User login
Antihistamines synergistically induce CLL cell death with TK inhibitors
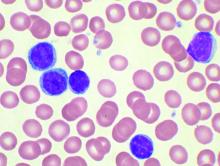
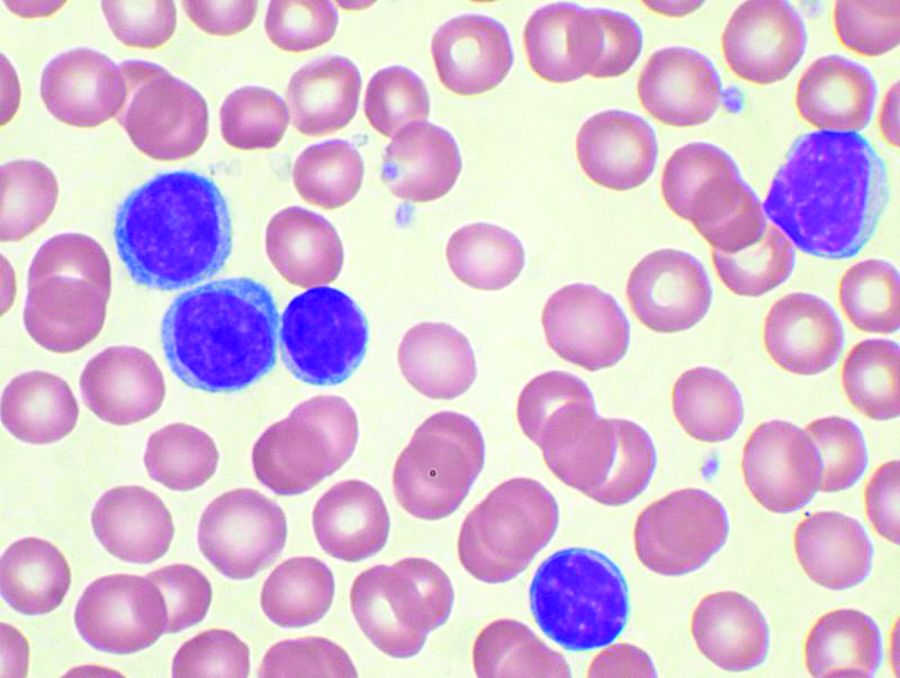
Three over-the-counter antihistamines, clemastine, desloratadine, and loratadine, preferentially induce cell death through lysosomal membrane permeabilization in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, compared with normal lymphocytes, according to the results of an in vitro study published in Leukemia Research.
In addition, the antihistamines showed a synergistic effect in killing off chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells when combined with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, ibrutinib, but not with chemotherapy, according to Aaron Chanas-Larue of CancerCare Manitoba, Winnipeg, Man., and colleagues.
Blood from CLL patients and age-matched healthy donors was collected, treated, and compared with two malignant B-cell lines. Cells were treated with the three different antihistamines at various concentrations alone and in the presence of ibrutinib. Cell death was determined by flow cytometry using fluorescent staining and EC50 (half-maximal effective concentration) values were calculated.
Of the three drugs, clemastine demonstrated the greatest degree of cytotoxicity, with a mean EC50 value of 12.3 mcmol in CLL cells. Desloratadine and loratadine also had a greater effect on leukemic cells, with mean EC50 values of 27.2 mcmol and 17.2 mcmol, respectively, according to the researchers.
Clemastine also showed the greatest tumor sensitivity, with an EC50 nearly three times lower for CLL cells (EC50, 12.3 mcmol) than for normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (EC50, 32 mcmol). In addition, clemastine induced cell death over a 72-hour time course in CLL cells, and was equally effective against CLL cells with del17p, unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain gene, or high Zeta-chain–associated protein kinase 70 expression.
Effective synergy
The researchers found that clemastine enhanced cell death when combined with targeted CLL therapies ibrutinib, idelalisib, or venetoclax, but did not enhance the activities of the chemotherapeutics fludarabine, chlorambucil, or bendamustine.
Ibrutinib increased cell death to the greatest degree when combined with antihistamines. The effect was demonstrated to be synergistic, showing “a unique interaction between the activities of the antihistamines and this inhibitor of the B-cell pathway, suggesting a clinical potential for this combination,” the authors stated.
“Repurposing well-characterized drugs such as antihistamines with defined mechanisms and toxicities allows for repositioning of these drugs to use in CLL treatment in the near future in the context of targeted therapies,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the Cancer Research Society and the CancerCare Manitoba Foundation. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Chanas-Larue A et al. Leuk Res. 2020 Jul 17. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106423.
Three over-the-counter antihistamines, clemastine, desloratadine, and loratadine, preferentially induce cell death through lysosomal membrane permeabilization in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, compared with normal lymphocytes, according to the results of an in vitro study published in Leukemia Research.
In addition, the antihistamines showed a synergistic effect in killing off chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells when combined with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, ibrutinib, but not with chemotherapy, according to Aaron Chanas-Larue of CancerCare Manitoba, Winnipeg, Man., and colleagues.
Blood from CLL patients and age-matched healthy donors was collected, treated, and compared with two malignant B-cell lines. Cells were treated with the three different antihistamines at various concentrations alone and in the presence of ibrutinib. Cell death was determined by flow cytometry using fluorescent staining and EC50 (half-maximal effective concentration) values were calculated.
Of the three drugs, clemastine demonstrated the greatest degree of cytotoxicity, with a mean EC50 value of 12.3 mcmol in CLL cells. Desloratadine and loratadine also had a greater effect on leukemic cells, with mean EC50 values of 27.2 mcmol and 17.2 mcmol, respectively, according to the researchers.
Clemastine also showed the greatest tumor sensitivity, with an EC50 nearly three times lower for CLL cells (EC50, 12.3 mcmol) than for normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (EC50, 32 mcmol). In addition, clemastine induced cell death over a 72-hour time course in CLL cells, and was equally effective against CLL cells with del17p, unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain gene, or high Zeta-chain–associated protein kinase 70 expression.
Effective synergy
The researchers found that clemastine enhanced cell death when combined with targeted CLL therapies ibrutinib, idelalisib, or venetoclax, but did not enhance the activities of the chemotherapeutics fludarabine, chlorambucil, or bendamustine.
Ibrutinib increased cell death to the greatest degree when combined with antihistamines. The effect was demonstrated to be synergistic, showing “a unique interaction between the activities of the antihistamines and this inhibitor of the B-cell pathway, suggesting a clinical potential for this combination,” the authors stated.
“Repurposing well-characterized drugs such as antihistamines with defined mechanisms and toxicities allows for repositioning of these drugs to use in CLL treatment in the near future in the context of targeted therapies,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the Cancer Research Society and the CancerCare Manitoba Foundation. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Chanas-Larue A et al. Leuk Res. 2020 Jul 17. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106423.
Three over-the-counter antihistamines, clemastine, desloratadine, and loratadine, preferentially induce cell death through lysosomal membrane permeabilization in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, compared with normal lymphocytes, according to the results of an in vitro study published in Leukemia Research.
In addition, the antihistamines showed a synergistic effect in killing off chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) cells when combined with the tyrosine kinase inhibitor, ibrutinib, but not with chemotherapy, according to Aaron Chanas-Larue of CancerCare Manitoba, Winnipeg, Man., and colleagues.
Blood from CLL patients and age-matched healthy donors was collected, treated, and compared with two malignant B-cell lines. Cells were treated with the three different antihistamines at various concentrations alone and in the presence of ibrutinib. Cell death was determined by flow cytometry using fluorescent staining and EC50 (half-maximal effective concentration) values were calculated.
Of the three drugs, clemastine demonstrated the greatest degree of cytotoxicity, with a mean EC50 value of 12.3 mcmol in CLL cells. Desloratadine and loratadine also had a greater effect on leukemic cells, with mean EC50 values of 27.2 mcmol and 17.2 mcmol, respectively, according to the researchers.
Clemastine also showed the greatest tumor sensitivity, with an EC50 nearly three times lower for CLL cells (EC50, 12.3 mcmol) than for normal peripheral blood mononuclear cells (EC50, 32 mcmol). In addition, clemastine induced cell death over a 72-hour time course in CLL cells, and was equally effective against CLL cells with del17p, unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain gene, or high Zeta-chain–associated protein kinase 70 expression.
Effective synergy
The researchers found that clemastine enhanced cell death when combined with targeted CLL therapies ibrutinib, idelalisib, or venetoclax, but did not enhance the activities of the chemotherapeutics fludarabine, chlorambucil, or bendamustine.
Ibrutinib increased cell death to the greatest degree when combined with antihistamines. The effect was demonstrated to be synergistic, showing “a unique interaction between the activities of the antihistamines and this inhibitor of the B-cell pathway, suggesting a clinical potential for this combination,” the authors stated.
“Repurposing well-characterized drugs such as antihistamines with defined mechanisms and toxicities allows for repositioning of these drugs to use in CLL treatment in the near future in the context of targeted therapies,” they concluded.
The study was supported by grants from the Cancer Research Society and the CancerCare Manitoba Foundation. The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Chanas-Larue A et al. Leuk Res. 2020 Jul 17. doi: 10.1016/j.leukres.2020.106423.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
BALL score predicts benefit from ibrutinib therapy in relapsed/refractory CLL patients
The BALL score was able to identify a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who particularly benefit from single-agent ibrutinib therapy, according to the results of a study of 111 patients followed from two different institutions.
The BALL model consists of four factors: serum beta₂-microglobulin at 5 mg/dL or greater, hemoglobin < 110 g/L for women or < 120 g/L for men, lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] > upper limit of normal [UNL], and time elapsed from last therapy less than 24 months. Each parameter was alloted 1 point, leading to a stratification of patients into three different prognostic groups: low risk (score 0-1), intermediate risk (2-3), and high risk (score 4), according to a report published online in Leukemia Research.
According to Stefano Molica, MD, of the Azienda Ospedaliera Pugliese-Ciaccio, Catanzaro, Italy, and his colleagues, the majority of patients (82%) were clinical Rai stage II-IV. The median patient age was 63 years and nearly 68% were men.
The researchers assessed four models for predicting overall survival. The modified version of CLL-International Prognostic Index (CLL-IPI) failed to provide prognostic information in relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL (P = .77) as did the Ahn et al. model (P = .95) and a simplified BALL model (P = .09). In contrast, the full BALL score captured two groups of patients with significant differences in survival (hazard ratio, 0.240; 95 % confidence interval, 0.10-0.54; P = .0005); however, because of the low number of patients in the high-risk category, these cases were combined with the intermediate-risk group.
The BALL score identified a subset of patients, accounting for about 50% of the whole population, who particularly benefit from single-agent ibrutinib, according to Dr. Molica and his colleagues. These patients had a survival rate of 85% at 3 years.
“In contrast, the outcome of subjects with intermediate-high risk is disappointing. These patients should be considered for a combination of targeted drugs or cellular-based therapies,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Molica S et al. Leuk Res. 2020 Jun 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.
The BALL score was able to identify a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who particularly benefit from single-agent ibrutinib therapy, according to the results of a study of 111 patients followed from two different institutions.
The BALL model consists of four factors: serum beta₂-microglobulin at 5 mg/dL or greater, hemoglobin < 110 g/L for women or < 120 g/L for men, lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] > upper limit of normal [UNL], and time elapsed from last therapy less than 24 months. Each parameter was alloted 1 point, leading to a stratification of patients into three different prognostic groups: low risk (score 0-1), intermediate risk (2-3), and high risk (score 4), according to a report published online in Leukemia Research.
According to Stefano Molica, MD, of the Azienda Ospedaliera Pugliese-Ciaccio, Catanzaro, Italy, and his colleagues, the majority of patients (82%) were clinical Rai stage II-IV. The median patient age was 63 years and nearly 68% were men.
The researchers assessed four models for predicting overall survival. The modified version of CLL-International Prognostic Index (CLL-IPI) failed to provide prognostic information in relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL (P = .77) as did the Ahn et al. model (P = .95) and a simplified BALL model (P = .09). In contrast, the full BALL score captured two groups of patients with significant differences in survival (hazard ratio, 0.240; 95 % confidence interval, 0.10-0.54; P = .0005); however, because of the low number of patients in the high-risk category, these cases were combined with the intermediate-risk group.
The BALL score identified a subset of patients, accounting for about 50% of the whole population, who particularly benefit from single-agent ibrutinib, according to Dr. Molica and his colleagues. These patients had a survival rate of 85% at 3 years.
“In contrast, the outcome of subjects with intermediate-high risk is disappointing. These patients should be considered for a combination of targeted drugs or cellular-based therapies,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Molica S et al. Leuk Res. 2020 Jun 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.
The BALL score was able to identify a subset of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who particularly benefit from single-agent ibrutinib therapy, according to the results of a study of 111 patients followed from two different institutions.
The BALL model consists of four factors: serum beta₂-microglobulin at 5 mg/dL or greater, hemoglobin < 110 g/L for women or < 120 g/L for men, lactate dehydrogenase [LDH] > upper limit of normal [UNL], and time elapsed from last therapy less than 24 months. Each parameter was alloted 1 point, leading to a stratification of patients into three different prognostic groups: low risk (score 0-1), intermediate risk (2-3), and high risk (score 4), according to a report published online in Leukemia Research.
According to Stefano Molica, MD, of the Azienda Ospedaliera Pugliese-Ciaccio, Catanzaro, Italy, and his colleagues, the majority of patients (82%) were clinical Rai stage II-IV. The median patient age was 63 years and nearly 68% were men.
The researchers assessed four models for predicting overall survival. The modified version of CLL-International Prognostic Index (CLL-IPI) failed to provide prognostic information in relapsed/refractory (R/R) CLL (P = .77) as did the Ahn et al. model (P = .95) and a simplified BALL model (P = .09). In contrast, the full BALL score captured two groups of patients with significant differences in survival (hazard ratio, 0.240; 95 % confidence interval, 0.10-0.54; P = .0005); however, because of the low number of patients in the high-risk category, these cases were combined with the intermediate-risk group.
The BALL score identified a subset of patients, accounting for about 50% of the whole population, who particularly benefit from single-agent ibrutinib, according to Dr. Molica and his colleagues. These patients had a survival rate of 85% at 3 years.
“In contrast, the outcome of subjects with intermediate-high risk is disappointing. These patients should be considered for a combination of targeted drugs or cellular-based therapies,” the researchers concluded.
The authors reported that they had no conflicts.
SOURCE: Molica S et al. Leuk Res. 2020 Jun 10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.leukres.2020.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
EMA gives green light to avapritinib for GIST, acalabrutinib for CLL
The CHMP recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for avapritinib (Ayvakit, Blueprint Medicines) for use in adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. About 6%-10% of GIST tumors harbor this mutation, and avapritinib is a selective and potent inhibitor of KIT and PDGFRA mutant kinases.
The CHMP also adopted a positive opinion for acalabrutinib (Calquence, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) as monotherapy in patients who are treatment-naive or have received at least one prior therapy.
The CHMP opinion on both drugs will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to grant marketing authorization for medicinal products in the EU.
Detailed recommendations for the use of both drugs will be provided in the summary of product characteristics, which will be published in the European public assessment report and made available in all official EU languages after the products receive marketing authorization by the European Commission.
First targeted therapy for mutation
If approved by the European Commission, avapritinib would be the first treatment in the EU indicated for patients with PDGFRA D842V-mutant GIST.
Avapritinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year for the aforementioned indication. The FDA approval was based on findings from the phase 1 NAVIGATOR trial, which included 43 patients with GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, including 38 patients with the most common mutation, PDGFRA D842V.
For patients harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, the overall response rate (ORR) was 84%, with 7% having a complete response and 77% having a partial response. Patients with the PDGFRA D842V mutation achieved an ORR of 89%, with 8% having a complete response and 82% having a partial response.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies ... Today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, in a statement at the time of approval.
The most common side effects (≥ 20% of patients) observed in patients taking avapritinib include nausea, fatigue, anemia, periorbital edema, face edema, hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, increased lacrimation, decreased appetite, and memory impairment. There may also be a risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in which case the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
In the EU, conditional marketing authorization is granted to a medicinal product that fulfills an unmet medical need when the benefit to public health of immediate availability outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required, the CHMP notes on its website.
Avapritinib had received an orphan medicine designation during development, which the EMA will review to determine if the designation can be maintained.
New treatment for CLL
Acalabrutinib is already approved in the United States, Canada, and Australia for the treatment of CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma. The product was approved at the same time by all three regulatory authorities last year. In the United States, acalabrutinib had previously been approved for use in mantle cell lymphoma.
The CHMP’s positive opinion of acalabrutinib is based on results from two phase 3 trials, ELEVATE TN and ASCEND.
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib was compared with investigator’s choice of idelalisib or bendamustine with rituximab. The trial, which involved 310 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, showed that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival (PFS).
At a median follow-up of 16.1 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib and was 16.5 months with investigator’s choice of therapy (P < .0001).
The most commonly reported adverse events seen with acalabrutinib were respiratory tract infections, headache, bruising, contusion, diarrhea, nausea, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased platelets.
In the ELEVATE TN trial, acalabrutinib was given alone or combined with obinutuzumab and compared to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in patients with previously untreated CLL. There were 535 patients randomized to receive acalabrutinib alone (n = 179), acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab (n = 179), and chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab (n = 177).
At a median follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib alone or with acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, but the median PFS was 22.6 months in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
The most common adverse events in the acalabrutinib arms were headache, diarrhea, neutropenia, and nausea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The CHMP recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for avapritinib (Ayvakit, Blueprint Medicines) for use in adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. About 6%-10% of GIST tumors harbor this mutation, and avapritinib is a selective and potent inhibitor of KIT and PDGFRA mutant kinases.
The CHMP also adopted a positive opinion for acalabrutinib (Calquence, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) as monotherapy in patients who are treatment-naive or have received at least one prior therapy.
The CHMP opinion on both drugs will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to grant marketing authorization for medicinal products in the EU.
Detailed recommendations for the use of both drugs will be provided in the summary of product characteristics, which will be published in the European public assessment report and made available in all official EU languages after the products receive marketing authorization by the European Commission.
First targeted therapy for mutation
If approved by the European Commission, avapritinib would be the first treatment in the EU indicated for patients with PDGFRA D842V-mutant GIST.
Avapritinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year for the aforementioned indication. The FDA approval was based on findings from the phase 1 NAVIGATOR trial, which included 43 patients with GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, including 38 patients with the most common mutation, PDGFRA D842V.
For patients harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, the overall response rate (ORR) was 84%, with 7% having a complete response and 77% having a partial response. Patients with the PDGFRA D842V mutation achieved an ORR of 89%, with 8% having a complete response and 82% having a partial response.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies ... Today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, in a statement at the time of approval.
The most common side effects (≥ 20% of patients) observed in patients taking avapritinib include nausea, fatigue, anemia, periorbital edema, face edema, hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, increased lacrimation, decreased appetite, and memory impairment. There may also be a risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in which case the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
In the EU, conditional marketing authorization is granted to a medicinal product that fulfills an unmet medical need when the benefit to public health of immediate availability outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required, the CHMP notes on its website.
Avapritinib had received an orphan medicine designation during development, which the EMA will review to determine if the designation can be maintained.
New treatment for CLL
Acalabrutinib is already approved in the United States, Canada, and Australia for the treatment of CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma. The product was approved at the same time by all three regulatory authorities last year. In the United States, acalabrutinib had previously been approved for use in mantle cell lymphoma.
The CHMP’s positive opinion of acalabrutinib is based on results from two phase 3 trials, ELEVATE TN and ASCEND.
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib was compared with investigator’s choice of idelalisib or bendamustine with rituximab. The trial, which involved 310 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, showed that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival (PFS).
At a median follow-up of 16.1 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib and was 16.5 months with investigator’s choice of therapy (P < .0001).
The most commonly reported adverse events seen with acalabrutinib were respiratory tract infections, headache, bruising, contusion, diarrhea, nausea, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased platelets.
In the ELEVATE TN trial, acalabrutinib was given alone or combined with obinutuzumab and compared to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in patients with previously untreated CLL. There were 535 patients randomized to receive acalabrutinib alone (n = 179), acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab (n = 179), and chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab (n = 177).
At a median follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib alone or with acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, but the median PFS was 22.6 months in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
The most common adverse events in the acalabrutinib arms were headache, diarrhea, neutropenia, and nausea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The CHMP recommended granting conditional marketing authorization for avapritinib (Ayvakit, Blueprint Medicines) for use in adults with unresectable or metastatic gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GIST) harboring a platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRA) exon 18 mutation, including PDGFRA D842V mutations. About 6%-10% of GIST tumors harbor this mutation, and avapritinib is a selective and potent inhibitor of KIT and PDGFRA mutant kinases.
The CHMP also adopted a positive opinion for acalabrutinib (Calquence, AstraZeneca) for the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) as monotherapy in patients who are treatment-naive or have received at least one prior therapy.
The CHMP opinion on both drugs will be reviewed by the European Commission, which has the authority to grant marketing authorization for medicinal products in the EU.
Detailed recommendations for the use of both drugs will be provided in the summary of product characteristics, which will be published in the European public assessment report and made available in all official EU languages after the products receive marketing authorization by the European Commission.
First targeted therapy for mutation
If approved by the European Commission, avapritinib would be the first treatment in the EU indicated for patients with PDGFRA D842V-mutant GIST.
Avapritinib was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) earlier this year for the aforementioned indication. The FDA approval was based on findings from the phase 1 NAVIGATOR trial, which included 43 patients with GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, including 38 patients with the most common mutation, PDGFRA D842V.
For patients harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation, the overall response rate (ORR) was 84%, with 7% having a complete response and 77% having a partial response. Patients with the PDGFRA D842V mutation achieved an ORR of 89%, with 8% having a complete response and 82% having a partial response.
“GIST harboring a PDGFRA exon 18 mutation do not respond to standard therapies ... Today’s approval provides patients with the first drug specifically approved for GIST harboring this mutation,” said Richard Pazdur, MD, director of the FDA’s Oncology Center of Excellence, in a statement at the time of approval.
The most common side effects (≥ 20% of patients) observed in patients taking avapritinib include nausea, fatigue, anemia, periorbital edema, face edema, hyperbilirubinemia, diarrhea, vomiting, peripheral edema, increased lacrimation, decreased appetite, and memory impairment. There may also be a risk of intracranial hemorrhage, in which case the dose should be reduced or the drug should be discontinued.
In the EU, conditional marketing authorization is granted to a medicinal product that fulfills an unmet medical need when the benefit to public health of immediate availability outweighs the risk inherent in the fact that additional data are still required, the CHMP notes on its website.
Avapritinib had received an orphan medicine designation during development, which the EMA will review to determine if the designation can be maintained.
New treatment for CLL
Acalabrutinib is already approved in the United States, Canada, and Australia for the treatment of CLL and small lymphocytic lymphoma. The product was approved at the same time by all three regulatory authorities last year. In the United States, acalabrutinib had previously been approved for use in mantle cell lymphoma.
The CHMP’s positive opinion of acalabrutinib is based on results from two phase 3 trials, ELEVATE TN and ASCEND.
In the ASCEND trial, acalabrutinib was compared with investigator’s choice of idelalisib or bendamustine with rituximab. The trial, which involved 310 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, showed that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival (PFS).
At a median follow-up of 16.1 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib and was 16.5 months with investigator’s choice of therapy (P < .0001).
The most commonly reported adverse events seen with acalabrutinib were respiratory tract infections, headache, bruising, contusion, diarrhea, nausea, rash, musculoskeletal pain, fatigue, decreased hemoglobin, and decreased platelets.
In the ELEVATE TN trial, acalabrutinib was given alone or combined with obinutuzumab and compared to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in patients with previously untreated CLL. There were 535 patients randomized to receive acalabrutinib alone (n = 179), acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab (n = 179), and chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab (n = 177).
At a median follow-up of 28 months, the median PFS was not reached with acalabrutinib alone or with acalabrutinib plus obinutuzumab, but the median PFS was 22.6 months in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm (P < .0001 for both comparisons).
The most common adverse events in the acalabrutinib arms were headache, diarrhea, neutropenia, and nausea.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In remission for 10 years: Long-term toxicity data on CAR T cells
When a patient with cancer hears there isn’t much left that doctors can do, it always stays fresh in the mind.
Doug Olson was first diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) over 20 years ago, in 1996. For several years, his doctors used the watch-and-wait approach. But then his cancer progressed and needed treatment. By 2010, it had mutated so much that it no longer responded to standard therapy.
He was rapidly running out of options. Back then, the only treatment left was a bone marrow transplant. Without one, his doctors said, he would have 1 or 2 years left to live.
“I was really trying to avoid a bone marrow transplant. You’re playing your last card if that doesn’t work. It’s a pretty rough procedure,” Olson told Medscape Medical News.
Looking back, Olson counts himself as lucky – for being in the right place, at the right time, with the right doctor. His oncologist was David Porter, MD, the principal investigator on a trial at the University of Pennsylvania that was investigating a brand new approach to treating cancer: chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
CAR T-cell therapy uses a patient’s own T cells engineered to express a receptor that targets proteins on cancer cells. CAR T cells are considered “living drugs” because they expand inside the body and stick around for years – maybe for a lifetime – to fight the cancer if it tries to come back.
“I was certainly intrigued by the approach. It had worked in mice, and it was the sort of thing that looked like it would work,” Olson recalled.
Science is not a foreign language to Olson. He holds a PhD in medicinal chemistry, spent most of his career in the in vitro diagnostics industry, and currently acts as chief executive officer of Buhlmann Diagnostics Corp.
So he read the clinical protocol for the first in-human trial of CAR T cells and agreed to become patient number two.
Olson’s T cells were harvested, engineered to attack the CD19 antigen found on malignant and normal B lymphocytes, and then were expanded into millions in the lab. After undergoing preconditioning with chemotherapy to minimize rejection and boost the CAR T cells’ expansion inside the body, he received several infusions of the new therapy over the course of 3 days.
Nothing really happened for 2 weeks. Then he developed severe flu-like symptoms – so bad that he was hospitalized.
Ironically, getting sick was a sign that the CAR T cells were working. Olson was experiencing one of the main short-term effects of CAR T-cell therapy: cytokine release syndrome. Symptoms include extremely high fevers and dangerous drops in blood pressure that can potentially cause end-organ damage.
In the early trials of these products, some patients experienced such a severe reaction that they needed intensive care, and some died. With increasing clinical experience, doctors have learned to control the reaction with the use of steroids and interleukein-6 inhibitors such as tocilizumab (Actemra).
Fortunately for Olson, the reaction passed, and he was eventually discharged.
Then the “aha moment” happened. Four weeks after receiving the CAR T cells, Olson found out that he was cancer free.
“It still gives me shivers,” he said. “Dr Porter said, ‘Your bone marrow’s completely free. We just can’t find a cancer cell anywhere.’ “
The remission has lasted, and it is now 10 years later.
Balancing long-term risks vs benefits
Long-term data have been accumulating for these novel therapies since Olson’s treatment in 2010. This is particularly important for CAR T-cell therapy, because of its longevity. Because these are living cells and are expected to persist in the body for years, there is great interest in longer-term data, especially the risks for toxicity.
The FDA requires clinical follow-up for at least 15 years for patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy or any other genetically modified cells.
So far, most of the experience with CAR T cells comes from anti-CD19-directed therapy, which has shown “remarkable” remission rates in the 50% to 85% range, said Nirali Shah, MD, head of the hematologic malignancies section of the Pediatric Oncology Branch at the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
The most recent results presented at this year’s annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology support earlier efficacy data, she noted. In the longest follow-up to date, researchers reported remissions lasting over 9 years in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma or CLL treated with Kite›s axicaptagene cilleucel (Yescarta), one of two anti-CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapies approved by the FDA in 2017 (the other is Novartis’ tisagenlecleucel [Kymriah]).
This study included 43 patients and showed an overall remission rate of 76%. Complete remission was achieved in 54% of patients, and 22% had partial remission.
The other focus is long-term safety. Although some of the long-term adverse effects are known and are manageable, others fall into the theoretical realm. In early May 2020, the NCI held a multidisciplinary virtual conference on CAR T-cell therapy «to encourage collaborative research about the subacute and potentially long-term toxicity profile of these treatments.»
“We know just a little at this point about late- and long-term effects of CAR-T therapy, because we are relatively early in the era of CAR T cells,” said Merav Bar, MD, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington.
B-cell aplasia and risk for new infections
What is known is that B-cell aplasia represents the most common long-term adverse effect of CAR T-cell therapy. B-cell aplasia results when anti-CD19 CAR-T therapy wipes out healthy B cells as well as the malignant ones responsible for leukemia/lymphoma.
As major players in the immune system, B cells are a key defense against viruses. So B-cell aplasia represents a very specific type of immunosuppression. It is generally less severe than immunosuppression that occurs after organ transplant, which hits the immune system pretty much across the board and carries a much higher risk for infection.
The main concern is what happens when someone with B-cell aplasia encounters a new pathogen, such as SARS-CoV-2.
After infection, B cells generate memory cells, which are not killed off by anti-CD19 therapy and that stick around for life. So a patient such as Olson would still make antibodies that fight infections they experienced before receiving CAR-T therapy, such as childhood chickenpox. But now they are unable to make new memory cells, so these patients receive monthly immunoglobulin infusions to protect against pathogens they have not previously encountered.
Olson takes this in stride and says he isn’t overly worried about COVID-19. He follows the recommended precautions for a man his age. He wears a mask, washes his hands frequently, and tries to maintain social distancing. But he doesn’t stay locked up in his New Hampshire home.
“I took the attitude when I was diagnosed with cancer that I’m going to live my life,” he said. “Quality of life to me is more important than quantity.”
Neuropsychiatric toxicity
Another problem is the possibility of neuropsychiatric toxicity. Past studies have reported a wide range of such toxicities associated with CAR T-cell therapy, including seizures and hallucinations. Most have occurred early in the course of treatment and appear to be short-lived and reversible. However, there remain questions about long-term neuropsychiatric problems.
In a long-term study of 40 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and ALL, nearly half of patients (47.5%, 19/40) self-reported at least one clinically meaningful negative neuropsychiatric outcome (anxiety, depression, or cognitive difficulty) 1 to 5 years after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. In addition, 37.5% (15/40) self-reported cognitive difficulties.
“Patients with more severe neurotoxicity showed a trend for more cognitive difficulties afterwards,» said Bar, senior author of the study.
However, teasing out the role that CAR T-cell therapy plays in these problems poses a challenge. All of these patients had been heavily pretreated with previous cancer therapy, which has also been associated with neuropsychiatric problems.
“So far, we don’t know what caused it,” Bar said. “Nevertheless, people need to pay attention to neuropsychiatric symptoms in CAR T-cell therapy. It is important to continue to monitor these patients for these issues.”
Graft-vs-host disease
Another potential problem is graft-vs-host disease (GVHD). This is not uncommon after hematopoietic stem cell transplants. It develops when the donor T cells view antigens on healthy recipient cells as foreign and attack them.
For patients who are treated with CAR T cells, GVHD is mostly a concern among individuals who have previously had a transplant and who are already at increased risk for it.
In a study of late effects among 86 adults treated with anti-CD19 CAR T cells for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Bar and colleagues found that GVHD occurred only among patients who had received a previous donor stem cell transplant. Of these, 20% (3/15) developed GVHD about 28 months after CAR-T therapy.
“The data for CAR T cells causing GVHD really hasn’t shown that it’s a huge problem, although we have seen it and are continuing to monitor for it,” the NCI’s Shah commented to Medscape Medical News.
Other Long-term Adverse Effects
A range of other long-term adverse effects have been reported with CAR-T therapy, including prolonged cytopenias (reduced mature blood cells), myelodysplasia (bone marrow failure), and second malignancies.
In the study with the longest follow-up to date, 16% (7/43) of patients developed second malignancies, which is comparable to data from Bar’s study in Seattle (15%, 13/86). The researchers in this study consider this rate to be no higher than expected: these patients had already received extensive chemotherapy, which increases the risk for other cancers, they point out.
However, this brings up theoretical concerns about the long-term effects of gene modification. CAR T cells are engineered using retroviruses (mainly lentiviruses), which randomly insert the CAR genes into the host genome. Doing so may cause mutations that could promote cancer. These lentiviruses also carry the theoretical risk of becoming capable of viral replication once inside the body.
To address these concerns, viruses used to engineer CAR T cells go through comprehensive safety testing. After therapy, patients are checked every few months during the first year and annually after that.
So far, there have been no reports of cancers associated with CAR T-cell therapy.
“Any type of cancer is a very theoretical risk,” Bar told Medscape Medical News. «Most likely the malignancies in our study were related to prior treatment that the patients received. None of them had any evidence of replication-competent lentivirus, or any other evidence that the malignancies were related to the CAR T cells.»
Another theoretical concern is the possibility of new-onset autoimmune disease, although, once again, no cases have been reported so far.
“We think of it as a theoretic possibility. Whenever you jack up the immune system, autoimmune disease is a potential risk,” said Carl June, MD, director of the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies at the University of Pennsylvania.
June was the co–principal investigator of the trial in which Olson participated. He is also the inventor on patents for CAR T cells licensed by the University of Pennsylvania to Novartis and Tmunity and is a scientific founder with equity in Tmunity.
Still, autoimmunity could occur, and scientists are looking out for it.
“We are continuing to be vigilant in our monitoring for autoimmune disease,” Shah added. “We’ve been doing CAR T-cell therapy since 2012, and I think we have yet to see true autoimmunity beyond GVHD.”
Future directions
In the 10 years since Olson received CAR T-cell therapy, an entire industry has sprung up. Over 100 companies worldwide are now developing CAR T-cell therapies targeting various antigens. These therapies are directed at about 60 different tumor types, including solid tumors. Nearly 200 clinical trials are underway, though most are still in early stages: as of September 2019, only 5% had reached phase 3.
Clinical data show promising results for CAR T-cell therapy directed against CD22 (overexpressed on ALL cells), and BCMA (found on almost all multiple myeloma cells). Yet questions remain as to whether CAR T cells will be as effective if they target antigens other than CD19 or cells other than B lymphocytes. One of the biggest research questions is whether they will be effective against solid tumors.
One research avenue being watched with great interest is the development of universal CAR T cells. So far, such products are at very early stages of development (phase 1 trials), but they are attractive because of the potential advantages they offer over bespoke CAR T cells. Automating the process holds the promise of immediate availability, standardizing production, expanding access, and lowering costs. And because the T cells for this universal product come from healthy donors, they may function better than T cells that have been battered and bruised by past cancer treatments, or even the cancer itself.
However, precisely because they are developed from healthy donor T cells, universal CAR T cells may pose increased risk for GVHD. Scientists are trying to get around this problem by engineering universal CAR T cells that lack the T-cell receptor involved in GVHD.
There are also other concerns. Nature has a penchant for mutation. Engineering CAR T cells without T-cell receptors means the body may no longer detect or reject a universal CAR T cell if it goes rogue. Also, gene insertion in universal CAR-T therapy is targeted rather than random (as in bespoke CAR T cells), which could create off-target effects. Both issues create a theoretical risk of such products inducing an untreatable CAR T-cell therapy–associated cancer.
“The theoretic risk with universal cells is that their safety profile may not be as good for long term,” June commented.
Hope for the future
From that first trial in which June and Porter used CAR T cells, two of three patients they treated are still alive 10 years later.
Olson is one of these two, and he still undergoes monitoring every 3 months to check for relapse. So far, none of his tests have shown signs of his cancer returning.
After going into remission, Doug spent the next 6 to 9 months regaining his health and strength.
“I figured if I had this amazing treatment that saved my life, I had an obligation to stay alive,” he said. “I’d better not die of something like a heart attack!”
He took up long distance running and has completed six half marathons. He became involved in the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, participating in fund-raising and helping newly diagnosed patients. Over the years, he has also given talks for researchers, people with cancer, and healthcare providers.
Doug is now 73. Today, he marvels at how rapidly the CAR-T field has progressed.
“Twenty years ago, if you had cancer, your prospects weren’t nearly as good as these days. In 2010, people still didn’t believe in CAR T-cell therapy,” he said. “My goal always in telling my story is a message of hope.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When a patient with cancer hears there isn’t much left that doctors can do, it always stays fresh in the mind.
Doug Olson was first diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) over 20 years ago, in 1996. For several years, his doctors used the watch-and-wait approach. But then his cancer progressed and needed treatment. By 2010, it had mutated so much that it no longer responded to standard therapy.
He was rapidly running out of options. Back then, the only treatment left was a bone marrow transplant. Without one, his doctors said, he would have 1 or 2 years left to live.
“I was really trying to avoid a bone marrow transplant. You’re playing your last card if that doesn’t work. It’s a pretty rough procedure,” Olson told Medscape Medical News.
Looking back, Olson counts himself as lucky – for being in the right place, at the right time, with the right doctor. His oncologist was David Porter, MD, the principal investigator on a trial at the University of Pennsylvania that was investigating a brand new approach to treating cancer: chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
CAR T-cell therapy uses a patient’s own T cells engineered to express a receptor that targets proteins on cancer cells. CAR T cells are considered “living drugs” because they expand inside the body and stick around for years – maybe for a lifetime – to fight the cancer if it tries to come back.
“I was certainly intrigued by the approach. It had worked in mice, and it was the sort of thing that looked like it would work,” Olson recalled.
Science is not a foreign language to Olson. He holds a PhD in medicinal chemistry, spent most of his career in the in vitro diagnostics industry, and currently acts as chief executive officer of Buhlmann Diagnostics Corp.
So he read the clinical protocol for the first in-human trial of CAR T cells and agreed to become patient number two.
Olson’s T cells were harvested, engineered to attack the CD19 antigen found on malignant and normal B lymphocytes, and then were expanded into millions in the lab. After undergoing preconditioning with chemotherapy to minimize rejection and boost the CAR T cells’ expansion inside the body, he received several infusions of the new therapy over the course of 3 days.
Nothing really happened for 2 weeks. Then he developed severe flu-like symptoms – so bad that he was hospitalized.
Ironically, getting sick was a sign that the CAR T cells were working. Olson was experiencing one of the main short-term effects of CAR T-cell therapy: cytokine release syndrome. Symptoms include extremely high fevers and dangerous drops in blood pressure that can potentially cause end-organ damage.
In the early trials of these products, some patients experienced such a severe reaction that they needed intensive care, and some died. With increasing clinical experience, doctors have learned to control the reaction with the use of steroids and interleukein-6 inhibitors such as tocilizumab (Actemra).
Fortunately for Olson, the reaction passed, and he was eventually discharged.
Then the “aha moment” happened. Four weeks after receiving the CAR T cells, Olson found out that he was cancer free.
“It still gives me shivers,” he said. “Dr Porter said, ‘Your bone marrow’s completely free. We just can’t find a cancer cell anywhere.’ “
The remission has lasted, and it is now 10 years later.
Balancing long-term risks vs benefits
Long-term data have been accumulating for these novel therapies since Olson’s treatment in 2010. This is particularly important for CAR T-cell therapy, because of its longevity. Because these are living cells and are expected to persist in the body for years, there is great interest in longer-term data, especially the risks for toxicity.
The FDA requires clinical follow-up for at least 15 years for patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy or any other genetically modified cells.
So far, most of the experience with CAR T cells comes from anti-CD19-directed therapy, which has shown “remarkable” remission rates in the 50% to 85% range, said Nirali Shah, MD, head of the hematologic malignancies section of the Pediatric Oncology Branch at the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
The most recent results presented at this year’s annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology support earlier efficacy data, she noted. In the longest follow-up to date, researchers reported remissions lasting over 9 years in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma or CLL treated with Kite›s axicaptagene cilleucel (Yescarta), one of two anti-CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapies approved by the FDA in 2017 (the other is Novartis’ tisagenlecleucel [Kymriah]).
This study included 43 patients and showed an overall remission rate of 76%. Complete remission was achieved in 54% of patients, and 22% had partial remission.
The other focus is long-term safety. Although some of the long-term adverse effects are known and are manageable, others fall into the theoretical realm. In early May 2020, the NCI held a multidisciplinary virtual conference on CAR T-cell therapy «to encourage collaborative research about the subacute and potentially long-term toxicity profile of these treatments.»
“We know just a little at this point about late- and long-term effects of CAR-T therapy, because we are relatively early in the era of CAR T cells,” said Merav Bar, MD, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington.
B-cell aplasia and risk for new infections
What is known is that B-cell aplasia represents the most common long-term adverse effect of CAR T-cell therapy. B-cell aplasia results when anti-CD19 CAR-T therapy wipes out healthy B cells as well as the malignant ones responsible for leukemia/lymphoma.
As major players in the immune system, B cells are a key defense against viruses. So B-cell aplasia represents a very specific type of immunosuppression. It is generally less severe than immunosuppression that occurs after organ transplant, which hits the immune system pretty much across the board and carries a much higher risk for infection.
The main concern is what happens when someone with B-cell aplasia encounters a new pathogen, such as SARS-CoV-2.
After infection, B cells generate memory cells, which are not killed off by anti-CD19 therapy and that stick around for life. So a patient such as Olson would still make antibodies that fight infections they experienced before receiving CAR-T therapy, such as childhood chickenpox. But now they are unable to make new memory cells, so these patients receive monthly immunoglobulin infusions to protect against pathogens they have not previously encountered.
Olson takes this in stride and says he isn’t overly worried about COVID-19. He follows the recommended precautions for a man his age. He wears a mask, washes his hands frequently, and tries to maintain social distancing. But he doesn’t stay locked up in his New Hampshire home.
“I took the attitude when I was diagnosed with cancer that I’m going to live my life,” he said. “Quality of life to me is more important than quantity.”
Neuropsychiatric toxicity
Another problem is the possibility of neuropsychiatric toxicity. Past studies have reported a wide range of such toxicities associated with CAR T-cell therapy, including seizures and hallucinations. Most have occurred early in the course of treatment and appear to be short-lived and reversible. However, there remain questions about long-term neuropsychiatric problems.
In a long-term study of 40 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and ALL, nearly half of patients (47.5%, 19/40) self-reported at least one clinically meaningful negative neuropsychiatric outcome (anxiety, depression, or cognitive difficulty) 1 to 5 years after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. In addition, 37.5% (15/40) self-reported cognitive difficulties.
“Patients with more severe neurotoxicity showed a trend for more cognitive difficulties afterwards,» said Bar, senior author of the study.
However, teasing out the role that CAR T-cell therapy plays in these problems poses a challenge. All of these patients had been heavily pretreated with previous cancer therapy, which has also been associated with neuropsychiatric problems.
“So far, we don’t know what caused it,” Bar said. “Nevertheless, people need to pay attention to neuropsychiatric symptoms in CAR T-cell therapy. It is important to continue to monitor these patients for these issues.”
Graft-vs-host disease
Another potential problem is graft-vs-host disease (GVHD). This is not uncommon after hematopoietic stem cell transplants. It develops when the donor T cells view antigens on healthy recipient cells as foreign and attack them.
For patients who are treated with CAR T cells, GVHD is mostly a concern among individuals who have previously had a transplant and who are already at increased risk for it.
In a study of late effects among 86 adults treated with anti-CD19 CAR T cells for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Bar and colleagues found that GVHD occurred only among patients who had received a previous donor stem cell transplant. Of these, 20% (3/15) developed GVHD about 28 months after CAR-T therapy.
“The data for CAR T cells causing GVHD really hasn’t shown that it’s a huge problem, although we have seen it and are continuing to monitor for it,” the NCI’s Shah commented to Medscape Medical News.
Other Long-term Adverse Effects
A range of other long-term adverse effects have been reported with CAR-T therapy, including prolonged cytopenias (reduced mature blood cells), myelodysplasia (bone marrow failure), and second malignancies.
In the study with the longest follow-up to date, 16% (7/43) of patients developed second malignancies, which is comparable to data from Bar’s study in Seattle (15%, 13/86). The researchers in this study consider this rate to be no higher than expected: these patients had already received extensive chemotherapy, which increases the risk for other cancers, they point out.
However, this brings up theoretical concerns about the long-term effects of gene modification. CAR T cells are engineered using retroviruses (mainly lentiviruses), which randomly insert the CAR genes into the host genome. Doing so may cause mutations that could promote cancer. These lentiviruses also carry the theoretical risk of becoming capable of viral replication once inside the body.
To address these concerns, viruses used to engineer CAR T cells go through comprehensive safety testing. After therapy, patients are checked every few months during the first year and annually after that.
So far, there have been no reports of cancers associated with CAR T-cell therapy.
“Any type of cancer is a very theoretical risk,” Bar told Medscape Medical News. «Most likely the malignancies in our study were related to prior treatment that the patients received. None of them had any evidence of replication-competent lentivirus, or any other evidence that the malignancies were related to the CAR T cells.»
Another theoretical concern is the possibility of new-onset autoimmune disease, although, once again, no cases have been reported so far.
“We think of it as a theoretic possibility. Whenever you jack up the immune system, autoimmune disease is a potential risk,” said Carl June, MD, director of the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies at the University of Pennsylvania.
June was the co–principal investigator of the trial in which Olson participated. He is also the inventor on patents for CAR T cells licensed by the University of Pennsylvania to Novartis and Tmunity and is a scientific founder with equity in Tmunity.
Still, autoimmunity could occur, and scientists are looking out for it.
“We are continuing to be vigilant in our monitoring for autoimmune disease,” Shah added. “We’ve been doing CAR T-cell therapy since 2012, and I think we have yet to see true autoimmunity beyond GVHD.”
Future directions
In the 10 years since Olson received CAR T-cell therapy, an entire industry has sprung up. Over 100 companies worldwide are now developing CAR T-cell therapies targeting various antigens. These therapies are directed at about 60 different tumor types, including solid tumors. Nearly 200 clinical trials are underway, though most are still in early stages: as of September 2019, only 5% had reached phase 3.
Clinical data show promising results for CAR T-cell therapy directed against CD22 (overexpressed on ALL cells), and BCMA (found on almost all multiple myeloma cells). Yet questions remain as to whether CAR T cells will be as effective if they target antigens other than CD19 or cells other than B lymphocytes. One of the biggest research questions is whether they will be effective against solid tumors.
One research avenue being watched with great interest is the development of universal CAR T cells. So far, such products are at very early stages of development (phase 1 trials), but they are attractive because of the potential advantages they offer over bespoke CAR T cells. Automating the process holds the promise of immediate availability, standardizing production, expanding access, and lowering costs. And because the T cells for this universal product come from healthy donors, they may function better than T cells that have been battered and bruised by past cancer treatments, or even the cancer itself.
However, precisely because they are developed from healthy donor T cells, universal CAR T cells may pose increased risk for GVHD. Scientists are trying to get around this problem by engineering universal CAR T cells that lack the T-cell receptor involved in GVHD.
There are also other concerns. Nature has a penchant for mutation. Engineering CAR T cells without T-cell receptors means the body may no longer detect or reject a universal CAR T cell if it goes rogue. Also, gene insertion in universal CAR-T therapy is targeted rather than random (as in bespoke CAR T cells), which could create off-target effects. Both issues create a theoretical risk of such products inducing an untreatable CAR T-cell therapy–associated cancer.
“The theoretic risk with universal cells is that their safety profile may not be as good for long term,” June commented.
Hope for the future
From that first trial in which June and Porter used CAR T cells, two of three patients they treated are still alive 10 years later.
Olson is one of these two, and he still undergoes monitoring every 3 months to check for relapse. So far, none of his tests have shown signs of his cancer returning.
After going into remission, Doug spent the next 6 to 9 months regaining his health and strength.
“I figured if I had this amazing treatment that saved my life, I had an obligation to stay alive,” he said. “I’d better not die of something like a heart attack!”
He took up long distance running and has completed six half marathons. He became involved in the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, participating in fund-raising and helping newly diagnosed patients. Over the years, he has also given talks for researchers, people with cancer, and healthcare providers.
Doug is now 73. Today, he marvels at how rapidly the CAR-T field has progressed.
“Twenty years ago, if you had cancer, your prospects weren’t nearly as good as these days. In 2010, people still didn’t believe in CAR T-cell therapy,” he said. “My goal always in telling my story is a message of hope.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
When a patient with cancer hears there isn’t much left that doctors can do, it always stays fresh in the mind.
Doug Olson was first diagnosed with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) over 20 years ago, in 1996. For several years, his doctors used the watch-and-wait approach. But then his cancer progressed and needed treatment. By 2010, it had mutated so much that it no longer responded to standard therapy.
He was rapidly running out of options. Back then, the only treatment left was a bone marrow transplant. Without one, his doctors said, he would have 1 or 2 years left to live.
“I was really trying to avoid a bone marrow transplant. You’re playing your last card if that doesn’t work. It’s a pretty rough procedure,” Olson told Medscape Medical News.
Looking back, Olson counts himself as lucky – for being in the right place, at the right time, with the right doctor. His oncologist was David Porter, MD, the principal investigator on a trial at the University of Pennsylvania that was investigating a brand new approach to treating cancer: chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy.
CAR T-cell therapy uses a patient’s own T cells engineered to express a receptor that targets proteins on cancer cells. CAR T cells are considered “living drugs” because they expand inside the body and stick around for years – maybe for a lifetime – to fight the cancer if it tries to come back.
“I was certainly intrigued by the approach. It had worked in mice, and it was the sort of thing that looked like it would work,” Olson recalled.
Science is not a foreign language to Olson. He holds a PhD in medicinal chemistry, spent most of his career in the in vitro diagnostics industry, and currently acts as chief executive officer of Buhlmann Diagnostics Corp.
So he read the clinical protocol for the first in-human trial of CAR T cells and agreed to become patient number two.
Olson’s T cells were harvested, engineered to attack the CD19 antigen found on malignant and normal B lymphocytes, and then were expanded into millions in the lab. After undergoing preconditioning with chemotherapy to minimize rejection and boost the CAR T cells’ expansion inside the body, he received several infusions of the new therapy over the course of 3 days.
Nothing really happened for 2 weeks. Then he developed severe flu-like symptoms – so bad that he was hospitalized.
Ironically, getting sick was a sign that the CAR T cells were working. Olson was experiencing one of the main short-term effects of CAR T-cell therapy: cytokine release syndrome. Symptoms include extremely high fevers and dangerous drops in blood pressure that can potentially cause end-organ damage.
In the early trials of these products, some patients experienced such a severe reaction that they needed intensive care, and some died. With increasing clinical experience, doctors have learned to control the reaction with the use of steroids and interleukein-6 inhibitors such as tocilizumab (Actemra).
Fortunately for Olson, the reaction passed, and he was eventually discharged.
Then the “aha moment” happened. Four weeks after receiving the CAR T cells, Olson found out that he was cancer free.
“It still gives me shivers,” he said. “Dr Porter said, ‘Your bone marrow’s completely free. We just can’t find a cancer cell anywhere.’ “
The remission has lasted, and it is now 10 years later.
Balancing long-term risks vs benefits
Long-term data have been accumulating for these novel therapies since Olson’s treatment in 2010. This is particularly important for CAR T-cell therapy, because of its longevity. Because these are living cells and are expected to persist in the body for years, there is great interest in longer-term data, especially the risks for toxicity.
The FDA requires clinical follow-up for at least 15 years for patients treated with CAR T-cell therapy or any other genetically modified cells.
So far, most of the experience with CAR T cells comes from anti-CD19-directed therapy, which has shown “remarkable” remission rates in the 50% to 85% range, said Nirali Shah, MD, head of the hematologic malignancies section of the Pediatric Oncology Branch at the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
The most recent results presented at this year’s annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology support earlier efficacy data, she noted. In the longest follow-up to date, researchers reported remissions lasting over 9 years in patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell lymphoma or CLL treated with Kite›s axicaptagene cilleucel (Yescarta), one of two anti-CD19-directed CAR T-cell therapies approved by the FDA in 2017 (the other is Novartis’ tisagenlecleucel [Kymriah]).
This study included 43 patients and showed an overall remission rate of 76%. Complete remission was achieved in 54% of patients, and 22% had partial remission.
The other focus is long-term safety. Although some of the long-term adverse effects are known and are manageable, others fall into the theoretical realm. In early May 2020, the NCI held a multidisciplinary virtual conference on CAR T-cell therapy «to encourage collaborative research about the subacute and potentially long-term toxicity profile of these treatments.»
“We know just a little at this point about late- and long-term effects of CAR-T therapy, because we are relatively early in the era of CAR T cells,” said Merav Bar, MD, from the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle, Washington.
B-cell aplasia and risk for new infections
What is known is that B-cell aplasia represents the most common long-term adverse effect of CAR T-cell therapy. B-cell aplasia results when anti-CD19 CAR-T therapy wipes out healthy B cells as well as the malignant ones responsible for leukemia/lymphoma.
As major players in the immune system, B cells are a key defense against viruses. So B-cell aplasia represents a very specific type of immunosuppression. It is generally less severe than immunosuppression that occurs after organ transplant, which hits the immune system pretty much across the board and carries a much higher risk for infection.
The main concern is what happens when someone with B-cell aplasia encounters a new pathogen, such as SARS-CoV-2.
After infection, B cells generate memory cells, which are not killed off by anti-CD19 therapy and that stick around for life. So a patient such as Olson would still make antibodies that fight infections they experienced before receiving CAR-T therapy, such as childhood chickenpox. But now they are unable to make new memory cells, so these patients receive monthly immunoglobulin infusions to protect against pathogens they have not previously encountered.
Olson takes this in stride and says he isn’t overly worried about COVID-19. He follows the recommended precautions for a man his age. He wears a mask, washes his hands frequently, and tries to maintain social distancing. But he doesn’t stay locked up in his New Hampshire home.
“I took the attitude when I was diagnosed with cancer that I’m going to live my life,” he said. “Quality of life to me is more important than quantity.”
Neuropsychiatric toxicity
Another problem is the possibility of neuropsychiatric toxicity. Past studies have reported a wide range of such toxicities associated with CAR T-cell therapy, including seizures and hallucinations. Most have occurred early in the course of treatment and appear to be short-lived and reversible. However, there remain questions about long-term neuropsychiatric problems.
In a long-term study of 40 patients with relapsed/refractory CLL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, and ALL, nearly half of patients (47.5%, 19/40) self-reported at least one clinically meaningful negative neuropsychiatric outcome (anxiety, depression, or cognitive difficulty) 1 to 5 years after anti-CD19 CAR T-cell therapy. In addition, 37.5% (15/40) self-reported cognitive difficulties.
“Patients with more severe neurotoxicity showed a trend for more cognitive difficulties afterwards,» said Bar, senior author of the study.
However, teasing out the role that CAR T-cell therapy plays in these problems poses a challenge. All of these patients had been heavily pretreated with previous cancer therapy, which has also been associated with neuropsychiatric problems.
“So far, we don’t know what caused it,” Bar said. “Nevertheless, people need to pay attention to neuropsychiatric symptoms in CAR T-cell therapy. It is important to continue to monitor these patients for these issues.”
Graft-vs-host disease
Another potential problem is graft-vs-host disease (GVHD). This is not uncommon after hematopoietic stem cell transplants. It develops when the donor T cells view antigens on healthy recipient cells as foreign and attack them.
For patients who are treated with CAR T cells, GVHD is mostly a concern among individuals who have previously had a transplant and who are already at increased risk for it.
In a study of late effects among 86 adults treated with anti-CD19 CAR T cells for relapsed/refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Bar and colleagues found that GVHD occurred only among patients who had received a previous donor stem cell transplant. Of these, 20% (3/15) developed GVHD about 28 months after CAR-T therapy.
“The data for CAR T cells causing GVHD really hasn’t shown that it’s a huge problem, although we have seen it and are continuing to monitor for it,” the NCI’s Shah commented to Medscape Medical News.
Other Long-term Adverse Effects
A range of other long-term adverse effects have been reported with CAR-T therapy, including prolonged cytopenias (reduced mature blood cells), myelodysplasia (bone marrow failure), and second malignancies.
In the study with the longest follow-up to date, 16% (7/43) of patients developed second malignancies, which is comparable to data from Bar’s study in Seattle (15%, 13/86). The researchers in this study consider this rate to be no higher than expected: these patients had already received extensive chemotherapy, which increases the risk for other cancers, they point out.
However, this brings up theoretical concerns about the long-term effects of gene modification. CAR T cells are engineered using retroviruses (mainly lentiviruses), which randomly insert the CAR genes into the host genome. Doing so may cause mutations that could promote cancer. These lentiviruses also carry the theoretical risk of becoming capable of viral replication once inside the body.
To address these concerns, viruses used to engineer CAR T cells go through comprehensive safety testing. After therapy, patients are checked every few months during the first year and annually after that.
So far, there have been no reports of cancers associated with CAR T-cell therapy.
“Any type of cancer is a very theoretical risk,” Bar told Medscape Medical News. «Most likely the malignancies in our study were related to prior treatment that the patients received. None of them had any evidence of replication-competent lentivirus, or any other evidence that the malignancies were related to the CAR T cells.»
Another theoretical concern is the possibility of new-onset autoimmune disease, although, once again, no cases have been reported so far.
“We think of it as a theoretic possibility. Whenever you jack up the immune system, autoimmune disease is a potential risk,” said Carl June, MD, director of the Center for Cellular Immunotherapies at the University of Pennsylvania.
June was the co–principal investigator of the trial in which Olson participated. He is also the inventor on patents for CAR T cells licensed by the University of Pennsylvania to Novartis and Tmunity and is a scientific founder with equity in Tmunity.
Still, autoimmunity could occur, and scientists are looking out for it.
“We are continuing to be vigilant in our monitoring for autoimmune disease,” Shah added. “We’ve been doing CAR T-cell therapy since 2012, and I think we have yet to see true autoimmunity beyond GVHD.”
Future directions
In the 10 years since Olson received CAR T-cell therapy, an entire industry has sprung up. Over 100 companies worldwide are now developing CAR T-cell therapies targeting various antigens. These therapies are directed at about 60 different tumor types, including solid tumors. Nearly 200 clinical trials are underway, though most are still in early stages: as of September 2019, only 5% had reached phase 3.
Clinical data show promising results for CAR T-cell therapy directed against CD22 (overexpressed on ALL cells), and BCMA (found on almost all multiple myeloma cells). Yet questions remain as to whether CAR T cells will be as effective if they target antigens other than CD19 or cells other than B lymphocytes. One of the biggest research questions is whether they will be effective against solid tumors.
One research avenue being watched with great interest is the development of universal CAR T cells. So far, such products are at very early stages of development (phase 1 trials), but they are attractive because of the potential advantages they offer over bespoke CAR T cells. Automating the process holds the promise of immediate availability, standardizing production, expanding access, and lowering costs. And because the T cells for this universal product come from healthy donors, they may function better than T cells that have been battered and bruised by past cancer treatments, or even the cancer itself.
However, precisely because they are developed from healthy donor T cells, universal CAR T cells may pose increased risk for GVHD. Scientists are trying to get around this problem by engineering universal CAR T cells that lack the T-cell receptor involved in GVHD.
There are also other concerns. Nature has a penchant for mutation. Engineering CAR T cells without T-cell receptors means the body may no longer detect or reject a universal CAR T cell if it goes rogue. Also, gene insertion in universal CAR-T therapy is targeted rather than random (as in bespoke CAR T cells), which could create off-target effects. Both issues create a theoretical risk of such products inducing an untreatable CAR T-cell therapy–associated cancer.
“The theoretic risk with universal cells is that their safety profile may not be as good for long term,” June commented.
Hope for the future
From that first trial in which June and Porter used CAR T cells, two of three patients they treated are still alive 10 years later.
Olson is one of these two, and he still undergoes monitoring every 3 months to check for relapse. So far, none of his tests have shown signs of his cancer returning.
After going into remission, Doug spent the next 6 to 9 months regaining his health and strength.
“I figured if I had this amazing treatment that saved my life, I had an obligation to stay alive,” he said. “I’d better not die of something like a heart attack!”
He took up long distance running and has completed six half marathons. He became involved in the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society, participating in fund-raising and helping newly diagnosed patients. Over the years, he has also given talks for researchers, people with cancer, and healthcare providers.
Doug is now 73. Today, he marvels at how rapidly the CAR-T field has progressed.
“Twenty years ago, if you had cancer, your prospects weren’t nearly as good as these days. In 2010, people still didn’t believe in CAR T-cell therapy,” he said. “My goal always in telling my story is a message of hope.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ibrutinib-venetoclax produces high MRD-negative rates in CLL/SLL
In patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), a once-daily oral regimen of ibrutinib and venetoclax was associated with deep molecular remissions in both bone marrow and peripheral blood, including in patients with high-risk disease, according to investigators in the phase 2 CAPTIVATE MRD trial.
An intention-to-treat analysis of 164 patients with CLL/SLL treated with the combination of ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta) showed a 75% rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity in peripheral blood, and a 68% rate of MRD negativity in bone marrow among patients who received up to 12 cycles of the combination, reported Tanya Siddiqi, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, Calif., and colleagues.
“This phase 2 study supports synergistic antitumor activity of the combination with notable deep responses across multiple compartments,” she said in an oral presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Not ready to change practice
A hematologist/oncologist who was not involved in the study said that the data from CAPTIVATE MRD look good, but it’s still not known whether concurrent or sequential administration of the agents is optimal, and whether other regimens may be more effective in the first line.
“I think this is promising, but the informative and practice-changing study would be to compare this combination to ibrutinib monotherapy or to venetoclax and obinutuzumab, and that’s actually the subject of the next large German cooperative group study, CLL17,” said Catherine C. Coombs, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of North Carolina, and the UNC Lineberger Cancer Center, Chapel Hill.
She noted that the combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) is also associated with high rates of MRD negativity in the first-line setting, and that use of this regimen allows clinicians to reserve ibrutinib or acalabrutinib (Calquence) for patients in the relapsed setting.
Prerandomization results
Dr. Siddiqi presented prerandomization results from the MRD cohort of the CAPTIVATE trial (NCT02910583), which is evaluating the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax for depth of MRD response. Following 12 cycles of the combinations, patients in this cohort are then randomized based on confirmed MRD status, with patients who are MRD negative randomized to maintenance with either ibrutinib or placebo, and patients with residual disease (MRD positive) randomized to maintenance with either ibrutinib alone or with venetoclax.
A total of 164 patients with previously untreated CLL/SLL and active disease requiring treatment who were under age 70 and had good performance status were enrolled. Following an ibrutinib lead-in period with the drug given at 420 mg once daily for three cycles of 28 days, the patients were continued on ibrutinib, and were started on venetoclax with a ramp up to 400 mg once daily, for 12 additional cycles.
As planned, patients were assessed after 15 cycles for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) risk assessment, MRD, and hematologic, clinical, imaging, and bone marrow exams for response.
The median patient age was 58, with poor-risk features such as deletion 17p seen in 16%, complex karyotype in 19%, and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) in 59%.
A total of 152 patients (90%) completed all 12 cycles of the combined agents, with a median treatment duration of 14.7 months on ibrutinib and 12 months on venetoclax. Eight patients had adverse events leading to discontinuation, but there were no treatment-related deaths.
A majority of patients had reductions in lymph node burden after the three-cycle ibrutinib lead in. TLS risk also decreased during the lead-in period, with 90% of patients who had a high baseline TLS risk shifting to medium or low-risk categories, and no patients moved into the high-risk category.
“Hospitalization because of this was no longer required in 66% of at-risk patients after three cycles of ibrutinib lead in, and 82% of patients initiated venetoclax ramp up without the need for hospitalization,” Dr. Siddiqi said.
The best response of undetectable MRD was seen in peripheral blood of 75% of 163 evaluable patients, and in bone marrow of 72% of 155 patients. As noted before, the respective rates of MRD negativity in the intention-to-treat population were 75% and 68%. The proportion of patients with undetectable MRD in peripheral blood increased over time, from 57% after six cycles of the combination, she said.
The overall response rate was 97%, including 51% complete responses (CR) or CR with incomplete bone marrow recovery (CRi), and 46% partial (PR) or nodular PR (nPR). Among patients with CR/CRi, 85% had undetectable MRD in peripheral blood and 80% were MRD negative in bone marrow. In patients with PR/nPR, the respective rates were 69% and 59%. The high rates of undetectable MRD were seen irrespective of baseline disease characteristics, including bulky disease, cytogenetic risk category, del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and complex karyotype.
The most common adverse events with the combination were grade 1 or 2 diarrhea, arthralgia, fatigue, headache, and nausea. Grade 3 neutropenia was seen in 17% of patients, and grade 4 neutropenia was seen in 16%. Grade 3 febrile neutropenia and laboratory confirmed TLS occurred in 2 patients each (1%), and there were no grade 4 instances of either adverse event.
Postrandomization follow-up and analyses are currently being conducted, and results will be reported at a future meeting, real or virtual. An analysis of data on a separate cohort of 159 patients treated with the ibrutinib-venetoclax combination for a fixed duration is currently ongoing.
Dr. Siddiqi disclosed research funding and speakers bureau activity for Pharmacyclics, which sponsored the study, and others, as well as consulting/advising for several companies. Dr. Coombs disclosed consulting for AbbVie.
SOURCE: Siddiqi T et al. EHA25. Abstract S158.
In patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), a once-daily oral regimen of ibrutinib and venetoclax was associated with deep molecular remissions in both bone marrow and peripheral blood, including in patients with high-risk disease, according to investigators in the phase 2 CAPTIVATE MRD trial.
An intention-to-treat analysis of 164 patients with CLL/SLL treated with the combination of ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta) showed a 75% rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity in peripheral blood, and a 68% rate of MRD negativity in bone marrow among patients who received up to 12 cycles of the combination, reported Tanya Siddiqi, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, Calif., and colleagues.
“This phase 2 study supports synergistic antitumor activity of the combination with notable deep responses across multiple compartments,” she said in an oral presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Not ready to change practice
A hematologist/oncologist who was not involved in the study said that the data from CAPTIVATE MRD look good, but it’s still not known whether concurrent or sequential administration of the agents is optimal, and whether other regimens may be more effective in the first line.
“I think this is promising, but the informative and practice-changing study would be to compare this combination to ibrutinib monotherapy or to venetoclax and obinutuzumab, and that’s actually the subject of the next large German cooperative group study, CLL17,” said Catherine C. Coombs, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of North Carolina, and the UNC Lineberger Cancer Center, Chapel Hill.
She noted that the combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) is also associated with high rates of MRD negativity in the first-line setting, and that use of this regimen allows clinicians to reserve ibrutinib or acalabrutinib (Calquence) for patients in the relapsed setting.
Prerandomization results
Dr. Siddiqi presented prerandomization results from the MRD cohort of the CAPTIVATE trial (NCT02910583), which is evaluating the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax for depth of MRD response. Following 12 cycles of the combinations, patients in this cohort are then randomized based on confirmed MRD status, with patients who are MRD negative randomized to maintenance with either ibrutinib or placebo, and patients with residual disease (MRD positive) randomized to maintenance with either ibrutinib alone or with venetoclax.
A total of 164 patients with previously untreated CLL/SLL and active disease requiring treatment who were under age 70 and had good performance status were enrolled. Following an ibrutinib lead-in period with the drug given at 420 mg once daily for three cycles of 28 days, the patients were continued on ibrutinib, and were started on venetoclax with a ramp up to 400 mg once daily, for 12 additional cycles.
As planned, patients were assessed after 15 cycles for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) risk assessment, MRD, and hematologic, clinical, imaging, and bone marrow exams for response.
The median patient age was 58, with poor-risk features such as deletion 17p seen in 16%, complex karyotype in 19%, and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) in 59%.
A total of 152 patients (90%) completed all 12 cycles of the combined agents, with a median treatment duration of 14.7 months on ibrutinib and 12 months on venetoclax. Eight patients had adverse events leading to discontinuation, but there were no treatment-related deaths.
A majority of patients had reductions in lymph node burden after the three-cycle ibrutinib lead in. TLS risk also decreased during the lead-in period, with 90% of patients who had a high baseline TLS risk shifting to medium or low-risk categories, and no patients moved into the high-risk category.
“Hospitalization because of this was no longer required in 66% of at-risk patients after three cycles of ibrutinib lead in, and 82% of patients initiated venetoclax ramp up without the need for hospitalization,” Dr. Siddiqi said.
The best response of undetectable MRD was seen in peripheral blood of 75% of 163 evaluable patients, and in bone marrow of 72% of 155 patients. As noted before, the respective rates of MRD negativity in the intention-to-treat population were 75% and 68%. The proportion of patients with undetectable MRD in peripheral blood increased over time, from 57% after six cycles of the combination, she said.
The overall response rate was 97%, including 51% complete responses (CR) or CR with incomplete bone marrow recovery (CRi), and 46% partial (PR) or nodular PR (nPR). Among patients with CR/CRi, 85% had undetectable MRD in peripheral blood and 80% were MRD negative in bone marrow. In patients with PR/nPR, the respective rates were 69% and 59%. The high rates of undetectable MRD were seen irrespective of baseline disease characteristics, including bulky disease, cytogenetic risk category, del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and complex karyotype.
The most common adverse events with the combination were grade 1 or 2 diarrhea, arthralgia, fatigue, headache, and nausea. Grade 3 neutropenia was seen in 17% of patients, and grade 4 neutropenia was seen in 16%. Grade 3 febrile neutropenia and laboratory confirmed TLS occurred in 2 patients each (1%), and there were no grade 4 instances of either adverse event.
Postrandomization follow-up and analyses are currently being conducted, and results will be reported at a future meeting, real or virtual. An analysis of data on a separate cohort of 159 patients treated with the ibrutinib-venetoclax combination for a fixed duration is currently ongoing.
Dr. Siddiqi disclosed research funding and speakers bureau activity for Pharmacyclics, which sponsored the study, and others, as well as consulting/advising for several companies. Dr. Coombs disclosed consulting for AbbVie.
SOURCE: Siddiqi T et al. EHA25. Abstract S158.
In patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), a once-daily oral regimen of ibrutinib and venetoclax was associated with deep molecular remissions in both bone marrow and peripheral blood, including in patients with high-risk disease, according to investigators in the phase 2 CAPTIVATE MRD trial.
An intention-to-treat analysis of 164 patients with CLL/SLL treated with the combination of ibrutinib (Imbruvica) and venetoclax (Venclexta) showed a 75% rate of minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity in peripheral blood, and a 68% rate of MRD negativity in bone marrow among patients who received up to 12 cycles of the combination, reported Tanya Siddiqi, MD, of City of Hope National Medical Center, Duarte, Calif., and colleagues.
“This phase 2 study supports synergistic antitumor activity of the combination with notable deep responses across multiple compartments,” she said in an oral presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Not ready to change practice
A hematologist/oncologist who was not involved in the study said that the data from CAPTIVATE MRD look good, but it’s still not known whether concurrent or sequential administration of the agents is optimal, and whether other regimens may be more effective in the first line.
“I think this is promising, but the informative and practice-changing study would be to compare this combination to ibrutinib monotherapy or to venetoclax and obinutuzumab, and that’s actually the subject of the next large German cooperative group study, CLL17,” said Catherine C. Coombs, MD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of North Carolina, and the UNC Lineberger Cancer Center, Chapel Hill.
She noted that the combination of venetoclax and obinutuzumab (Gazyva) is also associated with high rates of MRD negativity in the first-line setting, and that use of this regimen allows clinicians to reserve ibrutinib or acalabrutinib (Calquence) for patients in the relapsed setting.
Prerandomization results
Dr. Siddiqi presented prerandomization results from the MRD cohort of the CAPTIVATE trial (NCT02910583), which is evaluating the combination of ibrutinib and venetoclax for depth of MRD response. Following 12 cycles of the combinations, patients in this cohort are then randomized based on confirmed MRD status, with patients who are MRD negative randomized to maintenance with either ibrutinib or placebo, and patients with residual disease (MRD positive) randomized to maintenance with either ibrutinib alone or with venetoclax.
A total of 164 patients with previously untreated CLL/SLL and active disease requiring treatment who were under age 70 and had good performance status were enrolled. Following an ibrutinib lead-in period with the drug given at 420 mg once daily for three cycles of 28 days, the patients were continued on ibrutinib, and were started on venetoclax with a ramp up to 400 mg once daily, for 12 additional cycles.
As planned, patients were assessed after 15 cycles for tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) risk assessment, MRD, and hematologic, clinical, imaging, and bone marrow exams for response.
The median patient age was 58, with poor-risk features such as deletion 17p seen in 16%, complex karyotype in 19%, and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain variable (IGHV) in 59%.
A total of 152 patients (90%) completed all 12 cycles of the combined agents, with a median treatment duration of 14.7 months on ibrutinib and 12 months on venetoclax. Eight patients had adverse events leading to discontinuation, but there were no treatment-related deaths.
A majority of patients had reductions in lymph node burden after the three-cycle ibrutinib lead in. TLS risk also decreased during the lead-in period, with 90% of patients who had a high baseline TLS risk shifting to medium or low-risk categories, and no patients moved into the high-risk category.
“Hospitalization because of this was no longer required in 66% of at-risk patients after three cycles of ibrutinib lead in, and 82% of patients initiated venetoclax ramp up without the need for hospitalization,” Dr. Siddiqi said.
The best response of undetectable MRD was seen in peripheral blood of 75% of 163 evaluable patients, and in bone marrow of 72% of 155 patients. As noted before, the respective rates of MRD negativity in the intention-to-treat population were 75% and 68%. The proportion of patients with undetectable MRD in peripheral blood increased over time, from 57% after six cycles of the combination, she said.
The overall response rate was 97%, including 51% complete responses (CR) or CR with incomplete bone marrow recovery (CRi), and 46% partial (PR) or nodular PR (nPR). Among patients with CR/CRi, 85% had undetectable MRD in peripheral blood and 80% were MRD negative in bone marrow. In patients with PR/nPR, the respective rates were 69% and 59%. The high rates of undetectable MRD were seen irrespective of baseline disease characteristics, including bulky disease, cytogenetic risk category, del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and complex karyotype.
The most common adverse events with the combination were grade 1 or 2 diarrhea, arthralgia, fatigue, headache, and nausea. Grade 3 neutropenia was seen in 17% of patients, and grade 4 neutropenia was seen in 16%. Grade 3 febrile neutropenia and laboratory confirmed TLS occurred in 2 patients each (1%), and there were no grade 4 instances of either adverse event.
Postrandomization follow-up and analyses are currently being conducted, and results will be reported at a future meeting, real or virtual. An analysis of data on a separate cohort of 159 patients treated with the ibrutinib-venetoclax combination for a fixed duration is currently ongoing.
Dr. Siddiqi disclosed research funding and speakers bureau activity for Pharmacyclics, which sponsored the study, and others, as well as consulting/advising for several companies. Dr. Coombs disclosed consulting for AbbVie.
SOURCE: Siddiqi T et al. EHA25. Abstract S158.
FROM EHA 2020
Three-drug combo promising against high-risk CLL
For patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line therapy with a triple combination of targeted agents showed encouraging response rates in the phase 2 CLL2-GIVe trial.
Among 41 patients with untreated CLL bearing deleterious TP53 mutations and/or the 17p chromosomal deletion who received the GIVe regimen consisting of obinutuzumab (Gazyva), ibrutinib (Imbruvica), and venetoclax (Venclexta), the complete response rate at final restaging was 58.5%, and 33 patients with a confirmed response were negative for minimal residual disease after a median follow-up of 18.6 months, reported Henriette Huber, MD, of University Hospital Ulm, Germany.
“The GIVe regimen is promising first-line therapy for patients with high-risk CLL,” she said in a presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The overall safety profile of the combination was acceptable, she said, but added that “some higher-grade infections are of concern.” The rate of grade 3 or greater infections/infestations in the study was 19.5%.
Sound rationale (with caveat)
Another adverse event of concern is the rate of atrial fibrillation in the comparatively young patient population (median age 62), noted Alexey Danilov, MD, PhD, of City of Hope in Duarte Calif., who commented on the study for MDedge.
He pointed out that second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors such as acalabrutinib (Calquence) may pose a lower risk of atrial fibrillation than the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib used in the CLL2-GIVe study.
In general, however, the rationale for the combination is sound, Dr. Danilov said.
“Of all the patient populations that we deal with within CLL, this probably would be most appropriate for this type of therapy. Patients with deletion 17p or TP53 mutations still represent an unmet medical need compared to other patients who don’t have those mutations,” he said.
Patients with CLL bearing the mutations have lower clinical response rates to novel therapies and generally do not respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, he said.
“The question becomes whether using these all at the same time, versus sequential strategies – using one drug and then after that, at relapse, another – is better, and obviously this trial doesn’t address that,” he said.
Three targets
The investigators enrolled 24 men and 17 women with untreated CLL with del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations and adequate organ function (creatinine clearance rate of more than 50 mL/min). The median age was 62 (range 35-85 years); 78% of patients had Binet stage B or C disease. The median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) score was 3 (range 0 to 8).
All patients received treatment with the combination for 6 months. The CD20 inhibitor obinutuzumab was given in a dose of 1,000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib was given continuously at a dose of 420 mg per day beginning on the first day of the first cycle. Venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, was started on day 22 of cycle 1, and was increased to 400 mg per day over 5 weeks until the end of cycle 12.
If patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi) according to International Workshop on CLL criteria at final restaging (performed with imaging at the end of cycle 12 followed by bone marrow biopsy 2 months later), ibrutinib would be stopped beginning at cycle 15. Patients who did not have a CR or CRi would continue on ibrutinib until cycle 36.
Encouraging results
All but 3 of the 41 patients reached final restaging. Analyses of efficacy and safety included all 41 patients.
The CR/CRi rate at final restaging, the primary endpoint, was accomplished in 24 patients (58.8%), and 14 patients (34.1%) had a partial response.
Of the three patients for whom responses could not be assessed, two died (one from ovarian cancer which was retrospectively determined to have been present at enrollment, and one at cycle 9 from cardiac failure), and the third patient withdrew consent at cycle 10.
In all, 33 patients (80.5%) were MRD-negative in peripheral blood, 4 remained MRD positive, and 4 were not assessed. Per protocol, 22 patients with undetectable MRD and a CR or CRi discontinued therapy at week 15. An additional 13 patients also discontinued therapy because of adverse events or other reasons, and 6 remained on therapy beyond cycle 15.
The most frequent adverse events of any grade through the end of cycle 14 were gastrointestinal disorders in 83%, none higher than grade 2; infections and infestations in 70.7%, of which 19.5% were grade 3 or greater in severity; and blood and lymphatic system disorders in 58.5%, most of which (53.7%) were grade 3 or greater.
Cardiac disorders were reported in 19.5% of all patients, including 12.2% with atrial fibrillation; grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation occurred in 2.4% of patients.
There was one case each of cerebral aspergillosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (without PCR testing), urosepsis, staphylococcal sepsis and febrile infection.
Laboratory confirmed tumor lysis syndrome, all grade 3 or greater, was reported in 9.8% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported in 29.3% of patients, with a total of 7.3% being grade 3 or greater.
The trial was supported by Janssen-Cilag and Roche. Dr. Huber disclosed travel reimbursement from Novartis. Dr. Danilov disclosed consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Huber H et al. EHA Congress. Abstract S157.
For patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line therapy with a triple combination of targeted agents showed encouraging response rates in the phase 2 CLL2-GIVe trial.
Among 41 patients with untreated CLL bearing deleterious TP53 mutations and/or the 17p chromosomal deletion who received the GIVe regimen consisting of obinutuzumab (Gazyva), ibrutinib (Imbruvica), and venetoclax (Venclexta), the complete response rate at final restaging was 58.5%, and 33 patients with a confirmed response were negative for minimal residual disease after a median follow-up of 18.6 months, reported Henriette Huber, MD, of University Hospital Ulm, Germany.
“The GIVe regimen is promising first-line therapy for patients with high-risk CLL,” she said in a presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The overall safety profile of the combination was acceptable, she said, but added that “some higher-grade infections are of concern.” The rate of grade 3 or greater infections/infestations in the study was 19.5%.
Sound rationale (with caveat)
Another adverse event of concern is the rate of atrial fibrillation in the comparatively young patient population (median age 62), noted Alexey Danilov, MD, PhD, of City of Hope in Duarte Calif., who commented on the study for MDedge.
He pointed out that second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors such as acalabrutinib (Calquence) may pose a lower risk of atrial fibrillation than the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib used in the CLL2-GIVe study.
In general, however, the rationale for the combination is sound, Dr. Danilov said.
“Of all the patient populations that we deal with within CLL, this probably would be most appropriate for this type of therapy. Patients with deletion 17p or TP53 mutations still represent an unmet medical need compared to other patients who don’t have those mutations,” he said.
Patients with CLL bearing the mutations have lower clinical response rates to novel therapies and generally do not respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, he said.
“The question becomes whether using these all at the same time, versus sequential strategies – using one drug and then after that, at relapse, another – is better, and obviously this trial doesn’t address that,” he said.
Three targets
The investigators enrolled 24 men and 17 women with untreated CLL with del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations and adequate organ function (creatinine clearance rate of more than 50 mL/min). The median age was 62 (range 35-85 years); 78% of patients had Binet stage B or C disease. The median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) score was 3 (range 0 to 8).
All patients received treatment with the combination for 6 months. The CD20 inhibitor obinutuzumab was given in a dose of 1,000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib was given continuously at a dose of 420 mg per day beginning on the first day of the first cycle. Venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, was started on day 22 of cycle 1, and was increased to 400 mg per day over 5 weeks until the end of cycle 12.
If patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi) according to International Workshop on CLL criteria at final restaging (performed with imaging at the end of cycle 12 followed by bone marrow biopsy 2 months later), ibrutinib would be stopped beginning at cycle 15. Patients who did not have a CR or CRi would continue on ibrutinib until cycle 36.
Encouraging results
All but 3 of the 41 patients reached final restaging. Analyses of efficacy and safety included all 41 patients.
The CR/CRi rate at final restaging, the primary endpoint, was accomplished in 24 patients (58.8%), and 14 patients (34.1%) had a partial response.
Of the three patients for whom responses could not be assessed, two died (one from ovarian cancer which was retrospectively determined to have been present at enrollment, and one at cycle 9 from cardiac failure), and the third patient withdrew consent at cycle 10.
In all, 33 patients (80.5%) were MRD-negative in peripheral blood, 4 remained MRD positive, and 4 were not assessed. Per protocol, 22 patients with undetectable MRD and a CR or CRi discontinued therapy at week 15. An additional 13 patients also discontinued therapy because of adverse events or other reasons, and 6 remained on therapy beyond cycle 15.
The most frequent adverse events of any grade through the end of cycle 14 were gastrointestinal disorders in 83%, none higher than grade 2; infections and infestations in 70.7%, of which 19.5% were grade 3 or greater in severity; and blood and lymphatic system disorders in 58.5%, most of which (53.7%) were grade 3 or greater.
Cardiac disorders were reported in 19.5% of all patients, including 12.2% with atrial fibrillation; grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation occurred in 2.4% of patients.
There was one case each of cerebral aspergillosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (without PCR testing), urosepsis, staphylococcal sepsis and febrile infection.
Laboratory confirmed tumor lysis syndrome, all grade 3 or greater, was reported in 9.8% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported in 29.3% of patients, with a total of 7.3% being grade 3 or greater.
The trial was supported by Janssen-Cilag and Roche. Dr. Huber disclosed travel reimbursement from Novartis. Dr. Danilov disclosed consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Huber H et al. EHA Congress. Abstract S157.
For patients with high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), first-line therapy with a triple combination of targeted agents showed encouraging response rates in the phase 2 CLL2-GIVe trial.
Among 41 patients with untreated CLL bearing deleterious TP53 mutations and/or the 17p chromosomal deletion who received the GIVe regimen consisting of obinutuzumab (Gazyva), ibrutinib (Imbruvica), and venetoclax (Venclexta), the complete response rate at final restaging was 58.5%, and 33 patients with a confirmed response were negative for minimal residual disease after a median follow-up of 18.6 months, reported Henriette Huber, MD, of University Hospital Ulm, Germany.
“The GIVe regimen is promising first-line therapy for patients with high-risk CLL,” she said in a presentation during the virtual annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
The overall safety profile of the combination was acceptable, she said, but added that “some higher-grade infections are of concern.” The rate of grade 3 or greater infections/infestations in the study was 19.5%.
Sound rationale (with caveat)
Another adverse event of concern is the rate of atrial fibrillation in the comparatively young patient population (median age 62), noted Alexey Danilov, MD, PhD, of City of Hope in Duarte Calif., who commented on the study for MDedge.
He pointed out that second-generation Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitors such as acalabrutinib (Calquence) may pose a lower risk of atrial fibrillation than the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib used in the CLL2-GIVe study.
In general, however, the rationale for the combination is sound, Dr. Danilov said.
“Of all the patient populations that we deal with within CLL, this probably would be most appropriate for this type of therapy. Patients with deletion 17p or TP53 mutations still represent an unmet medical need compared to other patients who don’t have those mutations,” he said.
Patients with CLL bearing the mutations have lower clinical response rates to novel therapies and generally do not respond well to chemoimmunotherapy, he said.
“The question becomes whether using these all at the same time, versus sequential strategies – using one drug and then after that, at relapse, another – is better, and obviously this trial doesn’t address that,” he said.
Three targets
The investigators enrolled 24 men and 17 women with untreated CLL with del(17p) and/or TP53 mutations and adequate organ function (creatinine clearance rate of more than 50 mL/min). The median age was 62 (range 35-85 years); 78% of patients had Binet stage B or C disease. The median Cumulative Illness Rating Scale (CIRS) score was 3 (range 0 to 8).
All patients received treatment with the combination for 6 months. The CD20 inhibitor obinutuzumab was given in a dose of 1,000 mg on days 1, 8 and 15 of cycle 1 and day 1 of cycles 2-6. The BTK inhibitor ibrutinib was given continuously at a dose of 420 mg per day beginning on the first day of the first cycle. Venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 (BCL-2) inhibitor, was started on day 22 of cycle 1, and was increased to 400 mg per day over 5 weeks until the end of cycle 12.
If patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete recovery of blood counts (CRi) according to International Workshop on CLL criteria at final restaging (performed with imaging at the end of cycle 12 followed by bone marrow biopsy 2 months later), ibrutinib would be stopped beginning at cycle 15. Patients who did not have a CR or CRi would continue on ibrutinib until cycle 36.
Encouraging results
All but 3 of the 41 patients reached final restaging. Analyses of efficacy and safety included all 41 patients.
The CR/CRi rate at final restaging, the primary endpoint, was accomplished in 24 patients (58.8%), and 14 patients (34.1%) had a partial response.
Of the three patients for whom responses could not be assessed, two died (one from ovarian cancer which was retrospectively determined to have been present at enrollment, and one at cycle 9 from cardiac failure), and the third patient withdrew consent at cycle 10.
In all, 33 patients (80.5%) were MRD-negative in peripheral blood, 4 remained MRD positive, and 4 were not assessed. Per protocol, 22 patients with undetectable MRD and a CR or CRi discontinued therapy at week 15. An additional 13 patients also discontinued therapy because of adverse events or other reasons, and 6 remained on therapy beyond cycle 15.
The most frequent adverse events of any grade through the end of cycle 14 were gastrointestinal disorders in 83%, none higher than grade 2; infections and infestations in 70.7%, of which 19.5% were grade 3 or greater in severity; and blood and lymphatic system disorders in 58.5%, most of which (53.7%) were grade 3 or greater.
Cardiac disorders were reported in 19.5% of all patients, including 12.2% with atrial fibrillation; grade 3 or greater atrial fibrillation occurred in 2.4% of patients.
There was one case each of cerebral aspergillosis, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (without PCR testing), urosepsis, staphylococcal sepsis and febrile infection.
Laboratory confirmed tumor lysis syndrome, all grade 3 or greater, was reported in 9.8% of patients. Infusion-related reactions were reported in 29.3% of patients, with a total of 7.3% being grade 3 or greater.
The trial was supported by Janssen-Cilag and Roche. Dr. Huber disclosed travel reimbursement from Novartis. Dr. Danilov disclosed consulting for AbbVie, Janssen, and Genentech.
SOURCE: Huber H et al. EHA Congress. Abstract S157.
FROM EHA CONGRESS
MCC response varies based on immunosuppression type, especially CLL
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic immunosuppression may fare better or worse on immunotherapy based on the reason for immunosuppression, according to recent research at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
About 10% of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) are immunosuppressed at diagnosis, and these patients tend to have a more aggressive disease course and worse disease-specific survival compared with immunocompetent patients, Lauren Zawacki, a research assistant in the Nghiem Lab at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in her presentation. Although patients are receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 as treatments, the efficacy and side effects on immunosuppressed patients have not been well studied because many of these patients are not eligible for clinical trials.
Ms. Zawacki and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective Seattle registry of 1,442 patients with MCC, identifying 179 patients with MCC who had chronic immunosuppression due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), solid organ transplants, autoimmune disorders, other hematological malignancies, and HIV and AIDS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprised 7 of 8 patients in the group with other hematological malignancies, and Crohn’s disease made up 5 of 6 patients in the autoimmune disorder group. Of the 179 patients with MCC and immunosuppression, 31 patients were treated with either anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy.
There was an objective response rate of 52%, with 14 patients having a complete response, 2 patients having a partial response, and 15 patients experiencing disease progression. Of the patients with disease progression, 11 died of MCC. The response rate in immunocompromised patients is similar to results seen by her group in immunocompetent patients (Nghiem P et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:2542-52), said Ms. Zawacki. “While the overall objective response rate is comparable between immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients, the response rates vary greatly between the different types of immunosuppression,” she said.
When grouping response rates by immunosuppression type, they found 2 of 11 patients with CLL (18%) and 2 of 6 patients with autoimmune disease (33%) had an objective response, while 2 of 3 patients with HIV/AIDS (66%) and 7 of 7 patients with other hematologic malignancies (100%) had an objective response.
“While the numbers of the cohort are small, there still seems to be a considerable difference in the response rate between the different types of immune suppression, which is critical when we’re treating patients who typically have a more aggressive disease course,” said Ms. Zawacki.
In particular, the finding of no patients with MCC and CLL achieving a complete response interested Ms. Zawacki and her colleagues, since about one-fourth of patients in the Seattle registry have this combination of disease. “Not only did none of the CLL patients have a complete response, but 7 out of the 11 patients with CLL died from MCC,” she explained. When examining further, the researchers found 45% of patients in this group discontinued because of side effects of immunotherapy and had a median time to recurrence of 1.5 months. “This finding suggests that CLL in particular plays a large role in impairing the function of the immune system, leading to not only a more aggressive disease course, but a poorer response to immunotherapy,” she said.
“There is a significant need for improved interventions for patients with CLL and autoimmune disorders,” she added. “Research for immunosuppressed patients is critical given the associated aggressive disease course and their lack of inclusion in clinical trials.”
Ms. Zawacki acknowledged the small number of patients in the study as a limitation, and patients who received follow-up at outside facilities may have received slightly different care, which could impact adverse event reporting or reasons for study discontinuation.
“A multi-institutional study would be beneficial to expand the number of patients in that cohort and to help confirm the trend observed in this study. In addition, future studies should assess the role of combination systemic therapy, such as neutron radiation and immunotherapy together in order to see if the objective response can be approved among immunosuppressed patients,” she said.
This study was supported by funding from the MCC Patient Gift Fund, the National Cancer Institute, and a grant from NIH. Ms. Zawacki reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zawacki L. SID 2020, Abstract 497.
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic immunosuppression may fare better or worse on immunotherapy based on the reason for immunosuppression, according to recent research at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
About 10% of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) are immunosuppressed at diagnosis, and these patients tend to have a more aggressive disease course and worse disease-specific survival compared with immunocompetent patients, Lauren Zawacki, a research assistant in the Nghiem Lab at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in her presentation. Although patients are receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 as treatments, the efficacy and side effects on immunosuppressed patients have not been well studied because many of these patients are not eligible for clinical trials.
Ms. Zawacki and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective Seattle registry of 1,442 patients with MCC, identifying 179 patients with MCC who had chronic immunosuppression due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), solid organ transplants, autoimmune disorders, other hematological malignancies, and HIV and AIDS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprised 7 of 8 patients in the group with other hematological malignancies, and Crohn’s disease made up 5 of 6 patients in the autoimmune disorder group. Of the 179 patients with MCC and immunosuppression, 31 patients were treated with either anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy.
There was an objective response rate of 52%, with 14 patients having a complete response, 2 patients having a partial response, and 15 patients experiencing disease progression. Of the patients with disease progression, 11 died of MCC. The response rate in immunocompromised patients is similar to results seen by her group in immunocompetent patients (Nghiem P et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:2542-52), said Ms. Zawacki. “While the overall objective response rate is comparable between immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients, the response rates vary greatly between the different types of immunosuppression,” she said.
When grouping response rates by immunosuppression type, they found 2 of 11 patients with CLL (18%) and 2 of 6 patients with autoimmune disease (33%) had an objective response, while 2 of 3 patients with HIV/AIDS (66%) and 7 of 7 patients with other hematologic malignancies (100%) had an objective response.
“While the numbers of the cohort are small, there still seems to be a considerable difference in the response rate between the different types of immune suppression, which is critical when we’re treating patients who typically have a more aggressive disease course,” said Ms. Zawacki.
In particular, the finding of no patients with MCC and CLL achieving a complete response interested Ms. Zawacki and her colleagues, since about one-fourth of patients in the Seattle registry have this combination of disease. “Not only did none of the CLL patients have a complete response, but 7 out of the 11 patients with CLL died from MCC,” she explained. When examining further, the researchers found 45% of patients in this group discontinued because of side effects of immunotherapy and had a median time to recurrence of 1.5 months. “This finding suggests that CLL in particular plays a large role in impairing the function of the immune system, leading to not only a more aggressive disease course, but a poorer response to immunotherapy,” she said.
“There is a significant need for improved interventions for patients with CLL and autoimmune disorders,” she added. “Research for immunosuppressed patients is critical given the associated aggressive disease course and their lack of inclusion in clinical trials.”
Ms. Zawacki acknowledged the small number of patients in the study as a limitation, and patients who received follow-up at outside facilities may have received slightly different care, which could impact adverse event reporting or reasons for study discontinuation.
“A multi-institutional study would be beneficial to expand the number of patients in that cohort and to help confirm the trend observed in this study. In addition, future studies should assess the role of combination systemic therapy, such as neutron radiation and immunotherapy together in order to see if the objective response can be approved among immunosuppressed patients,” she said.
This study was supported by funding from the MCC Patient Gift Fund, the National Cancer Institute, and a grant from NIH. Ms. Zawacki reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zawacki L. SID 2020, Abstract 497.
Patients with Merkel cell carcinoma and chronic immunosuppression may fare better or worse on immunotherapy based on the reason for immunosuppression, according to recent research at the annual meeting of the Society for Investigative Dermatology, held virtually.
About 10% of patients with Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) are immunosuppressed at diagnosis, and these patients tend to have a more aggressive disease course and worse disease-specific survival compared with immunocompetent patients, Lauren Zawacki, a research assistant in the Nghiem Lab at the University of Washington, Seattle, said in her presentation. Although patients are receiving immune checkpoint inhibitors such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1 as treatments, the efficacy and side effects on immunosuppressed patients have not been well studied because many of these patients are not eligible for clinical trials.
Ms. Zawacki and colleagues analyzed data from a prospective Seattle registry of 1,442 patients with MCC, identifying 179 patients with MCC who had chronic immunosuppression due to chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), solid organ transplants, autoimmune disorders, other hematological malignancies, and HIV and AIDS. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma comprised 7 of 8 patients in the group with other hematological malignancies, and Crohn’s disease made up 5 of 6 patients in the autoimmune disorder group. Of the 179 patients with MCC and immunosuppression, 31 patients were treated with either anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 therapy.
There was an objective response rate of 52%, with 14 patients having a complete response, 2 patients having a partial response, and 15 patients experiencing disease progression. Of the patients with disease progression, 11 died of MCC. The response rate in immunocompromised patients is similar to results seen by her group in immunocompetent patients (Nghiem P et al. N Engl J Med 2016; 374:2542-52), said Ms. Zawacki. “While the overall objective response rate is comparable between immunocompetent and immunosuppressed patients, the response rates vary greatly between the different types of immunosuppression,” she said.
When grouping response rates by immunosuppression type, they found 2 of 11 patients with CLL (18%) and 2 of 6 patients with autoimmune disease (33%) had an objective response, while 2 of 3 patients with HIV/AIDS (66%) and 7 of 7 patients with other hematologic malignancies (100%) had an objective response.
“While the numbers of the cohort are small, there still seems to be a considerable difference in the response rate between the different types of immune suppression, which is critical when we’re treating patients who typically have a more aggressive disease course,” said Ms. Zawacki.
In particular, the finding of no patients with MCC and CLL achieving a complete response interested Ms. Zawacki and her colleagues, since about one-fourth of patients in the Seattle registry have this combination of disease. “Not only did none of the CLL patients have a complete response, but 7 out of the 11 patients with CLL died from MCC,” she explained. When examining further, the researchers found 45% of patients in this group discontinued because of side effects of immunotherapy and had a median time to recurrence of 1.5 months. “This finding suggests that CLL in particular plays a large role in impairing the function of the immune system, leading to not only a more aggressive disease course, but a poorer response to immunotherapy,” she said.
“There is a significant need for improved interventions for patients with CLL and autoimmune disorders,” she added. “Research for immunosuppressed patients is critical given the associated aggressive disease course and their lack of inclusion in clinical trials.”
Ms. Zawacki acknowledged the small number of patients in the study as a limitation, and patients who received follow-up at outside facilities may have received slightly different care, which could impact adverse event reporting or reasons for study discontinuation.
“A multi-institutional study would be beneficial to expand the number of patients in that cohort and to help confirm the trend observed in this study. In addition, future studies should assess the role of combination systemic therapy, such as neutron radiation and immunotherapy together in order to see if the objective response can be approved among immunosuppressed patients,” she said.
This study was supported by funding from the MCC Patient Gift Fund, the National Cancer Institute, and a grant from NIH. Ms. Zawacki reports no relevant conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Zawacki L. SID 2020, Abstract 497.
FROM SID 2020
Race and location appear to play a role in the incidence of CLL and DLBCL
Exposure to carcinogens has been implicated in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), suggesting that an examination of the environment on a population-based level might provide some insights. On that basis, researchers performed a study that found that living in an urban vs. rural area was associated with an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) among diverse, urban populations.
The study, published online in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, found an increased incidence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in urban vs. rural Hispanics, and a similar increased incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in non-metropolitan urban non-Hispanic blacks.
A total of 482,096 adults aged 20 years and older with incident NHL were reported to 21 Surveillance, Epidemiology,and End Results (SEER) population-based registries for the period 2000 to 2016. Deanna Blansky of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, N.Y., and her colleagues compared patients by NHL subtype and urban-rural status, using rural-urban continuum codes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The researchers found 136,197 DLBCL, 70,882 follicular lymphoma (FL), and 120,319 CLL cases of patients aged ≥ 20 years. The DLBCL patients comprised 73.6% non-Hispanic white, 11.8% Hispanic, and 7.3% non-Hispanic black, with a similar distribution observed for FL and CLL. Patients were adjusted for age, sex, and family poverty.
The study showed that, overall, there was a higher DLBCL incidence rate in metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas overall (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11-1.30). Most pronounced was an increased DLBCL incidence among Hispanics in urban areas, compared with rural areas (rural IRR = 1.00; non-metropolitan urban IRR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16-1.51; metropolitan urban = 1.55, 95% CI 1.36-1.76).
In contrast, metropolitan urban areas had a lower overall incidence of CLL than rural areas (8.4 vs. 9.7 per 100,000; IRR = .87; 95% CI .86-.89).
However, increased CLL incidence rates were found to be associated with non-metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas (IRR = 1.19; 95% CI 1.10-1.28), particularly among non-Hispanic Blacks (IRR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.27-1.72).
Unlike DLBCL and CLL, there were no differences observed in FL incidence rates by urban-rural status after adjusting for age, sex, and family poverty rates, the researchers reported.
“Overall, our findings suggest that factors related to urban status may be associated with DLBCL and CLL pathogenesis. Our results may help provide epidemiological clues to understanding the racial disparities seen among hematological malignancies, particularly regarding the risk of DLBCL in Hispanics and CLL in non-Hispanic Blacks,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The researchers did not report conflict information.
SOURCE: Blansky D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 May 15; doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2020.05.010.
Exposure to carcinogens has been implicated in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), suggesting that an examination of the environment on a population-based level might provide some insights. On that basis, researchers performed a study that found that living in an urban vs. rural area was associated with an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) among diverse, urban populations.
The study, published online in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, found an increased incidence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in urban vs. rural Hispanics, and a similar increased incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in non-metropolitan urban non-Hispanic blacks.
A total of 482,096 adults aged 20 years and older with incident NHL were reported to 21 Surveillance, Epidemiology,and End Results (SEER) population-based registries for the period 2000 to 2016. Deanna Blansky of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, N.Y., and her colleagues compared patients by NHL subtype and urban-rural status, using rural-urban continuum codes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The researchers found 136,197 DLBCL, 70,882 follicular lymphoma (FL), and 120,319 CLL cases of patients aged ≥ 20 years. The DLBCL patients comprised 73.6% non-Hispanic white, 11.8% Hispanic, and 7.3% non-Hispanic black, with a similar distribution observed for FL and CLL. Patients were adjusted for age, sex, and family poverty.
The study showed that, overall, there was a higher DLBCL incidence rate in metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas overall (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11-1.30). Most pronounced was an increased DLBCL incidence among Hispanics in urban areas, compared with rural areas (rural IRR = 1.00; non-metropolitan urban IRR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16-1.51; metropolitan urban = 1.55, 95% CI 1.36-1.76).
In contrast, metropolitan urban areas had a lower overall incidence of CLL than rural areas (8.4 vs. 9.7 per 100,000; IRR = .87; 95% CI .86-.89).
However, increased CLL incidence rates were found to be associated with non-metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas (IRR = 1.19; 95% CI 1.10-1.28), particularly among non-Hispanic Blacks (IRR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.27-1.72).
Unlike DLBCL and CLL, there were no differences observed in FL incidence rates by urban-rural status after adjusting for age, sex, and family poverty rates, the researchers reported.
“Overall, our findings suggest that factors related to urban status may be associated with DLBCL and CLL pathogenesis. Our results may help provide epidemiological clues to understanding the racial disparities seen among hematological malignancies, particularly regarding the risk of DLBCL in Hispanics and CLL in non-Hispanic Blacks,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The researchers did not report conflict information.
SOURCE: Blansky D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 May 15; doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2020.05.010.
Exposure to carcinogens has been implicated in the development of non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), suggesting that an examination of the environment on a population-based level might provide some insights. On that basis, researchers performed a study that found that living in an urban vs. rural area was associated with an increased risk of developing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) among diverse, urban populations.
The study, published online in Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma & Leukemia, found an increased incidence of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in urban vs. rural Hispanics, and a similar increased incidence of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in non-metropolitan urban non-Hispanic blacks.
A total of 482,096 adults aged 20 years and older with incident NHL were reported to 21 Surveillance, Epidemiology,and End Results (SEER) population-based registries for the period 2000 to 2016. Deanna Blansky of the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, N.Y., and her colleagues compared patients by NHL subtype and urban-rural status, using rural-urban continuum codes from the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The researchers found 136,197 DLBCL, 70,882 follicular lymphoma (FL), and 120,319 CLL cases of patients aged ≥ 20 years. The DLBCL patients comprised 73.6% non-Hispanic white, 11.8% Hispanic, and 7.3% non-Hispanic black, with a similar distribution observed for FL and CLL. Patients were adjusted for age, sex, and family poverty.
The study showed that, overall, there was a higher DLBCL incidence rate in metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas overall (incidence rate ratio [IRR] = 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11-1.30). Most pronounced was an increased DLBCL incidence among Hispanics in urban areas, compared with rural areas (rural IRR = 1.00; non-metropolitan urban IRR = 1.32, 95% CI 1.16-1.51; metropolitan urban = 1.55, 95% CI 1.36-1.76).
In contrast, metropolitan urban areas had a lower overall incidence of CLL than rural areas (8.4 vs. 9.7 per 100,000; IRR = .87; 95% CI .86-.89).
However, increased CLL incidence rates were found to be associated with non-metropolitan urban areas, compared with rural areas (IRR = 1.19; 95% CI 1.10-1.28), particularly among non-Hispanic Blacks (IRR = 1.49, 95% CI 1.27-1.72).
Unlike DLBCL and CLL, there were no differences observed in FL incidence rates by urban-rural status after adjusting for age, sex, and family poverty rates, the researchers reported.
“Overall, our findings suggest that factors related to urban status may be associated with DLBCL and CLL pathogenesis. Our results may help provide epidemiological clues to understanding the racial disparities seen among hematological malignancies, particularly regarding the risk of DLBCL in Hispanics and CLL in non-Hispanic Blacks,” the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the U.S. National Institutes of Health. The researchers did not report conflict information.
SOURCE: Blansky D et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2020 May 15; doi.org/10.1016/j.clml.2020.05.010.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA & LEUKEMIA
Interleukin-27 increased cytotoxic effects of bone marrow NK cells in CLL
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is characterized by significant immune perturbation, including significant impairment of natural killer (NK) cells, which leads to disease complications and reduced effectiveness of treatment.
However, the use of , according to an in vitro study conducted by Maral Hemati, a student researcher at the Semnan (Iran) University of Medical Sciences, and colleagues.
Ms. Hemati and her colleagues obtained bone marrow aspirates (BM) and peripheral blood samples (PB) were from 12 untreated CLL patients (9 men and 3 women) with a median age of 61 years. The cells were cultured in vitro, according to their report in International Immunopharmacology.
The researchers found that the use of recombinant human interleukin-27 (IL-27) stimulated NK cells in the cultured BM and PB cells of CLL patients, based upon assessment using cell surface flow cytometry and a cytotoxicity assay.
Treatment with IL-27 also increased CD69 (a marker for NK cell activity) on NK cells both in BM and PB. In addition, , whereas it did not improve NK cell activity of PB, according to the researchers.
The research was supported by Semnan (Iran) University of Medical Sciences. The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hemati M et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;82:doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106350.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is characterized by significant immune perturbation, including significant impairment of natural killer (NK) cells, which leads to disease complications and reduced effectiveness of treatment.
However, the use of , according to an in vitro study conducted by Maral Hemati, a student researcher at the Semnan (Iran) University of Medical Sciences, and colleagues.
Ms. Hemati and her colleagues obtained bone marrow aspirates (BM) and peripheral blood samples (PB) were from 12 untreated CLL patients (9 men and 3 women) with a median age of 61 years. The cells were cultured in vitro, according to their report in International Immunopharmacology.
The researchers found that the use of recombinant human interleukin-27 (IL-27) stimulated NK cells in the cultured BM and PB cells of CLL patients, based upon assessment using cell surface flow cytometry and a cytotoxicity assay.
Treatment with IL-27 also increased CD69 (a marker for NK cell activity) on NK cells both in BM and PB. In addition, , whereas it did not improve NK cell activity of PB, according to the researchers.
The research was supported by Semnan (Iran) University of Medical Sciences. The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hemati M et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;82:doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106350.
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is characterized by significant immune perturbation, including significant impairment of natural killer (NK) cells, which leads to disease complications and reduced effectiveness of treatment.
However, the use of , according to an in vitro study conducted by Maral Hemati, a student researcher at the Semnan (Iran) University of Medical Sciences, and colleagues.
Ms. Hemati and her colleagues obtained bone marrow aspirates (BM) and peripheral blood samples (PB) were from 12 untreated CLL patients (9 men and 3 women) with a median age of 61 years. The cells were cultured in vitro, according to their report in International Immunopharmacology.
The researchers found that the use of recombinant human interleukin-27 (IL-27) stimulated NK cells in the cultured BM and PB cells of CLL patients, based upon assessment using cell surface flow cytometry and a cytotoxicity assay.
Treatment with IL-27 also increased CD69 (a marker for NK cell activity) on NK cells both in BM and PB. In addition, , whereas it did not improve NK cell activity of PB, according to the researchers.
The research was supported by Semnan (Iran) University of Medical Sciences. The authors reported that they had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Hemati M et al. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;82:doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106350.
FROM INTERNATIONAL IMMUNOPHARMACOLOGY
FDA approves ibrutinib-rituximab combo for newly diagnosed CLL, SLL in adults
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for ibrutinib (Imbruvica) to allow its combination with rituximab for frontline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in adults.
The approval, announced April 21, was based on findings from the randomized, controlled, open-label, phase 3 E1912 trial of 529 patients, which demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) among those who received ibrutinib plus rituximab, compared with those who received fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) (87% vs. 75%; hazard ratio, 0.34). Median PFS was not reached in either arm after a median follow-up of 37 months.
E1912 was the first study to show superiority of a chemotherapy-free regimen over FCR chemoimmunotherapy, considered the gold standard for newly diagnosed CLL and SLL for the past 2 decades.
The recommended dosage for the newly approved combination is a once-daily 420-mg dose of ibrutinib taken with a glass of water, with rituximab initiation in the second cycle at doses of 50 mg/m2 on day 1, 325 mg/m2 on day 2, and 500 mg/m2 on days 1-5 of subsequent cycles for a total of six cycles.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for ibrutinib (Imbruvica) to allow its combination with rituximab for frontline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in adults.
The approval, announced April 21, was based on findings from the randomized, controlled, open-label, phase 3 E1912 trial of 529 patients, which demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) among those who received ibrutinib plus rituximab, compared with those who received fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) (87% vs. 75%; hazard ratio, 0.34). Median PFS was not reached in either arm after a median follow-up of 37 months.
E1912 was the first study to show superiority of a chemotherapy-free regimen over FCR chemoimmunotherapy, considered the gold standard for newly diagnosed CLL and SLL for the past 2 decades.
The recommended dosage for the newly approved combination is a once-daily 420-mg dose of ibrutinib taken with a glass of water, with rituximab initiation in the second cycle at doses of 50 mg/m2 on day 1, 325 mg/m2 on day 2, and 500 mg/m2 on days 1-5 of subsequent cycles for a total of six cycles.
The Food and Drug Administration has expanded the indication for ibrutinib (Imbruvica) to allow its combination with rituximab for frontline treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in adults.
The approval, announced April 21, was based on findings from the randomized, controlled, open-label, phase 3 E1912 trial of 529 patients, which demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) among those who received ibrutinib plus rituximab, compared with those who received fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) (87% vs. 75%; hazard ratio, 0.34). Median PFS was not reached in either arm after a median follow-up of 37 months.
E1912 was the first study to show superiority of a chemotherapy-free regimen over FCR chemoimmunotherapy, considered the gold standard for newly diagnosed CLL and SLL for the past 2 decades.
The recommended dosage for the newly approved combination is a once-daily 420-mg dose of ibrutinib taken with a glass of water, with rituximab initiation in the second cycle at doses of 50 mg/m2 on day 1, 325 mg/m2 on day 2, and 500 mg/m2 on days 1-5 of subsequent cycles for a total of six cycles.