User login
FFR-guided PCI falls short vs. surgery in multivessel disease: FAME 3
Coronary stenting guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) readings, considered to reflect the targeted lesion’s functional impact, was no match for coronary bypass surgery (CABG) in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) in a major international randomized trial.
Indeed, FFR-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using one of the latest drug-eluting stents (DES) seemed to perform poorly in the trial, compared with surgery, apparently upping the risk for clinical events by 50% over 1 year.
Designed statistically for noninferiority, the third Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial, with 1,500 randomized patients, showed that FFR-guided PCI was “not noninferior” to CABG. Of those randomized to PCI, 10.6% met the 1-year primary endpoint of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE), compared with only 6.9% of patients assigned to CABG.
The trial enrolled only patients with three-vessel coronary disease with no left-main coronary artery involvement, who were declared by their institution’s multidisciplinary heart team to be appropriate for either form of revascularization.
One of the roles of FFR for PCI guidance is to identify significant lesions “that are underrecognized by the angiogram,” which is less likely to happen in patients with very complex coronary anatomy, study chair William F. Fearon, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
“That’s what we saw in a subgroup analysis based on SYNTAX score,” an index of lesion complexity. “In patients with very high SYNTAX scores, CABG outperformed FFR-guided PCI. But if you look at patients with low SYNTAX scores, actually, FFR-guided PCI outperformed CABG for 1-year MACCE.”
Dr. Fearon is lead author on the study’s Nov. 4, 2021, publication in the New England Journal of Medicine, its release timed to coincide with his presentation of the trial at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
He noted that FAME-3 “wasn’t designed or powered to test for superiority,” so its results do not imply CABG is superior to FFR-PCI in patients with MVD, and remains “inconclusive” on that question.
“I think what this study does is provide both the physician and patients more contemporary data and information on options and expected outcomes in multivessel disease. So if you are a patient who has less complex disease, I think you can feel comfortable that you will get an equivalent result with FFR-guided PCI.” But, at least based on FAME-3, Dr. Fearon said, CABG provides better outcomes in patients with more complex disease.
“I think there are still patients that look at trade-offs. Some patients will accept a higher event rate in order to avoid a long recovery, and vice versa.” So the trial may allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, he said.
A main message of FAME-3 “is that we’re getting very good results with three-vessel PCI, but better results with surgery,” Ran Kornowski, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and Tel Aviv University, said as a discussant following Dr. Fearon’s presentation of the trial. The subanalysis by SYNTAX score, he agreed, probably could be used as part of shared decision-making with patients.
Not all that surprising
“It’s a well-designed study, with a lot of patients,” said surgeon Frank W. Sellke, MD, of Rhode Island Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Brown University, all in Providence.
“I don’t think it’s all that surprising,” he said in an interview. “It’s very consistent with what other studies have shown, that for three-vessel disease, surgery tends to have the edge,” even when pitted against FFR-guided PCI.
Indeed, pressure-wire FFR-PCI has a spotty history, even as an alternative to standard angiography-based PCI. For example, it has performed well in registry and other cohort studies but showed no advantage in the all-comers RIPCORD-2 trial or in the setting of complete revascularization PCI for acute MI in FLOWER-MI. And it emitted an increased-mortality signal in the prematurely halted FUTURE trial.
In FAME-3, “the 1-year follow-up was the best chance for FFR-PCI to be noninferior to CABG. The CABG advantage is only going to get better with time if prior experience and pathobiology is true,” Sanjay Kaul, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Overall, “the quality and quantity of evidence is insufficient to support FFR-guided PCI” in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), he said. “I would also argue that the evidence for FFR-guided PCI for simple CAD is also not high quality.”
Dr. Kaul also blasted the claim that FFR-PCI was seen to perform better against CABG in patients with low SYNTAX scores. “In general, one cannot use a positive subgroup in a null or negative trial, as is the case with FAME-3, to ‘rescue’ the treatment intervention.” Such a positive subgroup finding, he said, “would at best be deemed hypothesis-generating and not hypothesis validating.”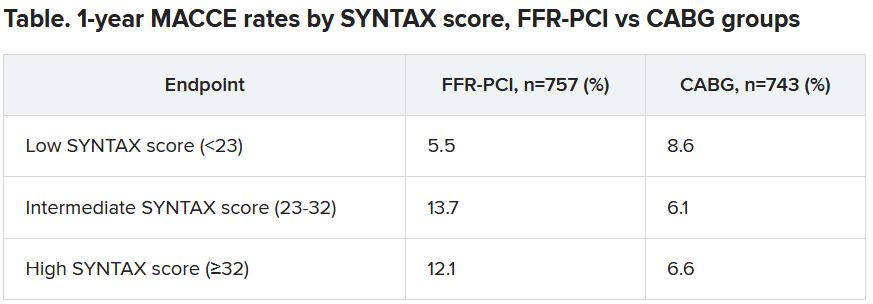
Dr. Fearon agreed that the subgroup analysis by SYNTAX score, though prespecified, was only hypothesis generating. “But I think that other studies have shown the same thing – that in less complex disease, the two strategies appear to perform in a similar fashion.”
The FAME-3 trial’s 1,500 patients were randomly assigned at 48 centers to undergo standard CABG or FFR-guided PCI with Resolute Integrity (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting DES. Lesions with a pressure-wire FFR of 0.80 or less were stented and those with higher FFR readings were deferred.
The 1-year hazard ratio for the primary endpoint—a composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or repeat revascularization – was 1.5 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.2) with a noninferiority P value of .35 for the comparison of FFR-PCI versus CABG.
FFR-guided PCI fared significantly better than CABG for some safety endpoints, including major bleeding (1.6% vs 3.8%, P < .01), arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%, P < .001), acute kidney injury (0.1% vs 0.9%, P < .04), and 30-day rehospitalization (5.5% vs 10.2%, P < .001).
Did the primary endpoint favor CABG?
At a media briefing prior to Dr. Fearon’s TCT 2021 presentation of the trail, Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, proposed that the inclusion of repeat revascularization in the trial’s composite primary endpoint tilted the outcome in favor of CABG. “To me, the FAME-3 results are predictable because repeat revascularization is in the equation.”
It’s well recognized that the endpoint is less likely after CABG than PCI. The latter treats focal lesions that are a limited part of a coronary artery in which CAD is still likely progressing. CABG, on the other hand, can bypass longer segments of diseased artery.
Indeed, as Dr. Fearon reported, the rates of death, MI, or stroke excluding repeat revascularization were 7.3% with FFR-PCI and 5.2% for CABG, for an HR of 1.4 (95% CI, 0.9-2.1).
Dr. Mehran also proposed that intravascular-ultrasound (IVUS) guidance, had it been part of the trial, could potentially have boosted the performance of FFR-PCI.
Repeat revascularization, Dr. Kaul agreed, “should not have been included” in the trial’s primary endpoint. It had been added “to amplify events and to minimize sample size. Not including revascularization would render the sample size prohibitive. There is always give and take in designing clinical trials.”
And he agreed that “IVUS-based PCI optimization would have further improved PCI outcomes.” However, “IVUS plus FFR adds to the procedural burden and limited resources available.” Dr. Fearon said when interviewed that the trial’s definition of procedural MI, a component of the primary endpoint, might potentially be seen as controversial. Procedural MIs in both the PCI and CABG groups were required to meet the standards of CABG-related type-5 MI according to the third and fourth Universal Definitions. The had also had to be accompanied by “a significant finding like new Q waves or a new wall-motion abnormality on echocardiography,” he said.
“That’s fairly strict. Because of that, we had a low rate of periprocedural MI and it was similar between the two groups, around 1.5% in both arms.”
FAME-3 was funded by Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Kaul disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kornowsky receives royalties from or holds intellectual property rights with CathWorks. Dr. Mehran disclosed financial ties to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies, and that she, her spouse, or her institution hold equity in Elixir Medical, Applied Therapeutics, and ControlRad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary stenting guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) readings, considered to reflect the targeted lesion’s functional impact, was no match for coronary bypass surgery (CABG) in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) in a major international randomized trial.
Indeed, FFR-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using one of the latest drug-eluting stents (DES) seemed to perform poorly in the trial, compared with surgery, apparently upping the risk for clinical events by 50% over 1 year.
Designed statistically for noninferiority, the third Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial, with 1,500 randomized patients, showed that FFR-guided PCI was “not noninferior” to CABG. Of those randomized to PCI, 10.6% met the 1-year primary endpoint of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE), compared with only 6.9% of patients assigned to CABG.
The trial enrolled only patients with three-vessel coronary disease with no left-main coronary artery involvement, who were declared by their institution’s multidisciplinary heart team to be appropriate for either form of revascularization.
One of the roles of FFR for PCI guidance is to identify significant lesions “that are underrecognized by the angiogram,” which is less likely to happen in patients with very complex coronary anatomy, study chair William F. Fearon, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
“That’s what we saw in a subgroup analysis based on SYNTAX score,” an index of lesion complexity. “In patients with very high SYNTAX scores, CABG outperformed FFR-guided PCI. But if you look at patients with low SYNTAX scores, actually, FFR-guided PCI outperformed CABG for 1-year MACCE.”
Dr. Fearon is lead author on the study’s Nov. 4, 2021, publication in the New England Journal of Medicine, its release timed to coincide with his presentation of the trial at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
He noted that FAME-3 “wasn’t designed or powered to test for superiority,” so its results do not imply CABG is superior to FFR-PCI in patients with MVD, and remains “inconclusive” on that question.
“I think what this study does is provide both the physician and patients more contemporary data and information on options and expected outcomes in multivessel disease. So if you are a patient who has less complex disease, I think you can feel comfortable that you will get an equivalent result with FFR-guided PCI.” But, at least based on FAME-3, Dr. Fearon said, CABG provides better outcomes in patients with more complex disease.
“I think there are still patients that look at trade-offs. Some patients will accept a higher event rate in order to avoid a long recovery, and vice versa.” So the trial may allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, he said.
A main message of FAME-3 “is that we’re getting very good results with three-vessel PCI, but better results with surgery,” Ran Kornowski, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and Tel Aviv University, said as a discussant following Dr. Fearon’s presentation of the trial. The subanalysis by SYNTAX score, he agreed, probably could be used as part of shared decision-making with patients.
Not all that surprising
“It’s a well-designed study, with a lot of patients,” said surgeon Frank W. Sellke, MD, of Rhode Island Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Brown University, all in Providence.
“I don’t think it’s all that surprising,” he said in an interview. “It’s very consistent with what other studies have shown, that for three-vessel disease, surgery tends to have the edge,” even when pitted against FFR-guided PCI.
Indeed, pressure-wire FFR-PCI has a spotty history, even as an alternative to standard angiography-based PCI. For example, it has performed well in registry and other cohort studies but showed no advantage in the all-comers RIPCORD-2 trial or in the setting of complete revascularization PCI for acute MI in FLOWER-MI. And it emitted an increased-mortality signal in the prematurely halted FUTURE trial.
In FAME-3, “the 1-year follow-up was the best chance for FFR-PCI to be noninferior to CABG. The CABG advantage is only going to get better with time if prior experience and pathobiology is true,” Sanjay Kaul, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Overall, “the quality and quantity of evidence is insufficient to support FFR-guided PCI” in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), he said. “I would also argue that the evidence for FFR-guided PCI for simple CAD is also not high quality.”
Dr. Kaul also blasted the claim that FFR-PCI was seen to perform better against CABG in patients with low SYNTAX scores. “In general, one cannot use a positive subgroup in a null or negative trial, as is the case with FAME-3, to ‘rescue’ the treatment intervention.” Such a positive subgroup finding, he said, “would at best be deemed hypothesis-generating and not hypothesis validating.”
Dr. Fearon agreed that the subgroup analysis by SYNTAX score, though prespecified, was only hypothesis generating. “But I think that other studies have shown the same thing – that in less complex disease, the two strategies appear to perform in a similar fashion.”
The FAME-3 trial’s 1,500 patients were randomly assigned at 48 centers to undergo standard CABG or FFR-guided PCI with Resolute Integrity (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting DES. Lesions with a pressure-wire FFR of 0.80 or less were stented and those with higher FFR readings were deferred.
The 1-year hazard ratio for the primary endpoint—a composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or repeat revascularization – was 1.5 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.2) with a noninferiority P value of .35 for the comparison of FFR-PCI versus CABG.
FFR-guided PCI fared significantly better than CABG for some safety endpoints, including major bleeding (1.6% vs 3.8%, P < .01), arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%, P < .001), acute kidney injury (0.1% vs 0.9%, P < .04), and 30-day rehospitalization (5.5% vs 10.2%, P < .001).
Did the primary endpoint favor CABG?
At a media briefing prior to Dr. Fearon’s TCT 2021 presentation of the trail, Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, proposed that the inclusion of repeat revascularization in the trial’s composite primary endpoint tilted the outcome in favor of CABG. “To me, the FAME-3 results are predictable because repeat revascularization is in the equation.”
It’s well recognized that the endpoint is less likely after CABG than PCI. The latter treats focal lesions that are a limited part of a coronary artery in which CAD is still likely progressing. CABG, on the other hand, can bypass longer segments of diseased artery.
Indeed, as Dr. Fearon reported, the rates of death, MI, or stroke excluding repeat revascularization were 7.3% with FFR-PCI and 5.2% for CABG, for an HR of 1.4 (95% CI, 0.9-2.1).
Dr. Mehran also proposed that intravascular-ultrasound (IVUS) guidance, had it been part of the trial, could potentially have boosted the performance of FFR-PCI.
Repeat revascularization, Dr. Kaul agreed, “should not have been included” in the trial’s primary endpoint. It had been added “to amplify events and to minimize sample size. Not including revascularization would render the sample size prohibitive. There is always give and take in designing clinical trials.”
And he agreed that “IVUS-based PCI optimization would have further improved PCI outcomes.” However, “IVUS plus FFR adds to the procedural burden and limited resources available.” Dr. Fearon said when interviewed that the trial’s definition of procedural MI, a component of the primary endpoint, might potentially be seen as controversial. Procedural MIs in both the PCI and CABG groups were required to meet the standards of CABG-related type-5 MI according to the third and fourth Universal Definitions. The had also had to be accompanied by “a significant finding like new Q waves or a new wall-motion abnormality on echocardiography,” he said.
“That’s fairly strict. Because of that, we had a low rate of periprocedural MI and it was similar between the two groups, around 1.5% in both arms.”
FAME-3 was funded by Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Kaul disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kornowsky receives royalties from or holds intellectual property rights with CathWorks. Dr. Mehran disclosed financial ties to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies, and that she, her spouse, or her institution hold equity in Elixir Medical, Applied Therapeutics, and ControlRad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Coronary stenting guided by fractional flow reserve (FFR) readings, considered to reflect the targeted lesion’s functional impact, was no match for coronary bypass surgery (CABG) in patients with multivessel disease (MVD) in a major international randomized trial.
Indeed, FFR-guided percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) using one of the latest drug-eluting stents (DES) seemed to perform poorly in the trial, compared with surgery, apparently upping the risk for clinical events by 50% over 1 year.
Designed statistically for noninferiority, the third Fractional Flow Reserve Versus Angiography for Multivessel Evaluation (FAME 3) trial, with 1,500 randomized patients, showed that FFR-guided PCI was “not noninferior” to CABG. Of those randomized to PCI, 10.6% met the 1-year primary endpoint of major adverse cardiac or cerebrovascular events (MACCE), compared with only 6.9% of patients assigned to CABG.
The trial enrolled only patients with three-vessel coronary disease with no left-main coronary artery involvement, who were declared by their institution’s multidisciplinary heart team to be appropriate for either form of revascularization.
One of the roles of FFR for PCI guidance is to identify significant lesions “that are underrecognized by the angiogram,” which is less likely to happen in patients with very complex coronary anatomy, study chair William F. Fearon, MD, Stanford (Calif.) University, said in an interview.
“That’s what we saw in a subgroup analysis based on SYNTAX score,” an index of lesion complexity. “In patients with very high SYNTAX scores, CABG outperformed FFR-guided PCI. But if you look at patients with low SYNTAX scores, actually, FFR-guided PCI outperformed CABG for 1-year MACCE.”
Dr. Fearon is lead author on the study’s Nov. 4, 2021, publication in the New England Journal of Medicine, its release timed to coincide with his presentation of the trial at the Transcatheter Cardiovascular Therapeutics annual meeting, held virtually and live in Orlando and sponsored by the Cardiovascular Research Foundation.
He noted that FAME-3 “wasn’t designed or powered to test for superiority,” so its results do not imply CABG is superior to FFR-PCI in patients with MVD, and remains “inconclusive” on that question.
“I think what this study does is provide both the physician and patients more contemporary data and information on options and expected outcomes in multivessel disease. So if you are a patient who has less complex disease, I think you can feel comfortable that you will get an equivalent result with FFR-guided PCI.” But, at least based on FAME-3, Dr. Fearon said, CABG provides better outcomes in patients with more complex disease.
“I think there are still patients that look at trade-offs. Some patients will accept a higher event rate in order to avoid a long recovery, and vice versa.” So the trial may allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, he said.
A main message of FAME-3 “is that we’re getting very good results with three-vessel PCI, but better results with surgery,” Ran Kornowski, MD, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and Tel Aviv University, said as a discussant following Dr. Fearon’s presentation of the trial. The subanalysis by SYNTAX score, he agreed, probably could be used as part of shared decision-making with patients.
Not all that surprising
“It’s a well-designed study, with a lot of patients,” said surgeon Frank W. Sellke, MD, of Rhode Island Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Brown University, all in Providence.
“I don’t think it’s all that surprising,” he said in an interview. “It’s very consistent with what other studies have shown, that for three-vessel disease, surgery tends to have the edge,” even when pitted against FFR-guided PCI.
Indeed, pressure-wire FFR-PCI has a spotty history, even as an alternative to standard angiography-based PCI. For example, it has performed well in registry and other cohort studies but showed no advantage in the all-comers RIPCORD-2 trial or in the setting of complete revascularization PCI for acute MI in FLOWER-MI. And it emitted an increased-mortality signal in the prematurely halted FUTURE trial.
In FAME-3, “the 1-year follow-up was the best chance for FFR-PCI to be noninferior to CABG. The CABG advantage is only going to get better with time if prior experience and pathobiology is true,” Sanjay Kaul, MD, Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in an interview.
Overall, “the quality and quantity of evidence is insufficient to support FFR-guided PCI” in patients with complex coronary artery disease (CAD), he said. “I would also argue that the evidence for FFR-guided PCI for simple CAD is also not high quality.”
Dr. Kaul also blasted the claim that FFR-PCI was seen to perform better against CABG in patients with low SYNTAX scores. “In general, one cannot use a positive subgroup in a null or negative trial, as is the case with FAME-3, to ‘rescue’ the treatment intervention.” Such a positive subgroup finding, he said, “would at best be deemed hypothesis-generating and not hypothesis validating.”
Dr. Fearon agreed that the subgroup analysis by SYNTAX score, though prespecified, was only hypothesis generating. “But I think that other studies have shown the same thing – that in less complex disease, the two strategies appear to perform in a similar fashion.”
The FAME-3 trial’s 1,500 patients were randomly assigned at 48 centers to undergo standard CABG or FFR-guided PCI with Resolute Integrity (Medtronic) zotarolimus-eluting DES. Lesions with a pressure-wire FFR of 0.80 or less were stented and those with higher FFR readings were deferred.
The 1-year hazard ratio for the primary endpoint—a composite of death from any cause, MI, stroke, or repeat revascularization – was 1.5 (95% confidence interval, 1.1-2.2) with a noninferiority P value of .35 for the comparison of FFR-PCI versus CABG.
FFR-guided PCI fared significantly better than CABG for some safety endpoints, including major bleeding (1.6% vs 3.8%, P < .01), arrhythmia including atrial fibrillation (2.4% vs. 14.1%, P < .001), acute kidney injury (0.1% vs 0.9%, P < .04), and 30-day rehospitalization (5.5% vs 10.2%, P < .001).
Did the primary endpoint favor CABG?
At a media briefing prior to Dr. Fearon’s TCT 2021 presentation of the trail, Roxana Mehran, MD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, proposed that the inclusion of repeat revascularization in the trial’s composite primary endpoint tilted the outcome in favor of CABG. “To me, the FAME-3 results are predictable because repeat revascularization is in the equation.”
It’s well recognized that the endpoint is less likely after CABG than PCI. The latter treats focal lesions that are a limited part of a coronary artery in which CAD is still likely progressing. CABG, on the other hand, can bypass longer segments of diseased artery.
Indeed, as Dr. Fearon reported, the rates of death, MI, or stroke excluding repeat revascularization were 7.3% with FFR-PCI and 5.2% for CABG, for an HR of 1.4 (95% CI, 0.9-2.1).
Dr. Mehran also proposed that intravascular-ultrasound (IVUS) guidance, had it been part of the trial, could potentially have boosted the performance of FFR-PCI.
Repeat revascularization, Dr. Kaul agreed, “should not have been included” in the trial’s primary endpoint. It had been added “to amplify events and to minimize sample size. Not including revascularization would render the sample size prohibitive. There is always give and take in designing clinical trials.”
And he agreed that “IVUS-based PCI optimization would have further improved PCI outcomes.” However, “IVUS plus FFR adds to the procedural burden and limited resources available.” Dr. Fearon said when interviewed that the trial’s definition of procedural MI, a component of the primary endpoint, might potentially be seen as controversial. Procedural MIs in both the PCI and CABG groups were required to meet the standards of CABG-related type-5 MI according to the third and fourth Universal Definitions. The had also had to be accompanied by “a significant finding like new Q waves or a new wall-motion abnormality on echocardiography,” he said.
“That’s fairly strict. Because of that, we had a low rate of periprocedural MI and it was similar between the two groups, around 1.5% in both arms.”
FAME-3 was funded by Medtronic and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Kaul disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Kornowsky receives royalties from or holds intellectual property rights with CathWorks. Dr. Mehran disclosed financial ties to numerous pharmaceutical and device companies, and that she, her spouse, or her institution hold equity in Elixir Medical, Applied Therapeutics, and ControlRad.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA class I recall of CardioSave hybrid/rescue IABPs
Datascope/Getinge/Maquet is recalling CardioSave Hybrid and Rescue intra-aortic balloon pumps (IABPs) because some battery packs may have a shortened run time and fail unexpectedly, according to a medical device recall notice posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
The FDA has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall, because of the risk for serious injury or death.
The recalled IABPs have substandard batteries that do not meet performance specifications and were mistakenly released to a limited number of customers.
If a patient requires life-supporting therapy with an IABP and the device does not work or stops working during use because of battery failure, the patient will be at risk for serious injury, including death, the FDA cautions.
Both IABP monitors display battery life and have low battery alarms when alternative power sources are needed.
Datascope/Getting/Maquet has received six complaints but no reports of injury or death related to this issue.
“However, there is a potential for underreporting since the end user reporting a failed battery or short battery run time cannot be aware that they originally received a substandard battery,” the FDA said.
The recall involves 137 battery packs distributed in the United States between Sept. 23, 2017, and Aug. 17, 2021. Product codes and lot numbers are available in the recall notice.
The company sent an urgent medical device removal letter to customers requesting that they check inventory to determine if there are any CardioSave LiIon battery packs with part number/reference number 0146-00-0097 and with serial numbers listed in the letter.
Customers are asked to replace any affected battery with an unaffected battery and remove the affected product from areas of use.
The company will issue credit or a replacement battery at no cost to the facility upon receipt of the response form attached to the letter.
Distributors who shipped any affected product to customers are asked to forward the device removal letter to customers.
All customers, regardless of whether or not they have defective batteries, are asked to complete and sign the response form to acknowledge that they received the notification and disposed of the affected batteries.
Completed forms can be scanned and emailed to Datascope/Getinge/Maquet at [email protected] or by FAX to 1-877-446-3360.
Customers who have questions about this recall should contact their Datascope/Getinge/Maquet sales representative or, for technical questions, customer service (1-888-943-8872, option 2), Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. ET.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled CardioSave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Datascope/Getinge/Maquet is recalling CardioSave Hybrid and Rescue intra-aortic balloon pumps (IABPs) because some battery packs may have a shortened run time and fail unexpectedly, according to a medical device recall notice posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
The FDA has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall, because of the risk for serious injury or death.
The recalled IABPs have substandard batteries that do not meet performance specifications and were mistakenly released to a limited number of customers.
If a patient requires life-supporting therapy with an IABP and the device does not work or stops working during use because of battery failure, the patient will be at risk for serious injury, including death, the FDA cautions.
Both IABP monitors display battery life and have low battery alarms when alternative power sources are needed.
Datascope/Getting/Maquet has received six complaints but no reports of injury or death related to this issue.
“However, there is a potential for underreporting since the end user reporting a failed battery or short battery run time cannot be aware that they originally received a substandard battery,” the FDA said.
The recall involves 137 battery packs distributed in the United States between Sept. 23, 2017, and Aug. 17, 2021. Product codes and lot numbers are available in the recall notice.
The company sent an urgent medical device removal letter to customers requesting that they check inventory to determine if there are any CardioSave LiIon battery packs with part number/reference number 0146-00-0097 and with serial numbers listed in the letter.
Customers are asked to replace any affected battery with an unaffected battery and remove the affected product from areas of use.
The company will issue credit or a replacement battery at no cost to the facility upon receipt of the response form attached to the letter.
Distributors who shipped any affected product to customers are asked to forward the device removal letter to customers.
All customers, regardless of whether or not they have defective batteries, are asked to complete and sign the response form to acknowledge that they received the notification and disposed of the affected batteries.
Completed forms can be scanned and emailed to Datascope/Getinge/Maquet at [email protected] or by FAX to 1-877-446-3360.
Customers who have questions about this recall should contact their Datascope/Getinge/Maquet sales representative or, for technical questions, customer service (1-888-943-8872, option 2), Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. ET.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled CardioSave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Datascope/Getinge/Maquet is recalling CardioSave Hybrid and Rescue intra-aortic balloon pumps (IABPs) because some battery packs may have a shortened run time and fail unexpectedly, according to a medical device recall notice posted on the U.S. Food and Drug Administration website.
The FDA has identified this as a class I recall, the most serious type of recall, because of the risk for serious injury or death.
The recalled IABPs have substandard batteries that do not meet performance specifications and were mistakenly released to a limited number of customers.
If a patient requires life-supporting therapy with an IABP and the device does not work or stops working during use because of battery failure, the patient will be at risk for serious injury, including death, the FDA cautions.
Both IABP monitors display battery life and have low battery alarms when alternative power sources are needed.
Datascope/Getting/Maquet has received six complaints but no reports of injury or death related to this issue.
“However, there is a potential for underreporting since the end user reporting a failed battery or short battery run time cannot be aware that they originally received a substandard battery,” the FDA said.
The recall involves 137 battery packs distributed in the United States between Sept. 23, 2017, and Aug. 17, 2021. Product codes and lot numbers are available in the recall notice.
The company sent an urgent medical device removal letter to customers requesting that they check inventory to determine if there are any CardioSave LiIon battery packs with part number/reference number 0146-00-0097 and with serial numbers listed in the letter.
Customers are asked to replace any affected battery with an unaffected battery and remove the affected product from areas of use.
The company will issue credit or a replacement battery at no cost to the facility upon receipt of the response form attached to the letter.
Distributors who shipped any affected product to customers are asked to forward the device removal letter to customers.
All customers, regardless of whether or not they have defective batteries, are asked to complete and sign the response form to acknowledge that they received the notification and disposed of the affected batteries.
Completed forms can be scanned and emailed to Datascope/Getinge/Maquet at [email protected] or by FAX to 1-877-446-3360.
Customers who have questions about this recall should contact their Datascope/Getinge/Maquet sales representative or, for technical questions, customer service (1-888-943-8872, option 2), Monday through Friday, 8:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m. ET.
Any adverse events or suspected adverse events related to the recalled CardioSave Hybrid/Rescue IABPs should be reported to the FDA through MedWatch, its adverse event reporting program.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves Abbott’s Portico valve for TAVR
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Portico with FlexNav (Abbott) transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) system for patients with “symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis who are at high or extreme risk for open-heart surgery,” the company has announced.
The approval indication is in line with the entry criteria of PORTICO IDE, the investigational device exemption trial from which the FDA largely made its decision.
With the self-expanding Portico valve, Abbott joins two other companies with TAVR valves on the U.S. market: Medtronic with the self-expanding Corevalve Evolut (Medtronic) line, and Edwards Lifesciences with its Sapien (Edwards Lifesciences) valves, both of which can be used in patients at low surgical risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Portico with FlexNav (Abbott) transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) system for patients with “symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis who are at high or extreme risk for open-heart surgery,” the company has announced.
The approval indication is in line with the entry criteria of PORTICO IDE, the investigational device exemption trial from which the FDA largely made its decision.
With the self-expanding Portico valve, Abbott joins two other companies with TAVR valves on the U.S. market: Medtronic with the self-expanding Corevalve Evolut (Medtronic) line, and Edwards Lifesciences with its Sapien (Edwards Lifesciences) valves, both of which can be used in patients at low surgical risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Portico with FlexNav (Abbott) transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) system for patients with “symptomatic, severe aortic stenosis who are at high or extreme risk for open-heart surgery,” the company has announced.
The approval indication is in line with the entry criteria of PORTICO IDE, the investigational device exemption trial from which the FDA largely made its decision.
With the self-expanding Portico valve, Abbott joins two other companies with TAVR valves on the U.S. market: Medtronic with the self-expanding Corevalve Evolut (Medtronic) line, and Edwards Lifesciences with its Sapien (Edwards Lifesciences) valves, both of which can be used in patients at low surgical risk.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Angiography can wait for cardiac arrest without ST-elevation
A protocol of immediate angiography provided no mortality benefit over a strategy or delayed or more selective angiography among patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and without ST-segment elevation, new randomized results show.
“Among patients with resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin, with shockable and nonshockable arrest rhythm and no ST-elevation, a strategy of immediate, unselected coronary angiography was not found to be beneficial over a delayed and selective approach with regard to the 30-day risk of all-cause death,” concluded principal investigator Steffen Desch, MD, University of Leipzig (Germany) Heart Center.
The results support previous results of the Coronary Angiography after Cardiac Arrest (COACT) trial, in patients with shockable rhythms, which also showed no differences in clinical outcomes between immediate and delayed coronary angiography at both 90 days and 1 year, he noted.
“What the clinicians wanted to know is, is it really necessary to get up at 3 a.m. in the morning to perform a coronary angiography on these patients, and that’s certainly out,” Dr. Desch said in an interview. “So, there’s really no room for this strategy anymore. You can take your time and wait a day or 2.”
These findings, from the TOMAHAWK trial, were presented Aug. 29 at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Larger group without ST-segment elevation
Prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is extremely poor, with an overall survival rate of less than 10%, Dr. Desch noted. “Actually, only 20% make it to the hospital; the vast majority of these patients die out in the field, so there’s really a great need in improving treatment.”
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for up to 60% of out-of-hospital arrests in which a cardiac cause has been identified, the authors wrote in their report. ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography “has good positive predictive value” for acute coronary lesions triggering the arrest, but in the far larger subgroup of patients without ST-segment elevation, “the spectrum of underlying causes is considerably broader and includes both cardiac and noncardiac causes.”
In patients with myocardial infarction, early revascularization would prevent negative consequences of myocardial injury, but unselected early coronary angiography would put patients not having an MI at unnecessary risk for procedural complications or delay in the diagnosis of the actual cause of their arrest, they noted.
In this trial, the researchers randomly assigned 554 patients from 31 sites in Germany and Denmark who were successfully resuscitated after cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin to immediate transfer for coronary angiography or to initial intensive care assessment with delayed or selective angiography after a minimum delay of at least 1 day.
In the end, the average delay in this arm was 2 days, Dr. Desch noted. If the clinical course indicated that a coronary cause was unlikely, angiography might not be performed at all in this group.
No patient had ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography. The primary endpoint was death from any cause at 30 days; secondary end points were death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days.
Results showed that 95% of patients in the immediate angiography group actually underwent the procedure, compared with 62% of those in the delayed group, a finding that was “logical” given the study design, he said.
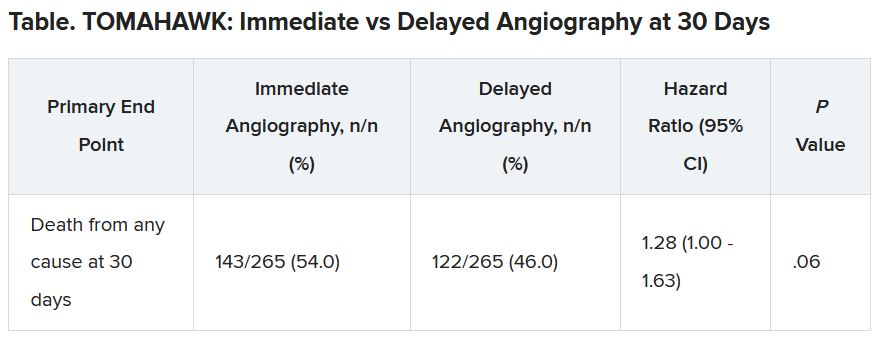
At 30 days, 54% of patients in the immediate angiography group and 46% in the delayed group had died, a nonsignificant difference (P = .06). Because the researchers had performed an interim analysis, Dr. Desch explained, the final P value for significance in this trial was not .05, but rather .034, to account for multiple comparisons.
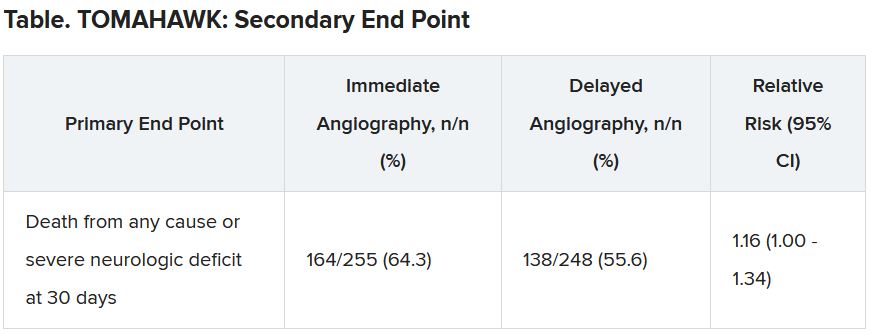
The secondary end point of death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days “was actually nominally significant in favor of the delayed group,” he said. “So, this is not corrected for multiple testing, it’s just a hypothesis that’s in the room, but it’s certainly worthy of discussion that the immediate strategy might actually cause harm.”
There was no difference between the groups in peak release of myocardial enzymes, or any other safety end points, including bleeding, stroke, or renal failure, Dr. Desch said.
Further analyses showed no large differences between subgroups, including age, diabetes, first monitored rhythm, confirmed MI as the trigger of the arrest, sex, and the time from cardiac arrest to the return of spontaneous circulation, he noted.
Opportunity to minimize harm
Discussant for the results during the presentation was Susanna Price, MBBS, PhD, Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
Dr. Price concluded: “What this means for me, is it gives me information that’s useful regarding the opportunity to minimize harm, which is a lot of what critical care is about, so we don’t necessarily now have to move these patients very acutely when they’ve just come in through the ED [emergency department]. It has implications for resource utilization, but also implications for mobilizing patients around the hospital during COVID-19.”
It’s also important to note that coronary angiography was still carried out in certain patients, “so we still have to have that dialogue with our interventional cardiologists for certain patients who may need to go to the cath lab, and what it should now allow us to do is give appropriate focus to how to manage these patients when they come in to the ED or to our ICUs [intensive care units],” she said.
Dr. Price added, though, that perhaps “the most important slide” in the presentation was that showing 90% of these patients had a witnessed cardiac arrest, “and yet a third of these patients, 168 of them, had no bystander CPR at all.”
She pointed to the “chain of survival” after cardiac arrest, of which Charles D. Deakin, MD, University Hospital Southampton (England), wrote that “not all links are equal.”
“Early recognition and calling for help, early CPR, early defibrillation where appropriate are very, very important, and we need to be addressing all of these, as well as what happens in the cath lab and after admission,” Dr. Price said.
This research was funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Desch and Dr. Price reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A protocol of immediate angiography provided no mortality benefit over a strategy or delayed or more selective angiography among patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and without ST-segment elevation, new randomized results show.
“Among patients with resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin, with shockable and nonshockable arrest rhythm and no ST-elevation, a strategy of immediate, unselected coronary angiography was not found to be beneficial over a delayed and selective approach with regard to the 30-day risk of all-cause death,” concluded principal investigator Steffen Desch, MD, University of Leipzig (Germany) Heart Center.
The results support previous results of the Coronary Angiography after Cardiac Arrest (COACT) trial, in patients with shockable rhythms, which also showed no differences in clinical outcomes between immediate and delayed coronary angiography at both 90 days and 1 year, he noted.
“What the clinicians wanted to know is, is it really necessary to get up at 3 a.m. in the morning to perform a coronary angiography on these patients, and that’s certainly out,” Dr. Desch said in an interview. “So, there’s really no room for this strategy anymore. You can take your time and wait a day or 2.”
These findings, from the TOMAHAWK trial, were presented Aug. 29 at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Larger group without ST-segment elevation
Prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is extremely poor, with an overall survival rate of less than 10%, Dr. Desch noted. “Actually, only 20% make it to the hospital; the vast majority of these patients die out in the field, so there’s really a great need in improving treatment.”
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for up to 60% of out-of-hospital arrests in which a cardiac cause has been identified, the authors wrote in their report. ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography “has good positive predictive value” for acute coronary lesions triggering the arrest, but in the far larger subgroup of patients without ST-segment elevation, “the spectrum of underlying causes is considerably broader and includes both cardiac and noncardiac causes.”
In patients with myocardial infarction, early revascularization would prevent negative consequences of myocardial injury, but unselected early coronary angiography would put patients not having an MI at unnecessary risk for procedural complications or delay in the diagnosis of the actual cause of their arrest, they noted.
In this trial, the researchers randomly assigned 554 patients from 31 sites in Germany and Denmark who were successfully resuscitated after cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin to immediate transfer for coronary angiography or to initial intensive care assessment with delayed or selective angiography after a minimum delay of at least 1 day.
In the end, the average delay in this arm was 2 days, Dr. Desch noted. If the clinical course indicated that a coronary cause was unlikely, angiography might not be performed at all in this group.
No patient had ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography. The primary endpoint was death from any cause at 30 days; secondary end points were death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days.
Results showed that 95% of patients in the immediate angiography group actually underwent the procedure, compared with 62% of those in the delayed group, a finding that was “logical” given the study design, he said.
At 30 days, 54% of patients in the immediate angiography group and 46% in the delayed group had died, a nonsignificant difference (P = .06). Because the researchers had performed an interim analysis, Dr. Desch explained, the final P value for significance in this trial was not .05, but rather .034, to account for multiple comparisons.

The secondary end point of death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days “was actually nominally significant in favor of the delayed group,” he said. “So, this is not corrected for multiple testing, it’s just a hypothesis that’s in the room, but it’s certainly worthy of discussion that the immediate strategy might actually cause harm.”

There was no difference between the groups in peak release of myocardial enzymes, or any other safety end points, including bleeding, stroke, or renal failure, Dr. Desch said.
Further analyses showed no large differences between subgroups, including age, diabetes, first monitored rhythm, confirmed MI as the trigger of the arrest, sex, and the time from cardiac arrest to the return of spontaneous circulation, he noted.
Opportunity to minimize harm
Discussant for the results during the presentation was Susanna Price, MBBS, PhD, Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
Dr. Price concluded: “What this means for me, is it gives me information that’s useful regarding the opportunity to minimize harm, which is a lot of what critical care is about, so we don’t necessarily now have to move these patients very acutely when they’ve just come in through the ED [emergency department]. It has implications for resource utilization, but also implications for mobilizing patients around the hospital during COVID-19.”
It’s also important to note that coronary angiography was still carried out in certain patients, “so we still have to have that dialogue with our interventional cardiologists for certain patients who may need to go to the cath lab, and what it should now allow us to do is give appropriate focus to how to manage these patients when they come in to the ED or to our ICUs [intensive care units],” she said.
Dr. Price added, though, that perhaps “the most important slide” in the presentation was that showing 90% of these patients had a witnessed cardiac arrest, “and yet a third of these patients, 168 of them, had no bystander CPR at all.”
She pointed to the “chain of survival” after cardiac arrest, of which Charles D. Deakin, MD, University Hospital Southampton (England), wrote that “not all links are equal.”
“Early recognition and calling for help, early CPR, early defibrillation where appropriate are very, very important, and we need to be addressing all of these, as well as what happens in the cath lab and after admission,” Dr. Price said.
This research was funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Desch and Dr. Price reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A protocol of immediate angiography provided no mortality benefit over a strategy or delayed or more selective angiography among patients resuscitated from out-of-hospital cardiac arrest and without ST-segment elevation, new randomized results show.
“Among patients with resuscitated out-of-hospital cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin, with shockable and nonshockable arrest rhythm and no ST-elevation, a strategy of immediate, unselected coronary angiography was not found to be beneficial over a delayed and selective approach with regard to the 30-day risk of all-cause death,” concluded principal investigator Steffen Desch, MD, University of Leipzig (Germany) Heart Center.
The results support previous results of the Coronary Angiography after Cardiac Arrest (COACT) trial, in patients with shockable rhythms, which also showed no differences in clinical outcomes between immediate and delayed coronary angiography at both 90 days and 1 year, he noted.
“What the clinicians wanted to know is, is it really necessary to get up at 3 a.m. in the morning to perform a coronary angiography on these patients, and that’s certainly out,” Dr. Desch said in an interview. “So, there’s really no room for this strategy anymore. You can take your time and wait a day or 2.”
These findings, from the TOMAHAWK trial, were presented Aug. 29 at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and simultaneously published online in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Larger group without ST-segment elevation
Prognosis after out-of-hospital cardiac arrest is extremely poor, with an overall survival rate of less than 10%, Dr. Desch noted. “Actually, only 20% make it to the hospital; the vast majority of these patients die out in the field, so there’s really a great need in improving treatment.”
Acute coronary syndrome accounts for up to 60% of out-of-hospital arrests in which a cardiac cause has been identified, the authors wrote in their report. ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography “has good positive predictive value” for acute coronary lesions triggering the arrest, but in the far larger subgroup of patients without ST-segment elevation, “the spectrum of underlying causes is considerably broader and includes both cardiac and noncardiac causes.”
In patients with myocardial infarction, early revascularization would prevent negative consequences of myocardial injury, but unselected early coronary angiography would put patients not having an MI at unnecessary risk for procedural complications or delay in the diagnosis of the actual cause of their arrest, they noted.
In this trial, the researchers randomly assigned 554 patients from 31 sites in Germany and Denmark who were successfully resuscitated after cardiac arrest of possible cardiac origin to immediate transfer for coronary angiography or to initial intensive care assessment with delayed or selective angiography after a minimum delay of at least 1 day.
In the end, the average delay in this arm was 2 days, Dr. Desch noted. If the clinical course indicated that a coronary cause was unlikely, angiography might not be performed at all in this group.
No patient had ST-segment elevation on postresuscitation electrocardiography. The primary endpoint was death from any cause at 30 days; secondary end points were death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days.
Results showed that 95% of patients in the immediate angiography group actually underwent the procedure, compared with 62% of those in the delayed group, a finding that was “logical” given the study design, he said.
At 30 days, 54% of patients in the immediate angiography group and 46% in the delayed group had died, a nonsignificant difference (P = .06). Because the researchers had performed an interim analysis, Dr. Desch explained, the final P value for significance in this trial was not .05, but rather .034, to account for multiple comparisons.

The secondary end point of death from any cause or severe neurologic deficit at 30 days “was actually nominally significant in favor of the delayed group,” he said. “So, this is not corrected for multiple testing, it’s just a hypothesis that’s in the room, but it’s certainly worthy of discussion that the immediate strategy might actually cause harm.”

There was no difference between the groups in peak release of myocardial enzymes, or any other safety end points, including bleeding, stroke, or renal failure, Dr. Desch said.
Further analyses showed no large differences between subgroups, including age, diabetes, first monitored rhythm, confirmed MI as the trigger of the arrest, sex, and the time from cardiac arrest to the return of spontaneous circulation, he noted.
Opportunity to minimize harm
Discussant for the results during the presentation was Susanna Price, MBBS, PhD, Royal Brompton Hospital, London.
Dr. Price concluded: “What this means for me, is it gives me information that’s useful regarding the opportunity to minimize harm, which is a lot of what critical care is about, so we don’t necessarily now have to move these patients very acutely when they’ve just come in through the ED [emergency department]. It has implications for resource utilization, but also implications for mobilizing patients around the hospital during COVID-19.”
It’s also important to note that coronary angiography was still carried out in certain patients, “so we still have to have that dialogue with our interventional cardiologists for certain patients who may need to go to the cath lab, and what it should now allow us to do is give appropriate focus to how to manage these patients when they come in to the ED or to our ICUs [intensive care units],” she said.
Dr. Price added, though, that perhaps “the most important slide” in the presentation was that showing 90% of these patients had a witnessed cardiac arrest, “and yet a third of these patients, 168 of them, had no bystander CPR at all.”
She pointed to the “chain of survival” after cardiac arrest, of which Charles D. Deakin, MD, University Hospital Southampton (England), wrote that “not all links are equal.”
“Early recognition and calling for help, early CPR, early defibrillation where appropriate are very, very important, and we need to be addressing all of these, as well as what happens in the cath lab and after admission,” Dr. Price said.
This research was funded by the German Center for Cardiovascular Research. Dr. Desch and Dr. Price reported no relevant disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
What is the most likely cause of this patient’s fever?
A 63-year-old man undergoes cardiac bypass surgery. He is able to be extubated at 8 hours. The next morning he has a fever to 38.5° C His exam shows no redness at the surgical site, or at his IV sites. His lung exam is unremarkable. His urinalysis is without white blood cells. His white blood cell count is 8,500, and his chest x-ray shows atelectasis without other abnormalities.
One of the earliest things I was taught in my clinical years were the causes of postoperative fever, or the 5Ws, which are wind, water, wound, walk, and wonder drug.
Atelectasis was touted as the cause of early postoperative fever. This became clear fact in my medical student mind, not something that I had ever questioned. But investigation into whether there is evidence of this shows it is only a myth. In actuality, there is scant evidence, if any, for atelectasis causing fever. Frequently, no cause of postoperative fever has been found, despite aggressive attempts to look for one.
What the research says
Fanning and colleagues prospectively looked at 537 women who were undergoing major gynecologic surgery.1 Postoperative fever occurred in 211 of them. In 92% of these patients, no cause for fever was found.
Atelectasis is frequently seen postoperatively. Schlenker and colleagues reported that, in patients with postoperative atelectasis, temperature elevation on the first postoperative day was directly related to the degree of atelectasis, but the white blood cell count elevation was inversely related.2
In this study, atelectasis was diagnosed by auscultation, with chest x-rays ordered at the discretion of the physician. There was little correlation with the auscultatory findings and presence or absence of atelectasis in the patients who did receive chest x-rays.
Engoren did a study to prospectively evaluate 100 postoperative patients with daily chest x-rays and continuous temperature monitoring.3 Results from the day of surgery (day 0) to the second postoperative day showed an increase in presence of atelectasis from 43% on the day of surgery to 79% by day 2.
Fever, defined as temperature greater than 38° C, fell from 37% on the day of surgery to 17% by day 2. Engoren found no association between fever and degree of atelectasis.
Mavros and colleagues did a comprehensive review to determine whether there was evidence to support atelectasis causing fever.4 They concluded that there was no clinical evidence supporting the concept that atelectasis is associated with early postoperative fever.
A possible cause of fever
Mavros and colleagues’ paper suggested that early postoperative fever was caused by stress derived by surgery, which can increase the patient’s interleukin-6 levels and thermostatic set point. This was demonstrated in a small study by Wortel and colleagues, who measured IL-6 levels in the portal and peripheral blood of patients following pancreaticoduodenectomy.5 They found IL-6 levels correlated strongly with peak body temperature.
In conclusion, atelectasis is not a well-established cause of postoperative fever.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Fanning J et al. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 6(6):252-5 .
2. Schlenker JD and Hubay CA. Arch Surg 1973;107:846-50
3. Engoren M. Chest. 1995;107(1):81-4 .
4. Michael N et al. Chest. 2011;140(2):418-24
5. Wortel CH et al. Surgery. 1993;114(3):564-70 .
A 63-year-old man undergoes cardiac bypass surgery. He is able to be extubated at 8 hours. The next morning he has a fever to 38.5° C His exam shows no redness at the surgical site, or at his IV sites. His lung exam is unremarkable. His urinalysis is without white blood cells. His white blood cell count is 8,500, and his chest x-ray shows atelectasis without other abnormalities.
One of the earliest things I was taught in my clinical years were the causes of postoperative fever, or the 5Ws, which are wind, water, wound, walk, and wonder drug.
Atelectasis was touted as the cause of early postoperative fever. This became clear fact in my medical student mind, not something that I had ever questioned. But investigation into whether there is evidence of this shows it is only a myth. In actuality, there is scant evidence, if any, for atelectasis causing fever. Frequently, no cause of postoperative fever has been found, despite aggressive attempts to look for one.
What the research says
Fanning and colleagues prospectively looked at 537 women who were undergoing major gynecologic surgery.1 Postoperative fever occurred in 211 of them. In 92% of these patients, no cause for fever was found.
Atelectasis is frequently seen postoperatively. Schlenker and colleagues reported that, in patients with postoperative atelectasis, temperature elevation on the first postoperative day was directly related to the degree of atelectasis, but the white blood cell count elevation was inversely related.2
In this study, atelectasis was diagnosed by auscultation, with chest x-rays ordered at the discretion of the physician. There was little correlation with the auscultatory findings and presence or absence of atelectasis in the patients who did receive chest x-rays.
Engoren did a study to prospectively evaluate 100 postoperative patients with daily chest x-rays and continuous temperature monitoring.3 Results from the day of surgery (day 0) to the second postoperative day showed an increase in presence of atelectasis from 43% on the day of surgery to 79% by day 2.
Fever, defined as temperature greater than 38° C, fell from 37% on the day of surgery to 17% by day 2. Engoren found no association between fever and degree of atelectasis.
Mavros and colleagues did a comprehensive review to determine whether there was evidence to support atelectasis causing fever.4 They concluded that there was no clinical evidence supporting the concept that atelectasis is associated with early postoperative fever.
A possible cause of fever
Mavros and colleagues’ paper suggested that early postoperative fever was caused by stress derived by surgery, which can increase the patient’s interleukin-6 levels and thermostatic set point. This was demonstrated in a small study by Wortel and colleagues, who measured IL-6 levels in the portal and peripheral blood of patients following pancreaticoduodenectomy.5 They found IL-6 levels correlated strongly with peak body temperature.
In conclusion, atelectasis is not a well-established cause of postoperative fever.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Fanning J et al. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 6(6):252-5 .
2. Schlenker JD and Hubay CA. Arch Surg 1973;107:846-50
3. Engoren M. Chest. 1995;107(1):81-4 .
4. Michael N et al. Chest. 2011;140(2):418-24
5. Wortel CH et al. Surgery. 1993;114(3):564-70 .
A 63-year-old man undergoes cardiac bypass surgery. He is able to be extubated at 8 hours. The next morning he has a fever to 38.5° C His exam shows no redness at the surgical site, or at his IV sites. His lung exam is unremarkable. His urinalysis is without white blood cells. His white blood cell count is 8,500, and his chest x-ray shows atelectasis without other abnormalities.
One of the earliest things I was taught in my clinical years were the causes of postoperative fever, or the 5Ws, which are wind, water, wound, walk, and wonder drug.
Atelectasis was touted as the cause of early postoperative fever. This became clear fact in my medical student mind, not something that I had ever questioned. But investigation into whether there is evidence of this shows it is only a myth. In actuality, there is scant evidence, if any, for atelectasis causing fever. Frequently, no cause of postoperative fever has been found, despite aggressive attempts to look for one.
What the research says
Fanning and colleagues prospectively looked at 537 women who were undergoing major gynecologic surgery.1 Postoperative fever occurred in 211 of them. In 92% of these patients, no cause for fever was found.
Atelectasis is frequently seen postoperatively. Schlenker and colleagues reported that, in patients with postoperative atelectasis, temperature elevation on the first postoperative day was directly related to the degree of atelectasis, but the white blood cell count elevation was inversely related.2
In this study, atelectasis was diagnosed by auscultation, with chest x-rays ordered at the discretion of the physician. There was little correlation with the auscultatory findings and presence or absence of atelectasis in the patients who did receive chest x-rays.
Engoren did a study to prospectively evaluate 100 postoperative patients with daily chest x-rays and continuous temperature monitoring.3 Results from the day of surgery (day 0) to the second postoperative day showed an increase in presence of atelectasis from 43% on the day of surgery to 79% by day 2.
Fever, defined as temperature greater than 38° C, fell from 37% on the day of surgery to 17% by day 2. Engoren found no association between fever and degree of atelectasis.
Mavros and colleagues did a comprehensive review to determine whether there was evidence to support atelectasis causing fever.4 They concluded that there was no clinical evidence supporting the concept that atelectasis is associated with early postoperative fever.
A possible cause of fever
Mavros and colleagues’ paper suggested that early postoperative fever was caused by stress derived by surgery, which can increase the patient’s interleukin-6 levels and thermostatic set point. This was demonstrated in a small study by Wortel and colleagues, who measured IL-6 levels in the portal and peripheral blood of patients following pancreaticoduodenectomy.5 They found IL-6 levels correlated strongly with peak body temperature.
In conclusion, atelectasis is not a well-established cause of postoperative fever.
Dr. Paauw is professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine at the University of Washington, Seattle, and he serves as third-year medical student clerkship director at the University of Washington. He is a member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News. Dr. Paauw has no conflicts to disclose. Contact him at [email protected].
References
1. Fanning J et al. Infect Dis Obstet Gynecol. 1998; 6(6):252-5 .
2. Schlenker JD and Hubay CA. Arch Surg 1973;107:846-50
3. Engoren M. Chest. 1995;107(1):81-4 .
4. Michael N et al. Chest. 2011;140(2):418-24
5. Wortel CH et al. Surgery. 1993;114(3):564-70 .
Docs fight back after losing hospital privileges, patients, and income
In April, a group of more than a dozen cardiologists at St. Louis Heart and Vascular (SLHV) lost their privileges at SSM Health, an eight-hospital system in St. Louis.
The physicians did not lose their privileges because of a clinical failure. Rather, it was because of SSM’s decision to enter into an exclusive contract with another set of cardiologists.
“The current situation is economically untenable for us,” said Harvey Serota, MD, founder and medical director of SLHV. “This is an existential threat to the practice.”
Because of the exclusive contract, many of SLHV’s patients are now being redirected to SSM-contracted cardiologists. Volume for the group’s new $15 million catheterization lab has plummeted. SLHV is suing SSM to restore its privileges, claiming lack of due process, restraint of trade, interference with its business, and breach of contract.
Losing privileges because a hospital seeks to increase their profits is becoming all too familiar for many independent specialists in fields such as cardiology, orthopedic surgery, and urology, as the hospitals that hosted them become their competitors and forge exclusive contracts with opposing groups.
What can these doctors do if they’re shut out? File a lawsuit, as SLHV has done? Demand a hearing before the medical staff and try to resolve the problem? Or simply give up their privileges and move on?
Unfortunately, none of these approaches offer a quick or certain solution, and each comes with risks.
Generally, courts have upheld hospitals’ use of exclusive contracts, which is also known as economic credentialing, says Barry F. Rosen, a health law attorney at Gordon Feinblatt, in Baltimore.
“Courts have long recognized exclusive contracts, and challenges by excluded doctors usually fail,” he says.
However, Mr. Rosen can cite several examples in which excluded doctors launched legal challenges that prevailed, owing to nuances in the law. The legal field in this area is tangled, and it varies by state.
Can hospitals make exclusive deals?
Hospitals have long used exclusive contracts for hospital-based specialists – anesthesiologists, radiologists, pathologists, emergency physicians, and hospitalists. They say that restricting patients to one group of anesthesiologists or radiologists enhances operational efficiency and that these contracts do not disrupt patients, because patients have no ties to hospital-based physicians. Such contracts are often more profitable for the hospital because of the negotiated rates.
Exclusive contracts in other specialties, however, are less accepted because they involve markedly different strategies and have different effects. In such cases, the hospital is no longer simply enhancing operational efficiency but is competing with physicians on staff, and the arrangement can disrupt the care of patients of the excluded doctors.
In the courts, these concerns might form the basis of an antitrust action or a claim of tortious interference with physicians’ ability to provide care for their patients, but neither claim is easy to win, Mr. Rosen says.
In antitrust cases, “the issue is not whether the excluded doctor was injured but whether the action harmed competition,” Mr. Rosen says. “Will the exclusion lead to higher prices?”
In the case of interference with patient care, “you will always find interference by one entity in the affairs of another,” he says, “but tortious interference applies to situations where something nefarious is going on, such as the other side was out to destroy your business and create a monopoly.”
Hospitals may try to restrict the privileges of physicians who invest in competing facilities such as cath labs and ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs), says Gregory Mertz, managing director of Physician Strategies Group, a consultancy in Virginia Beach.
“However, any revenge that a hospital might take against the doctors who started an ASC would usually not be publicly admitted,” Mr. Mertz says. “Revenge would be exacted in subtle ways.”
In the St. Louis situation, SSM did not cite SLHV’s cath lab as a reason for its exclusive contract. SSM stated in court documents that the decision was based on the recommendations of an expert panel. Furthermore, SSM said the board created the panel in response to a state report that cited the limited experience of some SLHV cardiologists in treating a rare type of heart attack.
Mr. Mertz says the board’s interest in the state’s concern and then its forming the special panel lent a great deal of legitimacy to SSM’s decision to start an exclusive contract. “SSM can show evidence that the board’s decision was based on a clinical matter and not on trying to squeeze out the cardiologists,” he says.
In SLHV’s defense, Dr. Serota says the practice offered to stop taking calls for the type of heart attack that was cited, but the hospital did not respond to its offer. He says SSM should have consulted the hospital’s medical staff to address the state’s concern and to create the exclusive contract, because these decisions involved clinical issues that the medical staff understands better than the board.
The law, however, does not require a hospital board to consult with its medical staff, says Alice G. Gosfield, a health care attorney in Philadelphia. “The board has ultimate legal control of everything in the hospital,” she says. However, the board often delegates certain functions to the medical staff in the hospital bylaws, and depending on the wording of the bylaws, it is still possible that the board violated the bylaws, Ms. Gosfield adds.
Can excluded physicians get peer review?
Can the hospital medical staff help restore the privileges of excluded physicians? Don’t these physicians have the right to peer review – a hearing before the medical staff?
Indeed, the Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals, states that the hospital must have “mechanisms, including a fair hearing and appeal process, for addressing adverse decisions for existing medical staff members and other individuals holding clinical privileges for renewal, revocation, or revision of clinical privileges.”
However, excluded physicians may not have a right to a hearing if they have not been fully stripped of privileges. SSM discontinued adult cardiology privileges for SLHV doctors but retained some doctors’ internal medicine privileges. Dr. Serota says internal medicine privileges are useless to cardiologists, but because the doctors’ privileges had not been fully removed, they cannot ask for a hearing.
More fundamentally, exclusive contracts are not a good fit for peer review. Mr. Rosen says the hearings were designed to review the physicians’ clinical competence or behavior, but excluded physicians do not have these problems. About all the hearing could focus on is the hospital’s policy, which the board would not want to allow. To avoid this, “the hospital might rule out a hearing as contrary to the intent of the bylaws,” Mr. Rosen says.
Furthermore, even if peer review goes forward, “what the medical staff decides is only advisory, and the hospital board makes the final decision,” Mr. Rosen says. He notes that the doctor could challenge the decision in court, but the hospital might still prevail.
Excluded physicians sometimes prevail
Although it is rare for excluded physicians to win a lawsuit against their hospital, it does happen, says Michael R. Callahan, health lawyer at Katten Muchin Rosenman, in Chicago.
Mr. Callahan cites a 2010 decision by the Arkansas Supreme Court that stopped the state’s largest health system from denying physicians’ privileges. Among other things, the hospital was found to have tortiously interfered with the physicians’ contracts with patients.
In a 2007 decision, a West Virginia court ruled that hospitals that have a mission to serve the public cannot exclude physicians for nonquality issues. In addition, some states, such as Texas, limit the economic factors that can be considered when credentialing decisions are made. Other states, such as Ohio, give hospitals a great deal of leeway to alter credentialing.
Dr. Serota is optimistic about his Missouri lawsuit. Although the judge in the case did not immediately grant SLHV’s request for restoration of privileges while the case proceeds, she did grant expedited discovery – allowing SLHV to obtain documents from SSM that could strengthen the doctors’ case – and she agreed to a hearing on SLHV’s request for a temporary restoration of privileges.
Ms. Gosfield says Dr. Serota’s optimism seems justified, but she adds that such cases cost a lot of money and that they may still not be winnable.
Often plaintiffs can settle lawsuits before they go to trial, but Mr. Callahan says hospitals are loath to restore privileges in a settlement because they don’t want to undermine an exclusivity deal. “The exclusive group expects a certain volume, which can’t be reached if the competing doctors are allowed back in,” he says.
Many physicians don’t challenge the exclusion
Quite often, excluded doctors decide not to challenge the decision. For example, Dr. Serota says groups of orthopedic surgeons and urologists have decided not to challenge similar decisions by SSM. “They wanted to move on,” he says.
Mr. Callahan says many excluded doctors also don’t even ask for a hearing. “They expect that the hospital’s decision will be upheld,” he says.
This was the case for Devendra K. Amin, MD, an independent cardiologist in Easton, Pa. Dr. Amin has not had any hospital privileges since July 2020. Even though he is board certified in interventional cardiology, which involves catheterization, Dr. Amin says he cannot perform these procedures because they can only be performed in a hospital in the area.
In the 1990s, Dr. Amin says, he had invasive cardiology privileges at five hospitals, but then those hospitals consolidated, and the remaining ones started constricting his privileges. First he could no longer work in the emergency department, then he could no longer read echocardiograms and interpret stress test results, because that work was assigned exclusively to employed doctors, he says.
Then the one remaining hospital announced that privileges would only be available to physicians by invitation, and he was not invited. Dr. Amin says he could have regained general cardiology privileges if he had accepted employment at the hospital, but he did not want to do this. A recruiter and the head of the cardiology section at the hospital even took him out to dinner 2 years ago to discuss employment, but there was a stipulation that the hospital would not agree to.
“I wanted to get back my interventional privileges back,” Dr. Amin says, “but they told me that would not be possible because they had an exclusive contract with a group.”
Dr. Amin says that now, he can only work as a general cardiologist with reduced volume. He says primary care physicians in the local hospital systems only refer to cardiologists within their systems. “When these patients do come to me, it is only because they specifically requested to see me,” Dr. Amin says.
He does not want to challenge the decisions regarding privileging. “Look, I am 68 years old,” Dr. Amin says. “I’m not retiring yet, but I don’t want to get into a battle with a hospital that has very deep pockets. I’m not a confrontational person to begin with, and I don’t want to spend the next 10 years of my life in litigation.”
Diverging expectations
The law on exclusive contracts does not provide easy answers for excluded doctors, and often it defies physicians’ conception of their own role in the hospital.
Many physicians expect the hospital to be a haven where they can do their work without being cut out by a competitor. This view is reinforced by organizations such as the American Medical Association.
The AMA Council on Medical Service states that privileges “can only be abridged upon recommendation of the medical staff and only for reason related to professional competence, adherence to standards of care, and other parameters agreed to by the medical staff.”
But the courts don’t tend to agree with that position. “Hospitals have a fiduciary duty to protect their own financial interests,” Mr. Callahan says. “This may involve anything that furthers the hospital’s mission to provide high-quality health care services to its patient community.”
At the same time, however, there are plenty of instances in which courts have ruled that exclusive contracts had gone too far. But usually it takes a lawyer experienced in these cases to know what those exceptions are.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In April, a group of more than a dozen cardiologists at St. Louis Heart and Vascular (SLHV) lost their privileges at SSM Health, an eight-hospital system in St. Louis.
The physicians did not lose their privileges because of a clinical failure. Rather, it was because of SSM’s decision to enter into an exclusive contract with another set of cardiologists.
“The current situation is economically untenable for us,” said Harvey Serota, MD, founder and medical director of SLHV. “This is an existential threat to the practice.”
Because of the exclusive contract, many of SLHV’s patients are now being redirected to SSM-contracted cardiologists. Volume for the group’s new $15 million catheterization lab has plummeted. SLHV is suing SSM to restore its privileges, claiming lack of due process, restraint of trade, interference with its business, and breach of contract.
Losing privileges because a hospital seeks to increase their profits is becoming all too familiar for many independent specialists in fields such as cardiology, orthopedic surgery, and urology, as the hospitals that hosted them become their competitors and forge exclusive contracts with opposing groups.
What can these doctors do if they’re shut out? File a lawsuit, as SLHV has done? Demand a hearing before the medical staff and try to resolve the problem? Or simply give up their privileges and move on?
Unfortunately, none of these approaches offer a quick or certain solution, and each comes with risks.
Generally, courts have upheld hospitals’ use of exclusive contracts, which is also known as economic credentialing, says Barry F. Rosen, a health law attorney at Gordon Feinblatt, in Baltimore.
“Courts have long recognized exclusive contracts, and challenges by excluded doctors usually fail,” he says.
However, Mr. Rosen can cite several examples in which excluded doctors launched legal challenges that prevailed, owing to nuances in the law. The legal field in this area is tangled, and it varies by state.
Can hospitals make exclusive deals?
Hospitals have long used exclusive contracts for hospital-based specialists – anesthesiologists, radiologists, pathologists, emergency physicians, and hospitalists. They say that restricting patients to one group of anesthesiologists or radiologists enhances operational efficiency and that these contracts do not disrupt patients, because patients have no ties to hospital-based physicians. Such contracts are often more profitable for the hospital because of the negotiated rates.
Exclusive contracts in other specialties, however, are less accepted because they involve markedly different strategies and have different effects. In such cases, the hospital is no longer simply enhancing operational efficiency but is competing with physicians on staff, and the arrangement can disrupt the care of patients of the excluded doctors.
In the courts, these concerns might form the basis of an antitrust action or a claim of tortious interference with physicians’ ability to provide care for their patients, but neither claim is easy to win, Mr. Rosen says.
In antitrust cases, “the issue is not whether the excluded doctor was injured but whether the action harmed competition,” Mr. Rosen says. “Will the exclusion lead to higher prices?”
In the case of interference with patient care, “you will always find interference by one entity in the affairs of another,” he says, “but tortious interference applies to situations where something nefarious is going on, such as the other side was out to destroy your business and create a monopoly.”
Hospitals may try to restrict the privileges of physicians who invest in competing facilities such as cath labs and ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs), says Gregory Mertz, managing director of Physician Strategies Group, a consultancy in Virginia Beach.
“However, any revenge that a hospital might take against the doctors who started an ASC would usually not be publicly admitted,” Mr. Mertz says. “Revenge would be exacted in subtle ways.”
In the St. Louis situation, SSM did not cite SLHV’s cath lab as a reason for its exclusive contract. SSM stated in court documents that the decision was based on the recommendations of an expert panel. Furthermore, SSM said the board created the panel in response to a state report that cited the limited experience of some SLHV cardiologists in treating a rare type of heart attack.
Mr. Mertz says the board’s interest in the state’s concern and then its forming the special panel lent a great deal of legitimacy to SSM’s decision to start an exclusive contract. “SSM can show evidence that the board’s decision was based on a clinical matter and not on trying to squeeze out the cardiologists,” he says.
In SLHV’s defense, Dr. Serota says the practice offered to stop taking calls for the type of heart attack that was cited, but the hospital did not respond to its offer. He says SSM should have consulted the hospital’s medical staff to address the state’s concern and to create the exclusive contract, because these decisions involved clinical issues that the medical staff understands better than the board.
The law, however, does not require a hospital board to consult with its medical staff, says Alice G. Gosfield, a health care attorney in Philadelphia. “The board has ultimate legal control of everything in the hospital,” she says. However, the board often delegates certain functions to the medical staff in the hospital bylaws, and depending on the wording of the bylaws, it is still possible that the board violated the bylaws, Ms. Gosfield adds.
Can excluded physicians get peer review?
Can the hospital medical staff help restore the privileges of excluded physicians? Don’t these physicians have the right to peer review – a hearing before the medical staff?
Indeed, the Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals, states that the hospital must have “mechanisms, including a fair hearing and appeal process, for addressing adverse decisions for existing medical staff members and other individuals holding clinical privileges for renewal, revocation, or revision of clinical privileges.”
However, excluded physicians may not have a right to a hearing if they have not been fully stripped of privileges. SSM discontinued adult cardiology privileges for SLHV doctors but retained some doctors’ internal medicine privileges. Dr. Serota says internal medicine privileges are useless to cardiologists, but because the doctors’ privileges had not been fully removed, they cannot ask for a hearing.
More fundamentally, exclusive contracts are not a good fit for peer review. Mr. Rosen says the hearings were designed to review the physicians’ clinical competence or behavior, but excluded physicians do not have these problems. About all the hearing could focus on is the hospital’s policy, which the board would not want to allow. To avoid this, “the hospital might rule out a hearing as contrary to the intent of the bylaws,” Mr. Rosen says.
Furthermore, even if peer review goes forward, “what the medical staff decides is only advisory, and the hospital board makes the final decision,” Mr. Rosen says. He notes that the doctor could challenge the decision in court, but the hospital might still prevail.
Excluded physicians sometimes prevail
Although it is rare for excluded physicians to win a lawsuit against their hospital, it does happen, says Michael R. Callahan, health lawyer at Katten Muchin Rosenman, in Chicago.
Mr. Callahan cites a 2010 decision by the Arkansas Supreme Court that stopped the state’s largest health system from denying physicians’ privileges. Among other things, the hospital was found to have tortiously interfered with the physicians’ contracts with patients.
In a 2007 decision, a West Virginia court ruled that hospitals that have a mission to serve the public cannot exclude physicians for nonquality issues. In addition, some states, such as Texas, limit the economic factors that can be considered when credentialing decisions are made. Other states, such as Ohio, give hospitals a great deal of leeway to alter credentialing.
Dr. Serota is optimistic about his Missouri lawsuit. Although the judge in the case did not immediately grant SLHV’s request for restoration of privileges while the case proceeds, she did grant expedited discovery – allowing SLHV to obtain documents from SSM that could strengthen the doctors’ case – and she agreed to a hearing on SLHV’s request for a temporary restoration of privileges.
Ms. Gosfield says Dr. Serota’s optimism seems justified, but she adds that such cases cost a lot of money and that they may still not be winnable.
Often plaintiffs can settle lawsuits before they go to trial, but Mr. Callahan says hospitals are loath to restore privileges in a settlement because they don’t want to undermine an exclusivity deal. “The exclusive group expects a certain volume, which can’t be reached if the competing doctors are allowed back in,” he says.
Many physicians don’t challenge the exclusion
Quite often, excluded doctors decide not to challenge the decision. For example, Dr. Serota says groups of orthopedic surgeons and urologists have decided not to challenge similar decisions by SSM. “They wanted to move on,” he says.
Mr. Callahan says many excluded doctors also don’t even ask for a hearing. “They expect that the hospital’s decision will be upheld,” he says.
This was the case for Devendra K. Amin, MD, an independent cardiologist in Easton, Pa. Dr. Amin has not had any hospital privileges since July 2020. Even though he is board certified in interventional cardiology, which involves catheterization, Dr. Amin says he cannot perform these procedures because they can only be performed in a hospital in the area.
In the 1990s, Dr. Amin says, he had invasive cardiology privileges at five hospitals, but then those hospitals consolidated, and the remaining ones started constricting his privileges. First he could no longer work in the emergency department, then he could no longer read echocardiograms and interpret stress test results, because that work was assigned exclusively to employed doctors, he says.
Then the one remaining hospital announced that privileges would only be available to physicians by invitation, and he was not invited. Dr. Amin says he could have regained general cardiology privileges if he had accepted employment at the hospital, but he did not want to do this. A recruiter and the head of the cardiology section at the hospital even took him out to dinner 2 years ago to discuss employment, but there was a stipulation that the hospital would not agree to.
“I wanted to get back my interventional privileges back,” Dr. Amin says, “but they told me that would not be possible because they had an exclusive contract with a group.”
Dr. Amin says that now, he can only work as a general cardiologist with reduced volume. He says primary care physicians in the local hospital systems only refer to cardiologists within their systems. “When these patients do come to me, it is only because they specifically requested to see me,” Dr. Amin says.
He does not want to challenge the decisions regarding privileging. “Look, I am 68 years old,” Dr. Amin says. “I’m not retiring yet, but I don’t want to get into a battle with a hospital that has very deep pockets. I’m not a confrontational person to begin with, and I don’t want to spend the next 10 years of my life in litigation.”
Diverging expectations
The law on exclusive contracts does not provide easy answers for excluded doctors, and often it defies physicians’ conception of their own role in the hospital.
Many physicians expect the hospital to be a haven where they can do their work without being cut out by a competitor. This view is reinforced by organizations such as the American Medical Association.
The AMA Council on Medical Service states that privileges “can only be abridged upon recommendation of the medical staff and only for reason related to professional competence, adherence to standards of care, and other parameters agreed to by the medical staff.”
But the courts don’t tend to agree with that position. “Hospitals have a fiduciary duty to protect their own financial interests,” Mr. Callahan says. “This may involve anything that furthers the hospital’s mission to provide high-quality health care services to its patient community.”
At the same time, however, there are plenty of instances in which courts have ruled that exclusive contracts had gone too far. But usually it takes a lawyer experienced in these cases to know what those exceptions are.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In April, a group of more than a dozen cardiologists at St. Louis Heart and Vascular (SLHV) lost their privileges at SSM Health, an eight-hospital system in St. Louis.
The physicians did not lose their privileges because of a clinical failure. Rather, it was because of SSM’s decision to enter into an exclusive contract with another set of cardiologists.
“The current situation is economically untenable for us,” said Harvey Serota, MD, founder and medical director of SLHV. “This is an existential threat to the practice.”
Because of the exclusive contract, many of SLHV’s patients are now being redirected to SSM-contracted cardiologists. Volume for the group’s new $15 million catheterization lab has plummeted. SLHV is suing SSM to restore its privileges, claiming lack of due process, restraint of trade, interference with its business, and breach of contract.
Losing privileges because a hospital seeks to increase their profits is becoming all too familiar for many independent specialists in fields such as cardiology, orthopedic surgery, and urology, as the hospitals that hosted them become their competitors and forge exclusive contracts with opposing groups.
What can these doctors do if they’re shut out? File a lawsuit, as SLHV has done? Demand a hearing before the medical staff and try to resolve the problem? Or simply give up their privileges and move on?
Unfortunately, none of these approaches offer a quick or certain solution, and each comes with risks.
Generally, courts have upheld hospitals’ use of exclusive contracts, which is also known as economic credentialing, says Barry F. Rosen, a health law attorney at Gordon Feinblatt, in Baltimore.
“Courts have long recognized exclusive contracts, and challenges by excluded doctors usually fail,” he says.
However, Mr. Rosen can cite several examples in which excluded doctors launched legal challenges that prevailed, owing to nuances in the law. The legal field in this area is tangled, and it varies by state.
Can hospitals make exclusive deals?
Hospitals have long used exclusive contracts for hospital-based specialists – anesthesiologists, radiologists, pathologists, emergency physicians, and hospitalists. They say that restricting patients to one group of anesthesiologists or radiologists enhances operational efficiency and that these contracts do not disrupt patients, because patients have no ties to hospital-based physicians. Such contracts are often more profitable for the hospital because of the negotiated rates.
Exclusive contracts in other specialties, however, are less accepted because they involve markedly different strategies and have different effects. In such cases, the hospital is no longer simply enhancing operational efficiency but is competing with physicians on staff, and the arrangement can disrupt the care of patients of the excluded doctors.
In the courts, these concerns might form the basis of an antitrust action or a claim of tortious interference with physicians’ ability to provide care for their patients, but neither claim is easy to win, Mr. Rosen says.
In antitrust cases, “the issue is not whether the excluded doctor was injured but whether the action harmed competition,” Mr. Rosen says. “Will the exclusion lead to higher prices?”
In the case of interference with patient care, “you will always find interference by one entity in the affairs of another,” he says, “but tortious interference applies to situations where something nefarious is going on, such as the other side was out to destroy your business and create a monopoly.”
Hospitals may try to restrict the privileges of physicians who invest in competing facilities such as cath labs and ambulatory surgery centers (ASCs), says Gregory Mertz, managing director of Physician Strategies Group, a consultancy in Virginia Beach.
“However, any revenge that a hospital might take against the doctors who started an ASC would usually not be publicly admitted,” Mr. Mertz says. “Revenge would be exacted in subtle ways.”
In the St. Louis situation, SSM did not cite SLHV’s cath lab as a reason for its exclusive contract. SSM stated in court documents that the decision was based on the recommendations of an expert panel. Furthermore, SSM said the board created the panel in response to a state report that cited the limited experience of some SLHV cardiologists in treating a rare type of heart attack.
Mr. Mertz says the board’s interest in the state’s concern and then its forming the special panel lent a great deal of legitimacy to SSM’s decision to start an exclusive contract. “SSM can show evidence that the board’s decision was based on a clinical matter and not on trying to squeeze out the cardiologists,” he says.
In SLHV’s defense, Dr. Serota says the practice offered to stop taking calls for the type of heart attack that was cited, but the hospital did not respond to its offer. He says SSM should have consulted the hospital’s medical staff to address the state’s concern and to create the exclusive contract, because these decisions involved clinical issues that the medical staff understands better than the board.
The law, however, does not require a hospital board to consult with its medical staff, says Alice G. Gosfield, a health care attorney in Philadelphia. “The board has ultimate legal control of everything in the hospital,” she says. However, the board often delegates certain functions to the medical staff in the hospital bylaws, and depending on the wording of the bylaws, it is still possible that the board violated the bylaws, Ms. Gosfield adds.
Can excluded physicians get peer review?
Can the hospital medical staff help restore the privileges of excluded physicians? Don’t these physicians have the right to peer review – a hearing before the medical staff?
Indeed, the Joint Commission, which accredits hospitals, states that the hospital must have “mechanisms, including a fair hearing and appeal process, for addressing adverse decisions for existing medical staff members and other individuals holding clinical privileges for renewal, revocation, or revision of clinical privileges.”
However, excluded physicians may not have a right to a hearing if they have not been fully stripped of privileges. SSM discontinued adult cardiology privileges for SLHV doctors but retained some doctors’ internal medicine privileges. Dr. Serota says internal medicine privileges are useless to cardiologists, but because the doctors’ privileges had not been fully removed, they cannot ask for a hearing.
More fundamentally, exclusive contracts are not a good fit for peer review. Mr. Rosen says the hearings were designed to review the physicians’ clinical competence or behavior, but excluded physicians do not have these problems. About all the hearing could focus on is the hospital’s policy, which the board would not want to allow. To avoid this, “the hospital might rule out a hearing as contrary to the intent of the bylaws,” Mr. Rosen says.
Furthermore, even if peer review goes forward, “what the medical staff decides is only advisory, and the hospital board makes the final decision,” Mr. Rosen says. He notes that the doctor could challenge the decision in court, but the hospital might still prevail.
Excluded physicians sometimes prevail
Although it is rare for excluded physicians to win a lawsuit against their hospital, it does happen, says Michael R. Callahan, health lawyer at Katten Muchin Rosenman, in Chicago.
Mr. Callahan cites a 2010 decision by the Arkansas Supreme Court that stopped the state’s largest health system from denying physicians’ privileges. Among other things, the hospital was found to have tortiously interfered with the physicians’ contracts with patients.
In a 2007 decision, a West Virginia court ruled that hospitals that have a mission to serve the public cannot exclude physicians for nonquality issues. In addition, some states, such as Texas, limit the economic factors that can be considered when credentialing decisions are made. Other states, such as Ohio, give hospitals a great deal of leeway to alter credentialing.
Dr. Serota is optimistic about his Missouri lawsuit. Although the judge in the case did not immediately grant SLHV’s request for restoration of privileges while the case proceeds, she did grant expedited discovery – allowing SLHV to obtain documents from SSM that could strengthen the doctors’ case – and she agreed to a hearing on SLHV’s request for a temporary restoration of privileges.
Ms. Gosfield says Dr. Serota’s optimism seems justified, but she adds that such cases cost a lot of money and that they may still not be winnable.
Often plaintiffs can settle lawsuits before they go to trial, but Mr. Callahan says hospitals are loath to restore privileges in a settlement because they don’t want to undermine an exclusivity deal. “The exclusive group expects a certain volume, which can’t be reached if the competing doctors are allowed back in,” he says.
Many physicians don’t challenge the exclusion
Quite often, excluded doctors decide not to challenge the decision. For example, Dr. Serota says groups of orthopedic surgeons and urologists have decided not to challenge similar decisions by SSM. “They wanted to move on,” he says.
Mr. Callahan says many excluded doctors also don’t even ask for a hearing. “They expect that the hospital’s decision will be upheld,” he says.
This was the case for Devendra K. Amin, MD, an independent cardiologist in Easton, Pa. Dr. Amin has not had any hospital privileges since July 2020. Even though he is board certified in interventional cardiology, which involves catheterization, Dr. Amin says he cannot perform these procedures because they can only be performed in a hospital in the area.
In the 1990s, Dr. Amin says, he had invasive cardiology privileges at five hospitals, but then those hospitals consolidated, and the remaining ones started constricting his privileges. First he could no longer work in the emergency department, then he could no longer read echocardiograms and interpret stress test results, because that work was assigned exclusively to employed doctors, he says.
Then the one remaining hospital announced that privileges would only be available to physicians by invitation, and he was not invited. Dr. Amin says he could have regained general cardiology privileges if he had accepted employment at the hospital, but he did not want to do this. A recruiter and the head of the cardiology section at the hospital even took him out to dinner 2 years ago to discuss employment, but there was a stipulation that the hospital would not agree to.
“I wanted to get back my interventional privileges back,” Dr. Amin says, “but they told me that would not be possible because they had an exclusive contract with a group.”
Dr. Amin says that now, he can only work as a general cardiologist with reduced volume. He says primary care physicians in the local hospital systems only refer to cardiologists within their systems. “When these patients do come to me, it is only because they specifically requested to see me,” Dr. Amin says.
He does not want to challenge the decisions regarding privileging. “Look, I am 68 years old,” Dr. Amin says. “I’m not retiring yet, but I don’t want to get into a battle with a hospital that has very deep pockets. I’m not a confrontational person to begin with, and I don’t want to spend the next 10 years of my life in litigation.”
Diverging expectations
The law on exclusive contracts does not provide easy answers for excluded doctors, and often it defies physicians’ conception of their own role in the hospital.
Many physicians expect the hospital to be a haven where they can do their work without being cut out by a competitor. This view is reinforced by organizations such as the American Medical Association.
The AMA Council on Medical Service states that privileges “can only be abridged upon recommendation of the medical staff and only for reason related to professional competence, adherence to standards of care, and other parameters agreed to by the medical staff.”
But the courts don’t tend to agree with that position. “Hospitals have a fiduciary duty to protect their own financial interests,” Mr. Callahan says. “This may involve anything that furthers the hospital’s mission to provide high-quality health care services to its patient community.”
At the same time, however, there are plenty of instances in which courts have ruled that exclusive contracts had gone too far. But usually it takes a lawyer experienced in these cases to know what those exceptions are.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Thousands of patients were implanted with heart pumps that the FDA knew could be dangerous
John Winkler II was dying of heart failure when doctors came to his hospital bedside, offering a chance to prolong his life. The HeartWare Ventricular Assist Device, or HVAD, could be implanted in Winkler’s chest until a transplant was possible. The heart pump came with disclaimers of risk, but Winkler wanted to fight for time. He was only 46 and had a loving wife and four children, and his second grandchild was on the way.
So, in August 2014, Winkler had surgery to implant the device. A golf-ball–sized rotor was attached to his left ventricle to pump blood through a tube and into his aorta. A cable threading out of a small incision in his waist connected to a battery-powered controller strapped to his body. If something went wrong, an alarm as loud as a fire drill would sound.
Winkler returned home weeks later and, as he regained his strength, became hopeful about the future. He started making plans to visit colleges with his daughter, and was able to host his parents and new grandchild for Christmas. “He was doing so much better,” his wife, Tina Winkler, said. “We thought he was coasting until he got his transplant.”
What John Winkler didn’t know: Months before his implant, the Food and Drug Administration put HeartWare on notice for not properly monitoring or repairing HVAD defects, such as faulty batteries and short circuits caused by static electricity, that had killed patients. The agency issued a warning letter, one of its most serious citations. It demanded fixes within 15 days, but took no decisive action as problems persisted.
Ten days after Christmas of 2014, Winkler’s two teenage children heard the HVAD’s piercing alarm and ran upstairs. They found their father collapsed on his bedroom floor, completely unresponsive. Kelly, 17, dropped to his side and tried to copy how people on television did CPR. She told her brother to call 911, and over the device’s siren did her best to hear instructions from the operator.
When paramedics arrived and assessed her father, one made a passing comment that has haunted Kelly ever since: “Well, his toes are already cold.” He died 2 days later. Medtronic, the company that acquired HeartWare in 2016, settled a lawsuit by the family last year, admitting no fault. Tina Winkler believes her children blamed themselves for their father’s death. “Those two kids have never been the same,” she said. “I think they feel like they didn’t do things they needed to do.”
But it was the FDA that failed to protect Winkler and thousands of other patients whose survival depended on the HVAD, a ProPublica investigation found.
As HeartWare and Medtronic failed inspection after inspection and reports of device-related deaths piled up, the FDA relied on the device makers to fix the problems voluntarily rather than compelling them to do so.
The HVAD was implanted into more than 19,000 patients, the majority of whom got it after the FDA found in 2014 that the device didn’t meet federal standards. By the end of last year, the agency had received more than 3,000 reports of patient deaths that may have been caused or contributed to by the device.
Among them were reports of deaths the company linked to serious device problems: a patient who vomited blood as a family member struggled to restart a defective HVAD; a patient who bled out internally and died after implant surgery because a tube attached to the pump tore open; a patient whose heart tissue was left charred after an HVAD short-circuited and voltage surged through the pump.
The ineffective regulatory oversight of the HVAD is emblematic of larger, more systemic weaknesses.
For decades, the FDA and its Center for Devices and Radiological Health have been responsible for ensuring that high-risk medical devices are safe and effective. Yet they rely mostly on manufacturers to identify and correct problems. The agency says it can seize products, order injunctions against companies, or issue fines, but it rarely does so, preferring instead for companies to make fixes voluntarily.
When federal investigators found repeated manufacturing issues with the HVAD for years, the FDA didn’t penalize the company, even as the company issued 15 serious recalls of the device starting in 2014, the most of any single high-risk device in the FDA’s database. Thousands of patients with recalled models needed to have external HVAD parts replaced or take extra caution while handling their devices and monitor them for signs of malfunctions that could cause injury or death.
Meanwhile, the processes to inform the public through formal FDA notices and messages to health care providers repeatedly failed and left patients in the dark about known problems with the HVAD.
“Patients have no idea, and they rely on the FDA to ensure the safety and effectiveness of high-risk devices,” said Dr. Rita Redberg, a cardiologist at the University of California, San Francisco, who studies medical device regulation. “How can you not take action on a warning letter with these serious issues with very sick patients?”
In response to ProPublica’s findings, the FDA said it had been closely monitoring issues with the HVAD. It said that after Medtronic acquired HeartWare in 2016, it met with the company more than 100 times to ensure problems were being fixed and to review safety concerns related to the heart pump. The agency also said it initiated formal reviews of new device modifications and continually tracked whether the HVAD had a “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness.”
“Our decisions that we made along the way have always been patient focused,” said Dr. William Maisel, director of product evaluation and quality at the FDA’s device division. He added that more than 80% of companies fix their problems by the time the FDA reinspects.
That did not happen with the HVAD. In 2016 and 2018, inspectors found that issues detailed in the 2014 warning letter remained unresolved. Medtronic told the FDA last year that it had fixed the problems, but, before the agency could verify the claim, inspections were paused because of the coronavirus pandemic.
In June, Medtronic stopped HVAD sales and implants. The company conceded that a competing device was safer after a new study showed the HVAD had higher rates of death and neurological injury. Medtronic also cited a 12-year-old problem with its devices not restarting if they disconnect from power, leaving patients’ hearts without support.
Medtronic declined to make Geoffrey Martha, CEO, or Nnamdi Njoku, president of mechanical heart support, available for interviews. In an email, a spokesperson said, “There is nothing more important to Medtronic than the safety and well-being of patients.”
The email continued: “Medtronic takes this matter very seriously and, over the past five years, we have worked closely with FDA and engaged external experts to resolve the issues noted in the warning letter. FDA is aware of the steps Medtronic has taken to address the underlying concerns.”
The company said it will have a support system in place for the 4,000 patients worldwide and 2,000 in the United States who still rely on the HVAD. Medtronic will station 20 specialists across the globe to help with device maintenance and patient education. A centralized engineering team will provide technical support and troubleshooting for patients and medical staff. Medtronic said it will offer financial assistance if insurance doesn’t fully cover the surgery to replace a device with a competing product, but only if a doctor decides it’s medically necessary.
Patients with HVADs have little choice but to hope the devices keep working: The surgery to remove HVADs is so risky that both Medtronic and the FDA advise against it. The device is meant to be left in place until its wearer gets a heart transplant. Or dies.
Warning signs
In late 2012, HeartWare, then an independent company headquartered in Massachusetts, won FDA approval to sell a new device that could keep heart failure patients alive and mobile while awaiting a transplant.
A competing device, the HeartMate, was already gaining attention, with high-profile patients like former Vice President Dick Cheney, a heart attack survivor who eventually got a transplant after using the device for 20 months.
The HVAD offered a smaller option that could even be used in children, and it led to a string of publicized successes. A fitness model was able to return to the gym. A 13-year-old with heart defects could attend school again. Medtronic’s YouTube page features 16 interviews with grateful patients and families.
The patients who received HVADs had already been in grave peril. They had advanced heart failure, serious enough to need blood pumped out of their hearts artificially. Most patients were older than 50, but there were also younger patients with heart defects or other cardiac conditions. The device provided help but brought its own risks. Implanting it required invasive open-heart surgery, and clots could develop inside the pump, which, in the worst cases, led to deadly strokes.
The device also came with a steep price tag. Each HVAD cost about $80,000, and, even though HeartWare never made a profit as an independent company, in 2015 device sales brought in $276 million in revenue.
For many severe heart failure patients, the opportunity to survive longer and return to normal life made the device worth the risks and cost.
But patients were unaware the FDA started finding manufacturing issues at HeartWare’s Miami Lakes, Florida, plant as early as 2011, when the device was still seeking approval.
Among the findings, a federal inspector expressed concerns that engineering staff “were not completely reviewing documents before approving them” and found one employee assigned to monitoring device quality had missed several required monthly trainings. HeartWare leadership promised quick corrective action, according to FDA documents.
Then, in 2014, the FDA found more serious lapses, detailed in federal inspection reports.
For example, HeartWare knew of 119 instances in which batteries failed unexpectedly, which could leave the pump powerless, stopping support for the patient’s heart. But the company didn’t test the batteries in inventory for defects, or the batteries of current patients, even though one person’s death had already been linked to battery failure.
The company also received complaints that static electricity could short-circuit its devices. It learned of at least 27 such cases between 2010 and 2013, including four that resulted in serious injuries and two that led to death. HVAD patients would need to avoid contact with certain household objects like televisions or vacuum cleaners — anything that could create strong static electricity. HeartWare added warnings to the patient manual and redesigned its shield to protect the device controller, but the FDA found that the company didn’t replace shields for devices already being used by current patients or produced and sitting in inventory.
Continuing quality control concerns led to the FDA warning letter in June 2014. The document labeled the HVAD as “adulterated,” meaning the device did not meet federal manufacturing standards. The agency gave HeartWare 15 days to correct the problems or face regulatory action.
Still, investment analysts who followed HeartWare believed the warning posed little risk to the company’s business prospects. One described it as being “as benign as possible.”
The 15-day deadline passed, and the FDA never penalized the company.
The agency told ProPublica it had provided additional time because HeartWare was a relatively new manufacturer and the HVAD was a complicated device. It also said it avoided punitive action to make sure patients with severe heart failure had access to this treatment option. “We’re talking about the sickest of the sick patients who really have very few alternatives,” Maisel, the head of device quality, said.
But the HeartMate, the competing device, was available and already being used by the majority of patients. When Medtronic stopped HVAD sales, both companies said the HeartMate could fill the gap.
Inspectors continued to find problems at HeartWare facilities in 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018. In the most recent report in 2018, inspectors identified seven separate violations at the HVAD plant, including three previously cited in the 2014 warning letter. The company was still mishandling newly discovered defects like pins connecting the controller to a power source that could bend and become unusable, and controllers built with incompatible parts that could chemically react and “attack” the plastic exterior.
Again, the inspection report said the company “promised to correct” the issues.
“What penalty is there for noncompliance? There isn’t one,” said Madris Kinard, a former public health analyst with the FDA and the CEO of Device Events, a software company that analyzes FDA device data. “There’s nothing the FDA is doing that penalizes, in any true sense of the matter, the manufacturer.”
By the time sales were halted last month, the HVAD had become the subject of 15 company-initiated “Class I” recalls for dangerous device problems that could cause injury or death.
One recall came with a warning sent to health care providers in December that said pumps were failing to start up properly. The pattern of malfunctions was almost as old as the device itself, the company later admitted when it halted device sales in June. But even recent patients were completely unaware of the problem.
“A no-brainer”
When children asked Latoya Johnson Keelen about the cable that came out of her side and connected to a controller on her hip, she told them she was Iron Woman.
For a while, she felt invulnerable with the HVAD on her heart.
Johnson Keelen, who lives in the Atlanta suburbs, learned she needed the device after delivering her fourth child, Isaiah, in early 2018. Doctors diagnosed her with postpartum cardiomyopathy, a rare and mysterious form of heart failure that afflicts mothers during pregnancy or after birth. Black mothers in the South have among the highest rates of the illness. Some mothers quickly regain heart function, some only partially recuperate and others never recover.
Tests showed that Johnson Keelen, then 42, was suddenly in end-stage heart failure.
Her body’s immune response at the time was too strong for her to receive a heart transplant. Doctors gave her two choices: an HVAD or end-of-life hospice care.
“It became a no-brainer,” she said. “I just had a baby. I just gave birth. I’m not ready to plan for a funeral.”
Johnson Keelen, a woman of faith, believed God would heal her, either through a medical advancement or a miracle. She thought the HVAD was the answer.
Living with a life-sustaining medical device was difficult at first for the fiercely independent mother. She had to leave her job as a public health communications specialist, ask her older sons to change her bandages and lean heavily on her new husband, only a year into their marriage.
But, for about three years, she found comfort in the soft humming of the HVAD’s spinning rotor at night. It served as a lullaby for her new baby when he lay on her chest.
She said she was never told about the manufacturing problems the FDA repeatedly found at HeartWare’s facilities or about device recalls, including one sent to patients in December 2020. The notice said the device sometimes wouldn’t restart properly, which had led to two patient deaths at that point. It warned that current patients should always keep at least one power source, a battery or an AC or DC adapter, connected at all times to avoid the need for a restart.
Two months after that notice, Johnson Keelen was getting her kids ready for school when the HVAD’s low-battery alarm blared. She had unplugged the battery to replace it without realizing her wall adapter was disconnected.
Once before, Johnson Keelen had simply plugged the charger back into the outlet and her device restarted. But this time it wouldn’t.
As an emergency alarm sounded, she called the ventricular-assist team assigned to her case, and a specialist directed her to switch out the device controller.
Nothing changed, and panic crept into the voice on the phone.
An ambulance took Johnson Keelen to a hospital where medical staff used several backup controllers to try to start the pump.
Still nothing.
Doctors and nurses tried to keep calm, but Johnson Keelen could see fear and shock on their faces. Without the HVAD, her only options were a transplant or a completely new pump.
Doctors scurried to locate a donor heart and airlifted her for an emergency transplant. But while running tests, the medical team was stunned to find that Johnson Keelen’s miracle had occurred: Her heart was once again pumping blood on its own.
She had a new choice. She could avoid the risks of transplant rejection and open heart surgery during the pandemic by leaving the device on her functioning heart, while cutting the wires, removing the external components and sealing the pump.
She chose to trust her newly functioning heart, and leave the decommissioned HVAD inside her.
Three months later, when Medtronic said it was stopping HeartWare sales and implants, its announcement cited the problem with pumps not restarting among the reasons.
Company-led oversight
If evidence suggests a medical device may be linked to a serious patient injury or death, hospitals and other health care facilities must submit a report to the manufacturer and the FDA. Device companies must also submit reports if they learn independently of any incidents.
By the end of 2020, roughly 3,000 death reports and 20,000 injury reports related to the HVAD had been filed with the FDA.
Any details that could identify patients, like their age or gender, are removed from the publicly available reports. Most only have limited details about circumstances surrounding deaths or injuries. But it’s clear from the reports on the HVAD that some of these outcomes could be linked to problems previously identified by FDA inspectors.
Doctors attempted CPR for two hours after an electrostatic shock short-circuited one patient’s device in 2014, a few months after the FDA inspection that year. An autopsy revealed voltage had caused “deep charring” of the tissue inside the patient’s chest.
Friends found another patient dead in the kitchen, with groceries still on the counter, in 2018 after their device, which did not have the recommended static shield, short-circuited.
Last year, paramedics found a patient with the device disconnected from power. They struggled to restart the device, but it wouldn’t plug back into the power source because the connector pins were bent. The patient would die at the hospital.
In most cases, the FDA turned to the company to investigate whether a malfunction caused or contributed to the incidents.
But the FDA has long known HeartWare and Medtronic could not be relied on to properly submit HVAD incident reports.
In 2014, the FDA cited HeartWare because in at least 10 cases, there were no documents showing the company attempted to investigate.
In 2016, the agency wrote another citation when the company was late in reporting more than 200 cases, some more than a year past their 30-day reporting deadlines, and failed to report malfunctions that occurred during clinical trials.
The FDA told ProPublica the agency increased its monitoring of HVAD reports, and Medtronic hired new employees to submit timely reports. But by 2018, its backlog had only grown, with 677 late case filings. Again, the FDA did nothing beyond telling the company to fix the problem and further increasing its monitoring.
In an email, Medtronic said it “has robust systems in place to monitor the safety of all of our products, including the HVAD device.”
The email said, “When any potential safety issues are identified, those issues are thoroughly investigated and relevant information is shared with regulators and healthcare providers.” The company didn’t respond to the pattern of late reports and incomplete investigations identified in FDA inspections.
Maisel, the director of FDA device evaluation and quality, once criticized asking companies to investigate their own devices. In 2008, as a practicing cardiologist, he testified to the U.S. House oversight committee about his concerns.
“In the majority of cases, FDA relies on industry to identify, correct and report the problems,” he said. “But there is obviously an inherent financial conflict of interest for the manufacturers, sometimes measured in billions of dollars.”
Maisel has since had a change of heart. When asked about his 2008 testimony, he told ProPublica that he now believes the regulatory system “generally serves patients well” and “most companies are well intentioned.”
HeartWare’s track record of questionable investigations was glaring in John Winkler II’s case.
A report submitted by HeartWare that matches the dates and details of Winkler’s case shows the company decided there was “no indication of any device malfunctions.” It told the FDA that the device couldn’t be removed from the body because the hospital said his family declined an autopsy. HeartWare added that the evidence of the device’s role in Winkler’s death was inconclusive.
Yet little of this appears to be true. Documents reviewed by ProPublica show an autopsy of the heart and lungs was performed a day after the death. Tina Winkler said she was told the pump was removed from her husband’s body and was available for inspection.
A year after John Winkler’s death, HeartWare recalled 18,000 potentially faulty batteries produced between 2013 and 2015. Tina Winkler came across the notice online and found her husband’s battery serial numbers on the list. The company never contacted her about it or any further investigation, she said.
Rewards, not penalties
As deaths and recalls mounted, HeartWare and Medtronic touted additional FDA approval to treat more patients and their attempts to develop new cutting-edge devices.
With the company on notice under the 2014 warning letter, HeartWare geared up to begin human trials on a smaller heart pump, called the MVAD or Miniaturized Ventricular Assist Device. It would be powered by a new algorithm to more efficiently pump blood. Industry analysts predicted robust sales.
In July 2015, implantations were set to begin on a select group of 60 patients in Europe and Australia. But they were abruptly stopped less than two months later after only 11 implants. Patients experienced numerous adverse events, including major bleeding, infection and device malfunction, according to published data.
HeartWare’s stock price plummeted from about $85 to $35 by October 2015. The next year, Medtronic bought HeartWare for $1.1 billion, replacing much of the company’s leadership shortly after.
Some former HeartWare investors filed a class action lawsuit in January 2016 alleging deception in the development of the MVAD.
According to the accounts of six anonymous former employees in the lawsuit, the details mirror the scandal surrounding Theranos, the former blood test company charged with fraud for raising more than $700 million by allegedly lying about its technology.
Where Theranos made empty promises of a test that only needed a few drops of blood, the suit alleges HeartWare promoted a life-sustaining medical device that former employees said had many problems and actually worsened blood flow, increasing clotting risks.
“Nothing really worked right,” one former HeartWare manager said in the lawsuit, citing “improper alarms, improper touch screen performance, gibberish on display screens — just so many alerts and problems.”
Leadership proceeded with human testing anyway, the suit alleges.
Months later, at an investor conference, HeartWare leadership acknowledged the pump and algorithm led to multiple adverse events. For two patients in particular, the algorithm would direct the pump to speed up so fast that it would try to suck up more blood than was available inside the heart for prolonged periods of time.
HeartWare and Medtronic settled the investor suit for $54.5 million in 2018, admitting no fault.
None of the allegations slowed the FDA as it gave Medtronic additional approval and support for its heart pump technologies.
In September 2017, the agency approved the HVAD as “destination therapy” for patients who were not heart transplant candidates and would rely on the device for the rest of their lives.
“We’re really excited about our HVAD destination therapy approval,” a Medtronic executive said on an investor earnings call. “That’s a real game changer for us in that market.”
Two years later, Medtronic announced it was developing a fully implantable version of the HVAD that would no longer need a cable coming through the waist to connect to power.
Even though issues with the HeartWare device had been unresolved for five years at that point, the FDA accepted the pitch into its new fast-track approval process for high-risk devices.
“Slipped Through The Cracks”
After Johnson Keelen’s pump failed in February, she found a news story about the recall notice sent to medical providers two months prior.
It said the company had identified a problem with pump restarts that could cause heart attacks or serious patient harm. Nineteen patients had been seriously injured so far, and two people had died. The recall warned that patients should be careful to avoid disconnecting the device’s power sources.
“I kept seeing Medtronic on record saying they notified patients,” Johnson Keelen said. “Who did they contact? No one told me.”
Her doctor later told her she must have “slipped through the cracks,” she said.
The current system for informing patients of new safety concerns with high-risk devices relies on a communication chain that can easily break. The device company contacts the FDA and health care providers that work with device patients. The FDA typically issues a public notice, while health professionals contact their patients.
But the agency admits most patients don’t know to look for formal FDA postings. And, experts say, the medical system can lose track of who needs to be notified, especially if a patient moves or switches primary care physicians.
Tina Winkler still wonders why she was never told about FDA-known safety issues with the HVAD. She said her husband’s medical team “had to teach me how to clean his wound, how to change his batteries and what to do if alarms go off. And they never mentioned any of this.”
She said, “If we had all the facts, there’s no way he would have gotten that device implanted in his heart.”
When FDA inspectors find serious safety issues with a medical device, inspection reports are not posted online or sent to patients. The public can obtain reports through a Freedom of Information Act request, but the agency’s records department has said new requests can be stuck behind a year-long backlog.
Patients can find warning letters online in a searchable database of thousands of letters from different FDA divisions, including the center for devices. But HeartWare’s 2014 letter is no longer available for public review because the website purges letters older than five years.
There are also few documents available in state courts about faulty products, because of restrictions on lawsuits related to medical devices. The restrictions date back to a 2008 Supreme Court decision in a case against Medtronic. The court found that U.S. law bars patients and their survivors from suing device makers in state court, essentially because their products go through such a rigorous FDA approval process.
Two recent patient lawsuits against HeartWare and Medtronic, including one filed by Tina Winkler, were moved from state court to federal court. In both cases, Medtronic filed to dismiss the cases because of the U.S. law that protects device companies. Medtronic and the families reached private settlements soon after.
Winkler and an attorney for the other family said they could not comment on their settlements.
Johnson Keelen, with a decommissioned HVAD still attached to her heart, wonders what that means for her and other patients’ chances of recourse.
“Why isn’t anyone now stepping up for the patient?” she asked. “They are now liable for taking care of us because we relied on them.”
“Run its course”
Deserae Cain, 33, is one of the 4,000 patients still relying on a HeartWare device.
She was implanted with the heart pump in late 2017, after suddenly being diagnosed with heart failure. Scans showed her heart was three times normal size. It took time for her to come to terms with needing a life-sustaining device — not long before her diagnosis, she had been going on five-mile runs. In the four years since, though, Cain has built a life around the HVAD with her fiance in their Dayton, Ohio, home.
They know the device can malfunction. In 2019, the pump failed for almost an hour as doctors at a nearby hospital struggled to restart it. Cain just tried to stay calm, knowing anxiety could threaten her unsupported weak heart. Months later, she needed an emergency experimental procedure to clear out blood clots developed within her HVAD.
Then, in 2020, Cain developed a widespread infection. Doctors told her she needed surgery to clean out and replace the pump.
Cain asked her medical team if she could switch to the alternative HeartMate device, which other patients told her presented fewer problems, she said. Doctors said the HVAD was better suited for her smaller frame.
But her new pump had problems soon after the surgery.
The device’s suction alarms, which alert when the pump is trying to pull in more blood than is available within the heart, sounded multiple times a day, for hours at a time, she said. Baffled by the issue for months, her medical team eventually turned off that specific alarm.
Soon after, her ventricular-assist specialist called her about a patient’s death linked to the belt that holds the device controller, she said. The belt had ripped and the equipment had fallen, yanking on the cable that connected the controller to the pump. Cain replaced her belt but it quickly frayed and had to be replaced again within six weeks.
Then, in June, she found out about Medtronic’s decision to stop sales and implants. Cain received a letter from her hospital mentioning a Medtronic support program, but it provided few specifics.
Cain wondered if things would be any different than before. Anxious about her future, she asked: “Are they just going to let it run its course until there is none of us left?”
This article first appeared on Propublica.
John Winkler II was dying of heart failure when doctors came to his hospital bedside, offering a chance to prolong his life. The HeartWare Ventricular Assist Device, or HVAD, could be implanted in Winkler’s chest until a transplant was possible. The heart pump came with disclaimers of risk, but Winkler wanted to fight for time. He was only 46 and had a loving wife and four children, and his second grandchild was on the way.
So, in August 2014, Winkler had surgery to implant the device. A golf-ball–sized rotor was attached to his left ventricle to pump blood through a tube and into his aorta. A cable threading out of a small incision in his waist connected to a battery-powered controller strapped to his body. If something went wrong, an alarm as loud as a fire drill would sound.
Winkler returned home weeks later and, as he regained his strength, became hopeful about the future. He started making plans to visit colleges with his daughter, and was able to host his parents and new grandchild for Christmas. “He was doing so much better,” his wife, Tina Winkler, said. “We thought he was coasting until he got his transplant.”
What John Winkler didn’t know: Months before his implant, the Food and Drug Administration put HeartWare on notice for not properly monitoring or repairing HVAD defects, such as faulty batteries and short circuits caused by static electricity, that had killed patients. The agency issued a warning letter, one of its most serious citations. It demanded fixes within 15 days, but took no decisive action as problems persisted.
Ten days after Christmas of 2014, Winkler’s two teenage children heard the HVAD’s piercing alarm and ran upstairs. They found their father collapsed on his bedroom floor, completely unresponsive. Kelly, 17, dropped to his side and tried to copy how people on television did CPR. She told her brother to call 911, and over the device’s siren did her best to hear instructions from the operator.
When paramedics arrived and assessed her father, one made a passing comment that has haunted Kelly ever since: “Well, his toes are already cold.” He died 2 days later. Medtronic, the company that acquired HeartWare in 2016, settled a lawsuit by the family last year, admitting no fault. Tina Winkler believes her children blamed themselves for their father’s death. “Those two kids have never been the same,” she said. “I think they feel like they didn’t do things they needed to do.”
But it was the FDA that failed to protect Winkler and thousands of other patients whose survival depended on the HVAD, a ProPublica investigation found.
As HeartWare and Medtronic failed inspection after inspection and reports of device-related deaths piled up, the FDA relied on the device makers to fix the problems voluntarily rather than compelling them to do so.
The HVAD was implanted into more than 19,000 patients, the majority of whom got it after the FDA found in 2014 that the device didn’t meet federal standards. By the end of last year, the agency had received more than 3,000 reports of patient deaths that may have been caused or contributed to by the device.
Among them were reports of deaths the company linked to serious device problems: a patient who vomited blood as a family member struggled to restart a defective HVAD; a patient who bled out internally and died after implant surgery because a tube attached to the pump tore open; a patient whose heart tissue was left charred after an HVAD short-circuited and voltage surged through the pump.
The ineffective regulatory oversight of the HVAD is emblematic of larger, more systemic weaknesses.
For decades, the FDA and its Center for Devices and Radiological Health have been responsible for ensuring that high-risk medical devices are safe and effective. Yet they rely mostly on manufacturers to identify and correct problems. The agency says it can seize products, order injunctions against companies, or issue fines, but it rarely does so, preferring instead for companies to make fixes voluntarily.
When federal investigators found repeated manufacturing issues with the HVAD for years, the FDA didn’t penalize the company, even as the company issued 15 serious recalls of the device starting in 2014, the most of any single high-risk device in the FDA’s database. Thousands of patients with recalled models needed to have external HVAD parts replaced or take extra caution while handling their devices and monitor them for signs of malfunctions that could cause injury or death.
Meanwhile, the processes to inform the public through formal FDA notices and messages to health care providers repeatedly failed and left patients in the dark about known problems with the HVAD.
“Patients have no idea, and they rely on the FDA to ensure the safety and effectiveness of high-risk devices,” said Dr. Rita Redberg, a cardiologist at the University of California, San Francisco, who studies medical device regulation. “How can you not take action on a warning letter with these serious issues with very sick patients?”
In response to ProPublica’s findings, the FDA said it had been closely monitoring issues with the HVAD. It said that after Medtronic acquired HeartWare in 2016, it met with the company more than 100 times to ensure problems were being fixed and to review safety concerns related to the heart pump. The agency also said it initiated formal reviews of new device modifications and continually tracked whether the HVAD had a “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness.”
“Our decisions that we made along the way have always been patient focused,” said Dr. William Maisel, director of product evaluation and quality at the FDA’s device division. He added that more than 80% of companies fix their problems by the time the FDA reinspects.
That did not happen with the HVAD. In 2016 and 2018, inspectors found that issues detailed in the 2014 warning letter remained unresolved. Medtronic told the FDA last year that it had fixed the problems, but, before the agency could verify the claim, inspections were paused because of the coronavirus pandemic.
In June, Medtronic stopped HVAD sales and implants. The company conceded that a competing device was safer after a new study showed the HVAD had higher rates of death and neurological injury. Medtronic also cited a 12-year-old problem with its devices not restarting if they disconnect from power, leaving patients’ hearts without support.
Medtronic declined to make Geoffrey Martha, CEO, or Nnamdi Njoku, president of mechanical heart support, available for interviews. In an email, a spokesperson said, “There is nothing more important to Medtronic than the safety and well-being of patients.”
The email continued: “Medtronic takes this matter very seriously and, over the past five years, we have worked closely with FDA and engaged external experts to resolve the issues noted in the warning letter. FDA is aware of the steps Medtronic has taken to address the underlying concerns.”
The company said it will have a support system in place for the 4,000 patients worldwide and 2,000 in the United States who still rely on the HVAD. Medtronic will station 20 specialists across the globe to help with device maintenance and patient education. A centralized engineering team will provide technical support and troubleshooting for patients and medical staff. Medtronic said it will offer financial assistance if insurance doesn’t fully cover the surgery to replace a device with a competing product, but only if a doctor decides it’s medically necessary.
Patients with HVADs have little choice but to hope the devices keep working: The surgery to remove HVADs is so risky that both Medtronic and the FDA advise against it. The device is meant to be left in place until its wearer gets a heart transplant. Or dies.
Warning signs
In late 2012, HeartWare, then an independent company headquartered in Massachusetts, won FDA approval to sell a new device that could keep heart failure patients alive and mobile while awaiting a transplant.
A competing device, the HeartMate, was already gaining attention, with high-profile patients like former Vice President Dick Cheney, a heart attack survivor who eventually got a transplant after using the device for 20 months.
The HVAD offered a smaller option that could even be used in children, and it led to a string of publicized successes. A fitness model was able to return to the gym. A 13-year-old with heart defects could attend school again. Medtronic’s YouTube page features 16 interviews with grateful patients and families.
The patients who received HVADs had already been in grave peril. They had advanced heart failure, serious enough to need blood pumped out of their hearts artificially. Most patients were older than 50, but there were also younger patients with heart defects or other cardiac conditions. The device provided help but brought its own risks. Implanting it required invasive open-heart surgery, and clots could develop inside the pump, which, in the worst cases, led to deadly strokes.
The device also came with a steep price tag. Each HVAD cost about $80,000, and, even though HeartWare never made a profit as an independent company, in 2015 device sales brought in $276 million in revenue.
For many severe heart failure patients, the opportunity to survive longer and return to normal life made the device worth the risks and cost.
But patients were unaware the FDA started finding manufacturing issues at HeartWare’s Miami Lakes, Florida, plant as early as 2011, when the device was still seeking approval.
Among the findings, a federal inspector expressed concerns that engineering staff “were not completely reviewing documents before approving them” and found one employee assigned to monitoring device quality had missed several required monthly trainings. HeartWare leadership promised quick corrective action, according to FDA documents.
Then, in 2014, the FDA found more serious lapses, detailed in federal inspection reports.
For example, HeartWare knew of 119 instances in which batteries failed unexpectedly, which could leave the pump powerless, stopping support for the patient’s heart. But the company didn’t test the batteries in inventory for defects, or the batteries of current patients, even though one person’s death had already been linked to battery failure.
The company also received complaints that static electricity could short-circuit its devices. It learned of at least 27 such cases between 2010 and 2013, including four that resulted in serious injuries and two that led to death. HVAD patients would need to avoid contact with certain household objects like televisions or vacuum cleaners — anything that could create strong static electricity. HeartWare added warnings to the patient manual and redesigned its shield to protect the device controller, but the FDA found that the company didn’t replace shields for devices already being used by current patients or produced and sitting in inventory.
Continuing quality control concerns led to the FDA warning letter in June 2014. The document labeled the HVAD as “adulterated,” meaning the device did not meet federal manufacturing standards. The agency gave HeartWare 15 days to correct the problems or face regulatory action.
Still, investment analysts who followed HeartWare believed the warning posed little risk to the company’s business prospects. One described it as being “as benign as possible.”
The 15-day deadline passed, and the FDA never penalized the company.
The agency told ProPublica it had provided additional time because HeartWare was a relatively new manufacturer and the HVAD was a complicated device. It also said it avoided punitive action to make sure patients with severe heart failure had access to this treatment option. “We’re talking about the sickest of the sick patients who really have very few alternatives,” Maisel, the head of device quality, said.
But the HeartMate, the competing device, was available and already being used by the majority of patients. When Medtronic stopped HVAD sales, both companies said the HeartMate could fill the gap.
Inspectors continued to find problems at HeartWare facilities in 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018. In the most recent report in 2018, inspectors identified seven separate violations at the HVAD plant, including three previously cited in the 2014 warning letter. The company was still mishandling newly discovered defects like pins connecting the controller to a power source that could bend and become unusable, and controllers built with incompatible parts that could chemically react and “attack” the plastic exterior.
Again, the inspection report said the company “promised to correct” the issues.
“What penalty is there for noncompliance? There isn’t one,” said Madris Kinard, a former public health analyst with the FDA and the CEO of Device Events, a software company that analyzes FDA device data. “There’s nothing the FDA is doing that penalizes, in any true sense of the matter, the manufacturer.”
By the time sales were halted last month, the HVAD had become the subject of 15 company-initiated “Class I” recalls for dangerous device problems that could cause injury or death.
One recall came with a warning sent to health care providers in December that said pumps were failing to start up properly. The pattern of malfunctions was almost as old as the device itself, the company later admitted when it halted device sales in June. But even recent patients were completely unaware of the problem.
“A no-brainer”
When children asked Latoya Johnson Keelen about the cable that came out of her side and connected to a controller on her hip, she told them she was Iron Woman.
For a while, she felt invulnerable with the HVAD on her heart.
Johnson Keelen, who lives in the Atlanta suburbs, learned she needed the device after delivering her fourth child, Isaiah, in early 2018. Doctors diagnosed her with postpartum cardiomyopathy, a rare and mysterious form of heart failure that afflicts mothers during pregnancy or after birth. Black mothers in the South have among the highest rates of the illness. Some mothers quickly regain heart function, some only partially recuperate and others never recover.
Tests showed that Johnson Keelen, then 42, was suddenly in end-stage heart failure.
Her body’s immune response at the time was too strong for her to receive a heart transplant. Doctors gave her two choices: an HVAD or end-of-life hospice care.
“It became a no-brainer,” she said. “I just had a baby. I just gave birth. I’m not ready to plan for a funeral.”
Johnson Keelen, a woman of faith, believed God would heal her, either through a medical advancement or a miracle. She thought the HVAD was the answer.
Living with a life-sustaining medical device was difficult at first for the fiercely independent mother. She had to leave her job as a public health communications specialist, ask her older sons to change her bandages and lean heavily on her new husband, only a year into their marriage.
But, for about three years, she found comfort in the soft humming of the HVAD’s spinning rotor at night. It served as a lullaby for her new baby when he lay on her chest.
She said she was never told about the manufacturing problems the FDA repeatedly found at HeartWare’s facilities or about device recalls, including one sent to patients in December 2020. The notice said the device sometimes wouldn’t restart properly, which had led to two patient deaths at that point. It warned that current patients should always keep at least one power source, a battery or an AC or DC adapter, connected at all times to avoid the need for a restart.
Two months after that notice, Johnson Keelen was getting her kids ready for school when the HVAD’s low-battery alarm blared. She had unplugged the battery to replace it without realizing her wall adapter was disconnected.
Once before, Johnson Keelen had simply plugged the charger back into the outlet and her device restarted. But this time it wouldn’t.
As an emergency alarm sounded, she called the ventricular-assist team assigned to her case, and a specialist directed her to switch out the device controller.
Nothing changed, and panic crept into the voice on the phone.
An ambulance took Johnson Keelen to a hospital where medical staff used several backup controllers to try to start the pump.
Still nothing.
Doctors and nurses tried to keep calm, but Johnson Keelen could see fear and shock on their faces. Without the HVAD, her only options were a transplant or a completely new pump.
Doctors scurried to locate a donor heart and airlifted her for an emergency transplant. But while running tests, the medical team was stunned to find that Johnson Keelen’s miracle had occurred: Her heart was once again pumping blood on its own.
She had a new choice. She could avoid the risks of transplant rejection and open heart surgery during the pandemic by leaving the device on her functioning heart, while cutting the wires, removing the external components and sealing the pump.
She chose to trust her newly functioning heart, and leave the decommissioned HVAD inside her.
Three months later, when Medtronic said it was stopping HeartWare sales and implants, its announcement cited the problem with pumps not restarting among the reasons.
Company-led oversight
If evidence suggests a medical device may be linked to a serious patient injury or death, hospitals and other health care facilities must submit a report to the manufacturer and the FDA. Device companies must also submit reports if they learn independently of any incidents.
By the end of 2020, roughly 3,000 death reports and 20,000 injury reports related to the HVAD had been filed with the FDA.
Any details that could identify patients, like their age or gender, are removed from the publicly available reports. Most only have limited details about circumstances surrounding deaths or injuries. But it’s clear from the reports on the HVAD that some of these outcomes could be linked to problems previously identified by FDA inspectors.
Doctors attempted CPR for two hours after an electrostatic shock short-circuited one patient’s device in 2014, a few months after the FDA inspection that year. An autopsy revealed voltage had caused “deep charring” of the tissue inside the patient’s chest.
Friends found another patient dead in the kitchen, with groceries still on the counter, in 2018 after their device, which did not have the recommended static shield, short-circuited.
Last year, paramedics found a patient with the device disconnected from power. They struggled to restart the device, but it wouldn’t plug back into the power source because the connector pins were bent. The patient would die at the hospital.
In most cases, the FDA turned to the company to investigate whether a malfunction caused or contributed to the incidents.
But the FDA has long known HeartWare and Medtronic could not be relied on to properly submit HVAD incident reports.
In 2014, the FDA cited HeartWare because in at least 10 cases, there were no documents showing the company attempted to investigate.
In 2016, the agency wrote another citation when the company was late in reporting more than 200 cases, some more than a year past their 30-day reporting deadlines, and failed to report malfunctions that occurred during clinical trials.
The FDA told ProPublica the agency increased its monitoring of HVAD reports, and Medtronic hired new employees to submit timely reports. But by 2018, its backlog had only grown, with 677 late case filings. Again, the FDA did nothing beyond telling the company to fix the problem and further increasing its monitoring.
In an email, Medtronic said it “has robust systems in place to monitor the safety of all of our products, including the HVAD device.”
The email said, “When any potential safety issues are identified, those issues are thoroughly investigated and relevant information is shared with regulators and healthcare providers.” The company didn’t respond to the pattern of late reports and incomplete investigations identified in FDA inspections.
Maisel, the director of FDA device evaluation and quality, once criticized asking companies to investigate their own devices. In 2008, as a practicing cardiologist, he testified to the U.S. House oversight committee about his concerns.
“In the majority of cases, FDA relies on industry to identify, correct and report the problems,” he said. “But there is obviously an inherent financial conflict of interest for the manufacturers, sometimes measured in billions of dollars.”
Maisel has since had a change of heart. When asked about his 2008 testimony, he told ProPublica that he now believes the regulatory system “generally serves patients well” and “most companies are well intentioned.”
HeartWare’s track record of questionable investigations was glaring in John Winkler II’s case.
A report submitted by HeartWare that matches the dates and details of Winkler’s case shows the company decided there was “no indication of any device malfunctions.” It told the FDA that the device couldn’t be removed from the body because the hospital said his family declined an autopsy. HeartWare added that the evidence of the device’s role in Winkler’s death was inconclusive.
Yet little of this appears to be true. Documents reviewed by ProPublica show an autopsy of the heart and lungs was performed a day after the death. Tina Winkler said she was told the pump was removed from her husband’s body and was available for inspection.
A year after John Winkler’s death, HeartWare recalled 18,000 potentially faulty batteries produced between 2013 and 2015. Tina Winkler came across the notice online and found her husband’s battery serial numbers on the list. The company never contacted her about it or any further investigation, she said.
Rewards, not penalties
As deaths and recalls mounted, HeartWare and Medtronic touted additional FDA approval to treat more patients and their attempts to develop new cutting-edge devices.
With the company on notice under the 2014 warning letter, HeartWare geared up to begin human trials on a smaller heart pump, called the MVAD or Miniaturized Ventricular Assist Device. It would be powered by a new algorithm to more efficiently pump blood. Industry analysts predicted robust sales.
In July 2015, implantations were set to begin on a select group of 60 patients in Europe and Australia. But they were abruptly stopped less than two months later after only 11 implants. Patients experienced numerous adverse events, including major bleeding, infection and device malfunction, according to published data.
HeartWare’s stock price plummeted from about $85 to $35 by October 2015. The next year, Medtronic bought HeartWare for $1.1 billion, replacing much of the company’s leadership shortly after.
Some former HeartWare investors filed a class action lawsuit in January 2016 alleging deception in the development of the MVAD.
According to the accounts of six anonymous former employees in the lawsuit, the details mirror the scandal surrounding Theranos, the former blood test company charged with fraud for raising more than $700 million by allegedly lying about its technology.
Where Theranos made empty promises of a test that only needed a few drops of blood, the suit alleges HeartWare promoted a life-sustaining medical device that former employees said had many problems and actually worsened blood flow, increasing clotting risks.
“Nothing really worked right,” one former HeartWare manager said in the lawsuit, citing “improper alarms, improper touch screen performance, gibberish on display screens — just so many alerts and problems.”
Leadership proceeded with human testing anyway, the suit alleges.
Months later, at an investor conference, HeartWare leadership acknowledged the pump and algorithm led to multiple adverse events. For two patients in particular, the algorithm would direct the pump to speed up so fast that it would try to suck up more blood than was available inside the heart for prolonged periods of time.
HeartWare and Medtronic settled the investor suit for $54.5 million in 2018, admitting no fault.
None of the allegations slowed the FDA as it gave Medtronic additional approval and support for its heart pump technologies.
In September 2017, the agency approved the HVAD as “destination therapy” for patients who were not heart transplant candidates and would rely on the device for the rest of their lives.
“We’re really excited about our HVAD destination therapy approval,” a Medtronic executive said on an investor earnings call. “That’s a real game changer for us in that market.”
Two years later, Medtronic announced it was developing a fully implantable version of the HVAD that would no longer need a cable coming through the waist to connect to power.
Even though issues with the HeartWare device had been unresolved for five years at that point, the FDA accepted the pitch into its new fast-track approval process for high-risk devices.
“Slipped Through The Cracks”
After Johnson Keelen’s pump failed in February, she found a news story about the recall notice sent to medical providers two months prior.
It said the company had identified a problem with pump restarts that could cause heart attacks or serious patient harm. Nineteen patients had been seriously injured so far, and two people had died. The recall warned that patients should be careful to avoid disconnecting the device’s power sources.
“I kept seeing Medtronic on record saying they notified patients,” Johnson Keelen said. “Who did they contact? No one told me.”
Her doctor later told her she must have “slipped through the cracks,” she said.
The current system for informing patients of new safety concerns with high-risk devices relies on a communication chain that can easily break. The device company contacts the FDA and health care providers that work with device patients. The FDA typically issues a public notice, while health professionals contact their patients.
But the agency admits most patients don’t know to look for formal FDA postings. And, experts say, the medical system can lose track of who needs to be notified, especially if a patient moves or switches primary care physicians.
Tina Winkler still wonders why she was never told about FDA-known safety issues with the HVAD. She said her husband’s medical team “had to teach me how to clean his wound, how to change his batteries and what to do if alarms go off. And they never mentioned any of this.”
She said, “If we had all the facts, there’s no way he would have gotten that device implanted in his heart.”
When FDA inspectors find serious safety issues with a medical device, inspection reports are not posted online or sent to patients. The public can obtain reports through a Freedom of Information Act request, but the agency’s records department has said new requests can be stuck behind a year-long backlog.
Patients can find warning letters online in a searchable database of thousands of letters from different FDA divisions, including the center for devices. But HeartWare’s 2014 letter is no longer available for public review because the website purges letters older than five years.
There are also few documents available in state courts about faulty products, because of restrictions on lawsuits related to medical devices. The restrictions date back to a 2008 Supreme Court decision in a case against Medtronic. The court found that U.S. law bars patients and their survivors from suing device makers in state court, essentially because their products go through such a rigorous FDA approval process.
Two recent patient lawsuits against HeartWare and Medtronic, including one filed by Tina Winkler, were moved from state court to federal court. In both cases, Medtronic filed to dismiss the cases because of the U.S. law that protects device companies. Medtronic and the families reached private settlements soon after.
Winkler and an attorney for the other family said they could not comment on their settlements.
Johnson Keelen, with a decommissioned HVAD still attached to her heart, wonders what that means for her and other patients’ chances of recourse.
“Why isn’t anyone now stepping up for the patient?” she asked. “They are now liable for taking care of us because we relied on them.”
“Run its course”
Deserae Cain, 33, is one of the 4,000 patients still relying on a HeartWare device.
She was implanted with the heart pump in late 2017, after suddenly being diagnosed with heart failure. Scans showed her heart was three times normal size. It took time for her to come to terms with needing a life-sustaining device — not long before her diagnosis, she had been going on five-mile runs. In the four years since, though, Cain has built a life around the HVAD with her fiance in their Dayton, Ohio, home.
They know the device can malfunction. In 2019, the pump failed for almost an hour as doctors at a nearby hospital struggled to restart it. Cain just tried to stay calm, knowing anxiety could threaten her unsupported weak heart. Months later, she needed an emergency experimental procedure to clear out blood clots developed within her HVAD.
Then, in 2020, Cain developed a widespread infection. Doctors told her she needed surgery to clean out and replace the pump.
Cain asked her medical team if she could switch to the alternative HeartMate device, which other patients told her presented fewer problems, she said. Doctors said the HVAD was better suited for her smaller frame.
But her new pump had problems soon after the surgery.
The device’s suction alarms, which alert when the pump is trying to pull in more blood than is available within the heart, sounded multiple times a day, for hours at a time, she said. Baffled by the issue for months, her medical team eventually turned off that specific alarm.
Soon after, her ventricular-assist specialist called her about a patient’s death linked to the belt that holds the device controller, she said. The belt had ripped and the equipment had fallen, yanking on the cable that connected the controller to the pump. Cain replaced her belt but it quickly frayed and had to be replaced again within six weeks.
Then, in June, she found out about Medtronic’s decision to stop sales and implants. Cain received a letter from her hospital mentioning a Medtronic support program, but it provided few specifics.
Cain wondered if things would be any different than before. Anxious about her future, she asked: “Are they just going to let it run its course until there is none of us left?”
This article first appeared on Propublica.
John Winkler II was dying of heart failure when doctors came to his hospital bedside, offering a chance to prolong his life. The HeartWare Ventricular Assist Device, or HVAD, could be implanted in Winkler’s chest until a transplant was possible. The heart pump came with disclaimers of risk, but Winkler wanted to fight for time. He was only 46 and had a loving wife and four children, and his second grandchild was on the way.
So, in August 2014, Winkler had surgery to implant the device. A golf-ball–sized rotor was attached to his left ventricle to pump blood through a tube and into his aorta. A cable threading out of a small incision in his waist connected to a battery-powered controller strapped to his body. If something went wrong, an alarm as loud as a fire drill would sound.
Winkler returned home weeks later and, as he regained his strength, became hopeful about the future. He started making plans to visit colleges with his daughter, and was able to host his parents and new grandchild for Christmas. “He was doing so much better,” his wife, Tina Winkler, said. “We thought he was coasting until he got his transplant.”
What John Winkler didn’t know: Months before his implant, the Food and Drug Administration put HeartWare on notice for not properly monitoring or repairing HVAD defects, such as faulty batteries and short circuits caused by static electricity, that had killed patients. The agency issued a warning letter, one of its most serious citations. It demanded fixes within 15 days, but took no decisive action as problems persisted.
Ten days after Christmas of 2014, Winkler’s two teenage children heard the HVAD’s piercing alarm and ran upstairs. They found their father collapsed on his bedroom floor, completely unresponsive. Kelly, 17, dropped to his side and tried to copy how people on television did CPR. She told her brother to call 911, and over the device’s siren did her best to hear instructions from the operator.
When paramedics arrived and assessed her father, one made a passing comment that has haunted Kelly ever since: “Well, his toes are already cold.” He died 2 days later. Medtronic, the company that acquired HeartWare in 2016, settled a lawsuit by the family last year, admitting no fault. Tina Winkler believes her children blamed themselves for their father’s death. “Those two kids have never been the same,” she said. “I think they feel like they didn’t do things they needed to do.”
But it was the FDA that failed to protect Winkler and thousands of other patients whose survival depended on the HVAD, a ProPublica investigation found.
As HeartWare and Medtronic failed inspection after inspection and reports of device-related deaths piled up, the FDA relied on the device makers to fix the problems voluntarily rather than compelling them to do so.
The HVAD was implanted into more than 19,000 patients, the majority of whom got it after the FDA found in 2014 that the device didn’t meet federal standards. By the end of last year, the agency had received more than 3,000 reports of patient deaths that may have been caused or contributed to by the device.
Among them were reports of deaths the company linked to serious device problems: a patient who vomited blood as a family member struggled to restart a defective HVAD; a patient who bled out internally and died after implant surgery because a tube attached to the pump tore open; a patient whose heart tissue was left charred after an HVAD short-circuited and voltage surged through the pump.
The ineffective regulatory oversight of the HVAD is emblematic of larger, more systemic weaknesses.
For decades, the FDA and its Center for Devices and Radiological Health have been responsible for ensuring that high-risk medical devices are safe and effective. Yet they rely mostly on manufacturers to identify and correct problems. The agency says it can seize products, order injunctions against companies, or issue fines, but it rarely does so, preferring instead for companies to make fixes voluntarily.
When federal investigators found repeated manufacturing issues with the HVAD for years, the FDA didn’t penalize the company, even as the company issued 15 serious recalls of the device starting in 2014, the most of any single high-risk device in the FDA’s database. Thousands of patients with recalled models needed to have external HVAD parts replaced or take extra caution while handling their devices and monitor them for signs of malfunctions that could cause injury or death.
Meanwhile, the processes to inform the public through formal FDA notices and messages to health care providers repeatedly failed and left patients in the dark about known problems with the HVAD.
“Patients have no idea, and they rely on the FDA to ensure the safety and effectiveness of high-risk devices,” said Dr. Rita Redberg, a cardiologist at the University of California, San Francisco, who studies medical device regulation. “How can you not take action on a warning letter with these serious issues with very sick patients?”
In response to ProPublica’s findings, the FDA said it had been closely monitoring issues with the HVAD. It said that after Medtronic acquired HeartWare in 2016, it met with the company more than 100 times to ensure problems were being fixed and to review safety concerns related to the heart pump. The agency also said it initiated formal reviews of new device modifications and continually tracked whether the HVAD had a “reasonable assurance of safety and effectiveness.”
“Our decisions that we made along the way have always been patient focused,” said Dr. William Maisel, director of product evaluation and quality at the FDA’s device division. He added that more than 80% of companies fix their problems by the time the FDA reinspects.
That did not happen with the HVAD. In 2016 and 2018, inspectors found that issues detailed in the 2014 warning letter remained unresolved. Medtronic told the FDA last year that it had fixed the problems, but, before the agency could verify the claim, inspections were paused because of the coronavirus pandemic.
In June, Medtronic stopped HVAD sales and implants. The company conceded that a competing device was safer after a new study showed the HVAD had higher rates of death and neurological injury. Medtronic also cited a 12-year-old problem with its devices not restarting if they disconnect from power, leaving patients’ hearts without support.
Medtronic declined to make Geoffrey Martha, CEO, or Nnamdi Njoku, president of mechanical heart support, available for interviews. In an email, a spokesperson said, “There is nothing more important to Medtronic than the safety and well-being of patients.”
The email continued: “Medtronic takes this matter very seriously and, over the past five years, we have worked closely with FDA and engaged external experts to resolve the issues noted in the warning letter. FDA is aware of the steps Medtronic has taken to address the underlying concerns.”
The company said it will have a support system in place for the 4,000 patients worldwide and 2,000 in the United States who still rely on the HVAD. Medtronic will station 20 specialists across the globe to help with device maintenance and patient education. A centralized engineering team will provide technical support and troubleshooting for patients and medical staff. Medtronic said it will offer financial assistance if insurance doesn’t fully cover the surgery to replace a device with a competing product, but only if a doctor decides it’s medically necessary.
Patients with HVADs have little choice but to hope the devices keep working: The surgery to remove HVADs is so risky that both Medtronic and the FDA advise against it. The device is meant to be left in place until its wearer gets a heart transplant. Or dies.
Warning signs
In late 2012, HeartWare, then an independent company headquartered in Massachusetts, won FDA approval to sell a new device that could keep heart failure patients alive and mobile while awaiting a transplant.
A competing device, the HeartMate, was already gaining attention, with high-profile patients like former Vice President Dick Cheney, a heart attack survivor who eventually got a transplant after using the device for 20 months.
The HVAD offered a smaller option that could even be used in children, and it led to a string of publicized successes. A fitness model was able to return to the gym. A 13-year-old with heart defects could attend school again. Medtronic’s YouTube page features 16 interviews with grateful patients and families.
The patients who received HVADs had already been in grave peril. They had advanced heart failure, serious enough to need blood pumped out of their hearts artificially. Most patients were older than 50, but there were also younger patients with heart defects or other cardiac conditions. The device provided help but brought its own risks. Implanting it required invasive open-heart surgery, and clots could develop inside the pump, which, in the worst cases, led to deadly strokes.
The device also came with a steep price tag. Each HVAD cost about $80,000, and, even though HeartWare never made a profit as an independent company, in 2015 device sales brought in $276 million in revenue.
For many severe heart failure patients, the opportunity to survive longer and return to normal life made the device worth the risks and cost.
But patients were unaware the FDA started finding manufacturing issues at HeartWare’s Miami Lakes, Florida, plant as early as 2011, when the device was still seeking approval.
Among the findings, a federal inspector expressed concerns that engineering staff “were not completely reviewing documents before approving them” and found one employee assigned to monitoring device quality had missed several required monthly trainings. HeartWare leadership promised quick corrective action, according to FDA documents.
Then, in 2014, the FDA found more serious lapses, detailed in federal inspection reports.
For example, HeartWare knew of 119 instances in which batteries failed unexpectedly, which could leave the pump powerless, stopping support for the patient’s heart. But the company didn’t test the batteries in inventory for defects, or the batteries of current patients, even though one person’s death had already been linked to battery failure.
The company also received complaints that static electricity could short-circuit its devices. It learned of at least 27 such cases between 2010 and 2013, including four that resulted in serious injuries and two that led to death. HVAD patients would need to avoid contact with certain household objects like televisions or vacuum cleaners — anything that could create strong static electricity. HeartWare added warnings to the patient manual and redesigned its shield to protect the device controller, but the FDA found that the company didn’t replace shields for devices already being used by current patients or produced and sitting in inventory.
Continuing quality control concerns led to the FDA warning letter in June 2014. The document labeled the HVAD as “adulterated,” meaning the device did not meet federal manufacturing standards. The agency gave HeartWare 15 days to correct the problems or face regulatory action.
Still, investment analysts who followed HeartWare believed the warning posed little risk to the company’s business prospects. One described it as being “as benign as possible.”
The 15-day deadline passed, and the FDA never penalized the company.
The agency told ProPublica it had provided additional time because HeartWare was a relatively new manufacturer and the HVAD was a complicated device. It also said it avoided punitive action to make sure patients with severe heart failure had access to this treatment option. “We’re talking about the sickest of the sick patients who really have very few alternatives,” Maisel, the head of device quality, said.
But the HeartMate, the competing device, was available and already being used by the majority of patients. When Medtronic stopped HVAD sales, both companies said the HeartMate could fill the gap.
Inspectors continued to find problems at HeartWare facilities in 2015, 2016, 2017 and 2018. In the most recent report in 2018, inspectors identified seven separate violations at the HVAD plant, including three previously cited in the 2014 warning letter. The company was still mishandling newly discovered defects like pins connecting the controller to a power source that could bend and become unusable, and controllers built with incompatible parts that could chemically react and “attack” the plastic exterior.
Again, the inspection report said the company “promised to correct” the issues.
“What penalty is there for noncompliance? There isn’t one,” said Madris Kinard, a former public health analyst with the FDA and the CEO of Device Events, a software company that analyzes FDA device data. “There’s nothing the FDA is doing that penalizes, in any true sense of the matter, the manufacturer.”
By the time sales were halted last month, the HVAD had become the subject of 15 company-initiated “Class I” recalls for dangerous device problems that could cause injury or death.
One recall came with a warning sent to health care providers in December that said pumps were failing to start up properly. The pattern of malfunctions was almost as old as the device itself, the company later admitted when it halted device sales in June. But even recent patients were completely unaware of the problem.
“A no-brainer”
When children asked Latoya Johnson Keelen about the cable that came out of her side and connected to a controller on her hip, she told them she was Iron Woman.
For a while, she felt invulnerable with the HVAD on her heart.
Johnson Keelen, who lives in the Atlanta suburbs, learned she needed the device after delivering her fourth child, Isaiah, in early 2018. Doctors diagnosed her with postpartum cardiomyopathy, a rare and mysterious form of heart failure that afflicts mothers during pregnancy or after birth. Black mothers in the South have among the highest rates of the illness. Some mothers quickly regain heart function, some only partially recuperate and others never recover.
Tests showed that Johnson Keelen, then 42, was suddenly in end-stage heart failure.
Her body’s immune response at the time was too strong for her to receive a heart transplant. Doctors gave her two choices: an HVAD or end-of-life hospice care.
“It became a no-brainer,” she said. “I just had a baby. I just gave birth. I’m not ready to plan for a funeral.”
Johnson Keelen, a woman of faith, believed God would heal her, either through a medical advancement or a miracle. She thought the HVAD was the answer.
Living with a life-sustaining medical device was difficult at first for the fiercely independent mother. She had to leave her job as a public health communications specialist, ask her older sons to change her bandages and lean heavily on her new husband, only a year into their marriage.
But, for about three years, she found comfort in the soft humming of the HVAD’s spinning rotor at night. It served as a lullaby for her new baby when he lay on her chest.
She said she was never told about the manufacturing problems the FDA repeatedly found at HeartWare’s facilities or about device recalls, including one sent to patients in December 2020. The notice said the device sometimes wouldn’t restart properly, which had led to two patient deaths at that point. It warned that current patients should always keep at least one power source, a battery or an AC or DC adapter, connected at all times to avoid the need for a restart.
Two months after that notice, Johnson Keelen was getting her kids ready for school when the HVAD’s low-battery alarm blared. She had unplugged the battery to replace it without realizing her wall adapter was disconnected.
Once before, Johnson Keelen had simply plugged the charger back into the outlet and her device restarted. But this time it wouldn’t.
As an emergency alarm sounded, she called the ventricular-assist team assigned to her case, and a specialist directed her to switch out the device controller.
Nothing changed, and panic crept into the voice on the phone.
An ambulance took Johnson Keelen to a hospital where medical staff used several backup controllers to try to start the pump.
Still nothing.
Doctors and nurses tried to keep calm, but Johnson Keelen could see fear and shock on their faces. Without the HVAD, her only options were a transplant or a completely new pump.
Doctors scurried to locate a donor heart and airlifted her for an emergency transplant. But while running tests, the medical team was stunned to find that Johnson Keelen’s miracle had occurred: Her heart was once again pumping blood on its own.
She had a new choice. She could avoid the risks of transplant rejection and open heart surgery during the pandemic by leaving the device on her functioning heart, while cutting the wires, removing the external components and sealing the pump.
She chose to trust her newly functioning heart, and leave the decommissioned HVAD inside her.
Three months later, when Medtronic said it was stopping HeartWare sales and implants, its announcement cited the problem with pumps not restarting among the reasons.
Company-led oversight
If evidence suggests a medical device may be linked to a serious patient injury or death, hospitals and other health care facilities must submit a report to the manufacturer and the FDA. Device companies must also submit reports if they learn independently of any incidents.
By the end of 2020, roughly 3,000 death reports and 20,000 injury reports related to the HVAD had been filed with the FDA.
Any details that could identify patients, like their age or gender, are removed from the publicly available reports. Most only have limited details about circumstances surrounding deaths or injuries. But it’s clear from the reports on the HVAD that some of these outcomes could be linked to problems previously identified by FDA inspectors.
Doctors attempted CPR for two hours after an electrostatic shock short-circuited one patient’s device in 2014, a few months after the FDA inspection that year. An autopsy revealed voltage had caused “deep charring” of the tissue inside the patient’s chest.
Friends found another patient dead in the kitchen, with groceries still on the counter, in 2018 after their device, which did not have the recommended static shield, short-circuited.
Last year, paramedics found a patient with the device disconnected from power. They struggled to restart the device, but it wouldn’t plug back into the power source because the connector pins were bent. The patient would die at the hospital.
In most cases, the FDA turned to the company to investigate whether a malfunction caused or contributed to the incidents.
But the FDA has long known HeartWare and Medtronic could not be relied on to properly submit HVAD incident reports.
In 2014, the FDA cited HeartWare because in at least 10 cases, there were no documents showing the company attempted to investigate.
In 2016, the agency wrote another citation when the company was late in reporting more than 200 cases, some more than a year past their 30-day reporting deadlines, and failed to report malfunctions that occurred during clinical trials.
The FDA told ProPublica the agency increased its monitoring of HVAD reports, and Medtronic hired new employees to submit timely reports. But by 2018, its backlog had only grown, with 677 late case filings. Again, the FDA did nothing beyond telling the company to fix the problem and further increasing its monitoring.
In an email, Medtronic said it “has robust systems in place to monitor the safety of all of our products, including the HVAD device.”
The email said, “When any potential safety issues are identified, those issues are thoroughly investigated and relevant information is shared with regulators and healthcare providers.” The company didn’t respond to the pattern of late reports and incomplete investigations identified in FDA inspections.
Maisel, the director of FDA device evaluation and quality, once criticized asking companies to investigate their own devices. In 2008, as a practicing cardiologist, he testified to the U.S. House oversight committee about his concerns.
“In the majority of cases, FDA relies on industry to identify, correct and report the problems,” he said. “But there is obviously an inherent financial conflict of interest for the manufacturers, sometimes measured in billions of dollars.”
Maisel has since had a change of heart. When asked about his 2008 testimony, he told ProPublica that he now believes the regulatory system “generally serves patients well” and “most companies are well intentioned.”
HeartWare’s track record of questionable investigations was glaring in John Winkler II’s case.
A report submitted by HeartWare that matches the dates and details of Winkler’s case shows the company decided there was “no indication of any device malfunctions.” It told the FDA that the device couldn’t be removed from the body because the hospital said his family declined an autopsy. HeartWare added that the evidence of the device’s role in Winkler’s death was inconclusive.
Yet little of this appears to be true. Documents reviewed by ProPublica show an autopsy of the heart and lungs was performed a day after the death. Tina Winkler said she was told the pump was removed from her husband’s body and was available for inspection.
A year after John Winkler’s death, HeartWare recalled 18,000 potentially faulty batteries produced between 2013 and 2015. Tina Winkler came across the notice online and found her husband’s battery serial numbers on the list. The company never contacted her about it or any further investigation, she said.
Rewards, not penalties
As deaths and recalls mounted, HeartWare and Medtronic touted additional FDA approval to treat more patients and their attempts to develop new cutting-edge devices.
With the company on notice under the 2014 warning letter, HeartWare geared up to begin human trials on a smaller heart pump, called the MVAD or Miniaturized Ventricular Assist Device. It would be powered by a new algorithm to more efficiently pump blood. Industry analysts predicted robust sales.
In July 2015, implantations were set to begin on a select group of 60 patients in Europe and Australia. But they were abruptly stopped less than two months later after only 11 implants. Patients experienced numerous adverse events, including major bleeding, infection and device malfunction, according to published data.
HeartWare’s stock price plummeted from about $85 to $35 by October 2015. The next year, Medtronic bought HeartWare for $1.1 billion, replacing much of the company’s leadership shortly after.
Some former HeartWare investors filed a class action lawsuit in January 2016 alleging deception in the development of the MVAD.
According to the accounts of six anonymous former employees in the lawsuit, the details mirror the scandal surrounding Theranos, the former blood test company charged with fraud for raising more than $700 million by allegedly lying about its technology.
Where Theranos made empty promises of a test that only needed a few drops of blood, the suit alleges HeartWare promoted a life-sustaining medical device that former employees said had many problems and actually worsened blood flow, increasing clotting risks.
“Nothing really worked right,” one former HeartWare manager said in the lawsuit, citing “improper alarms, improper touch screen performance, gibberish on display screens — just so many alerts and problems.”
Leadership proceeded with human testing anyway, the suit alleges.
Months later, at an investor conference, HeartWare leadership acknowledged the pump and algorithm led to multiple adverse events. For two patients in particular, the algorithm would direct the pump to speed up so fast that it would try to suck up more blood than was available inside the heart for prolonged periods of time.
HeartWare and Medtronic settled the investor suit for $54.5 million in 2018, admitting no fault.
None of the allegations slowed the FDA as it gave Medtronic additional approval and support for its heart pump technologies.
In September 2017, the agency approved the HVAD as “destination therapy” for patients who were not heart transplant candidates and would rely on the device for the rest of their lives.
“We’re really excited about our HVAD destination therapy approval,” a Medtronic executive said on an investor earnings call. “That’s a real game changer for us in that market.”
Two years later, Medtronic announced it was developing a fully implantable version of the HVAD that would no longer need a cable coming through the waist to connect to power.
Even though issues with the HeartWare device had been unresolved for five years at that point, the FDA accepted the pitch into its new fast-track approval process for high-risk devices.
“Slipped Through The Cracks”
After Johnson Keelen’s pump failed in February, she found a news story about the recall notice sent to medical providers two months prior.
It said the company had identified a problem with pump restarts that could cause heart attacks or serious patient harm. Nineteen patients had been seriously injured so far, and two people had died. The recall warned that patients should be careful to avoid disconnecting the device’s power sources.
“I kept seeing Medtronic on record saying they notified patients,” Johnson Keelen said. “Who did they contact? No one told me.”
Her doctor later told her she must have “slipped through the cracks,” she said.
The current system for informing patients of new safety concerns with high-risk devices relies on a communication chain that can easily break. The device company contacts the FDA and health care providers that work with device patients. The FDA typically issues a public notice, while health professionals contact their patients.
But the agency admits most patients don’t know to look for formal FDA postings. And, experts say, the medical system can lose track of who needs to be notified, especially if a patient moves or switches primary care physicians.
Tina Winkler still wonders why she was never told about FDA-known safety issues with the HVAD. She said her husband’s medical team “had to teach me how to clean his wound, how to change his batteries and what to do if alarms go off. And they never mentioned any of this.”
She said, “If we had all the facts, there’s no way he would have gotten that device implanted in his heart.”
When FDA inspectors find serious safety issues with a medical device, inspection reports are not posted online or sent to patients. The public can obtain reports through a Freedom of Information Act request, but the agency’s records department has said new requests can be stuck behind a year-long backlog.
Patients can find warning letters online in a searchable database of thousands of letters from different FDA divisions, including the center for devices. But HeartWare’s 2014 letter is no longer available for public review because the website purges letters older than five years.
There are also few documents available in state courts about faulty products, because of restrictions on lawsuits related to medical devices. The restrictions date back to a 2008 Supreme Court decision in a case against Medtronic. The court found that U.S. law bars patients and their survivors from suing device makers in state court, essentially because their products go through such a rigorous FDA approval process.
Two recent patient lawsuits against HeartWare and Medtronic, including one filed by Tina Winkler, were moved from state court to federal court. In both cases, Medtronic filed to dismiss the cases because of the U.S. law that protects device companies. Medtronic and the families reached private settlements soon after.
Winkler and an attorney for the other family said they could not comment on their settlements.
Johnson Keelen, with a decommissioned HVAD still attached to her heart, wonders what that means for her and other patients’ chances of recourse.
“Why isn’t anyone now stepping up for the patient?” she asked. “They are now liable for taking care of us because we relied on them.”
“Run its course”
Deserae Cain, 33, is one of the 4,000 patients still relying on a HeartWare device.
She was implanted with the heart pump in late 2017, after suddenly being diagnosed with heart failure. Scans showed her heart was three times normal size. It took time for her to come to terms with needing a life-sustaining device — not long before her diagnosis, she had been going on five-mile runs. In the four years since, though, Cain has built a life around the HVAD with her fiance in their Dayton, Ohio, home.
They know the device can malfunction. In 2019, the pump failed for almost an hour as doctors at a nearby hospital struggled to restart it. Cain just tried to stay calm, knowing anxiety could threaten her unsupported weak heart. Months later, she needed an emergency experimental procedure to clear out blood clots developed within her HVAD.
Then, in 2020, Cain developed a widespread infection. Doctors told her she needed surgery to clean out and replace the pump.
Cain asked her medical team if she could switch to the alternative HeartMate device, which other patients told her presented fewer problems, she said. Doctors said the HVAD was better suited for her smaller frame.
But her new pump had problems soon after the surgery.
The device’s suction alarms, which alert when the pump is trying to pull in more blood than is available within the heart, sounded multiple times a day, for hours at a time, she said. Baffled by the issue for months, her medical team eventually turned off that specific alarm.
Soon after, her ventricular-assist specialist called her about a patient’s death linked to the belt that holds the device controller, she said. The belt had ripped and the equipment had fallen, yanking on the cable that connected the controller to the pump. Cain replaced her belt but it quickly frayed and had to be replaced again within six weeks.
Then, in June, she found out about Medtronic’s decision to stop sales and implants. Cain received a letter from her hospital mentioning a Medtronic support program, but it provided few specifics.
Cain wondered if things would be any different than before. Anxious about her future, she asked: “Are they just going to let it run its course until there is none of us left?”
This article first appeared on Propublica.
A pacemaker that 'just disappears' and a magnetic diet device
Ignore this pacemaker and it will go away
At some point – and now seems to be that point – we have to say enough is enough. The throwaway culture that produces phones, TVs, and computers that get tossed in the trash because they can’t be repaired has gone too far. That’s right, we’re looking at you, medical science!
This time, it’s a pacemaker that just disappears when it’s no longer needed. Some lazy heart surgeon decided that it was way too much trouble to do another surgery to remove the leads when a temporary pacemaker was no longer needed. You know the type: “It sure would be nice if the pacemaker components were biocompatible and were naturally absorbed by the body over the course of a few weeks and wouldn’t need to be surgically extracted.” Slacker.
Well, get a load of this. Researchers at Northwestern and George Washington universities say that they have come up with a transient pacemaker that “harvests energy from an external, remote antenna using near-field communication protocols – the same technology used in smartphones for electronic payments and in RFID tags.”
That means no batteries and no wires that have to be removed and can cause infections. Because the infectious disease docs also are too lazy to do their jobs, apparently.
The lack of onboard infrastructure means that the device can be very small – it weighs less than half a gram and is only 250 microns thick. And yes, it is bioresorbable and completely harmless. It fully degrades and disappears in 5-7 weeks through the body’s natural biologic processes, “thereby avoiding the need for physical removal of the pacemaker electrodes. This is potentially a major victory for postoperative patients,” said Dr. Rishi Arora, one of the investigators.
A victory for patients, he says. Not a word about the time and effort saved by the surgeons. Typical.
It’s a mask! No, it’s a COVID-19 test!
Mask wearing has gotten more lax as people get vaccinated for COVID-19, but as wearing masks for virus prevention is becoming more normalized in western society, some saw an opportunity to make them work for diagnosis.
Researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have found a way to do just that with their wearable freeze-dried cell-free (wFDCF) technology. A single push of a button releases water from a reservoir in the mask that sequentially activates three different freeze-dried biological reactions, which detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the wearer’s breath.
Initially meant as a tool for the Zika outbreak in 2015, the team made a quick pivot in May 2020. But this isn’t just some run-of-the-mill, at-home test. The data prove that the wFDCF mask is comparable to polymerase chain reactions tests, the standard in COVID-19 detection. Plus there aren’t any extra factors to deal with, like room or instrument temperature to ensure accuracy. In just 90 minutes, the mask gives results on a readout in a way similar to that of a pregnancy test. Voilà! To have COVID-19 or not to have COVID-19 is an easily answered question.
At LOTME, we think this is a big improvement from having dogs, or even three-foot rats, sniffing out coronavirus.
But wait, there’s more. “In addition to face masks, our programmable biosensors can be integrated into other garments to provide on-the-go detection of dangerous substances including viruses, bacteria, toxins, and chemical agents,” said Peter Nguyen, PhD, study coauthor and research scientist at the Wyss Institute. The technology can be used on lab coats, scrubs, military uniforms, and uniforms of first responders who may come in contact with hazardous pathogens and toxins. Think of all the lives saved and possible avoidances.
If only it could diagnose bad breath.
Finally, an excuse for the all-beer diet
Weight loss is hard work. Extremely hard work, and, as evidenced by the constant inundation and advertisement of quick fixes, crash diets, and expensive gym memberships, there’s not really a solid, 100% solution to the issue. Until now, thanks to a team of doctors from New Zealand, who’ve decided that the best way to combat obesity is to leave you in constant agony.
The DentalSlim Diet Control device is certainly a radical yet comically logical attempt to combat obesity. The creators say that the biggest problem with dieting is compliance, and, well, it’s difficult to eat too much if you can’t actually open your mouth. The metal contraption is mounted onto your teeth and uses magnetic locks to prevent the user from opening their mouths more than 2 mm. That’s less than a tenth of an inch. Which is not a lot. So not a lot that essentially all you can consume is liquid.
Oh, and they’ve got results to back up their madness. In a small study, seven otherwise healthy obese women lost an average of 5.1% of their body weight after using the DentalSlim for 2 weeks, though they did complain that the device was difficult to use, caused discomfort and difficulty speaking, made them more tense, and in general made life “less satisfying.” And one participant was able to cheat the system and consume nonhealthy food like chocolate by melting it.
So, there you are, if you want a weight-loss solution that tortures you and has far bigger holes than the one it leaves for your mouth, try the DentalSlim. Or, you know, don’t eat that eighth slice of pizza and maybe go for a walk later. Your choice.
Ignore this pacemaker and it will go away
At some point – and now seems to be that point – we have to say enough is enough. The throwaway culture that produces phones, TVs, and computers that get tossed in the trash because they can’t be repaired has gone too far. That’s right, we’re looking at you, medical science!
This time, it’s a pacemaker that just disappears when it’s no longer needed. Some lazy heart surgeon decided that it was way too much trouble to do another surgery to remove the leads when a temporary pacemaker was no longer needed. You know the type: “It sure would be nice if the pacemaker components were biocompatible and were naturally absorbed by the body over the course of a few weeks and wouldn’t need to be surgically extracted.” Slacker.
Well, get a load of this. Researchers at Northwestern and George Washington universities say that they have come up with a transient pacemaker that “harvests energy from an external, remote antenna using near-field communication protocols – the same technology used in smartphones for electronic payments and in RFID tags.”
That means no batteries and no wires that have to be removed and can cause infections. Because the infectious disease docs also are too lazy to do their jobs, apparently.
The lack of onboard infrastructure means that the device can be very small – it weighs less than half a gram and is only 250 microns thick. And yes, it is bioresorbable and completely harmless. It fully degrades and disappears in 5-7 weeks through the body’s natural biologic processes, “thereby avoiding the need for physical removal of the pacemaker electrodes. This is potentially a major victory for postoperative patients,” said Dr. Rishi Arora, one of the investigators.
A victory for patients, he says. Not a word about the time and effort saved by the surgeons. Typical.
It’s a mask! No, it’s a COVID-19 test!
Mask wearing has gotten more lax as people get vaccinated for COVID-19, but as wearing masks for virus prevention is becoming more normalized in western society, some saw an opportunity to make them work for diagnosis.
Researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have found a way to do just that with their wearable freeze-dried cell-free (wFDCF) technology. A single push of a button releases water from a reservoir in the mask that sequentially activates three different freeze-dried biological reactions, which detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the wearer’s breath.
Initially meant as a tool for the Zika outbreak in 2015, the team made a quick pivot in May 2020. But this isn’t just some run-of-the-mill, at-home test. The data prove that the wFDCF mask is comparable to polymerase chain reactions tests, the standard in COVID-19 detection. Plus there aren’t any extra factors to deal with, like room or instrument temperature to ensure accuracy. In just 90 minutes, the mask gives results on a readout in a way similar to that of a pregnancy test. Voilà! To have COVID-19 or not to have COVID-19 is an easily answered question.
At LOTME, we think this is a big improvement from having dogs, or even three-foot rats, sniffing out coronavirus.
But wait, there’s more. “In addition to face masks, our programmable biosensors can be integrated into other garments to provide on-the-go detection of dangerous substances including viruses, bacteria, toxins, and chemical agents,” said Peter Nguyen, PhD, study coauthor and research scientist at the Wyss Institute. The technology can be used on lab coats, scrubs, military uniforms, and uniforms of first responders who may come in contact with hazardous pathogens and toxins. Think of all the lives saved and possible avoidances.
If only it could diagnose bad breath.
Finally, an excuse for the all-beer diet
Weight loss is hard work. Extremely hard work, and, as evidenced by the constant inundation and advertisement of quick fixes, crash diets, and expensive gym memberships, there’s not really a solid, 100% solution to the issue. Until now, thanks to a team of doctors from New Zealand, who’ve decided that the best way to combat obesity is to leave you in constant agony.
The DentalSlim Diet Control device is certainly a radical yet comically logical attempt to combat obesity. The creators say that the biggest problem with dieting is compliance, and, well, it’s difficult to eat too much if you can’t actually open your mouth. The metal contraption is mounted onto your teeth and uses magnetic locks to prevent the user from opening their mouths more than 2 mm. That’s less than a tenth of an inch. Which is not a lot. So not a lot that essentially all you can consume is liquid.
Oh, and they’ve got results to back up their madness. In a small study, seven otherwise healthy obese women lost an average of 5.1% of their body weight after using the DentalSlim for 2 weeks, though they did complain that the device was difficult to use, caused discomfort and difficulty speaking, made them more tense, and in general made life “less satisfying.” And one participant was able to cheat the system and consume nonhealthy food like chocolate by melting it.
So, there you are, if you want a weight-loss solution that tortures you and has far bigger holes than the one it leaves for your mouth, try the DentalSlim. Or, you know, don’t eat that eighth slice of pizza and maybe go for a walk later. Your choice.
Ignore this pacemaker and it will go away
At some point – and now seems to be that point – we have to say enough is enough. The throwaway culture that produces phones, TVs, and computers that get tossed in the trash because they can’t be repaired has gone too far. That’s right, we’re looking at you, medical science!
This time, it’s a pacemaker that just disappears when it’s no longer needed. Some lazy heart surgeon decided that it was way too much trouble to do another surgery to remove the leads when a temporary pacemaker was no longer needed. You know the type: “It sure would be nice if the pacemaker components were biocompatible and were naturally absorbed by the body over the course of a few weeks and wouldn’t need to be surgically extracted.” Slacker.
Well, get a load of this. Researchers at Northwestern and George Washington universities say that they have come up with a transient pacemaker that “harvests energy from an external, remote antenna using near-field communication protocols – the same technology used in smartphones for electronic payments and in RFID tags.”
That means no batteries and no wires that have to be removed and can cause infections. Because the infectious disease docs also are too lazy to do their jobs, apparently.
The lack of onboard infrastructure means that the device can be very small – it weighs less than half a gram and is only 250 microns thick. And yes, it is bioresorbable and completely harmless. It fully degrades and disappears in 5-7 weeks through the body’s natural biologic processes, “thereby avoiding the need for physical removal of the pacemaker electrodes. This is potentially a major victory for postoperative patients,” said Dr. Rishi Arora, one of the investigators.
A victory for patients, he says. Not a word about the time and effort saved by the surgeons. Typical.
It’s a mask! No, it’s a COVID-19 test!
Mask wearing has gotten more lax as people get vaccinated for COVID-19, but as wearing masks for virus prevention is becoming more normalized in western society, some saw an opportunity to make them work for diagnosis.
Researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology and the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard University have found a way to do just that with their wearable freeze-dried cell-free (wFDCF) technology. A single push of a button releases water from a reservoir in the mask that sequentially activates three different freeze-dried biological reactions, which detect the SARS-CoV-2 virus in the wearer’s breath.
Initially meant as a tool for the Zika outbreak in 2015, the team made a quick pivot in May 2020. But this isn’t just some run-of-the-mill, at-home test. The data prove that the wFDCF mask is comparable to polymerase chain reactions tests, the standard in COVID-19 detection. Plus there aren’t any extra factors to deal with, like room or instrument temperature to ensure accuracy. In just 90 minutes, the mask gives results on a readout in a way similar to that of a pregnancy test. Voilà! To have COVID-19 or not to have COVID-19 is an easily answered question.
At LOTME, we think this is a big improvement from having dogs, or even three-foot rats, sniffing out coronavirus.
But wait, there’s more. “In addition to face masks, our programmable biosensors can be integrated into other garments to provide on-the-go detection of dangerous substances including viruses, bacteria, toxins, and chemical agents,” said Peter Nguyen, PhD, study coauthor and research scientist at the Wyss Institute. The technology can be used on lab coats, scrubs, military uniforms, and uniforms of first responders who may come in contact with hazardous pathogens and toxins. Think of all the lives saved and possible avoidances.
If only it could diagnose bad breath.
Finally, an excuse for the all-beer diet
Weight loss is hard work. Extremely hard work, and, as evidenced by the constant inundation and advertisement of quick fixes, crash diets, and expensive gym memberships, there’s not really a solid, 100% solution to the issue. Until now, thanks to a team of doctors from New Zealand, who’ve decided that the best way to combat obesity is to leave you in constant agony.
The DentalSlim Diet Control device is certainly a radical yet comically logical attempt to combat obesity. The creators say that the biggest problem with dieting is compliance, and, well, it’s difficult to eat too much if you can’t actually open your mouth. The metal contraption is mounted onto your teeth and uses magnetic locks to prevent the user from opening their mouths more than 2 mm. That’s less than a tenth of an inch. Which is not a lot. So not a lot that essentially all you can consume is liquid.
Oh, and they’ve got results to back up their madness. In a small study, seven otherwise healthy obese women lost an average of 5.1% of their body weight after using the DentalSlim for 2 weeks, though they did complain that the device was difficult to use, caused discomfort and difficulty speaking, made them more tense, and in general made life “less satisfying.” And one participant was able to cheat the system and consume nonhealthy food like chocolate by melting it.
So, there you are, if you want a weight-loss solution that tortures you and has far bigger holes than the one it leaves for your mouth, try the DentalSlim. Or, you know, don’t eat that eighth slice of pizza and maybe go for a walk later. Your choice.
Patchy growth of TAVR programs leaves poorer communities behind
Inequities in the initial growth of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) programs in American hospitals has led to less use of the transformative procedure in poorer communities, a new cross-sectional study suggests.
Using Medicare claims data, investigators identified 554 new TAVR programs created between January 2012 and December 2018.
Of these, 98% were established in metropolitan areas (>50,000 residents) and 53% were started in areas with preexisting TAVR programs, “thereby increasing the number of programs but not necessarily increasing the geographic availability of the procedure,” said study author Ashwin Nathan, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Only 11 programs were started in nonmetropolitan areas over the study period, he noted during the featured clinical research presentation at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 annual scientific sessions, held virtually this year.
Hospitals that established TAVR programs, compared with those that did not, cared for patients with higher median household incomes (difference, $1,305; P = .03) and from areas with better economic well-being based on the Distressed Communities Index (difference, –3.15 units; P < .01), and cared for fewer patients with dual eligibility for Medicaid (difference, –3.15%; P < .01).
When the investigators looked at rates of TAVR between the core-based statistical areas, there were fewer TAVR procedures per 100,000 Medicare beneficiaries in areas with more Medicaid dual-eligible patients (difference, –1.19% per 1% increase), lower average median household incomes (difference, –0.62% per $1,000 decrease), and more average community distress (difference, –0.35% per 1 unit increase; P < .01 for all).
“What we can conclude is that the increased number of TAVR programs that we found during the study period did not necessarily translate to increased access to TAVR ... Wealthy, more privileged patients had more access to TAVR by virtue of the hospitals that serve them,” Dr. Nathan said.
Future steps, he said, are to identify the role of race and ethnicity in inequitable access to TAVR, identify system- and patient-level barriers to access, and to develop and test solutions to address inequitable care.
Elaborating on the latter point during a discussion of the results, study coauthor Jay S. Giri, MD, MPH, also from the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, observed that although the data showed rural areas are left behind, not every part of an urban area acts like the area more generally.
As a result, they’re delving into the 25 largest urban areas and trying to disaggregate, based on both socioeconomic status and race within the area, whether inequities exist, he said. “Believe it or not, in some urban areas where there clearly is access – there might even be a dozen TAVR programs within a 25 mile radius – do some of those areas still act like rural areas that don’t have access? So more to come on that.”
Session comoderator Steven Yakubov, MD, MidWest Cardiology Research Foundation in Columbus, Ohio, said the results show TAVR programs tend to be developed in well-served areas but asked whether some of the responsibility falls on patients to seek medical attention. “Do we just not give enough education to patients on how to access care?”
Dr. Giri responded by highlighting the complexity of navigating from even being diagnosed with aortic stenosis to making it through a multidisciplinary TAVR evaluation.
“Individuals with increased health literacy and more means are more likely to make it through that gauntlet. But from a public health perspective, obviously, I’d argue that the onus is probably more on the medical community at large to figure out how to roll these programs out more widespread,” he said.
“It looked to us like market forces overwhelmingly seemed to drive the development of new TAVR programs over access to care considerations,” Dr. Giri added. “And just to point out, those market forces aren’t at the level of the device manufacturers, who are often maligned for cost. This is really about the market forces at the level of hospitals and health systems.”
Session comoderator Megan Coylewright, MD, MPH, Erlanger Heart and Lung Institute, Chattanooga, Tenn., said, “I think that’s really well stated,” and noted that physicians may bear some responsibility as well.
“From a physician responsibility, especially for structural heart, we tended to all aggregate together, all of us that have structural heart training or that have trained in certain institutions,” she said. “It’s certainly on us to continue to spread out and go to the communities in need to ensure access. I think, as Dr. Giri said, there are a lot of solutions and that needs to be the focus for the next couple of years.”
Dr. Nathan reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Giri reported serving as a principal investigator for a research study for Boston Scientific, Inari Medical, Abbott, and Recor Medical; consulting for Boston Scientific; and serving on an advisory board for Inari Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Inequities in the initial growth of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) programs in American hospitals has led to less use of the transformative procedure in poorer communities, a new cross-sectional study suggests.
Using Medicare claims data, investigators identified 554 new TAVR programs created between January 2012 and December 2018.
Of these, 98% were established in metropolitan areas (>50,000 residents) and 53% were started in areas with preexisting TAVR programs, “thereby increasing the number of programs but not necessarily increasing the geographic availability of the procedure,” said study author Ashwin Nathan, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Only 11 programs were started in nonmetropolitan areas over the study period, he noted during the featured clinical research presentation at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 annual scientific sessions, held virtually this year.
Hospitals that established TAVR programs, compared with those that did not, cared for patients with higher median household incomes (difference, $1,305; P = .03) and from areas with better economic well-being based on the Distressed Communities Index (difference, –3.15 units; P < .01), and cared for fewer patients with dual eligibility for Medicaid (difference, –3.15%; P < .01).
When the investigators looked at rates of TAVR between the core-based statistical areas, there were fewer TAVR procedures per 100,000 Medicare beneficiaries in areas with more Medicaid dual-eligible patients (difference, –1.19% per 1% increase), lower average median household incomes (difference, –0.62% per $1,000 decrease), and more average community distress (difference, –0.35% per 1 unit increase; P < .01 for all).
“What we can conclude is that the increased number of TAVR programs that we found during the study period did not necessarily translate to increased access to TAVR ... Wealthy, more privileged patients had more access to TAVR by virtue of the hospitals that serve them,” Dr. Nathan said.
Future steps, he said, are to identify the role of race and ethnicity in inequitable access to TAVR, identify system- and patient-level barriers to access, and to develop and test solutions to address inequitable care.
Elaborating on the latter point during a discussion of the results, study coauthor Jay S. Giri, MD, MPH, also from the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, observed that although the data showed rural areas are left behind, not every part of an urban area acts like the area more generally.
As a result, they’re delving into the 25 largest urban areas and trying to disaggregate, based on both socioeconomic status and race within the area, whether inequities exist, he said. “Believe it or not, in some urban areas where there clearly is access – there might even be a dozen TAVR programs within a 25 mile radius – do some of those areas still act like rural areas that don’t have access? So more to come on that.”
Session comoderator Steven Yakubov, MD, MidWest Cardiology Research Foundation in Columbus, Ohio, said the results show TAVR programs tend to be developed in well-served areas but asked whether some of the responsibility falls on patients to seek medical attention. “Do we just not give enough education to patients on how to access care?”
Dr. Giri responded by highlighting the complexity of navigating from even being diagnosed with aortic stenosis to making it through a multidisciplinary TAVR evaluation.
“Individuals with increased health literacy and more means are more likely to make it through that gauntlet. But from a public health perspective, obviously, I’d argue that the onus is probably more on the medical community at large to figure out how to roll these programs out more widespread,” he said.
“It looked to us like market forces overwhelmingly seemed to drive the development of new TAVR programs over access to care considerations,” Dr. Giri added. “And just to point out, those market forces aren’t at the level of the device manufacturers, who are often maligned for cost. This is really about the market forces at the level of hospitals and health systems.”
Session comoderator Megan Coylewright, MD, MPH, Erlanger Heart and Lung Institute, Chattanooga, Tenn., said, “I think that’s really well stated,” and noted that physicians may bear some responsibility as well.
“From a physician responsibility, especially for structural heart, we tended to all aggregate together, all of us that have structural heart training or that have trained in certain institutions,” she said. “It’s certainly on us to continue to spread out and go to the communities in need to ensure access. I think, as Dr. Giri said, there are a lot of solutions and that needs to be the focus for the next couple of years.”
Dr. Nathan reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Giri reported serving as a principal investigator for a research study for Boston Scientific, Inari Medical, Abbott, and Recor Medical; consulting for Boston Scientific; and serving on an advisory board for Inari Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Inequities in the initial growth of transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) programs in American hospitals has led to less use of the transformative procedure in poorer communities, a new cross-sectional study suggests.
Using Medicare claims data, investigators identified 554 new TAVR programs created between January 2012 and December 2018.
Of these, 98% were established in metropolitan areas (>50,000 residents) and 53% were started in areas with preexisting TAVR programs, “thereby increasing the number of programs but not necessarily increasing the geographic availability of the procedure,” said study author Ashwin Nathan, MD, Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia.
Only 11 programs were started in nonmetropolitan areas over the study period, he noted during the featured clinical research presentation at the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI) 2021 annual scientific sessions, held virtually this year.
Hospitals that established TAVR programs, compared with those that did not, cared for patients with higher median household incomes (difference, $1,305; P = .03) and from areas with better economic well-being based on the Distressed Communities Index (difference, –3.15 units; P < .01), and cared for fewer patients with dual eligibility for Medicaid (difference, –3.15%; P < .01).
When the investigators looked at rates of TAVR between the core-based statistical areas, there were fewer TAVR procedures per 100,000 Medicare beneficiaries in areas with more Medicaid dual-eligible patients (difference, –1.19% per 1% increase), lower average median household incomes (difference, –0.62% per $1,000 decrease), and more average community distress (difference, –0.35% per 1 unit increase; P < .01 for all).
“What we can conclude is that the increased number of TAVR programs that we found during the study period did not necessarily translate to increased access to TAVR ... Wealthy, more privileged patients had more access to TAVR by virtue of the hospitals that serve them,” Dr. Nathan said.
Future steps, he said, are to identify the role of race and ethnicity in inequitable access to TAVR, identify system- and patient-level barriers to access, and to develop and test solutions to address inequitable care.
Elaborating on the latter point during a discussion of the results, study coauthor Jay S. Giri, MD, MPH, also from the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania, observed that although the data showed rural areas are left behind, not every part of an urban area acts like the area more generally.
As a result, they’re delving into the 25 largest urban areas and trying to disaggregate, based on both socioeconomic status and race within the area, whether inequities exist, he said. “Believe it or not, in some urban areas where there clearly is access – there might even be a dozen TAVR programs within a 25 mile radius – do some of those areas still act like rural areas that don’t have access? So more to come on that.”
Session comoderator Steven Yakubov, MD, MidWest Cardiology Research Foundation in Columbus, Ohio, said the results show TAVR programs tend to be developed in well-served areas but asked whether some of the responsibility falls on patients to seek medical attention. “Do we just not give enough education to patients on how to access care?”
Dr. Giri responded by highlighting the complexity of navigating from even being diagnosed with aortic stenosis to making it through a multidisciplinary TAVR evaluation.
“Individuals with increased health literacy and more means are more likely to make it through that gauntlet. But from a public health perspective, obviously, I’d argue that the onus is probably more on the medical community at large to figure out how to roll these programs out more widespread,” he said.
“It looked to us like market forces overwhelmingly seemed to drive the development of new TAVR programs over access to care considerations,” Dr. Giri added. “And just to point out, those market forces aren’t at the level of the device manufacturers, who are often maligned for cost. This is really about the market forces at the level of hospitals and health systems.”
Session comoderator Megan Coylewright, MD, MPH, Erlanger Heart and Lung Institute, Chattanooga, Tenn., said, “I think that’s really well stated,” and noted that physicians may bear some responsibility as well.
“From a physician responsibility, especially for structural heart, we tended to all aggregate together, all of us that have structural heart training or that have trained in certain institutions,” she said. “It’s certainly on us to continue to spread out and go to the communities in need to ensure access. I think, as Dr. Giri said, there are a lot of solutions and that needs to be the focus for the next couple of years.”
Dr. Nathan reported having no relevant disclosures. Dr. Giri reported serving as a principal investigator for a research study for Boston Scientific, Inari Medical, Abbott, and Recor Medical; consulting for Boston Scientific; and serving on an advisory board for Inari Medical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medtronic recall of almost 240,000 ICDs is class I, FDA says
The Food and Drug Administration has declared Medtronic’s recall of seven models of defibrillating cardiac rhythm devices, caused by a risk for premature battery depletion, as class I, which implies a potential risk for serious injury or death. A total of 444 complaints, but no deaths, have been reported in association with the 239,171 affected devices, the agency said in a statement on April 12, 2021.
Physicians were notified of the company’s recall in early February. It covered implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy–defibrillator (CRT-D) models Evera, Viva, Brava, Claria, Amplia, Compia, and Visia distributed from Aug. 31, 2012 to May 9, 2018.
The devices could be subject to “an unexpected and rapid decrease in battery life” because of a possible short circuit that could lead to a device-replacement alert “earlier than expected.” Some devices may experience full battery depletion “within as little as 1 day” after such an alert.
“If the user does not respond to the first warning, the device may stop functioning. The likelihood that this issue will occur is constant after approximately 3 years after device use,” the announcement said.
Medtronic recommends device replacement no more than 1 week after such an early warning for patients who are not pacing dependent or who have them for primary prevention, but right away for pacing-dependent patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
The Food and Drug Administration has declared Medtronic’s recall of seven models of defibrillating cardiac rhythm devices, caused by a risk for premature battery depletion, as class I, which implies a potential risk for serious injury or death. A total of 444 complaints, but no deaths, have been reported in association with the 239,171 affected devices, the agency said in a statement on April 12, 2021.
Physicians were notified of the company’s recall in early February. It covered implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy–defibrillator (CRT-D) models Evera, Viva, Brava, Claria, Amplia, Compia, and Visia distributed from Aug. 31, 2012 to May 9, 2018.
The devices could be subject to “an unexpected and rapid decrease in battery life” because of a possible short circuit that could lead to a device-replacement alert “earlier than expected.” Some devices may experience full battery depletion “within as little as 1 day” after such an alert.
“If the user does not respond to the first warning, the device may stop functioning. The likelihood that this issue will occur is constant after approximately 3 years after device use,” the announcement said.
Medtronic recommends device replacement no more than 1 week after such an early warning for patients who are not pacing dependent or who have them for primary prevention, but right away for pacing-dependent patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com
The Food and Drug Administration has declared Medtronic’s recall of seven models of defibrillating cardiac rhythm devices, caused by a risk for premature battery depletion, as class I, which implies a potential risk for serious injury or death. A total of 444 complaints, but no deaths, have been reported in association with the 239,171 affected devices, the agency said in a statement on April 12, 2021.
Physicians were notified of the company’s recall in early February. It covered implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) and cardiac resynchronization therapy–defibrillator (CRT-D) models Evera, Viva, Brava, Claria, Amplia, Compia, and Visia distributed from Aug. 31, 2012 to May 9, 2018.
The devices could be subject to “an unexpected and rapid decrease in battery life” because of a possible short circuit that could lead to a device-replacement alert “earlier than expected.” Some devices may experience full battery depletion “within as little as 1 day” after such an alert.
“If the user does not respond to the first warning, the device may stop functioning. The likelihood that this issue will occur is constant after approximately 3 years after device use,” the announcement said.
Medtronic recommends device replacement no more than 1 week after such an early warning for patients who are not pacing dependent or who have them for primary prevention, but right away for pacing-dependent patients.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com