User login
Pig heart successfully transplanted to man
A genetically modified pig heart has been successfully transplanted into a 57-year-old man who had no other treatment options but is “doing well” 3 days after the procedure, officials at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), Baltimore, announced Jan. 10.
“This organ transplant demonstrated for the first time that a genetically modified animal heart can function like a human heart without immediate rejection by the body,” they said.
Three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection had been knocked out in the pig supplying the transplanted heart, and six human genes associated with immune acceptance of the organ had been inserted into the pig’s genome, notes a UMMC press release.
“Lastly, one additional gene in the pig was knocked out to prevent excessive growth of the pig heart tissue, which totaled 10 unique gene edits made in the donor pig,” the release states.
The patient, Maryland resident David Bennett, had required mechanical circulatory support to stay alive but was rejected for standard heart transplantation at UMMC and other centers. He was ineligible for an implanted ventricular assist device due to ventricular arrhythmias.
Mr. Bennett “is being carefully monitored over the next days and weeks to determine whether the transplant provides lifesaving benefits,” the announcement says.
“We are proceeding cautiously, but we are also optimistic that this first-in-the-world surgery will provide an important new option for patients in the future,” notes a quote from Bartley P. Griffith, MD, the UMMC surgeon who performed the procedure.
The pig supplying the heart was provided to the center by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Virginia), a regenerative medicine company. An experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Massachusetts) was also used, in addition to standard immunosuppressants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A genetically modified pig heart has been successfully transplanted into a 57-year-old man who had no other treatment options but is “doing well” 3 days after the procedure, officials at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), Baltimore, announced Jan. 10.
“This organ transplant demonstrated for the first time that a genetically modified animal heart can function like a human heart without immediate rejection by the body,” they said.
Three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection had been knocked out in the pig supplying the transplanted heart, and six human genes associated with immune acceptance of the organ had been inserted into the pig’s genome, notes a UMMC press release.
“Lastly, one additional gene in the pig was knocked out to prevent excessive growth of the pig heart tissue, which totaled 10 unique gene edits made in the donor pig,” the release states.
The patient, Maryland resident David Bennett, had required mechanical circulatory support to stay alive but was rejected for standard heart transplantation at UMMC and other centers. He was ineligible for an implanted ventricular assist device due to ventricular arrhythmias.
Mr. Bennett “is being carefully monitored over the next days and weeks to determine whether the transplant provides lifesaving benefits,” the announcement says.
“We are proceeding cautiously, but we are also optimistic that this first-in-the-world surgery will provide an important new option for patients in the future,” notes a quote from Bartley P. Griffith, MD, the UMMC surgeon who performed the procedure.
The pig supplying the heart was provided to the center by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Virginia), a regenerative medicine company. An experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Massachusetts) was also used, in addition to standard immunosuppressants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A genetically modified pig heart has been successfully transplanted into a 57-year-old man who had no other treatment options but is “doing well” 3 days after the procedure, officials at the University of Maryland Medical Center (UMMC), Baltimore, announced Jan. 10.
“This organ transplant demonstrated for the first time that a genetically modified animal heart can function like a human heart without immediate rejection by the body,” they said.
Three genes associated with antibody-mediated rejection had been knocked out in the pig supplying the transplanted heart, and six human genes associated with immune acceptance of the organ had been inserted into the pig’s genome, notes a UMMC press release.
“Lastly, one additional gene in the pig was knocked out to prevent excessive growth of the pig heart tissue, which totaled 10 unique gene edits made in the donor pig,” the release states.
The patient, Maryland resident David Bennett, had required mechanical circulatory support to stay alive but was rejected for standard heart transplantation at UMMC and other centers. He was ineligible for an implanted ventricular assist device due to ventricular arrhythmias.
Mr. Bennett “is being carefully monitored over the next days and weeks to determine whether the transplant provides lifesaving benefits,” the announcement says.
“We are proceeding cautiously, but we are also optimistic that this first-in-the-world surgery will provide an important new option for patients in the future,” notes a quote from Bartley P. Griffith, MD, the UMMC surgeon who performed the procedure.
The pig supplying the heart was provided to the center by Revivicor (Blacksburg, Virginia), a regenerative medicine company. An experimental antirejection medication (Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals; Lexington, Massachusetts) was also used, in addition to standard immunosuppressants.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bleeding after reperfusion contributes to cardiac injury in MI
The damage to the heart caused by a myocardial infarction is not just a result of ischemia caused by the blocked artery but is also brought about by bleeding in the myocardium after the artery has been opened, a new study suggests.
This observation is leading to new approaches to limiting infarct size and treating MI.
“In MI treatment, we have always focused on opening up the artery as quickly as possible to limit the myocardial damage caused by ischemia,” the study’s senior author, Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, Indiana University, Indianapolis, told this news organization.
“We are pursuing a completely new approach focusing on limiting the damage after revascularization,” he said. “We are totally rethinking what a myocardial infarction is – what causes the injury and the time course of the injury – our results suggest that it’s not just ischemic damage and a lot of the harm is caused by hemorrhage after reperfusion.”
It has been known for many years that hemorrhage is often seen in the myocardium in large MIs, but it has not been established before now whether it contributes to the injury or not, Dr. Dharmakumar explained.
“This study was done to look at that – and we found that the hemorrhage drives a second layer of injury on top of the ischemia.”
Dr. Dharmakumar said this hemorrhage is part of the phenomenon known as reperfusion injury. “This has been known to exist for many years, but we haven’t fully understood all the factors contributing to it. Our results suggest that hemorrhage is a major component of reperfusion injury – probably the dominant factor,” he said.
The researchers are now working on therapeutic approaches to try to prevent this hemorrhage and/or to minimize its effect.
“We are studying how hemorrhage drives damage and how to block these biological processes,” Dr. Dharmakumar said. “Our studies suggest that hemorrhage could account for up to half of the damage caused by a myocardial infarction. If we can limit that, we should be able to reduce the size of the infarct and this should translate into better long-term outcomes.
“I’m very excited about these results,” he added. “We are already seeing a remarkable improvement in animal models with some of the potential therapeutic approaches we are working on.”
The current study is published in the January 2022 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The authors explain that it is now recognized that reperfusion injury can contribute to increasing infarct size, which they refer to as “infarct surge.” Previous studies have also shown that reperfusion injury can contribute to as much as 50% of the final infarct size, but the factors contributing to the observed variability are not known, and previous attempts to limit infarct surge from reperfusion injury have failed.
They noted that after reperfusion, microvessels can remain obstructed, resulting in intramyocardial hemorrhage. They conducted the current study to investigate whether such hemorrhage causes expansion of the infarct.
They studied 70 patients with ST-segment elevation MI who were categorized with cardiovascular MRI to have intramyocardial hemorrhage or not following primary PCI, and for whom serial cardiac troponin measures were used to assess infarct size.
Results showed that while troponin levels were not different before reperfusion, patients with intramyocardial hemorrhage had significantly higher cardiac troponin levels after reperfusion and these levels peaked earlier than in patients without hemorrhage.
In animal models, those with intramyocardial hemorrhage had a more rapid expansion of myocardial necrosis than did those without hemorrhage, and within 72 hours of reperfusion, a fourfold greater loss in salvageable myocardium was evident in hemorrhagic MIs.
“We have shown that damage to the heart continues after revascularization as measured by rapidly increasing troponin levels in the hearts that have had a hemorrhage,” Dr. Dharmakumar said.
“Hemorrhage in the myocardium was associated with larger infarctions, and in infarcts causing the same area of myocardium to be at risk, those with hemorrhage after revascularization lost a lot more of the salvageable myocardium than those without hemorrhage,” he added.
Dr. Dharmakumar estimates that such hemorrhage occurs in about half of MIs after revascularization, with risk factors including male gender, anterior wall MIs, and smoking.
He pointed out that previous attempts to treat or prevent reperfusion injury have not been successful, probably because they have not been addressing the key mechanism. “We have not been looking at hemorrhage in this regard until now. This is because it is only recently that we have had the tools to be able to identify hemorrhage in the heart with the use of cardiac MRI.”
Final frontier
In an accompanying editorial, Colin Berry, MBChB, University of Glasgow, and Borja Ibáñez, MD, Jiménez Díaz Foundation University Hospital, Madrid, said they applaud the investigators for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.
But they pointed out that it is difficult to completely dissect the impact of hemorrhage versus MI size on adverse remodeling, noting that it might be the case that more severe ischemia/reperfusion events are associated with large MI sizes and higher degree of hemorrhage.
However, they concluded that: “Intramyocardial hemorrhage represents the final frontier for preventing heart failure post-MI. It is readily detected using CMR, and clinical research of novel therapeutic approaches merits prioritization.”
This work was supported by grants from National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Dharmakumar and coauthor Robert Finney, PhD, have ownership interest in Cardiotheranostics. Dr. Berry is employed by the University of Glasgow, which holds consultancy and research agreements for his work with Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Causeway Therapeutics, Coroventis, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, HeartFlow, Menarini, Neovasc, Siemens Healthcare, and Valo Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The damage to the heart caused by a myocardial infarction is not just a result of ischemia caused by the blocked artery but is also brought about by bleeding in the myocardium after the artery has been opened, a new study suggests.
This observation is leading to new approaches to limiting infarct size and treating MI.
“In MI treatment, we have always focused on opening up the artery as quickly as possible to limit the myocardial damage caused by ischemia,” the study’s senior author, Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, Indiana University, Indianapolis, told this news organization.
“We are pursuing a completely new approach focusing on limiting the damage after revascularization,” he said. “We are totally rethinking what a myocardial infarction is – what causes the injury and the time course of the injury – our results suggest that it’s not just ischemic damage and a lot of the harm is caused by hemorrhage after reperfusion.”
It has been known for many years that hemorrhage is often seen in the myocardium in large MIs, but it has not been established before now whether it contributes to the injury or not, Dr. Dharmakumar explained.
“This study was done to look at that – and we found that the hemorrhage drives a second layer of injury on top of the ischemia.”
Dr. Dharmakumar said this hemorrhage is part of the phenomenon known as reperfusion injury. “This has been known to exist for many years, but we haven’t fully understood all the factors contributing to it. Our results suggest that hemorrhage is a major component of reperfusion injury – probably the dominant factor,” he said.
The researchers are now working on therapeutic approaches to try to prevent this hemorrhage and/or to minimize its effect.
“We are studying how hemorrhage drives damage and how to block these biological processes,” Dr. Dharmakumar said. “Our studies suggest that hemorrhage could account for up to half of the damage caused by a myocardial infarction. If we can limit that, we should be able to reduce the size of the infarct and this should translate into better long-term outcomes.
“I’m very excited about these results,” he added. “We are already seeing a remarkable improvement in animal models with some of the potential therapeutic approaches we are working on.”
The current study is published in the January 2022 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The authors explain that it is now recognized that reperfusion injury can contribute to increasing infarct size, which they refer to as “infarct surge.” Previous studies have also shown that reperfusion injury can contribute to as much as 50% of the final infarct size, but the factors contributing to the observed variability are not known, and previous attempts to limit infarct surge from reperfusion injury have failed.
They noted that after reperfusion, microvessels can remain obstructed, resulting in intramyocardial hemorrhage. They conducted the current study to investigate whether such hemorrhage causes expansion of the infarct.
They studied 70 patients with ST-segment elevation MI who were categorized with cardiovascular MRI to have intramyocardial hemorrhage or not following primary PCI, and for whom serial cardiac troponin measures were used to assess infarct size.
Results showed that while troponin levels were not different before reperfusion, patients with intramyocardial hemorrhage had significantly higher cardiac troponin levels after reperfusion and these levels peaked earlier than in patients without hemorrhage.
In animal models, those with intramyocardial hemorrhage had a more rapid expansion of myocardial necrosis than did those without hemorrhage, and within 72 hours of reperfusion, a fourfold greater loss in salvageable myocardium was evident in hemorrhagic MIs.
“We have shown that damage to the heart continues after revascularization as measured by rapidly increasing troponin levels in the hearts that have had a hemorrhage,” Dr. Dharmakumar said.
“Hemorrhage in the myocardium was associated with larger infarctions, and in infarcts causing the same area of myocardium to be at risk, those with hemorrhage after revascularization lost a lot more of the salvageable myocardium than those without hemorrhage,” he added.
Dr. Dharmakumar estimates that such hemorrhage occurs in about half of MIs after revascularization, with risk factors including male gender, anterior wall MIs, and smoking.
He pointed out that previous attempts to treat or prevent reperfusion injury have not been successful, probably because they have not been addressing the key mechanism. “We have not been looking at hemorrhage in this regard until now. This is because it is only recently that we have had the tools to be able to identify hemorrhage in the heart with the use of cardiac MRI.”
Final frontier
In an accompanying editorial, Colin Berry, MBChB, University of Glasgow, and Borja Ibáñez, MD, Jiménez Díaz Foundation University Hospital, Madrid, said they applaud the investigators for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.
But they pointed out that it is difficult to completely dissect the impact of hemorrhage versus MI size on adverse remodeling, noting that it might be the case that more severe ischemia/reperfusion events are associated with large MI sizes and higher degree of hemorrhage.
However, they concluded that: “Intramyocardial hemorrhage represents the final frontier for preventing heart failure post-MI. It is readily detected using CMR, and clinical research of novel therapeutic approaches merits prioritization.”
This work was supported by grants from National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Dharmakumar and coauthor Robert Finney, PhD, have ownership interest in Cardiotheranostics. Dr. Berry is employed by the University of Glasgow, which holds consultancy and research agreements for his work with Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Causeway Therapeutics, Coroventis, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, HeartFlow, Menarini, Neovasc, Siemens Healthcare, and Valo Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The damage to the heart caused by a myocardial infarction is not just a result of ischemia caused by the blocked artery but is also brought about by bleeding in the myocardium after the artery has been opened, a new study suggests.
This observation is leading to new approaches to limiting infarct size and treating MI.
“In MI treatment, we have always focused on opening up the artery as quickly as possible to limit the myocardial damage caused by ischemia,” the study’s senior author, Rohan Dharmakumar, PhD, Indiana University, Indianapolis, told this news organization.
“We are pursuing a completely new approach focusing on limiting the damage after revascularization,” he said. “We are totally rethinking what a myocardial infarction is – what causes the injury and the time course of the injury – our results suggest that it’s not just ischemic damage and a lot of the harm is caused by hemorrhage after reperfusion.”
It has been known for many years that hemorrhage is often seen in the myocardium in large MIs, but it has not been established before now whether it contributes to the injury or not, Dr. Dharmakumar explained.
“This study was done to look at that – and we found that the hemorrhage drives a second layer of injury on top of the ischemia.”
Dr. Dharmakumar said this hemorrhage is part of the phenomenon known as reperfusion injury. “This has been known to exist for many years, but we haven’t fully understood all the factors contributing to it. Our results suggest that hemorrhage is a major component of reperfusion injury – probably the dominant factor,” he said.
The researchers are now working on therapeutic approaches to try to prevent this hemorrhage and/or to minimize its effect.
“We are studying how hemorrhage drives damage and how to block these biological processes,” Dr. Dharmakumar said. “Our studies suggest that hemorrhage could account for up to half of the damage caused by a myocardial infarction. If we can limit that, we should be able to reduce the size of the infarct and this should translate into better long-term outcomes.
“I’m very excited about these results,” he added. “We are already seeing a remarkable improvement in animal models with some of the potential therapeutic approaches we are working on.”
The current study is published in the January 2022 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC).
The authors explain that it is now recognized that reperfusion injury can contribute to increasing infarct size, which they refer to as “infarct surge.” Previous studies have also shown that reperfusion injury can contribute to as much as 50% of the final infarct size, but the factors contributing to the observed variability are not known, and previous attempts to limit infarct surge from reperfusion injury have failed.
They noted that after reperfusion, microvessels can remain obstructed, resulting in intramyocardial hemorrhage. They conducted the current study to investigate whether such hemorrhage causes expansion of the infarct.
They studied 70 patients with ST-segment elevation MI who were categorized with cardiovascular MRI to have intramyocardial hemorrhage or not following primary PCI, and for whom serial cardiac troponin measures were used to assess infarct size.
Results showed that while troponin levels were not different before reperfusion, patients with intramyocardial hemorrhage had significantly higher cardiac troponin levels after reperfusion and these levels peaked earlier than in patients without hemorrhage.
In animal models, those with intramyocardial hemorrhage had a more rapid expansion of myocardial necrosis than did those without hemorrhage, and within 72 hours of reperfusion, a fourfold greater loss in salvageable myocardium was evident in hemorrhagic MIs.
“We have shown that damage to the heart continues after revascularization as measured by rapidly increasing troponin levels in the hearts that have had a hemorrhage,” Dr. Dharmakumar said.
“Hemorrhage in the myocardium was associated with larger infarctions, and in infarcts causing the same area of myocardium to be at risk, those with hemorrhage after revascularization lost a lot more of the salvageable myocardium than those without hemorrhage,” he added.
Dr. Dharmakumar estimates that such hemorrhage occurs in about half of MIs after revascularization, with risk factors including male gender, anterior wall MIs, and smoking.
He pointed out that previous attempts to treat or prevent reperfusion injury have not been successful, probably because they have not been addressing the key mechanism. “We have not been looking at hemorrhage in this regard until now. This is because it is only recently that we have had the tools to be able to identify hemorrhage in the heart with the use of cardiac MRI.”
Final frontier
In an accompanying editorial, Colin Berry, MBChB, University of Glasgow, and Borja Ibáñez, MD, Jiménez Díaz Foundation University Hospital, Madrid, said they applaud the investigators for providing new, mechanistic insights into a difficult clinical problem that has an unmet therapeutic need.
But they pointed out that it is difficult to completely dissect the impact of hemorrhage versus MI size on adverse remodeling, noting that it might be the case that more severe ischemia/reperfusion events are associated with large MI sizes and higher degree of hemorrhage.
However, they concluded that: “Intramyocardial hemorrhage represents the final frontier for preventing heart failure post-MI. It is readily detected using CMR, and clinical research of novel therapeutic approaches merits prioritization.”
This work was supported by grants from National Institutes of Health/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Dharmakumar and coauthor Robert Finney, PhD, have ownership interest in Cardiotheranostics. Dr. Berry is employed by the University of Glasgow, which holds consultancy and research agreements for his work with Abbott Vascular, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Causeway Therapeutics, Coroventis, Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, HeartFlow, Menarini, Neovasc, Siemens Healthcare, and Valo Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Similar 10-year survival after CABG, PCI in heavy calcification
Patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD) – either three-vessel disease and/or left main disease – who also had heavy coronary artery calcification (CAC) had greater all-cause mortality 10 years after revascularization, compared with those without such lesions.
However, perhaps unexpectedly, patients with heavily calcified lesions (HCLs) had similar 10-year survival whether they had undergone coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
These findings from a post hoc analysis of the SYNTAX Extended Survival (SYNTAXES) study led by Hideyuki Kawashima, MD, PhD, National University of Ireland, Galway, and the University of Amsterdam, were published online Dec. 29, 2021, in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
“There was an apparent lack of benefit at very long-term with CABG versus PCI in the presence of HCL,” Dr. Kawashima and corresponding author Patrick W. Serruys, MD, PhD, National University of Ireland and Imperial College London, summarized in a joint email to this news organization.
“Since HCLs – the final status of atherosclerosis and inflammation – reflect the aging process, complexity, and extensiveness of CAD, and comorbidity, it is possible that the currently available revascularization methods do not provide benefit in the prevention of long-term [10-year] mortality,” they suggested.
In an accompanying editorial, Usman Baber, MD, commented that this study provides a “novel insight.”
Specifically, while patients without HCLs had significantly lower 10-year mortality with CABG versus PCI (18.8% vs. 26.0%; P = .003), an opposite trend was observed among those with HCLs (39.0% vs. 34.0%; P = .26; P int = .005).
The patients with HCLs had higher SYNTAX scores (30.8 vs. 22.4; P < .001) and more complex CAD, so their lack of 10-year mortality benefit with CABG “is somewhat unexpected and warrants further scrutiny,” added Dr. Baber, from the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center in Oklahoma City.
Dr. Serruys and Dr. Kawashima agreed that “this study highlights the need for further research on this topic focusing on this specific population with HCLs,” which were 30% of the patients with complex lesions who participated in SYNTAXES.
Consider factors beyond coronary anatomy
The current findings reinforce “the importance of considering not just coronary anatomy, but patient age and other comorbid factors when evaluating mode of revascularization,” said Dr. Baber.
“Coronary calcification is a strong factor in deciding between CABG versus PCI, as multiple studies have shown that CAC increases risk after PCI, even with contemporary safe stent platforms,” he explained in an email.
The current study suggests the adverse prognosis associated with CAC also persists for patients treated with CABG.
Dr. Baber said that, “for patients in whom PCI may not be feasible due to extensive and bulky coronary calcification, it is important to emphasize that the benefits of CABG (versus PCI) may not be as significant or durable.”
“The lack of benefit with CABG,” he added, “is likely due to comorbid factors that tend to increase in prevalence with vascular calcification (older age, peripheral arterial disease, renal impairment, etc).”
This study reinforces “the importance of not just considering coronary complexity, but also additional noncoronary factors that influence long-term prognosis in patients with advanced multivessel CAD,” Dr. Baber stressed.
More aggressive lipid-lowering or antithrombotic therapy may improve the prognosis for such patients, he suggested.
“In general,” Dr. Serruys and Dr. Kawashima similarly noted, “for short-/mid-term outcomes, CABG is preferred to PCI in patients with HCLs because of a higher rate of complete revascularization and less need for repeat revascularization.”
“Our findings at 10 years are in line with the general findings preferring CABG in mid and long term, whereas the benefit of very long-term follow-up might be more complex to capture and comprehend,” they concluded. “Whether HCLs require special consideration when deciding the mode of revascularization beyond their contribution to the SYNTAX score deserves further evaluation.
“Newer PCI technology or CABG methods may become a game-changer in the future,” they speculated.
Worse clinical outcomes
Heavy coronary calcification is associated with worse clinical outcomes after PCI or CABG, but to date, no trial has compared 10-year outcomes after PCI or CABG in patients with complex CAD with versus without HCLs.
To look at this, Dr. Kawashima and colleagues performed a subanalysis of patients in the SYNTAXES study. The original SYNTAX trial had randomized 1,800 patients with complex CAD who were eligible for either PCI or CABG 1:1 to these two treatments, with a 5-year follow-up, and SYNTAXES extended the follow-up to 10 years.
Of the 1,800 patients, 532 (29.6%) had at least one HCL and the rest (70.4%) did not.
The median follow-up in SYNTAXES was 11.2 years overall and 11.9 years in survivors.
At baseline, compared with other patients, those with HCLs were older and had a lower body mass index and higher rates of insulin-treated diabetes, hypertension, previous cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, and heart failure.
After adjusting for multiple variables, having a HCL was an independent predictor of greater risk of 10-year mortality (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.69; P = .006).
In patients without HCLs, mortality was significantly higher after PCI than CABG (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.14-1.83; P = .003), whereas in those with HCLs, there was no significant difference (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.64-1.13; P = .264).
The location of the HCL did not have any impact on 10-year mortality regardless of the assigned treatment.
Among patients with at least one HCL who underwent CABG, those with at least two HCLs had greater 10-year all-cause mortality than those with one HCL; this difference was not seen among patients with at least one HCL who underwent PCI.
The researchers acknowledge study limitations include that it was a post hoc analysis, so it should be considered hypothesis generating.
In addition, SYNTAX was conducted between 2005 and 2007, when PCI mainly used first-generation paclitaxel drug-eluting stents, so the findings may not be generalizable to current practice.
SYNTAXES was supported by the German Foundation of Heart Research. SYNTAX, during 0- to 5-year follow-up, was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Serruys reported receiving personal fees from SMT, Philips/Volcano, Xeltis, Novartis, and Meril Life. Dr. Kawashima reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Baber reported receiving honoraria and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Biotronik, and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD) – either three-vessel disease and/or left main disease – who also had heavy coronary artery calcification (CAC) had greater all-cause mortality 10 years after revascularization, compared with those without such lesions.
However, perhaps unexpectedly, patients with heavily calcified lesions (HCLs) had similar 10-year survival whether they had undergone coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
These findings from a post hoc analysis of the SYNTAX Extended Survival (SYNTAXES) study led by Hideyuki Kawashima, MD, PhD, National University of Ireland, Galway, and the University of Amsterdam, were published online Dec. 29, 2021, in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
“There was an apparent lack of benefit at very long-term with CABG versus PCI in the presence of HCL,” Dr. Kawashima and corresponding author Patrick W. Serruys, MD, PhD, National University of Ireland and Imperial College London, summarized in a joint email to this news organization.
“Since HCLs – the final status of atherosclerosis and inflammation – reflect the aging process, complexity, and extensiveness of CAD, and comorbidity, it is possible that the currently available revascularization methods do not provide benefit in the prevention of long-term [10-year] mortality,” they suggested.
In an accompanying editorial, Usman Baber, MD, commented that this study provides a “novel insight.”
Specifically, while patients without HCLs had significantly lower 10-year mortality with CABG versus PCI (18.8% vs. 26.0%; P = .003), an opposite trend was observed among those with HCLs (39.0% vs. 34.0%; P = .26; P int = .005).
The patients with HCLs had higher SYNTAX scores (30.8 vs. 22.4; P < .001) and more complex CAD, so their lack of 10-year mortality benefit with CABG “is somewhat unexpected and warrants further scrutiny,” added Dr. Baber, from the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center in Oklahoma City.
Dr. Serruys and Dr. Kawashima agreed that “this study highlights the need for further research on this topic focusing on this specific population with HCLs,” which were 30% of the patients with complex lesions who participated in SYNTAXES.
Consider factors beyond coronary anatomy
The current findings reinforce “the importance of considering not just coronary anatomy, but patient age and other comorbid factors when evaluating mode of revascularization,” said Dr. Baber.
“Coronary calcification is a strong factor in deciding between CABG versus PCI, as multiple studies have shown that CAC increases risk after PCI, even with contemporary safe stent platforms,” he explained in an email.
The current study suggests the adverse prognosis associated with CAC also persists for patients treated with CABG.
Dr. Baber said that, “for patients in whom PCI may not be feasible due to extensive and bulky coronary calcification, it is important to emphasize that the benefits of CABG (versus PCI) may not be as significant or durable.”
“The lack of benefit with CABG,” he added, “is likely due to comorbid factors that tend to increase in prevalence with vascular calcification (older age, peripheral arterial disease, renal impairment, etc).”
This study reinforces “the importance of not just considering coronary complexity, but also additional noncoronary factors that influence long-term prognosis in patients with advanced multivessel CAD,” Dr. Baber stressed.
More aggressive lipid-lowering or antithrombotic therapy may improve the prognosis for such patients, he suggested.
“In general,” Dr. Serruys and Dr. Kawashima similarly noted, “for short-/mid-term outcomes, CABG is preferred to PCI in patients with HCLs because of a higher rate of complete revascularization and less need for repeat revascularization.”
“Our findings at 10 years are in line with the general findings preferring CABG in mid and long term, whereas the benefit of very long-term follow-up might be more complex to capture and comprehend,” they concluded. “Whether HCLs require special consideration when deciding the mode of revascularization beyond their contribution to the SYNTAX score deserves further evaluation.
“Newer PCI technology or CABG methods may become a game-changer in the future,” they speculated.
Worse clinical outcomes
Heavy coronary calcification is associated with worse clinical outcomes after PCI or CABG, but to date, no trial has compared 10-year outcomes after PCI or CABG in patients with complex CAD with versus without HCLs.
To look at this, Dr. Kawashima and colleagues performed a subanalysis of patients in the SYNTAXES study. The original SYNTAX trial had randomized 1,800 patients with complex CAD who were eligible for either PCI or CABG 1:1 to these two treatments, with a 5-year follow-up, and SYNTAXES extended the follow-up to 10 years.
Of the 1,800 patients, 532 (29.6%) had at least one HCL and the rest (70.4%) did not.
The median follow-up in SYNTAXES was 11.2 years overall and 11.9 years in survivors.
At baseline, compared with other patients, those with HCLs were older and had a lower body mass index and higher rates of insulin-treated diabetes, hypertension, previous cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, and heart failure.
After adjusting for multiple variables, having a HCL was an independent predictor of greater risk of 10-year mortality (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.69; P = .006).
In patients without HCLs, mortality was significantly higher after PCI than CABG (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.14-1.83; P = .003), whereas in those with HCLs, there was no significant difference (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.64-1.13; P = .264).
The location of the HCL did not have any impact on 10-year mortality regardless of the assigned treatment.
Among patients with at least one HCL who underwent CABG, those with at least two HCLs had greater 10-year all-cause mortality than those with one HCL; this difference was not seen among patients with at least one HCL who underwent PCI.
The researchers acknowledge study limitations include that it was a post hoc analysis, so it should be considered hypothesis generating.
In addition, SYNTAX was conducted between 2005 and 2007, when PCI mainly used first-generation paclitaxel drug-eluting stents, so the findings may not be generalizable to current practice.
SYNTAXES was supported by the German Foundation of Heart Research. SYNTAX, during 0- to 5-year follow-up, was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Serruys reported receiving personal fees from SMT, Philips/Volcano, Xeltis, Novartis, and Meril Life. Dr. Kawashima reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Baber reported receiving honoraria and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Biotronik, and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD) – either three-vessel disease and/or left main disease – who also had heavy coronary artery calcification (CAC) had greater all-cause mortality 10 years after revascularization, compared with those without such lesions.
However, perhaps unexpectedly, patients with heavily calcified lesions (HCLs) had similar 10-year survival whether they had undergone coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI).
These findings from a post hoc analysis of the SYNTAX Extended Survival (SYNTAXES) study led by Hideyuki Kawashima, MD, PhD, National University of Ireland, Galway, and the University of Amsterdam, were published online Dec. 29, 2021, in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
“There was an apparent lack of benefit at very long-term with CABG versus PCI in the presence of HCL,” Dr. Kawashima and corresponding author Patrick W. Serruys, MD, PhD, National University of Ireland and Imperial College London, summarized in a joint email to this news organization.
“Since HCLs – the final status of atherosclerosis and inflammation – reflect the aging process, complexity, and extensiveness of CAD, and comorbidity, it is possible that the currently available revascularization methods do not provide benefit in the prevention of long-term [10-year] mortality,” they suggested.
In an accompanying editorial, Usman Baber, MD, commented that this study provides a “novel insight.”
Specifically, while patients without HCLs had significantly lower 10-year mortality with CABG versus PCI (18.8% vs. 26.0%; P = .003), an opposite trend was observed among those with HCLs (39.0% vs. 34.0%; P = .26; P int = .005).
The patients with HCLs had higher SYNTAX scores (30.8 vs. 22.4; P < .001) and more complex CAD, so their lack of 10-year mortality benefit with CABG “is somewhat unexpected and warrants further scrutiny,” added Dr. Baber, from the University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center in Oklahoma City.
Dr. Serruys and Dr. Kawashima agreed that “this study highlights the need for further research on this topic focusing on this specific population with HCLs,” which were 30% of the patients with complex lesions who participated in SYNTAXES.
Consider factors beyond coronary anatomy
The current findings reinforce “the importance of considering not just coronary anatomy, but patient age and other comorbid factors when evaluating mode of revascularization,” said Dr. Baber.
“Coronary calcification is a strong factor in deciding between CABG versus PCI, as multiple studies have shown that CAC increases risk after PCI, even with contemporary safe stent platforms,” he explained in an email.
The current study suggests the adverse prognosis associated with CAC also persists for patients treated with CABG.
Dr. Baber said that, “for patients in whom PCI may not be feasible due to extensive and bulky coronary calcification, it is important to emphasize that the benefits of CABG (versus PCI) may not be as significant or durable.”
“The lack of benefit with CABG,” he added, “is likely due to comorbid factors that tend to increase in prevalence with vascular calcification (older age, peripheral arterial disease, renal impairment, etc).”
This study reinforces “the importance of not just considering coronary complexity, but also additional noncoronary factors that influence long-term prognosis in patients with advanced multivessel CAD,” Dr. Baber stressed.
More aggressive lipid-lowering or antithrombotic therapy may improve the prognosis for such patients, he suggested.
“In general,” Dr. Serruys and Dr. Kawashima similarly noted, “for short-/mid-term outcomes, CABG is preferred to PCI in patients with HCLs because of a higher rate of complete revascularization and less need for repeat revascularization.”
“Our findings at 10 years are in line with the general findings preferring CABG in mid and long term, whereas the benefit of very long-term follow-up might be more complex to capture and comprehend,” they concluded. “Whether HCLs require special consideration when deciding the mode of revascularization beyond their contribution to the SYNTAX score deserves further evaluation.
“Newer PCI technology or CABG methods may become a game-changer in the future,” they speculated.
Worse clinical outcomes
Heavy coronary calcification is associated with worse clinical outcomes after PCI or CABG, but to date, no trial has compared 10-year outcomes after PCI or CABG in patients with complex CAD with versus without HCLs.
To look at this, Dr. Kawashima and colleagues performed a subanalysis of patients in the SYNTAXES study. The original SYNTAX trial had randomized 1,800 patients with complex CAD who were eligible for either PCI or CABG 1:1 to these two treatments, with a 5-year follow-up, and SYNTAXES extended the follow-up to 10 years.
Of the 1,800 patients, 532 (29.6%) had at least one HCL and the rest (70.4%) did not.
The median follow-up in SYNTAXES was 11.2 years overall and 11.9 years in survivors.
At baseline, compared with other patients, those with HCLs were older and had a lower body mass index and higher rates of insulin-treated diabetes, hypertension, previous cerebrovascular disease, peripheral vascular disease, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, and heart failure.
After adjusting for multiple variables, having a HCL was an independent predictor of greater risk of 10-year mortality (hazard ratio, 1.36; 95% confidence interval, 1.09-1.69; P = .006).
In patients without HCLs, mortality was significantly higher after PCI than CABG (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.14-1.83; P = .003), whereas in those with HCLs, there was no significant difference (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.64-1.13; P = .264).
The location of the HCL did not have any impact on 10-year mortality regardless of the assigned treatment.
Among patients with at least one HCL who underwent CABG, those with at least two HCLs had greater 10-year all-cause mortality than those with one HCL; this difference was not seen among patients with at least one HCL who underwent PCI.
The researchers acknowledge study limitations include that it was a post hoc analysis, so it should be considered hypothesis generating.
In addition, SYNTAX was conducted between 2005 and 2007, when PCI mainly used first-generation paclitaxel drug-eluting stents, so the findings may not be generalizable to current practice.
SYNTAXES was supported by the German Foundation of Heart Research. SYNTAX, during 0- to 5-year follow-up, was funded by Boston Scientific. Dr. Serruys reported receiving personal fees from SMT, Philips/Volcano, Xeltis, Novartis, and Meril Life. Dr. Kawashima reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Baber reported receiving honoraria and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, Biotronik, and Amgen.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR INTERVENTIONS
Surgical groups push back against new revascularization guidelines
The new 2021 coronary revascularization guidelines are spurring controversy, as surgical associations raise concerns about the interpretation of the evidence behind key recommendations and the makeup of the writing committee.
The guideline was published in December by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (ACC/AHA/SCAI), and replaces the 2011 coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) and the 2011 and 2015 percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) guidelines.
The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) were part of the development of the document but have withdrawn their support, citing three areas of concern in a recent editorial in Annals of Thoracic Surgery.
“I do have to emphasize this is not just the AATS and STS – the European societies, Latin American societies, Asian societies, and even cardiologists are all coming out against these guidelines,” Joseph F. Sabik III, MD, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, lead author of the editorial, said in an interview. “So, I think that tells us that something didn’t go right here.”
The main objection is the downgrading of CABG surgery from a class 1 to weak 2b recommendation to improve survival in patients with three-vessel coronary artery disease (CAD) and normal left ventricular function.
The ISCHEMIA trial was used to support this two-level downgrade and a class 1 to 2a downgrade for CABG in three-vessel CAD with mild to moderate left ventricular dysfunction. But the trial wasn’t powered for survival, only 20% of patients underwent CABG as the initial invasive strategy, and patients were followed for less than 5 years, the editorialists observed.
At the same time, there’s plenty of observational and randomized studies such as SYNTAX, EXCEL, and FAME 3 showing a clear survival benefit of CABG over PCI, Dr. Sabik said. “The criticism is that these are old studies and aren’t applicable today, but we don’t understand downgrading without any evidence suggesting it [CABG] isn’t effective anymore.”
CABG and PCI treated as equal
AATS and STS also object to the new guidelines treating PCI and CABG as equivalent revascularization strategies in decreasing ischemic events. Both were given a 2b recommendation for survival with triple-vessel disease, but randomized trials have demonstrated not only lower mortality with surgery but fewer reinterventions and myocardial infarctions.
“None of that gets acknowledged in the guidelines; they are treated equally,” Dr. Sabik said. “So if you’re going to say that CABG isn’t any better than medical therapy, in our mind, you have to say that PCI is worse than medical therapy. And we don’t believe that, I want you to know. We just think that the logic doesn’t make any sense. The committee used what it wanted to but didn’t use many things that committees have used in the past to give CABG a level 1 recommendation.”
The downgrade is also at odds with the 2018 European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/ European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) guidelines, which give CABG a class 1 recommendation in three-vessel CAD as well as one- or two-vessel CAD with proximal left atrial descending artery stenosis.
In a Dec. 14 letter to the ACC/AHA Joint Committee, the Latin American Association of Cardiac and Endovascular Surgery (LACES) also called out the guideline committee for the 2b class of recommendation (COR) for PCI and CABG, saying it contradicts the text, which “clearly considers” the need to give a weaker endorsement for PCI than for CABG in patients with multivessel CAD.
“Considering that this section has the most significant impact due to the prevalence of stable ischemic heart disease in patients with multivessel CAD, such a contradiction may affect the lives and survival of millions of patients worldwide and have a major socioeconomic impact,” the letter states.
“Therefore, LACES respectfully but vehemently believes the Task Force should seriously reconsider the wording and recommendations in this specific large group of patients.”
Class I for radial conduit
AATS and STS also express concern about the new class 1 recommendation for the radial artery as a conduit in CABG. They note this is higher than bilateral internal mammary artery grafting and based on a meta-analysis of six relatively small studies with very strict inclusion criteria favorable for radial artery usage and patency.
“There’s a lot of studies that showed if you use the radial artery incorrectly, you have worse outcomes, and that’s what scares us a bit,” Dr. Sabik said. “If they’re giving it a class 1 recommendation, does that mean that becomes standard of care and could that cause patient harm? We think that level 1 is too high and that a [class] 2a with qualifications would be appropriate.”
Unequal footing
In a Dec. 23 letter, EACTS said it is “extremely concerned” about downgrading the COR for CABG without new randomized controlled trials to support the decision or to reject previously held evidence.
“The downgrading of CABG, and placing PCI at the same COR, does not meet our interpretation of the evidence, and may lead to avoidable loss of life,” EACTS officials said. “These guidelines also have implications on patient care: A COR IIb entails that CABG may not be reimbursable in some countries.”
EACTS called on AHA, ACC, and SCAI to review the evidence and called out the makeup of the guideline writing committee. “It is astonishing that no surgical association was involved, coauthored, or endorsed these guidelines.”
The AATS and STS each had a single representative on the guidelines’ writing committee but note that the six remaining surgeons were chosen by the ACC and AHA. Surgeons were also in the minority and only a majority was needed to approve the guidelines, highlighting the need to revisit the guideline development process to ensure equal representation by multidisciplinary experts across specialties.
“I hope the cardiology and surgical societies can come together and figure out how we do this better in the future, and we take a look again at these guidelines and come up with what we think is appropriate, especially since this is not just AATS and STS,” Dr. Sabik said.
In an emailed statement, the ACC/AHA said the AATS and STS representatives “actively participated throughout the writing process the past 3 years” and that the AATS and STS were involved in the “extensive peer review process” for the document with a reviewer from each organization. Nevertheless, AATS and STS both elected not to endorse the guidelines when at the organizational approval stage.
“Consequently, the AATS representative chose to stay with the committee and be recognized as having been appointed on behalf of the ACC and the AHA,” according to the statement. “The STS representative chose to withdraw from the committee and is not listed as a writing committee member on the final guideline. The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for coronary artery revascularization, as agreed by the ACC, AHA, SCAI, and the full writing committee.”
Despite pleas from the surgical groups to reconsider the evidence, “there is no further review process for the revascularization guideline,” the ACC/AHA spokesperson noted.
Jennifer S. Lawton, MD, chief of cardiac surgery at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and guideline writing committee chair, did not respond to numerous requests for comment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new 2021 coronary revascularization guidelines are spurring controversy, as surgical associations raise concerns about the interpretation of the evidence behind key recommendations and the makeup of the writing committee.
The guideline was published in December by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (ACC/AHA/SCAI), and replaces the 2011 coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) and the 2011 and 2015 percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) guidelines.
The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) were part of the development of the document but have withdrawn their support, citing three areas of concern in a recent editorial in Annals of Thoracic Surgery.
“I do have to emphasize this is not just the AATS and STS – the European societies, Latin American societies, Asian societies, and even cardiologists are all coming out against these guidelines,” Joseph F. Sabik III, MD, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, lead author of the editorial, said in an interview. “So, I think that tells us that something didn’t go right here.”
The main objection is the downgrading of CABG surgery from a class 1 to weak 2b recommendation to improve survival in patients with three-vessel coronary artery disease (CAD) and normal left ventricular function.
The ISCHEMIA trial was used to support this two-level downgrade and a class 1 to 2a downgrade for CABG in three-vessel CAD with mild to moderate left ventricular dysfunction. But the trial wasn’t powered for survival, only 20% of patients underwent CABG as the initial invasive strategy, and patients were followed for less than 5 years, the editorialists observed.
At the same time, there’s plenty of observational and randomized studies such as SYNTAX, EXCEL, and FAME 3 showing a clear survival benefit of CABG over PCI, Dr. Sabik said. “The criticism is that these are old studies and aren’t applicable today, but we don’t understand downgrading without any evidence suggesting it [CABG] isn’t effective anymore.”
CABG and PCI treated as equal
AATS and STS also object to the new guidelines treating PCI and CABG as equivalent revascularization strategies in decreasing ischemic events. Both were given a 2b recommendation for survival with triple-vessel disease, but randomized trials have demonstrated not only lower mortality with surgery but fewer reinterventions and myocardial infarctions.
“None of that gets acknowledged in the guidelines; they are treated equally,” Dr. Sabik said. “So if you’re going to say that CABG isn’t any better than medical therapy, in our mind, you have to say that PCI is worse than medical therapy. And we don’t believe that, I want you to know. We just think that the logic doesn’t make any sense. The committee used what it wanted to but didn’t use many things that committees have used in the past to give CABG a level 1 recommendation.”
The downgrade is also at odds with the 2018 European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/ European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) guidelines, which give CABG a class 1 recommendation in three-vessel CAD as well as one- or two-vessel CAD with proximal left atrial descending artery stenosis.
In a Dec. 14 letter to the ACC/AHA Joint Committee, the Latin American Association of Cardiac and Endovascular Surgery (LACES) also called out the guideline committee for the 2b class of recommendation (COR) for PCI and CABG, saying it contradicts the text, which “clearly considers” the need to give a weaker endorsement for PCI than for CABG in patients with multivessel CAD.
“Considering that this section has the most significant impact due to the prevalence of stable ischemic heart disease in patients with multivessel CAD, such a contradiction may affect the lives and survival of millions of patients worldwide and have a major socioeconomic impact,” the letter states.
“Therefore, LACES respectfully but vehemently believes the Task Force should seriously reconsider the wording and recommendations in this specific large group of patients.”
Class I for radial conduit
AATS and STS also express concern about the new class 1 recommendation for the radial artery as a conduit in CABG. They note this is higher than bilateral internal mammary artery grafting and based on a meta-analysis of six relatively small studies with very strict inclusion criteria favorable for radial artery usage and patency.
“There’s a lot of studies that showed if you use the radial artery incorrectly, you have worse outcomes, and that’s what scares us a bit,” Dr. Sabik said. “If they’re giving it a class 1 recommendation, does that mean that becomes standard of care and could that cause patient harm? We think that level 1 is too high and that a [class] 2a with qualifications would be appropriate.”
Unequal footing
In a Dec. 23 letter, EACTS said it is “extremely concerned” about downgrading the COR for CABG without new randomized controlled trials to support the decision or to reject previously held evidence.
“The downgrading of CABG, and placing PCI at the same COR, does not meet our interpretation of the evidence, and may lead to avoidable loss of life,” EACTS officials said. “These guidelines also have implications on patient care: A COR IIb entails that CABG may not be reimbursable in some countries.”
EACTS called on AHA, ACC, and SCAI to review the evidence and called out the makeup of the guideline writing committee. “It is astonishing that no surgical association was involved, coauthored, or endorsed these guidelines.”
The AATS and STS each had a single representative on the guidelines’ writing committee but note that the six remaining surgeons were chosen by the ACC and AHA. Surgeons were also in the minority and only a majority was needed to approve the guidelines, highlighting the need to revisit the guideline development process to ensure equal representation by multidisciplinary experts across specialties.
“I hope the cardiology and surgical societies can come together and figure out how we do this better in the future, and we take a look again at these guidelines and come up with what we think is appropriate, especially since this is not just AATS and STS,” Dr. Sabik said.
In an emailed statement, the ACC/AHA said the AATS and STS representatives “actively participated throughout the writing process the past 3 years” and that the AATS and STS were involved in the “extensive peer review process” for the document with a reviewer from each organization. Nevertheless, AATS and STS both elected not to endorse the guidelines when at the organizational approval stage.
“Consequently, the AATS representative chose to stay with the committee and be recognized as having been appointed on behalf of the ACC and the AHA,” according to the statement. “The STS representative chose to withdraw from the committee and is not listed as a writing committee member on the final guideline. The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for coronary artery revascularization, as agreed by the ACC, AHA, SCAI, and the full writing committee.”
Despite pleas from the surgical groups to reconsider the evidence, “there is no further review process for the revascularization guideline,” the ACC/AHA spokesperson noted.
Jennifer S. Lawton, MD, chief of cardiac surgery at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and guideline writing committee chair, did not respond to numerous requests for comment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new 2021 coronary revascularization guidelines are spurring controversy, as surgical associations raise concerns about the interpretation of the evidence behind key recommendations and the makeup of the writing committee.
The guideline was published in December by the American College of Cardiology, American Heart Association, and Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (ACC/AHA/SCAI), and replaces the 2011 coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) and the 2011 and 2015 percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) guidelines.
The American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AATS) and Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) were part of the development of the document but have withdrawn their support, citing three areas of concern in a recent editorial in Annals of Thoracic Surgery.
“I do have to emphasize this is not just the AATS and STS – the European societies, Latin American societies, Asian societies, and even cardiologists are all coming out against these guidelines,” Joseph F. Sabik III, MD, University Hospitals Cleveland Medical Center, lead author of the editorial, said in an interview. “So, I think that tells us that something didn’t go right here.”
The main objection is the downgrading of CABG surgery from a class 1 to weak 2b recommendation to improve survival in patients with three-vessel coronary artery disease (CAD) and normal left ventricular function.
The ISCHEMIA trial was used to support this two-level downgrade and a class 1 to 2a downgrade for CABG in three-vessel CAD with mild to moderate left ventricular dysfunction. But the trial wasn’t powered for survival, only 20% of patients underwent CABG as the initial invasive strategy, and patients were followed for less than 5 years, the editorialists observed.
At the same time, there’s plenty of observational and randomized studies such as SYNTAX, EXCEL, and FAME 3 showing a clear survival benefit of CABG over PCI, Dr. Sabik said. “The criticism is that these are old studies and aren’t applicable today, but we don’t understand downgrading without any evidence suggesting it [CABG] isn’t effective anymore.”
CABG and PCI treated as equal
AATS and STS also object to the new guidelines treating PCI and CABG as equivalent revascularization strategies in decreasing ischemic events. Both were given a 2b recommendation for survival with triple-vessel disease, but randomized trials have demonstrated not only lower mortality with surgery but fewer reinterventions and myocardial infarctions.
“None of that gets acknowledged in the guidelines; they are treated equally,” Dr. Sabik said. “So if you’re going to say that CABG isn’t any better than medical therapy, in our mind, you have to say that PCI is worse than medical therapy. And we don’t believe that, I want you to know. We just think that the logic doesn’t make any sense. The committee used what it wanted to but didn’t use many things that committees have used in the past to give CABG a level 1 recommendation.”
The downgrade is also at odds with the 2018 European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/ European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) guidelines, which give CABG a class 1 recommendation in three-vessel CAD as well as one- or two-vessel CAD with proximal left atrial descending artery stenosis.
In a Dec. 14 letter to the ACC/AHA Joint Committee, the Latin American Association of Cardiac and Endovascular Surgery (LACES) also called out the guideline committee for the 2b class of recommendation (COR) for PCI and CABG, saying it contradicts the text, which “clearly considers” the need to give a weaker endorsement for PCI than for CABG in patients with multivessel CAD.
“Considering that this section has the most significant impact due to the prevalence of stable ischemic heart disease in patients with multivessel CAD, such a contradiction may affect the lives and survival of millions of patients worldwide and have a major socioeconomic impact,” the letter states.
“Therefore, LACES respectfully but vehemently believes the Task Force should seriously reconsider the wording and recommendations in this specific large group of patients.”
Class I for radial conduit
AATS and STS also express concern about the new class 1 recommendation for the radial artery as a conduit in CABG. They note this is higher than bilateral internal mammary artery grafting and based on a meta-analysis of six relatively small studies with very strict inclusion criteria favorable for radial artery usage and patency.
“There’s a lot of studies that showed if you use the radial artery incorrectly, you have worse outcomes, and that’s what scares us a bit,” Dr. Sabik said. “If they’re giving it a class 1 recommendation, does that mean that becomes standard of care and could that cause patient harm? We think that level 1 is too high and that a [class] 2a with qualifications would be appropriate.”
Unequal footing
In a Dec. 23 letter, EACTS said it is “extremely concerned” about downgrading the COR for CABG without new randomized controlled trials to support the decision or to reject previously held evidence.
“The downgrading of CABG, and placing PCI at the same COR, does not meet our interpretation of the evidence, and may lead to avoidable loss of life,” EACTS officials said. “These guidelines also have implications on patient care: A COR IIb entails that CABG may not be reimbursable in some countries.”
EACTS called on AHA, ACC, and SCAI to review the evidence and called out the makeup of the guideline writing committee. “It is astonishing that no surgical association was involved, coauthored, or endorsed these guidelines.”
The AATS and STS each had a single representative on the guidelines’ writing committee but note that the six remaining surgeons were chosen by the ACC and AHA. Surgeons were also in the minority and only a majority was needed to approve the guidelines, highlighting the need to revisit the guideline development process to ensure equal representation by multidisciplinary experts across specialties.
“I hope the cardiology and surgical societies can come together and figure out how we do this better in the future, and we take a look again at these guidelines and come up with what we think is appropriate, especially since this is not just AATS and STS,” Dr. Sabik said.
In an emailed statement, the ACC/AHA said the AATS and STS representatives “actively participated throughout the writing process the past 3 years” and that the AATS and STS were involved in the “extensive peer review process” for the document with a reviewer from each organization. Nevertheless, AATS and STS both elected not to endorse the guidelines when at the organizational approval stage.
“Consequently, the AATS representative chose to stay with the committee and be recognized as having been appointed on behalf of the ACC and the AHA,” according to the statement. “The STS representative chose to withdraw from the committee and is not listed as a writing committee member on the final guideline. The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for coronary artery revascularization, as agreed by the ACC, AHA, SCAI, and the full writing committee.”
Despite pleas from the surgical groups to reconsider the evidence, “there is no further review process for the revascularization guideline,” the ACC/AHA spokesperson noted.
Jennifer S. Lawton, MD, chief of cardiac surgery at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and guideline writing committee chair, did not respond to numerous requests for comment.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early SAVR tops watchful waiting in severe, asymptomatic aortic stenosis: AVATAR
Better to intervene early with a new valve in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS) who are asymptomatic, even during exercise, than to wait for the disease to progress and symptoms to emerge before operating, suggests a small, randomized trial that challenges the guidelines.
Of the trial’s 157 patients, all with negative results on stress tests and normal left ventricular (LV) function despite severe AS, those assigned to early surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR), compared with standard watchful waiting, showed a better-than-50% drop in risk for death or major adverse cardiac events (MACE) over 2-3 years. The benefit appeared driven by fewer hospitalizations for heart failure (HF) and deaths in the early-surgery group.
The findings “advocate for early surgery once aortic stenosis becomes significant and regardless of symptom status,” Marko Banovic, MD, PhD, said during his presentation at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Banovic, from the University of Belgrade Medical School in Serbia, is coprincipal investigator on the trial, called AVATAR (Aortic Valve Replacement vs. Conservative Treatment in Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis). He is also lead author on the study’s publication in Circulation, timed to coincide with his AHA presentation.
“The AVATAR findings provide additional evidence to help clinicians in guiding their decision when seeing a patient with significant aortic stenosis, normal left ventricular function, overall low surgical risk, and without significant comorbidities,” Dr. Banovic told this news organization.
European and North American Guidelines favor watchful waiting for asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis, with surgery upon development of symptoms or LV dysfunction, observed Victoria Delgado, MD, PhD, Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, an invited discussant for the AVATAR presentation.
AVATAR does suggest that “early surgery in truly asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and preserved ejection fraction seems to provide better outcomes as compared to the conservative treatment,” she said. “But I think that the long-term follow-up for potential events, such as valve durability or endocarditis, is still needed.”
The trial has strengths, compared with the recent RECOVERY trial, which also concluded in favor of early SAVR over watchful waiting in patients described as asymptomatic with severe aortic stenosis. Dr. Delgado and other observers, however, have pointed out limitations of that trial, including questions about whether the patients were truly asymptomatic – stress testing wasn›t routinely performed.
In AVATAR, all patients were negative at stress testing, which required them to reach their estimated maximum heart rate, Dr. Banovic noted. As he and his colleagues write, the trial expands on RECOVERY “by providing evidence of the benefit of early surgery in a setting representative of a dilemma in decision making, in truly asymptomatic patients with severe but not critical aortic stenosis and normal LV function.”
A role for TAVR?
Guidelines in general “can be very conservative and lag behind evidence a bit,” Patricia A. Pellikka, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., who is not associated with AVATAR, said in an interview.
“I think when we see patients clinically, we can advise them that if they don’t have symptoms and they do have severe aortic stenosis,” she said, “they’re likely going to get symptoms within a reasonably short period of time, according to our retrospective databases, and that doing the intervention early may yield better long-term outcomes.”
The results of AVATAR, in which valve replacement consisted only of SAVR, “probably could be extrapolated” to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), Dr. Pellikka observed. “Certainly, TAVR is the procedure that patients come asking for. It’s attractive to avoid a major surgery, and it seems very plausible that TAVR would have yielded similar results if that had been a therapy in this trial.”
In practice, patient age and functional status would figure heavily in deciding whether early valve replacement, and which procedure, is appropriate, Dr. Banovic said in an interview. Importantly, the trial’s patients were at low surgical risk and free of major chronic diseases or other important health concerns.
“Frailty and older age are known risk factors for suboptimal recovery” after SAVR, Dr. Banovic said when interviewed. Therefore, frail patients, who were not many in AVATAR, might be “more suitable for TAVR than SAVR, based on the TAVR-vs.-SAVR results in symptomatic AS patients,” he said.
“One might extrapolate experience from AVATAR trial to TAVR, which may lower the bar for TAVR indications,” but that would require more supporting evidence, Dr. Banovic said.
Confirmed asymptomatic
AVATAR, conducted at nine centers in seven countries in the European Union, randomly assigned 157 adults with severe AS by echocardiography and a LV ejection fraction (LVEF) greater than 50% to early SAVR or conservative management. They averaged 67 years in age, and 43% were women.
The trial excluded anyone with dyspnea, syncope, presyncope, angina, or LV dysfunction and anyone with a history of atrial fibrillation or significant cardiac, renal, or lung disease. The cohort’s average Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 1.7%.
The 78 patients in the early-surgery group “were expected” to have the procedure within 8 weeks of randomization, the published report states; the median time was 55 days. Six of them ultimately did not have the surgery. There was only one periprocedural death, for an operative mortality of 1.4%.
The 79 patients assigned to conservative care were later referred for surgery if they developed symptoms, their LVEF dropped below 50%, or they showed a 0.3-m/sec jump in peak aortic jet velocity at follow-up echocardiography. That occurred with 25 patients a median of 400 days after randomization.
The rate of the primary endpoint – death from any cause, acute myocardial infarction, stroke, or unplanned HF hospitalization – was 16.6% in the early-surgery group and 32.9% for those managed conservatively over a median of 32 months. The hazard ratio by intention-to-treat analysis was 0.46 (95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.90; P = .02). The HR for death from any cause or HF hospitalization was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.19-0.84; P = .013). Any differences in the individual endpoints of death, first HF hospitalizations, thromboembolic complications, or major bleeding were not significant.
If early aortic valve replacement is better for patients like those in AVATAR, some sort of screening for previously unknown severe aortic stenosis may seem attractive for selected populations. “Echocardiography would be the screening test for aortic stenosis, but it’s fairly expensive and therefore has never been advocated as a test to screen everyone,” Dr. Pellikka observed.
“But things are changing,” given innovations such as point-of-care ultrasonography and machine learning, she noted. “Artificial intelligence is progressing in its application to echocardiography, and it’s conceivable that in the future, there might be some abbreviated or screening type of test. But I don’t think we’re quite there yet.”
Dr. Banovic had no conflicts; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Delgado disclosed speaker fees from Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, and GE Healthcare and unrestricted research grants to her institution from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Biotronik, Bioventrix, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, GE Healthcare, Ionis, and Medtronic. Dr. Pellikka disclosed receiving a research grant from Ultromics and having unspecified modest relationships with GE Healthcare, Lantheus, and OxThera.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Better to intervene early with a new valve in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS) who are asymptomatic, even during exercise, than to wait for the disease to progress and symptoms to emerge before operating, suggests a small, randomized trial that challenges the guidelines.
Of the trial’s 157 patients, all with negative results on stress tests and normal left ventricular (LV) function despite severe AS, those assigned to early surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR), compared with standard watchful waiting, showed a better-than-50% drop in risk for death or major adverse cardiac events (MACE) over 2-3 years. The benefit appeared driven by fewer hospitalizations for heart failure (HF) and deaths in the early-surgery group.
The findings “advocate for early surgery once aortic stenosis becomes significant and regardless of symptom status,” Marko Banovic, MD, PhD, said during his presentation at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Banovic, from the University of Belgrade Medical School in Serbia, is coprincipal investigator on the trial, called AVATAR (Aortic Valve Replacement vs. Conservative Treatment in Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis). He is also lead author on the study’s publication in Circulation, timed to coincide with his AHA presentation.
“The AVATAR findings provide additional evidence to help clinicians in guiding their decision when seeing a patient with significant aortic stenosis, normal left ventricular function, overall low surgical risk, and without significant comorbidities,” Dr. Banovic told this news organization.
European and North American Guidelines favor watchful waiting for asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis, with surgery upon development of symptoms or LV dysfunction, observed Victoria Delgado, MD, PhD, Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, an invited discussant for the AVATAR presentation.
AVATAR does suggest that “early surgery in truly asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and preserved ejection fraction seems to provide better outcomes as compared to the conservative treatment,” she said. “But I think that the long-term follow-up for potential events, such as valve durability or endocarditis, is still needed.”
The trial has strengths, compared with the recent RECOVERY trial, which also concluded in favor of early SAVR over watchful waiting in patients described as asymptomatic with severe aortic stenosis. Dr. Delgado and other observers, however, have pointed out limitations of that trial, including questions about whether the patients were truly asymptomatic – stress testing wasn›t routinely performed.
In AVATAR, all patients were negative at stress testing, which required them to reach their estimated maximum heart rate, Dr. Banovic noted. As he and his colleagues write, the trial expands on RECOVERY “by providing evidence of the benefit of early surgery in a setting representative of a dilemma in decision making, in truly asymptomatic patients with severe but not critical aortic stenosis and normal LV function.”
A role for TAVR?
Guidelines in general “can be very conservative and lag behind evidence a bit,” Patricia A. Pellikka, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., who is not associated with AVATAR, said in an interview.
“I think when we see patients clinically, we can advise them that if they don’t have symptoms and they do have severe aortic stenosis,” she said, “they’re likely going to get symptoms within a reasonably short period of time, according to our retrospective databases, and that doing the intervention early may yield better long-term outcomes.”
The results of AVATAR, in which valve replacement consisted only of SAVR, “probably could be extrapolated” to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), Dr. Pellikka observed. “Certainly, TAVR is the procedure that patients come asking for. It’s attractive to avoid a major surgery, and it seems very plausible that TAVR would have yielded similar results if that had been a therapy in this trial.”
In practice, patient age and functional status would figure heavily in deciding whether early valve replacement, and which procedure, is appropriate, Dr. Banovic said in an interview. Importantly, the trial’s patients were at low surgical risk and free of major chronic diseases or other important health concerns.
“Frailty and older age are known risk factors for suboptimal recovery” after SAVR, Dr. Banovic said when interviewed. Therefore, frail patients, who were not many in AVATAR, might be “more suitable for TAVR than SAVR, based on the TAVR-vs.-SAVR results in symptomatic AS patients,” he said.
“One might extrapolate experience from AVATAR trial to TAVR, which may lower the bar for TAVR indications,” but that would require more supporting evidence, Dr. Banovic said.
Confirmed asymptomatic
AVATAR, conducted at nine centers in seven countries in the European Union, randomly assigned 157 adults with severe AS by echocardiography and a LV ejection fraction (LVEF) greater than 50% to early SAVR or conservative management. They averaged 67 years in age, and 43% were women.
The trial excluded anyone with dyspnea, syncope, presyncope, angina, or LV dysfunction and anyone with a history of atrial fibrillation or significant cardiac, renal, or lung disease. The cohort’s average Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 1.7%.
The 78 patients in the early-surgery group “were expected” to have the procedure within 8 weeks of randomization, the published report states; the median time was 55 days. Six of them ultimately did not have the surgery. There was only one periprocedural death, for an operative mortality of 1.4%.
The 79 patients assigned to conservative care were later referred for surgery if they developed symptoms, their LVEF dropped below 50%, or they showed a 0.3-m/sec jump in peak aortic jet velocity at follow-up echocardiography. That occurred with 25 patients a median of 400 days after randomization.
The rate of the primary endpoint – death from any cause, acute myocardial infarction, stroke, or unplanned HF hospitalization – was 16.6% in the early-surgery group and 32.9% for those managed conservatively over a median of 32 months. The hazard ratio by intention-to-treat analysis was 0.46 (95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.90; P = .02). The HR for death from any cause or HF hospitalization was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.19-0.84; P = .013). Any differences in the individual endpoints of death, first HF hospitalizations, thromboembolic complications, or major bleeding were not significant.
If early aortic valve replacement is better for patients like those in AVATAR, some sort of screening for previously unknown severe aortic stenosis may seem attractive for selected populations. “Echocardiography would be the screening test for aortic stenosis, but it’s fairly expensive and therefore has never been advocated as a test to screen everyone,” Dr. Pellikka observed.
“But things are changing,” given innovations such as point-of-care ultrasonography and machine learning, she noted. “Artificial intelligence is progressing in its application to echocardiography, and it’s conceivable that in the future, there might be some abbreviated or screening type of test. But I don’t think we’re quite there yet.”
Dr. Banovic had no conflicts; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Delgado disclosed speaker fees from Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, and GE Healthcare and unrestricted research grants to her institution from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Biotronik, Bioventrix, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, GE Healthcare, Ionis, and Medtronic. Dr. Pellikka disclosed receiving a research grant from Ultromics and having unspecified modest relationships with GE Healthcare, Lantheus, and OxThera.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Better to intervene early with a new valve in patients with severe aortic stenosis (AS) who are asymptomatic, even during exercise, than to wait for the disease to progress and symptoms to emerge before operating, suggests a small, randomized trial that challenges the guidelines.
Of the trial’s 157 patients, all with negative results on stress tests and normal left ventricular (LV) function despite severe AS, those assigned to early surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR), compared with standard watchful waiting, showed a better-than-50% drop in risk for death or major adverse cardiac events (MACE) over 2-3 years. The benefit appeared driven by fewer hospitalizations for heart failure (HF) and deaths in the early-surgery group.
The findings “advocate for early surgery once aortic stenosis becomes significant and regardless of symptom status,” Marko Banovic, MD, PhD, said during his presentation at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
Dr. Banovic, from the University of Belgrade Medical School in Serbia, is coprincipal investigator on the trial, called AVATAR (Aortic Valve Replacement vs. Conservative Treatment in Asymptomatic Severe Aortic Stenosis). He is also lead author on the study’s publication in Circulation, timed to coincide with his AHA presentation.
“The AVATAR findings provide additional evidence to help clinicians in guiding their decision when seeing a patient with significant aortic stenosis, normal left ventricular function, overall low surgical risk, and without significant comorbidities,” Dr. Banovic told this news organization.
European and North American Guidelines favor watchful waiting for asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis, with surgery upon development of symptoms or LV dysfunction, observed Victoria Delgado, MD, PhD, Leiden (the Netherlands) University Medical Center, an invited discussant for the AVATAR presentation.
AVATAR does suggest that “early surgery in truly asymptomatic patients with severe aortic stenosis and preserved ejection fraction seems to provide better outcomes as compared to the conservative treatment,” she said. “But I think that the long-term follow-up for potential events, such as valve durability or endocarditis, is still needed.”
The trial has strengths, compared with the recent RECOVERY trial, which also concluded in favor of early SAVR over watchful waiting in patients described as asymptomatic with severe aortic stenosis. Dr. Delgado and other observers, however, have pointed out limitations of that trial, including questions about whether the patients were truly asymptomatic – stress testing wasn›t routinely performed.
In AVATAR, all patients were negative at stress testing, which required them to reach their estimated maximum heart rate, Dr. Banovic noted. As he and his colleagues write, the trial expands on RECOVERY “by providing evidence of the benefit of early surgery in a setting representative of a dilemma in decision making, in truly asymptomatic patients with severe but not critical aortic stenosis and normal LV function.”
A role for TAVR?
Guidelines in general “can be very conservative and lag behind evidence a bit,” Patricia A. Pellikka, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., who is not associated with AVATAR, said in an interview.
“I think when we see patients clinically, we can advise them that if they don’t have symptoms and they do have severe aortic stenosis,” she said, “they’re likely going to get symptoms within a reasonably short period of time, according to our retrospective databases, and that doing the intervention early may yield better long-term outcomes.”
The results of AVATAR, in which valve replacement consisted only of SAVR, “probably could be extrapolated” to transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR), Dr. Pellikka observed. “Certainly, TAVR is the procedure that patients come asking for. It’s attractive to avoid a major surgery, and it seems very plausible that TAVR would have yielded similar results if that had been a therapy in this trial.”
In practice, patient age and functional status would figure heavily in deciding whether early valve replacement, and which procedure, is appropriate, Dr. Banovic said in an interview. Importantly, the trial’s patients were at low surgical risk and free of major chronic diseases or other important health concerns.
“Frailty and older age are known risk factors for suboptimal recovery” after SAVR, Dr. Banovic said when interviewed. Therefore, frail patients, who were not many in AVATAR, might be “more suitable for TAVR than SAVR, based on the TAVR-vs.-SAVR results in symptomatic AS patients,” he said.
“One might extrapolate experience from AVATAR trial to TAVR, which may lower the bar for TAVR indications,” but that would require more supporting evidence, Dr. Banovic said.
Confirmed asymptomatic
AVATAR, conducted at nine centers in seven countries in the European Union, randomly assigned 157 adults with severe AS by echocardiography and a LV ejection fraction (LVEF) greater than 50% to early SAVR or conservative management. They averaged 67 years in age, and 43% were women.
The trial excluded anyone with dyspnea, syncope, presyncope, angina, or LV dysfunction and anyone with a history of atrial fibrillation or significant cardiac, renal, or lung disease. The cohort’s average Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 1.7%.
The 78 patients in the early-surgery group “were expected” to have the procedure within 8 weeks of randomization, the published report states; the median time was 55 days. Six of them ultimately did not have the surgery. There was only one periprocedural death, for an operative mortality of 1.4%.
The 79 patients assigned to conservative care were later referred for surgery if they developed symptoms, their LVEF dropped below 50%, or they showed a 0.3-m/sec jump in peak aortic jet velocity at follow-up echocardiography. That occurred with 25 patients a median of 400 days after randomization.
The rate of the primary endpoint – death from any cause, acute myocardial infarction, stroke, or unplanned HF hospitalization – was 16.6% in the early-surgery group and 32.9% for those managed conservatively over a median of 32 months. The hazard ratio by intention-to-treat analysis was 0.46 (95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.90; P = .02). The HR for death from any cause or HF hospitalization was 0.40 (95% CI, 0.19-0.84; P = .013). Any differences in the individual endpoints of death, first HF hospitalizations, thromboembolic complications, or major bleeding were not significant.
If early aortic valve replacement is better for patients like those in AVATAR, some sort of screening for previously unknown severe aortic stenosis may seem attractive for selected populations. “Echocardiography would be the screening test for aortic stenosis, but it’s fairly expensive and therefore has never been advocated as a test to screen everyone,” Dr. Pellikka observed.
“But things are changing,” given innovations such as point-of-care ultrasonography and machine learning, she noted. “Artificial intelligence is progressing in its application to echocardiography, and it’s conceivable that in the future, there might be some abbreviated or screening type of test. But I don’t think we’re quite there yet.”
Dr. Banovic had no conflicts; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Delgado disclosed speaker fees from Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, Medtronic, Merck, Novartis, and GE Healthcare and unrestricted research grants to her institution from Abbott Vascular, Bayer, Biotronik, Bioventrix, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, GE Healthcare, Ionis, and Medtronic. Dr. Pellikka disclosed receiving a research grant from Ultromics and having unspecified modest relationships with GE Healthcare, Lantheus, and OxThera.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2021
CABG safe 3 days after stopping ticagrelor: RAPID CABG
Patients with acute coronary syndromes who have been taking the antiplatelet medication, ticagrelor, and who need coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be able to safely have the procedure earlier than typically recommended, a new randomized trial suggests.
The RAPID CABG trial found that early surgery 2-3 days after ticagrelor cessation was noninferior in incurring severe or massive perioperative bleeding, compared with waiting 5-7 days. There was also no significant difference in TIMI CABG or Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) type 4 or 5 bleeding.
Patients in the delayed group had a numerically higher number of ischemic events requiring earlier surgery and had a longer hospital stay.
The study was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“RAPID CABG is the first and only randomized controlled trial evaluating the safety of early surgery in patients taking ticagrelor,” said lead investigator Derek So, MD.
Dr. So, a cardiologist at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute and a professor at the University of Ottawa, explained that ticagrelor is a first-line antiplatelet agent for patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), but around 10% of patients presenting with ACS require CABG surgery.
A major concern among patients requiring bypass surgery is perioperative bleeding, and it has been shown that patients undergoing urgent bypass within 24 hours of the last dose of ticagrelor have increased mortality. Accordingly, guidelines suggest a waiting period for patients not requiring urgent bypass surgery, Dr. So noted.
Current North American guidelines suggest a waiting period of at least 5 days after stopping ticagrelor before bypass surgery. In contrast, the updated European and Japanese guidelines suggest a waiting period of 3 days.
Dr. So noted that all of the guidelines are based on cohort studies and pharmacodynamic studies, with no randomized evidence. Pharmacodynamic studies have shown that at 48 hours after the last dose of ticagrelor, the level of platelet inhibition drops to the same levels seen with long-term treatment with clopidogrel, a weaker antiplatelet drug, and after 120 hours (5 days) the effect has completely worn off.
Dr. So concluded that these new results from the RAPID CABG trial “may influence future iterations of North American guidelines with reduced waiting prior to bypass surgery” for patients receiving ticagrelor, and “they could also strengthen the level of evidence in European and Asian guidelines.”
Designated discussant of the RAPID CABG trial, Roxana Mehran, MD, professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said this was a “very important study,” being the only randomized trial to look at this issue to date.
Dr. Mehran noted that the results showed a similar number of major life-threatening bleeding events in the early and delayed groups and met the noninferiority endpoint, but she pointed out that the trial had a small sample size and a small number of events. “Therefore, larger trials are needed to verify these important and encouraging results.”
However, she concluded that these results should be considered in decisions about the timing of bypass surgery in patients receiving ticagrelor. “I will be changing my practice and sending patients earlier based on this data,” she said.
RAPID CABG
RAPID CABG was a physician-initiated multicenter randomized study evaluating the safety of early surgery at 2-3 days after ticagrelor cessation, compared with a delay of 5-7 days among patients presenting with ACS who required nonemergency CABG surgery.
The study enrolled 143 patients with ACS who were receiving ticagrelor and needed CABG surgery. Patients with stenting for culprit lesions, those requiring urgent surgery (less than 24 hours after presentation), and those requiring valve surgery were excluded.
Three patients declined surgery, and several others underwent surgery outside the assigned time window, so the results were based on the per protocol analysis of patients who actually had CABG in the assigned time window: 65 patients in the early CABG group and 58 in the delayed group.
The mean time from last ticagrelor dose to surgery was 3 days in the early group and 6 days in the delayed group.
Platelet reactivity on the VerifyNow test showed more residual antiplatelet activity in the early group, with P2Y12 reaction unit (PRU) levels of 200 (vs. 251 in the delayed group). This test measures the extent of platelet aggregation in the presence of P2Y12-inhibitor drugs, with lower PRU levels showing stronger antiplatelet effects.
The primary outcome of the study was severe or massive bleeding by Universal Definition of Perioperative Bleeding (UDPB) class 3 or 4. This is defined as a blood transfusions of more than 5 units of red blood cells or plasma within 24 hours of surgical closure, chest tube drainage of over 1,000 mL in the first 12 hours, and reoperation for bleeding.
Results showed that 4.6% of the early-surgery group had a primary outcome bleeding event, compared with 5.2% of the delayed surgery group, meeting the criteria for noninferiority (P = .0253 for noninferiority).
Individual components of the primary endpoint showed three class 3 (severe) bleeding events in both groups and no class 4 (massive) bleeding events in either group.
In terms of other bleeding outcomes, TIMI CABG bleeding occurred in two patients (3.1%) in the early-surgery group vs. no patients in the delayed group; BARC 4 bleeding occurred in two patients (3.1%) in the early group versus none in the delayed group, and there were no BARC 5 bleeding events in either group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, ischemic events before surgery occurred in six patients (8.7%) in the delayed group (one myocardial infarction, four cases of recurrent ischemia, and one ventricular tachycardia) versus none in the early group.
Cumulative 6-month ischemic events occurred in nine patients (13.0%) in the delayed group vs. four patients (5.6%) in the early group, the difference being driven by nonfatal MI and recurrent ischemia.
There were no cardiovascular deaths in either group and one all-cause death in both groups.
Patients undergoing early surgery also had a shorter hospitalization, with a median length of stay of 9 days versus 12 days in the delayed group.
Larger trial needed
Commenting on the RAPID CABG study at an AHA press conference, Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of the cardiac surgery department at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said the results were in line with her practice.
“These results confirm what I already think is safe,” she said. “I’m comfortable going within 48 hours. But we individualize our approach, so it was helpful that the study investigators included platelet reactivity data. The interesting thing for me in this study was the number of adverse events in patients who waited longer.”
Dr. Chikwe said her top-line message was that “Surgery looked incredibly safe; there was amazingly low mortality. And if a patient has an indication for surgery, waiting does not serve you well.”
However, she also cautioned that the trial was somewhat underpowered, with a small number of events that drove the primary outcome, leading to some uncertainty on the results.
“The RAPID trial was helpful, and although it confirms my practice, I think physicians may want to see a larger-powered trial to be convincingly compelled that they should change their practice,” Dr. Chikwe noted.
She added that clinical trials in cardiac surgery are driven by inherent challenges. “Cardiac surgery is not very common, and it is hard to recruit patients into these trials, so you are generally tied to a small number of patients, and you therefore have to be extremely thoughtful about the study design. It is almost a given that you will need to use surrogate endpoints, and the choice of the surrogate endpoint can determine which way the trial goes.”
The RAPID CABG study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. So reports research support, consultancy, or speaker’s fees from AggreDyne, Roche Diagnostics, Fujimori Kogyo, and AstraZeneca Canada. Dr. Mehran reports that her institution has received significant trial funding from AstraZeneca (the manufacturer of ticagrelor).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes who have been taking the antiplatelet medication, ticagrelor, and who need coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be able to safely have the procedure earlier than typically recommended, a new randomized trial suggests.
The RAPID CABG trial found that early surgery 2-3 days after ticagrelor cessation was noninferior in incurring severe or massive perioperative bleeding, compared with waiting 5-7 days. There was also no significant difference in TIMI CABG or Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) type 4 or 5 bleeding.
Patients in the delayed group had a numerically higher number of ischemic events requiring earlier surgery and had a longer hospital stay.
The study was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“RAPID CABG is the first and only randomized controlled trial evaluating the safety of early surgery in patients taking ticagrelor,” said lead investigator Derek So, MD.
Dr. So, a cardiologist at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute and a professor at the University of Ottawa, explained that ticagrelor is a first-line antiplatelet agent for patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), but around 10% of patients presenting with ACS require CABG surgery.
A major concern among patients requiring bypass surgery is perioperative bleeding, and it has been shown that patients undergoing urgent bypass within 24 hours of the last dose of ticagrelor have increased mortality. Accordingly, guidelines suggest a waiting period for patients not requiring urgent bypass surgery, Dr. So noted.
Current North American guidelines suggest a waiting period of at least 5 days after stopping ticagrelor before bypass surgery. In contrast, the updated European and Japanese guidelines suggest a waiting period of 3 days.
Dr. So noted that all of the guidelines are based on cohort studies and pharmacodynamic studies, with no randomized evidence. Pharmacodynamic studies have shown that at 48 hours after the last dose of ticagrelor, the level of platelet inhibition drops to the same levels seen with long-term treatment with clopidogrel, a weaker antiplatelet drug, and after 120 hours (5 days) the effect has completely worn off.
Dr. So concluded that these new results from the RAPID CABG trial “may influence future iterations of North American guidelines with reduced waiting prior to bypass surgery” for patients receiving ticagrelor, and “they could also strengthen the level of evidence in European and Asian guidelines.”
Designated discussant of the RAPID CABG trial, Roxana Mehran, MD, professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said this was a “very important study,” being the only randomized trial to look at this issue to date.
Dr. Mehran noted that the results showed a similar number of major life-threatening bleeding events in the early and delayed groups and met the noninferiority endpoint, but she pointed out that the trial had a small sample size and a small number of events. “Therefore, larger trials are needed to verify these important and encouraging results.”
However, she concluded that these results should be considered in decisions about the timing of bypass surgery in patients receiving ticagrelor. “I will be changing my practice and sending patients earlier based on this data,” she said.
RAPID CABG
RAPID CABG was a physician-initiated multicenter randomized study evaluating the safety of early surgery at 2-3 days after ticagrelor cessation, compared with a delay of 5-7 days among patients presenting with ACS who required nonemergency CABG surgery.
The study enrolled 143 patients with ACS who were receiving ticagrelor and needed CABG surgery. Patients with stenting for culprit lesions, those requiring urgent surgery (less than 24 hours after presentation), and those requiring valve surgery were excluded.
Three patients declined surgery, and several others underwent surgery outside the assigned time window, so the results were based on the per protocol analysis of patients who actually had CABG in the assigned time window: 65 patients in the early CABG group and 58 in the delayed group.
The mean time from last ticagrelor dose to surgery was 3 days in the early group and 6 days in the delayed group.
Platelet reactivity on the VerifyNow test showed more residual antiplatelet activity in the early group, with P2Y12 reaction unit (PRU) levels of 200 (vs. 251 in the delayed group). This test measures the extent of platelet aggregation in the presence of P2Y12-inhibitor drugs, with lower PRU levels showing stronger antiplatelet effects.
The primary outcome of the study was severe or massive bleeding by Universal Definition of Perioperative Bleeding (UDPB) class 3 or 4. This is defined as a blood transfusions of more than 5 units of red blood cells or plasma within 24 hours of surgical closure, chest tube drainage of over 1,000 mL in the first 12 hours, and reoperation for bleeding.
Results showed that 4.6% of the early-surgery group had a primary outcome bleeding event, compared with 5.2% of the delayed surgery group, meeting the criteria for noninferiority (P = .0253 for noninferiority).
Individual components of the primary endpoint showed three class 3 (severe) bleeding events in both groups and no class 4 (massive) bleeding events in either group.
In terms of other bleeding outcomes, TIMI CABG bleeding occurred in two patients (3.1%) in the early-surgery group vs. no patients in the delayed group; BARC 4 bleeding occurred in two patients (3.1%) in the early group versus none in the delayed group, and there were no BARC 5 bleeding events in either group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, ischemic events before surgery occurred in six patients (8.7%) in the delayed group (one myocardial infarction, four cases of recurrent ischemia, and one ventricular tachycardia) versus none in the early group.
Cumulative 6-month ischemic events occurred in nine patients (13.0%) in the delayed group vs. four patients (5.6%) in the early group, the difference being driven by nonfatal MI and recurrent ischemia.
There were no cardiovascular deaths in either group and one all-cause death in both groups.
Patients undergoing early surgery also had a shorter hospitalization, with a median length of stay of 9 days versus 12 days in the delayed group.
Larger trial needed
Commenting on the RAPID CABG study at an AHA press conference, Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of the cardiac surgery department at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said the results were in line with her practice.
“These results confirm what I already think is safe,” she said. “I’m comfortable going within 48 hours. But we individualize our approach, so it was helpful that the study investigators included platelet reactivity data. The interesting thing for me in this study was the number of adverse events in patients who waited longer.”
Dr. Chikwe said her top-line message was that “Surgery looked incredibly safe; there was amazingly low mortality. And if a patient has an indication for surgery, waiting does not serve you well.”
However, she also cautioned that the trial was somewhat underpowered, with a small number of events that drove the primary outcome, leading to some uncertainty on the results.
“The RAPID trial was helpful, and although it confirms my practice, I think physicians may want to see a larger-powered trial to be convincingly compelled that they should change their practice,” Dr. Chikwe noted.
She added that clinical trials in cardiac surgery are driven by inherent challenges. “Cardiac surgery is not very common, and it is hard to recruit patients into these trials, so you are generally tied to a small number of patients, and you therefore have to be extremely thoughtful about the study design. It is almost a given that you will need to use surrogate endpoints, and the choice of the surrogate endpoint can determine which way the trial goes.”
The RAPID CABG study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. So reports research support, consultancy, or speaker’s fees from AggreDyne, Roche Diagnostics, Fujimori Kogyo, and AstraZeneca Canada. Dr. Mehran reports that her institution has received significant trial funding from AstraZeneca (the manufacturer of ticagrelor).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes who have been taking the antiplatelet medication, ticagrelor, and who need coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG) may be able to safely have the procedure earlier than typically recommended, a new randomized trial suggests.
The RAPID CABG trial found that early surgery 2-3 days after ticagrelor cessation was noninferior in incurring severe or massive perioperative bleeding, compared with waiting 5-7 days. There was also no significant difference in TIMI CABG or Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) type 4 or 5 bleeding.
Patients in the delayed group had a numerically higher number of ischemic events requiring earlier surgery and had a longer hospital stay.
The study was presented at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
“RAPID CABG is the first and only randomized controlled trial evaluating the safety of early surgery in patients taking ticagrelor,” said lead investigator Derek So, MD.
Dr. So, a cardiologist at the University of Ottawa Heart Institute and a professor at the University of Ottawa, explained that ticagrelor is a first-line antiplatelet agent for patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS), but around 10% of patients presenting with ACS require CABG surgery.
A major concern among patients requiring bypass surgery is perioperative bleeding, and it has been shown that patients undergoing urgent bypass within 24 hours of the last dose of ticagrelor have increased mortality. Accordingly, guidelines suggest a waiting period for patients not requiring urgent bypass surgery, Dr. So noted.
Current North American guidelines suggest a waiting period of at least 5 days after stopping ticagrelor before bypass surgery. In contrast, the updated European and Japanese guidelines suggest a waiting period of 3 days.
Dr. So noted that all of the guidelines are based on cohort studies and pharmacodynamic studies, with no randomized evidence. Pharmacodynamic studies have shown that at 48 hours after the last dose of ticagrelor, the level of platelet inhibition drops to the same levels seen with long-term treatment with clopidogrel, a weaker antiplatelet drug, and after 120 hours (5 days) the effect has completely worn off.
Dr. So concluded that these new results from the RAPID CABG trial “may influence future iterations of North American guidelines with reduced waiting prior to bypass surgery” for patients receiving ticagrelor, and “they could also strengthen the level of evidence in European and Asian guidelines.”
Designated discussant of the RAPID CABG trial, Roxana Mehran, MD, professor of medicine at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, said this was a “very important study,” being the only randomized trial to look at this issue to date.
Dr. Mehran noted that the results showed a similar number of major life-threatening bleeding events in the early and delayed groups and met the noninferiority endpoint, but she pointed out that the trial had a small sample size and a small number of events. “Therefore, larger trials are needed to verify these important and encouraging results.”
However, she concluded that these results should be considered in decisions about the timing of bypass surgery in patients receiving ticagrelor. “I will be changing my practice and sending patients earlier based on this data,” she said.
RAPID CABG
RAPID CABG was a physician-initiated multicenter randomized study evaluating the safety of early surgery at 2-3 days after ticagrelor cessation, compared with a delay of 5-7 days among patients presenting with ACS who required nonemergency CABG surgery.
The study enrolled 143 patients with ACS who were receiving ticagrelor and needed CABG surgery. Patients with stenting for culprit lesions, those requiring urgent surgery (less than 24 hours after presentation), and those requiring valve surgery were excluded.
Three patients declined surgery, and several others underwent surgery outside the assigned time window, so the results were based on the per protocol analysis of patients who actually had CABG in the assigned time window: 65 patients in the early CABG group and 58 in the delayed group.
The mean time from last ticagrelor dose to surgery was 3 days in the early group and 6 days in the delayed group.
Platelet reactivity on the VerifyNow test showed more residual antiplatelet activity in the early group, with P2Y12 reaction unit (PRU) levels of 200 (vs. 251 in the delayed group). This test measures the extent of platelet aggregation in the presence of P2Y12-inhibitor drugs, with lower PRU levels showing stronger antiplatelet effects.
The primary outcome of the study was severe or massive bleeding by Universal Definition of Perioperative Bleeding (UDPB) class 3 or 4. This is defined as a blood transfusions of more than 5 units of red blood cells or plasma within 24 hours of surgical closure, chest tube drainage of over 1,000 mL in the first 12 hours, and reoperation for bleeding.
Results showed that 4.6% of the early-surgery group had a primary outcome bleeding event, compared with 5.2% of the delayed surgery group, meeting the criteria for noninferiority (P = .0253 for noninferiority).
Individual components of the primary endpoint showed three class 3 (severe) bleeding events in both groups and no class 4 (massive) bleeding events in either group.
In terms of other bleeding outcomes, TIMI CABG bleeding occurred in two patients (3.1%) in the early-surgery group vs. no patients in the delayed group; BARC 4 bleeding occurred in two patients (3.1%) in the early group versus none in the delayed group, and there were no BARC 5 bleeding events in either group.
In the intention-to-treat analysis, ischemic events before surgery occurred in six patients (8.7%) in the delayed group (one myocardial infarction, four cases of recurrent ischemia, and one ventricular tachycardia) versus none in the early group.
Cumulative 6-month ischemic events occurred in nine patients (13.0%) in the delayed group vs. four patients (5.6%) in the early group, the difference being driven by nonfatal MI and recurrent ischemia.
There were no cardiovascular deaths in either group and one all-cause death in both groups.
Patients undergoing early surgery also had a shorter hospitalization, with a median length of stay of 9 days versus 12 days in the delayed group.
Larger trial needed
Commenting on the RAPID CABG study at an AHA press conference, Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of the cardiac surgery department at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said the results were in line with her practice.
“These results confirm what I already think is safe,” she said. “I’m comfortable going within 48 hours. But we individualize our approach, so it was helpful that the study investigators included platelet reactivity data. The interesting thing for me in this study was the number of adverse events in patients who waited longer.”
Dr. Chikwe said her top-line message was that “Surgery looked incredibly safe; there was amazingly low mortality. And if a patient has an indication for surgery, waiting does not serve you well.”
However, she also cautioned that the trial was somewhat underpowered, with a small number of events that drove the primary outcome, leading to some uncertainty on the results.
“The RAPID trial was helpful, and although it confirms my practice, I think physicians may want to see a larger-powered trial to be convincingly compelled that they should change their practice,” Dr. Chikwe noted.
She added that clinical trials in cardiac surgery are driven by inherent challenges. “Cardiac surgery is not very common, and it is hard to recruit patients into these trials, so you are generally tied to a small number of patients, and you therefore have to be extremely thoughtful about the study design. It is almost a given that you will need to use surrogate endpoints, and the choice of the surrogate endpoint can determine which way the trial goes.”
The RAPID CABG study was funded by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. So reports research support, consultancy, or speaker’s fees from AggreDyne, Roche Diagnostics, Fujimori Kogyo, and AstraZeneca Canada. Dr. Mehran reports that her institution has received significant trial funding from AstraZeneca (the manufacturer of ticagrelor).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2021
Concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery beneficial but with a trade-off
Tricuspid valve repair at the time of mitral valve surgery reduces tricuspid regurgitation progression, but at the cost of more than a fivefold increase in permanent pacemakers, results of a new Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network study show.
The results were presented during the opening late-breaking science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is common among patients undergoing mitral valve surgery, and there’s broad agreement to intervene when a patient has severe TR. There’s uncertainty, however, about the management of moderate or less TR during mitral valve surgery, which is reflected in current guidelines on the basis of observational data, explained coprimary investigator James Gammie, MD, codirector and surgical director of the Johns Hopkins Heart and Vascular Institute, Baltimore. As a result, rates of concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery range from 5% to 75% at various centers.
To help fill the gap, Dr. Gammie and colleagues screened 5,208 patients at 29 centers in the United States, Canada, and Germany undergoing surgery for degenerative mitral regurgitation, and randomly assigned 401 patients (75% male) to mitral valve surgery alone or with tricuspid annuloplasty.
Patients had either moderate TR (37%) or less than moderate TR with a dilated tricuspid annulus of at least 40 mm or at least 21 mm/m2 indexed for body surface area. Importantly, there was a uniform surgical approach using undersized (26-30 mm) rigid nonplanar annuloplasty rings to repair the tricuspid valve, he said.
The study’s primary outcome of treatment failure at 2 years was defined as the composite of death, reoperation for TR, or progression of TR from baseline by 2 grades or severe TR.
The primary endpoint occurred in 10.2% of patients who underwent mitral valve surgery alone and 3.9% who underwent concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty (relative risk, 0.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.16-0.86; P = .02).
The endpoint was driven exclusively by less TR progression in the annuloplasty group, with no TR reoperations in either group, observed Dr. Gammie. At 2 years, just 0.6% of the annuloplasty group had severe TR, compared with 5.6% of the surgery-alone group.
The rate of permanent pacemaker implantations, however, jumped from 2.5% with surgery alone to 14.1% with concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty (rate ratio, 5.75; 95% CI, 2.27-14.60). More than half of pacemakers were placed during the first 2 days after surgery.
There was no between-group difference in 2-year rates of all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events, readmission, quality of life, or functional status.
Less than moderate TR
In a post hoc analysis stratified by baseline TR severity, treatment failure was significantly less common with surgery plus tricuspid annuloplasty among patients with moderate TR (4.5% vs. 18.1%) but not among those with less than moderate TR and tricuspid annular dilation (3.4% vs. 6.1%).
Although the trial was not powered for the subgroup analysis, “these results call into question the idea that less than moderate TR with annular dilation should be an indication for tricuspid valve repair,” Dr. Gammie told this news organization.
“I did not repair the tricuspid valve in the setting of less than moderate TR before the trial, and my practice won’t change; but it will be based on much better evidence,” he added. “Of course, long-term data from our trial will be of great interest.”
Discussant Joseph Woo, MD, chair of surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, congratulated the authors on a “landmark trial” that addresses a highly relevant problem without a clear-cut indication.
In the 2020 AHA/American College of Cardiology heart valve disease guideline, tricuspid valve surgery is a class I recommendation when there’s severe TR (stages C and D) and left-sided valve surgery but a class IIa recommendation in patients with progressive TR (stage B) with an annular dilation of at least 40 mm.
“The interesting findings in this study include that moderate TR was only 37% of the enrolled patients, and only 97% of the patients with degenerative MR received a mitral valve repair,” Dr. Woo said. “This level of mitral valve repair is perhaps lower than what we might expect at these centers and lower, certainly, than what the AHA/ACC guidelines recommend for surgery on asymptomatic severe mitral regurgitation.”
Panelist Roxanna Mehran, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York said, “What I was struck by is that we, as clinicians, believe that if you fix the mitral valve, maybe the tricuspid regurgitation will improve. And it seems like that is not what’s happening, and I think that’s a big takeaway.”
Session comoderator Joanna Chikwe, MD, head of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said, “I think we can all agree that severe tricuspid regurgitation is a disaster for patients, and I think the fact the trial is designed for an additional 5 years’ follow-up will hopefully give us some insights into the clinical impact of severe tricuspid regurgitation.”
For now, “a back of the envelope calculation suggests that, for every 20 patients with moderate tricuspid regurgitation who we repair the tricuspid valve in, we would prevent severe tricuspid valve regurgitation in 1 at the price of pacemakers in 2,” she said.
Dr. Chikwe said in an interview that “transcatheter tricuspid repair is increasingly helping these patients, but if you could avoid it with a technique that doesn’t cause incremental harm beyond, perhaps, the need for pacemakers, then this is helpful data that supports that approach.”
The pacemaker burden is not negligible, she said, but also not surprising to surgeons. “If you look at national practice of mitral-tricuspid surgery, it’s about 15% after that, and it’s simply because the conduction tissue is so close to the tricuspid annulus.”
Pacemaker implantation rates, like those for concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery, are also highly variable, and in some single-center series only around 2%, Dr. Chikwe said. “So that suggests there are technical approaches that can minimize the pacemaker rate [such as] being extremely careful to avoid suture placement around the area of the conduction tissues.”
For some the trade-off between reduced TR progression and the risk of a permanent pacemaker is worth it. “But the fact that the trial didn’t show a difference in survival, a difference in symptoms or quality of life, might suggest that patients you anticipated were high risk for surgery or didn’t have a longer projected survival aren’t going to benefit from what is quite an aggressive surgical approach,” Dr. Chikwe said.
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Chikwe and Mario Gaudino, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, also point out that the “very dynamic nature of tricuspid regurgitation and wide variability in assessing tricuspid annular dilatation are additional compelling reasons to leave lesser regurgitation alone.”
Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, Kings College and tricuspid service lead at Guys and St. Thomas NHS, London, also pointed to the need for longer-term follow-up but said increased use of imaging markers is also needed to help pinpoint TR progression in these patients. “For the moment, the results should remind imagers and clinicians to refer patients earlier.”
“As a valvular heart physician, I see more and more patients coming in with significant severe tricuspid regurgitation post–mitral valve surgery and because of the time that’s passed, there’s dysfunction of the right heart, the left heart, and it’s very hard to suggest an operation because they’re at high risk,” she said. “So we’re discussing with these patients whether to do an intervention or medical management.”
“Now, with this study, and the pending longer follow-up by the authors, I’m optimistic that the class II recommendation will be class I in order to help our patients treat tricuspid regurgitation earlier than late,” said Dr. Grapsa, who is also editor-in-chief of JACC: Case Reports.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Gammie reports a consultant/stockholder relationship with Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Grapsa reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Chikwe reports that as coprincipal investigator/study director of NCT 05051033 (an NHLBI-sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network trial), she collaborates with several of the study authors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tricuspid valve repair at the time of mitral valve surgery reduces tricuspid regurgitation progression, but at the cost of more than a fivefold increase in permanent pacemakers, results of a new Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network study show.
The results were presented during the opening late-breaking science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is common among patients undergoing mitral valve surgery, and there’s broad agreement to intervene when a patient has severe TR. There’s uncertainty, however, about the management of moderate or less TR during mitral valve surgery, which is reflected in current guidelines on the basis of observational data, explained coprimary investigator James Gammie, MD, codirector and surgical director of the Johns Hopkins Heart and Vascular Institute, Baltimore. As a result, rates of concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery range from 5% to 75% at various centers.
To help fill the gap, Dr. Gammie and colleagues screened 5,208 patients at 29 centers in the United States, Canada, and Germany undergoing surgery for degenerative mitral regurgitation, and randomly assigned 401 patients (75% male) to mitral valve surgery alone or with tricuspid annuloplasty.
Patients had either moderate TR (37%) or less than moderate TR with a dilated tricuspid annulus of at least 40 mm or at least 21 mm/m2 indexed for body surface area. Importantly, there was a uniform surgical approach using undersized (26-30 mm) rigid nonplanar annuloplasty rings to repair the tricuspid valve, he said.
The study’s primary outcome of treatment failure at 2 years was defined as the composite of death, reoperation for TR, or progression of TR from baseline by 2 grades or severe TR.
The primary endpoint occurred in 10.2% of patients who underwent mitral valve surgery alone and 3.9% who underwent concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty (relative risk, 0.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.16-0.86; P = .02).
The endpoint was driven exclusively by less TR progression in the annuloplasty group, with no TR reoperations in either group, observed Dr. Gammie. At 2 years, just 0.6% of the annuloplasty group had severe TR, compared with 5.6% of the surgery-alone group.
The rate of permanent pacemaker implantations, however, jumped from 2.5% with surgery alone to 14.1% with concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty (rate ratio, 5.75; 95% CI, 2.27-14.60). More than half of pacemakers were placed during the first 2 days after surgery.
There was no between-group difference in 2-year rates of all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events, readmission, quality of life, or functional status.
Less than moderate TR
In a post hoc analysis stratified by baseline TR severity, treatment failure was significantly less common with surgery plus tricuspid annuloplasty among patients with moderate TR (4.5% vs. 18.1%) but not among those with less than moderate TR and tricuspid annular dilation (3.4% vs. 6.1%).
Although the trial was not powered for the subgroup analysis, “these results call into question the idea that less than moderate TR with annular dilation should be an indication for tricuspid valve repair,” Dr. Gammie told this news organization.
“I did not repair the tricuspid valve in the setting of less than moderate TR before the trial, and my practice won’t change; but it will be based on much better evidence,” he added. “Of course, long-term data from our trial will be of great interest.”
Discussant Joseph Woo, MD, chair of surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, congratulated the authors on a “landmark trial” that addresses a highly relevant problem without a clear-cut indication.
In the 2020 AHA/American College of Cardiology heart valve disease guideline, tricuspid valve surgery is a class I recommendation when there’s severe TR (stages C and D) and left-sided valve surgery but a class IIa recommendation in patients with progressive TR (stage B) with an annular dilation of at least 40 mm.
“The interesting findings in this study include that moderate TR was only 37% of the enrolled patients, and only 97% of the patients with degenerative MR received a mitral valve repair,” Dr. Woo said. “This level of mitral valve repair is perhaps lower than what we might expect at these centers and lower, certainly, than what the AHA/ACC guidelines recommend for surgery on asymptomatic severe mitral regurgitation.”
Panelist Roxanna Mehran, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York said, “What I was struck by is that we, as clinicians, believe that if you fix the mitral valve, maybe the tricuspid regurgitation will improve. And it seems like that is not what’s happening, and I think that’s a big takeaway.”
Session comoderator Joanna Chikwe, MD, head of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said, “I think we can all agree that severe tricuspid regurgitation is a disaster for patients, and I think the fact the trial is designed for an additional 5 years’ follow-up will hopefully give us some insights into the clinical impact of severe tricuspid regurgitation.”
For now, “a back of the envelope calculation suggests that, for every 20 patients with moderate tricuspid regurgitation who we repair the tricuspid valve in, we would prevent severe tricuspid valve regurgitation in 1 at the price of pacemakers in 2,” she said.
Dr. Chikwe said in an interview that “transcatheter tricuspid repair is increasingly helping these patients, but if you could avoid it with a technique that doesn’t cause incremental harm beyond, perhaps, the need for pacemakers, then this is helpful data that supports that approach.”
The pacemaker burden is not negligible, she said, but also not surprising to surgeons. “If you look at national practice of mitral-tricuspid surgery, it’s about 15% after that, and it’s simply because the conduction tissue is so close to the tricuspid annulus.”
Pacemaker implantation rates, like those for concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery, are also highly variable, and in some single-center series only around 2%, Dr. Chikwe said. “So that suggests there are technical approaches that can minimize the pacemaker rate [such as] being extremely careful to avoid suture placement around the area of the conduction tissues.”
For some the trade-off between reduced TR progression and the risk of a permanent pacemaker is worth it. “But the fact that the trial didn’t show a difference in survival, a difference in symptoms or quality of life, might suggest that patients you anticipated were high risk for surgery or didn’t have a longer projected survival aren’t going to benefit from what is quite an aggressive surgical approach,” Dr. Chikwe said.
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Chikwe and Mario Gaudino, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, also point out that the “very dynamic nature of tricuspid regurgitation and wide variability in assessing tricuspid annular dilatation are additional compelling reasons to leave lesser regurgitation alone.”
Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, Kings College and tricuspid service lead at Guys and St. Thomas NHS, London, also pointed to the need for longer-term follow-up but said increased use of imaging markers is also needed to help pinpoint TR progression in these patients. “For the moment, the results should remind imagers and clinicians to refer patients earlier.”
“As a valvular heart physician, I see more and more patients coming in with significant severe tricuspid regurgitation post–mitral valve surgery and because of the time that’s passed, there’s dysfunction of the right heart, the left heart, and it’s very hard to suggest an operation because they’re at high risk,” she said. “So we’re discussing with these patients whether to do an intervention or medical management.”
“Now, with this study, and the pending longer follow-up by the authors, I’m optimistic that the class II recommendation will be class I in order to help our patients treat tricuspid regurgitation earlier than late,” said Dr. Grapsa, who is also editor-in-chief of JACC: Case Reports.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Gammie reports a consultant/stockholder relationship with Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Grapsa reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Chikwe reports that as coprincipal investigator/study director of NCT 05051033 (an NHLBI-sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network trial), she collaborates with several of the study authors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tricuspid valve repair at the time of mitral valve surgery reduces tricuspid regurgitation progression, but at the cost of more than a fivefold increase in permanent pacemakers, results of a new Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network study show.
The results were presented during the opening late-breaking science session at the American Heart Association scientific sessions and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is common among patients undergoing mitral valve surgery, and there’s broad agreement to intervene when a patient has severe TR. There’s uncertainty, however, about the management of moderate or less TR during mitral valve surgery, which is reflected in current guidelines on the basis of observational data, explained coprimary investigator James Gammie, MD, codirector and surgical director of the Johns Hopkins Heart and Vascular Institute, Baltimore. As a result, rates of concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery range from 5% to 75% at various centers.
To help fill the gap, Dr. Gammie and colleagues screened 5,208 patients at 29 centers in the United States, Canada, and Germany undergoing surgery for degenerative mitral regurgitation, and randomly assigned 401 patients (75% male) to mitral valve surgery alone or with tricuspid annuloplasty.
Patients had either moderate TR (37%) or less than moderate TR with a dilated tricuspid annulus of at least 40 mm or at least 21 mm/m2 indexed for body surface area. Importantly, there was a uniform surgical approach using undersized (26-30 mm) rigid nonplanar annuloplasty rings to repair the tricuspid valve, he said.
The study’s primary outcome of treatment failure at 2 years was defined as the composite of death, reoperation for TR, or progression of TR from baseline by 2 grades or severe TR.
The primary endpoint occurred in 10.2% of patients who underwent mitral valve surgery alone and 3.9% who underwent concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty (relative risk, 0.37; 95% confidence interval, 0.16-0.86; P = .02).
The endpoint was driven exclusively by less TR progression in the annuloplasty group, with no TR reoperations in either group, observed Dr. Gammie. At 2 years, just 0.6% of the annuloplasty group had severe TR, compared with 5.6% of the surgery-alone group.
The rate of permanent pacemaker implantations, however, jumped from 2.5% with surgery alone to 14.1% with concomitant tricuspid annuloplasty (rate ratio, 5.75; 95% CI, 2.27-14.60). More than half of pacemakers were placed during the first 2 days after surgery.
There was no between-group difference in 2-year rates of all-cause mortality, major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events, readmission, quality of life, or functional status.
Less than moderate TR
In a post hoc analysis stratified by baseline TR severity, treatment failure was significantly less common with surgery plus tricuspid annuloplasty among patients with moderate TR (4.5% vs. 18.1%) but not among those with less than moderate TR and tricuspid annular dilation (3.4% vs. 6.1%).
Although the trial was not powered for the subgroup analysis, “these results call into question the idea that less than moderate TR with annular dilation should be an indication for tricuspid valve repair,” Dr. Gammie told this news organization.
“I did not repair the tricuspid valve in the setting of less than moderate TR before the trial, and my practice won’t change; but it will be based on much better evidence,” he added. “Of course, long-term data from our trial will be of great interest.”
Discussant Joseph Woo, MD, chair of surgery at Stanford (Calif.) University, congratulated the authors on a “landmark trial” that addresses a highly relevant problem without a clear-cut indication.
In the 2020 AHA/American College of Cardiology heart valve disease guideline, tricuspid valve surgery is a class I recommendation when there’s severe TR (stages C and D) and left-sided valve surgery but a class IIa recommendation in patients with progressive TR (stage B) with an annular dilation of at least 40 mm.
“The interesting findings in this study include that moderate TR was only 37% of the enrolled patients, and only 97% of the patients with degenerative MR received a mitral valve repair,” Dr. Woo said. “This level of mitral valve repair is perhaps lower than what we might expect at these centers and lower, certainly, than what the AHA/ACC guidelines recommend for surgery on asymptomatic severe mitral regurgitation.”
Panelist Roxanna Mehran, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in New York said, “What I was struck by is that we, as clinicians, believe that if you fix the mitral valve, maybe the tricuspid regurgitation will improve. And it seems like that is not what’s happening, and I think that’s a big takeaway.”
Session comoderator Joanna Chikwe, MD, head of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said, “I think we can all agree that severe tricuspid regurgitation is a disaster for patients, and I think the fact the trial is designed for an additional 5 years’ follow-up will hopefully give us some insights into the clinical impact of severe tricuspid regurgitation.”
For now, “a back of the envelope calculation suggests that, for every 20 patients with moderate tricuspid regurgitation who we repair the tricuspid valve in, we would prevent severe tricuspid valve regurgitation in 1 at the price of pacemakers in 2,” she said.
Dr. Chikwe said in an interview that “transcatheter tricuspid repair is increasingly helping these patients, but if you could avoid it with a technique that doesn’t cause incremental harm beyond, perhaps, the need for pacemakers, then this is helpful data that supports that approach.”
The pacemaker burden is not negligible, she said, but also not surprising to surgeons. “If you look at national practice of mitral-tricuspid surgery, it’s about 15% after that, and it’s simply because the conduction tissue is so close to the tricuspid annulus.”
Pacemaker implantation rates, like those for concomitant tricuspid-mitral surgery, are also highly variable, and in some single-center series only around 2%, Dr. Chikwe said. “So that suggests there are technical approaches that can minimize the pacemaker rate [such as] being extremely careful to avoid suture placement around the area of the conduction tissues.”
For some the trade-off between reduced TR progression and the risk of a permanent pacemaker is worth it. “But the fact that the trial didn’t show a difference in survival, a difference in symptoms or quality of life, might suggest that patients you anticipated were high risk for surgery or didn’t have a longer projected survival aren’t going to benefit from what is quite an aggressive surgical approach,” Dr. Chikwe said.
In an accompanying editorial, Dr. Chikwe and Mario Gaudino, MD, of Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, also point out that the “very dynamic nature of tricuspid regurgitation and wide variability in assessing tricuspid annular dilatation are additional compelling reasons to leave lesser regurgitation alone.”
Julia Grapsa, MD, PhD, Kings College and tricuspid service lead at Guys and St. Thomas NHS, London, also pointed to the need for longer-term follow-up but said increased use of imaging markers is also needed to help pinpoint TR progression in these patients. “For the moment, the results should remind imagers and clinicians to refer patients earlier.”
“As a valvular heart physician, I see more and more patients coming in with significant severe tricuspid regurgitation post–mitral valve surgery and because of the time that’s passed, there’s dysfunction of the right heart, the left heart, and it’s very hard to suggest an operation because they’re at high risk,” she said. “So we’re discussing with these patients whether to do an intervention or medical management.”
“Now, with this study, and the pending longer follow-up by the authors, I’m optimistic that the class II recommendation will be class I in order to help our patients treat tricuspid regurgitation earlier than late,” said Dr. Grapsa, who is also editor-in-chief of JACC: Case Reports.
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute and the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Gammie reports a consultant/stockholder relationship with Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Grapsa reports no conflicts of interest. Dr. Chikwe reports that as coprincipal investigator/study director of NCT 05051033 (an NHLBI-sponsored Cardiothoracic Surgical Trials Network trial), she collaborates with several of the study authors.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2021
VEST: External sheath for CABG vein grafts shows promise
A novel, stent-shaped device that provides external buttressing to saphenous vein grafts placed during coronary artery bypass surgery was safe, but failed to improve 12-month patency of vein grafts, in a prospective study with 224 patients.
Despite the neutral result, “we are cautiously optimistic” about the prospects for the device to reduce the risk for failure of coronary vein grafts caused by intimal hyperplasia of the internal lining of the vein graft that leads to graft occlusion, said John D. Puskas, MD, lead investigator of the study, who reported the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
In the trial, called VEST, each buttressed vein graft was compared with a similar, unbuttressed graft in the same patient. Perhaps the biggest issue faced by the study was the unexpectedly high 42% rate of vein-graft occlusion or diffuse disease seen in the studied grafts 12 months after placement. This rate included both the vein grafts placed within the external buttressing device and control vein grafts that underwent the same postharvest preparation but weren’t placed within an external sheath, which is formed from woven cobalt chromium wire.
Dr. Puskas attributed this high failure rate to the need to remove all adventitia tissue and fat from the harvested saphenous vein segments before grafting, a step required to allow the vein conduit to fit inside the wire sheath. The potential exists to further optimize this step, he said in an interview.
“I was very surprised by the low 12-month patency rates” in both treatment arms of the study, commented Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
External scaffold to counter blood pressure
The concept behind the external buttressing sheath is that the walls of saphenous vein grafts are not structured to accommodate arterial blood pressure, and over time this pressure produces accelerated atherosclerotic changes and premature occlusion and graft failure. The external support is supposed to impede vein wall dilatation, reduce irregularities of the inner lumen surface, and improve hemodynamics and shear stress.
The VEST trial ran at 14 U.S. and 3 Canadian centers and enrolled 224 patients scheduled for coronary artery bypass grafting with planned use of at least two saphenous vein grafts, along with an internal mammary artery graft for the left anterior descending coronary artery. The patients averaged 66 years of age, 21% were women, and 51% had diabetes.
All patients successfully underwent their surgery, with 203 returning after 12 months for their primary follow-up examination by intravascular ultrasound. However, because of the high rate of vein occlusion or development of diffuse intragraft disease, successful intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) examination of both vein grafts occurred in only 113 patients.
The IVUS examinations showed that the study’s primary endpoint, the intimal hyperplasia area in all 224 patients who received vein grafts, averaged 5.11 mm2 in the grafts placed within the wire sleeve and 5.79 mm2 for control grafts not placed in the wire sheath, a difference that fell short of significance (P = .072). However, in a sensitivity analysis that focused on only the 113 patients who had both vein grafts successfully assayed by IVUS, the average area of intimal hyperplasia was 4.58 mm2 in the grafts within a wire sheath and 5.12 mm2 in the control grafts, a significant difference (P = .043).
The combined rate of major adverse cardiovascular events after 12 months was 7%, including a 2% mortality rate, a 3% stroke rate, and 3% rate of Mis, outcomes that suggested “no safety signals,” said Dr. Puskas, chair of cardiovascular surgery at Mount Sinai St. Luke’s in New York.
Although a large body of evidence has shown the superiority of arterial grafts for long-term graft patency, vein grafts have many advantages that have maintained them as the most widely used conduits worldwide for coronary artery bypass surgery, Dr. Puskas said.
Saphenous vein segments are readily available from patients and easy to harvest; they nicely conform to the coronary arteries that require bypass, rarely leak, are easy to work with, and can successfully hold stitches. Surgeons performing coronary artery bypass are unlikely to abandon vein grafts anytime soon, which makes improving the performance of vein grafts a priority, Dr. Puskas said.
The study was sponsored by Vascular Graft Solutions, the company developing the venous graft external support. Dr. Puskas and Dr. Chikwe had no disclosures related to the study.
A novel, stent-shaped device that provides external buttressing to saphenous vein grafts placed during coronary artery bypass surgery was safe, but failed to improve 12-month patency of vein grafts, in a prospective study with 224 patients.
Despite the neutral result, “we are cautiously optimistic” about the prospects for the device to reduce the risk for failure of coronary vein grafts caused by intimal hyperplasia of the internal lining of the vein graft that leads to graft occlusion, said John D. Puskas, MD, lead investigator of the study, who reported the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
In the trial, called VEST, each buttressed vein graft was compared with a similar, unbuttressed graft in the same patient. Perhaps the biggest issue faced by the study was the unexpectedly high 42% rate of vein-graft occlusion or diffuse disease seen in the studied grafts 12 months after placement. This rate included both the vein grafts placed within the external buttressing device and control vein grafts that underwent the same postharvest preparation but weren’t placed within an external sheath, which is formed from woven cobalt chromium wire.
Dr. Puskas attributed this high failure rate to the need to remove all adventitia tissue and fat from the harvested saphenous vein segments before grafting, a step required to allow the vein conduit to fit inside the wire sheath. The potential exists to further optimize this step, he said in an interview.
“I was very surprised by the low 12-month patency rates” in both treatment arms of the study, commented Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
External scaffold to counter blood pressure
The concept behind the external buttressing sheath is that the walls of saphenous vein grafts are not structured to accommodate arterial blood pressure, and over time this pressure produces accelerated atherosclerotic changes and premature occlusion and graft failure. The external support is supposed to impede vein wall dilatation, reduce irregularities of the inner lumen surface, and improve hemodynamics and shear stress.
The VEST trial ran at 14 U.S. and 3 Canadian centers and enrolled 224 patients scheduled for coronary artery bypass grafting with planned use of at least two saphenous vein grafts, along with an internal mammary artery graft for the left anterior descending coronary artery. The patients averaged 66 years of age, 21% were women, and 51% had diabetes.
All patients successfully underwent their surgery, with 203 returning after 12 months for their primary follow-up examination by intravascular ultrasound. However, because of the high rate of vein occlusion or development of diffuse intragraft disease, successful intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) examination of both vein grafts occurred in only 113 patients.
The IVUS examinations showed that the study’s primary endpoint, the intimal hyperplasia area in all 224 patients who received vein grafts, averaged 5.11 mm2 in the grafts placed within the wire sleeve and 5.79 mm2 for control grafts not placed in the wire sheath, a difference that fell short of significance (P = .072). However, in a sensitivity analysis that focused on only the 113 patients who had both vein grafts successfully assayed by IVUS, the average area of intimal hyperplasia was 4.58 mm2 in the grafts within a wire sheath and 5.12 mm2 in the control grafts, a significant difference (P = .043).
The combined rate of major adverse cardiovascular events after 12 months was 7%, including a 2% mortality rate, a 3% stroke rate, and 3% rate of Mis, outcomes that suggested “no safety signals,” said Dr. Puskas, chair of cardiovascular surgery at Mount Sinai St. Luke’s in New York.
Although a large body of evidence has shown the superiority of arterial grafts for long-term graft patency, vein grafts have many advantages that have maintained them as the most widely used conduits worldwide for coronary artery bypass surgery, Dr. Puskas said.
Saphenous vein segments are readily available from patients and easy to harvest; they nicely conform to the coronary arteries that require bypass, rarely leak, are easy to work with, and can successfully hold stitches. Surgeons performing coronary artery bypass are unlikely to abandon vein grafts anytime soon, which makes improving the performance of vein grafts a priority, Dr. Puskas said.
The study was sponsored by Vascular Graft Solutions, the company developing the venous graft external support. Dr. Puskas and Dr. Chikwe had no disclosures related to the study.
A novel, stent-shaped device that provides external buttressing to saphenous vein grafts placed during coronary artery bypass surgery was safe, but failed to improve 12-month patency of vein grafts, in a prospective study with 224 patients.
Despite the neutral result, “we are cautiously optimistic” about the prospects for the device to reduce the risk for failure of coronary vein grafts caused by intimal hyperplasia of the internal lining of the vein graft that leads to graft occlusion, said John D. Puskas, MD, lead investigator of the study, who reported the results at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
In the trial, called VEST, each buttressed vein graft was compared with a similar, unbuttressed graft in the same patient. Perhaps the biggest issue faced by the study was the unexpectedly high 42% rate of vein-graft occlusion or diffuse disease seen in the studied grafts 12 months after placement. This rate included both the vein grafts placed within the external buttressing device and control vein grafts that underwent the same postharvest preparation but weren’t placed within an external sheath, which is formed from woven cobalt chromium wire.
Dr. Puskas attributed this high failure rate to the need to remove all adventitia tissue and fat from the harvested saphenous vein segments before grafting, a step required to allow the vein conduit to fit inside the wire sheath. The potential exists to further optimize this step, he said in an interview.
“I was very surprised by the low 12-month patency rates” in both treatment arms of the study, commented Joanna Chikwe, MD, chair of cardiac surgery at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center in Los Angeles.
External scaffold to counter blood pressure
The concept behind the external buttressing sheath is that the walls of saphenous vein grafts are not structured to accommodate arterial blood pressure, and over time this pressure produces accelerated atherosclerotic changes and premature occlusion and graft failure. The external support is supposed to impede vein wall dilatation, reduce irregularities of the inner lumen surface, and improve hemodynamics and shear stress.
The VEST trial ran at 14 U.S. and 3 Canadian centers and enrolled 224 patients scheduled for coronary artery bypass grafting with planned use of at least two saphenous vein grafts, along with an internal mammary artery graft for the left anterior descending coronary artery. The patients averaged 66 years of age, 21% were women, and 51% had diabetes.
All patients successfully underwent their surgery, with 203 returning after 12 months for their primary follow-up examination by intravascular ultrasound. However, because of the high rate of vein occlusion or development of diffuse intragraft disease, successful intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) examination of both vein grafts occurred in only 113 patients.
The IVUS examinations showed that the study’s primary endpoint, the intimal hyperplasia area in all 224 patients who received vein grafts, averaged 5.11 mm2 in the grafts placed within the wire sleeve and 5.79 mm2 for control grafts not placed in the wire sheath, a difference that fell short of significance (P = .072). However, in a sensitivity analysis that focused on only the 113 patients who had both vein grafts successfully assayed by IVUS, the average area of intimal hyperplasia was 4.58 mm2 in the grafts within a wire sheath and 5.12 mm2 in the control grafts, a significant difference (P = .043).
The combined rate of major adverse cardiovascular events after 12 months was 7%, including a 2% mortality rate, a 3% stroke rate, and 3% rate of Mis, outcomes that suggested “no safety signals,” said Dr. Puskas, chair of cardiovascular surgery at Mount Sinai St. Luke’s in New York.
Although a large body of evidence has shown the superiority of arterial grafts for long-term graft patency, vein grafts have many advantages that have maintained them as the most widely used conduits worldwide for coronary artery bypass surgery, Dr. Puskas said.
Saphenous vein segments are readily available from patients and easy to harvest; they nicely conform to the coronary arteries that require bypass, rarely leak, are easy to work with, and can successfully hold stitches. Surgeons performing coronary artery bypass are unlikely to abandon vein grafts anytime soon, which makes improving the performance of vein grafts a priority, Dr. Puskas said.
The study was sponsored by Vascular Graft Solutions, the company developing the venous graft external support. Dr. Puskas and Dr. Chikwe had no disclosures related to the study.
FROM AHA 2021
Fully endovascular mitral valve replacement a limited success in feasibility study
It remains early days for transcatheter mitral-valve replacement (TMVR) as a minimally invasive way to treat severe, mitral regurgitation (MR), but it’s even earlier days for TMVR as an endovascular procedure. Most of the technique’s limited experience with a dedicated mitral prosthesis has involved transapical delivery.
But now a 15-patient study of transfemoral, transeptal TMVR – with a prosthesis designed for the mitral position and previously tested only transapically – has shown good 30-day results in that MR was essentially abolished with virtually no paravalvular leakage.
Nor were there adverse clinical events such as death, stroke, reintervention, or new need for a pacemaker in any of the high-surgical-risk patients with MR in this feasibility study of the transfemoral Intrepid TMVR System (Medtronic). Implantation failed, however, in one patient who then received a surgical valve via sternotomy.
The current cohort is part of a larger ongoing trial that will track whether patients implanted transfemorally with the Intrepid also show reverse remodeling and good clinical outcomes over at least a year. That study, called APOLLO, is one of several exploring dedicated TMVR valves from different companies, with names like SUMMIT, MISCEND, and TIARA-2.
Currently, TMVR is approved in the United States only using one device designed for the aortic position and only for treating failed surgical mitral bioprostheses in high-risk patients.
If the Intrepid transfemoral system has an Achilles’ heel, at least in the current iteration, it might be its 35 F catheter delivery system that requires surgical access to the femoral vein. Seven of the patients in the small series experienced major bleeding events, including six at the femoral access site, listed as major vascular complications.
Overall, the study’s patients “were extremely sick with a lot of comorbidity. A lot of them had atrial fibrillation, a lot of them were on anticoagulation to start with,” observed Firas Zahr, MD, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, as part of his presentation of the study at Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2021, held virtually as well as onsite in Orlando, Florida.
All had moderate-to-severe, usually primary MR; two thirds of the cohort had been in NYHA class III or IV at baseline, and 40% had been hospitalized for heart failure within the past year. Eight had a history of cardiovascular surgery, and eight had diabetes. Their mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 4.7, Dr. Zahr reported.
“At 30 days, there was a significant improvement in their heart failure classification; the vast majority of the patients were [NYHA] class I and class II,” said Dr. Zahr, who is also lead author on the study’s Nov. 6 publication in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Observers of the study at TCT 2021 seemed enthusiastic about the study’s results but recognized that TMVR in its current form still has formidable limitations.
“This is clearly an exciting look into the future and very reassuring to a degree, aside from the complications, which are somewhat expected as we go with 30-plus French devices,” Rajiv Tayal, MD, MPH, said at a press conference on the Intrepid study held before Dr. Zahr’s formal presentation. Dr. Tayal is an interventional cardiologist with Valley Health System, Ridgewood, New Jersey, and New York Medical College, Valhalla.
“I think we’ve all learned that transapical [access] is just not a viable procedure for a lot of these patients, and so we’ve got to get to transfemoral,” Susheel K. Kodali, MD, interventional cardiologist at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, said at the same forum.
A 35 F device “is going to be too big,” he said. However, “it is the first step to iterate to a smaller device.” Dr. Kodali said his center contributed a patient to the study, and he is listed as a coauthor on the publication.
The delivery system’s large profile is only part of the vascular complication issue. Not only did the procedure require surgical cutdown for venous access, but “we were fairly aggressive in anticoagulating these patients with the fear of thrombus formation,” Dr. Zahr said in the discussion following his presentation.
“A postprocedure anticoagulation regimen is recommended within the protocol, but ultimate therapy was left to the discretion of the treating site physician,” the published report states, noting that all 14 patients with successful TMVR were discharged on warfarin. They included 12 who were also put on a single antiplatelet and one given dual antiplatelet therapy on top of the oral anticoagulant.
“One thing that we learned is that we probably should standardize our approach to perioperative anticoagulation,” Dr. Zahr observed. Also, a 29 F sheath for the system is in the works, “and we’re hoping that with smaller sheath size, and hopefully going even to percutaneous, might have an impact on lowering the vascular complications.”
Explanations for the “higher-than-expected vascular complication rate” remains somewhat unclear, agreed an editorial accompanying the study’s publication, “but may include a learning curve with the system, the large introducer sheath, the need for surgical cutdown, and postprocedural anticoagulation.”
For trans-septal TMVR to become a default approach, “venous access will need to be achieved percutaneously and vascular complications need to be infrequent,” contends the editorial, with lead author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
“These data provide a glimpse into the future of TMVR. The excellent short-term safety and effectiveness of this still very early-stage procedure represent a major step forward in the field,” they write.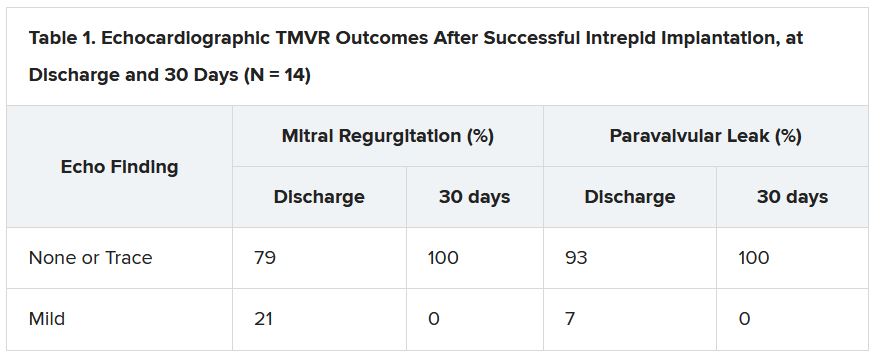
“The main question that the Intrepid early feasibility data raise is whether transfemoral, trans-septal TMVR will evolve to become the preferred strategy over transapical TMVR,” as occurred with transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR), the editorial states. “The answer is likely yes, but a few matters specific to trans-septal route will need be addressed first.”
Among those matters: The 35 F catheter leaves behind a considerable atrial septal defect (ASD). At operator discretion in this series, 11 patients received an ASD closure device.
None of the remaining four patients “developed significant heart failure or right ventricular dysfunction,” Dr. Zahr observed. “So, it seems like those patients who had their ASD left open tolerated it fairly well, at least until 30 days.”
But “we still need to learn what to do with those ASDs,” he said. “What is an acceptable residual shunt and what is an acceptable ASD size is to be determined.”
In general, the editorial notes, “the TMVR population has a high prevalence of cardiomyopathy, and a large residual iatrogenic ASD may lead to worsening volume overload and heart failure decompensation in some patients.”
Insertion of a closure device has its own issues, it continues. “Closure of the ASD might impede future access to the left atrium, which could impact life-long management of this high-risk population. A large septal occluder may hinder potentially needed procedures such as paravalvular leak closure, left atrial appendage closure, or pulmonary vein isolation.”
Patients like those in the current series, Dr. Kodali observed, will face “a lifetime of management challenges, and you want to make sure you don’t take away other options.”
The study was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Zahr reported institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Kodali disclosed consultant fees from Admedus and Dura Biotech; equity in Dura Biotech, Microinterventional Devices, Thubrika Aortic Valve, Supira, Admedus, TriFlo, and Anona; and institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve. The editorial writers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tayal disclosed consultant fees or honoraria from or serving on a speakers bureau for Abiomed, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, and Shockwave Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It remains early days for transcatheter mitral-valve replacement (TMVR) as a minimally invasive way to treat severe, mitral regurgitation (MR), but it’s even earlier days for TMVR as an endovascular procedure. Most of the technique’s limited experience with a dedicated mitral prosthesis has involved transapical delivery.
But now a 15-patient study of transfemoral, transeptal TMVR – with a prosthesis designed for the mitral position and previously tested only transapically – has shown good 30-day results in that MR was essentially abolished with virtually no paravalvular leakage.
Nor were there adverse clinical events such as death, stroke, reintervention, or new need for a pacemaker in any of the high-surgical-risk patients with MR in this feasibility study of the transfemoral Intrepid TMVR System (Medtronic). Implantation failed, however, in one patient who then received a surgical valve via sternotomy.
The current cohort is part of a larger ongoing trial that will track whether patients implanted transfemorally with the Intrepid also show reverse remodeling and good clinical outcomes over at least a year. That study, called APOLLO, is one of several exploring dedicated TMVR valves from different companies, with names like SUMMIT, MISCEND, and TIARA-2.
Currently, TMVR is approved in the United States only using one device designed for the aortic position and only for treating failed surgical mitral bioprostheses in high-risk patients.
If the Intrepid transfemoral system has an Achilles’ heel, at least in the current iteration, it might be its 35 F catheter delivery system that requires surgical access to the femoral vein. Seven of the patients in the small series experienced major bleeding events, including six at the femoral access site, listed as major vascular complications.
Overall, the study’s patients “were extremely sick with a lot of comorbidity. A lot of them had atrial fibrillation, a lot of them were on anticoagulation to start with,” observed Firas Zahr, MD, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, as part of his presentation of the study at Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2021, held virtually as well as onsite in Orlando, Florida.
All had moderate-to-severe, usually primary MR; two thirds of the cohort had been in NYHA class III or IV at baseline, and 40% had been hospitalized for heart failure within the past year. Eight had a history of cardiovascular surgery, and eight had diabetes. Their mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 4.7, Dr. Zahr reported.
“At 30 days, there was a significant improvement in their heart failure classification; the vast majority of the patients were [NYHA] class I and class II,” said Dr. Zahr, who is also lead author on the study’s Nov. 6 publication in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Observers of the study at TCT 2021 seemed enthusiastic about the study’s results but recognized that TMVR in its current form still has formidable limitations.
“This is clearly an exciting look into the future and very reassuring to a degree, aside from the complications, which are somewhat expected as we go with 30-plus French devices,” Rajiv Tayal, MD, MPH, said at a press conference on the Intrepid study held before Dr. Zahr’s formal presentation. Dr. Tayal is an interventional cardiologist with Valley Health System, Ridgewood, New Jersey, and New York Medical College, Valhalla.
“I think we’ve all learned that transapical [access] is just not a viable procedure for a lot of these patients, and so we’ve got to get to transfemoral,” Susheel K. Kodali, MD, interventional cardiologist at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, said at the same forum.
A 35 F device “is going to be too big,” he said. However, “it is the first step to iterate to a smaller device.” Dr. Kodali said his center contributed a patient to the study, and he is listed as a coauthor on the publication.
The delivery system’s large profile is only part of the vascular complication issue. Not only did the procedure require surgical cutdown for venous access, but “we were fairly aggressive in anticoagulating these patients with the fear of thrombus formation,” Dr. Zahr said in the discussion following his presentation.
“A postprocedure anticoagulation regimen is recommended within the protocol, but ultimate therapy was left to the discretion of the treating site physician,” the published report states, noting that all 14 patients with successful TMVR were discharged on warfarin. They included 12 who were also put on a single antiplatelet and one given dual antiplatelet therapy on top of the oral anticoagulant.
“One thing that we learned is that we probably should standardize our approach to perioperative anticoagulation,” Dr. Zahr observed. Also, a 29 F sheath for the system is in the works, “and we’re hoping that with smaller sheath size, and hopefully going even to percutaneous, might have an impact on lowering the vascular complications.”
Explanations for the “higher-than-expected vascular complication rate” remains somewhat unclear, agreed an editorial accompanying the study’s publication, “but may include a learning curve with the system, the large introducer sheath, the need for surgical cutdown, and postprocedural anticoagulation.”
For trans-septal TMVR to become a default approach, “venous access will need to be achieved percutaneously and vascular complications need to be infrequent,” contends the editorial, with lead author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
“These data provide a glimpse into the future of TMVR. The excellent short-term safety and effectiveness of this still very early-stage procedure represent a major step forward in the field,” they write.
“The main question that the Intrepid early feasibility data raise is whether transfemoral, trans-septal TMVR will evolve to become the preferred strategy over transapical TMVR,” as occurred with transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR), the editorial states. “The answer is likely yes, but a few matters specific to trans-septal route will need be addressed first.”
Among those matters: The 35 F catheter leaves behind a considerable atrial septal defect (ASD). At operator discretion in this series, 11 patients received an ASD closure device.
None of the remaining four patients “developed significant heart failure or right ventricular dysfunction,” Dr. Zahr observed. “So, it seems like those patients who had their ASD left open tolerated it fairly well, at least until 30 days.”
But “we still need to learn what to do with those ASDs,” he said. “What is an acceptable residual shunt and what is an acceptable ASD size is to be determined.”
In general, the editorial notes, “the TMVR population has a high prevalence of cardiomyopathy, and a large residual iatrogenic ASD may lead to worsening volume overload and heart failure decompensation in some patients.”
Insertion of a closure device has its own issues, it continues. “Closure of the ASD might impede future access to the left atrium, which could impact life-long management of this high-risk population. A large septal occluder may hinder potentially needed procedures such as paravalvular leak closure, left atrial appendage closure, or pulmonary vein isolation.”
Patients like those in the current series, Dr. Kodali observed, will face “a lifetime of management challenges, and you want to make sure you don’t take away other options.”
The study was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Zahr reported institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Kodali disclosed consultant fees from Admedus and Dura Biotech; equity in Dura Biotech, Microinterventional Devices, Thubrika Aortic Valve, Supira, Admedus, TriFlo, and Anona; and institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve. The editorial writers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tayal disclosed consultant fees or honoraria from or serving on a speakers bureau for Abiomed, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, and Shockwave Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
It remains early days for transcatheter mitral-valve replacement (TMVR) as a minimally invasive way to treat severe, mitral regurgitation (MR), but it’s even earlier days for TMVR as an endovascular procedure. Most of the technique’s limited experience with a dedicated mitral prosthesis has involved transapical delivery.
But now a 15-patient study of transfemoral, transeptal TMVR – with a prosthesis designed for the mitral position and previously tested only transapically – has shown good 30-day results in that MR was essentially abolished with virtually no paravalvular leakage.
Nor were there adverse clinical events such as death, stroke, reintervention, or new need for a pacemaker in any of the high-surgical-risk patients with MR in this feasibility study of the transfemoral Intrepid TMVR System (Medtronic). Implantation failed, however, in one patient who then received a surgical valve via sternotomy.
The current cohort is part of a larger ongoing trial that will track whether patients implanted transfemorally with the Intrepid also show reverse remodeling and good clinical outcomes over at least a year. That study, called APOLLO, is one of several exploring dedicated TMVR valves from different companies, with names like SUMMIT, MISCEND, and TIARA-2.
Currently, TMVR is approved in the United States only using one device designed for the aortic position and only for treating failed surgical mitral bioprostheses in high-risk patients.
If the Intrepid transfemoral system has an Achilles’ heel, at least in the current iteration, it might be its 35 F catheter delivery system that requires surgical access to the femoral vein. Seven of the patients in the small series experienced major bleeding events, including six at the femoral access site, listed as major vascular complications.
Overall, the study’s patients “were extremely sick with a lot of comorbidity. A lot of them had atrial fibrillation, a lot of them were on anticoagulation to start with,” observed Firas Zahr, MD, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, as part of his presentation of the study at Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics (TCT) 2021, held virtually as well as onsite in Orlando, Florida.
All had moderate-to-severe, usually primary MR; two thirds of the cohort had been in NYHA class III or IV at baseline, and 40% had been hospitalized for heart failure within the past year. Eight had a history of cardiovascular surgery, and eight had diabetes. Their mean Society of Thoracic Surgeons Predicted Risk of Mortality (STS-PROM) score was 4.7, Dr. Zahr reported.
“At 30 days, there was a significant improvement in their heart failure classification; the vast majority of the patients were [NYHA] class I and class II,” said Dr. Zahr, who is also lead author on the study’s Nov. 6 publication in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
Observers of the study at TCT 2021 seemed enthusiastic about the study’s results but recognized that TMVR in its current form still has formidable limitations.
“This is clearly an exciting look into the future and very reassuring to a degree, aside from the complications, which are somewhat expected as we go with 30-plus French devices,” Rajiv Tayal, MD, MPH, said at a press conference on the Intrepid study held before Dr. Zahr’s formal presentation. Dr. Tayal is an interventional cardiologist with Valley Health System, Ridgewood, New Jersey, and New York Medical College, Valhalla.
“I think we’ve all learned that transapical [access] is just not a viable procedure for a lot of these patients, and so we’ve got to get to transfemoral,” Susheel K. Kodali, MD, interventional cardiologist at New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, said at the same forum.
A 35 F device “is going to be too big,” he said. However, “it is the first step to iterate to a smaller device.” Dr. Kodali said his center contributed a patient to the study, and he is listed as a coauthor on the publication.
The delivery system’s large profile is only part of the vascular complication issue. Not only did the procedure require surgical cutdown for venous access, but “we were fairly aggressive in anticoagulating these patients with the fear of thrombus formation,” Dr. Zahr said in the discussion following his presentation.
“A postprocedure anticoagulation regimen is recommended within the protocol, but ultimate therapy was left to the discretion of the treating site physician,” the published report states, noting that all 14 patients with successful TMVR were discharged on warfarin. They included 12 who were also put on a single antiplatelet and one given dual antiplatelet therapy on top of the oral anticoagulant.
“One thing that we learned is that we probably should standardize our approach to perioperative anticoagulation,” Dr. Zahr observed. Also, a 29 F sheath for the system is in the works, “and we’re hoping that with smaller sheath size, and hopefully going even to percutaneous, might have an impact on lowering the vascular complications.”
Explanations for the “higher-than-expected vascular complication rate” remains somewhat unclear, agreed an editorial accompanying the study’s publication, “but may include a learning curve with the system, the large introducer sheath, the need for surgical cutdown, and postprocedural anticoagulation.”
For trans-septal TMVR to become a default approach, “venous access will need to be achieved percutaneously and vascular complications need to be infrequent,” contends the editorial, with lead author Mohamad Alkhouli, MD, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
“These data provide a glimpse into the future of TMVR. The excellent short-term safety and effectiveness of this still very early-stage procedure represent a major step forward in the field,” they write.
“The main question that the Intrepid early feasibility data raise is whether transfemoral, trans-septal TMVR will evolve to become the preferred strategy over transapical TMVR,” as occurred with transcatheter aortic-valve replacement (TAVR), the editorial states. “The answer is likely yes, but a few matters specific to trans-septal route will need be addressed first.”
Among those matters: The 35 F catheter leaves behind a considerable atrial septal defect (ASD). At operator discretion in this series, 11 patients received an ASD closure device.
None of the remaining four patients “developed significant heart failure or right ventricular dysfunction,” Dr. Zahr observed. “So, it seems like those patients who had their ASD left open tolerated it fairly well, at least until 30 days.”
But “we still need to learn what to do with those ASDs,” he said. “What is an acceptable residual shunt and what is an acceptable ASD size is to be determined.”
In general, the editorial notes, “the TMVR population has a high prevalence of cardiomyopathy, and a large residual iatrogenic ASD may lead to worsening volume overload and heart failure decompensation in some patients.”
Insertion of a closure device has its own issues, it continues. “Closure of the ASD might impede future access to the left atrium, which could impact life-long management of this high-risk population. A large septal occluder may hinder potentially needed procedures such as paravalvular leak closure, left atrial appendage closure, or pulmonary vein isolation.”
Patients like those in the current series, Dr. Kodali observed, will face “a lifetime of management challenges, and you want to make sure you don’t take away other options.”
The study was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Zahr reported institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Medtronic. Dr. Kodali disclosed consultant fees from Admedus and Dura Biotech; equity in Dura Biotech, Microinterventional Devices, Thubrika Aortic Valve, Supira, Admedus, TriFlo, and Anona; and institutional grant support from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve. The editorial writers have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Tayal disclosed consultant fees or honoraria from or serving on a speakers bureau for Abiomed, Edwards Lifesciences, Abbott Vascular, and Shockwave Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA panel slams Endologix response to stent-graft safety issues
The Food and Drug Administration has long kept a watchful eye over successive iterations of endovascular stent graphs in the Endologix AFX line, designed for repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). For years, the devices, first approved in 2011, have drawn safety alerts and recalls , stemming from what the agency says was a “higher than expected” risk for potentially injurious or fatal type III endoleaks.
As part of the latest review process, Endologix recently showed regulators data from a rare randomized trial of the AAA endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) technique. The company said the recent postmarket study LEOPARD suggested the type III endoleaks – blood seeping around or through the device into the aneurysm – are no more common with the current AFX2 system than with other available AAA stent-grafts.
Technical upgrades to its AFX line of EVAR devices in recent years have largely resolved the safety issues identified in previous models, the company argued.
But the company’s case was unconvincing for a majority of the FDA Circulatory System Devices Advisory Panel that assembled virtually on Nov. 2. A number of panelists questioned the earnestness with which Endologix worked to rectify the safety alert and recall issues. Many also decried the real-world relevance of the randomized trial presented as evidence, with its follow-up time of only a few years.
The panel that included more than a dozen clinicians – mostly surgeons or interventional cardiologists or radiologists – were not instructed to formally vote on the issues. But it ultimately advised the FDA that more exacting studies with longer follow-ups appear needed to show that the device’s benefits in routine use outweigh its risks, especially for type III endoleaks.
“There isn’t a tremendous amount of confidence” that Endologix had enacted sufficient risk-mitigation measures in the wake of the safety alerts and recalls, chair Richard A. Lange, MD, MBA, Foster School of Medicine and Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, said when summarizing the panel’s take on the day’s proceedings.
Although the stent-graft’s safety seemed improved with recent design changes, the panel wasn’t convinced the upgrades could take the credit, or even that they were aimed specifically at preventing endoleaks, Dr. Lange said. “Nobody feels assurance that the problem has been solved.”
“I believe that the type-three endoleaks pose a challenge to patients, and I have not seen enough data to assure me with a degree of certainty that that problem no longer persists,” said panelist Joaquin E. Cigarroa, MD, a cardiologist at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. His take on the LEOPARD trial, moreover, is that it “does not refute that there is an issue, given the duration of follow-up.”
On the other hand, a majority of the panel agreed that, currently, the AFX2’s benefits would likely outweigh risks for patients in narrowly defined high-risk anatomic or clinical scenarios and those with no other endovascular or surgical option.
“I do believe that there are patient subsets where the Endologix graft can play an important and vital role,” surgeon Keith B. Allen, MD, St. Luke’s Mid America Heart & Vascular Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, offered from the panel.
“In patients that don’t have aneurysmal disease but have distal bifurcation proximal iliac disease, it can be a very nice graft to use and solves a problem,” he said. “To remove that graft completely from the market, I believe, would deny a subset of patients.”
But for aortic aneurysms in routine practice, Dr. Allen said, “I think there are some red flags with it.”
Joining the day’s proceedings as a public commenter, surgeon Mark Conrad, MD, St. Elizabeth’s Hospital, Boston, agreed that “there’s not one commercial device out there that is able to handle every anatomy.”
Having options for patients is important, he said, because “the biggest problems we run into are when somebody only uses one graft, and they try to make that fit everything.”
Another public commenter offered a similar take. “I think we haven’t done a great job in the vascular surgery community really honing in on the detailed nuances that separate one device from another,” said Naiem Nassiri, MD, Yale New Haven Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Connecticut.
The Endologix device, he said, “serves a very specific role under certain anatomic configurations and limitations, and really, truly fills a gap” left by other available grafts. It suits a very specific niche, “and I think it needs to be explored further for that.”
Endologix representatives who advise clinicians could play a better role in familiarizing operators with the EVAR system’s strengths and limitations, proposed several panelists, including Minhaj S. Khaja, MD, MBA, interventional radiologist at UVA Health and the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“There definitely needs to be more education of the clinical reps as well as the physicians implanting these devices,” he said, regarding the type III leaks, patient selection issues, appropriate imaging follow-up, “and the potential for increased reintervention.”
All public commenters, Dr. Lange observed, had been invited to disclose potential conflicts of interest, but it was not mandatory and none did so during the public forum. Disclosures of potential conflicts for the panelists are available on the FDA site.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has long kept a watchful eye over successive iterations of endovascular stent graphs in the Endologix AFX line, designed for repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). For years, the devices, first approved in 2011, have drawn safety alerts and recalls , stemming from what the agency says was a “higher than expected” risk for potentially injurious or fatal type III endoleaks.
As part of the latest review process, Endologix recently showed regulators data from a rare randomized trial of the AAA endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) technique. The company said the recent postmarket study LEOPARD suggested the type III endoleaks – blood seeping around or through the device into the aneurysm – are no more common with the current AFX2 system than with other available AAA stent-grafts.
Technical upgrades to its AFX line of EVAR devices in recent years have largely resolved the safety issues identified in previous models, the company argued.
But the company’s case was unconvincing for a majority of the FDA Circulatory System Devices Advisory Panel that assembled virtually on Nov. 2. A number of panelists questioned the earnestness with which Endologix worked to rectify the safety alert and recall issues. Many also decried the real-world relevance of the randomized trial presented as evidence, with its follow-up time of only a few years.
The panel that included more than a dozen clinicians – mostly surgeons or interventional cardiologists or radiologists – were not instructed to formally vote on the issues. But it ultimately advised the FDA that more exacting studies with longer follow-ups appear needed to show that the device’s benefits in routine use outweigh its risks, especially for type III endoleaks.
“There isn’t a tremendous amount of confidence” that Endologix had enacted sufficient risk-mitigation measures in the wake of the safety alerts and recalls, chair Richard A. Lange, MD, MBA, Foster School of Medicine and Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, said when summarizing the panel’s take on the day’s proceedings.
Although the stent-graft’s safety seemed improved with recent design changes, the panel wasn’t convinced the upgrades could take the credit, or even that they were aimed specifically at preventing endoleaks, Dr. Lange said. “Nobody feels assurance that the problem has been solved.”
“I believe that the type-three endoleaks pose a challenge to patients, and I have not seen enough data to assure me with a degree of certainty that that problem no longer persists,” said panelist Joaquin E. Cigarroa, MD, a cardiologist at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. His take on the LEOPARD trial, moreover, is that it “does not refute that there is an issue, given the duration of follow-up.”
On the other hand, a majority of the panel agreed that, currently, the AFX2’s benefits would likely outweigh risks for patients in narrowly defined high-risk anatomic or clinical scenarios and those with no other endovascular or surgical option.
“I do believe that there are patient subsets where the Endologix graft can play an important and vital role,” surgeon Keith B. Allen, MD, St. Luke’s Mid America Heart & Vascular Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, offered from the panel.
“In patients that don’t have aneurysmal disease but have distal bifurcation proximal iliac disease, it can be a very nice graft to use and solves a problem,” he said. “To remove that graft completely from the market, I believe, would deny a subset of patients.”
But for aortic aneurysms in routine practice, Dr. Allen said, “I think there are some red flags with it.”
Joining the day’s proceedings as a public commenter, surgeon Mark Conrad, MD, St. Elizabeth’s Hospital, Boston, agreed that “there’s not one commercial device out there that is able to handle every anatomy.”
Having options for patients is important, he said, because “the biggest problems we run into are when somebody only uses one graft, and they try to make that fit everything.”
Another public commenter offered a similar take. “I think we haven’t done a great job in the vascular surgery community really honing in on the detailed nuances that separate one device from another,” said Naiem Nassiri, MD, Yale New Haven Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Connecticut.
The Endologix device, he said, “serves a very specific role under certain anatomic configurations and limitations, and really, truly fills a gap” left by other available grafts. It suits a very specific niche, “and I think it needs to be explored further for that.”
Endologix representatives who advise clinicians could play a better role in familiarizing operators with the EVAR system’s strengths and limitations, proposed several panelists, including Minhaj S. Khaja, MD, MBA, interventional radiologist at UVA Health and the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“There definitely needs to be more education of the clinical reps as well as the physicians implanting these devices,” he said, regarding the type III leaks, patient selection issues, appropriate imaging follow-up, “and the potential for increased reintervention.”
All public commenters, Dr. Lange observed, had been invited to disclose potential conflicts of interest, but it was not mandatory and none did so during the public forum. Disclosures of potential conflicts for the panelists are available on the FDA site.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has long kept a watchful eye over successive iterations of endovascular stent graphs in the Endologix AFX line, designed for repair of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). For years, the devices, first approved in 2011, have drawn safety alerts and recalls , stemming from what the agency says was a “higher than expected” risk for potentially injurious or fatal type III endoleaks.
As part of the latest review process, Endologix recently showed regulators data from a rare randomized trial of the AAA endovascular aneurysm repair (EVAR) technique. The company said the recent postmarket study LEOPARD suggested the type III endoleaks – blood seeping around or through the device into the aneurysm – are no more common with the current AFX2 system than with other available AAA stent-grafts.
Technical upgrades to its AFX line of EVAR devices in recent years have largely resolved the safety issues identified in previous models, the company argued.
But the company’s case was unconvincing for a majority of the FDA Circulatory System Devices Advisory Panel that assembled virtually on Nov. 2. A number of panelists questioned the earnestness with which Endologix worked to rectify the safety alert and recall issues. Many also decried the real-world relevance of the randomized trial presented as evidence, with its follow-up time of only a few years.
The panel that included more than a dozen clinicians – mostly surgeons or interventional cardiologists or radiologists – were not instructed to formally vote on the issues. But it ultimately advised the FDA that more exacting studies with longer follow-ups appear needed to show that the device’s benefits in routine use outweigh its risks, especially for type III endoleaks.
“There isn’t a tremendous amount of confidence” that Endologix had enacted sufficient risk-mitigation measures in the wake of the safety alerts and recalls, chair Richard A. Lange, MD, MBA, Foster School of Medicine and Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center, El Paso, said when summarizing the panel’s take on the day’s proceedings.
Although the stent-graft’s safety seemed improved with recent design changes, the panel wasn’t convinced the upgrades could take the credit, or even that they were aimed specifically at preventing endoleaks, Dr. Lange said. “Nobody feels assurance that the problem has been solved.”
“I believe that the type-three endoleaks pose a challenge to patients, and I have not seen enough data to assure me with a degree of certainty that that problem no longer persists,” said panelist Joaquin E. Cigarroa, MD, a cardiologist at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland. His take on the LEOPARD trial, moreover, is that it “does not refute that there is an issue, given the duration of follow-up.”
On the other hand, a majority of the panel agreed that, currently, the AFX2’s benefits would likely outweigh risks for patients in narrowly defined high-risk anatomic or clinical scenarios and those with no other endovascular or surgical option.
“I do believe that there are patient subsets where the Endologix graft can play an important and vital role,” surgeon Keith B. Allen, MD, St. Luke’s Mid America Heart & Vascular Institute, Kansas City, Missouri, offered from the panel.
“In patients that don’t have aneurysmal disease but have distal bifurcation proximal iliac disease, it can be a very nice graft to use and solves a problem,” he said. “To remove that graft completely from the market, I believe, would deny a subset of patients.”
But for aortic aneurysms in routine practice, Dr. Allen said, “I think there are some red flags with it.”
Joining the day’s proceedings as a public commenter, surgeon Mark Conrad, MD, St. Elizabeth’s Hospital, Boston, agreed that “there’s not one commercial device out there that is able to handle every anatomy.”
Having options for patients is important, he said, because “the biggest problems we run into are when somebody only uses one graft, and they try to make that fit everything.”
Another public commenter offered a similar take. “I think we haven’t done a great job in the vascular surgery community really honing in on the detailed nuances that separate one device from another,” said Naiem Nassiri, MD, Yale New Haven Hospital Heart & Vascular Center, Connecticut.
The Endologix device, he said, “serves a very specific role under certain anatomic configurations and limitations, and really, truly fills a gap” left by other available grafts. It suits a very specific niche, “and I think it needs to be explored further for that.”
Endologix representatives who advise clinicians could play a better role in familiarizing operators with the EVAR system’s strengths and limitations, proposed several panelists, including Minhaj S. Khaja, MD, MBA, interventional radiologist at UVA Health and the University of Virginia, Charlottesville.
“There definitely needs to be more education of the clinical reps as well as the physicians implanting these devices,” he said, regarding the type III leaks, patient selection issues, appropriate imaging follow-up, “and the potential for increased reintervention.”
All public commenters, Dr. Lange observed, had been invited to disclose potential conflicts of interest, but it was not mandatory and none did so during the public forum. Disclosures of potential conflicts for the panelists are available on the FDA site.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.