vaccination within the requested time (P < .0001).
The two nudging strategies – a letter highlighting potential cardiovascular benefits of influenza vaccination or a repeat letter – that were effective in boosting flu shot rates in the main analysis were also effective in all major CVD subgroups (ischemic heart disease, pulmonary heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerotic CVD, embolic or thrombotic disease, and congenital heart disease).
Despite strong guideline endorsement, “influenza vaccination rates remain suboptimal in patients with high-risk cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Morin and colleagues write, possibly because of “insufficient knowledge among patients and providers of potential clinical benefits, concerns about vaccine safety, and other forms of vaccine hesitancy.”
Their findings suggest that “select digital behaviorally informed nudges delivered in advance of vaccine availability might be utilized to increase influenza vaccinate uptake in individuals with cardiovascular disease.”
NUDGE-HF was funded by Sanofi. Dr. Johansen and Dr. Modin have no disclosures. The disclosures of the other authors are listed with the articles. Dr. Stockwell has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two types of electronically delivered letter strategies – a letter highlighting potential cardiovascular benefits of influenza vaccination and a repeat reminder letter – increased flu shot uptake, compared with usual care alone, in a national study of seniors in Denmark.
And in a prespecified subanalysis focusing on older adults with cardiovascular disease, these two strategies were also effective in boosting vaccine uptake in those with or without CVD.
The findings are from the Nationwide Utilization of Danish Government Electronic Letter System for Increasing Influenza Vaccine Uptake (NUDGE-FLU) trial, which compared usual care alone with one of nine different electronic letter “behavioral nudge” strategies during the 2022-2023 flu season in people aged 65 years and older.
Niklas Dyrby Johansen, MD, Hospital–Herlev and Gentofte and Copenhagen University, presented the main study findings in a late-breaking clinical trial session at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation, and the article was simultaneously published in The Lancet
The subanalysis in patients with CVD was published online March 5 in Circulation.
“Despite modest effect sizes, the results may have important implications when translated to a population level,” Dr. Dyrby Johansen concluded during his presentation. Still, the authors write, “the low-touch (no person-to-person interaction), inexpensive, and highly scalable nature of these electronic letters might have important population-level public health implications.”
They note that, among approximately 63 million Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, a 0.89–percentage point absolute increase in vaccination rate achieved through the most successful electronic letter in NUDGE-FLU, the one highlighting cardiovascular gain, would be expected to lead to 500,000 additional vaccinations and potentially prevent 7,849 illnesses, 4,395 medical visits, 714 hospitalizations, and 66 deaths each year.
Electronic letter systems similar to the one used in this trial are already in place in several European countries, including Sweden, Norway, and Ireland, the researchers note.
In countries such as the United States, where implementing a nationwide government electronic letter system might not be feasible, nudges could be done via email, text message, or other systems, but whether this would be as effective remains to be seen.
Commenting on the findings, David Cho, MD, UCLA Health and chair of the ACC Health Care Innovation Council, commended the researchers on engaging patients with more than a million separate nudges sent out during one flu season, and randomly assigning participants to 10 different types of nudges, calling it “impressive.”
“I think the concept that the nudge is to plant an idea that leads to an action is pretty much the basis of a lot of these health care interventions, which seems like a small way to have a big impact at outcome,” Dr. Cho noted. “The behavioral science aspects of the nudges are also fascinating to me personally, and I think to a lot of the cardiologists in the audience – about how you actually get people to act. I think it’s been a lifelong question for people in general, how do you get people to follow through on an action?”
“So I found the fact that secondary gain from a cardiovascular health standpoint, but also the repeated nudges were sort of simple ways that you could have people take ownership and get their flu vaccination,” he said.
“This is ACC, this is a cardiovascular conference, but the influence of vaccine is not just a primary care problem, it is also directly affecting cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Cho concluded.
‘Small but important effect’
In an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2023 Mar 5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00453-1), Melissa Stockwell, MD, Columbia University, New York, writes, “The study by Johansen and colleagues highlights the small but still important effect of scalable, digital interventions across an entire at-risk population.”
A difference of 0.89% in the entire study population of over 960,000 adults age 65 years or older would be more than 8,500 additional adults protected, she notes. “That increase is important for a scalable intervention that has a low cost per letter.”
Moreover, “that the cardiovascular gain–framed messages worked best in those who had not been vaccinated in the previous season further highlights the potential impact on a more vaccine-hesitant population,” Dr. Stockwell notes.
However, with the mandatory government electronic notification system in Denmark, “notifications are sent via regular email and SMS message, and recipients log in through a portal or smartphone app to view the letter.” Similar studies in the United States that included this extra step of needing to sign in online have not been effective in older populations.
Another limitation is that the intervention may have a different effect in populations for which there is a digital divide between people with or without Internet access of sufficient data on their mobile phones.
First-of-its kind, nationwide pragmatic trial
The NUDGE-FLU protocol was previously published in the American Heart Journal. NUDGE-FLU is a first-of-its kind nationwide, pragmatic, registry-based, cluster-randomized implementation trial of electronically delivered nudges to increase influenza vaccination uptake, the researchers note.
They identified 964,870 individuals who were 65 years or older (or would turn 65 by Jan. 15, 2023) who lived in one of 691,820 households in Denmark.
This excluded individuals who lived in a nursing home or were exempt from the government’s mandatory electronic letter system that is used for official communications.
Households were randomly assigned 9:1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1 to receive usual care alone or to one of nine electronic letter strategies based on different behavioral science approaches to encourage influenza vaccination uptake:
- Standard electronic letter
- Standard electronic letter sent at randomization and again 14 days later (repeated letter)
- Depersonalized letter without the recipient’s name
- Gain-framing nudge (“Vaccinations help end pandemics, like COVID-19 and the flu. Protect yourself and your loved ones.”)
- Loss-framing nudge (“When too few people get vaccinated, pandemics from diseases like COVID-19 and the flu can spread and place you and your loved ones at risk.”)
- Collective-goal nudge (“78% of Danes 65 and above were vaccinated against influenza last year. Help us achieve an even higher goal this year.”)
- Active choice or implementation-intention prompt (“We encourage you to record your appointment time here.”)
- Cardiovascular gain–framing nudge (“In addition to its protection against influenza infection, influenza vaccination also seems to protect against cardiovascular disease such as heart attacks and heart failure.”)
- Expert-authority statement (“I recommend everyone over the age of 65 years to get vaccinated against influenza – Tyra Grove Krause, Executive Vice President, Statens Serum Institut.”)
The electronic letters were sent out Sept. 16, 2022, and the primary endpoint was vaccine receipt on or before Jan. 1, 2023.
All individuals received an informative vaccination encouragement letter from the Danish Health Authority (usual care) delivered via the same electronic letter system during Sept. 17 through Sept. 21, 2022.
The individuals had a mean age of 73.8 years, 51.5% were women, and 27.4% had chronic cardiovascular disease.
The analyses were done in one randomly selected individual per household.
Influenza vaccination rates were significantly higher in the cardiovascular gain–framing nudge group vs. usual care (81.00% vs. 80.12%; difference, 0.89 percentage points; P < .0001) and in the repeat-letter group vs. usual care (80.85% vs 80.12%; difference, 0.73 percentage points; P = .0006).
These two strategies also improved vaccination rates across major subgroups.
The cardiovascular gain–framed letter was particularly effective among participants who had not been vaccinated for influenza in the previous season.
The seven other letter strategies did not increase flu shot uptake.
Subanalysis in CVD
In the prespecified subanalysis of the NUDGE-FLU trial of patients aged 65 and older that focused on patients with CVD, Daniel Modin, MB, and colleagues report that 83.1% of patients with CVD vs. 79.2% of patients without CVD received influenza vaccination within the requested time (P < .0001).
The two nudging strategies – a letter highlighting potential cardiovascular benefits of influenza vaccination or a repeat letter – that were effective in boosting flu shot rates in the main analysis were also effective in all major CVD subgroups (ischemic heart disease, pulmonary heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerotic CVD, embolic or thrombotic disease, and congenital heart disease).
Despite strong guideline endorsement, “influenza vaccination rates remain suboptimal in patients with high-risk cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Morin and colleagues write, possibly because of “insufficient knowledge among patients and providers of potential clinical benefits, concerns about vaccine safety, and other forms of vaccine hesitancy.”
Their findings suggest that “select digital behaviorally informed nudges delivered in advance of vaccine availability might be utilized to increase influenza vaccinate uptake in individuals with cardiovascular disease.”
NUDGE-HF was funded by Sanofi. Dr. Johansen and Dr. Modin have no disclosures. The disclosures of the other authors are listed with the articles. Dr. Stockwell has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two types of electronically delivered letter strategies – a letter highlighting potential cardiovascular benefits of influenza vaccination and a repeat reminder letter – increased flu shot uptake, compared with usual care alone, in a national study of seniors in Denmark.
And in a prespecified subanalysis focusing on older adults with cardiovascular disease, these two strategies were also effective in boosting vaccine uptake in those with or without CVD.
The findings are from the Nationwide Utilization of Danish Government Electronic Letter System for Increasing Influenza Vaccine Uptake (NUDGE-FLU) trial, which compared usual care alone with one of nine different electronic letter “behavioral nudge” strategies during the 2022-2023 flu season in people aged 65 years and older.
Niklas Dyrby Johansen, MD, Hospital–Herlev and Gentofte and Copenhagen University, presented the main study findings in a late-breaking clinical trial session at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation, and the article was simultaneously published in The Lancet
The subanalysis in patients with CVD was published online March 5 in Circulation.
“Despite modest effect sizes, the results may have important implications when translated to a population level,” Dr. Dyrby Johansen concluded during his presentation. Still, the authors write, “the low-touch (no person-to-person interaction), inexpensive, and highly scalable nature of these electronic letters might have important population-level public health implications.”
They note that, among approximately 63 million Medicare beneficiaries in the United States, a 0.89–percentage point absolute increase in vaccination rate achieved through the most successful electronic letter in NUDGE-FLU, the one highlighting cardiovascular gain, would be expected to lead to 500,000 additional vaccinations and potentially prevent 7,849 illnesses, 4,395 medical visits, 714 hospitalizations, and 66 deaths each year.
Electronic letter systems similar to the one used in this trial are already in place in several European countries, including Sweden, Norway, and Ireland, the researchers note.
In countries such as the United States, where implementing a nationwide government electronic letter system might not be feasible, nudges could be done via email, text message, or other systems, but whether this would be as effective remains to be seen.
Commenting on the findings, David Cho, MD, UCLA Health and chair of the ACC Health Care Innovation Council, commended the researchers on engaging patients with more than a million separate nudges sent out during one flu season, and randomly assigning participants to 10 different types of nudges, calling it “impressive.”
“I think the concept that the nudge is to plant an idea that leads to an action is pretty much the basis of a lot of these health care interventions, which seems like a small way to have a big impact at outcome,” Dr. Cho noted. “The behavioral science aspects of the nudges are also fascinating to me personally, and I think to a lot of the cardiologists in the audience – about how you actually get people to act. I think it’s been a lifelong question for people in general, how do you get people to follow through on an action?”
“So I found the fact that secondary gain from a cardiovascular health standpoint, but also the repeated nudges were sort of simple ways that you could have people take ownership and get their flu vaccination,” he said.
“This is ACC, this is a cardiovascular conference, but the influence of vaccine is not just a primary care problem, it is also directly affecting cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Cho concluded.
‘Small but important effect’
In an accompanying editorial (Lancet. 2023 Mar 5. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(23)00453-1), Melissa Stockwell, MD, Columbia University, New York, writes, “The study by Johansen and colleagues highlights the small but still important effect of scalable, digital interventions across an entire at-risk population.”
A difference of 0.89% in the entire study population of over 960,000 adults age 65 years or older would be more than 8,500 additional adults protected, she notes. “That increase is important for a scalable intervention that has a low cost per letter.”
Moreover, “that the cardiovascular gain–framed messages worked best in those who had not been vaccinated in the previous season further highlights the potential impact on a more vaccine-hesitant population,” Dr. Stockwell notes.
However, with the mandatory government electronic notification system in Denmark, “notifications are sent via regular email and SMS message, and recipients log in through a portal or smartphone app to view the letter.” Similar studies in the United States that included this extra step of needing to sign in online have not been effective in older populations.
Another limitation is that the intervention may have a different effect in populations for which there is a digital divide between people with or without Internet access of sufficient data on their mobile phones.
First-of-its kind, nationwide pragmatic trial
The NUDGE-FLU protocol was previously published in the American Heart Journal. NUDGE-FLU is a first-of-its kind nationwide, pragmatic, registry-based, cluster-randomized implementation trial of electronically delivered nudges to increase influenza vaccination uptake, the researchers note.
They identified 964,870 individuals who were 65 years or older (or would turn 65 by Jan. 15, 2023) who lived in one of 691,820 households in Denmark.
This excluded individuals who lived in a nursing home or were exempt from the government’s mandatory electronic letter system that is used for official communications.
Households were randomly assigned 9:1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1:1 to receive usual care alone or to one of nine electronic letter strategies based on different behavioral science approaches to encourage influenza vaccination uptake:
- Standard electronic letter
- Standard electronic letter sent at randomization and again 14 days later (repeated letter)
- Depersonalized letter without the recipient’s name
- Gain-framing nudge (“Vaccinations help end pandemics, like COVID-19 and the flu. Protect yourself and your loved ones.”)
- Loss-framing nudge (“When too few people get vaccinated, pandemics from diseases like COVID-19 and the flu can spread and place you and your loved ones at risk.”)
- Collective-goal nudge (“78% of Danes 65 and above were vaccinated against influenza last year. Help us achieve an even higher goal this year.”)
- Active choice or implementation-intention prompt (“We encourage you to record your appointment time here.”)
- Cardiovascular gain–framing nudge (“In addition to its protection against influenza infection, influenza vaccination also seems to protect against cardiovascular disease such as heart attacks and heart failure.”)
- Expert-authority statement (“I recommend everyone over the age of 65 years to get vaccinated against influenza – Tyra Grove Krause, Executive Vice President, Statens Serum Institut.”)
The electronic letters were sent out Sept. 16, 2022, and the primary endpoint was vaccine receipt on or before Jan. 1, 2023.
All individuals received an informative vaccination encouragement letter from the Danish Health Authority (usual care) delivered via the same electronic letter system during Sept. 17 through Sept. 21, 2022.
The individuals had a mean age of 73.8 years, 51.5% were women, and 27.4% had chronic cardiovascular disease.
The analyses were done in one randomly selected individual per household.
Influenza vaccination rates were significantly higher in the cardiovascular gain–framing nudge group vs. usual care (81.00% vs. 80.12%; difference, 0.89 percentage points; P < .0001) and in the repeat-letter group vs. usual care (80.85% vs 80.12%; difference, 0.73 percentage points; P = .0006).
These two strategies also improved vaccination rates across major subgroups.
The cardiovascular gain–framed letter was particularly effective among participants who had not been vaccinated for influenza in the previous season.
The seven other letter strategies did not increase flu shot uptake.
Subanalysis in CVD
In the prespecified subanalysis of the NUDGE-FLU trial of patients aged 65 and older that focused on patients with CVD, Daniel Modin, MB, and colleagues report that 83.1% of patients with CVD vs. 79.2% of patients without CVD received influenza vaccination within the requested time (P < .0001).
The two nudging strategies – a letter highlighting potential cardiovascular benefits of influenza vaccination or a repeat letter – that were effective in boosting flu shot rates in the main analysis were also effective in all major CVD subgroups (ischemic heart disease, pulmonary heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, cerebrovascular disease, atherosclerotic CVD, embolic or thrombotic disease, and congenital heart disease).
Despite strong guideline endorsement, “influenza vaccination rates remain suboptimal in patients with high-risk cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Morin and colleagues write, possibly because of “insufficient knowledge among patients and providers of potential clinical benefits, concerns about vaccine safety, and other forms of vaccine hesitancy.”
Their findings suggest that “select digital behaviorally informed nudges delivered in advance of vaccine availability might be utilized to increase influenza vaccinate uptake in individuals with cardiovascular disease.”
NUDGE-HF was funded by Sanofi. Dr. Johansen and Dr. Modin have no disclosures. The disclosures of the other authors are listed with the articles. Dr. Stockwell has no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACC 2023
EHR alerts boosted MRA prescribing to patients with HFrEF
NEW ORLEANS – EHR-embedded alerts that a patient with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is a great candidate for treatment with a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) more than doubled prescribing of this “pillar” class for HFrEF, compared with control practices that used usual care and no alerts.
That’s according to results of BETTER CARE-HF, a single-center, randomized trial with more than 2,000 patients and involving 180 cardiologists.
“EHR-embedded tools cans be a rapid, low-cost, and high-impact method to increase prescription of life-saving therapies across large populations,” said Amrita Mukhopadhyay, MD, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
Her study targeted underprescribing of an MRA – spironolactone or eplerenone (Inspra) – because of its “vastly underprescribed” status in U.S. practice, where roughly two-thirds of patients with HFrEF do not receive an MRA despite clear recommendations from several medical groups that it is an essential part of treatment for most patients with HFrEF. Dr. Mukhopadhyay estimated that more comprehensive prescribing of MRAs to U.S. patients with HFrEF could prevent more than 20,000 deaths annually.
She also explained that the EHR-embedded alert was carefully devised, through interviews with cardiologists and pilot testing, to optimize the nudge so that it was less intrusive but effective for capturing attention and initiating action.
‘Clinically relevant, impressive results’
“This is a really important study, because despite overwhelming evidence for more than a decade favoring MRA use for patients with HFrEF there is an incredibly large treatment gap. MRAs can reduce all-cause death in people with HFrEF by 25%-30%, as well as reduce hospitalizations for heart failure, at a cost of less than $50 a year,” commented Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. The study showed “very clinically relevant, impressive results” for individualized, patient-specific alerts to prescribe an MRA and order the laboratory tests, particularly for serum potassium levels, needed to safely start the treatment, Dr. Fonarow said in an interview.
The BETTER CARE-HF study ran at more than 60 practices in the New York City region operated by the NYU Langone Health system, which sponsored the study. The trial randomized 180 cardiologists from these practices in a cluster format to one of three study arms: Sixty cardiologists received the EHR-embedded alerts for their relevant patients (755 patients) when the patient was in the physician’s office; another 60 cardiologists received a less tailored, monthly message that flagged all patients with HFrEF in a cardiologist’s practice who remained untreated candidates for MRA intervention (812 patients); and a third arm of 60 cardiologists and their HFrEF patients served as controls where the clinicians received no alert or message (644 patients).
The study included 2,211 patients with HFrEF and not on MRA treatment at baseline who were all identified as good candidates for starting treatment with the class, with no contraindications, no preexisting hyperkalemia, and no advanced-stage renal dysfunction.
The study’s primary outcome was the percentage of patients in each subgroup who received a new prescription for an MRA. This occurred in 29.6% of the patients whose physicians received an alert, in 15.6% of the patients whose physicians received a monthly message, and in 11.7% of patients in the control practices. Statistical analyses showed that the alerts led to a significant 2.53-fold increase in MRA prescribing, while the messages linked with a significant 67% increase in prescribing, compared with the control practices, reported Dr. Mukhopadhyay, a health services researcher at NYU Langone Health in New York. Simultaneously with her report, the results also appeared in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The findings also showed that the alert and message had no significant impact on the prescribing of any other medication classes for HFrEF, compared with the controls. And the alert intervention had minimal adverse effects. While patients in the alert arm showed a significant, 45% relative increase in the incidence of hyperkalemia episodes, compared with control patients (because of a 4.5% absolute increase in hyperkalemia events), the rate of “significant” hyperkalemia with a value of at least 5.5 mmol/L, occurred in 5.0% of patients in the alert group and 5.1% of patients in the control arm.
Potassium testing poses another barrier
Even though the alerts substantially improved MRA prescribing, 70% of patients deemed MRA eligible in the alert subgroup still failed to receive a prescription. One additional barrier specific to MRA prescribing is the need it triggers for serial laboratory testing to monitor serum potassium levels. “Potassium testing generates additional work outside the index visit, which along with the risk for hyperkalemia exists as a barrier,” commented Lee R. Goldberg, MD, a heart failure specialist and professor at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. “This may be the next aspect to focus on to improve MRA uptake,” he said as a designated discussant for the report.
“It’s not enough to just prompt medication treatment. We also need to prompt appropriate laboratory testing,” noted Dr. Fonarow.
He also said that the approach tested by Dr. Mukhopadhyay could now be expanded to outpatient cardiologists. “The onus is on everyone involved in caring for patients with HFrEF failure to explain why maximum effort is not being made to deploy” all of the guideline-directed medical therapies for the disorder.
EHR alerts “are one way to bridge the prescribing gap, but we need multiple approaches so that all eligible patients receive guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Fonarow said.
BETTER CARE-HF received no commercial funding, and Dr. Mukhopadhyay had no disclosures. Dr. Fonarow has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Amgen, Cytokinetics, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Dr. Goldberg has received personal fees from Abbott, VisCardia, and Zoll/Respircardia.
NEW ORLEANS – EHR-embedded alerts that a patient with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is a great candidate for treatment with a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) more than doubled prescribing of this “pillar” class for HFrEF, compared with control practices that used usual care and no alerts.
That’s according to results of BETTER CARE-HF, a single-center, randomized trial with more than 2,000 patients and involving 180 cardiologists.
“EHR-embedded tools cans be a rapid, low-cost, and high-impact method to increase prescription of life-saving therapies across large populations,” said Amrita Mukhopadhyay, MD, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
Her study targeted underprescribing of an MRA – spironolactone or eplerenone (Inspra) – because of its “vastly underprescribed” status in U.S. practice, where roughly two-thirds of patients with HFrEF do not receive an MRA despite clear recommendations from several medical groups that it is an essential part of treatment for most patients with HFrEF. Dr. Mukhopadhyay estimated that more comprehensive prescribing of MRAs to U.S. patients with HFrEF could prevent more than 20,000 deaths annually.
She also explained that the EHR-embedded alert was carefully devised, through interviews with cardiologists and pilot testing, to optimize the nudge so that it was less intrusive but effective for capturing attention and initiating action.
‘Clinically relevant, impressive results’
“This is a really important study, because despite overwhelming evidence for more than a decade favoring MRA use for patients with HFrEF there is an incredibly large treatment gap. MRAs can reduce all-cause death in people with HFrEF by 25%-30%, as well as reduce hospitalizations for heart failure, at a cost of less than $50 a year,” commented Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. The study showed “very clinically relevant, impressive results” for individualized, patient-specific alerts to prescribe an MRA and order the laboratory tests, particularly for serum potassium levels, needed to safely start the treatment, Dr. Fonarow said in an interview.
The BETTER CARE-HF study ran at more than 60 practices in the New York City region operated by the NYU Langone Health system, which sponsored the study. The trial randomized 180 cardiologists from these practices in a cluster format to one of three study arms: Sixty cardiologists received the EHR-embedded alerts for their relevant patients (755 patients) when the patient was in the physician’s office; another 60 cardiologists received a less tailored, monthly message that flagged all patients with HFrEF in a cardiologist’s practice who remained untreated candidates for MRA intervention (812 patients); and a third arm of 60 cardiologists and their HFrEF patients served as controls where the clinicians received no alert or message (644 patients).
The study included 2,211 patients with HFrEF and not on MRA treatment at baseline who were all identified as good candidates for starting treatment with the class, with no contraindications, no preexisting hyperkalemia, and no advanced-stage renal dysfunction.
The study’s primary outcome was the percentage of patients in each subgroup who received a new prescription for an MRA. This occurred in 29.6% of the patients whose physicians received an alert, in 15.6% of the patients whose physicians received a monthly message, and in 11.7% of patients in the control practices. Statistical analyses showed that the alerts led to a significant 2.53-fold increase in MRA prescribing, while the messages linked with a significant 67% increase in prescribing, compared with the control practices, reported Dr. Mukhopadhyay, a health services researcher at NYU Langone Health in New York. Simultaneously with her report, the results also appeared in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The findings also showed that the alert and message had no significant impact on the prescribing of any other medication classes for HFrEF, compared with the controls. And the alert intervention had minimal adverse effects. While patients in the alert arm showed a significant, 45% relative increase in the incidence of hyperkalemia episodes, compared with control patients (because of a 4.5% absolute increase in hyperkalemia events), the rate of “significant” hyperkalemia with a value of at least 5.5 mmol/L, occurred in 5.0% of patients in the alert group and 5.1% of patients in the control arm.
Potassium testing poses another barrier
Even though the alerts substantially improved MRA prescribing, 70% of patients deemed MRA eligible in the alert subgroup still failed to receive a prescription. One additional barrier specific to MRA prescribing is the need it triggers for serial laboratory testing to monitor serum potassium levels. “Potassium testing generates additional work outside the index visit, which along with the risk for hyperkalemia exists as a barrier,” commented Lee R. Goldberg, MD, a heart failure specialist and professor at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. “This may be the next aspect to focus on to improve MRA uptake,” he said as a designated discussant for the report.
“It’s not enough to just prompt medication treatment. We also need to prompt appropriate laboratory testing,” noted Dr. Fonarow.
He also said that the approach tested by Dr. Mukhopadhyay could now be expanded to outpatient cardiologists. “The onus is on everyone involved in caring for patients with HFrEF failure to explain why maximum effort is not being made to deploy” all of the guideline-directed medical therapies for the disorder.
EHR alerts “are one way to bridge the prescribing gap, but we need multiple approaches so that all eligible patients receive guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Fonarow said.
BETTER CARE-HF received no commercial funding, and Dr. Mukhopadhyay had no disclosures. Dr. Fonarow has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Amgen, Cytokinetics, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Dr. Goldberg has received personal fees from Abbott, VisCardia, and Zoll/Respircardia.
NEW ORLEANS – EHR-embedded alerts that a patient with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) is a great candidate for treatment with a mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) more than doubled prescribing of this “pillar” class for HFrEF, compared with control practices that used usual care and no alerts.
That’s according to results of BETTER CARE-HF, a single-center, randomized trial with more than 2,000 patients and involving 180 cardiologists.
“EHR-embedded tools cans be a rapid, low-cost, and high-impact method to increase prescription of life-saving therapies across large populations,” said Amrita Mukhopadhyay, MD, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
Her study targeted underprescribing of an MRA – spironolactone or eplerenone (Inspra) – because of its “vastly underprescribed” status in U.S. practice, where roughly two-thirds of patients with HFrEF do not receive an MRA despite clear recommendations from several medical groups that it is an essential part of treatment for most patients with HFrEF. Dr. Mukhopadhyay estimated that more comprehensive prescribing of MRAs to U.S. patients with HFrEF could prevent more than 20,000 deaths annually.
She also explained that the EHR-embedded alert was carefully devised, through interviews with cardiologists and pilot testing, to optimize the nudge so that it was less intrusive but effective for capturing attention and initiating action.
‘Clinically relevant, impressive results’
“This is a really important study, because despite overwhelming evidence for more than a decade favoring MRA use for patients with HFrEF there is an incredibly large treatment gap. MRAs can reduce all-cause death in people with HFrEF by 25%-30%, as well as reduce hospitalizations for heart failure, at a cost of less than $50 a year,” commented Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, interim chief of cardiology at the University of California, Los Angeles. The study showed “very clinically relevant, impressive results” for individualized, patient-specific alerts to prescribe an MRA and order the laboratory tests, particularly for serum potassium levels, needed to safely start the treatment, Dr. Fonarow said in an interview.
The BETTER CARE-HF study ran at more than 60 practices in the New York City region operated by the NYU Langone Health system, which sponsored the study. The trial randomized 180 cardiologists from these practices in a cluster format to one of three study arms: Sixty cardiologists received the EHR-embedded alerts for their relevant patients (755 patients) when the patient was in the physician’s office; another 60 cardiologists received a less tailored, monthly message that flagged all patients with HFrEF in a cardiologist’s practice who remained untreated candidates for MRA intervention (812 patients); and a third arm of 60 cardiologists and their HFrEF patients served as controls where the clinicians received no alert or message (644 patients).
The study included 2,211 patients with HFrEF and not on MRA treatment at baseline who were all identified as good candidates for starting treatment with the class, with no contraindications, no preexisting hyperkalemia, and no advanced-stage renal dysfunction.
The study’s primary outcome was the percentage of patients in each subgroup who received a new prescription for an MRA. This occurred in 29.6% of the patients whose physicians received an alert, in 15.6% of the patients whose physicians received a monthly message, and in 11.7% of patients in the control practices. Statistical analyses showed that the alerts led to a significant 2.53-fold increase in MRA prescribing, while the messages linked with a significant 67% increase in prescribing, compared with the control practices, reported Dr. Mukhopadhyay, a health services researcher at NYU Langone Health in New York. Simultaneously with her report, the results also appeared in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
The findings also showed that the alert and message had no significant impact on the prescribing of any other medication classes for HFrEF, compared with the controls. And the alert intervention had minimal adverse effects. While patients in the alert arm showed a significant, 45% relative increase in the incidence of hyperkalemia episodes, compared with control patients (because of a 4.5% absolute increase in hyperkalemia events), the rate of “significant” hyperkalemia with a value of at least 5.5 mmol/L, occurred in 5.0% of patients in the alert group and 5.1% of patients in the control arm.
Potassium testing poses another barrier
Even though the alerts substantially improved MRA prescribing, 70% of patients deemed MRA eligible in the alert subgroup still failed to receive a prescription. One additional barrier specific to MRA prescribing is the need it triggers for serial laboratory testing to monitor serum potassium levels. “Potassium testing generates additional work outside the index visit, which along with the risk for hyperkalemia exists as a barrier,” commented Lee R. Goldberg, MD, a heart failure specialist and professor at the University of Pennsylvania in Philadelphia. “This may be the next aspect to focus on to improve MRA uptake,” he said as a designated discussant for the report.
“It’s not enough to just prompt medication treatment. We also need to prompt appropriate laboratory testing,” noted Dr. Fonarow.
He also said that the approach tested by Dr. Mukhopadhyay could now be expanded to outpatient cardiologists. “The onus is on everyone involved in caring for patients with HFrEF failure to explain why maximum effort is not being made to deploy” all of the guideline-directed medical therapies for the disorder.
EHR alerts “are one way to bridge the prescribing gap, but we need multiple approaches so that all eligible patients receive guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Fonarow said.
BETTER CARE-HF received no commercial funding, and Dr. Mukhopadhyay had no disclosures. Dr. Fonarow has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Amgen, Cytokinetics, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, and Pfizer. Dr. Goldberg has received personal fees from Abbott, VisCardia, and Zoll/Respircardia.
AT ACC 2023
BIOVASC: Immediate complete revascularization beneficial in ACS
Immediate complete revascularization during the index procedure might become the new treatment paradigm in patients with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and multivessel disease, based on results of the BIOVASC trial.
In the trial, in patients presenting with ACS and multivessel disease, immediate complete revascularization was noninferior to staged complete revascularization for the primary composite outcome and was associated with a reduction in myocardial infarction and unplanned ischemia-driven revascularization.
The BIOVASC trial was presented on March 5 by Roberto Diletti, MD, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The study was simultaneously published online in The Lancet.
“We did not detect an early safety signal against an immediate complete revascularization strategy,” the authors state in the Lancet paper, adding: “Treating physicians should not be concerned about potential risks associated with immediate treatment of nonculprit lesions.”
They note, “This strategy might be particularly effective in patients with only two-vessel disease and reasonably simple lesions, with a high likelihood of procedural success without excessive use of radiation, contrast dye, or other resources.”
The trial also showed a shorter hospital stay with an immediate complete revascularization strategy.
“Immediate complete revascularization might have potential health economic benefits because of the lower rate of myocardial infarction, including spontaneous myocardial infarction, and unplanned revascularizations, and the shorter overall hospital stay,” the researchers conclude.
Introducing his presentation, Dr. Diletti explained that multiple studies have established the clinical benefit of complete coronary revascularization as compared with exclusive reperfusion of the culprit lesion, but the optimal timing for nonculprit lesion revascularization remains unclear.
The BIOVASC trial, conducted in Belgium, Italy, the Netherlands, and Spain, involved 1,525 patients with ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) or non-STEMI ACS and multivessel coronary artery disease with a clearly identifiable culprit lesion.
They were randomly assigned to undergo immediate complete revascularization (percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI] of the culprit lesion first, followed by other nonculprit lesions deemed to be clinically significant by the operator during the index procedure) or staged complete revascularization (PCI of only the culprit lesion during the index procedure and PCI of all nonculprit lesions deemed to be clinically significant within 6 weeks after the index procedure).
The primary outcome was the composite of all-cause mortality, MI, any unplanned ischemia-driven revascularization, or cerebrovascular events at 1 year after the index procedure.
The trial had a noninferiority design, with noninferiority of immediate to staged complete revascularization considered to be met if the upper boundary of the 95% confidence interval of the hazard ratio for the primary outcome did not exceed 1.39.
Among the trial population, 40% of patients had STEMI, 52% had non-STEMI, and 8% had unstable angina.
In the immediate complete revascularization group, 16 patients did not receive complete revascularization during the index procedure primarily because of prolonged procedure time, procedural complexity, or excessive contrast dye use.
In the staged group, 30% of patients underwent all subsequent procedures during the index hospitalization.
Results showed that the primary composite outcome at 1 year occurred in 7.6% of the immediate revascularization group and in 9.4% of the staged group, meeting the noninferiority criteria (HR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.55-1.11; P for noninferiority = .0011).
Superiority of the immediate over the staged complete revascularization strategy was not met at 1-year follow-up (P for superiority = .17).
However, in the prespecified analysis of clinical events at 30 days after the index procedure, immediate complete revascularization was superior to staged revascularization in terms of the composite primary outcome (2.2% vs. 5.8%; HR, 0.38; P for superiority = .0007).
One-year results showed no difference in all-cause death between the two groups, but the immediate complete revascularization group appeared to have a reduction in MI (1.9% vs. 4.5%) and fewer unplanned ischemia-driven revascularizations (4.2% vs. 6.7%).
The difference in MI was mainly driven by spontaneous MIs (not procedure related) that predominantly occurred in the time window between the index procedure and the planned date for the staged intervention, and an originally nonculprit lesion was identified as the cause for these events in almost all cases.
Subgroup analysis showed similar results across the patient population, including age, sex, and STEMI vs. non-STEMI presentation.
High rate of MI in staged group
Discussant of the study at the ACC session, Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, University of California, Irvine, said this was a “very important trial.”
She expressed surprise over the “remarkably high rate” of MI in the staged procedure group and asked Dr. Diletti why that might have occurred.
He responded that the operator may have misjudged the culprit lesion or that patients with ACS may have multiple unstable plaques and “treating the culprit lesion alone does not do the job.”
He added: “We need to look at the data more thoroughly to better understand this, but in both scenarios, immediate complete revascularization would prevent these events.”
Dr. Itchhaporia also pointed out a low rate of functional imaging used in the study.
Dr. Diletti replied that this reflected current European practice, but he acknowledged that, “in my opinion this reduces our ability to detect the culprit lesion.”
Commenting at an ACC press conference, David Moliterno, MD, Gill Heart and Vascular Institute, Lexington, Ky., said the trial poses the question “Can we fix it all at once?” and the results suggest “Yes, we can.”
He said this approach had the advantage of removing any uncertainly as to which was the culprit lesion. “We just fix everything – leave no blockage behind.”
But he pointed out that for some patients this may not be appropriate, such as those with compromised renal function, in whom excessive amounts of contrast material should be avoided.
CABG still needs to be considered
In a comment accompanying the Lancet publication, Tobias Pustjens, MD, Pieter Vriesendorp, MD, and Arnoud W.J. van’t Hof, MD, Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht (the Netherlands), note that more than half of the patients presenting with an ACS have multivessel coronary disease.
They say the trial results suggest that “pursuing an immediate complete revascularisation strategy, especially in times of reduced hospital capacity and staff scarcity, not only benefits the individual patient in clinical outcomes but can also safely reduce the pressure on health care systems.”
But they also point out that the possibility of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) should not be omitted, and that CABG is still the treatment of choice in patients with diabetes or complex coronary artery disease.
They conclude: “The results of the BIOVASC study move clinical practice forward from culprit-only to an immediate, complete revascularisation strategy. … However, further fine tuning of this treatment strategy to substantiate a role for intracoronary physiology assessment, intracoronary imaging, and guidance of the heart team decision is needed.”
The BIOVASC trial was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Biotronik AG. Dr. Diletti has received institutional research grants from Biotronik, Medtronic, ACIST Medical Systems, and Boston Scientific. Dr. van’t Hof has received institutional research grants from Biotronik.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immediate complete revascularization during the index procedure might become the new treatment paradigm in patients with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and multivessel disease, based on results of the BIOVASC trial.
In the trial, in patients presenting with ACS and multivessel disease, immediate complete revascularization was noninferior to staged complete revascularization for the primary composite outcome and was associated with a reduction in myocardial infarction and unplanned ischemia-driven revascularization.
The BIOVASC trial was presented on March 5 by Roberto Diletti, MD, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The study was simultaneously published online in The Lancet.
“We did not detect an early safety signal against an immediate complete revascularization strategy,” the authors state in the Lancet paper, adding: “Treating physicians should not be concerned about potential risks associated with immediate treatment of nonculprit lesions.”
They note, “This strategy might be particularly effective in patients with only two-vessel disease and reasonably simple lesions, with a high likelihood of procedural success without excessive use of radiation, contrast dye, or other resources.”
The trial also showed a shorter hospital stay with an immediate complete revascularization strategy.
“Immediate complete revascularization might have potential health economic benefits because of the lower rate of myocardial infarction, including spontaneous myocardial infarction, and unplanned revascularizations, and the shorter overall hospital stay,” the researchers conclude.
Introducing his presentation, Dr. Diletti explained that multiple studies have established the clinical benefit of complete coronary revascularization as compared with exclusive reperfusion of the culprit lesion, but the optimal timing for nonculprit lesion revascularization remains unclear.
The BIOVASC trial, conducted in Belgium, Italy, the Netherlands, and Spain, involved 1,525 patients with ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) or non-STEMI ACS and multivessel coronary artery disease with a clearly identifiable culprit lesion.
They were randomly assigned to undergo immediate complete revascularization (percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI] of the culprit lesion first, followed by other nonculprit lesions deemed to be clinically significant by the operator during the index procedure) or staged complete revascularization (PCI of only the culprit lesion during the index procedure and PCI of all nonculprit lesions deemed to be clinically significant within 6 weeks after the index procedure).
The primary outcome was the composite of all-cause mortality, MI, any unplanned ischemia-driven revascularization, or cerebrovascular events at 1 year after the index procedure.
The trial had a noninferiority design, with noninferiority of immediate to staged complete revascularization considered to be met if the upper boundary of the 95% confidence interval of the hazard ratio for the primary outcome did not exceed 1.39.
Among the trial population, 40% of patients had STEMI, 52% had non-STEMI, and 8% had unstable angina.
In the immediate complete revascularization group, 16 patients did not receive complete revascularization during the index procedure primarily because of prolonged procedure time, procedural complexity, or excessive contrast dye use.
In the staged group, 30% of patients underwent all subsequent procedures during the index hospitalization.
Results showed that the primary composite outcome at 1 year occurred in 7.6% of the immediate revascularization group and in 9.4% of the staged group, meeting the noninferiority criteria (HR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.55-1.11; P for noninferiority = .0011).
Superiority of the immediate over the staged complete revascularization strategy was not met at 1-year follow-up (P for superiority = .17).
However, in the prespecified analysis of clinical events at 30 days after the index procedure, immediate complete revascularization was superior to staged revascularization in terms of the composite primary outcome (2.2% vs. 5.8%; HR, 0.38; P for superiority = .0007).
One-year results showed no difference in all-cause death between the two groups, but the immediate complete revascularization group appeared to have a reduction in MI (1.9% vs. 4.5%) and fewer unplanned ischemia-driven revascularizations (4.2% vs. 6.7%).
The difference in MI was mainly driven by spontaneous MIs (not procedure related) that predominantly occurred in the time window between the index procedure and the planned date for the staged intervention, and an originally nonculprit lesion was identified as the cause for these events in almost all cases.
Subgroup analysis showed similar results across the patient population, including age, sex, and STEMI vs. non-STEMI presentation.
High rate of MI in staged group
Discussant of the study at the ACC session, Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, University of California, Irvine, said this was a “very important trial.”
She expressed surprise over the “remarkably high rate” of MI in the staged procedure group and asked Dr. Diletti why that might have occurred.
He responded that the operator may have misjudged the culprit lesion or that patients with ACS may have multiple unstable plaques and “treating the culprit lesion alone does not do the job.”
He added: “We need to look at the data more thoroughly to better understand this, but in both scenarios, immediate complete revascularization would prevent these events.”
Dr. Itchhaporia also pointed out a low rate of functional imaging used in the study.
Dr. Diletti replied that this reflected current European practice, but he acknowledged that, “in my opinion this reduces our ability to detect the culprit lesion.”
Commenting at an ACC press conference, David Moliterno, MD, Gill Heart and Vascular Institute, Lexington, Ky., said the trial poses the question “Can we fix it all at once?” and the results suggest “Yes, we can.”
He said this approach had the advantage of removing any uncertainly as to which was the culprit lesion. “We just fix everything – leave no blockage behind.”
But he pointed out that for some patients this may not be appropriate, such as those with compromised renal function, in whom excessive amounts of contrast material should be avoided.
CABG still needs to be considered
In a comment accompanying the Lancet publication, Tobias Pustjens, MD, Pieter Vriesendorp, MD, and Arnoud W.J. van’t Hof, MD, Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht (the Netherlands), note that more than half of the patients presenting with an ACS have multivessel coronary disease.
They say the trial results suggest that “pursuing an immediate complete revascularisation strategy, especially in times of reduced hospital capacity and staff scarcity, not only benefits the individual patient in clinical outcomes but can also safely reduce the pressure on health care systems.”
But they also point out that the possibility of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) should not be omitted, and that CABG is still the treatment of choice in patients with diabetes or complex coronary artery disease.
They conclude: “The results of the BIOVASC study move clinical practice forward from culprit-only to an immediate, complete revascularisation strategy. … However, further fine tuning of this treatment strategy to substantiate a role for intracoronary physiology assessment, intracoronary imaging, and guidance of the heart team decision is needed.”
The BIOVASC trial was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Biotronik AG. Dr. Diletti has received institutional research grants from Biotronik, Medtronic, ACIST Medical Systems, and Boston Scientific. Dr. van’t Hof has received institutional research grants from Biotronik.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immediate complete revascularization during the index procedure might become the new treatment paradigm in patients with an acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and multivessel disease, based on results of the BIOVASC trial.
In the trial, in patients presenting with ACS and multivessel disease, immediate complete revascularization was noninferior to staged complete revascularization for the primary composite outcome and was associated with a reduction in myocardial infarction and unplanned ischemia-driven revascularization.
The BIOVASC trial was presented on March 5 by Roberto Diletti, MD, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The study was simultaneously published online in The Lancet.
“We did not detect an early safety signal against an immediate complete revascularization strategy,” the authors state in the Lancet paper, adding: “Treating physicians should not be concerned about potential risks associated with immediate treatment of nonculprit lesions.”
They note, “This strategy might be particularly effective in patients with only two-vessel disease and reasonably simple lesions, with a high likelihood of procedural success without excessive use of radiation, contrast dye, or other resources.”
The trial also showed a shorter hospital stay with an immediate complete revascularization strategy.
“Immediate complete revascularization might have potential health economic benefits because of the lower rate of myocardial infarction, including spontaneous myocardial infarction, and unplanned revascularizations, and the shorter overall hospital stay,” the researchers conclude.
Introducing his presentation, Dr. Diletti explained that multiple studies have established the clinical benefit of complete coronary revascularization as compared with exclusive reperfusion of the culprit lesion, but the optimal timing for nonculprit lesion revascularization remains unclear.
The BIOVASC trial, conducted in Belgium, Italy, the Netherlands, and Spain, involved 1,525 patients with ST-segment elevation MI (STEMI) or non-STEMI ACS and multivessel coronary artery disease with a clearly identifiable culprit lesion.
They were randomly assigned to undergo immediate complete revascularization (percutaneous coronary intervention [PCI] of the culprit lesion first, followed by other nonculprit lesions deemed to be clinically significant by the operator during the index procedure) or staged complete revascularization (PCI of only the culprit lesion during the index procedure and PCI of all nonculprit lesions deemed to be clinically significant within 6 weeks after the index procedure).
The primary outcome was the composite of all-cause mortality, MI, any unplanned ischemia-driven revascularization, or cerebrovascular events at 1 year after the index procedure.
The trial had a noninferiority design, with noninferiority of immediate to staged complete revascularization considered to be met if the upper boundary of the 95% confidence interval of the hazard ratio for the primary outcome did not exceed 1.39.
Among the trial population, 40% of patients had STEMI, 52% had non-STEMI, and 8% had unstable angina.
In the immediate complete revascularization group, 16 patients did not receive complete revascularization during the index procedure primarily because of prolonged procedure time, procedural complexity, or excessive contrast dye use.
In the staged group, 30% of patients underwent all subsequent procedures during the index hospitalization.
Results showed that the primary composite outcome at 1 year occurred in 7.6% of the immediate revascularization group and in 9.4% of the staged group, meeting the noninferiority criteria (HR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.55-1.11; P for noninferiority = .0011).
Superiority of the immediate over the staged complete revascularization strategy was not met at 1-year follow-up (P for superiority = .17).
However, in the prespecified analysis of clinical events at 30 days after the index procedure, immediate complete revascularization was superior to staged revascularization in terms of the composite primary outcome (2.2% vs. 5.8%; HR, 0.38; P for superiority = .0007).
One-year results showed no difference in all-cause death between the two groups, but the immediate complete revascularization group appeared to have a reduction in MI (1.9% vs. 4.5%) and fewer unplanned ischemia-driven revascularizations (4.2% vs. 6.7%).
The difference in MI was mainly driven by spontaneous MIs (not procedure related) that predominantly occurred in the time window between the index procedure and the planned date for the staged intervention, and an originally nonculprit lesion was identified as the cause for these events in almost all cases.
Subgroup analysis showed similar results across the patient population, including age, sex, and STEMI vs. non-STEMI presentation.
High rate of MI in staged group
Discussant of the study at the ACC session, Dipti Itchhaporia, MD, University of California, Irvine, said this was a “very important trial.”
She expressed surprise over the “remarkably high rate” of MI in the staged procedure group and asked Dr. Diletti why that might have occurred.
He responded that the operator may have misjudged the culprit lesion or that patients with ACS may have multiple unstable plaques and “treating the culprit lesion alone does not do the job.”
He added: “We need to look at the data more thoroughly to better understand this, but in both scenarios, immediate complete revascularization would prevent these events.”
Dr. Itchhaporia also pointed out a low rate of functional imaging used in the study.
Dr. Diletti replied that this reflected current European practice, but he acknowledged that, “in my opinion this reduces our ability to detect the culprit lesion.”
Commenting at an ACC press conference, David Moliterno, MD, Gill Heart and Vascular Institute, Lexington, Ky., said the trial poses the question “Can we fix it all at once?” and the results suggest “Yes, we can.”
He said this approach had the advantage of removing any uncertainly as to which was the culprit lesion. “We just fix everything – leave no blockage behind.”
But he pointed out that for some patients this may not be appropriate, such as those with compromised renal function, in whom excessive amounts of contrast material should be avoided.
CABG still needs to be considered
In a comment accompanying the Lancet publication, Tobias Pustjens, MD, Pieter Vriesendorp, MD, and Arnoud W.J. van’t Hof, MD, Cardiovascular Research Institute Maastricht (the Netherlands), note that more than half of the patients presenting with an ACS have multivessel coronary disease.
They say the trial results suggest that “pursuing an immediate complete revascularisation strategy, especially in times of reduced hospital capacity and staff scarcity, not only benefits the individual patient in clinical outcomes but can also safely reduce the pressure on health care systems.”
But they also point out that the possibility of coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) should not be omitted, and that CABG is still the treatment of choice in patients with diabetes or complex coronary artery disease.
They conclude: “The results of the BIOVASC study move clinical practice forward from culprit-only to an immediate, complete revascularisation strategy. … However, further fine tuning of this treatment strategy to substantiate a role for intracoronary physiology assessment, intracoronary imaging, and guidance of the heart team decision is needed.”
The BIOVASC trial was supported by an unrestricted research grant from Biotronik AG. Dr. Diletti has received institutional research grants from Biotronik, Medtronic, ACIST Medical Systems, and Boston Scientific. Dr. van’t Hof has received institutional research grants from Biotronik.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACS 2023
Atorvastatin cut anthracycline cardiac dysfunction in lymphoma
NEW ORLEANS – Atorvastatin treatment of patients with lymphoma undergoing treatment with an anthracycline significantly cut the incidence of incident cardiac dysfunction by about two-thirds during 12 months of treatment, in a multicenter, randomized trial with 300 enrolled patients.
“These data support the use of atorvastatin among patients with lymphoma being treated with anthracyclines where prevention of cardiac systolic dysfunction is important,” concluded Tomas G. Neilan, MD, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
He highlighted that an important difference between the new study, STOP-CA, and a major prior study with a neutral effect published in 2022, was that STOP-CA “was powered for a major change” in cardiac function as the study’s primary outcome, a decline from baseline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 10% that also reduced ejection fraction to less than 55%.
“We can consider these medications [atorvastatin] for patients at higher risk for cardiac toxicity from anthracyclines, such as patients who receive a higher dose of an anthracycline, older patients, people with obesity, and women, commented Anita Deswal, MD, professor and chair of the department of cardiology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who was not involved with the study.
A basis for an ‘important discussion’ with patients
“For patients receiving higher doses of anthracyclines, the STOP-CA trial says that whether to start a statin for cardiac protection is now an important discussion” for these patients to have with their treating clinicians. ”That was not the case before today,” commented Ronald M. Witteles, MD, a cardiologist and professor who specializes in cardio-oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
“For a patient being treated for lymphoma or for another cancer and treated with equal or higher anthracycline doses, such as patients with a sarcoma, this trial’s results at the very least warrant a discussion between physicians and patients to make the decision,” Dr. Witteles, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. But he also cautioned that “whether an individual patient should take a statin in this scenario is still not a no-brainer. While the trial was positive, it was for an imaging rather than for a clinical endpoint.”
Experts noted that a similar study with the clinical endpoint of heart failure would require both many more randomized patients as well as much longer follow-up. STOP-CA was not powered for this endpoint. During its 12-month duration, a total of 11 patients developed heart failure, with no between group difference.
STOP-CA enrolled adults with lymphoma (Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin) and scheduled to undergo anthracycline treatment at eight U.S. centers and one in Canada, and excluded patients already on statin treatment or those for whom a statin was already indicated. Of the 300 enrolled patients, 286 had 12-month follow-up. Randomization assigned patients to receive either 40 mg daily of atorvastatin or placebo.
Their cumulative, median anthracycline dose was 300 mg/m2, which is typical for treating lymphoma, but higher than the typical dose use for patients with breast cancer. At baseline, average LVEF was 63%, and after 12 months this had declined to 59%. Forty-six of the 286 patients assessed after 12 months fulfilled the primary outcome of at least a 10–percentage point reduction from baseline in their LVEF and a decline in LVEF to less than 55%. Researchers used cardiac MR to assess LVEF at baseline, and in most patients at follow-up, but a minority of patients had their follow-up assessments by echocardiography because of logistical issues. Greater than 90% of patients were adherent to their assigned regimen.
Tripled incidence of cardiac dysfunction in placebo patients
The incidence of this outcome was 9% among the patients who received atorvastatin, and 22% among those on placebo, a significant difference. The calculated odds of the primary outcome was 2.9-fold more likely among the patients treated with placebo, compared with those who received atorvastatin, also a significant difference.
The study’s secondary outcome was patients who had at least a 5% drop from baseline in their LVEF and with a LVEF of less than 55% after 12 months. This outcome occurred in 13% of patients treated with atorvastatin and in 29% of those who received placebo, a significant difference.
The atorvastatin and placebo arms showed no significant differences in adverse events during the study, with roughly similar incidence rates for muscle pain, elevated liver enzymes, and renal failure. None of the enrolled patients developed myositis.
Atorvastatin treatment also produced an expected average 37% decline from baseline in levels of LDL cholesterol.
“This was a well-designed and important trial,” said Dr. Witteles. “Anthracyclines remain a mainstay of cancer therapies for a number of malignancies, such as lymphoma and sarcoma, and the cardiac side effects of development of cardiac dysfunction are unequivocally real.”
The importance of a clinically meaningful effect
The results especially contrast with the findings from the PREVENT study, published in 2022, which compared a daily, 40-mg atorvastatin treatment with placebo in 279 randomized patients with breast cancer and treated for 24 months. However, patients in PREVENT had a cumulative, median anthracycline dose of 240 mg/m2, and the study’s primary outcome was the average change from baseline in LVEF after 24 months of treatment, which was a reduction of 0.08 percentage points in the placebo arm, a nonsignificant difference.
In STOP-CA, the average change in LVEF from baseline was a 1–percentage point reduction in the placebo arm, compared with the atorvastatin-treated patients, a difference that was statistically significant, but “not clinically significant,” said Dr. Neilan, director of the cardio-oncology program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. He cited the good fortune of the STOP-CA investigators when they received a recommendation from reviewers early on to design their study to track a clinically meaningful change in LVEF rather than just looking at the average overall change.
Dr. Deswal also noted that it is unlikely that future studies will examine the efficacy of a statin for preventing LVEF in patients across the range of cancers that are eligible for anthracycline treatment. As a result, she predicted that “we may have to extrapolate” the results from STOP-CA to patients with other cancer types.
STOP-CA received no commercial funding. Dr. Neilan has been a consultant for and received fees from Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRC Oncology, Genentech, Roche, and Sanofi, and has received grant funding from AstraZeneca and Bristol Myers Squib. Dr. Deswal and Dr. Witteles had no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – Atorvastatin treatment of patients with lymphoma undergoing treatment with an anthracycline significantly cut the incidence of incident cardiac dysfunction by about two-thirds during 12 months of treatment, in a multicenter, randomized trial with 300 enrolled patients.
“These data support the use of atorvastatin among patients with lymphoma being treated with anthracyclines where prevention of cardiac systolic dysfunction is important,” concluded Tomas G. Neilan, MD, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
He highlighted that an important difference between the new study, STOP-CA, and a major prior study with a neutral effect published in 2022, was that STOP-CA “was powered for a major change” in cardiac function as the study’s primary outcome, a decline from baseline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 10% that also reduced ejection fraction to less than 55%.
“We can consider these medications [atorvastatin] for patients at higher risk for cardiac toxicity from anthracyclines, such as patients who receive a higher dose of an anthracycline, older patients, people with obesity, and women, commented Anita Deswal, MD, professor and chair of the department of cardiology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who was not involved with the study.
A basis for an ‘important discussion’ with patients
“For patients receiving higher doses of anthracyclines, the STOP-CA trial says that whether to start a statin for cardiac protection is now an important discussion” for these patients to have with their treating clinicians. ”That was not the case before today,” commented Ronald M. Witteles, MD, a cardiologist and professor who specializes in cardio-oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
“For a patient being treated for lymphoma or for another cancer and treated with equal or higher anthracycline doses, such as patients with a sarcoma, this trial’s results at the very least warrant a discussion between physicians and patients to make the decision,” Dr. Witteles, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. But he also cautioned that “whether an individual patient should take a statin in this scenario is still not a no-brainer. While the trial was positive, it was for an imaging rather than for a clinical endpoint.”
Experts noted that a similar study with the clinical endpoint of heart failure would require both many more randomized patients as well as much longer follow-up. STOP-CA was not powered for this endpoint. During its 12-month duration, a total of 11 patients developed heart failure, with no between group difference.
STOP-CA enrolled adults with lymphoma (Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin) and scheduled to undergo anthracycline treatment at eight U.S. centers and one in Canada, and excluded patients already on statin treatment or those for whom a statin was already indicated. Of the 300 enrolled patients, 286 had 12-month follow-up. Randomization assigned patients to receive either 40 mg daily of atorvastatin or placebo.
Their cumulative, median anthracycline dose was 300 mg/m2, which is typical for treating lymphoma, but higher than the typical dose use for patients with breast cancer. At baseline, average LVEF was 63%, and after 12 months this had declined to 59%. Forty-six of the 286 patients assessed after 12 months fulfilled the primary outcome of at least a 10–percentage point reduction from baseline in their LVEF and a decline in LVEF to less than 55%. Researchers used cardiac MR to assess LVEF at baseline, and in most patients at follow-up, but a minority of patients had their follow-up assessments by echocardiography because of logistical issues. Greater than 90% of patients were adherent to their assigned regimen.
Tripled incidence of cardiac dysfunction in placebo patients
The incidence of this outcome was 9% among the patients who received atorvastatin, and 22% among those on placebo, a significant difference. The calculated odds of the primary outcome was 2.9-fold more likely among the patients treated with placebo, compared with those who received atorvastatin, also a significant difference.
The study’s secondary outcome was patients who had at least a 5% drop from baseline in their LVEF and with a LVEF of less than 55% after 12 months. This outcome occurred in 13% of patients treated with atorvastatin and in 29% of those who received placebo, a significant difference.
The atorvastatin and placebo arms showed no significant differences in adverse events during the study, with roughly similar incidence rates for muscle pain, elevated liver enzymes, and renal failure. None of the enrolled patients developed myositis.
Atorvastatin treatment also produced an expected average 37% decline from baseline in levels of LDL cholesterol.
“This was a well-designed and important trial,” said Dr. Witteles. “Anthracyclines remain a mainstay of cancer therapies for a number of malignancies, such as lymphoma and sarcoma, and the cardiac side effects of development of cardiac dysfunction are unequivocally real.”
The importance of a clinically meaningful effect
The results especially contrast with the findings from the PREVENT study, published in 2022, which compared a daily, 40-mg atorvastatin treatment with placebo in 279 randomized patients with breast cancer and treated for 24 months. However, patients in PREVENT had a cumulative, median anthracycline dose of 240 mg/m2, and the study’s primary outcome was the average change from baseline in LVEF after 24 months of treatment, which was a reduction of 0.08 percentage points in the placebo arm, a nonsignificant difference.
In STOP-CA, the average change in LVEF from baseline was a 1–percentage point reduction in the placebo arm, compared with the atorvastatin-treated patients, a difference that was statistically significant, but “not clinically significant,” said Dr. Neilan, director of the cardio-oncology program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. He cited the good fortune of the STOP-CA investigators when they received a recommendation from reviewers early on to design their study to track a clinically meaningful change in LVEF rather than just looking at the average overall change.
Dr. Deswal also noted that it is unlikely that future studies will examine the efficacy of a statin for preventing LVEF in patients across the range of cancers that are eligible for anthracycline treatment. As a result, she predicted that “we may have to extrapolate” the results from STOP-CA to patients with other cancer types.
STOP-CA received no commercial funding. Dr. Neilan has been a consultant for and received fees from Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRC Oncology, Genentech, Roche, and Sanofi, and has received grant funding from AstraZeneca and Bristol Myers Squib. Dr. Deswal and Dr. Witteles had no relevant disclosures.
NEW ORLEANS – Atorvastatin treatment of patients with lymphoma undergoing treatment with an anthracycline significantly cut the incidence of incident cardiac dysfunction by about two-thirds during 12 months of treatment, in a multicenter, randomized trial with 300 enrolled patients.
“These data support the use of atorvastatin among patients with lymphoma being treated with anthracyclines where prevention of cardiac systolic dysfunction is important,” concluded Tomas G. Neilan, MD, at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation.
He highlighted that an important difference between the new study, STOP-CA, and a major prior study with a neutral effect published in 2022, was that STOP-CA “was powered for a major change” in cardiac function as the study’s primary outcome, a decline from baseline in left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 10% that also reduced ejection fraction to less than 55%.
“We can consider these medications [atorvastatin] for patients at higher risk for cardiac toxicity from anthracyclines, such as patients who receive a higher dose of an anthracycline, older patients, people with obesity, and women, commented Anita Deswal, MD, professor and chair of the department of cardiology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, who was not involved with the study.
A basis for an ‘important discussion’ with patients
“For patients receiving higher doses of anthracyclines, the STOP-CA trial says that whether to start a statin for cardiac protection is now an important discussion” for these patients to have with their treating clinicians. ”That was not the case before today,” commented Ronald M. Witteles, MD, a cardiologist and professor who specializes in cardio-oncology at Stanford (Calif.) University.
“For a patient being treated for lymphoma or for another cancer and treated with equal or higher anthracycline doses, such as patients with a sarcoma, this trial’s results at the very least warrant a discussion between physicians and patients to make the decision,” Dr. Witteles, who was not involved in the study, said in an interview. But he also cautioned that “whether an individual patient should take a statin in this scenario is still not a no-brainer. While the trial was positive, it was for an imaging rather than for a clinical endpoint.”
Experts noted that a similar study with the clinical endpoint of heart failure would require both many more randomized patients as well as much longer follow-up. STOP-CA was not powered for this endpoint. During its 12-month duration, a total of 11 patients developed heart failure, with no between group difference.
STOP-CA enrolled adults with lymphoma (Hodgkin or non-Hodgkin) and scheduled to undergo anthracycline treatment at eight U.S. centers and one in Canada, and excluded patients already on statin treatment or those for whom a statin was already indicated. Of the 300 enrolled patients, 286 had 12-month follow-up. Randomization assigned patients to receive either 40 mg daily of atorvastatin or placebo.
Their cumulative, median anthracycline dose was 300 mg/m2, which is typical for treating lymphoma, but higher than the typical dose use for patients with breast cancer. At baseline, average LVEF was 63%, and after 12 months this had declined to 59%. Forty-six of the 286 patients assessed after 12 months fulfilled the primary outcome of at least a 10–percentage point reduction from baseline in their LVEF and a decline in LVEF to less than 55%. Researchers used cardiac MR to assess LVEF at baseline, and in most patients at follow-up, but a minority of patients had their follow-up assessments by echocardiography because of logistical issues. Greater than 90% of patients were adherent to their assigned regimen.
Tripled incidence of cardiac dysfunction in placebo patients
The incidence of this outcome was 9% among the patients who received atorvastatin, and 22% among those on placebo, a significant difference. The calculated odds of the primary outcome was 2.9-fold more likely among the patients treated with placebo, compared with those who received atorvastatin, also a significant difference.
The study’s secondary outcome was patients who had at least a 5% drop from baseline in their LVEF and with a LVEF of less than 55% after 12 months. This outcome occurred in 13% of patients treated with atorvastatin and in 29% of those who received placebo, a significant difference.
The atorvastatin and placebo arms showed no significant differences in adverse events during the study, with roughly similar incidence rates for muscle pain, elevated liver enzymes, and renal failure. None of the enrolled patients developed myositis.
Atorvastatin treatment also produced an expected average 37% decline from baseline in levels of LDL cholesterol.
“This was a well-designed and important trial,” said Dr. Witteles. “Anthracyclines remain a mainstay of cancer therapies for a number of malignancies, such as lymphoma and sarcoma, and the cardiac side effects of development of cardiac dysfunction are unequivocally real.”
The importance of a clinically meaningful effect
The results especially contrast with the findings from the PREVENT study, published in 2022, which compared a daily, 40-mg atorvastatin treatment with placebo in 279 randomized patients with breast cancer and treated for 24 months. However, patients in PREVENT had a cumulative, median anthracycline dose of 240 mg/m2, and the study’s primary outcome was the average change from baseline in LVEF after 24 months of treatment, which was a reduction of 0.08 percentage points in the placebo arm, a nonsignificant difference.
In STOP-CA, the average change in LVEF from baseline was a 1–percentage point reduction in the placebo arm, compared with the atorvastatin-treated patients, a difference that was statistically significant, but “not clinically significant,” said Dr. Neilan, director of the cardio-oncology program at Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston. He cited the good fortune of the STOP-CA investigators when they received a recommendation from reviewers early on to design their study to track a clinically meaningful change in LVEF rather than just looking at the average overall change.
Dr. Deswal also noted that it is unlikely that future studies will examine the efficacy of a statin for preventing LVEF in patients across the range of cancers that are eligible for anthracycline treatment. As a result, she predicted that “we may have to extrapolate” the results from STOP-CA to patients with other cancer types.
STOP-CA received no commercial funding. Dr. Neilan has been a consultant for and received fees from Abbvie, Amgen, Bristol-Myers Squibb, CRC Oncology, Genentech, Roche, and Sanofi, and has received grant funding from AstraZeneca and Bristol Myers Squib. Dr. Deswal and Dr. Witteles had no relevant disclosures.
AT ACC 2023